A collection of TED Talks (and more) on the topic of Trust.

Talks about Trust

5 steps to fix any problem at work

The awesome potential of many metaverses

What Wikipedia teaches us about balancing truth and beliefs

7 tools for building a business people trust

How your brain responds to stories -- and why they're crucial for leaders

An aerialist on listening to your body's signals

Dignity isn't a privilege. It's a worker's right

The future of digital communication and privacy

Why winning doesn't always equal success

How to break bad management habits before they reach the next generation of leaders

Confessions of a recovering micromanager

What to trust in a "post-truth" world

The age-old sharing economies of Africa -- and why we should scale them

How to build (and rebuild) trust

A better way to talk about love

How the blockchain will radically transform the economy
Exclusive articles about trust, 7 ways to build greater trust in all of your partnerships, how to raise kids who will grow into secure, trustworthy adults, where in the world will you find the most advanced e-government estonia..
- Presentation Hacks
6 Ways to Build Trust With Any Audience | Public Speaking
- By: Scott Schwertly
Trust. We desire it in all of our relationships whether it is our spouse, parent, or best friend. Why should presentation environments be any different? The best presenters know how to build and maintain trust with their audience. They establish it in the beginning, hold it throughout their talk, and finish with it.
Are you curious how you can create and maintain trust? I’ve got six recommendations for you.
Presentations that are built on trust add value. Plain and simple. The speaker has the intentional goal to improve the lives of their audience. The lift them up, and they empower them with information they did not before the session.
The question to ask yourself: “Am I adding value?”
Information
We live in a very Google-centric society where anyone can find anything they are looking for at any given time. So, you have two main challenges: 1. Is your information accurate? and more importantly, 2. Does the information you are providing help with the business decision making process?
For instance, if you are asking your audience to invest time to hear you make a pitch, is the information you are sharing empower them enough to make a decision when you are done or do you have gaps in your content that are still left unanswered.
The question to ask yourself: “Is my information empowering them to make a decision?”
Influence. We all seek it because we all want to make an impact on the people in our life. In the case of presentations, the only way you are going to be influential is if you are confident. And, confidence comes from preparation.
The elephant in the room on preparation is how many times should you present. My answer to this question is something I like to call the “Plus 10” rule. Simply, take the number of minutes of your talk, add 10, and that is how many times you should practice your talk. In other words, a 30 minute talk (plus 10) would be mean you should rehearse 40 times.
The question to ask yourself: “Did I practice my talk enough?”
We’ve been told most of our lives to “just be yourself.” It sounds generic but there is a reason why this advice continues to live on. Integrity is accomplished by being you and not someone else. As an audience member, it is super easy to pinpoint that poser or faker. You don’t want to be that victim so you need to be diligent about tapping into your public speaking strengths and let them shine.
The question to ask yourself: “Am I authentic with my message and approach?”
This next section is all about the headline – did you make an impact on your audience? Solid presentations are memorable. They create discussion. They create wonder. They get people talking about important issues. It is your responsibility as a presenter, to create those memorable moments for your audience by crafting a message and providing a delivery of that content in the most impactful way.
The question to ask yourself: “Is my presentation going to be memorable?”
And finally, we have the last component which is all about ignition. This concept is about whether you have actually ignited your audience to do something. To put it in a business context, did you include a call-to-action. Every presentation must have a call-to-action. It’s the entire reason why your talk exists so make sure you provide a mission and purpose behind your message.
The question to ask yourself: “Do I have a call-to-action?”
Building trust is an effort which takes time and intentionality. However, it can be accomplished in a presentation environment if you apply the above six principles. They will give you an amazing foundation to work from and you should be earning and maintaining credibility with every person in the room.
Scott Schwertly
Join our newsletter today.
© 2006-2024 Ethos3 – An Award Winning Presentation Design and Training Company ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Diversity and Inclusion
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

17 templates

9 templates

tropical rainforest
29 templates

summer vacation
19 templates

islamic history
36 templates

american history
70 templates
Trust Building for Teams Meeting
Trust building for teams meeting presentation, free google slides theme and powerpoint template.
Your team at work is who you spend most of your time with, who you learn with and who you spend your hardest days with. That’s why your workplace should be a safe environment full of trust. How can you build it? Speak about it with this design for a meeting and help your coworkers build healthy relationships between each other with this beautiful presentation
Features of this template
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- 27 different slides to impress your audience
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics such as graphs, maps, tables, timelines and mockups
- Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides and Microsoft PowerPoint
- 16:9 widescreen format suitable for all types of screens
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the resources used
How can I use the template?
Am I free to use the templates?
How to attribute?
Attribution required If you are a free user, you must attribute Slidesgo by keeping the slide where the credits appear. How to attribute?
Related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access

Sales | Business | Persuasion
4 ways to establish trust in your presentation or sales pitch.
Written by Eugene Cheng

There’s no doubt that a riveting story structure and a visually arresting deck are both requisites of a great presentation or pitch. However, apart from the other presentation mistakes you might make , all your work developing your presentation might be for naught if your audiences don’t trust you. If you can’t establish credibility early on in your presentation, it’s as good as not delivering the presentation in the first place as your messages will likely fall on deaf ears and you can’t influence your audience.
The adage: “Trust isn’t given, it’s earned.” usually rings true here. Problem is, trust is typically hard to earn and sometimes, you simply don’t have the luxury of time to build trust quickly from scratch on the first contact with your audience.
Unlike personal selling, you don’t always get to build rapport with your audience on a one-to-one basis. Instead, it’s likely you’ll only be able to speak to a group of people at a time when you’re delivering a presentation.
From our experience, your credibility during a presentation depends on a few factors
i) If the audiences feel you are authentic and honest as a speaker
Nobody likes a sleazy salesperson. If you appear to be untrustworthy or evasive when delivering your presentation, you can expect to face obstacles getting them to take action or believe what you say.
ii) Whether you are perceived as an expert on your topic of choice
There are way too many people calling themselves gurus in the market and audience members are quick to make snap judgments based on whether you have the requisite knowledge or expertise.
iii) How well you can appeal to your audiences
Even if you hit all the right notes in the other two areas, you might not always be able to appeal to certain audience members that might have deep-seated prejudices which go against your cause.
Here are 5 ways to implicitly build and establish trust as you’re delivering your presentation :
1. Back up what you say with evidence
It’s easy to make sweeping claims like: “We’re the best company in this industry”, but supporting these audacious statements with hard facts and data is where it gets challenging.
Naturally, you won’t always have research papers to back up every assertion or opinion you might have. Here are some ways to reference other people or hard evidence in varying degrees of credibility:
Referencing actual research papers and aggregated statistics

You’d be surprised at the extent of research that has been published. Scientists have conducted experiments and research on anything from cognitive biases on how to be more persuasive to stats on mobile penetration in specific countries.
For example, in a formal business presentation setting, there’ll be occasions where you’ll need to reference quantitative evidence on why certain business decisions need to be made. These obviously can’t be based on your own personal opinion but hard, indisputable factual evidence. Using data in your presentations is essential to building trust.
Quote respected authorities or experts

In some cases where you’re trying to make a case to take action on something that you can’t find quantitative data on, citing a strong ‘endorsement’ or quote from an authority figure is the next best thing.
Similarly to how we trust authority figures purely via conditioned behaviour in our lives (doctors, police, teachers) as theorized by Robert Cialdini in his book, Influence , we tend to lend trust to people whoare considered authorities in their respective fields (aka the Principle of Authority). Principles from Influence also apply in presentations.
For example, Jack Ma of Alibaba has risen to fame as an entrepreneur and business magnate to the extent that his foresight on market climates and the ‘future’ of industries is widely cited. Can we say that his statements are 100% accurate? No. Yet, we still afford his words credibility because of his stature, background, and inherent expertise.
2. Develop your expert identity

A Nielsen research study found that consumers in a marketing setting unanimously seek out information and take action on content provided by companies or journalists they perceive to be experts.
It is integral that when you’re speaking on a topic, you have to be perceived as someone that has the relevant expertise and that you ‘know what you’re talking about’.
A way to do this implicitly is weaving a mix of client testimonials, credentials and relevant awards to signify your deep domain knowledge and expertise.
Show past client testimonials and credentials

A great way to immediately build credibility is having someone else talk about you in a positive light. Testimonials are a quick way to do this without seeming like you’re selling yourself – instead, it’s someone else doing the selling.
In Robert Cialdini’s epic, Influence: The Psychology Of Persuasion , this effect is known as ‘Social Proof’ where we augment our behaviors to match what is perceived to be socially acceptable or correct behaviour as dictated by the masses. It’s almost like a herd mentality of sorts. He goes even further to talk about the more pronounced effects of it when the source of social proof is similar to the subject that needs to be persuaded.
What this means is that if you quote clients that are similar to your audience during your presentation, you’ll have a much easier time establishing trust from the get-go. At the same time, showing a list of past clientele can also help to assure listeners that others have put their trust in you prior and this can improve your image of trustworthiness.
Look the part
We tend to make snap-judgments on different unconscious signals by salespeople or presenters. It could be a hint of contempt in their microexpressions or the way they shake hands, but half the battle is sometimes won by simply looking the part. The visual aspect and first impression lends to build part of your expert identity.
If you try to make someone pay for an expensive meal that’s wrapped in cling wrap in a dingy little store versus a posh, clean and well-designed restaurant, you’ll definitely get push back. In most cases, presentations aren’t too different.
First impressions can be affected by anything from sloppy dressing to cluttered slides. Venngage put together an excellent resource on expert presentation design styles you can adapt for your next presentation.
Have an unconventional opinion
True experts are expected to have original ideas that sometimes go against the grain of commonly touted advice or industry norms. It’s not to say that you should actively seek to be contrarian for the sake of it, but being able to hold your ground and have a clear stance is indicative of an expert that knows what he/she is talking about. For example, Gary Vaynerchuk can be considered a prolific and polarizing figure because of his irreverent way of speaking as well as his contrarian opinions.
An easy way to do this is to identify a common, but misguided belief that the industry has and logically debunk it with your own theory. Having an original stance and supporting it with evidence can quickly help you become perceived as an expert.
We buy into the brand of industry moguls like Steve Jobs and Elon Musk precisely because they seem to offer ideas that are novel and unique. At the same time, because their ideas are at odds with the current status quo, we’re drawn to their narratives because of either the Underdog Effect (e.g. when Apple is up against conglomerates like IBM) or the protagonist-antagonist dynamic of their vision(e.g. Elon Musk fighting against pollution and innovating beyond the public’s current perception of what’s possible).
Share relevant credentials that matter to your audience

Different audiences have various ways that they use to evaluate speakers on trustworthiness. Being aware of these early on will give you an edge in establishing trust with your audience.
For example, if you’re aware that your audience values globalized insights, having a slide that validates your experience in a global setting can help you develop a strong position of authority.
In certain industries, even factors like age can play a part in whether your audiences listen to your or discount your views on first-impression. For example, in tech companies, older workers are perceived to take longer to ‘get to grips with new skills’.
Hence if you’re speaking at a tech-related event, it might not be the best strategy to try to boost your credibility by boasting about your age via public speaking . Being prepared for the right context can make or break your presentation.
Only after establishing the needs in #1 should you “formally” introduce yourself or your company to make yourself relevant
3. Have genuine intent to add value to your audience
Remember that the presentation is never about you, it’s about your audience. It’s about what they want to achieve and how you can help them get there.
As such, it’s imperative that you find out as much about them as possible prior to developing your presentation and work towards adding value to them, instead of force-feeding them a solution that they don’t need.
The best way to do this is to put in a couple of extra hours to deliver timely, relevant content coupled with effective presentation design that’s obviously tailored to your audience.
Use examples that your audiences resonate with

Think back to when you were back in school, listening to your lecturer offer examples that didn’t interest you in the least bit. Similarly, if you were speaking to a group of millennials today, they would have specific areas of interest that you can take advantage of.
Referencing recent trending news and drawing relationships between what you’re speaking about and what they might find relevant is an easy way to build rapport quickly. If you’re talking about a business-related topic, try referencing popular companies like SnapChat or Instagram that they interact with on a daily basis. You can be sure they’ll sit up and listen if it hits close to home. That way, you’ll have their attention and appreciation for taking the time to put together relevant examples.
4. Have a process for execution
According to an Accenture study, 94% of B2B buyers conduct online research at some point in the buying process. This makes it difficult for you to try and breeze through the sales conversation without any real substance.
In another study by Bain , 375 companies were asked if they believe they delivered a superior value proposition to clients. Eighty percent said yes. Bain then asked the clients of these actual companies if they agreed that the specific company that they bought from actually delivered this superior value proposition. You know what’s funny? Only eight percent agreed.
Buyers that need to make purchases quickly now rely on how believable you are rather than make logical comparisons on the actual value proposition.
For those that are selling a product or service, a great way to quickly establish trust to get you closer to buy-in is to detail a process of execution especially for sales presentations or investor presentations . Generally, when we’re buying anything in today’s age, we have unlimited access to information online to make comparisons that lead to an informed choice.
Showing that you or your company follows a repeatable process helps to put your buyer’s mind at ease. Instead of putting their trust in a single individual doing guesswork, they can now rely on a proven methodology or framework rather than just the words of the person they’re speaking to. In some cases, this is communicated at the end to conclude your presentation and to suggest next steps.
Whenever you’re in doubt as to whether your presentations will establish trust during your sales pitch or presentation, ask yourself if it fulfills these four criteria:
- Back Up What You Say With Evidence
- Develop Your Expert Identity
- Have Genuine Intent To Add Value To Your Audience
- Have A Process Of Execution
There you have it, four ways to almost immediately establish trust during your presentations on-stage, in the boardroom or digitally. —— Originally published on Business.com: https://www.business.com/articles/how-to-establish-trust/
Article Written By: Eugene Cheng
You may also like….

Patrice Choong: Stepping Out of Your Comfort Zone
by Kai Xin Koh
Read on as Patrice shares on how stories can be used to inspire you to step out of your comfort zone.

Val Yap: Delivering Success Through Effective Communication
Success is not dictated by the hard work of one person alone. A great leader is also a great story-teller because effective communication is the foundation of any successful organisation.

