

7 Tips to Draft a Compelling Budget for Grant Proposal
While financial support is crucial for conducting research, acquiring funds for your research is a challenging task and so is planning the budget for grant proposal !
The key requisites of a successful grant proposal are:
- Uniqueness of the research problem
- Best possible plan for solving the problem
- Appropriate budget planning
In an attempt to grab the attention of funders, researchers strive to submit innovative research proposals and often overlook other elements when creating a successful grant proposal. One such neglected section is the budget for grant proposals . It is important for funders to know how finances are being utilized. Therefore, adequately estimating how much the project will cost and how the finances will be distributed can make all the difference. In simpler words, your grant proposal must explain your request in both textual and numeral forms.
It is often a challenge for budding researchers to present an estimated cost of their research. However, remember that the grant budget is not an organizational budget! Furthermore, in today’s age of stiff competition, even senior researchers will benefit from improving their budgeting skills. In this article, we will discuss ways on how to draft a compelling budget for grant proposal.
Why is the Budget Section Important for a Grant Proposal?
A grant budget is important to paint the financial picture of your research proposal to the funders. The budget for grant proposal provides the following:
- Details of the possible expenditures for the proposed research project .
- Reassurance to funders that the researchers have a realistic sense of the expenses to complete the work proposed.
- List of other income sources for costs not covered in the grant proposal.
- Guarantees an optimal use of the funds.
- Makes practical implementation of the research project smoother.
What Constitutes a Budget for Grant Proposal?
An estimated budget quantifies the financial plan for possible expenses during the research project. The budget for grant proposals must demonstrate and serve a plan for funders on how the researcher/s will utilize the money for both operational aspects of the project and miscellaneous expenses associated with the research.
In order to stand out from other applicants, researchers can customize the budget for grant proposal as per the funding agencies’ guidelines. However, the major elements of the budget plan comprise two broad categories: Direct and Indirect Costs
- Direct Costs
Direct costs are perhaps the most critical part of your budget section. These expenses are solely incurred for executing your research. It broadly includes expenses towards:
- Personnel (payroll)
- Consumables
Furthermore, direct costs are sub-categorized into the below two forms based on their occurrence during the research:
- Recurring expenses
- Non-recurring expenses
As human resources are required for the study, salaries with allowances must be budgeted as per funding agency guidelines. The human resources may include personnel such as site manager, research assistant, junior research fellow (JRF), senior research fellow (SRF), research associate, technician, or data entry operator, and attender.
- Recurring expenses:
These expenses are variable and may keep on occurring throughout the study period. Consumables, chemicals, glassware, laboratory test charges , diagnostic kits, stationery, prints, photocopies, communication, postage, telephone charges, survey tools, questionnaires, publication charges, reprints, binding, etc. are some of the particulars in this category. Additionally, recurring expenses could also include allowances for patients/participants, food charges, and medical charges.
- Non-recurring expenses:
These are expenses that are one-time in nature and do not recur at regular intervals throughout the research duration. Equipment or instruments along with its accessories, software programs, computers, printers, electronic accessories of existing instruments in your lab, etc. are some of the particulars covered under non-recurring expenses.
- Traveling expenses:
Travelling expenses can be used for attending meetings, conferences, workshops, and training programs relevant to your research study. Some funding agencies allow both foreign and domestic travel, whereas, some do not. You can mention traveling expenses for collection of data, survey, and visit to other centers in a multi-centric study in this sub-section.
The detailed budget for grant proposal should be clear, well organized and easy to understand. Below is an example for grant proposal. The costs described below are direct costs:
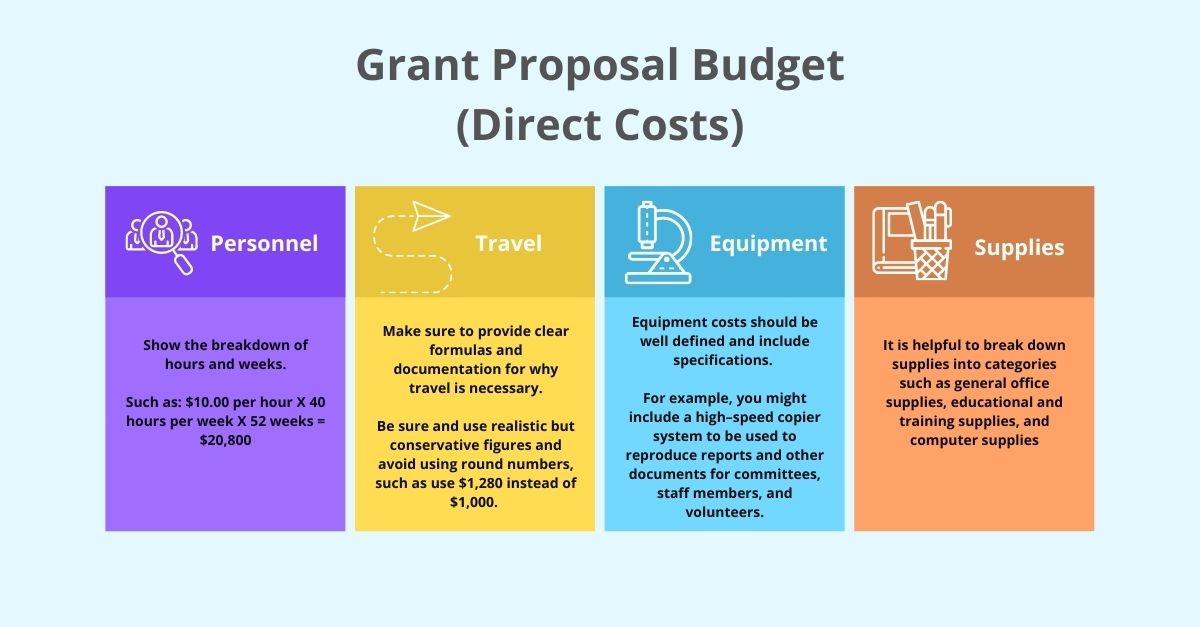
- Indirect Costs
These do not directly attribute to specific expenses of a research, but rather act as an accomplice to run a project. These are also termed as overhead charges. Particulars such as electricity bill, water, library membership, accommodation charges, administrative charges, etc. are included in indirect costs. Generally, about 5–15% of the total budget is provisioned as overhead charges, which is credited to the institution directly. However, this range may vary as per the funding agency.

Tips to Draft a Compelling Budget for Grant Proposal
So when does your budget planning begin? It’s usually when you have your research question and a suitable study design ready!
Here are seven top tips to follow whilst drafting a compelling budget for grant proposal :
- Focus on Uniqueness of Study Essentials
Study design, testing procedures, sample collection methods, and research settings are the essential factors that need to be focused on to resolve the research problem. The uniqueness and complexity of these essentials increases the chances of being incorporated in the budget.
- Follow Funding Agency Guidelines
You must abide by the budget rules and limitations provided by your potential funder and draft the budget accordingly. Scrutinize each instruction and do not deviate from its actual meaning. Most importantly, stick to the list of requisites provided by the funding agencies.
- Categorization of Each Item
Breakup all particulars with their costs under related categories as mentioned earlier. Furthermore, follow an item-wise and year-wise tabulation method to present your budget.
- Value for Money
Funders like to see that the investigators are valuing the finances provided and not splurging on irrelevant particulars. For instance, you must mention if you can redirect resources such as equipment or instruments that are already available from your previous study and can be used in your present study.
- Include Expenses and Revenue
While you are seeking for funds , the funder is interested in investing in projects that bring other resources to the table. Owing to this, your budget section must include two sections:
Inclusion of expenses is obviously the major part of the budget section. Likewise, mentioning revenue in this case means other sources that will pay for your research.
You’d wonder—why do the potential funders care about where the other money is coming from? Well, it is to instill trust in the funders. Acquiring some or most of the needed funds gives credibility to your research and ensures the funder that organizations are willing to invest in non-profit research.
- Do Not Over-Estimate Your Budget
It is critical to base your budgeted expenses on the true costs of your project requisites. But pulling numbers out of thin air will lead to confusion and tally errors. Make sure that you find the cost of all particulars from trusted sources and quote them accurately in your budget. Avoid over-estimating your budget, as it may repel the funder. As you know, “something is better than nothing”! So stick to the narrative of your research and align the budget of grant proposal to it. Subsequently, it is important to keep in mind that a very low budget will raise eyebrows to suspicion. Thus, make sure what you request for is reasonable.
- Tracking Expenses
Describe your methodology to track the expenses throughout the project. You must mention how you plan to effectively manage your expenses and review them. Additionally, give references of some tools that you will be using to manage your finances.
Have you been facing challenges in drafting the budget for grant proposal ? What did you do to improve your budgeting skills? Try these tips while drafting the next budget for your grant proposal and let us know how it works out for you and your colleagues.
Hi , can i please get a template? for research grant
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Expert Interviews
Empowering Scholarly Endeavors: Insights on grants, funding, and diversity in academia
Funding plays an indispensable role in a researcher’s career. In our unwavering commitment to improve…

- Diversity and Inclusion
- Trending Now
The Silent Struggle: Confronting gender bias in science funding
In the 1990s, Dr. Katalin Kariko’s pioneering mRNA research seemed destined for obscurity, doomed by…

- Industry News
Optimizing Funding Strategies: Clarivate unveils Web of Science Grants Index for researchers
Clarivate Plc, a global leader in providing information services, has recently launched the Web of…

Addressing Socioeconomic Disparities in Academic Funding: Inclusivity in research grant allocation
Research grant allocation is a critical process that determines the distribution of funds to various…

- Thought Leadership
Knowledge Without Walls: Enago’s comprehensive global survey report on open-access publishing
In the ever-evolving landscape of scholarly communication, the global expansion of open-access (OA) publishing has…
Opening Doors to Academic Inclusivity: The significance of open access funding
Investing in Visibility: Incorporating publishing funds effectively in grant…
How to Write an Exceptional Research Scholarship Motivation Letter
Learn How to Write a Persuasive Letter of Support for Grant

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?
3 Examples of Grant Budgets That Will Win Over Funders [With Template]
Reviewed by:
April 28, 2022
Last Updated:
January 29, 2024
Table of Contents
It doesn’t matter if you’re applying for a government, corporation, or foundation grant, a well-crafted budget will make or break your proposal.
We interviewed over a dozen grant consultants and professionals to understand what grant budgets need to pass the sniff test with funders and convince them to open up checkbooks.
In this guide, we are going to share examples of effective grant budgets and highlight advice from seasoned grant writers. We’ll cover:
- Different budget types
- Real-world budget examples
- A downloadable budget template
- Expert advice from grant administrators and funders
Let’s dive in!
Your Grant Budget Will Make or Break Your Proposal
A grant budget is one of the most important parts of your grant proposal.
A grant budget is a detailed financial plan that outlines the estimated expenses of your proposed project or program for which you’re seeking funding. If the budget isn’t carefully crafted or doesn’t fall in line with the requirements of the funder, it could cause you to lose the award.

In general, the steps to creating a grant budget , include identifying all your potential expenses, delineating between direct and indirect costs, and giving yourself some buffer for unexpected costs.
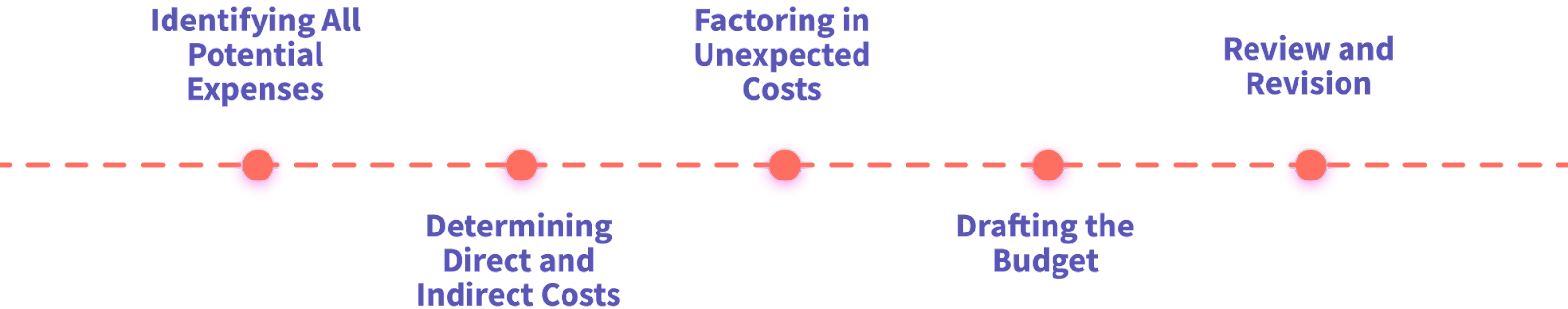
Likewise, always budget time for yourself to share the budget with your board and finance team so everyone’s on the same page, and you can make changes if need be before you get down to the wire with submission deadlines.
In many cases, funders will skip to your budget first before reading anything else in your proposal to make sure it meets their criteria, including:
- Alignment With Their Priorities. Most grants will specify what types of projects or operational expenses they are looking to fund, so your team should ensure your grant budget aligns with these priorities.
- Evidence of Need. Grant budgets must provide evidence of need to ensure the funding will be used to address urgent problems within your community. This evidence should coincide with the needs statement in the proposal.
- Feasibility and Transparency. Feasible and transparent grant budgets prove to the funder that you plan on using their monies in an appropriate and effective way.
- Sustainability. Funders want to support sustainable initiatives that will continue to thrive in the future (even after the grant funds run out). This is essential if you are applying for a program or project grant.
- Measurable Outcomes and Evaluation. You need to have measurable outcomes and a way to prove the impact of your proposed initiative. This includes a step-by-step plan that demonstrates how you will evaluate the success of your grant-funded project.
- Compliance and Accountability. Every grant has different compliance and accountability requirements, so it’s important to ensure your budget meets these specifications.
- Clear and Compelling Narrative. Knowing how to write a clear, compelling, and organized budget narrative is imperative to justifying your project’s costs that are attributed in each line item or category within the budget. This will enhance the credibility of the funding request.
For example, if your budget is too high, a funder might immediately pass you over. If your budget is too low, you could be setting yourself up for failure.
The NIH Central Resource for Grants and Funding Information , a leader in grant funding, further emphasizes the importance of properly estimating your budget:
“Significant over- or under-estimating suggests you may not understand the scope of the work.” - The NIH Central Resource for Grants and Funding Information
Even if you have the perfect idea for a new project, you will still lose out on funding if your grant budget isn’t feasible and in line with the funder’s priorities.

Santa Clara County Office of Education covers several more helpful tips for building grant proposal budgets in their webinar (starting at 3:27).
There Are Several Types of Grant Budgets You Might Use in an Application
There are several types of grant budgets you might use in a grant proposal.
Below we’ve outlined five of the most common budgets and explained when and why they might be used:
- Operating Budget: This type of budget is used for funding an organization's ongoing operational expenses, such as staff salaries, rent, utilities, and administrative costs. Operating budgets are often used for grants that support the general functioning of an organization.
- Program and Project Budgets: The most common types of grant budgets are used for specific programs or projects. For example, your nonprofit might be starting a new after-school program for disadvantaged youth and your budget would include all of the materials and supplies needed to run the program. Program and project budgets can be used to jumpstart new initiatives or support existing ones.
- Capital Budget: This type of budget is used for large-scale construction projects, purchasing new facilities, making renovations, or even purchasing new equipment. These budgets are large in size because they are used to fund capital projects that support the long-term operational needs of an organization.
- Research Budget: This type of budget is for research projects and community programs. For example, an environmental nonprofit organization may want to conduct research on pollution in their area’s streams and rivers. Their research budget could include the cost of the testing equipment, the researchers’ salaries, and more.
- Multi-Year Budget: Multi-year budgets simply refer to budgets that span over multiple years. The funder usually specifies if they are awarding a multi-year grant, which means you will need to detail in your budget how you will sustain your project, research, or initiative over a longer period of time.
Click to find the best grants for your nonprofit from 12,000+ active opportunities.
Search 150+ subcategories
Examples of Grant Budgets for Different Types of Nonprofits
Grant budgets will look different depending on what they’re for. But each budget will include direct costs, those expenses related to the project or program you’re funding, as well as indirect costs that go along with running an organization. Depending on the type of grant you win, the award will cover only direct costs, or, if a general operating grant , it may cover much more.

