Rubric Best Practices, Examples, and Templates
A rubric is a scoring tool that identifies the different criteria relevant to an assignment, assessment, or learning outcome and states the possible levels of achievement in a specific, clear, and objective way. Use rubrics to assess project-based student work including essays, group projects, creative endeavors, and oral presentations.
Rubrics can help instructors communicate expectations to students and assess student work fairly, consistently and efficiently. Rubrics can provide students with informative feedback on their strengths and weaknesses so that they can reflect on their performance and work on areas that need improvement.

How to Get Started
Best practices, moodle how-to guides.
- Workshop Recording (Fall 2022)
- Workshop Registration
Step 1: Analyze the assignment
The first step in the rubric creation process is to analyze the assignment or assessment for which you are creating a rubric. To do this, consider the following questions:
- What is the purpose of the assignment and your feedback? What do you want students to demonstrate through the completion of this assignment (i.e. what are the learning objectives measured by it)? Is it a summative assessment, or will students use the feedback to create an improved product?
- Does the assignment break down into different or smaller tasks? Are these tasks equally important as the main assignment?
- What would an “excellent” assignment look like? An “acceptable” assignment? One that still needs major work?
- How detailed do you want the feedback you give students to be? Do you want/need to give them a grade?
Step 2: Decide what kind of rubric you will use
Types of rubrics: holistic, analytic/descriptive, single-point
Holistic Rubric. A holistic rubric includes all the criteria (such as clarity, organization, mechanics, etc.) to be considered together and included in a single evaluation. With a holistic rubric, the rater or grader assigns a single score based on an overall judgment of the student’s work, using descriptions of each performance level to assign the score.
Advantages of holistic rubrics:
- Can p lace an emphasis on what learners can demonstrate rather than what they cannot
- Save grader time by minimizing the number of evaluations to be made for each student
- Can be used consistently across raters, provided they have all been trained
Disadvantages of holistic rubrics:
- Provide less specific feedback than analytic/descriptive rubrics
- Can be difficult to choose a score when a student’s work is at varying levels across the criteria
- Any weighting of c riteria cannot be indicated in the rubric
Analytic/Descriptive Rubric . An analytic or descriptive rubric often takes the form of a table with the criteria listed in the left column and with levels of performance listed across the top row. Each cell contains a description of what the specified criterion looks like at a given level of performance. Each of the criteria is scored individually.
Advantages of analytic rubrics:
- Provide detailed feedback on areas of strength or weakness
- Each criterion can be weighted to reflect its relative importance
Disadvantages of analytic rubrics:
- More time-consuming to create and use than a holistic rubric
- May not be used consistently across raters unless the cells are well defined
- May result in giving less personalized feedback
Single-Point Rubric . A single-point rubric is breaks down the components of an assignment into different criteria, but instead of describing different levels of performance, only the “proficient” level is described. Feedback space is provided for instructors to give individualized comments to help students improve and/or show where they excelled beyond the proficiency descriptors.
Advantages of single-point rubrics:
- Easier to create than an analytic/descriptive rubric
- Perhaps more likely that students will read the descriptors
- Areas of concern and excellence are open-ended
- May removes a focus on the grade/points
- May increase student creativity in project-based assignments
Disadvantage of analytic rubrics: Requires more work for instructors writing feedback
Step 3 (Optional): Look for templates and examples.
You might Google, “Rubric for persuasive essay at the college level” and see if there are any publicly available examples to start from. Ask your colleagues if they have used a rubric for a similar assignment. Some examples are also available at the end of this article. These rubrics can be a great starting point for you, but consider steps 3, 4, and 5 below to ensure that the rubric matches your assignment description, learning objectives and expectations.
Step 4: Define the assignment criteria
Make a list of the knowledge and skills are you measuring with the assignment/assessment Refer to your stated learning objectives, the assignment instructions, past examples of student work, etc. for help.
Helpful strategies for defining grading criteria:
- Collaborate with co-instructors, teaching assistants, and other colleagues
- Brainstorm and discuss with students
- Can they be observed and measured?
- Are they important and essential?
- Are they distinct from other criteria?
- Are they phrased in precise, unambiguous language?
- Revise the criteria as needed
- Consider whether some are more important than others, and how you will weight them.
Step 5: Design the rating scale
Most ratings scales include between 3 and 5 levels. Consider the following questions when designing your rating scale:
- Given what students are able to demonstrate in this assignment/assessment, what are the possible levels of achievement?
- How many levels would you like to include (more levels means more detailed descriptions)
- Will you use numbers and/or descriptive labels for each level of performance? (for example 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 and/or Exceeds expectations, Accomplished, Proficient, Developing, Beginning, etc.)
- Don’t use too many columns, and recognize that some criteria can have more columns that others . The rubric needs to be comprehensible and organized. Pick the right amount of columns so that the criteria flow logically and naturally across levels.
Step 6: Write descriptions for each level of the rating scale
Artificial Intelligence tools like Chat GPT have proven to be useful tools for creating a rubric. You will want to engineer your prompt that you provide the AI assistant to ensure you get what you want. For example, you might provide the assignment description, the criteria you feel are important, and the number of levels of performance you want in your prompt. Use the results as a starting point, and adjust the descriptions as needed.
Building a rubric from scratch
For a single-point rubric , describe what would be considered “proficient,” i.e. B-level work, and provide that description. You might also include suggestions for students outside of the actual rubric about how they might surpass proficient-level work.
For analytic and holistic rubrics , c reate statements of expected performance at each level of the rubric.
- Consider what descriptor is appropriate for each criteria, e.g., presence vs absence, complete vs incomplete, many vs none, major vs minor, consistent vs inconsistent, always vs never. If you have an indicator described in one level, it will need to be described in each level.
- You might start with the top/exemplary level. What does it look like when a student has achieved excellence for each/every criterion? Then, look at the “bottom” level. What does it look like when a student has not achieved the learning goals in any way? Then, complete the in-between levels.
- For an analytic rubric , do this for each particular criterion of the rubric so that every cell in the table is filled. These descriptions help students understand your expectations and their performance in regard to those expectations.
Well-written descriptions:
- Describe observable and measurable behavior
- Use parallel language across the scale
- Indicate the degree to which the standards are met
Step 7: Create your rubric
Create your rubric in a table or spreadsheet in Word, Google Docs, Sheets, etc., and then transfer it by typing it into Moodle. You can also use online tools to create the rubric, but you will still have to type the criteria, indicators, levels, etc., into Moodle. Rubric creators: Rubistar , iRubric
Step 8: Pilot-test your rubric
Prior to implementing your rubric on a live course, obtain feedback from:
- Teacher assistants
Try out your new rubric on a sample of student work. After you pilot-test your rubric, analyze the results to consider its effectiveness and revise accordingly.
- Limit the rubric to a single page for reading and grading ease
- Use parallel language . Use similar language and syntax/wording from column to column. Make sure that the rubric can be easily read from left to right or vice versa.
- Use student-friendly language . Make sure the language is learning-level appropriate. If you use academic language or concepts, you will need to teach those concepts.
- Share and discuss the rubric with your students . Students should understand that the rubric is there to help them learn, reflect, and self-assess. If students use a rubric, they will understand the expectations and their relevance to learning.
- Consider scalability and reusability of rubrics. Create rubric templates that you can alter as needed for multiple assignments.
- Maximize the descriptiveness of your language. Avoid words like “good” and “excellent.” For example, instead of saying, “uses excellent sources,” you might describe what makes a resource excellent so that students will know. You might also consider reducing the reliance on quantity, such as a number of allowable misspelled words. Focus instead, for example, on how distracting any spelling errors are.
Example of an analytic rubric for a final paper
Example of a holistic rubric for a final paper, single-point rubric, more examples:.
- Single Point Rubric Template ( variation )
- Analytic Rubric Template make a copy to edit
- A Rubric for Rubrics
- Bank of Online Discussion Rubrics in different formats
- Mathematical Presentations Descriptive Rubric
- Math Proof Assessment Rubric
- Kansas State Sample Rubrics
- Design Single Point Rubric
Technology Tools: Rubrics in Moodle
- Moodle Docs: Rubrics
- Moodle Docs: Grading Guide (use for single-point rubrics)
Tools with rubrics (other than Moodle)
- Google Assignments
- Turnitin Assignments: Rubric or Grading Form
Other resources
- DePaul University (n.d.). Rubrics .
- Gonzalez, J. (2014). Know your terms: Holistic, Analytic, and Single-Point Rubrics . Cult of Pedagogy.
- Goodrich, H. (1996). Understanding rubrics . Teaching for Authentic Student Performance, 54 (4), 14-17. Retrieved from
- Miller, A. (2012). Tame the beast: tips for designing and using rubrics.
- Ragupathi, K., Lee, A. (2020). Beyond Fairness and Consistency in Grading: The Role of Rubrics in Higher Education. In: Sanger, C., Gleason, N. (eds) Diversity and Inclusion in Global Higher Education. Palgrave Macmillan, Singapore.
Rubric Design
Main navigation, articulating your assessment values.
Reading, commenting on, and then assigning a grade to a piece of student writing requires intense attention and difficult judgment calls. Some faculty dread “the stack.” Students may share the faculty’s dim view of writing assessment, perceiving it as highly subjective. They wonder why one faculty member values evidence and correctness before all else, while another seeks a vaguely defined originality.
Writing rubrics can help address the concerns of both faculty and students by making writing assessment more efficient, consistent, and public. Whether it is called a grading rubric, a grading sheet, or a scoring guide, a writing assignment rubric lists criteria by which the writing is graded.
Why create a writing rubric?
- It makes your tacit rhetorical knowledge explicit
- It articulates community- and discipline-specific standards of excellence
- It links the grade you give the assignment to the criteria
- It can make your grading more efficient, consistent, and fair as you can read and comment with your criteria in mind
- It can help you reverse engineer your course: once you have the rubrics created, you can align your readings, activities, and lectures with the rubrics to set your students up for success
- It can help your students produce writing that you look forward to reading
How to create a writing rubric
Create a rubric at the same time you create the assignment. It will help you explain to the students what your goals are for the assignment.
- Consider your purpose: do you need a rubric that addresses the standards for all the writing in the course? Or do you need to address the writing requirements and standards for just one assignment? Task-specific rubrics are written to help teachers assess individual assignments or genres, whereas generic rubrics are written to help teachers assess multiple assignments.
- Begin by listing the important qualities of the writing that will be produced in response to a particular assignment. It may be helpful to have several examples of excellent versions of the assignment in front of you: what writing elements do they all have in common? Among other things, these may include features of the argument, such as a main claim or thesis; use and presentation of sources, including visuals; and formatting guidelines such as the requirement of a works cited.
- Then consider how the criteria will be weighted in grading. Perhaps all criteria are equally important, or perhaps there are two or three that all students must achieve to earn a passing grade. Decide what best fits the class and requirements of the assignment.
Consider involving students in Steps 2 and 3. A class session devoted to developing a rubric can provoke many important discussions about the ways the features of the language serve the purpose of the writing. And when students themselves work to describe the writing they are expected to produce, they are more likely to achieve it.
At this point, you will need to decide if you want to create a holistic or an analytic rubric. There is much debate about these two approaches to assessment.
Comparing Holistic and Analytic Rubrics
Holistic scoring .
Holistic scoring aims to rate overall proficiency in a given student writing sample. It is often used in large-scale writing program assessment and impromptu classroom writing for diagnostic purposes.
General tenets to holistic scoring:
- Responding to drafts is part of evaluation
- Responses do not focus on grammar and mechanics during drafting and there is little correction
- Marginal comments are kept to 2-3 per page with summative comments at end
- End commentary attends to students’ overall performance across learning objectives as articulated in the assignment
- Response language aims to foster students’ self-assessment
Holistic rubrics emphasize what students do well and generally increase efficiency; they may also be more valid because scoring includes authentic, personal reaction of the reader. But holistic sores won’t tell a student how they’ve progressed relative to previous assignments and may be rater-dependent, reducing reliability. (For a summary of advantages and disadvantages of holistic scoring, see Becker, 2011, p. 116.)
Here is an example of a partial holistic rubric:
Summary meets all the criteria. The writer understands the article thoroughly. The main points in the article appear in the summary with all main points proportionately developed. The summary should be as comprehensive as possible and should be as comprehensive as possible and should read smoothly, with appropriate transitions between ideas. Sentences should be clear, without vagueness or ambiguity and without grammatical or mechanical errors.
A complete holistic rubric for a research paper (authored by Jonah Willihnganz) can be downloaded here.
Analytic Scoring
Analytic scoring makes explicit the contribution to the final grade of each element of writing. For example, an instructor may choose to give 30 points for an essay whose ideas are sufficiently complex, that marshals good reasons in support of a thesis, and whose argument is logical; and 20 points for well-constructed sentences and careful copy editing.
General tenets to analytic scoring:
- Reflect emphases in your teaching and communicate the learning goals for the course
- Emphasize student performance across criterion, which are established as central to the assignment in advance, usually on an assignment sheet
- Typically take a quantitative approach, providing a scaled set of points for each criterion
- Make the analytic framework available to students before they write
Advantages of an analytic rubric include ease of training raters and improved reliability. Meanwhile, writers often can more easily diagnose the strengths and weaknesses of their work. But analytic rubrics can be time-consuming to produce, and raters may judge the writing holistically anyway. Moreover, many readers believe that writing traits cannot be separated. (For a summary of the advantages and disadvantages of analytic scoring, see Becker, 2011, p. 115.)
For example, a partial analytic rubric for a single trait, “addresses a significant issue”:
- Excellent: Elegantly establishes the current problem, why it matters, to whom
- Above Average: Identifies the problem; explains why it matters and to whom
- Competent: Describes topic but relevance unclear or cursory
- Developing: Unclear issue and relevance
A complete analytic rubric for a research paper can be downloaded here. In WIM courses, this language should be revised to name specific disciplinary conventions.
Whichever type of rubric you write, your goal is to avoid pushing students into prescriptive formulas and limiting thinking (e.g., “each paragraph has five sentences”). By carefully describing the writing you want to read, you give students a clear target, and, as Ed White puts it, “describe the ongoing work of the class” (75).
Writing rubrics contribute meaningfully to the teaching of writing. Think of them as a coaching aide. In class and in conferences, you can use the language of the rubric to help you move past generic statements about what makes good writing good to statements about what constitutes success on the assignment and in the genre or discourse community. The rubric articulates what you are asking students to produce on the page; once that work is accomplished, you can turn your attention to explaining how students can achieve it.
Works Cited
Becker, Anthony. “Examining Rubrics Used to Measure Writing Performance in U.S. Intensive English Programs.” The CATESOL Journal 22.1 (2010/2011):113-30. Web.
White, Edward M. Teaching and Assessing Writing . Proquest Info and Learning, 1985. Print.
Further Resources
CCCC Committee on Assessment. “Writing Assessment: A Position Statement.” November 2006 (Revised March 2009). Conference on College Composition and Communication. Web.
Gallagher, Chris W. “Assess Locally, Validate Globally: Heuristics for Validating Local Writing Assessments.” Writing Program Administration 34.1 (2010): 10-32. Web.
Huot, Brian. (Re)Articulating Writing Assessment for Teaching and Learning. Logan: Utah State UP, 2002. Print.
Kelly-Reilly, Diane, and Peggy O’Neil, eds. Journal of Writing Assessment. Web.
McKee, Heidi A., and Dànielle Nicole DeVoss DeVoss, Eds. Digital Writing Assessment & Evaluation. Logan, UT: Computers and Composition Digital Press/Utah State University Press, 2013. Web.
O’Neill, Peggy, Cindy Moore, and Brian Huot. A Guide to College Writing Assessment . Logan: Utah State UP, 2009. Print.
Sommers, Nancy. Responding to Student Writers . Macmillan Higher Education, 2013.
Straub, Richard. “Responding, Really Responding to Other Students’ Writing.” The Subject is Writing: Essays by Teachers and Students. Ed. Wendy Bishop. Boynton/Cook, 1999. Web.
White, Edward M., and Cassie A. Wright. Assigning, Responding, Evaluating: A Writing Teacher’s Guide . 5th ed. Bedford/St. Martin’s, 2015. Print.
Eberly Center
Teaching excellence & educational innovation, creating and using rubrics.
A rubric is a scoring tool that explicitly describes the instructor’s performance expectations for an assignment or piece of work. A rubric identifies:
- criteria: the aspects of performance (e.g., argument, evidence, clarity) that will be assessed
- descriptors: the characteristics associated with each dimension (e.g., argument is demonstrable and original, evidence is diverse and compelling)
- performance levels: a rating scale that identifies students’ level of mastery within each criterion
Rubrics can be used to provide feedback to students on diverse types of assignments, from papers, projects, and oral presentations to artistic performances and group projects.
Benefitting from Rubrics
- reduce the time spent grading by allowing instructors to refer to a substantive description without writing long comments
- help instructors more clearly identify strengths and weaknesses across an entire class and adjust their instruction appropriately
- help to ensure consistency across time and across graders
- reduce the uncertainty which can accompany grading
- discourage complaints about grades
- understand instructors’ expectations and standards
- use instructor feedback to improve their performance
- monitor and assess their progress as they work towards clearly indicated goals
- recognize their strengths and weaknesses and direct their efforts accordingly
Examples of Rubrics
Here we are providing a sample set of rubrics designed by faculty at Carnegie Mellon and other institutions. Although your particular field of study or type of assessment may not be represented, viewing a rubric that is designed for a similar assessment may give you ideas for the kinds of criteria, descriptions, and performance levels you use on your own rubric.
- Example 1: Philosophy Paper This rubric was designed for student papers in a range of courses in philosophy (Carnegie Mellon).
- Example 2: Psychology Assignment Short, concept application homework assignment in cognitive psychology (Carnegie Mellon).
- Example 3: Anthropology Writing Assignments This rubric was designed for a series of short writing assignments in anthropology (Carnegie Mellon).
- Example 4: History Research Paper . This rubric was designed for essays and research papers in history (Carnegie Mellon).
- Example 1: Capstone Project in Design This rubric describes the components and standards of performance from the research phase to the final presentation for a senior capstone project in design (Carnegie Mellon).
- Example 2: Engineering Design Project This rubric describes performance standards for three aspects of a team project: research and design, communication, and team work.
Oral Presentations
- Example 1: Oral Exam This rubric describes a set of components and standards for assessing performance on an oral exam in an upper-division course in history (Carnegie Mellon).
- Example 2: Oral Communication This rubric is adapted from Huba and Freed, 2000.
- Example 3: Group Presentations This rubric describes a set of components and standards for assessing group presentations in history (Carnegie Mellon).
Class Participation/Contributions
- Example 1: Discussion Class This rubric assesses the quality of student contributions to class discussions. This is appropriate for an undergraduate-level course (Carnegie Mellon).
- Example 2: Advanced Seminar This rubric is designed for assessing discussion performance in an advanced undergraduate or graduate seminar.
See also " Examples and Tools " section of this site for more rubrics.
CONTACT US to talk with an Eberly colleague in person!
- Faculty Support
- Graduate Student Support
- Canvas @ Carnegie Mellon
- Quick Links