Zia Zaman: How a World-Class Speaker brings Storytelling, Experimentation & Empathy into Business
Any businessperson understands the value of selling and the art of storytelling. They are indispensable and inevitable, yet only a few have truly...
Sign Up for Winning With Stories!
- First Name *
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
The 3 Elements of Trust
- Jack Zenger
- Joseph Folkman

And which one is most important for leaders.
As a leader, you want the people in your organization to trust you. And with good reason. In our coaching with leaders, we often see that trust is a leading indicator of whether others evaluate them positively or negatively. But how to create that trust, or perhaps more importantly, how reestablish it when you’ve lost it isn’t always that straightforward. By analyzing over 80,000 360-degree reviews, the authors found that there are three elements that predict whether a leader will be trusted by his direct reports, peers, and other colleagues. These are positive relationships, consistency, and good judgment/expertise. When a leader was above average on each of these elements, they were more likely to be trusted, and positive relationships appeared to be the most important element in that, without it, a leader’s trust rating fell most significantly. Trust is an important currency in organizations and any leader would be wise to invest time in building it by focusing on these three elements.
As a leader, you want the people in your organization to trust you. And with good reason. In our coaching with leaders, we often see that trust is a leading indicator of whether others evaluate them positively or negatively. But creating that trust or, perhaps more importantly, reestablishing it when you’ve lost it isn’t always that straightforward.
- Jack Zenger is the CEO of Zenger/Folkman, a leadership development consultancy. He is a coauthor of the October 2011 HBR article “ Making Yourself Indispensable ” and the book The New Extraordinary Leader: Turning Good Managers into Great Leaders (McGraw Hill, 2019). Connect with Jack on LinkedIn .
- Joseph Folkman is the president of Zenger/Folkman, a leadership development consultancy. He is a coauthor of the October 2011 HBR article “ Making Yourself Indispensable ” and the book The Trifecta of Trust: The Proven Formula for Building and Restoring Trust (River Grove, 2022). Connect with Joe on LinkedIn .
Partner Center
- All Resource
PPT Templates
Single slides.
- Pitch Deck 209 templates
- Animation 326 templates
- Vertical Report 316 templates
- Business 803 templates
- Finance 56 templates
- Construction 45 templates
- IT/Commerce 171 templates
- Medical 64 templates
- Education 45 templates
- Lifestyle 394 templates
- Pitch Decks 138 templates
- Business 541 templates
- Finance 20 templates
- Construction 75 templates
- IT/Commerce 73 templates
- Medical 27 templates
- Lifestyle 578 templates
- Pitch Decks 140 templates
- Business 469 templates
- Finance 19 templates
- Construction 64 templates
- IT/Commerce 72 templates
- Medical 29 templates
- Education 39 templates
- Lifestyle 490 templates
- Cover 266 templates
- Agenda 97 templates
- Overview 216 templates
- CEO 28 templates
- Our Team 142 templates
- Organization 48 templates
- History 38 templates
- Vision, Mission 109 templates
- Problem, Solution 193 templates
- Opportunity 154 templates
- Business Model 158 templates
- Product, Services 299 templates
- Technology 65 templates
- Market 155 templates
- Prices 56 templates
- Customers 55 templates
- Competitor 113 templates
- Business Process 151 templates
- Analysis 222 templates
- Strategy 120 templates
- Marketing, Sales 61 templates
- Profit, Loss 69 templates
- Financials 247 templates
- Timeline 122 templates
- Proposal 40 templates
- Contact Us 272 templates
- Break Slides 16 templates
- List 361 templates
- Process 351 templates
- Cycle 177 templates
- Hierarchy 98 templates
- Relationship 152 templates
- Matrix 86 templates
- Pyramid 67 templates
- Tables 145 templates
- Map 96 templates
- Puzzles 163 templates
- Graph 217 templates
- Infographics 436 templates
- SWOT 111 templates
- Icon 418 templates
- Theme Slides 138 templates
- Mockup 42 templates
- Column 315 templates
- Line 199 templates
- Pie 139 templates
- Bar 179 templates
- Area 130 templates
- X Y,Scatter 16 templates
- Stock 59 templates
- Surface 3 templates
- Doughnut 256 templates
- Bubble 65 templates
- Radar 83 templates
- Free PPT Templates 2,101 templates
- Free Keynote 2,017 templates
- Free Google Slides 2,098 templates
- Free Theme Slides 35 templates
- Free Diagram 126 templates
- Free Chart 49 templates
- New Updates
Result for ' trust '
52 Templates are available.
- Sort by Accuracy
- Sort by Newest

Do not let your hearts be troubled. Trust in God; trust also in me. - Jesus Christ The best way to find out if you can trust somebody is to trust them. - Ernest Hemingway The Best Proof of love is trust. -Joyce Brothers

Love yourself for who you are, and trust me, if you are happy from within, you are the most beautiful person, and your smile is your best asset. - Ileana D'Cruz Love me or hate me, both are in my favour. If you love me, I will always be in your heart, and if you hate me, I will be in your mind. - Qandeel Baloch The beauty of a woman must be seen from in her eyes, because that is the doorway to her heart, the place where love resides. - Audrey Hepburn Love myself I do. Not everything, but I love the good as well as the bad. I love my crazy lifestyle, and I love my hard discipline. I love my freedom of speech and the way my eyes get dark when I'm tired. I love that I have learned to trust people with my heart, even if it will get broken. I am proud of everything that I am and will become. - Johnny Weir

Negotiation Startup PPT Templates
Easy to edit and customize Easy to change colors Data charts (editable via Excel) Landscape orientation style Professional business presentation

Information Privacy Action plan PPT
Easy to change colors Smart and innovative presentation slides Created by professionals Created with high quality slides All elements are editable

Biometric Authentication PowerPoint Templates for Presentation
Replaceable the image into placeholder Created by professionals Created with high quality slides Premade color variation Suitable for each industries

Success Project PowerPoint Templates Design
Modern, simple, and clean design Highly editable presentation template. Easy to change colors Easy editable data driven charts (pie, bar, line) No animation template Format: PowerPoint (.pptx) - designed with Microsoft PowerPoint 2016 Master layout with text placeholders

Relationship
A good friend is my nearest relation. - Thomas Fuller The relationship between husband and wife should be one of closest friends. - B. R. Ambedkar Great companies that build an enduring brand have an emotional relationship with customers that has no barrier. And that emotional relationship is on the most important characteristic, which is trust. - Howard Schultz

Do not dwell in the past, do not dream of the future, concentrate the mind on the present moment. - Buddha DREAM You have to dream before your dreams can come true. - A. P. J. Abdul Kalam Every human is an artist. The dream of your life is to make beautiful art. - Don Miguel Ruiz

Pregnancy and motherhood are the most beautiful and significantly life-altering events that I have ever experienced. - Elisabeth Hasselbeck Pregnancy is a kind of miracle. Especially so in that it proves that a man and woman can conspire to force God to create a new soul. - Robert Anton Wilson Preg nancy changed my body; it changed the way I walk. - Andie MacDowell

Communication
Words are singularly the most powerful force available to humanity. We can choose to use this force constructively with words of encouragement, or destructively using words of despair. Words have energy and power with the ability to help, to heal, to hinder, to hurt, to harm, to humiliate and to humble. - Yehuda Berg

Finance Presentation PowerPoint Templates Design
Easy customization 100% fully editable PowerPoint slides 100% vector (fully editable maps, infographic, icons) No animation template Modern and clean design Modern layouts based on master slides

Lovely Pet Simple PowerPoint Templates
100% fully editable PowerPoint slides Easy to change colors Easy to edit in PowerPoint

Simple Pitch Deck Template PPT Templates
Easy to change colors Free images and artwork Modern and clean design Non-animated Drag & drop friendly

Investment Proposal PPT Presentation
Easy customization Quick and easy to customize Data charts editable via Excel Shapes: fully editable vector graphics All elements are editable

The Proposal Theme PT Templates
Modern, simple, and clean design Data charts editable via Excel Shapes: fully editable vector graphics All elements are editable

Senior Businessman Design brief Templates
Easy customization Fully editable content (graphics and text) via PowerPoint - No Photoshop needed! Easy to change colors Easy editable data driven charts (pie, bar, line) Shapes: fully editable vector graphics Non-animated

Investor Deck Template creating PowerPoint Presentations
Modern, simple, and clean design Fully editable content (graphics and text) via PowerPoint - No Photoshop needed! Data charts (editable via Excel) Shapes: fully editable vector graphics Modern layouts based on master slides

STARTUP Pitch Background PowerPoint
Modern, simple, and clean design Free images and artwork Shapes: fully editable vector graphics

Orthopedics PowerPoint Presentations Samples
Data charts (editable via Excel) 100% vector objects & icons Free images and artwork No animation template 16:9 aspect ratio Professional business presentation

Data Analysis Best PPT Templates
Easy customization Quick and easy to customize 100% fully editable PowerPoint slides Easy to change colors Vector icons 100% editable Professional business presentation
Free Slides
Slide Members
All Rights Reserved 2024 © Copyright Slide Members
Information
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
Recent Slides
- 26+ Latest weekly update Powerpoint Templates & Google slides
- 19+ Recently Powerpoint Templates & Google slides Update
- 9+ New Powerpoint Templates & Google Slides Update

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 40 Teamwork and Collaboration PowerPoint Templates for Timely Achievement of Company’s Goals

Deepali Khatri
Everyone is looking forward for increasing organizational productivity and for learning to work together effectively. Whether you choose a private-sector career or an academic, you’ll need to know how to work together with the members of your group. Learning to work collectively for a common goal is vital these days.
Even while seeking a job, people look for a company with a happy work culture rather than a company that offers the best perks and designations. And, this is because working together effectively helps in increasing the outcome, quality and boosts up the morale of the employees.
If you wish to conduct a comprehensive training for your team and colleagues on conflict management, access our training module here that will provide all the hands-on material you need to make for an effective experience.

Click here to access our Comprehensive Training Curriculum on Conflict Management
Here we present to you top 40 teamwork and collaboration templates that will aid you in improving your teamwork and collaboration skills. Incorporating these PPT templates will help you make most out of the team’s collective strengths and experience. Employing these predesigned editable PowerPoint slides will enable you to build a team of people for the timely achievement of company’s goals.
Partnership Graphic With Teamwork Success Growth And Collaborate-1

Get This Partnership Graphic with Teamwork Success Growth and Collaborate PowerPoint Template
Achieve common goals of the organization in the most effective and efficient way using this readymade partnership graphic with a teamwork success growth PowerPoint template. Give your employees a common goal for which they can work together and familiarize them with the benefits of working together.
Activities and Team Marketing Manufacturing Management Treasury Finance-2

Grab this Activities and Team PPT Layout
This is a deck consisting of 9 slides that can be used for illustrating team building activities for a company. Present the steps of building an effective team using this editable PPT slide design. The benefits one can gain by working in a team can be easily elucidated taking the assistance of this activities and team template. Divide various responsibilities and activities between different team members through this slide.
Involvement of People Teamwork PPT PowerPoint Presentation Pictures Brochure-3

Download this Involvement of People Teamwork PPT Layout
Incorporate this involvement of people teamwork PPT template and make your team stronger by involving the team members in the decision-making process. This teamwork and collaborations PPT template will assist you in understanding each other and building friendly relations. Showcase how people work together using their individual skills through this amazingly curated PowerPoint slide.
Collaboration Teamwork PPT PowerPoint Presentation Professional Master Slide-4
Download this Collaboration Teamwork PowerPoint Slide Design
Showcase the value of working together for achieving a common goal. This PowerPoint layout provides every team member with equal opportunities to participate and communicate their ideas. Having collaborations can help in increasing retention rates. Work together by sharing your ideas to reach the set goals.
Collaboration Teamwork Forecasting Budgeting PPT PowerPoint Presentation model Brochure-5
Download this Collaboration Teamwork Forecasting Budgeting PowerPoint Slide Show
Display the significance of working collectively in a team taking the assistance of this teamwork forecasting budgeting PowerPoint model. The slide will enable you to illustrate the importance of working as a team. Use this predesigned PPT template to enhance participants' skills while practicing teamwork concepts.
Teamwork Chain Template PowerPoint Slide Images-6
Download this Readymade Teamwork Chain Template PowerPoint Slide Design
Display how the functional business teams are connected with the help of this creatively designed teamwork chain PPT template. Illustrate the process of managing teams and motivate your employees to work as per the set guidelines. This template can be the best tool for introducing your team members to the clients for attaining projects. Showcase the connection between various departments and how these departments together work for achieving the organizational objectives.
Collaboration Skills Teamwork PPT PowerPoint Presentation Model Design Ideas-7
Download this Collaboration Skills Teamwork PowerPoint Diagram
Use this PowerPoint template to build and develop an efficient, effective and powerful team. Mention the skills required for teamwork and collaboration. Illustrate how problem-solving, interpersonal and communication skills can help you reach your organizational goals quickly. Use this editable slide to depict the principles of effective collaboration.
Coordination Icon for Business Collaboration-8
Download this Coordination for Business Collaboration PowerPoint Layout
Employ this coordination icon for business collaboration PowerPoint slide design to devise strategies that will motivate employees to work towards the achievement of common goals. Discuss the tasks that need to be done for building strong relations with the other team members. Jot down the important plans that will help you in building a strong team using this slide.
Organizational Effectiveness Teamwork Achievement Successful Strategy-9