To make it more concrete, let's look at 3 examples of grant budgets. We'll show an operating budget, a project budget, and a capital budget.
Operating Budget for Violence Prevention and Intervention
Operating budgets are easier to develop because you can estimate the amounts based on the day-to-day costs in your organizational budget from the prior year.
Some common operational expenses could include the following:
- Salaries and benefits for staff members
- Office rent and utilities
- Administrative and office supplies
- Marketing and outreach expenses
- Accounting and legal fees
- Fundraising expenses
As an example, the operating budget below details the total expenses for a General Operating Grant for $40,000 for a Chicago-area violence prevention and intervention nonprofit. This example even includes explanations of variances between the budget and actual amounts:

Project Budget for a Community Education Program
Project budgets should outline your overall spending plan for your entire project, from successfully executing it to evaluating its impact and sustainability.
Line items usually found in a project plan include:
- Project coordinator's salary
- Outreach and education materials
- Training sessions and workshops
- Equipment and supplies
- Evaluation and data analysis costs
The Council of New Jersey Grantmakers has a project budget sample for a Community Education Initiative that lays out each budgetary requirement clearly and accurately for the funder:

Capital Budget for a School Renovation Project
Capital grants are usually for large-scale items like construction, renovations, or equipment.
Budgetary items include:
- Construction and renovation costs
- Architectural and engineering fees
- Building permits and inspections
- Furniture and fixtures
- Technology infrastructure
- Contingency for unexpected construction issues
Western Kentucky University had numerous improvements they wanted to complete on their campus. They created a capital budget that detailed the capital expenditures over a multi-year life of a possible grant. The entire capital budget can be found here , and a sample of their budgetary items is shown below and can be used as a budget template:

Downloadable Grant Budget Templates
There are many resources to assist you with creating your own budget after you’ve considered all of the direct and indirect costs of your project.
For example, one of the helpful grant budget examples comes from the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA). You can download this example here and repurpose it to use as your own budget template.
This sheet provides a great sample of staffing and personnel needs for a proposed project. It also walks the reader through a budget justification and includes matching grant funds.

You can also use Instrumentl's Grant Budget Template sample from the U.S. General Services Administration, which is a simple budget in Google Sheets that can be tailored to your specific budget line items.

This is another helpful example that you can repurpose with your own budgetary information.
Expert Advice on Building Your Grant Budget
There’s a lot of advice you’ll hear through the grape vine regrading grant budgets. To help pick out the signal from the noise, we interviewed several seasoned grant professionals. Here’s what they had to share.
Details Matter
All experts agree that details matter when compiling your budget. If the details aren’t clear or don’t add up, a funder will see through your numbers.
Elizabeth Morgan Burrows, JD, principal of Burrows Consulting , stresses that you should have a detailed budget that lists each of your expected expenditures for the entirety of your project. That way, the funder has a clear understanding that your nonprofit has the means and manpower to complete the proposed project.

Some general line items you will want to prioritize include:
- The people working on the project and their respective salaries being funded by the grant.
- Any technology required for the project and/or the reporting requirements.
- Costs associated with specific tasks and responsibilities.
- Revenue that comes into the nonprofit for the program.
Be Consistent With Your Narrative
Each line item in your budget should align with your overall narrative. If there is an activity explained in your narrative that requires funding, it must be a line item in your budget.
Lyndel King , Chair, Board of Overseers at Hill Museum & Manuscript Library, stresses that you need to "make sure that the item is somehow accounted for in the narrative. Everything in the budget should be able to be tied back to the project narrative.”
A clear budget will instil confidence. Anything less could arouse suspicion or doubt, costing you the award.

With that said, Sarah Lange , a grant consultant, advises grant teams not to undersell themselves either.
“Funders want to see reasonable costs, but please don’t fall prey to pressure to keep overhead low! Your program costs what it costs, and your staff deserves a living wage!”
Stay Realistic and Feasible
Earlier, we discussed the importance of staying realistic and feasible. Jacob B. Chase from Chase Consulting Solutions , agrees.
He's quick to remind his clients that a realistic budget is a winning budget. It shows that your "and organization has thoroughly considered the financial aspects of the project."

Connect the Budget to Your Goals
Finally, your budget needs to establish a clear connection between the numbers and your goals.
A funder will more than likely skip over your proposal if your budget doesn’t meet the needs of the intended audience.
CEO of Chase Consulting Solutions , Jacob B. Chase, shares,
“Demonstrate a clear connection between the budget and the project goals outlined in the proposal. Funders want to see that resources are allocated to activities that directly contribute to the project's success.”
Rachel Grusin, Project Coordinator for the Legal Aid Society of San Diego , further explains that nonprofits can't expect to slide in a line item without a clear explanation for why it belongs.

Ready To Submit Your Grant Budget?
It should be clear by now that your grant budget can make or break your chances of winning funding. The examples, insights, and expert advice in this guide should provide you with the resources you need to craft an effective and compelling budget in your next proposal.
For even more helpful advice, check out these 24 tips for stronger grant proposals .
Get access to weekly advice and grant writing templates

10k+ grant writers have already subscribed

Stephanie Paul Morrow
Stephanie Morrows holds a Ph.D. in Media and Communications and is a professor at PennState Harrisburg.
Become a Stronger Grant Writer in Just 5 Minutes
Share this article, related posts, 5 tips for using ai to write grants: 4 experts putting it to the test.
These days, it feels like Artificial Intelligence (AI) is everywhere. We spoke to four industry experts to learn how they are—or are not—using AI to support their grant-seeking efforts.
How to Make Your Letter of Inquiry Stand Out To Funders
Learn how to write compelling Letters of Inquiry (LOIs) with practical advice from grant experts. Discover essential tips from recorded events with Arnisha Johnson and Margit Brazda Poirier to increase your chances of success in securing funding for your nonprofit.
These Grant Writers Raised Millions: Tactics They Swear By To Win Over Funders
Unlock the secrets to becoming a game-changing grants professional with insights from industry experts who have secured millions in funding. Learn from their years of experience.
Try Instrumentl
The best tool for finding & organizing grants
128 reviews | High Performer status on g2.com


- Conduct , Grants and Funding
How to Plan and Write a Budget for Research Grant Proposal
Conductscience.
Need equipment for your lab?
To be a successful candidate for a research grant, you need perfect budget formulation and justification. Here, we will help you plan the research budget for your grant proposal and give you handy tips to transform it into a convincible form.
Budget as a Skeletal Support
Your budget is the skeleton of your grant proposal. It provides the estimated finance your research needs to be completed in a particular time range. It also gives the funders an exact knowledge about where their funds will be used and how will they be financed ( Asya, 2008 ). It is your responsibility to postulate clearly how you will manage the funds if granted. An excellent budget plan will compel your funders to assume that you have thought about every financial detail concerning your project.
Specific Terminologies to Know Beforehand
Certain wordings are preferred to convey your research budget information better. It is important to familiarize with them before constructing the budget section of the proposals. The lexis includes:
Direct Costs
These are the expenses that are utilized solely for executing your research. For example, expenses on your research staff members, tools, materials, and travel finance.
Facilities & Administrative Costs (Indirect Costs)
These are the overhead charges reserved for institutional facilities that you avail yourself while conducting your research. For example, institutional laboratory, electricity, and water usage costs.
Fringe Benefits
These are the additional benefits provided to the personnel, along with their basic salaries. Every institution has its own set of fringe benefits rates.
Research Consortium
It is a group of institutions that apply for a grant together as one. They have reached a grant agreement, and one of the institutions represents them all. The budget is divided between them.
Types of Budget
There are two budget designs used in the NIH grant applications. Specific points will decide the type of budget design form you have to use for your application. These are:
Modular Design Budget
Your budget design is considered modular when your research fulfills the following criteria:
- Your direct costs are equal to or less than $250,000 annually
- You are applying for research grants or their equivalents
- Your institution is located in the United States
Detailed Design Budget
Your budget design should be in detailed form if your research project fulfills any of the below-mentioned criteria:
- Your direct costs are more than $250,000 per annum
- You are applying for grants other than research grant type or its equivalents
- Your institution is situated outside the United States
For the modular design, you have to fill out the PHS 398 modular budget application form, and for the detailed design budget, you have to use the R & R detailed budget application form.
Planning your Budget
Your budget planning starts when you find the research question and decide on a suitable study design. You should also be able to guess the unpredictable charges that can arise while conducting your research ( Sudheesh, Devika & Nethra, 2016 ). There are five main points to keep in mind while planning your research budget:
Pin-point the Budget Essentials
Think about all the things that will affect your research budget. These are mainly the study design, testing procedures, sample collection methods, and research settings. The more complicated and unique these essentials will be, the higher will be your budget requirements. Also, observe the already present resources and will they benefit your research budget.
Follow the Instructions of the Funding Agency
The next point to consider while planning your budget is to abide by the budget rules and limitations of your particular funding agency. Read each instruction carefully and remember not to deviate from it. It is expected of you to provide the exact list of items necessary for your project.
Categorization of Each Item
Thirdly, a breakdown of each item into its related category should be made along with its cost. A breakdown of the budget item-wise and year-wise with cost calculation should be done. Point out the recurring and nonrecurring items that are directly related to your research. All this planning is done beforehand to ensure proper budget management.
Justification of Each Item
For every enlisted item, you should be able to provide a solid justification for its importance in your research. Only a well-justified budget document can win the confidence of the peer reviewers.
Review & Verification of the Budget Items
Reviewing is the most significant step for every document or proposal. You can ask your team members to review your budget document for you. Also, recalculate the cost of each item and the total items combined cost per annum. Keep in mind that too low or high budget will only raise suspicion in the mind of your reviewers. So, make sure you plan a research budget range, not more than the maximum limit set by your funding agency ( Michael et al., 2019 ).
Scripting your Budget onto the Grant Application
Projecting your finances into your application requires skills. When writing, we primarily divide our budget into two sub-sections. These include:
As mentioned before, these are the direct expenses on which your research is largely dependent. So, firstly, give the heading of direct costs and then further give the following subheadings with explanations.
Personnel Involved
If your research project involves resource team members, here is where you have to mention them. Your resource team includes the technicians, laboratory attendants, site caretakers, data entry personnel, junior researchers, and the senior researcher involved. Specify their allowances and salaries in an organized manner.
Recurring Expenditure
These expenses occur regularly and yet cannot be avoided. These include equipment usage, laboratory-conducted diagnostic tests, telecommunication charges, chemicals, and any other essential items. Fees for human subjects involved in your research are also stated here.
Non-recurring Expenditure
These are the costs of items for which you have to pay one-time charges, and then their use is free. These include buying charges for the printer, computer, or other electronic items. Once you buy them, they are charge-free. Thus, you have to specify all the non-recurring charges in your budget form.
Traveling Expenditure
In this subheading, specify the amount spent on your traveling for research purposes. Separately mention your traveling costs for attending research-related conferences, seminars, and training. Also, mention the travel expenses for the surveys and data collection. Visiting expenses to other institutions for the sake of a research study can also be mentioned here.
Indirect Costs
The second sub-section is indirect expenditure. It includes facilities that are indirectly related to your research project. These can be library facilities, electricity, and water usage for your experiments and test conduction. These are also called overhead charges that are paid specifically to the institution for providing such facilities ( Ahmed & Abdullah, 2017 ).
Budget Overview
In the final paragraph, write a short finalizing note relating your budget outlining the main point. This should be a 4 to 5-lined paragraph.
Budget Justification
Most of the funding agencies separately require justification for each item that you specified in your above-mentioned budget form. This document is also known as the budget narrative page. It reasons the importance of that item for your research conduction. Each item is mentioned in the same order as in your budget form and should be justified respectively ( Al-Jundi & Salah, 2016 ). It is best to make a three-columned table with the name of the item in the first column, the quantity and cost in the second column, and a justification statement in the third column.
Budget Summary
In the last, you have to provide a summarized form of your budget for your proposed research. It is written at the end when you have completed writing your whole application. In this, you have to specify every item with its cost per annum. The non-recurring items will only be specified under the first-year heading as they have a one-time expense. Likewise, the recurring items will be mentioned in both years, along with their costs.
Esthetical Considerations
The following points will enhance the esthetics of your budget section:
Headings & Bullet points
Writing the budget items under a categorized heading will make it easy for the reviewers to retrieve the necessary points in your budget. You can use bullet marks or checklist signs to highlight your main points. This will show the reviewers that you have the budget representation skills and that your enlisted budget finance is authentic.
Tabulations
Try to write your budget essentials in a tabulated form with three main columns. The first column represents the item name. The second column specifies the cost of that particular essential. The third column signifies the importance of your particular essential in performing your research. This will save both time and effort of reviewers who have to scrutinize many applications at a time.
Organization
The pattern you follow for each essential specification in the budget form should be followed in the same manner while writing the budget justification document. There should be a flow in your budget data and which will further enhance its esthetics.
Elementary Language
Your language should be simple enough to be understood by a common person. Complicated terms and phrases will only make it difficult for reviewers to reach your point of view.
Your budget prepares you for all the financial aids you need to conduct your research. It informs you about the expenses of each research item and method. In this way, you can choose an economical procedure for your research. The budget section is considered as the key factor of success or failure for your proposal. This section requires a skillful approach and should be handled delicately. Nowadays, research writers record their budget in the form of electronic spreadsheets. It is easy to manage the budget essentials and the expenses via these excel spreadsheets. You just need to point out and categorize the direct and indirect costs in the already drawn tabulated budget spreadsheet. Hence, you will be able to plan and compose a well-scripted budget by following the instructions given in this article.
- Al-Riyami, A. (2008, April). How to Prepare a Research Proposal. Oman Medical Journal , 23 (2), 66–69. http://europepmc.org/articles/PMC3282423
- Duggappa, D.R., Nethra, S.S. & Sudheesh, K. (2016, September). How to Write a Research Proposal? Indian Journal of Anaesthesia , 60 (9), 631–634. https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5049.190617
- Burkhardt, J., Carlson, J.N., Gottlieb, M., King, A.M., Lee, S., Santen, S.A. & Wong, A.H. (2019, January). Show Me the Money: Successfully Obtaining Grant Funding in Medical Education. The Western Journal of Emergency Medicine , 20 (1), 71–77. https://doi.org/10.5811/westjem.2018.10.41269
- Al-Maniri, A. & Al-Shukaili, A. (2017). Writing a Research Proposal to the Research Council of Oman. Oman Medical Journal , 32 (3), 180–188. https://doi.org/10.5001/omj.2017.35
- Azzam, A. & Sakka, S. (2016, November). Protocol Writing in Clinical Research. Journal of Clinical & Diagnostic Research, 10(11), Z10–Z13. https://doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2016/21426.8865
Related Articles

Best Microchannel Pipettes: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction Pipetting, at first glance, would seem a fairly simple and easy task. Essentially described as glass or plastic tubes used to measure and transfer

Resource Identification Initiative
Resource Identification Initiative: A Key to Scientific Success and Analytics The key to success can be found in the essential principles of the Resource Identification

Best Microcentrifuges: A Comprehensive Guide
INTRODUCTION AND BRIEF HISTORY One of the most important pieces of equipment in the laboratory is the centrifuge, which facilitates the separation of samples of

Best Benchtop Centrifuges: A Comprehensive Guide
Top sales products.