Designing Writing Assignments
Designing Writing Assignments designing-assignments
As you think about creating writing assignments, use these five principles:
- Tie the writing task to specific pedagogical goals.
- Note rhetorical aspects of the task, i.e., audience, purpose, writing situation.
- Make all elements of the task clear.
- Include grading criteria on the assignment sheet.
- Break down the task into manageable steps.
You'll find discussions of these principles in the following sections of this guide.
Writing Should Meet Teaching Goals
Working backwards from goals, guidelines for writing assignments, resource: checksheets, resources: sample assignments.
- Citation Information
To guarantee that writing tasks tie directly to the teaching goals for your class, ask yourself questions such as the following:
- What specific course objectives will the writing assignment meet?
- Will informal or formal writing better meet my teaching goals?
- Will students be writing to learn course material, to master writing conventions in this discipline, or both?
- Does the assignment make sense?
Although it might seem awkward at first, working backwards from what you hope the final papers will look like often produces the best assignment sheets. We recommend jotting down several points that will help you with this step in writing your assignments:
- Why should students write in your class? State your goals for the final product as clearly and concretely as possible.
- Determine what writing products will meet these goals and fit your teaching style/preferences.
- Note specific skills that will contribute to the final product.
- Sequence activities (reading, researching, writing) to build toward the final product.
Successful writing assignments depend on preparation, careful and thorough instructions, and on explicit criteria for evaluation. Although your experience with a given assignment will suggest ways of improving a specific paper in your class, the following guidelines should help you anticipate many potential problems and considerably reduce your grading time.
- Explain the purpose of the writing assignment.
- Make the format of the writing assignment fit the purpose (format: research paper, position paper, brief or abstract, lab report, problem-solving paper, etc.).
II. The assignment
- Provide complete written instructions.
- Provide format models where possible.
- Discuss sample strong, average, and weak papers.
III. Revision of written drafts
Where appropriate, peer group workshops on rough drafts of papers may improve the overall quality of papers. For example, have students critique each others' papers one week before the due date for format, organization, or mechanics. For these workshops, outline specific and limited tasks on a checksheet. These workshops also give you an opportunity to make sure that all the students are progressing satisfactorily on the project.
IV. Evaluation
On a grading sheet, indicate the percentage of the grade devoted to content and the percentage devoted to writing skills (expression, punctuation, spelling, mechanics). The grading sheet should indicate the important content features as well as the writing skills you consider significant.
Visitors to this site are welcome to download and print these guidelines
Checksheet 1: (thanks to Kate Kiefer and Donna Lecourt)
- written out the assignment so that students can take away a copy of the precise task?
- made clear which course goals this writing task helps students meet?
- specified the audience and purpose of the assignment?
- outlined clearly all required sub-parts of the assignment (if any)?
- included my grading criteria on the assignment sheet?
- pointed students toward appropriate prewriting activities or sources of information?
- specified the format of the final paper (including documentation, headings or sections, page layout)?
- given students models or appropriate samples?
- set a schedule that will encourage students to review each other's drafts and revise their papers?
Checksheet 2: (thanks to Jean Wyrick)
- Is the assignment written clearly on the board or on a handout?
- Do the instructions explain the purpose(s) of the assignment?
- Does the assignment fit the purpose?
- Is the assignment stated in precise language that cannot be misunderstood?
- If choices are possible, are these options clearly marked?
- Are there instructions for the appropriate format? (examples: length? typed? cover sheet? type of paper?)
- Are there any special instructions, such as use of a particular citation format or kinds of headings? If so, are these clearly stated?
- Is the due date clearly visible? (Are late assignments accepted? If so, any penalty?)
- Are any potential problems anticipated and explained?
- Are the grading criteria spelled out as specifically as possible? How much does content count? Organization? Writing skills? One grade or separate grades on form and content? Etc.
- Does the grading criteria section specifically indicate which writing skills the teacher considers important as well as the various aspects of content?
- What part of the course grade is this assignment?
- Does the assignment include use of models (strong, average, weak) or samples outlines?
Sample Full-Semester Assignment from Ag Econ 4XX
Good analytical writing is a rigorous and difficult task. It involves a process of editing and rewriting, and it is common to do a half dozen or more drafts. Because of the difficulty of analytical writing and the need for drafting, we will be completing the assignment in four stages. A draft of each of the sections described below is due when we finish the class unit related to that topic (see due dates on syllabus). I will read the drafts of each section and provide comments; these drafts will not be graded but failure to pass in a complete version of a section will result in a deduction in your final paper grade. Because of the time both you and I are investing in the project, it will constitute one-half of your semester grade.
Content, Concepts and Substance
Papers will focus on the peoples and policies related to population, food, and the environment of your chosen country. As well as exploring each of these subsets, papers need to highlight the interrelations among them. These interrelations should form part of your revision focus for the final draft. Important concepts relevant to the papers will be covered in class; therefore, your research should be focused on the collection of information on your chosen country or region to substantiate your themes. Specifically, the paper needs to address the following questions.
- Population - Developing countries have undergone large changes in population. Explain the dynamic nature of this continuing change in your country or region and the forces underlying the changes. Better papers will go beyond description and analyze the situation at hand. That is, go behind the numbers to explain what is happening in your country with respect to the underlying population dynamics: structure of growth, population momentum, rural/urban migration, age structure of population, unanticipated populations shocks, etc. DUE: WEEK 4.
- Food - What is the nature of food consumption in your country or region? Is the average daily consumption below recommended levels? Is food consumption increasing with economic growth? What is the income elasticity of demand? Use Engel's law to discuss this behavior. Is production able to stay abreast with demand given these trends? What is the nature of agricultural production: traditional agriculture or green revolution technology? Is the trend in food production towards self-sufficiency? If not, can comparative advantage explain this? Does the country import or export food? Is the politico-economic regime supportive of a progressive agricultural sector? DUE: WEEK 8.
- Environment - This is the third issue to be covered in class. It is crucial to show in your paper the environmental impact of agricultural production techniques as well as any direct impacts from population changes. This is especially true in countries that have evolved from traditional agriculture to green revolution techniques in the wake of population pressures. While there are private benefits to increased production, the use of petroleum-based inputs leads to environmental and human health related social costs which are exacerbated by poorly defined property rights. Use the concepts of technological externalities, assimilative capacity, property rights, etc. to explain the nature of this situation in your country or region. What other environmental problems are evident? Discuss the problems and methods for economically measuring environmental degradation. DUE: WEEK 12.
- Final Draft - The final draft of the project should consider the economic situation of agriculture in your specified country or region from the three perspectives outlined above. Key to such an analysis are the interrelationships of the three perspectives. How does each factor contribute to an overall analysis of the successes and problems in agricultural policy and production of your chosen country or region? The paper may conclude with recommendations, but, at the very least, it should provide a clear summary statement about the challenges facing your country or region. DUE: WEEK15.
Landscape Architecture 3XX: Design Critique
Critical yet often overlooked components of the landscape architect's professional skills are the ability to critically evaluate existing designs and the ability to eloquently express him/herself in writing. To develop your skills at these fundamental components, you are to professionally critique a built project with which you are personally and directly familiar. The critique is intended for the "informed public" as might be expected to be read in such features in The New York Times or Columbus Monthly ; therefore, it should be insightful and professionally valid, yet also entertaining and eloquent. It should reflect a sophisticated knowledge of the subject without being burdened with professional jargon.
As in most critiques or reviews, you are attempting not only to identify the project's good and bad features but also to interpret the project's significance and meaning. As such, the critique should have a clear "point of view" or thesis that is then supported by evidence (your description of the place) that persuades the reader that your thesis is valid. Note, however, that your primary goal is not to force the reader to agree with your point of view but rather to present a valid discussion that enriches and broadens the reader's understanding of the project.
To assist in the development of the best possible paper, you are to submit a typed draft by 1:00 pm, Monday, February 10th. The drafts will be reviewed as a set and will then serve as a basis of an in-class writing improvement seminar on Friday, February 14th. The seminar will focus on problems identified in the set of drafts, so individual papers will not have been commented on or marked. You may also submit a typed draft of your paper to the course instructor for review and comment at any time prior to the final submission.
Final papers are due at 2:00 pm, Friday, February 23rd.
Animal/Dairy/Poultry Science 2XX: Comparative Animal Nutrition
Purpose: Students should be able to integrate lecture and laboratory material, relate class material to industry situations, and improve their problem-solving abilities.
Assignment 1: Weekly laboratory reports (50 points)
For the first laboratory, students will be expected to provide depth and breadth of knowledge, creativity, and proper writing format in a one-page, typed, double-spaced report. Thus, conciseness will be stressed. Five points total will be possible for the first draft, another five points possible will be given to a student peer-reviewer of the draft, and five final points will be available for a second draft. This assignment, in its entirety, will be due before the first midterm (class 20). Any major writing flaws will be addressed early so that students can grasp concepts stressed by the instructors without major impact on their grades. Additional objectives are to provide students with skills in critically reviewing papers and to acquaint writers and reviewers of the instructors' expectations for assignments 2 and 3, which are weighted much more heavily.
Students will submit seven one-page handwritten reports from each week's previous laboratory. These reports will cover laboratory classes 2-9; note that one report can be dropped and week 10 has no laboratory. Reports will be graded (5 points each) by the instructors for integration of relevant lecture material or prior experience with the current laboratory.
Assignment 2: Group problem-solving approach to a nutritional problem in the animal industry (50 points)
Students will be divided into groups of four. Several problems will be offered by the instructors, but a group can choose an alternative, approved topic. Students should propose a solution to the problem. Because most real-life problems are solved by groups of employees and (or) consultants, this exercise should provide students an opportunity to practice skills they will need after graduation. Groups will divide the assignment as they see fit. However, 25 points will be based on an individual's separate assignment (1-2 typed pages), and 25 points will be based on the group's total document. Thus, it is assumed that papers will be peer-reviewed. The audience intended will be marketing directors, who will need suitable background, illustrations, etc., to help their salespersons sell more products. This assignment will be started in about the second week of class and will be due by class 28.
Assignment 3: Students will develop a topic of their own choosing (approved by instructors) to be written for two audiences (100 points).
The first assignment (25 points) will be written in "common language," e.g., to farmers or salespersons. High clarity of presentation will be expected. It also will be graded for content to assure that the student has developed the topic adequately. This assignment will be due by class 38.
Concomitant with this assignment will be a first draft of a scientific term paper on the same subject. Ten scientific articles and five typed, double-spaced pages are minimum requirements. Basic knowledge of scientific principles will be incorporated into this term paper written to an audience of alumni of this course working in a nutrition-related field. This draft (25 points) will be due by class 38. It will be reviewed by a peer who will receive up to 25 points for his/her critique. It will be returned to the student and instructor by class 43. The final draft, worth an additional 25 points, will be due before class 50 and will be returned to the student during the final exam period.
Integration Papers - HD 3XX
Two papers will be assigned for the semester, each to be no more than three typewritten pages in length. Each paper will be worth 50 points.
Purpose: The purpose of this assignment is to aid the student in learning skills necessary in forming policy-making decisions and to encourage the student to consider the integral relationship between theory, research, and social policy.
Format: The student may choose any issue of interest that is appropriate to the socialization focus of the course, but the issue must be clearly stated and the student is advised to carefully limit the scope of the issue question.
There are three sections to the paper:
First: One page will summarize two conflicting theoretical approaches to the chosen issue. Summarize only what the selected theories may or would say about the particular question you've posed; do not try to summarize the entire theory. Make clear to a reader in what way the two theories disagree or contrast. Your text should provide you with the basic information to do this section.
Second: On the second page, summarize (abstract) one relevant piece of current research. The research article must be chosen from a professional journal (not a secondary source) written within the last five years. The article should be abstracted and then the student should clearly show how the research relates to the theoretical position(s) stated earlier, in particular, and to the socialization issue chosen in general. Be sure the subjects used, methodology, and assumptions can be reasonably extended to your concern.
Third: On the third page, the student will present a policy guideline (for example, the Colorado courts should be required to include, on the child's behalf, a child development specialist's testimony at all custody hearings) that can be supported by the information gained and presented in the first two pages. My advice is that you picture a specific audience and the final purpose or use of such a policy guideline. For example, perhaps as a child development specialist you have been requested to present an informed opinion to a federal or state committee whose charge is to develop a particular type of human development program or service. Be specific about your hypothetical situation and this will help you write a realistic policy guideline.
Sample papers will be available in the department reading room.
SP3XX Short Essay Grading Criteria
A (90-100): Thesis is clearly presented in first paragraph. Every subsequent paragraph contributes significantly to the development of the thesis. Final paragraph "pulls together" the body of the essay and demonstrates how the essay as a whole has supported the thesis. In terms of both style and content, the essay is a pleasure to read; ideas are brought forth with clarity and follow each other logically and effortlessly. Essay is virtually free of misspellings, sentence fragments, fused sentences, comma splices, semicolon errors, wrong word choices, and paragraphing errors.
B (80-89): Thesis is clearly presented in first paragraph. Every subsequent paragraph contributes significantly to the development of the thesis. Final paragraph "pulls together" the body of the essay and demonstrates how the essay as a whole has supported the thesis. In terms of style and content, the essay is still clear and progresses logically, but the essay is somewhat weaker due to awkward word choice, sentence structure, or organization. Essay may have a few (approximately 3) instances of misspellings, sentence fragments, fused sentences, comma splices, semicolon errors, wrong word choices, and paragraphing errors.
C (70-79): There is a thesis, but the reader may have to hunt for it a bit. All the paragraphs contribute to the thesis, but the organization of these paragraphs is less than clear. Final paragraph simply summarizes essay without successfully integrating the ideas presented into a unified support for thesis. In terms of style and content, the reader is able to discern the intent of the essay and the support for the thesis, but some amount of mental gymnastics and "reading between the lines" is necessary; the essay is not easy to read, but it still has said some important things. Essay may have instances (approximately 6) of misspellings, sentence fragments, fused sentences, comma splices, semicolon errors, wrong word choices, and paragraphing errors.
D (60-69): Thesis is not clear. Individual paragraphs may have interesting insights, but the paragraphs do not work together well in support of the thesis. In terms of style and content, the essay is difficult to read and to understand, but the reader can see there was a (less than successful) effort to engage a meaningful subject. Essay may have several instances (approximately 6) of misspellings, sentence fragments, fused sentences, comma splices, semicolon errors, wrong word choices, and paragraphing errors.
Teacher Comments
Patrick Fitzhorn, Mechanical Engineering: My expectations for freshman are relatively high. I'm jaded with the seniors, who keep disappointing me. Often, we don't agree on the grading criteria.
There's three parts to our writing in engineering. The first part, is the assignment itself.
The four types: lab reports, technical papers, design reports, and proposals. The other part is expectations in terms of a growth of writing style at each level in our curriculum and an understanding of that from students so they understand that high school writing is not acceptable as a senior in college. Third, is how we transform our expectations into justifiable grades that have real feedback for the students.
To the freshman, I might give a page to a page and one half to here's how I want the design report. To the seniors it was three pages long. We try to capture how our expectations change from freshman to senior. I bet the structure is almost identical...
We always give them pretty rigorous outlines. Often times, the way students write is to take the outline we give them and students write that chunk. Virtually every writing assignment we give, we provide a writing outline of the writing style we want. These patterns are then used in industry. One organization style works for each of the writing styles. Between faculty, some minute details may change with organization, but there is a standard for writers to follow.
Interviewer: How do students determine purpose
Ken Reardon, Chemical Engineerin: Students usually respond to an assignment. That tells them what the purpose is. . . . I think it's something they infer from the assignment sheet.
Interviewer What types of purposes are there?
Ken Reardon: Persuading is the case with proposals. And informing with progress and the final results. Informing is to just "Here are the results of analysis; here's the answer to the question." It's presenting information. Persuasion is analyzing some information and coming to a conclusion. More of the writing I've seen engineers do is a soft version of persuasion, where they're not trying to sell. "Here's my analysis, here's how I interpreted those results and so here's what I think is worthwhile." Justifying.
Interviewer: Why do students need to be aware of this concept?
Ken Reardon: It helps to tell the reader what they're reading. Without it, readers don't know how to read.
Kiefer, Kate. (1997). Designing Writing Assignments. Writing@CSU . Colorado State University. https://writing.colostate.edu/teaching/guide.cfm?guideid=101
- U.S. Locations
- UMGC Europe
- Learn Online
- Find Answers
- 855-655-8682
- Current Students
Online Guide to Writing and Research
Assessing your writing, explore more of umgc.
- Online Guide to Writing
How Is Writing Graded?

