Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center


Organisational Behaviour: A case study of Coca-Cola Company

Abstract: The paper contains a detail analysis of organizational behavior discussing issues facing cutting age organizations on leadership behavior, organizational effectiveness, organizational structures and human resource management. The paper further analyzed the structure and culture of Coca-Cola Company with emphasis on issues relating to ricks and uncertainties in the company’s decision making. Recommendations are laid based on the study to address the company’s issues and align decision-making with the company’s structure
Related Papers
Angelina Mar
Ibrahim Dan-Musa
This is a research on the question “Does Culture play a significant role in Organisational Change?” This paper aims at giving a critical analysis on the subject matter “organisational change” (“an alteration of an organization’s environment, structure, culture, technology, or people” [Michael Crandall 2006]) and how much role culture (the collective programming of the human mind that distinguishes the members of one human group from those of another” [Hofstede 1981]) plays in organisational change. It aims to answer the question whether culture contributes a significant role in organisational change. It would also look at the impact of leadership on organisational change and the significance of leadership in organisational change. It would also show the correlation and catalyst effect of leadership on culture in making an organisational change. The research would then give an example of the role of culture in organisational change using the case study of Petro-Kazakhstan and China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC) to illustrate the role of culture in organisational change. The paper would end with a conclusion and recommendation on the dissertation question, “Does culture play a significant role in organisational change?”
Assignment on change management 3000 words with references.
Oghenethoja Umuteme
A review of both old and new leadership theories from a psychological perspective is presented in this work. Organisational leadership as a term is being discussed in various academic and business circles, leading to several definitions of the term. The inability of the business and academic world to accept a universal definition explains that leadership itself is complex. This can be attributed to various factors such as personality traits, organisational culture, current world issues, etc., that various theories tries to explain.
Vidushi Manoraj
Samuel Babatunji Adedeji
The purpose of this paper is to determine the extent to which organisational culture is an explanatory variable for firm’s corporate performance especially now that entities interact in globally knowledge based economies. A review of theoretical and empirical studies were carried out on some developed, emerging and developing nations with particular reference to traits characterised in specific organisational cultural environments in relation to their effects on corporate performance. Those reviews show that organisational culture needs to focus on knowledge management, knowledge conversion, team work, human capital formation, organisational climate and adaptive culture. The studies reviewed focused more on cross-national research design with less attention on the longitudinal aspect. It was not possible to review papers written in non-English language, and those published reviews with access denied to some online. There is a need for more empirical evidence to further justify the relevance of this study area for assessment of organisational culture and corporate performance. This review adds value with the recognition of the need to gear up researchers and policy making bodies to encourage advancement of studies on intellectual capital and knowledge management to enhance sustainable corporate culture and performance.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
The Coca-Cola Company: Personal Management and Organizational Behavior Term Paper
Introduction.
The Coca-Cola Company started functioning as a one man business which was hardly known to anyone. The drink itself was invented by Doctor John Pemberton in 1886 in Atlanta, Georgia. Later, the same tear, a prohibition law made Pemberton change the formula for this nerve tonic and a headache remedy. The drink remained a nerve stimulant, but wine which used to be one of its ingredients was changed for sugar; despite this, however, the drinnk’s inventor continued calling it a “temperance drink.”
After Pemberton’s death in 1888, the trademark which he and his partners created became unbelievably popular. By the end of 1890s, Coca-Cola became the most popular fountain drink among the Americans. Back then it was headed by Griggs Candler, another pharmacist from Atlanta, who managed to increase the sales of the syrup by 4000%.
One of the facts which remains unknown is that Candler and one of Pemberton’s former partners, Frank Robinson, changed the recipe of the syrup and “perfected” the drink by adding several new ingredients and taking out some of the others. Besides, namely Robinson created the name of the drink and its script logo, as well as the slogan “delicious and refreshing.” The name itself symbolizes “the company’s main product, which stands for refreshment.” (Truitt, 2006, p.132)
After 1900, Candler and his partners started selling the syrup to independent bottling companies who had the license allowing them to sell this drink. Due to this, Coca-Cola bottling factories started springing up across America bringing fame and richness to their owners. The Coke brand imprinted itself upon a number of other cultures appearing in song lyrics, movies, and even sculptures and paintings.
The company, which was headed by Don Keough and Roberto Goizueta, attracted numerous investors, because Wall Street labeled it as a growth stock. By the late 1990s the Coca-Cola Company became “a sprawling empire employing 29,000 people worldwide.” (Feigenbaum, 2003, p.175) These days, there is hardly a country where Coca-Cola Company does not sell beverages; at this, two-thirds of the company’s sales come from outside the USA. The company sells large amounts of the products increasing its profits daily:
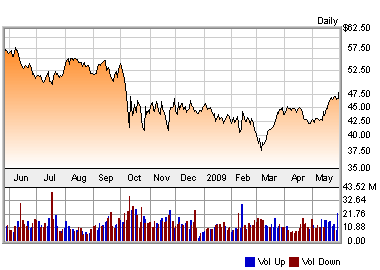
The company serves 9 million stores which sell the drinks; to succeed in this, “the company has contracts with hundreds of bottlers, which add water to the company’s trademark concentrate and distribute the soft drinks in cans and bottles.” (Certo, 2005, p.99) There exist three types of bottlers to which the company sells syrups and concentrates: “First are independent bottlers in which the company has no ownership interest. Second are bottlers in which the company has a minority equity position.
Third are bottlers in which the company has a controlling interest.” (Steiner, 2005, p. 348) Apart from carbonated drinks, the company is currently selling juices, tea, bottle water, and the like products (the company diversified its products already in 1960-1970 when it acquired the Minute Maid, the Duncan Foods Corporation, the Belmon Springs Water Company, Inc., Taylor Wines Company, and others).
It is also engaged in the activities which benefit the communities in which the company has businesses. For instance, in 2001 it signed a three-year partnership with UNAIDS (the United Nations Agency which coordinates activities in fighting with AIDS and HIV); Coca-Cola Company provided “multiple services throughout Africa to support AIDS education; distribute[d] preventive measures, such as AIDS testing kits and condoms; and publicize[d] treatment programs.” (Steiner, 2005, p.349) Coca-Cola Company is known not only for its soft drinks of high quality; the company takes care about the emotional health of its employees, regularly improves customer services, and is always open for changes and innovations if they help to meet the customers’ needs.
Emotional Health of Employees
The Coca-Cola Company management has almost a full control of their employees’ emotions and is known for its good working conditions, training and education classes for employees, as well as for the employees’ loyalty to the company. The latter is one of the most important factors for the company’s welfare, since some of the employees have an access to the “secret formula,” or the recipe of the famous Coca-Cola syrup which the company sells to other bottlers.
This is one of the reasons why “Coca-Cola has created an atmosphere of “fierce Loyalty” among its employees.” (Grossman & Jennings, 2002, p.202) Such atmosphere has been maintained in the company over the decades. Since some of the employees know the formula, they sign a non-compete agreement which prevents them from using it. However, this agreement is more of a formality for Coca-Cola employees, because the history of the company abounds with the cases when the Coke employees refused even to use the products manufactured by Pepsi and other manufacturers which are Coca-Cola’s competitors, let alone sharing the formula with these companies.
According to Ryan, Gasparski, & Enderle 2000, in 1995 and 1996 “The Coca-Cola Company occupied the first position on the list of the most admired American companies, in a survey conducted by Fortune … Coke’s CEO Robert Goizueta believes that employees with integrity are the ones that build the company’s reputation.” (p. 62) The management of the company believes that the welfare and satisfaction of the employees result in better performance of the company, because the employee who is satisfied with the working conditions and the work in general works better and produces the products or services of higher quality.
Quality of the manufactured products is the most important for the Coca-Cola Company this why commitment to quality is the way of life for each of the employees. (Ryan et al, 2000, p.63) The company continually hires new workers because it considers growth to be an essential part of the corporate culture, “the primary reason for growth being not financial but spiritual, since it produces a winning spirit; it creates a vital, enthusiastic atmosphere in the corporation where people see genuine personal opportunity.” (Ryan et al, 2000, p. 63)
Due to such emotional health of the employees and the company’s caring about the employees’ emotions, the products which the company manufactures are used by more than 94% of the world’s population with Coca-Cola being the most admired trademark in the world:
