
Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download

Case Study Questions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shape
- Last modified on: 8 months ago
- Reading Time: 9 Minutes

Here in this article, we are providing case study questions for class 6 maths. Here you will find case study questions for class 6 maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shape .
Case Study Question 1:
The figure below shows a combination of shapes.

(i) Arun joins S and Q, SQ is an extension of US. Which type of quadrilateral is PQUV? Justify your answer.
Sol. PQUV is a parallelogram as opposite side UV is parallel; to QP, and UQ is parallel to VP.
(ii) Which of the following quadrilaterals is regular? (a) PQRS (b) PSUV (c) RWUT (d) PQTV
Ans. Option (a) is correct. Explanation: PQRS is a square and regular quadrilateral.
(iii) Looking at the figure, Raji claims that, ‘PWUS is a rhombus’. Do we have sufficient information to accept her claim? Justify your answer.
Sol. No, neither the length or angles of PWUS are not given.
Related Posts
Maths class 6 chapter list, latest chapter list (2023-24).
Chapter 1 Knowing Our Numbers Case Study Questions Chapter 2 Whole Numbers Case Study Questions Chapter 3 Playing with Numbers Case Study Questions Chapter 4 Basic Geometrical Ideas Case Study Questions Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shape Case Study Questions Chapter 6 Integers Case Study Questions Chapter 7 Fractions Case Study Questions Chapter 8 Decimals Case Study Questions Chapter 9 Data Handling Case Study Questions Chapter 10 Mensuration Case Study Questions Chapter 11 Algebra Case Study Questions Chapter 12 Ratio and Proportion Case Study Questions
Old Chapter List
Chapter 1 Knowing Our Numbers Chapter 2 Whole Numbers Chapter 3 Playing with Numbers Chapter 4 Basic Geometrical Ideas Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shape Chapter 6 Integers Chapter 7 Fractions Chapter 8 Decimals Chapter 9 Data Handling Chapter 10 Mensuration Chapter 11 Algebra Chapter 12 Ratio and Proportion Chapter 13 Symmetry Chapter 14 Practical Geometry
Deleted Chapter:
Tips for Answering Case Study Questions for Class 6 Maths in Exam

1. Comprehensive Reading for Context: Prioritize a thorough understanding of the provided case study. Absorb the contextual details and data meticulously to establish a strong foundation for your solution.
2. Relevance Identification: Pinpoint pertinent mathematical concepts applicable to the case study. By doing so, you can streamline your thinking process and apply appropriate methods with precision.
3. Deconstruction of the Problem: Break down the complex problem into manageable components or steps. This approach enhances clarity and facilitates organized problem-solving.
4. Highlighting Key Data: Emphasize critical information and data supplied within the case study. This practice aids quick referencing during the problem-solving process.
5. Application of Formulas: Leverage pertinent mathematical formulas, theorems, and principles to solve the case study. Accuracy in formula selection and unit usage is paramount.
6. Transparent Workflow Display: Document your solution with transparency, showcasing intermediate calculations and steps taken. This not only helps track progress but also offers insight into your analytical process.
7. Variable Labeling and Definition: For introduced variables or unknowns, offer clear labels and definitions. This eliminates ambiguity and reinforces a structured solution approach.
8. Step Explanation: Accompany each step with an explanatory note. This reinforces your grasp of concepts and demonstrates effective application.
9. Realistic Application: When the case study pertains to real-world scenarios, infuse practical reasoning and logic into your solution. This ensures alignment with real-life implications.
10. Thorough Answer Review: Post-solving, meticulously review your answer for accuracy and coherence. Assess its compatibility with the case study’s context.
11. Solution Recap: Before submission, revisit your solution to guarantee comprehensive coverage of the problem and a well-organized response.
12. Previous Case Study Practice: Boost your confidence by practicing with past case study questions from exams or textbooks. This familiarity enhances your readiness for the question format.
13. Efficient Time Management: Strategically allocate time for each case study question based on its complexity and the overall exam duration.
14. Maintain Composure and Confidence: Approach questions with poise and self-assurance. Your preparation equips you to conquer the challenges presented.
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course
Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
You are learning...
Chapter 5 Class 6 Understanding Elementary Shapes
Click on any of the links below to start learning from Teachoo ...
Updated for new NCERT Book .
NCERT Solutions of all execise questions and examples of Chapter 5 Class 6 Understanding Elementary Shapes is available free at teachoo. Each and every question is explained in an easy to understand way.
In the last chapter , we studied some basic shapes like line, line segment, angle, triangle, quadrilateral, polygon.
In this chapter, we will learn
- How to compare length of line segments - using observation, tracing and divider & ruler
- Right and straight angle in terms of revolutions
- Right angle and straight angle in a clock
- Acute , Obtuse and Reflex Angles
- Measuring angles using protractor
- Measure of right angle, straight angle, reflex angle, acute angle, obtuse angle
- Perpendicular line s and
- Perpendicular bisector
- Classifying triangles based on sides - scalene, isosceles, equilateral triangle
- and on angles - acute, obtuse, right angled triangles
- Different types of quadrilateral s like - Kite, Trapezium, Parallelogram, Rhombus, Rectangle, Square
- Different types of polygons - Triangle, Quadrilateral, Pentagon, Hexagon, Heptagon
- Introduction to 3 Dimensional Shapes - Cube, Cuboid, Cylinder, Cone, Sphere,
Click on exercise link below to study from the NCERT Book way.
Or you can study the teachoo way. Click on a topic below to study the concept first, and then the questions. Questions have been ordered from easy to difficult for your reference.
Click on a topic below to begin
Serial order wise
Concept wise.
What's in it?
Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.
NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 maths chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes enables the students to understand and observe shapes around them. This chapter will also help students develop key skills with the help of which they can compare different shapes and figures. We will learn the different methods of comparison like observation, tracing, etc. NCERT Solutions Class 6 maths chapter 5 can also help students develop visualization skills, thus enabling them to analyze different figures precisely.
This chapter will enable kids to develop tools that will help them measure and compare the sizes of objects. This is one of the most important chapters as it will help the students gain practical knowledge on the subject. In order to compare objects, one needs to find the relationship between them. For example, to compare any two line segments, we find a relation between their lengths. The Class 6 maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes challenges the students to use their logical skills. The detailed solution set of these solutions can be found using the links given below:
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Ex 5.1
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Ex 5.2
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Ex 5.3
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Ex 5.4
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Ex 5.5
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Ex 5.6
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Ex 5.7
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Ex 5.8
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Ex 5.9
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 PDF
This chapter also covers the concept of angles such as acute, obtuse, and reflex angles. Also, each method of comparison of shapes is explained with the help of figures. The strategic approach to solving all the questions of this chapter has been outlined in the NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 5.
☛ Download Class 6 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes
NCERT Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Download PDF

NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes
We can see different shapes like circles, triangles, rectangles, squares, etc., everywhere around us. These shapes are made up of line segments, curves, corners, edges, etc., with the help of which we compare their shapes and sizes. This chapter will teach kids how different shapes can be compared. An exercise-wise analysis of the NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes is provided below:
- Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Ex 5.1 - 7 Questions
- Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Ex 5.2 - 7 Questions
- Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Ex 5.3 - 2 Questions
- Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Ex 5.4 - 9 Questions
- Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Ex 5.5 - 11 Questions
- Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Ex 5.6 - 4 Questions
- Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Ex 5.7 - 3 Questions
- Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Ex 5.8 - 5 Questions
- Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Ex 5.9 - 2 Questions
☛ Download Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 NCERT Book
Topics covered : The topics covered in the class 6 maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 5 are measuring line segments , types of angles , measuring angles , perpendicular lines , classification of triangles , quadrilateral polygons, and three-dimensional shapes .
Total Questions: Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes consists of 43 key questions, of which 20 are easy, 13 are medium-level sums, and 10 problems require some brainstorming as they are challenging.
List of Formulas in NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 5
NCERT Class 6 maths chapter 5 encompasses different concepts of shapes, their comparison, and properties. The concepts in this chapter work to simplify tough problems that would otherwise prove to be very difficult. Kids are required to understand the important crucial concepts like the comparison of line segments with different methods such as tracing, observation, and measurement using a ruler. There are no formulas covered in this chapter; however certain points that are important have been reflected in this section. Let us go through these points one by one:
- Based on the angles, triangles can be categorized as follows:
If each angle is acute - Acute angled triangle
If one angle is a right angle - A right-angled triangle
If one angle is obtuse- Obtuse angled triangle
- We can measure the angle using a protractor.
- An angle is acute if its measure is less than a right angle and obtuse if its measure is larger than a right angle but less than a straight angle.
- A reflex angle is more than twice as large as a straight angle.
- The ruler and divider can be used to compare the length of the segments.
Important Questions for Class 6 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 5
Faqs on ncert solutions class 6 maths chapter 5, why are ncert solutions class 6 maths chapter 5 vital for scoring well.
NCERT Solutions Class 6 maths chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes has surprising applications not just in mathematics but in real life as well. Since shapes and angles are everywhere, we need to know how to compare and differentiate them. Hence, it is important to have a strong foundation of this topic to score well in exams.
Do I Need to Practice all Questions Given in Class 6 Maths NCERT Solutions Understanding Elementary Shapes?
The questions for the CBSE examinations are mainly picked from the NCERT Solutions that cover topics like classification of triangles, working of a protractor, quadrilaterals, and many more. The CBSE also recommends the NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths as it is the perfect study material. Hence, it is advisable for the students to solve all the questions from the NCERT solutions to gain confidence and score exceptionally well.
What are the Important Topics Covered in NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 5?
The important topics covered in NCERT solutions class 6 maths chapter 5 are types of angles, measuring angles, perpendicular lines, classification of triangles, quadrilateral polygons, and three-dimensional shapes. Students should be able to solve all the questions related to these topics as these are important from an exam perspective.
How Many Questions are there in NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes?
The NCERT Solutions class 6 maths chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes consists of 43 well-researched questions. These 43 sums are well-placed concerning the theory's setting. These problems are interesting as they come in different formats such as long answer type, word problems, proof-based questions, and many more.
What are the Important Formulas in NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 5?
There are no formulas in the NCERT Solutions class 6 maths chapter 5 however certain important concepts like comparison of angles, line segments, quadrilaterals, angles, etc., have been highlighted in the NCERT Solutions. Students must actively revise these concepts and solve questions to get a rock-solid foundation.
Why Should I Practice NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Understanding Elementary Shapes Chapter 5?
NCERT Solutions assists the students in reinforcing their understanding of concepts while attempting questions from the chapter. These questions not only boost the mathematical but the problem-solving and reasoning skills of a student as well. Moreover, questions related to the properties of shapes like trapezium, parallelogram, rectangle, rhombus, etc., are often asked in exams, hence, the students must practice all the questions in the NCERT Solutions Class 6 maths Understanding Elementary Shapes Chapter 5.
- CBSE Class 10th
CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore
Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Main Question Paper
- JEE Main Cutoff
- JEE Main Answer Key
- JEE Main Result
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- JEE Advanced Registration
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2023
- CAT 2023 College Predictor
- CMAT 2024 Registration
- TS ICET 2024 Registration
- CMAT Exam Date 2024
- MAH MBA CET Cutoff 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- DNB CET College Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Application Form 2024
- NEET PG Application Form 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- LSAT India 2024
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top Law Collages in Indore
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- AIBE 18 Result 2023
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Animation Courses
- Animation Courses in India
- Animation Courses in Bangalore
- Animation Courses in Mumbai
- Animation Courses in Pune
- Animation Courses in Chennai
- Animation Courses in Hyderabad
- Design Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Bangalore
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Fashion Design Colleges in Pune
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Hyderabad
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Design Colleges in India
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission 2024
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- LPU NEST 2024
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET Exam City Intimation Slip 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET Mock Test 2024
- CUET Admit card 2024
- CUET PG Syllabus 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Syllabus 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- IGNOU Result
- CUET Courses List 2024
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Access premium articles, webinars, resources to make the best decisions for career, course, exams, scholarships, study abroad and much more with
Plan, Prepare & Make the Best Career Choices
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes provided here. 6 Class students can access NCERT Class 6 Maths solutions chapter 5 in this article. All the shapes that you see around yourself are formed using lines and curves. Class 6 NCERT Maths solutions chapter 5 are covering problems related to line segments, circle and other shapes. NCERT Maths Class 6 chapter 5 solutions are prepared, based on the problems available in NCERT Class 6 Syllabus .
Latest: Important Maths Formulas for Class 6 - Chapterwise
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 - Important Formulae And Points
Ncert solutions for class 6 maths chapter 5 understanding elementary shapes (intext questions and exercise), ncert solutions for class 6 maths topic: angles, ncert solutions for class 6 mathematics chapter wise, how to use ncert solutions for class 6 maths chapter 5 understanding elementary shapes, ncert solutions for class 6 - subject wise.

It is one of the most important chapters of this Class as well as of the geometry part. So students should prepare well and refer to NCERT solutions for Class 6 Maths chapter 5, in case of any doubt. CBSE NCERT Class 6 Maths solutions chapter 5 is covering the solution of all the subtopics. In this chapter of NCERT , there are 45 questions in 9 exercises. NCERT Maths Class 6 chapter 5 solutions to all these 45 problems are covered and provided below. Check NCERT Solutions for other classes and subjects. Download - NCERT Books for Class 6
Straight angle = 180 degrees and right angle = 90 degrees.
Acute angle: When an angle is smaller than a right angle, we call it an acute angle.
Obtuse angle: When an angle is bigger than a right angle but smaller than a straight angle, we call it an obtuse angle.
Reflex angle: When an angle is larger than a straight angle, we call it a reflex angle.
Sum of interior angles of a triangle=180 degree
Sum of all interior angles of a polygon with n side=(n - 2)180 degrees
Triangle And Its Type
Quadrilaterals.
Download PDF
Q1 What is the disadvantage in comparing line segments by mere observation?
Answer: The disadvantage in comparing line segments by mere observation is that our estimation may be inaccurate and therefore a divider must be used.
Q2 Why is it better to use a divider than a ruler, while measuring the length of a line segment?
Answer: While measuring the length of a line segment using error might creep in due to the thickness and translucency of the ruler and because of angular viewing. We can get rid of these errors using a divider.
Q3 Draw any line segment, say AB. Take any point C lying in between A and B. Measure the lengths of AB, BC and AC. Is AB = AC + CB?
[Note : If A,B,C are any three points on a line such that AC + CB = AB, then we can be sure that C lies between A and B.]

Q4 If A, B, C are three points on a line such that AB = 5 cm, BC = 3 cm and AC = 8 cm, which one of them lies between the other two?
Answer: AB = 5 cm BC = 3 cm AC = 8 cm Therefore AB + BC = AC Therefore point B lies between points A and C.
Q5 Verify, whether D is the midpoint of AG.

Answer: AD = 4 - 1 = 3 DG = 7 - 4 = 3 Therefore, AD = DG Therefore, D is the midpoint of AG.
Q6 If B is the midpoint of AC and C is the midpoint of BD, where A, B, C, D lie on a straight line, say why AB = CD?
Q7 Draw five triangles and measure their sides. Check in each case, if the sum of the lengths of any two sides is always less than the third side.

After measuring their sides we have found that the sum of lengths of any two sides of a triangle is always greater than the third side.
Q1 What is the angle name for half a revolution?
Q2 What is the angle name for one-fourth revolution?
Q3 Draw five other situations of one-fourth, half and three-fourth revolution on a clock.

NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Exercise: 5.2
Q1 What fraction of a clockwise revolution does the hour hand of a clock turn through, when it goes from
(a) 3 to 9 (b) 4 to 7 (c) 7 to 10
(d) 12 to 9 (e) 1 to 10 (f) 6 to 3
Answer: (a) Half. (b) One fourth. (c) One fourth. (d) Three fourth. (e) Three fourth. (f) Three fourth.
Answer: (a) West. (b) West. (c) North. (d) South. No need to specify clockwise or anti-clockwise for the last question as after one complete revolution we would be facing in the same direction.
Q4 What part of a revolution have you turned through if you stand facing (a) east and turn clockwise to face north? (b) south and turn clockwise to face east? (c) west and turn clockwise to face east?
Q5 Find the number of right angles turned through by the hour hand of a clock when it goes from
(a) 3 to 6 (b) 2 to 8 (c) 5 to 11
(d) 10 to 1 (e) 12 to 9 (f) 12 to 6
Answer: Number of right angles turned through by the hour hand of a clock when it goes from (a) 3 to 6, (b) 2 to 8, (c) 5 to 11, (d) 10 to 1, (e) 12 to 9, (f) 12 to 6 are
(a) 1. (b) 2. (c) 2. (d) 1. (e) 3. (f) 2.
Q6 How many right angles do you make if you start facing (a) south and turn clockwise to west? (b) north and turn anti-clockwise to east? (c) west and turn to west? (d) south and turn to north?
Answer: The number of right angles we can make from the given conditions are- (a) 1. (b) 3. (c) 4. (d) 2.
Q7 Where will the hour hand of a clock stop if it starts
(a) from 6 and turns through 1 right angle?
(b) from 8 and turns through 2 right angles?
(c) from 10 and turns through 3 right angles?
(d) from 7 and turns through 2 straight angles?
Answer: (a) Starting from 6 and turns through 1 right angle the hour hand stops at 9. (b) Starting from 8 and turns through 2 right angles the hour hand stops at 2. (c) Starting from 10 and turns through 3 right angles the hour hand stops at 7. (d) Starting from 7 and turns through 2 straight angles the hour hand stops at 7.
NCERT solutions for class 6 maths topic: Angles
Q1 The hour hand of a clock moves from 12 to 5. Is the revolution of the hour hand more than 1 right angle?

Q2 What does the angle made by the hour hand of the clock look like when it moves from 5 to 7. Is the angle moved more than 1 right angle?

NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Exercise: 5.3
Q1 Match the following
Q2 Classify each one of the following angles as right, straight, acute, obtuse or reflex :

- (b) Obtuse.
- (d) Reflex.
- (e) Straight.
- (f) Acute, acute.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Exercise: 5.4
Q1 What is the measure of (i) a right angle? (ii) a straight angle?
Answer: (i) 90 o (ii) 180 o
Q2 Say True or False :
- (a) The measure of an acute angle < 90°.
- (b) The measure of an obtuse angle < 90°.
- (c) The measure of a reflex angle > 180°.
- (d) The measure of one complete revolution = 360°.
- (e) If m A∠ = 53° and m B∠ = 35°, then m A∠ > m B.
Q3 Write down the measures of (a) some acute angles. (b) some obtuse angles. (give at least two examples of each).
- (a) 30 o , 45 o and 60 o
- (b) 120 o , 135 o and 150 o
Q4 Measure the angles given below using the Protractor and write down the measure.

- (d) 60 o , 90 o and 125 o
Q5 Which angle has a large measure? First, estimate and then measure.

Measure of Angle A = Measure of Angle B =
Answer: Measure of Angle A = 40 o Measure of Angle B = 60 o
Q6 From these two angles which has larger measure? Estimate and then confirm by measuring them.