Students often want to know how their writing assignments are graded—that is, what is an A paper, a B paper, and so on. Generally speaking, there are two basic ways to determine how your papers will be graded.
Understand your assignment, which often will include a rubric.
Understand general grading standards professors usually apply to papers.
Assignments and What Rubrics Have To Do with Them
Virtually every college and graduate-level assignment will include instructions from your professor. Often, rubrics, which provide criteria for each possible grade you might receive, will accompany your assignments.
Some rubrics can be quite detailed, breaking down the assignment and describing the grading criteria for each requirement. Other rubrics merely provide general writing standards associated with each grade. In either case, your first and best source for understanding assignment’s associated grading standards is the content of the assignment itself.
As you familiarize yourself with an assignment and its rubric, keep in mind the following:
Prioritize the criteria for a particular assignment over the criteria listed in the section below.
When an assignment comes with a rubric, study the rubric and familiarize yourself with it. Aside from your professor, this is the best guide to successfully meeting the assignment requirements.
Prioritize your professor’s advice above all. College and graduate professors often provide their own descriptions of their assignments and a list of requirements. Sometimes these can differ from the accompanying rubric. If you are ever in doubt about your assignment and its requirements, contact your professor with your questions.
Some General (Though Not Exhaustive) Grading Standards for Academic Papers
Although each professor and class is unique, there are some general qualities that attach to each grade. The following grading standards may be useful as you assess your own writing, but remember, a number of factors ultimately contribute to your grade, including your specific instructor's guidelines and preferences. Always defer to your assignment-specific or class-specific standards for grading information, and reach out to your instructor with any questions.
- The Grade of A
- The Grade of B
- The Grade of C
- The Grade of D
- The Grade of F
The A paper is characterized by outstanding writing marked by superior readability and command of content.
The paper thoroughly addresses the assignment prompt.
The paper proceeds in a clear, logical fashion that makes the information accessible to the reader.
The paper’s purpose is clear, followed by details reflecting this purpose.
The style throughout the paper accommodates the reader.
The diction throughout the paper, and sentence construction, contribute to understanding.
The student’s grammar, mechanics, and format are flawless.
The B paper is characterized by distinguished writing and fulfills the assignment requirements; however, the writing contains some of the following weaknesses:
The paper is well organized, but the presentation of content sometimes inhibits understanding.
The audience for which the paper is intended is sometimes unclear.
The student’s diction at times is vague and hinders precise communication.
The student’s grammar, mechanics, and formatting flaws interfere with reading and comprehension.
The C paper is characterized by satisfactory writing that is generally effective but contains any one of the following weaknesses:
The paper lacks clear organization, or some material is not clearly explained; the paper’s audience and purpose are not clear.
The student’s sentences, although grammatically correct, often make information difficult to extract.
The student’s diction throughout the paper interferes with readability, but the reader can still glean the meaning; sections of the paper require rereading.
The paper contains repeated errors in grammar, mechanics, or format.
The D paper struggles to communicate information and contains weak writing. In a professional work environment, such writing would be considered incompetent because it suffers from any one of the following problems:
The paper contains two or more of the problems listed for the C paper.
The paper lacks evidence of audience accommodation.
The paper contains poor diction, such as garbled wording that prevents understanding.
The student’s sentences have mechanical errors, such as persistent run‑on sentences and comma splices.
The student’s grammar, spelling, or format problems create frequent obstacles to understanding.
The paper fails on multiple levels. A failing grade on a writing assignment usually means that your paper contains two or more of the problems listed for the D paper.
Mailing Address: 3501 University Blvd. East, Adelphi, MD 20783 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License . © 2022 UMGC. All links to external sites were verified at the time of publication. UMGC is not responsible for the validity or integrity of information located at external sites.
Table of Contents: Online Guide to Writing
Chapter 1: College Writing
How Does College Writing Differ from Workplace Writing?
What Is College Writing?
Why So Much Emphasis on Writing?
Chapter 2: The Writing Process
Doing Exploratory Research
Getting from Notes to Your Draft
Introduction
Prewriting - Techniques to Get Started - Mining Your Intuition
Prewriting: Targeting Your Audience
Prewriting: Techniques to Get Started
Prewriting: Understanding Your Assignment
Rewriting: Being Your Own Critic
Rewriting: Creating a Revision Strategy
Rewriting: Getting Feedback
Rewriting: The Final Draft
Techniques to Get Started - Outlining
Techniques to Get Started - Using Systematic Techniques
Thesis Statement and Controlling Idea
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Freewriting
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Summarizing Your Ideas
Writing: Outlining What You Will Write
Chapter 3: Thinking Strategies
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone: Style Through Vocabulary and Diction
Critical Strategies and Writing
Critical Strategies and Writing: Analysis
Critical Strategies and Writing: Evaluation
Critical Strategies and Writing: Persuasion
Critical Strategies and Writing: Synthesis
Developing a Paper Using Strategies
Kinds of Assignments You Will Write
Patterns for Presenting Information
Patterns for Presenting Information: Critiques
Patterns for Presenting Information: Discussing Raw Data
Patterns for Presenting Information: General-to-Specific Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Problem-Cause-Solution Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Specific-to-General Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Summaries and Abstracts
Supporting with Research and Examples
Writing Essay Examinations
Writing Essay Examinations: Make Your Answer Relevant and Complete
Writing Essay Examinations: Organize Thinking Before Writing
Writing Essay Examinations: Read and Understand the Question
Chapter 4: The Research Process
Planning and Writing a Research Paper
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Ask a Research Question
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Cite Sources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Collect Evidence
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Decide Your Point of View, or Role, for Your Research
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Draw Conclusions
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Find a Topic and Get an Overview
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Manage Your Resources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Outline
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Survey the Literature
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Work Your Sources into Your Research Writing
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Human Resources
Research Resources: What Are Research Resources?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Electronic Resources
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Print Resources
Structuring the Research Paper: Formal Research Structure
Structuring the Research Paper: Informal Research Structure
The Nature of Research
The Research Assignment: How Should Research Sources Be Evaluated?
The Research Assignment: When Is Research Needed?
The Research Assignment: Why Perform Research?
Chapter 5: Academic Integrity
Academic Integrity
Giving Credit to Sources
Giving Credit to Sources: Copyright Laws
Giving Credit to Sources: Documentation
Giving Credit to Sources: Style Guides
Integrating Sources
Practicing Academic Integrity
Practicing Academic Integrity: Keeping Accurate Records
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Paraphrasing Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Quoting Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Summarizing Your Sources
Types of Documentation
Types of Documentation: Bibliographies and Source Lists
Types of Documentation: Citing World Wide Web Sources
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - APA Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - CSE/CBE Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - Chicago Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - MLA Style
Types of Documentation: Note Citations
Chapter 6: Using Library Resources
Finding Library Resources
Chapter 7: Assessing Your Writing
How Is Writing Graded?: A General Assessment Tool
The Draft Stage
The Draft Stage: The First Draft
The Draft Stage: The Revision Process and the Final Draft
The Draft Stage: Using Feedback
The Research Stage
Using Assessment to Improve Your Writing
Chapter 8: Other Frequently Assigned Papers
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Article and Book Reviews
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Reaction Papers
Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Adapting the Argument Structure
Writing Arguments: Purposes of Argument
Writing Arguments: References to Consult for Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Anticipate Active Opposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Determine Your Organization
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Develop Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Introduce Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - State Your Thesis or Proposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Write Your Conclusion
Writing Arguments: Types of Argument
Appendix A: Books to Help Improve Your Writing
Dictionaries
General Style Manuals
Researching on the Internet
Special Style Manuals
Writing Handbooks
Appendix B: Collaborative Writing and Peer Reviewing
Collaborative Writing: Assignments to Accompany the Group Project
Collaborative Writing: Informal Progress Report
Collaborative Writing: Issues to Resolve
Collaborative Writing: Methodology
Collaborative Writing: Peer Evaluation
Collaborative Writing: Tasks of Collaborative Writing Group Members
Collaborative Writing: Writing Plan
General Introduction
Peer Reviewing
Appendix C: Developing an Improvement Plan
Working with Your Instructor’s Comments and Grades
Appendix D: Writing Plan and Project Schedule
Devising a Writing Project Plan and Schedule
Reviewing Your Plan with Others
By using our website you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about how we use cookies by reading our Privacy Policy .

