- Editorial Board
- Open Access
- List of Issues
- FOOD Website

GUIDE TO CONTRIBUTORS
Original Articles Only Research papers, Review articles, Notes and Short Communication are accepted on the understanding that they have not been and will not be published elsewhere without the Chief Editor’s permission. When submitting notes and short communications, authors should make clear that their work is to be treated as such. Authors should suggest keywords and a short running title for their articles. Papers accepted become the copyright of the Journal. Authors are requested to submit the names and full contact details (address, affiliation and e-mail) of three potential reviewers for the manuscript. Manuscript Style Research papers should be divided into the following sections: (a) An abstract embodying the main conclusion and giving the essential information. It should be intelligible without reference to the paper itself; (b) Introduction – should give the aim of the investigation and a brief statement of previous relevant work with references; (c) Materials and Methods – only new techniques need to be described in detail but known methods must have adequate reference; (d) Results – must be presented with tables and figures for clarity; (e) Discussion – Conclusions - usually interprets the results and the Conclusions should not merely repeat points made in the preceding sections; (g) Acknowledgement – should be kept to the absolute minimum; and (h) References. A short running title must also be provided. Tables, Graphs, Figures and Photographs Tables, graphs and figures should be displayed on separate pages in the manuscript after the reference section. Tables and figures should be captioned. Scanned or digital photographs should be in high resolution, minimum 300 dpi in the PC format. For colour reproduction in print, you will receive information regarding the costs from the Editor-in-Chief after receipt of your accepted article. Keep the numbers of Figures and Tables used in the article to the minimum (maximum allowed is a total of 5 Figures and Tables altogether). Footnotes Footnotes should be kept to a minimum; in most cases, it will be possible to incorporate the information in the text. If footnotes are used, they should be numbered in the text, indicated by superscript numbers and kept as brief as possible. References References should be cited in the text by the author. All references in the text must be listed at the end of the paper, with the names of authors arranged alphabetically, and titles of papers given. No underlining, italics or bold face should be used. References in incorrect format will be returned for correction. Examples of reference styles are given below: Journal Collins, S. J., Bester, B. H. and McGill, A. E. J. 1993. Influence of psychrotrophic bacterial growth in raw milk on the sensory acceptance of UHT skim milk. Journal of Food Protection 56 (5): 418-425. Monograph Connel, J. J. 1990. Control of fish quality. 2nd edn. London: Fishing News Books. Chapter in Book Hart, R. J. 1998. Food Science and the transport of food. In Heap, R., Kierstan, M. and Ford, G. (Eds). Food Transportation, p. 1-21. London: Thomson Science. Proceedings Jinap, S. and Yusof, S. 1994. Development of juice from cocoa pulp. In Jinap, S., Bong, C. L., Tan, K. L. and Wan Rahimah, W. I. (Eds). Proceedings of the Malaysian International Conference, p. 351. Kuala Lumpur: Malaysian Cocoa Board. Internet Internet: Food and Drug Administration 2000. Bad bug book – Aflatoxins. Downloaded from http:vm.cfsan.fda.gov/¬mow/chap41.html on 3/3/2000. Report Lontoc, A. V. 1981. Existing food analytical methods and problems in the Philippines. Report of the ASEAN Workshop on Analytical Techniques. Singapore: ASEAN Subcommittee on Protein. Thesis Yusep, I. 1997. The effect of fermentation and soaking times on pyrazines and acidity concentration of Thai Forastero cocoa beans. Bangkok, Thailand: Kasertsart University, MSc thesis. Submission Submissions by email are preferred. However, submissions of hard copies by surface, airmail, express mail or courier are also acceptable. If submitting hard copies, two manuscripts printed on one side of white A4 paper should be sent. Manuscripts should be double-spaced, typed using 12 point Arial or equivalent typeface with a margin of 4 cm on all four sides. Refer to the latest issue of International Food Research Journal for the format of manuscript preparation. The corresponding author will be provided with PDF copy of the manuscript. Manuscripts and other communication must be directed to the secretariat of the Journal at the following address: Professor Dr. Son Radu Editor International Food Research Journal Faculty of Food Science and Technology Universiti Putra Malaysia 43400 UPM Serdang Selangor Malaysia Phone: +603-89468361 Fax: +603- 89423552 Email: [email protected]
International Food Research Journal carries no page charge.
© 2008 IFRJ, Faculty of Food Science & Technology, UPM.