Click Here to Download this Organizational Effectiveness Teamwork Achievement Successful Strategy
Use this slide to depict how people can cooperate using their individual skills and provide constructive decisions or solutions. Incorporate the template to illustrate what are the qualities one should acquire to be an effective member of the team. This template depicts different people holding hands which is a symbol of strength. Build a successful strategy and present it in front of your team members with this predesigned PowerPoint template.
3D Men With Jigsaw Puzzle Teamwork PPT Graphics Icons PowerPoint-10
Click Here to Get this 3d Men with Jigsaw Puzzle Teamwork PowerPoint Slide Show
This 3D men with jigsaw puzzle teamwork PPT graphics is a metaphor for business and strategy PowerPoint presentation. The template will let you break down a complex piece of information in a simpler manner. This template has been crafted by our experts for your convenience which allows you to enter the text in the text placeholders. The interconnected puzzle shows connectivity and flow among several steps.
Teamwork and Collaboration Sample Presentation PPT-11
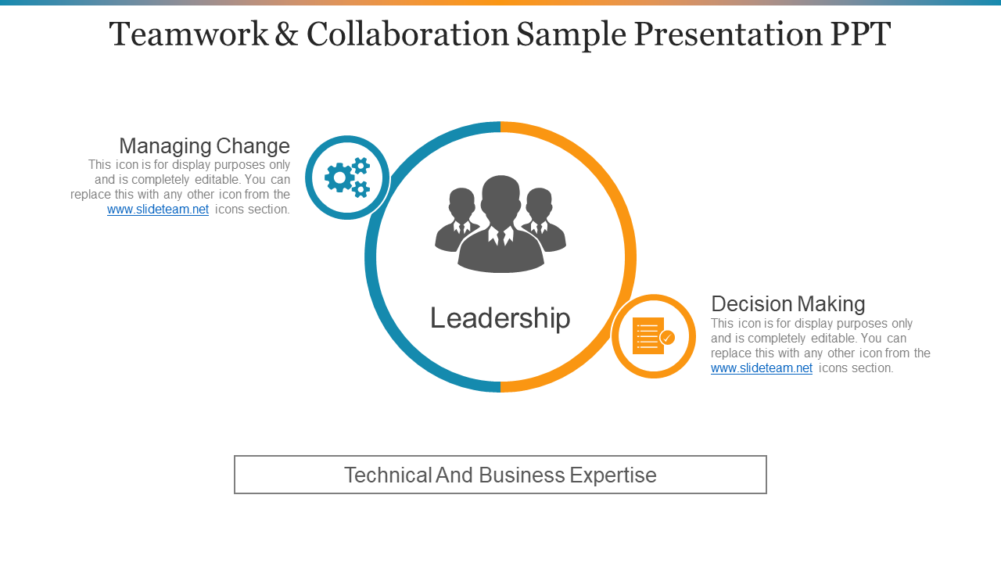
Get this Teamwork and Collaboration Sample PowerPoint Presentation
Incorporate this slide to build a team for the timely achievement of your company’s goal. The slide will let you showcase how good leadership can encourage better interactions amongst your team members. Showcase how teamwork and personal growth can help in appropriate decision making. Make your organization work smoothly with the help of this readily available teamwork and collaboration PowerPoint slide show.
Strategic Partnership Showing Collaboration Teamwork Plan And Strategy-12
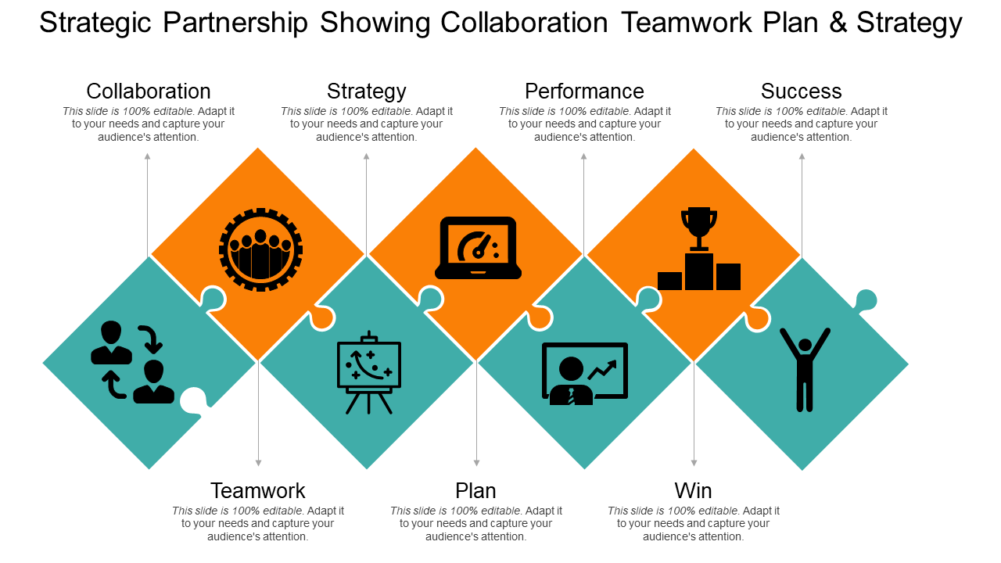
Download this Customizable Strategic Partnership Showing Collaboration Teamwork Plan and Strategy
This PPT template will assist small businesses to grow their customer base and improve their business. Formulate appropriate plans for growth of your business organization and mention the ways through which you can build strategic partnership that will enhance your organizational productivity. Guide your viewers about the various types of strategic partnerships via this professionally designed PowerPoint slide design.
Commitment Showing Collaboration Between Group-13
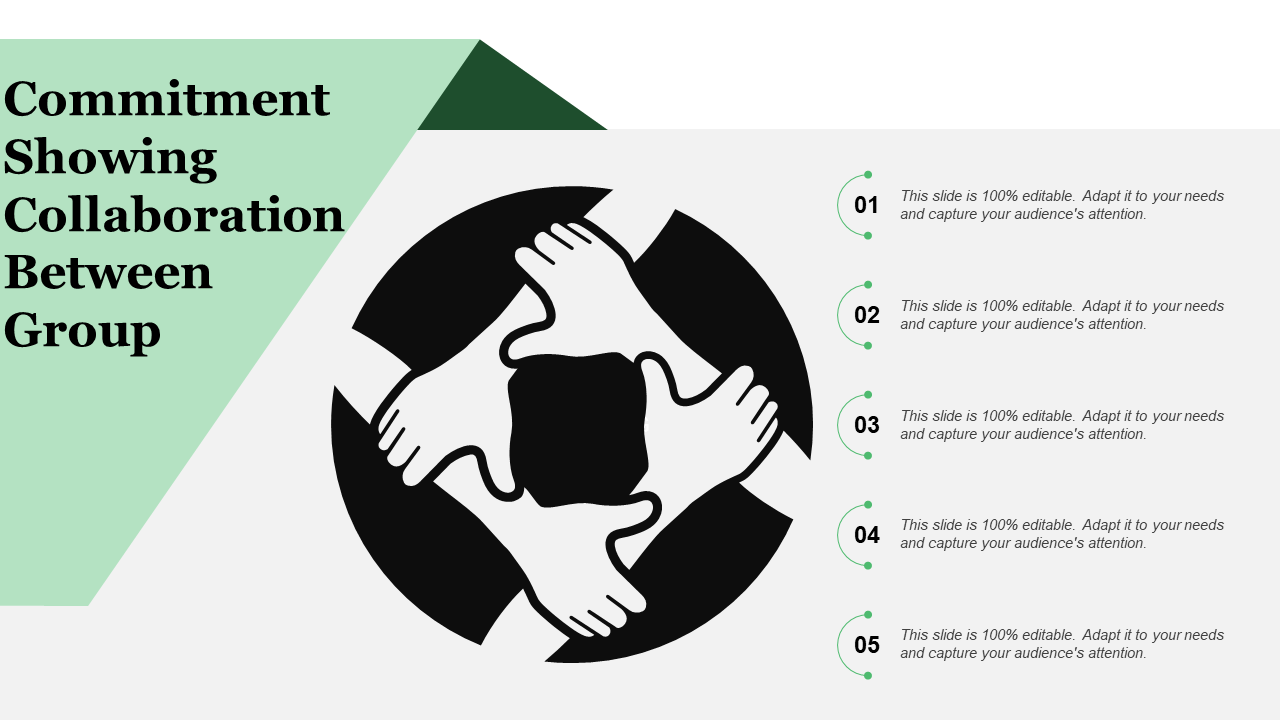
Download this PowerPoint Template Now
Display the most important skills required for teamwork and collaboration using this amazingly curated PowerPoint slide. The slide can also be used to depict the effects of commitment on teamwork and organizational productivity. With the commitment between team members and groups, your organization will benefit from more ideas, thereby increasing the profits of the organization.
Collaboration Continuum Diagram PowerPoint Slide-14
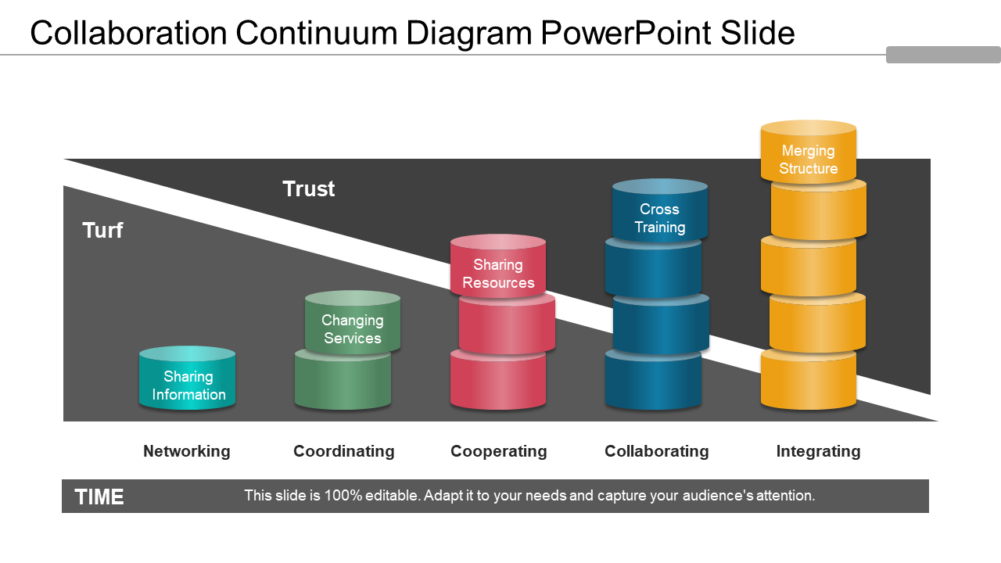
Download this Collaboration Continuum Diagram PowerPoint Template
Communicate efficiently taking the assistance of this collaboration business model. The template consists of five stages showcasing networking, coordination, cooperation, collaboration, and integration. This PPT design is divided in two parts displaying trust and turf which makes easier for you to share information. The collaboration continuum will help in achieving goals collectively that otherwise cannot be achieved by a single agent.
3 Important Skills Teamwork Collaboration PPT PowerPoint Presentation Outline Good-15
Download this Readymade 3 Important Skills Teamwork Collaboration PPT Template
Elucidate the skills required for effective teamwork and collaborations. Let your viewers be aware of how communication skills, credibility, accommodation, and other important skills can help in working collectively for the common organizational goals. If you are to work with others on a long term basis, you need to possess certain skills. Display the skills that your employees must acquire for efficient working within the business organization.
Team With Bulb Puzzle And Icons Flat PowerPoint Design-16
Grab this Team with Bulb Puzzle and Icons Flat PowerPoint Slide Design
Find a solution for your business problems by discussing on the matter through this amazingly designed PPT template. Showcase how collaboration helps the organization to achieve the desired objectives. Showcase the problem-solving concept in an organization and illustrate the ways and methods to tackle with the given situation. This team with bulb puzzle template allows you to convey your ideas and messages for reaching to a conclusion collectively.
Teamwork for Project Completion in Coordination Icon-17
Get this Teamwork for Project Completion in Coordination Icon PPT Template
Take the assistance of this readily available teamwork for project completion in the coordination template and showcase how working together in a team assists you in completing the projects keeping in mind the deadlines. Using this slide one can ensure that resources are well managed, and less time is needed to complete the project. This PPT template will let you assign duties and responsibilities to the workforce. Let your staff members be aware of who is accountable to whom.
3d Business Peoples for Teamwork PowerPoint Template-18

Get this 3d Business People For Teamwork PPT Slide Design
Get this teamwork PPT template and guide your workforce about the benefits of working together in a team. Introduce the members in your team who are involved in working for a particular project. The slide consists of sample text that can be replaced with your own text. Keep it as an introductory slide to introduce your team with the audience.
Company Culture Strategic Planning Leadership Development Team Dynamic-19

Grab this Company Culture Strategic Planning Leadership Development Team Dynamic PowerPoint Slide Show
This is a complete deck consisting of 13 slides that can be used to depict company culture and teamwork. Showcase how different individual contribute their opinions and that leads to collective decision making. Present the contribution of each employee for the organizational objectives and display how the individual contribution leads to a bigger achievement using this editable PowerPoint template.
Importance Of Leadership In Teamwork-20

Download this Readily Available Importance of Leadership PowerPoint Template
Display the importance of leadership in teamwork and present how a leader showcases a vision to your team members for your business. Depict the effects of leadership on teamwork and why leadership is important for an organization. Leadership can create and encourage team members to meet their responsibilities and this can be easily done using this slide.
3D Men Holding Jigsaw Puzzle Pieces Teamwork Business PPT Graphics Icons-21
Get This Readily Available 3d Men Holding Jigsaw Puzzle Teamwork Ppt Layout
This jigsaw puzzle PPT template can be used to depict how teamwork and working collectively can help in solving organizational puzzles. This shows that employees must work together for completing a puzzle quickly. You can incorporate this template to guide your employees and subordinated about the same using this creative jigsaw puzzle teamwork PPT diagram.
3D Red White Team standing together unity PPT Graphics Icons-22
Get this 3d Red White Team Standing Together Unity PPT Graphics
When you are working within the organization you get expose to diverse people that helps you become a better person. This 3D red and white PPT template will help you enhance the quality of work helping you to complete the project within specified timeframe. Teamwork can help in maximizing the effectiveness of an organization and that can be presented with the help of this creative 3D PPT slide.
Rowing Team People Teamwork PowerPoint Template-23

Download this Rowing Team People Teamwork PPT Slide
Showcase how interdependent individuals who work together towards a common goal can achieve them efficiently. Present various characteristics that the members of the team must possess for open communication and building trust. Present the basic team dynamics such as communication, collaboration, coordination and interdependence with the help of this template.
Working Together 3 Gears-24

Get this Working Together 3 Gears PowerPoint Template
Present the ideas of your team in a visually appealing manner taking the assistance of this predesigned working together 3 gears PPT slide. The slide has been designed keeping in mind the concept of focus groups, where a group of individuals collectively conceptualize and develop a new product to fulfill the market needs.
Corporate Teamwork PPT PowerPoint Presentation Ideas Introduction-25
Get this Corporate Teamwork PPT Presentation Slide
Motivate your workers to work together for achieving the targets taking advantage of this eye-catching PPT template. Showcase how cooperation is important for building a strong team. Display how mutual support and shared goals provide workplace synergy using this customizable PPT template. Present the quality of good teamwork using this 5 stage teamwork PPT template.
Team with Puzzles And Icons Teamwork Problem Solving Flat PowerPoint Design-26
Download This Team with Puzzles and Icons Teamwork PPT Template
Depict the idea of collaboration of team spirit and problem-solving using this editable PowerPoint slide show. Strategize with the available resources and present your plans and ideas in a visually appealing way. This readymade PPT slide is useful for business entities, educational institutes, researchers, finance consultants, etc.
Teamwork Strategies for The Workplace PPT Slide-27

Download this Teamwork Strategies for The Workplace PPT Slide Design
Devise strategies for building a strong team using this predesigned teamwork strategy for the workplace PPT template. Promote teamwork in the workplace taking the assistance of this readily available teamwork strategies. The qualities that a team leader must possess can be showcased via this creative teamwork strategy PowerPoint template.
Leadership Model PPT Inspiration Infographic Template Connection To Community-28

Click here to Get this Leadership Model PowerPoint Slide Show
Showcase the importance of having a leader for building a strong and effective team for your organization. This deck consists of 10 slides that can be incorporated for depicting cultural system within the organization. Effective leadership is a vital element for successful business operations. Include this slide in your presentation and guide your viewers of the same.
Team Engagement Ideas PPT Model-29
Click here to Get this Team Engagement Ideas PPT Model
Employ this team engagement ideas PowerPoint template and invite ideas from people within your organization. Mention the ways with the help of which one can work towards increasing employee engagement. This customizable PowerPoint template depicts a bulb as a symbol of idea generation. Motivate your team members to participate in the decision-making process taking the assistance of this readily available PowerPoint slide show.
Teamwork For Idea Implementation Flat PowerPoint Design-30
Click Here to Get this Teamwork for Idea Implementation Flat PowerPoint Template
Implement a plan or action to strengthen your teamwork using this teamwork for implementation PPT slide. Teamwork is important to collaborate and communicate properly and for implementing the ideas generated. Take into consideration the ideas contributed by each individual and reach to a conclusion through mutual consent. This slide depicts how working collectively can lead to appropriate decision making.
Collaboration Word Cloud Showing Teamwork Icon-31
Download this Collaboration Word Cloud Showing Teamwork Icon
Showcase the concept of cloud computing and display how the files are shared using cloud computing where the documents are uploaded to a central “cloud” for storage from where others can also access it. This PPT template will let you guide your employees to work together on documents and other related data.
Team Performance Teamwork Leadership Togetherness Unity Analysis-32