Executives in Atlanta office say that if the place was obliterated off the earth, they could go to the bank and borrow $100 million and rebuild Coca-Cola in a matter of months just on he strength of he brand. Employees are proud to be able to work for the company that sells one of he most famous and admired products and speak of the brand with respect. (Ryan, e al, 2000, p.64)
Therefore, emotions, as one of the concepts of organizational behavior, are the key factor in Coca-Cola’s development and performance. This is what Robbins and Judge (2007) refer to as “positive organizational behavior” which helps the companies “develop human strengths, foster vitality and resilience, and unlock potential.” (p.25) Since the quality of the products manufactured by Coca-Cola Company depends on the employees’ treatment of their work, the management of the company does everything possible to sustain their emotional health.
Improving Customer Service
A company which manufactures products and services cannot exist without customers this is why creating customer-responsive culture in the organization is vital for its performance and overall existence. It is the responsibility of the company’s management to create “cultures in which employees are friendly and courteous, accessible, knowledgeable, prompt in responding to customer needs, and willing to do what’s necessary to please the customer.” (Robbins & Judge, 2007, p. 22)
Customer service is one of the means to show that the company cares about its customers. A professional customer service program helps the company reduce marketing expenditures, because handling the customers’ complaints results in saving the customers. (Tschohl & Franzmeier, 2008, p. 35)
The Coca-Cola Company, like no other company, is customer-oriented this is why it has “an amazing global customer support infrastructure,” (McKenna, 2002, p.142) and the quality of customer support is continually improving by its bottlers all around the world. For instance, one of its bottlers, Coca Cola Bottling Unit (Lambeg) installed a single customer service touchpoint already in 1996 when the survey conducted among the customers showed that they needed a single contact point for customer service, even though they were totally satisfied with the quality of the products. Absence of such a touchpoint hindered considerably the analysis of the call content and had an impact on the quality of responses:
The company resolved these problems by introducing a single touchpoint for all service issues and implementing the service automation product, HEAT. HEAT is used to monitor product codes found on packaging and products; when the support team finds three or more complaints that refer to any of these items then an alert message is sent direct to the incident team who investigate the situation. (Buttle, 2008, p. 456)
What’s more, the company’s implementation of service level agreements allowed automatically escalating the phone calls if they were not resolved in an identified period of time. The management ensured intensive training of the customer service team, which enabled each employee “to close standard queries and improve[d] the service customers receive.” (Buttle, 2008, p.456) All these operations not only helped the company retain a large number of customers, but attracted new ones. Thus, it can be stated that the Coca-Cola Company values its vast consumer network and tries to preserve it through improving its customer service.
Stimulating Innovation and Change
Modern companies and organizations have to cope with a great number of competitors which enter the market daily. Mastering the art of change and fostering innovation is extremely important for the organizations, because the chance to survive is given only to those companies which “maintain their flexibility, continually improve their quality, and beat their competition to the marketplace with a constant stream of innovative products and services.” (Robbins & Judge, 2007, p. 23)
The main task of the company’s management with respect to this problem is to stimulate the creativity of the employees and to teach them to easily and readily accept the changes. (Robbins & Judge, 2007, p. 23) The Coca-Cola Company is an example of how the organization should adapt to possible changes in consumers’ preferences and how the brilliant performance may sometimes help to avoid changing the manufactured products.
For most of the other companies which produce soft drinks or food, innovation is an integral part of the company’s existence, because consumers’ tastes change all the time and it becomes difficult to meet their needs. The experience of the Coca-Cola Company in the 1990s proved that well-established manufacturers need diversification, rather than modernization, change, or innovation. The company got convinced that diversification of the product would attract more customers than changing the already existing drinks; moreover, it would help to save the old consumers.
In 1985, the organization started producing New Coke in response to Pepsi’s stating that its drink had a “better tasting”. Trying not to lose the customers, Coca-Cola changed the formula of the drink, but people refused to accept it. This was when both the company and the consumers realized that “Coke was not just a cola. It was a tradition, owned not by the company but by the whole community.” (Kiuch & Shireman, 2002, p.118)
Doug Daft, who initiated the manufacturing of New Coke, had to bring Coca-Cola Classic back to the market for he recognized that Coca-Cola’s future lied not in the best-tasting soft drink, but “in its social license, the trust and esteem with which people held the company, a contract more binding than anything written on the paper.” (Kiuch & Shireman, 2002, p.118) From that moment, the only change the company made regarding the products was diversifying them.
Diversification of the products was beneficial for everyone starting with the stakeholders and shareholders and ending with consumers; at this, the latter benefited most of all, because diversification expanded the variety of products and gave them a possibility to choose, which was the most important since the choice created value. (Kiuch & Shireman, 2002, p.118) In addition, diversification made the company more resistant to any change in the market, as well as secured the integrity of the Coke brand.
This means that such organizations as Coca-Cola Company may not need other changes except for diversification of already existing products. The company’s negative experience with changing the taste of the drink which the consumers liked so much has shown that the consumers’ respect and devotion to the product may bring far more profits than any kind of change or innovation.
The Coca-Cola Company is an organization which can serve as an example for the companies developing in the modern market. Its rich history shows how much the company has gone through on its way to the success it enjoys today. Despite high popularity, the company continues caring about the employees’ welfare, particularly emotional welfare, for its management knows that only people who are totally satisfied with their work and salary are able to produce the products of high quality.
Coca-Cola is a customer-oriented company this is why the employees are trained to create a responsive environment which is maintained through the customer service where all the complaints are handled. Lastly, the company does not experiment with changing the taste of the products anymore opting to diversify them instead, which makes the company even stronger and attracts new customers and investors.
Buttle, F. (2008). Customer Relationship Management: Concepts and Technologies. Boston : Butterworth-Heinemann.
Cetro, S. (2005). Supervision: Concepts and Skill-Building. New York: McGraw-Hill Professional.
Feigenbaum, A.V. (2003). The Power of Management Capital: Utilizing the New Drivers of Innovation, Profitability, and Growth in a Demanding Global Economy. New York: McGraw-Hill Professional.
Grossman, L.H. & Jennings, M. (2002). Building a Business through Good Times and Bad: Lessons From 15 Companies, Each with a Century of Dividends. New York: Greenwood Publishing Group.
Interactive Stock Chart. (2009). [Graph Illustration]. Coca Cola Company . Web.
Kiuch, T. &Shireman, W.K. (2002). What We Learned in the Rainforest: Business Lessons from Nature : Innovation, Growth, Profit, and Sustainability At 20 of The World’s Top Companies. San Francisco: Berrett-Koehler Publishers.
McKenna, R. (2002). Total Access: Giving Customers What They Want In an Anytime, Anywhere World . Boston: Harvard Business Press.
Ryan, L.V., Gasparsky, W., & Enderle, G. (2000). Business Students Focus on Ethics . New Brunswick and London: Transaction Publishers.
Steiner, J.F. (2005). Business, Government and Society: A Managerial Perspective. New York: McGraw-Hill Professional.
Truitt, W.B. (2006). The Corporation. New York: Greenwood Publishing Group.
Tschol, J. & Franzmeir, S. (1996). Achieving Excellence Through Customer Service . New York: Best Sellers Publishing.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, March 13). The Coca-Cola Company: Personal Management and Organizational Behavior. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-coca-cola-company-personal-management-and-organizational-behavior/
"The Coca-Cola Company: Personal Management and Organizational Behavior." IvyPanda , 13 Mar. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/the-coca-cola-company-personal-management-and-organizational-behavior/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'The Coca-Cola Company: Personal Management and Organizational Behavior'. 13 March.
IvyPanda . 2024. "The Coca-Cola Company: Personal Management and Organizational Behavior." March 13, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-coca-cola-company-personal-management-and-organizational-behavior/.
1. IvyPanda . "The Coca-Cola Company: Personal Management and Organizational Behavior." March 13, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-coca-cola-company-personal-management-and-organizational-behavior/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "The Coca-Cola Company: Personal Management and Organizational Behavior." March 13, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-coca-cola-company-personal-management-and-organizational-behavior/.
- High Fructose Corn Syrup: Something to Be Avoided
- History. A Coca-Cola Bottle as a Cultural Artifact
- Coca-Cola Company Strategies
- Coordination and Motivation as a Firm's Purpose
- Merck: Company Mission and Strategies
- HBG UK Ltd: Company Performance Audit
- Starbucks Corporation's Mission: Responsibility and Growth
- Gap Inc.: Going to France Strategy
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Shaking Things Up at Coca-Cola
- An Interview with Muhtar Kent by Adi Ignatius

