- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research

Research Hypothesis: What It Is, Types + How to Develop?

A research study starts with a question. Researchers worldwide ask questions and create research hypotheses. The effectiveness of research relies on developing a good research hypothesis. Examples of research hypotheses can guide researchers in writing effective ones.
In this blog, we’ll learn what a research hypothesis is, why it’s important in research, and the different types used in science. We’ll also guide you through creating your research hypothesis and discussing ways to test and evaluate it.
What is a Research Hypothesis?
A hypothesis is like a guess or idea that you suggest to check if it’s true. A research hypothesis is a statement that brings up a question and predicts what might happen.
It’s really important in the scientific method and is used in experiments to figure things out. Essentially, it’s an educated guess about how things are connected in the research.
A research hypothesis usually includes pointing out the independent variable (the thing they’re changing or studying) and the dependent variable (the result they’re measuring or watching). It helps plan how to gather and analyze data to see if there’s evidence to support or deny the expected connection between these variables.
Importance of Hypothesis in Research
Hypotheses are really important in research. They help design studies, allow for practical testing, and add to our scientific knowledge. Their main role is to organize research projects, making them purposeful, focused, and valuable to the scientific community. Let’s look at some key reasons why they matter:
- A research hypothesis helps test theories.
A hypothesis plays a pivotal role in the scientific method by providing a basis for testing existing theories. For example, a hypothesis might test the predictive power of a psychological theory on human behavior.
- It serves as a great platform for investigation activities.
It serves as a launching pad for investigation activities, which offers researchers a clear starting point. A research hypothesis can explore the relationship between exercise and stress reduction.
- Hypothesis guides the research work or study.
A well-formulated hypothesis guides the entire research process. It ensures that the study remains focused and purposeful. For instance, a hypothesis about the impact of social media on interpersonal relationships provides clear guidance for a study.
- Hypothesis sometimes suggests theories.
In some cases, a hypothesis can suggest new theories or modifications to existing ones. For example, a hypothesis testing the effectiveness of a new drug might prompt a reconsideration of current medical theories.
- It helps in knowing the data needs.
A hypothesis clarifies the data requirements for a study, ensuring that researchers collect the necessary information—a hypothesis guiding the collection of demographic data to analyze the influence of age on a particular phenomenon.
- The hypothesis explains social phenomena.
Hypotheses are instrumental in explaining complex social phenomena. For instance, a hypothesis might explore the relationship between economic factors and crime rates in a given community.
- Hypothesis provides a relationship between phenomena for empirical Testing.
Hypotheses establish clear relationships between phenomena, paving the way for empirical testing. An example could be a hypothesis exploring the correlation between sleep patterns and academic performance.
- It helps in knowing the most suitable analysis technique.
A hypothesis guides researchers in selecting the most appropriate analysis techniques for their data. For example, a hypothesis focusing on the effectiveness of a teaching method may lead to the choice of statistical analyses best suited for educational research.
Characteristics of a Good Research Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a specific idea that you can test in a study. It often comes from looking at past research and theories. A good hypothesis usually starts with a research question that you can explore through background research. For it to be effective, consider these key characteristics:
- Clear and Focused Language: A good hypothesis uses clear and focused language to avoid confusion and ensure everyone understands it.
- Related to the Research Topic: The hypothesis should directly relate to the research topic, acting as a bridge between the specific question and the broader study.
- Testable: An effective hypothesis can be tested, meaning its prediction can be checked with real data to support or challenge the proposed relationship.
- Potential for Exploration: A good hypothesis often comes from a research question that invites further exploration. Doing background research helps find gaps and potential areas to investigate.
- Includes Variables: The hypothesis should clearly state both the independent and dependent variables, specifying the factors being studied and the expected outcomes.
- Ethical Considerations: Check if variables can be manipulated without breaking ethical standards. It’s crucial to maintain ethical research practices.
- Predicts Outcomes: The hypothesis should predict the expected relationship and outcome, acting as a roadmap for the study and guiding data collection and analysis.
- Simple and Concise: A good hypothesis avoids unnecessary complexity and is simple and concise, expressing the essence of the proposed relationship clearly.
- Clear and Assumption-Free: The hypothesis should be clear and free from assumptions about the reader’s prior knowledge, ensuring universal understanding.
- Observable and Testable Results: A strong hypothesis implies research that produces observable and testable results, making sure the study’s outcomes can be effectively measured and analyzed.
When you use these characteristics as a checklist, it can help you create a good research hypothesis. It’ll guide improving and strengthening the hypothesis, identifying any weaknesses, and making necessary changes. Crafting a hypothesis with these features helps you conduct a thorough and insightful research study.
Types of Research Hypotheses
The research hypothesis comes in various types, each serving a specific purpose in guiding the scientific investigation. Knowing the differences will make it easier for you to create your own hypothesis. Here’s an overview of the common types:
01. Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis states that there is no connection between two considered variables or that two groups are unrelated. As discussed earlier, a hypothesis is an unproven assumption lacking sufficient supporting data. It serves as the statement researchers aim to disprove. It is testable, verifiable, and can be rejected.
For example, if you’re studying the relationship between Project A and Project B, assuming both projects are of equal standard is your null hypothesis. It needs to be specific for your study.
02. Alternative Hypothesis
The alternative hypothesis is basically another option to the null hypothesis. It involves looking for a significant change or alternative that could lead you to reject the null hypothesis. It’s a different idea compared to the null hypothesis.
When you create a null hypothesis, you’re making an educated guess about whether something is true or if there’s a connection between that thing and another variable. If the null view suggests something is correct, the alternative hypothesis says it’s incorrect.
For instance, if your null hypothesis is “I’m going to be $1000 richer,” the alternative hypothesis would be “I’m not going to get $1000 or be richer.”
03. Directional Hypothesis
The directional hypothesis predicts the direction of the relationship between independent and dependent variables. They specify whether the effect will be positive or negative.
If you increase your study hours, you will experience a positive association with your exam scores. This hypothesis suggests that as you increase the independent variable (study hours), there will also be an increase in the dependent variable (exam scores).
04. Non-directional Hypothesis
The non-directional hypothesis predicts the existence of a relationship between variables but does not specify the direction of the effect. It suggests that there will be a significant difference or relationship, but it does not predict the nature of that difference.
For example, you will find no notable difference in test scores between students who receive the educational intervention and those who do not. However, once you compare the test scores of the two groups, you will notice an important difference.
05. Simple Hypothesis
A simple hypothesis predicts a relationship between one dependent variable and one independent variable without specifying the nature of that relationship. It’s simple and usually used when we don’t know much about how the two things are connected.
For example, if you adopt effective study habits, you will achieve higher exam scores than those with poor study habits.
06. Complex Hypothesis
A complex hypothesis is an idea that specifies a relationship between multiple independent and dependent variables. It is a more detailed idea than a simple hypothesis.
While a simple view suggests a straightforward cause-and-effect relationship between two things, a complex hypothesis involves many factors and how they’re connected to each other.
For example, when you increase your study time, you tend to achieve higher exam scores. The connection between your study time and exam performance is affected by various factors, including the quality of your sleep, your motivation levels, and the effectiveness of your study techniques.