- Articles in Press
- Vol. 8│Issue 2
- Vol. 8 | Supplementary 2
- Vol. 8│Issue 1
- Vol. 8 | Supplementary 1
- Vol. 7│Issue 1
- Vol. 7│Issue 2
- Vol. 7│Issue 3
- Vol. 7│Issue 4
- Vol. 7│Issue 5
- Vol. 7│Issue 6
- Vol. 7 | Supplementary 1
- Vol. 7 | Supplementary 2
- Vol. 7 | Supplementary 3
- Vol. 7 | Supplementary 4
- Vol. 7 | Supplementary 5
- Vol. 6│Issue 1
- Vol. 6│Issue 2
- Vol. 6│Issue 3
- Vol. 6│Issue 4
- Vol. 6│Issue 5
- Vol. 6│Issue 6
- Vol. 6│Supplementary 1
- Vol. 6│Supplementary 2
- Vol. 6│Supplementary 3
- Vol. 6│Supplementary 4
- Vol. 5│Issue 1
- Vol. 5│Issue 2
- Vol. 5│Issue 3
- Vol. 5│Issue 4
- Vol. 5│Issue 5
- Vol. 5│Issue 6
- Vol. 5│Supplementary 1
- Vol. 5│Supplementary 2
- Vol. 5│Supplementary 3
- Vol. 5│Supplementary 4
- Vol. 4│Issue 1
- Vol. 4│Issue 2
- Vol. 4│Issue 3
- Vol. 4│Issue 4
- Vol. 4│Issue 5
- Vol. 4│Issue 6
- Vol. 4│Supplementary 1
- Vol. 4│Supplementary 2
- Vol. 4│Supplementary 3
- Vol. 4│Supplementary 4
- Vol. 4│Supplementary 5
- Vol. 4│Supplementary 6
- Vol. 3│Issue 1
- Vol. 3│Issue 2
- Vol. 3│Issue 3
- Vol. 3│Issue 4
- Vol. 3│Issue 5
- Vol. 3│Issue 6
- Vol. 2│Issue 1
- Vol. 2│Issue 2
- Vol. 2│Issue 3
- Vol. 2│Issue 4
- Vol. 2│Issue 5
- Vol. 2│Issue 6
- Vol. 1│Issue 1
- Vol. 1│Issue 2
- Vol. 1│Issue 3
- Vol. 1│Issue 4
- Vol. 1│Issue 5
- Vol. 1│Issue 6
- Editorial Board
- Author Guidelines
- Submit Your Manuscript
- Peer Review Process
- For Referees

- Food science and food chemistry
- Food technology, food processing, and food engineering
- Food safety and quality - microbiological and chemical
- Sensory, habits, consumer behaviour/practice and preference
- Nutrition and Dietetics
- Nutraceuticals and functional food
- Food service management
- Food trends, innovation and business
- Post-harvest and agribusiness
- Food security
- Food packaging
Article In Press