Listen to an excerpt of the interview.Download this podcast Since Muhtar Kent took the helm of Coca-Cola, in July 2008, he has set a course for ambitious, long-term growth—even in a supposedly mature U.S. market—with the goal of doubling revenue by 2020. Kent has tried to rejuvenate an inward-looking, “arrogant” corporate culture and has reinvested […]
Reprint: R1110F
When Muhtar Kent took the helm at Coke, in 2008, he had two top priorities: to establish a long-term vision and to restore growth in North America. The vision called for doubling Coke’s business in 10 years—something “not for the fainthearted,” Kent says, “but clearly doable.” In this edited interview he talks about the role of social media (Coke has 33 million Facebook fans), which today get 20% of the company’s total media spend; the importance of creating sustainable communities to preserve the future of the business; and Coke’s commitment to water neutrality by 2020—which means giving back a liter of water for every one the company uses. As the CEO of a company with 140,000 employees, Kent says, “you can only influence.” He takes a low-key approach, treasures the team, and loves to visit supermarkets and observe customers.
Partner Center
The Brand Impact on Culture: Case of Coca Cola Cultural Issues in India
- Conference paper
- First Online: 13 March 2021
- Cite this conference paper

- Asaad Ali Karam 12 , 13
Part of the book series: Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems ((LNNS,volume 194))
Included in the following conference series:
- International Conference on Business and Technology
2740 Accesses
3 Citations
The study purpose was culture assumes a pivotal role in brand and relying on underlying cultural philosophies. The Indian culture differences impacts on Coca-Cola brand; culture affects other brands very strongly. Productive brands have been able to adopt this dominant cultural paradigm. The measurements are based on the quantitative methods with criteria that were framed by culture and brand factors through customer perceived value to find out Coca-Cola’s brand cultural issues, the SmartPLS analysis was generated to study conceptual framework that was conducted restricting samples size of (N = 500). The study found that the culture and brand factors were effects on customer perceived value which was explained by (R 2 Adj. = 78.5%), While, the whole model was effective by Coca-Cola cultural issues with (R 2 Adj. = 80.9%). Further, culture has a significant effect on firm performance. Results of examination help companies to realize the significance of brand culture and product identity on the target market. The originality of this paper gives clear observations into the integration and combining of cultural fibers that make the brand prosper in the target market. It also clearly shows that several brands were successfully integrating and combining Indian culture in the market.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Yogi, K.S.: Assessment of process capability: the case of soft drinks processing unit. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 330 (1) (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/330/1/012064
Chaklader, B., Gautam, N.: Efficient water management through public-private partnership model: an experiment in CSR by coca-cola india. Vikalpa 38 (4), 97–104 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1177/0256090920130407
Article Google Scholar
Budhwar, P.S., Varma, A.: Doing Business in India, Doing Business in India. Routledge, London and New York (2010). https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203840931
Book Google Scholar
Karnani, A.: Working Paper of the Commons - Case Study : Coca-Cola India Case Study : Coca-Cola India. Ross School of Business Working Paper Working Paper No. 1173 (2012)
Google Scholar
Vedwan, N.: Pesticide in coca-cola and pepsi: consumerism, brand image, and public interest in a globalizing India. Cult. Anthropol. 22 (4), 659–684 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1525/can.2007.22.4.659
Kuntara, P., Thomas, W.: Venture capital in China: a culture shock for Western investors. Manag. Decis. 45 (4), 708–731 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1108/00251740710745999
De Mooij, M.: Global Marketing and Advertising, 5th edn. International Marketing Review. SAGE Publications Limited https://doi.org/10.1108/02651330610712184
Yin, J., Jamali, D.: Strategic corporate social responsibility of multinational companies subsidiaries in emerging markets: evidence from China. Long Range Plan. 49 (5), 541–558 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lrp.2015.12.024
Loftus, B., Goold, B., Giollabhui, S.M.: From a visible spectacle to an invisible presence: the working culture of covert policing. Br. J. Criminol. 56 (4), 629–645 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1093/bjc/azv076
Taneja, S., Sewell, S.S., Odom, R.Y.: A culture of employee engagement: a strategic perspective for global managers. J. Bus. Strat. 36 (3), 46–56 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1108/JBS-06-2014-0062
Vogel, R.M., Mitchell, M.S., Tepper, B.J., Restubog, S.L., Hu, C., Hua, W., Huang, J.C.: A cross-cultural examination of subordinates’ perceptions of and reactions to abusive supervision. J. Organ. Behav. 36 (5), 720–745 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/job.1984
Buil, I., de Chernatony, L., Hem, L.E.: Brand extension strategies: perceived fit, brand type, and culture influences. Eur. J. Mark. 43 (11), 1300–1324 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1108/03090560910989902
Matzler, K., Strobl, A., Stokburger-Sauer, N., Bobovnicky, A., Bauer, F.: Brand personality and culture: the role of cultural differences on the impact of brand personality perceptions on tourists’ visit intentions. Tour. Manag. 52 , 507–520 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2015.07.017
Harrigan, P., Evers, U., Miles, M.P., Daly, T.: Customer engagement and the relationship between involvement, engagement, self-brand connection and brand usage intent. J. Bus. Res. 88 , 388–396 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2017.11.046
Kim, S.S., Choe, J.Y.J., Petrick, J.F.: The effect of celebrity on brand awareness, perceived quality, brand image, brand loyalty, and destination attachment to a literary festival. J. Dest. Mark. Manag. 320–329 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdmm.2018.03.006 .
Karam, A.A., Saydam, S.: An analysis study of improving brand awareness and its impact on consumer behavior via media in North Cyprus (a case study of fast food restaurants). Int. J. Bus. Soc. Sci. 6 (1) (2015)
Foroudi, P.: Influence of brand signature, brand awareness, brand attitude, brand reputation on hotel industry’s brand performance. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 76 , 271–285 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2018.05.016
Martínez-Ferrero, J., García-Sánchez, I.-M.: The level of sustainability assurance: the effects of brand reputation and industry specialisation of assurance providers. J. Bus. Ethics 150 (4), 971–990 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-016-3159-x
Karam, A.A., Hamo, R.H., Rashid, H.M., Jarjes, D.A., Mohammed, C.S., Obaid, S.H.: The effect of marketing strategy implementation on organization performance as a private business: case of Cihan University Duhok Camps KRG-Iraq. Int. J. Bus. Manag. Econ. Res. (IJBMER) (2018)
de Chernatony, L.: Brand management through narrowing the gap between brand identity and brand reputation. J. Mark. Manag. 15 (1–3), 157–179 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1362/026725799784870432
Islam, J.U., Rahman, Z., Hollebeek, L.D.: Consumer engagement in online brand communities: a solicitation of congruity theory. Internet Res. 28 (1) (2018). https://doi.org/10.1108/IntR-09-2016-0279
Yatundu, F.A., Otiso, K.N., Rajab, F.N.: Brand awareness and its effect on performance of public sugar manufacturing firms in Western Kenya. Int. J. Adv. Manag. Econ. 5 (1), 42–47 (2016)
Sultan, K., Akram, S., Abdulhaliq, S., Jamal, D., Saleem, R.: A strategic approach to the consumer perception of brand on the basis of brand awareness and brand loyalty. Int. J. Res. Bus. Soc. Sci. (2147-4478), 8 (3), 33–44 (2019)
Buil, I., Martínez, E., de Chernatony, L.: The influence of brand equity on consumer responses. J. Cons. Mark. 30 (1), 62–74 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1108/07363761311290849
Crass, D., Czarnitzki, D., Toole, A.A.: The dynamic relationship between investments in brand equity and firm profitability: evidence using trademark registrations. . Int. J. Econ. Bus. 26 (1), 157–176 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/13571516.2019.1553292
Karam, A.A.: An investigation of marketing crisis, and outcomes influence on buyer behavior. Bus. Res. Rev. 2 (1), 51–72 (2016)
Berggren, A.: Empowerment according to whom? A critical assessment of Coca-Cola’s Corporate Social Responsibility initiative Parivartan (5by20) in India (2015)
Smith, P.B., Peterson, M.F., Schwartz, S.H.: Cultural values, sources of guidance, and their relevance to managerial behavior: a 47-nation study. J. Cross Cult. Psychol. 33 (2), 188–208 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1177/0022022102033002005
Byeong-Joon, M., Hoon, O.C.: The impact of CSR on consumer-corporate connection and brand loyalty: a cross cultural investigation. Int. Mark. Rev. 32 (5), 518–539(2015) https://doi.org/10.1108/IMR-03-2014-0089
