📕 Studying HQ
Ultimate guide to writing a reflective essay, carla johnson.
- June 14, 2023
- Essay Topics and Ideas , How to Guides
Writing about yourself is a powerful way to learn and grow as a person. It is a type of writing that makes you think about your thoughts, feelings, and experiences and how they have affected your personal and professional growth. A reflective essay is a type of writing that lets you talk about your own experiences, thoughts, and insights. In this article , we’ll tell you everything you need to know about writing a reflective essay, from how to define it and figure out what it’s for to how to do it well.
What You'll Learn

Definition of a Reflective Essay
A reflective essay is a type of writing in which you write about your own thoughts, feelings, and experiences. It is a type of personal writing that lets you talk about your own thoughts and experiences and share them with other people. Students are often asked to write reflective essays for school, but they can also be used for personal or professional growth.
Purpose of a Reflective Essay
The goal of a reflective essay is to get you to think about your life and how it has affected your personal and professional growth. Reflective essays can help you learn more about yourself and your experiences, as well as find places where you can grow and improve. They can also help you get better at writing and better at getting your ideas across.
Importance of Reflective Writing
Writing about yourself and your work is an important way to grow personally and professionally. It can help you learn more about yourself, figure out where you need to grow and change, and learn more about how you think and feel. Writing about yourself can also help you get better at critical thinking and analysis , and it can help you get your ideas across better. It is a useful tool for anyone who wants to grow personally and professionally, and it can be used in many different situations, from academic writing to keeping a personal journal.
Writing about yourself and your work is a powerful way to grow personally and professionally. Reflective essays give you a chance to think about your own life and how it has affected your personal and professional growth. By writing about your thoughts and feelings, you can learn more about them, find ways to grow and improve, and improve your writing and communication skills . In the next parts of this article, we’ll show you how to write a good reflective essay step by step, from choosing a topic and organizing your thoughts to writing and revising your essay.
Elements of a Reflective Essay
A reflective essay is a type of writing that allows you to reflect on your personal experiences, thoughts, and feelings. There are several essential elements that should be included in a reflective essay to ensure that it is effective in conveying your personal reflections and experiences.
Personal Reflection
The first essential element of a reflective essay is personal reflection. This involves exploring your own thoughts and feelings about the experience you are reflecting on. It is important to be honest and open about your thoughts and feelings, as this will make your essay more authentic and meaningful.
Description of the Experience
The second element of a reflective essay is a description of the experience that you are reflecting on. This includes providing details about the experience, such as where it took place, who was involved, and what happened. The description should be clear and concise, and should provide enough detail for the reader to understand the context of your reflection.
Analysis of the Experience
The third element of a reflective essay is analysis of the experience. This involves exploring the experience in more depth, and examining your thoughts and feelings about it. You should consider what you learned from the experience, and how it impacted your personal and professional growth .
Evaluation of the Experience
The fourth element of a reflective essay is evaluation of the experience. This involves examining the experience from different perspectives, and considering its strengths and weaknesses. You should reflect on what you would do differently if you were in the same situation again, and how you could improve your response or approach.
Identification of Key Learning
The fifth element of a reflective essay is identifying the key learning that you gained from the experience. This involves reflecting on the insights and lessons that you learned from the experience, and how these have impacted your personal and professional growth. This can include new skills, knowledge, or perspectives that you gained from the experience.
Planning for Future Action
The final element of a reflective essay is planning for future action. This involves considering how you can apply the lessons and insights gained from the experience to improve your future actions. You should reflect on how you can use what you learned to approach similar situations differently in the future.
How to Write a Reflective Essay
Writing a reflective essay can be a challenging task, but by following a few simple steps, you can write an effective and meaningful essay .
Steps for Writing a Reflective Essay:
1. Brainstorming and Selecting a Topic
Begin by brainstorming and selecting a topic for your reflective essay. Think about a personal experience or event that had a significant impact on your personal or professional growth.
2. Creating an Outline
Create an outline for your essay . This should include an introduction, body, and conclusion, as well as sections for each of the essential elements described above.
3. Writing the Introduction
Write the introduction for your essay . This should include a brief overview of the experience that you will be reflecting on, as well as the purpose and focus of your essay.
4. Writing the Body
Write the body of your essay, which should include the personal reflection, description of the experience, analysis of the experience, evaluation of the experience, identification of key learning, and planning for future action . Make sure to use specific examples and details to support your reflection.
5. Writing the Conclusion
Write the conclusion for your essay , which should summarize the key points of your reflection and provide closure for the reader. You can also include a final reflection on the experience and what it means to you.
6. Revising and Editing
Pay close attention to grammar, spelling, and sentence structure as you reread and edit your essay . Make sure your essay is easy to read and flows well. You might also want someone else to look over your essay and give you feedback and ideas.
If you follow these steps, you should be able to write a good reflective essay. Remember to be honest and open about your thoughts and feelings, and to support your reflection with specific examples and details. You can become a good reflective writer with practice , and you can use this skill to help your personal and professional growth.
Reflective Essay Topics
Reflective essays can be written on a wide range of topics, as they are based on personal experiences and reflections. Here are some common categories of reflective essay topics:
Personal Experiences
– A time when you overcame a personal challenge
– A difficult decision you had to make
– A significant event in your life that changed you
– A moment when you learned an important lesson
– A relationship that had a significant impact on you
Professional Experiences
– A challenging project or assignment at work
– A significant accomplishment or success in your career
– A time when you had to deal with a difficult colleague or boss
– A failure or setback in your career and what you learned from it
– A career change or transition that had a significant impact on you
Academic Experiences
– A challenging course or assignment in school
– A significant accomplishment or success in your academic career
– A time when you struggled with a particular subject or topic and how you overcame it
– A research project or paper that had a significant impact on you
– A teacher or mentor who had a significant impact on your academic career
Cultural Experiences
– A significant trip or travel experience
– A significant cultural event or celebration you participated in
– A time when you experienced culture shock
– A significant interaction with someone from a different culture
– A time when you learned something new about a different culture and how it impacted you
Social Issues
– A personal experience with discrimination or prejudice
– A time when you volunteered or worked for a social cause or organization
– A significant event or moment related to a social issue (e.g. protest, rally, community event)
– A time when you had to confront your own biases or privilege
– A social issue that you are passionate about and how it has impacted you personally
Reflective Essay Examples
Example 1: Reflecting on a Personal Challenge
In this reflective essay, the writer reflects on a personal challenge they faced and how they overcame it. They explore their thoughts, feelings, and actions during this time, and reflect on the lessons they learned from the experience.