- Subject Guides
Academic writing: a practical guide
Assessment & feedback.
- Academic writing
- The writing process
- Academic writing style
- Structure & cohesion
- Criticality in academic writing
- Working with evidence
- Referencing
- Dissertations
- Reflective writing
- Examination writing
- Academic posters
- Feedback on Structure and Organisation
- Feedback on Argument, Analysis, and Critical Thinking
- Feedback on Writing Style and Clarity
- Feedback on Referencing and Research
- Feedback on Presentation and Proofreading
What markers are looking for in your work and using feedback to improve your writing.
Assessment criteria
Most written assignments are marked using assessment criteria, which show the areas the work is marked on and what's expected at each grade band. Each department has its own assessment criteria, and sometimes modules have a specific set of criteria too.
Assessment criteria can be organised as a list of descriptions for each grade band, as a grid with descriptions for each marking area and grade band, or as marking areas rated on a scale.

Marking areas
Criteria have different areas (or categories) that work is marked against. Marking areas can vary across departments or assignments, but there are some key areas that often appear. Here are some ideas of what markers may be looking for:
Content & relevance
This area looks at how far the assignment meets the task requirements and the relevance of the information included.
Addressing the question/task
Make sure you read the assessment instructions carefully!
- How far does the work address the question/task?
- Are all parts of the question/task addressed?
- Is the work within +/- 10% of the stated word count?
Relevance of content
- Are points and sources relevant to the question/task?
- Are the relevant ideas/principles from the module included?
- For higher scores, does the work include relevant ideas from reading beyond the module content?
- Are sources used relevant, up to date and reliable?
More information:

Argument & analysis
This category focuses on the quality of your argument and critical analysis relating to the topic. It's also sometimes called 'originality of thought' or 'engagement with ideas'.
An important aspect of academic writing is incorporating relevant previous research and thinking as well as your own findings. However, it's not enough just to describe or summarise this information - to get higher marks, you also need to critically analyse it. What does it mean in terms of your overall argument? If the content is the 'what', the analysis and argument are more like 'so what?'.
Relating this to Bloom's Taxonomy , this requires more complex processes; analysing, evaluating and creating.
Questions markers may ask:
- Is the argument logical and well developed, with enough relevant supporting evidence?
- Is the work analytical, rather than just descriptive?
- Have connections or comparisons been made across sources?
- Are source information and/or research findings evaluated in terms of the argument?
Critical analysis is spread throughout assignments in small critical comments and is also usually the major focus of the discussion or conclusion. To help you critically analyse source information or your own findings, ask questions like why? how? and so what?
- Why did paper A find different results to papers B and C?
- How might this information influence policy?
- Plant A grew faster than Plant B - so what?

This area focuses on the structure and organisation of the assignment, which is important to help the reader follow the argument easily.
- Is the overall structure and argument clear?
- Are points logically ordered to create the argument?
- Are paragraphs structured clearly, with one central idea?
- Are ideas linked smoothly within and between paragraphs?
- Does the work meet structural requirements for the type of writing (eg, does a report include section headings)?
Style & presentation
This area is about the surface aspects of your work - how does it look and feel?
Referencing style
- Are citations and references formatted correctly in the required referencing style?
- Is all source information acknowledged appropriately?
You can find examples of correctly formatted citations and references in our practical guide to referencing styles .
Presentation
- Are the format and presentation appropriate to the task?
- Have formatting guidelines or requirements been followed?
- Is formatting consistent?
Use of language
- Is an academic writing style used that is appropriate to the assignment?
- Is spelling, grammar and punctuation correct?
- Is the writing clear and concise?
What to do with assessment criteria?

Find your assessment criteria
Your module learning outcomes and assessment criteria could be found in your programme handbook, an induction or module VLE site, or the module catalogue.

Read & understand the criteria
You need to know what markers' expectations are, so read the criteria carefully. Consider:
- Which key areas is your work marked on?
- What are the expectations at different grade bands?
Apply the criteria
You can use the criteria in a few ways to help improve your assignments:
- Evaluate example assignments using the criteria - why were they awarded that grade?
- Use with feedback on previous assignments to help identify strengths and areas to improve (also see the Feedback box).
- Use them while writing assignments to remind you what markers are looking for.
If you have questions about the marking criteria, ask your module tutor, your academic supervisor, or book a Writing Centre appointment .
View this information in a new window: Assessment criteria [Google Doc]
Using feedback to improve writing
Feedback comes in many forms:
- written comments about your work
- highlighting sections of the assessment criteria
- verbally in an audio or video clip, or in a conversation
- model answers to compare your work to
- advice on common issues (especially for formative work)

Feedback is an opportunity to develop and improve. It's not always nice to read, but don't ignore it !
Feedback can...
...show what you've done well.
The essay is structured well and your argument is easy to follow.
Your literature review comprises highly relevant studies, which you link back to in your discussion of the results.
Overall, you demonstrate a good understanding of the quantitative statistical analyses you have conducted.
These comments help you understand the strengths of your writing. For example, If you know that your structure was clear, you can use the same approach in your next assignments.
Also, they make you feel good - give yourself a pat on the back!
...identify areas for improvement
You raise some (potentially) interesting points in your essay, but these are very often not supported with a reference to relevant evidence.
The third paragraph is quite off-topic, and doesn't help you answer the essay question.
Your arguments are not clear in several places due to errors in grammar and wording.
It might not be very nice to hear about aspects of your work that are not so good, but these comments are the most useful to help you improve!
This type of comment often includes phrases like:
- [something positive], but/however [something to improve]
- make sure you...
- pay attention to...
- you could have...
- it would have helped to...
- [some part of the assignment] could be more...
See the sections below for tips on dealing with some common problems identified in feedback.
...help extend your understanding
What might be the implications of this policy for schools?
How far could your findings be generalised to other working environments?
You mention some theories of aggression, but don't go into detail - why are these particular theories relevant?
Comments like this can give you ideas to consider or further reading to help deepen your knowledge on a topic. This is especially useful if you want to explore this topic further in later modules or your dissertation. They could also highlight gaps in your understanding. In this case, it might be worthwhile to go back and revise the module content to help you in your later modules.

What to do with feedback?