If you sleep well, stay highly motivated, and use effective study strategies, you may observe a more robust positive correlation between the time you spend studying and your exam scores, unlike those who may lack these factors.
07. Associative Hypothesis
An associative hypothesis proposes a connection between two things without saying that one causes the other. Basically, it suggests that when one thing changes, the other changes too, but it doesn’t claim that one thing is causing the change in the other.
For example, you will likely notice higher exam scores when you increase your study time. You can recognize an association between your study time and exam scores in this scenario.
Your hypothesis acknowledges a relationship between the two variables—your study time and exam scores—without asserting that increased study time directly causes higher exam scores. You need to consider that other factors, like motivation or learning style, could affect the observed association.
08. Causal Hypothesis
A causal hypothesis proposes a cause-and-effect relationship between two variables. It suggests that changes in one variable directly cause changes in another variable.
For example, when you increase your study time, you experience higher exam scores. This hypothesis suggests a direct cause-and-effect relationship, indicating that the more time you spend studying, the higher your exam scores. It assumes that changes in your study time directly influence changes in your exam performance.
09. Empirical Hypothesis
An empirical hypothesis is a statement based on things we can see and measure. It comes from direct observation or experiments and can be tested with real-world evidence. If an experiment proves a theory, it supports the idea and shows it’s not just a guess. This makes the statement more reliable than a wild guess.
For example, if you increase the dosage of a certain medication, you might observe a quicker recovery time for patients. Imagine you’re in charge of a clinical trial. In this trial, patients are given varying dosages of the medication, and you measure and compare their recovery times. This allows you to directly see the effects of different dosages on how fast patients recover.
This way, you can create a research hypothesis: “Increasing the dosage of a certain medication will lead to a faster recovery time for patients.”
10. Statistical Hypothesis
A statistical hypothesis is a statement or assumption about a population parameter that is the subject of an investigation. It serves as the basis for statistical analysis and testing. It is often tested using statistical methods to draw inferences about the larger population.
In a hypothesis test, statistical evidence is collected to either reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis or fail to reject the null hypothesis due to insufficient evidence.
For example, let’s say you’re testing a new medicine. Your hypothesis could be that the medicine doesn’t really help patients get better. So, you collect data and use statistics to see if your guess is right or if the medicine actually makes a difference.
If the data strongly shows that the medicine does help, you say your guess was wrong, and the medicine does make a difference. But if the proof isn’t strong enough, you can stick with your original guess because you didn’t get enough evidence to change your mind.
How to Develop a Research Hypotheses?
Step 1: identify your research problem or topic..
Define the area of interest or the problem you want to investigate. Make sure it’s clear and well-defined.
Start by asking a question about your chosen topic. Consider the limitations of your research and create a straightforward problem related to your topic. Once you’ve done that, you can develop and test a hypothesis with evidence.
Step 2: Conduct a literature review
Review existing literature related to your research problem. This will help you understand the current state of knowledge in the field, identify gaps, and build a foundation for your hypothesis. Consider the following questions:
- What existing research has been conducted on your chosen topic?
- Are there any gaps or unanswered questions in the current literature?
- How will the existing literature contribute to the foundation of your research?
Step 3: Formulate your research question
Based on your literature review, create a specific and concise research question that addresses your identified problem. Your research question should be clear, focused, and relevant to your field of study.
Step 4: Identify variables
Determine the key variables involved in your research question. Variables are the factors or phenomena that you will study and manipulate to test your hypothesis.
- Independent Variable: The variable you manipulate or control.
- Dependent Variable: The variable you measure to observe the effect of the independent variable.
Step 5: State the Null hypothesis
The null hypothesis is a statement that there is no significant difference or effect. It serves as a baseline for comparison with the alternative hypothesis.
Step 6: Select appropriate methods for testing the hypothesis
Choose research methods that align with your study objectives, such as experiments, surveys, or observational studies. The selected methods enable you to test your research hypothesis effectively.
Creating a research hypothesis usually takes more than one try. Expect to make changes as you collect data. It’s normal to test and say no to a few hypotheses before you find the right answer to your research question.
Testing and Evaluating Hypotheses
Testing hypotheses is a really important part of research. It’s like the practical side of things. Here, real-world evidence will help you determine how different things are connected. Let’s explore the main steps in hypothesis testing:
- State your research hypothesis.
Before testing, clearly articulate your research hypothesis. This involves framing both a null hypothesis, suggesting no significant effect or relationship, and an alternative hypothesis, proposing the expected outcome.
- Collect data strategically.
Plan how you will gather information in a way that fits your study. Make sure your data collection method matches the things you’re studying.
Whether through surveys, observations, or experiments, this step demands precision and adherence to the established methodology. The quality of data collected directly influences the credibility of study outcomes.
- Perform an appropriate statistical test.
Choose a statistical test that aligns with the nature of your data and the hypotheses being tested. Whether it’s a t-test, chi-square test, ANOVA, or regression analysis, selecting the right statistical tool is paramount for accurate and reliable results.
- Decide if your idea was right or wrong.
Following the statistical analysis, evaluate the results in the context of your null hypothesis. You need to decide if you should reject your null hypothesis or not.
- Share what you found.
When discussing what you found in your research, be clear and organized. Say whether your idea was supported or not, and talk about what your results mean. Also, mention any limits to your study and suggest ideas for future research.
The Role of QuestionPro to Develop a Good Research Hypothesis
QuestionPro is a survey and research platform that provides tools for creating, distributing, and analyzing surveys. It plays a crucial role in the research process, especially when you’re in the initial stages of hypothesis development. Here’s how QuestionPro can help you to develop a good research hypothesis:
- Survey design and data collection: You can use the platform to create targeted questions that help you gather relevant data.
- Exploratory research: Through surveys and feedback mechanisms on QuestionPro, you can conduct exploratory research to understand the landscape of a particular subject.
- Literature review and background research: QuestionPro surveys can collect sample population opinions, experiences, and preferences. This data and a thorough literature evaluation can help you generate a well-grounded hypothesis by improving your research knowledge.
- Identifying variables: Using targeted survey questions, you can identify relevant variables related to their research topic.
- Testing assumptions: You can use surveys to informally test certain assumptions or hypotheses before formalizing a research hypothesis.
- Data analysis tools: QuestionPro provides tools for analyzing survey data. You can use these tools to identify the collected data’s patterns, correlations, or trends.
- Refining your hypotheses: As you collect data through QuestionPro, you can adjust your hypotheses based on the real-world responses you receive.
A research hypothesis is like a guide for researchers in science. It’s a well-thought-out idea that has been thoroughly tested. This idea is crucial as researchers can explore different fields, such as medicine, social sciences, and natural sciences. The research hypothesis links theories to real-world evidence and gives researchers a clear path to explore and make discoveries.
QuestionPro Research Suite is a helpful tool for researchers. It makes creating surveys, collecting data, and analyzing information easily. It supports all kinds of research, from exploring new ideas to forming hypotheses. With a focus on using data, it helps researchers do their best work.
Are you interested in learning more about QuestionPro Research Suite? Take advantage of QuestionPro’s free trial to get an initial look at its capabilities and realize the full potential of your research efforts.
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS

