Accessibility Links
- Skip to content
- Skip to search IOPscience
- Skip to Journals list
- Accessibility help
- Accessibility Help
Click here to close this panel.

Engineering Research Express

As a society-owned publisher with a legacy of serving scientific communities, we are committed to offering a home to all scientifically valid and rigorously reviewed research. In doing so, we aim to accelerate the dissemination of scientific knowledge and the advancement of scholarly communications to benefit all.
Engineering Research Express supports this mission and actively demonstrates our core values of inclusive publishing and trusted science . To find out more about these values and how they can help you publish your next paper with us, visit our journal scope .
Purpose-led Publishing is a coalition of three not-for-profit publishers in the field of physical sciences: AIP Publishing, the American Physical Society and IOP Publishing.
Together, as publishers that will always put purpose above profit, we have defined a set of industry standards that underpin high-quality, ethical scholarly communications.
We are proudly declaring that science is our only shareholder.
Engineering Research Express (ERX) is a broad, multidisciplinary journal devoted to publishing new experimental and theoretical research covering topics extending across all areas of engineering science including interdisciplinary fields.
- Trustworthy science backed by rigorous peer review
- Inclusive publishing practices focused on scientific validity
- Find out more about our scope
Open all abstracts , in this tab
Mohammed Asadullah Khan et al 2021 Eng. Res. Express 3 022005
Magnetic field sensors are an integral part of many industrial and biomedical applications, and their utilization continues to grow at a high rate. The development is driven both by new use cases and demand like internet of things as well as by new technologies and capabilities like flexible and stretchable devices. Magnetic field sensors exploit different physical principles for their operation, resulting in different specifications with respect to sensitivity, linearity, field range, power consumption, costs etc. In this review, we will focus on solid state magnetic field sensors that enable miniaturization and are suitable for integrated approaches to satisfy the needs of growing application areas like biosensors, ubiquitous sensor networks, wearables, smart things etc. Such applications require a high sensitivity, low power consumption, flexible substrates and miniaturization. Hence, the sensor types covered in this review are Hall Effect, Giant Magnetoresistance, Tunnel Magnetoresistance, Anisotropic Magnetoresistance and Giant Magnetoimpedance.
Eshaan Gupta et al 2022 Eng. Res. Express 4 025039
The objective of this research paper is to design, simulate and compare components of a race car braking system. The Racecar is an FSAE car that is designed around the rules and regulations of the FSAE rulebook, the main aim of this project is to make components lightweight and improve their performance as compared to their OEM counterparts. The braking system involves the mathematical calculation of pedal ratio, brake torque, heat generated in brake discs, and required clamping force using MATLAB to achieve peak deceleration after which these values would be used to design and simulate the components. The paper presents some innovative new ideas applied in an FSAE car and also involves designing techniques like topology optimization which was done using Altair inspire. Finally, all the components were designed in Solidworks, and simulations like Factor of safety, von mises stress, and strain were performed using ANSYS 18.1. The paper also compares the work of other authors as well and explains the differentiating factors between our and their design.
Erteza Tawsif Efaz et al 2021 Eng. Res. Express 3 032001
Thin-film solar cells are preferable for their cost-effective nature, least use of material, and an optimistic trend in the rise of efficiency. This paper presents a holistic review regarding 3 major types of thin-film solar cells including cadmium telluride (CdTe), copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS), and amorphous silicon ( α -Si) from their inception to the best laboratory-developed module. The remarkable evolution, cell configuration, limitations, cell performance, and global market share of each technology are discussed. The reliability, availability of cell materials, and comparison of different properties are equally explored for the corresponding technologies. The emerging solar cell technologies holding some key factors and solutions for future development are also mentioned. The summarized part of this comparative study is targeted to help the readers to decipher possible research scopes considering proper applications and productions of solar cells.
Thiago F Santos et al 2024 Eng. Res. Express 6 012501
This systematic review focuses on the exploration and advancement of sustainable and eco-friendly polymer composite materials derived from bast fibers. Bast fibers, obtained from the phloem of certain plants like flax, hemp, jute, and kenaf, represent a renewable and environmentally benign resource. Their integration into polymer based composites has gained significant attention due to the growing environmental concerns and the need for sustainable material development. The importance of this study lies in its comprehensive examination of bast fibers as viable alternatives to the synthetic fibers in polymer composite materials. By harnessing the natural strength, light weight, and biodegradability of bast fibers, this review contributes to the creation of materials that are not only environmentally sustainable but also possess enhanced mechanical properties suitable for various industrial and domestic applications.
Kaltrine Jakupi et al 2024 Eng. Res. Express 6 025005
This study employs Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) technology to investigate surface roughness in stainless steel 316L 3D printing processes. Utilizing the Taguchi method in experimental design, we examine the influence of independent variables—laser power, scan speed, and hatch spacing - on surface roughness quality. Results indicate that laser power has the greatest impact, followed by scan speed and hatch spacing. Notably, both laser power and hatch spacing positively affect surface roughness, while scan speed adversely affects the top surface quality of printed components. This research enhances comprehension of the intricate relationship between process parameters and surface quality in DMLS-based 3D printing, offering insights for optimizing surface roughness in stainless steel 316L applications. The study holds practical significance for enhancing the quality and performance of 3D-printed components across diverse engineering and manufacturing sectors.
Angshuman Khan et al 2022 Eng. Res. Express 4 035040
This study presents an ultrasound speckle suppression method to detect the stones in the human kidney. An initial image is first improved using image enhancement techniques, which are used to change the image's intensities. Next, median filters smooth the picture and eliminate noise. Pre-processed images are segmented using a thresholding technique. The median filter extracts impulsive noise from salt-and-pepper noise. The suggested approach locates stones using location coordinates. Hospital and clinical ultrasound images were used to evaluate the proposed scheme and algorithm. The suggested scheme has been assessed by different performance measuring parameters. Physicians are likely to benefit from the research in terms of clinical diagnosis and educational training. Based on 50 test cases, the proposed plan was correct 96.82% of the time and sensitive 92.16% of the time. Furthermore, the peak signal to noise ratio is 1.82, and the average signal to noise ratio is 1.58, demonstrating the efficacy of the proposed approach.
Asra Tariq et al 2023 Eng. Res. Express 5 032002
Shear sensors are used for measuring shear stress and shear strain in solid bodies when mechanical forces are applied. For the preparation of these sensors, researchers reported innovative materials either alone or in the form of blends, alloys, and composites. Shear sensors are not easily available for purchase, therefore, this review focuses on the working principles of various kinds of shear sensors being explored by researchers. Several technologies and materials are used, such as piezoelectric materials, piezoresistive materials, Fiber Bragg Grating, capacitive sensing, and structural colors. This article also looks at fabrication-based challenges that restrict the commercial use of shear sensors. A variety of shear sensor devices are evaluated for measuring shear stress/strain for many different applications such as health monitoring and biomedical, robotics, and or fracture in materials.
Jasjeevan Singh et al 2021 Eng. Res. Express 3 012002
Cutting fluids provide cooling at the cutting tool and on the surface of work piece, lubricate the tool-workpiece interface and evacuate chips from the cutting zone in the machining processes. The primary reason for using cutting fluid is to reduce the temperature at cutting zone and friction wear either through cooling or lubrication. To maximize the efficiency of cutting fluids in machining processes the knowledge of machining conditions and cutting fluid types are critically important. However, misemploy of the cutting fluid and non efficient method of disposal can raise health issues and environmental impact. In this paper, an attempt has been made to provide overview of cutting fluids type, cooling techniques and main alternatives as dry machining, cryogenic cooling, minimum quantity lubrication and hybrid cooling minimizing use of cutting fluids. The inclusion of solid lubricants, nano fluids in lubrication/cooling techniques results in increase in the productivity of the process due to reduction in friction and heat at the cutting zone. The cutting parameters and type of tools utilized by various researchers have been summed up and introduced in this paper to provide useful information to various researcher works.
Sakshi Anand and Rakesh Sharma 2024 Eng. Res. Express 6 022201
In last decades, remote sensing technology has rapidly progressed, leading to the development of numerous earth satellites such as Landsat 7, QuickBird, SPOT, Sentinel-2, and IKONOS. These satellites provide multispectral images with a lower spatial resolution and panchromatic images with a higher spatial resolution. However, satellite sensors are unable to capture images with high spatial and spectral resolutions simultaneously due to storage and bandwidth constraints, among other things. Image fusion in remote sensing has emerged as a powerful tool for improving image quality and integrating important features from multiple source images into one, all while maintaining the integrity of critical features. It is especially useful for high-resolution remote sensing applications that need to integrate features from multiple sources and hence a vital pre-processing step for various applications, including medical, computer vision, and satellite imaging. This review initially gives a basic framework for image fusion, followed by statistical analysis and a comprehensive review of various state-of-the-art image fusion methods, where they are classified based on the number of sensors used, processing levels, and type of information being fused. Subsequently, a thorough analysis of STF and pansharpening techniques for remote sensing applications has been covered, where the dataset of the DEIMOS-2 satellite is employed for evaluating various pansharpening methods while MODIS and Landsat images are employed in the spatiotemporal fusion method. A comparative evaluation of several approaches has been carried out to assess the merits and drawbacks of the current approaches. Several real-time applications of remote sensing image fusion have been explored, and current and future directions in fusion research for remote sensing have been discussed, along with the obstacles they present.