Answer: By estimation followed by confirmation by measurement we know that the second angle is greater.
Q7 Fill in the blanks with acute, obtuse, right or straight :
- (a) An angle whose measure is less than that of a right angle is______.
- (b) An angle whose measure is greater than that of a right angle is ______.
- (c) An angle whose measure is the sum of the measures of two right angles is _____.
- (d) When the sum of the measures of two angles is that of a right angle, then each one of them is ______.
- (e) When the sum of the measures of two angles is that of a straight angle and if one of them is acute then the other should be _______.
- (a) An angle whose measure is less than that of a right angle is acute .
- (b) An angle whose measure is greater than that of a right angle is obtuse .
- (c) An angle whose measure is the sum of the measures of two right angles is straight .
- (d) When the sum of the measures of two angles is that of a right angle, then each one of them is acute .
- (e) When the sum of the measures of two angles is that of a straight angle and if one of them is acute then the other should be obtuse .
Q8 Find the measure of the angle shown in each figure. (First estimate with your eyes and then find the actual measure with a protractor).

- (a) Measure of the given along = 40 o
- (b) Measure of the given along = 130 o
- (c) Measure of the given along = 65 o
- (d) Measure of the given along = 135 o
Q9 Find the angle measure between the hands of the clock in each figure :

Answer: The angle measure between the hands of the clock in each figure is
Q11 Measure and classify each angle :

NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Exercise: 5.5
Q1 Which of the following are models for perpendicular lines :
- (a) The adjacent edges of a table-top.
- (b) The lines of a railway track.
- (c) The line segments forming the letter ‘L’.
- (d) The letter V.
- (a) The adjacent edges of a table-top are models for perpendicular lines.
- (b) The lines of a railway track are not models for perpendicular lines as they are parallel to each other.
- (c) The line segments forming the letter ‘L’ are models for perpendicular lines.
- (d) The line segments forming the letter ‘V’ are models for perpendicular lines.
Q3 There are two set-squares in your box. What are the measures of the angles that are formed at their corners? Do they have any angle measure that is common?
Answer: The angles of the two set squares are (i) 90 o , 60 o and 30 o (ii) 90 o , 45 o, and 45 o Yes they have the common angle measure 90 o
- (a) Is CE = EG?
- (b) Does PE bisect CG?
- (c) Identify any two line segments for which PE is the perpendicular bisector.
- (i) AC > FG
- (ii) CD = GH
- (iii) BC < EH.

- (a) CE = 5 - 3 = 2 units EG = 7 - 5 = 2 units Therefore CE = EG.
- (b) CE = EG therefore PE bisects CG.
- (c) PE is the perpendicular bisector for line segments DF and BH
- (i) AC = 3 - 1 = 2 units FG = 7 - 6 = 1 unit Therefore AC > FG True
- (ii) CD = 4 - 3 = 1 unit GH = 8 - 7 = 1 unit Therefore CD = GH True
- (iii) BC = 3 - 2 = 1 unit EH = 8 - 5 = 3 units Therefore BC < EH True.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Topic: Classification of Triangles
Q1 Try to draw rough sketches of
- (a) a scalene acute-angled triangle.
- (b) an obtuse-angled isosceles triangle.

NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Exercise: 5.6
Q1 Name the types of following triangles :
- (a) Triangle with lengths of sides 7 cm, 8 cm and 9 cm.
- (a) Scalene Triangle.
- (b) Scalene Triangle.
- (c) Equilateral Triangle.
- (d) Right-angled Triangle.
- (e) Right-angled isosceles Triangle.
- (f) Acute angled Triangle.
Q2 Match the following :
Q3 Name each of the following triangles in two different ways: (you may judge the nature of the angle by observation)

- (a)(i) Acute angled triangle.
- (ii) Isosceles triangle.
- (b)(i) Right-angled triangle.
- (ii) Scalane triangle.
- (c)(i) Obtuse angled triangle.
- (d)(i) Right-angled triangle.
- (e)(i) Acute angled triangle.
- (ii) Equilateral triangle.
- (f)(i) Obtuse angled triangle.
- (ii) Scalene triangle.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Topic: Quadrilaterals
Q1 Place a pair of unequal sticks such that they have their endpoints joined at one end. Now place another such pair meeting the free ends of the first pair. What is the figure enclosed? It is a quadrilateral, like the one you see here. The sides of the quadrilateral are AB, BC, ___, ___. There are 4 angles for this quadrilateral. They are given by ∠BAD, ∠ADC, ∠DCB and _____. BD is one diagonal. What is the other? Measure the length of the sides and the diagonals. Measure all the angles also.

Q2 Using four unequal sticks, as you did in the above activity, see if you can form a quadrilateral such that
(a) all the four angles are acute.
(b) one of the angles is obtuse.
(c) one of the angles is right-angled.
(d) two of the angles are obtuse.
(e) two of the angles are right-angled.
(f) the diagonals are perpendicular to one another

NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Exercise 5.7
Q1 Say True or False :
- (a) Each angle of a rectangle is a right angle.
- (b) The opposite sides of a rectangle are equal in length.
- (c) The diagonals of a square are perpendicular to one another.
- (d) All the sides of a rhombus are of equal length.
- (e) All the sides of a parallelogram are of equal length.
- (f) The opposite sides of a trapezium are parallel.
Q2 (a) Give reasons for the following: A square can be thought of as a special rectangle.
Answer: A square can be thought of as a special rectangle as it is a rectangle only but with all sides equal.
Q2 (b) Give reasons for the following: A rectangle can be thought of as a special parallelogram.
Answer: A rectangle can be thought of as a special parallelogram as it s a parallelogram only but with all angles equal to ninety degrees.
Q2 (c) Give reasons for the following: A square can be thought of as a special rhombus.
Answer: A square can be thought of as a special rhombus because like a rhombus it has all sides equal but all its angles are also equal.
Q2 (d) Give reasons for the following: Squares, rectangles, parallelograms are all quadrilaterals.
Answer: Squares, rectangles, parallelograms are all quadrilaterals as they all have four sides.
Q2 (e) Give reasons for the following: Square is also a parallelogram.
Answer: Square is also a parallelogram as its opposite sides are parallel.
Q3 A figure is said to be regular if its sides are equal in length and angles are equal in measure. Can you identify the regular quadrilateral?
Answer: Square is the only quadrilateral with sides equal in length and angles equal in measure, therefore, a square is the regular quadrilateral.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Exercise: 5.8
Q1 Examine whether the following are polygons. If anyone among them is not, say why?

- (a) The given figure is not a polygon as it is not a closed figure.
- (b) The given figure is a polygon.
- (c) The given figure is not a polygon as a polygon is enclosed only by line segments.
- (d) The given figure is not a polygon as a polygon is enclosed only by line segments.
Q2 Name each polygon.

Make two more examples of each of these.
(a) Quadrilateral

(b) Triangle

(c) Pentagon

(d) Octagon

Q3 Draw a rough sketch of a regular hexagon. Connecting any three of its vertices, draw a triangle. Identify the type of triangle you have drawn.

We have drawn the regular Hexagon ABCDEF and by joining the vertices B, D and F we have formed the Equilateral Triangle BDF.
Q4 Draw a rough sketch of a regular octagon. (Use squared paper if you wish). Draw a rectangle by joining exactly four of the vertices of the octagon.

We have made the regular octagon ABCDEFGH and by joining vertices H, C, D and G we have formed the rectangle HCDG
Q5 A diagonal is a line segment that joins any two vertices of the polygon and is not a side of the polygon. Draw a rough sketch of a pentagon and draw its diagonals.

We have drawn the pentagon ABCDE and by joining its vertices he has drawn the diagonals AC, CE, EB, BD and DA.
NCERT Solutions of Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Topic: Three Dimensional Shapes
Q2 A cube is a cuboid whose edges are all of equal length.
- It has ______ faces.
- Each face has ______ edges.
- Each face has ______ vertices.

Q3 A triangular pyramid has a triangle as its base. It is also known as a tetrahedron.
- Faces : _______
- Edges : _______
- Corners : _______

Answer: The number of
Q4 A square pyramid has a square as its base.

Q5 A triangular prism looks like the shape of a Kaleidoscope. It has triangles as its bases.

NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Exercise: 5.9
Q1 Match the following :

