How to Write a Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples

Noah Parsons
24 min. read
Updated March 18, 2024
Writing a business plan doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to write a business plan that’s detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
- The basics of business planning
If you’re reading this guide, then you already know why you need a business plan .
You understand that planning helps you:
- Raise money
- Grow strategically
- Keep your business on the right track
As you start to write your plan, it’s useful to zoom out and remember what a business plan is .
At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow.
A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It’s also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals.
After completing your plan, you can use it as a management tool to track your progress toward your goals. Updating and adjusting your forecasts and budgets as you go is one of the most important steps you can take to run a healthier, smarter business.
We’ll dive into how to use your plan later in this article.
There are many different types of plans , but we’ll go over the most common type here, which includes everything you need for an investor-ready plan. However, if you’re just starting out and are looking for something simpler—I recommend starting with a one-page business plan . It’s faster and easier to create.
It’s also the perfect place to start if you’re just figuring out your idea, or need a simple strategic plan to use inside your business.
Dig deeper : How to write a one-page business plan
Brought to you by

Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What to include in your business plan
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it’s a summary of the complete business plan.
Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan.
In fact, it’s common for investors to ask only for the executive summary when evaluating your business. If they like what they see in the executive summary, they’ll often follow up with a request for a complete plan, a pitch presentation , or more in-depth financial forecasts .
Your executive summary should include:
- A summary of the problem you are solving
- A description of your product or service
- An overview of your target market
- A brief description of your team
- A summary of your financials
- Your funding requirements (if you are raising money)
Dig Deeper: How to write an effective executive summary
Products and services description
This is where you describe exactly what you’re selling, and how it solves a problem for your target market. The best way to organize this part of your plan is to start by describing the problem that exists for your customers. After that, you can describe how you plan to solve that problem with your product or service.
This is usually called a problem and solution statement .
To truly showcase the value of your products and services, you need to craft a compelling narrative around your offerings. How will your product or service transform your customers’ lives or jobs? A strong narrative will draw in your readers.
This is also the part of the business plan to discuss any competitive advantages you may have, like specific intellectual property or patents that protect your product. If you have any initial sales, contracts, or other evidence that your product or service is likely to sell, include that information as well. It will show that your idea has traction , which can help convince readers that your plan has a high chance of success.
Market analysis
Your target market is a description of the type of people that you plan to sell to. You might even have multiple target markets, depending on your business.
A market analysis is the part of your plan where you bring together all of the information you know about your target market. Basically, it’s a thorough description of who your customers are and why they need what you’re selling. You’ll also include information about the growth of your market and your industry .
Try to be as specific as possible when you describe your market.
Include information such as age, income level, and location—these are what’s called “demographics.” If you can, also describe your market’s interests and habits as they relate to your business—these are “psychographics.”
Related: Target market examples
Essentially, you want to include any knowledge you have about your customers that is relevant to how your product or service is right for them. With a solid target market, it will be easier to create a sales and marketing plan that will reach your customers. That’s because you know who they are, what they like to do, and the best ways to reach them.
Next, provide any additional information you have about your market.
What is the size of your market ? Is the market growing or shrinking? Ideally, you’ll want to demonstrate that your market is growing over time, and also explain how your business is positioned to take advantage of any expected changes in your industry.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write a market analysis
Competitive analysis
Part of defining your business opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage is. To do this effectively, you need to know as much about your competitors as your target customers.
Every business has some form of competition. If you don’t think you have competitors, then explore what alternatives there are in the market for your product or service.
For example: In the early years of cars, their main competition was horses. For social media, the early competition was reading books, watching TV, and talking on the phone.
A good competitive analysis fully lays out the competitive landscape and then explains how your business is different. Maybe your products are better made, or cheaper, or your customer service is superior. Maybe your competitive advantage is your location – a wide variety of factors can ultimately give you an advantage.
Dig Deeper: How to write a competitive analysis for your business plan
Marketing and sales plan
The marketing and sales plan covers how you will position your product or service in the market, the marketing channels and messaging you will use, and your sales tactics.
The best place to start with a marketing plan is with a positioning statement .
This explains how your business fits into the overall market, and how you will explain the advantages of your product or service to customers. You’ll use the information from your competitive analysis to help you with your positioning.
For example: You might position your company as the premium, most expensive but the highest quality option in the market. Or your positioning might focus on being locally owned and that shoppers support the local economy by buying your products.
Once you understand your positioning, you’ll bring this together with the information about your target market to create your marketing strategy .
This is how you plan to communicate your message to potential customers. Depending on who your customers are and how they purchase products like yours, you might use many different strategies, from social media advertising to creating a podcast. Your marketing plan is all about how your customers discover who you are and why they should consider your products and services.
While your marketing plan is about reaching your customers—your sales plan will describe the actual sales process once a customer has decided that they’re interested in what you have to offer.
If your business requires salespeople and a long sales process, describe that in this section. If your customers can “self-serve” and just make purchases quickly on your website, describe that process.
A good sales plan picks up where your marketing plan leaves off. The marketing plan brings customers in the door and the sales plan is how you close the deal.
Together, these specific plans paint a picture of how you will connect with your target audience, and how you will turn them into paying customers.
Dig deeper: What to include in your sales and marketing plan
Business operations
The operations section describes the necessary requirements for your business to run smoothly. It’s where you talk about how your business works and what day-to-day operations look like.
Depending on how your business is structured, your operations plan may include elements of the business like:
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing processes
- Equipment and technology
- Distribution
Some businesses distribute their products and reach their customers through large retailers like Amazon.com, Walmart, Target, and grocery store chains.
These businesses should review how this part of their business works. The plan should discuss the logistics and costs of getting products onto store shelves and any potential hurdles the business may have to overcome.
If your business is much simpler than this, that’s OK. This section of your business plan can be either extremely short or more detailed, depending on the type of business you are building.
For businesses selling services, such as physical therapy or online software, you can use this section to describe the technology you’ll leverage, what goes into your service, and who you will partner with to deliver your services.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write the operations chapter of your plan
Key milestones and metrics
Although it’s not required to complete your business plan, mapping out key business milestones and the metrics can be incredibly useful for measuring your success.
Good milestones clearly lay out the parameters of the task and set expectations for their execution. You’ll want to include:
- A description of each task
- The proposed due date
- Who is responsible for each task
If you have a budget, you can include projected costs to hit each milestone. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section—just list key milestones you want to hit and when you plan to hit them. This is your overall business roadmap.
Possible milestones might be:
- Website launch date
- Store or office opening date
- First significant sales
- Break even date
- Business licenses and approvals
You should also discuss the key numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common metrics worth tracking include:
- Conversion rates
- Customer acquisition costs
- Profit per customer
- Repeat purchases
It’s perfectly fine to start with just a few metrics and grow the number you are tracking over time. You also may find that some metrics simply aren’t relevant to your business and can narrow down what you’re tracking.
Dig Deeper: How to use milestones in your business plan
Organization and management team
Investors don’t just look for great ideas—they want to find great teams. Use this chapter to describe your current team and who you need to hire . You should also provide a quick overview of your location and history if you’re already up and running.
Briefly highlight the relevant experiences of each key team member in the company. It’s important to make the case for why yours is the right team to turn an idea into a reality.
Do they have the right industry experience and background? Have members of the team had entrepreneurial successes before?
If you still need to hire key team members, that’s OK. Just note those gaps in this section.
Your company overview should also include a summary of your company’s current business structure . The most common business structures include:
- Sole proprietor
- Partnership
Be sure to provide an overview of how the business is owned as well. Does each business partner own an equal portion of the business? How is ownership divided?
Potential lenders and investors will want to know the structure of the business before they will consider a loan or investment.
Dig Deeper: How to write about your company structure and team
Financial plan
Last, but certainly not least, is your financial plan chapter.
Entrepreneurs often find this section the most daunting. But, business financials for most startups are less complicated than you think, and a business degree is certainly not required to build a solid financial forecast.
A typical financial forecast in a business plan includes the following:
- Sales forecast : An estimate of the sales expected over a given period. You’ll break down your forecast into the key revenue streams that you expect to have.
- Expense budget : Your planned spending such as personnel costs , marketing expenses, and taxes.
- Profit & Loss : Brings together your sales and expenses and helps you calculate planned profits.
- Cash Flow : Shows how cash moves into and out of your business. It can predict how much cash you’ll have on hand at any given point in the future.
- Balance Sheet : A list of the assets, liabilities, and equity in your company. In short, it provides an overview of the financial health of your business.
A strong business plan will include a description of assumptions about the future, and potential risks that could impact the financial plan. Including those will be especially important if you’re writing a business plan to pursue a loan or other investment.
Dig Deeper: How to create financial forecasts and budgets
This is the place for additional data, charts, or other information that supports your plan.
Including an appendix can significantly enhance the credibility of your plan by showing readers that you’ve thoroughly considered the details of your business idea, and are backing your ideas up with solid data.
Just remember that the information in the appendix is meant to be supplementary. Your business plan should stand on its own, even if the reader skips this section.
Dig Deeper : What to include in your business plan appendix
Optional: Business plan cover page
Adding a business plan cover page can make your plan, and by extension your business, seem more professional in the eyes of potential investors, lenders, and partners. It serves as the introduction to your document and provides necessary contact information for stakeholders to reference.
Your cover page should be simple and include:
- Company logo
- Business name
- Value proposition (optional)
- Business plan title
- Completion and/or update date
- Address and contact information
- Confidentiality statement
Just remember, the cover page is optional. If you decide to include it, keep it very simple and only spend a short amount of time putting it together.
Dig Deeper: How to create a business plan cover page
How to use AI to help write your business plan
Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT can speed up the business plan writing process and help you think through concepts like market segmentation and competition. These tools are especially useful for taking ideas that you provide and converting them into polished text for your business plan.
The best way to use AI for your business plan is to leverage it as a collaborator , not a replacement for human creative thinking and ingenuity.
AI can come up with lots of ideas and act as a brainstorming partner. It’s up to you to filter through those ideas and figure out which ones are realistic enough to resonate with your customers.
There are pros and cons of using AI to help with your business plan . So, spend some time understanding how it can be most helpful before just outsourcing the job to AI.
Learn more: 10 AI prompts you need to write a business plan
- Writing tips and strategies
To help streamline the business plan writing process, here are a few tips and key questions to answer to make sure you get the most out of your plan and avoid common mistakes .
Determine why you are writing a business plan
Knowing why you are writing a business plan will determine your approach to your planning project.
For example: If you are writing a business plan for yourself, or just to use inside your own business , you can probably skip the section about your team and organizational structure.
If you’re raising money, you’ll want to spend more time explaining why you’re looking to raise the funds and exactly how you will use them.
Regardless of how you intend to use your business plan , think about why you are writing and what you’re trying to get out of the process before you begin.
Keep things concise
Probably the most important tip is to keep your business plan short and simple. There are no prizes for long business plans . The longer your plan is, the less likely people are to read it.
So focus on trimming things down to the essentials your readers need to know. Skip the extended, wordy descriptions and instead focus on creating a plan that is easy to read —using bullets and short sentences whenever possible.
Have someone review your business plan
Writing a business plan in a vacuum is never a good idea. Sometimes it’s helpful to zoom out and check if your plan makes sense to someone else. You also want to make sure that it’s easy to read and understand.
Don’t wait until your plan is “done” to get a second look. Start sharing your plan early, and find out from readers what questions your plan leaves unanswered. This early review cycle will help you spot shortcomings in your plan and address them quickly, rather than finding out about them right before you present your plan to a lender or investor.
If you need a more detailed review, you may want to explore hiring a professional plan writer to thoroughly examine it.
Use a free business plan template and business plan examples to get started
Knowing what information you need to cover in a business plan sometimes isn’t quite enough. If you’re struggling to get started or need additional guidance, it may be worth using a business plan template.
If you’re looking for a free downloadable business plan template to get you started, download the template used by more than 1 million businesses.
Or, if you just want to see what a completed business plan looks like, check out our library of over 550 free business plan examples .
We even have a growing list of industry business planning guides with tips for what to focus on depending on your business type.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
It’s easy to make mistakes when you’re writing your business plan. Some entrepreneurs get sucked into the writing and research process, and don’t focus enough on actually getting their business started.
Here are a few common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Not talking to your customers : This is one of the most common mistakes. It’s easy to assume that your product or service is something that people want. Before you invest too much in your business and too much in the planning process, make sure you talk to your prospective customers and have a good understanding of their needs.
- Overly optimistic sales and profit forecasts: By nature, entrepreneurs are optimistic about the future. But it’s good to temper that optimism a little when you’re planning, and make sure your forecasts are grounded in reality.
- Spending too much time planning: Yes, planning is crucial. But you also need to get out and talk to customers, build prototypes of your product and figure out if there’s a market for your idea. Make sure to balance planning with building.
- Not revising the plan: Planning is useful, but nothing ever goes exactly as planned. As you learn more about what’s working and what’s not—revise your plan, your budgets, and your revenue forecast. Doing so will provide a more realistic picture of where your business is going, and what your financial needs will be moving forward.
- Not using the plan to manage your business: A good business plan is a management tool. Don’t just write it and put it on the shelf to collect dust – use it to track your progress and help you reach your goals.
- Presenting your business plan
The planning process forces you to think through every aspect of your business and answer questions that you may not have thought of. That’s the real benefit of writing a business plan – the knowledge you gain about your business that you may not have been able to discover otherwise.
With all of this knowledge, you’re well prepared to convert your business plan into a pitch presentation to present your ideas.
A pitch presentation is a summary of your plan, just hitting the highlights and key points. It’s the best way to present your business plan to investors and team members.
Dig Deeper: Learn what key slides should be included in your pitch deck
Use your business plan to manage your business
One of the biggest benefits of planning is that it gives you a tool to manage your business better. With a revenue forecast, expense budget, and projected cash flow, you know your targets and where you are headed.
And yet, nothing ever goes exactly as planned – it’s the nature of business.
That’s where using your plan as a management tool comes in. The key to leveraging it for your business is to review it periodically and compare your forecasts and projections to your actual results.
Start by setting up a regular time to review the plan – a monthly review is a good starting point. During this review, answer questions like:
- Did you meet your sales goals?
- Is spending following your budget?
- Has anything gone differently than what you expected?
Now that you see whether you’re meeting your goals or are off track, you can make adjustments and set new targets.
Maybe you’re exceeding your sales goals and should set new, more aggressive goals. In that case, maybe you should also explore more spending or hiring more employees.
Or maybe expenses are rising faster than you projected. If that’s the case, you would need to look at where you can cut costs.
A plan, and a method for comparing your plan to your actual results , is the tool you need to steer your business toward success.
Learn More: How to run a regular plan review
Free business plan templates and examples
Kickstart your business plan writing with one of our free business plan templates or recommended tools.

Free business plan template
Download a free SBA-approved business plan template built for small businesses and startups.
Download Template

One-page plan template
Download a free one-page plan template to write a useful business plan in as little as 30-minutes.