Here's a handy three-step process to use your feedback to write better assignments.
- Read the feedback carefully. What are you doing well? What do you need to improve?
- Look back at your assignment - can you find the good things and issues mentioned?
- If the feedback isn't clear, ask your tutor to explain or book a Writing Centre appointment to discuss it.
- Look for patterns in feedback across assignments to identify what to focus on.
- For areas to improve on, make a plan to address this. For example, if the structure needs to be clearer, you could spend more time planning next time.
- For things you're doing well, how can you apply this to future assignments?
Do something!
- Apply your plans from the Reflect stage when you write your next assignments.
- When you get the feedback for these assignments, think about what you did differently - have you addressed the issues?
And then the cycle begins again!
You can use this template to review your feedback to identify areas for improvement and work out what you need to focus on:

Common feedback issues & how to avoid them
The issues below are often identified in feedback. Open each for advice on how to address them in your next assignments. Some are easier to deal with than others!
Proofreading, spelling and grammar errors
Work on improving the clarity of your writing, including grammar and choice of words.
There are numerous errors in spelling and grammar, eg 'the survey contain 10 questions'.
Make sure to proofread your work carefully, there are lots of typos.
Feedback like this is very common, as the mistakes are easy for markers to spot.
It shows you need to check your work carefully for small mistakes or typos in spelling, grammar, punctuation or word choice before you submit. This checking is often called ' proofreading '.
More detail & advice:

Referencing style errors
The format of your references in the text does not always follow the APA format.
There are some instances of citing and referencing format being incorrect.
Pay attention to following Harvard style correctly.
Each referencing style has specific formatting requirements for in-text citations, footnotes and the reference list/bibliography (as used in that style). For example, in APA style (Tanaka & Smith, 2007) is correctly formatted, but (Tanaka and Smith 2007) is not. These can seem like small details, but they're very important to get right!
To avoid making referencing style errors, check all of your citations and references carefully before you submit. Common errors include:
- incorrect author names or missing out authors
- missing out some information needed in the reference
- not using the correct punctuation and text formatting, especially full stops, commas, ampersand (&) and italics
- putting an in-text citation outside the sentence instead of before the full stop
- citing a source in the text, but not including it in the reference list (or vice versa)
You can find examples of correctly formatted citations and references for each style in our practical guide to referencing styles . You can also use reference management software to generate citations and references from your sources - this can save a lot of time! They're not always 100% correct though, so you'll need to check them still.

More critical analysis/stronger argument needed
The style is often somewhat descriptive, and you could have added more critical discussion of the findings.
Relevant texts are reviewed, but there is only limited criticality towards their content.
The argument lacks development, with minimal indication of original thought.
Comments like this suggest that your writing focuses on the more descriptive processes - remembering, understanding and applying. To access higher marks, you also need to demonstrate more critical skills - analysis, evaluation and processing. This is considering what the information means in terms of your argument.
More information on what criticality is and how to add it to your work:
Structure isn't clear
The argument wasn't always clear, so a more logical structure to the assignment would have helped.
Your results section could be more organised - it seems like you just report everything you found.
Some paragraphs contain unrelated information, which is a bit distracting.
Assignments need a clear overall structure. This usually means a linear structure, where paragraphs have one central idea and build on each other towards the final argument. You can think of this as a flight of stairs going from your title at the bottom to your conclusion at the top. A key way to improve your structure is to plan out your points and arrange them before you start writing.
Cohesion is also an important part of structure. There are lots of words and phrases that you can use to link your ideas more clearly. These phrases don't really add any information, but they make the links clear to the reader so it's easier for them to follow your argument
For more in-depth information, see our advice on structuring academic writing:
Writing style isn't academic enough
Very long sentences sometimes make the essay difficult to follow.
Personal remarks are inadequate for developing an academic argument.
There are numerous colloquialisms (‘the next thing to do’, ‘pour their knowledge into our heads’) in this work.
Academic writing uses a very different style to other types of writing. Some of the key features are:
- being clear and concise
- using neutral words and avoiding informal, conversational or colloquial language
- avoiding personal language
For more in-depth information, see our advice on academic writing style:
Assignment doesn't meet task requirements
Your literature review is quite good, but the remainder of the assignment is not in the style of a research report.
The first part of the essay is relevant to the question, but the second half is largely off-topic.
You haven’t done any analysis, which was a central part of this assessment.
To get a good mark, you have to complete the assignment that was set! This means answering all parts of the task, staying relevant and using an appropriate structure and style. Make sure to read the assessment brief carefully to find out what you need to do.
For more information see our advice on understanding task requirements:
Use of source information / course content
There is heavy reliance on just a few references, which all come from the module reading list.
There are some up to date and relevant sources, but you could have used more recent references.
Your sources all support your argument. What about research with different findings?
In most assignments, you need to refer to information in sources to support your argument - without evidence from sources, your points are just your opinion, and it's very difficult to show any critical analysis.
Make sure you:
- use sources that are credible, up-to-date and relevant to the task.
- don't rely on just a couple of sources, as this will limit your argument.
- extend module content and find some sources yourself.
- don't ignore sources with different findings/points - be complete in your argument.
Find on choosing suitable sources and how to find them on these pages:

View this information in a new window: Using feedback to improve writing [Google Doc]
- << Previous: Referencing
- Next: Tools >>
- Last Updated: Apr 3, 2024 4:02 PM
- URL: https://subjectguides.york.ac.uk/academic-writing
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Understanding the Writing Assignment
Before you begin working on an essay or a writing assignment, don’t forget to spend some quality time analyzing the assignment sheet. By closely reading and breaking down the assignment sheet, you are setting yourself up for an easier time planning and composing the assignment.
Understanding what you need to do
- First , carefully read the assignment sheet and search for the required page length, due dates, and other submission-based information.
- Second , determine the genre of the assignment
- Third , identify the core assignment questions that you need to answer
- Fourth , locate the evaluation and grading criteria
Identifying Writing Requirements & Disciplinary Expectations
Some instructors offer indications of what certain parts of the essay/composition should contain. Does the assignment sheet offer suggestions or requirements for the Intro paragraph? For the thesis statement? For the structure or content of the body paragraphs or conclusion paragraphs?
Depending on the discipline in which you are writing, different features and formats of your writing may be expected. Always look closely at key terms and vocabulary in the writing assignment, and be sure to note what type of evidence and citation style your instructor expects.
- Does the essay need to be in MLA, APA, CMS, or another style?
- Does the professor require any specific submission elements or formats?
Writing Genre
What, in the broadest sense, are you being asked to do? What writing genre is expected?
- Narrative – The act of telling a story through an essay. Also note that narrative includes the act of writing about yourself, which is exceptionally difficult for most writers but is nonetheless required for many circumstances in and out of college.
- Analysis – Analysis questions often contain words like how, in what ways, and what are some of the ____. Analysis asks you to examine small pieces of the larger whole and indicate their meaning or significance.
- Synthesis – If you are asked to draw from and connect several different sources, then you will be synthesizing.
- Argument – Any text in which you are attempting to get a reader to accept your claim. Argument is persuasive writing, and it can include things like argument-based research papers or critiques/evaluations of others’ work.
- Explanation – Any text in which you merely report (as opposed to attempting to persuade) is going to be an explanation paper. None of your own opinions is being sought. Summaries, annotations, and reports are often explanatory.
- Compare and Contrast – This essay is usually between two ideas. The primary aim of comparing and contrasting in college writing is to clarify meaningful, non-obvious features of similarity and difference.
Answer the Assignment Questions & Implied Questions
Sometimes, a list of prompts or questions may appear with an assignment. Likely, your instructor will not expect you to answer all of the questions listed. They are simply offering you some ideas so that you can think of your questions to ask.
- Circle all assignment questions that you see on the assignment sheet
- Put a star next to the question that is either the most important OR that you will pursue in creating the assignment
A prompt may not include a clear ‘how’ or ‘why’ question, though one is always implied by the language of the prompt. For example:
“Discuss the effects of the No Child Left Behind Act on special education programs” is asking you to write how the act has affected special education programs. “Consider the recent rise of autism diagnoses” is asking you to write why the diagnoses of autism are on the rise.
Identifying Evaluation Criteria
Many assignment sheets contain a grading rubric or some other indication of evaluation criteria for the assignment. You can use these criteria to both begin the writing process and to guide your revision and editing process. If you do not see any rubric or evaluation criteria on the assignment sheet — ask!
Attributions
A Guide to Rhetoric, Genre, and Success in First-Year Writing by Melanie Gagich & Emilie Zickel is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
This chapter has additions, edits, and organization by James Charles Devlin.
Understanding the Writing Assignment Copyright © by James Charles Devlin is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Understanding Writing Assignments