Example 2: Reflecting on a Professional Experience
In this reflective essay, the writer reflects on a challenging project they worked on at work and how they overcame obstacles to successfully complete it. They explore their thoughts and feelings about the experience and reflect on the skills and knowledge they gained from it.
Example 3: Reflecting on an Academic Assignment
In this reflective essay, the writer reflects on a challenging academic assignment they completed and how they overcame difficulties to successfully complete it. They explore their thoughts and feelings about the experience and reflect on the skills and knowledge they gained from it.
Example 4: Reflecting on a Cultural Experience
In this reflective essay, the writer reflects on a significant cultural experience they had, such as traveling to a new country or participating in a cultural event. Theyexplore their thoughts and feelings about the experience, reflect on what they learned about the culture, and how it impacted them personally.
Example 5: Reflecting on a Social Issue
In this reflective essay, the writer reflects on their personal experiences with discrimination or prejudice and how it impacted them. They explore their thoughts and feelings about the experience, reflect on what they learned about themselves and the issue, and how they can take action to address it.
These examples demonstrate how reflective essays can be used to explore a wide range of personal experiences and reflections. By exploring your own thoughts and feelings about an experience, you can gain insights into your personal and professional growth and identify areas for further development . Reflective writing is a powerful tool for self-reflection and personal growth, and it can be used in many different contexts to help you gain a deeper understanding of yourself and the world around you.
Reflective Essay Outline
A reflective essay should follow a basic outline that includes an introduction, body, and conclusion. Here is a breakdown of each section:
Introduction: The introduction should provide an overview of the experience you will be reflecting on and a preview of the key points you will be discussing in your essay .
Body: The body of the essay should include several paragraphs that explore your personal reflection, description of the experience, analysis of the experience, evaluation of the experience, identification of key learning, and planning for future action.
Conclusion: The conclusion should summarize the key points of your reflection and provide closure for the reader.
Reflective Essay Thesis
A reflective essay thesis is a statement that summarizes the main points of your essay and provides a clear focus for your writing. A strong thesis statement is essential for a successful reflective essay, as it helps to guide your writing and ensure that your essay is focused and coherent.
Importance of a Strong Thesis Statement
A strong thesis statement is important for several reasons. First, it provides a clear focus for your writing, which helps to ensure that your essay is coherent and well-organized. Second, it helps to guide your writing and ensure that you stay on topic throughout your essay . Finally, it helps to engage your reader and provide them with a clear understanding of what your essay is about.
Tips for Writing a Thesis Statement
To write a strong thesis statement for your reflective essay, follow these tips:
– Be clear and concise: Yourthesis statement should clearly state the main focus and purpose of your essay in a concise manner.
– Use specific language: Use specific language to describe the experience you will be reflecting on and the key points you will be discussing in your essay .
– Make it arguable: A strong thesis statement should be arguable and provide some insight or perspective on the experience you are reflecting on.
– Reflect on the significance: Reflect on the significance of the experience you are reflecting on and why it is important to you.
Reflective Essay Structure
The structure of a reflective essay is important for ensuring that your essay is well-organized and easy to read. A clear structure helps to guide the reader through your thoughts and reflections, and it makes it easier for them to understand your main points.
The Importance of a Clear Structure
A clear structure is important for several reasons. First, it helps to ensure that your essay is well-organized and easy to read. Second, it helps to guide your writing and ensure that you stay on topic throughout your essay. Finally, it helps to engage your reader and provide them with a clear understanding of the key points you are making.
Tips for Structuring a Reflective Essay
To structure your reflective essay effectively, follow these tips:
– Start with an introduction that provides an overview of the experience you are reflecting on and a preview of the key points you will be discussing in your essay .
– Use body paragraphs to explore your personal reflection, description of the experience, analysisof the experience, evaluation of the experience, identification of key learning, and planning for future action. Ensure that each paragraph has a clear focus and supports your thesis statement .
– Use transition words and phrases to connect your paragraphs and make your essay flow smoothly.
– End your essay with a conclusion that summarizes the key points of your reflection and provides closure for the reader.
– Consider using subheadings to organize your essay and make it more structured and easy to read.
By following these tips, you can create a clear and well-structured reflective essay that effectively communicates your personal experiences and reflections. Remember to use specific examples and details to support your reflection, and to keep your focus on the main topic and thesis statement of your essay .
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. what is a reflective essay.
A reflective essay is a type of writing that allows you to reflect on your personal experiences, thoughts, and feelings. It involves exploring your own thoughts and feelings about an experience, and reflecting on what you learned from it.
2. What are the elements of a reflective essay?
The essential elements of a reflective essay include personal reflection, description of the experience, analysis of the experience, evaluation of the experience, identification of key learning, and planning for future action.
3. How do I choose a topic for a reflective essay?
To choose a topic for a reflective essay, think about a personal experience or event that had a significant impact on your personal or professional growth. You may also consider professional experiences, academic experiences, cultural experiences, or social issues that have impacted you personally.
Reflective writing is a powerful tool for personal and professional development. By exploring your own thoughts and feelings about an experience, you can gain insights into your personal and professional growth and identify areas for further development. To write an effective reflective essay, it is important to follow a clear structure, use specific examples and details to support your reflection, and stay focused on the main topic and thesis statement of your essay . By following these tips and guidelines, you can become a skilled reflective writer and use this tool to improve your personal and professional growth.
Start by filling this short order form order.studyinghq.com
And then follow the progressive flow.
Having an issue, chat with us here
Cathy, CS.
New Concept ? Let a subject expert write your paper for You
Have a subject expert write for you now, have a subject expert finish your paper for you, edit my paper for me, have an expert write your dissertation's chapter, popular topics.
Business StudyingHq Essay Topics and Ideas How to Guides Samples
- Nursing Solutions
- Study Guides
- Free Study Database for Essays
- Privacy Policy
- Writing Service
- Discounts / Offers
Study Hub:
- Studying Blog
- Topic Ideas
- How to Guides
- Business Studying
- Nursing Studying
- Literature and English Studying
Writing Tools
- Citation Generator
- Topic Generator
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Conclusion Maker
- Research Title Generator
- Thesis Statement Generator
- Summarizing Tool
- Terms and Conditions
- Confidentiality Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Refund and Revision Policy
Our samples and other types of content are meant for research and reference purposes only. We are strongly against plagiarism and academic dishonesty.
Contact Us:
📞 +15512677917
2012-2024 © studyinghq.com. All rights reserved

What Is Reflective Writing? (Explained W/ 20+ Examples)
I’ll admit, reflecting on my experiences used to seem pointless—now, I can’t imagine my routine without it.
What is reflective writing?
Reflective writing is a personal exploration of experiences, analyzing thoughts, feelings, and learnings to gain insights. It involves critical thinking, deep analysis, and focuses on personal growth through structured reflection on past events.
In this guide, you’ll learn everything you need to know about reflective writing — with lots of examples.
What Is Reflective Writing (Long Description)?