Optogenetics Optical Fiber

Stereotaxic Portable Digital System for Rat & Mouse
Hess Tissue Forceps

Protective Virus Shield for Counter & Desk – Freestanding Clear Acrylic Shield 36″ x 24″
Elschling 1×2 Teeth Tissue Forceps
St. Martin 1×2 Teeth Tissue Forceps

Our Location
Conduct science.
- Become a Partner
- Social Media
- Career /Academia
- Privacy Policy
- Shipping & Returns
- Request a quote
Customer service
- Account details
- Lost password
DISCLAIMER: ConductScience and affiliate products are NOT designed for human consumption, testing, or clinical utilization. They are designed for pre-clinical utilization only. Customers purchasing apparatus for the purposes of scientific research or veterinary care affirm adherence to applicable regulatory bodies for the country in which their research or care is conducted.
The Ultimate Grant Writing Guide (and How to Find and Apply for Grants)
Securing grants requires strategic planning. Identifying relevant opportunities, building collaborations, and crafting a comprehensive grant proposal are crucial steps. Read our ultimate guide on grant writing, finding grants, and applying for grants to get the funding for your research.
Updated on February 22, 2024

Embarking on a journey of groundbreaking research and innovation always requires more than just passion and dedication, it demands financial support. In the academic and research domains, securing grants is a pivotal factor for transforming these ideas into tangible outcomes.
Grant awards not only offer the backing needed for ambitious projects but also stand as a testament to the importance and potential impact of your work. The process of identifying, pursuing, and securing grants, however, is riddled with nuances that necessitate careful exploration.
Whether you're a seasoned researcher or a budding academic, navigating this complex world of grants can be challenging, but we’re here to help. In this comprehensive guide, we'll walk you through the essential steps of applying for grants, providing expert tips and insights along the way.
Finding grant opportunities
Prior to diving into the application phase, the process of finding grants involves researching and identifying those that are relevant and realistic to your project. While the initial step may seem as simple as entering a few keywords into a search engine, the full search phase takes a more thorough investigation.
By focusing efforts solely on the grants that align with your goals, this pre-application preparation streamlines the process while also increasing the likelihood of meeting all the requirements. In fact, having a well thought out plan and a clear understanding of the grants you seek both simplifies the entire activity and sets you and your team up for success.
Apply these steps when searching for appropriate grant opportunities:
1. Determine your need
Before embarking on the grant-seeking journey, clearly articulate why you need the funds and how they will be utilized. Understanding your financial requirements is crucial for effective grant research.
2. Know when you need the money
Grants operate on specific timelines with set award dates. Align your grant-seeking efforts with these timelines to enhance your chances of success.
3. Search strategically
Build a checklist of your most important, non-negotiable search criteria for quickly weeding out grant options that absolutely do not fit your project. Then, utilize the following resources to identify potential grants:
- Online directories
- Small Business Administration (SBA)
- Foundations
4. Develop a tracking tool
After familiarizing yourself with the criteria of each grant, including paperwork, deadlines, and award amounts, make a spreadsheet or use a project management tool to stay organized. Share this with your team to ensure that everyone can contribute to the grant cycle.
Here are a few popular grant management tools to try:
- Jotform : spreadsheet template
- Airtable : table template
- Instrumentl : software
- Submit : software
Tips for Finding Research Grants
Consider large funding sources : Explore major agencies like NSF and NIH.
Reach out to experts : Consult experienced researchers and your institution's grant office.
Stay informed : Regularly check news in your field for novel funding sources.
Know agency requirements : Research and align your proposal with their requisites.
Ask questions : Use the available resources to get insights into the process.
Demonstrate expertise : Showcase your team's knowledge and background.
Neglect lesser-known sources : Cast a wide net to diversify opportunities.
Name drop reviewers : Prevent potential conflicts of interest.
Miss your chance : Find field-specific grant options.
Forget refinement : Improve proposal language, grammar, and clarity.
Ignore grant support services : Enhance the quality of your proposal.
Overlook co-investigators : Enhance your application by adding experience.
Grant collaboration
Now that you’ve taken the initial step of identifying potential grant opportunities, it’s time to find collaborators. The application process is lengthy and arduous. It requires a diverse set of skills. This phase is crucial for success.
With their valuable expertise and unique perspectives, these collaborators play instrumental roles in navigating the complexities of grant writing. While exploring the judiciousness that goes into building these partnerships, we will underscore why collaboration is both advantageous and indispensable to the pursuit of securing grants.
Why is collaboration important to the grant process?
Some grant funding agencies outline collaboration as an outright requirement for acceptable applications. However, the condition is more implied with others. Funders may simply favor or seek out applications that represent multidisciplinary and multinational projects.
To get an idea of the types of collaboration major funders prefer, try searching “collaborative research grants” to uncover countless possibilities, such as:
- National Endowment for the Humanities
- American Brain Tumor Association
For exploring grants specifically for international collaboration, check out this blog:
- 30+ Research Funding Agencies That Support International Collaboration
Either way, proposing an interdisciplinary research project substantially increases your funding opportunities. Teaming up with multiple collaborators who offer diverse backgrounds and skill sets enhances the robustness of your research project and increases credibility.
This is especially true for early career researchers, who can leverage collaboration with industry, international, or community partners to boost their research profile. The key lies in recognizing the multifaceted advantages of collaboration in the context of obtaining funding and maximizing the impact of your research efforts.
How can I find collaborators?
Before embarking on the search for a collaborative partner, it's essential to crystallize your objectives for the grant proposal and identify the type of support needed. Ask yourself these questions:
1)Which facet of the grant process do I need assistance with:
2) Is my knowledge lacking in a specific:
- Population?
3) Do I have access to the necessary:
Use these questions to compile a detailed list of your needs and prioritize them based on magnitude and ramification. These preliminary step ensure that search for an ideal collaborator is focused and effective.
Once you identify targeted criteria for the most appropriate partners, it’s time to make your approach. While a practical starting point involves reaching out to peers, mentors, and other colleagues with shared interests and research goals, we encourage you to go outside your comfort zone.
Beyond the first line of potential collaborators exists a world of opportunities to expand your network. Uncover partnership possibilities by engaging with speakers and attendees at events, workshops, webinars, and conferences related to grant writing or your field.
Also, consider joining online communities that facilitate connections among grant writers and researchers. These communities offer a space to exchange ideas and information. Sites like Collaboratory , NIH RePorter , and upwork provide channels for canvassing and engaging with feasible collaborators who are good fits for your project.
Like any other partnership, carefully weigh your vetted options before committing to a collaboration. Talk with individuals about their qualifications and experience, availability and work style, and terms for grant writing collaborations.
Transparency on both sides of this partnership is imperative to forging a positive work environment where goals, values, and expectations align for a strong grant proposal.
Putting together a winning grant proposal
It’s time to assemble the bulk of your grant application packet – the proposal itself. Each funder is unique in outlining the details for specific grants, but here are several elements fundamental to every proposal:
- Executive Summary
- Needs assessment
- Project description
- Evaluation plan
- Team introduction
- Sustainability plan
This list of multi-faceted components may seem daunting, but careful research and planning will make it manageable.
Start by reading about the grant funder to learn:
- What their mission and goals are,
- Which types of projects they have funded in the past, and
- How they evaluate and score applications.
Next, view sample applications to get a feel for the length, flow, and tone the evaluators are looking for. Many funders offer samples to peruse, like these from the NIH , while others are curated by online platforms , such as Grantstation.
Also, closely evaluate the grant application’s requirements. they vary between funding organizations and opportunities, and also from one grant cycle to the next. Take notes and make a checklist of these requirements to add to an Excel spreadsheet, Google smartsheet, or management system for organizing and tracking your grant process.
Finally, understand how you will submit the final grant application. Many funders use online portals with character or word limits for each section. Be aware of these limits beforehand. Simplify the editing process by first writing each section in a Word document to be copy and pasted into the corresponding submission fields.
If there is no online application platform, the funder will usually offer a comprehensive Request for Proposal (RFP) to guide the structure of your grant proposal. The RFP:
- Specifies page constraints
- Delineates specific sections
- Outlines additional attachments
- Provides other pertinent details
Components of a grant proposal
Cover letter.
Though not always explicitly requested, including a cover letter is a strategic maneuver that could be the factor determining whether or not grant funders engage with your proposal. It’s an opportunity to give your best first impression by grabbing the reviewer’s attention and compelling them to read further.
Cover letters are not the place for excessive emotion or detail, keep it brief and direct, stating your financial needs and purpose confidently from the outset. Also, try to clearly demonstrate the connection between your project and the funder’s mission to create additional value beyond the formal proposal.
Executive summary
Like an abstract for your research manuscript, the executive summary is a brief synopsis that encapsulates the overarching topics and key points of your grant proposal. It must set the tone for the main body of the proposal while providing enough information to stand alone if necessary.
Refer to How to Write an Executive Summary for a Grant Proposal for detailed guidance like:
- Give a clear and concise account of your identity, funding needs, and project roadmap.
- Write in an instructive manner aiming for an objective and persuasive tone
- Be convincing and pragmatic about your research team's ability.
- Follow the logical flow of main points in your proposal.
- Use subheadings and bulleted lists for clarity.
- Write the executive summary at the end of the proposal process.
- Reference detailed information explained in the proposal body.
- Address the funder directly.
- Provide excessive details about your project's accomplishments or management plans.
- Write in the first person.
- Disclose confidential information that could be accessed by competitors.
- Focus excessively on problems rather than proposed solutions.
- Deviate from the logical flow of the main proposal.
- Forget to align with evaluation criteria if specified
Project narrative
After the executive summary is the project narrative . This is the main body of your grant proposal and encompasses several distinct elements that work together to tell the story of your project and justify the need for funding.
Include these primary components:
Introduction of the project team
Briefly outline the names, positions, and credentials of the project’s directors, key personnel, contributors, and advisors in a format that clearly defines their roles and responsibilities. Showing your team’s capacity and ability to meet all deliverables builds confidence and trust with the reviewers.
Needs assessment or problem statement
A compelling needs assessment (or problem statement) clearly articulates a problem that must be urgently addressed. It also offers a well-defined project idea as a possible solution. This statement emphasizes the pressing situation and highlights existing gaps and their consequences to illustrate how your project will make a difference.
To begin, ask yourself these questions:
- What urgent need are we focusing on with this project?
- Which unique solution does our project offer to this urgent need?
- How will this project positively impact the world once completed?
Here are some helpful examples and templates.
Goals and objectives
Goals are broad statements that are fairly abstract and intangible. Objectives are more narrow statements that are concrete and measurable. For example :
- Goal : “To explore the impact of sleep deprivation on cognitive performance in college students.”
- Objective : “To compare cognitive test scores of students with less than six hours of sleep and those with 8 or more hours of sleep.”
Focus on outcomes, not processes, when crafting goals and objectives. Use the SMART acronym to align them with the proposal's mission while emphasizing their impact on the target audience.
Methods and strategies
It is vitally important to explain how you intend to use the grant funds to fulfill the project’s objectives. Detail the resources and activities that will be employed. Methods and strategies are the bridge between idea and action. They must prove to reviewers the plausibility of your project and the significance of their possible funding.
Here are some useful guidelines for writing your methods section that are outlined in " Winning Grants: Step by Step ."
- Firmly tie your methods to the proposed project's objectives and needs assessment.
- Clearly link them to the resources you are requesting in the proposal budget.
- Thoroughly explain why you chose these methods by including research, expert opinion, and your experience.
- Precisely list the facilities and capital equipment that you will use in the project.
- Carefully structure activities so that the program moves toward the desired results in a time-bound manner.
A comprehensive evaluation plan underscores the effectiveness and accountability of a project for both the funders and your team. An evaluation is used for tracking progress and success. The evaluation process shows how to determine the success of your project and measure the impact of the grant award by systematically gauging and analyzing each phase of your project as it compares to the set objectives.
Evaluations typically fall into two standard categories:
1. Formative evaluation : extending from project development through implementation, continuously provides feedback for necessary adjustments and improvements.
2. Summative evaluation : conducted post-project completion, critically assesses overall success and impact by compiling information on activities and outcomes.
Creating a conceptual model of your project is helpful when identifying these key evaluation points. Then, you must consider exactly who will do the evaluations, what specific skills and resources they need, how long it will take, and how much it will cost.
Sustainability
Presenting a solid plan that illustrates exactly how your project will continue to thrive after the grant money is gone builds the funder's confidence in the project’s longevity and significance. In this sustainability section, it is vital to demonstrate a diversified funding strategy for securing the long-term viability of your program.
There are three possible long term outcomes for projects with correlated sustainability options:
- Short term projects: Though only implemented once, will have ongoing maintenance costs, such as monitoring, training, and updates.
(E.g., digitizing records, cleaning up after an oil spill)
- Projects that will generate income at some point in the future: must be funded until your product or service can cover operating costs with an alternative plan in place for deficits.
(E.g., medical device, technology, farming method)
- Ongoing projects: will eventually need a continuous stream of funding from a government entity or large organization.
(E.g., space exploration, hurricane tracking)
Along with strategies for funding your program beyond the initial grant, reference your access to institutional infrastructure and resources that will reduce costs.
Also, submit multi-year budgets that reflect how sustainability factors are integrated into the project’s design.
The budget section of your grant proposal, comprising both a spreadsheet and a narrative, is the most influential component. It should be able to stand independently as a suitable representation of the entire endeavor. Providing a detailed plan to outline how grant funds will be utilized is crucial for illustrating cost-effectiveness and careful consideration of project expenses.
A comprehensive grant budget offers numerous benefits to both the grantor , or entity funding the grant, and the grantee , those receiving the funding, such as:
- Grantor : The budget facilitates objective evaluation and comparison between multiple proposals by conveying a project's story through responsible fund management and financial transparency.
- Grantee : The budget serves as a tracking tool for monitoring and adjusting expenses throughout the project and cultivates trust with funders by answering questions before they arise.
Because the grant proposal budget is all-encompassing and integral to your efforts for securing funding, it can seem overwhelming. Start by listing all anticipated expenditures within two broad categories, direct and indirect expenses , where:
- Direct : are essential for successful project implementation, are measurable project-associated costs, such as salaries, equipment, supplies, travel, and external consultants, and are itemized and detailed in various categories within the grant budget.
- Indirect : includes administrative costs not directly or exclusively tied to your project, but necessary for its completion, like rent, utilities, and insurance, think about lab or meeting spaces that are shared by multiple project teams, or Directors who oversee several ongoing projects.
After compiling your list, review sample budgets to understand the typical layout and complexity. Focus closely on the budget narratives , where you have the opportunity to justify each aspect of the spreadsheet to ensure clarity and validity.

While not always needed, the appendices consist of relevant supplementary materials that are clearly referenced within your grant application. These might include:
- Updated resumes that emphasize staff members' current positions and accomplishments.
- Letters of support from people or organizations that have authority in the field of your research, or community members that may benefit from the project.
- Visual aids like charts, graphs, and maps that contribute directly to your project’s story and are referred to previously in the application.
Finalizing your grant application
Now that your grant application is finished, make sure it's not just another document in the stack Aim for a grant proposal that captivates the evaluator. It should stand out not only for presenting an excellent project, but for being engaging and easily comprehended .
Keep the language simple. Avoid jargon. Prioritizing accuracy and conciseness. Opt for reader-friendly formatting with white space, headings, standard fonts, and illustrations to enhance readability.
Always take time for thorough proofreading and editing. You can even set your proposal aside for a few days before revisiting it for additional edits and improvements. At this stage, it is helpful to seek outside feedback from those familiar with the subject matter as well as novices to catch unnoticed mistakes and improve clarity.
If you want to be absolutely sure your grant proposal is polished, consider getting it edited by AJE .
How can AI help the grant process?
When used efficiently, AI is a powerful tool for streamlining and enhancing various aspects of the grant process.
- Use AI algorithms to review related studies and identify knowledge gaps.
- Employ AI for quick analysis of complex datasets to identify patterns and trends.
- Leverage AI algorithms to match your project with relevant grant opportunities.
- Apply Natural Language Processing for analyzing grant guidelines and tailoring proposals accordingly.
- Utilize AI-powered tools for efficient project planning and execution.
- Employ AI for tracking project progress and generating reports.
- Take advantage of AI tools for improving the clarity, coherence, and quality of your proposal.
- Rely solely on manual efforts that are less comprehensive and more time consuming.
- Overlook the fact that AI is designed to find patterns and trends within large datasets.
- Minimize AI’s ability to use set parameters for sifting through vast amounts of data quickly.
- Forget that the strength of AI lies in its capacity to follow your prompts without divergence.
- Neglect tools that assist with scheduling, resource allocation, and milestone tracking.
- Settle for software that is not intuitive with automated reminders and updates.
- Hesitate to use AI tools for improving grammar, spelling, and composition throughout the writing process.
Remember that AI provides a diverse array of tools; there is no universal solution. Identify the most suitable tool for your specific task. Also, like a screwdriver or a hammer, AI needs informed human direction and control to work effectively.
Looking for tips when writing your grant application?
Check out these resources:
- 4 Tips for Writing a Persuasive Grant Proposal
- Writing Effective Grant Applications
- 7 Tips for Writing an Effective Grant Proposal
- The best-kept secrets to winning grants
- The Best Grant Writing Books for Beginner Grant Writers
- Research Grant Proposal Funding: How I got $1 Million
Final thoughts
The bottom line – applying for grants is challenging. It requires passion, dedication, and a set of diverse skills rarely found within one human being.
Therefore, collaboration is key to a successful grant process . It encourages everyone’s strengths to shine. Be honest and ask yourself, “Which elements of this grant application do I really need help with?” Seek out experts in those areas.
Keep this guide on hand to reference as you work your way through this funding journey. Use the resources contained within. Seek out answers to all the questions that will inevitably arise throughout the process.
The grants are out there just waiting for the right project to present itself – one that shares the funder’s mission and is a benefit to our communities. Find grants that align with your project goals, tell your story through a compelling proposal, and get ready to make the world a better place with your research.