P K Dinesh Kumar and S Darius Gnanaraj 2023 Eng. Res. Express 5 022002
In an automotive vehicle, the brake discs, also known as rotors, contribute significant weight to the engine chassis. Hence, lightweight aluminum brake discs are in the developmental stage as a popular alternative to traditional cast iron or steel brake discs. Weight reduction is desirable to improve vehicle performance and fuel efficiency. Monolithic aluminum is not a practical choice as an alternative to existing commercial brake discs because of its poor operational temperature and wear performance. Literature suggests that Aluminum Metal Matrix composite (AMC) can be an ideal choice for brake discs. AMC brake discs are more resistant to warping and cracking than cast iron discs. They also have better heat dissipation properties, which help reduce brake fade and prolong the life of the brake pads. This study examines the different types of aluminum alloys, reinforcements, and manufacturing processes for manufacturing ideal AMC brake discs. The significance of silicon as the principal alloying element to improve thermal characteristics and incorporate various reinforcements to increase the AMC's wear resistance and frictional stability for brake disc applications is outlined. This article focuses on the thermal and tribological behavior of the AMC brake discs' performance over traditional rotors. The review discusses the different equipment required to assess the tribological characteristics of brake discs to meet industrial requirements. In addition to experimental validation, this paper addresses the necessity of proper rotor design selection and numerical analysis to evaluate the thermo-mechanical behavior of the brake disc at various braking events. The article points out that aluminum metal matrix composites have great potential to replace conventional grey cast iron brake discs. Finally, this review discusses possible future research avenues for developing an AMC rotor disc.
Latest articles
Ajeet K Yadav et al 2024 Eng. Res. Express 6 025323
The Tunnel Field Effect Transistor (TFET) often suffers from low ON current ( I ON ), charge traps, and thermal variability, which limits its performance and reliability. To address these issues, the source work function engineered Ge Charge Plasma Double Gate Tunnel Field Effect Transistor (CP-DGTFET) device structure with HfO 2 /Al 2 O 3 bilayer gate dielectric is designed and investigated using numerical TCAD simulations. The proposed Ti/HfO 2 /Al 2 O 3 /Ge CP-DGTFET device structure showed excellent DC characteristics with exceptional I ON , I ON / I OFF ratio, and minimal sub-threshold swing ( S ) of ∼3.04 × 10 −4 A μ m −1 , ∼1.2 × 10 10 , and ∼3.4 mV/dec, respectively. Furthermore, the device's analog characteristics displayed good transconductance, cut-off frequency, and gain bandwidth product of ∼0.75 mS/ μ m, ∼0.97 THz, and ∼102 GHz, respectively. Moreover, the charge trap exploration divulges that positive ITCs can enhance device performance, whereas negative ITCs can adversely impact the electrical characteristics of CP-DGTFET. Additionally, the temperature-dependent analysis showed that the OFF-state leakage current increases from ∼1.7 × 10 −15 A μ m −1 to 2.4 × 10 −10 A μ m −1 with temperature fluctuations from 275 K to 375 K. Overall, the work function-engineered CP-based Ti/HfO 2 /Al 2 O 3 /Ge DGTFET device structure shows great potential for improving the performance and reliability of Ge TFET technology.
Nekkanti Gowthami and Shalanti Vineetha Blessy 2024 Eng. Res. Express 6 025007
Recognition models achieved exceptional performance in object detection during the computer vision era, but they still rely on Small-Scale Object Detection (SSOD). SSOD remains difficult due to the variety of shapes and orientations of the object, as well as fixed prediction heads at the detection stage. To overcome these challenges, our paper proposed an auto anchor module, a Spatial Pyramid Pooling Faster layer (SPPF) in the feature refinement network, and an extremely small-scale prediction head at the detection stage of the model. With the auto anchor feature, the model is able to adjust the anchor boxes dynamically during training, which can improve its overall performance. The SPPF layer divides the feature map into five pyramid levels, each corresponding to a different scale. This enables the model to detect objects of different sizes by pooling features from all pyramid levels. Extreme Small Scale prediction head is specifically designed for small object detection and uses anchor boxes with small sizes and feature re-sampling techniques to improve the accuracy of SSOD. We perform quantitative evaluations on the VOC and achieved 85.4% mAP, 79.8% precision, 80.3% recall, and 80% F1-score. These reliable results prove that the suggested model performs better than existing models in detecting small-scale objects.
Isaiah Adebayo et al 2024 Eng. Res. Express 6 025322
Due to power losses, a sizeable portion of the electrical power produced is lost, which causes voltage deviation and instability as a result of rising load demand at the radial distribution network (RDN). Shunt capacitor penetration will enhance the RDN's efficiency by reducing power losses, improving the voltage profile and stability. For the best sizing and allocation of shunt capacitors (SCs) in RDN, a novel human-based metaheuristic heap-based optimizer (HBO) influenced by the ideas of corporate rank hierarchy (CRH) of standard organization is presented. The real power loss, voltage variation, and voltage stability index are all minimized while equality and inequality criteria are met by the HBO optimal allocation of SCs. One, two, and three numbers of SCs were investigated when installing the reactive compensating devices. Using typical IEEE 33-bus and 69-bus RDNs, covering a range of scenarios in the form of single- and multi-objective functions, the effectiveness of the HBO technique was examined. The real power loss for the conventional IEEE 33-bus and 69-bus RDN was reduced by 34.46% and 35.50%, respectively compared to their respective base cases. By contrasting the outcomes of the power loss with well-established and new optimization approaches, the efficacy and superiority of the suggested HBO were demonstrated.
Pengfei Ma et al 2024 Eng. Res. Express 6 025321
In this paper, a 128-channel non-uniform optical phased array is proposed. The antenna is based on a silicon nitride waveguide with a large cross-sectional area (3 μ m × 1.2 μ m) and a silicon nitride grating with a small diffraction window (grating width of 200 nm), enabling high optical power transmission and a wide 1 dB field of view. As a result, the designed sparse optical phased array achieves less than 1 dB of main lobe attenuation over a 94° field of view. Within this field of view, the main lobe will not fall below 80% of the maximum main lobe. This allows the minimum detection distance to still be about 89% of the maximum detection distance without increasing the input power. In this field of view, the maximum side-lobe suppression of the designed sparse optical phased array is 13.4 dB, and the minimum side-lobe suppression is higher than 11.9 dB. This is useful for simultaneously achieving a large field of view, low main lobe attenuation, stable side-lobe suppression, and long detection distance.
Review articles
Baruna Kumar Turuk and Basudeba Behera 2024 Eng. Res. Express 6 022302
In recent years, with the rapid growth of communication technology and the necessity for Radiofrequency (RF) front-end devices, the one-port Surface Acoustic Wave Resonator (SAWR) has turned out to be a significant component in the design of a SAW device. Hence, the present study concentrates on and around one-port multi-layer SAW resonators with their applications in communication systems. A comparative and critical analysis of various parameters is explored including temperature coefficient of frequency (TCF), Quality factor (Q-factor), phase velocity, impedance ratio, bandwidth, sensitivity, metallization ratio, etc to discuss the advantages and disadvantages of conventional one-port multi-layer SAW resonator. Through the analysis, future research trends as well as the applications of one port multi-layer SAW resonator are also discussed. The study also explores that the one port multi-layer SAW resonator finds employability in various applications like multimedia and mobile communication, medical field sensing technology, broadband signal processing at high frequencies, etc. Thus, significant, and efficient parameters of the resonator can be easily identified through comparative and critical analysis. The outcome of this study will help the researchers to enhance their work in this specific field in the future.
Shashi Kumar et al 2024 Eng. Res. Express 6 022101
The review paper deals with a literature review on buckling analysis by different methods of laminated plates with different types of stiffeners which has been conducted in recent years. Analytical studies, experimental studies, finite element analysis, and other computational methods have been implemented by researchers on the stiffened panels under compression and shear for determination of the buckling behavior of the panel with I-type, blade-type, T-type, and hat-stiffeners. Some literature has been found on the panel with the influence of variation of the stiffener depth for the determination of buckling capacity. Very few literatures, non-linear finite element (FE) have been implemented for the determination of the effect of debonding damage between plate-stiffener of the panel but have not been reported parametric data about the effect of cohesive parameters of plate-stiffener and delamination of plies of the composites stiffened panel for post-buckling analysis. This paper also provides a literature survey based on the buckling performance of the plates with the application of different shapes of stiffeners.
Muhammad Nafiz Hamidi et al 2024 Eng. Res. Express 6 012402
Recently, there has been rising interest in 4D printing (4DP) technology. It is a new technology that emerged from 3D printing technology but can produce a dynamic product that can change its shape and properties when subjected to external stimuli. 4DP is an additive manufacturing process that uses materials receptive to stimuli, such as shape memory polymer (SMP), that can alter its shape once exposed to applied stimuli like heat, water, light, electricity, pressure, etc. Two frequently used SMPs are polylactic acid (PLA) and thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU), owing to their excellent shape memory properties, biodegradability, and biocompatibility. The shape memory performance of the 4D printed SMP is quantified by shape recovery ratio (R r ) and shape fixity ratio (R f ), which is highly dependent on the printing parameters. Some of the important printing parameters that influence shape memory performance are printing speed, raster angle, layer thickness, and nozzle temperature. Due to 4DP's ability to produce a dynamic product, it is widely used to revolutionize several fields such as biomedical, textile, aerospace, soft robotic, and electronic fields. This review paper discusses and provides a better understanding of the 4DP technology, the shape recovery mechanism, the effect of 4DP parameters on shape recovery performance, applications of 4DP technology, challenges faced, and future perspectives regarding the 4DP technology.
Adarsh Mathew Abraham and S Venkatesan 2024 Eng. Res. Express 6 012508
Implants play a vital role in a person's life because losing any body part to function less actively, which makes the sufferer uncomfortable. Implants should be both biocompatible and non-toxic to the body is essential to achieve its biocompatibility nature. To create orthopaedic, dental, and surgical implants, biomaterials were divided into three categories: metallic, polymeric, and ceramic. Materials based on polymers indicate their degree of adaptability in terms of sutures, medication delivery, etc. Ceramic materials are known for their high compressive strength and inert behaviour, which combine aesthetic qualities. Metallic biomaterials are enhanced by their high strength and resistance to fracture. One of the most promising techniques for improving a material's mechanical qualities is powder metallurgy. Powder metallurgy involves blending of powders, compaction of blended powder, sintering and mechanical test. Samples with varying compact pressures, sintering temperatures, and sintering times were created using the powder metallurgy process. The aim of the research work is to get the concept of powder metallurgy, biomaterials commercially available for orthopaedic and dental applications, properties of biomaterial and methods to fabricate the material effectively.