Table of Contents
Reflective writing is a method used to examine and understand personal experiences more deeply.
This kind of writing goes beyond mere description of events or tasks.
Instead, it involves looking back on these experiences, analyzing them, and learning from them.
It’s a process that encourages you to think critically about your actions, decisions, emotions, and responses.
By reflecting on your experiences, you can identify areas for improvement, make connections between theory and practice, and enhance your personal and professional development. Reflective writing is introspective, but it should also be analytical and critical.
It’s not just about what happened.
It’s about why it happened, how it affected you, and what you can learn from it.
This type of writing is commonly used in education, professional development, and personal growth, offering a way for individuals to gain insights into their personal experiences and behaviors.
Types of Reflective Writing
Reflective writing can take many forms, each serving different purposes and providing various insights into the writer’s experiences.
Here are ten types of reflective writing, each with a unique focus and approach.
Journaling – The Daily Reflection
Journaling is a type of reflective writing that involves keeping a daily or regular record of experiences, thoughts, and feelings.
It’s a private space where you can freely express yourself and reflect on your day-to-day life.
Example: Today, I realized that the more I try to control outcomes, the less control I feel. Letting go isn’t about giving up; it’s about understanding that some things are beyond my grasp.
Example: Reflecting on the quiet moments of the morning, I realized how much I value stillness before the day begins. It’s a reminder to carve out space for peace in my routine.
Learning Logs – The Educational Tracker
Learning logs are used to reflect on educational experiences, track learning progress, and identify areas for improvement.
They often focus on specific learning objectives or outcomes.
Example: This week, I struggled with understanding the concept of reflective writing. However, after reviewing examples and actively engaging in the process, I’m beginning to see how it can deepen my learning.
Example: After studying the impact of historical events on modern society, I see the importance of understanding history to navigate the present. It’s a lesson in the power of context.
Critical Incident Journals – The Turning Point
Critical incident journals focus on a significant event or “critical incident” that had a profound impact on the writer’s understanding or perspective.
These incidents are analyzed in depth to extract learning and insights.
Example: Encountering a homeless person on my way home forced me to confront my biases and assumptions about homelessness. It was a moment of realization that has since altered my perspective on social issues.
Example: Missing a crucial deadline taught me about the consequences of procrastination and the value of time management. It was a wake-up call to prioritize and organize better.
Project Diaries – The Project Chronicle
Project diaries are reflective writings that document the progress, challenges, and learnings of a project over time.
They provide insights into decision-making processes and project management strategies.
Example: Launching the community garden project was more challenging than anticipated. It taught me the importance of community engagement and the value of patience and persistence.
Example: Overcoming unexpected technical issues during our project showed me the importance of adaptability and teamwork. Every obstacle became a stepping stone to innovation.
Portfolios – The Comprehensive Showcase
Portfolios are collections of work that also include reflective commentary.
They showcase the writer’s achievements and learning over time, reflecting on both successes and areas for development.
Example: Reviewing my portfolio, I’m proud of how much I’ve grown as a designer. Each project reflects a step in my journey, highlighting my evolving style and approach.
Example: As I added my latest project to my portfolio, I reflected on the journey of my skills evolving. Each piece is a chapter in my story of growth and learning.
Peer Reviews – The Collaborative Insight
Peer reviews involve writing reflectively about the work of others, offering constructive feedback while also considering one’s own learning and development.
Example: Reviewing Maria’s project, I admired her innovative approach, which inspired me to think more creatively about my own work. It’s a reminder of the value of diverse perspectives.
Example: Seeing the innovative approach my peer took on a similar project inspired me to rethink my own methods. It’s a testament to the power of sharing knowledge and perspectives.
Personal Development Plans – The Future Blueprint
Personal development plans are reflective writings that outline goals, strategies, and actions for personal or professional growth.
They include reflections on strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Example: My goal to become a more effective communicator will require me to step out of my comfort zone and seek opportunities to speak publicly. It’s daunting but necessary for my growth.
Example: Identifying my fear of public speaking in my plan pushed me to take a course on it. Acknowledging weaknesses is the first step to turning them into strengths.
Reflective Essays – The Structured Analysis
Reflective essays are more formal pieces of writing that analyze personal experiences in depth.
They require a structured approach to reflection, often including theories or models to frame the reflection.
Example: Reflecting on my leadership role during the group project, I applied Tuckman’s stages of group development to understand the dynamics at play. It helped me appreciate the natural progression of team development.
Example: In my essay, reflecting on a failed project helped me understand the role of resilience in success. Failure isn’t the opposite of success; it’s part of its process.
Reflective Letters – The Personal Correspondence
Reflective letters involve writing to someone (real or imagined) about personal experiences and learnings.
It’s a way to articulate thoughts and feelings in a structured yet personal format.
Example: Dear Future Self, Today, I learned the importance of resilience. Faced with failure, I found the strength to persevere a nd try again. This lesson, I hope, will stay with me as I navigate the challenges ahead.
Example: Writing a letter to my past self, I shared insights on overcoming challenges with patience and persistence. It’s a reminder of how far I’ve come and the hurdles I’ve overcome.
Blogs – The Public Journal
Blogs are a form of reflective writing that allows writers to share their experiences, insights, and learnings with a wider audience.
They often combine personal narrative with broader observations about life, work, or society.