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
How to Decipher the Paper Assignment
Many instructors write their assignment prompts differently. By following a few steps, you can better understand the requirements for the assignment. The best way, as always, is to ask the instructor about anything confusing.
- Read the prompt the entire way through once. This gives you an overall view of what is going on.
- Underline or circle the portions that you absolutely must know. This information may include due date, research (source) requirements, page length, and format (MLA, APA, CMS).
- Underline or circle important phrases. You should know your instructor at least a little by now - what phrases do they use in class? Does he repeatedly say a specific word? If these are in the prompt, you know the instructor wants you to use them in the assignment.
- Think about how you will address the prompt. The prompt contains clues on how to write the assignment. Your instructor will often describe the ideas they want discussed either in questions, in bullet points, or in the text of the prompt. Think about each of these sentences and number them so that you can write a paragraph or section of your essay on that portion if necessary.
- Rank ideas in descending order, from most important to least important. Instructors may include more questions or talking points than you can cover in your assignment, so rank them in the order you think is more important. One area of the prompt may be more interesting to you than another.
- Ask your instructor questions if you have any.
After you are finished with these steps, ask yourself the following:
- What is the purpose of this assignment? Is my purpose to provide information without forming an argument, to construct an argument based on research, or analyze a poem and discuss its imagery?
- Who is my audience? Is my instructor my only audience? Who else might read this? Will it be posted online? What are my readers' needs and expectations?
- What resources do I need to begin work? Do I need to conduct literature (hermeneutic or historical) research, or do I need to review important literature on the topic and then conduct empirical research, such as a survey or an observation? How many sources are required?
- Who - beyond my instructor - can I contact to help me if I have questions? Do you have a writing lab or student service center that offers tutorials in writing?
(Notes on prompts made in blue )
Poster or Song Analysis: Poster or Song? Poster!
Goals : To systematically consider the rhetorical choices made in either a poster or a song. She says that all the time.
Things to Consider: ah- talking points
- how the poster addresses its audience and is affected by context I'll do this first - 1.
- general layout, use of color, contours of light and shade, etc.
- use of contrast, alignment, repetition, and proximity C.A.R.P. They say that, too. I'll do this third - 3.
- the point of view the viewer is invited to take, poses of figures in the poster, etc. any text that may be present
- possible cultural ramifications or social issues that have bearing I'll cover this second - 2.
- ethical implications
- how the poster affects us emotionally, or what mood it evokes
- the poster's implicit argument and its effectiveness said that was important in class, so I'll discuss this last - 4.
- how the song addresses its audience
- lyrics: how they rhyme, repeat, what they say
- use of music, tempo, different instruments
- possible cultural ramifications or social issues that have bearing
- emotional effects
- the implicit argument and its effectiveness
These thinking points are not a step-by-step guideline on how to write your paper; instead, they are various means through which you can approach the subject. I do expect to see at least a few of them addressed, and there are other aspects that may be pertinent to your choice that have not been included in these lists. You will want to find a central idea and base your argument around that. Additionally, you must include a copy of the poster or song that you are working with. Really important!
I will be your audience. This is a formal paper, and you should use academic conventions throughout.
Length: 4 pages Format: Typed, double-spaced, 10-12 point Times New Roman, 1 inch margins I need to remember the format stuff. I messed this up last time =(
Academic Argument Essay
5-7 pages, Times New Roman 12 pt. font, 1 inch margins.
Minimum of five cited sources: 3 must be from academic journals or books
- Design Plan due: Thurs. 10/19
- Rough Draft due: Monday 10/30
- Final Draft due: Thurs. 11/9
Remember this! I missed the deadline last time
The design plan is simply a statement of purpose, as described on pages 40-41 of the book, and an outline. The outline may be formal, as we discussed in class, or a printout of an Open Mind project. It must be a minimum of 1 page typed information, plus 1 page outline.
This project is an expansion of your opinion editorial. While you should avoid repeating any of your exact phrases from Project 2, you may reuse some of the same ideas. Your topic should be similar. You must use research to support your position, and you must also demonstrate a fairly thorough knowledge of any opposing position(s). 2 things to do - my position and the opposite.
Your essay should begin with an introduction that encapsulates your topic and indicates 1 the general trajectory of your argument. You need to have a discernable thesis that appears early in your paper. Your conclusion should restate the thesis in different words, 2 and then draw some additional meaningful analysis out of the developments of your argument. Think of this as a "so what" factor. What are some implications for the future, relating to your topic? What does all this (what you have argued) mean for society, or for the section of it to which your argument pertains? A good conclusion moves outside the topic in the paper and deals with a larger issue.
You should spend at least one paragraph acknowledging and describing the opposing position in a manner that is respectful and honestly representative of the opposition’s 3 views. The counterargument does not need to occur in a certain area, but generally begins or ends your argument. Asserting and attempting to prove each aspect of your argument’s structure should comprise the majority of your paper. Ask yourself what your argument assumes and what must be proven in order to validate your claims. Then go step-by-step, paragraph-by-paragraph, addressing each facet of your position. Most important part!
Finally, pay attention to readability . Just because this is a research paper does not mean that it has to be boring. Use examples and allow your opinion to show through word choice and tone. Proofread before you turn in the paper. Your audience is generally the academic community and specifically me, as a representative of that community. Ok, They want this to be easy to read, to contain examples I find, and they want it to be grammatically correct. I can visit the tutoring center if I get stuck, or I can email the OWL Email Tutors short questions if I have any more problems.
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
II. Getting Started
2.2 Understanding the Writing Assignment: Quick Reference
Robin Jeffrey; Emilie Zickel; Kathy Anders; and Terri Pantuso
Before you begin working on an essay or a writing assignment, don’t forget to spend some quality time analyzing the assignment sheet. By closely reading and breaking down the assignment sheet, you are setting yourself up for an easier time of planning and composing the assignment. You might find it helpful to use the following steps:
- First, determine the genre of the assignment;
- Second, identify the core assignment questions that you need to answer;
- Third, note what types of secondary sources are required as well as how many;
- Fourth, locate the evaluation and grading criteria; carefully read the assignment sheet and search for the required page length, due dates, and other submission-based information;
- Finally, identify the disciplinary conventions with which you are expected to write.
Writing Genre
Loosely speaking, genre refers to a category of work that generally shares similar characteristics. When determining the genre in which you are being asked to write, if it is not explicitly stated ask yourself what, in the broadest sense, are you being asked to do?
How to Answer the Assignment Question(s)
Sometimes, a list of prompts or questions may appear with an assignment given to you by your instructor. It is likely that your instructor will not expect you to answer all of the questions listed. They are simply offering you some ideas so that you can think of your own questions to ask. When this occurs, it can be useful to:
- Circle all assignment questions that you see on the assignment sheet;
- Put a star next to the question that is either the most important OR that you will pursue in creating the assignment;
- Underline the topic about which you feel most passionate. If you are interested in the topic, you will produce a better paper.
Recognizing Implied Questions
A prompt may not include a clear ‘how’ or ‘why’ question, though one is always implied by the language of the prompt. For example, “Discuss the effects of the No Child Left Behind Act on special education programs” is asking you to write how the act has affected special education programs, while “Consider the recent rise of autism diagnoses” is asking you to write why the diagnoses of autism are on the rise. If it is not relatively clear what is implied in the question or prompt, check with your instructor or a writing center tutor.
Identifying Writing Requirements
Some instructors offer indications of what certain parts of the essay/composition should contain. As you read the assignment sheet, look for an indication of elements to be included. Does the assignment sheet offer suggestions or requirements for the introductory paragraph? For the thesis statement? For the structure or content of the body paragraphs or conclusion paragraphs? If not, check with your instructor or visit your university writing center for suggestions and guidance.
Identifying Source Information Requirements
When you receive an assignment, note what types of information you will need in order to respond to the questions in the prompt. Your instructor may indicate that you need to use a certain number of secondary sources in your assignment and may even tell you what types of sources, e.g. newspaper stories, magazine articles, interviews, or scholarly journal articles. It may also be the case that apart from the requirements for the writing assignment, you need to find background information on the topic so that you can begin to formulate your own ideas or your claim. For example, say you are in a nutrition class and you receive the following prompt:
“Evaluate the benefits and drawbacks of a ketogenic diet for a population with a health issue of your choosing, i.e., epilepsy, liver disease, kidney disease, obesity, etc. Use at least four scholarly sources in your paper.”
If you are not already familiar with what a ketogenic diet is, you will have to do some background research on the concept itself as you begin to address the topic of your essay. You might also need to do some research about the health issue upon which you focus. As you write, you will also need to find and incorporate four scholarly sources into your paper likely addressing the specific question about the ketogenic diet and the population group you chose. You might choose to include even more sources depending upon how you want to address the topic. However, remember that when you are using secondary sources you keep your voice and claim prominent in the essay, and not the voices of your secondary sources.
Identifying Evaluation Criteria
Many assignment sheets contain a grading rubric or some other indication of evaluation criteria for the assignment. You can use these criteria to both begin the writing process and to guide your revision and editing process. If you do not see any rubric or evaluation criteria on the assignment sheet — ask!
Recognizing Disciplinary Expectations
Depending on the discipline in which you are writing, different features and formats of your writing may be expected. Always look closely at key terms and vocabulary in the writing assignment, and be sure to note what type of evidence and citations style your instructor expects.
- Does the essay need to be in MLA, APA, Chicago or another style?
- Does the instructor require any specific submission elements or formats?
This section contains material from:
Jeffrey, Robin, and Emilie Zickel. “Understanding the Writing Assignment.” In A Guide to Rhetoric, Genre, and Success in First-Year Writing , by Melanie Gagich and Emilie Zickel. Cleveland: MSL Academic Endeavors. Accessed July 2019. https://pressbooks.ulib.csuohio.edu/csu-fyw-rhetoric/chapter/understanding-assignments/. Licensed u nder a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License .
To hint; to suggest indirectly without mentioning the topic explicitly. An implied argument is one that does not obviously appear to be an argument but is nevertheless persuasive.
A statement, usually one sentence, that summarizes an argument that will later be explained, expanded upon, and developed in a longer essay or research paper. In undergraduate writing, a thesis statement is often found in the introductory paragraph of an essay. The plural of thesis is theses .
Sources that provide information on a primary source; the presentation of non-original data; the analysis of someone else’s research.
When something is described as scholarly, that means that has been written by and for the academic community. The term scholarly is commonly used as shorthand to indicate that information that has been peer reviewed or examined by other experts of the same academic field or discipline. Sometimes, the terms academic, scholarly, and peer reviewed are confused as synonyms; peer reviewed is a narrower term referring to an item that has been reviewed by experts in the field prior to publication, while academic is a broader term that also includes works that are written by and for academics, but that have not been peer reviewed.
An ambiguous or amorphous quality to writing comprising the vocabulary, word choice, tone, point of view, syntax, attitude, emotion, and style of a writer. Because writing is a personal and individual exercise, every writer has their own unique voice.
An arguable statement; a point that a writer, researcher, or speaker makes in order to prove their thesis.
The explicit set of criteria, point distribution, and expectations set forth by a grader. A rubric is almost always standardized out of fairness for all the people whose work is being graded.
2.2 Understanding the Writing Assignment: Quick Reference Copyright © 2022 by Robin Jeffrey; Emilie Zickel; Kathy Anders; and Terri Pantuso is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Writing Assignments
Kate Derrington; Cristy Bartlett; and Sarah Irvine

Introduction
Assignments are a common method of assessment at university and require careful planning and good quality research. Developing critical thinking and writing skills are also necessary to demonstrate your ability to understand and apply information about your topic. It is not uncommon to be unsure about the processes of writing assignments at university.
- You may be returning to study after a break
- You may have come from an exam based assessment system and never written an assignment before
- Maybe you have written assignments but would like to improve your processes and strategies
This chapter has a collection of resources that will provide you with the skills and strategies to understand assignment requirements and effectively plan, research, write and edit your assignments. It begins with an explanation of how to analyse an assignment task and start putting your ideas together. It continues by breaking down the components of academic writing and exploring the elements you will need to master in your written assignments. This is followed by a discussion of paraphrasing and synthesis, and how you can use these strategies to create a strong, written argument. The chapter concludes with useful checklists for editing and proofreading to help you get the best possible mark for your work.
Task Analysis and Deconstructing an Assignment
It is important that before you begin researching and writing your assignments you spend sufficient time understanding all the requirements. This will help make your research process more efficient and effective. Check your subject information such as task sheets, criteria sheets and any additional information that may be in your subject portal online. Seek clarification from your lecturer or tutor if you are still unsure about how to begin your assignments.
The task sheet typically provides key information about an assessment including the assignment question. It can be helpful to scan this document for topic, task and limiting words to ensure that you fully understand the concepts you are required to research, how to approach the assignment, and the scope of the task you have been set. These words can typically be found in your assignment question and are outlined in more detail in the two tables below (see Table 19.1 and Table 19.2 ).
Table 19.1 Parts of an Assignment Question
Make sure you have a clear understanding of what the task word requires you to address.
Table 19.2 Task words
The criteria sheet , also known as the marking sheet or rubric, is another important document to look at before you begin your assignment. The criteria sheet outlines how your assignment will be marked and should be used as a checklist to make sure you have included all the information required.
The task or criteria sheet will also include the:
- Word limit (or word count)
- Referencing style and research expectations
- Formatting requirements
Task analysis and criteria sheets are also discussed in the chapter Managing Assessments for a more detailed discussion on task analysis, criteria sheets, and marking rubrics.
Preparing your ideas
Brainstorm or concept map: List possible ideas to address each part of the assignment task based on what you already know about the topic from lectures and weekly readings.
Finding appropriate information: Learn how to find scholarly information for your assignments which is
See the chapter Working With Information for a more detailed explanation .
What is academic writing?
Academic writing tone and style.
Many of the assessment pieces you prepare will require an academic writing style. This is sometimes called ‘academic tone’ or ‘academic voice’. This section will help you to identify what is required when you are writing academically (see Table 19.3 ). The best way to understand what academic writing looks like, is to read broadly in your discipline area. Look at how your course readings, or scholarly sources, are written. This will help you identify the language of your discipline field, as well as how other writers structure their work.
Table 19.3 Comparison of academic and non-academic writing
Thesis statements.
Essays are a common form of assessment that you will likely encounter during your university studies. You should apply an academic tone and style when writing an essay, just as you would in in your other assessment pieces. One of the most important steps in writing an essay is constructing your thesis statement. A thesis statement tells the reader the purpose, argument or direction you will take to answer your assignment question. A thesis statement may not be relevant for some questions, if you are unsure check with your lecturer. The thesis statement:
- Directly relates to the task . Your thesis statement may even contain some of the key words or synonyms from the task description.
- Does more than restate the question.
- Is specific and uses precise language.
- Let’s your reader know your position or the main argument that you will support with evidence throughout your assignment.
- The subject is the key content area you will be covering.
- The contention is the position you are taking in relation to the chosen content.
Your thesis statement helps you to structure your essay. It plays a part in each key section: introduction, body and conclusion.
Planning your assignment structure

When planning and drafting assignments, it is important to consider the structure of your writing. Academic writing should have clear and logical structure and incorporate academic research to support your ideas. It can be hard to get started and at first you may feel nervous about the size of the task, this is normal. If you break your assignment into smaller pieces, it will seem more manageable as you can approach the task in sections. Refer to your brainstorm or plan. These ideas should guide your research and will also inform what you write in your draft. It is sometimes easier to draft your assignment using the 2-3-1 approach, that is, write the body paragraphs first followed by the conclusion and finally the introduction.
Writing introductions and conclusions
Clear and purposeful introductions and conclusions in assignments are fundamental to effective academic writing. Your introduction should tell the reader what is going to be covered and how you intend to approach this. Your conclusion should summarise your argument or discussion and signal to the reader that you have come to a conclusion with a final statement. These tips below are based on the requirements usually needed for an essay assignment, however, they can be applied to other assignment types.
Writing introductions

