Copyright Note
- Preferences


What is Operating System and its Types | Uses - PowerPoint PPT Presentation

What is Operating System and its Types | Uses
The operating system (os) acts as a host for the application program that runs on the machine. as a host, one purpose of the operating system is to handle the operating details of the hardware. – powerpoint ppt presentation.
- Process Management
- Memory Management
- Disk And File System
- Graphical User Interfaces
- User Interface
- Job Management
- Task Management
- Windows Mobile
- Simple Batch System
- Multiprogramming Batch System
- Multiprocessor System
- Desktop System
- Distributed Operating System
- Clustered System
- Real time Operating System
- Handheld System
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics , the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.


Types of Operating Systems
Jul 29, 2014
290 likes | 922 Views
Types of Operating Systems. Computer Engineering Department Computer Graphics Course Asst. Prof. Dr. Ahmet Sayar Kocaeli University - Fall 201 2. Uniprocessor Operating Systems. An OS acts as a resource manager or an arbitrator Manages CPU, I/O devices, memory
Share Presentation
- large kernel
- transferring data
- distributed oss
- multiprocessor operating systems
- developing distributed systems

Presentation Transcript
Types of Operating Systems Computer Engineering Department Computer Graphics Course Asst. Prof. Dr. AhmetSayar Kocaeli University - Fall 2012
Uniprocessor Operating Systems • An OS acts as a resource manager or an arbitrator • Manages CPU, I/O devices, memory • OS provides a virtual interface that is easier to use than hardware • Structure of uniprocessor operating systems • Monolithic (e.g., MS-DOS, early UNIX) • One large kernel that handles everything • Layered design • Functionality is decomposed into N layers • Each layer uses services of layer N-1 and implements new service(s) for layer N+1
Uniprocessor Operating Systems • Microkernel architecture • Small kernel • user-level servers implement additional functionality
Distributed Operating System-Multi-computer- • Manages resources in a distributed system • Seamlessly and transparently to the user • Looks to the user like a centralized OS • But operates on multiple independent CPUs • Provides transparency • Location, migration, concurrency, replication,… • Presents users with a virtual uniprocessor
Multi-computer Systems • How to run multiprocessor software on multicomputer systems ?
Multiprocessor Operating Systems • Multi-core • Like a uniprocessor operating system • Manages multiple CPUs transparently to the user • Shared main memory and controlled by a single OS instance • Each processor has its own hardware cache • Maintain consistency of cached data
Multiprocessor Operating - Contd SystemsHardware Concept
Multiprocessor Operating Systems -Contd • A bus-based multiprocessor • A representation of shared memory super computing
Distributed Operating Systems (1) • Example: MOSIX cluster - single system image
Distributed Operating Systems (2) • Gives illusion of single system • Users not aware of multiplicity of machines • Access to remote resources similar to access to local resources • Data Migration – transfer data by transferring entire file, or transferring only those portions of the file necessary for the immediate task • Computation Migration – transfer the computation, rather than the data, across the system
Network Operating System (1)
Network Operating System (2) • Users are aware of multiplicity of machines. Access to resources of various machines is done explicitly by: • Remote logging into the appropriate remote machine (telnet, ssh) • Remote Desktop (Microsoft Windows) • Transferring data from remote machines to local machines, via the File Transfer Protocol (FTP) mechanism
Middleware-based Systems
Types of Distributed OSs
Comparison between Systems
Pitfalls when Developing Distributed Systems • False assumptions made by first time developer: • The network is reliable. • The network is secure. • The network is homogeneous. • Latency is zero. • Bandwidth is infinite. • Transport cost is zero. • There is one administrator.
Summary • Distributed Systems … autonomous computers • working together to give the appearance of a single, coherent system. • They are transparent, scalable and open. • Unfortunately, they also tend to be complex
Overview challenges • Concurrency • Shared access to resources must be possible • Openness • Interfaces should be publicly available to ease adding new components • Security • The system should only be used in the way intended
- More by User

CS 333 Introduction to Operating Systems Class 20 - History and Types of Operating Systems
Jonathan Walpole Computer Science Portland State University. CS 333 Introduction to Operating Systems Class 20 - History and Types of Operating Systems. About the Instructor & TA. Instructor - Jonathan Walpole Ph.D. Comp. Science. – Lancaster Uni., UK, 1987
1.32k views • 85 slides