Example: In my latest blog post, I explored the journey of embracing vulnerability. Sharing my own experiences of failure and doubt not only helped me process these feelings but also connected me with readers going through similar struggles. It’s a powerful reminder of the strength found in sharing our stories.
Example: In a blog post about starting a new career path, I shared the fears and excitement of stepping into the unknown. It’s a journey of self-discovery and embracing new challenges.
What Are the Key Features of Reflective Writing?
Reflective writing is characterized by several key features that distinguish it from other types of writing.
These features include personal insight, critical analysis, descriptive narrative, and a focus on personal growth.
- Personal Insight: Reflective writing is deeply personal, focusing on the writer’s internal thoughts, feelings, and reactions. It requires introspection and a willingness to explore one’s own experiences in depth.
- Critical Analysis: Beyond simply describing events, reflective writing involves analyzing these experiences. This means looking at the why and how, not just the what. It involves questioning, evaluating, and interpreting your experiences in relation to yourself, others, and the world.
- Descriptive Narrative: While reflective writing is analytical, it also includes descriptive elements. Vivid descriptions of experiences, thoughts, and feelings help to convey the depth of the reflection.
- Focus on Growth: A central aim of reflective writing is to foster personal or professional growth. It involves identifying lessons learned, recognizing patterns, and considering how to apply insights gained to future situations.
These features combine to make reflective writing a powerful tool for learning and development.
It’s a practice that encourages writers to engage deeply with their experiences, challenge their assumptions, and grow from their reflections.
What Is the Structure of Reflective Writing?
The structure of reflective writing can vary depending on the context and purpose, but it typically follows a general pattern that facilitates deep reflection.
A common structure includes an introduction, a body that outlines the experience and the reflection on it, and a conclusion.
- Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for the reflective piece. It briefly introduces the topic or experience being reflected upon and may include a thesis statement that outlines the main insight or theme of the reflection.
- Body: The body is where the bulk of the reflection takes place. It often follows a chronological order, detailing the experience before moving into the reflection. This section should explore the writer’s thoughts, feelings, reactions, and insights related to the experience. It’s also where critical analysis comes into play, examining causes, effects, and underlying principles.
- Conclusion: The conclusion wraps up the reflection, summarizing the key insights gained and considering how these learnings might apply to future situations. It’s an opportunity to reflect on personal growth and the broader implications of the experience.
This structure is flexible and can be adapted to suit different types of reflective writing.
However, the focus should always be on creating a coherent narrative that allows for deep personal insight and learning.
How Do You Start Reflective Writing?
Starting reflective writing can be challenging, as it requires diving into personal experiences and emotions.
Here are some tips to help initiate the reflective writing process:
- Choose a Focus: Start by selecting an experience or topic to reflect upon. It could be a specific event, a general period in your life, a project you worked on, or even a book that made a significant impact on you.
- Reflect on Your Feelings: Think about how the experience made you feel at the time and how you feel about it now. Understanding your emotional response is a crucial part of reflective writing.
- Ask Yourself Questions: Begin by asking yourself questions related to the experience. What did you learn from it? How did it challenge your assumptions? How has it influenced your thinking or behavior?
- Write a Strong Opening: Your first few sentences should grab the reader’s attention and clearly indicate what you will be reflecting on. You can start with a striking fact, a question, a quote, or a vivid description of a moment from the experience.
- Keep It Personal: Remember that reflective writing is personal. Use “I” statements to express your thoughts, feelings, and insights. This helps to maintain the focus on your personal experience and learning journey.
Here is a video about reflective writing that I think you’ll like:
Reflective Writing Toolkit
Finding the right tools and resources has been key to deepening my reflections and enhancing my self-awareness.
Here’s a curated toolkit that has empowered my own reflective practice:
- Journaling Apps: Apps like Day One or Reflectly provide structured formats for daily reflections, helping to capture thoughts and feelings on the go.
- Digital Notebooks: Tools like Evernote or Microsoft OneNote allow for organized, searchable reflections that can include text, images, and links.
- Writing Prompts: Websites like WritingPrompts.com offer endless ideas to spark reflective writing, making it easier to start when you’re feeling stuck.
- Mind Mapping Software: Platforms like MindMeister help organize thoughts visually, which can be especially helpful for reflective planning or brainstorming.
- Blogging Platforms: Sites like WordPress or Medium offer a space to share reflective writings publicly, fostering community and feedback. You’ll need a hosting platform. I recommend Bluehost or Hostarmada for beginners.
- Guided Meditation Apps: Apps such as Headspace or Calm can support reflective writing by clearing the mind and fostering a reflective state before writing.
- Audio Recording Apps: Tools like Otter.ai not only allow for verbal reflection but also transcribe conversations, which can then be reflected upon in writing.
- Time Management Apps: Resources like Forest or Pomodoro Technique apps help set dedicated time for reflection, making it a regular part of your routine.
- Creative Writing Software: Platforms like Scrivener cater to more in-depth reflective projects, providing extensive organizing and formatting options.
- Research Databases: Access to journals and articles through databases like Google Scholar can enrich reflective writing with theoretical frameworks and insights.
Final Thoughts: What Is Reflective Writing?
Reflective writing, at its core, is a deeply personal practice.
Yet, it also holds the potential to bridge cultural divides. By sharing reflective writings that explore personal experiences through the lens of different cultural backgrounds, we can foster a deeper understanding and appreciation of diverse worldviews.
Read This Next:
- What Is a Prompt in Writing? (Ultimate Guide + 200 Examples)
- What Is A Personal Account In Writing? (47 Examples)
- Why Does Academic Writing Require Strict Formatting?
- What Is A Lens In Writing? (The Ultimate Guide)