Download this Customizable Team Performance Teamwork Leadership Togetherness Unity Analysis PPT Slide
Promote an atmosphere that fosters friendship and loyalty within your organization. Learning and working together enables them develop understanding with each other. Teams will be able to share vision of what they actually want to achieve and will make plans for achieving the goals together. This slide can be customized as per your requirements. Devise strategies and formulate plans to implement the devised strategies.
Hand Holding Hands Teamwork PowerPoint Slide Introduction-33
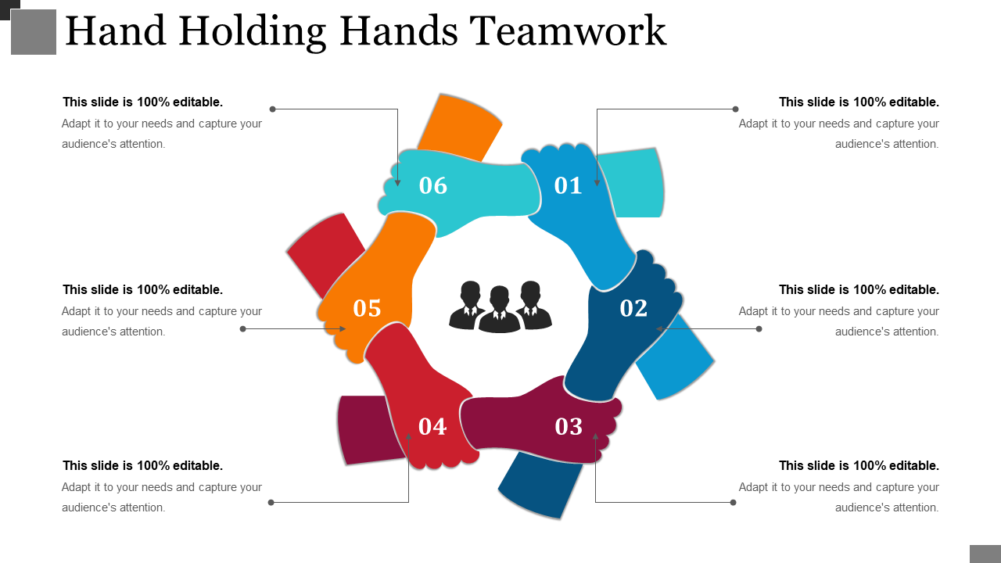
Download this Predesigned Hand Holding Hands Teamwork PowerPoint Slide Show
This readily available PPT template depicts hands holding together that can be used to guide the workforce about the concept of strength and unity. Get your audience have an idea about your team and capabilities. Represent the symbolic meaning of holding hands using this hands holding teamwork PowerPoint template. Elucidate how timely support and assistance amongst your team members can lead your company towards success.
Our Team Communication Teamwork PPT PowerPoint Presentation Icon-34
Get this Customizable Our Team Communication Teamwork PPT Presentation
Introduce your team member in a better way through this professionally designed our team PowerPoint template. An introductory slide like this can give a better idea to your audience about your teammates. Mention the name of the manager and the head of the departments in the text place holders. Give a clear picture of your company and provide an overview of the company’s profile. Present the key performers of your organization in an attractive way.
Growth Arrow With Business Peoples Teamwork And Unity Flat PowerPoint Design-35
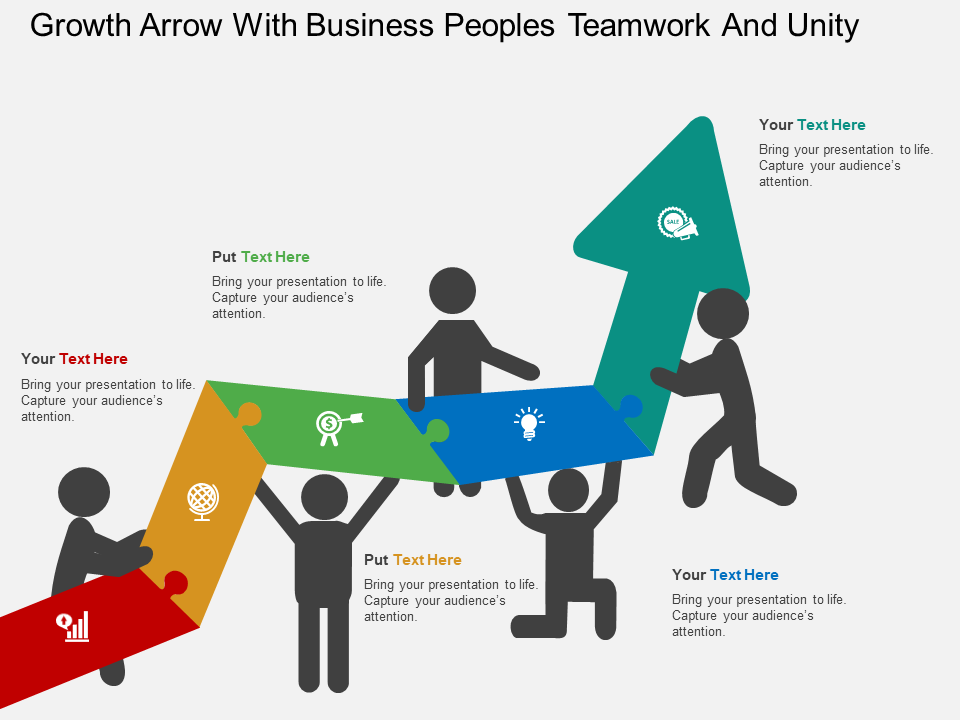
Download this Growth Arrow with Businesspeople Teamwork and Unity Flat PowerPoint Example
This growth arrow with businesspeople PowerPoint template demonstrates the concept of teamwork in business development. The predesigned PowerPoint template depicts the growth of your business organization. Work together towards the achievement of the goals and targets and depict the same using this PowerPoint layout.
Team Collaboration Process Brainstorm Interaction and Share Ideas-36
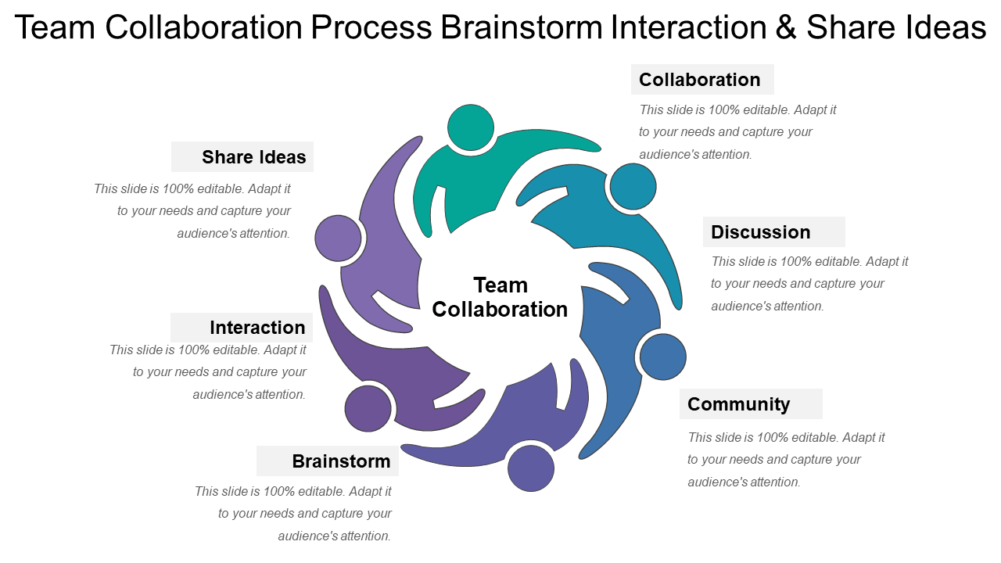
Download this Customizable Team Collaboration Process Brainstorm Interaction and Share Idea PPT Template
Raise the level of morale, expertise and learning by employing this creative team collaboration process brainstorm PowerPoint layout. Depict the steps of the entire procedure of brainstorming. Mention the rules and techniques of brainstorming and let your viewers be aware how individual ideas form a part of a bigger idea. Elucidate the benefits of working together in a team by incorporating this PowerPoint layout.
Working Together 4 Human Gears Working Together for Change-37

Get this Working Together 4 Human Gears PowerPoint Slide
Working together will help a group to achieve a common aim quickly and this can be presented with the assistance of this customizable working together PowerPoint template. Explain how teamwork and collaboration can contribute in completing the tasks faster. This template showcases number of people joining hands together and can also be used as a metaphor for unity and strength.
Business Collaboration Partnership Steps Circular Puzzle PPT Slide-38
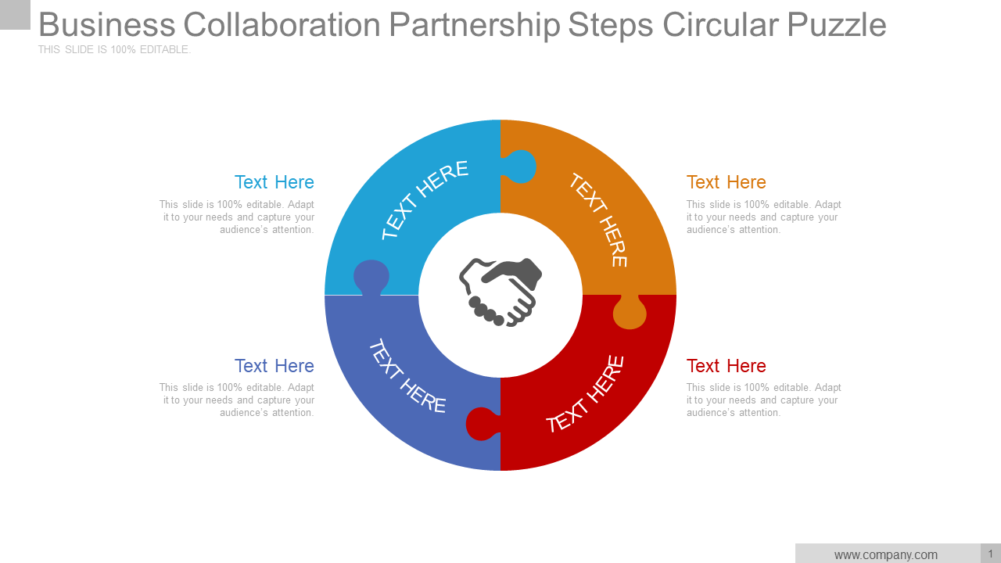
Click Here to Download this Editable Business Collaboration Partnership Steps Circular Puzzle PPT Slide
Illustrate the process of business collaboration and familiarize the audience with the steps using this creatively designed PowerPoint template. This template is completely customizable that can serve as a great tool for individuals to work together for the common purpose of business benefit. Present the four major strategies of collaboration through this circular puzzle PPT template.
Quotes Unity Is Strength Collaboration Teamwork Achieved-39

Click Here to Get This Quotes Unity is Strength Collaboration Teamwork Achieved
Incorporate this template to motivate your employees, subordinates and other staff members to work in unity. Present the quotes related to unity, teamwork, and collaborations. Inspire your team members to work collectively thereby increasing the organizational productivity. Familiarize them with the benefits of working together using this PPT slide.
3D People Standing With Cubes Of Teamwork Stock Photo-40

Download this Amazingly Designed 3d People Standing with Cubes of Teamwork Stock Photo Template
This PPT template consists of people standing with cubes and can be used as an introductory template for a PPT presentation on the topic of teamwork and collaboration. Familiarize your audience with the collaboration tools for business. Let your viewers be aware of the benefits of teamwork and collaboration using this editable PowerPoint slide design.
These readymade templates will save a lot of your valuable time. Get access to these slides just by clicking on the download button and prepare impactful presentations without any hassle.

Related posts:
- Top 10 PowerPoint Slides for Productive Collaboration
- Top 20 Team Building PowerPoint Templates to Present Your Ideas and Strategies
- How to Design the Perfect Service Launch Presentation [Custom Launch Deck Included]
- Quarterly Business Review Presentation: All the Essential Slides You Need in Your Deck
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Top 40 Planning and Timelines PowerPoint Templates used by Managers and Consultants

Top 30 Valentine’s Day PowerPoint Templates to Make Your Loved One Feel Special!
![presentations on trust [Updated 2023] Top 30 Stock Market PowerPoint Templates to help Analysts and Managers Analyze Better!](https://www.slideteam.net/wp/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/Banner-25-335x146.png)
[Updated 2023] Top 30 Stock Market PowerPoint Templates to help Analysts and Managers Analyze Better!
![presentations on trust [Updated 2023] Top 50 Scorecards and Dashboards PowerPoint Templates to Analyze your Business Performance](https://www.slideteam.net/wp/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/Banner-26-335x146.png)
[Updated 2023] Top 50 Scorecards and Dashboards PowerPoint Templates to Analyze your Business Performance
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

Sales funnel results presentation layouts
3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Future plan powerpoint template slide

Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

Agenda powerpoint slide show

Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

Meet our team representing in circular format


The Importance of Trust
Apr 05, 2019
580 likes | 1.27k Views
The Importance of Trust. October 23, 2007 Dr. Sandra Lindsay. What is trust? Why does it matter?. Trust Building Activity. Car-Car Listen carefully to the directions given by the presenter. Complete the activity. Analyze the importance of trust to the successful completion of this activity.
Share Presentation
- intensive case study research
- different school communities
- break confidences
- violate expectations