Most writing at university will require a strong and logically structured introduction. An effective introduction should provide some background or context for your assignment, clearly state your thesis and include the key points you will cover in the body of the essay in order to prove your thesis.
Usually, your introduction is approximately 10% of your total assignment word count. It is much easier to write your introduction once you have drafted your body paragraphs and conclusion, as you know what your assignment is going to be about. An effective introduction needs to inform your reader by establishing what the paper is about and provide four basic things:
- A brief background or overview of your assignment topic
- A thesis statement (see section above)
- An outline of your essay structure
- An indication of any parameters or scope that will/ will not be covered, e.g. From an Australian perspective.
The below example demonstrates the four different elements of an introductory paragraph.
1) Information technology is having significant effects on the communication of individuals and organisations in different professions. 2) This essay will discuss the impact of information technology on the communication of health professionals. 3) First, the provision of information technology for the educational needs of nurses will be discussed. 4) This will be followed by an explanation of the significant effects that information technology can have on the role of general practitioner in the area of public health. 5) Considerations will then be made regarding the lack of knowledge about the potential of computers among hospital administrators and nursing executives. 6) The final section will explore how information technology assists health professionals in the delivery of services in rural areas . 7) It will be argued that information technology has significant potential to improve health care and medical education, but health professionals are reluctant to use it.
1 Brief background/ overview | 2 Indicates the scope of what will be covered | 3-6 Outline of the main ideas (structure) | 7 The thesis statement
Note : The examples in this document are taken from the University of Canberra and used under a CC-BY-SA-3.0 licence.
Writing conclusions
You should aim to end your assignments with a strong conclusion. Your conclusion should restate your thesis and summarise the key points you have used to prove this thesis. Finish with a key point as a final impactful statement. Similar to your introduction, your conclusion should be approximately 10% of the total assignment word length. If your assessment task asks you to make recommendations, you may need to allocate more words to the conclusion or add a separate recommendations section before the conclusion. Use the checklist below to check your conclusion is doing the right job.
Conclusion checklist
- Have you referred to the assignment question and restated your argument (or thesis statement), as outlined in the introduction?
- Have you pulled together all the threads of your essay into a logical ending and given it a sense of unity?
- Have you presented implications or recommendations in your conclusion? (if required by your task).
- Have you added to the overall quality and impact of your essay? This is your final statement about this topic; thus, a key take-away point can make a great impact on the reader.
- Remember, do not add any new material or direct quotes in your conclusion.
This below example demonstrates the different elements of a concluding paragraph.
1) It is evident, therefore, that not only do employees need to be trained for working in the Australian multicultural workplace, but managers also need to be trained. 2) Managers must ensure that effective in-house training programs are provided for migrant workers, so that they become more familiar with the English language, Australian communication norms and the Australian work culture. 3) In addition, Australian native English speakers need to be made aware of the differing cultural values of their workmates; particularly the different forms of non-verbal communication used by other cultures. 4) Furthermore, all employees must be provided with clear and detailed guidelines about company expectations. 5) Above all, in order to minimise communication problems and to maintain an atmosphere of tolerance, understanding and cooperation in the multicultural workplace, managers need to have an effective knowledge about their employees. This will help employers understand how their employee’s social conditioning affects their beliefs about work. It will develop their communication skills to develop confidence and self-esteem among diverse work groups. 6) The culturally diverse Australian workplace may never be completely free of communication problems, however, further studies to identify potential problems and solutions, as well as better training in cross cultural communication for managers and employees, should result in a much more understanding and cooperative environment.
1 Reference to thesis statement – In this essay the writer has taken the position that training is required for both employees and employers . | 2-5 Structure overview – Here the writer pulls together the main ideas in the essay. | 6 Final summary statement that is based on the evidence.
Note: The examples in this document are taken from the University of Canberra and used under a CC-BY-SA-3.0 licence.
Writing paragraphs
Paragraph writing is a key skill that enables you to incorporate your academic research into your written work. Each paragraph should have its own clearly identified topic sentence or main idea which relates to the argument or point (thesis) you are developing. This idea should then be explained by additional sentences which you have paraphrased from good quality sources and referenced according to the recommended guidelines of your subject (see the chapter Working with Information ). Paragraphs are characterised by increasing specificity; that is, they move from the general to the specific, increasingly refining the reader’s understanding. A common structure for paragraphs in academic writing is as follows.
Topic Sentence
This is the main idea of the paragraph and should relate to the overall issue or purpose of your assignment is addressing. Often it will be expressed as an assertion or claim which supports the overall argument or purpose of your writing.
Explanation/ Elaboration
The main idea must have its meaning explained and elaborated upon. Think critically, do not just describe the idea.
These explanations must include evidence to support your main idea. This information should be paraphrased and referenced according to the appropriate referencing style of your course.
Concluding sentence (critical thinking)
This should explain why the topic of the paragraph is relevant to the assignment question and link to the following paragraph.
Use the checklist below to check your paragraphs are clear and well formed.
Paragraph checklist
- Does your paragraph have a clear main idea?
- Is everything in the paragraph related to this main idea?
- Is the main idea adequately developed and explained?
- Do your sentences run together smoothly?
- Have you included evidence to support your ideas?
- Have you concluded the paragraph by connecting it to your overall topic?
Writing sentences
Make sure all the sentences in your paragraphs make sense. Each sentence must contain a verb to be a complete sentence. Avoid sentence fragments . These are incomplete sentences or ideas that are unfinished and create confusion for your reader. Avoid also run on sentences . This happens when you join two ideas or clauses without using the appropriate punctuation. This also confuses your meaning (See the chapter English Language Foundations for examples and further explanation).
Use transitions (linking words and phrases) to connect your ideas between paragraphs and make your writing flow. The order that you structure the ideas in your assignment should reflect the structure you have outlined in your introduction. Refer to transition words table in the chapter English Language Foundations.
Paraphrasing and Synthesising
Paraphrasing and synthesising are powerful tools that you can use to support the main idea of a paragraph. It is likely that you will regularly use these skills at university to incorporate evidence into explanatory sentences and strengthen your essay. It is important to paraphrase and synthesise because:
- Paraphrasing is regarded more highly at university than direct quoting.
- Paraphrasing can also help you better understand the material.
- Paraphrasing and synthesising demonstrate you have understood what you have read through your ability to summarise and combine arguments from the literature using your own words.
What is paraphrasing?
Paraphrasing is changing the writing of another author into your words while retaining the original meaning. You must acknowledge the original author as the source of the information in your citation. Follow the steps in this table to help you build your skills in paraphrasing (see Table 19.4 ).
Table 19.4 Paraphrasing techniques
Example of paraphrasing.
Please note that these examples and in text citations are for instructional purposes only.
Original text
Health care professionals assist people often when they are at their most vulnerable . To provide the best care and understand their needs, workers must demonstrate good communication skills . They must develop patient trust and provide empathy to effectively work with patients who are experiencing a variety of situations including those who may be suffering from trauma or violence, physical or mental illness or substance abuse (French & Saunders, 2018).
Poor quality paraphrase example
This is a poor example of paraphrasing. Some synonyms have been used and the order of a few words changed within the sentences however the colours of the sentences indicate that the paragraph follows the same structure as the original text.
Health care sector workers are often responsible for vulnerable patients. To understand patients and deliver good service , they need to be excellent communicators . They must establish patient rapport and show empathy if they are to successfully care for patients from a variety of backgrounds and with different medical, psychological and social needs (French & Saunders, 2018).
A good quality paraphrase example
This example demonstrates a better quality paraphrase. The author has demonstrated more understanding of the overall concept in the text by using the keywords as the basis to reconstruct the paragraph. Note how the blocks of colour have been broken up to see how much the structure has changed from the original text.
Empathetic communication is a vital skill for health care workers. Professionals in these fields are often responsible for patients with complex medical, psychological and social needs. Empathetic communication assists in building rapport and gaining the necessary trust to assist these vulnerable patients by providing appropriate supportive care (French & Saunders, 2018).
The good quality paraphrase example demonstrates understanding of the overall concept in the text by using key words as the basis to reconstruct the paragraph. Note how the blocks of colour have been broken up, which indicates how much the structure has changed from the original text.
What is synthesising?
Synthesising means to bring together more than one source of information to strengthen your argument. Once you have learnt how to paraphrase the ideas of one source at a time, you can consider adding additional sources to support your argument. Synthesis demonstrates your understanding and ability to show connections between multiple pieces of evidence to support your ideas and is a more advanced academic thinking and writing skill.
Follow the steps in this table to improve your synthesis techniques (see Table 19.5 ).
Table 19.5 Synthesising techniques
Example of synthesis
There is a relationship between academic procrastination and mental health outcomes. Procrastination has been found to have a negative effect on students’ well-being (Balkis, & Duru, 2016). Yerdelen, McCaffrey, and Klassens’ (2016) research results suggested that there was a positive association between procrastination and anxiety. This was corroborated by Custer’s (2018) findings which indicated that students with higher levels of procrastination also reported greater levels of the anxiety. Therefore, it could be argued that procrastination is an ineffective learning strategy that leads to increased levels of distress.
Topic sentence | Statements using paraphrased evidence | Critical thinking (student voice) | Concluding statement – linking to topic sentence
This example demonstrates a simple synthesis. The author has developed a paragraph with one central theme and included explanatory sentences complete with in-text citations from multiple sources. Note how the blocks of colour have been used to illustrate the paragraph structure and synthesis (i.e., statements using paraphrased evidence from several sources). A more complex synthesis may include more than one citation per sentence.
Creating an argument
What does this mean.
Throughout your university studies, you may be asked to ‘argue’ a particular point or position in your writing. You may already be familiar with the idea of an argument, which in general terms means to have a disagreement with someone. Similarly, in academic writing, if you are asked to create an argument, this means you are asked to have a position on a particular topic, and then justify your position using evidence.
What skills do you need to create an argument?
In order to create a good and effective argument, you need to be able to:
- Read critically to find evidence
- Plan your argument
- Think and write critically throughout your paper to enhance your argument
For tips on how to read and write critically, refer to the chapter Thinking for more information. A formula for developing a strong argument is presented below.
A formula for a good argument
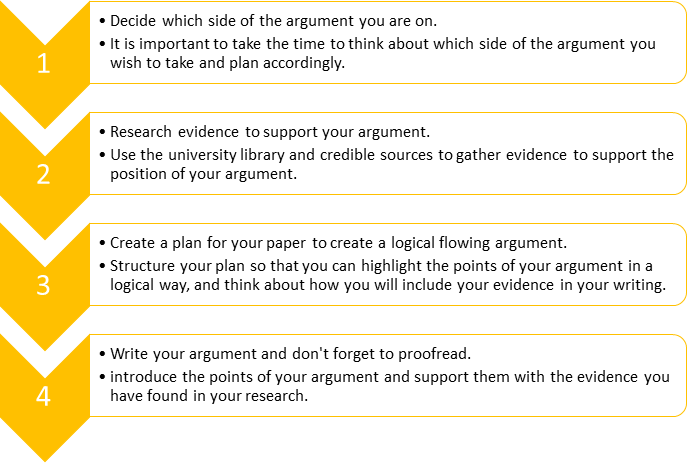
What does an argument look like?
As can be seen from the figure above, including evidence is a key element of a good argument. While this may seem like a straightforward task, it can be difficult to think of wording to express your argument. The table below provides examples of how you can illustrate your argument in academic writing (see Table 19.6 ).
Table 19.6 Argument
Editing and proofreading (reviewing).
Once you have finished writing your first draft it is recommended that you spend time revising your work. Proofreading and editing are two different stages of the revision process.
- Editing considers the overall focus or bigger picture of the assignment
- Proofreading considers the finer details
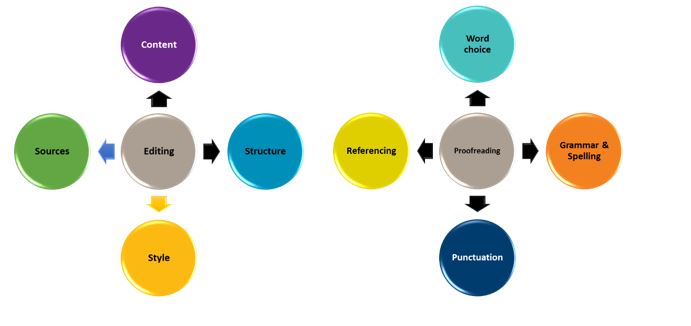
As can be seen in the figure above there are four main areas that you should review during the editing phase of the revision process. The main things to consider when editing include content, structure, style, and sources. It is important to check that all the content relates to the assignment task, the structure is appropriate for the purposes of the assignment, the writing is academic in style, and that sources have been adequately acknowledged. Use the checklist below when editing your work.
Editing checklist
- Have I answered the question accurately?
- Do I have enough credible, scholarly supporting evidence?
- Is my writing tone objective and formal enough or have I used emotive and informal language?
- Have I written in the third person not the first person?
- Do I have appropriate in-text citations for all my information?
- Have I included the full details for all my in-text citations in my reference list?
There are also several key things to look out for during the proofreading phase of the revision process. In this stage it is important to check your work for word choice, grammar and spelling, punctuation and referencing errors. It can be easy to mis-type words like ‘from’ and ‘form’ or mix up words like ‘trail’ and ‘trial’ when writing about research, apply American rather than Australian spelling, include unnecessary commas or incorrectly format your references list. The checklist below is a useful guide that you can use when proofreading your work.
Proofreading checklist
- Is my spelling and grammar accurate?
- Are they complete?
- Do they all make sense?
- Do they only contain only one idea?
- Do the different elements (subject, verb, nouns, pronouns) within my sentences agree?
- Are my sentences too long and complicated?
- Do they contain only one idea per sentence?
- Is my writing concise? Take out words that do not add meaning to your sentences.
- Have I used appropriate discipline specific language but avoided words I don’t know or understand that could possibly be out of context?
- Have I avoided discriminatory language and colloquial expressions (slang)?
- Is my referencing formatted correctly according to my assignment guidelines? (for more information on referencing refer to the Managing Assessment feedback section).
This chapter has examined the experience of writing assignments. It began by focusing on how to read and break down an assignment question, then highlighted the key components of essays. Next, it examined some techniques for paraphrasing and summarising, and how to build an argument. It concluded with a discussion on planning and structuring your assignment and giving it that essential polish with editing and proof-reading. Combining these skills and practising them, can greatly improve your success with this very common form of assessment.
- Academic writing requires clear and logical structure, critical thinking and the use of credible scholarly sources.
- A thesis statement is important as it tells the reader the position or argument you have adopted in your assignment. Not all assignments will require a thesis statement.
- Spending time analysing your task and planning your structure before you start to write your assignment is time well spent.
- Information you use in your assignment should come from credible scholarly sources such as textbooks and peer reviewed journals. This information needs to be paraphrased and referenced appropriately.
- Paraphrasing means putting something into your own words and synthesising means to bring together several ideas from sources.
- Creating an argument is a four step process and can be applied to all types of academic writing.
- Editing and proofreading are two separate processes.
Academic Skills Centre. (2013). Writing an introduction and conclusion . University of Canberra, accessed 13 August, 2013, http://www.canberra.edu.au/studyskills/writing/conclusions
Balkis, M., & Duru, E. (2016). Procrastination, self-regulation failure, academic life satisfaction, and affective well-being: underregulation or misregulation form. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 31 (3), 439-459.
Custer, N. (2018). Test anxiety and academic procrastination among prelicensure nursing students. Nursing education perspectives, 39 (3), 162-163.
Yerdelen, S., McCaffrey, A., & Klassen, R. M. (2016). Longitudinal examination of procrastination and anxiety, and their relation to self-efficacy for self-regulated learning: Latent growth curve modeling. Educational Sciences: Theory & Practice, 16 (1).
Writing Assignments Copyright © 2021 by Kate Derrington; Cristy Bartlett; and Sarah Irvine is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Assignment Biography: Student Criteria and Rubric for Writing
Researching an Individual Aligned to Common Core Writing Standards
- Tips & Strategies
- An Introduction to Teaching
- Policies & Discipline
- Community Involvement
- School Administration
- Technology in the Classroom
- Teaching Adult Learners
- Issues In Education
- Teaching Resources
- Becoming A Teacher
- Assessments & Tests
- Elementary Education
- Secondary Education
- Special Education
- Homeschooling
- M.A., English, Western Connecticut State University
- B.S., Education, Southern Connecticut State University
The genre of biography can also be categorized in the sub-genre of narrative nonfiction/historical nonfiction. When a teacher assigns a biography as a writing assignment, the purpose is to have a student utilize multiple research tools to gather and to synthesize information that may be used as evidence in a written report about an individual. The evidence gained from research can include a person’s words, actions, journals, reactions, related books, interviews with friends, relatives, associates, and enemies. The historical context is equally important. Since there are people who have influenced every academic discipline, assigning a biography can be a cross-disciplinary or inter-disciplinary writing assignment.
Middle and high school teachers should allow students to have a choice in selecting the subject for a biography. Providing student choice, particularly for students in grades 7-12, increases their engagement and their motivation especially if students select individuals they care about. Students would find it difficult to write about a person they do not like. Such an attitude compromises the process of researching and writing the biography.
According to by Judith L. Irvin, Julie Meltzer and Melinda S. Dukes in their book Taking Action on Adolescent Literacy:
"As humans, we are motivated to engage when we are interested or have real purpose for doing so. So motivation to engage [students] is the first step on the road to improving literacy habits and skills" (Chapter 1).
Students should find at least three different sources (if possible) to make sure the biography is accurate. A good biography is well-balanced and objective. That means if there is disagreement between sources, the student can use the evidence to state that there is a conflict. Students should know that a good biography is more than a timeline of events in a person's life.
The context of a person's life is important. Students should include information about the historical time period in which a subject lived and did her/his work.
In addition, the student should have a purpose for researching another person's life. For example, the purpose for a student to research and write a biography can be in a response to the prompt:
"How does this writing this biography help me to understand the influence of this person on history, and quite possibly, this person's impact on me?"
The following standards-based criteria and scoring rubrics can be used to grade a student-selected biography. Both criteria and rubrics should be given to students before they begin their work.
Criteria for a Student Biography aligned to Common Core State Standards
A General Outline for Biography Details
- Birthdate /Birthplace
- Death (if applicable).
- Family Members.
- Miscellaneous (religion, titles, etc).
Education/Influences
- Schooling.Training.
- Work Experiences.
- Contemporaries/Relationships.
Accomplishments/ Significance
- Evidence of major accomplishments.
- Evidence of minor accomplishments (if relevant).
- The analysis that supports why the individual was worthy of note in their field of expertise during his or her life.
- Analysis why this individual is worthy of note in their field of expertise today.
Quotes/Publications
- Statements made.
- Works published.
Biography Organization using the CCSS Anchor Writing Standards
- Transitions are effective in assisting the reader to understand shifts.
- Ideas within each paragraph are fully developed.
- Each point is supported by evidence.
- All evidence is relevant.
- Important terms are explained to the reader.
- Purpose of each paragraph (introduction, body paragraphs, conclusion) is clear.
- Clear relationship between topic sentence(s) and paragraph(s) that came before is evident.
Grading Rubric: Holistic Standards with Letter Grade Conversions
(based on extended response Smarter Balanced Assessment writing rubric)
Score: 4 or Letter Grade: A
Student response is a thorough elaboration of the support/evidence on the topic (individual) including the effective use of source material. The response clearly and effectively develops ideas, using precise language:
- Comprehensive evidence (facts and details) from source materials are integrated.
- Relevant, and specific clear citations or attribution to source materials.
- Effective use of a variety of elaborative techniques.
- Vocabulary is clearly appropriate for the audience and purpose.
- Effective, appropriate style enhances content.
Score: 3 Letter Grade: B
Student response is an adequate elaboration of the support/evidence in the biography that includes the use of source materials. The student response adequately develops ideas, employing a mix of precise and more general language:
- Adequate evidence (facts and details) from the source materials is integrated and relevant, yet the evidence and explanation may be general.
- Adequate use of citations or attribution to the source material.
- Adequate use of some elaborative techniques.
- Vocabulary is generally appropriate for the audience and purpose.
- The style is generally appropriate for the audience and purpose.
Score: 2 Letter Grade: C
Student response is uneven with a cursory elaboration of the support/evidence in the biography that includes the uneven or limited use of source material. The student response develops ideas unevenly, using simplistic language:
- Some evidence (facts and details) from the source materials may be weakly integrated, imprecise, repetitive, vague, and/or copied.
- Weak use of citations or attribution to source materials.
- Weak or uneven use of elaborative techniques.
- Development may consist primarily of source summaries.
- Vocabulary use is uneven or somewhat ineffective for the audience and purpose.
- Inconsistent or weak attempt to create the appropriate style.
Score: 1 Letter Grade: D
Student response provides a minimal elaboration of the support/evidence in the biography that includes little or no use of source material. The student response is vague, lacks clarity, or is confusing:
- Evidence (facts and details) from the source material is minimal, irrelevant, absent, incorrectly used.
- Insufficient use of citations or attribution to the source material.
- Minimal, if any, use of elaborative techniques.
- Vocabulary is limited or ineffective for the audience and purpose.
- Little or no evidence of appropriate style.
- Insufficient or plagiarized (copied without credit) text.
- Off-topic.
- Off-purpose.
- Pros and Cons to Flexible Grouping in Middle and High School
- Grading for Proficiency in the World of 4.0 GPAs
- What Is an Annotated Bibliography?
- How to Write an Interesting Biography
- T.E.S.T. Season for Grades 7-12
- Topics for a Lesson Plan Template
- The Whys and How-tos for Group Writing in All Content Areas
- How to Create a Rubric in 6 Steps
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
- Beef Up Critical Thinking and Writing Skills: Comparison Essays
- What Is Plagiarism?
- 10 Test Question Terms and What They Ask Students to Do
- Higher Level Thinking: Synthesis in Bloom's Taxonomy
- What Is a Rubric?
- Writing Prompt (Composition)
- Rubrics - Quick Guide for all Content Areas