Sample business plan library
Explore over 500 real-world business plan examples from a wide variety of industries.
View Sample Plans
How to write a business plan FAQ
What is a business plan?
A document that describes your business , the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy, how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan helps you understand where you want to go with your business and what it will take to get there. It reduces your overall risk, helps you uncover your business’s potential, attracts investors, and identifies areas for growth.
Having a business plan ultimately makes you more confident as a business owner and more likely to succeed for a longer period of time.
What are the 7 steps of a business plan?
The seven steps to writing a business plan include:
- Write a brief executive summary
- Describe your products and services.
- Conduct market research and compile data into a cohesive market analysis.
- Describe your marketing and sales strategy.
- Outline your organizational structure and management team.
- Develop financial projections for sales, revenue, and cash flow.
- Add any additional documents to your appendix.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
There are plenty of mistakes that can be made when writing a business plan. However, these are the 5 most common that you should do your best to avoid:
- 1. Not taking the planning process seriously.
- Having unrealistic financial projections or incomplete financial information.
- Inconsistent information or simple mistakes.
- Failing to establish a sound business model.
- Not having a defined purpose for your business plan.
What questions should be answered in a business plan?
Writing a business plan is all about asking yourself questions about your business and being able to answer them through the planning process. You’ll likely be asking dozens and dozens of questions for each section of your plan.
However, these are the key questions you should ask and answer with your business plan:
- How will your business make money?
- Is there a need for your product or service?
- Who are your customers?
- How are you different from the competition?
- How will you reach your customers?
- How will you measure success?
How long should a business plan be?
The length of your business plan fully depends on what you intend to do with it. From the SBA and traditional lender point of view, a business plan needs to be whatever length necessary to fully explain your business. This means that you prove the viability of your business, show that you understand the market, and have a detailed strategy in place.
If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don’t necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary information in place.
What are the different types of business plans?
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan: The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used when applying for funding or pitching to investors. This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix.
Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
One-page business plan: This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences. It’s most useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Lean Plan: The Lean Plan is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance. It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision.
However, when approached correctly, your business plan can actually function as a strategic plan as well. If kept lean, you can define your business, outline strategic steps, and track ongoing operations all with a single plan.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- Use AI to help write your plan
- Common planning mistakes
- Manage with your business plan
- Templates and examples
Related Articles

9 Min. Read
Airbnb rental business plan

5 Min. Read
Life coaching business plan

3 Min. Read
Outline your marketing strategy

Break-even analysis
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Simple Business Plan
By Joe Weller | October 11, 2021
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
A business plan is the cornerstone of any successful company, regardless of size or industry. This step-by-step guide provides information on writing a business plan for organizations at any stage, complete with free templates and expert advice.
Included on this page, you’ll find a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan and a chart to identify which type of business plan you should write . Plus, find information on how a business plan can help grow a business and expert tips on writing one .
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that communicates a company’s goals and ambitions, along with the timeline, finances, and methods needed to achieve them. Additionally, it may include a mission statement and details about the specific products or services offered.
A business plan can highlight varying time periods, depending on the stage of your company and its goals. That said, a typical business plan will include the following benchmarks:
- Product goals and deadlines for each month
- Monthly financials for the first two years
- Profit and loss statements for the first three to five years
- Balance sheet projections for the first three to five years
Startups, entrepreneurs, and small businesses all create business plans to use as a guide as their new company progresses. Larger organizations may also create (and update) a business plan to keep high-level goals, financials, and timelines in check.
While you certainly need to have a formalized outline of your business’s goals and finances, creating a business plan can also help you determine a company’s viability, its profitability (including when it will first turn a profit), and how much money you will need from investors. In turn, a business plan has functional value as well: Not only does outlining goals help keep you accountable on a timeline, it can also attract investors in and of itself and, therefore, act as an effective strategy for growth.
For more information, visit our comprehensive guide to writing a strategic plan or download free strategic plan templates . This page focuses on for-profit business plans, but you can read our article with nonprofit business plan templates .
Business Plan Steps
The specific information in your business plan will vary, depending on the needs and goals of your venture, but a typical plan includes the following ordered elements:
- Executive summary
- Description of business
- Market analysis
- Competitive analysis
- Description of organizational management
- Description of product or services
- Marketing plan
- Sales strategy
- Funding details (or request for funding)
- Financial projections
If your plan is particularly long or complicated, consider adding a table of contents or an appendix for reference. For an in-depth description of each step listed above, read “ How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step ” below.
Broadly speaking, your audience includes anyone with a vested interest in your organization. They can include potential and existing investors, as well as customers, internal team members, suppliers, and vendors.
Do I Need a Simple or Detailed Plan?
Your business’s stage and intended audience dictates the level of detail your plan needs. Corporations require a thorough business plan — up to 100 pages. Small businesses or startups should have a concise plan focusing on financials and strategy.
How to Choose the Right Plan for Your Business
In order to identify which type of business plan you need to create, ask: “What do we want the plan to do?” Identify function first, and form will follow.
Use the chart below as a guide for what type of business plan to create:
Is the Order of Your Business Plan Important?
There is no set order for a business plan, with the exception of the executive summary, which should always come first. Beyond that, simply ensure that you organize the plan in a way that makes sense and flows naturally.
The Difference Between Traditional and Lean Business Plans
A traditional business plan follows the standard structure — because these plans encourage detail, they tend to require more work upfront and can run dozens of pages. A Lean business plan is less common and focuses on summarizing critical points for each section. These plans take much less work and typically run one page in length.
In general, you should use a traditional model for a legacy company, a large company, or any business that does not adhere to Lean (or another Agile method ). Use Lean if you expect the company to pivot quickly or if you already employ a Lean strategy with other business operations. Additionally, a Lean business plan can suffice if the document is for internal use only. Stick to a traditional version for investors, as they may be more sensitive to sudden changes or a high degree of built-in flexibility in the plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step
Writing a strong business plan requires research and attention to detail for each section. Below, you’ll find a 10-step guide to researching and defining each element in the plan.
Step 1: Executive Summary
The executive summary will always be the first section of your business plan. The goal is to answer the following questions:
- What is the vision and mission of the company?
- What are the company’s short- and long-term goals?
See our roundup of executive summary examples and templates for samples. Read our executive summary guide to learn more about writing one.
Step 2: Description of Business
The goal of this section is to define the realm, scope, and intent of your venture. To do so, answer the following questions as clearly and concisely as possible:
- What business are we in?
- What does our business do?
Step 3: Market Analysis
In this section, provide evidence that you have surveyed and understand the current marketplace, and that your product or service satisfies a niche in the market. To do so, answer these questions:
- Who is our customer?
- What does that customer value?
Step 4: Competitive Analysis
In many cases, a business plan proposes not a brand-new (or even market-disrupting) venture, but a more competitive version — whether via features, pricing, integrations, etc. — than what is currently available. In this section, answer the following questions to show that your product or service stands to outpace competitors:
- Who is the competition?
- What do they do best?
- What is our unique value proposition?
Step 5: Description of Organizational Management
In this section, write an overview of the team members and other key personnel who are integral to success. List roles and responsibilities, and if possible, note the hierarchy or team structure.
Step 6: Description of Products or Services
In this section, clearly define your product or service, as well as all the effort and resources that go into producing it. The strength of your product largely defines the success of your business, so it’s imperative that you take time to test and refine the product before launching into marketing, sales, or funding details.
Questions to answer in this section are as follows:
- What is the product or service?
- How do we produce it, and what resources are necessary for production?
Step 7: Marketing Plan
In this section, define the marketing strategy for your product or service. This doesn’t need to be as fleshed out as a full marketing plan , but it should answer basic questions, such as the following:
- Who is the target market (if different from existing customer base)?
- What channels will you use to reach your target market?
- What resources does your marketing strategy require, and do you have access to them?
- If possible, do you have a rough estimate of timeline and budget?
- How will you measure success?
Step 8: Sales Plan
Write an overview of the sales strategy, including the priorities of each cycle, steps to achieve these goals, and metrics for success. For the purposes of a business plan, this section does not need to be a comprehensive, in-depth sales plan , but can simply outline the high-level objectives and strategies of your sales efforts.
Start by answering the following questions:
- What is the sales strategy?
- What are the tools and tactics you will use to achieve your goals?
- What are the potential obstacles, and how will you overcome them?
- What is the timeline for sales and turning a profit?
- What are the metrics of success?
Step 9: Funding Details (or Request for Funding)
This section is one of the most critical parts of your business plan, particularly if you are sharing it with investors. You do not need to provide a full financial plan, but you should be able to answer the following questions:
- How much capital do you currently have? How much capital do you need?
- How will you grow the team (onboarding, team structure, training and development)?
- What are your physical needs and constraints (space, equipment, etc.)?
Step 10: Financial Projections
Apart from the fundraising analysis, investors like to see thought-out financial projections for the future. As discussed earlier, depending on the scope and stage of your business, this could be anywhere from one to five years.
While these projections won’t be exact — and will need to be somewhat flexible — you should be able to gauge the following:
- How and when will the company first generate a profit?
- How will the company maintain profit thereafter?
Business Plan Template

Download Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Smartsheet
This basic business plan template has space for all the traditional elements: an executive summary, product or service details, target audience, marketing and sales strategies, etc. In the finances sections, input your baseline numbers, and the template will automatically calculate projections for sales forecasting, financial statements, and more.
For templates tailored to more specific needs, visit this business plan template roundup or download a fill-in-the-blank business plan template to make things easy.
If you are looking for a particular template by file type, visit our pages dedicated exclusively to Microsoft Excel , Microsoft Word , and Adobe PDF business plan templates.
How to Write a Simple Business Plan
A simple business plan is a streamlined, lightweight version of the large, traditional model. As opposed to a one-page business plan , which communicates high-level information for quick overviews (such as a stakeholder presentation), a simple business plan can exceed one page.
Below are the steps for creating a generic simple business plan, which are reflected in the template below .
- Write the Executive Summary This section is the same as in the traditional business plan — simply offer an overview of what’s in the business plan, the prospect or core offering, and the short- and long-term goals of the company.
- Add a Company Overview Document the larger company mission and vision.
- Provide the Problem and Solution In straightforward terms, define the problem you are attempting to solve with your product or service and how your company will attempt to do it. Think of this section as the gap in the market you are attempting to close.
- Identify the Target Market Who is your company (and its products or services) attempting to reach? If possible, briefly define your buyer personas .
- Write About the Competition In this section, demonstrate your knowledge of the market by listing the current competitors and outlining your competitive advantage.
- Describe Your Product or Service Offerings Get down to brass tacks and define your product or service. What exactly are you selling?
- Outline Your Marketing Tactics Without getting into too much detail, describe your planned marketing initiatives.
- Add a Timeline and the Metrics You Will Use to Measure Success Offer a rough timeline, including milestones and key performance indicators (KPIs) that you will use to measure your progress.
- Include Your Financial Forecasts Write an overview of your financial plan that demonstrates you have done your research and adequate modeling. You can also list key assumptions that go into this forecasting.
- Identify Your Financing Needs This section is where you will make your funding request. Based on everything in the business plan, list your proposed sources of funding, as well as how you will use it.
Simple Business Plan Template

Download Simple Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF | Smartsheet
Use this simple business plan template to outline each aspect of your organization, including information about financing and opportunities to seek out further funding. This template is completely customizable to fit the needs of any business, whether it’s a startup or large company.
Read our article offering free simple business plan templates or free 30-60-90-day business plan templates to find more tailored options. You can also explore our collection of one page business templates .
How to Write a Business Plan for a Lean Startup
A Lean startup business plan is a more Agile approach to a traditional version. The plan focuses more on activities, processes, and relationships (and maintains flexibility in all aspects), rather than on concrete deliverables and timelines.
While there is some overlap between a traditional and a Lean business plan, you can write a Lean plan by following the steps below:
- Add Your Value Proposition Take a streamlined approach to describing your product or service. What is the unique value your startup aims to deliver to customers? Make sure the team is aligned on the core offering and that you can state it in clear, simple language.
- List Your Key Partners List any other businesses you will work with to realize your vision, including external vendors, suppliers, and partners. This section demonstrates that you have thoughtfully considered the resources you can provide internally, identified areas for external assistance, and conducted research to find alternatives.
- Note the Key Activities Describe the key activities of your business, including sourcing, production, marketing, distribution channels, and customer relationships.
- Include Your Key Resources List the critical resources — including personnel, equipment, space, and intellectual property — that will enable you to deliver your unique value.
- Identify Your Customer Relationships and Channels In this section, document how you will reach and build relationships with customers. Provide a high-level map of the customer experience from start to finish, including the spaces in which you will interact with the customer (online, retail, etc.).
- Detail Your Marketing Channels Describe the marketing methods and communication platforms you will use to identify and nurture your relationships with customers. These could be email, advertising, social media, etc.
- Explain the Cost Structure This section is especially necessary in the early stages of a business. Will you prioritize maximizing value or keeping costs low? List the foundational startup costs and how you will move toward profit over time.
- Share Your Revenue Streams Over time, how will the company make money? Include both the direct product or service purchase, as well as secondary sources of revenue, such as subscriptions, selling advertising space, fundraising, etc.
Lean Business Plan Template for Startups

Download Lean Business Plan Template for Startups
Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF
Startup leaders can use this Lean business plan template to relay the most critical information from a traditional plan. You’ll find all the sections listed above, including spaces for industry and product overviews, cost structure and sources of revenue, and key metrics, and a timeline. The template is completely customizable, so you can edit it to suit the objectives of your Lean startups.
See our wide variety of startup business plan templates for more options.
How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
A business plan for a loan, often called a loan proposal , includes many of the same aspects of a traditional business plan, as well as additional financial documents, such as a credit history, a loan request, and a loan repayment plan.
In addition, you may be asked to include personal and business financial statements, a form of collateral, and equity investment information.
Download free financial templates to support your business plan.
Tips for Writing a Business Plan
Outside of including all the key details in your business plan, you have several options to elevate the document for the highest chance of winning funding and other resources. Follow these tips from experts:.
- Keep It Simple: Avner Brodsky , the Co-Founder and CEO of Lezgo Limited, an online marketing company, uses the acronym KISS (keep it short and simple) as a variation on this idea. “The business plan is not a college thesis,” he says. “Just focus on providing the essential information.”
- Do Adequate Research: Michael Dean, the Co-Founder of Pool Research , encourages business leaders to “invest time in research, both internal and external (market, finance, legal etc.). Avoid being overly ambitious or presumptive. Instead, keep everything objective, balanced, and accurate.” Your plan needs to stand on its own, and you must have the data to back up any claims or forecasting you make. As Brodsky explains, “Your business needs to be grounded on the realities of the market in your chosen location. Get the most recent data from authoritative sources so that the figures are vetted by experts and are reliable.”
- Set Clear Goals: Make sure your plan includes clear, time-based goals. “Short-term goals are key to momentum growth and are especially important to identify for new businesses,” advises Dean.
- Know (and Address) Your Weaknesses: “This awareness sets you up to overcome your weak points much quicker than waiting for them to arise,” shares Dean. Brodsky recommends performing a full SWOT analysis to identify your weaknesses, too. “Your business will fare better with self-knowledge, which will help you better define the mission of your business, as well as the strategies you will choose to achieve your objectives,” he adds.
- Seek Peer or Mentor Review: “Ask for feedback on your drafts and for areas to improve,” advises Brodsky. “When your mind is filled with dreams for your business, sometimes it is an outsider who can tell you what you’re missing and will save your business from being a product of whimsy.”
Outside of these more practical tips, the language you use is also important and may make or break your business plan.
Shaun Heng, VP of Operations at Coin Market Cap , gives the following advice on the writing, “Your business plan is your sales pitch to an investor. And as with any sales pitch, you need to strike the right tone and hit a few emotional chords. This is a little tricky in a business plan, because you also need to be formal and matter-of-fact. But you can still impress by weaving in descriptive language and saying things in a more elegant way.
“A great way to do this is by expanding your vocabulary, avoiding word repetition, and using business language. Instead of saying that something ‘will bring in as many customers as possible,’ try saying ‘will garner the largest possible market segment.’ Elevate your writing with precise descriptive words and you'll impress even the busiest investor.”
Additionally, Dean recommends that you “stay consistent and concise by keeping your tone and style steady throughout, and your language clear and precise. Include only what is 100 percent necessary.”
Resources for Writing a Business Plan
While a template provides a great outline of what to include in a business plan, a live document or more robust program can provide additional functionality, visibility, and real-time updates. The U.S. Small Business Association also curates resources for writing a business plan.
Additionally, you can use business plan software to house data, attach documentation, and share information with stakeholders. Popular options include LivePlan, Enloop, BizPlanner, PlanGuru, and iPlanner.
How a Business Plan Helps to Grow Your Business
A business plan — both the exercise of creating one and the document — can grow your business by helping you to refine your product, target audience, sales plan, identify opportunities, secure funding, and build new partnerships.
Outside of these immediate returns, writing a business plan is a useful exercise in that it forces you to research the market, which prompts you to forge your unique value proposition and identify ways to beat the competition. Doing so will also help you build (and keep you accountable to) attainable financial and product milestones. And down the line, it will serve as a welcome guide as hurdles inevitably arise.
Streamline Your Business Planning Activities with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Business Plan, Step by Step

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
What is a business plan?
1. write an executive summary, 2. describe your company, 3. state your business goals, 4. describe your products and services, 5. do your market research, 6. outline your marketing and sales plan, 7. perform a business financial analysis, 8. make financial projections, 9. summarize how your company operates, 10. add any additional information to an appendix, business plan tips and resources.
A business plan outlines your business’s financial goals and explains how you’ll achieve them over the next three to five years. Here’s a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan that will offer a strong, detailed road map for your business.