- Subject Guides
Academic writing: a practical guide
Reflective writing.
- Academic writing
- The writing process
- Academic writing style
- Structure & cohesion
- Criticality in academic writing
- Working with evidence
- Referencing
- Assessment & feedback
- Dissertations
- Examination writing
- Academic posters
- Feedback on Structure and Organisation
- Feedback on Argument, Analysis, and Critical Thinking
- Feedback on Writing Style and Clarity
- Feedback on Referencing and Research
- Feedback on Presentation and Proofreading
Writing reflectively is essential to many academic programmes and also to completing applications for employment. This page considers what reflective writing is and how to do it.
What is reflection?
Reflection is something that we do everyday as part of being human. We plan and undertake actions, then think about whether each was successful or not, and how we might improve next time. We can also feel reflection as emotions, such as satisfaction and regret, or as a need to talk over happenings with friends. See below for an introduction to reflection as a concept.
Reflection in everyday life [Google Slides]

What is reflective writing?
Reflective writing should be thought of as recording reflective thinking. This can be done in an everyday diary entry, or instruction in a recipe book to change a cooking method next time. In academic courses, reflective is more complex and focussed. This section considers the main features of reflective writing.
Reflective writing for employability
When applying for jobs, or further academic study, students are required to think through what they have done in their degrees and translate it into evaluative writing that fulfils the criteria of job descriptions and person specifications. This is a different style of writing, the resource below will enable you to think about how to begin this transition.
There are also lots of resources available through the university's careers service and elsewhere on the Skills Guides. The links below are to pages that can offer further support and guidance.
- Careers and Placements Service resources Lots of resources that relate to all aspects of job applications, including tailored writing styles and techniques.
The language of reflective writing
Reflective academic writing is:
- almost always written in the first person.
- evaluative - you are judging something.
- partly personal, partly based on criteria.
- analytical - you are usually categorising actions and events.
- formal - it is for an academic audience.
- carefully constructed.
Look at the sections below to see specific vocabulary types and sentence constructions that can be useful when writing reflectively.
Language for exploring outcomes
A key element of writing reflectively is being able to explain to the reader what the results of your actions were. This requires careful grading of language to ensure that what you write reflects the evidence of what happened and to convey clearly what you achieved or did not achieve.
Below are some ideas and prompts of how you can write reflectively about outcomes, using clarity and graded language.
Expressing uncertainty when writing about outcomes:
- It is not yet clear that…
- I do not yet (fully) understand...
- It is unclear...
- It is not yet fully clear...
- It is not yet (fully?) known…
- It appears to be the case that…
- It is too soon to tell....
Often, in academic learning, the uncertainty in the outcomes is a key part of the learning and development that you undertake. It is vital therefore that you explain this clearly to the reader using careful choices in your language.
Writing about how the outcome relates to you:
- I gained (xxxx) skills…
- I developed…
- The experience/task/process taught me…
- I achieved…
- I learned that…
- I found that…
In each case you can add in words like, ‘significantly’, ‘greatly’, ‘less importantly’ etc. The use of evaluative adjectives enables you to express to the reader the importance and significance of your learning in terms of the outcomes achieved.
Describing how you reached your outcomes:
- Having read....
- Having completed (xxxx)...
- I analysed…
- I applied…
- I learned…
- I experienced…
- Having reflected…
This gives the reader an idea of the nature of the reflection they are reading. How and why you reach the conclusions and learning that you express in your reflective writing is important so the reader can assess the validity and strength of your reflections.
Projecting your outcomes into the future:
- If I completed a similar task in the future I would…
- Having learned through this process I would…
- Next time I will…
- I will need to develop…. (in light of the outcomes)
- Next time my responses would be different....
When showing the reader how you will use your learning in the future, it is important to be specific and again, to use accurate graded language to show how and why what you choose to highlight matters. Check carefully against task instructions to see what you are expected to reflect into the future about.
When reflecting in academic writing on outcomes, this can mean either the results of the task you have completed, for example, the accuracy of a titration in a Chemistry lab session, or what you have learned/developed within the task, for example, ensuring that an interview question is written clearly enough to produce a response that reflects what you wished to find out.
Language choices are important in ensuring the reader can see what you think in relation to the reflection you have done.
Language for interpretation
When you interpret something you are telling the reader how important it is, or what meaning is attached to it.
You may wish to indicate the value of something:
- superfluous
- non-essential
E.g. 'the accuracy of the transcription was essential to the accuracy of the eventual coding and analysis of the interviews undertaken. The training I undertook was critical to enabling me to transcribe quickly and accurately'
You may wish to show how ideas, actions or some other aspect developed over time:
- Initially
- subsequently
- in sequence
E.g. 'Before we could produce the final version of the presentation, we had to complete both the research and produce a plan. This was achieved later than expected, leading to subsequent rushing of creating slides, and this contributed to a lower grade'.
You may wish to show your viewpoint or that of others:
- did not think
- articulated
- did/did not do something
Each of these could be preceded by 'we' or 'I'.
E.g. 'I noticed that the model of the bridge was sagging. I expressed this to the group, and as I did so I noticed that two members did not seem to grasp how serious the problem was. I proposed a break and a meeting, during which I intervened to show the results of inaction.'
There is a huge range of language that can be used for interpretation, the most important thing is to remember your reader and be clear with them about what your interpretation is, so they can see your thinking and agree or disagree with you.
Language for analysis
When reflecting, it is important to show the reader that you have analysed the tasks, outcomes, learning and all other aspects that you are writing about. In most cases, you are using categories to provide structure to your reflection. Some suggestions of language to use when analysing in reflective writing are below:
Signposting that you are breaking down a task or learning into categories:
- An aspect of…
- An element of…
- An example of…
- A key feature of the task was... (e.g. teamwork)
- The task was multifaceted… (then go on to list or describe the facets)
- There were several experiences…
- ‘X’ is related to ‘y’
There may be specific categories that you should consider in your reflection. In teamwork, it could be individual and team performance, in lab work it could be accuracy and the reliability of results. It is important that the reader can see the categories you have used for your analysis.
Analysis by chronology:
- Subsequently
- Consequently
- Stage 1 (or other)
In many tasks the order in which they were completed matters. This can be a key part of your reflection, as it is possible that you may learn to do things in a different order next time or that the chronology influenced the outcomes.
Analysis by perspective:
- I considered
These language choices show that you are analysing purely by your own personal perspective. You may provide evidence to support your thinking, but it is your viewpoint that matters.
- What I expected from the reading did not happen…
- The Theory did not appear in our results…
- The predictions made were not fulfilled…
- The outcome was surprising because… (and link to what was expected)
These language choices show that you are analysing by making reference to academic learning (from an academic perspective). This means you have read or otherwise learned something and used it to form expectations, ideas and/or predictions. You can then reflect on what you found vs what you expected. The reader needs to know what has informed our reflections.
- Organisation X should therefore…
- A key recommendation is…
- I now know that organisation x is…
- Theory A can be applied to organisation X
These language choices show that analysis is being completed from a systems perspective. You are telling the reader how your learning links into the bigger picture of systems, for example, what an organisation or entity might do in response to what you have learned.
Analysing is a key element of being reflective. You must think through the task, ideas, or learning you are reflecting on and use categories to provide structure to your thought. This then translates into structure and language choices in your writing, so your reader can see clearly how you have used analysis to provide sense and structure to your reflections.
Language for evaluation
Reflecting is fundamentally an evaluative activity. Writing about reflection is therefore replete with evaluative language. A skillful reflective writer is able to grade their language to match the thinking it is expressing to the reader.
Language to show how significant something is:
- Most importantly
- Significantly
- The principal lesson was…
- Consequential
- Fundamental
- Insignificant
- In each case the language is quantifying the significance of the element you are describing, telling the reader the product of your evaluative thought.
For example, ‘when team working I initially thought that we would succeed by setting out a plan and then working independently, but in fact, constant communication and collaboration were crucial to success. This was the most significant thing I learned.’
Language to show the strength of relationships:
- X is strongly associated with Y
- A is a consequence of B
- There is a probable relationship between…
- C does not cause D
- A may influence B
- I learn most strongly when doing A
In each case the language used can show how significant and strong the relationship between two factors are.
For example, ‘I learned, as part of my research methods module, that the accuracy of the data gained through surveys is directly related to the quality of the questions. Quality can be improved by reading widely and looking at surveys in existing academic papers to inform making your own questions’
Language to evaluate your viewpoint:
- I was convinced...
- I have developed significantly…
- I learned that...
- The most significant thing that I learned was…
- Next time, I would definitely…
- I am unclear about…
- I was uncertain about…
These language choices show that you are attaching a level of significance to your reflection. This enables the reader to see what you think about the learning you achieved and the level of significance you attach to each reflection.
For example, ‘when using systematic sampling of a mixed woodland, I was convinced that method A would be most effective, but in reality, it was clear that method B produced the most accurate results. I learned that assumptions based on reading previous research can lead to inaccurate predictions. This is very important for me as I will be planning a similar sampling activity as part of my fourth year project’
Evaluating is the main element of reflecting. You need to evaluate the outcomes of the activities you have done, your part in them, the learning you achieved and the process/methods you used in your learning, among many other things. It is important that you carefully use language to show the evaluative thinking you have completed to the reader.
Varieties of reflective writing in academic studies
There are a huge variety of reflective writing tasks, which differ between programmes and modules. Some are required by the nature of the subject, like in Education, where reflection is a required standard in teaching.
Some are required by the industry area graduates are training for, such as 'Human Resources Management', where the industry accreditation body require evidence of reflective capabilities in graduates.
In some cases, reflection is about the 'learning to learn' element of degree studies, to help you to become a more effective learner. Below, some of the main reflective writing tasks found in University of York degrees are explored. In each case the advice, guidance and materials do not substitute for those provided within your modules.
Reflective essay writing
Reflective essay tasks vary greatly in what they require of you. The most important thing to do is to read the assessment brief carefully, attend any sessions and read any materials provided as guidance and to allocate time to ensure you can do the task well.