Presentation Transcript
The Importance of Trust October 23, 2007 Dr. Sandra Lindsay
What is trust?Why does it matter?
Trust Building Activity • Car-Car • Listen carefully to the directions given by the presenter. Complete the activity. • Analyze the importance of trust to the successful completion of this activity.
“Car-car,” was developed by David Earl Platts of the Findhorn Foundation. Trust and responsibility are two very important qualities in leaders and followers. This activity will help you experience how you feel about trust. Choose two people from each group. This is a silent exercise. Car-Car
One person, “the car,” stands in front with his or her eyes closed and hands held in front of the chest with palms outward as your bumpers. The second person, “the driver,” with eyes open, stands behind with hands on the shoulders of the car. Keeping his/her eyes open, the driver will steer the sightless car around the area, avoiding collisions with other pairs. Remember that the safety of the other person is your responsibility, so you must show compassion and care. Any questions? Car-Car, continued
Examining Trust • Look at the “Personalities” on the cards assigned to your group. • How would trust factor into your working relationship with these individuals? • In your group, discuss what elements of trust are exhibited or omitted by the characters.
The Importance of Trust • Anticipating the emotional effects that decisions and actions might have on others • Responding tactfully and respectfully in emotional situations • Eliciting the perceptions, feelings, and concerns of others • Recognizing that conflict is inevitable and using it to strengthen relationships
Trust • Following through on commitments and keeping one’s word • Using the name of the other person when conversing with him or her • Showing courtesy and respect • Questioning, clarifying, and correcting others in a positive and professional manner
Trust • Suggesting compromises • Paraphrasing the speaker’s views, feelings, and concerns • Helping others save face when taking a different position (Muse, Sperry, Voelker, Harrington, & Harris, pp. 1-23)
Trust in Schools …a growing body of case studies and clinical narratives directs our attention to the engaging but elusive idea of social trust as essential for meaningful school improvement. Anthony S. Bryk and Barbara Schneider
Trust in Schools …we conducted almost a decade of intensive case study research and longitudinal statistical analyses from more than 400 Chicago elementary schools. We spent approximately four years in 12 different school communities observing school meetings and events; conducting interviews and focus groups with principals, teachers, parents, and community leaders; observing classroom instruction; and talking to teachers about the progress and problems in their reform efforts. Anthony S. Bryk and Barbara Schneider
Trust • High trust • “Growing trust” • Low trust • Two out of three tell the story!
The Speed of TrustStephen M. R. Covey Dr. Sandra R. Lindsay
The Economics of Trust Trust = Speed Cost Trust = Speed Cost
The 4 Cores of Credibility • Integrity Character • Intent • Capabilities Competence • Results
Activity • Take the deck of cards at your table or share with a small group around you. • Covey’s 13 behaviors are on one set of cards and the “opposite” of each behavior is found on a card in the other deck. Spend some time talking about the behaviors and their opposites as you match the behavior and its opposite together.
Behavior 1: Talk Straight • Be honest. • Tell the truth. • Let people know where you stand. • Use simple language. • Call things what they are. • Demonstrate integrity. • Don’t manipulate people or distort facts. • Don’t spin the truth. • Don’t leave false impressions.
Behavior 2: Demonstrate Respect • Genuinely care for others. • Show you care. • Respect the dignity of every person and every role. • Treat everyone with respect, especially those who can’t do anything for you. • Show kindness in the little things. • Don’t fake caring. • Don’t attempt to be “efficient” with people.
Behavior 3: Create Transparency • Tell the truth in a way people can verify. • Get real and genuine. • Be open and authentic. • Err on the side of disclosure. • Operate on the premise of “What you see is what you get.” • Don’t have hidden agendas. • Don’t hide information.
Behavior 4: Right Wrongs • Make things right when you are wrong. • Apologize quickly. • Make restitution where possible. • Practice “service recoveries.” • Demonstrate personal humility. • Don’t cover things up. • Don’t let pride get in the way of doing things right.
Behavior 5: Show Loyalty • Give credit freely. • Acknowledge the contributions of others. • Speak about people as if they were present. • Represent others who aren’t there to speak for themselves. • Don’t bad mouth others behind their backs. • Don’t disclose others’ private information.
Behavior 6: Deliver Results • Establish a track record of results. • Get the right things done. • Make things happen. • Accomplish what you’re hired to do. • Be on time and within budget. • Don’t overpromise and underdeliver. • Don’t make excuses for not delivering.
Behavior 7: Get Better • Continuously improve. • Increase your capabilities. • Be a constant learner. • Develop feedback systems—both formal and informal. • Act on the feedback you receive. • Thank people for feedback. • Don’t consider yourself above feedback. • Don’t assume today’s knowledge and skills will be sufficient for tomorrow’s challenges.
Behavior 8: Confront Reality • Address the tough stuff directly. • Acknowledge the unsaid. • Lead out courageously in conversation. • Remove the “sword from their hands.” • Don’t skirt the real issues. • Don’t bury your head in the sand.
Behavior 9: Clarify Expectations • Disclose and reveal expectations. • Discuss them. • Validate them. • Renegotiate them if needed and possible. • Don’t violate expectations. • Don’t assume that expectations are clear or shared.
Behavior 10: Practice Accountability • Hold yourself accountable. • Hold others accountable. • Take responsibility for results. • Be clear on how you’ll communicate how you are doing—and how others are doing. • Don’t avoid or shirk responsibility. • Don’t blame others or point fingers when things go wrong.
Behavior 11: Listen First • Listen before you speak. • Understand. • Diagnose. • Listen with your ears—and your eyes and heart. • Find out what the most important behaviors are to the people with whom you’re working. • Don’t assume you know what matters most to others. • Don’t presume you have all the answers—or all the questions.
Behavior 12: Keep Commitments • Say what you’re going to do, then do what you say you’re going to do. • Make commitments carefully and keep them. • Make keeping commitments the symbol of your honor. • Don’t break confidences. • Don’t attempt to PR your way out of a commitment you’ve broken.
Behavior 13: Extend Trust • Demonstrate a propensity to trust. • Extend trust abundantly to those who have earned your trust. • Extend conditionally to those who are earning your trust. • Learn how to extend trust appropriately to others, based in the situation, risk, and credibility (character and competence) of the people involved. But have a propensity to trust. • Don’t withhold trust because there is risk involved.
Activity: Trust Behaviors • Use the first grid in each block on the activity sheet provided to rate yourself in each of the trust behaviors. • Use the second grid in each block to rate your organization in each of the trust behaviors. • Decide what you can do next to make the biggest difference in your personal behavior and in your organization to make a difference.
Regaining Trust Whether you lose the trust of others through a conscious act of betrayal, poor judgment, an honest mistake, a failure of competence, or a simple misunderstanding, the path to restoration is the same—to increase your personal credibility and behave in ways that inspire trust.
- More by User

The Importance of
ETHICS. The Importance of. in. SCHOLASTIC JOURNALISM. Maggie Cogar Kent State University. “Ethics requires that intelligence fuse with intuition, that the process be internalized, and that decisions be made quickly and naturally." - Rushworth Kidder.
429 views • 12 slides

The Impact of Trust
The Impact of Trust. Bruce E. Brown www.proactivecoaching.info. Liberal Arts – 43% Education – 52% Medical – 63% Law – 63% Business – 75%. The Importance of Trust on Teams. “Trust men and the will be true to you. Treat them greatly and they will show themselves great.” Emerson
353 views • 21 slides

The Speed of Trust
The Speed of Trust. Stephen M.R. Covey. Trust Myths. Myth – Trust is nice to have - social virtue Reality – Trust is hard-edged economic driver gives speed & low costs that can be measured Myth – Trust is slow
2.75k views • 11 slides

ETHICS. The Importance of . in. SCHOLASTIC JOURNALISM. Maggie Cogar Kent State University. “Ethics requires that intelligence fuse with intuition, that the process be internalized, and that decisions be made quickly and naturally." - Rushworth Kidder.
373 views • 12 slides

The Trust. Council of Governors 6 July 2011. The area. ‘Outer NEL’ 859,000 pop. 2500 staff. ‘SW Essex’ 420,000 pop. 1470 staff. Redbridge. Waltham Forest. South West Essex. Barking & Dagenham. Havering. The journey so far. June 2008 Achieved Foundation Trust status. July 2009
321 views • 7 slides

The Speed of Trust. The One Thing That Changes Everything Author: Stephen M. R. Covey With Rebecca R. Merrill Bridgett Smith Change Theory Summer 2007. “Leadership” is getting results in a way that inspires trust.
7.31k views • 32 slides

Architects of Trust: Building Trust in the Workplace
Architects of Trust: Building Trust in the Workplace. Ann Brown, MA A&R Brown Business Group Inc. www.bccq.org. Some Survey Numbers. 70% of employees believe that trust and loyalty within the firms is declining 60% do not believe that their management is upright, ethical and honest
1.79k views • 40 slides

Building Trust in the Age of Trust-Busters
Building Trust in the Age of Trust-Busters. Prepared by: Elise M. Farnham CPCU, ARM, AIM, CPIW President, Illumine Consulting www.elisefarnham.com 770-367-3148 [email protected]. Advantages Demonstration of shared moral values Leads to authenticity
331 views • 11 slides

The Power of Trust
The Power of Trust. Dr Robert Ghanea-Hercock www.agentdynamics.com. What is trust?. Who should I trust?. Trust.
732 views • 50 slides

The importance of……?
“ THE SHIFT FROM FOOD-GATHERING TO FOOD-PRODUCING CULTURES REPRESENTS ONE OF THE GREATEST BREAKTHROUGHS IN WORLD HISTORY. ”. The importance of……?. Part A Make a list of the snacks and meals that you ate yesterday and today. Where do all these foods and drinks originate from? Part B
491 views • 31 slides

The importance of……?. Make a list of the snacks and meals that you ate yesterday and today. Where do all these foodstuffs and drinks originate from? Make a list of everything that exists in the modern world around you.
331 views • 17 slides

Series: The Importance of... The Importance Of Helpers
Series: The Importance of... The Importance Of Helpers. The Importance Of Helpers In the beginning... Genesis 2:18(KJV) 18 And the LORD God said, It is not good that the man should be alone; I will make him an help meet for him.
777 views • 52 slides

The importance of
The importance of. REPENTANCE. PART 2. ALSO IN THE NEW TESTAMENT. LET US LOOK AT SOME WHO TAUGHT REPENTANCE. Mark 1:4 John the Baptist burst onto the scene- denouncing SIN- and calling on the people to repent. preaching a BAPTISM OF REPENTANCE -for forgiveness of sins.
503 views • 30 slides

Trust The Pain, Trust The Diagnosis
Joint pain can be excruciating. May be it’s time to get it checked. And if you’re unsure how it’s going to work, your arthroscopy doctor can explain things better to you. Learn all about joint pain and its possible treatments in the points below. Make sure you get under your skin to see where the problem lies. Let your doctor handle the rest! http://www.advfas.com/
205 views • 8 slides

The Importance And Ways Of Building High-Trust Organizations
Despite the significant role it plays in building a growth-oriented and culturally rich organization, trust is often taken most for-granted within an organization. Building a high-trust organization is not something that can be accomplished overnight. Rather, it is requires investment of considerable efforts and a great deal of care on part of each employee within the organization to attain this objective. In this context, the executive search firms in China, stress on the importance of using correct tools and methodologies for building a high-trust organization. • Benefits Of Building A High-Trust Organization • Ways To Build High-Trust Organization • Encouraging Transparency In Communication • Ensure Greater Employee Engagement In Decision Making • Developing A Positive Attitude To Constructive Criticism Involving the employees in the decision making processes can go a long way in building their trust in management. Such initiatives make the employees feel like being an integral and vital part of the organization and this naturally enhances their level of loyalty. On their part, the employees need to trust the organization management about having their best interests in mind while making key policy decisions. The process of building a high-trust organization is continuous one and needs to be carried out through the use of right methods. The top executive search firms in China have identified the following ways that can help businesses to become high-trust organizations in effective manner.
113 views • 11 slides

The Speed of Trust. Based on the book by Stephen MR Covey. INTRODUCTION. Trust means confidence. When we trust people, we have confidence in them – in their integrity and in their abilities. When we distrust people, we are suspicious of them.
473 views • 33 slides

525 views • 50 slides

The Blessing of Trust
The Blessing of Trust. Peter Fitch, St. Croix Vineyard Sunday, November 8, 2015. Proverbs 3:5-6. 5 Trust in the LORD with all your heart And do not lean on your own understanding. 6 In all your ways acknowledge Him, And He will make your paths straight. Timely.
194 views • 15 slides

The importance of. REPENTANCE. PART 1. A turn around. ECNATNEPER. REPENTANCE. As ECNATNEPER makes no sense; neither does REPENTANCE without fruits!. “Bring forth therefore fruits worthy of repentance” (Luke 3:8). The Importance of REPENTANCE. OBSERVATION
334 views • 22 slides

The Speed of Trust. Stephen M. R. Covey. What is trust?. What are two key areas where confidence is important if trust is to be established? Integrity Abilities. Distrust. Distrust involves suspicion of a person’s integrity, agenda, capabilities, and/or track record.
765 views • 28 slides

Importance of Private Trust Fund
you will be capable to increase the network of administrators. It is a junior trust fund area section untaxed savings accounts that were on the market for youngsters born between one Sep 2002 and a couplet of Gregorian calendar month 2011
61 views • 5 slides