ZenBusiness
A business plan is a document that explains what your business does, how it makes money and who its customers are. Internally, writing a business plan should help you clarify your vision and organize your operations. Externally, you can share it with potential lenders and investors to show them you’re on the right track.
Business plans are living documents; it’s OK for them to change over time. Startups may update their business plans often as they figure out who their customers are and what products and services fit them best. Mature companies might only revisit their business plan every few years. Regardless of your business’s age, brush up this document before you apply for a business loan .
» Need help writing? Learn about the best business plan software .
This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your business offers and a broad summary of your financial growth plans.
Though the executive summary is the first thing your investors will read, it can be easier to write it last. That way, you can highlight information you’ve identified while writing other sections that go into more detail.
» MORE: How to write an executive summary in 6 steps
Next up is your company description. This should contain basic information like:
Your business’s registered name.
Address of your business location .
Names of key people in the business. Make sure to highlight unique skills or technical expertise among members of your team.
Your company description should also define your business structure — such as a sole proprietorship, partnership or corporation — and include the percent ownership that each owner has and the extent of each owner’s involvement in the company.
Lastly, write a little about the history of your company and the nature of your business now. This prepares the reader to learn about your goals in the next section.
» MORE: How to write a company overview for a business plan

The third part of a business plan is an objective statement. This section spells out what you’d like to accomplish, both in the near term and over the coming years.
If you’re looking for a business loan or outside investment, you can use this section to explain how the financing will help your business grow and how you plan to achieve those growth targets. The key is to provide a clear explanation of the opportunity your business presents to the lender.
For example, if your business is launching a second product line, you might explain how the loan will help your company launch that new product and how much you think sales will increase over the next three years as a result.
» MORE: How to write a successful business plan for a loan
In this section, go into detail about the products or services you offer or plan to offer.
You should include the following:
An explanation of how your product or service works.
The pricing model for your product or service.
The typical customers you serve.
Your supply chain and order fulfillment strategy.
You can also discuss current or pending trademarks and patents associated with your product or service.
Lenders and investors will want to know what sets your product apart from your competition. In your market analysis section , explain who your competitors are. Discuss what they do well, and point out what you can do better. If you’re serving a different or underserved market, explain that.
Here, you can address how you plan to persuade customers to buy your products or services, or how you will develop customer loyalty that will lead to repeat business.
Include details about your sales and distribution strategies, including the costs involved in selling each product .
» MORE: R e a d our complete guide to small business marketing
If you’re a startup, you may not have much information on your business financials yet. However, if you’re an existing business, you’ll want to include income or profit-and-loss statements, a balance sheet that lists your assets and debts, and a cash flow statement that shows how cash comes into and goes out of the company.
Accounting software may be able to generate these reports for you. It may also help you calculate metrics such as:
Net profit margin: the percentage of revenue you keep as net income.
Current ratio: the measurement of your liquidity and ability to repay debts.
Accounts receivable turnover ratio: a measurement of how frequently you collect on receivables per year.
This is a great place to include charts and graphs that make it easy for those reading your plan to understand the financial health of your business.
This is a critical part of your business plan if you’re seeking financing or investors. It outlines how your business will generate enough profit to repay the loan or how you will earn a decent return for investors.
Here, you’ll provide your business’s monthly or quarterly sales, expenses and profit estimates over at least a three-year period — with the future numbers assuming you’ve obtained a new loan.
Accuracy is key, so carefully analyze your past financial statements before giving projections. Your goals may be aggressive, but they should also be realistic.
NerdWallet’s picks for setting up your business finances:
The best business checking accounts .
The best business credit cards .
The best accounting software .
Before the end of your business plan, summarize how your business is structured and outline each team’s responsibilities. This will help your readers understand who performs each of the functions you’ve described above — making and selling your products or services — and how much each of those functions cost.
If any of your employees have exceptional skills, you may want to include their resumes to help explain the competitive advantage they give you.
Finally, attach any supporting information or additional materials that you couldn’t fit in elsewhere. That might include:
Licenses and permits.
Equipment leases.
Bank statements.
Details of your personal and business credit history, if you’re seeking financing.
If the appendix is long, you may want to consider adding a table of contents at the beginning of this section.
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
Here are some tips to write a detailed, convincing business plan:
Avoid over-optimism: If you’re applying for a business bank loan or professional investment, someone will be reading your business plan closely. Providing unreasonable sales estimates can hurt your chances of approval.
Proofread: Spelling, punctuation and grammatical errors can jump off the page and turn off lenders and prospective investors. If writing and editing aren't your strong suit, you may want to hire a professional business plan writer, copy editor or proofreader.
Use free resources: SCORE is a nonprofit association that offers a large network of volunteer business mentors and experts who can help you write or edit your business plan. The U.S. Small Business Administration’s Small Business Development Centers , which provide free business consulting and help with business plan development, can also be a resource.
On a similar note...
Find small-business financing
Compare multiple lenders that fit your business

How to make a business plan
Table of Contents
How to make a good business plan: step-by-step guide.
A business plan is a strategic roadmap used to navigate the challenging journey of entrepreneurship. It's the foundation upon which you build a successful business.
A well-crafted business plan can help you define your vision, clarify your goals, and identify potential problems before they arise.
But where do you start? How do you create a business plan that sets you up for success?
This article will explore the step-by-step process of creating a comprehensive business plan.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a formal document that outlines a business's objectives, strategies, and operational procedures. It typically includes the following information about a company:
Products or services
Target market
Competitors
Marketing and sales strategies
Financial plan
Management team
A business plan serves as a roadmap for a company's success and provides a blueprint for its growth and development. It helps entrepreneurs and business owners organize their ideas, evaluate the feasibility, and identify potential challenges and opportunities.
As well as serving as a guide for business owners, a business plan can attract investors and secure funding. It demonstrates the company's understanding of the market, its ability to generate revenue and profits, and its strategy for managing risks and achieving success.
Business plan vs. business model canvas
A business plan may seem similar to a business model canvas, but each document serves a different purpose.
A business model canvas is a high-level overview that helps entrepreneurs and business owners quickly test and iterate their ideas. It is often a one-page document that briefly outlines the following:
Key partnerships
Key activities
Key propositions
Customer relationships
Customer segments
Key resources
Cost structure
Revenue streams
On the other hand, a Business Plan Template provides a more in-depth analysis of a company's strategy and operations. It is typically a lengthy document and requires significant time and effort to develop.
A business model shouldn’t replace a business plan, and vice versa. Business owners should lay the foundations and visually capture the most important information with a Business Model Canvas Template . Because this is a fast and efficient way to communicate a business idea, a business model canvas is a good starting point before developing a more comprehensive business plan.
A business plan can aim to secure funding from investors or lenders, while a business model canvas communicates a business idea to potential customers or partners.
Why is a business plan important?
A business plan is crucial for any entrepreneur or business owner wanting to increase their chances of success.
Here are some of the many benefits of having a thorough business plan.
Helps to define the business goals and objectives
A business plan encourages you to think critically about your goals and objectives. Doing so lets you clearly understand what you want to achieve and how you plan to get there.
A well-defined set of goals, objectives, and key results also provides a sense of direction and purpose, which helps keep business owners focused and motivated.
Guides decision-making
A business plan requires you to consider different scenarios and potential problems that may arise in your business. This awareness allows you to devise strategies to deal with these issues and avoid pitfalls.
With a clear plan, entrepreneurs can make informed decisions aligning with their overall business goals and objectives. This helps reduce the risk of making costly mistakes and ensures they make decisions with long-term success in mind.
Attracts investors and secures funding
Investors and lenders often require a business plan before considering investing in your business. A document that outlines the company's goals, objectives, and financial forecasts can help instill confidence in potential investors and lenders.
A well-written business plan demonstrates that you have thoroughly thought through your business idea and have a solid plan for success.
Identifies potential challenges and risks
A business plan requires entrepreneurs to consider potential challenges and risks that could impact their business. For example:
Is there enough demand for my product or service?
Will I have enough capital to start my business?
Is the market oversaturated with too many competitors?
What will happen if my marketing strategy is ineffective?
By identifying these potential challenges, entrepreneurs can develop strategies to mitigate risks and overcome challenges. This can reduce the likelihood of costly mistakes and ensure the business is well-positioned to take on any challenges.
Provides a basis for measuring success
A business plan serves as a framework for measuring success by providing clear goals and financial projections . Entrepreneurs can regularly refer to the original business plan as a benchmark to measure progress. By comparing the current business position to initial forecasts, business owners can answer questions such as:
Are we where we want to be at this point?
Did we achieve our goals?
If not, why not, and what do we need to do?
After assessing whether the business is meeting its objectives or falling short, business owners can adjust their strategies as needed.
How to make a business plan step by step
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include.
1. Create an executive summary
Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
Keep your executive summary concise and clear with the Executive Summary Template . The simple design helps readers understand the crux of your business plan without reading the entire document.
2. Write your company description
Provide a detailed explanation of your company. Include information on what your company does, the mission statement, and your vision for the future.
Provide additional background information on the history of your company, the founders, and any notable achievements or milestones.
3. Conduct a market analysis
Conduct an in-depth analysis of your industry, competitors, and target market. This is best done with a SWOT analysis to identify your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Next, identify your target market's needs, demographics, and behaviors.
Use the Competitive Analysis Template to brainstorm answers to simple questions like:
What does the current market look like?
Who are your competitors?
What are they offering?
What will give you a competitive advantage?
Who is your target market?
What are they looking for and why?
How will your product or service satisfy a need?
These questions should give you valuable insights into the current market and where your business stands.
4. Describe your products and services
Provide detailed information about your products and services. This includes pricing information, product features, and any unique selling points.
Use the Product/Market Fit Template to explain how your products meet the needs of your target market. Describe what sets them apart from the competition.
5. Design a marketing and sales strategy
Outline how you plan to promote and sell your products. Your marketing strategy and sales strategy should include information about your:
Pricing strategy
Advertising and promotional tactics
Sales channels
The Go to Market Strategy Template is a great way to visually map how you plan to launch your product or service in a new or existing market.
6. Determine budget and financial projections
Document detailed information on your business’ finances. Describe the current financial position of the company and how you expect the finances to play out.
Some details to include in this section are:
Startup costs
Revenue projections
Profit and loss statement
Funding you have received or plan to receive
Strategy for raising funds
7. Set the organization and management structure
Define how your company is structured and who will be responsible for each aspect of the business. Use the Business Organizational Chart Template to visually map the company’s teams, roles, and hierarchy.
As well as the organization and management structure, discuss the legal structure of your business. Clarify whether your business is a corporation, partnership, sole proprietorship, or LLC.
8. Make an action plan
At this point in your business plan, you’ve described what you’re aiming for. But how are you going to get there? The Action Plan Template describes the following steps to move your business plan forward. Outline the next steps you plan to take to bring your business plan to fruition.
Types of business plans
Several types of business plans cater to different purposes and stages of a company's lifecycle. Here are some of the most common types of business plans.
Startup business plan
A startup business plan is typically an entrepreneur's first business plan. This document helps entrepreneurs articulate their business idea when starting a new business.
Not sure how to make a business plan for a startup? It’s pretty similar to a regular business plan, except the primary purpose of a startup business plan is to convince investors to provide funding for the business. A startup business plan also outlines the potential target market, product/service offering, marketing plan, and financial projections.
Strategic business plan
A strategic business plan is a long-term plan that outlines a company's overall strategy, objectives, and tactics. This type of strategic plan focuses on the big picture and helps business owners set goals and priorities and measure progress.
The primary purpose of a strategic business plan is to provide direction and guidance to the company's management team and stakeholders. The plan typically covers a period of three to five years.
Operational business plan
An operational business plan is a detailed document that outlines the day-to-day operations of a business. It focuses on the specific activities and processes required to run the business, such as:
Organizational structure
Staffing plan
Production plan
Quality control
Inventory management
Supply chain
The primary purpose of an operational business plan is to ensure that the business runs efficiently and effectively. It helps business owners manage their resources, track their performance, and identify areas for improvement.
Growth-business plan
A growth-business plan is a strategic plan that outlines how a company plans to expand its business. It helps business owners identify new market opportunities and increase revenue and profitability. The primary purpose of a growth-business plan is to provide a roadmap for the company's expansion and growth.
The 3 Horizons of Growth Template is a great tool to identify new areas of growth. This framework categorizes growth opportunities into three categories: Horizon 1 (core business), Horizon 2 (emerging business), and Horizon 3 (potential business).
One-page business plan
A one-page business plan is a condensed version of a full business plan that focuses on the most critical aspects of a business. It’s a great tool for entrepreneurs who want to quickly communicate their business idea to potential investors, partners, or employees.
A one-page business plan typically includes sections such as business concept, value proposition, revenue streams, and cost structure.
Best practices for how to make a good business plan
Here are some additional tips for creating a business plan:
Use a template
A template can help you organize your thoughts and effectively communicate your business ideas and strategies. Starting with a template can also save you time and effort when formatting your plan.
Miro’s extensive library of customizable templates includes all the necessary sections for a comprehensive business plan. With our templates, you can confidently present your business plans to stakeholders and investors.
Be practical
Avoid overestimating revenue projections or underestimating expenses. Your business plan should be grounded in practical realities like your budget, resources, and capabilities.
Be specific
Provide as much detail as possible in your business plan. A specific plan is easier to execute because it provides clear guidance on what needs to be done and how. Without specific details, your plan may be too broad or vague, making it difficult to know where to start or how to measure success.
Be thorough with your research
Conduct thorough research to fully understand the market, your competitors, and your target audience . By conducting thorough research, you can identify potential risks and challenges your business may face and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Get input from others
It can be easy to become overly focused on your vision and ideas, leading to tunnel vision and a lack of objectivity. By seeking input from others, you can identify potential opportunities you may have overlooked.
Review and revise regularly
A business plan is a living document. You should update it regularly to reflect market, industry, and business changes. Set aside time for regular reviews and revisions to ensure your plan remains relevant and effective.
Create a winning business plan to chart your path to success
Starting or growing a business can be challenging, but it doesn't have to be. Whether you're a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting, a well-written business plan can make or break your business’ success.
The purpose of a business plan is more than just to secure funding and attract investors. It also serves as a roadmap for achieving your business goals and realizing your vision. With the right mindset, tools, and strategies, you can develop a visually appealing, persuasive business plan.
Ready to make an effective business plan that works for you? Check out our library of ready-made strategy and planning templates and chart your path to success.
Get on board in seconds
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.

How to Write a Business Plan in 2023: The Ultimate Guide for Every Entrepreneur
Are you starting a new business or trying to get a loan for your existing venture? If so, you’re going to need to know how to write a business plan. Business plans give entrepreneurs the opportunity to formally analyze and define every aspect of their business idea .
In this post, you’ll learn how to put together a business plan and find the best resources to help you along the way.
Start selling online now with Shopify

What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a formal document that outlines your business’s goals and how you will achieve those goals. Entrepreneurs who start out with business plans are 16 percent more likely to build successful companies , according to the Harvard Business Review. Developing a business plan ensures sustainable success, guiding you as you grow your business, legitimizing your venture, and helping you secure funding (among countless other benefits).
What Are the Main Purposes of a Business Plan?
Most financial institutions and service providers require you to submit a detailed business plan to obtain funding for your business. Online businesses will likely have a low overhead to start, so they may not need funding and therefore may not feel the need to write a business plan. That said, writing a business plan is still a good idea as it can help you secure a drastic increase limit on your credit card as your business grows or open a business account. This varies per bank.
If you’re growing your business, use it to help you raise expansion capital, create a growth strategy, find opportunities, and mitigate risks.Palo Alto software found that companies who make business plans are twice as likely to secure funding . .
→ Click Here to Launch Your Online Business with Shopify
If you’re just starting your business, making a business plan can help you identify your strengths and weaknesses, communicate your vision to others, and develop accurate forecasts.

How to Make a Business Plan: The Prerequisites
Here are the prerequisites to creating a solid business plan:
- Establish goals
- Understand your audience
- Determine your business plan format
- Get to writing!
Establish Goals
There are two key questions to ask here:
- What are you hoping to accomplish with your business?
- What are you hoping to accomplish with your business plan?
Approaching your business plan through that lens will help you focus on the end goal throughout the writing process. These also provide metrics to measure success against.
Before writing your business plan, gather the content and data needed to inform what goes in it. This includes researching your market and industry – spanning everything from customer research to legalities you’ll need to consider. It’s a lot easier to start with the information already in front of you instead of researching each section individually as you go.
Turn to guides, samples, and small business plan templates to help. Many countries have an official administration or service dedicated to providing information, resources, and tools to help entrepreneurs and store owners plan, launch, manage, and grow their businesses.
The following will take you to online business plan guides and templates for specific countries.
- United States Small Business Administration (SBA) – The “write your business plan page” includes traditional and lean startup business plan formats, three downloadable sample business plans, a template, and a step-by-step build a business plan tool.
- Australian Government – The “business plan template” page includes a downloadable template, guide, and business plan creation app.
- UK Government Business and Self-Employed – The “write a business plan” page includes links to a downloadable business plan template and resources from trusted UK businesses. .
- Canada Business Network – The “writing your business plan” page includes a detailed guide to writing your business plan and links to business plan templates from Canadian business development organizations and banks.
These business resource sites also offer a wealth of valuable information for entrepreneurs including local and regional regulations, structuring, tax obligations, funding programs, market research data, and much more. Visit the sites above or do the following Google searches to find official local business resources in your area:
- your country government business services
- your state/province government business services
- your city government business services
Some Chamber of Commerce websites offer resources for business owners, including business plan guides and templates. Check your local chapter to see if they have any.
Banks that offer business funding also often have a resource section for entrepreneurs. Do a Google search to find banks that offer business funding as well as business plan advice to see the business plans that get funding. If your bank doesn’t offer any advice, search for the largest banks in your area:
- business plan guide bank name
- business plan samples bank name
- business plan template bank name
If you’re looking for more sample business plans, Bplans has over 500 free business plan samples organized by business type as well as a business plan template. Their collection includes 116 business plans for retail and online stores. Shopify also offers business plan templates intended to help small business owners and aspiring entrepreneurs identify functional areas of a business they may not have considered.