Q2 What shape is (a) Your instrument box? (b) A brick? (c) A matchbox? (d) A road-roller? (e) A sweet laddu?
Answer: T he shape of the following things are
- (a) Your instrument box- Cuboid
- (b) A brick- Cuboid
- (c) A matchbox-Cuboid
- (d) A road-roller- Cylinder
- (e) A sweet laddu-Sphere
Understanding Elementary Shape Class 6 Maths Chapter 5-Summary
In Class 6 Maths Chapter 5, "Understanding Elementary Shapes," the following topics are covered:
Measuring Line Segment: This topic focuses on measuring the length of a line segment using a ruler or a measuring scale. Students learn how to read measurements in centimeters (cm) and millimeters (mm) and understand the concept of units of length.
Angles - 'Right' and 'Straight': Students are introduced to angles and learn about two specific types: right angles and straight angles. A right angle measures exactly 90 degrees and forms the shape of an "L." A straight angle measures exactly 180 degrees and forms a straight line.
Angles - 'Acute', 'Obtuse', and 'Reflex': This topic expands on angles by introducing acute angles, which are less than 90 degrees, and obtuse angles, which are greater than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees. Students also learn about reflex angles, which measure greater than 180 degrees but less than 360 degrees.
Measuring Angles: Students explore how to measure and draw angles using a protractor. They understand that the measure of an angle is represented in degrees and learn how to determine the measurement of an angle accurately.
Perpendicular Line: This topic introduces the concept of perpendicular lines. Students learn that perpendicular lines are two lines that intersect at a right angle, forming four right angles at the point of intersection.
Classification of Triangles: Students learn about the classification of triangles based on their sides and angles. They study equilateral triangles (all sides and angles are equal), isosceles triangles (two sides and two angles are equal), and scalene triangles (all sides and angles are different).
Quadrilaterals: This topic focuses on quadrilaterals, which are polygons with four sides. Students learn about different types of quadrilaterals, such as squares, rectangles, parallelograms, and trapezoids. They understand the properties and characteristics of each type.
Polygons: Students delve into the concept of polygons in general, which are closed figures formed by line segments. They explore the properties of polygons and study various types, including triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, hexagons, and so on.
Three-Dimensional Shape: This topic introduces three-dimensional shapes, also known as solid shapes. Students learn about common three-dimensional shapes like cubes, cuboids, cylinders, cones, and spheres. They understand the distinguishing features and characteristics of each shape.
Also Check -
NCERT Books and NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books Class 6 Maths
- NCERT Syllabus Class 6 Maths
- NCERT Books Class 6
- NCERT Syllabus Class 6
- You must have covered the previous chapter Basic Geometrical Ideas of class 6 hindi chapter 5 .
- Read the conceptual text given in the NCERT textbook and then refer to NCERT Solutions for Class 6 .
- Learn the application of all these concepts in the problems.
- When you are done with all the above three points, you can practice it.
- While practicing you can utilize solutions of NCERT for Class 6 Maths chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes.
Keep learning and working hard!
Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
A triangular prism has six corners, also known as vertices. In a triangular prism, there are three vertices at the top triangle and three vertices at the bottom triangle. These vertices are connected by edges to form the prism.
In a rectangle, each angle measures 90 degrees. A rectangle is a quadrilateral with four right angles (90-degree angles). The opposite sides of a rectangle are parallel, and all four angles are equal, measuring 90 degrees each. This property of rectangles makes them useful for various geometric and architectural applications. Students can study understanding elementary shapes class 6 pdf after downloading form the website.
If a triangle has three equal sides, it is called an equilateral triangle. In an equilateral triangle, all three angles are equal. Since the sum of angles in any triangle is always 180 degrees, each angle of an equilateral triangle measures 60 degrees. Also these concepts are discussed in class 6 maths chapter 5 pdf which can be downloaded from careers360 website.
There are 9 exercise solved in the maths class 6 chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes.
- Latest Articles
- Popular Articles
Explore Premium
Understand your attachment style and learn how you can reform your relationships, 7 tips to convey your struggles to your loved ones, decision-making: common challenges faced, tips to make good decisions, how stay-at-home parents can care for themselves, teenage relationships: tips to help your teenager deal with a breakup, getting over the pink and blue divide: revising gender roles, artificial rain: concept and techniques, what is lenz’s law in electricity and magnetism and why is it true, cancer treatment: why chemotherapy does not suit all patients, upcoming school exams, national institute of open schooling 12th examination.
Admit Card Date : 28 March,2024 - 22 May,2024
National Institute of Open Schooling 10th examination
Punjab board of secondary education 12th examination.
Exam Date : 05 April,2024 - 27 April,2024
Bihar Board 12th Examination
Admit Card Date : 19 April,2024 - 11 May,2024
Nagaland Board High School Leaving Certificate Examination
Result Date : 26 April,2024 - 26 April,2024
Popular Questions
A block of mass 0.50 kg is moving with a speed of 2.00 ms -1 on a smooth surface. It strikes another mass of 1.00 kg and then they move together as a single body. The energy loss during the collision is
A person trying to lose weight by burning fat lifts a mass of 10 kg upto a height of 1 m 1000 times. Assume that the potential energy lost each time he lowers the mass is dissipated. How much fat will he use up considering the work done only when the weight is lifted up ? Fat supplies 3.8×10 7 J of energy per kg which is converted to mechanical energy with a 20% efficiency rate. Take g = 9.8 ms −2 :
An athlete in the olympic games covers a distance of 100 m in 10 s. His kinetic energy can be estimated to be in the range
In the reaction,
If we consider that 1/6, in place of 1/12, mass of carbon atom is taken to be the relative atomic mass unit, the mass of one mole of a substance will
With increase of temperature, which of these changes?
Number of atoms in 558.5 gram Fe (at. wt.of Fe = 55.85 g mol -1 ) is
A pulley of radius 2 m is rotated about its axis by a force F = (20t - 5t 2 ) newton (where t is measured in seconds) applied tangentially. If the moment of inertia of the pulley about its axis of rotation is 10 kg m 2 , the number of rotations made by the pulley before its direction of motion if reversed, is
Colleges After 12th
Popular course after 12th.
- DUET (DU JAT)
- BHU UET,BUMAT,
- MAH CET Law
- JEE Advanced
- COMEDK UGET
- JEE Main Paper 2
- AAT (JEE Advanced)
- ISI Admission Test
Explore Career Options (By Industry)
- Construction
- Entertainment
- Manufacturing
- Information Technology
Data Administrator
Database professionals use software to store and organise data such as financial information, and customer shipping records. Individuals who opt for a career as data administrators ensure that data is available for users and secured from unauthorised sales. DB administrators may work in various types of industries. It may involve computer systems design, service firms, insurance companies, banks and hospitals.
Bio Medical Engineer
The field of biomedical engineering opens up a universe of expert chances. An Individual in the biomedical engineering career path work in the field of engineering as well as medicine, in order to find out solutions to common problems of the two fields. The biomedical engineering job opportunities are to collaborate with doctors and researchers to develop medical systems, equipment, or devices that can solve clinical problems. Here we will be discussing jobs after biomedical engineering, how to get a job in biomedical engineering, biomedical engineering scope, and salary.
Ethical Hacker
A career as ethical hacker involves various challenges and provides lucrative opportunities in the digital era where every giant business and startup owns its cyberspace on the world wide web. Individuals in the ethical hacker career path try to find the vulnerabilities in the cyber system to get its authority. If he or she succeeds in it then he or she gets its illegal authority. Individuals in the ethical hacker career path then steal information or delete the file that could affect the business, functioning, or services of the organization.
GIS officer work on various GIS software to conduct a study and gather spatial and non-spatial information. GIS experts update the GIS data and maintain it. The databases include aerial or satellite imagery, latitudinal and longitudinal coordinates, and manually digitized images of maps. In a career as GIS expert, one is responsible for creating online and mobile maps.
Data Analyst
The invention of the database has given fresh breath to the people involved in the data analytics career path. Analysis refers to splitting up a whole into its individual components for individual analysis. Data analysis is a method through which raw data are processed and transformed into information that would be beneficial for user strategic thinking.
Data are collected and examined to respond to questions, evaluate hypotheses or contradict theories. It is a tool for analyzing, transforming, modeling, and arranging data with useful knowledge, to assist in decision-making and methods, encompassing various strategies, and is used in different fields of business, research, and social science.
Geothermal Engineer
Individuals who opt for a career as geothermal engineers are the professionals involved in the processing of geothermal energy. The responsibilities of geothermal engineers may vary depending on the workplace location. Those who work in fields design facilities to process and distribute geothermal energy. They oversee the functioning of machinery used in the field.
Database Architect
If you are intrigued by the programming world and are interested in developing communications networks then a career as database architect may be a good option for you. Data architect roles and responsibilities include building design models for data communication networks. Wide Area Networks (WANs), local area networks (LANs), and intranets are included in the database networks. It is expected that database architects will have in-depth knowledge of a company's business to develop a network to fulfil the requirements of the organisation. Stay tuned as we look at the larger picture and give you more information on what is db architecture, why you should pursue database architecture, what to expect from such a degree and what your job opportunities will be after graduation. Here, we will be discussing how to become a data architect. Students can visit NIT Trichy , IIT Kharagpur , JMI New Delhi .
Remote Sensing Technician
Individuals who opt for a career as a remote sensing technician possess unique personalities. Remote sensing analysts seem to be rational human beings, they are strong, independent, persistent, sincere, realistic and resourceful. Some of them are analytical as well, which means they are intelligent, introspective and inquisitive.
Remote sensing scientists use remote sensing technology to support scientists in fields such as community planning, flight planning or the management of natural resources. Analysing data collected from aircraft, satellites or ground-based platforms using statistical analysis software, image analysis software or Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is a significant part of their work. Do you want to learn how to become remote sensing technician? There's no need to be concerned; we've devised a simple remote sensing technician career path for you. Scroll through the pages and read.
Budget Analyst
Budget analysis, in a nutshell, entails thoroughly analyzing the details of a financial budget. The budget analysis aims to better understand and manage revenue. Budget analysts assist in the achievement of financial targets, the preservation of profitability, and the pursuit of long-term growth for a business. Budget analysts generally have a bachelor's degree in accounting, finance, economics, or a closely related field. Knowledge of Financial Management is of prime importance in this career.
Underwriter
An underwriter is a person who assesses and evaluates the risk of insurance in his or her field like mortgage, loan, health policy, investment, and so on and so forth. The underwriter career path does involve risks as analysing the risks means finding out if there is a way for the insurance underwriter jobs to recover the money from its clients. If the risk turns out to be too much for the company then in the future it is an underwriter who will be held accountable for it. Therefore, one must carry out his or her job with a lot of attention and diligence.
Finance Executive
Product manager.
A Product Manager is a professional responsible for product planning and marketing. He or she manages the product throughout the Product Life Cycle, gathering and prioritising the product. A product manager job description includes defining the product vision and working closely with team members of other departments to deliver winning products.
Operations Manager
Individuals in the operations manager jobs are responsible for ensuring the efficiency of each department to acquire its optimal goal. They plan the use of resources and distribution of materials. The operations manager's job description includes managing budgets, negotiating contracts, and performing administrative tasks.
Stock Analyst
Individuals who opt for a career as a stock analyst examine the company's investments makes decisions and keep track of financial securities. The nature of such investments will differ from one business to the next. Individuals in the stock analyst career use data mining to forecast a company's profits and revenues, advise clients on whether to buy or sell, participate in seminars, and discussing financial matters with executives and evaluate annual reports.
A Researcher is a professional who is responsible for collecting data and information by reviewing the literature and conducting experiments and surveys. He or she uses various methodological processes to provide accurate data and information that is utilised by academicians and other industry professionals. Here, we will discuss what is a researcher, the researcher's salary, types of researchers.
Welding Engineer
Welding Engineer Job Description: A Welding Engineer work involves managing welding projects and supervising welding teams. He or she is responsible for reviewing welding procedures, processes and documentation. A career as Welding Engineer involves conducting failure analyses and causes on welding issues.
Transportation Planner
A career as Transportation Planner requires technical application of science and technology in engineering, particularly the concepts, equipment and technologies involved in the production of products and services. In fields like land use, infrastructure review, ecological standards and street design, he or she considers issues of health, environment and performance. A Transportation Planner assigns resources for implementing and designing programmes. He or she is responsible for assessing needs, preparing plans and forecasts and compliance with regulations.
Environmental Engineer
Individuals who opt for a career as an environmental engineer are construction professionals who utilise the skills and knowledge of biology, soil science, chemistry and the concept of engineering to design and develop projects that serve as solutions to various environmental problems.
Safety Manager
A Safety Manager is a professional responsible for employee’s safety at work. He or she plans, implements and oversees the company’s employee safety. A Safety Manager ensures compliance and adherence to Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) guidelines.
Conservation Architect
A Conservation Architect is a professional responsible for conserving and restoring buildings or monuments having a historic value. He or she applies techniques to document and stabilise the object’s state without any further damage. A Conservation Architect restores the monuments and heritage buildings to bring them back to their original state.
Structural Engineer
A Structural Engineer designs buildings, bridges, and other related structures. He or she analyzes the structures and makes sure the structures are strong enough to be used by the people. A career as a Structural Engineer requires working in the construction process. It comes under the civil engineering discipline. A Structure Engineer creates structural models with the help of computer-aided design software.
Highway Engineer
Highway Engineer Job Description: A Highway Engineer is a civil engineer who specialises in planning and building thousands of miles of roads that support connectivity and allow transportation across the country. He or she ensures that traffic management schemes are effectively planned concerning economic sustainability and successful implementation.
Field Surveyor
Are you searching for a Field Surveyor Job Description? A Field Surveyor is a professional responsible for conducting field surveys for various places or geographical conditions. He or she collects the required data and information as per the instructions given by senior officials.
Orthotist and Prosthetist
Orthotists and Prosthetists are professionals who provide aid to patients with disabilities. They fix them to artificial limbs (prosthetics) and help them to regain stability. There are times when people lose their limbs in an accident. In some other occasions, they are born without a limb or orthopaedic impairment. Orthotists and prosthetists play a crucial role in their lives with fixing them to assistive devices and provide mobility.
Pathologist
A career in pathology in India is filled with several responsibilities as it is a medical branch and affects human lives. The demand for pathologists has been increasing over the past few years as people are getting more aware of different diseases. Not only that, but an increase in population and lifestyle changes have also contributed to the increase in a pathologist’s demand. The pathology careers provide an extremely huge number of opportunities and if you want to be a part of the medical field you can consider being a pathologist. If you want to know more about a career in pathology in India then continue reading this article.
Veterinary Doctor
Speech therapist, gynaecologist.
Gynaecology can be defined as the study of the female body. The job outlook for gynaecology is excellent since there is evergreen demand for one because of their responsibility of dealing with not only women’s health but also fertility and pregnancy issues. Although most women prefer to have a women obstetrician gynaecologist as their doctor, men also explore a career as a gynaecologist and there are ample amounts of male doctors in the field who are gynaecologists and aid women during delivery and childbirth.
Audiologist
The audiologist career involves audiology professionals who are responsible to treat hearing loss and proactively preventing the relevant damage. Individuals who opt for a career as an audiologist use various testing strategies with the aim to determine if someone has a normal sensitivity to sounds or not. After the identification of hearing loss, a hearing doctor is required to determine which sections of the hearing are affected, to what extent they are affected, and where the wound causing the hearing loss is found. As soon as the hearing loss is identified, the patients are provided with recommendations for interventions and rehabilitation such as hearing aids, cochlear implants, and appropriate medical referrals. While audiology is a branch of science that studies and researches hearing, balance, and related disorders.
An oncologist is a specialised doctor responsible for providing medical care to patients diagnosed with cancer. He or she uses several therapies to control the cancer and its effect on the human body such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, radiation therapy and biopsy. An oncologist designs a treatment plan based on a pathology report after diagnosing the type of cancer and where it is spreading inside the body.
Are you searching for an ‘Anatomist job description’? An Anatomist is a research professional who applies the laws of biological science to determine the ability of bodies of various living organisms including animals and humans to regenerate the damaged or destroyed organs. If you want to know what does an anatomist do, then read the entire article, where we will answer all your questions.
For an individual who opts for a career as an actor, the primary responsibility is to completely speak to the character he or she is playing and to persuade the crowd that the character is genuine by connecting with them and bringing them into the story. This applies to significant roles and littler parts, as all roles join to make an effective creation. Here in this article, we will discuss how to become an actor in India, actor exams, actor salary in India, and actor jobs.
Individuals who opt for a career as acrobats create and direct original routines for themselves, in addition to developing interpretations of existing routines. The work of circus acrobats can be seen in a variety of performance settings, including circus, reality shows, sports events like the Olympics, movies and commercials. Individuals who opt for a career as acrobats must be prepared to face rejections and intermittent periods of work. The creativity of acrobats may extend to other aspects of the performance. For example, acrobats in the circus may work with gym trainers, celebrities or collaborate with other professionals to enhance such performance elements as costume and or maybe at the teaching end of the career.
Video Game Designer
Career as a video game designer is filled with excitement as well as responsibilities. A video game designer is someone who is involved in the process of creating a game from day one. He or she is responsible for fulfilling duties like designing the character of the game, the several levels involved, plot, art and similar other elements. Individuals who opt for a career as a video game designer may also write the codes for the game using different programming languages.
Depending on the video game designer job description and experience they may also have to lead a team and do the early testing of the game in order to suggest changes and find loopholes.
Radio Jockey
Radio Jockey is an exciting, promising career and a great challenge for music lovers. If you are really interested in a career as radio jockey, then it is very important for an RJ to have an automatic, fun, and friendly personality. If you want to get a job done in this field, a strong command of the language and a good voice are always good things. Apart from this, in order to be a good radio jockey, you will also listen to good radio jockeys so that you can understand their style and later make your own by practicing.
A career as radio jockey has a lot to offer to deserving candidates. If you want to know more about a career as radio jockey, and how to become a radio jockey then continue reading the article.
Choreographer
The word “choreography" actually comes from Greek words that mean “dance writing." Individuals who opt for a career as a choreographer create and direct original dances, in addition to developing interpretations of existing dances. A Choreographer dances and utilises his or her creativity in other aspects of dance performance. For example, he or she may work with the music director to select music or collaborate with other famous choreographers to enhance such performance elements as lighting, costume and set design.
Social Media Manager
A career as social media manager involves implementing the company’s or brand’s marketing plan across all social media channels. Social media managers help in building or improving a brand’s or a company’s website traffic, build brand awareness, create and implement marketing and brand strategy. Social media managers are key to important social communication as well.
Photographer
Photography is considered both a science and an art, an artistic means of expression in which the camera replaces the pen. In a career as a photographer, an individual is hired to capture the moments of public and private events, such as press conferences or weddings, or may also work inside a studio, where people go to get their picture clicked. Photography is divided into many streams each generating numerous career opportunities in photography. With the boom in advertising, media, and the fashion industry, photography has emerged as a lucrative and thrilling career option for many Indian youths.
An individual who is pursuing a career as a producer is responsible for managing the business aspects of production. They are involved in each aspect of production from its inception to deception. Famous movie producers review the script, recommend changes and visualise the story.
They are responsible for overseeing the finance involved in the project and distributing the film for broadcasting on various platforms. A career as a producer is quite fulfilling as well as exhaustive in terms of playing different roles in order for a production to be successful. Famous movie producers are responsible for hiring creative and technical personnel on contract basis.
Copy Writer
In a career as a copywriter, one has to consult with the client and understand the brief well. A career as a copywriter has a lot to offer to deserving candidates. Several new mediums of advertising are opening therefore making it a lucrative career choice. Students can pursue various copywriter courses such as Journalism , Advertising , Marketing Management . Here, we have discussed how to become a freelance copywriter, copywriter career path, how to become a copywriter in India, and copywriting career outlook.
In a career as a vlogger, one generally works for himself or herself. However, once an individual has gained viewership there are several brands and companies that approach them for paid collaboration. It is one of those fields where an individual can earn well while following his or her passion.
Ever since internet costs got reduced the viewership for these types of content has increased on a large scale. Therefore, a career as a vlogger has a lot to offer. If you want to know more about the Vlogger eligibility, roles and responsibilities then continue reading the article.
For publishing books, newspapers, magazines and digital material, editorial and commercial strategies are set by publishers. Individuals in publishing career paths make choices about the markets their businesses will reach and the type of content that their audience will be served. Individuals in book publisher careers collaborate with editorial staff, designers, authors, and freelance contributors who develop and manage the creation of content.
Careers in journalism are filled with excitement as well as responsibilities. One cannot afford to miss out on the details. As it is the small details that provide insights into a story. Depending on those insights a journalist goes about writing a news article. A journalism career can be stressful at times but if you are someone who is passionate about it then it is the right choice for you. If you want to know more about the media field and journalist career then continue reading this article.
Individuals in the editor career path is an unsung hero of the news industry who polishes the language of the news stories provided by stringers, reporters, copywriters and content writers and also news agencies. Individuals who opt for a career as an editor make it more persuasive, concise and clear for readers. In this article, we will discuss the details of the editor's career path such as how to become an editor in India, editor salary in India and editor skills and qualities.
Individuals who opt for a career as a reporter may often be at work on national holidays and festivities. He or she pitches various story ideas and covers news stories in risky situations. Students can pursue a BMC (Bachelor of Mass Communication) , B.M.M. (Bachelor of Mass Media) , or MAJMC (MA in Journalism and Mass Communication) to become a reporter. While we sit at home reporters travel to locations to collect information that carries a news value.
Corporate Executive
Are you searching for a Corporate Executive job description? A Corporate Executive role comes with administrative duties. He or she provides support to the leadership of the organisation. A Corporate Executive fulfils the business purpose and ensures its financial stability. In this article, we are going to discuss how to become corporate executive.
Multimedia Specialist
A multimedia specialist is a media professional who creates, audio, videos, graphic image files, computer animations for multimedia applications. He or she is responsible for planning, producing, and maintaining websites and applications.
Quality Controller
A quality controller plays a crucial role in an organisation. He or she is responsible for performing quality checks on manufactured products. He or she identifies the defects in a product and rejects the product.
A quality controller records detailed information about products with defects and sends it to the supervisor or plant manager to take necessary actions to improve the production process.
Production Manager
A QA Lead is in charge of the QA Team. The role of QA Lead comes with the responsibility of assessing services and products in order to determine that he or she meets the quality standards. He or she develops, implements and manages test plans.
Process Development Engineer
The Process Development Engineers design, implement, manufacture, mine, and other production systems using technical knowledge and expertise in the industry. They use computer modeling software to test technologies and machinery. An individual who is opting career as Process Development Engineer is responsible for developing cost-effective and efficient processes. They also monitor the production process and ensure it functions smoothly and efficiently.
AWS Solution Architect
An AWS Solution Architect is someone who specializes in developing and implementing cloud computing systems. He or she has a good understanding of the various aspects of cloud computing and can confidently deploy and manage their systems. He or she troubleshoots the issues and evaluates the risk from the third party.
Azure Administrator
An Azure Administrator is a professional responsible for implementing, monitoring, and maintaining Azure Solutions. He or she manages cloud infrastructure service instances and various cloud servers as well as sets up public and private cloud systems.
Computer Programmer
Careers in computer programming primarily refer to the systematic act of writing code and moreover include wider computer science areas. The word 'programmer' or 'coder' has entered into practice with the growing number of newly self-taught tech enthusiasts. Computer programming careers involve the use of designs created by software developers and engineers and transforming them into commands that can be implemented by computers. These commands result in regular usage of social media sites, word-processing applications and browsers.
Information Security Manager
Individuals in the information security manager career path involves in overseeing and controlling all aspects of computer security. The IT security manager job description includes planning and carrying out security measures to protect the business data and information from corruption, theft, unauthorised access, and deliberate attack
ITSM Manager
Automation test engineer.
An Automation Test Engineer job involves executing automated test scripts. He or she identifies the project’s problems and troubleshoots them. The role involves documenting the defect using management tools. He or she works with the application team in order to resolve any issues arising during the testing process.
Applications for Admissions are open.

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

ALLEN NEET Coaching
Ace your NEET preparation with ALLEN Online Programs


SAT® | CollegeBoard
Registeration closing on 19th Apr for SAT® | One Test-Many Universities | 90% discount on registrations fee | Free Practice | Multiple Attempts | no penalty for guessing

TOEFL ® Registrations 2024
Thinking of Studying Abroad? Think the TOEFL® test. Register now & Save 10% on English Proficiency Tests with Gift Cards

PTE Exam 2024 Registrations
Register now for PTE & Save 5% on English Proficiency Tests with Gift Cards
Everything about Education
Latest updates, Exclusive Content, Webinars and more.
Explore on Careers360
- Board Exams
- Top Schools
- Navodaya Vidyalaya
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 6
NCERT Exemplars
- NCERT Exemplar
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 solutions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 10 solutions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Solutions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Solutions
- NCERT Books for class 6
- NCERT Books for class 7
- NCERT Books for class 8
- NCERT Books for class 9
- NCERT Books for Class 10
- NCERT Books for Class 11
- NCERT Books for Class 12
- NCERT Notes for Class 9
- NCERT Notes for Class 10
- NCERT Notes for Class 11
- NCERT Notes for Class 12
- NCERT Syllabus for Class 6
- NCERT Syllabus for Class 7
- NCERT Syllabus for class 8
- NCERT Syllabus for class 9
- NCERT Syllabus for Class 10
- NCERT Syllabus for Class 11
- NCERT Syllabus for Class 12
- CBSE Date Sheet
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Admit Card
- CBSE Result
- CBSE Result Name and State Wise
- CBSE Passing Marks
CBSE Class 10
- CBSE Board Class 10th
- CBSE Class 10 Date Sheet
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
- CBSE 10th Exam Pattern
- CBSE Class 10 Answer Key
- CBSE 10th Admit Card
- CBSE 10th Result
- CBSE 10th Toppers
- CBSE Board Class 12th
- CBSE Class 12 Date Sheet
- CBSE Class 12 Admit Card
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Exam Pattern
- CBSE Class 12 Answer Key
- CBSE 12th Result
- CBSE Class 12 Toppers
CISCE Board 10th
- ICSE 10th time table
- ICSE 10th Syllabus
- ICSE 10th exam pattern
- ICSE 10th Question Papers
- ICSE 10th Result
- ICSE 10th Toppers
- ISC 12th Board
- ISC 12th Time Table
- ISC Syllabus
- ISC 12th Question Papers
- ISC 12th Result
- IMO Syllabus
- IMO Sample Papers
- IMO Answer Key
- IEO Syllabus
- IEO Answer Key
- NSO Syllabus
- NSO Sample Papers
- NSO Answer Key
- NMMS Application form
- NMMS Scholarship
- NMMS Eligibility
- NMMS Exam Pattern
- NMMS Admit Card
- NMMS Question Paper
- NMMS Answer Key
- NMMS Syllabus
- NMMS Result
- NTSE Application Form
- NTSE Eligibility Criteria
- NTSE Exam Pattern
- NTSE Admit Card
- NTSE Syllabus
- NTSE Question Papers
- NTSE Answer Key
- NTSE Cutoff
- NTSE Result
Schools By Medium
- Malayalam Medium Schools in India
- Urdu Medium Schools in India
- Telugu Medium Schools in India
- Karnataka Board PUE Schools in India
- Bengali Medium Schools in India
- Marathi Medium Schools in India
By Ownership
- Central Government Schools in India
- Private Schools in India
- Schools in Delhi
- Schools in Lucknow
- Schools in Kolkata
- Schools in Pune
- Schools in Bangalore
- Schools in Chennai
- Schools in Mumbai
- Schools in Hyderabad
- Schools in Gurgaon
- Schools in Ahmedabad
- Schools in Uttar Pradesh
- Schools in Maharashtra
- Schools in Karnataka
- Schools in Haryana
- Schools in Punjab
- Schools in Andhra Pradesh
- Schools in Madhya Pradesh
- Schools in Rajasthan
- Schools in Tamil Nadu
- NVS Admit Card
- Navodaya Result
- Navodaya Exam Date
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission Class 6
- JNVST admit card for class 6
- JNVST class 6 answer key
- JNVST class 6 Result
- JNVST Class 6 Exam Pattern
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission
- JNVST class 9 exam pattern
- JNVST class 9 answer key
- JNVST class 9 Result
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Cetifications
We Appeared in