Engelhard, F., Garg, R.: The influence of intra-cultural diversity on self-efficacy beliefs: evidence from India . Int. J. Indian Cult. Bus. Manag. 16 (2), 131–155 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1504/IJICBM.2018.090086
Wegner, L., Rhoda, A.: The influence of cultural beliefs on the utilisation of rehabilitation services in a rural South African context: therapists’ perspective. African J. Disab. 4 (1), 1–8 (2015). https://doi.org/10.4102/ajod.v4i1.128
Dirani, K.M.: Cultural differences and improving performance: how values and beliefs influence organizational performance . J. Eur. Ind. Train. 35 (2), 184–186 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1108/03090591111109370
Bailey, F.G.: Structure and change in Indian society . Pacific Affairs 42 (4), 494–502 (1969). https://doi.org/10.2307/2754130
Booth, A.: Whose Diwali is it? Diaspora, identity, and festivalization. Tour. Cult. Commun. 15 (3), 215–226 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3727/109830415X14483038034209
Banerjee, S.: Dimensions of Indian culture, core cultural values and marketing implications: an analysis. Cross Cult. Manag. Int. J. 15 (4), 367–378 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1108/13527600810914157
Hardenberg, R.J.: Categories of relatedness: Rituals as a form of classification in a central Indian society. Contrib. Indian Sociol. 43 (1), 61–87 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1177/006996670904300103
Taylor, M.: Cultural variance as a challenge to global public relations: a case study of the Coca-Cola scare in Europe. Public Relat. Rev. 26 (3), 277–293 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0363-8111(00)00048-5
Aaker, J.L., Sengupta, J.: Additivity versus attenuation: the role of culture in the resolution of information incongruity. J. Consum. Psychol. 9 (2), 67–82 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327663jcp0902_2
Schroeder, J.E.: The artist in brand culture. Marketing The Arts: A Fresh Approach, pp. 18–30 (2010). https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203855072
Yoo, B., Donthu, N.: Testing cross-cultural invariance of the brand equity creation process. J. Prod. Brand Manag. 11 (6), 380–398 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1108/10610420210445505
Namhoon, K., Eunha, C., Eunju, K.: Country of origin effects on brand image, brand evaluation, and purchase intention: a closer look at Seoul, New York, and Paris fashion collection. Int. Mark. Rev. 34 (2), 254–271 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1108/IMR-03-2015-0071
Hegner, S.M., Jevons, C.: Brand trust: a cross-national validation in Germany, India, and South Africa. J. Prod. Brand Manag. 25 (1), 58–68 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1108/JPBM-02-2015-0814
Liao, P.-S., Fu, Y.-C., Yi, C.-C.: Perceived quality of life in Taiwan and Hong Kong: an intra-culture comparison. J. Happiness Stud. 6 (1), 43–67 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-004-1753-6
Jiang, L., Jun, M., Yang, Z.: Customer-perceived value and loyalty: how do key service quality dimensions matter in the context of B2C e-commerce? Serv. Bus. 10 (2), 301–317 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11628-015-0269-y
El-Adly, M.I., Eid, R.: An empirical study of the relationship between shopping environment, customer perceived value, satisfaction, and loyalty in the UAE malls context . J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 31 , 217–227 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2016.04.002
Hult, G.T.M., Morgeson, F.V., Morgan, N.A., Mithas, S., Fornell, C.: Do managers know what their customers think and why? J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 45 (1), 37–54 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-016-0487-4
Nikhashemi, S.R., Tarofder, A.K., Gaur, S.S., Haque, A.: The effect of customers’ perceived value of retail store on relationship between store attribute and customer brand loyalty: some insights from Malaysia. Procedia Econ. Finance 37 , pp. 432–438 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/s2212-5671(16)30148-4
Karam, A.A., Kitana, A.F.: An exploratory study to identify the impact of leadership styles on achieving institutional excellence in the public sector: United Arab Emirates . Int. J. Bus. Manag. 15 (6), 16 (2020). https://doi.org/10.5539/ijbm.v15n6p16
Hays, R.D., Liu, H., Kapteyn, A.: Use of Internet panels to conduct surveys. Behav. Res. Methods 47 (3), 685–690 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3758/s13428-015-0617-9
Karam, A.A., Kitana, A.F.: The impact of social media on human resource management scope activities in Al-Futtaim and Al-Etihad Group UAE. Int. Bus. Res. 11 (12), 145 (2018). https://doi.org/10.5539/ibr.v11n12p145
Kladou, S., Kavaratzis, M., Rigopoulou, I., Salonika, E.: The role of brand elements in destination branding. J. Dest. Mark. Manag. 6 (4), 426–435 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdmm.2016.06.011
Goldstine, J., Kintala, C.M.R., Wotschke, D.: Multiple Criteria Decision Analysis. Springer, New York (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-3094-4
Hair, J.F., Risher, J.J., Sarstedt, M., Ringle, C.M.: When to use and how to report the results of PLS-SEM. Eur. Bus. Rev. 31 (1), 2–4 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1108/EBR-11-2018-0203
Raykov, T., Gabler, S., Dimitrov, D.M.: Maximal reliability and composite reliability: examining their difference for multicomponent measuring instruments using latent variable modeling. Struct. Eq. Model. 23 (3), 384–391 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/10705511.2014.966369
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Salmerón, R., García, C.B., García, J.: Variance inflation factor and condition number in multiple linear regression. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 88 (12), 2365–2384 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/00949655.2018.1463376
Article MathSciNet MATH Google Scholar
Karam, A.A.: The impact of training and development on different cultural employees performance through interaction employees motivation in erbil public and private banks. Mediter. J. Soc. Sci. 10 (1), 193–206 (2019). https://doi.org/10.2478/mjss-2019-0017
Voorhees, C.M., Brady, M.K., Calantone, R., Ramirez, E.: Discriminant validity testing in marketing: an analysis, causes for concern, and proposed remedies. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 44 (1), 119–134 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-015-0455-4
Bijoy, C.R.: Kerala’s Plachimada Struggle. Econ. Polit. Weekly 5 (1), 4332–4339 (2006)
Nassar, M., Battour, M.: The impact of marketing ethics on customer loyalty: a conceptual framework. Int. J. Bus. Ethics Govern. 3 (2), 1–12 (2020)
Ali Saad, A.Z., Mohd Noor, A.B., Sharofiddin, A.: Effect of applying total quality management in improving the performance of Al-Waqf of Albr societies in Saudi Arabia: a theoretical framework for “Deming’s Model”. Int. J. Bus. Ethics Govern. 3 (2), 13–33 (2020)
Joseph Ekhayemhe, A., Oguzie, S.: Assessing the relationship between rewards and employees’ motivation in some selected non-profit organizations in Abuja, Nigeria. Int. J. Bus. Ethics Govern. 1 (1), 1–4 (2018)
Aljamal, S.: The practice of transformational management and its role in achieving institutional excellence from the point of view of workers in the directorates of education in Hebron. Int. J. Bus. Ethics Govern. 1 (1), 64–90 (2018)
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Duhok, Zakho Street 38, 1006, Duhok Kurdistan Region, Iraq
Asaad Ali Karam
City University College of Ajman, Sheikh Ammar Road, Ajman, United Arab Emirates
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Asaad Ali Karam .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Middle East Technical University-Northern Cyprus Campus, Güzelyurt, Turkey
Bahaaeddin Alareeni
College of Business and Finance, Ahlia University, Manama, Bahrain
Allam Hamdan
Islam Elgedawy
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper.
Karam, A.A. (2021). The Brand Impact on Culture: Case of Coca Cola Cultural Issues in India. In: Alareeni, B., Hamdan, A., Elgedawy, I. (eds) The Importance of New Technologies and Entrepreneurship in Business Development: In The Context of Economic Diversity in Developing Countries. ICBT 2020. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 194. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-69221-6_42
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-69221-6_42
Published : 13 March 2021
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-69220-9
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-69221-6
eBook Packages : Engineering Engineering (R0)
Share this paper
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Harvard Business School →
- Faculty & Research →
- HBS Case Collection
Coca-Cola: Preparing for the Next 100 Years
- Format: Print
- | Language: English
- | Pages: 28
About The Author
Cynthia A. Montgomery
More from the authors.
- September 2023
- Faculty Research
Icahn Enterprises: Ponzi Scheme or Sound Investment
- September 2023 (Revised January 2024)
- August 2023
BYD, China, and Global Electric Vehicle Rivalry
- Icahn Enterprises: Ponzi Scheme or Sound Investment By: Aiyesha Dey, Jonas Heese and James Weber
- BYD, China, and Global Electric Vehicle Rivalry By: Cynthia A. Montgomery and Max Hancock
Brought to you by:

Coca-Cola: Preparing for the Next 100 Years
By: Cynthia A. Montgomery, James Weber
In early 2020, James Quincey, the 14th chair of the 133-year old The Coca-Cola Company, was in the midst of a years-long transformation of Coca-Cola from being the leading carbonated soft drink (CSD)…
- Length: 28 page(s)
- Publication Date: Apr 1, 2021
- Discipline: Strategy
- Product #: 721359-PDF-ENG
What's included:
- Educator Copy
$4.95 per student
degree granting course
$8.95 per student
non-degree granting course
Get access to this material, plus much more with a free Educator Account:
- Access to world-famous HBS cases
- Up to 60% off materials for your students
- Resources for teaching online
- Tips and reviews from other Educators
Already registered? Sign in
- Student Registration
- Non-Academic Registration
- Included Materials
In early 2020, James Quincey, the 14th chair of the 133-year old The Coca-Cola Company, was in the midst of a years-long transformation of Coca-Cola from being the leading carbonated soft drink (CSD) beverage company into a total beverage company. The company's flagship product, Coca-Cola, had been the world's best-selling beverage for 100 years, yet some consumers were turning away from CSDs due to health concerns over sugar consumption and a proliferation of other beverage options. The company had both acquired and developed many new beverage brands. It was in the process of changing its culture to be faster moving and more willing to take risks, and a culture where the new brands meant as much to the company as did its flagship product, which was still the company's largest selling beverage. Coca-Cola was also working to improve its environmental sustainability and social consciousness activities, and building a company where people were proud to work. The case also provides a historical look at the company's development, its relations with bottlers, competition with rival PepsiCo, and ends with emerging issues in the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Apr 1, 2021
Discipline:
Geographies:
United States
Industries:
Food and beverage sector
Harvard Business School
721359-PDF-ENG
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
- CRM Asignment Help
- MBA Assignment Help
- Statistics Assignment Help
- Market Analysis Assignment Help
- Business Development Assignment Help
- 4p of Marketing Assignment Help
- Pricing Strategy Assignment Help
- Operations Management Assignment Help
- Corporate Strategy Assignment Help
- Change Management Assignment Help
- Supply Chain Management Assignment Help
- Human Resource Assignment Help
- Management Assignment Help
- Marketing Assignment Help
- Strategy Assignment Help
- Operation Assignment Help
- Marketing Research Assignment Help
- Strategic Marketing Assignment Help
- Project Management Assignment Help
- Strategic Management Assignment Help
- Marketing Management Assignment Help
- Business Assignment Help
- Business Ethics Assignment Help
- Consumer Behavior Assignment Help
- Conflict Management Assignment Help
- Business Statistics Assignment Help
- Managerial Economics Assignment Help
- Project Risk Management Assignment Help
- Nursing Assignment Help
- Clinical Reasoning Cycle
- Nursing Resume Writing
- Medical Assignment Help
- Financial Accounting Assignment Help
- Financial Services Assignment Help
- Finance Planning Assignment Help
- Finance Assignment Help
- Forex Assignment Help
- Behavioral Finance Assignment Help
- Personal Finance Assignment Help
- Capital Budgeting Assignment Help
- Corporate Finance Planning Assignment Help
- Financial Statement Analysis Assignment Help
- Accounting Assignment Help
- Solve My Accounting Paper
- Taxation Assignment Help
- Cost Accounting Assignment Help
- Managerial Accounting Assignment Help
- Business Accounting Assignment Help
- Activity-Based Accounting Assignment Help
- Economics Assignment Help
- Microeconomics Assignment Help
- Econometrics Assignment Help
- IT Management Assignment Help
- Robotics Assignment Help
- Business Intelligence Assignment Help
- Information Technology Assignment Help
- Database Assignment Help
- Data Mining Assignment Help
- Data Structure Assignment Help
- Computer Network Assignment Help
- Operating System Assignment Help
- Data Flow Diagram Assignment Help
- UML Diagram Assignment Help
- Solidworks Assignment Help
- Cookery Assignment Help
- R Studio Assignment Help
- Law Assignment Help
- Law Assignment Sample
- Criminology Assignment Help
- Taxation Law Assignment Help
- Constitutional Law Assignment Help
- Business Law Assignment Help
- Consumer Law Assignment Help
- Employment Law Assignment Help
- Commercial Law Assignment Help
- Criminal Law Assignment Help
- Environmental Law Assignment Help
- Contract Law Assignment Help
- Company Law Assignment Help
- Corp. Governance Law Assignment Help
- Science Assignment Help
- Physics Assignment Help
- Chemistry Assignment Help
- Sports Science Assignment Help
- Chemical Engineering Assignment Help
- Biology Assignment Help
- Bioinformatics Assignment Help
- Biochemistry Assignment Help
- Biotechnology Assignment Help
- Anthropology Assignment Help
- Paleontology Assignment Help
- Engineering Assignment Help
- Autocad Assignment Help
- Mechanical Assignment Help
- Fluid Mechanics Assignment Help
- Civil Engineering Assignment Help
- Electrical Engineering Assignment Help
- Ansys Assignment Help
- Humanities Assignment Help
- Sociology Assignment Help
- Philosophy Assignment Help
- English Assignment Help
- Geography Assignment Help
- History Assignment Help
- Agroecology Assignment Help
- Psychology Assignment Help
- Social Science Assignment Help
- Public Relations Assignment Help
- Political Science Assignment Help
- Mass Communication Assignment Help
- Auditing Assignment Help
- Dissertation Writing Help
- Sociology Dissertation Help
- Marketing Dissertation Help
- Biology Dissertation Help
- Nursing Dissertation Help
- MATLAB Dissertation Help
- Law Dissertation Help
- Geography Dissertation Help
- English Dissertation Help
- Architecture Dissertation Help
- Doctoral Dissertation Help
- Dissertation Statistics Help
- Academic Dissertation Help
- Cheap Dissertation Help
- Dissertation Help Online
- Dissertation Proofreading Services
- Do My Dissertation
- Business Report Writing
- Programming Assignment Help
- Java Programming Assignment Help
- C Programming Assignment Help
- PHP Assignment Help
- Python Assignment Help
- Perl Assignment Help
- SAS Assignment Help
- Web Designing Assignment Help
- Android App Assignment Help
- JavaScript Assignment Help
- Linux Assignment Help
- Mathematics Assignment Help
- Geometry Assignment Help
- Arithmetic Assignment Help
- Trigonometry Assignment Help
- Calculus Assignment Help
- Arts Architecture Assignment Help
- Arts Assignment Help
- Case Study Assignment Help
- History Case Study
- Case Study Writing Services
- Write My Case Study For Me
- Business Law Case Study
- Civil Law Case Study Help
- Marketing Case Study Help
- Nursing Case Study Help
- ZARA Case Study
- Amazon Case Study
- Apple Case Study
- Coursework Assignment Help
- Finance Coursework Help
- Coursework Writing Services
- Marketing Coursework Help
- Maths Coursework Help
- Chemistry Coursework Help
- English Coursework Help
- Do My Coursework
- Custom Coursework Writing Service
- Thesis Writing Help
- Thesis Help Online
- Write my thesis for me
- CDR Writing Services
- CDR Engineers Australia
- CDR Report Writers
- Homework help
- Algebra Homework Help
- Psychology Homework Help
- Statistics Homework Help
- English Homework Help
- CPM homework help
- Do My Homework For Me
- Online Exam Help
- Pay Someone to Do My Homework
- Do My Math Homework
- Macroeconomics Homework Help
- Jiskha Homework Help
- Research Paper Help
- Edit my paper
- Research Paper Writing Service
- Write My Paper For Me
- Buy Term Papers Online
- Buy College Papers
- Paper Writing Services
- Research Proposal Help
- Proofread My Paper
- Report Writing Help
- Story Writing Help
- Grant Writing Help
- DCU Assignment Cover Sheet Help Ireland
- CHCDIV001 Assessment Answers
- BSBWOR203 Assessment Answers
- CHC33015 Assessment Answers
- CHCCCS015 Assessment Answers
- CHCECE018 Assessment Answers
- CHCLEG001 Assessment Answers
- CHCPRP001 Assessment Answers
- CHCPRT001 Assessment Answers
- HLTAAP001 Assessment Answers
- HLTINF001 Assessment Answers
- HLTWHS001 Assessment Answers
- SITXCOM005 Assessment Answers
- SITXFSA001 Assessment Answers
- BSBMED301 Assessment Answers
- BSBWOR502 Assessment Answers
- CHCAGE001 Assessment Answers
- CHCCCS011 Assessment Answers
- CHCCOM003 Assessment Answers
- CHCCOM005 Assessment Answers
- CHCDIV002 Assessment Answers
- CHCECE001 Assessment Answers
- CHCECE017 Assessment Answers
- CHCECE023 Assessment Answers
- CHCPRP003 Assessment Answers
- HLTWHS003 Assessment Answers
- SITXWHS001 Assessment Answers
- BSBCMM401 Assessment Answers
- BSBDIV501 Assessment Answers
- BSBSUS401 Assessment Answers
- BSBWOR501 Assessment Answers
- CHCAGE005 Assessment Answers
- CHCDIS002 Assessment Answers
- CHCECE002 Assessment Answers
- CHCECE007 Assessment Answers
- CHCECE025 Assessment Answers
- CHCECE026 Assessment Answers
- CHCLEG003 Assessment Answers
- HLTAID003 Assessment Answers
- SITXHRM002 Assessment Answers
- Elevator Speech
- Maid Of Honor Speech
- Problem Solutions Speech
- Award Presentation Speech
- Tropicana Speech Topics
- Write My Assignment
- Personal Statement Writing
- Narrative Writing help
- Academic Writing Service
- Resume Writing Services
- Assignment Writing Tips
- Writing Assignment for University
- Custom Assignment Writing Service
- Assignment Provider
- Assignment Assistance
- Solve My Assignment
- Pay For Assignment Help
- Assignment Help Online
- HND Assignment Help
- SPSS Assignment Help
- Buy Assignments Online
- Assignment Paper Help
- Assignment Cover Page
- Urgent Assignment Help
- Perdisco Assignment Help
- Make My Assignment
- College Assignment Help
- Get Assignment Help
- Cheap Assignment Help
- Assignment Help Tutors
- TAFE Assignment Help
- Study Help Online
- Do My Assignment
- Do Assignment For Me
- My Assignment Help
- All Assignment Help
- Academic Assignment Help
- Student Assignment Help
- University Assignment Help
- Instant Assignment Help
- Powerpoint Presentation Service
- Last Minute Assignment Help
- World No 1 Assignment Help Company
- Mentorship Assignment Help
- Legit Essay
- Essay Writing Services
- Essay Outline Help
- Descriptive Essay Help
- History Essay Help
- Research Essay Help
- English Essay Writing
- Literature Essay Help
- Essay Writer for Australia
- Online Custom Essay Help
- Essay Writing Help
- Custom Essay Help
- Essay Help Online
- Writing Essay Papers
- Essay Homework Help
- Professional Essay Writer
- Illustration Essay Help
- Scholarship Essay Help
- Need Help Writing Essay
- Plagiarism Free Essays
- Write My Essay
- Response Essay Writing Help
- Essay Assistance
- Essay Typer
- APA Reference Generator
- Harvard Reference Generator
- Vancouver Reference Generator
- Oscola Referencing Generator
- Deakin Referencing Generator
- Griffith Referencing Tool
- Turabian Citation Generator
- UTS Referencing Generator
- Swinburne Referencing Tool
- AGLC Referencing Generator
- AMA Referencing Generator
- MLA Referencing Generator
- CSE Citation Generator
- ASA Referencing
- Oxford Referencing Generator
- LaTrobe Referencing Tool
- ACS Citation Generator
- APSA Citation Generator
- Central Queensland University
- Holmes Institute
- Monash University
- Torrens University
- Victoria University
- Federation University
- Griffith University
- Deakin University
- Murdoch University
- The University of Sydney
- The London College
- Ulster University
- University of derby
- University of West London
- Bath Spa University
- University of Warwick
- Newcastle University
- Anglia Ruskin University
- University of Northampton
- The University of Manchester
- University of Michigan
- University of Chicago
- University of Pennsylvania
- Cornell University
- Georgia Institute of Technology
- National University
- University of Florida
- University of Minnesota
- Help University
- INTI International University
- Universiti Sains Malaysia
- Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
- University of Malaya
- ERC Institute
- Nanyang Technological University
- Singapore Institute of Management
- Singapore Institute of Technology
- United Kingdom
- Jobs near Deakin University
- Jobs Near CQUniversity
- Jobs Near La Trobe University
- Jobs Near Monash University
- Jobs Near Torrens University
- Jobs Near Cornell University
- Jobs Near National University
- Jobs Near University of Chicago
- Jobs Near University of Florida
- Jobs Near University of Michigan
- Jobs Near Bath Spa University
- Jobs Near Coventry University
- Jobs Near Newcastle University
- Jobs Near University of Bolton
- Jobs Near university of derby
- Search Assignments
- Connect Seniors
- Essay Rewriter
- Knowledge Series
- Conclusion Generator
- GPA Calculator
- Factoring Calculator
- Plagiarism Checker
- Word Page Counter
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Living Calculator
- Quadratic Equation
- Algebra Calculator
- Integral Calculator
- Chemical Balancer
- Equation Solver
- Fraction Calculator
- Slope Calculator
- Fisher Equation
- Summary Generator
- Essay Topic Generator
- Alphabetizer
- Case Converter
- Antiderivative Calculator
- Kinematics Calculator
- Truth Table Generator
- Financial Calculator
- Reflection calculator
- Projectile Motion Calculator
- Paper Checker
- Inverse Function Calculator