Understand Your Audience
Because business plans serve different purposes, you’re not always presenting it to the same audience. It’s important to understand who’s going to be reading your business plan, what you’re trying to convince them to do, and what hesitations they might have.
That way, you can adapt your business plan accordingly. As such, your audience also determines which type of business plan format you use. Which brings us to our next point…
Which Business Plan Format Should You Use?
The United States Small Business Administration (SBA) presents two business plan formats:
- The traditional business plan format is for entrepreneurs who want to create a detailed plan for themselves or for business funding.
- The lean startup business plan format, on the other hand, is for business owners that want to create a condensed, single-page business plan.
If the business plan is just for you and internal folks, draft a lean startup business plan or a customized version of the traditional business plan with only the sections you need. If you need it for business funding or other official purposes, choose the formal business plan and thoroughly complete the required sections while paying extra attention to financial projections.
If your business operates outside the U.S., clarify the preferred format with your bank.
How to Create a Business Plan: Questions to Ask Yourself
As you write a business plan, take time to not only analyze your business idea, but yourself as well. Ask the following questions to help you analyze your business idea along the way:
- Why do I want to start or expand my business?
- Do my goals (personal and professional) and values align with my business idea?
- What income do I need to generate for myself?
- What education, experience, and skills do I bring to my business?

How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step
According to the business plan template created by SCORE, Deluxe, and the SBA , a traditional business plan encompasses the following sections.
- Executive summary
- Company description
- Products & services
- Market analysis
- Marketing & sales
- Management & organization
- Funding request
- Financial projections
- SWOT analysis
Since not everyone is aware of the key details to include in each section, we’ve listed information you can copy to fill in your business plan outline. Here’s how to build a business plan step by step.
Executive Summary
The Executive Summary is the first part of your business plan, so this is where you need to hook readers in. Every business plan starts this way — even a simple business plan template should kick off with the Executive Summary. Summarize your entire business plan in a single page, highlighting details about your business that will excite potential investors and lenders.
Explain what your business has to offer, your target market , what separates you from the competition, a little bit about yourself and the core people behind your business, and realistic projections about your business’ success.
While this is the first section of your business plan, write it after you’ve completed the rest of your business plan. It’s a lot easier because you can pull from the sections you’ve already written, and it’s easier to identify the best parts of your business plan to include on the first page.
Company Description
In the Company Description, share 411 about your business. Include basic details like:
- Legal structure (sole proprietor, partnership, corporation, etc.)
- Business and tax ID numbers
- When the business started
- Ownership information
- Number of employees
Your mission statement , philosophy and values, vision, short- and long-term goals, and milestones along with a brief overview of your industry, market, outlook, and competitors should also be in the Company Description.
Pro tip: These are the details you’ll use each time you create a business profile, whether that's on social media, business directories, or other networks. Keep your information consistent to reduce confusion and instill more confidence in potential customers.
Products & Services
The Products & Services section details what you plan to sell to customers. For a dropshipping business , this section should explain which trending products you’re going to sell, the pain points your products solve for customers, how you’ll price your products compared to your competitors, expected profit margin, and production and delivery details.
Remember to include any unique selling points for specific products or product groupings, such as low overhead, exclusive agreements with vendors, the ability to obtain products that are in short supply / high demand based on your connections, personalized customer service, or other advantages.
For dropshipping businesses selling hundreds or even thousands of products, detail the main categories of products and the number of products you plan to offer within each category. By doing this, it’s easier to visualize your business offerings as a whole to determine if you need more products in one category to fully flesh out your online store.
Market Analysis
The Market Analysis section of your business plan allows you to share the research you have done to learn about your target audience — the potential buyers of your products. People requesting a business plan will want to know that you have a solid understanding of your industry, the competitive landscape, who’s most likely to become your customers. It’s important to demonstrate that there’s a large enough market for your product to make it profitable and/or to make a strong return on investment .
To complete the Market Analysis component of your business plan, check out the following resources for industry, market, and local economic research:
- U.S. Embassy websites in most countries have a business section with information for people who want to sell abroad. Business sections include a basic “getting started” guide, links to economic and data reports, trade events, and additional useful business links for a particular region.
- IBISWorld is a provider of free and paid industry research and procurement research reports for the United States , United Kingdom , Australia , and New Zealand .
- Statista offers free and paid statistics and studies from over 18,000 sources including industry reports, country reports, market studies, outlook reports, and consumer market reports.
Use these websites and others to learn about the projected growth of your industry and your potential profitability. You can also use social media tools like Facebook Audience Insights to estimate the size of your target market on the largest social network
Another way to research your market and products is through Google Trends . This free tool will allow you to see how often people search for the products your business offers over time. Be sure to explain how your business plans to capitalize on increasing and decreasing search trends accordingly.
Marketing & Sales
Knowing your target market is half the battle. In the Marketing & Sales section, share how you plan to reach and sell products to your target market. Outline the marketing and advertising strategies you intend to use to market your product to potential customers – search marketing , social media marketing , email marketing , and influencer marketing methods .
If you’re unsure how to market your business’ products, analyze your competitors for some inspiration. Discovering your competition’s marketing tactics will help you customize your own strategy for building a customer base and ultimately taking your business to the next level.
Do a Google search for your competitor’s business name to find the websites, social accounts, and content they’ve created to market their products. Look at the ways your competitor uses each online entity to drive new customers to their website and product pages.
Then come up with a plan to convert a similar audience with your marketing and advertising messages. For dropshipping businesses, conversions will typically take place on your website as people purchase your products and/or by phone if you take orders over the phone.
Management & Organization
In the Management & Organization piece of your business plan, describe the structure of your business. In terms of legal structure and incorporation, most businesses are classified as sole proprietorships (one owner), partnerships (two or more owners), corporations, or S corporations.
Draft a condensed resume for each of the key members of your business. If you’re a solopreneur , include how your past education and work experience will help you run each aspect of your business. If you have one or more partner(s) and employee(s), include their relevant education and experience as well.
Think of this as a great way to evaluate the strengths of each individual running your business. When self-evaluating, you’ll be able to identify the aspects of your business that’ll be easier to manage and which ones to delegate to freelancers, contractors, employees, and third-party services. This also makes it easier to find the best way to utilize their strengths for business growth.
Funding Request
Chances are, you don’t have a funding request for a startup dropshipping business since the appeal to dropshipping is the low upfront investment . If you’re looking for a loan, however, this would be the section where you outline the dollar amount you need, what you plan to invest in, and how you see the return on your investment.
Another way to use this section is to analyze the investment you have or plan to make when starting or growing your business. This should include everything from the computer you use to run your website to the monthly fee for business services.
Financial Projections
In Financial Projections, share your projected revenue and expenses for the first or next five years of your business. The idea here is to demonstrate that the revenue you’re anticipating will easily lead to a return on any investment, whether from your personal finances or a capital lending service.

If you’re looking for funding, you’ll need to go into detail with projected income statements, balance sheets, cash flow statements, and capital expenditure budgets. If you aren’t looking for funding, it won’t hurt to create these types of financial projections so you can realistically plan for the future of your business.
The Appendix of your business plan includes any supplemental documents needed throughout the sections of your business plan. These may include, but are not limited to:
- Credit histories
- Product brochures
- Legal forms
- Supplier contracts
If you’re submitting your business plan for funding, contact the lender to see what documentation they want included with your funding request.
SWOT Analysis
In addition to the above sections, some business plans also include a SWOT Analysis. This is a one-page summary of your business’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. The strengths and weaknesses you include will be internal, whereas opportunities and threats you include will be external.
Depending on the revelations of this section, you may or may not want to make a SWOT analysis when submitting your business plan formally unless it is requested.

Summary: How to Create a Business Plan
As you can see, creating a business plan for your dropshipping business is a great way to validate your business idea , discover your business’s strengths and weaknesses, and make a blueprint for your business's future.
In summary, here are the sections you will need to write for your business plan, step by step:
- SWOT analysis (Optional)
If you haven’t already, take the time to create a business plan to launch or grow your business in 2023!
Want to Learn More?
- How to Start a Dropshipping Business
- How to Register a Business in the USA
- How to Launch Your Ecommerce Store in Less Than 30 Minutes Flat
- 30+ Amazing Startup Business Ideas That’ll Make You Money

How to Start an Ecommerce Business: 2024 Edition
Discover how to launch your own ecommerce business in 2024. Find practical steps and the latest strategies for success.

18 Best Logo Design Companies to Consider in 2024
Looking for the best logo design companies? Here are 18 agencies that can create a stunning and professional logo for y…

10 Best Ecommerce Hosting Providers in 2024
Who’s the best ecommerce hosting provider out there? That’s what this post aims to help you find out.
Oberlo uses cookies to provide necessary site functionality and improve your experience. By using our website, you agree to our privacy policy.

How to Write Your First Business Plan
Bryce Warnes
Reviewed by
April 8, 2021
This article is Tax Professional approved
A business plan lays out where your business stands in the present and where it’s headed in the future. If you’re applying for a loan or bringing on investors, your business plan proves that your business is making money, and that you’re well positioned to make more.
I am the text that will be copied.
But even if you aren’t looking for working capital, having a business plan can be a huge benefit. It helps you set future goals, put together strategies to help you reach them, and make decisions along the way.
What a business plan tells you
Every business plan is different. The way you create yours will depend on the nature of your business. However, it should include the following:
- The value you offer customers or clients
- How your business makes money
- The resources you rely on to operate
- New products or services you may provide in the future
- Your position in the market versus competitors
- How you plan for your business to grow
- Current financial report
- Financial projections
There are different ways to communicate this information—we’ll get to those shortly.
Reasons to write a business plan
A business plan is like a Swiss Army knife—it can do a lot of things really well. And once you have one, it soon becomes indispensable.
While each industry’s business plan will look different— an ecommerce business plan will be different than a medical tech company—there are very basic commonalities. Broadly speaking, here are five important goals you can achieve with a business plan.
1. Test out your business idea
Maybe you’re considering turning your side hustle into a full-time gig, or maybe it’s still just a twinkle in your eye. Either way, writing a plan is a good way to see if it’s feasible before you start investing serious time and money.
Working through a business plan can lay bare your idea’s strengths and weaknesses, and flag any roadblocks you may face down the line. Specifically, when you do market and competitor analysis for your prospective business, you should quickly be able to tell whether it will be profitable. Financial projections can help you determine what type of income you’ll be earning, and what you need for funding.
2. Get funding
If you’re applying for a small business loan, having a thorough business plan is essential. Lenders want to be sure you’ll be able to pay off the loan, with interest. A business plan shows them how you’ll do that.
3. Attract investors
Similar to lenders, investors—whether they’re angel investors, venture capital firms, or even friends and family—want to know your business will turn a profit. After all, they’ll want a good return on their investment. Most investors expect to see your business plan before they risk their money.
4. Plan for the future
With financial projections and marketing objectives, your business plan sets a roadmap for the future. That can help you decide what to do in the here and now, and prepare for the years to come.
5. Make decisions more easily
When you’ve got a map guiding you, you spend less time at the crossroads picking a direction to take. As you face decisions during periods of business growth, your business plan acts as a powerful tool.
Should you open a brick-and-mortar location, or offer a wider range of products online? Should you apply for a loan now, or wait until next year? If your business plan is thorough, you already have the answers. That means less time debating, and more time acting.
Steps to writing a business plan
1. Determine its purpose
First, decide what goals you hope your business plan will help you achieve. Your business plan’s purpose will determine how you format it, what type of documentation you need to support it, and the kind of research you’ll need to conduct. For instance, if your aim is to secure financing, your plan will be different than it would be if you were using it internally to make business decisions.
2. Pick your audience
Who will read your business plan? Potential investors, lenders, or buyers? Employees? All of the above? Write your plan, choosing the language you use and the information you present with your specific audience in mind.
3. Do the research
Any claims you make need to be supported by hard facts. Research will take up the bulk of the time you spend creating your business plan. For instance, if your business plan assumes your industry is on the upswing, you should have the numbers to prove it.
Some questions you should be prepared to answer with the support of research:
- Who are your main competitors?
- What services/products are your target clients or customers looking for?
- Where is your industry headed?
- What is the history of your industry or niche?
- What types of roadblocks could you potentially face down the line?
4. Get documentation together
The most important documents in your business plan are your financial records . Past tax returns, financial reports, and comprehensive bookkeeping demonstrate your company’s history and future viability. You’ll use them to create financial projections.
You’ll also need a list of all employees and their positions within the company. And if your business relies on licensing agreements or intellectual property, be prepared to compile those as well.
5. Create a company profile
Your company profile is a public-facing document. For inspiration, make a list of companies you admire and then check their website’s “About” page and their LinkedIn profile.
Your company profile should explain:
- The problems your business solves for customers and clients
- What sets you apart from the competition
- The resources you use to get the job done
- Your company’s history
- What inspired you to go into business
- Your mission statement and vision for the future
This should be a short document, no longer than one page. These topics will be covered in greater detail within the business statement itself, but spelling out all the info now can help you get started and guide you as you write it.
6. Write the business plan
When you’ve decided what you’re aiming to achieve and who you’re addressing, compiled all the information you need, and laid the groundwork with a company profile, you’re ready to write your plan. Don’t start until you’ve covered the previous five steps—it’s better to over prepare for writing your plan rather than scramble for information when you’re in the thick of it.
It’s also best practice to include a cover page . It should be simple and introduce the key information of your business including a logo and legal information.
7. (Optional) Prepare a presentation
If you’re looking for funding or sharing your work with partners and employees, you may want to create a business plan presentation. This can take the form of a speech, slideshow, promotional video, audio track, or any combination of the above.
Think of it as a pitch for your company and your plans for the future. Boil down the information in your business plan into a digestible format, with the goal of getting your audience excited.
Types of business plans: traditional vs. lean
Business plans can be split into two categories: traditional and lean (or “startup”). Each has its own strengths and weaknesses. Choosing the type that’s relevant to your business will depend on how you intend to use your business plan.
Traditional
A traditional business plan is highly detailed, and relies on plenty of research. This is the type favored by investors and lenders—if you’re seeking out more working capital, it’s a good choice.
The drawback? Traditional plans take longer to research, plan, and write than lean business plans.
A lean business plan is less detailed than a traditional one, relying on less research. Specifically, it doesn’t feature financial projections or detailed competitor and market analysis. It’s relatively quick to write, and leaves you more flexibility—you can write a lean business plan now, and a traditional one later on. That makes it a great choice for startups still sketching out exactly what their business will look like.
Since it’s less detailed than a traditional plan, if you present a lean business plan to lenders or investors, they may ask you for more information. A lean plan is best used as a “rough draft” to help guide you in the early days of your business.
Business plan formats
Even if you’re seeking funding, the traditional format may seem like overkill. But each of the following nine parts plays an important role—feel free to adjust them to suit your needs.
The lean business plan is based on the Lean Business Model Canvas , a classic format for startup business plans. When creating a lean business plan, keep it brief and digestible. It can be as short as one page.
Even if you aren’t using your business plan to seek funding, including financial projections offers major benefits. By looking into the future of your business, you can make plans for growth and set realistic goals to reach along the way. Get started with our guide to financial forecasting .
Join over 140,000 fellow entrepreneurs who receive expert advice for their small business finances
Get a regular dose of educational guides and resources curated from the experts at Bench to help you confidently make the right decisions to grow your business. No spam. Unsubscribe at any time.

Starting a Business | How To
How to Write a Business Plan in 7 Steps
Published February 2, 2024
Published Feb 2, 2024
WRITTEN BY: Mary King
Get Your Free Ebook
Your Privacy is important to us.
This article is part of a larger series on Starting a Business .
Starting A Business?