Try Process AI free
How to improve customer satisfaction in a powerpoint presentation.
Are you struggling to keep your audience engaged during PowerPoint presentations? Do you want to leave a lasting impression on your clients? Look no further, as this article will guide you on how to improve customer satisfaction in your presentations, leading to increased interest and better results.
What Is Customer Satisfaction?
Customer satisfaction refers to the level of satisfaction a person feels after using a product or service. It encompasses the customer’s perception of the value received in relation to their expectations. Factors such as product quality, service delivery, and overall customer experience contribute to customer satisfaction. Understanding what customer satisfaction is is essential for businesses to identify areas for improvement and maintain customer loyalty.
Why Is Customer Satisfaction Important?
Customer satisfaction is vital for the success of any business. When customers are satisfied, they are more likely to return, refer others, and leave positive reviews. This, in turn, can lead to increased loyalty and a higher customer lifetime value. It is also crucial to understand the importance of customer satisfaction in order to identify areas for improvement and improve overall business performance.
How Does Customer Satisfaction Affect Business?
- Customer Retention: Satisfied customers are likely to remain loyal, leading to repeat purchases and long-term relationships.
- Positive Word of Mouth: Happy customers act as brand advocates, attracting new customers through recommendations and positive reviews.
- Increased Profits: Satisfied customers contribute to higher sales, enhanced brand reputation, and reduced marketing costs.
- Reduced Churn Rate: High customer satisfaction lowers the likelihood of customers switching to competitors, thus reducing churn rate.
To understand the impact of customer satisfaction on business, it is important to consider how it affects various aspects such as customer retention, positive word of mouth, increased profits, and reduced churn rate. To achieve these benefits, businesses should focus on consistent quality, exceptional service, competitive pricing, and continuous improvement based on customer feedback.
What Are the Factors That Influence Customer Satisfaction?
When it comes to customer satisfaction, there are various factors that can greatly influence a customer’s perception of a product or service. In this section, we will discuss the key elements that can impact customer satisfaction and how they play a role in creating a positive customer experience. From the quality of the product or service to the level of customer service, we will uncover the different factors that businesses must consider in order to improve customer satisfaction.
1. Quality of Product/Service
- Conduct market research to gain insight into customer needs and expectations regarding the quality of our products and services.
- Implement quality control measures to maintain consistency and reliability in our offerings.
- Train employees to provide high-quality service and effectively address any product-related inquiries.
- Solicit feedback and reviews from customers to identify areas for improvement in our product and service quality.
- Regularly update and innovate our products and services based on customer feedback and industry trends, ensuring the highest level of quality.
In a similar approach, a local bakery improved the quality of their products by sourcing organic ingredients, resulting in a significant increase in customer satisfaction and loyalty.
2. Customer Service
- Train your staff to be empathetic and attentive towards customers.
- Implement a system for swift resolution of customer issues.
- Establish clear communication channels for efficient customer support.
- Personalize the customer experience to build strong relationships.
- Solicit and take action on customer feedback for continual improvement of services.
In 1909, Harry Gordon Selfridge, an American retail magnate, revolutionized the concept of customer service by introducing the motto ‘ The customer is always right ‘ at his department store in London. This set a new standard for businesses to prioritize the needs and satisfaction of their customers.
- Understand market pricing and customer expectations.
- Offer transparent pricing with no hidden costs.
- Provide value through competitive pricing strategies, taking into account the crucial factor of 3. price.
- Implement loyalty programs or discounts for returning customers.
- Regularly review pricing strategies to stay competitive and profitable, keeping in mind the importance of 3. price in influencing customer satisfaction and purchase decisions.
Did you know that 3. price is a crucial factor influencing customer satisfaction and purchase decisions?
4. Brand Reputation
Brand reputation is crucial when it comes to customer satisfaction. A positive brand image, based on reliability and trust, promotes customer loyalty and contentment. When a brand consistently follows through on its promises, customers are more likely to support the brand and remain satisfied with their experiences.
In 1985, Coca-Cola introduced New Coke , which received significant backlash due to its altered taste. This had a negative impact on the brand’s reputation, resulting in customer dissatisfaction and a decline in sales.
5. Convenience
- Location: Ensure convenient access to your products or services through multiple channels and extended opening hours.
- Communication: Provide clear and concise information about your offerings, policies, and procedures to make things more convenient for customers.
- Technology: Implement user-friendly online platforms and mobile apps for seamless transactions and interactions, adding to the convenience factor.
- Feedback: Act on customer feedback to streamline processes and enhance overall convenience.
In the early 20th century, the introduction of self-service supermarkets revolutionized convenience for shoppers, allowing them to independently browse and select items, reshaping the retail landscape.
How Can You Measure Customer Satisfaction?
In order to improve customer satisfaction, it is important to have a way to measure it. This section will discuss various methods for gauging customer satisfaction, including surveys, Net Promoter Score (NPS), and customer feedback. By utilizing these tools, you can gain valuable insights into the level of satisfaction your customers have with your products or services, and make necessary improvements to enhance their overall experience.
- Establish the objectives of the survey and identify the specific information that you wish to collect.
- Create clear and concise questions that align with the objectives.
- Choose the most suitable survey method, whether it be phone, email, or online platforms.
- Take into account the timing and frequency of the survey to ensure accurate feedback is captured.
- Analyze and interpret the survey data to pinpoint areas that can be improved upon.
2. Net Promoter Score
- Understand Net Promoter Score (NPS): Familiarize yourself with the NPS system and its scale from 0 to 10, which is used to measure customer loyalty and satisfaction.
- Survey Implementation: Utilize NPS surveys to gather customer feedback by asking the ‘likelihood to recommend’ question.
- Segment Responses: Categorize responses into promoters, passives, and detractors based on their rating.
- Analyze and Act: Regularly analyze NPS results and take action to enhance customer satisfaction, with a focus on detractors in order to convert them into promoters.
- Continuous Improvement: Use NPS as a continuous improvement tool, tracking changes in scores over time.
3. Customer Feedback
Customer feedback , a crucial component of ensuring customer satisfaction, can be gathered through a variety of channels including surveys, online reviews, and direct communication.
How to Improve Customer Satisfaction in a PowerPoint Presentation?
When giving a PowerPoint presentation, it is important to not only convey information but also engage and satisfy your audience. In this section, we will discuss five key strategies for improving customer satisfaction in a PowerPoint presentation. From understanding your audience to using visual aids and incorporating a call to action, these techniques will help you create a memorable and effective presentation that leaves your audience feeling satisfied and informed.
1. Know Your Audience
- Evaluate the demographics, interests, and knowledge level of your audience.
- Understand the needs, preferences, and expectations of your audience.
- Adapt the content, tone, and delivery method to resonate with your audience.
- Anticipate potential questions or concerns and address them proactively.
- Ensure the presentation aligns with the audience’s objectives and values.
2. Use Visual Aids
- Utilize high-quality images and graphics to enhance understanding and retention.
- Include charts and graphs to effectively present data and statistics.
- Incorporate videos or animations to engage and illustrate complex concepts.
When creating a PowerPoint presentation on improving customer satisfaction, visual aids play a crucial role in capturing and maintaining audience attention.
3. Tell a Story
- Craft a narrative with a beginning, middle, and end to illustrate a customer’s journey.
- Personalize the story by incorporating relatable characters or situations.
- Highlight challenges faced by the customer and how your product/service resolved them.
- Use visuals to enhance the storytelling experience and evoke emotions.
- End with a satisfying resolution that emphasizes the positive impact of customer satisfaction.
To captivate your audience, infuse your presentation with engaging anecdotes and captivating storytelling techniques, ensuring a memorable and impactful delivery.
4. Use Data and Statistics
Utilizing data and statistics is essential for improving customer satisfaction. By analyzing customer feedback, purchase patterns, and demographic information, businesses can identify areas for improvement.
For example, tracking customer service response times and resolution rates can reveal operational inefficiencies. Additionally, utilizing statistical models can help predict customer behavior and personalize offerings.
Presenting these insights in a PowerPoint presentation can effectively demonstrate the impact of data-driven strategies on customer satisfaction.
5. Include a Call to Action
- Evaluate the desired action: Determine what specific action you want your audience to take.
- Create a sense of urgency: Encourage immediate action by setting a deadline or offering limited-time promotions.
- Provide clear instructions: Clearly outline the steps your audience needs to take to fulfill the call to action.
- Use compelling language: Use persuasive and compelling language to motivate your audience to act.
- Offer incentives: Provide incentives to encourage your audience to respond to the call to action, such as discounts or free trials.
In 2007, during the launch of the iPhone, Apple included a call to action in their marketing campaign, urging customers to ‘Experience the iPhone today at your nearest Apple Store.’ This call to action prompted a surge in customer engagement and sales.