Food Research
Food Research International
Subject Area and Category
- Food Science
Elsevier Ltd
Publication type
09639969, 18737145
Information
How to publish in this journal
The set of journals have been ranked according to their SJR and divided into four equal groups, four quartiles. Q1 (green) comprises the quarter of the journals with the highest values, Q2 (yellow) the second highest values, Q3 (orange) the third highest values and Q4 (red) the lowest values.
The SJR is a size-independent prestige indicator that ranks journals by their 'average prestige per article'. It is based on the idea that 'all citations are not created equal'. SJR is a measure of scientific influence of journals that accounts for both the number of citations received by a journal and the importance or prestige of the journals where such citations come from It measures the scientific influence of the average article in a journal, it expresses how central to the global scientific discussion an average article of the journal is.
Evolution of the number of published documents. All types of documents are considered, including citable and non citable documents.
This indicator counts the number of citations received by documents from a journal and divides them by the total number of documents published in that journal. The chart shows the evolution of the average number of times documents published in a journal in the past two, three and four years have been cited in the current year. The two years line is equivalent to journal impact factor ™ (Thomson Reuters) metric.
Evolution of the total number of citations and journal's self-citations received by a journal's published documents during the three previous years. Journal Self-citation is defined as the number of citation from a journal citing article to articles published by the same journal.
Evolution of the number of total citation per document and external citation per document (i.e. journal self-citations removed) received by a journal's published documents during the three previous years. External citations are calculated by subtracting the number of self-citations from the total number of citations received by the journal’s documents.
International Collaboration accounts for the articles that have been produced by researchers from several countries. The chart shows the ratio of a journal's documents signed by researchers from more than one country; that is including more than one country address.
Not every article in a journal is considered primary research and therefore "citable", this chart shows the ratio of a journal's articles including substantial research (research articles, conference papers and reviews) in three year windows vs. those documents other than research articles, reviews and conference papers.
Ratio of a journal's items, grouped in three years windows, that have been cited at least once vs. those not cited during the following year.
Leave a comment
Name * Required
Email (will not be published) * Required
* Required Cancel
The users of Scimago Journal & Country Rank have the possibility to dialogue through comments linked to a specific journal. The purpose is to have a forum in which general doubts about the processes of publication in the journal, experiences and other issues derived from the publication of papers are resolved. For topics on particular articles, maintain the dialogue through the usual channels with your editor.

Follow us on @ScimagoJR Scimago Lab , Copyright 2007-2024. Data Source: Scopus®

Cookie settings
Cookie Policy
Legal Notice
Privacy Policy
Identifiers
Linking ISSN (ISSN-L): 2231-7546
URL http://www.ifrj.upm.edu.my/
Google https://www.google.com/search?q=ISSN+%221985-4668%22
Bing https://www.bing.com/search?q=ISSN+%221985-4668%22
Yahoo https://search.yahoo.com/search?p=ISSN%20%221985-4668%22
ISSN Malaysia https://opac.pnm.gov.my/search/query?match_1=PHRASE&field_1=issn&term_1=1985-4668&match_2=PHRASE&field_2=text&match_3=SHOULD&field_3=text&match_4=NOT&field_4=text&filter_format=Serial&theme=PNM2
Resource information
Title proper: International food research journal
Country: Malaysia
Medium: Print
Record information
Last modification date: 26/05/2023
Type of record: Confirmed
ISSN Center responsible of the record: ISSN National Centre for Malaysia
downloads requested
Discover all the features of the complete ISSN records
Display mode x.
Labelled view
MARC21 view
UNIMARC view
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
Latest science news, discoveries and analysis

Bird flu in US cows: is the milk supply safe?

Future of Humanity Institute shuts: what's next for ‘deep future’ research?

Judge dismisses superconductivity physicist’s lawsuit against university

NIH pay raise for postdocs and PhD students could have US ripple effect
Hello puffins, goodbye belugas: changing arctic fjord hints at our climate future, china's moon atlas is the most detailed ever made, ‘shut up and calculate’: how einstein lost the battle to explain quantum reality, rat neurons repair mouse brains — and restore sense of smell, ecologists: don’t lose touch with the joy of fieldwork chris mantegna.

Should the Maldives be creating new land?

Lethal AI weapons are here: how can we control them?

Algorithm ranks peer reviewers by reputation — but critics warn of bias

How gliding marsupials got their ‘wings’
Audio long read: why loneliness is bad for your health, nato is boosting ai and climate research as scientific diplomacy remains on ice, plastic pollution: three numbers that support a crackdown, the maldives is racing to create new land. why are so many people concerned.
Retractions are part of science, but misconduct isn’t — lessons from a superconductivity lab

Any plan to make smoking obsolete is the right step

Citizenship privilege harms science
European ruling linking climate change to human rights could be a game changer — here’s how charlotte e. blattner, will ai accelerate or delay the race to net-zero emissions, current issue.