Coca Cola Case Study: An Analysis Of Organizational Behavior
Task: Drawing on your own personal workplace experience , write a mini case-study (max 1200 words ) on: The key components of my effective team.
Following the case-study, two questions are to be posed which encourage the reader to analyse different aspects of the case in close detail. Students should also provide a brief 200-250 word example answer for each question in order to demonstrate the potential learning outcomes of the case. A minimum of four distinct references from academic journals are to be included in the assignment. They can be part of the case, the example answers, or spread across the two sections.
Introduction Organizational behavior in this coca cola case study refers to the study of activities or behavior of the employees inside a commercial enterprise. The reflective case study has been made depending on the issues faced the famous soft drink company Coca Cola. The aim of this coca cola case study is to figure out the strategies with which the company can utilize it human capital in order to make the organization a better place to work. At the same time, I have described the opportunities through which the company can continue its growth in the local market.
Subscribe our YouTube channel for more related videos
Background Coco Cola has been serving the world for more than 130 years however, the organization is facing extreme problem in the market of the island country like Sri Lanka. The company is facing a downtrend regarding its brand value. In the year 2014 the brand value of Coca Cola a around 34 billion dollar whereas it has decreased to nearly 32billion dollar in the year 2018. It means the company has faced an acute loss of around 5.4 percent. In this coca cola case study discovered certain factors that have caused such an acute downfall of the branded organization. One of the factors is the mismanagement inside the organization. In the following coca cola case study, I have highlighted how the improper workforce management of Coca Cola has leaded the company to such an adverse situation.
Reasons of the downfall of Coca Cola Company Communication: In order to identify problem lied behind the downfall of the Coca Cola Company discussed in this coca cola case study, I found certain issues and communication is one of such issues. The entire set up of the organization is so much corporate like that the employees hardly get time as well as scope to share their opinion or thought with other. It has affected the growth of the company in two different ways. First of all the staffs has could not get chance to share their problem with their leader. As a result, they could not develop their skill in order to improve their performance. On the contrary, the company lost the opportunities of utilizing the innovative ideas of the workers that could have been fruitful for the Coca Cola Company.
Feedback sharing: The HR of the team leader did not pay proper attention on sharing the feedback with the staffs of the. As a result, the employees did not get the chance to improve their skill. Sometimes, they lacked of the proper knowledge of using the latest technology while producing the various products. This situation had a negative repercussion on the company’s growth as a lot of employee left the firm out of lack of dissatisfaction. As an irreversible effect, the company had to face an acute shortage of labour that has hindered the production rate. In my opinion the shortage of the human capital is one of the most important factors that has affect the growth of Coca Cola Company in a profound way.
Motivation: I think motivation is one of the factors that are responsible for the shortage of the staffs inside the organization. It is true that Sri Lanka is one of the densely populated area in South Asia. As per the recent report held on 8th May, in the year 2019, which is refered in this coca cola case study the entire population of the country is 21,008,582 (Chandrajith et al., 2019, pp-12, pp-37) which is approximately 0.27 percent of the entire population of the world (Wijesuriya et al., 2019). As a result of such huge population the country enjoys the facility of plenty human capital. May be that is the reason that the company treated its staff as a factor that can easily be replaced by some other employ. The management of the company did not pay attention in order to motivate the employees. For instance in this coca cola case study, they did not arrange proper compensation or increment which was quite demotivating for the staffs. As a result, the employee showed less interest in order to enhance their performance.
Absence of proper training: I found in this coca cola case study that one of the reasons of the downfall of Coca Cola Company is the lack of training the needed to be provided to the employee in order to enhance their performance. Like other country like Australia, UK and many more the company did not have proper training facility for their employees. I think, that is the reason why the staffs that were unable to perform well were easily demotivated. In addition, the management did not take any measure in order to increase the efficiency of their workers. This situation had a adverse effect on their work performance which consequently followed by the decrease in products’ quality.
Improper human resource management: Before writing this coca cola case study, I had gone through certain researches, which illustrate the error of the human resource management of Coca Cola Company. For instance, the company has collaborated with four bottling firms that created a big issue as the organization brought around ten thousand workers (Chiu, Fischer and Friedman, 2019, pp-109). It was actually double of the entire work force. As a result of such collaboration the company had to encounter with the problem of complexity of the unnecessary staffs as well as resignation of termination of employees (Chiu, Fischer and Friedman, 2019, pp-98). It created an unstable situation inside the organization that had a negative impact on the reputation of the company. In addition, the human resource managers did not show proper interest in order to attract or retain the quality employee who could play significant role in betterment of the company.
Attitude of team leader: The team leader failed to motivate their team members. Most of the time they could not encourage their subordinate staffs and thus they could take proper initiative in order to achieve the company’s target. In addition, the team leader r the supervisors did not perform the proper monitoring of the tasks of their subordinate team members. Even they showed reluctant to share proper feedback which could improve the quality of the performance of their team members. The irresponsibility of the team member or the management of the Coca Cola Company has increased the uncertainty among the subordinate staffs of the organization. In my opinion this kind of attitude of the higher authority was quite responsible for the loss of status of the world famous Coca Cola Company.
Relation between the management and the staffs: I discovered that the company management was failed to build a lateral relation between the employees as well as the team leader inside the company premises. I have discussed earlier in this report that the workers hardly got chance to talk about their problems whatever they faced at the time of performing their task. The management of Coca Cola Company hardly arranged meetings in order to discuss the problems of their staffs as well as the possible remedies to resolve those problems.
Proper working environment: The management failed to create the proper working environment that can encourage or motivate the employees to give their best performance (Jones and Comfort, 2018, pp-43). As I have earlier mentioned that Coca Cola Company provided a strict corporate environment to its employees. This situation created obstruction in building an emotional attachment between the workers as well as the management of the organization. As a result, the employees failed to understand that their improvement was closely related to the success of the company (Jones and Comfort, 2018). That was the reason in this coca cola case study why the workers of the Coca Cola Company did not take enough enthusiasm in order to provide their best performance for the organization’s upliftment.
Questions and Answers Question 1: What are the factors that are responsible for the downfall of the Coca Cola Company in Sri Lanka? The coca cola case study has been resulted in the identification of the downfall reasons for the successful execution of the works for the company. The study had narrowed the reasons for the major issue alignment including the lack of the information, absence of the training and development, and lesser motivational strategies had resulted in the downfall of the company. The integration had resulted in the major issues for the development of the facilities and implying the management of the works for enduring the continuation of the facilities. The lack of information was the major reason behind the implication of the issues of the Coca Cola for the enduring of the works. The information management had resulted in the cognitive management of the factors aligning the successful and effective completion of the development.
The issues in the team management had also ensured the cohesive and managed performance development for the work information management. The human resource management issues resulted in the major setback for the continuation of the innovative work alignment and development. The formation would also enable the effective formation of the works that can result in the major issues of the continuation and development. The issues of the works would result for making compilation issues in the formation of the effective work development. The major issues in the alignment of the human team management of Coca Cola were issues in the HR department for implying effective communication process.
Question 2: Suggest some possible remedies through which the company can overcome such situation? The major identified issues of the Coca Cola were the lack of the information, absence of the training and development, and lesser motivational strategies that had resulted in the major setback for the company. The coca cola case study resulted in highlighting the major issues in the completion of the works. However, the use of the effective strategies can result in the cohesive and effective development of the plan for easing the operations of the Coca Cola. Some of them have been explained below,
Proper Training and Development: The proper training and development referred in this coca cola organizational behavior would be marked for managing the effective formation of the works that can endure the management of the works. The training and development would also ensure the compilation of the works. The ensuring of the facilities would also make sure that the works are effective completion of the works.
Induction and Communication Program: The induction and communication program would be developed for the enduring the continuation of the works for aligning the management of the works. The communication and induction program would enable the completion of the works. The alignment would also ensure the completion of the works.
Information Sourcing from Credible Sources: The sourcing of the information from the credible sources can be used for ensuring the effective development and improvement of the information for Coca Cola. The sources in this coca cola organizational behavior would be genuine and provide authentic information for the completion of the strategy development. The information management would also ensure the successful completion of the works.
Coca cola case study assignments are being prepared by our online management assignment help experts from top universities which let us to provide you a reliable homework assignment help online service.
Reference List Chandrajith, R., Weerasingha, A., Premaratne, K.M., Gamage, D., Abeygunasekera, A.M., Joachimski, M.M. & Senaratne, A., 2019. Mineralogical, compositional and isotope characterization of human kidney stones (urolithiasis) in a Sri Lankan population. Environmental geochemistry and health, pp.1-14.
Chiu, H., Fischer, D. & Friedman, H., 2019. Board Diversity in Audit and Finance Committees: A Case Study of Coca-Cola. In Diversity within Diversity Management: Types of Diversity in Organizations (pp. 95-113). Emerald Publishing Limited.
Jones, P. & Comfort, D., 2018. The Coca Cola Brand and Sustainability. Indonesian Journal of Applied Business and Economic Research, vol. 1, no. 1, pp.34-46.
CHECK THE PRICE FOR YOUR PROJECT
Number of pages/words you require, choose your assignment deadline, related samples.
- Enhancing Leadership and Management Strategies at Chesterfield Mayfair Hotel
- Herbal Tea Enlightenment: A Comprehensive Digital Campaign Proposal for Twinnings Tea
- Navigating Professional Growth: A Reflection on Co-operative Education Experience at Post Haste
- Adapting Strategies: Navigating the Impact of Macro-Environment Factors on Kroger's Marketing Approach
- Harmony in the Park: A Sustainable Outdoor Music Event Marketing Plan
- Unveiling Marketing Strategies: A Personal Evaluation of Samsung S22 Purchase
- Journey through Entrepreneurial Leadership: A Reflection and Case Study Analysis
- Navigating Ethical Challenges: A Case Study on Wells Fargo's Sales Culture
- Unlocking the Power of Employee Motivation in Effective Management
- Impact of effective leadership strategies on the business performance of UK retail firms- A Case of Tesco
- Analysing the operational aspects for a new resort
- Analysing leadership approaches within a project environment
- Safeguarding Children's Welfare: Legal Protection Against Abuse
- Navigating Compassion and Law Enforcement: A Case Study Analysis
- Unveiling the Shadows: Understanding Drug Addiction in Australia
- Enhancing Patient Safety Through Medication Administration: A Case Study Analysis
- Climate Change's Impact on Corporate Social Responsibility: A Case Study of Viva Energies Australia
- Analyzing narrative techniques in a given reading
- Planning a web-based reporting system for Rimu Art
- The effects of technological implementations on sustainable development in the UK construction industry
- Child protection policy that has emphasis on an adoption approach versus child protection policy that has emphasis on use of intensive family support programs
- Reflective essay on understanding human development across the lifespan
- Evaluating different management support systems relating to information systems
- Evaluating gender discrimination in early childhood education in Australia
- Improving Early Education Standards for children and families