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- ML Aggarwal Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- Important Info
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Sample Papers
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes PDF Download
The NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes provides detailed and explained Solutions for all Questions in the textbook. By referring to the Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes answers, students can understand each and every step; accordingly can form their own strategies to solve Questions in a proper and systematic way during further preparations.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes PDF
The NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes PDF prove to be worthy as it provides a lot of Questions to solve; accordingly they can score well. Students can access the Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Questions of Class 6 Maths through the Selfstudys website from their comfort zone. In the process of solving Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Questions, students can build a strong and solid foundation for the chapter.
Where can Students Find the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes?
Students can find the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes from the Selfstudys website; steps to download are clearly explained:
- Visit the Selfstudys website.
- Bring the arrow towards the NCERT Books & Solutions which can be clearly seen in the navigation bar.
- Automatically a drop menu will appear, select NCERT Solutions from the list.
- A new page will appear, select Class 6th from the list of classes.
- Now click Maths from the list of subjects and select Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes from the list of chapters.
Characteristics of NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes PDF
The characteristics of NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes PDF is the distinctive quality which each and every student needs to know; some of the important features are discussed below:
- All the Exercises are Covered: In the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes revision, all the exercises of the textbook are covered so that students can get an idea about how to solve Questions.
- Pictorial Representation is Given: Pictorial representations are often represented as icons, symbols, pictures, etc; these pictorial representations are given in the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes theory.
- Formulas are Included: Formula is a group of signs, letters or numbers that are used to solve Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Questions; these formulas are included in the Class 6 Maths NCERT Solutions.
- All Topics are Covered: In the Class 6 NCERT Maths Solutions, all the topics of Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes are covered so that students can have a deep understanding of the concepts.
- Available in the PDF: Students can easily access the Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Questions from the Class 6 NCERT Solutions as it is available in portable document format.
- Step By Step Approach: The Questions of Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes in the Class 6 Maths NCERT Solutions are solved in a step by step approach so that students can understand each and every step.
How Can NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Help Students?
The NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes can help in several ways; those ways are discussed below:
- Focuses on Fundamental Concepts: The Questions in the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes focuses on fundamental concepts; so by solving and referring to it students can have crystal clear knowledge about the concepts.
- Improves Problem Solving Skills: Problem solving skills helps students determine the source of Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Questions and to find an effective solution; to improve problem solving skills, students can refer to the NCERT Class 6 Maths Solutions.
- Helps in Better Grades: By using the Class 6 Maths NCERT Solutions of Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes, students can develop their understanding of concepts and accordingly they can improve their grades.
- Explained in a Simple Language: The Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Questions of NCERT Class 6 Solutions are explained in a simple language so that students can understand a lot of complex Questions easily.
- Designed According to the Exam Pattern: It is believed that the Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Questions from the NCERT Class 6 Maths Solutions are designed according to the latest exam pattern.
- Saves Time: The Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Questions of Class 6 Maths NCERT Solutions are available ready made which saves most of time; otherwise students would be wasting precious time in searching for answers.
A Comprehensive Guide to Solve Questions from NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes PDF
To solve Questions from the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes PDF in a comprehensive way, students need to follow the given steps; those steps are:
- Read the Question Carefully: Before attempting the Questions from the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes, students need to read the question carefully so that they can understand what is being asked.
- Understand the Concepts: Students should make sure that they need to understand Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes concepts which are related to Questions; then only they can solve Questions from the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes revision.
- Use the Formula or Method: Depending upon the types of Questions in the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes theory, students need to use the required formula and method; through this students can score well.
- Look for Clues in the Questions: Students are advised to look for clues in the Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Questions in the NCERT Class 6 Maths Solutions so that they can conclude the answers.
- Check the Answers: After solving the Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Questions from the NCERT Solutions, students need to check the answers with their own answers then they can get an idea about the mistakes.
- Set Some Goals: To solve Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Questions from the NCERT Class 6 Maths Solutions, students need to set some goals rather than just thinking to complete the Questions.
How to Improve Confidence With the Help of NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes?
To improve confidence during the preparations, students can refer to the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes; some of the scenarios to improve confidence are discussed below:
- Questions are Based on the Textbook: The Questions in the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes revision are based on the textbook. So by solving Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Questions, students can gain confidence and score well in the test.
- Enhances the Basic Knowledge: Once students start solving Questions from the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes theory it can enhance the basic knowledge and improve their confidence; which can be implemented while attempting the final exams.
- Covers the Difficult Topics: It is obvious that the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes PDF covers difficult and complex topics; so by solving these Questions students can have a better understanding of concepts; accordingly they can improve their confidence level.
- Students Will Learn How to Answer Questions: By solving Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Questions from the NCERT Solutions of Class 6 Maths, students can learn to have different and creative approaches; this can help students to improve their confidence level.
- Are Great for Revision: The NCERT Class 6 Maths Solutions of Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes are great for revising all topics and concepts; automatically they can improve their confidence level.
- Provide Accurate Answers: The answers of Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Questions of NCERT Class 6 Maths Solutions are accurate so by referring to it; students can improve their confidence level.
What are the Difficulties Faced While Solving Questions from the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes PDF?
Students may face difficulty while solving Questions from the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes PDF; some of the difficulties are discussed below:
- Lack of Understanding of the Concepts: If in case, students don’t have an understanding for the concepts; then they may face difficulty while solving Questions from the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes.
- Difficulty in Calculations: If students are struggling with basic calculations then they can also face the same difficulty while solving Questions from the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes revision.
- Confusions With the Formulas: If in case students are not familiar with the usage of right formulas and right method, then they can face difficulty in attempting Questions from the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes PDF.
- Misreading of the Question: Students may face difficulty in solving Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Questions from the NCERT Class 6 Maths Solutions if they have misunderstood the question or misinterpreted it.
- Fear of Failure: It is obvious that students may be afraid of making mistakes; for them it may be very difficult in solving Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Questions from the NCERT Class 6 Maths Solutions. This fear can lead to anxiety and stress level, this can be eliminated by completing the Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes concepts in a proper way.
- Lack of Organisation: Students may face difficulty in solving Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Questions from the NCERT Class 6 Maths Solutions if they are not organised in a proper way.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

One Last Step...

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Understanding Elementary Shapes Class 6 Notes CBSE Maths Chapter 5 (Free PDF Download)
- Revision Notes

Revision Notes for CBSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 - Free PDF Download
It is important to have excellent command over the Understanding Elementary Shapes Class 6 Notes as it not merely helps students to learn various important topics given in the chapter but also helps them to revise the chapter effectively before the exam. The experts at Vedantu are strongly engaged in formulating the optimum study material that meets the requirements of the students. We assure you that your doubts related to the topic Understanding Elementary Shapes would be cleared.
Register Online for NCERT Class 6 Science tuition on Vedantu.com to score more marks in CBSE board examination. Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials for students. Maths Students who are looking for the better solutions ,they can download Class 6 Maths NCERT Solutions to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Access Class 6 Mathematics Chapter 5 - Understanding Elementary Shapes Notes in 30 Minutes
Measurement of Line Segment:
A line segment is defined as a segment of a line that is fixed in place. This enables the measurement of a line segment.
The length of a line segment is the distance between its endpoints.
When comparing the lengths of line segments, a graduated ruler and a divider are used. These methods give accurate length distances.
Also, we can compare the two line segments by observation or with the help of trace paper. But, both the methods have very little accuracy and we can’t trace the lengths every time.
Angles – ‘Right’ and ‘Straight’:
An example of an angle is when the hand of a clock shifts from one location to another.
A right angle is used to turn from north to east.
A full turn is made by turning in the same direction by two straight angles (or four right angles).
The angle for one revolution is called a complete angle.
One revolution's angle is a full angle.
A protractor is used to calculate the size of an angle in degrees.
A $\dfrac{1}{4}$ revolution is a right angle, whereas a $\dfrac{1}{2}$ revolution is a straight angle.
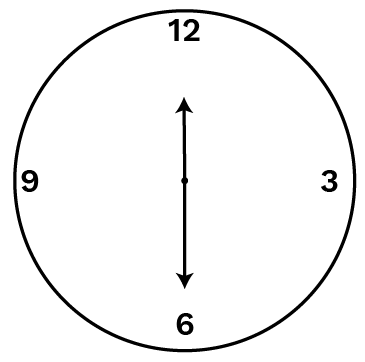
From above,
Clock $1$ represents $\dfrac{1}{2}$ of revolution or $2$ right angles.
Clock $2$ represents $\dfrac{1}{4}$ of revolution or $1$ right angles, and
Clock $3$ represents $\dfrac{3}{4}$ of revolution or $3$ right angles.
A right angle is $\dfrac{1}{4}$ a revolution and a straight angle is $\dfrac{1}{2}$ a revolution.
Protractor is an instrument used to measure the size of an angle in degrees.
The measure of a right angle is ${{90}^{0}}$ and hence that of a straight angle is ${{180}^{0}}$.
An angle is said to be acute if its measure is less than that of a right angle and is said to be obtuse if its measure is more than that of a right angle but is less than a straight angle.
Sea-saw, rooftop, opening book, etc. are examples of an acute angle.
House, desk for book reading, etc. are examples of an obtuse angle.
A reflex angle is larger than a straight angle.
Two intersecting lines are perpendicular if the angle between them is ${{90}^{0}}$.
The perpendicular bisector of a line segment is perpendicular to the line segment that divides it into two equal parts.
Triangles Can Be Classified As Follows Based on Their Angles:
Angles – ‘Acute’, ‘Obtuse’ and ‘Reflex’:
An acute angle is an angle smaller than a right angle.
An obtuse angle is one that is greater than a right angle but smaller than a straight one.
A reflex angle is more than twice as large as a straight angle.
Triangles can be classified as follows based on the lengths of their sides:
Polygons are named based on their sides:
Quadrilaterals are further classified with reference to their properties:
Faces, Edges, and vertices:
We see around us many three-dimensional shapes. Cubes, cuboids, spheres,
Cylinders, cones, prisms, and pyramids are some of them.
Each side of the cube is a flat surface called a flat face (or simply a face).
Two faces meet at a line segment called an edge.
Three edges meet at a point called a vertex.
The triangular prism has a triangular base, whereas the rectangular prism has a rectangular base.
Understanding Elementary Shapes Notes - Free Download
Our experts at Vedantu had put an extensive effort to formulate Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 notes in a short and precise manner. The students can effectively use the Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Notes to have a quick revision of the topic just before the examination.
It is mandatory to study all the important concepts related to different geometrical figures given in Understanding Elementary Shapes Class 6 Notes in order to score better marks in the exam and to have a thorough understanding of the important topics given in the chapter. As the chapter is so vast, we have segregated the chapter in different sections. A detailed explanation of every topic is provided in our Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 notes. These detailed explanations will help students solve every question given in different exercise productions.
Students can make use of Understanding Elementary Shapes notes and gain the necessary information to prepare the complete chapter in a better way. Instead of studying the last minutes, all students need to do is to refer to Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 notes, as they are very precise and all the important concepts are explained extremely well. With this, students will surely be able to answer all the Understanding Elementary Shapes questions that may come up in the examination.
Rather than cramming the last minute for their examination and getting useless stress, the Understanding Elementary Shapes notes can be used in a smart way to gain the best out of it for the exam. Students can also evaluate their strengths and weaknesses and prepare the chapter accordingly to score maximum marks in the exam. The Understanding Elementary Shapes notes are available free of cost. Students can download Understanding Elementary Shapes notes in a PDF format just with a single click on the PDF link given below.
Understanding Elementary Shapes Introduction
We can see many different shapes around us that are drawn using curves or lines. We can see open curves, close curves, edges, corners in our surroundings. We use them to form angles, circles, triangles, line segments, and polygons of different sizes and measurements. In this chapter, we will learn how geometrical shapes such as triangles, circles, polygons, etc of different sizes and measurements are constructed using a ruler or divider.
The chapter Understanding Elementary Shapes is divided into 10 sections and 9 exercises.
The first section is the basic introduction to Understanding elementary shapes having examples from the surroundings that are formed using curves or lines.
The second section introduces the methods of comparing two or more than two line segments of different lengths.
The third section introduces the concept of right angle and straight angles by directions.
The fourth section introduces different angles such as acute angle, obtuse angle, right angle, straight angle, and reflex angle.
The fifth section discusses how to measure different angles using the protractor and ruler.
The sixth section discusses perpendicular lines and their constructions.
This seventh section introduces different types of a triangle like a scalene triangle, an equilateral triangle, an isosceles triangle, an acute angle triangle, an obtuse angle triangle, and a right-angled triangle.
The eight sections introduce different types of quadrilaterals such as rectangle, square, parallelogram, rhombus, and trapezium.
The ninth section introduces a classification of polygons on the basis of their sizes and vertices.
The tenth section introduces three-dimensional shapes such as cone, cube, cylinder, pyramid, and sphere. This section also discusses the number of faces, edges, and vertices in different three-dimensional shapes.
Benefits of Understanding Elementary Shapes Notes by Vedantu
Understanding Elementary Shapes Class 6 Notes have been prepared in accordance with the latest academic year syllabus so that students don't find any confusion if any changes have been made by the CBSE board.
Prepared by the teachers who have extensive experience and know what exactly is required to mention.
The students will be able to observe short keynotes of the chapter that will boost their exam preparation.
Available in a free downloadable PDF format so that students can easily refer to it when required.
Vedantu made an effort to facilitate the students with the perfect Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 notes which definitely assure them to get better marks.
Conclusion
Vedantu's free PDF notes on CBSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 , "Understanding Elementary Shapes," are a valuable educational resource for young learners. These notes offer a comprehensive understanding of basic geometric concepts, ensuring that students have access to high-quality study materials that align with the CBSE curriculum. Vedantu's commitment to providing accessible educational content empowers students to delve into the world of shapes and geometry. These notes facilitate a deeper comprehension of elementary shapes, fostering essential mathematical skills and spatial reasoning abilities. By utilising these resources, students can enhance their mathematical knowledge, critical thinking skills, and overall academic performance, making them an indispensable asset for maths enthusiasts and educators alike.