The AJE Team
See our "Privacy Policy"
The Research Whisperer
Just like the thesis whisperer – but with more money, how to make a simple research budget.

Every research project needs a budget*.
If you are applying for funding, you must say what you are planning to spend that funding on. More than that, you need to show how spending that money will help you to answer your research question .
So, developing the budget is the perfect time to plan your project clearly . A good budget shows the assessors that you have thought about your research in detail and, if it is done well, it can serve as a great, convincing overview of the project.
Here are five steps to create a simple budget for your research project.
1. List your activities
Make a list of everything that you plan to do in the project, and who is going to do it.
Take your methodology and turn it into a step-by-step plan. Have you said that you will interview 50 people? Write it on your list.
Are you performing statistical analysis on your sample? Write it down.
Think through the implications of what you are going to do. Do you need to use a Thingatron? Note down that you will need to buy it, install it, and commission it.
What about travel? Write down each trip separately. Be specific. You can’t just go to ‘South East Asia’ to do fieldwork. You need to go to Kuala Lumpur to interview X number of people over Y weeks, then the same again for Singapore and Jakarta.
Your budget list might look like this:
- I’m going to do 10 interviews in Kuala Lumpur; 10 interviews in Singapore; 10 interviews in Jakarta by me.
- I’ll need teaching release for three months for fieldwork.
- I’ll need Flights to KL, Singapore, Jakarta and back to Melbourne.
- I’ll need Accommodation for a month in each place, plus per diem.
- The transcription service will transcribe the 30 interviews.
- I’ll analysis the transcribed results. (No teaching release required – I’ll do it in my meagre research time allowance.)
- I’ll need a Thingatron X32C to do the trials.
- Thing Inc will need to install the Thingatron. (I wonder how long that will take.)
- The research assistant will do three trials a month with the Thingatron.
- I’ll need to hire a research assistant (1 day per week for a year at Level B1.)
- The research assistant will do the statistical analysis of the Thingatron results.
- I’ll do the writing up in my research allowance time.
By the end, you should feel like you have thought through the entire project in detail. You should be able to walk someone else through the project, so grab a critical friend and read the list to them. If they ask questions, write down the answers.
This will help you to get to the level of specificity you need for the next step.
2. Check the rules again
You’ve already read the funding rules, right? If not, go and read them now – I’ll wait right here until you get back.
Once you’ve listed everything you want to do, go back and read the specific rules for budgets again. What is and isn’t allowed? The funding scheme won’t pay for equipment – you’ll need to fund your Thingatron from somewhere else. Cross it off.
Some schemes won’t fund people. Others won’t fund travel. It is important to know what you need for your project. It is just as important to know what you can include in the application that you are writing right now.
Most funding schemes won’t fund infrastructure (like building costs) and other things that aren’t directly related to the project. Some will, though. If they do, you should include overheads (i.e. the general costs that your organisation needs to keep running). This includes the cost of basics like power and lighting; desks and chairs; and cleaners and security staff. It also includes service areas like the university library. Ask your finance officer for help with this. Often, it is a percentage of the overall cost of the project.
If you are hiring people, don’t forget to use the right salary rate and include salary on-costs. These are the extra costs that an organisation has to pay for an employee, but that doesn’t appear in their pay check. This might include things like superannuation, leave loading, insurance, and payroll tax. Once again, your finance officer can help with this.
Your budget list might now look like this:
- 10 interviews in Kuala Lumpur; 10 interviews in Singapore; 10 interviews in Jakarta by me.
- Teaching release for three months for fieldwork.
- Flights to KL, Singapore, Jakarta and back to Melbourne.
- Accommodation for a month in each place, plus per diem, plus travel insurance (rule 3F).
- Transcription of 30 interviews, by the transcription service.
- Analysis of transcribed results, by me. No teaching release required.
- Purchase and install Thingatron X32C, by Thing Inc . Not allowed by rule 3C . Organise access to Thingatron via partner organistion – this is an in-kind contribution to the project.
- Three trials a month with Thingatron, by research assistant.
- Statistical analysis of Thingatron results, by research assistant.
- Research assistant: 1 day per week for a year at Level B1, plus 25.91% salary on-costs.
- Overheads at 125% of total cash request, as per rule 3H.
3. Cost each item
For each item on your list, find a reasonable cost for it . Are you going to interview the fifty people and do the statistical analysis yourself? If so, do you need time release from teaching? How much time? What is your salary for that period of time, or how much will it cost to hire a replacement? Don’t forget any hidden costs, like salary on-costs.
If you aren’t going to do the work yourself, work out how long you need a research assistant for. Be realistic. Work out what level you want to employ them at, and find out how much that costs.
How much is your Thingatron going to cost? Sometimes, you can just look that stuff up on the web. Other times, you’ll need to ring a supplier, particularly if there are delivery and installation costs.
Jump on a travel website and find reasonable costs for travel to Kuala Lumpur and the other places. Find accommodation costs for the period that you are planning to stay, and work out living expenses. Your university, or your government, may have per diem rates for travel like this.
Make a note of where you got each of your estimates from. This will be handy later, when you write the budget justification.
- 10 interviews in Kuala Lumpur; 10 interviews in Singapore; 10 interviews in Jakarta by me (see below for travel costs).
- Teaching release for three months for fieldwork = $25,342 – advice from finance officer.
- Flights to KL ($775), Singapore ($564), Jakarta ($726), Melbourne ($535) – Blue Sky airlines, return economy.
- Accommodation for a month in each place (KL: $3,500; Sing: $4,245; Jak: $2,750 – long stay, three star accommodation as per TripAdviser).
- Per diem for three months (60 days x $125 per day – University travel rules).
- Travel insurance (rule 3F): $145 – University travel insurance calculator .
- Transcription of 30 interviews, by the transcription service: 30 interviews x 60 minutes per interview x $2.75 per minute – Quote from transcription service, accented voices rate.
- Analysis of transcribed results, by me. No teaching release required. (In-kind contribution of university worth $2,112 for one week of my time – advice from finance officer ).
- Purchase and install Thingatron X32C, by Thing Inc . Not allowed by rule 3C. Organise access to Thingatron via partner organistion – this is an in-kind contribution to the project. ($2,435 in-kind – quote from partner organisation, at ‘favoured client’ rate.)
- Research assistant: 1 day per week for a year at Level B1, plus 25.91% salary on-costs. $12,456 – advice from finance officer.
Things are getting messy, but the next step will tidy it up.
4. Put it in a spreadsheet
Some people work naturally in spreadsheets (like Excel). Others don’t. If you don’t like Excel, tough. You are going to be doing research budgets for the rest of your research life.
When you are working with budgets, a spreadsheet is the right tool for the job, so learn to use it! Learn enough to construct a simple budget – adding things up and multiplying things together will get you through most of it. Go and do a course if you have to.
For a start, your spreadsheet will multiply things like 7 days in Kuala Lumpur at $89.52 per day, and it will also add up all of your sub-totals for you.
If your budget doesn’t add up properly (because, for example, you constructed it as a table in Word), two things will happen. First, you will look foolish. Secondly, and more importantly, people will lose confidence in all your other numbers, too. If your total is wrong, they will start to question the validity of the rest of your budget. You don’t want that.
If you are shy of maths, then Excel is your friend. It will do most of the heavy lifting for you.
For this exercise, the trick is to put each number on a new line. Here is how it might look.

5. Justify it
Accompanying every budget is a budget justification. For each item in your budget, you need to answer two questions:
- Why do you need this money?
- Where did you get your figures from?
The budget justification links your budget to your project plan and back again. Everything item in your budget should be listed in your budget justification, so take the list from your budget and paste it into your budget justification.
For each item, give a short paragraph that says why you need it. Refer back to the project plan and expand on what is there. For example, if you have listed a research assistant in your application, this is a perfect opportunity to say what the research assistant will be doing.
Also, for each item, show where you got your figures from. For a research assistant, this might mean talking about the level of responsibility required, so people can understand why you chose the salary level. For a flight, it might be as easy as saying: “Blue Sky airlines economy return flight.”
Here is an example for just one aspect of the budget:
Fieldwork: Kuala Lumpur
Past experience has shown that one month allows enough time to refine and localise interview questions with research partners at University of Malaya, test interview instrument, recruit participants, conduct ten x one-hour interviews with field notes. In addition, the novel methodology will be presented at CONF2015, to be held in Malaysia in February 2015.
Melbourne – Kuala Lumpur economy airfare is based on current Blue Sky Airlines rates. Note that airfares have been kept to a minimum by travelling from country to country, rather than returning to Australia.
1 month accommodation is based on three star, long stay accommodation rates provided by TripAdvisor.
30 days per diem rate is based on standard university rates for South-East Asia.
Pro tip: Use the same nomenclature everywhere. If you list a Thingatron X32C in your budget, then call it a Thingatron X32C in your budget justification and project plan. In an ideal world, someone should be able to flip from the project plan, to the budget and to the budget justification and back again and always know exactly where they are.
- Project plan: “Doing fieldwork in Malaysia? Whereabouts?” Flips to budget.
- Budget: “A month in Kuala Lumpur – OK. Why a month?” Flips to budget justification.
- Budget justification: “Ah, the field work happens at the same time as the conference. Now I get it. So, what are they presenting at the conference?” Flips back to the project description…
So, there you have it: Make a list; check the rules; cost everything; spreadsheet it; and then justify it. Budget done. Good job, team!
This article builds on several previous articles. I have shamelessly stolen from them.
- Constructing your budget – Jonathan O’Donnell.
- What makes a winning budget ? – Jonathan O’Donnell.
- How NOT to pad your budget – Tseen Khoo.
- Conquer the budget, conquer the project – Tseen Khoo.
- Research on a shoestring – Emily Kothe.
- How to make a simple Gantt chart – Jonathan O’Donnell.
* Actually, there are some grant schemes that give you a fixed amount of money, which I think is a really great idea . However, you will still need to work out what you are going to spend the money on, so you will still need a budget at some stage, even if you don’t need it for the application.
Also in the ‘simple grant’ series:
- How to write a simple research methods section .
- How to make a simple Gantt chart .
Share this:
28 comments.
This has saved my day!
Happy to help, Malba.
Like Liked by 1 person
[…] you be putting in a bid for funding? Are there costs involved, such as travel or equipment costs? Research Whisperer’s post on research budgets may help you […]
I’ve posted a link to this article of Jonathan’s in the Australasian Research Management Society LinkedIn group as well, as I’m sure lots of other people will want to share this.
Thanks, Miriam.
This is great! Humorous way to talk explain a serious subject and could be helpful in designing budgets for outreach grants, as well. Thanks!
Thanks, Jackie
If you are interested, I have another one on how to do a timeline: https://theresearchwhisperer.wordpress.com/2011/09/13/gantt-chart/
[…] really useful information regarding budget development can be found on the Research Whisperer Blog here. Any other thoughts and suggestions are welcome – what are your tips to developing a good […]
[…] it gets you to the level of specificity that you need for a detailed methods section. Similarly, working out a budget for your workshops will force you to be specific about how many people will be attending (venue […]
A friend of mine recently commented by e-mail:
I was interested in your blog “How to make a simple research budget”, particularly the statement: “Think through the implications of what you are going to do. Do you need to use a Thingatron? Note down that you will need to buy it, install it, and commission it.”
From my limited experience so far, I’d think you could add:
“Who else is nearby who might share the costs of the Thingatron? If it’s a big capital outlay, and you’re only going to use it to 34% of it’s capacity, sharing can make the new purchase much easier to justify. But how will this fit into your grant? And then it’s got to be maintained – the little old chap who used to just do all that odd mix of electrickery and persuasion to every machine in the lab got retrenched in the last round. You can run it into the ground. But that means you won’t have a reliable, stable Thingatron all ready to run when you apply for the follow-on grant in two years.”
[…] (For more on this process, take a look at How to Write a Simple Project Budget.) […]
[…] Source: How to make a simple research budget […]
This is such a big help! Thank You!
No worries, Claudine. Happy to help.
Would you like to share the link of the article which was wrote about funding rules? I can’t find it. Many thanks!
Hello there – do you mean this post? https://theresearchwhisperer.wordpress.com/2012/02/14/reading-guidelines
Thank @tseen khoo, very useful tips. I also want to understand more about 3C 3F 3H. What do they stand for? Can you help me find out which posts talk about that. Thank again.
[…] mount up rapidly, even if you are in a remote and developing part of the world. Putting together a half decent budget early on and being aware of funding opportunities can help to avoid financial disaster half way […]
This is so amazing, it really helpful and educative. Happy unread this last week before my proposal was drafted.
Happy to help, Babayomi. Glad you liked it.
really useful! thanks kate
[…] “How to Make a Simple Research Budget,” by Jonathan O’Donnell on The Research Whisperer […]
[…] offering services that ran pretty expensive. until I found this one. It guided me through making a simple budget. The information feels sort of like a university graduate research paper but having analysed […]
[…] Advice on writing research proposals for industry […]
[…] research serves as the bedrock of informed budgeting. Explore the average costs of accommodation, transportation, meals, and activities in your chosen […]
Leave a comment Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER COLUMN
- 14 January 2021
The power of a budget plan in grant writing
- Ethan Wilk 0
Ethan Wilk is a secondary-school student researching sustainable economics and finance at BASIS Scottsdale in Arizona.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
I awoke one morning last June to a blaring bedside alarm that nearly gave me a heart attack. That shock, however, paled in comparison to the one that followed when I read my e-mail — I had won a Harvard CBE Sustainability Grant , an environmental award of up to US$20,000 that is typically conferred on a cohort of students and faculty members at Harvard University in Cambridge, Massachusetts. I’m an 18-year-old high-school student.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-021-00096-x
This is an article from the Nature Careers Community, a place for Nature readers to share their professional experiences and advice. Guest posts are encouraged .
Patil, S. G. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 10 , 139–142 (2019).
Article Google Scholar
Kanji, S. Can. J. Hosp. Pharm. 68 , 458–464 (2015).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Download references
Related Articles

How I harnessed media engagement to supercharge my research career
Career Column 09 APR 24

How we landed job interviews for professorships straight out of our PhD programmes
Career Column 08 APR 24

Three ways ChatGPT helps me in my academic writing
How to break big tech’s stranglehold on AI in academia
Correspondence 09 APR 24
Use fines from EU social-media act to fund research on adolescent mental health

‘Without these tools, I’d be lost’: how generative AI aids in accessibility
Technology Feature 08 APR 24

India is booming — but there are worries ahead for basic science
News 10 APR 24

Brazil budget cuts could leave science labs without power and water
News 08 APR 24

Will the Gates Foundation’s preprint-centric policy help open access?
News 04 APR 24
Junior Group Leader Position at IMBA - Institute of Molecular Biotechnology
The Institute of Molecular Biotechnology (IMBA) is one of Europe’s leading institutes for basic research in the life sciences. IMBA is located on t...
Austria (AT)
IMBA - Institute of Molecular Biotechnology
Open Rank Faculty, Center for Public Health Genomics
Center for Public Health Genomics & UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center seek 2 tenure-track faculty members in Cancer Precision Medicine/Precision Health.
Charlottesville, Virginia
Center for Public Health Genomics at the University of Virginia
Husbandry Technician I
Memphis, Tennessee
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital (St. Jude)
Lead Researcher – Department of Bone Marrow Transplantation & Cellular Therapy
Researcher in the center for in vivo imaging and therapy.
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