NPS Survey Platform: Types, Tips, 11 Best Platforms & Tools
Apr 26, 2024
User Journey vs User Flow: Differences and Similarities

Best 7 Gap Analysis Tools to Empower Your Business
Apr 25, 2024

12 Best Employee Survey Tools for Organizational Excellence
Other categories.
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Ohio State nav bar
The Ohio State University
- BuckeyeLink
- Find People
- Search Ohio State
Research Questions & Hypotheses
Generally, in quantitative studies, reviewers expect hypotheses rather than research questions. However, both research questions and hypotheses serve different purposes and can be beneficial when used together.
Research Questions
Clarify the research’s aim (farrugia et al., 2010).
- Research often begins with an interest in a topic, but a deep understanding of the subject is crucial to formulate an appropriate research question.
- Descriptive: “What factors most influence the academic achievement of senior high school students?”
- Comparative: “What is the performance difference between teaching methods A and B?”
- Relationship-based: “What is the relationship between self-efficacy and academic achievement?”
- Increasing knowledge about a subject can be achieved through systematic literature reviews, in-depth interviews with patients (and proxies), focus groups, and consultations with field experts.
- Some funding bodies, like the Canadian Institute for Health Research, recommend conducting a systematic review or a pilot study before seeking grants for full trials.
- The presence of multiple research questions in a study can complicate the design, statistical analysis, and feasibility.
- It’s advisable to focus on a single primary research question for the study.
- The primary question, clearly stated at the end of a grant proposal’s introduction, usually specifies the study population, intervention, and other relevant factors.
- The FINER criteria underscore aspects that can enhance the chances of a successful research project, including specifying the population of interest, aligning with scientific and public interest, clinical relevance, and contribution to the field, while complying with ethical and national research standards.
- The P ICOT approach is crucial in developing the study’s framework and protocol, influencing inclusion and exclusion criteria and identifying patient groups for inclusion.
- Defining the specific population, intervention, comparator, and outcome helps in selecting the right outcome measurement tool.
- The more precise the population definition and stricter the inclusion and exclusion criteria, the more significant the impact on the interpretation, applicability, and generalizability of the research findings.
- A restricted study population enhances internal validity but may limit the study’s external validity and generalizability to clinical practice.
- A broadly defined study population may better reflect clinical practice but could increase bias and reduce internal validity.
- An inadequately formulated research question can negatively impact study design, potentially leading to ineffective outcomes and affecting publication prospects.
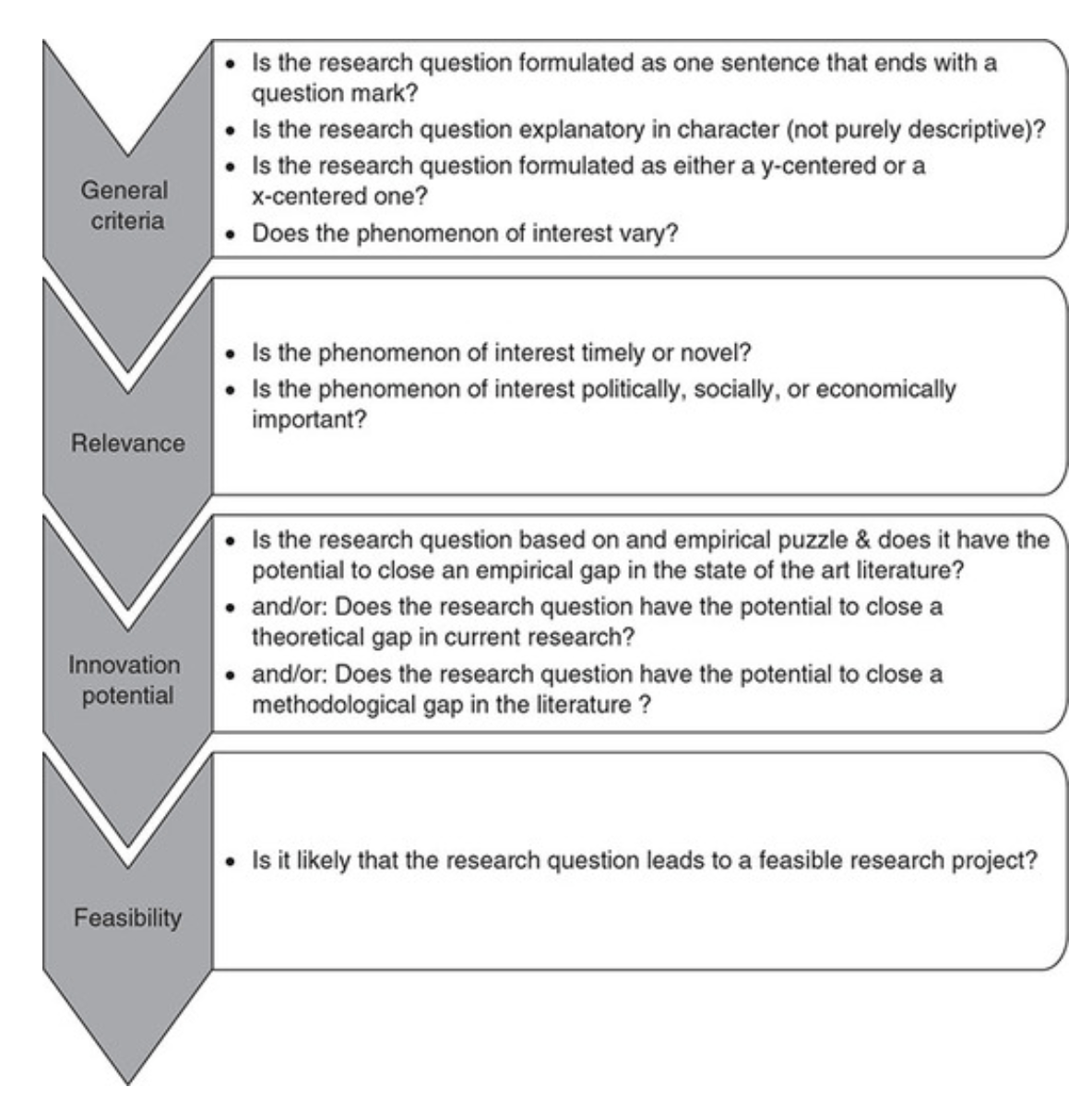
Checklist: Good research questions for social science projects (Panke, 2018)
Research Hypotheses
Present the researcher’s predictions based on specific statements.
- These statements define the research problem or issue and indicate the direction of the researcher’s predictions.
- Formulating the research question and hypothesis from existing data (e.g., a database) can lead to multiple statistical comparisons and potentially spurious findings due to chance.
- The research or clinical hypothesis, derived from the research question, shapes the study’s key elements: sampling strategy, intervention, comparison, and outcome variables.
- Hypotheses can express a single outcome or multiple outcomes.
- After statistical testing, the null hypothesis is either rejected or not rejected based on whether the study’s findings are statistically significant.
- Hypothesis testing helps determine if observed findings are due to true differences and not chance.
- Hypotheses can be 1-sided (specific direction of difference) or 2-sided (presence of a difference without specifying direction).
- 2-sided hypotheses are generally preferred unless there’s a strong justification for a 1-sided hypothesis.
- A solid research hypothesis, informed by a good research question, influences the research design and paves the way for defining clear research objectives.
Types of Research Hypothesis
- In a Y-centered research design, the focus is on the dependent variable (DV) which is specified in the research question. Theories are then used to identify independent variables (IV) and explain their causal relationship with the DV.
- Example: “An increase in teacher-led instructional time (IV) is likely to improve student reading comprehension scores (DV), because extensive guided practice under expert supervision enhances learning retention and skill mastery.”
- Hypothesis Explanation: The dependent variable (student reading comprehension scores) is the focus, and the hypothesis explores how changes in the independent variable (teacher-led instructional time) affect it.
- In X-centered research designs, the independent variable is specified in the research question. Theories are used to determine potential dependent variables and the causal mechanisms at play.
- Example: “Implementing technology-based learning tools (IV) is likely to enhance student engagement in the classroom (DV), because interactive and multimedia content increases student interest and participation.”
- Hypothesis Explanation: The independent variable (technology-based learning tools) is the focus, with the hypothesis exploring its impact on a potential dependent variable (student engagement).
- Probabilistic hypotheses suggest that changes in the independent variable are likely to lead to changes in the dependent variable in a predictable manner, but not with absolute certainty.
- Example: “The more teachers engage in professional development programs (IV), the more their teaching effectiveness (DV) is likely to improve, because continuous training updates pedagogical skills and knowledge.”
- Hypothesis Explanation: This hypothesis implies a probable relationship between the extent of professional development (IV) and teaching effectiveness (DV).
- Deterministic hypotheses state that a specific change in the independent variable will lead to a specific change in the dependent variable, implying a more direct and certain relationship.
- Example: “If the school curriculum changes from traditional lecture-based methods to project-based learning (IV), then student collaboration skills (DV) are expected to improve because project-based learning inherently requires teamwork and peer interaction.”
- Hypothesis Explanation: This hypothesis presumes a direct and definite outcome (improvement in collaboration skills) resulting from a specific change in the teaching method.
- Example : “Students who identify as visual learners will score higher on tests that are presented in a visually rich format compared to tests presented in a text-only format.”
- Explanation : This hypothesis aims to describe the potential difference in test scores between visual learners taking visually rich tests and text-only tests, without implying a direct cause-and-effect relationship.
- Example : “Teaching method A will improve student performance more than method B.”
- Explanation : This hypothesis compares the effectiveness of two different teaching methods, suggesting that one will lead to better student performance than the other. It implies a direct comparison but does not necessarily establish a causal mechanism.
- Example : “Students with higher self-efficacy will show higher levels of academic achievement.”
- Explanation : This hypothesis predicts a relationship between the variable of self-efficacy and academic achievement. Unlike a causal hypothesis, it does not necessarily suggest that one variable causes changes in the other, but rather that they are related in some way.
Tips for developing research questions and hypotheses for research studies
- Perform a systematic literature review (if one has not been done) to increase knowledge and familiarity with the topic and to assist with research development.
- Learn about current trends and technological advances on the topic.
- Seek careful input from experts, mentors, colleagues, and collaborators to refine your research question as this will aid in developing the research question and guide the research study.
- Use the FINER criteria in the development of the research question.
- Ensure that the research question follows PICOT format.
- Develop a research hypothesis from the research question.
- Ensure that the research question and objectives are answerable, feasible, and clinically relevant.
If your research hypotheses are derived from your research questions, particularly when multiple hypotheses address a single question, it’s recommended to use both research questions and hypotheses. However, if this isn’t the case, using hypotheses over research questions is advised. It’s important to note these are general guidelines, not strict rules. If you opt not to use hypotheses, consult with your supervisor for the best approach.
Farrugia, P., Petrisor, B. A., Farrokhyar, F., & Bhandari, M. (2010). Practical tips for surgical research: Research questions, hypotheses and objectives. Canadian journal of surgery. Journal canadien de chirurgie , 53 (4), 278–281.
Hulley, S. B., Cummings, S. R., Browner, W. S., Grady, D., & Newman, T. B. (2007). Designing clinical research. Philadelphia.
Panke, D. (2018). Research design & method selection: Making good choices in the social sciences. Research Design & Method Selection , 1-368.
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