Accepted manuscripts
KARAKAS et al
Natural and organic-based composite materials are widely used in many industrial applications due to their low cost, easy recyclability, economic feasibility, and ready availability. In this study, a polymer-based composite friction material consisting of Hemp-Colemanite composition (HCFCo) has been developed for the automotive sector to exhibit lower cost, environmentally friendly characteristics, and suitable friction-wear behaviors. For this purpose, three different ratios (%4, %8 and %12) of HCFCo composites were produced using a coating technique called impregnation process with a specially designed device. During the production stage, homogeneity of the composites was ensured, and then the final shape was given by the hot pressing method. Properties such as hardness, density, water and oil absorption, friction coefficient, and specific wear of HCFCo samples were examined. In addition, the microstructures of HCFCo composites were investigated to determine the bonding form between hemp fiber and colemanite. The results obtained revealed that the friction coefficient values decreased with an increase in temperature, while no significant change was observed in hardness and density values. Throughout the entire testing process, the friction coefficients varied between 0.14 and 0.29 on average. It was concluded that the developed fiber-reinforced composite can be reliably used in industrial applications and can contribute significantly to innovations in the literature.
A et al
Ceramic Matrix Composites (CMC) are widely used for manufacturing automobile parts aircraft components, biomedical and electronic devices. In recent years, graphene has found extensive applications in various fields like effective reinforcement in the development of metal matrix, polymer matrix and ceramic matrix composites. Literature reveals that more focus was on polymer and metal matrix composites reinforced with graphene when compared to ceramic matrix composites. In this manuscript, the effect and suitability of graphene as a reinforcement for fabricating ceramic matrix composite are presented. Further, the property evaluation, including mechanical and physical, characterization and microstructural evaluation of the CMCs developed with graphene as reinforcement is elaborated. The investigation of the reinforcing mechanisms and failure behavior of ceramic matrix composites reinforced with graphene, together with the development of novel processing techniques to solve manufacturing difficulties, are key areas of focus. Although many investigations have concentrated on enhancing the mechanical and electrical characteristics of ceramics by integrating graphene, more investigation is required to investigate the interfacial interaction between graphene and the ceramic matrix, as well as the influence of graphene size on the properties of the composite. Furthermore, there is a need for future research to explore the possibility of using graphene-reinforced ceramic composites in several multifunctional applications, including microwave absorption, electromagnetic interference shielding, ballistic armors, self-monitoring damage sensors, and energy storage and conversion. Future research should focus on developing innovative processing procedures that guarantee the uniform distribution and precise alignment of graphene sheets within the ceramic matrix. The incorporation of graphene into ceramic matrix composites presents novel prospects for augmenting the characteristics and capabilities of ceramics, rendering it a very interesting area for further investigation.
Pradeep Kumar et al
In the present investigation, self-lubricating cutting tools were fabricated by adding various elements such as NiCr, Ag, Mo, SrSO4, and CaF2 to Zirconia Toughened Alumina in order to overcome the difficulties that occurred in dry machining. Three significant process parameters; cutting speed (50, 125, 200, and 275 m/min), feed rate (0.1 and 0.2 mm/rev), and depth of cut (0.1 and 0.2 mm) were selected for the machining process. The performance measures such as chip thickness ratio, shear angle, and tool wear, were investigated. The experimental runs were conducted with Taguchi L8 mixed-level orthogonal array. Technique for Order of Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution is a multi-criteria decision-making method used to determine the best alternative from a set of options. Turning experiments have been performed on the AISI 4340 steel workpiece with various combinations of machining parameters. The findings revealed the incorporation of SrSO4 and Mo at 10Wt.% and CaF2 at 5Wt.% (i.e., self-lubricating cutting tool-4) achieved better mechanical properties and wear resistance due to the formation of a self-lubrication layer on the rake face of the cutting tool. A confirmation experiment is executed in order to verify the outcomes in the end. Finally, there is a noticeable improvement in the outcomes compared to the base cutting tool, i.e., chip thickness ratio is 35.77%, shear angle is 27.31%, and tool wear is 58%. The mechanism for improving performance measures is discussed in detail.
Liu et al
Steel-timber composite structures are a novel hybrid structural system that combines the advantages of both steel and wood structures, holding great promise for various applications. In this paper, the seismic behaviors of steel- timber composite columns are investigated based on finite element analysis. The reliability of the finite element model is validated by quasi-static test results. Numerical analysis results indicate that the proposed steel- timber composite systems is with high ultimate bearing capacity, full hysteresis loops, and strong displacement ductility, demonstrating excellent seismic performance. The axial compression ratio, steel tube thickness, and flexural point height significantly influence the seismic resistance of the structure.
Asalekar et al
This research investigates the performance of high-speed CNC milling operations on Ti6Al4V alloy by employing a novel ZnO-Ag hybrid nanofluid. The study involves the preparation and characterization of nanofluids with varying concentrations of nanoparticles, focusing on thermal conductivity and stability. The machining experiments encompass four critical input parameters: Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL) flow rate, cutting speed, nanofluid concentration, and feed rate. Performance evaluation is based on average surface roughness (Ra) and cutting temperature. Key findings include a remarkable 21.05% improvement in thermal conductivity for the ZnO-Ag-based sunflower oil at 0.2% volume concentration compared to 0.05% concentration. The prepared nanofluids exhibit good stability. Moreover, cutting speed and MQL flow rate emerge as significant contributors to Ra, accounting for 35.62% and 34.82%, respectively. Interestingly, MQL flow rate is identified as the most influential factor, surpassing even cutting speed. SEM images for tool wear reveals that the ZnO-Ag based sunflower oil reduced tool wear significantly. In conclusion, the proposed ZnO-Ag-based sunflower oil at 0.2% concentration emerges as the good option for sustainable high-speed machining of Ti6Al4V alloy, showcasing
More Accepted manuscripts
Open access
Hamdi KARAKAS et al 2024 Eng. Res. Express
Adnan Khadim and Naveed Ahmad 2024 Eng. Res. Express 6 025105
Asphalt is a viscoelastic material which performs to resist rutting, fatigue cracking, and moisture susceptibility under different loading and temperature conditions. The use of innovative and renewable pavement construction materials is inevitable due to high axle loads, rapidly increasing traffic volumes, and varying climatic conditions. This study aims to assess the effect as well as the optimum dosage of paper waste lignin for use in hot mix asphalt (HMA). Lignin from the paper industry with dosage ratios of 5, 10, 15, and 20%, was utilized to study the effect of the addition of lignin to the asphalt binder. Virgin and lignin-modified binder samples, before and after the aging process, were subjected to physical testing through penetration, softening point, ductility, viscosity and specific gravity and rheological characteristics through dynamic shear rheometer (DSR), bending beam rheometer (BBR), and rational viscometer (RV). The fractional composition was assessed through saturates, aromatics, resins and asphaltenes (SARA) fractional composition technique. Statistical analysis was also performed to find correlation of different physical and rheological parameters. Furthermore, based on optimum dosage, the performance of asphalt mixtures was studied against rutting, fatigue cracking, and moisture susceptibility. The results indicated that the addition of lignin has improved the physical properties significantly. The amount of asphaltene decreased and aromatics increased in SARA fractional analysis. Moreover, the Colloidal Instability Index (CII) has also indicated a stable structure of the binder. The rheological characteristics are improved after modification. The asphalt mixture tests revealed that addition of lignin with optimum dosage (10%) has improved the performance against rutting, fatigue cracking and moisture susceptibility. Statistical analysis indicated good co-relation among different physical and rheological parameters. This study concludes that 10% dosage is the optimum dosage that can successfully replace the virgin asphalt binder for performance of hot mix asphalt.
Xiaowei Zhao et al 2024 Eng. Res. Express 6 025319
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) has revolutionized retinal imaging by offering non-invasive high-resolution three-dimensional visualization capabilities. OCT has become the standard of care in routine ophthalmological practice, especially for the posterior segment. Given its widespread clinical applications, establishing standardized test devices and methods for key OCT parameters is imperative to ensure both optimal imaging performance and diagnostic accuracy and treatment effectiveness. As a widely applied standard, ISO 16971:2015 published by the International Organization for Standardization specifies the minimum requirements, test device, and methods for OCT for the posterior segment of the human eye. Notably, these standards lacked experimental validation. In the present study, we implement the test device according to ISO 16971:2015, and assess a commercially available ophthalmic OCT instrument with the suggested test device and methods. Results show that the test device and methods could facilitate a rudimentary evaluation of OCT key parameters. Nevertheless, refinements of the test device and methods are requisite to enhance measurement accuracy, reliability, traceability, and practicability, catering to the diverse needs of manufacturers, end-users, and regulatory entities.
Krishnanunni S et al 2024 Eng. Res. Express
The automotive industry's relentless pursuit of improved safety, performance, and durability has spurred a continuous search for innovative solutions for crucial components like brake discs. These components endure extreme thermal and mechanical stresses, making them highly susceptible to corrosion and wear. Inadequate corrosion resistance and excessive wear of brake disc material during service remain significant concerns, with the latter resulting in brake emissions in the form of dust and particulate matter that pose health risks to humans. As exhaust emission standards grow more stringent, it becomes imperative to address brake disc wear issues while maintaining material braking performance. This paper provides an extensive examination of recent advancements in brake disc coatings, specifically designed to combat both corrosion and wear challenges. It explores how these protective coatings interact with the broader automotive ecosystem, highlighting their pivotal role in ensuring safer, more resilient, and environmentally responsible vehicles. This paper also evaluates traditional coating technologies and materials alongside emerging alternatives for brake disc applications.