Surprise hybrid origins of a butterfly species
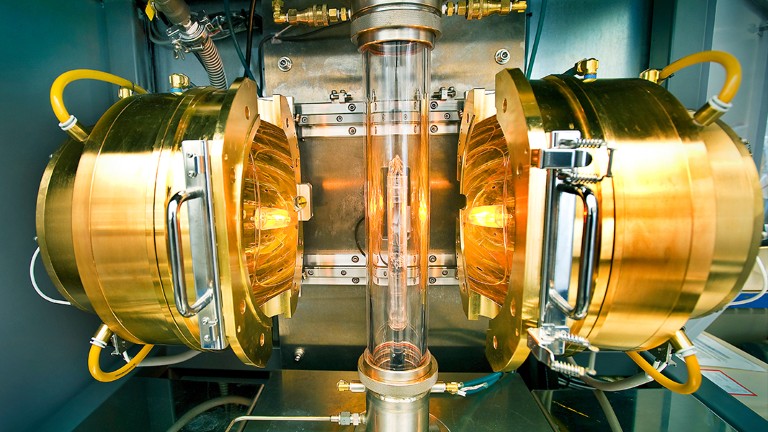
Stripped-envelope supernova light curves argue for central engine activity, optical clocks at sea, research analysis.


Ancient DNA traces family lines and political shifts in the Avar empire
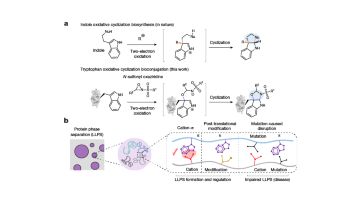
A chemical method for selective labelling of the key amino acid tryptophan
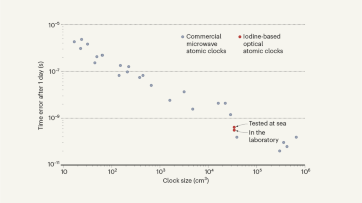
Robust optical clocks promise stable timing in a portable package
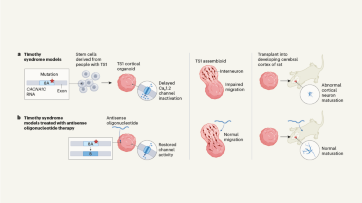
Targeting RNA opens therapeutic avenues for Timothy syndrome
Bioengineered ‘mini-colons’ shed light on cancer progression, galaxy found napping in the primordial universe, tumours form without genetic mutations, marsupial genomes reveal how a skin membrane for gliding evolved.

Scientists urged to collect royalties from the ‘magic money tree’

Breaking ice, and helicopter drops: winning photos of working scientists

Shrouded in secrecy: how science is harmed by the bullying and harassment rumour mill
How ground glass might save crops from drought on a caribbean island, londoners see what a scientist looks like up close in 50 photographs, books & culture.

How volcanoes shaped our planet — and why we need to be ready for the next big eruption

Dogwhistles, drilling and the roots of Western civilization: Books in brief

Cosmic rentals
Las borinqueñas remembers the forgotten puerto rican women who tested the first pill, dad always mows on summer saturday mornings, nature podcast.