Step 1: Gather Your Information
Step 2: outline your business plan, step 3: write each section, step 4: organize your appendix, step 5: add final details, step 6: add a table of contents, step 7: get feedback, bottom line.
A solid business plan helps you forecast your future business and is a critical tool for raising money or attracting key employees or business partners. A business plan is also an opportunity to show why and how your business will become a success. Learning how to write a business plan successfully requires planning ahead and conducting financial and market research.
How to write a business plan step-by-step:
- Gather your information
- Outline your business plan
- Write each section
- Organize your appendix
- Add final details
- Add a table of contents
- Get feedback.
Your first step is to get organized by gathering all your relevant business information. This will save you time completing the various sections of your business plan. At a minimum, you’ll want to have the following handy:
- Business name, contact information, and address
- Owner(s) names, contact information, and addresses
- Names, contact information, and addresses of any business partners (if you will be working with partners)
- Resume and relevant work history for yourself and any key partners or employees
- Any significant sales, commerce, traffic, and financial data and forecasts
- Customer data (if applicable)
- Any significant data about your nearest competitors’ commerce, traffic, or finances
Now it’s time to outline your business plan, making note of the sections you need to include and what data you want to include in each section. You can create an outline on your own or use a business plan template to help. Whichever route you choose, it is common to include these sections in your business plan outline:
- Introduction
- Executive summary
- Company overview
- Products and services
- Market and industry analysis
- Marketing strategy
- Sales strategy
- Management and organization
- Financial data, analysis, and forecasts
Connect the data you gathered in step one to specific sections of your outline. Make a note if you need to convert some information into charts or images to make them more compelling for potential investors. For example, you’ll want to include relevant work history in your management section and convert your sales forecasts into charts for your financial data section.
Now it’s time to write your business plan. Attack this one section at a time, adding the relevant data as you go.
Executive Summary
The executive summary is an overview of the business plan and should ideally be one, but no more than two, pages in length. Some investors actually only request the executive summary. So make it an informative, persuasive, and concise version of your business plan.
It can be easier to write the executive summary last, after the other sections. Then you can more clearly understand which sections of your business plan are the most important to highlight in the executive summary.
When learning how to write an executive summary for a business plan, remember to include the following:
- Business objectives : Your business objectives are specific and attainable goals for your business. Create at least four business objectives organized by bullet point. If you’re not sure how to phrase your objectives, read our SMART goals examples to understand how to do so.
- Mission statement: The mission statement discusses the aim, purpose, and values of your business. It’s typically a short statement from one sentence to several sentences in length. You may find that your mission statement evolves as your business grows. Learn more on how to write your mission statement in our guide.
Consider also including the following in your executive summary:
- Business description : Similar to a 30-second pitch, describing your business and what makes it unique
- Products and services : The type of products and services you’re providing and their costs
- Competitors : Your biggest competitors and why your business will succeed despite them
- Management and organization : The owners’ backgrounds and how they will help the business succeed; management structure within the business
- Business location (or facility) : Location benefits and the surrounding area
- Target market and ideal customer : Who your ideal customers are and why they’re going to purchase your products or services
- Financial data and projections : Provide brief financial data and projections relevant to your business, such as startup costs, at what month the business will be profitable, and forecasted sales data
- Financing needed : Explanation of the startup funding sources and the amount of financing being requested
The bullets above can be combined into several paragraphs. You can add or remove sections based on your business’ needs. For example, if you don’t have a physical location, you might remove that piece of information. Or, if a web presence is crucial to your success, include two to three sentences about your online strategy .
Company Overview
The company overview (sometimes also called a “business overview”) section highlights your company successes (if you’re already in business) or why it will be successful (if you’re a startup). In the opening paragraph or paragraphs, provide information like location, owners, hours of operation, products, and services.
How you structure this section depends on whether you’re a startup or an established business. A startup will discuss the general expenses and steps needed to open the business, such as permits, build-outs, rent, and marketing. An established business will briefly discuss the company’s financial performance over the past three years.
If you’re trying to raise capital from an investor or bank, include a chart listing the items your business will acquire with the capital. For example, if you’re purchasing equipment with the additional funding, list each piece of equipment and the associated cost. At the bottom of the chart, show the total of all expenses, which should be the requested amount of funding.
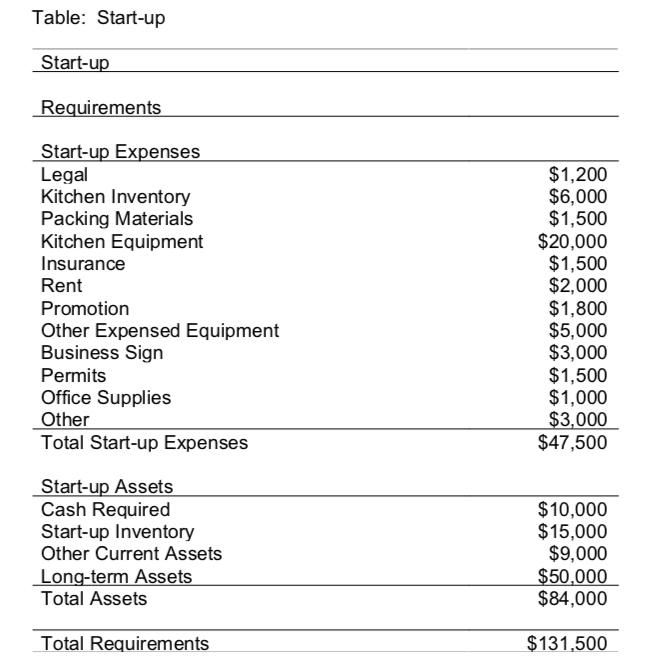
This startup cost table for a pizza restaurant separates startup expenses from startup assets.
Your company overview should cover the following:
- Location & Facilities : If you have a brick-and-mortar location or a facility, like a warehouse, describe it here. Detail the benefits of your location and the surrounding areas. Write about square footage, leases or ownership, the surrounding area, and a brief description of the population.
- Ownership : Briefly mention the company ownership team and their backgrounds. Show why these owners are likely to be successful in operating this business by providing certain details, such as each owner’s industry experience, previous employers, education, and awards. This will be discussed more in-depth in the management and organization section below.
- Competitive advantage : Ideally, your competitive advantage is what your business can do that your competitors cannot. It’s the one big differentiator that will make your company successful. Many investors are looking for specific competitive advantages, such as patents, proprietary tech, data, and industry relationships. If you don’t have these, describe the top aspect in which your business will do better than competitors, such as quality of products, quality of services, relationships with vendors, or marketing strategy.
Products & Services
The products and services section is the most flexible section because its structure depends on what your business sells. Regardless of what you’re selling, include a description of your business model to explain how your business makes money. Also include future products or services your business could provide one, two, or five years down the road.
List and describe all physical and digital products you plan to sell, as well as any services the business provides. Services don’t necessarily have to be sold for a cost—your business might offer entertainment, like live music or bar games as a free service.
Whether you’re selling products, services, or both, it’s important to discuss fulfillment, or how each will be delivered. If you make or sell physical products, describe how products will be sold, assembled, packed, and shipped. If your business is service-based, describe how a service, such as a window installation, will be ordered and completed. Where will the glass be purchased from and acquired, how will customers place orders, and how will the window be installed?
Market & Industry Analysis
The market and industry analysis section is where you analyze potential customers and the forces that influence your industry. This section is where you make the case as to why your business should succeed, ideally backed by data. You’ll want to do a deep dive into your competitors and discuss their challenges and successes. Learn more about sales targeting to improve how you approach your sales strategy.
Market Segmentation
Market segmentation, or your target market, consists of the customers who are most likely to purchase your products or services. Describe these groups of customers based on demographics, including attributes like age, income, location, and buying habits. Additionally, if you’ll be operating with a business-to-business (B2B) model, use characteristics to describe the ideal businesses to which you’ll sell.
Once your target market is segmented into groups, use market research data to show that those customers are physically located near your business (or are likely to do business with you if you’re online). If you’re opening a daycare, for example, you’ll want to show the data on how many families are in a certain mile radius around your business. You can obtain this kind of data from a free resource, like the U.S. Census and ReferenceUSA .
Once you have at least three segments, briefly outline the strategy you’ll use to reach them. Most likely it will be a combination of marketing, pricing, networking, and sales.
Learn the best approach to product pricing in our guide.
Industry Analysis
Take a look at your business’s industry and explain why it’s a great idea to start a business in that niche. If you’re in a growing industry, a bank is more likely to lend your business capital because it’s predicted to be in demand and have additional customers. Learn about how to find a niche market .
Find industry statistics from a free tool, like the Bureau of Labor Statistics , or a paid tool like the Hoovers Industry Research , which provides professionally curated reports for over 1,000 industries.
Competitor Research
Wrap up the market and industry analysis section by analyzing at least five competitors within a five-mile radius (expand the radius, if needed). Create a table with the five competitors and mention their distance from your business (if applicable), along with their challenges, and successes.
During your analysis, you’ll want to frame their challenges as something you can improve upon. Persuade your reader that your business will provide superior products and services than the competitors.
Marketing Strategy & Implementation Summary
In the opening paragraphs of your marketing strategy and implementation summary, give an overview of the subsections below.
Include any industry trends you may take advantage of. If applicable, include the advertising strategy and budget, stating specific channels. Mention who in the business will be responsible for overseeing the marketing.
Include any platforms and tools the business will use, like your website, social media, email marketing, and video. If you’re hiring a company to do any online work, like creating a website or managing social media, briefly describe them and the overall cost (you can elaborate more on costs in the financial data section ).
Don’t forget to include a subsection for your traditional marketing plan. Traditional marketing encompasses anything not online, such as business cards, flyers, local media, direct mail, magazine advertising, and signage.
Sales Strategy
If sales is an important component of your business, include a section about your sales strategy. Describe the role of the salesperson (or persons), strategies they’ll use to close the deal with clients, lead follow-up procedures, and networking they’ll attend. Also, list any training your sales staff will attend.
Sales Forecast Table
A sales forecast table gives a high-level summary of where you expect your sales and expenses to occur for each of the next three years in business. In the paragraph before the table, state where you expect growth to come from and include a growth percentage rate. The annual sales forecast chart will be broken down further in the financial projections section below.
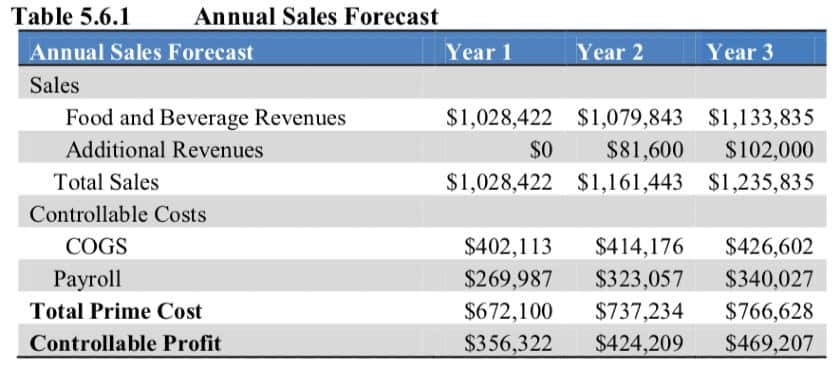
The annual sales forecast for this restaurant summarizes sales, cost, and profit for the first three years in business.
Pricing Strategy
In the pricing strategy section, discuss product/service pricing, competitor pricing, sales promotions , and discounts—basically anything related to the pricing of what you sell. You should discuss pricing in relation to product and service quality as well. Consider including an overview of pricing for specific products, e.g., pizza price discounts when ordering a specific number of pizzas for catering.
Milestones in a business plan are typically displayed in a table. They outline important tasks to do before the business opens (or expands, if already in business). For each milestone, include the name, estimated start and completion date, cost, person responsible, and department responsible (or outside company responsible). List at least seven milestones.
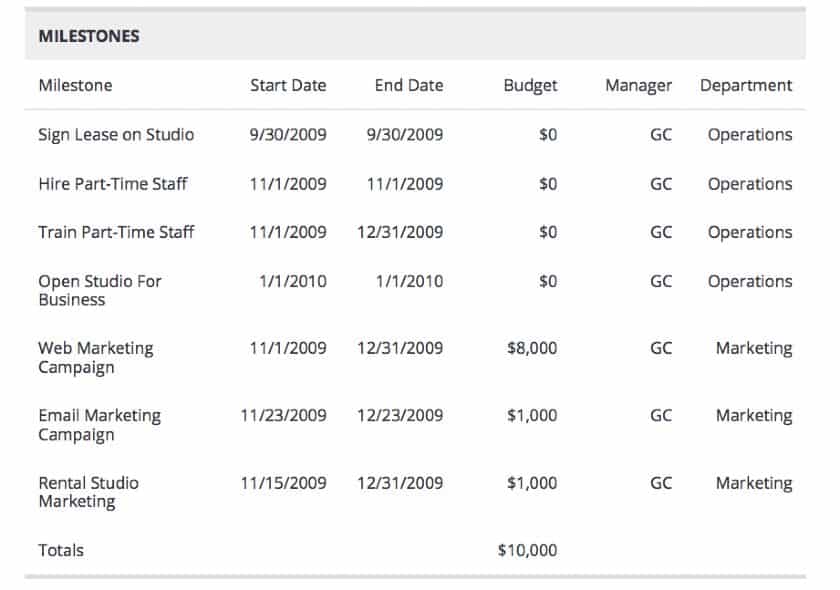
Milestones for this commercial photography business include hiring staff and completing marketing campaigns.
Management & Organization Summary
The management and organization summary is an in-depth look at the ownership background and key personnel. This is an important section because many investors say they don’t invest in companies, they invest in people. In this section, make the case why you and your team have the experience and knowledge to make this business a success.
Ownership Background
Discuss the owners’ backgrounds and place an emphasis on why that background will ensure the business succeeds. If you don’t have experience managing a retail business, consider finding a co-owner who does. Typically, banks won’t lend to someone who doesn’t have experience in the type of business they’re trying to open.
Management Team Gaps
If there are any experience or knowledge gaps within the management team, state them. List the consultants or employees you will hire to cover the gaps. Investors who know your industry well may recognize gaps within your business plan, and it’s important to state the gaps without waiting for the investor to bring it up. This makes it appear that you know the industry well.
Personnel Plan
The personnel plan outlines every position within your business for at least the next three years. In the opening paragraph, discuss the roles within the company and who will report to whom. Include a table with at least three years of salary projections for each employee in your business. Include a total salary figure at the bottom. This table may be broken down further into salaries for each month in the financial projections or appendix.
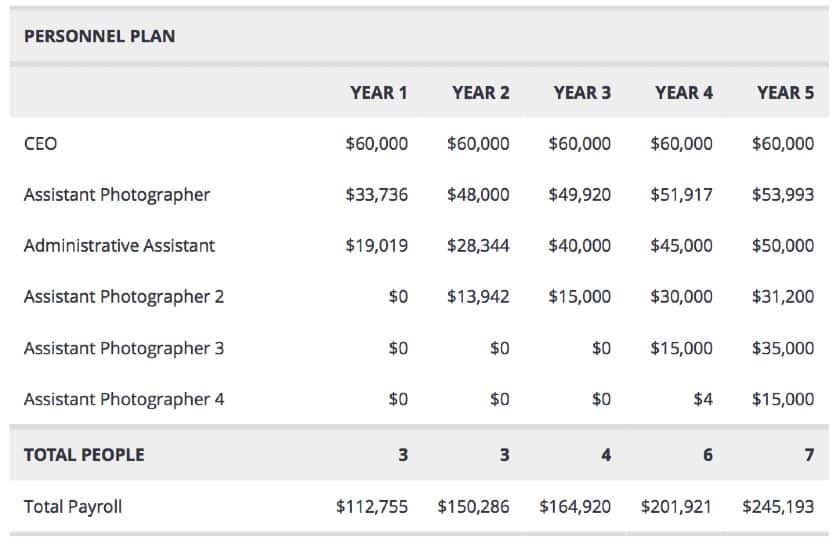
This commercial photography business has the CEO at the same salary every year, with their employees’ salaries increasing year over year.
Financial Data & Analysis
The financial data and analysis section is the most difficult part of a business plan. This section requires you to forecast income and expenses for the next three years. You’ll need a working knowledge of common financial statements, like the profit and loss statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement.
In the opening paragraphs of the financial data and analysis section, give an overview of the sections below. Discuss the break-even point and the projected profit at the first, second, and third year in business. State the assets and liabilities from the projected balance sheet as well.
If you’re getting a loan from a bank, say how long and from what source the loan will be repaid. One of the main pieces of information bankers want to ascertain from financial forecasting is if they will be paid back and how likely that is to happen.
You might also include the following financial reports:
- Break-even analysis : Break-even is when your business starts to make money. Break-even analysis is where you illustrate the point at which your revenue exceeds expenses and a profit occurs. In this section’s opening paragraph, state your monthly fixed costs and average percent variable costs (cost that changes with output, like labor or cost of goods). In the example below, variable costs increase 8% for every additional dollar made.
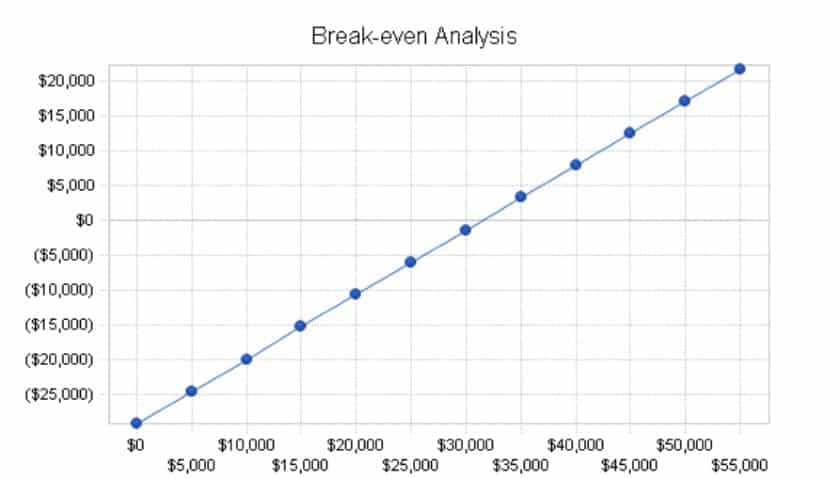
The break-even point for this document shredding business is $31,500 in a month.
- Projected profit & loss: The profit and loss table is a month-by-month breakdown of income and expenses (including startup expenses). Typically, you should expect your business to show a profit within the first year of operating and increase in years two and three. Be sure to show income and expenses month-by-month for the first two years in operation. Create a separate chart that shows income and expenses year-by-year for the first three years.
- Projected cash flow : The cash flow section shows your business’s monthly incoming and outgoing cash. It should cover the first two years in business. Mention what you plan to do with excess cash. See how to run a statement cash flow in QuickBooks Online .
- Projected balance sheet: The balance sheet shows the net worth of the business and the financial position of the company on a specific date. It focuses on the assets and liabilities of the business. Ideally, the balance sheet should show that the net worth of your business increases. Prepare a projected year-by-year balance sheet for the first three years.
- Business ratios: Also called financial ratios, these are a way to evaluate business performance. It’s helpful to compare your projected business ratios to the industry standard. Project your business ratios by year for the first three years.
The appendix is where you put information about the business that doesn’t fit in the above categories. What you put here largely depends on the type of business you’re creating. It’s a good idea to put any visual components in the appendix. A restaurant might add an image of the menu and an artist rendering of the interior and exterior, for example.
Consider including the following items in your business plan appendix:
- Artist mock-up of interior
- Building permits
- Equipment documentation
- Incorporation documents
- Leases and agreements
- Letters of recommendation
- Licenses and permits
- Marketing materials
- Media coverage
- Supplier agreements
An appendix isn’t required in a business plan, but it’s highly recommended for additional persuasion. Documents like media coverage, agreements, and equipment documentation show the investor and banker you’re serious about the business. If your appendix is more than 10 pages, consider creating a second table of contents just for the appendix.
Detailed Financial Projections
Put the more detailed projections in the appendix. The financial projections in the previous section is typically a year-by-year breakdown for three years in the future. But many bankers and investors want to see the first two years broken down month-by-month for at least the profit and loss statement, balance sheet, cash flow, and personnel plan.
Typically, you can print out the spreadsheet in smaller font and include it in the appendix. You don’t need to create additional charts for the appendix.
With all of your information organized, now it’s time to add the final details, like cover pages and a nondisclosure agreement (NDA).
- Cover Page: The cover page provides contact information about the business and its owner. The cover page should have the business name and who prepared it, including your name, address, phone number, and email address. Additionally, if the registered company name with the state is different from the business name, you may want to add that as a “company name.”
- Nondisclosure Agreement: An NDA ((also called a confidentiality agreement) is a legal document that safeguards business information. You’d want someone to sign it before reading your business plan if you believe they could use the information to their advantage and your disadvantage, such as to steal your business idea or marketing strategy.