GyeChol Sin et al 2024 Eng. Res. Express 6 025006
Composite transparent conductive electrodes (TCEs) consisting of silver nanowires (AgNWs) and conductive metal oxides are very promising for flexible optoelectronic devices due to their smooth surface morphology and high chemical stability. However, it is still challenging to ensure high optoelectronic performance and long-term stability in practical applications. Here, we solved these problems by coating antimony-doped tin oxide (ATO) nanoparticles dispersion on ultra-long AgNWs network using waterborne polyurethane (WPU) binder. Ultra-long nanowires occupy less wire-wire junctions and space than short nanowires, thus increasing the optoelectronic performance and flexibility of the composite TCE. WPU improves the adhesion and stability of ATO nanoparticles to the substrate and AgNWs network. The fabricated composite TCE showed a low sheet resistance of 11.9 Ω sq −1 , good optical transmittance of 83% at 550 nm and a figure of merit (FOM) of 162 compared to PET/ITO electrode. It also showed excellent mechanical flexibility, adhesion to the substrate and solvent stability. Furthermore, the long-term conductivity was maintained under ambient conditions for 60 days.
Saravanan Subramanian et al 2024 Eng. Res. Express
Confirming the pozzolanic activity is crucial to ensure their compatibility and performance in geopolymer composite (GC) applications, as it improves the geopolymerization process and optimizes the strength characteristics of GCs. This work evaluates the pozzolanic properties of Fly ash (FA), Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF) slag, and Iron Ore Tailings (IOT) for their potential use in the development of Engineered Geopolymer Composites (EGC). IOT partially substitutes fine aggregate, while FA and BOF slag are the major precursors. Pozzolanic properties of the aforementioned materials were assessed through the Frattini, saturated lime test (SLT), and strength activity index (SAI). The Frattini test values recorded were 90, 47, and 30 % of CaO removal, denoting their degree of pozzolanicity respectively for BOF Slag, FA, and IOT. In the SLT, the formation of stable calcium silicate hydrates and aluminates are verified by the reaction of the test pozzolans with lime, thereby conforming their pozzolanicity. The results from the Frattini and SAI tests showed a significant correlation, indicating an effective pozzolanicity measure of the test materials. However, the results from the SLT did not align with the outcomes from the Frattini and SAI tests. This contradiction suggests that the SLT is ineffective compared to the other two test methods in measuring the pozzolanic activity of the test materials. The research findings provide valuable insights into the potential usage of these materials (pozzolans) as sustainable building materials in the construction industry.
Vijayalaxmi H M et al 2024 Eng. Res. Express 6 025205
The medical images of people are important and sensitive and cannot be shared with the public considering privacy measures. Maintaining the confidentiality of the medical image is essential, and leakage of such information can cause great loss. Therefore, the information has to be secured while being transferred through a third party, which can be any network medium. Thus, there is a need for developing a robust encryption algorithm. These algorithms improve the security of the ongoing pictures by compromising the nature of the picture and utilizing complex calculations. Algorithms that work on the nature of the picture by utilizing complex cycles, for example, error diffusion, halftoning, wavelet transform, and dithering, lead to time complexity. Thus, a compact and efficient cryptographic algorithm is proposed with fewer mathematical computations that ensure the secured transmission and reception of medical images through the medium using Significant Visual Cryptography (SVC). In SVC, initially, the quality of the secret images (SI) is improved by using the Error Abatement Technique (EAT). The output of EAT is used to generate random share values, which are then implanted in cover pictures. The shares that are transmitted do not reveal the secret information present in the original image because of the steganography features involved in this technique. The integrated check value (ICV) is calculated over the region of interest (ROI) at the encryption and decryption sides to provide additional security. Quality and security analyses have been carried out to ensure the robustness of the algorithm. The detailed study proved that the proposed algorithm beat the constraints of the current calculations. The concept of checking the integrity value and steganography features enhanced the effectiveness of the algorithm.
Shenghan Guo et al 2024 Eng. Res. Express
This study examines a new intelligent control method for a single-link flexible manipulator that addresses backlash and model uncertainty. First, a smooth backlash inverse model is constructed to mitigate backlash nonlinearity. Subsequently, a "disturbance-like" term is formulated to recharacterize the coupled term composed of external disturbances and model uncertainty. A new adaptive controller is proposed to compensate for the unknown "disturbance-like" term. Using the proposed control method, the stability of the system is evaluated using the direct Lyapunov theory, ensuring uniform ultimate boundedness. Finally, numerical simulation and experiment are conducted using the Quanser platform. The numerical simulation and experimental results show that the proposed control can ensure a faster convergence rate and effectively reduce actuator input chattering.
Narayan Joshi 2024 Eng. Res. Express
Optimum efficiency and fault tolerance are the most demanding and challenging issues in the domain of performance and reliability management in cloud computing environments. Optimized resource utilization is a key aspect for yielding efficiency in cloud platforms. Workload balancing through resource sharing is one of the key solutions for attaining performance in cloud environments. In addition, multiple cloud environments join hands to offer performance and fault tolerance through resource sharing. We provide a better and cloud-instances' priority-based efficient load balancing method for collaborative cloud platforms. The recommended efficient load balancing method shortens the waiting timespan and overcomes the starvation problem of low priority instances in intercloud environments. A functional prototype of the recommended load balancing method was deployed on a physical cloud infrastructure which was setup with the OpenStack cloud software on the Fedora Linux operating system. The pilot project execution findings exhibit a reduction in the timespan borne by instances for executing load balancing. This technique is useful for attaining fault tolerance and efficient resource utilization in intracloud and intercloud environments.
Sadegh Mahmoudkhani et al 2024 Eng. Res. Express 6 025308
Steel tendons commonly used in pre-stressed/post-tensioned concrete structural systems can lose cross-section due to corrosion, eventually leading to acoustic emission (AE) events when the stress exceeds the breaking strength of the wires that make up the tendons. Reliable differentiation of wire break AE events from traffic or grout crack events is critical for monitoring large structures, even where the distance between sensors may produce highly attenuated signals. In this paper, the Fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm was employed to differentiate AEs released from breaking wires of steel tendons from a database of 13464 AEs, including wire breaks, environmental and grout crack AEs. Wire breaks and grout crack AEs were collected from axial loading tests of grouted tendons in which the load increased until a wire broke. Environmental acoustic signals were collected from a bridge. Then all the collected AEs were gathered in a database and post-processed to simulate attenuation of up to 20 m from source to sensor. To optimize the speed and reliability of the Fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm, a non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm-II (NSGA-II) was used to find the minimum number of acoustic features needed. The NSGA-II algorithm started with 201 possible acoustic features and found 12 combinations of features that resulted in more than 80% wire break detection accuracy. In contrast, less than 3% of grout cracks and 0% of environmental signals were detected as wire breaks. The proposed method is suitable for deployment in a large sensor network and has sufficiently low-computational requirements for at-the-sensor processing, eliminating the need to send high-frequency sampled data outside the sensor node.
More Open Access articles
Journal links
- Submit an article
- About the journal
- Editorial Board
- Author guidelines
- Review for this journal
- Publication charges
- Journal collections
- Pricing and ordering
Journal information
- 2019-present Engineering Research Express doi: 10.1088/issn.2631-8695 Online ISSN: 2631-8695
- ASME Foundation
- Sections & Divisions
- Sign In/Create Account
- Publications & Submissions
- Find Journal
- Journal of Manufacturing Science & En...
Journal of Manufacturing Science & Engineering
This Standard was last reviewed and reaffirmed in {{activeProduct.ReaffirmationYear}}. Therefore this version remains in effect.
{{activeProduct.DisplayTitle}}
Digital products are restricted to one per purchase.
{{activeProduct.CurrencySymbol}}{{ formatPrice(activeProduct.ListPrice) }} activeProduct.ListPrice"> was {{activeProduct.CurrencySymbol}}{{ formatPrice(originalPrice) }}
{{activeProduct.CurrencySymbol}}{{ formatPrice(activeProduct.ListPriceSale) }} activeProduct.ListPriceSale"> was {{activeProduct.CurrencySymbol}}{{ formatPrice(activeProduct.ListPrice) }}
{{activeProduct.CurrencySymbol}}{{ formatPrice(activeProduct.ListPriceSale) }} activeProduct.ListPriceSale"> was {{activeProduct.CurrencySymbol}}{{ formatPrice(originalPrice) }}
0}"> {{activeProduct.CurrencySymbol}}{{ formatPrice(activeProduct.MemberPrice) }} activeProduct.MemberPrice"> was {{activeProduct.CurrencySymbol}}{{ formatPrice(originalPrice) }}
0"> {{activeProduct.CurrencySymbol}}{{ formatPrice(activeProduct.MemberPriceSale) }} activeProduct.MemberPriceSale"> was {{activeProduct.CurrencySymbol}}{{ formatPrice(originalPrice) }}
Become a member
*Excluding Lite Members
Final invoices will include applicable sales and use tax.
Print or Share
Product options.
- Format Availability Order No. Price List Price Member Price
- Print Journal Immediately MANU List $1343 Member $134.30 $1343 $134.30 Select Selected
- Online Journal Immediately MANUOL List $1000 Member $100 $1000 $100 Select Selected
Containing cutting-edge research in the multi-disciplinary area of engineering for industry, this journal presents technical papers, discussions, technical briefs, and more. Specific topics of interest are: computer-related manufacturing; design for manufacturing; expert sustems in manufacturing; grinding and abrasive machining; inspection and quality control; machine tool control manufacturing automation; metal forming and forging; material removal by machining; nontraditional manufacturing processes; process simulation; production systems optimization; rail transportation; robotics and flexible tooling; sensors; textile production; and welding. Published: Monthly
Subscriptions currently include the years 2000 - present. Access to archived content prior to the year 2000 can be obtained with an instututional subscription or an ASME Member Article Pack.
Please allow three to five days for electronic subscription activation.