Latest videos
Nature briefing.
An essential round-up of science news, opinion and analysis, delivered to your inbox every weekday.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Spatial Variations of the Activity of 137 Cs and the Contents of Heavy Metals and Petroleum Products in the Polluted Soils of the City of Elektrostal
- DEGRADATION, REHABILITATION, AND CONSERVATION OF SOILS
- Open access
- Published: 15 June 2022
- Volume 55 , pages 840–848, ( 2022 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- D. N. Lipatov 1 ,
- V. A. Varachenkov 1 ,
- D. V. Manakhov 1 ,
- M. M. Karpukhin 1 &
- S. V. Mamikhin 1
1460 Accesses
2 Citations
Explore all metrics
The levels of specific activity of 137 Cs and the contents of mobile forms (1 M ammonium acetate extraction) of heavy metals (Zn, Cu, Ni, Co, Cr, Pb) and petroleum products were studied in the upper soil horizon of urban landscapes of the city of Elektrostal under conditions of local radioactive and chemical contamination were studied. In the soils within a short radius (0–100 m) around the heavy engineering plant, the specific activity of 137 Cs and the contents of mobile forms of Pb, Cu, and Zn were increased. The lognormal distribution law of 137 Cs was found in the upper (0–10 cm) soil layer; five years after the radiation accident, the specific activity of 137 Cs varied from 6 to 4238 Bq/kg. The coefficients of variation increased with an increase in the degree of soil contamination in the following sequence: Co < Ni < petroleum products < Cr < 137 Cs < Zn < Pb < Cu ranging from 50 to 435%. Statistically significant direct correlation was found between the specific activity of 137 Cs and the contents of mobile forms of Pb, Cu, and Zn in the upper horizon of urban soils, and this fact indicated the spatial conjugacy of local spots of radioactive and polymetallic contamination in the studied area. It was shown that the specific activity of 137 Cs, as well as the content of heavy metals and petroleum products in the upper layer (0–10 cm) of the soils disturbed in the course of decontamination, earthwork and reclamation is reduced.
Similar content being viewed by others
Accumulation and migration of heavy metals in soils of the rostov region, south of russia.

Geographical Features of Pollution of the Territory of Yakutia With Cesium-137

Activity Concentration of Natural Radionuclides and Total Heavy Metals Content in Soils of Urban Agglomeration
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
INTRODUCTION
Contaminants migrate and accumulate in urban ecosystems under the impact of both natural and technogenic factors. The processes of technogenic migration of 137 Cs are most pronounced in radioactively contaminated territories. It was found in urboecological studies that the intensity of sedimentation of aerosol particles containing radionuclides and heavy metals is determined by the types of the surfaces of roofs, walls, roads, lawns, and parks and by their position within the urban wind field [ 12 , 26 ]. Traffic in the cities results in significant transport of dust and associated contaminants and radionuclides [ 15 , 24 ]. During decontamination measures in the areas of Chernobyl radioactive trace, not only the decrease in the level of contamination but also the possibility of secondary radioactive contamination because of the transportation of contaminated soil particles by wind or water, or anthropogenic transfer of transferring of ground were observed [ 5 , 6 ]. Rainstorm runoff and hydrological transport of dissolved and colloidal forms of 137 Cs can result in the accumulation of this radionuclide in meso- and microdepressions, where sedimentation takes place [ 10 , 16 ]. Different spatial distribution patterns of 137 Cs in soils of particular urban landscapes were found in the city of Ozersk near the nuclear fuel cycle works [ 17 ]. Natural character of 137 Cs migration in soils of Moscow forest-parks and a decrease in its specific activity in industrial areas have been revealed [ 10 ]. Determination of the mean level and parameters of spatial variations of 137 Cs in soils is one of primary tasks of radioecological monitoring of cities, including both unpolluted (background) and contaminated territories.
Emissions and discharges from numerous sources of contamination can cause the accumulation of a wide range of toxicants in urban soils: heavy metals (HMs), oil products (OPs), polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), and other chemical substances. Soil contamination by several groups of toxicants is often observed in urban landscapes [ 20 , 23 ] because of the common contamination source or close pathways of the migration of different contaminants. A comprehensive analysis of contamination of urban soils by radionuclides and heavy metals has been performed in some studies [ 21 , 25 ]. The determination of possible spatial interrelationships between radioactive and chemical contaminations in urban soils is an important problem in urban ecology.
A radiation accident took place in the Elektrostal heavy engineering works (EHEW) in April 2013: a capacious source of 137 Cs entered the smelt furnace, and emission of radioactive aerosols from the aerating duct into the urban environment took place. The activity of molten source was estimated at about 1000–7000 Ci [ 14 ]. The area of contamination in the territory of the plant reached 7500 m 2 . However, radioactive aerosols affected a much larger area around the EHEW, including Krasnaya and Pervomaiskaya streets, and reached Lenin Prospect.
Geochemical evaluation of contamination of the upper soil horizon in the city of Elektrostal was carried out in 1989–1991. This survey indicated the anomalies of concentrations of wolfram, nickel, molybdenum, chromium, and other heavy metals related to accumulation of alloying constituent and impurities of non-ferrous metals in the emissions of steelmaking works [ 19 ].
The aim of our work was to determine the levels of specific activity of 137 Cs, concentrations of mobile forms of heavy metals (Zn, Cu, Ni, Co, Cr, and Pb) and oil products in the upper soil horizons in different urban landscapes of the city of Elektrostal under the conditions of local radioactive and chemical contamination.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Lomonosov Moscow State University, 119991, Moscow, Russia
D. N. Lipatov, V. A. Varachenkov, D. V. Manakhov, M. M. Karpukhin & S. V. Mamikhin
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to D. N. Lipatov .
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by T. Chicheva
Rights and permissions
Open Access. This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Lipatov, D.N., Varachenkov, V.A., Manakhov, D.V. et al. Spatial Variations of the Activity of 137 Cs and the Contents of Heavy Metals and Petroleum Products in the Polluted Soils of the City of Elektrostal. Eurasian Soil Sc. 55 , 840–848 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229322060072
Download citation
Received : 21 October 2021
Revised : 22 December 2021
Accepted : 30 December 2021
Published : 15 June 2022
Issue Date : June 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229322060072
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- urban soils
- urban ecosystems
- radiation monitoring
- decontamination
- Urban Technosols
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