FAQs on Understanding Elementary Shapes Class 6 Notes CBSE Maths Chapter 5 (Free PDF Download)
Q1. What do you understand about elementary shapes ?
The Chapter of Class 6 Maths which is The Elementary Shapes very important as they will be introduced to lines, angles and triangles. They will learn the types and the properties of the elementary shapes. The students will learn about a straight line which is starting from a point and will end at a fixed point. The formation of angles is by joining two line segments and the measure of angle by protractor. These are the basic geometry and the students have to learn with full attention.
Q2. What are the basic geometrical ideas?
Geometry is the study of the various shapes and their positions and measurement of the same. The basic geometrical ideas give an idea of the basic terms used. Some of them are;
The point gives a definite location that cannot be moved.
The line is a collection of points.
A ray is a line that has a fixed point and can be indefinitely extended from the other direction.
A part of a line that has a definite length is called a line segment.
A plane is a surface of any solid that can be flat or even curved.
Collinear and non-collinear points If three or more points lie in the same line is collinear and if three or more points do not lie in the same line are non-collinear points.
The curve is a continuous line without any sharp edges.
Polygons are made of the line segments which are connected.
Angles are formed by the joining of the two rays at a point.
A triangle is a closed plane surface with three lines segments.
Q3. What is an angle?
An angle is formed by two different rays which are joined at the point. If you are taking two rays namely AB and BC and if they are made to join at the vertex B then the angle formed can be named angle ABC. The middle letter will represent an angle. Students in Class 6 Maths will be learning different types of angles and their construction. The details of the chapter can be well captured in Vedantu from NCERT solutions. The explanations are given in easy steps and comprehensively structured.
Q4. Why should we not compare line segments by mere observation?
The two-line segments cannot be compared by mere observation. Sometimes it might be seen as the two are of the same length but even a slight difference will make a difference in the value and the numerical might go wrong. The mathematical calculation should be accurate and there is no guesswork. Especially when you are working on a geometrical topic you should be sure that your pencils are sharp so your value is perfect.
These solutions are available on Vedantu's official website( vedantu.com ) and mobile app free of cost.
Q5. What are the properties of parallelogram and rectangle?
The main properties of a parallelogram are that;
Opposite sides are parallel and equal to each other, opposite angles are equal, diagonals bisect each other if one angle is 90 degrees then all the other angles will be 90.
A parallelogram is divided by the diagonal into two congruent triangles.
Rectangle has all angles as the right angle.
Opposite sides are equal.
Diagonals are equal and bisect each other.
Every rectangle has at least one right angle and it is a parallelogram.
Students should be thorough with these properties and the differences. They should develop conceptual knowledge from the start of the chapters.
NCERT Solutions
Cbse links for class 6.
RS Aggarwal Solutions for Class 6 Math Chapter 5 - Understanding Elementary Shapes
- RS Aggarwal Solutions
- Understanding Elementary Shapes
RS Aggarwal Solutions for Class 6 Math Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes are provided here with simple step-by-step explanations. These solutions for Understanding Elementary Shapes are extremely popular among class 6 students for Math Understanding Elementary Shapes Solutions come handy for quickly completing your homework and preparing for exams. All questions and answers from the RS Aggarwal Book of class 6 Math Chapter 5 are provided here for you for free. You will also love the ad-free experience on Meritnation’s RS Aggarwal Solutions. All RS Aggarwal Solutions for class 6 Math are prepared by experts and are 100% accurate.
Page No 88:
Question 1:.
What is the disadvantage in comparing line segments by mere observation?
By mere observation, we cannot be absolutely sure about the judgement. When we compare two line segments of almost same lengths, we cannot be sure about the line segment of greater length. Therefore, it is not an appropriate method to compare line segments having a slight difference between their lengths. This is the disadvantage in comparing line segments by mere observation.
Question 2:
Why is it better to use a divider than a ruler, while measuring the length of a line segment?
It is better to use a divider than a ruler because while using a ruler, positioning error may occur due to the incorrect positioning of the eye.
Question 3:
[Note: If A, B, C are any three points on a line such that AC + CB = AB, then we can be sure that C lies between A and B]
For example,
Hence, relation AB = AC + CB is verified.
Page No 89:
Question 4:.
If A, B, C are three points on a line such that AB = 5 cm, BC = 3 cm and AC = 8 cm, which one of them lies between the other two?
Given that,
It can be observed that AC = AB + BC
Clearly, point B is lying between A and C.
Question 5:
From the given figure, it can be observed that
Clearly, D is the mid-point of AG.
Question 6:
Since B is the mid-point of AC,
AB = BC (1)
Since C is the mid-point of BD,
BC = CD (2)
From equation (1) and (2), we may find that
Page No 91:
What fraction of a clock wise revolution does the hour hand of a clock turn through when it goes from
(a) 3 to 9 (b) 4 to 7 (c) 7 to 10
(d) 12 to 9 (e) 1 to 10 (f) 6 to 3
We may observe that in 1 complete clockwise revolution, the hour hand will
rotate by 360º.
(a) When the hour hand goes from 3 to 9 clockwise, it will rotate by 2 right angles or 180º.
(b) When the hour hand goes from 4 to 7 clockwise, it will rotate by 1 right angle or 90º.
(c) When the hour hand goes from 7 to 10 clockwise, it will rotate by 1 right angle or 90º.
(d) When the hour hand goes from 12 to 9 clockwise, it will rotate by 3 right angles or 270º.
(e) When the hour hand goes from 1 to 10 clockwise, it will rotate by 3 right angles or 270º.
(f) When the hour hand goes from 6 to 3 clockwise, it will rotate by 3 right angles or 270º.
Video Solution for Understanding Elementary Shapes (Page: 91 , Q.No.: 1)
NCERT Solution for Class 6 math - Understanding Elementary Shapes 91 , Question 1
Where will the hand of a clock stop if it
In 1 complete clockwise revolution, the hand of a clock will rotate by 360º.
Video Solution for Understanding Elementary Shapes (Page: 91 , Q.No.: 2)
NCERT Solution for Class 6 math - Understanding Elementary Shapes 91 , Question 2
Which direction will you face if you start facing
(d) South and make one full revolution?
(Should we specify clockwise or anti-clockwise for this last question? Why not? )
(d) If we start facing South and make a full revolution, then we will again
face the South direction.
In case of revolving by 1 complete round, the direction in which we are revolving does not matter. In both cases, clockwise or anti-clockwise, we will be back at our initial position.
Video Solution for Understanding Elementary Shapes (Page: 91 , Q.No.: 3)
NCERT Solution for Class 6 math - Understanding Elementary Shapes 91 , Question 3
What part of a revolution have you turned through if you stand facing
(a) East and turn clock wise to face north?
(b) South and turn clockwise to face east?
(c) West and turn clockwise to face east?
Video Solution for Understanding Elementary Shapes (Page: 91 , Q.No.: 4)
NCERT Solution for Class 6 math - Understanding Elementary Shapes 91 , Question 4
Find the number of right angles turned through by the hour hand of a clock when it goes from
(a) 3 to 6 (b) 2 to 8 (c) 5 to 11
(d) 10 to 1 (e) 12 to 9 (f) 12 to 6
The hour hand of a clock revolves by 360º or 4 right angles in 1 complete round.
(a) The hour hand of a clock revolves by 90º or 1 right angle when it goes from 3 to 6.
(b) The hour hand of a clock revolves by 180º or 2 right angles when it goes from 2 to 8.
(c) The hour hand of a clock revolves by 180º or 2 right angles when it goes from 5 to 11.
(d) The hour hand of a clock revolves by 90º or 1 right angle when it goes from 10 to 1.
(e) The hour hand of a clock revolves by 270º or 3 right angles when it goes from 12 to 9.
(f) The hour hand of a clock revolves by 180º or 2 right angles when it goes from 12 to 6.
Video Solution for Understanding Elementary Shapes (Page: 91 , Q.No.: 5)
NCERT Solution for Class 6 math - Understanding Elementary Shapes 91 , Question 5
Page No 92:
How many right angles do you make if you start facing
(a) South and turn clockwise to west?
(b) North and turn anti-clockwise to east?
(c) West and turn to west?
(d) South and turn to north?
If we revolve one complete round in either clockwise or anti-clockwise direction, then we will revolve by 360º or 4 right angles and the two adjacent directions will be at 90º or 1 right angle away from each other.
(a) If we start facing South and turn clockwise to West, then we make 1 right angle.
(b) If we start facing North and turn anti-clockwise to East, then we make 3 right angles.
(c) If we start facing West and turn to West, then we make 1 complete round or 4 right angles.
(d) If we start facing South and turn to North, then we make 2 right angles.
Question 7:
Q7. Where will the hour hand of a clock stop if it starts
(a) From 6 and turns through 1 right angle?
(b) From 8 and turns through 2 right angles?
(c) From 10 and turns through 3 right angles?
(d) From 7 and turns through 2 straight angles?
In 1 complete revolution (clockwise or anti-clockwise), the hour hand of a clock will rotate by 360º or 4 right angles.
If the hour hand of a clock starts from 6 and turns through 1 right angle, then it will stop at 9.
If the hour hand of a clock starts from 8 and turns through 2 right angles, then it will stop at 2.
If the hour hand of a clock starts from 10 and turns through 3 right angles, then it will stop at 7.
If the hour hand of a clock starts from 7 and turns through 2 straight angles, then it will stop at 7.
Page No 94:
Match the following:
(i) Straight angle (a) Less than one-fourth of a revolution
(ii) Right angle (b) More than half a revolution
(iii) Acute angle (c) Half of a revolution
(iv) Obtuse angle (d) One-fourth of a revolution
(f) One complete revolution
(i) Straight angle is of 180º and half of a revolution is 180º.
Hence, (i) ↔ (c)
(ii) Right angle is of 90º and one-fourth of a revolution is 90º.
Hence, (ii) ↔ (d)
(iii) Acute angles are the angles less than 90º. Also, less than one-fourth of a revolution is the angle less than 90º.
Hence, (iii) ↔ (a)
Hence, (iv) ↔ (e)
(v) Reflex angles are the angles greater than 180º but less than 360º. Also, more than half a revolution is the angle whose measure is greater than 180º.
Hence, (v) ↔ (b)
Page No 95:
Classify each one of the following angles as right, straight, acute, obtuse or reflex:
(a) Acute angle as its measure is less than 90º.
(b) Obtuse angle as its measure is more than 90º but less than 180º.
(c) Right angle as its measure is 90º.
(d) Reflex angle as its measure is more than 180º but less than 360º.
(e) Straight angle as its measure is 180º.
(f) Acute angle as its measure is less than 90º.
Page No 97:
What is the measure of (i) a right angle? (ii) a straight angle?
(i) The measure of a right angle is 90°.
(ii) The measure of a straight angle is 180°.
Say True or False:
(a) The measure of an acute angle < 90°
(b) The measure of an obtuse angle < 90°
(c) The measure of a reflex angle > 180°
(d) The measure of one complete revolution = 360°
(e) If m∠A = 53° and m∠B = 35°, then m∠A > m∠B.
The measure of an acute angle is less than 90°.
The measure of an obtuse angle is greater than 90º but less than 180º.
The measure of a reflex angle is greater than 180°.
The measure of one complete revolution is 360º.
Write down the measures of
(a) Some acute angles. (b) Some obtuse angles.
(Give at least two examples of each).
(a) 45°, 70°
(b) 105°, 132°
Measure the angles given below using the Protractor and write down the measure.
(a) 45º
(b) 120º
(c) 90º
(d) 60º, 90º, and 130º
Page No 98:
Which angle has a large measure? First estimate and then measure.
Measure of angle A =
Measure of angle B =
Measure of angle A = 40º
Measure of angle B = 68º
∠B has the greater measure than ∠A.
From these two angles which has larger measure? Estimate and then confirm by measuring them.
The measures of these angles are 45º and 55º. Therefore, the angle shown in 2 nd figure is greater.
Fill in the blanks with acute, obtuse, right or straight:
(a) An angle whose measure is less than that of a right angle is _______.
(b) An angle whose measure is greater than that of a right angle is _______.
(c) An angle whose measure is the sum of the measures of two right angles is _______.
(d) When the sum of the measures of two angles is that of a right angle, then each one of them is _______.
(e) When the sum of the measures of two angles is that of a straight angle, and if one of them is acute then the other should be _______.
(a) Acute angle
(b) Obtuse angle (if the angle is less than 180º)
(c) Straight angle
(d) Acute angle
(e) Obtuse angle
Question 8:
Find the measure of the angle shown in each figure. (First estimate with your eyes and then find the actual measure with a protractor).
The measures of the angles shown in the above figure are 40º, 130º, 65º, 135º respectively.
Question 9:
Find the angle measure between the hands of the clock in each figure:
(a) 90°
(b) 30°
(c) 180°
Page No 99:
Question 10:.
Investigate
In the given figure, the angle measures 30°. Look at the same figure through a magnifying glass. Does the angle become larger? Does the size of the angle change?
The measure of this angle will not change.
Question 11:
Measure and classify each angle:
Page No 100:
Which of the following are models for perpendicular lines:
(a) The adjacent edges of a table top.
(b) The lines of a railway track.
(c) The line segments forming the letter ’L’
(d) The letter V.
(a) The adjacent edges of a table top are perpendicular to each other.
(b) The lines of a railway track are parallel to each other.
(c) The line segments forming the letter ’L’ are perpendicular to each other.
(d) The sides of letter V are inclined at some acute angle on each other.
Hence, (a) and (c) are the models for perpendicular lines.
From the figure, it can be easily observed that the measure of ∠PAY is 90°.
There are two set-squares in your box. What are the measures of the angles that are formed at their corners? Do they have any angle measure that is common?
One has a measure of 90°, 45°, 45°.
Other has a measure of 90°, 30°, 60°.
Therefore, the angle of 90° measure is common between them.
Study the diagram. The line l is perpendicular to line m .
(a) Is CE = EG?
(b) Does PE bisect CG?
(c) Identify any two line segments for which PE is the perpendicular bisector.
(d) Are these true?
(i) AC > FG.
(ii) CD = GH.
(iii) BC < EH.
(a) Yes. As CE = EG = 2 units
(b) Yes. PE bisects CG since CE = EG.
(d) (i) True. As length of AC and FG are of 2 units and 1 unit respectively.
(ii) True. As both have 1 unit length.
(iii) True. As the length of BC and EH are of 1 unit and 3 units respectively.
Page No 103:
Name the types of following triangles:
(a) Triangle with lengths of sides 7 cm, 8 cm and 9 cm.
(b) ΔABC with AB = 8.7 cm, AC = 7 cm and BC = 6 cm.
(c) ΔPQR such that PQ = QR = PR = 5 cm.
(d) ΔDEF with m∠D = 90°
(e) ΔXYZ with m∠Y = 90° and XY = YZ.
(f) ΔLMN with m∠L = 30°, m∠M = 70° and m∠N = 80°
(a) Scalene triangle
(b) Scalene triangle
(c) Equilateral triangle
(d) Right-angled triangle
(e) Right-angled isosceles triangle
(f) Acute-angled triangle
(i) Equilateral (e)
(ii) Isosceles (g)
(iii) Scalene (a)
(iv) Acute-angled (f)
(v) Right-angled (d)
(vi) Obtuse-angled (c)
(vii) Isosceles right-angled (b)
Name each of the following triangles in two different ways: (you may judge the nature of the angle by observation)
(a) Acute-angled and isosceles
(b) Right-angled and scalene
(c) Obtuse-angled and isosceles
(d) Right-angled and isosceles
(e) Acute-angled and equilateral
(f) Obtuse-angled and scalene
Page No 104:
Try to construct triangles using match sticks. Some are shown here. Can you make a triangle with
(a) 3 matchsticks?
(b) 4 matchsticks?
(c) 5 matchsticks?
(d)6 matchsticks?
(Remember you have to use all the available matchsticks in each case)
Name the type of triangle in each case. If you cannot make a triangle, think of reasons for it.
(a) By using 3 matchsticks, we can form a triangle as
(b) By using 4 matchsticks, we cannot form a triangle. This is because the sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is always greater than the length of the remaining side of the triangle.
(c) By using 5 matchsticks, we can form a triangle as
(d) By using 6 matchsticks, we can form a triangle as
Page No 106:
Say True of False:
(a) Each angle of a rectangle is a right angle.
(b) The opposite sides of a rectangle are equal in length.
(c) The diagonals of a square are perpendicular to one another.
(d) All the sides of a rhombus are of equal length.
(e) All the sides of a parallelogram are of equal length.
(f) The opposite sides of a trapezium are parallel.
Give reasons for the following:
(a) A square can be thought of as a special rectangle.
(b) A rectangle can be thought of as a special parallelogram.
(c) A square can be thought of as a special rhombus.
(d) Squares, rectangles, parallelograms are all quadrilaterals.
(e) Square is also a parallelogram.
(a) In a rectangle, all the interior angles are of the same measure, i.e., 90º and only the opposite sides of the rectangle are of the same length whereas in case of a square, all the interior angles are of 90° and all the sides are of the same length. In other words, a rectangle with all sides equal becomes a square. Therefore, a square is a special rectangle.
(b) Opposite sides of a parallelogram are parallel and equal. In a rectangle, the opposite sides are parallel and equal. Also, all the interior angles of the rectangle are of the same measure, i.e., 90º. In other words, a parallelogram with each angle a right angle becomes a rectangle. Therefore, a rectangle can be thought of as a special parallelogram.
(c) All sides of a rhombus and a square are equal. However, in case of a square, all interior angles are of 90º measure. A rhombus with each angle a right angle becomes a square. Therefore, a square can be thought of as a special rhombus.
(d) All are closed figures made of 4 line segments. Therefore, all these are quadrilaterals.
(e) Opposite sides of a parallelogram are parallel and equal. In a square, the opposite sides are parallel and the lengths of all the four sides are equal. Therefore, a square can be thought of as a special parallelogram.
A figure is said to be regular if its sides are equal in length and angles are equal in measure. Can you identify the regular quadrilateral?
In a square, all the interior angles are of 90° and all the sides are of the same length. Therefore, a square is a regular quadrilateral.
Page No 108:
Examine whether the following are polygons. If any one among them is not, say why?
(a) It is not a polygon as it is not a closed figure.
(b) Yes, it is a polygon made of 6 sides.
(c) No, it is not made of line segments.
(d) No, it is not made of only line segments.
Name each polygon.
Make two more examples of each of these.
(a) The given figure is a quadrilateral as this closed figure is made of 4
line segments. Two more examples are
(b) The given figure is a triangle as this closed figure is made of 3 line segments. Two more examples are
(c) The given figure is a pentagon as this closed figure is made of 5 line segments. Two more examples are
(d) The given figure is an octagon as this closed figure is made of 8 line segments. Two more examples are
Draw a rough sketch of a regular hexagon. Connecting any three of its vertices, draw a triangle. Identify the type of the triangle you have drawn.
An isosceles triangle by joining three of the vertices of a hexagon can be drawn as follows.
Draw a rough sketch of a regular octagon. (Use squared paper if you wish). Draw a rectangle by joining exactly four of the vertices of the octagon.
A diagonal is a line segment that joins any two vertices of the polygon and is not a side of the polygon. Draw a rough sketch of a pentagon and draw its diagonals.
It can be observed here that AC, AD, BD, BE, CE are the diagonals.
Page No 111:
Give two new examples of each shape.
What shape is
(a) Your instrument box? (b) A brick?
(c) A match box? (d) A road-roller?
(e) A sweet laddu?
(d) Cylinder
View NCERT Solutions for all chapters of Class 6

NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes

Here you will find NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes so that students may learn more efficiently. Students can download these resources in PDF format to practice offline. For practically all subjects, INFINITY Learn’s provides online learning materials such as notes, question papers, sample problems, and other materials that students can use as worksheets to prepare for exams. Students can use these NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes to help them prepare for their exams. Students will gain a better grasp of how to tackle different types of questions by practicing these NCERT Class 6 Chapter 5 solved problems.
Fill Out the Form for Expert Academic Guidance!
Please indicate your interest Live Classes Books Test Series Self Learning
Verify OTP Code (required)
I agree to the terms and conditions and privacy policy .
Fill complete details
Target Exam ---
Download PDF for Free. Study without Internet (Offline)
Grade --- Class 1 Class 2 Class 3 Class 4 Class 5 Class 6 Class 7 Class 8 Class 9 Class 10 Class 11 Class 12
Target Exam JEE NEET CBSE
Preferred time slot for the call --- 9 am 10 am 11 am 12 pm 1 pm 2 pm 3 pm 4 pm 5 pm 6 pm 7 pm 8pm 9 pm 10pm
Language --- English Hindi Marathi Tamil Telugu Malayalam
Are you a Sri Chaitanya student? No Yes
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 – Understanding Elementary Shapes
Different shapes that occur in the world around us have been discussed in Chapter 5 of Class 6 Mathematics. It is critical for pupils to have a firm grasp of various geometrical shapes, and this answer aids them in this endeavor.
This chapter contains ten themes, each of which addresses a different concept. It starts with the measurement of various line segments and progresses to more advanced ideas of angles and geometrical shapes.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 is an important study resource for class six students. It provides a thorough yet simple explanation of this fundamental mathematical idea. It aids pupils in swiftly grasping concepts and improving their exam preparation.
NCERT Solution for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Topic-Wise Discussion
Following are the subtopics discussed in this chapter:
- Introduction
The chapter starts with an overview of various geometric shapes and how they are formed using various lines. It discusses how shapes use straight, curved, and other types of lines. With real-life examples, this chapter gives for a more in-depth understanding of Elementary shapes Class 6.
- Measuring Line Segment
A line segment is a section of a line that can be drawn in any direction. Students will learn how to measure various sorts of lines as well as the instruments required for the work in this chapter. In this chapter of NCERT Class 6 Maths Chapter 5, kids will also learn how to compare between distinct line segments.
- Right and Straight Angles
The next sub-topic in this NCERT Maths Book Class 6 Chapter 5 solutions discusses angles, which is an important subject in geometry. Students learn about two important angles in this section: right-angle and straight-angle.
90 degrees is a right angle, and 180 degrees is a straight angle. To help pupils understand this concept, there are several examples of directions and the position of clock hands.
- Acute, Obtuse, and Reflex Angles
There are three basic classes of angles, in addition to right-angle and straight-angle.
- An acute angle is a smaller angle than a straight angle.
- An obtuse angle is a type of angle that is greater than a right angle but less than a straight angle.
- The reflex angle is greater than a straight angle.
The fourth section of NCERT Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 delves into these three perspectives in depth. Real-life examples are used to make these concepts more relevant to students.
- Measuring Angles
Angle measurement is discussed extensively in Class 6 Understanding Elementary Shapes. Students will learn how to accurately measure various angles in this subject. They’ll learn how to use a protractor and how it can help them measure angles accurately.
- Perpendicular Lines
Perpendicular lines are formed when two parallel lines intersect at a right angle. This concept is covered in full in the next chapter of Elementary Shapes Class 6.
- Classification of Triangles
Candidates will learn about various triangles in-depth in this sub-topic of NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5. Students will learn how to name triangles based on their sides and the degree of their angles, in addition to their qualities.
This section introduces several sorts of triangles, such as scalene, isosceles, and equilateral triangles, which are named after the sides of a triangle. Students will also learn about the different names for triangles based on their angle size, such as right-angle triangle, obtuse-angled triangle, acute-angle triangle, and so on.
- Quadrilaterals
A polygon with four sides is known as a quadrilateral. However, there is more to it, as students will discover in this Class 6th Maths Chapter 5 lesson. Set-squares can be used to create a variety of quadrilaterals by students.
The following lesson of Class 6 Maths Understanding Elementary Shapes expands on the concept of a polygon. A polygon with three or four sides is called a triangle or a quadrilateral. Students will encounter different polygon types such as pentagon, hexagon, and octagon during this topic. This chapter also includes a few real-life examples of polygon representations to help students comprehend.
- Three-Dimensional Shapes
Finally, Chapter 5 of CBSE Class 6 Maths offers a discussion of 3-D shapes. Students have already learned about 2-D shapes, but they will now progress to more sophisticated concepts. These three-dimensional shapes can be found all around us, and using them as an example makes it easier for pupils to understand such complex issues.
It also goes through the number of edges, faces, and vertices that 3-D figures have in detail.
Following are the Exercises covered in this Chapter:
EXERCISE 5.1 – 7 Questions with Solutions
EXERCISE 5.2 – 7 Questions with Solutions
EXERCISE 5.3 – 2 Questions with Solutions
EXERCISE 5.4 – 11 Questions with Solutions
EXERCISE 5.5 – 4 Questions with Solutions
EXERCISE 5.6 – 4 Questions with Solutions
EXERCISE 5.7 – 3 Questions with Solutions
EXERCISE 5.8 – 5 Questions with Solutions
EXERCISE 5.9 – 2 Questions with Solutions.
Key Features:
Students may learn a lot from NCERT Solutions on INFINITY Learn’s official website. It’s similar to an assorted back with a wide range of requirements. The following are some of the advantages of NCERT solutions:
- The explanation will be simple to grasp and tailored to the student’s level.
- It includes a test purpose and enough unresolved problems to become proficient in that subject for each chapter.
- The pupils will profit from the free PDF in a variety of ways, and parents will no longer have to worry about the cost.
- Students’ doubts can be cleared by participating in a live session on the official website.
- Define angles and their types as given in Chapter 5 of the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths?
- Explain the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths topic of solid shapes.
- Is INFINITY Learn the most dependable solution in NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5?
1. Define angles and their types as given in Chapter 5 of the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths?
Any two rays with the same endpoint or starting point make up an angle. The movement of clock hands can help you understand it better. When the hand of a clock moves, it creates an angle. A protractor is used to measure the angle. It’s worth noting that a right angle is 90 degrees and a straight angle is 180 degrees.
An angle can be categorized into three sorts based on its degree:
- Acute angle: An acute angle is defined as a measurement of an angle that is less than a right angle.
- Obtuse angle: An obtuse angle is one that is larger than a right angle but smaller than a straight one.
- Reflex angle: A reflex angle is defined as an angle that is larger than a straight angle.
2. Explain the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths topic of solid shapes.
A solid shape, also known as a three-dimensional shape (3D shape), is an item that can be measured in three dimensions: length, width, and height. Cylinder, cube, cuboid, sphere, and other 3D shapes are examples.
3. Is INFINITY Learn the most dependable solution in NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5?
INFINITY Learn has the most accurate and dependable NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 accessible. Students can quickly download and view the solutions, which are available in PDF format, during their exam preparation. The solutions are framed and prepared by a group of experienced academics with years of experience in the various areas. The most in-depth solutions to the exercise-by-exercise difficulties have been compiled with the goal of assisting students in acing the exam without worry.
Related content
Talk to our academic expert!
Get access to free Mock Test and Master Class
Register to Get Free Mock Test and Study Material
Offer Ends in 5:00
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes are provided below. Our solutions covered each questions of the chapter and explains every concept with a clarified explanation. It helps the students to understand slowly and to get practice well to become perfect and again a good score in their examination.
These materials are prepared based on Class 6 NCERT syllabus, taking the types of questions asked in the NCERT textbook into consideration. Further, all the CBSE Class 6 Solutions Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes are in accordance with the latest CBSE guidelines and marking schemes
Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Exercise 5.1 Solutions

Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Exercise 5.2 Solutions
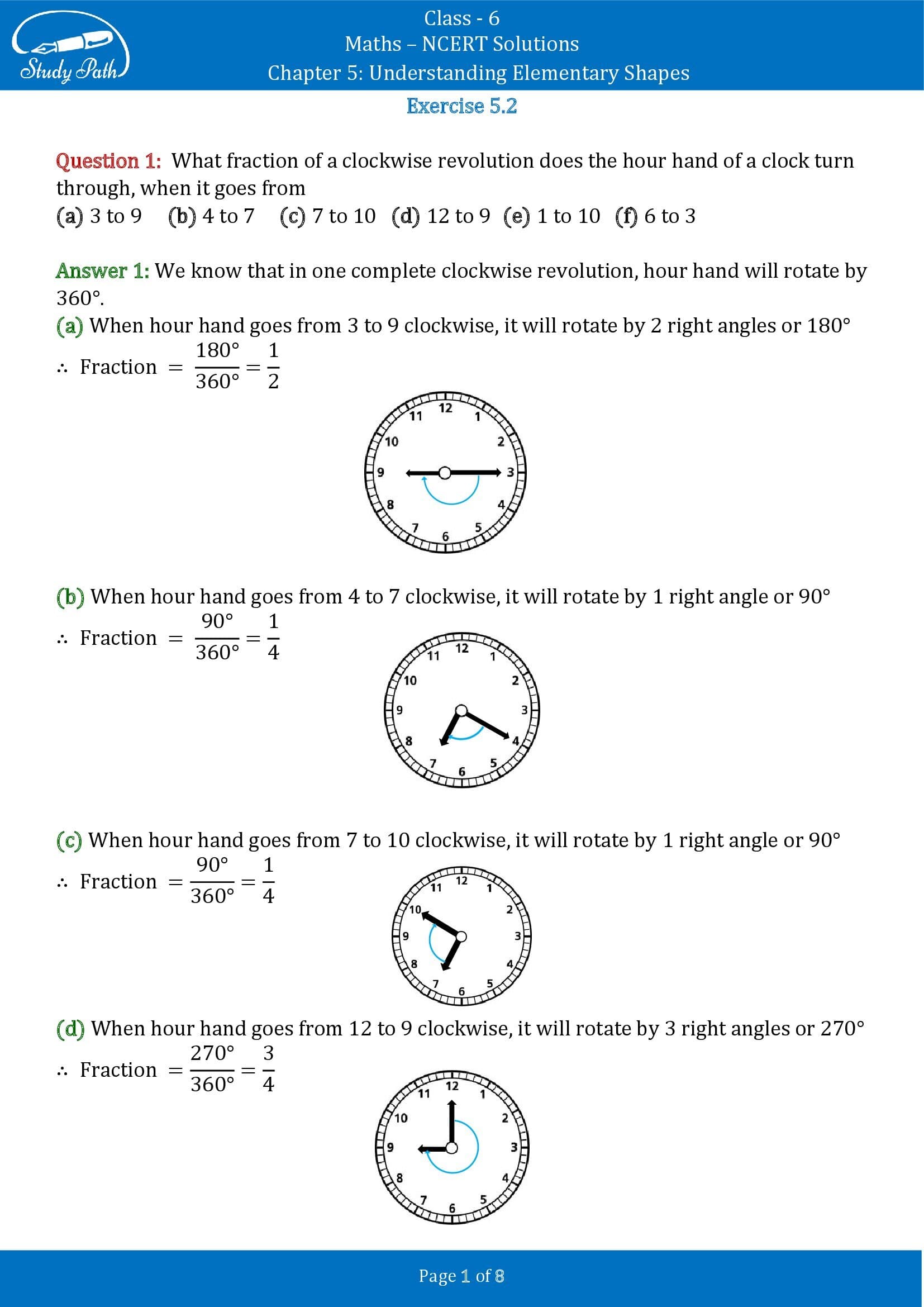
Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Exercise 5.3 Solutions

Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Exercise 5.4 Solutions

Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Exercise 5.5 Solutions

Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Exercise 5.6 Solutions

Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Exercise 5.7 Solutions

Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Exercise 5.8 Solutions
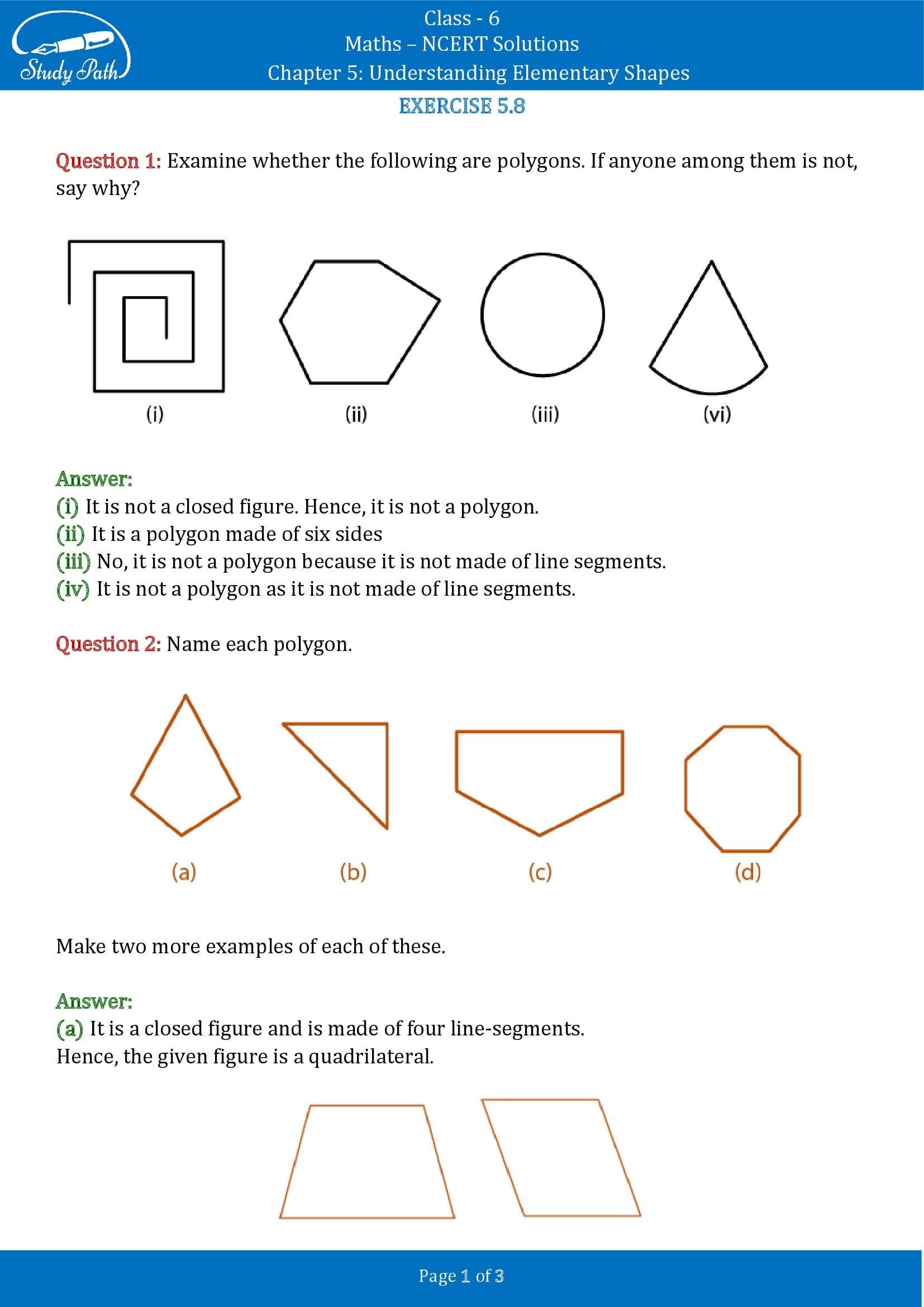
Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Exercise 5.9 Solutions
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes

- Exercise 5.1 Chapter 5 Class 6 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Exercise 5.2 Chapter 5 Class 6 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Exercise 5.3 Chapter 5 Class 6 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Exercise 5.4 Chapter 5 Class 6 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Exercise 5.5 Chapter 5 Class 6 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Exercise 5.6 Chapter 5 Class 6 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Exercise 5.7 Chapter 5 Class 6 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Exercise 5.8 Chapter 5 Class 6 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Exercise 5.9 Chapter 5 Class 6 Maths NCERT Solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapters:
How many exercises in chapter 5 understanding elementary shapes, what is a rhombus, what is perpendicular bisector of the line segment, what do you mean by parallelogram, contact form.
- School Solutions
- Star Program
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Statistics
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Hindi
- NCERT Books Class 12
- NCERT Books Class 11
- NCERT Books Class 10
- NCERT Books Class 9
- NCERT Books Class 8
- NCERT Books Class 7
- NCERT Books Class 6
- NCERT Books Class 5
- NCERT Books Class 4
- NCERT Books Class 3
- NCERT Books Class 2
- NCERT Books Class 1
- Important Questions Class 12
- Important Questions Class 11
- Important Questions Class 10
- Important Questions Class 9
- Important Questions Class 8
- Important Questions Class 7
- important questions class 6
- CBSE Class 12 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 8 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 6 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 11 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 9 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 8 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 7 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 6 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 5 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 4 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 3 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 2 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 1 Syllabus
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 5
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 4
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 3
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 2
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 1
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Science
- NEET 2021 Question Paper
- NEET 2020 Question Paper
- NEET 2019 Question Paper
- NEET 2018 Question Paper
- NEET 2017 Question Paper
- NEET 2016 Question Paper
- NEET 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Physics Questions
- NEET Chemistry Questions
- NEET Biology Questions
- NEET Sample Papers
- NEET Physics Syllabus
- NEET Chemistry Syllabus
- NEET Biology Syllabus
- NEET Mock Test
- NEET Eligibility Criteria
- JEE Main 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Main Sample Papers
- JEE Main Physics Syllabus
- JEE Main Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Main Maths Syllabus
- JEE Main Physics Questions
- JEE Main Chemistry Questions
- JEE Main Maths Questions
- JEE main revision notes
- JEE Main Mock Test
- JEE Advanced Physics Questions
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Questions
- JEE Advanced Maths Questions
- JEE Advanced 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced Physics Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Maths Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Mock Test
- ISC Class 12 Syllabus
- ISC Class 11 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 10 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 9 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 8 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 7 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 6 Syllabus
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 6
- ICSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- ICSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- ISC Important Questions for Class 12
- ISC Important Questions for Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 6
- ISC Class 12 Question Paper
- ICSE Class 10 Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Syllabus
- Maharashtra Board Sample Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Previous Year Question Paper
- AP Board Syllabus
- AP Board Sample Question Paper
- AP Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Board Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Telangana Board Syllabus
- Telangana Board Sample Question Paper
- Telangana Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Syllabus
- Karnataka Board Sample Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Examination Full Forms
- Physics Full Forms
- Chemistry Full Forms
- Biology Full Forms
- Educational Full Form
- CUET Eligibility Criteria
- CUET Exam Pattern
- CUET Cutoff
- CUET Syllabus
- CUET Admit Card
- CUET Counselling
- CUET Previous Year Question Papers
- CUET Application Form
- CUET Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Centers
- CUET Exam Dates
- CUET Results
- Physics Formulas
- Chemistry Formulas
- Math Formulas
- Algebra Formulas
- Geometry Formulas
- Trigonometry Formulas
- Subscription
Important Questions for CBSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 – Understanding Elementary Shapes
Home » CBSE » Important Questions for CBSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 – Understanding Elementary Shapes

- CBSE Important Questions
- Important Questions Class 6
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers
- CBSE Revision Notes
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Extra Questions
- CBSE Sample Papers
- ISC & ICSE Syllabus
- ICSE Syllabus Class 9
- ICSE Syllabus Class 8
- ICSE Syllabus Class 7
- ICSE Syllabus Class 6
- ICSE Syllabus Class 10
- ICSE Question Paper
- ICSE Sample Question Papers
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- ICSE Revision Notes
- ICSE Important Questions
- ISC Important Questions For Class 12
- ISC Important Questions For Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 6
- Maharashtra board
- Rajasthan-Board
- Andhrapradesh Board
- AP Board syllabus
- Telangana Board
- Tamilnadu Board
- Tamilnadu Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Previous Year Question Paper
- NCERT Solutions Class 12
- NCERT Solutions Class 10
- NCERT Solutions Class 11
- NCERT Solutions Class 9
- NCERT Solutions Class 8
- NCERT Solutions Class 7
- NCERT Solutions Class 6
- NCERT Solutions Class 5
- NCERT Solutions Class 4
- NCERT Solutions Class 3
- NCERT Solutions Class 2
- NCERT Solutions Class 1
- JEE Main Question Papers
- JEE Main Syllabus
- JEE Main Questions
- JEE Main Revision Notes
- JEE Advanced Question Papers
- JEE Advanced Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Questions
- JEE Advanced Sample Papers
- NEET Question Papers
- Neet 2021 Question Paper
- Neet 2020 Question Paper
- Neet 2019 Question Paper
- Neet 2018 Question Paper
- Neet 2017 Question Paper
- Neet 2016 Question Paper
- Neet 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Syllabus