Add a new code entry for this paper
Remove a code repository from this paper, mark the official implementation from paper authors, add a new evaluation result row, remove a task, add a method, remove a method, edit datasets, human factors in model-driven engineering: future research goals and initiatives for mde.
29 Apr 2024 · Grischa Liebel , Jil Klünder , Regina Hebig , Christopher Lazik , Inês Nunes , Isabella Graßl , Jan-Philipp Steghöfer , Joeri Exelmans , Julian Oertel , Kai Marquardt , Katharina Juhnke , Kurt Schneider , Lucas Gren , Lucia Happe , Marc Herrmann , Marvin Wyrich , Matthias Tichy , Miguel Goulão , Rebekka Wohlrab , Reyhaneh Kalantari , Robert Heinrich , Sandra Greiner , Satrio Adi Rukmono , Shalini Chakraborty , Silvia Abrahão , Vasco Amaral · Edit social preview
Purpose: Software modelling and Model-Driven Engineering (MDE) is traditionally studied from a technical perspective. However, one of the core motivations behind the use of software models is inherently human-centred. Models aim to enable practitioners to communicate about software designs, make software understandable, or make software easier to write through domain-specific modelling languages. Several recent studies challenge the idea that these aims can always be reached and indicate that human factors play a role in the success of MDE. However, there is an under-representation of research focusing on human factors in modelling. Methods: During a GI-Dagstuhl seminar, topics related to human factors in modelling were discussed by 26 expert participants from research and industry. Results: In breakout groups, five topics were covered in depth, namely modelling human aspects, factors of modeller experience, diversity and inclusion in MDE, collaboration and MDE, and teaching human-aware MDE. Conclusion: We summarise our insights gained during the discussions on the five topics. We formulate research goals, questions, and propositions that support directing future initiatives towards an MDE community that is aware of and supportive of human factors and values.
Code Edit Add Remove Mark official
Datasets edit.
Princeton University
Princeton engineering, the science of static shock jolted into the 21st century.
By Scott Lyon
April 9, 2024