Grant Proposals (or Give me the money!)
What this handout is about.
This handout will help you write and revise grant proposals for research funding in all academic disciplines (sciences, social sciences, humanities, and the arts). It’s targeted primarily to graduate students and faculty, although it will also be helpful to undergraduate students who are seeking funding for research (e.g. for a senior thesis).
The grant writing process
A grant proposal or application is a document or set of documents that is submitted to an organization with the explicit intent of securing funding for a research project. Grant writing varies widely across the disciplines, and research intended for epistemological purposes (philosophy or the arts) rests on very different assumptions than research intended for practical applications (medicine or social policy research). Nonetheless, this handout attempts to provide a general introduction to grant writing across the disciplines.
Before you begin writing your proposal, you need to know what kind of research you will be doing and why. You may have a topic or experiment in mind, but taking the time to define what your ultimate purpose is can be essential to convincing others to fund that project. Although some scholars in the humanities and arts may not have thought about their projects in terms of research design, hypotheses, research questions, or results, reviewers and funding agencies expect you to frame your project in these terms. You may also find that thinking about your project in these terms reveals new aspects of it to you.
Writing successful grant applications is a long process that begins with an idea. Although many people think of grant writing as a linear process (from idea to proposal to award), it is a circular process. Many people start by defining their research question or questions. What knowledge or information will be gained as a direct result of your project? Why is undertaking your research important in a broader sense? You will need to explicitly communicate this purpose to the committee reviewing your application. This is easier when you know what you plan to achieve before you begin the writing process.
Diagram 1 below provides an overview of the grant writing process and may help you plan your proposal development.
Applicants must write grant proposals, submit them, receive notice of acceptance or rejection, and then revise their proposals. Unsuccessful grant applicants must revise and resubmit their proposals during the next funding cycle. Successful grant applications and the resulting research lead to ideas for further research and new grant proposals.
Cultivating an ongoing, positive relationship with funding agencies may lead to additional grants down the road. Thus, make sure you file progress reports and final reports in a timely and professional manner. Although some successful grant applicants may fear that funding agencies will reject future proposals because they’ve already received “enough” funding, the truth is that money follows money. Individuals or projects awarded grants in the past are more competitive and thus more likely to receive funding in the future.
Some general tips
- Begin early.
- Apply early and often.
- Don’t forget to include a cover letter with your application.
- Answer all questions. (Pre-empt all unstated questions.)
- If rejected, revise your proposal and apply again.
- Give them what they want. Follow the application guidelines exactly.
- Be explicit and specific.
- Be realistic in designing the project.
- Make explicit the connections between your research questions and objectives, your objectives and methods, your methods and results, and your results and dissemination plan.
- Follow the application guidelines exactly. (We have repeated this tip because it is very, very important.)
Before you start writing
Identify your needs and focus.
First, identify your needs. Answering the following questions may help you:
- Are you undertaking preliminary or pilot research in order to develop a full-blown research agenda?
- Are you seeking funding for dissertation research? Pre-dissertation research? Postdoctoral research? Archival research? Experimental research? Fieldwork?
- Are you seeking a stipend so that you can write a dissertation or book? Polish a manuscript?
- Do you want a fellowship in residence at an institution that will offer some programmatic support or other resources to enhance your project?
- Do you want funding for a large research project that will last for several years and involve multiple staff members?
Next, think about the focus of your research/project. Answering the following questions may help you narrow it down:
- What is the topic? Why is this topic important?
- What are the research questions that you’re trying to answer? What relevance do your research questions have?
- What are your hypotheses?
- What are your research methods?
- Why is your research/project important? What is its significance?
- Do you plan on using quantitative methods? Qualitative methods? Both?
- Will you be undertaking experimental research? Clinical research?
Once you have identified your needs and focus, you can begin looking for prospective grants and funding agencies.
Finding prospective grants and funding agencies
Whether your proposal receives funding will rely in large part on whether your purpose and goals closely match the priorities of granting agencies. Locating possible grantors is a time consuming task, but in the long run it will yield the greatest benefits. Even if you have the most appealing research proposal in the world, if you don’t send it to the right institutions, then you’re unlikely to receive funding.
There are many sources of information about granting agencies and grant programs. Most universities and many schools within universities have Offices of Research, whose primary purpose is to support faculty and students in grant-seeking endeavors. These offices usually have libraries or resource centers to help people find prospective grants.
At UNC, the Research at Carolina office coordinates research support.
The Funding Information Portal offers a collection of databases and proposal development guidance.
The UNC School of Medicine and School of Public Health each have their own Office of Research.
Writing your proposal
The majority of grant programs recruit academic reviewers with knowledge of the disciplines and/or program areas of the grant. Thus, when writing your grant proposals, assume that you are addressing a colleague who is knowledgeable in the general area, but who does not necessarily know the details about your research questions.
Remember that most readers are lazy and will not respond well to a poorly organized, poorly written, or confusing proposal. Be sure to give readers what they want. Follow all the guidelines for the particular grant you are applying for. This may require you to reframe your project in a different light or language. Reframing your project to fit a specific grant’s requirements is a legitimate and necessary part of the process unless it will fundamentally change your project’s goals or outcomes.
Final decisions about which proposals are funded often come down to whether the proposal convinces the reviewer that the research project is well planned and feasible and whether the investigators are well qualified to execute it. Throughout the proposal, be as explicit as possible. Predict the questions that the reviewer may have and answer them. Przeworski and Salomon (1995) note that reviewers read with three questions in mind:
- What are we going to learn as a result of the proposed project that we do not know now? (goals, aims, and outcomes)
- Why is it worth knowing? (significance)
- How will we know that the conclusions are valid? (criteria for success) (2)
Be sure to answer these questions in your proposal. Keep in mind that reviewers may not read every word of your proposal. Your reviewer may only read the abstract, the sections on research design and methodology, the vitae, and the budget. Make these sections as clear and straightforward as possible.
The way you write your grant will tell the reviewers a lot about you (Reif-Lehrer 82). From reading your proposal, the reviewers will form an idea of who you are as a scholar, a researcher, and a person. They will decide whether you are creative, logical, analytical, up-to-date in the relevant literature of the field, and, most importantly, capable of executing the proposed project. Allow your discipline and its conventions to determine the general style of your writing, but allow your own voice and personality to come through. Be sure to clarify your project’s theoretical orientation.
Develop a general proposal and budget
Because most proposal writers seek funding from several different agencies or granting programs, it is a good idea to begin by developing a general grant proposal and budget. This general proposal is sometimes called a “white paper.” Your general proposal should explain your project to a general academic audience. Before you submit proposals to different grant programs, you will tailor a specific proposal to their guidelines and priorities.
Organizing your proposal
Although each funding agency will have its own (usually very specific) requirements, there are several elements of a proposal that are fairly standard, and they often come in the following order:
- Introduction (statement of the problem, purpose of research or goals, and significance of research)
Literature review
- Project narrative (methods, procedures, objectives, outcomes or deliverables, evaluation, and dissemination)
- Budget and budget justification
Format the proposal so that it is easy to read. Use headings to break the proposal up into sections. If it is long, include a table of contents with page numbers.
The title page usually includes a brief yet explicit title for the research project, the names of the principal investigator(s), the institutional affiliation of the applicants (the department and university), name and address of the granting agency, project dates, amount of funding requested, and signatures of university personnel authorizing the proposal (when necessary). Most funding agencies have specific requirements for the title page; make sure to follow them.
The abstract provides readers with their first impression of your project. To remind themselves of your proposal, readers may glance at your abstract when making their final recommendations, so it may also serve as their last impression of your project. The abstract should explain the key elements of your research project in the future tense. Most abstracts state: (1) the general purpose, (2) specific goals, (3) research design, (4) methods, and (5) significance (contribution and rationale). Be as explicit as possible in your abstract. Use statements such as, “The objective of this study is to …”
Introduction
The introduction should cover the key elements of your proposal, including a statement of the problem, the purpose of research, research goals or objectives, and significance of the research. The statement of problem should provide a background and rationale for the project and establish the need and relevance of the research. How is your project different from previous research on the same topic? Will you be using new methodologies or covering new theoretical territory? The research goals or objectives should identify the anticipated outcomes of the research and should match up to the needs identified in the statement of problem. List only the principle goal(s) or objective(s) of your research and save sub-objectives for the project narrative.
Many proposals require a literature review. Reviewers want to know whether you’ve done the necessary preliminary research to undertake your project. Literature reviews should be selective and critical, not exhaustive. Reviewers want to see your evaluation of pertinent works. For more information, see our handout on literature reviews .
Project narrative
The project narrative provides the meat of your proposal and may require several subsections. The project narrative should supply all the details of the project, including a detailed statement of problem, research objectives or goals, hypotheses, methods, procedures, outcomes or deliverables, and evaluation and dissemination of the research.
For the project narrative, pre-empt and/or answer all of the reviewers’ questions. Don’t leave them wondering about anything. For example, if you propose to conduct unstructured interviews with open-ended questions, be sure you’ve explained why this methodology is best suited to the specific research questions in your proposal. Or, if you’re using item response theory rather than classical test theory to verify the validity of your survey instrument, explain the advantages of this innovative methodology. Or, if you need to travel to Valdez, Alaska to access historical archives at the Valdez Museum, make it clear what documents you hope to find and why they are relevant to your historical novel on the ’98ers in the Alaskan Gold Rush.
Clearly and explicitly state the connections between your research objectives, research questions, hypotheses, methodologies, and outcomes. As the requirements for a strong project narrative vary widely by discipline, consult a discipline-specific guide to grant writing for some additional advice.
Explain staffing requirements in detail and make sure that staffing makes sense. Be very explicit about the skill sets of the personnel already in place (you will probably include their Curriculum Vitae as part of the proposal). Explain the necessary skill sets and functions of personnel you will recruit. To minimize expenses, phase out personnel who are not relevant to later phases of a project.
The budget spells out project costs and usually consists of a spreadsheet or table with the budget detailed as line items and a budget narrative (also known as a budget justification) that explains the various expenses. Even when proposal guidelines do not specifically mention a narrative, be sure to include a one or two page explanation of the budget. To see a sample budget, turn to Example #1 at the end of this handout.
Consider including an exhaustive budget for your project, even if it exceeds the normal grant size of a particular funding organization. Simply make it clear that you are seeking additional funding from other sources. This technique will make it easier for you to combine awards down the road should you have the good fortune of receiving multiple grants.
Make sure that all budget items meet the funding agency’s requirements. For example, all U.S. government agencies have strict requirements for airline travel. Be sure the cost of the airline travel in your budget meets their requirements. If a line item falls outside an agency’s requirements (e.g. some organizations will not cover equipment purchases or other capital expenses), explain in the budget justification that other grant sources will pay for the item.
Many universities require that indirect costs (overhead) be added to grants that they administer. Check with the appropriate offices to find out what the standard (or required) rates are for overhead. Pass a draft budget by the university officer in charge of grant administration for assistance with indirect costs and costs not directly associated with research (e.g. facilities use charges).
Furthermore, make sure you factor in the estimated taxes applicable for your case. Depending on the categories of expenses and your particular circumstances (whether you are a foreign national, for example), estimated tax rates may differ. You can consult respective departmental staff or university services, as well as professional tax assistants. For information on taxes on scholarships and fellowships, see https://cashier.unc.edu/student-tax-information/scholarships-fellowships/ .
Explain the timeframe for the research project in some detail. When will you begin and complete each step? It may be helpful to reviewers if you present a visual version of your timeline. For less complicated research, a table summarizing the timeline for the project will help reviewers understand and evaluate the planning and feasibility. See Example #2 at the end of this handout.
For multi-year research proposals with numerous procedures and a large staff, a time line diagram can help clarify the feasibility and planning of the study. See Example #3 at the end of this handout.
Revising your proposal
Strong grant proposals take a long time to develop. Start the process early and leave time to get feedback from several readers on different drafts. Seek out a variety of readers, both specialists in your research area and non-specialist colleagues. You may also want to request assistance from knowledgeable readers on specific areas of your proposal. For example, you may want to schedule a meeting with a statistician to help revise your methodology section. Don’t hesitate to seek out specialized assistance from the relevant research offices on your campus. At UNC, the Odum Institute provides a variety of services to graduate students and faculty in the social sciences.
In your revision and editing, ask your readers to give careful consideration to whether you’ve made explicit the connections between your research objectives and methodology. Here are some example questions:
- Have you presented a compelling case?
- Have you made your hypotheses explicit?
- Does your project seem feasible? Is it overly ambitious? Does it have other weaknesses?
- Have you stated the means that grantors can use to evaluate the success of your project after you’ve executed it?
If a granting agency lists particular criteria used for rating and evaluating proposals, be sure to share these with your own reviewers.
Example #1. Sample Budget
Jet travel $6,100 This estimate is based on the commercial high season rate for jet economy travel on Sabena Belgian Airlines. No U.S. carriers fly to Kigali, Rwanda. Sabena has student fare tickets available which will be significantly less expensive (approximately $2,000).
Maintenance allowance $22,788 Based on the Fulbright-Hays Maintenance Allowances published in the grant application guide.
Research assistant/translator $4,800 The research assistant/translator will be a native (and primary) speaker of Kinya-rwanda with at least a four-year university degree. They will accompany the primary investigator during life history interviews to provide assistance in comprehension. In addition, they will provide commentary, explanations, and observations to facilitate the primary investigator’s participant observation. During the first phase of the project in Kigali, the research assistant will work forty hours a week and occasional overtime as needed. During phases two and three in rural Rwanda, the assistant will stay with the investigator overnight in the field when necessary. The salary of $400 per month is based on the average pay rate for individuals with similar qualifications working for international NGO’s in Rwanda.
Transportation within country, phase one $1,200 The primary investigator and research assistant will need regular transportation within Kigali by bus and taxi. The average taxi fare in Kigali is $6-8 and bus fare is $.15. This figure is based on an average of $10 per day in transportation costs during the first project phase.
Transportation within country, phases two and three $12,000 Project personnel will also require regular transportation between rural field sites. If it is not possible to remain overnight, daily trips will be necessary. The average rental rate for a 4×4 vehicle in Rwanda is $130 per day. This estimate is based on an average of $50 per day in transportation costs for the second and third project phases. These costs could be reduced if an arrangement could be made with either a government ministry or international aid agency for transportation assistance.
Email $720 The rate for email service from RwandaTel (the only service provider in Rwanda) is $60 per month. Email access is vital for receiving news reports on Rwanda and the region as well as for staying in contact with dissertation committee members and advisors in the United States.
Audiocassette tapes $400 Audiocassette tapes will be necessary for recording life history interviews, musical performances, community events, story telling, and other pertinent data.
Photographic & slide film $100 Photographic and slide film will be necessary to document visual data such as landscape, environment, marriages, funerals, community events, etc.
Laptop computer $2,895 A laptop computer will be necessary for recording observations, thoughts, and analysis during research project. Price listed is a special offer to UNC students through the Carolina Computing Initiative.
NUD*IST 4.0 software $373.00 NUD*IST, “Nonnumerical, Unstructured Data, Indexing, Searching, and Theorizing,” is necessary for cataloging, indexing, and managing field notes both during and following the field research phase. The program will assist in cataloging themes that emerge during the life history interviews.
Administrative fee $100 Fee set by Fulbright-Hays for the sponsoring institution.
Example #2: Project Timeline in Table Format
Example #3: project timeline in chart format.