COMMENTS
The International Food Research Journal (IFRJ) publishes papers in English, six (6) issues a year. The scope of the Journal includes: Food chemistry. Food microbiology. Food safety. Food processing. Food engineering. Food quality. Food toxicology.
Food Research International is an open access journal that publishes novel and high impact research in food science, technology, engineering and nutrition. It covers topics such as food chemistry, microbiology, toxicology, engineering, sensory science, quality, health and nutrition, and nanotechnology.
The International Food Research Journal (IFRJ) publishes papers in English, six (6) issues a year. The scope of the Journal includes: -Food chemistry- Food microbiology- Food safety- Food processing- Food engineering- Food quality- Food toxicology- Food nutritional chemistry- Food analysis- Food packagingy- Sensory science- Post-harvest ...
A peer-reviewed journal that publishes original research articles on various aspects of food science and technology. The latest issue covers topics such as amaranth proteins, pennywort leaves, red wine, konar fruits, oregano and thyme essential oils, and more.
International Food Research Journal Volume 29 Issue 1, 2022 Review Main functional ingredients, nutritional, and medicinal values of common wild edible fungi: a review
Browse the latest articles of Food Research International, a peer-reviewed journal covering all aspects of food science and technology. Find issues from 2005 to 2024, formerly known as Canadian Institute of Food Science and Technology Journal.
Development and validation of a predictive model for the effect of temperature, pH and water activity on the growth kinetics of Bacillus coagulans in non-refrigerated ready-to-eat food products. Ourania Misiou, Christina Zourou, Konstantinos Koutsoumanis. Article 110705.
ISSN 2231-7546 (Online) | International food research journal. Skip to main content. Leave this field blank . Log In; Automatic login IP; PUBLISHERS' AREA DISCOVER ISSN SERVICES SEARCH OPEN ACCESS RESOURCES KEEPERS REGISTRY ISSN INTERNATIONAL CENTER. Username or e-mail * Password * Forgot Password. Home Record ...
This study evaluates the nutritional quality and level of processing of food and beverage products advertised on television channels most watched by children, in Italy. Data were collected over 20 non-consecutive days from the five top channels in Italy. A total of 209 food items were analysed using the Nutri-Score and the NOVA classification.
International Food Research Journal Faculty of Food Science and Technology Universiti Putra Malaysia 43400 UPM Serdang Selangor Malaysia Phone: +603-89468361 Fax: +603- 89423552 Email: [email protected]. International Food Research Journal carries no page charge.
Food Research is an O pen Access journal that publishes reviews, original research articles and short communications focusing on f ood science and technology, food service management, nutrition, nutraceuticals, food innovation, and agriculture food science. Studies should be of general interest to the international community of food researchers.
A multidisciplinary journal that publishes research on food science topics, such as shelf life, food engineering, and food processing. Browse the latest articles, meet the editorial board, and propose a special issue.
Suwen Liu, Jincheng Yu, Mengfan Fu, Xinfang Wang, Xuedong Chang. Article 110239. View PDF. Article preview. Read the latest articles of Food Research International at ScienceDirect.com, Elsevier's leading platform of peer-reviewed scholarly literature.
Scope. Food Research International provides a forum for the rapid dissemination of significant novel and high impact research in food science, technology, engineering and nutrition. The journal only publishes novel, high quality and high impact review papers, original research papers and letters to the editors, in the various disciplines ...