No credit card required
Your projects are processes, Take control of them today.
- Open access
- Published: 18 April 2024
Research ethics and artificial intelligence for global health: perspectives from the global forum on bioethics in research
- James Shaw 1 , 13 ,
- Joseph Ali 2 , 3 ,
- Caesar A. Atuire 4 , 5 ,
- Phaik Yeong Cheah 6 ,
- Armando Guio Español 7 ,
- Judy Wawira Gichoya 8 ,
- Adrienne Hunt 9 ,
- Daudi Jjingo 10 ,
- Katherine Littler 9 ,
- Daniela Paolotti 11 &
- Effy Vayena 12
BMC Medical Ethics volume 25 , Article number: 46 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
973 Accesses
6 Altmetric
Metrics details
The ethical governance of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in health care and public health continues to be an urgent issue for attention in policy, research, and practice. In this paper we report on central themes related to challenges and strategies for promoting ethics in research involving AI in global health, arising from the Global Forum on Bioethics in Research (GFBR), held in Cape Town, South Africa in November 2022.
The GFBR is an annual meeting organized by the World Health Organization and supported by the Wellcome Trust, the US National Institutes of Health, the UK Medical Research Council (MRC) and the South African MRC. The forum aims to bring together ethicists, researchers, policymakers, research ethics committee members and other actors to engage with challenges and opportunities specifically related to research ethics. In 2022 the focus of the GFBR was “Ethics of AI in Global Health Research”. The forum consisted of 6 case study presentations, 16 governance presentations, and a series of small group and large group discussions. A total of 87 participants attended the forum from 31 countries around the world, representing disciplines of bioethics, AI, health policy, health professional practice, research funding, and bioinformatics. In this paper, we highlight central insights arising from GFBR 2022.
We describe the significance of four thematic insights arising from the forum: (1) Appropriateness of building AI, (2) Transferability of AI systems, (3) Accountability for AI decision-making and outcomes, and (4) Individual consent. We then describe eight recommendations for governance leaders to enhance the ethical governance of AI in global health research, addressing issues such as AI impact assessments, environmental values, and fair partnerships.
Conclusions
The 2022 Global Forum on Bioethics in Research illustrated several innovations in ethical governance of AI for global health research, as well as several areas in need of urgent attention internationally. This summary is intended to inform international and domestic efforts to strengthen research ethics and support the evolution of governance leadership to meet the demands of AI in global health research.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
The ethical governance of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in health care and public health continues to be an urgent issue for attention in policy, research, and practice [ 1 , 2 , 3 ]. Beyond the growing number of AI applications being implemented in health care, capabilities of AI models such as Large Language Models (LLMs) expand the potential reach and significance of AI technologies across health-related fields [ 4 , 5 ]. Discussion about effective, ethical governance of AI technologies has spanned a range of governance approaches, including government regulation, organizational decision-making, professional self-regulation, and research ethics review [ 6 , 7 , 8 ]. In this paper, we report on central themes related to challenges and strategies for promoting ethics in research involving AI in global health research, arising from the Global Forum on Bioethics in Research (GFBR), held in Cape Town, South Africa in November 2022. Although applications of AI for research, health care, and public health are diverse and advancing rapidly, the insights generated at the forum remain highly relevant from a global health perspective. After summarizing important context for work in this domain, we highlight categories of ethical issues emphasized at the forum for attention from a research ethics perspective internationally. We then outline strategies proposed for research, innovation, and governance to support more ethical AI for global health.
In this paper, we adopt the definition of AI systems provided by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) as our starting point. Their definition states that an AI system is “a machine-based system that can, for a given set of human-defined objectives, make predictions, recommendations, or decisions influencing real or virtual environments. AI systems are designed to operate with varying levels of autonomy” [ 9 ]. The conceptualization of an algorithm as helping to constitute an AI system, along with hardware, other elements of software, and a particular context of use, illustrates the wide variety of ways in which AI can be applied. We have found it useful to differentiate applications of AI in research as those classified as “AI systems for discovery” and “AI systems for intervention”. An AI system for discovery is one that is intended to generate new knowledge, for example in drug discovery or public health research in which researchers are seeking potential targets for intervention, innovation, or further research. An AI system for intervention is one that directly contributes to enacting an intervention in a particular context, for example informing decision-making at the point of care or assisting with accuracy in a surgical procedure.
The mandate of the GFBR is to take a broad view of what constitutes research and its regulation in global health, with special attention to bioethics in Low- and Middle- Income Countries. AI as a group of technologies demands such a broad view. AI development for health occurs in a variety of environments, including universities and academic health sciences centers where research ethics review remains an important element of the governance of science and innovation internationally [ 10 , 11 ]. In these settings, research ethics committees (RECs; also known by different names such as Institutional Review Boards or IRBs) make decisions about the ethical appropriateness of projects proposed by researchers and other institutional members, ultimately determining whether a given project is allowed to proceed on ethical grounds [ 12 ].
However, research involving AI for health also takes place in large corporations and smaller scale start-ups, which in some jurisdictions fall outside the scope of research ethics regulation. In the domain of AI, the question of what constitutes research also becomes blurred. For example, is the development of an algorithm itself considered a part of the research process? Or only when that algorithm is tested under the formal constraints of a systematic research methodology? In this paper we take an inclusive view, in which AI development is included in the definition of research activity and within scope for our inquiry, regardless of the setting in which it takes place. This broad perspective characterizes the approach to “research ethics” we take in this paper, extending beyond the work of RECs to include the ethical analysis of the wide range of activities that constitute research as the generation of new knowledge and intervention in the world.
Ethical governance of AI in global health
The ethical governance of AI for global health has been widely discussed in recent years. The World Health Organization (WHO) released its guidelines on ethics and governance of AI for health in 2021, endorsing a set of six ethical principles and exploring the relevance of those principles through a variety of use cases. The WHO guidelines also provided an overview of AI governance, defining governance as covering “a range of steering and rule-making functions of governments and other decision-makers, including international health agencies, for the achievement of national health policy objectives conducive to universal health coverage.” (p. 81) The report usefully provided a series of recommendations related to governance of seven domains pertaining to AI for health: data, benefit sharing, the private sector, the public sector, regulation, policy observatories/model legislation, and global governance. The report acknowledges that much work is yet to be done to advance international cooperation on AI governance, especially related to prioritizing voices from Low- and Middle-Income Countries (LMICs) in global dialogue.
One important point emphasized in the WHO report that reinforces the broader literature on global governance of AI is the distribution of responsibility across a wide range of actors in the AI ecosystem. This is especially important to highlight when focused on research for global health, which is specifically about work that transcends national borders. Alami et al. (2020) discussed the unique risks raised by AI research in global health, ranging from the unavailability of data in many LMICs required to train locally relevant AI models to the capacity of health systems to absorb new AI technologies that demand the use of resources from elsewhere in the system. These observations illustrate the need to identify the unique issues posed by AI research for global health specifically, and the strategies that can be employed by all those implicated in AI governance to promote ethically responsible use of AI in global health research.
RECs and the regulation of research involving AI
RECs represent an important element of the governance of AI for global health research, and thus warrant further commentary as background to our paper. Despite the importance of RECs, foundational questions have been raised about their capabilities to accurately understand and address ethical issues raised by studies involving AI. Rahimzadeh et al. (2023) outlined how RECs in the United States are under-prepared to align with recent federal policy requiring that RECs review data sharing and management plans with attention to the unique ethical issues raised in AI research for health [ 13 ]. Similar research in South Africa identified variability in understanding of existing regulations and ethical issues associated with health-related big data sharing and management among research ethics committee members [ 14 , 15 ]. The effort to address harms accruing to groups or communities as opposed to individuals whose data are included in AI research has also been identified as a unique challenge for RECs [ 16 , 17 ]. Doerr and Meeder (2022) suggested that current regulatory frameworks for research ethics might actually prevent RECs from adequately addressing such issues, as they are deemed out of scope of REC review [ 16 ]. Furthermore, research in the United Kingdom and Canada has suggested that researchers using AI methods for health tend to distinguish between ethical issues and social impact of their research, adopting an overly narrow view of what constitutes ethical issues in their work [ 18 ].
The challenges for RECs in adequately addressing ethical issues in AI research for health care and public health exceed a straightforward survey of ethical considerations. As Ferretti et al. (2021) contend, some capabilities of RECs adequately cover certain issues in AI-based health research, such as the common occurrence of conflicts of interest where researchers who accept funds from commercial technology providers are implicitly incentivized to produce results that align with commercial interests [ 12 ]. However, some features of REC review require reform to adequately meet ethical needs. Ferretti et al. outlined weaknesses of RECs that are longstanding and those that are novel to AI-related projects, proposing a series of directions for development that are regulatory, procedural, and complementary to REC functionality. The work required on a global scale to update the REC function in response to the demands of research involving AI is substantial.
These issues take greater urgency in the context of global health [ 19 ]. Teixeira da Silva (2022) described the global practice of “ethics dumping”, where researchers from high income countries bring ethically contentious practices to RECs in low-income countries as a strategy to gain approval and move projects forward [ 20 ]. Although not yet systematically documented in AI research for health, risk of ethics dumping in AI research is high. Evidence is already emerging of practices of “health data colonialism”, in which AI researchers and developers from large organizations in high-income countries acquire data to build algorithms in LMICs to avoid stricter regulations [ 21 ]. This specific practice is part of a larger collection of practices that characterize health data colonialism, involving the broader exploitation of data and the populations they represent primarily for commercial gain [ 21 , 22 ]. As an additional complication, AI algorithms trained on data from high-income contexts are unlikely to apply in straightforward ways to LMIC settings [ 21 , 23 ]. In the context of global health, there is widespread acknowledgement about the need to not only enhance the knowledge base of REC members about AI-based methods internationally, but to acknowledge the broader shifts required to encourage their capabilities to more fully address these and other ethical issues associated with AI research for health [ 8 ].
Although RECs are an important part of the story of the ethical governance of AI for global health research, they are not the only part. The responsibilities of supra-national entities such as the World Health Organization, national governments, organizational leaders, commercial AI technology providers, health care professionals, and other groups continue to be worked out internationally. In this context of ongoing work, examining issues that demand attention and strategies to address them remains an urgent and valuable task.
The GFBR is an annual meeting organized by the World Health Organization and supported by the Wellcome Trust, the US National Institutes of Health, the UK Medical Research Council (MRC) and the South African MRC. The forum aims to bring together ethicists, researchers, policymakers, REC members and other actors to engage with challenges and opportunities specifically related to research ethics. Each year the GFBR meeting includes a series of case studies and keynotes presented in plenary format to an audience of approximately 100 people who have applied and been competitively selected to attend, along with small-group breakout discussions to advance thinking on related issues. The specific topic of the forum changes each year, with past topics including ethical issues in research with people living with mental health conditions (2021), genome editing (2019), and biobanking/data sharing (2018). The forum is intended to remain grounded in the practical challenges of engaging in research ethics, with special interest in low resource settings from a global health perspective. A post-meeting fellowship scheme is open to all LMIC participants, providing a unique opportunity to apply for funding to further explore and address the ethical challenges that are identified during the meeting.
In 2022, the focus of the GFBR was “Ethics of AI in Global Health Research”. The forum consisted of 6 case study presentations (both short and long form) reporting on specific initiatives related to research ethics and AI for health, and 16 governance presentations (both short and long form) reporting on actual approaches to governing AI in different country settings. A keynote presentation from Professor Effy Vayena addressed the topic of the broader context for AI ethics in a rapidly evolving field. A total of 87 participants attended the forum from 31 countries around the world, representing disciplines of bioethics, AI, health policy, health professional practice, research funding, and bioinformatics. The 2-day forum addressed a wide range of themes. The conference report provides a detailed overview of each of the specific topics addressed while a policy paper outlines the cross-cutting themes (both documents are available at the GFBR website: https://www.gfbr.global/past-meetings/16th-forum-cape-town-south-africa-29-30-november-2022/ ). As opposed to providing a detailed summary in this paper, we aim to briefly highlight central issues raised, solutions proposed, and the challenges facing the research ethics community in the years to come.
In this way, our primary aim in this paper is to present a synthesis of the challenges and opportunities raised at the GFBR meeting and in the planning process, followed by our reflections as a group of authors on their significance for governance leaders in the coming years. We acknowledge that the views represented at the meeting and in our results are a partial representation of the universe of views on this topic; however, the GFBR leadership invested a great deal of resources in convening a deeply diverse and thoughtful group of researchers and practitioners working on themes of bioethics related to AI for global health including those based in LMICs. We contend that it remains rare to convene such a strong group for an extended time and believe that many of the challenges and opportunities raised demand attention for more ethical futures of AI for health. Nonetheless, our results are primarily descriptive and are thus not explicitly grounded in a normative argument. We make effort in the Discussion section to contextualize our results by describing their significance and connecting them to broader efforts to reform global health research and practice.
Uniquely important ethical issues for AI in global health research
Presentations and group dialogue over the course of the forum raised several issues for consideration, and here we describe four overarching themes for the ethical governance of AI in global health research. Brief descriptions of each issue can be found in Table 1 . Reports referred to throughout the paper are available at the GFBR website provided above.
The first overarching thematic issue relates to the appropriateness of building AI technologies in response to health-related challenges in the first place. Case study presentations referred to initiatives where AI technologies were highly appropriate, such as in ear shape biometric identification to more accurately link electronic health care records to individual patients in Zambia (Alinani Simukanga). Although important ethical issues were raised with respect to privacy, trust, and community engagement in this initiative, the AI-based solution was appropriately matched to the challenge of accurately linking electronic records to specific patient identities. In contrast, forum participants raised questions about the appropriateness of an initiative using AI to improve the quality of handwashing practices in an acute care hospital in India (Niyoshi Shah), which led to gaming the algorithm. Overall, participants acknowledged the dangers of techno-solutionism, in which AI researchers and developers treat AI technologies as the most obvious solutions to problems that in actuality demand much more complex strategies to address [ 24 ]. However, forum participants agreed that RECs in different contexts have differing degrees of power to raise issues of the appropriateness of an AI-based intervention.
The second overarching thematic issue related to whether and how AI-based systems transfer from one national health context to another. One central issue raised by a number of case study presentations related to the challenges of validating an algorithm with data collected in a local environment. For example, one case study presentation described a project that would involve the collection of personally identifiable data for sensitive group identities, such as tribe, clan, or religion, in the jurisdictions involved (South Africa, Nigeria, Tanzania, Uganda and the US; Gakii Masunga). Doing so would enable the team to ensure that those groups were adequately represented in the dataset to ensure the resulting algorithm was not biased against specific community groups when deployed in that context. However, some members of these communities might desire to be represented in the dataset, whereas others might not, illustrating the need to balance autonomy and inclusivity. It was also widely recognized that collecting these data is an immense challenge, particularly when historically oppressive practices have led to a low-trust environment for international organizations and the technologies they produce. It is important to note that in some countries such as South Africa and Rwanda, it is illegal to collect information such as race and tribal identities, re-emphasizing the importance for cultural awareness and avoiding “one size fits all” solutions.
The third overarching thematic issue is related to understanding accountabilities for both the impacts of AI technologies and governance decision-making regarding their use. Where global health research involving AI leads to longer-term harms that might fall outside the usual scope of issues considered by a REC, who is to be held accountable, and how? This question was raised as one that requires much further attention, with law being mixed internationally regarding the mechanisms available to hold researchers, innovators, and their institutions accountable over the longer term. However, it was recognized in breakout group discussion that many jurisdictions are developing strong data protection regimes related specifically to international collaboration for research involving health data. For example, Kenya’s Data Protection Act requires that any internationally funded projects have a local principal investigator who will hold accountability for how data are shared and used [ 25 ]. The issue of research partnerships with commercial entities was raised by many participants in the context of accountability, pointing toward the urgent need for clear principles related to strategies for engagement with commercial technology companies in global health research.
The fourth and final overarching thematic issue raised here is that of consent. The issue of consent was framed by the widely shared recognition that models of individual, explicit consent might not produce a supportive environment for AI innovation that relies on the secondary uses of health-related datasets to build AI algorithms. Given this recognition, approaches such as community oversight of health data uses were suggested as a potential solution. However, the details of implementing such community oversight mechanisms require much further attention, particularly given the unique perspectives on health data in different country settings in global health research. Furthermore, some uses of health data do continue to require consent. One case study of South Africa, Nigeria, Kenya, Ethiopia and Uganda suggested that when health data are shared across borders, individual consent remains necessary when data is transferred from certain countries (Nezerith Cengiz). Broader clarity is necessary to support the ethical governance of health data uses for AI in global health research.
Recommendations for ethical governance of AI in global health research
Dialogue at the forum led to a range of suggestions for promoting ethical conduct of AI research for global health, related to the various roles of actors involved in the governance of AI research broadly defined. The strategies are written for actors we refer to as “governance leaders”, those people distributed throughout the AI for global health research ecosystem who are responsible for ensuring the ethical and socially responsible conduct of global health research involving AI (including researchers themselves). These include RECs, government regulators, health care leaders, health professionals, corporate social accountability officers, and others. Enacting these strategies would bolster the ethical governance of AI for global health more generally, enabling multiple actors to fulfill their roles related to governing research and development activities carried out across multiple organizations, including universities, academic health sciences centers, start-ups, and technology corporations. Specific suggestions are summarized in Table 2 .
First, forum participants suggested that governance leaders including RECs, should remain up to date on recent advances in the regulation of AI for health. Regulation of AI for health advances rapidly and takes on different forms in jurisdictions around the world. RECs play an important role in governance, but only a partial role; it was deemed important for RECs to acknowledge how they fit within a broader governance ecosystem in order to more effectively address the issues within their scope. Not only RECs but organizational leaders responsible for procurement, researchers, and commercial actors should all commit to efforts to remain up to date about the relevant approaches to regulating AI for health care and public health in jurisdictions internationally. In this way, governance can more adequately remain up to date with advances in regulation.
Second, forum participants suggested that governance leaders should focus on ethical governance of health data as a basis for ethical global health AI research. Health data are considered the foundation of AI development, being used to train AI algorithms for various uses [ 26 ]. By focusing on ethical governance of health data generation, sharing, and use, multiple actors will help to build an ethical foundation for AI development among global health researchers.
Third, forum participants believed that governance processes should incorporate AI impact assessments where appropriate. An AI impact assessment is the process of evaluating the potential effects, both positive and negative, of implementing an AI algorithm on individuals, society, and various stakeholders, generally over time frames specified in advance of implementation [ 27 ]. Although not all types of AI research in global health would warrant an AI impact assessment, this is especially relevant for those studies aiming to implement an AI system for intervention into health care or public health. Organizations such as RECs can use AI impact assessments to boost understanding of potential harms at the outset of a research project, encouraging researchers to more deeply consider potential harms in the development of their study.
Fourth, forum participants suggested that governance decisions should incorporate the use of environmental impact assessments, or at least the incorporation of environment values when assessing the potential impact of an AI system. An environmental impact assessment involves evaluating and anticipating the potential environmental effects of a proposed project to inform ethical decision-making that supports sustainability [ 28 ]. Although a relatively new consideration in research ethics conversations [ 29 ], the environmental impact of building technologies is a crucial consideration for the public health commitment to environmental sustainability. Governance leaders can use environmental impact assessments to boost understanding of potential environmental harms linked to AI research projects in global health over both the shorter and longer terms.
Fifth, forum participants suggested that governance leaders should require stronger transparency in the development of AI algorithms in global health research. Transparency was considered essential in the design and development of AI algorithms for global health to ensure ethical and accountable decision-making throughout the process. Furthermore, whether and how researchers have considered the unique contexts into which such algorithms may be deployed can be surfaced through stronger transparency, for example in describing what primary considerations were made at the outset of the project and which stakeholders were consulted along the way. Sharing information about data provenance and methods used in AI development will also enhance the trustworthiness of the AI-based research process.
Sixth, forum participants suggested that governance leaders can encourage or require community engagement at various points throughout an AI project. It was considered that engaging patients and communities is crucial in AI algorithm development to ensure that the technology aligns with community needs and values. However, participants acknowledged that this is not a straightforward process. Effective community engagement requires lengthy commitments to meeting with and hearing from diverse communities in a given setting, and demands a particular set of skills in communication and dialogue that are not possessed by all researchers. Encouraging AI researchers to begin this process early and build long-term partnerships with community members is a promising strategy to deepen community engagement in AI research for global health. One notable recommendation was that research funders have an opportunity to incentivize and enable community engagement with funds dedicated to these activities in AI research in global health.
Seventh, forum participants suggested that governance leaders can encourage researchers to build strong, fair partnerships between institutions and individuals across country settings. In a context of longstanding imbalances in geopolitical and economic power, fair partnerships in global health demand a priori commitments to share benefits related to advances in medical technologies, knowledge, and financial gains. Although enforcement of this point might be beyond the remit of RECs, commentary will encourage researchers to consider stronger, fairer partnerships in global health in the longer term.
Eighth, it became evident that it is necessary to explore new forms of regulatory experimentation given the complexity of regulating a technology of this nature. In addition, the health sector has a series of particularities that make it especially complicated to generate rules that have not been previously tested. Several participants highlighted the desire to promote spaces for experimentation such as regulatory sandboxes or innovation hubs in health. These spaces can have several benefits for addressing issues surrounding the regulation of AI in the health sector, such as: (i) increasing the capacities and knowledge of health authorities about this technology; (ii) identifying the major problems surrounding AI regulation in the health sector; (iii) establishing possibilities for exchange and learning with other authorities; (iv) promoting innovation and entrepreneurship in AI in health; and (vi) identifying the need to regulate AI in this sector and update other existing regulations.
Ninth and finally, forum participants believed that the capabilities of governance leaders need to evolve to better incorporate expertise related to AI in ways that make sense within a given jurisdiction. With respect to RECs, for example, it might not make sense for every REC to recruit a member with expertise in AI methods. Rather, it will make more sense in some jurisdictions to consult with members of the scientific community with expertise in AI when research protocols are submitted that demand such expertise. Furthermore, RECs and other approaches to research governance in jurisdictions around the world will need to evolve in order to adopt the suggestions outlined above, developing processes that apply specifically to the ethical governance of research using AI methods in global health.
Research involving the development and implementation of AI technologies continues to grow in global health, posing important challenges for ethical governance of AI in global health research around the world. In this paper we have summarized insights from the 2022 GFBR, focused specifically on issues in research ethics related to AI for global health research. We summarized four thematic challenges for governance related to AI in global health research and nine suggestions arising from presentations and dialogue at the forum. In this brief discussion section, we present an overarching observation about power imbalances that frames efforts to evolve the role of governance in global health research, and then outline two important opportunity areas as the field develops to meet the challenges of AI in global health research.
Dialogue about power is not unfamiliar in global health, especially given recent contributions exploring what it would mean to de-colonize global health research, funding, and practice [ 30 , 31 ]. Discussions of research ethics applied to AI research in global health contexts are deeply infused with power imbalances. The existing context of global health is one in which high-income countries primarily located in the “Global North” charitably invest in projects taking place primarily in the “Global South” while recouping knowledge, financial, and reputational benefits [ 32 ]. With respect to AI development in particular, recent examples of digital colonialism frame dialogue about global partnerships, raising attention to the role of large commercial entities and global financial capitalism in global health research [ 21 , 22 ]. Furthermore, the power of governance organizations such as RECs to intervene in the process of AI research in global health varies widely around the world, depending on the authorities assigned to them by domestic research governance policies. These observations frame the challenges outlined in our paper, highlighting the difficulties associated with making meaningful change in this field.
Despite these overarching challenges of the global health research context, there are clear strategies for progress in this domain. Firstly, AI innovation is rapidly evolving, which means approaches to the governance of AI for health are rapidly evolving too. Such rapid evolution presents an important opportunity for governance leaders to clarify their vision and influence over AI innovation in global health research, boosting the expertise, structure, and functionality required to meet the demands of research involving AI. Secondly, the research ethics community has strong international ties, linked to a global scholarly community that is committed to sharing insights and best practices around the world. This global community can be leveraged to coordinate efforts to produce advances in the capabilities and authorities of governance leaders to meaningfully govern AI research for global health given the challenges summarized in our paper.
Limitations
Our paper includes two specific limitations that we address explicitly here. First, it is still early in the lifetime of the development of applications of AI for use in global health, and as such, the global community has had limited opportunity to learn from experience. For example, there were many fewer case studies, which detail experiences with the actual implementation of an AI technology, submitted to GFBR 2022 for consideration than was expected. In contrast, there were many more governance reports submitted, which detail the processes and outputs of governance processes that anticipate the development and dissemination of AI technologies. This observation represents both a success and a challenge. It is a success that so many groups are engaging in anticipatory governance of AI technologies, exploring evidence of their likely impacts and governing technologies in novel and well-designed ways. It is a challenge that there is little experience to build upon of the successful implementation of AI technologies in ways that have limited harms while promoting innovation. Further experience with AI technologies in global health will contribute to revising and enhancing the challenges and recommendations we have outlined in our paper.
Second, global trends in the politics and economics of AI technologies are evolving rapidly. Although some nations are advancing detailed policy approaches to regulating AI more generally, including for uses in health care and public health, the impacts of corporate investments in AI and political responses related to governance remain to be seen. The excitement around large language models (LLMs) and large multimodal models (LMMs) has drawn deeper attention to the challenges of regulating AI in any general sense, opening dialogue about health sector-specific regulations. The direction of this global dialogue, strongly linked to high-profile corporate actors and multi-national governance institutions, will strongly influence the development of boundaries around what is possible for the ethical governance of AI for global health. We have written this paper at a point when these developments are proceeding rapidly, and as such, we acknowledge that our recommendations will need updating as the broader field evolves.
Ultimately, coordination and collaboration between many stakeholders in the research ethics ecosystem will be necessary to strengthen the ethical governance of AI in global health research. The 2022 GFBR illustrated several innovations in ethical governance of AI for global health research, as well as several areas in need of urgent attention internationally. This summary is intended to inform international and domestic efforts to strengthen research ethics and support the evolution of governance leadership to meet the demands of AI in global health research.
Data availability
All data and materials analyzed to produce this paper are available on the GFBR website: https://www.gfbr.global/past-meetings/16th-forum-cape-town-south-africa-29-30-november-2022/ .
Clark P, Kim J, Aphinyanaphongs Y, Marketing, Food US. Drug Administration Clearance of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Enabled Software in and as Medical devices: a systematic review. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(7):e2321792–2321792.
Article Google Scholar
Potnis KC, Ross JS, Aneja S, Gross CP, Richman IB. Artificial intelligence in breast cancer screening: evaluation of FDA device regulation and future recommendations. JAMA Intern Med. 2022;182(12):1306–12.
Siala H, Wang Y. SHIFTing artificial intelligence to be responsible in healthcare: a systematic review. Soc Sci Med. 2022;296:114782.
Yang X, Chen A, PourNejatian N, Shin HC, Smith KE, Parisien C, et al. A large language model for electronic health records. NPJ Digit Med. 2022;5(1):194.
Meskó B, Topol EJ. The imperative for regulatory oversight of large language models (or generative AI) in healthcare. NPJ Digit Med. 2023;6(1):120.
Jobin A, Ienca M, Vayena E. The global landscape of AI ethics guidelines. Nat Mach Intell. 2019;1(9):389–99.
Minssen T, Vayena E, Cohen IG. The challenges for Regulating Medical Use of ChatGPT and other large Language models. JAMA. 2023.
Ho CWL, Malpani R. Scaling up the research ethics framework for healthcare machine learning as global health ethics and governance. Am J Bioeth. 2022;22(5):36–8.
Yeung K. Recommendation of the council on artificial intelligence (OECD). Int Leg Mater. 2020;59(1):27–34.
Maddox TM, Rumsfeld JS, Payne PR. Questions for artificial intelligence in health care. JAMA. 2019;321(1):31–2.
Dzau VJ, Balatbat CA, Ellaissi WF. Revisiting academic health sciences systems a decade later: discovery to health to population to society. Lancet. 2021;398(10318):2300–4.
Ferretti A, Ienca M, Sheehan M, Blasimme A, Dove ES, Farsides B, et al. Ethics review of big data research: what should stay and what should be reformed? BMC Med Ethics. 2021;22(1):1–13.
Rahimzadeh V, Serpico K, Gelinas L. Institutional review boards need new skills to review data sharing and management plans. Nat Med. 2023;1–3.
Kling S, Singh S, Burgess TL, Nair G. The role of an ethics advisory committee in data science research in sub-saharan Africa. South Afr J Sci. 2023;119(5–6):1–3.
Google Scholar
Cengiz N, Kabanda SM, Esterhuizen TM, Moodley K. Exploring perspectives of research ethics committee members on the governance of big data in sub-saharan Africa. South Afr J Sci. 2023;119(5–6):1–9.
Doerr M, Meeder S. Big health data research and group harm: the scope of IRB review. Ethics Hum Res. 2022;44(4):34–8.
Ballantyne A, Stewart C. Big data and public-private partnerships in healthcare and research: the application of an ethics framework for big data in health and research. Asian Bioeth Rev. 2019;11(3):315–26.
Samuel G, Chubb J, Derrick G. Boundaries between research ethics and ethical research use in artificial intelligence health research. J Empir Res Hum Res Ethics. 2021;16(3):325–37.
Murphy K, Di Ruggiero E, Upshur R, Willison DJ, Malhotra N, Cai JC, et al. Artificial intelligence for good health: a scoping review of the ethics literature. BMC Med Ethics. 2021;22(1):1–17.
Teixeira da Silva JA. Handling ethics dumping and neo-colonial research: from the laboratory to the academic literature. J Bioethical Inq. 2022;19(3):433–43.
Ferryman K. The dangers of data colonialism in precision public health. Glob Policy. 2021;12:90–2.
Couldry N, Mejias UA. Data colonialism: rethinking big data’s relation to the contemporary subject. Telev New Media. 2019;20(4):336–49.
Organization WH. Ethics and governance of artificial intelligence for health: WHO guidance. 2021.
Metcalf J, Moss E. Owning ethics: corporate logics, silicon valley, and the institutionalization of ethics. Soc Res Int Q. 2019;86(2):449–76.
Data Protection Act - OFFICE OF THE DATA PROTECTION COMMISSIONER KENYA [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 Sep 30]. https://www.odpc.go.ke/dpa-act/ .
Sharon T, Lucivero F. Introduction to the special theme: the expansion of the health data ecosystem–rethinking data ethics and governance. Big Data & Society. Volume 6. London, England: SAGE Publications Sage UK; 2019. p. 2053951719852969.
Reisman D, Schultz J, Crawford K, Whittaker M. Algorithmic impact assessments: a practical Framework for Public Agency. AI Now. 2018.
Morgan RK. Environmental impact assessment: the state of the art. Impact Assess Proj Apprais. 2012;30(1):5–14.
Samuel G, Richie C. Reimagining research ethics to include environmental sustainability: a principled approach, including a case study of data-driven health research. J Med Ethics. 2023;49(6):428–33.
Kwete X, Tang K, Chen L, Ren R, Chen Q, Wu Z, et al. Decolonizing global health: what should be the target of this movement and where does it lead us? Glob Health Res Policy. 2022;7(1):3.
Abimbola S, Asthana S, Montenegro C, Guinto RR, Jumbam DT, Louskieter L, et al. Addressing power asymmetries in global health: imperatives in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. PLoS Med. 2021;18(4):e1003604.
Benatar S. Politics, power, poverty and global health: systems and frames. Int J Health Policy Manag. 2016;5(10):599.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the outstanding contributions of the attendees of GFBR 2022 in Cape Town, South Africa. This paper is authored by members of the GFBR 2022 Planning Committee. We would like to acknowledge additional members Tamra Lysaght, National University of Singapore, and Niresh Bhagwandin, South African Medical Research Council, for their input during the planning stages and as reviewers of the applications to attend the Forum.
This work was supported by Wellcome [222525/Z/21/Z], the US National Institutes of Health, the UK Medical Research Council (part of UK Research and Innovation), and the South African Medical Research Council through funding to the Global Forum on Bioethics in Research.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Physical Therapy, Temerty Faculty of Medicine, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada
Berman Institute of Bioethics, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA
Bloomberg School of Public Health, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA
Department of Philosophy and Classics, University of Ghana, Legon-Accra, Ghana
Caesar A. Atuire
Centre for Tropical Medicine and Global Health, Nuffield Department of Medicine, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK
Mahidol Oxford Tropical Medicine Research Unit, Faculty of Tropical Medicine, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand
Phaik Yeong Cheah
Berkman Klein Center, Harvard University, Bogotá, Colombia
Armando Guio Español
Department of Radiology and Informatics, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA, USA
Judy Wawira Gichoya
Health Ethics & Governance Unit, Research for Health Department, Science Division, World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland
Adrienne Hunt & Katherine Littler
African Center of Excellence in Bioinformatics and Data Intensive Science, Infectious Diseases Institute, Makerere University, Kampala, Uganda
Daudi Jjingo
ISI Foundation, Turin, Italy
Daniela Paolotti
Department of Health Sciences and Technology, ETH Zurich, Zürich, Switzerland
Effy Vayena
Joint Centre for Bioethics, Dalla Lana School of Public Health, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
JS led the writing, contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. JA contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. CA contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. PYC contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. AE contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. JWG contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. AH contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. DJ contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. KL contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. DP contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. EV contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to James Shaw .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Shaw, J., Ali, J., Atuire, C.A. et al. Research ethics and artificial intelligence for global health: perspectives from the global forum on bioethics in research. BMC Med Ethics 25 , 46 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-024-01044-w
Download citation
Received : 31 October 2023
Accepted : 01 April 2024
Published : 18 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-024-01044-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Artificial intelligence
- Machine learning
- Research ethics
- Global health
BMC Medical Ethics
ISSN: 1472-6939
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Perpetual in talks with KKR for corporate trust and wealth management unit sale