Some closing advice
Some of us may feel ashamed or embarrassed about asking for money or promoting ourselves. Often, these feelings have more to do with our own insecurities than with problems in the tone or style of our writing. If you’re having trouble because of these types of hang-ups, the most important thing to keep in mind is that it never hurts to ask. If you never ask for the money, they’ll never give you the money. Besides, the worst thing they can do is say no.
UNC resources for proposal writing
Research at Carolina http://research.unc.edu
The Odum Institute for Research in the Social Sciences https://odum.unc.edu/
UNC Medical School Office of Research https://www.med.unc.edu/oor
UNC School of Public Health Office of Research http://www.sph.unc.edu/research/
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Holloway, Brian R. 2003. Proposal Writing Across the Disciplines. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Levine, S. Joseph. “Guide for Writing a Funding Proposal.” http://www.learnerassociates.net/proposal/ .
Locke, Lawrence F., Waneen Wyrick Spirduso, and Stephen J. Silverman. 2014. Proposals That Work . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Przeworski, Adam, and Frank Salomon. 2012. “Some Candid Suggestions on the Art of Writing Proposals.” Social Science Research Council. https://s3.amazonaws.com/ssrc-cdn2/art-of-writing-proposals-dsd-e-56b50ef814f12.pdf .
Reif-Lehrer, Liane. 1989. Writing a Successful Grant Application . Boston: Jones and Bartlett Publishers.
Wiggins, Beverly. 2002. “Funding and Proposal Writing for Social Science Faculty and Graduate Student Research.” Chapel Hill: Howard W. Odum Institute for Research in Social Science. 2 Feb. 2004. http://www2.irss.unc.edu/irss/shortcourses/wigginshandouts/granthandout.pdf.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

How to Create More Accurate Budgets for Research Grant Proposals

Breaking down research costs
One of the most challenging aspects of budget development is identifying relevant costs. Remember, this financial plan quantifies only the expenses incurred while conducting research. It is not the organizational budget.
Begin by assessing the costs associated with the research essentials, i.e., the study design, study settings, testing procedures, and sample and data collection methods. These expenses can be divided into direct and indirect expenses.
Direct expenses
Direct expenses are costs arising solely from performing research. They must be allowable, allocable, reasonable, and consistent. Examples include:
- Personnel expenses: The salary and any benefits associated with the human resources necessary to conduct research, such as site managers, research assistants, research associates, data entry operators, etc.
- Recurring expenses: Costs that will continue throughout the study period, including consumables, materials, food, and medical charges
- Nonrecurring expenses: Single expenses incurred once during the study, such as the cost of equipment, instruments, software programs, computers, and electronic accessories
- Travel expenses: Costs incurred while traveling to collect data or visit other centers in cases of multicenter research. They may also include costs to attend meetings or conferences relevant to the research project.
Indirect expenses
Also known as overheads, these costs are not directly attributed to your specific study but are incurred while performing research. They include electricity and water bills, accommodation charges, administrative fees, library memberships, etc. Generally, these expenses make up 5-15% of a proposal budget.
The proposal budget should also include any direct or indirect expenses already covered. This means identifying any material or equipment previously paid for or made available by other sources.
Drafting the proposal budget
With all the relevant expenses identified, revisit the funding agency’s guidelines. Study each budgeting instruction line by line to ensure you understand the rules and limitations, from the maximum amount of funds you can request to any expenses not allowed. With this information, you now have a framework to build your grant budget.
Next, chronologically categorize each expense as direct or indirect, as well as weekly, monthly, or yearly, depending on your research project’s timeline.
With each item, justify the expense with specified rates and calculations. If the cost of an item is already covered, include the pertinent information. This meticulous approach demonstrates you will value any funding provided and will not splurge on unnecessary particulars.
Consider the example below of a sample travel budget illustrating this methodology:
* These rates are examples and will vary from actual rates.
Base all expense calculations on true costs quoted from trusted sources. Sponsors know overestimations when they see them. Underestimations also raise suspicion and may appear under-researched. Therefore, be as reasonable and accurate as possible.
Finally, include your methodology for tracking expenses throughout the research period, highlighting any tools or technologies to be used. This reassures sponsors you have all your bases covered.
Using integrated technology
Given the complexities of a grant proposal budget, traditional enterprise resource planning (ERP) platforms cannot support the level of precision and collaboration necessary for adequate budgeting. But by integrating advanced technology, such as Cayuse’s Fund Manager and Sponsored Projects, you can upgrade these legacy systems for optimized budgeting and proposal development.
Fund Manager allows for granular accounting and is accessible to all stakeholders through a customizable dashboard. Not only does it manage internal expenses and faculty salary splits, but it also supplements what-if planning and average monthly projections on a grant-by-grant basis.
With Sponsored Projects , administrators can track proposals, awards, contracts, and agreements via a user-specific dashboard. Its modern, user-friendly interface provides instant access, full visibility, and a collaboration workspace, relieving administrative burdens.
Boost your budgeting accuracy
Regardless of how appealing or innovative your research project might be, without justifiable numbers to back it up, it may be tossed aside. Don’t take this risk. Instead, leverage integrated technology, such as Cayuse’s Fund Manager and Sponsored Projects, to develop more accurate proposal budgets and maximize your chances to win funding.
Featured Resource:

6 ways to minimize risk in research administration
Get ebook >>
Sample Budget Justifications
Sponsor requirements differ, and sample budget justifications should be seen only as a starting point. Guidelines for sponsor requirements are in the annotated budget justifications. Read the solicitation and the sponsor’s proposal preparation guidelines for each proposal's requirements.
For Research Sponsors
- Sample Budget Justification for Non-Federal Research [DOCX] - April 6, 2023
- Annotated Budget Justification - Non-Federal Research
- Sample Budget Justification for Federal Research [DOCX] - April 6, 2023
- Annotated Budget Justification - Federal Research
For Non-Research Sponsors:
- Sample Budget Justification for Non-Federal Non-Research [DOCX] - July 29, 2022
- Annotated Budget Justification - Non-Federal Non-Research
- Sample Budget Justification for Federal Non-Research [DOCX] - July 29, 2022
- Annotated Budget Justification - Federal Non-Research
- Uniform Guidance Fixed Rate Requirements
- F&A Methodology
- F&A Components
- MIT Use of a de minimis Rate
- Fund Account Overhead Rates
- Allocation Rates
- Determination of On-Campus and Off-Campus Rates
- Employee Benefits (EB) Rates
- Vacation Accrual Rates
- Graduate Research Assistant Tuition Subsidy
- Historical RA Salary Levels
- MIT Facts and Profile Information
- Classification of Sponsored Projects
- Types of Sponsored Awards
- How Are Sponsored Projects Generated?
- Cost Principles and Unallowable Costs
- Direct and Indirect Costs
- Pre-Proposals / Letters of Intent
- MIT Investigator Status
- Components of a Proposal
- Special Reviews
- Applying Through Workspace
- Proposal Preparation Checklist
- Proposals and Confidential Information
- Personnel Costs
- Subcontracts and Consultants
- Kuali Coeus Approval Mapping
- Roles and Responsibilities
- Submission of Revised Budgets
- Standard Contract Terms and Conditions
- Contractual Obligations and Problematic Terms and Conditions
- Review and Negotiation of Federal Contract and Grant Terms and Conditions
- Industrial Collaboration
- International Activities
- MIT Export Control - Export Policies
- Nondisclosure and Confidentiality Agreements
- Negative Confirmation On Award Notices
- Routing and Acceptance of the Award Notice
- COI and Special Review Hold Notice Definitions
- Limiting Long-Term WBS Account Structures
- SAP Project WBS Element Conditions
- Kuali Coeus Electronic Document Storage (EDS)
- Billing Agreements
- PI Absence from Project
- Cost Transfers
- Equipment Threshold
- Uniform Guidance and the FAR
- MIT Standard Terms and Policies
- Guidelines for Charging Faculty Summer Salary
- Key Personnel
- Limitations on Funds - Federal Contracts
- Managing Salary Costs
- Monitoring Project Budgets
- Monthly Reconciliation and Review
- No-Cost Extensions
- Reporting Requirements
- Return of Unexpended Funds to Foundations
- Determining the Sponsor Approved Budget (SAB)
- Working With the Sponsor Approved Budget (SAB)
- Sponsor Approved Budget (SAB) and Child Account Budgets
- Sponsor Approved Budget (SAB) and Prior Approvals
- Submitting an SAB Change Request
- When a PI Leaves MIT
- Research Performance Progress Reports
- Closing Out Fixed Price Awards
- Closeout of Subawards
- Record Retention
- Early Termination
- Reporting FAQs
- Using SciENcv
- AFOSR No-Cost Extension Process
- Terms and Conditions
- New ONR Account Set Ups
- Department of Defense Disclosure Guidance
- Department of Energy / Office of Science Disclosure Guidance
- Introduction to Industrial Sponsors
- General Considerations for Industrial Proposals
- SRC Guidance to Faculty Considering Applying for SRC Funding
- Find Specific RFP Information
- Industrial Proposal Checklist
- Proposal Formats
- Special Requirements
- Deadline Cycles
- Model Proposals
- Non-Competitive Industrial Proposals
- Master and Alliance Agreements With Non-Standard Proposal Processes
- Template Agreements
- New Consortium Agreements
- Competitive Industrial Proposals
- Collaborative (No-cost) Research Agreements
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration Disclosure Guidance
- NASA Graduate Research Fellowship Programs
- NASA PI Status and Definitions
- NIH Checklists and Preparation Guides
- National Institutes of Health Disclosure Guidance
- Human Subjects and NIH Proposals
- NIH Data Management and Sharing
- NIH Research Performance Progress Reports
- Grant Opportunities for Academic Liaison with Industry (GOALI) proposals
- MIT Guidance Regarding the NSF CAREER Program
- Research Experiences for Undergraduates (REU) Supplements
- National Science Foundation Disclosure Guidance
- NSF Proposals: Administrative Review Stage
- NSF Collaborations
- NSF Pre-Award and Post-Award Actions
- NSF Reporting
- NSF Frequently Asked Questions
- NSF Safe and Inclusive Working Environment
- Process, Roles and Responsibilities
- What Is Allowable/Eligible Cost Sharing?
- MIT’s Preferred Cost Sharing Funds
- Third-Party Cost Sharing
- Showing Cost Sharing in a Proposal Budget
- Sponsor Specific Instructions Regarding Location in the Proposal
- Funding F&A Costs as Cost Sharing
- Using Faculty Effort for Cost Sharing
- Information about Completing the Cost Sharing Template
- NSF Cost Sharing Policy
- Tracking/Reporting Cost Sharing
- Special Cost Sharing Topics
- International Activities Examples
- Rubicon Fellowships
- Marie Skłodowska-Curie Fellowships
- Criteria for Subrecipients
- Subawards at Proposal
- Requesting New Subawards
- Managing Subawards
- RAS Subaward Team Contacts
- Funding and Approval
- Proposal Phase
- Award Set-up
- Monitoring Research During Project Period
- Closeout Phase
- Voluntary Cost Sharing
- Sponsor-Specific Guidance
- Audits and Auditors
- Upcoming Trainings and Events
- Research Administration Practices (RAP)
- NCURA Virtual Workshops and Webinars
- Guide to RA Resources and Training
- Career Paths
- Newsletters
- Tools and Systems
- Award Closeout & Audits
- Award Setup
- Cost Sharing
- Export Control
- Financial Conflict of Interest
- Kuali Coeus
- Project Monitoring
- Proposal Preparation & Submission
- Research Sub Awards
- Research Administration Email Lists
- RAS Operations
- VPR Research Administration Organization Chart
- By department
- By administrator
- Research Administrator Day
- News & Announcements
- Onsite searching on the VPR public websites
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian Dermatol Online J
- v.12(1); Jan-Feb 2021
Research Funding—Why, When, and How?
Shekhar neema.
Department of Dermatology, Armed Forces Medical College, Pune, Maharashtra, India
Laxmisha Chandrashekar
1 Department of Dermatology, Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research (JIPMER), Dhanvantari Nagar, Puducherry, India
Research funding is defined as a grant obtained for conducting scientific research generally through a competitive process. To apply for grants and securing research funding is an essential part of conducting research. In this article, we will discuss why should one apply for research grants, what are the avenues for getting research grants, and how to go about it in a step-wise manner. We will also discuss how to write research grants and what to be done after funding is received.
Introduction
The two most important components of any research project is idea and execution. The successful execution of the research project depends not only on the effort of the researcher but also on available infrastructure to conduct the research. The conduct of a research project entails expenses on man and material and funding is essential to meet these requirements. It is possible to conduct many research projects without any external funding if the infrastructure to conduct the research is available with the researcher or institution. It is also unethical to order tests for research purpose when it does not benefit patient directly or is not part of the standard of care. Research funding is required to meet these expenses and smooth execution of research projects. Securing funding for the research project is a topic that is not discussed during postgraduation and afterwards during academic career especially in medical science. Many good ideas do not materialize into a good research project because of lack of funding.[ 1 ] This is an art which can be learnt only by practising and we intend to throw light on major hurdles faced to secure research funding.
Why Do We Need the Funds for Research?
It is possible to publish papers without any external funding; observational research and experimental research with small sample size can be conducted without external funding and can result in meaningful papers like case reports, case series, observational study, or small experimental study. However, when studies like multi-centric studies, randomized controlled trial, experimental study or observational study with large sample size are envisaged, it may not be possible to conduct the study within the resources of department or institution and a source of external funding is required.
Basic Requirements for Research Funding
The most important requirement is having an interest in the particular subject, thorough knowledge of the subject, and finding out the gap in the knowledge. The second requirement is to know whether your research can be completed with internal resources or requires external funding. The next step is finding out the funding agencies which provide funds for your subject, preparing research grant and submitting the research grant on time.
What Are the Sources of Research Funding? – Details of Funding Agencies
Many local, national, and international funding bodies can provide grants necessary for research. However, the priorities for different funding agencies on type of research may vary and this needs to be kept in mind while planning a grant proposal. Apart from this, different funding agencies have different timelines for proposal submission and limitation on funds. Details about funding bodies have been tabulated in Table 1 . These details are only indicative and not comprehensive.
Details of funding agencies
Application for the Research Grant
Applying for a research grant is a time-consuming but rewarding task. It not only provides an opportunity for designing a good study but also allows one to understand the administrative aspect of conducting research. In a publication, the peer review is done after the paper is submitted but in a research grant, peer review is done at the time of proposal, which helps the researcher to improve his study design even if the grant proposal is not successful. Funds which are available for research is generally limited; resulting in reviewing of a research grant on its merit by peer group before the proposal is approved. It is important to be on the lookout for call for proposal and deadlines for various grants. Ideally, the draft research proposal should be ready much before the call for proposal and every step should be meticulously planned to avoid rush just before the deadline. The steps of applying for a research grant are mentioned below and every step is essential but may not be conducted in a particular order.
- Idea: The most important aspect of research is the idea. After having the idea in mind, it is important to refine your idea by going through literature and finding out what has already been done in the subject and what are the gaps in the research. FINER framework should be used while framing research questions. FINER stands for feasibility, interesting, novel, ethical, and relevant
- Designing the study: Well-designed study is the first step of a well-executed research project. It is difficult to correct flawed study design when the project is advanced, hence it should be planned well and discussed with co-workers. The help of an expert epidemiologist can be sought while designing the study
- Collaboration: The facility to conduct the study within the department is often limited. Inter-departmental and inter-institutional collaboration is the key to perform good research. The quality of project improves by having a subject expert onboard and it also makes acceptance of grant easier. The availability of the facility for conduct of research in department and institution should be ascertained before planning the project
- Scientific and ethical committee approval: Most of the research grants require the project to be approved by the institutional ethical committee (IEC) before the project is submitted. IEC meeting usually happens once in a quarter; hence pre-planning the project is essential. Some institutes also conduct scientific committee meeting before the proposal can be submitted for funding. A project/study which is unscientific is not ethical, therefore it is a must that a research proposal should pass both the committees’ scrutiny
- Writing research grant: Writing a good research grant decides whether research funding can be secured or not. So, we will discuss this part in detail.
How to write a research grant proposal [ 13 , 14 , 15 ] The steps in writing a research grant are as follows
- Identifying the idea and designing the study. Study design should include details about type of study, methodology, sampling, blinding, inclusion and exclusion criteria, outcome measurements, and statistical analysis
- Identifying the prospective grants—the timing of application, specific requirements of grant and budget available in the grant
- Discussing with collaborators (co-investigators) about the requirement of consumables and equipment
- Preparing a budget proposal—the two most important part of any research proposal is methodology and budget proposal. It will be discussed separately
- Preparing a specific proposal as outlined in the grant document. This should contain details about the study including brief review of literature, why do you want to conduct this study, and what are the implications of the study, budget requirement, and timeline of the study
- A timeline or Gantt chart should always accompany any research proposal. This gives an idea about the major milestones of the project and how the project will be executed
- The researcher should also be ready for revising the grant proposal. After going through the initial proposal, committee members may suggest some changes in methodology and budgetary outlay
- The committee which scrutinizes grant proposal may be composed of varied specialities. Hence, proposal should be written in a language which even layman can understand. It is also a good idea to get the proposal peer reviewed before submission.
Budgeting for the Research Grant
Budgeting is as important as the methodology for grant proposal. The first step is to find out what is the monetary limit for grant proposal and what are the fund requirements for your project. If these do not match, even a good project may be rejected based on budgetary limitations. The budgetary layout should be prepared with prudence and only the amount necessary for the conduct of research should be asked. Administrative cost to conduct the research project should also be included in the proposal. The administrative cost varies depending on the type of research project.
Research fund can generally be used for the following requirement but not limited to these; it is helpful to know the subheads under which budgetary planning is done. The funds are generally allotted in a graded manner as per projected requirement and to the institution, not to the researcher.
- Purchase of equipment which is not available in an institution (some funding bodies do not allow equipment to be procured out of research funds). The equipment once procured out of any research fund is owned by the institute/department
- Consumables required for the conduct of research (consumables like medicines for the conduct of the investigator-initiated trials and laboratory consumables)
- The hiring of trained personnel—research assistant, data entry operator for smooth conduct of research. The remuneration details of trained personnel can be obtained from the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) website and the same can be used while planning the budget
- Stationary—for the printing of forms and similar expense
- Travel expense—If the researcher has to travel to present his finding or for some other reason necessary for the conduct of research, travel grant can be part of the research grant
- Publication expense: Some research bodies provide publication expense which can help the author make his findings open access which allows wider visibility to research
- Contingency: Miscellaneous expenditure during the conduct of research can be included in this head
- Miscellaneous expenses may include expense toward auditing the fund account, and other essential expenses which may be included in this head.
Once the research funding is granted. The fund allotted has to be expended as planned under budgetary planning. Transparency, integrity, fairness, and competition are the cornerstones of public procurement and should be remembered while spending grant money. The hiring of trained staff on contract is also based on similar principles and details of procurement and hiring can be read at the ICMR website.[ 4 ] During the conduct of the study, many of grant guidelines mandate quarterly or half-yearly progress report of the project. This includes expense on budgetary layout and scientific progress of the project. These reports should be prepared and sent on time.
Completion of a Research Project
Once the research project is completed, the completion report has to be sent to the funding agency. Most funding agencies also require period progress report and project should ideally progress as per Gantt chart. The completion report has two parts. The first part includes a scientific report which is like writing a research paper and should include all subheads (Review of literature, material and methods, results, conclusion including implications of research). The second part is an expense report including how money was spent, was it according to budgetary layout or there was any deviation, and reasons for the deviation. Any unutilized fund has to be returned to the funding agency. Ideally, the allotted fund should be post audited by a professional (chartered accountant) and an audit report along with original bills of expenditure should be preserved for future use in case of any discrepancy. This is an essential part of any funded project that prevents the researcher from getting embroiled in any accusations of impropriety.
Sharing of scientific findings and thus help in scientific advancement is the ultimate goal of any research project. Publication of findings is the part of any research grant and many funding agencies have certain restrictions on publications and presentation of the project completed out of research funds. For example, Indian Association of Dermatologists, Venereologists and Leprologists (IADVL) research projects on completion have to be presented in a national conference and the same is true for most funding agencies. It is imperative that during presentation and publication, researcher mentions the source of funding.
Research funding is an essential part of conducting research. To be able to secure a research grant is a matter of prestige for a researcher and it also helps in the advancement of career.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.