The Craft of Writing a Strong Hypothesis

Table of Contents
Writing a hypothesis is one of the essential elements of a scientific research paper. It needs to be to the point, clearly communicating what your research is trying to accomplish. A blurry, drawn-out, or complexly-structured hypothesis can confuse your readers. Or worse, the editor and peer reviewers.
A captivating hypothesis is not too intricate. This blog will take you through the process so that, by the end of it, you have a better idea of how to convey your research paper's intent in just one sentence.
What is a Hypothesis?
The first step in your scientific endeavor, a hypothesis, is a strong, concise statement that forms the basis of your research. It is not the same as a thesis statement , which is a brief summary of your research paper .
The sole purpose of a hypothesis is to predict your paper's findings, data, and conclusion. It comes from a place of curiosity and intuition . When you write a hypothesis, you're essentially making an educated guess based on scientific prejudices and evidence, which is further proven or disproven through the scientific method.
The reason for undertaking research is to observe a specific phenomenon. A hypothesis, therefore, lays out what the said phenomenon is. And it does so through two variables, an independent and dependent variable.
The independent variable is the cause behind the observation, while the dependent variable is the effect of the cause. A good example of this is “mixing red and blue forms purple.” In this hypothesis, mixing red and blue is the independent variable as you're combining the two colors at your own will. The formation of purple is the dependent variable as, in this case, it is conditional to the independent variable.
Different Types of Hypotheses

Types of hypotheses
Some would stand by the notion that there are only two types of hypotheses: a Null hypothesis and an Alternative hypothesis. While that may have some truth to it, it would be better to fully distinguish the most common forms as these terms come up so often, which might leave you out of context.
Apart from Null and Alternative, there are Complex, Simple, Directional, Non-Directional, Statistical, and Associative and casual hypotheses. They don't necessarily have to be exclusive, as one hypothesis can tick many boxes, but knowing the distinctions between them will make it easier for you to construct your own.
1. Null hypothesis
A null hypothesis proposes no relationship between two variables. Denoted by H 0 , it is a negative statement like “Attending physiotherapy sessions does not affect athletes' on-field performance.” Here, the author claims physiotherapy sessions have no effect on on-field performances. Even if there is, it's only a coincidence.
2. Alternative hypothesis
Considered to be the opposite of a null hypothesis, an alternative hypothesis is donated as H1 or Ha. It explicitly states that the dependent variable affects the independent variable. A good alternative hypothesis example is “Attending physiotherapy sessions improves athletes' on-field performance.” or “Water evaporates at 100 °C. ” The alternative hypothesis further branches into directional and non-directional.
- Directional hypothesis: A hypothesis that states the result would be either positive or negative is called directional hypothesis. It accompanies H1 with either the ‘<' or ‘>' sign.
- Non-directional hypothesis: A non-directional hypothesis only claims an effect on the dependent variable. It does not clarify whether the result would be positive or negative. The sign for a non-directional hypothesis is ‘≠.'
3. Simple hypothesis
A simple hypothesis is a statement made to reflect the relation between exactly two variables. One independent and one dependent. Consider the example, “Smoking is a prominent cause of lung cancer." The dependent variable, lung cancer, is dependent on the independent variable, smoking.
4. Complex hypothesis
In contrast to a simple hypothesis, a complex hypothesis implies the relationship between multiple independent and dependent variables. For instance, “Individuals who eat more fruits tend to have higher immunity, lesser cholesterol, and high metabolism.” The independent variable is eating more fruits, while the dependent variables are higher immunity, lesser cholesterol, and high metabolism.
5. Associative and casual hypothesis
Associative and casual hypotheses don't exhibit how many variables there will be. They define the relationship between the variables. In an associative hypothesis, changing any one variable, dependent or independent, affects others. In a casual hypothesis, the independent variable directly affects the dependent.
6. Empirical hypothesis
Also referred to as the working hypothesis, an empirical hypothesis claims a theory's validation via experiments and observation. This way, the statement appears justifiable and different from a wild guess.
Say, the hypothesis is “Women who take iron tablets face a lesser risk of anemia than those who take vitamin B12.” This is an example of an empirical hypothesis where the researcher the statement after assessing a group of women who take iron tablets and charting the findings.
7. Statistical hypothesis
The point of a statistical hypothesis is to test an already existing hypothesis by studying a population sample. Hypothesis like “44% of the Indian population belong in the age group of 22-27.” leverage evidence to prove or disprove a particular statement.
Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis
Writing a hypothesis is essential as it can make or break your research for you. That includes your chances of getting published in a journal. So when you're designing one, keep an eye out for these pointers:
- A research hypothesis has to be simple yet clear to look justifiable enough.
- It has to be testable — your research would be rendered pointless if too far-fetched into reality or limited by technology.
- It has to be precise about the results —what you are trying to do and achieve through it should come out in your hypothesis.
- A research hypothesis should be self-explanatory, leaving no doubt in the reader's mind.
- If you are developing a relational hypothesis, you need to include the variables and establish an appropriate relationship among them.
- A hypothesis must keep and reflect the scope for further investigations and experiments.
Separating a Hypothesis from a Prediction
Outside of academia, hypothesis and prediction are often used interchangeably. In research writing, this is not only confusing but also incorrect. And although a hypothesis and prediction are guesses at their core, there are many differences between them.
A hypothesis is an educated guess or even a testable prediction validated through research. It aims to analyze the gathered evidence and facts to define a relationship between variables and put forth a logical explanation behind the nature of events.
Predictions are assumptions or expected outcomes made without any backing evidence. They are more fictionally inclined regardless of where they originate from.
For this reason, a hypothesis holds much more weight than a prediction. It sticks to the scientific method rather than pure guesswork. "Planets revolve around the Sun." is an example of a hypothesis as it is previous knowledge and observed trends. Additionally, we can test it through the scientific method.
Whereas "COVID-19 will be eradicated by 2030." is a prediction. Even though it results from past trends, we can't prove or disprove it. So, the only way this gets validated is to wait and watch if COVID-19 cases end by 2030.
Finally, How to Write a Hypothesis

Quick tips on writing a hypothesis
1. Be clear about your research question
A hypothesis should instantly address the research question or the problem statement. To do so, you need to ask a question. Understand the constraints of your undertaken research topic and then formulate a simple and topic-centric problem. Only after that can you develop a hypothesis and further test for evidence.
2. Carry out a recce
Once you have your research's foundation laid out, it would be best to conduct preliminary research. Go through previous theories, academic papers, data, and experiments before you start curating your research hypothesis. It will give you an idea of your hypothesis's viability or originality.
Making use of references from relevant research papers helps draft a good research hypothesis. SciSpace Discover offers a repository of over 270 million research papers to browse through and gain a deeper understanding of related studies on a particular topic. Additionally, you can use SciSpace Copilot , your AI research assistant, for reading any lengthy research paper and getting a more summarized context of it. A hypothesis can be formed after evaluating many such summarized research papers. Copilot also offers explanations for theories and equations, explains paper in simplified version, allows you to highlight any text in the paper or clip math equations and tables and provides a deeper, clear understanding of what is being said. This can improve the hypothesis by helping you identify potential research gaps.
3. Create a 3-dimensional hypothesis
Variables are an essential part of any reasonable hypothesis. So, identify your independent and dependent variable(s) and form a correlation between them. The ideal way to do this is to write the hypothetical assumption in the ‘if-then' form. If you use this form, make sure that you state the predefined relationship between the variables.
In another way, you can choose to present your hypothesis as a comparison between two variables. Here, you must specify the difference you expect to observe in the results.
4. Write the first draft
Now that everything is in place, it's time to write your hypothesis. For starters, create the first draft. In this version, write what you expect to find from your research.
Clearly separate your independent and dependent variables and the link between them. Don't fixate on syntax at this stage. The goal is to ensure your hypothesis addresses the issue.
5. Proof your hypothesis
After preparing the first draft of your hypothesis, you need to inspect it thoroughly. It should tick all the boxes, like being concise, straightforward, relevant, and accurate. Your final hypothesis has to be well-structured as well.
Research projects are an exciting and crucial part of being a scholar. And once you have your research question, you need a great hypothesis to begin conducting research. Thus, knowing how to write a hypothesis is very important.
Now that you have a firmer grasp on what a good hypothesis constitutes, the different kinds there are, and what process to follow, you will find it much easier to write your hypothesis, which ultimately helps your research.
Now it's easier than ever to streamline your research workflow with SciSpace Discover . Its integrated, comprehensive end-to-end platform for research allows scholars to easily discover, write and publish their research and fosters collaboration.
It includes everything you need, including a repository of over 270 million research papers across disciplines, SEO-optimized summaries and public profiles to show your expertise and experience.
If you found these tips on writing a research hypothesis useful, head over to our blog on Statistical Hypothesis Testing to learn about the top researchers, papers, and institutions in this domain.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. what is the definition of hypothesis.
According to the Oxford dictionary, a hypothesis is defined as “An idea or explanation of something that is based on a few known facts, but that has not yet been proved to be true or correct”.
2. What is an example of hypothesis?
The hypothesis is a statement that proposes a relationship between two or more variables. An example: "If we increase the number of new users who join our platform by 25%, then we will see an increase in revenue."
3. What is an example of null hypothesis?
A null hypothesis is a statement that there is no relationship between two variables. The null hypothesis is written as H0. The null hypothesis states that there is no effect. For example, if you're studying whether or not a particular type of exercise increases strength, your null hypothesis will be "there is no difference in strength between people who exercise and people who don't."
4. What are the types of research?
• Fundamental research
• Applied research
• Qualitative research
• Quantitative research
• Mixed research
• Exploratory research
• Longitudinal research
• Cross-sectional research
• Field research
• Laboratory research
• Fixed research
• Flexible research
• Action research
• Policy research
• Classification research
• Comparative research
• Causal research
• Inductive research
• Deductive research
5. How to write a hypothesis?
• Your hypothesis should be able to predict the relationship and outcome.
• Avoid wordiness by keeping it simple and brief.
• Your hypothesis should contain observable and testable outcomes.
• Your hypothesis should be relevant to the research question.
6. What are the 2 types of hypothesis?
• Null hypotheses are used to test the claim that "there is no difference between two groups of data".
• Alternative hypotheses test the claim that "there is a difference between two data groups".
7. Difference between research question and research hypothesis?
A research question is a broad, open-ended question you will try to answer through your research. A hypothesis is a statement based on prior research or theory that you expect to be true due to your study. Example - Research question: What are the factors that influence the adoption of the new technology? Research hypothesis: There is a positive relationship between age, education and income level with the adoption of the new technology.
8. What is plural for hypothesis?
The plural of hypothesis is hypotheses. Here's an example of how it would be used in a statement, "Numerous well-considered hypotheses are presented in this part, and they are supported by tables and figures that are well-illustrated."