Static electricity has puzzled scientists for thousands of years. Above, water ions carry charge between two electrically insulating materials. The blue mesh represents the flow of charge that could be felt as a spark. Image courtesy of the researchers
Shuffling across the carpet to zap a friend may be the oldest trick in the book, but on a deep level that prank still mystifies scientists, even after thousands of years of study.
Now Princeton researchers have sparked new life into static. Using millions of hours of computational time to run detailed simulations, the researchers found a way to describe static charge atom-by-atom with the mathematics of heat and work. Their paper appeared in Nature Communications on March 23.
The study looked specifically at how charge moves between materials that do not allow the free flow of electrons, called insulating materials, such as vinyl and acrylic. The researchers said there is no established view on what mechanisms drive these jolts, despite the ubiquity of static: the crackle and pop of clothes pulled from a dryer, packing peanuts that cling to a box.
“We know it’s not electrons,” said Mike Webb , assistant professor of chemical and biological engineering , who led the study. “What is it?”
Webb first asked himself that question as a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Chicago. He puzzled over it with colleagues, baffled that such a common phenomenon could be so poorly understood. But the more they looked, the more insurmountable the questions became. “It just seemed out of reach,” he said.

It had been out of reach since Thales of Miletus first rubbed amber with fur and watched the amber (Greek: elektron ) collect feathers and dust — 26 centuries ago. Thales was one of the first people to explain nature through reason rather than supernatural forces. He played a critical role in the development of philosophy and eventually science. Despite the depth and breadth of knowledge accumulated over subsequent millennia, despite the myriad technologies born of that knowledge, science, in all that time, never cracked static. Maybe it never would.
At Princeton Webb got to talking to his colleague Sankaran Sundaresan , a leading expert in chemical reaction engineering who specializes in the flow of materials in gaseous chambers. In those environments, loaded with volatile chemicals, a stray spark could be deadly. Sundaresan had worked with static charge for decades, using reliable experimental data to predict but not fully fathom how charge moved in these systems.
“I treat that like a black box,” said Sundaresan, the Norman John Sollenberger Professor in Engineering. “We do some experiments and the experiments tell me: This is what happens. This is the charge.” He works down to the limit and carefully notes what he sees. What happens inside the black box remains a mystery.
One thing you find no matter where you look, though, according to Sundaresan, is trace amounts of water. Charged water molecules are everywhere, in nearly everything, clinging to virtually every surface on Earth. Even in extremely arid conditions, under intense heat, stray water ions pool into microscopic oases that harbor electrical charge.
Incidentally, Thales is best known not for his work on electricity but for an even grander project. He proposed that the entirety of nature was made of water, that water was the ur-substance, the essential stuff. It was the first attempt at a unified theory of everything. Aristotle wrote it all down.
Over the arc of Sundaresan’s career, he and his colleagues shrunk that black box so that the mysteries have been pushed ever deeper. But mysteries they remain.
The conversation between him and Webb led to a mutual realization: Sundaresan had decades of insight into data from reactors, and Webb could apply sophisticated atom-scale computational techniques to look at these water ions from the perspective of thermodynamics. How much energy would it take for a water ion to bolt from surface to surface? Maybe that would explain what was happening inside Sundaresan’s black box. The unresolved puzzle from Webb’s postdoc days came unlocked.
By modeling the relationship between charged water molecules and the amount of energy those molecules have available to propel them between surfaces, Webb and graduate student Hang Zhang demonstrated a very precise mathematical approximation of how electrical charge moves between two insulating materials.
In other words, they used math to simulate the movement of around 80,000 atoms. Those simulations matched real-life observations with a very high degree of precision. It turns out, in all likelihood, static shock is a function of water, and more specifically, the free energy of stray water ions. With that framework, Webb and Zhang revealed the molecular underpinnings of those familiar shocks in infinitesimal detail. They blew Sundaresan’s black box wide open. If only Thales could see.
The paper “Thermodynamic driving forces in contact electrification between polymeric materials” was published March 23 in the journal Nature Communications. Support for this work was provided by the Princeton Innovation Project X Fund and the U.S. Department of Energy. The simulations and analyses were performed using the resources of Princeton Research Computing.
Related News

Holographic displays offer a glimpse into an immersive future

Elke Weber receives BBVA Frontiers of Knowledge Award

Grad alum Avi Wigderson wins Turing Award for groundbreaking insights in computer science

Episode 4: Bethany Beardslee Winham and Chris Winham

Retro-reflectors could help future cities keep their cool

Episode 3: Haydn Seek

Michael A. Webb

Sankaran Sundaresan

Materials Science and Engineering
Related departments and centers.

Chemical and Biological Engineering

Princeton Materials Institute
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Artificial Intelligence
Title: crispr-gpt: an llm agent for automated design of gene-editing experiments.
Abstract: The introduction of genome engineering technology has transformed biomedical research, making it possible to make precise changes to genetic information. However, creating an efficient gene-editing system requires a deep understanding of CRISPR technology, and the complex experimental systems under investigation. While Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promise in various tasks, they often lack specific knowledge and struggle to accurately solve biological design problems. In this work, we introduce CRISPR-GPT, an LLM agent augmented with domain knowledge and external tools to automate and enhance the design process of CRISPR-based gene-editing experiments. CRISPR-GPT leverages the reasoning ability of LLMs to facilitate the process of selecting CRISPR systems, designing guide RNAs, recommending cellular delivery methods, drafting protocols, and designing validation experiments to confirm editing outcomes. We showcase the potential of CRISPR-GPT for assisting non-expert researchers with gene-editing experiments from scratch and validate the agent's effectiveness in a real-world use case. Furthermore, we explore the ethical and regulatory considerations associated with automated gene-editing design, highlighting the need for responsible and transparent use of these tools. Our work aims to bridge the gap between beginner biological researchers and CRISPR genome engineering techniques, and demonstrate the potential of LLM agents in facilitating complex biological discovery tasks.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
Aerospace engineering articles from across Nature Portfolio
Aerospace engineering is the branch of engineering that designs and builds machines for flight. This includes craft used both inside (aeronautical engineering) and outside (astronautical engineering) the Earth’s atmosphere. Aerospace engineering combines an understanding of fluid dynamics, robust but lightweight materials and the chemistry and thermodynamics of engines.
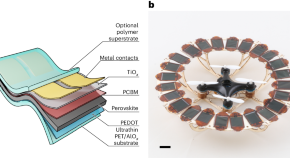
Ultralightweight perovskite solar cells for use in drones
Ultralightweight perovskite solar cells that achieve a specific power of up to 44 W g –1 and good stability are developed through engineering of the photoactive layer and substrate. These solar cells can be integrated into a drone to enable energy-autonomous flight.
Latest Research and Reviews
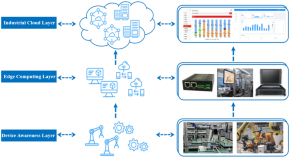
An imbalance data quality monitoring based on SMOTE-XGBOOST supported by edge computing
- Guotian Huang
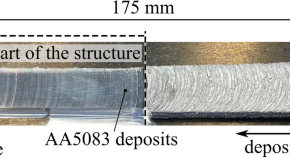
Corrosion behavior of multi-layer friction surfaced structure from dissimilar aluminum alloys
- Eduardo Antunes Duda
- Zina Kallien
- Benjamin Klusemann
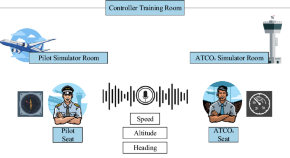

SLKIR: A framework for extracting key information from air traffic control instructions Using small sample learning
- Peiyuan Jiang
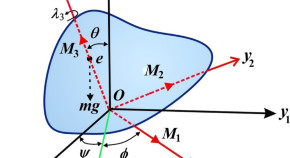
Analyzing the dynamics of a charged rotating rigid body under constant torques
- H. F. El-Kafly
- A. A. Galal
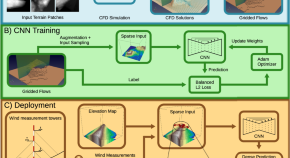
WindSeer: real-time volumetric wind prediction over complex terrain aboard a small uncrewed aerial vehicle
Wind has a large impact on the safety and efficiency of small uncrewed aerial vehicles. Here, the authors present a neural network-based method for estimating the wind at meter-scale resolution around complex terrain solely based on terrain knowledge and local onboard wind observations.
- Florian Achermann
- Thomas Stastny
- Nicholas Lawrance
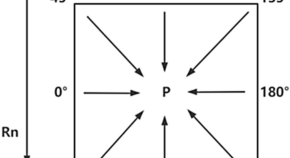
A dense matching method for remote sensing images fused with CPS denoising
News and Comment
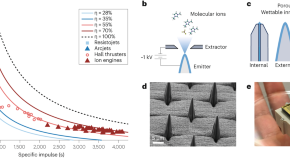
Design and microstructuring of materials to boost spacecraft ion propulsion
As new materials and manufacturing techniques are discovered, their benefits transform every branch of science and engineering. In spacecraft propulsion, a new generation of ion engines could provide unprecedented performance and flexibility in space mission design.
- Paulo C. Lozano
Domains of life sciences in spacefaring: what, where, and how to get involved
The integration of biology and spacefaring has led to the development of three interrelated fields: Astrobiology, Bioastronautics, and Space Bioprocess Engineering. Astrobiology is concerned with the study of the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe, while Bioastronautics focuses on the effects of spaceflight on biological systems, including human physiology and psychology. Space Bioprocess Engineering, on the other hand, deals with the design, deployment, and management of biotechnology for human exploration. This paper highlights the unique contributions of each field and outlines opportunities for biologists to engage in these exciting avenues of research. By providing a clear overview of the major fields of biology and spacefaring, this paper serves as a valuable resource for scientists and researchers interested in exploring the integration of these disciplines.
- Aaron J. Berliner
- Spencer Zezulka
- Adam P. Arkin
Propelling the widespread adoption of large-scale 3D printing
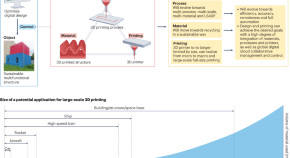
3D printing can be used to automate the manufacturing of building elements for large-scale structures such as skyscrapers, aircraft, rockets and space bases without human intervention. However, challenges in materials, processes, printers and software control must first be overcome for large-scale 3D printing to be adopted for widespread applications.
- Wouter De Corte
- Viktor Mechtcherine
Europe’s Ariane woes
With the retirement of Ariane 5, Europe lost its only heavy-lift rocket — one that carried most of ESA’s fleet of large astronomy missions. The long-term future of independent access to space for Europe is not straightforward and can complicate the European space exploration roadmap.