Reflective learning statements
Reflective learning statements are often attached to dissertations and projects, as well as practical activities. They are an opportunity to think about and tell the reader what you have learned, how you will use the learning, what you can do better next time and to link to other areas, such as your intended career.
Making a judgement about academic performance
Think of this type of writing as producing your own feedback. How did you do? Why? What could you improve next time? These activities may be a part of modules, they could be attached to a bigger piece of work like a dissertation or essay, or could be just a part of your module learning.
The four main questions to ask yourself when reflecting on your academic performance.
- Why exactly did you achieve the grade you have been awarded? Look at your feedback, the instructions, the marking scheme and talk to your tutors to find out if you don't know.
- How did your learning behaviours affect your academic performance? This covers aspects such as attendance, reading for lectures/seminars, asking questions, working with peers... the list goes on.
- How did your performance compare to others? Can you identify when others did better or worse? Can you talk to your peers to find out if they are doing something you are not or being more/less effective?
- What can you do differently to improve your performance? In each case, how will you ensure you can do it? Do you need training? Do you need a guide book or resources?
When writing about each of the above, you need to keep in mind the context of how you are being asked to judge your performance and ensure the reader gains the detail they need (and as this is usually a marker, this means they can give you a high grade!).
Writing a learning diary/blog/record
A learning diary or blog has become a very common method of assessing and supporting learning in many degree programmes. The aim is to help you to think through your day-to-day learning and identify what you have and have not learned, why that is and what you can improve as you go along. You are also encouraged to link your learning to bigger thinking, like future careers or your overall degree.
Other support for reflective writing
Online resources.
The general writing pages of this site offer guidance that can be applied to all types of writing, including reflective writing. Also check your department's guidance and VLE sites for tailored resources.
Other useful resources for reflective writing:

Appointments and workshops

- << Previous: Dissertations
- Next: Examination writing >>
- Last Updated: Apr 3, 2024 4:02 PM
- URL: https://subjectguides.york.ac.uk/academic-writing

How to Write a Reflective Essay: Easy Guide with Pro Tips

Defining What is a Reflective Essay: Purpose + Importance
Being present is a cornerstone of mindfulness and meditation. You must have often heard that staying in the moment helps you appreciate your surroundings, connects you with people and nature, and allows you to feel whatever emotions you must feel without anxiety. While this is helpful advice as you become more focused and avoid getting lost in thought, how can you truly appreciate the present without reflecting on your past experiences that have led you to the current moment?
We don't say that you should dwell on the past and get carried away with a constant thought process, but hey, hear us out - practice reflective thinking! Think back on your previous life events, paint a true picture of history, and make connections to your present self. This requires you to get a bit analytical and creative. So you might as well document your critical reflection on a piece of paper and give direction to your personal observations. That's when the need for reflective essays steps in!
In a reflective essay, you open up about your thoughts and emotions to uncover your mindset, personality, traits of character, and background. Your reflective essay should include a description of the experience/literature piece as well as explanations of your thoughts, feelings, and reactions. In this article, our essay writer service will share our ultimate guide on how to write a reflective essay with a clear format and reflective essay examples that will inspire you.
How to Write a Reflective Essay with a Proper Reflective Essay Outline
To give you a clear idea of structuring a reflective essay template, we broke down the essential steps below. Primarily, the organization of a reflective essay is very similar to other types of papers. However, our custom writers got more specific with the reflective essay outline to ease your writing process.
Reflective Essay Introduction
When wondering how to start a reflective essay, it is no surprise that you should begin writing your paper with an introductory paragraph. So, what's new and different with the reflection essay introduction? Let's dissect:
- Open your intro with an attention-seizing hook that engages your audience into reflective thinking with you. It can be something like: 'As I was sitting on my bed with my notebook placed on my shaky lap waiting for the letter of acceptance, I could not help but reflect, was enrolling in college the path I wanted to take in the future?'
- Provide context with a quick overview of the reflective essay topic. Don't reveal too much information at the start to prevent your audience from becoming discouraged to continue reading.
- Make a claim with a strong reflective essay thesis statement. It should be a simple explanation of the essay's main point, in this example, a specific event that had a big impact on you.
Reflective Essay Body Paragraphs
The next step is to develop the body of your essay. This section of the paper may be the most challenging because it's simple to ramble and replicate yourself both in the outline and the actual writing. Planning the body properly requires a lot of time and work, and the following advice can assist you in doing this effectively:
- Consider using a sequential strategy. This entails reviewing everything you wish to discuss in the order it occurred. This method ensures that your work is structured and cohesive.
- Make sure the body paragraph is well-rounded and employs the right amount of analysis. The body should go into the effects of the event on your life and the insights you've gained as a consequence.
- Prioritize reflecting rather than summarizing your points. In addition to giving readers insight into your personal experience, a reflective stance will also show off your personality and demonstrate your ability to handle certain challenges.
Reflective Essay Conclusion
The goal of your reflective essay conclusion should be to tie everything together by summarizing the key ideas raised throughout, as well as the lessons you were able to take away from experience.
- Don't forget to include the reasons for and the methods used to improve your beliefs and actions. Think about how your personality and skills have changed as well.
- What conclusions can you draw about your behavior in particular circumstances? What could you do differently if the conditions were the same in the future?
Remember that your instructor will be searching for clear signs of reflection.
Understanding a Reflection Paper Format
The format of reflective essay greatly differs from an argumentative or research paper. A reflective essay is more of a well-structured story or a diary entry rife with insight and reflection. You might be required to arrange your essay using the APA style or the MLA format.
And the typical reflection paper length varies between 300 and 700 words, but ask your instructor about the word length if it was assigned to you. Even though this essay is about you, try to avoid too much informal language.
If your instructor asks you to use an APA or MLA style format for reflective essay, here are a few shortcuts:
Reflective Essay in MLA Format
- Times New Roman 12pt font double spaced;
- 1" margins;
- The top right includes the last name and page number on every page;
- Titles are centered;
- The header should include your name, your professor's name, course number, and the date (dd/mm/yy);
- The last page includes a Works Cited.
Reflective Essay in APA Style
- Include a page header on the top of every page;
- Insert page number on the right;
- Your reflective essay should be divided into four parts: Title Page, Abstract, Main Body, and References.
Reflective Essay Writing Tips
You may think we've armed you with enough tips and pointers for reflective writing, but it doesn't stop here. Below we gathered some expert-approved tips for constructing uncontested reflection papers.