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Your professor may use a slightly different rubric, but the standard rubric at AUR will assess your writing according to the following standards: A (4) B (3) C (2) D/F (1/0) Focus: Purpose. Purpose is clear. Shows awareness of purpose. Shows limited awareness of purpose.
Disadvantage of analytic rubrics: Requires more work for instructors writing feedback. Step 3 (Optional): Look for templates and examples. ... Step 4: Define the assignment criteria. Make a list of the knowledge and skills are you measuring with the assignment/assessment Refer to your stated learning objectives, the assignment instructions ...
Additional tips for writing an Assignment Prompt. Consider the learning objectives for the unit and which ones you'd like to assess in this writing assignment. ... A rubric is the evaluation and grading criteria created for an assignment, especially a detailed assignment such as a written assignment. A rubric will indicate what the instructor ...
Writing rubrics can help address the concerns of both faculty and students by making writing assessment more efficient, consistent, and public. Whether it is called a grading rubric, a grading sheet, or a scoring guide, a writing assignment rubric lists criteria by which the writing is graded.
Here is a sample of a rubric with a range of points within each performance level. Step 4: Create a format for the rubric. When the specific criteria and levels of success have been named and ranked, they can be sorted into a variety of formats and distributed with the assignment.
Rubrics are tools for communicating grading criteria and assessing student progress. Rubrics take a variety of forms, from grids to checklists, and measure a range of writing tasks, from conceptual design to sentence-level considerations. As with any assessment tool, a rubric's effectiveness is entirely dependent upon its design and its ...
criteria: the aspects of performance (e.g., argument, evidence, clarity) that will be assessed; ... Example 3: Anthropology Writing Assignments This rubric was designed for a series of short writing assignments in anthropology (Carnegie Mellon). Example 4: History Research Paper. This rubric was designed for essays and research papers in ...
Step One: Identifying Criteria. The first step involved in creating assignment-specific rubrics is revisiting an assignment's intended outcomes. These objectives can be considered, prioritized, and reworded to create a rubric's criteria. If, for example, an instructor assigns a literature review hoping that students might become skilled at ...
Designing Writing Assignments designing-assignments. As you think about creating writing assignments, use these five principles: Tie the writing task to specific pedagogical goals. Note rhetorical aspects of the task, i.e., audience, purpose, writing situation. Make all elements of the task clear. Include grading criteria on the assignment ...
Read more about sequencing assignments. Clear criteria will help students connect an assignment's relevance to larger scale course outcomes. The literature on assignment design strongly encourages instructors to make the grading criteria explicit to students before the assignment is collected and assessed. ... (Re)Designing a Writing ...
Holistic scoring is a quick method of evaluating a composition based on the reader's general impression of the overall quality of the writing—you can generally read a student's composition and assign a score to it in two or three minutes. Holistic scoring is usually based on a scale of 0-4, 0-5, or 0-6.
Prioritize the criteria for a particular assignment over the criteria listed in the section below. When an assignment comes with a rubric, study the rubric and familiarize yourself with it. Aside from your professor, this is the best guide to successfully meeting the assignment requirements. Prioritize your professor's advice above all.
Use with feedback on previous assignments to help identify strengths and areas to improve (also see the Feedback box). Use them while writing assignments to remind you what markers are looking for. If you have questions about the marking criteria, ask your module tutor, your academic supervisor, or book a Writing Centre appointment.
1. Writing Assessment Scale 2. Writing Assessment subscales 1. Assessment criteria 2. Assessment categories Each piece of writing gets four sets of marks for each of the subscales, from 0 (lowest) to 5 (highest). Bands (0-5) marks / scores / grades These terms are commonly used to refer to Cambridge English Qualifications. There are also some
Understanding what you need to do. First, carefully read the assignment sheet and search for the required page length, due dates, and other submission-based information. Second, determine the genre of the assignment. Third, identify the core assignment questions that you need to answer. Fourth, locate the evaluation and grading criteria.
Writing is coherent and logically organized with transitions used between ideas and paragraphs to create coherence. Overall unity of ideas is present. Writing shows high degree of attention to logic and reasoning of points. Unity clearly leads the reader to the conclusion and stirs thought regarding the topic.
Many instructors write their assignment prompts differently. By following a few steps, you can better understand the requirements for the assignment. The best way, as always, is to ask the instructor about anything confusing. Read the prompt the entire way through once. This gives you an overall view of what is going on.
Many assignment sheets contain a grading rubric or some other indication of evaluation criteria for the assignment. You can use these criteria to both begin the writing process and to guide your revision and editing process. If you do not see any rubric or evaluation criteria on the assignment sheet — ask! Recognizing Disciplinary ...
The criteria sheet, also known as the marking sheet or rubric, is another important document to look at before you begin your assignment. The criteria sheet outlines how your assignment will be marked and should be used as a checklist to make sure you have included all the information required. The task or criteria sheet will also include the:
When a teacher assigns a biography as a writing assignment, the purpose is to have a student utilize multiple research tools to gather and to synthesize information that may be used as evidence in a written report about an individual. The evidence gained from research can include a person's words, actions, journals, reactions, related books ...
Before writing assessment criteria it is important to understand how assessment criteria relate to course design. The following diagram illustrates how assessment criteria both inform and are informed by ... Imagine what the ideal assignment (that aligns with the learning outcome(s)) would look like and list all the elements it should contain.