Looking for Your Assignment?

FREE PARAPHRASING TOOL

FREE PLAGIARISM CHECKER

FREE ESSAY TYPER TOOL
Other assignment services.
- SCM Assignment Help
- HRM Assignment Help
- Dissertation Assignment Help
- Marketing Analysis Assignment Help
- Corporate Finance Assignment Help


FREE WORD COUNT AND PAGE CALCULATOR

QUESTION BANK
ESCALATION EMAIL
To get answer.
Please Fill the following Details
Thank you !
We have sent you an email with the required document.
MBA Knowledge Base
Business • Management • Technology
Home » Management Case Studies » Case Study: Analysis of the Ethical Behavior of Coca Cola
Case Study: Analysis of the Ethical Behavior of Coca Cola
Coca-Cola is the world’s largest beverage company that operates the largest distribution system in the world. This allows Coca-Cola companies to serve more than 1 billion of its products to customers each day. The marketing strategy for Coca-Cola promotes products from four out of the five top selling soft drinks to earn sales such as Coke, Diet Coke, Fanta and Sprite. This process builds strong customer relationships , which gives the opportunity for these businesses to be identified and satisfied. With that being said, customers will be more willing to help Coca-Cola produce and grow.

Pepsi and Coca-Cola, between them, hold the dominant share of the world market. Even though Coca-Cola produces and sells big across the United States, in order for the company to expand and grow, they had to build their global soft drink market by selling to customers internationally. For example, both companies continued to target international markets focusing on traditional soft drinks, new-age drinks and expanding into the snack-food businesses. With these new changes, Pepsi has 60% of the U.S. Snack-food market while Coca-Cola contributes 85% of its sales outside of the United States.
Increasing market share is one of the most vital goals for a business such as Coca-Cola and Pepsi. Competitions between other soft drink companies, false market share reports and other business conducts can cause certain obstacles if the top selling companies allow them too. However, Coca Cola’s strategy, from the early and late 1800s, of achieving goals such as the international mergers , big market shares, snack food production and overall performance allowed them to strive then and continue to succeed today. Today, most of coke sales are spread throughout the world in the 2004 Annual Report, “Coca Cola had gallon sales distributed as follows: 28% in the United States, 26% in Mexico, Brazil, Japan and China and 46% in spread throughout the world”. This means that Coca Cola makes 70% of its profits from other countries. Coca-Cola must remain vigilant to keep their brand untarnished and their ethical issues to a minimum; their brand is their main key to success.
Coca Cola’s Reputation
Coca-Cola is admired and known for its strength of brand. It is the most well recognized logo and brand across the world. Coca-Colas strong emphasis on reputation they have created loyalty, trust among their customers, and the strongest brand recognition of all time. Coca-Cola retains a commitment and plan to attract, satisfy, and keep customers for the long run. The company has a reputation of having the most loyal customers of the industry. It is this reason that has made Coca-Cola the market leader in the beverage industry year after year. Coca-Cola continues to earn numerous awards including Responsible CEO of the year (2010), most socially responsible company (2008), Worlds most accountable companies (2007), and top 50 most admired companies (2010). Coca-Cola has sought not only to be the world’s largest beverage company but also to improve the quality of life of the communities they serve.
Coca-Cola is extremely active in all aspects of society and environmental issues. Coca-Cola has made numerous steps to prevent harm to the environment in its production of products. Some of these steps include eco friendly facilities and equipment. Coke has been a leader when it comes to environmental issues throughout the years with a major goal of being water neutral, which means every drop of water used by the company will be replenished by 2020. Coca Cola also has a commitment to helping the local aspect by collaborating with different groups and organizations to help with many local and health issues. An example of this would be Coca Cola’s collaborating with UNAIDS to help with the HIV/Aids epidemic throughout the world. Coca Cola has also had a vast impact on improving education. They have had many programs over the years, which include a scholarship program that has given out over 22 million dollars in grants.
Social Responsibility Focus
Many companies do not realize the importance of having a connection with the community and to be seen in their eyes as a very strong ethical company. Coca-Cola has taken up a few different social projects that have given them a good amount of support from the public. For example, they have done a philanthropy known as “Education On Wheels,” in which children are placed into a classroom that history is brought to life, giving them a very rich learning environment. They do different activities that really get the children thinking and force them to develop critical thinking methods. This is a huge thing for Coca-Cola and in our opinion for companies as a whole. The first thing that you must engage in a customer is their emotions , the strongest buying point that people act on. If people start recognizing that a company is doing community based activities for children, they are going to be very prone and likely to want to support and buy the products from the company.
The second thing that Coca-Cola has done is setup multiple scholarship funds available for high-school seniors as they make their way into college and the real world. Coca-Cola was very smart when they went about setting up these different funds for students. There is a huge market with kids graduating high school and those who are currently in college, appealing to these kids will grow a strong interest in their company and will build up their brand image more than ever. It states in the book that it is beneficial to the shareholders by doing this. This is so true with every company because shareholders and people who are invested in the company want to make sure that they are involved in a company that is making ethical decisions and who are giving back to the community in some way, shape or form.
As long as Coca-Cola keeps being persistent with how they give back into the community and monitor what they are doing on an ethical standpoint, they will keep their customers and stakeholders happy.
Crisis Situations
Coca-Cola has not always been a squeaky-clean company that never had problems. The stock price of the company is the same price as it was 10 years ago, and this is due to the ethical and legal issues that were associated with the company. A small problem occurred in Belgium in 1999 when a few children fell ill after drinking a product with the Coca-Cola brand on it. They had a recall on the product there in Belgium, but soon after, every item Coca-Cola made was pulled off the shelves in every store. This caused a loss of reputation, which, in turn, made people lose respect for the company and investors started selling their stocks in Coca-Cola. Neighboring countries, such as Luxembourg and the Netherlands, soon followed suit and recalled all products throughout both countries.
After Coca-Cola found the root of the problem, that being a bad batch of carbon dioxide, they made an announcement regarding the situation. Being a few days after all this happened was a little too slow for the media, and they ate up the story making Coca-Cola look worse than what was said about them. However, this was not the only occurrence. France supposedly had about one hundred people become sick due to mold in the products they consumed. Every single product was banned throughout France until the problem was resolved, but Coca-Cola had yet another slow response to the problem and their reputation was further diminished.
During this crisis, Coca-Cola started to run into different problems with their marketing in European countries with anti-trust laws. They wanted to create a merger with themselves and Orangina, a French company, but their overaggressive style turned off the other companies in the deal, which became a problem. Their strong-arm tactics proved to be too much for the foreign countries, and creating a competitive advantage seemed to cross the line of the anti-trust laws in which they were sued for the by the country of Italy. Italy won the court-case, which caused investigations of the company’s competitive practices, which is never a good thing for business.
Racial Discrimination Allegations
Coca-Cola faced a lawsuit in the spring of 1999. Fifteen hundred African American employees sued Coca-Cola for racial discrimination . Later, the number grew to 2,000 current and former employees. The company was being charged because they put African Americans at the bottom of the pay scale. An African American could have the same job as a Caucasian, but the African American would make $26,000 less each year. This is a huge difference in pay especially if it is only based on the color of a person’s skin. In the lawsuit, it states that the top management of Coca-Cola knew about the discrimination for four years and did nothing to stop it. The company denied the accusations, but the public had strong reactions to the case. To rebuild their image, Coca-Cola created a diversity council and paid $193 million to settle the racial discrimination lawsuit.
Problems with the Burger King Market Test
Just three years after the racial discrimination lawsuit, Coca-Cola found themselves in another allegation. Matthew Whitley, a mid-level Coca-Cola executive filed a whistle-blowing suit. Whitley revealed fraud in a market study that Coca-Cola did on behalf of Burger King. In 2002, Coca-Cola wanted to increase sales so they paired up with Burger King to launch a frozen Coke as a child’s snack. Before launching nationally, Burger King wanted to test the product out in the market. Burger King launched a three-week trial run in Richmond, Virginia to see if it was worth the investment. Customers received a coupon for a free frozen Coke when they purchased a Value Meal. When the test first started, sales of the frozen Coke were not looking good. Therefore, Coca-Cola decided to pay at least one individual $10,000 to take hundreds of children to Burger King to purchase Value Meals including the frozen Coke. U.S. attorney general for the North District of Georgia discovered and investigated the fraud. Coca-Cola had to pay Burger King $21 million, the whistle-blower $540,000, and a $9 million pretax write off had to be taken. Coca-Cola disputed the claim; however, it was extremely costly for the company. Not only did they lose millions of dollars, but also the case attracted a lot of negative publicity. In addition, it ruined any relationship that they had with Burger King.
Inflated Earnings Related to Channel Stuffing
Along with the other ethical dilemmas Coca-Cola was faced with, the company was accused of practicing channel stuffing. Channel stuffing is the practice of shipping extra inventory to wholesalers and retailers at an excessive rate, typically before the end of a quarter. The use of channel stuffing is deceptive and a company utilizes it to inflate their sales and earnings figures. When a company ships out their product to a distributor, it is counted as a sale. However, when a company participates in channel stuffing, they count the sale and usually the product is returned or it remains in a warehouse. The company sends their retailers more than they can sell, falsely demonstrating that there is a high demand for the product. It can also be used to hide when the demand of a product declines.
The benefit the company would receive from channel stuffing is more earnings on their financial statements and misinforming their investors. In Coca Cola’s situation, they were accused of sending extra concentrate to Japanese bottlers from 1997 to 1999 to dishonestly inflate their profits. Even though Coca-Cola settled the accusation, the Securities and Exchange Commission concluded that channel stuffing did occur. The company then pressured bottlers into purchasing extra concentrate in return for extended credit.
Coca-Cola promised the SEC to avoid engaging in channel stuffing in the future. At this time, the company created an ethics and compliance office, who verifies each financial quarter that they have not altered the terms of payment or extended special credit. Coca-Cola agreed to try to reduce the amount of concentrate held by the international bottlers. Even though they settled the predicament with the SEC, Coca-Cola still faces a lawsuit with shareholders for channel stuffing in Japan, North America, Europe, and South Africa.
Trouble with Distributors
Coca-Cola also faced serious issues with their distributors beginning in 2006. The company had deliveries of Powerade sent to Wal-Mart in a small Texas test area. When they tried to expand the delivery of Powerade directly to Wal-Mart warehouses all over the US, fifty-four of their bottlers filed lawsuits. Coca-Cola had an agreement regarding Powerade bottlers and that it was a breach of the agreement to provide warehouse delivery to Wal-Mart, even with the use of a subsidiary agent for warehouse delivery. The subsidiary agent, CCE, and Coca-Cola claim that they were trying to meet a request from Wal-Mart for warehouse delivery, just how PepsiCo distributes Gatorade. CCE proposed making payments to some other bottlers in return for taking over the distribution of Powerade. The bottlers were concerned that the proposed arrangement would violate antitrust laws. In addition, they believed that moving forward with their warehouse delivery would deteriorate the value of the bottlers’ businesses.
This dilemma had a serious impact on the reputation of the company. When one firm in a channel structure suffers, all the firms in the supply chain suffer in some way as well. Coca-Cola adopted a new enterprise resource system that made their classified information available to a group of partners. Since there is a lack of integrity between Coca-Cola and their partners, the partners assume a greater risk when forming a partnership with the company. These problems with their distributors took a toll on their partner companies, their stakeholders, and finally, their bottom lines.
Problems with Unions and Coke Trade Secrets
Amongst other international problems faced by Coca-Cola, they ran into trouble related to labor unions as well. The major cause of these problems occurred in Columbia where there were unfortunate deaths of Coca-Cola workers as well as forty-eight who went into hiding and another sixty-five who received death threats. The labor unions claimed that Coca-Cola chose to be involved with illegal dealings surrounding these deaths, death threats and disappearances. Coca-Cola denied any of the allegations and claimed that only one of the deaths was on the premises of the bottling plant that Coke worked with while the other ones were located off the premises where Coke had no involvement. Rather than take swift action Coca-Cola made itself look bad by not offering to help to any of the workers or their families. The further denial along with not providing any aid or action caused animosity with labor unions regarding the case and put another black mark on Coca-Cola’s currently sliding ethical reputation. Sure there may have been other circumstances behind the problems in Columbia but Coca-Cola did nothing to help anyone else or themselves in the situation.
Another problem Coca-Cola faced came a little closer to home. Coca-Cola had three employees get arrested in 2006 for fraudulently and unlawfully stealing and selling trade secrets from Coca-Cola. One of the people accused in the case contacted Pepsi and told them he was a high level employee with Coca-Cola. He then offered them very confidential and detailed information regarding the Coca-Cola Company. Coca-Cola then received a letter from Pepsi about the offer and contacted the FBI. The FBI found out the informant’s name was Ibrahim Dimson from Bronx, NY. He provided the FBI with fourteen pages worth of confidential information marked classified as well as top secret products from the Coca-Cola company. Ibrahim got his information from Joya Williams who was an executive administrative assistant for Coca-Cola’s global brand in Atlanta . She had access to all of the information given to the FBI by Dimson who is known in the case as “Dirk”. This is a big problem for Coca-Cola because not only are the actions of employees a direct responsibility of the company but it also makes the company look bad if there is internal problems. Any company that has people who are willing to give trade secrets to the direct competition need to evaluate the people who are in charge and make a change if the employees feel that disloyal towards a company that is very well known and successful globally. The company should have a system in place to protect it’s secrets because otherwise any person on the street can go take the syrup formula from Coke and give it to its competitors. This is another ethical situation where the right leadership and system in place could have resolved the issue before it started. Because of poor leadership now Coca-Cola’s reputation is once again tarnished ethically and 3 company employees are being charged with serious crimes.
Ethical Recovery?
Even after all of these problems presents, the customers in Europe said that they still feel like coke would behave correctly during these times of crises. Even after all of this they are still ranked third in a PricewaterhouseCoopers survey of the most respected companies in the world. Coke then donated $50 million to a foundation to support programs in minority programs, and hired an ombudsman who reports directly to the CEO in order to settle the racial discrimination lawsuit shown above. Coke is taking the initiative to fix their problems and the international community is seeing that. It seems that since they are taking these precautions to prevent further problems in the future, the European nations, in addition to the United States will be more trusting of Coke in their decisions in the future.
Related posts:
- Case Study: The Coca-Cola Company Struggles with Ethical Crisis
- Case Study: Quality Management System at Coca Cola Company
- SWOT Analysis of Coca Cola
- Ethical Behavior in Business
- Case Study on Business Ethics: Holiday Cheer or Ethical Dilemma?
- Case Study on Consumer Behavior: Gillette
- Case Study: Henry Ford’s Contributions to Organizational Behavior and Leadership
- Case Study on Business Ethics: Napster Copyright Infringement Case
- Case Study: Pfizer’s Strategy Analysis
- Case Study: Ryanair Business Strategy Analysis
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

How Coca-Cola Underwent a Massive Organizational Pivot
- Creative Tips + Tools , People + Things We Love , The Future Of , What We Design
It was in the news: Coca-Cola Company was under fire. For starters, Coke was missing a strong message for sustainable practices. But there was something more going on. Coca-Cola’s market share was dropping. Their relationships were suffering from the inside and out. Their employees, their customers, their bottlers, and their vendors were disconnected from the company’s mission.