Types of Operating System
http://www.amischool.edu.pk
1.29k views • 32 slides

Structure of Operating Systems
409 views • 24 slides

Functionalities of Operating Systems
Functionalities of Operating Systems. Types of Operating Systems. Real-time systems Time-critical environments Batch systems Throughput Interactive systems Time-sharing Hybrid systems Combination of batch and interactive. Real-Time System
226 views • 0 slides

Different types of operating system
iOS (previously iPhone OS) is a mobile operating system developed and distributed by Apple Inc. Originally unveiled in 2007 for the iPhone. It got made by apple .
2.85k views • 1 slides

FUNCTIONS OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
Memory Management. Utility. FUNCTIONS OF OPERATING SYSTEMS. Interfaces . Security. Interrupt Handling. Security. Login back up/system restore utility software. JOB SCHEDULING. FCFS – fist come, first served
402 views • 7 slides

Different types of Operating systems
Different types of Operating systems. Windows: Windows was developed by Bill Gates and it is widely used in most computer systems and laptops. Examples are Window X p and W indows 7.
227 views • 1 slides

Types of Operating Systems . Real Time OS Batch OS Time Sharing OS Why do we have different Operating Systems Common types of Operating Systems . Process Management. Memory Management. GUI. Operating System. Device Drivers. Disk Management. Security. Networking.
2.89k views • 27 slides

Function of Operating Systems
Function of Operating Systems. Introduction. The Operating System MUST:. provide and manage hardware resources provide an interface between the user and the machine provide an interface between applications software and the machine provide security for the data on the system
1.1k views • 9 slides

Characteristics of operating systems
Characteristics of operating systems. What is a program? A program is an inactive unit such as a file stored on a disk. A unit of work submitted by a user. What is a process? A program in execution
741 views • 20 slides
Different types of operating systems
Different types of operating systems. Mac OS was made by Apple inc. It is used in different types of Apple computers The latest version is the OS X Mavericks. Windows was made by is Bill G ate and Paul Allen
612 views • 1 slides
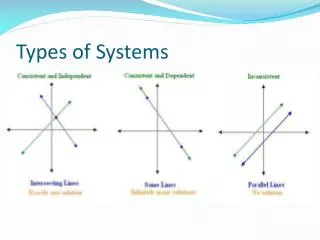
Types of Systems
Types of Systems . Inconsistent of consistent?. Example 1: 3x – y = 2 6x – 2y = 3 Example 2: x + y = -2 x -2y = 7. Inconsistent or Consistent?. Example 3: x + 2y + z = 1 -x – y + 2z = 0 y + 3z = 4 . Dependent vs. Independent.
266 views • 7 slides

Network Operating Systems versus Operating Systems
Network Operating Systems versus Operating Systems. Computer Networks. NOS have dedicated servers C lient server networks Servers provide a variety of services for other computers on the network. Network Operating System (NOS). Networks that don’t use NOS are peer-to-peer networks
437 views • 14 slides

Overview of Operating Systems
Chapters 1 and 2. Overview of Operating Systems. Introduction. Twin aims of an operating system are: User convenience System performance Performance measures depend on the computing environment Number of requests serviced per unit time, etc. Introduction. Fundamental tasks of an OS
434 views • 25 slides

Principles of Operating Systems
Principles of Operating Systems. Lecture 6 and 7 - Process Synchronization. Outline. Cooperating Processes The Bounded Buffer Producer-Consumer Problem The Critical Section Problem Synchronization Hardware Semaphores Classical Problems of Synchronization Critical Regions Monitors.
737 views • 58 slides

Principles of Operating Systems. Lectures 8 and 9 - Deadlocks. Outline. System Model Deadlock Characterization Methods for handling deadlocks Deadlock Prevention Deadlock Avoidance Deadlock Detection Recovery from Deadlock Combined Approach to Deadlock Handling. The Deadlock Problem.
627 views • 45 slides

Operating Systems Real-Time Operating Systems
Operating Systems Real-Time Operating Systems. Chalermek Intanagonwiwat. Slides courtesy of Subhashis Banerjee. Real-Time Systems. Result in severe consequences if logical and timing correctness are not met Two types exist Soft real-time Tasks are performed as fast as possible
2.02k views • 80 slides