Fit Small Business provides a free non-disclosure agreement.
Once your final details are added, proofread all the sections of your business plan, ensuring that the information is accurate and that all spelling and grammar are correct. If there are any illustrations, projections, or additional information you forgot to include, now is the time to add it.
The final step is adding a table of contents so that bankers and potential investors can easily navigate your business plan. A table of contents lists the sections and subsections of your business plan. All of the headers above (Executive Summary, Business Objectives, Company Overview, Products and Services, and so on) are considered sections of a business plan. You can number the sections for additional organization. For example, 1.0 is the executive summary, 1.1 is the business objectives, and 1.2 is the mission statement.
Editing and formatting can change the pagination of your business plan. So you’ll save yourself work if you finalize the business plan content first, then arrange the table of contents at the end.
Congratulations! You’ve captured your business idea and plan for profitability on paper. Before you send this business plan to loan officers and potential investors, ask friends, family, and other supportive business owners to read it and provide feedback. They may notice typos or other errors that you missed. They may also identify details you can add to make your business plan more persuasive.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About How to Write a Business Plan
These are the most common questions I hear about writing a business plan.
What needs to be in a business plan?
What you should put in a business plan depends on its purpose and your industry. If you’re seeking funding from a bank or investor, you’re going to need most of the sections above, with a strong focus on your financial projections. If you are using your business plan to attract key employees (like a chef for your restaurant), mock-ups and vendor agreements will be more useful. Think about the information that will help your target reader make a decision about whether to get involved with your business—whether that is a location, a business model, or product idea—and be sure your business plan includes that information.
How do you write a business plan for a startup?
The business plan for a startup is similar to a business plan for an established business. The startup business plan will include startup costs, which will be listed by item and factored into the financial projections. Additionally, since your business hasn’t proven it can be successful yet, you may need additional information about the ownership, business model, market, and industry to convince the reader your business will succeed.
How long does it take to write a business plan?
A simple business plan may only take a couple of hours. However, for the business plan provided with this template, which includes financial projections, it may take over 60 hours to research the income and costs associated with running your business. You also have to format those costs into a chart, because it’s best to showcase the data with easy-to-understand charts.
Is writing a business plan hard?
Creating a business plan for funding from a bank or investor is a detailed process. Unless you have a background in financial statements, the financial projections may be difficult for the average business owner. But you can ask for help; it is common to hire a bookkeeper or accountant to assist you with financial projects to ensure your math is correct. Outside of the projections, most other business plan sections are simple, though you’ll want to give yourself time to make each section persuasive.
Every type of business, whether it’s a side hustle or a multimillion-dollar business, should have a business plan. The industry analysis and market segmentation sections validate your business idea. Researching and forecasting financial projections helps you logically think through income and expenses, which lessens the risk of business failure. Remember to get feedback on your business plan from business employees and associates. If necessary, have them sign an NDA before they review the plan.
About the Author

Find Mary On LinkedIn Twitter
Mary King is an expert restaurant and small business contributor at Fit Small Business. With more than a decade of small business experience, Mary has worked with some of the best restaurants in the world, and some of the most forward-thinking hospitality programs in the country. Mary’s firsthand operational experience ranges from independent food trucks to the grand scale of Michelin-starred restaurants, from small trades-based businesses to cutting-edge co-working spaces.
Join Fit Small Business
Sign up to receive more well-researched small business articles and topics in your inbox, personalized for you. Select the newsletters you’re interested in below.

- Case Studies
- Flexible Products

- Expert Insights
- Research Studies

- Creativity and Culture
- Management and Leadership
- Business Solutions
- Member Spotlight
- Employee Spotlight
How to write a business plan in seven simple steps
When written effectively, a business plan can help raise capital, inform decisions, and draw new talent.

Companies of all sizes have one thing in common: They all began as small businesses. Starting small is the corner for those just getting off the ground. Learn about how to make that first hire, deal with all things administrative, and set yourself up for success.
Writing a business plan is often the first step in transforming your business from an idea into something tangible . As you write, your thoughts begin to solidify into strategy, and a path forward starts to emerge. But a business plan is not only the realm of startups; established companies can also benefit from revisiting and rewriting theirs. In any case, the formal documentation can provide the clarity needed to motivate staff , woo investors, or inform future decisions.
No matter your industry or the size of your team, the task of writing a business plan—a document filled with so much detail and documentation—can feel daunting. Don’t let that stop you, however; there are easy steps to getting started.
What is a business plan and why does it matter?
A business plan is a formal document outlining the goals, direction, finances, team, and future planning of your business. It can be geared toward investors, in a bid to raise capital, or used as an internal document to align teams and provide direction. It typically includes extensive market research, competitor analysis, financial documentation, and an overview of your business and marketing strategy. When written effectively, a business plan can help prescribe action and keep business owners on track to meeting business goals.
Who needs a business plan?
A business plan can be particularly helpful during a company’s initial growth and serve as a guiding force amid the uncertainty, distractions, and at-times rapid developments involved in starting a business . For enterprise companies, a business plan should be a living, breathing document that guides decision-making and facilitates intentional growth.
“You should have a game plan for every major commitment you’ll have, from early-stage founder agreements to onboarding legal professionals,” says Colin Keogh, CEO of the Rapid Foundation—a company that brings technology and training to communities in need—and a WeWork Labs mentor in the UK . “You can’t go out on funding rounds or take part in accelerators without any planning.”
How to make a business plan and seven components every plan needs
While there is no set format for writing a business plan, there are several elements that are typically included. Here’s what’s important to consider when writing your business plan.
1. Executive summary
No longer than half a page, the executive summary should briefly introduce your business and describe the purpose of the business plan. Are you writing the plan to attract capital? If so, specify how much money you hope to raise, and how you’re going to repay the loan. If you’re writing the plan to align your team and provide direction, explain at a high level what you hope to achieve with this alignment, as well as the size and state of your existing team.
The executive summary should explain what your business does, and provide an introductory overview of your financial health and major achievements to date.
2. Company description
To properly introduce your company, it’s important to also describe the wider industry. What is the financial worth of your market? Are there market trends that will affect the success of your company? What is the state of the industry and its future potential? Use data to support your claims and be sure to include the full gamut of information—both positive and negative—to provide investors and your employees a complete and accurate portrayal of your company’s milieu.
Go on to describe your company and what it provides your customers. Are you a sole proprietor , LLC, partnership, or corporation? Are you an established company or a budding startup? What does your leadership team look like and how many employees do you have? This section should provide both historical and future context around your business, including its founding story, mission statement , and vision for the future.
It’s essential to showcase your point of difference in your company description, as well as any advantages you may have in terms of expert talent or leading technology. This is typically one of the first pieces of the plan to be written.
3. Market analysis and opportunity
Research is key in completing a business plan and, ideally, more time should be spent on research and analysis than writing the plan itself. Understanding the size, growth, history, future potential, and current risks inherent to the wider market is essential for the success of your business, and these considerations should be described here.
In addition to this, it’s important to include research into the target demographic of your product or service. This might be in the form of fictional customer personas, or a broader overview of the income, location, age, gender, and buying habits of your existing and potential customers.
Though the research should be objective, the analysis in this section is a good place to reiterate your point of difference and the ways you plan to capture the market and surpass your competition.
4. Competitive analysis
Beyond explaining the elements that differentiate you from your competition, it’s important to provide an in-depth analysis of your competitors themselves.
This research should delve into the operations, financials, history, leadership, and distribution channels of your direct and indirect competitors. It should explore the value propositions of these competitors, and explain the ways you can compete with, or exploit, their strengths and weaknesses.
5. Execution plan: operations, development, management
This segment provides details around how you’re going to do the work necessary to fulfill this plan. It should include information about your organizational structure and the everyday operations of your team, contractors, and physical and digital assets.
Consider including your company’s organizational chart, as well as more in-depth information on the leadership team: Who are they? What are their backgrounds? What do they bring to the table? Potentially include the résumés of key people on your team.
For startups, your execution plan should include how long it will take to begin operations, and then how much longer to reach profitability. For established companies, it’s a good idea to outline how long it will take to execute your plan, and the ways in which you will change existing operations.
If applicable, it’s also beneficial to include your strategy for hiring new team members and scaling into different markets.
6. Marketing plan
It’s essential to have a comprehensive marketing plan in place as you scale operations or kick off a new strategy—and this should be shared with your stakeholders and employees. This segment of your business plan should show how you’re going to promote your business, attract customers, and retain existing clients.
Include brand messaging, marketing assets, and the timeline and budget for engaging consumers across different channels. Potentially include a marketing SWOT analysis into your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Evaluate the way your competitors market themselves, and how your target audience responds—or doesn’t respond—to these messages.

7. Financial history and projections
It’s essential to disclose all finances involved in running your company within your business plan. This is so your shareholders properly understand how you’re projected to perform going forward, and the progress you’ve made so far.
You should include your income statement, which outlines annual net profits or losses; a cash flow statement, which shows how much money you need to launch or scale operations; and a balance sheet that shows financial liabilities and assets.
“An income statement is the measure of your financial results for a certain period and the most accurate report of business activities during that time, [whereas a balance sheet] presents your assets, liabilities, and equity,” Amit Perry, a corporate finance expert, explained at a WeWork Labs educational session in Israel.
It’s crucial to understand the terms correctly so you know how to present your finances when you’re speaking to investors. Amit Perry, CEO and founder of Perryllion Ltd.
In addition, if you’re asking for funding, you will need to outline exactly how much money you need as well as where this money will go and how you plan to pay it back.
12 quick tips for writing a business plan
Now that you know what components are traditionally included in a business plan, it’s time to consider how you’ll actually construct the document.
Here are 12 key factors to keep in mind when writing a business plan. These overarching principles will help you write a business plan that serves its purpose (whatever that may be) and becomes an easy reference in the years ahead.
1. Don’t be long-winded
Use clear, concise language and avoid jargon. When business plans are too long-winded, they’re less likely to be used as intended and more likely to be forgotten or glazed over by stakeholders.
2. Show why you care
Let your passion for your business shine through; show employees and investors why you care (and why they should too).
3. Provide supporting documents
Don’t be afraid to have an extensive list of appendices, including the CVs of team members, built-out customer personas, product demonstrations, and examples of internal or external messaging.
4. Reference data
All information regarding the market, your competitors, and your customers should reference authoritative and relevant data points.
5. Research, research, research
The research that goes into your business plan should take you longer than the writing itself. Consider tracking your research as supporting documentation.
6. Clearly demonstrate your points of difference
At every opportunity, it’s important to drive home the way your product or service differentiates you from your competition and helps solve a problem for your target audience. Don’t shy away from reiterating these differentiating factors throughout the plan.
7. Be objective in your research
As important as it is to showcase your company and the benefits you provide your customers, it’s also important to be objective in the data and research you reference. Showcase the good and the bad when it comes to market research and your financials; you want your shareholders to know you’ve thought through every possible contingency.
8. Know the purpose of your plan
It’s important you understand the purpose of your plan before you begin researching and writing. Be clear about whether you’re writing this plan to attract investment, align teams, or provide direction.
9. Identify your audience
The same way your business plan must have a clearly defined purpose, you must have a clearly defined audience. To whom are you writing? New investors? Current employees? Potential collaborators? Existing shareholders?
Related articles

10. Avoid jargon
Avoid using industry-specific jargon, unless completely unavoidable, and try making your business plan as easy to understand as possible—for all potential stakeholders.
11. Don’t be afraid to change it
Your business plan should evolve with your company’s growth, which means your business plan document should evolve as well. Revisit and rework your business plan as needed, and remember the most important factor: having a plan in place, even if it changes.
A business plan shouldn’t just be a line on your to-do list; it should be referenced and used as intended going forward. Keep your business plan close, and use it to inform decisions and guide your team in the years ahead.
Creating a business plan is an important step in growing your company
Whether you’re just starting out or running an existing operation, writing an effective business plan can be a key predictor of future success. It can be a foundational document from which you grow and thrive . It can serve as a constant reminder to employees and clients about what you stand for, and the direction in which you’re moving. Or, it can prove to investors that your business, team, and vision are worth their investment.
No matter the size or stage of your business, WeWork can help you fulfill the objectives outlined in your business plan—and WeWork’s coworking spaces can be a hotbed for finding talent and investors, too. The benefits of coworking spaces include intentionally designed lounges, conference rooms, and private offices that foster connection and bolster creativity, while a global network of professionals allows you to expand your reach and meet new collaborators.
Using these steps to write a business plan will put you in good stead to not only create a document that fulfills a purpose but one that also helps to more clearly understand your market, competition, point of difference, and plan for the future.
For more tips on growing teams and building a business, check out all our articles on Ideas by WeWork.
Caitlin Bishop is a writer for WeWork’s Ideas by WeWork , based in New York City. Previously, she was a journalist and editor at Mamamia in Sydney, Australia, and a contributing reporter at Gotham Gazette .

Learn the differences between Class A, Class B, and Class C buildings based on their visual appeal, location, and amenities to see which of them best suits your business.