A 3D-printed alloy that can face extreme environments
An article in Nature reports an alloy that can be 3D printed and has improved mechanical properties at high temperatures compared with current state-of-the-art 3D-printable alloys.
- Charlotte Allard
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

Recent Developments in Structural Engineering, Volume 1
- Conference proceedings
- © 2024
- Manmohan Dass Goel 0 ,
- Ratnesh Kumar 1 ,
- Sangeeta S. Gadve 2
Department of Applied Mechanics, Visvesvaraya National Institute of Technology, Nagpur, India
You can also search for this editor in PubMed Google Scholar
- Presents the select proceedings of 13th Structural Engineering Convention
- Covers the latest research in multidisciplinary areas within structural engineering
- Covers topics such as structural dynamics, structural mechanics, finite element methods, etc.
Part of the book series: Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering (LNCE, volume 52)
Included in the following conference series:
- SEC: Structural Engineering Convention
Conference proceedings info: SEC 2023.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this book
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Other ways to access
Licence this eBook for your library
Institutional subscriptions
Table of contents (65 papers)
Front matter, optimum sph parameters for ballistic impact on ceramic tiles: a parametric study.
- M. D. Umbharatwala, P. Vinoth, Manmohan Dass Goel
Blast Retrofitting of Reinforced Concrete Structures Using Jacketing Schemes
- Rohan G. Raikar, Muhammed Zain Kangda, Nilesh Mate, Sandeep Sathe
A Comparative Study of AdaBoost and K-Nearest Neighbor Regressors for the Prediction of Compressive Strength of Ultra-High Performance Concrete
- Rakesh Kumar, Baboo Rai, Pijush Samui
Design Perspectives of the Structural Modes for Ground Liquid Storage Steel Tanks
- Zalakkumar R. Chhaya, Vipul Prakash
Reliability Based Design Optimization (RBDO) of Randomly Imperfect Thin Cylindrical Shells Against Post-Critical Drop
- Rohan Majumder, Sudib K. Mishra
Investigation on Influence of Embedment Depth of Foundation on Seismic Response of Building Considering Soil—Structure Interaction
- Vaibhav Mittal, Manojit Samanta
Structural Response of Shaped Concrete Units Subjected to Blast Loading: A Parametric Study
- Sreekumar Punnappilly, K. Baskar
Numerical Study of Damage Evaluation of Plain Concrete Under Projectile Impact
- Ajay Kumar, Kailash Kumar, M. A. Iqbal
Numerical Study on Ballistic Resistance of Whipple Shield Under Different Ellipsoid Projectiles Against Hypervelocity Impact
- Kailash Kumar, Ajay Kumar, M. A. Iqbal, P. K. Gupta
A Review on the Usage of Graphene in Cementitious Material
- Malaiappan Sindhu Muthu, Mallikarjun Perumalla
Prediction of Stress Fields in Particulate Polymer Composites Using Micromechanics-Based Artificial Intelligence Model
- Sristi Gupta, Tanmoy Mukhopadhyay, Divyesh Varade, Vinod Kushvaha
Underground Blast Induced Vibration Control of Building Isolated with Shape Memory Alloy Friction Pendulum
- Mohammad Yasir Mohammad Hasan Shaikh, Sourav Gur
Response of Aluminum and CFRP Plates to Successive Blast Loads
- Yash M. Chordiya, Manmohan Dass Goel, Vasant A. Matsagar
Should EBFs Be Preferred Over CBFs in EQRD?
- P. N. Panda, R. Selot, A. Chakrabarti, V. Prakash
Preliminary Static Analysis of Suspension Bridges
- R. Selot, P. N. Panda, V. Prakash
A Reduced Order Model for Damage Detection of Dynamic Problems
- Samrul Hoda, Biswarup Bhattacharyya
Cross-Section Based Performance Assessment of Buckling Restrained Braces
- Prachi Mishra, Arvind Y. Vyavahare
Experimental Analysis of Traditional Kath-Kuni Wall System
- Chetival Survesh, Chikermane Sanjay
Effect of Dynamic Material Strength on Blast Response of Earthquake-Resistant RC Buildings
- Shivalinga Baddipalli, Mahipal Kulariya, Sandip Kumar Saha
Other volumes
- Structural Fire Engineering
- Earthquake Engineering /Structural Dynamics/ Seismic Control
- AI and Machine Learning in Structural Engineering
- Concrete Structures
- Steel Structures
About this book
The book presents the select proceedings of 13th Structural Engineering Convention. It covers the latest research in multidisciplinary areas within structural engineering. Various topics covered include structural dynamics, structural mechanics, finite element methods, structural vibration control, advanced cementitious and composite materials, bridge engineering, soil-structure interaction, blast, impact, fire, material and many more. The book will be a useful reference material for structural engineering researchers and practicing engineers.
Editors and Affiliations
Manmohan Dass Goel, Ratnesh Kumar, Sangeeta S. Gadve
About the editors
Dr. Manmohan Dass Goel completed his Bachelor of Engineering from Yeshwantrao Chavan College of Engineering, Nagpur. He was awarded three gold medals by Nagpur University for academic excellence. He completed Master of Technology (M. Tech.) in offshore engineering from Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Bombay, Mumbai in year 2003. His Ph. D. is from Department of Civil Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Delhi and University of Federal Armed Forces, Munich, Germany under German Academic Exchange Service (DAAD) Sandwich Fellowship in year 2013. The topic of his doctoral research was "Blast Response of Structures and Its Mitigation Using Advanced Lightweight Materials". He was awarded Surendranath Mukherjee Memorial Medal for best research paper by Institution of Engineers (India) in year 2009. He has been selected Young Ambassador by German Academic Exchange Services (DAAD) for consecutively for two years. His doctoral thesis has been awarded as the bestthesis by the Indian National Academy of Engineering under "Innovative Student Project Award 2013" at doctoral level in Civil Engineering discipline. He has been awarded “CSIR Young Scientist Awards-2014” in Engineering Sciences by CSIR. He is recipient of “Young Engineer Award” from Institution of Engineers (India) in 2014. He has been nominated as “DAAD Research Ambassador” by German Academic Exchange Services (DAAD). He is also recipient of “Young Associate”, Maharashtra Academy of Sciences, Maharashtra in year 2015. His paper has been awarded IGS-HEICO Biennial Award- 2017 by Indian Geotechnical Society (IGS), India as a best paper on “Rock Mechanics” published in Indian Geotechnical Journal through Indian Geotechnical Society (IGS). He has been interviewed by Rajya Sabha TV under popular science program “Eureka” in recognition of contribution to the R&D in Engineering Sciences. He has been a Senate Member of ACSIR (Academy of Scientific & Innovative Research) CSIR, Delhi. Currently he is serving as Associate Professor, Department of Applied Mechanics, Visvesvaraya National Institute of Technology (VNIT), Nagpur. Prior to this, he served CSIR-AMPRI Bhopal and CSIR-National Environmental Engineering Research Institute (NEERI) Nagpur, India as a Scientist. He has more than 150 international and national journal/conference publications to his credit. His areas of research interest include blast analysis, blast resistant structures, lightweight materials, composite structures, low, medium and high strain rate material characterization and computational mechanics. He is looking forward to contribute in the broader areas of structural protection systems used against blast and impact loading.
Dr. Ratnesh Kumar is Professor in the Department of Applied Mechanics at Visvesvaraya National Institute of Technology (VNIT), Nagpur, where he has been since 2012. Prior to VNIT he was associated with various academia and industry; he worked with Earthquake Engineering Department, Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee as Fellow B, Assistant Professor at School of Engineering, Gautam Buddha University and Head of Structural Design Division in Privitech Consulting Engineers Pvt. Limited, New Delhi. He received Bachelor of Civil Engineering from Bangalore University in the year 2000, M. Tech and Ph. D from Earthquake Engineering Department, Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee. His research interests span both in structural engineering and earthquake engineering. Much of his work has been on improving the understanding, design, and performance of reinforced concrete structures. He is also working in the area of seismic evaluation and retrofitting and seismic risk assessment. He is also heading various laboratories such as: Advanced Computing, Earthquake Engineering and Structural Fire Engineering laboratory at VNIT. He has guided 3 Ph. D. and 28 M. Tech thesis and presently two Ph.D. students are working under his guidance. He has given more than twenty-five invited talks and tutorials at various academic and industrial forum, coordinated fifteen short-term courses and workshops on various aspects of structural and earthquake engineering and published more than sixty research papers in reputed journals and conferences. He is associated with various research projects of more than fifteen million rupees and handled consultancy project of more than twenty million rupees. He received Sir Arthur Cotton Memorial Prize (IEI) in 2011. He is member of Indian Water Works Association, Institution of Engineers (India), Bamboo Society of India and Indian Society of Earthquake Technology. In the later he also served as executive committee member during 2011-12. He is reviewer of many journals such as American Concrete Institute, Engineering Structures, Bulletin of Earthquake Engineering, Journal of Structural Fire Engineering and many more.