OPERATING SYSTEMS SYSTEMS
OPERATING SYSTEMS SYSTEMS. 9 th January 11CS10002. BATCH SYSTEMS. In these systems though there are many jobs in the job pool only one job is entered into the memory and no other job is selected till the current running job is terminated. OS. J1. J0. J2. J3. J4. LIMITATIONS.
659 views • 7 slides

Structure of Operating Systems. UNIT 2. Introduction. Operation of an OS Structure of an Operating System Operating Systems with Monolithic Structure. Operation of an OS. When a computer is switched on, boot procedure
1.79k views • 24 slides

Principles of Operating Systems. Lectures 3 and 4 - Processes and Threads. Outline. Process Concept Process Scheduling Operations on Processes Cooperating Processes Threads Interprocess Communication. Process Concept. An operating system executes a variety of programs
661 views • 56 slides

Principles of Operating Systems. Lecture 5 - CPU Scheduling. Outline. Scheduling Objectives Levels of Scheduling Scheduling Criteria Scheduling Algorithms FCFS, Shortest Job First, Priority, Round Robin, Multilevel Multiple Processor Scheduling Real-time Scheduling Algorithm Evaluation.
623 views • 37 slides

Types of Systems. Closed system and Open System. Closed system. Self contained. MATTER stays in. Energy moves freely in and out Example:. Open System. Matter and energy move in and out freely More complicated Very common in nature Example: river. Open or closed system?.
924 views • 48 slides

VIDEO
COMMENTS
Types of Operating System • SingleUser • Multi-user • Multi-tasking • Interactive • Real Time • Batch Processing • Distributed Systems. Single User • standard OS for a standalone computer systems • only one person can use the computer system at any one time • can support multiple accounts but only one used at a time ...
The slides are authorized for personal use, and for use in conjunction with a course for which Operating System Concepts is the prescribed text. Instructors are free to modify the slides to their taste, as long as the modified slides acknowledge the source and the fact that they have been modified. Paper copies of the slides may be sold ...
Operating System Concepts - slides. Avi Silberschatz. Peter Baer Galvin. Greg Gagne. We provide a set of slides to accompany each chapter. Click on the links below to download the slides in Powerpoint format. We also provide zip files of the all Powerpoint files , PDF files, and all figures used in the text. Chapter.
The slides are authorized for personal use, and for use in conjunction with a course for which Operating System Concepts is the prescribed text. Instructors are free to modify the slides to their taste, as long as the modified slides acknowledge the source and the fact that they have been modified. Paper copies of the slides may be sold ...
The first button is the minimize button and it will hide the window. The window can be opened again by clicking its button on the taskbar. The second button is maximize, which makes the window take. up all the screen space. Clicking again turns the window back to the size it was.
virtual address space, set of resources (object handles), and one or more threads. A thread are the unit of dispatching. Each thread has: scheduling state (ready, running, etc.), other scheduling parameters (priority, etc), context slot, and (generally) an associated process.
The slides are authorized for personal use, and for use in conjunction with a course for which Operating System Concepts is the prescribed text. Instructors are free to modify the slides to their taste, as long as the modified slides acknowledge the source and the fact that they have been modified. Paper copies of the slides may be sold ...
The operating system (OS) acts as a host for the application program that runs on the machine. As a host, one purpose of the operating system is to handle the operating details of the hardware. - A free PowerPoint PPT presentation (displayed as an HTML5 slide show) on PowerShow.com - id: 8d47ec-ZmMyM
A program that acts as an intermediary between a user of a computer and the computer hardware. Operating system goals: Execute user programs and make solving user problems easier. Make the computer system convenient to use. Use the computer hardware in an efficient manner.
A program that acts as an intermediary between a user of a computer and the computer hardware Operating system goals: O Execute user programs and make solving user problems easier Make the computer system convenient to use Use the computer hardware in an efficient manner. Computer System Structure Computer system can be divided into four ...
Middleware-based Systems. Types of Distributed OSs. Comparison between Systems. Pitfalls when Developing Distributed Systems • False assumptions made by first time developer: • The network is reliable. • The network is secure. • The network is homogeneous. • Latency is zero. • Bandwidth is infinite. • Transport cost is zero.