9. What is the red queen hypothesis?
The red queen hypothesis in evolutionary biology states that species must constantly evolve to avoid extinction because if they don't, they will be outcompeted by other species that are evolving. Leigh Van Valen first proposed it in 1973; since then, it has been tested and substantiated many times.
10. Who is known as the father of null hypothesis?
The father of the null hypothesis is Sir Ronald Fisher. He published a paper in 1925 that introduced the concept of null hypothesis testing, and he was also the first to use the term itself.
11. When to reject null hypothesis?
You need to find a significant difference between your two populations to reject the null hypothesis. You can determine that by running statistical tests such as an independent sample t-test or a dependent sample t-test. You should reject the null hypothesis if the p-value is less than 0.05.
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
What Is A Research (Scientific) Hypothesis? A plain-language explainer + examples
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020
If you’re new to the world of research, or it’s your first time writing a dissertation or thesis, you’re probably noticing that the words “research hypothesis” and “scientific hypothesis” are used quite a bit, and you’re wondering what they mean in a research context .
“Hypothesis” is one of those words that people use loosely, thinking they understand what it means. However, it has a very specific meaning within academic research. So, it’s important to understand the exact meaning before you start hypothesizing.
Research Hypothesis 101
- What is a hypothesis ?
- What is a research hypothesis (scientific hypothesis)?
- Requirements for a research hypothesis
- Definition of a research hypothesis
- The null hypothesis
What is a hypothesis?
Let’s start with the general definition of a hypothesis (not a research hypothesis or scientific hypothesis), according to the Cambridge Dictionary:
Hypothesis: an idea or explanation for something that is based on known facts but has not yet been proved.
In other words, it’s a statement that provides an explanation for why or how something works, based on facts (or some reasonable assumptions), but that has not yet been specifically tested . For example, a hypothesis might look something like this:
Hypothesis: sleep impacts academic performance.
This statement predicts that academic performance will be influenced by the amount and/or quality of sleep a student engages in – sounds reasonable, right? It’s based on reasonable assumptions , underpinned by what we currently know about sleep and health (from the existing literature). So, loosely speaking, we could call it a hypothesis, at least by the dictionary definition.
But that’s not good enough…
Unfortunately, that’s not quite sophisticated enough to describe a research hypothesis (also sometimes called a scientific hypothesis), and it wouldn’t be acceptable in a dissertation, thesis or research paper . In the world of academic research, a statement needs a few more criteria to constitute a true research hypothesis .
What is a research hypothesis?
A research hypothesis (also called a scientific hypothesis) is a statement about the expected outcome of a study (for example, a dissertation or thesis). To constitute a quality hypothesis, the statement needs to have three attributes – specificity , clarity and testability .
Let’s take a look at these more closely.
Need a helping hand?
Hypothesis Essential #1: Specificity & Clarity
A good research hypothesis needs to be extremely clear and articulate about both what’ s being assessed (who or what variables are involved ) and the expected outcome (for example, a difference between groups, a relationship between variables, etc.).
Let’s stick with our sleepy students example and look at how this statement could be more specific and clear.
Hypothesis: Students who sleep at least 8 hours per night will, on average, achieve higher grades in standardised tests than students who sleep less than 8 hours a night.
As you can see, the statement is very specific as it identifies the variables involved (sleep hours and test grades), the parties involved (two groups of students), as well as the predicted relationship type (a positive relationship). There’s no ambiguity or uncertainty about who or what is involved in the statement, and the expected outcome is clear.
Contrast that to the original hypothesis we looked at – “Sleep impacts academic performance” – and you can see the difference. “Sleep” and “academic performance” are both comparatively vague , and there’s no indication of what the expected relationship direction is (more sleep or less sleep). As you can see, specificity and clarity are key.

Hypothesis Essential #2: Testability (Provability)
A statement must be testable to qualify as a research hypothesis. In other words, there needs to be a way to prove (or disprove) the statement. If it’s not testable, it’s not a hypothesis – simple as that.
For example, consider the hypothesis we mentioned earlier:
Hypothesis: Students who sleep at least 8 hours per night will, on average, achieve higher grades in standardised tests than students who sleep less than 8 hours a night.
We could test this statement by undertaking a quantitative study involving two groups of students, one that gets 8 or more hours of sleep per night for a fixed period, and one that gets less. We could then compare the standardised test results for both groups to see if there’s a statistically significant difference.
Again, if you compare this to the original hypothesis we looked at – “Sleep impacts academic performance” – you can see that it would be quite difficult to test that statement, primarily because it isn’t specific enough. How much sleep? By who? What type of academic performance?
So, remember the mantra – if you can’t test it, it’s not a hypothesis 🙂

Defining A Research Hypothesis
You’re still with us? Great! Let’s recap and pin down a clear definition of a hypothesis.
A research hypothesis (or scientific hypothesis) is a statement about an expected relationship between variables, or explanation of an occurrence, that is clear, specific and testable.
So, when you write up hypotheses for your dissertation or thesis, make sure that they meet all these criteria. If you do, you’ll not only have rock-solid hypotheses but you’ll also ensure a clear focus for your entire research project.
What about the null hypothesis?
You may have also heard the terms null hypothesis , alternative hypothesis, or H-zero thrown around. At a simple level, the null hypothesis is the counter-proposal to the original hypothesis.
For example, if the hypothesis predicts that there is a relationship between two variables (for example, sleep and academic performance), the null hypothesis would predict that there is no relationship between those variables.
At a more technical level, the null hypothesis proposes that no statistical significance exists in a set of given observations and that any differences are due to chance alone.
And there you have it – hypotheses in a nutshell.
If you have any questions, be sure to leave a comment below and we’ll do our best to help you. If you need hands-on help developing and testing your hypotheses, consider our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the research journey.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