Millets are small-seeded cereals belonging to the family Poaceae. They are considered to be climate-resilient and future nutritional food cereals for humans. Millets are resistant to biotic and abiotic stressors compared to other major cereals and thrive in low-quality soils with little maintenance and less rainfall. The importance of millets is still not well known to many people due to the ...
Abstract. The possibility of using furfurol for the production of ash-free high-strength active carbons with spheroidal particles as adsorbents and catalyst supports is substantiated. A single-stage process that incorporates the resinification of furfurol, the molding of a spherical product, and its hardening while allowing the process cycle ...
Features of the macrostructure and microstructure of uranium dioxide powders are considered. Assumptions are made on the mechanisms of the behavior of powders of various natures during pelletizing. Experimental data that reflect the effect of these powders on the quality of fuel pellets, which is evaluated by modern procedures, are presented. To investigate the structure of the powders, modern ...
A tool for varietal selection. Ángela Díaz-Fernández, Emilia Díaz-Losada, Daniel Moreno, M. Esperanza Valdés Sánchez. Article 110983. View PDF. Article preview. Read the latest articles of Food Research International at ScienceDirect.com, Elsevier's leading platform of peer-reviewed scholarly literature.
The basic parameters of testing the fuel pellets produced by powder metallurgy for resintering, which should be provided by repeated heat treatment, are stated. The expressions for calculating the pellet resintering level and describing the procedure developed at OAO Mashinostroitel'nii zavod (Elektrostal') for evaluating the resintering of various types of fuel pellets are presented.
A peer-reviewed journal that publishes original research articles and reviews on various aspects of food science and technology. The current issue covers topics such as fermented food products, natural products, foodborne diseases, halal meat, silkworm pupal oil, coffee beans, goat's milk, lemon myrtle, potato starches, olive leaves, ginger, mangostana, clitoria ternatea, soybean, buckwheat, spelt, maize, jasmine flower, resistant starch, and food packaging.
ISSN 1985-4668 (Print) | International food research journal. Skip to main content. Leave this field blank . Log In; Automatic login IP; PUBLISHERS' AREA DISCOVER ISSN SERVICES SEARCH OPEN ACCESS RESOURCES KEEPERS REGISTRY ISSN INTERNATIONAL CENTER. Username or e-mail * Password * Forgot Password. Home Record ...
Find breaking science news and analysis from the world's leading research journal.
Introduction Food Research International is the successor to the Canadian Institute of Food Science and Technology Journal. Building on the quality and strengths of its predecessor, Food Research International has been developed to create a truly international forum for the communication of research in food science. Food Research International provides a forum for the rapid dissemination of ...
Changes in food quality and microbial composition of Russian sturgeon (Acipenser gueldenstaedti) fillets treated with low temperature vacuum heating method during storage at 4 °C. Shi-ke Shen, Yue-wen Chen, Xiu-ping Dong, Fei-jian Liu, ... Yi-ran Wang.
Field research was carried out in the city of Elektrostal, Moscow oblast, in July 2018, i.e. 5 years and 3 months after the local fallout of 137 Cs in the result of radiation accident. The emission of 137 Cs from the chimney of steel melting plant spread to the west of heavy engineering works in April 2013 in the day of radiation accident [].The surveyed part of the city near the plant ...