- Harvard Library
- Research Guides
- Harvard Graduate School of Design - Frances Loeb Library
Write and Cite
- Grants and Fellowships
- Academic Integrity
- Citing Sources
- Fair Use, Permissions, and Copyright
- Writing Resources
Quick Start Workflow
Notes on style, writing a proposal, writing a budget, writing a timeline, research methodologies for designers, funding opportunities, external resources.
Define your project + Identify your needs.
- Develop a key research question. What is your methodology? What outcomes do you expect to see?
- Establish realistic goals. What is your timeline? What other responsibilities do you have? What can you truly accomplish in the amount of time you have?
- Assess your needs. Are you undertaking preliminary research and in search of seed funding? Or, do you have an ongoing project which has developed into a full-blown research agenda? Scale is important in writing a research agenda: large-scale, long-term projects are often only funded if you can demonstrate seed funding or matched funds.
- Why is your research/project important? What is its significance? Will you be undertaking experimental research? Contextualize project relevance.
- Sketch a project budget and timeline.
- Define deliverables clearly.
Identify potential funding sources.
- Determine your category: dissertation, archival, experimental, fieldwork, or manuscript? Funders will usually list these categories in the CFP.
- Try to align your project goals with those of your funder’s. Make sure you’re “speaking the same language."
- Most importantly, apply early and often.
Develop a proposal and budget
- Follow the application guidelines exactly.
- Adjust your project to fit the CFP guidelines. Check that your methodology aligns to your project budget and timeline.
- Be clear and concise. Use images, diagrams, drawings, and maps where applicable.
- Use active, persuasive language. When describing outcomes, don’t use conditional/hedging words like might / may / maybe / would / could.
- Seek feedback and write many drafts.
Submit the proposal before the deadline.
Carry out the project.
File reports / send deliverables.
Writing for proposals is not the same as for academic work. It needs to be highly accessible with limited use of industry-specific terminology. Do not assume that the reviewer of your application has expertise in your field.
- Use short, clear sentences
- Employ an active voice (I or we)
- Remain future-focused
- Commit to strong, persuasive phrasing
- Convey enthusiasm and confidence
A grant proposal must always complete two tasks:
- Clearly articulate the hypothesis of your research in its broadest strokes.
- Demonstrate that your goals in the research endeavor and the goals of the funding institution are symbiotic.
Introduction/Abstract
As early in the proposal as possible, identify and explicitly state the question your research will answer. Avoid empty verbs like “shaped,” “influenced,” “sheds light,” “nuances,” and “complicates” that allude to the existence of an argument but do not state what that argument is. You might consider writing the abstract last even though it will be the first thing readers see in your proposal.
Though all grant CFPs (calls for proposals) vary, most call for a “grant narrative.” If they don’t ask for a separate abstract, incorporate the abstract into the first paragraph of your narrative. A successful abstract will accurately reflect the proposal and should quickly address your key question, research methodology, and relevance to the funding institution. Reviewers will have to sort through dozens or even hundreds of applications so state the who, what, why, where, when, how, how much, to what end(s) clearly and early. You can elaborate in the body of the grant narrative.
In a grant, it is more important to demonstrate the urgency of your research and relevance to the funding institution than to frame the “gaps” in the literature (as you would in a research paper). Frame research in schools of thought without much detail about individual scholars. Offer avenues for reviewers from other fields (historians, ecologists, sociologists, etc) to enter your intellectual world by relating your research questions to broader issues.
In the body, establish your general topic before you introduce your own argument about that topic. This framing will make your intervention’s relevance to the field evident. You can expand upon the historical or theoretical background to the project and explain how some of the research you’ve already done has led you to your key questions.
Research/Methodology
Be sure to give the fellowship committee some sense of your research process. You don’t need to re-invent the wheel when formulating a research strategy. In Writing Services, students often come to us with successful grant proposals, save for when they discuss methodologies. Research methodologies (aka research process) is either left out entirely, or students spend a good chunk of their word count trying to describe how they are going to conduct research. When writing a grant application, draw on extant methodologies to communicate to your reviewers how (and within what intellectual tradition) you’ll be conducting research. For a comprehensive list of methodologies in the design fields, see below.
Institutional Goals
A successful project will address the goals of the funding institution. Sometimes these goals are clear (example: the grant is for dissertation research, and you need funding to travel to an archive to finish your dissertation). However, you will usually need to construct an argument relating your project to the aims of the CFP. Find the mission statement for the institution that offers the grant. Use this statement to identify how your research will advance the institution’s goals. Figure out the reason the funding exists and devote serious thought to how your project relates to that reason. Even if the relevance seems obvious to you, clearly state it; the grant review committee goes through a mountain of applications, so don’t trust that they will make these connections on their own. Also, articulate the specific reasons why you need this money. What will it allow you to do that you couldn’t do otherwise? And why are you the best person to do this project?
A grant budget is usually comprised of two things: a spreadsheet of how the grant will be used on expenses and a budget narrative (justification). A budget narrative is a paragraph which should explain the expenses. Even when proposal guidelines do not specifically mention a narrative, be sure to include one. This budget narrative can exist at the bottom of the table and should provide a brief overview of the budget.
- Spell out project costs via a spreadsheet or table with the budget detailed as line items and include a budget narrative to explain and justify the table.
- Make sure that all budget items meet the funding agency’s requirements.
- Factor in the estimated taxes applicable for your case.
Certain grants will ask for a timeline in your budget proposal. This timeline should list all the activities you will need to carry out to meet each of your objectives.
Your timeline may be written as a narrative, but it can also be put into a table. A visual representation of your timeline may be easier for reviewers to understand.
Divide your timeline by quarters or months, depending on how long the funding period is. Place each activity into a quarter or month as opposed to specifying specific dates. These activities might include preliminary research, fieldwork, visits to archives, installation, model-making, publication design, etc. Include all activities from the day funding is awarded to the last day of funding.
Include when deliverables will be finished (or when you will fulfill reporting deadlines) and when/how you will assess the project’s progress and address any inadequacies.
If collaborating with other designers and researchers, be sure to address who is responsible for completing each task.
Keep the timeline realistic.
- Research Methods for Architecture by Rumiko Handa (Hollis online access)
- Architectural Research Methods by Linda Groat (Loeb Library stacks)
- Research Methods for the Architectura Profession by Ajla Aksamija (Loeb Library stacks)
- Research in Landscape Architecture: Methods and Methodology by Oxon Abingdon (Loeb Library stacks)
- The Little Book of Research Writing by Varanya Chaubey (Kennedy School Library)
- Operative Design: a Catalogue of Spatial Verbs by Anthoni Di Mari (Loeb Library stacks)
- Landscape Architectural Research: Inquiry, Strategy, Design by Elen Deming (HOLLIS online access)
- CARAT database of grants and fellowships
- Spin database of sponsored funding opportunities
- Graham Foundation
- Scholarships for International Students
- Travelling Fellowships at the GSD
- Architecture Fellowships, Prizes, and Travel Programs
- Fellowship Writing by the Yale Poorvu Center for Teaching and Learning
- Grant Writing Tips from Harvard Catalyst
- Fellowships from the Harvard Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
- << Previous: Writing Resources
- Last Updated: Mar 27, 2024 1:18 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.harvard.edu/gsd/write
Harvard University Digital Accessibility Policy
How to plan and write a budget for research grant proposal?
Affiliation.
- 1 Department of Physiology, Sri B. M. Patil Medical College, Hospital and Research Centre, BLDE University, Bijapur, Karnataka, India. Electronic address: [email protected].
- PMID: 29089186
- PMCID: PMC6598805
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaim.2017.08.005
Medical research can have an enormous positive impact on human health. Health research improves the quality of human lives and society which plays a vital role in social and economic development of the nation. Financial support is crucial for research. However, winning a research grant is a difficult task. A successful grant-winning application requires two key elements: one is an innovative research problem with best probable idea/plan for tackling it and appropriate planning of budget. The aim of the present paper is to give an insight on funding agencies providing funding for health research including traditional Indian medicine (from an Indian perspective) and key points for planning and writing budget section of a grant application.
Keywords: Grant writing; Planning budget; Research grant.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Publication types
How To Write a Grant Proposal: Guide + Templates
Fundraising practices.
Megan Allison
Share this article.

Nonprofit grant proposals can be a daunting task for fundraisers, but it’s a key way to help gain more sustainable funding for your organization. From finding the right grants to writing and applying for them, grant proposals require a lot of research and attention to detail! Even experienced fundraisers can feel overwhelmed, but by following a planned process and some best practices, you can take the stress out of appealing to grant funders.
- What is a grant proposal?
- 5 best practices for writing a convincing grant proposal
How to write a grant proposal for nonprofits in 11 basic steps
- Where to find grant opportunities
- Grant proposal templates
- Grant proposal do’s and don’ts
What is a grant proposal?
A grant proposal is a structured document that outlines the need for funding, your nonprofit’s objectives, the proposed project’s scope, and the budget you need to accomplish your project. It serves as your voice when grant funders are reviewing proposals, and it can decide whether you secure the grant or not.
Nonprofit grant proposals need to tell a moving story about your organization’s mission and vision while adhering to the stringent guidelines set forth by the grant maker. Writing a good grant proposal requires attention to detail, strategic thinking, and a compelling solution to a problem.
What do you write in a grant proposal?
Before you start writing your grant proposal, you need to know the key parts to include when writing your proposal .
- Cover letter: Your cover letter is the first impression you make on the grant review committee. Include big accomplishments and details that will help persuade the reviewers of the success of your work.
- Executive summary: The summary is a snapshot of your proposal. Create a concise but compelling way to capture your mission, the project’s scope, and the budget in a single page.
- Statement of need: Dive deep into the problem your nonprofit is trying to solve with grant funding. Use data to make a clear case for why the funder’s support is crucial to the impact you can make.
- Project description: Your description details how your organization intends to address the problem identified in your statement of need. Approach this with clear and tangible solutions to the issue at hand.
- Organization background : Show your nonprofit’s history, current programs, and any previous successes that demonstrate your capacity to handle the project you’re proposing for the grant.
- Budget: Go into detail about how exactly you plan to use the grant funding for your program.
- Sustainability plan: The fundraising world is looking more to sustainability to ensure organizations are getting to the root of a problem rather than just applying a short-term bandage. Outline how your program can continue long-term to help the problem at hand.
- Overall impact: Bring the grant review committee back to the main goal of your proposal by highlighting the overall impact your project aims to achieve.
Each component of your grant proposal serves a unique purpose! Use your nonprofit’s voice to help ensure the work you do is highlighted through each part.

5 best practices for writing a convincing grant proposal
1. make sure you have everything you need for your application. .
The guidelines for the grant you’re applying for should have all the information you’ll need to collect to apply for the grant. Two things you should make sure you have before you apply are your mission statement and any required paperwork. Your mission statement should be clear and explain your nonprofit’s purpose to provide a first impression for funders.
There are a few types of paperwork you may need to meet the grant’s eligibility requirements. Funders may request financial statements or annual reports, as well as other documentation on your nonprofit to be submitted with your proposal. Make sure you can match all the eligibility criteria before preparing your proposal to avoid wasting energy on applications that are ineligible for approval.
2. Tell a powerful story.
Grant funders are looking for projects that can create a lasting impact in their communities. To show your organization can create long-term change, use success stories that can be backed with data to show what your nonprofit can do. Emotional pull is an important part of the grant writing process, but numbers help solidify your funding request.
Craft a story that paints a clear image of your nonprofit’s identity, both visually and narratively. Share both successes and challenges to build a realistic visual of how your organization solves problems.
3. Research previous winners.
Before writing, research the grant you’re applying for and who the previous grant awardees are. Understand what the grant funders value to ensure your proposal is aligned with those priorities. Studying winning proposals from the past can provide insight into what works best for a specific funder. Look for common elements across different winners and structure your proposal in a similar fashion without losing your nonprofit’s voice.
4. Writing clearly and concisely.
Avoid using overly specific jargon and be as clear as possible. You’re an expert in your field, but the grant funders might not be. Your proposal might make perfect sense to you, but to others, it could take too much time to understand. Your communication needs to come across clearly, convey why your project matters, and how it will address the funder’s priorities. Make a checklist to guarantee you hit every point in your narrative.
5. Double check your work.
Proofread your proposal multiple times and have others review it as well. Typos and grammatical errors can detract from the power of your message. It also helps you ensure that your messaging is consistent throughout the proposal and that you’ve met all necessary guidelines.