Short-term leases can offer startups and established companies some much-needed flexibility

From federal taxes to 401(k)s, figuring out payroll deductions can be a headache. Here’s how to get started
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research Research Tools and Apps
How to Write a Perfect Business Plan: Step-By-Step Guide
Whether you’re just starting out or have been running your business for years, a business plan is one of the best ways to clarify the long-term goals you have for your business. By developing a plan for a business, you can put all of your business goals, objectives, structures, and marketing ideas in one central place.
Not every plan looks the same, but there are vital things to consider when making yours. These will help you and your business in the long run.
Use this step-by-step guide to write a good business plan for your business.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a strategy map. It shows where you and your business are, including your resources, skills, and goals. It also shows where you will be in the future and how you will get there. It’s just a plan for how your business will work and how you will make it succeed.
It is a written description or blueprint of your business’s future. All you need is a document that says what you want to do and how you want to do it.
LEARN ABOUT: Service Blueprint
Entrepreneurs who want to get money from investors use the business plan to explain their vision to potential investors. Second, they can be used by companies that want to attract key employees, look for new business, deal with suppliers, or figure out how to run their companies better.
A step-by-step guide
Start creating an executive summary.
The first step in making a good business plan is writing an executive summary. Think of an executive summary as your company’s elevator pitch in writing. You’ll want to keep it short but still get across the important parts of your business.
It should have your mission statement, a short description of your business’s products or services, a breakdown of who owns the business, and an overall business plan summary.
Create a company description
You also need to write a description of your business, which is just what it sounds like. This document will have important information about your business, such as its name, physical address(es), key employees, and important facts about its history.
In the company description, you can talk more about your business, its goals, its ideal customers, the problems it solves, and what makes it different from its competitors.
Conduct a market analysis
Market analysis is one of the most important parts of a business plan. With a market analysis, it will be easier to understand your industry, your target market, and how to stand out from your competition.
Start by doing comprehensive research on the market your business is entering. No matter how big or small your business is, if you know the trends and opportunities in your market, you can make a better marketing plan to grow your business.
Market research looks at everything from demographics to how people act as customers. When you do a market analysis, you can also learn about your competitors and determine their strengths and weaknesses. This analysis might also help you find potential customers or new products you could sell.
For a competitive information analysis, look at how they are growing, what changes they are making, and where they are having trouble in the market that you can take advantage of. You can conduct your market analysis with QuestionPro survey software.
Define your business structure
Your business structure needs to be mapped out in your business plan. Making an organizational chart allows you to see how your business is set up. Write down the roles and responsibilities of your company’s leaders and other key employees. Remember to include the company’s structure in your organizational chart.
Describe your products and services
This step gives you more information about the products and services you offer. When you list your products and services, include details about how they are made, what materials are needed, how you pay for them, how much they cost, and any other relevant information.
Write a plan for marketing and selling
It’s not enough to sell products or provide services. Your marketing and sales plan can be a partially-fledged marketing strategy, but it should clarify who you’re targeting and how. Include which platforms or marketing methods you will use to reach your target audience. Also, mention your marketing budget.
You should also include a high-level summary of your company’s sales strategy. A sales plan should include details about your sales process, your sales goals, and the steps you’ll take to reach those goals.
Think about what marketing and selling success looks like for your business. Include details about how you plan to succeed with your marketing and sales efforts.
Get your business’s financials together
Your business plan should also include information about how your company makes money. The following details should be included in this section:
- Statements of cash flow
- Statements of profits and losses
- Balance sheets
- Business expenses
- Income statements
Most of these documents can be made with spreadsheets, although accounting software can also help organize financial data. Your small business checking account should be able to work with the accounting software you use.
Describe your financial projections
The financials section of your business plan reflects previous and present company performance. It is especially important if you want investors to give you money. You can also include a roadmap that goes into detail about your business’s financial plans.
Include charts and other visuals in your financial projections to show how your company wants to grow. Try to see at least five years into the future to get a clear picture of where your business is going. Also, be realistic about what you think will happen. Give your financial plan some background and materials to back it up.
Write out your funding request
If you want to get funds for your business, you should include a list of any requests and requirements. Explain why you want to fund it and what it will be used for. Clearly state the terms and conditions of the funding and the type of funding that is needed.
Make an appendix
The last step of your business plan is the appendix. The appendix has documents that back up your business plans and extra information that isn’t found anywhere else in your plan. You can add the following documents to your appendix:
- Bank statements
- History of a business’s credit
- Legal document
- Reference letters
Consider adding a table of contents to help keep the appendix organized.
Whether you write the plan yourself or hire someone else to do it, it is well worth your time to take the time to write a strong and detailed business plan that can guide your business and convince outside team members to join.
Business plans are key to connecting with investors, lenders, partners, and vendors. They can help you explain why your business will be successful and why it’s a great investment for everyone involved. They’re also helpful in guiding your internal staff during the early years of managing the business.
Market research is essential for developing a business plan. To create a business plan, you need to know the current and past market details, audience, and customer’s point of view. QuestionPro will assist you in analyzing your market and audience to provide insight into your business.
QuestionPro is a survey software that lets you create and design a survey to meet your goals and analyze the data for your business. QuestionPro can help you with your business plans by analyzing your customers’ experiences. Contact us for further details.
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS

Unlocking Creativity With 10 Top Idea Management Software
Mar 23, 2024

20 Best Website Optimization Tools to Improve Your Website
Mar 22, 2024

15 Best Digital Customer Experience Software of 2024

15 Best Product Experience Software of 2024
Other categories.
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-14343635291-33bf053f368c43f6a792e94775285bbd.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- Sample Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Upmetrics AI Assistant: Simplifying Business Planning through AI-Powered Insights. Learn How
- 400+ Sample Business Plans
Customers Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Strategic Canvas Templates
E-books, Guides & More
Business consultants
Entrepreneurs and Small Business
Accelerators and Incubators
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai pitch deck generator
Stratrgic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
Small Business Tools
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Strategic Planning
Business Planning Process: Create a Business Plan That Works

Free Business Startup Checklist
Radhika Agarwal
- December 15, 2023

If you are planning to start or grow your business, you might have heard about the importance of the business planning process countless times. And yes, it is necessary to have a plan. After all, it’ll be your roadmap to success.
But how would you go about it? Where will you start? And most importantly is there a tried and tested process that can make your job easier? What if we told you there is such a process?
And through this article, we’ll walk you through everything from what is business planning to the steps of the business planning process .
What is Business Planning?
Business planning is the process of giving structure to your business idea. It acts as a roadmap to your business journey, helps you get through obstacles, and maximizes opportunities.
It also helps you set realistic goals and pursue the same with a structured action plan.
Moreover, through a business plan, you can analyze your company’s strengths and weaknesses, and understand how that would impact your company while dealing with market competition and how your strengths would help you achieve your goal.
Above all, doing business with a well-written business plan increases your chances of success.
Steps of the Business Planning Process
Although there’s no sole right way to go about the process of planning your business, here’s a compilation of steps that’ll make your planning process faster and easier.
1. Carry out your research

The first step to creating a business plan is to do thorough research about the business and industry you are trying to get into. Tap into all the information you can get about your target audience, potential customer base, competitors, market and industry trends, cost of business, etc.
You can give a form to your research by asking yourself the following questions:
- What are your goals?
- Where does your business stand currently?
- What are the prevailing market trends?
- What strategies is your competitor following?
You can find your answers by conducting market surveys , talking to customers and industry experts, designing good questionnaires, reading articles, blogs, and news updates about your industry and related ones, and so on.
Also, it is a good practice to conduct a SWOT analysis for your company to understand how your company’s strengths and weaknesses would help you stand apart from your competitors based on the current market statistics.
2. Make a Framework

Once you’re done with your research the next step is to make a framework or a set of strategies for your business based on your research and business goals. You can either design strategies from scratch or reframe previously tried and tested successful strategies to fit your business goals.
But remember that you’ll have to tweak strategies to fit your unique competitive advantages and goals. Hence, strategies that are already being used can act as a good foundation, but it is essential to remember that you’ll have to expand upon them or improvise them for your business.
This step can be completed by taking a deep dive into your customer’s buying motivations and challenges that your product can help solve. Based on that, make a marketing plan, operations plan, and cost structure for your business at least for the first few years of your business.
3. Formulate your Financial Forecasts

No matter how tedious finances might seem, they are an integral part of any business. When you map out your finances it is essential to note down all the costs you’ll incur as you grow and run your business for the next five years and what would be your potential revenue , and if or not it would leave room for profit.
You can get your financial forecast by adding your financial assumptions to a financial system which will give you your cash flow statements and give you an idea of what amount of funds you’ll need to start and run your business for the first year.
This step is especially helpful if you want to acquire funding for your business. Nonetheless, it helps you prepare to deal with the financial aspects of your business.
A financial statement essentially provides details of a company’s expenses and profits. It also provides an overview of the company’s current financial stance, including its assets and liabilities.
Through this section try to write down and explain how you plan to use your investments and how would the same give a return.
4. Draft a Plan

As you’re done with creating business strategies and planning your finances, it is time to draft your business plan and compile everything into a single document. As you are done with all the technical aspects, this step should feel relatively easy.
But if you need help drafting a business plan and making it look presentable, you can subscribe to business plan software that comes with predesigned templates and tools to make your work easier .
5. Recheck and Improvise

Now as you’re done with writing your plan, it is a good idea to give it enough time to edit it. Check for any unclear sentences, irrelevant phrases, or confusing terms.
Take suggestions from your team members who are familiar with the functioning of your business. Finally, proofread for any grammar or punctuation errors. One of the most popular and useful pieces of editing advice is to put your work aside for a while and then look at it with fresh eyes to edit it better.
6. Create an Impressive Business Plan Presentation

Now, as you’re done with writing your business plan, it is time to create a presentation that leaves an excellent impression on your audience. Highlight all the important and relevant points.
Also, add references for your investors like your financial reports , resumes of your key team members, snippets of your marketing plan, and past sales reports to have a well-rounded presentation.
It is true that starting a business is intimidating. It includes a bunch of emotions, chaotic ideas, and a will to take risks. ( Risks are a part and parcel of starting a business, no matter how much you plan, but yes planning helps you prepare for it.) But in the end, all of us know that all of it is worth it if you have a profitable business in the end.
And business planning is something that takes you one step closer to your idea of success. Moreover, a plan keeps you going in the face of challenges and adversities, and helps you push yourself a little harder to achieve your dreams when things get tougher.
Above all, a business plan helps you take action and turn ideas into a real and functioning business. So, what are you waiting for? Go ahead and start planning !
And while you’re at it, to check out Upmetrics’s business planning software to make business planning easier and faster.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.

About the Author

Radhika is an economics graduate and likes to read about every subject and idea she comes across. Apart from that she can discuss her favorite books to lengths( to the point you\'ll start feeling a little annoyed) and spends most of her free time on Google word coach.
Related Articles

How to Write a Business Plan Complete Guide

17 Reasons Why do you Need a Business Plan?

How to Prepare a Financial Plan for Startup Business (w/ example)
Reach your goals with accurate planning.
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates


How To Write A Business Plan [Step-By-Step Guide]
Have a business idea and want to know how to write a business plan, then here is the step-by-step guide for you. Writing a business plan is the first step to get started with your entrepreneurial journey.
Whether you’re gearing up to be the next apprentice on a TV show, facing dragons in the den, or embarking on your entrepreneurial journey , seeking sponsors for your business, the initial and crucial step is crafting a business plan.
Now, where do you kick things off?
The positive takeaway is that you don’t have to invest days in formulating your strategy. Opting for a professional business plan consultant can expedite the process, enabling you to translate your ideas into a comprehensive business plan seamlessly.
However, if you prefer a hands-on approach, fear not – we’ve got you covered.
Let’s delve into the steps of drafting your own business plan.
What is a Business Plan?
To bring any vision to life, it’s imperative to have a well-thought-out action plan. Your business plan serves precisely that purpose: it’s a roadmap that outlines the goals you aspire to achieve, the strategies you intend to employ to conquer these objectives, and the timelines within which you aim to make significant strides.
Given that business plans play a pivotal role in steering company operations and fostering growth, they hold immense importance for businesses of all scales – be it the newest startups or the most well-established organizations.
Types of Business Plans
Frequently, startup companies develop business plans to communicate their vision to potential investors, with the goal of securing funding. There are also other reasons, such as bringing aboard potential collaborators or establishing a clear, strategic course of action to be shared within the team.
There are basically 3 types of business plans:
● One-page business plan
● Lean business plan
● Traditional business plan
The tone, structure, and length of business plans can vary depending on the desired outcomes, as outlined below:
One-page business plan:
● The one-page business plan provides a concise snapshot of essential priorities and direction. It proves handy when sketching out the initial stages of a startup or as a brief pitching document.
Lean business plan:
● On the other hand, the “lean” business plan spans a few pages. Differing from traditional plans, it bypasses lengthy summaries and intricate details, focusing instead on specific deadlines, budgets, and milestones.
Traditional business plan:
● Meanwhile, the traditional business plan tends to be around 30 pages in length. It encompasses comprehensive sections like an executive summary, descriptions of products and services, target market analysis, and financial forecasting.
Why Should You Write a Business Plan?
Making the creation of your business plan a top priority is crucial, as it serves as a powerful tool to draw in new investors and business partners. Offering them a clear roadmap of the strategic steps you plan to take establishes the essential trust needed for a successful partnership.
Beyond just convincing investors to invest in your products or services, your business plan becomes a valuable guide for steering growth and managing operations in the initial phases of your venture. Your future self will appreciate having a detailed plan to rely on, keeping you on course – and the team members you bring on board will appreciate it too.
How To Write a Business Plan?
Now that you understand the immense value of a business plan, let’s delve into the optimal way to structure it. The step-by-step guide outlined below pertains to crafting a traditional business plan, the most comprehensive among the three types, featuring in-depth analyses and thorough descriptions.
How to write a business plan (8 Steps):
1. Step 1: Start with an executive summary
2. Step 2: Write up a business description and overview
3. Step 3: Describe your products or services
4. Step 4: Outline your marketing strategy
5. Step 5: Include a competitor analysis
6. Step 6: Get into design and development
7. Step 7: Provide details about operation and management
8. Step 8: End on financial factors
Step 1: Start with an executive summary
This serves as the opening to your business plan, providing a summary of what will be detailed in the upcoming pages. It should be as engaging as a captivating story, setting the tone right. Remember, if the initial chapter doesn’t grab attention, people might not be inclined to continue reading.
Clearly articulate the content goals of your comprehensive plan, covering all the key points. This section is particularly crucial if you’re seeking investors through your proposal.
Make sure to incorporate essential background information about your business, the market opportunity, capital requirements, a mission statement, an overview of management, details about competitors, your firm’s competitive advantages, and a snapshot of your financial projections for the next three years.
Step 2: Write up a business description and overview
This segment is crafted for you to offer additional insights into your business.
Inform your readers about the purpose of your business. Are you a fresh fashion brand exclusively dedicated to sportswear for tennis players? What drove your decision to establish this company?
Prepare a mission statement, lay out your business model strategy, and highlight any existing strategic relationships. Don’t forget to include the current outlook along with future possibilities. Consider other markets within the industry; will these new products and advancements positively impact or potentially pose challenges to your corporation?
Step 3: Describe your products or services
This is where you spotlight the core essence of your business: the standout product or service.
Clearly articulate what you’re offering and explain why your products or services outshine the competition.
If you’re in the business of selling products, specify whether you serve as the manufacturer, distributor, and retailer. Provide insights into your manufacturing process, the availability of materials, and your approach to managing inventory and fulfillment.
It’s crucial to include any patent, copyright, or trademark information at this juncture. If there are plans to introduce new products or services in the future, include that information here as well.
Step 4: Outline your marketing strategy
In this section, lay out your marketing strategy, delving into the specifics of your market analysis, sales approach, customer service, advertising, and public relations.
Explain how you connect with your target customers. What promotional tactics and digital marketing channels are currently in play? Define the desired brand positioning for each.
Many businesses leverage this space to showcase their vision for why their business will thrive, supported by market research pinpointing their target market, industry trends, and customer behaviors. Include details on both your planned and past marketing strategies.
Step 5: Include a competitor analysis
Competitor analysis seamlessly aligns with market research; for success, a thorough understanding of what rival companies offer is essential.
After accomplishing this, elucidate why and how you intend to surpass them in success. Who are your competitors, and what are their key strengths and weaknesses? Identify the areas where you already have or plan to gain a competitive advantage, and articulate the strategies that will facilitate this success.
Step 6: Get into design and development
This is the substantial core of your plan. Here, furnish the specifics of your sales strategy. What’s your action plan? How do you anticipate reaching your target audience and establishing dominance in the market?
In the design and development section, delineate how you intend to run the business across the entire cycle to achieve its objectives. Offer investors an overview of the product’s design, the development trajectory, and the allocated budget.
Step 7: Provide details about operation and management
If your business plan is crafted to attract investors, it’s essential to include information about the current executives and managers steering the company, showcasing examples of how they’ve contributed to achieving your business goals.
“For investors, knowing who these individuals are and understanding their experience is a crucial element,” emphasizes Tim Berry, president and founder of Palo Alto Software. The operations and management plan aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of how the business operates on an ongoing basis.
This section will spotlight the organization’s logistics, detailing the responsibilities of the management team, the tasks assigned to each division within the company, and the capital and expense requirements associated with the business operations.
Step 8: End on financial factors
In the financial segment, you present the quantifiable income, payouts, and profit corresponding to the information discussed in the previous seven sections. This is where you incorporate your projected profit-and-loss statements, balance sheets, and cash flow for the next three years.
Engaging a certified accountant to assist in compiling this section is a wise move. The numbers here should substantiate all the claims you’ve made in your proposal.
Common Mistakes To Avoid When You Write a Business Plan
Your business plan serves as the bedrock of your company. Allocating sufficient time to plan, draft, and meticulously edit it is crucial, as it can be the deciding factor between sealing the deal or losing it.
To enhance the likelihood of turning your product or service idea into reality, strive to steer clear of the five most common business plan mistakes outlined below.
1. Rushing through your executive summary
2. Making it too long
3. Setting unrealistic goals
4. Using poor formatting and grammar
5. Not creating a business plan at all
1. Rushing through your executive summary
Consider your executive summary as the opening act of your plan. As the most crucial section of your business strategy, it not only has to capture attention but also serve as a page-turner. Ensure it’s concise, well-written, and limited to less than 10% of your entire plan’s length.
2. Making it too long
You aim for your business plan to captivate your audience and keep them engaged until the very end. To prevent it from becoming overly dense with information, incorporate bold visuals such as graphs and charts instead of lengthy sentences. Maintain a smooth flow in your writing by using appendices for any supporting data or information.
3. Setting unrealistic goals
When crafting a business plan, adopting an honest approach with yourself and your audience is one of the best strategies. Avoid including unrealistic earnings projections or underestimating your competitors; otherwise, you risk coming across as lacking credibility or knowledge. Instead, conduct thorough research and emphasize presenting factual information.
4. Using poor formatting and grammar
Ensure you’ve gone through your business plan multiple times. While editing, take regular breaks, and enlist a friend or business partner to review it as well. The more thoroughly you examine it, the more visually appealing it will become, encouraging potential investors to spend more time with it.
5. Not creating a business plan at all
Young entrepreneurs are often so eager to dive into business that they might view putting things in writing as a poor use of time. However, just as writers begin with plot outlines and architects with blueprints, you should consider this initial phase as a crucial part of the process. It will undoubtedly prove beneficial in the long term!
Final Thoughts
We trust this guide has equipped you for crafting your very first business plan. Before you switch to a new window and start typing away, let’s sum up the crucial points:
● Conduct thorough research and incorporate your findings as supporting information.
● Strive for conciseness. Use graphs and appendices to make it a more digestible read.
● Customize your plan to your audience. Are you addressing new investors, potential collaborators, or existing shareholders?
● Be authentic. Let your audience sense your enthusiasm for what you do.
Enjoy laying the foundation for your new venture!
In the meantime, if you have any questions or wish to share your insights about writing a business plan, feel free to let us know in the comments section below.