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The authors identified five competencies a leader can utilize to gain buy-in and build trust in the context of a presentation: clarity, compassion, competency, connection, consistency. A few years ...
Trust is soft. • Trust is hard, real & quantifiable, it is measurable affects both speed & cost - productivity. Trust is slow. • Nothing is as fast as the speed of trust. Trust is built solely on integrity. • Trust is a function of character (including integrity) and competence. You either have trust or you don't.
2.Follow through on your. 3.Show care for others. It. 4.Connect to the bigger. 5.Communicate conscientiously. Expressiveness connects to. 6.Manage conversation and conflict. 7.Be open to different. 7 Steps to Building Trust in the Workplace - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
7 ways to build greater trust in all of your partnerships. Jean Oelwang, the president and founding CEO of Virgin Unite, has interviewed hundreds of people to figure out the key elements behind great partnerships. One of the most critical (and tricky) is trust -- and she explains how you can foster it. Posted Mar 2022.
Presentations that are built on trust add value. Plain and simple. The speaker has the intentional goal to improve the lives of their audience. The lift them up, and they empower them with information they did not before the session.
Communicate openly and frequently. 3. Collaborate creatively and constructively. 4. Support and empower your team members. 5. Adapt and improvise when necessary. 6. Reflect and improve as a team.
Free Google Slides theme and PowerPoint template. Your team at work is who you spend most of your time with, who you learn with and who you spend your hardest days with. That's why your workplace should be a safe environment full of trust. How can you build it? Speak about it with this design for a meeting and help your coworkers build ...
Building trust. Jul 25, 2015 • Download as PPTX, PDF •. 17 likes • 19,079 views. K. Kristin_Anderson_1. We know that healthy, respectful, and trusting teacher-student relationships nearly double the rate at which a student can learn. While not measured in the same fashion, building rapport and trust among adults has been proven to garner ...
We use Pecha Kucha presentations in which our five students and the coaching team members have 20 slides each to get to know each other through pictures. The students take turns introducing ...
The fiduciary (trustee) of a domestic decedent's estate, trust, or bankruptcy estate uses Form 1041 to report: Income. Deductions. Gains and losses of the estate or trust. Income will be accumulated and held for future distribution or distributed currently to the beneficiaries - based on the trust document.
Here are 5 ways to implicitly build and establish trust as you're delivering your presentation: 1. Back up what you say with evidence. It's easy to make sweeping claims like: "We're the best company in this industry", but supporting these audacious statements with hard facts and data is where it gets challenging.
By analyzing over 80,000 360-degree reviews, the authors found that there are three elements that predict whether a leader will be trusted by his direct reports, peers, and other colleagues. These ...
Presenting Building Trust and Confidence with Prospects to Boost Sales. These slides are 100 percent made in PowerPoint and are compatible with all screen types and monitors. They also support Google Slides. Premium Customer Support available. Suitable for use by managers, employees, and organizations.
It has PPT slides covering wide range of topics showcasing all the core areas of your business needs. This complete deck focuses on Effective Leadership Influence Trust And Respect Communication Change Management Strategy and consists of professionally designed templates with suitable graphics and appropriate content.
Free Theme Slides. Free Diagram. Free Chart. trust PPT Templates,Google Slides FREE for commercial and personal use! Download over 6,300+ complete free templates in high resolution. Unique slides with a clean and professional look.
This PPT design is divided in two parts displaying trust and turf which makes easier for you to share information. The collaboration continuum will help in achieving goals collectively that otherwise cannot be achieved by a single agent. 3 Important Skills Teamwork Collaboration PPT PowerPoint Presentation Outline Good-15
Trust Presentation 1. The Cultivation and Manifestation of Trust By Mark Connolly, Ed.D Director of Elementary Education Kelso School District [email_address] edu
The Speed of TrustStephen M. R. Covey Dr. Sandra R. Lindsay. The Economics of Trust Trust = Speed Cost Trust = Speed Cost. The 4 Cores of Credibility • Integrity Character • Intent • Capabilities Competence • Results. Activity • Take the deck of cards at your table or share with a small group around you.
Include charts and graphs to effectively present data and statistics. Incorporate videos or animations to engage and illustrate complex concepts. When creating a PowerPoint presentation on improving customer satisfaction, visual aids play a crucial role in capturing and maintaining audience attention. 3. Tell a Story.
The forum consisted of 6 case study presentations, 16 governance presentations, and a series of small group and large group discussions. ... The GFBR is an annual meeting organized by the World Health Organization and supported by the Wellcome Trust, the US National Institutes of Health, the UK Medical Research Council (MRC) and the South ...
Australia's Perpetual ASX:PPT on Monday confirmed it had entered into exclusive talks with global investment firm KKR & Co NYSE:KKR for the potential acquisition of the financial services firm's corporate trust and wealth management business.
Overview of the Presentation • The goal of this presentation is to give you a "30,000 view" of trusts, to enable you to speak about them with your clients and prospective clients in a competent manner. • The information contained in this presentation is based in the Uniform Trust Code, last revised in 2005 and available online at the ...
The following slide deck was published by Mapletree Logistics Trust in conjunction with their 2024 Q4 earnings call. ... Earnings Call Presentation. Apr. 29, 2024 8:43 AM ET Mapletree Logistics ...
Presentation on trusts-_final. 1. TAXATION OF PRIVATE BENEFICIARY AND CHARITABLE TRUST. 2. 3. Comparison among Trust, Society & Section 25 Company Points of Differences Trust Society Section 25 Company Statute / Legislation Relevant State Trust Act or Indian Trust Act, 1882 Societies Registration Act, 1860 Indian Companies Act, 1956 ...