1. Finding the right grants to apply to
Look through well-established grant databases, set up Google alerts, check out company foundations, and network with other nonprofits to keep track of available grants that align with your mission and find one that will fit your program needs.
2. Making a list of guidelines you must match
Create a checklist of the grant’s guidelines that need to be met in the proposal you submit. This helps you ensure accuracy and thoroughness throughout the writing process and provides an easy resource when double checking your work
3. Summarizing your work
In a few sentences, summarize what your nonprofit does and the primary focus of your work and the project you’re submitting for the grant. You can use this summary as a baseline for creating your nonprofit voice for the proposal, as well as use it to make first impressions when networking with potential funders.
4. Illustrating the problem you solve
Use real examples and statistics to help you illustrate the problem you’re tackling. You can show the urgency and need for solutions to the problem by providing tangible evidence of the issues occurring within your community.
5. Specifying goals and objectives
Your project needs to have specific goals with metrics you can measure to show your success. These goals should be directly related to resolving the problem you’ve identified in your community. Your objectives should also be something you can reasonably accomplish.
6. Explaining your project plan
Detail the steps of your project to achieve your objectives. Be specific about who will do what, when, and how to give an overview of the proposed timeline. You should also include how each step will help you move towards your objectives.
7. Proposing your budget
The budget is a key component of your grant proposal. Every line item should be justified and directly tied to activities that will help you achieve your goals. Your budget needs to be reasonable and fit within what the grant is able to offer in funding.
8. Planning your evaluation
Decide which metrics you’ll use to measure the success of your project. This part of your proposal demonstrates your commitment to accountability and your capacity to manage the grant. Pick a few key ways the funders can evaluate your program.
9. Ensuring sustainability
Show how you’ll maintain the project’s success after the funds from the grant are exhausted. Present a realistic, long-term plan for continuation. Your grant proposal doesn’t just fund a project with short-term results–it should initiate a change or growth that’s sustainable without continuous support from the funder.
10. Revising your proposal
Never rush the review process! After completing your first draft, provide a copy to a few reviewers to ensure your message gets across. You should also review yourself a few days after finishing up your draft to get a fresh look. You’ll be surprised how a clear head can help provide new insights.
11. Following Up
If you haven’t heard back within a reasonable time, it’s okay to follow up with the grant funders. Keep it simple and check if they’ve had a chance to review your proposal. You can also ask the grant review committee to provide feedback on your proposal to help you improve for your next proposal.

Where to find grant opportunities
There are a couple places you can look when trying to find grant opportunities . Well-known grant databases, such as grants.gov or GrantWatch , can be great resources to do a wide search of grants. You can also look at large corporations to check if they provide grants, such as Carnegie Foundation or Bank of America . Local government branches that work within your cause are also great resources for grants. You can also network with your board members or other nonprofits to find grant opportunities that you already have a connection with.
Here are 10 more places to find grants:
- National Endowment for the Arts
- GrantFinder
- Economic Development Directory
- Walmart Foundation
- Coca-Cola Foundation
- Aldi Cares Community Grants
- Candid’s Foundation Directory
- GrantStation
- Home Depot Foundation
Grant proposal templates
If you’re looking for a place to start, use this grant proposal template:
Cover letter
Dear [Grantor’s name],
Introduce your organization and thank the grantor for the opportunity to apply. Then, provide a brief overview of your nonprofit, including your mission, goals, and any unique strengths that set your organization apart.
Next, describe the specific project you’re seeking funding for. Explain the problem or need it addresses, the objectives of the project, why your organization is well-suited, and the intended outcomes. Include one or two examples of relevant experience that show your organization’s ability to complete the project.
Thank the grantor for considering your application and provide contact information to answer any questions they may have.
Executive summary
Provide a brief summary of your proposal that provides the grantor the most important details of your project. Explain what your organization does, why the project is important, who the project helps, and an overview of your suggested budget in a concise manner. Be sure to include the items listed below.
- Mission statement
- Problem statement
- Objective of the project
- Intended outcomes
- Funding request
Statement of need
Provide context about the issue or challenge that your organization is addressing with this project. Describe the problem in depth and highlight its impact on the community using key statistics about the problem. Provide examples of how this project aligns with your nonprofit, as well. Include images and data graphs to provide a visual of the issue.
Project description
Provide an overview of your proposed project, including its objectives, activities, and intended impact. Outline the specific activities and steps needed to achieve the project’s purpose, as well as details about each activity. Let the grantor see your staffing structure and what responsibilities each role will have in the project.
Include a timeline of key deadlines for your project into smaller phases and explain which activities will take place during each phase. The goal of this section is to show a thorough and transparent plan to the grantor. Break this section down into the sections listed below.
- Activities and action plan
- Staffing structure
- Project manager
- Roles and responsibilities
Organizational background
Use this section to introduce your organization to the grant reviewer and establish credibility. Restate your missions and values, and describe the different services and programs currently offered by your nonprofit to show your experience in similar projects.
Detail any previous achievements your organization had serving the community to provide credibility and a record of success to your proposal. Include any relevant qualifications your nonprofit has in your cause that could help with accomplishing your proposed project.
Provide an explanation and estimation for each expense of your project (materials, marketing, technology, administration, etc.). The grantor will want to know exactly how you plan to use the funds provided by the grant, so be as specific as possible in your budget when showing how your expenses directly contribute to achieving the project objectives.
Link each line item from the proposed budget to your project’s goal to show each expenses’ part in achieving the desired impact. Provide a chart or graph to add a visual representation of the budget.
Sustainability plan
Outline your nonprofit’s strategy for creating long-term sustainability of the proposed project. These plans should include where future funding will come from, what plans you have for long-term staffing of the project, and what ongoing support the program will receive from your organization.
This section is to show the grantor that the project will provide a reliable solution for the problem and not a short-term fix that relies purely on the grant fund.
Overall impact
Provide a detailed overview of the impact the proposed project will have on the community. Describe what the long-term benefits of the project will be on the community and how this impact can be measured by the grantor. Specify objective metrics that the grantor can use to examine the accomplishments of the project and include what metrics would need to be reached to indicate success.
AI prompt ideas
Consider using AI to generate new ideas for the different sections of your proposal. It can help you add a fresh perspective to your proposal or save you from writer’s block. Here some prompt ideas to help you fuel your writing process:
- “Write a one-page executive summary of [insert proposal sections] highlighting [your organization] accomplishments.”
- “Create a data table of [public program data] to show the success of [program name].”
- “Describe how [project mission] could help solve [community problem].”
- “Use [project estimates] to create a budget for [program name].”
- “Define the overall impact of [project plan] on [community problem].”

Grant proposal do’s and don’ts
Use these grants do’s and don’ts as a reminder for writing the best grant proposal you can.
Do prepare well ahead of time
Grant proposals need to be a well-planned effort, not a last-minute scramble. Planning ahead can help you make a more polished proposal.
Do communicate a consistent message
If it doesn’t feel like your proposal matches your mission, you’ll be less likely to receive the grant. Ensure the messaging of your proposal matches your nonprofit’s mission and branding.
Do show transparency
Be open about how your nonprofit works and how you use funds. Transparency shows the grant funders that your organization is trustworthy to follow through with your proposal.
Don’t submit without creating a connection
Your proposal isn’t just a document–it’s an overall approach to creating financial partnerships for your organization. Don’t submit your proposal without reaching out and connecting with your potential funder.
Don’t skim the guidelines
The guidelines provided for each grant are specific to the grant and are required by the funders to get their funding. Missing out on a guideline can mean you lose your chance at the grant.
Don’t be vague on your impact
The grant funders want to see results. Making vague claims about what your organization can do without backing it with data can undermine your credibility.
Final thoughts
The grant proposal process can be challenging, but the results are well worth the effort. Successfully securing a grant can provide more sustainable financial support needed to accomplish your nonprofit’s next big project and make a meaningful impact in your community.
Every word in your proposal should lead the review committee back to the main problem your project can solve with the help of the grant. Tell your story and make a compelling case for why your nonprofit deserves funding and how you can change the world.
Additional resources
Use these additional resources to help you find and write grant proposals for your organization.
- Quick Guide to Grants for Nonprofits: Tips, Resources & More . Use this guide for more tips and resources for writing grant proposals.
- How to Find & Engage The Right Grant Funders For Your Nonprofit . Find grant funds to apply to using this guide.
- How To Find And Get Grants . Check out this webinar on how to find and get grants.
- Demystifying the Grants Lifecycle: Grant Seeking Lessons and Pro-tips from the Field . Watch this video to learn tips on getting grants from experts in the field.

About the Author
Megan is a writer at Qgiv who takes pride in helping nonprofits. In her freetime, she enjoys reading, music, and playing with her two cats.
You might enjoy

How to Host a Benefit Concert for Your Nonprofit
Fundraising Events

15 Donor Appreciation Event Ideas for Every Budget
Donor Acquisition and Retention

Quick Guide to Corporate Giving Programs for Nonprofits
Fundraising Ideas
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience. Thanks!

- Funding Opportunities
- Proposal Development
The Office of the Vice President for Research invites you to attend
Write winning nih grant proposals, virtual workshops.
January 8, 9, and 10, 2024
Presenter: John D. Robertson, Ph.D.
Grant Writers’ Seminars & Workshops, LLC*
SBU Faculty and Staff must Register before December 1, 2023
Workbooks will be purchased for Stony Brook participants by the OVPR.
The workshops will focus on two types of extramural funding pursuits:
Writing Winning NIH Proposals
Agenda and Seminar Overview
Two half-day sessions:
- Monday, January 8, 2024, from 9 am to 12:30 pm
- Tuesday, January 9, 2024, from 9 am to 12:30 pm
Writing NIH Renewals and Resubmissions
One half-day session:
- Wednesday, January 10, 2024, from 9 am to 12:30 pm
These widely acclaimed must-attend workshops comprehensively address both practical and conceptual aspects that are important to the proposal-writing process. Emphasis is given to such things as idea development, identification of the most appropriate institute, how to write for reviewers, and tips and strategies that are of proven value in presenting an applicant's case to reviewers.
Participants are taught to write with a linear progression of logic, which leads reviewers through their applications. It is stressed that applicants are writing for two different audiences – the assigned reviewers, who have read the application in its entirety, and non-assigned reviewers, who may have read little or nothing of the proposal before the meeting of the study section. Strategies, tools, and tips designed to merit a fundable priority score are emphasized. The focus of this seminar will be on proposals for submission to all NIH institutes.
The half-day NIH Renewal and Resubmission workshop helps maximize the likelihood of success upon resubmission. Discussion will include NIH's resubmission policy and strategies related to triaged applications, common causes of resubmission success/failure, common mistakes to avoid, and how to seek and use input from the Program Officer and Scientific Review Officer in responding to the criticism received.
Please direct any questions and comments to [email protected]
* Grant Writers’ Seminars & Workshops, LLC was founded by academicians, for academicians to help researchers obtain formal training in how to support their work with grant proposal writing.
Dr. John Robertson holds a Doctorate in Pharmacology/Toxicology and has been an Associate Member at Grant Writers’ Seminars & Workshops since 2010. In 2017, he became the Managing Member. He has been the recipient of competitive extramural funding from both the NIH and non-federal sources. He has authored 30 peer-reviewed journal articles and three book chapters. In addition, he has been a member of grant review panels, a reviewer for a number of biomedical journals, and served on editorial boards. He has also been routinely recognized for excellence in teaching.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Budget plan is a key element of a grant application. It demonstrates the required cost for the proposed project. It is a prediction of expenses and serves a plan for funders on how the organization will operate the project, spend the money in a given set of period and where their money will go.
An estimated budget quantifies the financial plan for possible expenses during the research project. The budget for grant proposals must demonstrate and serve a plan for funders on how the researcher/s will utilize the money for both operational aspects of the project and miscellaneous expenses associated with the research. In order to stand ...
Depending on the type of grant you win, the award will cover only direct costs, or, if a general operating grant, it may cover much more. To make it more concrete, let's look at 3 examples of grant budgets. We'll show an operating budget, a project budget, and a capital budget. .
A precise estimate of the budget is really the best approach to win a grant. And importantly, once your proposal has been funded, you will find that having carefully estimated the different costs at the application stage will not only guarantee an optimal use of the funds, but also make the practical implementation of the research project ...
Try to write your budget essentials in a tabulated form with three main columns. The first column represents the item name. The second column specifies the cost of that particular essential. The third column signifies the importance of your particular essential in performing your research.
same page about what a budget actually is. A budget is a financial proposal that reflects the work proposed. It outlines the expected project costs in detail, and should mirror the project description. A budget is presented as a categorical list of anticipated project costs that represent the
Give a clear and concise account of your identity, funding needs, and project roadmap. Write in an instructive manner aiming for an objective and persuasive tone. Be convincing and pragmatic about your research team's ability. Follow the logical flow of main points in your proposal.
An item-wise and year wise summary of the total budget is usually required in most of the applications. Budget summary outlines the proposed grant and often (most of the format) appears at the beginning of the proposal. It should always be prepared at the end, after the grant proposal has been completely developed.
Example: Professor Smith is commitment 10% effort for the project year − and has a 12-month appointment. 10% × 12 = 1.2 Person-months h. If an investigator is committing effort only during certain months of the year, such as during the Summer or Academic year, calculate their effort commitment as follows.
A good budget shows the assessors that you have thought about your research in detail and, if it is done well, it can serve as a great, convincing overview of the project. Here are five steps to create a simple budget for your research project. 1. List your activities. Make a list of everything that you plan to do in the project, and who is ...
I learnt that as part of a grant application, a budget plan allows funders to understand exactly where the money will be going and what researchers will be doing with it at any given point ...
Writing a successful grant proposal and detailed budget. In order for the grant selection committee to fully understand the nature of your project, and its budgetary implications, we ask that you reference the following guide. Good luck! Writing the Proposal: Each submitted proposal should include the following: 1.
Applicants must write grant proposals, submit them, receive notice of acceptance or rejection, and then revise their proposals. Unsuccessful grant applicants must revise and resubmit their proposals during the next funding cycle. Successful grant applications and the resulting research lead to ideas for further research and new grant proposals.
A successful grant-winning application requires two key elements: (1) innovative research prob lem with best probable idea/plan for. tackling it and (2) appropriate planning of budget. The aim of ...
Drafting the proposal budget. With all the relevant expenses identified, revisit the funding agency's guidelines. Study each budgeting instruction line by line to ensure you understand the rules and limitations, from the maximum amount of funds you can request to any expenses not allowed. With this information, you now have a framework to ...
Sample Budget Justifications. Sponsor requirements differ, and sample budget justifications should be seen only as a starting point. Guidelines for sponsor requirements are in the annotated budget justifications. Read the solicitation and the sponsor's proposal preparation guidelines for each proposal's requirements.
Research funding is defined as a grant obtained for conducting scientific research generally through a competitive process. To apply for grants and securing research funding is an essential part of conducting research. In this article, we will discuss why should one apply for research grants, what are the avenues for getting research grants ...
A grant proposal must always complete two tasks: Clearly articulate the hypothesis of your research in its broadest strokes. Demonstrate that your goals in the research endeavor and the goals of the funding institution are symbiotic. Introduction/Abstract. As early in the proposal as possible, identify and explicitly state the question your ...
This commentary provides a summary of the key points a researcher needs to consider when writing a research grant proposal, outlining how to conceptualise the research idea, how to find the right funding call, the importance of planning, and key questions for reflection during preparation. Expand. 3. PDF.
However, winning a research grant is a difficult task. A successful grant-winning application requires two key elements: one is an innovative research problem with best probable idea/plan for tackling it and appropriate planning of budget. The aim of the present paper is to give an insight on funding agencies providing funding for health ...
A successful grant-winning application requires two key elements: one is an innovative research problem with best probable idea/plan for tackling it and appropriate planning of budget.
For multi-centric grants different organizations may have different roles and responsibilities. 9. Be prepared as time from call for proposal to last date may only be 1-2 weeks. 10. Have a maximum of three to four research objectives in the grant application. 11. Detail the preliminary work like that of a publication.
3. Research previous winners. Before writing, research the grant you're applying for and who the previous grant awardees are. Understand what the grant funders value to ensure your proposal is aligned with those priorities. Studying winning proposals from the past can provide insight into what works best for a specific funder.
The Office of the Vice President for Research invites you to attend Write Winning NIH Grant Proposals Virtual Workshops. January 8, 9, and 10, 2024. Presenter: John D. Robertson, Ph.D. Grant Writers' Seminars & Workshops, LLC* SBU Faculty and Staff must Register before December 1, 2023. Workbooks will be purchased for Stony Brook participants ...