Important Questions Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 – Understanding Elementary Shapes
Maths is a major subject that is taught in school. You may wonder why we study Maths in school. This subject has great applicability in our life. Maths is needed everywhere, from daily accounting to large-scale constructions to space science.
Quick Links
Understanding Elementary Shapes Class 6 Important Questions
In this chapter, you will learn how to measure a line and an angle, different types of angles, clock and anti-clock and faces, edges and vertices of a three-dimensional object. This chapter is very important, and students must practise questions regularly to score better in exams.
Extramarks is a leading company that provides important study material to students. Our experts have prepared the Important Questions Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 to help students solve questions. They have collected questions from different sources such as textbook exercises, CBSE sample papers and CBSE past years’ question papers. They have also provided the solutions in this question series.
Extramarks provided a wide range of study material to students. You will find the CBSE syllabus , CBSE past years’ question papers, CBSE sample papers, CBSE revision notes, CBSE extra questions , NCERT syllabus, NCERT exemplar, NCERT solutions, NCERT solutions, important questions, vital formulas and many more. You may register on our official website to download these resources of study material.
Get Access to CBSE Class 6 Maths Important Questions with Solutions
Also, get access to CBSE Class 6 Maths Important Questions for other chapters too:
Understanding Elementary Shapes Class 6 Extra Questions with Solutions
Subject experts at Extramarks have collated these questions from several sources. They have taken help from the textbook syllabus, CBSE sample papers and NCERT exemplar. They have also included a few questions from past years’ question papers so that students may have ideas about possible exam questions. They have included the solutions to the questions in the Important Questions Class 6 Maths Chapter 5. Experienced professionals have further checked the answers to ensure the best content quality. The questions are-
Question 1. What is the measure of – (i) a right angle? (ii) a straight angle?
Answer 1.
(i) The exact measure of a right angle is 90°.
(ii) The exact measure of a straight angle is 180°.
Question 2.
Draw a rough sketch of the following:
(a) Acute angle
(b) Obtuse angle
(c) Reflex angle
Answer 2.
Question 3. Classify each one of the following given angles as right, straight, acute, obtuse or reflex:
Answer 3.
(a) Acute angle – as its measure is less than 90º.
(b) Obtuse angle – as its measure is more than 90º but less than 180º.
(c) Right angle – as its measure is 90º.
(d) Reflex angle – as its measure is more than 180º but less than 360º.
(e) Straight angle – as its measure is 180º.
(f) Acute angle – as its measure is less than 90º.
Question 4. What is the main disadvantage of comparing line segments by just mere observation?
By mere observation, we cannot be sure about our judgement. When we have to compare two line segments of almost the same length, we cannot be certain which is the line segment of greater length. Hence, it is not an appropriate method to compare the line segments having a slight difference in their lengths. This is the disadvantage of comparing line segments by mere observation.
Question 5. W hy is it a good choice to use a divider rather than a ruler while measuring the length of a line segment?
It is a better choice to use a divider rather than a ruler because while using a ruler, positioning errors may happen due to the incorrect positioning of the eye.
Question 6. Draw any line segment, say AB. Now, take any point C between A and B. Measure the lengths of – AB, BC and AC. Is AB = AC + CB?
Answer 6.
Since it is given that point C lies between A and B. Hence, all points lie on the same line segment
- Therefore, for each and every situation at which point C is lying between A and B, we may say that.
AB = AC + CB
For example:
AB is a line segment of 7 cm, and C is a point which is between A and B so that AC = 3 cm and CB = 4 cm.
Hence, AC + CB = 7 cm
Since, AB = 7 cm
∴ AB = AC + CB is verified.
Question 7. If A, B, and C are three points that are present on a line so that AB = 5 cm, BC is equal to 3 cm and AC is equal to 8 cm, which one of these lies between the other two?
Given that AB = 5 cms
Now, it is clear that we have AC = AB + BC,
Therefore, point B lies between A and C.
Question 8. Draw any five triangles and measure their sides. Check in each and every case if the sum of the length of any two sides is always less than the third side.
We will be using the concept knowledge of triangles to solve this.
Case I. In ∆ABC
Consider that AB = 2.5 cms, BC = 4.8 cms and AC = 5.2 cms
AB + BC = 2.5 cms + 4.8 cms = 7.3 cm
As we know, 7.3 > 5.2 and AB + BC > AC
Hence, the sum of any of the two sides of the triangle is greater than the third side.
Case II. In ∆PQR, Consider that PQ = 2 cms, QR = 2.5 cms and PR = 3.5 cms
PQ + QR = 2 cms + 2.5 cms = 4.5 cms
As we know, 4.5 > 3.5, PQ + QR > PR
Hence, the sum of any of the two sides of the triangle is greater than the third triangle side.
Case III. In ∆XYZ,
Consider that XY = 5 cms, YZ = 3 cms and ZX = 6.8 cm
XY + YZ = 5 cm + 3 cm = 8 cm
As, we know 8 > 6.8 and XY + YZ > ZX
Hence, the sum of any of the two sides of a triangle is greater than the third side.
Case IV. In ∆MNS,
Consider that MN = 2.7 cm, NS = 4 cm and MS = 4.7 cm
MN + NS = 2.7 cm + 4 cm = 6.7 cm
As we know, 6.7 >4.7 and MN + NS > MS
Hence, the sum of any of the two sides of a triangle is greater than the third side.
Case V. In ∆KLM,
Consider that KL = 3.5 cm, LM = 3.5 cm and KM = 3.5 cm
KL + LM = 3.5 cm + 3.5 cm = 7 cm
Since we know 7 cm > 3.5 cm and KL + LM > KM
Hence, the sum of any of the two sides of a triangle is greater than the third side. Hence, we will conclude that the sum of any two sides of a triangle is never less than the third side.
Question 9.
Write down the measures of
(a) some acute angles
(b) some obtuse angles
(a) 25°, 63° and 72° are acute angles.
(b) 105°, 120° and 135° are obtuse angles.
Question 10.
State true(T) or false(F):
(a) The measure of an acute angle is < 90°.
(b) The measure of an obtuse angle is < 90°.
(c) The measure of a reflex angle is > 180°.
(d) The measure of one complete revolution is equal to 360°.
(e) If m ∠A = 53° and ∠B = 35°, then is m∠A > m∠B.
Answer 10.
Question 11.
How many right angles will you make if you start facing
(a) South(S) and turn clockwise to the West(W)?
(b) North(N) and turn anti-clockwise to the East(E)?
(c) West(W) and turn to West(W)?
(d) South(S) and turn to the North(N)?
Answer 11.
Suppose we revolve one complete round in either a clockwise or anti-clockwise direction. In that case, we will revolve by 360º or four right angles, and the two adjacent directions will be at 90º or one right angle away from each other.
</spa (a) Now, if we start facing South and turn clockwise to West, we make one right angle (90 degrees).
(b) If we start facing North(N) and turn anti-clockwise to East(E), we make three right angles (90 degrees).
(c) If we start facing West(W) and turn to West(W), then we make one complete round or four right angles (90 degrees).
(d) If we start facing South(S) and turn to North(N), then we make two right angles (90 degrees).
Question 12.
Complete each of the following statements so as to make a true statement –
(i) A _______ is a rectangle with a pair of adjacent sides equal.
(ii) A parallelogram with a pair of adjacent sides equal is called a _______.
(iii) A quadrilateral having exactly one pair of parallel sides is called a _______.
(iv) A quadrilateral having both pairs of opposite sides parallel is called a _______.
(v) A parallelogram whose each angle is a right angle is called a _______.
Answer 12.
(ii) rhombus
(iii) trapezium
(iv) parallelogram
(v) rectangle.
Question 13.
A figure is regular if its all sides are equal in length and all angles are equal in measure. Can you identify a regular quadrilateral?
Answer 13.
In a square, for example, all the interior angles are 90°, and all the sides are of the same length. Therefore, a square is a regular quadrilateral.
Question 14.
Fill in the blanks with – acute, obtuse, right or straight angle:
(i) An angle whose measure is less than that of a right angle is ______
(ii) An angle whose measure is greater than that of a right angle is ______
(iii) An angle whose measure is the sum of the measures of two right angles is ______
(iv) When the sum of the measures of two angles is that of a right angle, then each one of them is ______
(v) When the sum of the measures of the two angles of that of a straight angle, and if one of them is an acute angle, then the other angle should be ______
(ii) obtuse
(iii) straight
Question 15.
Which of the following are the models for perpendicular lines?
(a) The adjacent edges of a tabletop
(b) The lines of a railway track
(c) The line segments form the letter ‘L’
(d) The letter V
Answer 15.
(a) Yes, the adjacent edges of a tabletop are the models of perpendicular lines.
(b) No, the lines of railway tracks are parallel to each other. So they are not the model for perpendicular lines.
(c) Yes, the two line segments of ‘L’ are a model for perpendicular lines.
(d) No, the two line segments of the letter ‘V’ are not the model for perpendicular lines.
Question 16.
Name the types of the following triangles –
(i) Triangle with lengths of the sides 7 cm, 8 cm and 9 cm.
(ii) Triangle ABC with sides AB = 8.7 cm, AC = 7 cm and BC = 6 cm.
(iii) Triangle PQR such that side PQ = QR = PR = 5 cm.
(iv) Triangle DEF with m∠D = 90°
(v) Triangle XYZ with m∠Y = 90° and XY = YZ.
(vi) Triangle ∆LMN with m∠L = 30° m∠M = 70° and m∠N = 80°.
Answer 16.
(i) Lengths of the sides of the triangle are given as 7 cm, 8 cm and 9 cm.
Since all the given sides of the given triangle are different.
Hence, it is a Scalene triangle.
(ii) Given that: AB = 8.7 cm, AC = 7 cm and BC = 6 cm
Here AB ≠ AC ≠ BC Hence, ∆ABC is the Scalene triangle.
(iii) Given that: PQ = QR = PR = 5 cm
Since all sides are equal.
Hence, it is an equilateral triangle.
(iv) Given that: In ∆DEF, m∠D = 90°
Hence it is a right-angled triangle.
(v) Given that: In ∆XYZ, m∠Y = 90° and XY = YZ
(vi) Given that: ∆LMN, m∠L = 30°, m ∠M = 70° and m∠N = 80°.
Hence it is an acute-angled triangle.
Question 17.
Examine whether the following figures are polygons. If anyone among them is not a polygon, give the reason why.
</spa Answer 17.
(a) It is not a polygon because it is not a closed figure.
(b) Yes, it is a polygon as it is made of 6 sides.
(c) No, it is not made of any line segments.
(d) No, it is not made only from line segments.
Question 18.
A diagonal is a line segment that will join any of the two vertices of the polygon and is not any side of the polygon. Draw a sketch of a pentagon and also draw its diagonals.
It can be observed from the question that AC, AD, BD, BE, and CE are the diagonals. Question 19.
State true(T) or false(F) –
(i) Each angle of the rectangle is a right angle.
(ii) The opposite sides of a rectangle are always equal in length.
(iii) The diagonals of a square are always perpendicular to one another.
(iv) All the sides of a rhombus are of equal length.
(v) All the sides of a parallelogram are of equal length.
(vi) The opposite sides of the trapezium are parallel.
Question 20.
Give reasons for the following:
(i) A square can be thought of as a special rectangle.
(ii) A rectangle can be thought of as a special parallelogram.
(iii) A square can be thought of as a special rhombus.
(iv) Squares, rectangles, and parallelograms are all quadrilaterals.
(v) A square is also a parallelogram.
(i) A square has all the properties of a rectangle. So, it is a special rectangle.
(ii) A rectangle has the same properties as a parallelogram. So, it is a special parallelogram.
(iii) A square has the same properties as that of a rhombus. So, it is a special rhombus.
(iv) Squares, rectangles and parallelograms are all quadrilaterals as they are all enclosed by four sides.
Question 21.
The measure of two angles of a triangle is 720 and 550. Find the measure of the third angle.
Let ∠A,∠B,and ∠C are the three angles of a triangle.
Let the required missing triangle be x∘
∠A+∠B+∠C=180∘(By angle sum property of triangle)
72∘+55∘+x∘=180∘
127∘+x∘=180∘
x∘=180∘−127∘
Question 22.
Match the following statements :
Measures of Triangle Type of Triangle
(i) 3 sides present of equal length (a) Scalene
(ii) 2 sides present of equal length (b) Isosceles right-angled
(iii) All of the sides are of different length (c) Obtuse-angled
(iv) 3 acute angles (d) Right-angled
(v) 1 right angle (e) Equilateral
(vi) 1 obtuse angle (f) Acute-angled
(vii) 1 right angle with only two sides of equal length (g) Isosceles
Answer 22.
(i) Equilateral (e)
(ii) Isosceles (g)
(iii) Scalene (a)
(iv) Acute-angled (f)
(v) Right-angled (d)
(vi) Obtuse-angled (c)
(vii) Isosceles right-angled (b)
Question 23.
What part of a revolution will you turn through if you stand facing
(i) east and turn clockwise to face north?
(ii) south and turn clockwise to face east?
(iii) west and turn clockwise to face east?
If we revolve one complete round in either clockwise or in an anti-clockwise direction, then we will revolve it by 360º, and the two adjacent directions will be at 90º or 1/4 of a complete revolution away from each other.
(a) If we start facing east and turn clockwise to face north, then we have to make 3/4 of a revolution.
(b) If we start facing south and turn clockwise to face east, then we have to make 3/4 of a revolution.
(c) If we start facing west and turn clockwise to face wast, then we have to make 1/2 of a revolution.
Question 24.
Find the number of right angles that are turned through by the hour hand of a clock when it goes from
(i) 3 to 6 (ii) 2 to 8 (iii) 5 to 11
(iv) 10 to 1 (v) 12 to 9 (vi) 12 to 6
The hour hand of the clock revolves by 360º or four right angles in 1 complete round.
(i) The hour hand of a clock revolves by 90º or one right angle when it goes from 3 to 6.
(ii) The hour hand of a clock revolves by 180º or two right angles when it goes from 2 to 8.
(iii) The hour hand of a clock revolves by 180º or two right angles when it goes from 5 to 11.
(iv) The hour hand of a clock revolves by 90º or one right angle when it goes from 10 to 1.
(v) The hour hand of a clock revolves by 270º or three right angles when it goes from 12 to 9.
(vi) The hour hand of a clock revolves by 180º or two right angles when it goes from 12 to 6.
Question 25.
There are only two set squares in your box. What will be the measures of the angles that are formed at their corners? Will they have any angle measure that is common?
One has a measure of 90°, 45°, and 45°.
Others have a measure of 90°, 30°, and 60°.
Therefore, the angle of 90° is common between them.
Question 26.
What shape is
(a) your instrument box? (b) a brick?
(c) a matchbox? (d) a road-roller?
(e) a sweet laddu?
(d) Cylinder
(e) Sphere
Question 27.
Study the diagram. Line l is perpendicular to the line m.
(i) Is CE = EG?
(ii) Does PE bisect CG?
(iii) Identify any two line segments for which PE is the perpendicular bisector.
(iv) Are these true?
(a) AC > FG.
(b) CD = GH.
(c) BC < EH.
Answer 27.
(i) Yes. As CE = EG = 2 units
(ii) Yes. PE bisects CG since CE = EG.
(iii) Line DF and BH.
(iv) (a) True. As the length of AC and FG are two units and 1 unit, respectively.
(b) True. Because both of them will have 1 unit length.
(c) True. As the length of BC and EH are 1 unit and three units, respectively.
Benefits of Solving Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Extra Questions
Practice is crucial to score better in exams. In Maths, practice is important for various reasons. It helps students clear their doubts and build their basic concepts. Many students fear maths because they don’t get the subject matter. In such cases, they must solve sums to boost their confidence and clear their ideas. The Important Questions Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 will help students build practice habits. There will be other benefits to solving these questions too. They are-
- The experts have collected the questions from different sources. They have included the questions from the textbook exercise, CBSE sample papers, CBSE past years’ question papers, NCERT exemplar and important reference books. So, students can follow these questions and don’t have to search for questions from different sources. Sometimes, the textbook exercise is not enough for preparation. Then, students can follow the Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Important Questions because they will find various questions here.
- The experts have not only collected questions, they have also provided the answers. It is because students may not solve some questions. On the other hand, they can also tally their answers with the answers provided by the experts. Experienced professionals have further checked these solutions and ensured the best quality of content for students. Thus, the Maths Class 6 Chapter 5 Important Questions will help students clear their doubts, build concepts and boost confidence.
- The experts have tried to include questions from all over the chapter. They have attempted to incorporate every important concept of this chapter. For this purpose, they have taken help from several sources. Apart from this, they have also included questions from past years’ question papers so that students may know possible types of questions in exams. Thus, Chapter 5 Class 6 Maths Important Questions will help students greatly. It will not help them to practise questions regularly but also boost their preparation for exams. Thus, it will help to bring extra marks in exams.
Extramarks is a leading educational company in India that provides all the study material related to CBSE and NCERT. We understand the needs of students and try to supply study material according to their demands. One may register on our official website of Extramarks and download this material. You will find the CBSE syllabus, CBSE revision notes , CBSE extra questions, NCERT solutions, NCERT Exemplar, NCERT important questions, CBSE past years’ question papers, vital formulas and many more. Like the Important Questions Class 6 Maths Chapter 5, you will also find important questions for other chapters. Some links to study material are given below-
- NCERT books
- Important questions
- CBSE syllabus
- CBSE sample papers
- CBSE past years’ question papers
- Important formulas
- CBSE extra questions
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
Q.1 How many faces, edges and vertices does a cuboid have?
2 faces, 4 edges and 6 vertices
4 faces, 6 edges and 6 vertices
5 faces, 10 edges and 8 vertices
6 faces, 12 edges and 8 vertices

Q.2 A minute hand of a clock starts from 3 and makes an angle of 180° after some time. The minute hand stops at:

Q.3 In which of the following quadrilaterals, the diagonals intersect each other at 90 degrees? (a) Rhombus
(b) Trapezium
(c) Rectangle
(d) Parallelogram
(a) Rhombus

Q.4 Can a triangle have two obtuse angles ?
No, because the sum of two obtuse angles is more than 180 and this is not possible in the triangle.
Q.5 State true or false : A reflex angle is less than a straight angle.
A reflex angle is an angle which is more than 180 and less than 360. Also a straight angle is equal to 180°.
Hence, a reflex angle is larger than a straight angle.
Please register to view this section
Chapter 1 - knowing our numbers.

Chapter 2 - Whole Numbers
Chapter 3 - playing with numbers, chapter 4 - basic geometrical ideas, chapter 6 - integers, chapter 7 - fractions, chapter 8 - decimals, chapter 9 - data handling, chapter 10 - mensuration, chapter 11 - algebra, chapter 12 - ratio and proportion, chapter 13 - symmetry, chapter 14 - practical geometry, faqs (frequently asked questions), 1. what are the concepts discussed in class 6 maths chapter 5.
Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 discusses the measurement of lines and angles. It also teaches the different types of angles, such as acute and absolute angles. Students will learn about edges, vertices and faces of geometric objects and their definitions. This is a relatively easy and scoring chapter; students will get the concepts easily if they follow the textbook. Lines and other aspects are discussed in the chapter and easily solve the questions. For practice, they can take help from the Important Questions Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 prepared by the experts of Extramarks.
2. How can the Important Questions Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 help students?
Extramarks is a leading company that provides students with a wide range of study material. Our experts have made the question series after collecting the question from different sources. They have accumulated the questions from the textbook exercise, CBSE sample papers, CBSE past years’ question papers and important reference books. Apart from this, they solved the questions by giving a step-by-step solution process. Experienced professionals have further checked these answers to ensure the best quality of students. Thus, the Important Questions Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 prepared by Extramarks will help students in better preparation and higher marks in exams.
CBSE Related Links

Fill this form to view question paper
Otp verification.
The Site is down as we are performing important server maintenance, during which time the server will be unavailable for approximately 24 hours. Please hold off on any critical actions until we are finished. As always your feedback is appreciated.

- Study Packages
- NCERT Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Online Test

- Questions Bank
- Mathematics
- Understanding Elementary Shapes
- Test Series
- Ncert Solutions
- Solved Papers
- Current Affairs
- JEE Main & Advanced
- Pre-Primary
- MP State Exams
- UP State Exams
- Rajasthan State Exams
- Jharkhand State Exams
- Chhattisgarh State Exams
- Bihar State Exams
- Haryana State Exams
- Gujarat State Exams
- MH State Exams
- Himachal State Exams
- Delhi State Exams
- Uttarakhand State Exams
- Punjab State Exams
- J&K State Exams
6th Class Mathematics Understanding Elementary Shapes Question Bank
Done understanding elementary shapes total questions - 43.

question_answer 1) How many centimetres make 3m?
A) 100 done clear
B) 30 done clear
C) 300 done clear
D) 3000 done clear
question_answer 2) How many metres is 805 cm?
A) 80 m 5 cm done clear
B) 8 m 50 cm done clear
C) 8 m 50 cm done clear
D) 8 m 5 cm done clear
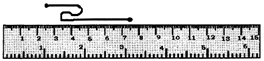
A) 7cm done clear
B) 8cm done clear
C) 9 cm done clear
D) 6 cm done clear
question_answer 4) Which is the longest rectangle ?

question_answer 5) What is an angle which measures more than \[\text{0 }\!\!{}^\circ\!\!\text{ }\] and less than \[\text{90 }\!\!{}^\circ\!\!\text{ }\]called?
A) Obtuse angle done clear
B) Acute angle done clear
C) Right angle done clear
D) Straight angle done clear
question_answer 6) How is the measure of an angle expressed?
A) Compasses done clear
B) Protractor done clear
C) Degrees done clear
D) Centimetres done clear
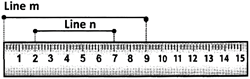
A) 1 cm done clear
B) 2 cm done clear
C) 3 cm done clear
D) 4 cm done clear
question_answer 8) An angle which measures \[\text{0 }\!\!{}^\circ\!\!\text{ }\] is called a/an ___ angle.
A) zero done clear
B) straight done clear
C) obtuse done clear
D) right done clear
A) An obtuse angle done clear
B) A right angle done clear
C) An acute tangle done clear
D) A straight angle done clear
question_answer 10) What is an angle which measures \[\text{180 }\!\!{}^\circ\!\!\text{ }\]called?
A) A zero angle done clear
B) A right angle done clear
C) A straight angle done clear
D) An acute angle done clear
question_answer 11) At 5:20 what type of angle is formed between the two hands of a clock?
A) An obtuse angle done clear
C) An acute angle done clear
D) A reflex angle done clear
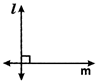
A) \[\text{0 }\!\!{}^\circ\!\!\text{ }\] done clear
B) \[\text{90 }\!\!{}^\circ\!\!\text{ }\] done clear
C) \[\text{90 }\!\!{}^\circ\!\!\text{ }\] done clear
D) \[\text{90 }\!\!{}^\circ\!\!\text{ }\] done clear
question_answer 13) \[\text{179 }\!\!{}^\circ\!\!\text{ }\] is an example of which of these angles?
A) An obtuse angle done clear
B) An acute angle done clear
C) A right angle done clear
question_answer 14) What is \[\text{89 }\!\!{}^\circ\!\!\text{ }\] an example of?
A) An obtuse angle done clear
B) An acute angle done clear
C) A right angle done clear
question_answer 15) When an arm of an angle is extended then how does its measure change?
A) Doubled done clear
B) Tripled done clear
C) Remains the same done clear
D) Halved done clear
question_answer 16) In \[\angle \text{RST}\], what is the vertex ?
A) R done clear
B) T done clear
C) S done clear
D) \[\overrightarrow{\text{OP}}\] done clear
question_answer 17) In\[\angle \text{PRQ}\], which of the following are the two arms?
A) \[\overrightarrow{\text{PR}}\text{, }\overrightarrow{\text{RQ}}\] done clear
B) \[\overrightarrow{\text{RP}}\text{, }\overrightarrow{\text{RQ}}\] done clear
C) \[\overrightarrow{\text{QR}}\text{, }\overrightarrow{\text{QP}}\] done clear
D) \[\overrightarrow{\text{PQ}}\text{, }\overrightarrow{\text{QR}}\] done clear
question_answer 18) How do we write "\[\overrightarrow{\text{PQ}}\] is perpendicular to \[\overrightarrow{\text{RS}}\,\,\text{''}\] symbolically?
A) \[\overleftrightarrow{\text{PQ}}\bot \overleftrightarrow{\text{RS}}\] done clear
B) \[\overleftrightarrow{\text{PQ}}//\overleftrightarrow{\text{RS}}\] done clear
C) \[\overleftrightarrow{\text{PQ}}\ne \overleftrightarrow{\text{RS}}\] done clear
D) \[\overleftrightarrow{\text{PQ}}=\overleftrightarrow{\text{RS}}\] done clear
question_answer 19) What are the lines which lie on the same plane and do not intersect at any point?
A) Perpendicular done clear
B) Intersecting done clear
C) Parallel done clear
D) Collinear done clear