16 Comments
Very useful information. I benefit more from getting more information in this regard.
Very great insight,educative and informative. Please give meet deep critics on many research data of public international Law like human rights, environment, natural resources, law of the sea etc
In a book I read a distinction is made between null, research, and alternative hypothesis. As far as I understand, alternative and research hypotheses are the same. Can you please elaborate? Best Afshin
This is a self explanatory, easy going site. I will recommend this to my friends and colleagues.
Very good definition. How can I cite your definition in my thesis? Thank you. Is nul hypothesis compulsory in a research?
It’s a counter-proposal to be proven as a rejection
Please what is the difference between alternate hypothesis and research hypothesis?
It is a very good explanation. However, it limits hypotheses to statistically tasteable ideas. What about for qualitative researches or other researches that involve quantitative data that don’t need statistical tests?
In qualitative research, one typically uses propositions, not hypotheses.
could you please elaborate it more
I’ve benefited greatly from these notes, thank you.
This is very helpful
well articulated ideas are presented here, thank you for being reliable sources of information
Excellent. Thanks for being clear and sound about the research methodology and hypothesis (quantitative research)
I have only a simple question regarding the null hypothesis. – Is the null hypothesis (Ho) known as the reversible hypothesis of the alternative hypothesis (H1? – How to test it in academic research?
this is very important note help me much more
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- What Is Research Methodology? Simple Definition (With Examples) - Grad Coach - […] Contrasted to this, a quantitative methodology is typically used when the research aims and objectives are confirmatory in nature. For example,…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

- Manuscript Preparation
What is and How to Write a Good Hypothesis in Research?
- 4 minute read
- 302.7K views
Table of Contents
One of the most important aspects of conducting research is constructing a strong hypothesis. But what makes a hypothesis in research effective? In this article, we’ll look at the difference between a hypothesis and a research question, as well as the elements of a good hypothesis in research. We’ll also include some examples of effective hypotheses, and what pitfalls to avoid.
What is a Hypothesis in Research?
Simply put, a hypothesis is a research question that also includes the predicted or expected result of the research. Without a hypothesis, there can be no basis for a scientific or research experiment. As such, it is critical that you carefully construct your hypothesis by being deliberate and thorough, even before you set pen to paper. Unless your hypothesis is clearly and carefully constructed, any flaw can have an adverse, and even grave, effect on the quality of your experiment and its subsequent results.
Research Question vs Hypothesis
It’s easy to confuse research questions with hypotheses, and vice versa. While they’re both critical to the Scientific Method, they have very specific differences. Primarily, a research question, just like a hypothesis, is focused and concise. But a hypothesis includes a prediction based on the proposed research, and is designed to forecast the relationship of and between two (or more) variables. Research questions are open-ended, and invite debate and discussion, while hypotheses are closed, e.g. “The relationship between A and B will be C.”
A hypothesis is generally used if your research topic is fairly well established, and you are relatively certain about the relationship between the variables that will be presented in your research. Since a hypothesis is ideally suited for experimental studies, it will, by its very existence, affect the design of your experiment. The research question is typically used for new topics that have not yet been researched extensively. Here, the relationship between different variables is less known. There is no prediction made, but there may be variables explored. The research question can be casual in nature, simply trying to understand if a relationship even exists, descriptive or comparative.
How to Write Hypothesis in Research
Writing an effective hypothesis starts before you even begin to type. Like any task, preparation is key, so you start first by conducting research yourself, and reading all you can about the topic that you plan to research. From there, you’ll gain the knowledge you need to understand where your focus within the topic will lie.
Remember that a hypothesis is a prediction of the relationship that exists between two or more variables. Your job is to write a hypothesis, and design the research, to “prove” whether or not your prediction is correct. A common pitfall is to use judgments that are subjective and inappropriate for the construction of a hypothesis. It’s important to keep the focus and language of your hypothesis objective.
An effective hypothesis in research is clearly and concisely written, and any terms or definitions clarified and defined. Specific language must also be used to avoid any generalities or assumptions.
Use the following points as a checklist to evaluate the effectiveness of your research hypothesis:
- Predicts the relationship and outcome
- Simple and concise – avoid wordiness
- Clear with no ambiguity or assumptions about the readers’ knowledge
- Observable and testable results
- Relevant and specific to the research question or problem
Research Hypothesis Example
Perhaps the best way to evaluate whether or not your hypothesis is effective is to compare it to those of your colleagues in the field. There is no need to reinvent the wheel when it comes to writing a powerful research hypothesis. As you’re reading and preparing your hypothesis, you’ll also read other hypotheses. These can help guide you on what works, and what doesn’t, when it comes to writing a strong research hypothesis.
Here are a few generic examples to get you started.
Eating an apple each day, after the age of 60, will result in a reduction of frequency of physician visits.
Budget airlines are more likely to receive more customer complaints. A budget airline is defined as an airline that offers lower fares and fewer amenities than a traditional full-service airline. (Note that the term “budget airline” is included in the hypothesis.
Workplaces that offer flexible working hours report higher levels of employee job satisfaction than workplaces with fixed hours.
Each of the above examples are specific, observable and measurable, and the statement of prediction can be verified or shown to be false by utilizing standard experimental practices. It should be noted, however, that often your hypothesis will change as your research progresses.
Language Editing Plus
Elsevier’s Language Editing Plus service can help ensure that your research hypothesis is well-designed, and articulates your research and conclusions. Our most comprehensive editing package, you can count on a thorough language review by native-English speakers who are PhDs or PhD candidates. We’ll check for effective logic and flow of your manuscript, as well as document formatting for your chosen journal, reference checks, and much more.

- Research Process
Systematic Literature Review or Literature Review?

What is a Problem Statement? [with examples]
You may also like.

Make Hook, Line, and Sinker: The Art of Crafting Engaging Introductions

Can Describing Study Limitations Improve the Quality of Your Paper?

A Guide to Crafting Shorter, Impactful Sentences in Academic Writing

6 Steps to Write an Excellent Discussion in Your Manuscript

How to Write Clear and Crisp Civil Engineering Papers? Here are 5 Key Tips to Consider

The Clear Path to An Impactful Paper: ②

The Essentials of Writing to Communicate Research in Medicine

Changing Lines: Sentence Patterns in Academic Writing
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
Ingham Institute

click here to donate please
Home / Why the research question is so important
Why the research question is so important
04/05/2018 at 5:42 am
A research question is a sentence that defines what you will examine, within which population, and what the outcome of interest will be. Defining a clear research question is the first and most important part of the project. Though it sounds simple, writing a research question is tricky even for experienced researchers. This video will build your understanding of where to start looking for research questions, how to write them, and why it is important to work with a solid research question from the beginning of the project.
Share this post
CALD clinical clinical data clinical practice clinical trials clinicians conducting surveys data database degree degrees diverse communities engagement guidelines linguistic masters PhD question research research journey research project statistical statistics study design support survey SWSLHD
Additional Content
Links to useful research papers.
Farrugia P, Petrisor BA, Farrokhyar F, Bhandari M. Research questions, hypotheses and objectives. Canadian Journal of Surgery. 2010;53(4):278-281. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2912019/
Aslam, S., & Emmanuel, P. (2010). Formulating a researchable question: A critical step for facilitating good clinical research. Indian J Sex Transm Dis, 31(1), 47-50. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21808439
Beitz, J. M. (2006). Writing the researchable question. J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs, 33(2), 122-124. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16572009
Links to useful websites
Centre for Clinical Effectivenbess
http://www.monashhealth.org/page/Resources
Centre for Evidence Based Medicine
https://www.cebm.net/category/ebm-resources/tools/
Libraries in SWSLHD
https://www.swslhd.health.nsw.gov.au/liverpool/library/default.html
https://www.swslhd.health.nsw.gov.au/ccq/library/
https://www.swslhd.health.nsw.gov.au/Fairfield/library/
https://www.swslhd.health.nsw.gov.au/bankstown/library/
Useful Information
Research questions examples
Useful resources to download

Help us improve!
Would you please take a moment to answer these 2 quick questions, to what extent did this resource increase your understanding of the topic, to what extent did this resource help you find further information on this topic , wow this is awesome.
Many people are getting problem in using bootstrap modal, so here I'm with custom modal which you can use anywhere.
100% of your donation goes to medical research
Clarifying the Research Questions or Hypotheses
- First Online: 28 March 2017
Cite this chapter

- Kenan Dikilitaş 3 &
- Carol Griffiths 4
1042 Accesses
This chapter deals with the important, but often neglected, issue of establishing research questions or hypotheses, whether this is done before or (in the “real world”) often after the study has been conducted. The point is made that, in fact, research questions tend to be more common than hypotheses in action research, and guidelines are suggested for delineating such questions and deciding on appropriate question types according to the research purpose. Some example questions are provided to stimulate ideas, and an example action research study which will proceed in stages throughout the book is begun here.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Educational Sciences, Bahçeşehir University, Istanbul, Turkey
Kenan Dikilitaş
Freelance, Istanbul, Turkey
Carol Griffiths
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Dikilitaş, K., Griffiths, C. (2017). Clarifying the Research Questions or Hypotheses. In: Developing Language Teacher Autonomy through Action Research. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-50739-2_2
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-50739-2_2
Published : 28 March 2017
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-50738-5
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-50739-2
eBook Packages : Social Sciences Social Sciences (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Can J Hosp Pharm
- v.67(1); Jan-Feb 2014