Dr. Sangeeta Gadve is Professor in the Department of Applied Mechanics at Visvesvaraya National Institute of Technology (VNIT), Nagpur. She joined VNIT, Nagpur in 2012, prior to which she was working with Sardar Patel College of Engineering, Mumbai as an Associate Professor since 1994. Dr. Gadve received her Bachelor of Civil Engineering from VNIT (then VRCE) in the year 1991, Masters in Structural Engineering from Mumbai University and Ph. D from Department of Civil Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Mumbai. Her research interest lies in Concrete Technology with specialization in Corrosion of rebar in concrete. Other than rebar corrosion in concrete, she has worked in evaluation of various concrete properties that include shear strength and Elasticity Modulus of plain concrete. She also works in the field of repairs and rehabilitation of reinforced concrete structures. He has set up an Advanced Concrete Technology Laboratory at VNIT which has got state of the art testing facilities. She has guided 4 Ph.D. and over 40 M.Tech dissertations. She has delivered over 30 invited talks at various academic and industrial forums. She has published more than fifty research papers in reputed journals and conferences. She has three Patents granted to her credit. She is working on various industry sponsored research projects as well as handled various consultancy projects. She is member of Indian Water Works Association, Institution of Engineers (India), Indian Society of Technical Education, Indian Concrete Institute, Association of Structural Rehabilitation. She is reviewer of journals such as American Concrete Institute, Indian Concrete Institute Engineering Structures.
Bibliographic Information
Book Title : Recent Developments in Structural Engineering, Volume 1
Editors : Manmohan Dass Goel, Ratnesh Kumar, Sangeeta S. Gadve
Series Title : Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-9625-4
Publisher : Springer Singapore
eBook Packages : Engineering , Engineering (R0)
Copyright Information : The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd. 2024
Hardcover ISBN : 978-981-99-9624-7 Published: 03 May 2024
Softcover ISBN : 978-981-99-9627-8 Due: 03 June 2024
eBook ISBN : 978-981-99-9625-4 Published: 02 May 2024
Series ISSN : 2366-2557
Series E-ISSN : 2366-2565
Edition Number : 1
Number of Pages : XVII, 689
Number of Illustrations : 54 b/w illustrations, 324 illustrations in colour
Topics : Building Construction and Design , Solid Construction , Sustainable Architecture/Green Buildings , Structural Materials
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Read the latest Research articles in Engineering from Scientific Reports. ... Research on the method of determining the block size for an open-pit mine integrating mining parameters and shovel ...
Journal of Engineering Research (JER) is an international, peer reviewed journal which publishes full length original research papers, reviews and case studies related to all areas of Engineering such as: Civil, Mechanical, Industrial, Electrical, Computer, Chemical, Petroleum, Aerospace, Architectural, etc. JER is intended to serve a wide range of educationists, scientists, specialists ...
Sage publishes over 50 engineering journals. The collection includes the 18 journals of the Institution for Mechanical Engineers as well other research in robotics, computing and textiles. The collection also features the leading open access journal in its field, Advances in Mechanical Engineering. Download new special issues, collections, and ...
Mechanical engineering articles from across Nature Portfolio. Mechanical engineering is the branch of engineering that deals with moving machines and their components. A central principle of ...
Engineering Reports is an open access engineering and computer science journal with a broad scope, addressing questions relevant to academia, industry or government. We quickly publish rigorously peer reviewed, well-conducted scientific research, covering areas including biological, chemical, civil, software, electrical, industrial, and mechanical engineering, as well as other engineering ...
Engineering Research Express. ISSN: 2631-8695. SUPPORTS OPEN ACCESS. Engineering Research Express (ERX) is a broad, multidisciplinary journal devoted to publishing new experimental and theoretical research covering topics extending across all areas of engineering science including interdisciplinary fields.
Advances in Mechanical Engineering (AIME) is a JCR Ranked, peer-reviewed, open access journal which publishes a wide range of original research and review articles. The journal Editorial Board welcomes manuscripts in both fundamental and applied research areas, and encourages submissions which contribute novel and innovative insights to the field of mechanical engineering.
Research in Engineering Design is a journal that publishes research papers on design theory and methodology across all engineering fields. Focuses on mechanical, civil, architectural, and manufacturing engineering. Emphasizes the underlying principles of engineering design. Examines theories of design, foundations of design environments, and ...
The disciplines of engineering are all described as the application of science to realistic systems which benefit humankind [1]. Engineering research is therefore based on the principles of scientific research which, in turn, are based on the scientific method, in which observations (experiments), theories, calculations and models are derived ...
ASCE Library. Celebrating 150 Volumes 2024. ASCE flagship journals reach the 150th volume milestone. Read select papers that reflect on our past and help us imagine the future. Read More. Standard 2022.
A research paper should not exceed 12,000 words. Beyond this amount, a mandatory excess-page charge can be assessed. These charges are described here: Publication Charges. To estimate figures and tables: 1 journal page = 1000 words. Half-journal page or a single column = 500 words. Half-column = 250 words.
Paper types considered are original research articles, case histories, and comprehensive reviews. Case studies, in particular, should emphasize why the paper is of interest to the international readership of this journal, and/or what new or novel research or theoretical methods are being presented. ... Engineering Geology 2023 Best Papers Award ...
Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering is a civil engineering journal bridging advances in computer technology with civil & infrastructure engineering. Abstract In this paper, we present a method based on an ensemble of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for the prediction of residual drift capacity in unreinforced damaged ...
can follow to write a good and interesting engineering research paper.. Guide to write Engineering research Paper. Plan your research early: Many students who are less comfortable with research ...
This collection highlights our most downloaded* engineering papers published in 2022. Featuring authors from around the world, these papers showcase valuable research from an international community.
1 Introduction. The term origami refers to the commonly known ancient art of paper folding. It finds its roots in the composition of the Japanese words oru, which means "fold," and kami, which means "paper." [] In the course of its long tradition, it has been known by a variety of names including orisue [] and orikata. [] Despite its popularity, it might be surprising to know that the ...
This paper provides a scoping literature review of STT in engineering education, focusing on research purposes, methodologies, findings, and potential gaps. Our examination of 25 papers indicates that research on STT in engineering education covers a variety of purposes and methodologies. Key findings in the literature provide a better ...
Get papers online in the ASME Digital Collection. This journal presents technical papers, discussions & technical briefs from a cutting-edge research in the multi-disciplinary area of engineering.
Methods: During a GI-Dagstuhl seminar, topics related to human factors in modelling were discussed by 26 expert participants from research and industry. Results: In breakout groups, five topics were covered in depth, namely modelling human aspects, factors of modeller experience, diversity and inclusion in MDE, collaboration and MDE, and ...
The science of static shock jolted into the 21st century. Static electricity has puzzled scientists for thousands of years. Above, water ions carry charge between two electrically insulating materials. The blue mesh represents the flow of charge that could be felt as a spark. Image courtesy of the researchers.
The introduction of genome engineering technology has transformed biomedical research, making it possible to make precise changes to genetic information. However, creating an efficient gene-editing system requires a deep understanding of CRISPR technology, and the complex experimental systems under investigation. While Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promise in various tasks, they ...
In this paper the analysis of real methods of calculation of heat losses of underground tunnel is accomplished. ... Bodrov, M. Bodrov, K. Lushin International Journal of Applied Engineering Research 22, 43277-43280 (2015) 9. A. G. Rymarov, Natural and technical sciences 63, 380-382 (2013) 10. A. G. Rymarov, Academia.
Adhesion and agglomeration of small sticky particles, i.e., microstickies, onto paper and paper machines cause serious problems for recycling mills. Because associations between materials with similar surface energies are strongest, we propose an "adhesives collect stickies" strategy to physically remove microstickies from whitewater systems. We characterized deposits from a commercial ...
Aerospace engineering articles from across Nature Portfolio. Aerospace engineering is the branch of engineering that designs and builds machines for flight. This includes craft used both inside ...
This paper mainly explore the analyze the construction technology of the prestressed reinforced concrete pipe in municipal water supply and drainage engineering. View full-text Article
The book presents the select proceedings of 13th Structural Engineering Convention. It covers the latest research in multidisciplinary areas within structural engineering. Various topics covered include structural dynamics, structural mechanics, finite element methods, structural vibration control, advanced cementitious and composite materials ...
This paper examines the history and social life of the underground public spaces in three Moscow Metro stations just north of Red Square and the Kremlin: Okhotny Ryad, Tverskaya, and Ploshchad Revolyutsii stations. Moscow's subway originated from two motivations: to improve the public transit system and to revitalize Moscow's centre instead ...