A) 2 done clear
B) 1 done clear
C) 4 done clear
D) 3 done clear
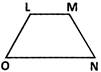
A) 1 done clear
B) 2 done clear
C) 3 done clear
D) 4 done clear
A) 5 done clear
B) 3 done clear
C) 2 done clear
D) 4 done clear
question_answer 23) Which of the following has a definite length?
A) A ray done clear
B) A straight line done clear
C) A line segment done clear
D) An angle done clear
question_answer 24) Which of the following statements is false?
A) Using a protractor, an angle of any measure between \[\text{0 }\!\!{}^\circ\!\!\text{ }\] and \[\text{180 }\!\!{}^\circ\!\!\text{ }\] can be drawn. done clear
B) A line has two end points. done clear
C) An angle whose measure is greater than \[\text{90 }\!\!{}^\circ\!\!\text{ }\] is an obtuse angle. done clear
D) Two coinciding rays with a common end point form an angle of measure\[\text{0 }\!\!{}^\circ\!\!\text{ }\]. done clear
question_answer 25) How many interior angles are formed in a triangle?
A) 1 done clear
C) 3 done clear
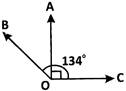
A) \[\text{90 }\!\!{}^\circ\!\!\text{ }\] done clear
B) \[\text{44 }\!\!{}^\circ\!\!\text{ }\] done clear
C) \[\text{224 }\!\!{}^\circ\!\!\text{ }\] done clear
D) \[\text{134 }\!\!{}^\circ\!\!\text{ }\] done clear
question_answer 27) What is an angle measuring \[\text{360 }\!\!{}^\circ\!\!\text{ }\]called ?
A) A right angle done clear
B) A complete angle done clear
C) An acute angle done clear
D) An obtuse angle done clear
question_answer 28) At 6 O'clock, what type of an angle is formed between the hands of a clock?
A) A straight angle done clear
C) An acute angle done clear
D) An obtuse angle done clear
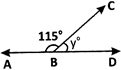
A) \[\text{65 }\!\!{}^\circ\!\!\text{ }\] done clear
B) \[\text{85 }\!\!{}^\circ\!\!\text{ }\] done clear
C) \[\text{75 }\!\!{}^\circ\!\!\text{ }\] done clear
D) \[\text{80 }\!\!{}^\circ\!\!\text{ }\] done clear
question_answer 30) What is a triangle with one right angle and two acute angles called?
A) A right angled triangle done clear
B) An acute angled triangle done clear
C) An equilateral triangle done clear
D) A scalene triangle done clear
question_answer 31) What is a quadrilateral in which both pairs of opposite sides are parallel called?
A) Trapezium done clear
B) Quadrilateral done clear
C) Cube done clear
D) Parallelogram done clear
question_answer 32) A triangle with sides measuring 5 cm, 6 cm and 4 cm is called a/an
A) equilateral triangle. done clear
B) isosceles triangle. done clear
C) scalene triangle. done clear
D) right angled triangle. done clear
question_answer 33) Which of the following statement(s) is/are true?
A) A parallelogram in which two adjacent angles are equal is a rectangle. done clear
B) A quadrilateral in which both pairs of opposite angles are equal is a parallelogram. done clear
C) In a parallelogram the number of acute angles is two. done clear
D) All the above. done clear
question_answer 34) A triangle with one obtuse and two acute angles is called a/an
A) right angled triangle done clear
B) acute angled triangle done clear
C) obtuse angled triangle done clear
D) reflex angled triangle done clear
question_answer 35) Of what shape are the faces of a cube?
A) Circle done clear
B) Triangle done clear
C) Square done clear
D) Pentagon done clear
question_answer 36) Which of the following is the best example of a sphere?
question_answer 37) What do you call the distance between the ends of a line segment?
A) Length of a line segment. done clear
B) Width of the line segment. done clear
C) Diameter of the line segment. done clear
D) Perimeter of the line segment. done clear
question_answer 38) A gas pipe is an example of which of the following?
A) Cuboid done clear
B) Cube done clear
C) Cone done clear
D) Cylinder done clear
question_answer 39) Of which of these is a football an example?
A) Cylinder done clear
B) Cone done clear
C) Sphere done clear
D) Circle done clear
A) 12 done clear
B) 8 done clear
C) 6 done clear
A) A square and a triangle. done clear
B) A square and a trapezium. done clear
C) A rectangle and a triangle. done clear
D) A rectangle and a parallelogram. done clear
question_answer 43) Find the odd figure in the given alternatives.
Study Package

Question - Understand Element Shapes
Related question.

Reset Password.
OTP has been sent to your mobile number and is valid for one hour
Mobile Number Verified
Your mobile number is verified.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Course: Class 6 > Unit 5
How we measure line segments.
- Understanding elementary shapes 5.1
Want to join the conversation?
Video transcript.
NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Class 6
- NCERT 6 Maths
- Chapter 5: Understanding Elementary Shapes
- Exercise 5.2
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Exercise 5.2
By practising the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Exercise 5.2, students can get an idea about the problems related to angles and their various types. These Class 6 Maths NCERT Solutions are designed in a step-wise manner to boost the confidence of students while solving problems.
- Chapter 1 Knowing Our Numbers
- Chapter 2 Whole Numbers
- Chapter 3 Playing with Numbers
- Chapter 4 Basic Geometrical Ideas
- Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes
- Chapter 6 Integers
- Chapter 7 Fractions
- Chapter 8 Decimals
- Chapter 9 Data Handling
- Chapter 10 Mensuration
- Chapter 11 Algebra
- Chapter 12 Ratio and Proportion
- Chapter 13 Introduction to Symmetry
- Chapter 14 Practical Geometry
- Exercise 5.1 Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes
- Exercise 5.2 Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes
- Exercise 5.3 Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes
- Exercise 5.4 Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes
- Exercise 5.5 Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes
- Exercise 5.6 Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes
- Exercise 5.7 Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes
- Exercise 5.8 Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes
- Exercise 5.9 Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Exercise 5.2
carouselExampleControls112

Previous Next
Access NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Chapter 5: Understanding Elementary Shapes Exercise 5.2
1. What fraction of a clockwise revolution does the hour hand of a clock turn through when it goes from
(c) 7 to 10
(d) 12 to 9
(e) 1 to 10
We know that in one complete clockwise revolution, the hour hand will rotate by 360 0
(a) When the hour hand goes from 3 to 9 clockwise, it will rotate by 2 right angles or 180 0
∴ Fraction = 180 0 /360 0

(b) When the hour hand goes from 4 to 7 clockwise, it will rotate by 1 right angle or 90 0
∴ Fraction = 90 0 /360 0

(c) When the hour hand goes from 7 to 10 clockwise, it will rotate by 1 right angle or 90 0

(d) When the hour hand goes from 12 to 9 clockwise, it will rotate by 3 right angles or 270 0
∴ Fraction = 270 0 /360 0

(e) When the hour hand of a clock goes from 1 to 10 clockwise, it will rotate by 3 right angles or 270 0

(f) When the hour hand goes from 6 to 3 clockwise, it will rotate by 3 right angles or 270 0

2. Where will the hand of a clock stop if it
(a) starts at 12 and makes 1/2 of a revolution, clockwise?
(b) starts at 2 and makes 1/2 of a revolution, clockwise?
(c) starts at 5 and makes 1/4 of a revolution, clockwise?
(d) starts at 5 and makes 3/4 of a revolution, clockwise?
(a) When the hour hand of a clock starts at 12 and makes 1/2 of a revolution clockwise, it will rotate by 180 0 .
Hence, the hour hand of a clock will stop at 6.

(b) When the hour hand of a clock starts at 2 and makes 1/2 of a revolution clockwise, it will rotate by 180 0
Hence, the hour hand of a clock will stop at 8.

(c) When the hour hand of a clock starts at 5 and makes 1/4 of a revolution clockwise, it will rotate by 90 0

(d) When the hour hand of a clock starts at 5 and makes 3/4 of a revolution clockwise, it will rotate by 270 0
Hence, the hour hand of a clock will stop at 2.

3. Which direction will you face if you start facing
(a) east and make 1/2 of a revolution clockwise?
(b) east and make 1½ of a revolution clockwise?
(c) west and make 3/4 of a revolution anti-clockwise?
(d) south and make one full revolution?
(Should we specify clockwise or anti-clockwise for the last question? Why not?)
Revolving one complete round in a clockwise or an anti-clockwise direction, we will revolve by 360 0 , and two adjacent directions are at 90 0 or 1/4 of a complete revolution away from each other.
(a) If we start facing towards the east and make 1/2 of a revolution clockwise, we will face towards the west direction.

(b) If we start facing towards the east and make 1½ of a revolution clockwise, we will face towards the west direction.

(c) If we start facing towards the west and make 3/4 of a revolution anti-clockwise, we will face towards the north direction.

(d) If we start facing the south and make one full revolution, again, we will face the south direction.

In the case of revolving 1 complete revolution, either clockwise or anti-clockwise, we will be back at the original position.
4. What part of a revolution have you turned through if you stand facing
(a) east and turn clockwise to face north?
(b) south and turn clockwise to face east
(c) west and turn clockwise to face east?
By revolving one complete revolution either in a clockwise or anti-clockwise direction, we will revolve by 360 0, and two adjacent directions are at 90 0 or 1/4 of a complete revolution away from each other.
(a) If we start facing towards the east and turn clockwise to face north, we have to make 3/4 of a revolution.

(b) If we start facing towards the south and turn clockwise to face east, we have to make 3/4 of a revolution.

(c) If we start facing towards the west and turn clockwise to face east, we have to make 1/2 of a revolution.

5. Find the number of right angles turned through by the hour hand of a clock when it goes from
(c) 5 to 11
(d) 10 to 1
(e) 12 to 9
(f) 12 to 6
The hour hand of a clock revolves by 360 0 , or it covers 4 right angles in one complete revolution.
(a) If the hour hand of a clock goes from 3 to 6, it revolves by 90 0 or 1 right angle.

(b) If the hour hand of a clock goes from 2 to 8, it revolves by 180 0 or 2 right angles.

(c) If the hour hand of a clock goes from 5 to 11, it revolves by 180 0 or 2 right angles.

(d) If the hour hand of a clock goes from 10 to 1, it revolves by 90 0 or 1 right angle.

(e) If the hour hand of a clock goes from 12 to 9, it revolves by 270 0 or 3 right angles.

(f) If the hour hand of a clock goes from 12 to 6, it revolves by 180 0 or 2 right angles.

6. How many right angles do you make if you start facing
(a) south and turn clockwise to the west?
(b) north and turn anti-clockwise to the east?
(c) west and turn to the west?
(d) south and turn to the north?
By revolving one complete round in either a clockwise or anti-clockwise direction, we will revolve by 360 0, and two adjacent directions are 90 0 away from each other.
(a) If we start facing towards the south and turn clockwise to the west, we have to make one right angle.

(b) If we start facing towards the north and turn anti-clockwise to east, we have to make 3 right angles.

(c) If we start facing towards the west and turn to the west, we have to make one complete round or 4 right angles.

(d) If we start facing towards the south and turn to the north, we have to make 2 right angles.

7. Where will the hour hand of a clock stop if it starts
(a) from 6 and turns through 1 right angle?
(b) from 8 and turns through 2 right angles?
(c) from 10 and turns through 3 right angles?
(d) from 7 and turns through 2 straight angles?
We know that in 1 complete revolution in either a clockwise or anticlockwise direction, the hour hand of a clock will rotate by 360 0 or 4 right angles.
(a) If the hour hand of a clock starts from 6 and turns through 1 right angle, it will stop at 9.

(b) If the hour hand of a clock starts from 8 and turns through 2 right angles, it will stop at 2.

(c) If the hour hand of a clock starts from 10 and turns through 3 right angles, it will stop at 7.

(d) If the hour hand of a clock starts from 7 and turns through 2 straight angles, it will stop at 7.

Also, explore –
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5
NCERT Solutions for Class 6
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
It is very good and useful
Good all answers are correct
Very good👍👍👍👍
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Case Study Questions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shape Here in this article, we are providing case study questions for class 6 maths. Here you will find case study questions for class 6 maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shape. Case Study Question 1: The figure below shows a combination of shapes. In … Continue reading Case Study Questions for Class 6 Maths ...
These materials in PDF format can be downloaded by the students to practise offline. BYJU'S offers online learning materials such as notes, question papers, exemplar problems, etc. for almost all the classes which students can use as worksheets to prepare well for exams. NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes ...
Class 6. 12 units · 56 skills. Unit 1. Knowing our numbers. Unit 2. Whole numbers. Unit 3. Playing with numbers. Unit 4. Basic geometrical ideas. ... Understanding elementary shapes 5.6 Get 6 of 8 questions to level up! Understanding elementary shapes 5.7. Learn. Intro to quadrilaterals (Opens a modal)
In the fascinating realm of mathematics, the study of shapes forms a fundamental cornerstone. Chapter 5 of NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths, titled 'Understanding Elementary Shapes,' invites students on an illuminating journey into the captivating world of geometric forms and their properties.This chapter is a gateway to comprehending the basic principles of shapes, angles, and lines, which ...
Understanding Elementary Shapes. 5.1 Introduction. All the shapes we see around us are formed using curves or lines. We can see corners, edges, planes, open curves and closed curves in our surroundings. We organise them into line segments, angles, triangles, polygons and circles. We find that they have different sizes and measures.
The PDF solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Important Questions based on the Understanding of Elementary Shapes are prepared by the expert to provide the top-notch solutions to students. All the Questions and solutions are prepared according to the NCERT curriculum so that this solution will help the students to score good marks in their ...
Updated for new NCERT Book. NCERT Solutions of all execise questions and examples of Chapter 5 Class 6 Understanding Elementary Shapes is available free at teachoo. Each and every question is explained in an easy to understand way. In the last chapter, we studied some basic shapes like line, line segment, angle, triangle, quadrilateral, polygon.
This chapter will teach kids how different shapes can be compared. An exercise-wise analysis of the NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes is provided below: ☛ Download Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 NCERT Book. Topics covered: The topics covered in the class 6 maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 5 are measuring line ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Exercise 5.7. Q1 Say True or False : (a) Each angle of a rectangle is a right angle. (b) The opposite sides of a rectangle are equal in length. (c) The diagonals of a square are perpendicular to one another.
The NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes PDF prove to be worthy as it provides a lot of Questions to solve; accordingly they can score well. Students can access the Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Questions of Class 6 Maths through the Selfstudys website from their comfort zone.
Vedantu's free PDF notes on CBSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 5, "Understanding Elementary Shapes," are a valuable educational resource for young learners. These notes offer a comprehensive understanding of basic geometric concepts, ensuring that students have access to high-quality study materials that align with the CBSE curriculum.
Solid Shapes or 3D Shapes. A solid shape or three-dimensional shape (3D shape) can be defined as the objects which can be measured in three directions i.e. length, breadth, and height. Examples of 3d shapes are cylinder, cube, cuboid, sphere, etc. Check out three-dimensional shapes to learn more about them and to get acquainted with the terms ...
Class 6 (Old) 12 units · 127 skills. Unit 1. Knowing our numbers. Unit 2. Whole numbers. Unit 3. Playing with numbers. Unit 4. Integers. Unit 5. Fractions. Unit 6. Decimals. Unit 7. ... Understanding elementary shapes: Quiz 2; Identify parts of 3D shapes; Identify geometric solids (3D shapes) Understanding elementary shapes: Unit test ...
Basic Geometrical Ideas Class 6 Extra Questions Long Answer Type. Question 15. Verify the 'Euler's formula' V + F = E + 2 for the given figures. (a) A triangular prism having 5 faces, 9 edges and 6 vertices. (b) A rectangular prism with 6 faces, 12 edges and 8 vertices. (c) A pentagonal prism with 7 faces, 15 edges and 10 vertices.
These solutions for Understanding Elementary Shapes are extremely popular among class 6 students for Math Understanding Elementary Shapes Solutions come handy for quickly completing your homework and preparing for exams. All questions and answers from the RS Aggarwal Book of class 6 Math Chapter 5 are provided here for you for free.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 is an important study resource for class six students. It provides a thorough yet simple explanation of this fundamental mathematical idea. ... The following lesson of Class 6 Maths Understanding Elementary Shapes expands on the concept of a polygon. A polygon with three or four sides is called a ...
These materials are prepared based on Class 6 NCERT syllabus, taking the types of questions asked in the NCERT textbook into consideration. Further, all the CBSE Class 6 Solutions Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes are in accordance with the latest CBSE guidelines and marking schemes . Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Exercise 5.1 Solutions
Understanding Elementary Shapes NCERT Solutions is very essential for scoring good marks in the class test examinations. In this chapter, we will talk about lines and angles, two dimensional figures and also about three dimensional figures.
Important Questions Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 - Understanding Elementary Shapes. Maths is a major subject that is taught in school. You may wonder why we study Maths in school. This subject has great applicability in our life. Maths is needed everywhere, from daily accounting to large-scale constructions to space science.
Free Question Bank for 6th Class Mathematics Understanding Elementary Shapes Understanding Elementary Shapes. Customer Care : 6267349244. Toggle navigation ... 6th Class Mathematics Understanding Elementary Shapes Question Bank ... Study Package. Question - Understand Element Shapes.
Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. Khan Academy is a nonprofit with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere.
Access NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Chapter 5: Understanding Elementary Shapes Exercise 5.7. 1. Say True or False: (a) Each angle of a rectangle is a right angle. (b) The opposite sides of a rectangle are equal in length. (c) The diagonals of a square are perpendicular to one another. (d) All the sides of a rhombus are of equal length.
Solutions: We know that in one complete clockwise revolution, the hour hand will rotate by 360 0. (a) When the hour hand goes from 3 to 9 clockwise, it will rotate by 2 right angles or 180 0. ∴ Fraction = 180 0 /360 0. = 1/2. (b) When the hour hand goes from 4 to 7 clockwise, it will rotate by 1 right angle or 90 0. ∴ Fraction = 90 0 /360 0.