The Challenge: Coke had stopped growing
Coca-Cola, one of the most successful companies in history, was missing a strategy for growth. Inappropriately, bottlers were managing resources. When pressed, employees were having difficulty understanding their roles at the company. Company-wide, morale was spiraling downward.
The Solution: Building a culture of collaboration, growth, and sustainability
Coca-Cola management realized they had to do something very big to uncover what was going wrong. They knew they had to re-build the company. But how? Coca-Cola reoriented themselves to growth and sustainability by promoting a shift in their culture.
1st step: Diagnose the current state of the organization
Coca-Cola partnered with McKinsey to help analyze the current state of the company and create a manifesto for growth. They collected reams of information on every aspect of the company, from culture to strategy.
2nd step: Use graphic facilitation to enable leaders to visualize the data and use it to rebuild the culture
Now that the information was collected, a snapshot was needed to help leaders peer into the Coca-Cola mirror so they could see what was happening, better define company relationships, rebuild the culture, and re-inspire the brand. Coca-Cola hired IDEA360 Graphic Facilitators to help McKinsey unpack the data and coalesce ideas into a visual story that would illuminate the current state and inspire important Aha! moments — breakthrough realizations — on the way to forging a Manifesto for Growth that would inspire the necessary shift in the company culture.
3rd step: Use visual collaboration tools to facilitate change
IDEA360 created six 4’ x 8’ graphic maps to capture this visual story and begin the Coca-Cola change journey. These maps were used as tools throughout the two-year change process to communicate the thoughts, needs, and ideas of Coca-Cola employees. They fueled and focused conversations within the company, allowing leadership and the employees to step away, evaluate, and then see the big picture. Responding to the visuals, employees were then able to work toward solutions.
The outcome: A Realigned & Recharged Coca-Cola Company
The IDEA360 maps revealed the big picture to Coca-Cola , helping build their Manifesto for Growth, which produced a new emotional and logistic framework of the company and a way to fulfill the mission and vision of the organization.
As a result of this visual and human-centered organizational change process , Coca-Cola took a loosely affiliated group of executives and employees and turned them into one cohesive global team, rallied around a clear vision for sustainable growth. They identified and filled talent gaps at the executive level and built a culture of modeling the leadership behaviors they wanted to see across the organization. They stopped losing high-caliber employees. They reinvested in the organization and its people, integrating marketing, strategy, and innovation.
Two years later, Coca-Cola won the Strategic HR Leadership Award from the Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM): “ The Coca-Cola Company, Atlanta, Ga., for its “Manifesto for Growth.” The Coca-Cola Company’s 71,000 employees embarked on a journey inspired by the desire for sustainable growth. Manifesto is the company’s strategic initiative to reinvent itself and reinvigorate growth through the partnership of senior leaders, human resources, and aligning and leveraging the power of their global network.”
Within 7 years, Coca-Cola had nearly doubled its revenue , becoming a true case study in what’s possible when visionary leadership meets visual storytelling.
Most Recent Read
Gifting experiences and supporting dreams.

Planting Seeds of Connection and Creativity

Unlocking tomorrow with a ‘VISION 2024’

Living Case Study: Exploring the Power of Immersive Imagination in Health Centers

- Culture Change , road map , strategy story

This Denver-based consulting business brings visual learning and the facilitated process together to activate creative business and community strategies that engage the individual along with the entire system.
- 303-578-6984
- [email protected]
- Denver, Colorado
Social Media
Copyright © idea360 2011 – 2024 all rights reserved., thank you for your support.
Click on the button to download your playbook.

Managing Human Capital: A Case Study of Coca Cola's Organizational Behavior
Added on 2023-06-12

End of preview
Want to access all the pages? Upload your documents or become a member.
Management: Putting Theory into Practice (LDT3103) lg ...
Communication issues in coca-cola company: analysis and recommendations lg ..., recruitment and selection process - coca cola lg ..., (doc) assignment: corporate social responsibility lg ..., strategic plan development for coca cola: competitive strategy options and impact on organisation lg ..., managing people during covid-19 pandemic: a case study of coca cola hbc lg ....

COMMENTS
Abstract: The paper contains a detail analysis of organizational behavior discussing issues facing cutting age organizations on leadership behavior, organizational effectiveness, organizational structures and human resource management. The paper ... (2000) "cultural variance as a challenge to global public relations: case study of coca-cola ...
Since the 1990s Coca-Cola has been accused of unethical behavior in a number of areas, in- cluding product safety, anti-competitiveness, racial discrimination, channel stuffing, dis- tributor conflicts, intimidation of union workers, pollution, depletion of natural resources, and health concerns.
The Coca-Cola Company (NYSE: KO) is a total beverage company, offering over 500 brands in more than 200 countries and territories. In addition to the company...
Coca-Cola Organizational Analysis. July 2022. DOI: 10.13140/RG.2.2.21638.04165. Authors: Peter Maina. Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology. Preprints and early-stage research may ...
The Coca-Cola Company started functioning as a one man business which was hardly known to anyone. The drink itself was invented by Doctor John Pemberton in 1886 in Atlanta, Georgia. Later, the same tear, a prohibition law made Pemberton change the formula for this nerve tonic and a headache remedy. The drink remained a nerve stimulant, but wine ...
Summary. When Muhtar Kent took the helm at Coke, in 2008, he had two top priorities: to establish a long-term vision and to restore growth in North America. The vision called for doubling Coke's ...
The study found that the culture and brand factors were effects on customer perceived value which was explained by (R 2 Adj. = 78.5%), While, the whole model was effective by Coca-Cola cultural issues with (R 2 Adj. = 80.9%). Further, culture has a significant effect on firm performance. Results of examination help companies to realize the ...
The Impact of Change Management on Organizational Performance in the light of global changes: A Case Study of Coca-Cola Company Eng. Hatem Mohammed Alshmrani Projects Manager, MBA in Process, Universidad Catolica San Antonio de Murcia (UCAM) ... A Case Study of Coca-Cola Company Nat Sci 2021;19(4):76-91].ISSN 1545-0740
In early 2020, James Quincey, the 14th chair of the 133-year old The Coca-Cola Company, was in the midst of a years-long transformation of Coca-Cola from being the leading carbonated soft drink (CSD) beverage company into a total beverage company. The company's flagship product, Coca-Cola, had been the world's best-selling beverage for 100 ...
In early 2020, James Quincey, the 14th chair of the 133-year old The Coca-Cola Company, was in the midst of a years-long transformation of Coca-Cola from being the leading carbonated soft drink (CSD) beverage company into a total beverage company. The company's flagship product, Coca-Cola, had been the world's best-selling beverage for 100 years, yet some consumers were turning away from CSDs ...
Answer. Organizational behavior in this coca cola case study refers to the study of activities or behavior of the employees inside a commercial enterprise. The reflective case study has been made depending on the issues faced the famous soft drink company Coca Cola. The aim of this coca cola case study is to figure out the strategies with which ...
Coca-Cola grew to an international beverage giant by consistently innovating its organizational structure. See this demonstrated through the history of Coca-Cola's management process from 1980 to ...
Coca-Cola has 200 brands worldwide and thanks to the excellent marketing of The Coca-Cola Company, its products are available in over 200 countries worldwide [3, 4]. While being the largest ...
Case Study: Analysis of the Ethical Behavior of Coca Cola. Coca-Cola is the world's largest beverage company that operates the largest distribution system in the world. This allows Coca-Cola companies to serve more than 1 billion of its products to customers each day. The marketing strategy for Coca-Cola promotes products from four out of the ...
The IDEA360 maps revealed the big picture to Coca-Cola, helping build their Manifesto for Growth, which produced a new emotional and logistic framework of the company and a way to fulfill the mission and vision of the organization.. As a result of this visual and human-centered organizational change process, Coca-Cola took a loosely affiliated group of executives and employees and turned them ...
study as well as recommendations to resolve problems and improve situations. TASK Introduces the case, including the background and the scenario Introduction of the case: This case study is related to the Coca-Cola's organizational behaviour of the employees inside a commercial enterprise. This case study depends on the issue faced by the ...
The paper further analyzed the structure and culture of Coca-Cola Company with emphasis on issues relating to ricks and uncertainties in the company's decision making. Recommendations are laid based on the study to address the company's issues and align decision-making with the company's structure. Organizational Behavior
The impact of organizational reward system on workers attitude and motivation to work (case study of Coca-Cola, Sokoto) @inproceedings{Ekeoma2014TheIO, title={The impact of organizational reward system on workers attitude and motivation to work (case study of Coca-Cola, Sokoto)}, author={Mavis Chioma Ekeoma}, year={2014}, url={https://api ...
PDF | On Jan 1, 2016, Mary Elector Odukah published Factors Influencing Staff Motivation among Employees: A Case Study of Equator Bottlers (Coca Cola) Kenya | Find, read and cite all the research ...
Coca Cola Case Study: An Analysis of Organizational Behaviour Introduction Organizational behavior in this coca cola case study refers to the study of activities or behavior of the employees inside a commercial enterprise. The reflective case study has been made depending on the issues faced the famous soft drink company Coca Cola. The aim of this coca cola case study is to figure out the ...
5. Impact of Brand Storytelling on Coca-Cola's Brand Identity. Brand storytelling has played a significant role in shaping Coca-Cola's brand identity. The strategic use of narratives and emotional appeals has had several key impacts on the brand's perception, consumer loyalty, and global consistency.
Organizational behavior in this coca cola case study refers to the study ofactivities or behavior of the employees inside a commercial enterprise. Thereflective case study has been made depending on the issues faced thefamous soft drink company Coca Cola. The aim of this coca cola case studyis to figure out the strategies with which the company ...
Coca Cola has served their signature beverage for over 130 years all around the world! They have dominated and crushed the competition multiple times. Howeve...