Research: Articulating Questions, Generating Hypotheses, and Choosing Study Designs
Introduction.
Articulating a clear and concise research question is fundamental to conducting a robust and useful research study. Although “getting stuck into” the data collection is the exciting part of research, this preparation stage is crucial. Clear and concise research questions are needed for a number of reasons. Initially, they are needed to enable you to search the literature effectively. They will allow you to write clear aims and generate hypotheses. They will also ensure that you can select the most appropriate research design for your study.
This paper begins by describing the process of articulating clear and concise research questions, assuming that you have minimal experience. It then describes how to choose research questions that should be answered and how to generate study aims and hypotheses from your questions. Finally, it describes briefly how your question will help you to decide on the research design and methods best suited to answering it.
TURNING CURIOSITY INTO QUESTIONS
A research question has been described as “the uncertainty that the investigator wants to resolve by performing her study” 1 or “a logical statement that progresses from what is known or believed to be true to that which is unknown and requires validation”. 2 Developing your question usually starts with having some general ideas about the areas within which you want to do your research. These might flow from your clinical work, for example. You might be interested in finding ways to improve the pharmaceutical care of patients on your wards. Alternatively, you might be interested in identifying the best antihypertensive agent for a particular subgroup of patients. Lipowski 2 described in detail how work as a practising pharmacist can be used to great advantage to generate interesting research questions and hence useful research studies. Ideas could come from questioning received wisdom within your clinical area or the rationale behind quick fixes or workarounds, or from wanting to improve the quality, safety, or efficiency of working practice.
Alternatively, your ideas could come from searching the literature to answer a query from a colleague. Perhaps you could not find a published answer to the question you were asked, and so you want to conduct some research yourself. However, just searching the literature to generate questions is not to be recommended for novices—the volume of material can feel totally overwhelming.
Use a research notebook, where you regularly write ideas for research questions as you think of them during your clinical practice or after reading other research papers. It has been said that the best way to have a great idea is to have lots of ideas and then choose the best. The same would apply to research questions!
When you first identify your area of research interest, it is likely to be either too narrow or too broad. Narrow questions (such as “How is drug X prescribed for patients with condition Y in my hospital?”) are usually of limited interest to anyone other than the researcher. Broad questions (such as “How can pharmacists provide better patient care?”) must be broken down into smaller, more manageable questions. If you are interested in how pharmacists can provide better care, for example, you might start to narrow that topic down to how pharmacists can provide better care for one condition (such as affective disorders) for a particular subgroup of patients (such as teenagers). Then you could focus it even further by considering a specific disorder (depression) and a particular type of service that pharmacists could provide (improving patient adherence). At this stage, you could write your research question as, for example, “What role, if any, can pharmacists play in improving adherence to fluoxetine used for depression in teenagers?”
TYPES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS
Being able to consider the type of research question that you have generated is particularly useful when deciding what research methods to use. There are 3 broad categories of question: descriptive, relational, and causal.
Descriptive
One of the most basic types of question is designed to ask systematically whether a phenomenon exists. For example, we could ask “Do pharmacists ‘care’ when they deliver pharmaceutical care?” This research would initially define the key terms (i.e., describing what “pharmaceutical care” and “care” are), and then the study would set out to look for the existence of care at the same time as pharmaceutical care was being delivered.
When you know that a phenomenon exists, you can then ask description and/or classification questions. The answers to these types of questions involve describing the characteristics of the phenomenon or creating typologies of variable subtypes. In the study above, for example, you could investigate the characteristics of the “care” that pharmacists provide. Classifications usually use mutually exclusive categories, so that various subtypes of the variable will have an unambiguous category to which they can be assigned. For example, a question could be asked as to “what is a pharmacist intervention” and a definition and classification system developed for use in further research.
When seeking further detail about your phenomenon, you might ask questions about its composition. These questions necessitate deconstructing a phenomenon (such as a behaviour) into its component parts. Within hospital pharmacy practice, you might be interested in asking questions about the composition of a new behavioural intervention to improve patient adherence, for example, “What is the detailed process that the pharmacist implicitly follows during delivery of this new intervention?”
After you have described your phenomena, you may then be interested in asking questions about the relationships between several phenomena. If you work on a renal ward, for example, you may be interested in looking at the relationship between hemoglobin levels and renal function, so your question would look something like this: “Are hemoglobin levels related to level of renal function?” Alternatively, you may have a categorical variable such as grade of doctor and be interested in the differences between them with regard to prescribing errors, so your research question would be “Do junior doctors make more prescribing errors than senior doctors?” Relational questions could also be asked within qualitative research, where a detailed understanding of the nature of the relationship between, for example, the gender and career aspirations of clinical pharmacists could be sought.
Once you have described your phenomena and have identified a relationship between them, you could ask about the causes of that relationship. You may be interested to know whether an intervention or some other activity has caused a change in your variable, and your research question would be about causality. For example, you may be interested in asking, “Does captopril treatment reduce blood pressure?” Generally, however, if you ask a causality question about a medication or any other health care intervention, it ought to be rephrased as a causality–comparative question. Without comparing what happens in the presence of an intervention with what happens in the absence of the intervention, it is impossible to attribute causality to the intervention. Although a causality question would usually be answered using a comparative research design, asking a causality–comparative question makes the research design much more explicit. So the above question could be rephrased as, “Is captopril better than placebo at reducing blood pressure?”
The acronym PICO has been used to describe the components of well-crafted causality–comparative research questions. 3 The letters in this acronym stand for Population, Intervention, Comparison, and Outcome. They remind the researcher that the research question should specify the type of participant to be recruited, the type of exposure involved, the type of control group with which participants are to be compared, and the type of outcome to be measured. Using the PICO approach, the above research question could be written as “Does captopril [ intervention ] decrease rates of cardiovascular events [ outcome ] in patients with essential hypertension [ population ] compared with patients receiving no treatment [ comparison ]?”
DECIDING WHETHER TO ANSWER A RESEARCH QUESTION
Just because a question can be asked does not mean that it needs to be answered. Not all research questions deserve to have time spent on them. One useful set of criteria is to ask whether your research question is feasible, interesting, novel, ethical, and relevant. 1 The need for research to be ethical will be covered in a later paper in the series, so is not discussed here. The literature review is crucial to finding out whether the research question fulfils the remaining 4 criteria.
Conducting a comprehensive literature review will allow you to find out what is already known about the subject and any gaps that need further exploration. You may find that your research question has already been answered. However, that does not mean that you should abandon the question altogether. It may be necessary to confirm those findings using an alternative method or to translate them to another setting. If your research question has no novelty, however, and is not interesting or relevant to your peers or potential funders, you are probably better finding an alternative.
The literature will also help you learn about the research designs and methods that have been used previously and hence to decide whether your potential study is feasible. As a novice researcher, it is particularly important to ask if your planned study is feasible for you to conduct. Do you or your collaborators have the necessary technical expertise? Do you have the other resources that will be needed? If you are just starting out with research, it is likely that you will have a limited budget, in terms of both time and money. Therefore, even if the question is novel, interesting, and relevant, it may not be one that is feasible for you to answer.
GENERATING AIMS AND HYPOTHESES
All research studies should have at least one research question, and they should also have at least one aim. As a rule of thumb, a small research study should not have more than 2 aims as an absolute maximum. The aim of the study is a broad statement of intention and aspiration; it is the overall goal that you intend to achieve. The wording of this broad statement of intent is derived from the research question. If it is a descriptive research question, the aim will be, for example, “to investigate” or “to explore”. If it is a relational research question, then the aim should state the phenomena being correlated, such as “to ascertain the impact of gender on career aspirations”. If it is a causal research question, then the aim should include the direction of the relationship being tested, such as “to investigate whether captopril decreases rates of cardiovascular events in patients with essential hypertension, relative to patients receiving no treatment”.
The hypothesis is a tentative prediction of the nature and direction of relationships between sets of data, phrased as a declarative statement. Therefore, hypotheses are really only required for studies that address relational or causal research questions. For the study above, the hypothesis being tested would be “Captopril decreases rates of cardiovascular events in patients with essential hypertension, relative to patients receiving no treatment”. Studies that seek to answer descriptive research questions do not test hypotheses, but they can be used for hypothesis generation. Those hypotheses would then be tested in subsequent studies.
CHOOSING THE STUDY DESIGN