Hey, I am Sachin Ramdurg. I run and manage futuredecider.com website that helps students, graduates, and professionals, to find and decide on their future career with ultimate future career advices and future career guides. I have an overall 12+ years of career guidance experience in multiple domains which has helped multiple students, graduates, and professionals to find the best career path for their future.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
How to create a business plan: a beginner's guide
Creating a well-written business plan is an essential first step to starting your own business

What is a business plan?
Key concepts for writing a business plan, main components of a business plan, tips for writing a business plan.
A well-written business plan holds a lot of value. It’s where your ideas start to take shape and the direction of your new enterprise becomes clear – but it can seem intimidating.
Business plans require focus: you’re stating why you’re doing what you’re doing, and how you expect to do it. There can be a lot to note down.
Ultimately, though, your business plan is going to become an essential guide for you, your team, and anyone involved in your company.
So let’s uncover what it takes to write a business plan, and find out how it can benefit you.
- Also check out our roundup of the best small business software
In short, a business plan is a description of your business and everything that goes into it.
As well as helping to clarify the business idea that you have, it brings into focus elements like financing, staffing, revenue targets, and marketing strategies.
Business plans aren’t exclusive to startups, either. If you’re regenerating an existing company, a detailed and structured plan is enormously useful.
Are you a pro? Subscribe to our newsletter
Sign up to the TechRadar Pro newsletter to get all the top news, opinion, features and guidance your business needs to succeed!
Not all success stories have required business plans, but a comprehensive plan will help you to identify any immediate routes to failure.
Although you’re putting a business concept on paper and announcing your mission statement, a plan has to be structured, not fanciful.
The first person it’s trying to convince is you. Are you ready to spend time and money on this?
After that, you should be considering any potential investors and your team members. Will they be motivated and excited? You’ll need to achieve the following with your business plan:
- A clear vision and purpose for the business – why is it important?
- A guide that can be used as a reference throughout the company’s growth.
- An objective outlook on the market potential of what it is your business is doing.
There is no one-size-fits-all business plan template, but the most successful plans have the same key components.
For small business owners writing a business plan, whether it's during the startup process or further down the road during a period of change, these are the essentials to include:
1. Executive summary
Think of your executive summary as an elevator pitch: it should be a concise, engaging, and persuasive overview of your business.
Keep this section to less than one page in length – after all, it is a summary.
While it’s the opening to your business plan, we recommend writing it last. That way, you can collate all of the key points raised in the rest of the document.
Here’s what you should summarize in this part of your business plan:
- A quick description - Outline what your business is about – if it’s a new business, what’s the mission? If you’re changing direction, what’s the concept?
- The products or services you’ll provide - Offer a brief value proposition – what makes your business idea unique?
- A picture of your target market - Give evidence that you’ve carried out market research and know who the end user should be.
- Your marketing strategy - Write a few lines about your intended marketing efforts to provide an idea of business reach.
- A snapshot of the company’s financial health - What’s the current business revenue and what are you forecasting to earn?
- A clear view of your financial needs - If you’re raising money, how much does the business require?
- The company’s key personnel - Whether you’re a startup business or an existing operation, who are the employees to mention?
- We've also featured the best online marketing services
2. Company description and overview
Next up, give a more detailed description of your business. Even if you’ve decided to write a business plan only for your own benefit, imagine what other people would want to know.
Make clear what you think is going to bring your business success in the long run.
This should help to demonstrate that the ideas you have are worth pursuing. For example, what problem can you solve? What experience can you bring to the table?
Here’s how to structure the company description part of your business plan:
Pinpoint the industry that your business is in, plus any insights or industry trends that you intend to adopt or disrupt.
Describe your business model and its structure – is it incorporated, a limited partnership, or perhaps a sole proprietorship?
Mention your target audience and highlight which problems or opportunities you have identified for the business.
Clarify your mission statement and value proposition to ensure that everyone is on the same page when it comes to business focus.
Provide some background on the company, like when it was founded, who by, and where it’s based.
Highlight the key employees in your team. If it’s a small business, that could be everyone, or maybe just a select few people.
It can be tricky to take a step back and consider your overall business goals and objectives, but remember that this is the whole point of writing a business plan.
Business plans can be great tools to use if you’re not even sure whether the venture is worth doing – writing an ambitious company description will help you to find that out.
3. Market analysis and opportunities
Whether you run a small business or a big business, you’ll have competitors. Knowing about the other companies in your industry will be invaluable.
That knowledge can inform your marketing plans, pricing decisions, and product selections.
You’ll also need to know about your target market. An understanding of your customer profile will help your business reach the right people and maintain a competitive advantage.
So, how does all of your market research come together in a business plan? Here’s how:
Illustrate your market analysis - Use charts and graphs to show where the business is going to sit within its industry. In terms of your price points, product offer, and service proposition, how will it compare to other businesses?
Explain who your potential customers are - Use survey tools to help you specify key demographics like age, profession, and location – if you’re only just starting out, it’s fine to make informed guesses about your ideal customer profile.
Include a SWOT analysis - Identifying the key strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of a business is at the heart of every competitive analysis. Present this part in a grid layout to draw attention to it within your business plan.
Be clear about the competition - It’s tough to find a market that isn’t already saturated, so show how your product or service will be different. Although it’s useful to have friendly rivals, you’ll need some competitive advantages.
4. Products and services
Earlier in your business plan, you hinted at what you’ll be selling, and now’s the time to describe it. It’s worth remembering at this point that industry jargon should be avoided.
Explaining the products or services your business offers should be clear, but exciting.
This section should describe why and how your product exists, how much money it will cost to develop, and how much business planning has gone into your decisions.
Whether you keep it brief, or go into detail about manufacturing, here’s how to shape this part:
- Outline the development process - If you’re selling products, will you be manufacturing them too, or sourcing from elsewhere? What’s the timeline?
- Overview the business model - This is particularly important for retailers, as you’ll need to clarify how your products will reach your customers.
- Cover off the costs - Financial projections and cost management will come up a lot in your business plan. In this part, discuss your profit margin expectations.
- Explain what sets your business apart - Chances are there will be versions of your product or service on the market – what’s your unique selling point (USP)?
- Talk about intellectual property - Mention any patents or copyrights you have applied for and emphasise how your work will be protected.
5. Business management and organization
By this part of your business plan, you will have described in detail the ideas behind your company or its expansion. The next step is to explain how you plan to execute them.
Start by talking about the people in your business and how they’ll contribute to its success.
You will have highlighted key employees at the start of the business plan document, so use this opportunity to go into more detail about the team.
After all, they’ll be driving the business with you – here’s what you can show:
An organizational chart - This will be a great way to sense check the structure you have created – are there too many people in senior roles? How does the team work together? Is there enough room for growth?
The backgrounds of your key players - A strong management team requires people with a range of skills and expertise. Although your employees don’t need to have years of experience, they should be bringing something interesting to the table.
Your hiring strategies - A big part of business planning is finding the right people – after all, salaries form part of the fixed costs you have to pay for. How do you expect to reach the right talent pool as you grow the company?
The company’s legal structure - If you are creating a startup, go into more detail about how your business will be run. For example, will it be a limited liability company (LLC), sole proprietorship, or partnership?
6. Marketing strategy
You have a customer profile, so now you need to think about how you’re going to manage customer relationships. Nailing this in your business plan is a really smart move.
First of all, understanding your marketing objectives will help you find the right channels.
It will also uncover the financial data around your company’s promotional efforts. What will your campaigns cost? What can you afford to spend on marketing?
Here are the key marketing components that you will need to consider:
Your website - While social media is effective, websites are essential. They’re easy to get – a website builder like Zyro or Squarespace will help you to create a bespoke platform and get online quickly and at a low cost.
Its marketing tools - The other major advantage to website builders is that they provide users with integrations, software, and insights to help drive marketing strategies. You’ll be getting an online presence and the tools to promote your business.
Third-party assistance - You can also use online marketing services to help you structure each marketing plan and drive a difference between you and your competitors. Who would you work with, and what will that cost?
Other marketing channels - Where will your audience be? You’ll most likely benefit from using social media platforms, but which ones? Find out if it’s worth investing time into Instagram, or if LinkedIn will be more profitable.
How your business will stand out - When you write a business plan, you’re making predictions about the future – what will you do if your marketing strategy fails? Understand some key digital marketing trends to help inform your ideas.
- Check out our complete list of the best small business website builders
7. Business operations and logistics
Now we’re getting really granular. Breaking down the proposed logistics in your business plan will be incredibly useful for you as you work out financial projections.
Getting a clear picture of business operations will also help you formulate a contingency plan.
It may be that your business model is very niche and needs testing – how will you account for any failures? While it isn't fun to think about worst case scenarios, it’s better to do this now.
Plus, if you need to secure funding, this section is important. Here’s what to cover:
- Business facilities - If the company plans to open retail spaces or venues, where are they and how big are they? Will there be an office for employees?
- Supply chain - Will you be sourcing products or materials from manufacturers? Explain where they are based and what policies you will implement
- Inventory management - Retailers should describe how and where they plan to manage stock and customer orders
- Fulfillment model - Another vital component for retail businesses, this covers how you expect to receive products and ship them out to customers
- Business equipment - Even small business administration costs money. How will you source office supplies? Will you need a bank loan?
- Financial operations - Before you delve into this part of the business plan, mention how you plan to track and manage cash flow
8. Financial plan
Whether you need to secure funding, take out a business loan, or simply take note of your income statements, every business plan needs to cover financial planning.
It helps to take a look at your finance software options to construct this part of the document.
Being upfront about your company’s financial outlook is critical, both for you and anyone else who is planning to invest in the organization.
There are three key components that you’ll need to include in your business plan:
An income statement , which shows the most accurate picture (or estimation) of your company’s profit and loss over a period of time.
A cash flow statement . To understand how much money you need to scale the business, and if it’s viable, you’ll need to provide cash flow statements.
Balance sheets . A balance sheet discloses your business assets and liabilities – in other words, what you owe to others.
On top of your financial statements, you should also include a breakeven analysis of your company in your business plan.
Critical for startups, this shows at what point you expect to start making a profit and for what duration you anticipate to be running at a loss.
Once you know what goes into a good business plan, you’ll need to know how to make it a document that people actually want to read.
In addition to the main segments, you can include supporting documents to help people further contextualize what it is you’re doing.
That will also help you to keep track of your plans, especially if you’re only writing the document to help yourself and your team, not investors.
Either way, you want to avoid writing a total snooze-fest. While a lot of detail goes into a business plan, it also needs to be engaging and exciting throughout.
So, to write a really solid business plan, remember to:
- Keep it brief - Nobody wants to have to flick through a 100-page manifesto, not even future you. An effective business plan is concise and memorable
- Make it shareable - Business plans written on paper won’t really go anywhere – make sure yours is published in an easily transferable format
- Be clear - Only use industry jargon when it’s totally unavoidable, otherwise you risk alienating (and boring) the readers of your business plan
- Show your research - Implement charts, provide supporting documents, and make sure that it’s abundantly clear how much thought you put into your business
- Remember your passion - Don’t be put off by traditional business plans with bland statements – make it clear in your own business plan how exciting this venture is
- We've also featured the best business plan software

Désiré has been musing and writing about technology during a career spanning four decades. He dabbled in website builders and web hosting when DHTML and frames were in vogue and started narrating about the impact of technology on society just before the start of the Y2K hysteria at the turn of the last millennium.
Allyant review: a document accessibility partner that looks good on paper
Adobe Acrobat Pro (2024) review
Quordle today – hints and answers for Sunday, March 24 (game #790)
Most Popular
By Charlotte Henry March 21, 2024
By Aatif Sulleyman March 21, 2024
By Will Hall March 21, 2024
By Jennifer Allen March 21, 2024
By Tom Wiggins March 21, 2024
By Andy Murray March 21, 2024
By Daniel Pateman March 19, 2024
By Will Hall March 19, 2024
By Aatif Sulleyman March 17, 2024
By Emma Street March 17, 2024
By Sofia Elizabella Wyciślik-Wilson March 16, 2024
- 2 Taylor Swift’s Eras Tour set a new Disney Plus record but its popularity is nothing compared to Netflix
- 3 Nvidia CEO says don't give up learning new skills — just maybe leave programming to AI
- 4 House of the Dragon season 2 gets an official Max release date and three fiery showdown-style trailers
- 5 Fujifilm X-T50 rumored to follow up the in-demand X100VI – and it could be the better buy
- 2 Nvidia has virtually recreated the entire planet — and now it wants to use its digital twin to crack weather forecasting for good
- 3 Windows 11 gets new features for Settings app as Microsoft continues with its ‘death by a thousand cuts’ for Control Panel
- 4 We could soon see an end to OLED burn-in – here’s why
- 5 Another Microsoft vulnerability is being used to spread malware

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Download Now: Free Business Plan Template. Writing a business plan doesn't have to be complicated. In this step-by-step guide, you'll learn how to write a business plan that's detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
Step #3: Conduct Your Market Analysis. Step #4: Research Your Competition. Step #5: Outline Your Products or Services. Step #6: Summarize Your Financial Plan. Step #7: Determine Your Marketing Strategy. Step #8: Showcase Your Organizational Chart. 14 Business Plan Templates to Help You Get Started.
Write the Executive Summary. This section is the same as in the traditional business plan — simply offer an overview of what's in the business plan, the prospect or core offering, and the short- and long-term goals of the company. Add a Company Overview. Document the larger company mission and vision.
Step 7: Financial Analysis and Projections. It doesn't matter if you include a request for funding in your plan, you will want to include a financial analysis here. You'll want to do two things here: Paint a picture of your business's performance in the past and show it will grow in the future.
Learn about the best business plan software. 1. Write an executive summary. This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your ...
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include. 1. Create an executive summary. Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
The following will take you to online business plan guides and templates for specific countries. United States Small Business Administration (SBA) - The "write your business plan page" includes traditional and lean startup business plan formats, three downloadable sample business plans, a template, and a step-by-step build a business plan ...
While it comes first in your business plan, you should write it last, once you've put together all your information in the following sections. Try to keep the executive summary concise—no more than one or two pages. - Your mission statement. - A description of your product/service. - Where your business is based.
Step 1: Gather Your Information. Your first step is to get organized by gathering all your relevant business information. This will save you time completing the various sections of your business plan. At a minimum, you'll want to have the following handy: Business name, contact information, and address. Owner (s) names, contact information ...
This is typically one of the first pieces of the plan to be written. 3. Market analysis and opportunity. Research is key in completing a business plan and, ideally, more time should be spent on research and analysis than writing the plan itself. Understanding the size, growth, history, future potential, and current risks inherent to the wider ...
Creating a strong business plan is the first step in your entrepreneurial journey to start a business. It gives your business a sense of direction and helps you make strategic decisions. However, crafting one can seem intimidating. It involves organizing your ideas, determining the right structure, performing market research, projecting ...
The first step in making a good business plan is writing an executive summary. Think of an executive summary as your company's elevator pitch in writing. You'll want to keep it short but still get across the important parts of your business. It should have your mission statement, a short description of your business's products or services ...
Step 5: Outline your organization and management structure. The strength and experience of your team can be a major factor in securing investor confidence and ensuring your business's success. That's why you'll need to showcase the team in this section. Begin by describing the organizational framework.
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
1. Carry out your research. The first step to creating a business plan is to do thorough research about the business and industry you are trying to get into. Tap into all the information you can get about your target audience, potential customer base, competitors, market and industry trends, cost of business, etc.
Whatever it is, mention and explain it. In essence, expand the competitive advantage you mentioned in the "company description" part of your plan. When you're done, use a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats) chart to summarize your findings. 6. Explain your sales and marketing strategy.
Have a business idea and want to know how to write a business plan, then here is the step-by-step guide for you. Writing a business plan is the first step to get started with your entrepreneurial journey. Whether you're gearing up to be the next apprentice on a TV show, facing dragons in the den, or embarking on your entrepreneurial journey, seeking sponsors for your business, the initial ...
1. Executive summary. Think of your executive summary as an elevator pitch: it should be a concise, engaging, and persuasive overview of your business. Keep this section to less than one page in ...
15+ Business Plan Examples to Help You Write Your Own. Having a clear business plan and sharing your goals with investors and stakeholders is an important first step to starting a successful business. It's like Utibe Samuel Mbom said, "Those who work hard, work alone. Those who work smart, work as a team.".
Creating a winning business plan is the first step to achieving your entrepren... Are you tired of working for someone else and want to start your own business? Creating a winning business plan is ...