The research question is paramount in deciding what research design and methods you are going to use. There are no inherently bad research designs. The rightness or wrongness of the decision about the research design is based simply on whether it is suitable for answering the research question that you have posed.
It is possible to select completely the wrong research design to answer a specific question. For example, you may want to answer one of the research questions outlined above: “Do pharmacists ‘care’ when they deliver pharmaceutical care?” Although a randomized controlled study is considered by many as a “gold standard” research design, such a study would just not be capable of generating data to answer the question posed. Similarly, if your question was, “Is captopril better than placebo at reducing blood pressure?”, conducting a series of in-depth qualitative interviews would be equally incapable of generating the necessary data. However, if these designs are swapped around, we have 2 combinations (pharmaceutical care investigated using interviews; captopril investigated using a randomized controlled study) that are more likely to produce robust answers to the questions.
The language of the research question can be helpful in deciding what research design and methods to use. Subsequent papers in this series will cover these topics in detail. For example, if the question starts with “how many” or “how often”, it is probably a descriptive question to assess the prevalence or incidence of a phenomenon. An epidemiological research design would be appropriate, perhaps using a postal survey or structured interviews to collect the data. If the question starts with “why” or “how”, then it is a descriptive question to gain an in-depth understanding of a phenomenon. A qualitative research design, using in-depth interviews or focus groups, would collect the data needed. Finally, the term “what is the impact of” suggests a causal question, which would require comparison of data collected with and without the intervention (i.e., a before–after or randomized controlled study).
CONCLUSIONS
This paper has briefly outlined how to articulate research questions, formulate your aims, and choose your research methods. It is crucial to realize that articulating a good research question involves considerable iteration through the stages described above. It is very common that the first research question generated bears little resemblance to the final question used in the study. The language is changed several times, for example, because the first question turned out not to be feasible and the second question was a descriptive question when what was really wanted was a causality question. The books listed in the “Further Reading” section provide greater detail on the material described here, as well as a wealth of other information to ensure that your first foray into conducting research is successful.
This article is the second in the CJHP Research Primer Series, an initiative of the CJHP Editorial Board and the CSHP Research Committee. The planned 2-year series is intended to appeal to relatively inexperienced researchers, with the goal of building research capacity among practising pharmacists. The articles, presenting simple but rigorous guidance to encourage and support novice researchers, are being solicited from authors with appropriate expertise.
Previous article in this series:
Bond CM. The research jigsaw: how to get started. Can J Hosp Pharm . 2014;67(1):28–30.
Competing interests: Mary Tully has received personal fees from the UK Renal Pharmacy Group to present a conference workshop on writing research questions and nonfinancial support (in the form of travel and accommodation) from the Dubai International Pharmaceuticals and Technologies Conference and Exhibition (DUPHAT) to present a workshop on conducting pharmacy practice research.
Further Reading
- Cresswell J. Research design: qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods approaches. London (UK): Sage; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Haynes RB, Sackett DL, Guyatt GH, Tugwell P. Clinical epidemiology: how to do clinical practice research. 3rd ed. Philadelphia (PA): Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins; 2006. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kumar R. Research methodology: a step-by-step guide for beginners. 3rd ed. London (UK): Sage; 2010. [ Google Scholar ]
- Smith FJ. Conducting your pharmacy practice research project. London (UK): Pharmaceutical Press; 2005. [ Google Scholar ]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research question. Interest in a particular topic usually begins the research process, but it is the familiarity with the subject that helps define an appropriate research question for a study. 1 Questions then arise out of a perceived knowledge deficit within a subject area or field of study. 2 Indeed, Haynes suggests that it is important to know "where the boundary between current ...
Hence, a comprehensive review of the topic is imperative, as it allows the researcher to identify this gap in the literature, formulate a hypothesis and develop a research question. To this end, it is crucial to be attentive to new ideas, keep the imagination roaming with reflective attitude, and remain sceptical to the new-gained information ...
Abstract. Formulation of research question (RQ) is an essentiality before starting any research. It aims to explore an existing uncertainty in an area of concern and points to a need for deliberate investigation. It is, therefore, pertinent to formulate a good RQ. The present paper aims to discuss the process of formulation of RQ with stepwise ...
A research hypothesis helps test theories. A hypothesis plays a pivotal role in the scientific method by providing a basis for testing existing theories. For example, a hypothesis might test the predictive power of a psychological theory on human behavior. It serves as a great platform for investigation activities.
A good research question is essential to guide your research paper, dissertation, or thesis. All research questions should be: Focused on a single problem or issue. Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources. Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints. Specific enough to answer thoroughly.
The primary research question should originate from the hypothesis, not the data, and be established before starting the study. Formulating the research question and hypothesis from existing data (e.g., a database) can lead to multiple statistical comparisons and potentially spurious findings due to chance.
This column is about research questions, the beginning of the researcher's process. For the reader, the question driving the researcher's inquiry is the first place to start when examining the quality of their work because if the question is flawed, the quality of the methods and soundness of the researchers' thinking does not matter.
Quick tips on writing a hypothesis. 1. Be clear about your research question. A hypothesis should instantly address the research question or the problem statement. To do so, you need to ask a question. Understand the constraints of your undertaken research topic and then formulate a simple and topic-centric problem.
A hypothesis (from the Greek, foundation) is a logical construct, interposed between a problem and its solution, which represents a proposed answer to a research question. It gives direction to the investigator's thinking about the problem and, therefore, facilitates a solution. Unlike facts and assumptions (presumed true and, therefore, not ...
DEVELOPING HYPOTHESES & RESEARCH QUESTIONS. Nature of Hypothesis. It can be tested - verifiable or falsifiable Hypotheses are not moral or ethical questions It is neither too specific nor to general It is a prediction of consequences It is considered valuable even if proven false. DEVELOPING HYPOTHESES & RESEARCH QUESTIONS.
Research Questions and Hypotheses I nvestigators place signposts to carry the reader through a plan for a study. The first signpost is the purpose statement, which establishes the ... Designing Research Example 7.3 A Null Hypothesis An investigator might examine three types of reinforcement for children with autism: verbal cues, a reward, and ...
INTRODUCTION. Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses.1,2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results.3,4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the ...
It seeks to explore and understand a particular aspect of the research subject. In contrast, a research hypothesis is a specific statement or prediction that suggests an expected relationship between variables. It is formulated based on existing knowledge or theories and guides the research design and data analysis. 7.
A research hypothesis (also called a scientific hypothesis) is a statement about the expected outcome of a study (for example, a dissertation or thesis). To constitute a quality hypothesis, the statement needs to have three attributes - specificity, clarity and testability. Let's take a look at these more closely.
The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not focused or researchable. The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically feasible. For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries.
It's important to keep the focus and language of your hypothesis objective. An effective hypothesis in research is clearly and concisely written, and any terms or definitions clarified and defined. Specific language must also be used to avoid any generalities or assumptions. Use the following points as a checklist to evaluate the ...
04/05/2018 at 5:42 am. A research question is a sentence that defines what you will examine, within which population, and what the outcome of interest will be. Defining a clear research question is the first and most important part of the project. Though it sounds simple, writing a research question is tricky even for experienced researchers.
In fact, publicly discussing research questions on platforms of news outlets, such as Reddit, may shape hypotheses on health-related issues of global importance, such as obesity.40 Analyzing Twitter comments, researchers may reveal both potentially valuable ideas and unfounded claims that surround groundbreaking research ideas.41 Social media ...
After constructing a purpose statement, research questions must be . crafted that flow from the purpose statement. For qualitative designs, a central, overarching research question is typical, followed by subques-tions. The central research question should include a broad question that denotes the exploration of the central phenomenon under study.
Research questions are essential because they: • Define an investigation. • Set boundaries. • Provide direction. • Act as a frame of reference for assessing your work. Now I don't want to make it sound like research questions are reductionist devices that take all exploration, creativity and fluidity out of the research process.
In fact, deciding the research topic and clarifying the question/s or hypothesis/es can often be the hardest part of any research project. But clarifying the research question/s or hypothesis/es early in the process can save a lot of wasted time, prevent missed opportunities, and avoid overlooking important details which may cause problems ...
Articulating a clear and concise research question is fundamental to conducting a robust and useful research study. Although "getting stuck into" the data collection is the exciting part of research, this preparation stage is crucial. Clear and concise research questions are needed for a number of reasons. Initially, they are needed to ...
Research problems and hypotheses are important means for attaining valuable knowledge. They are pointers or guides to such knowledge, or as formulated by Kerlinger ( 1986, p. 19): " … they direct investigation.". There are many kinds of problems and hypotheses, and they may play various roles in knowledge construction.