- Be as detailed as possible while writing. To make your reflective essay writing come to life, you should employ several tactics such as symbolism, sentence patterns, etc.
- Keep your audience in mind. The reader will become frustrated if you continue writing in the first person without taking a moment to convey something more important, even though you will likely speak about something from your own perspective.
- Put forth the effort to allow the reader to feel the situation or emotion you are attempting to explain.
- Don't preach; demonstrate. Instead of just reporting what happened, use description appropriately to paint a clear picture of the event or sensation.
- Plan the wording and structure of your reflective essay around a central emotion or subject, such as joy, pleasure, fear, or grief.
- Avoid adding dull elements that can lessen the effect of your work. Why include it if it won't enhance the emotion or understanding you wish to convey?
- There must be a constant sense of progression. Consider whether the event has transformed you or others around you.
- Remember to double-check your grammar, syntax, and spelling.
Ready to Shine a Light on Your Innermost Thoughts?
Order your reflection essays now and let a wider audience hear your unique story
Reflective Essay Topic Ideas
As a reflective essay should be about your own views and experiences, you generally can't use someone else's ideas. But to help you get started, here are some suggestions for writing topics:
- An experience you will never forget.
- The moment you overcame a fear.
- The most difficult choice you had to make.
- A time your beliefs were challenged.
- A time something changed your life.
- The happiest or most frightening moment of your life so far.
- Ways you think you or people can make the world a better place.
- A time you felt lost.
- An introspective look at your choices or a time you made the wrong choice.
- A moment in your life you would like to relive.
You may find it convenient to create a chart or table to keep track of your ideas. Split your chart into three parts:

- In the first column, write key experiences or your main points. You can arrange them from most important to least important.
- In the second column, list your response to the points you stated in the first column.
- In the third column, write what, from your response, you would like to share in the essay.
Meanwhile, if you're about to enroll in your dream university and your mind is constantly occupied with - 'how to write my college admissions essay?', order an academic essay on our platform to free you of unnecessary anxiety.
Reflective Essay Sample
Referring to reflective essay examples can help you a lot. A reflective essay sample can provide you with useful insight into how your essay should look like. You can also buy an essay online if you need one customized to your specific requirements.
How to Conclude a Reflective Essay
As we come to an end, it's only logical to reflect on the main points discussed above in the article. By now, you should clearly understand what is a reflective essay and that the key to writing a reflective essay is demonstrating what lessons you have taken away from your experiences and why and how these lessons have shaped you. It should also have a clear reflective essay format, with an opening, development of ideas, and resolution.
Now that you have the tools to create a thorough and accurate reflective paper, you might want to hand over other tasks like writing definition essay examples to our experienced writers. In this case, feel free to buy an essay online on our platform and reflect on your past events without worrying about future assignments!
Want to Easily Impress Your Professors?
Count on the support of our professional writers for a top-notch academic paper
Related Articles
.webp)
- Essay Guides
- Main Academic Essays
How to Write a Reflective Essay: A Quick Guide + Examples
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
A reflective essay is a type of writing where you explore how an event, experience, or concept has influenced your development or perspective. It involves deep thinking, self-analysis, and personal reflection. In a reflective essay, you explai what you learned and how you changed as a result of that experience.
In this article, you will learn how to write a reflective essay, and how to highlight impactful experiences. A reflection essay seems easy as you don’t have to defend one’s point of view or convince the reader of something. But it has its challenges, so we recommend to keep on reading and find out everything you need to know about this type of essay. More complex examples are available down below.

What Is a Reflective Essay: Definition
A good question to start with is, “What is a reflective essay?” A reflective essay is a type of academic writing, in which the student has to test personal life experience/position towards a particular topic. Unlike in argumentative writing, the student does not have to defend the personal position. It does not require a complicated, professional language with some terminology. Do not define something - focus on sharing personal life experience, skills, development, and the most vivid examples to illustrate the topic.
Reflective Essay Format
A reflection essay student writes to meet the college writing standards has a different format from the one a magazine writer should present to reach the issue’s audience. However, each reflective paper has a similar outline. Reflective essay format depends on the general requirements your teacher provides. Some of them can ask for a specific format for your essay. APA writing style , MLA, and Chicago are the basic formats you can use. But if you don’t know exactly which formatting to use, you can use reflective essay apa format. This is the most common college essay format, so knowing its requirements is critical: Font: Times New Roman, 12 points Interval: Double interval Margins: 1 inch all round Page Numbers: Insert a title in the upper left corner of each page.
Reflective Essay Outline and Structure
Knowing how to write a reflective essay is essential. Even if you feel confident about your thoughts and knowledge, don’t start your writing without a clear and well-designed plan. Without logical essay structure , your essay will likely achieve lower marks. To avoid this situation, follow 10 easy steps we provided below. The first thing every student needs to understand how to write a good reflective essay is an effective, detailed outline. It has 3 typical sections: introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Writing a reflective essay does not require any references – the only person to refer is the student who decides to share his thoughts & ideas. Let’s look at 4 main reasons to include an outline of reflective essays.
- An outline assists in laying out the details the student wants to leave after narrowing down the draft before working on the final paper. It prevents them from concluding the essay by realizing something is missing.
- An outline provides a clear, concise roadmap, which prevents the writer from taking curvy paths and facing dead ends. It shows the way like a compass in the woods.
- An outline helps to save a lot of time.
- An outline helps the potential readers, including teachers & classmates, to avoid falling off the main point when reading the essay partially.
Reflective essay outline is not much different from other types of essays. Use this reflective essay template in creating your perfect reflective essay:

How to Start a Reflective Essay: Creating an Introduction
Let’s figure out how to write a reflective essay introduction. Start with stating the primary focus of the personal reflection. Avoid being indirect and covering a range of topics; stay direct and concise by underlining the basic purpose of sharing a life experience. Professional Opinion:
“Giving a preview of the most exciting part of the story is a clue. The target reader may lack time to read the full piece from cover to cover. “There are many things I have learned from Marketing class. The most valuable lesson I have obtained is checking the effectiveness of 2 different approaches or services through utilizing so-called A/B testing.” It will make the reader think about what is special about this specific method. The reader will go on reading the body paragraphs to find out!” Professor Hemsworth, History & Anthropology teacher and academic writer at StudyCrumb
Another way to attract attention in the introductory paragraph is to come up with the intriguing hook for essay sentences like statistics, fact, quote, metaphor, rhetorical question, or joke. It depends on the mood of your reflective narrative.
Working on Reflective Essay Thesis
Some people may say that a reflective essay does not need a thesis. However, the example shared in the previous section talking about introduction is an example of the inspiring thesis statement. Include at least a reflective summary of the primary idea. The best idea would be to focus on previewing the peak of the plot development or highlighting the most valuable lesson learned. Let’s take a look at this little reflective essay thesis sample.

If you find it challenging, rely on our professional essay writing service and have your reflective essay done with academic standards in mind.
Writing a Reflection Essay Body Paragraph
What is the purpose of a body paragraph ? The body paragraphs of the reflective analysis interpret the way the author evolved or what he/she has absorbed from a particular life lesson (mention 3 different lessons). When writing your reflective essay you should mention the circumstances that forced you to pass a certain way. If you study a subject like English Literature or Arts, the paper’s prompt may ask you to describe how you changed as a field professional during the course of study. It is important to choose a specific interval of time to list the improvements. Compare & contrast the initial skills to the knowledge you have today. It is a great idea to tell the audience the ways various tasks, challenges, and lessons made the author grow since the beginning of his education. There is no need to conduct research to collect the supporting evidence. The author alone is responsible for defending every stated claim with the help of vivid samples that describe the topic the best. Example: In case the student has become more professional in the field of writing, he should list the causes of those changes (new English teacher, more practice at home, part-time job related to the field of writing). Who knows – some of the ideas may be used by other students to succeed!
How to Write a Reflective Essay Conclusion
The question of how to end a reflection paper is not less important. The last challenge is to prepare an impressive, inspiring, and powerful conclusion, which will make the target readers want to develop the same positive way. Write a reflective summary regarding the way you have changed over a given period of time. Share some forecast by looking ahead: how the experiences listed in the essay would influence further personal development. By looking at the past events, decide which of them was the most important. The good idea is to compare & contrast past and future events to stress the gaps between the obtained skills and experience, possibly gained in the future. Don't want to bother with writing any conclusions? Use a summary maker to generate e reflective essay conlusion in seconds.
How to Write a Reflective Essay: 10 Easy Steps
Writing personal reflection helps students to stress their individuality by highlighting various skills, knowledge, behavior, feelings, and even mood. The purpose of writing a reflective essay is to show how the person changed over time and what factors played an important role in those metamorphoses. Keep on reading this section to learn steps that will make your reflective writing perfect. Step 1: Think of the questions that interest you the most. It may be your experience, feelings, or an event in life. Make sure you analyzed the question well. Check credible sources and collect relevant information. Step 2: Decide what you want to write about. Make sure you know how to title an essay . Identify the topic. Step 3: After you decided on a topic, create an appealing title that will entice readers. Make sure your title is clear and to the point. Step 4: Create an outline of your essay. Step 5: Create an attention-grabbing hook for reflective essay. It should be some intriguing sentence or phrase that will arouse the interest of your readers. Step 6: Create an introduction of your reflection paper. Step 7: Think what you will include in the main body of your text. Start writing your body paragraphs. Step 8: Diversify your text with all the necessary details to make your readers see a clear picture of the environment in your story. It can be some place, people, atmosphere, etc. Step 9: After the reader is already familiar with the setting and characters, you should tell about yourself. What were your feelings? How has the situation affected you? What did you learn from this situation? Step 10: Conclude your reflective essay. Briefly summarize all the points that were mentioned in your text and provide a short moral with recommendations. You can use these steps as a checklist for your writing process. In case you need another step-by-step guide on response essays or any other type of writing, we've got you covered.
>> Read more: How to Write Essays
Reflective Essays Sample From Successful College Students
No recommendations, tips & tricks help the students to understand the way a particular assignment should look like in the end as effectively as the examples. The article contains one of the up-to-date reflective essay examples from a college student.
Writing a Reflective Essay: Bottom Line
Congratulations, we have learned how to write a reflective essay. We really do hope that our guidelines, tips, and examples were useful to you. Now, you can definitely work on your reflection assignment with a clear understanding of its structure and main points. So start your writing, and the sky's the limit!
In case you need more writing tips, feel free to browse our Blog. Be it a diagnostic essay , a synthesis essay or a response paper , we have tutorials for any type of writing.
Consider buying essay papers in case you've got other plans for the evening. Submit your details to StudyCrumb and get an astounding paper written in line with your requirements. Your assigned writer will handle any assignment with a blink of an eye!
Frequently Asked Questions about Writing a Reflective Essay
1. what is a common mistake when writing a reflective essay.
A common mistake when writing a reflective essay is to drift away from the subject you're writing about. It usually happens when you don’t stick to your initial plan. So plan your writing well and if you feel that you go a bit off topic, be sure that you return to the same topic you originally discussed.
2. What is the purpose of writing a reflective essay?
The purpose of writing a reflective essay is to make a student write about their personal experience, explore it, reflect on it and find positive and negative aspects. The goal is to analyze how a student changed due to this experience and what made them change. What lesson a student learned is an essential point in persuasive writing.
3. How to write a reflective essay on a book?
If you are writing a reflective essay on a book, the main task is to show your teacher how you reflect on a chosen book, how you understand the problem presented by an author. To create a good essay, start with brief information about the author. Then, without spoilers, briefly summarize the main points of a book. After that explain the main conflicts, share your impressions. Ask questions like: “What are the peculiarities of the main characters?”, “What did an author want to say by indicating the main issues?”

Daniel Howard is an Essay Writing guru. He helps students create essays that will strike a chord with the readers.
You may also like

Reflective Essay Guide
Writing Reflective Essay
Last updated on: Feb 9, 2023
A Step by Step Guide to Writing a Reflective Essay
By: John K.
Reviewed By: Jacklyn H.
Published on: May 11, 2021

If you have been assigned the task of writing a reflective essay, it will be an excellent opportunity to polish your creativity and writing skills.
A reflective essay is slightly different from other essays as it requires a personal point of view of a chosen subject. Thus, you need to analyze a particular subject with your personal experience, understanding, and knowledge.
The only key to write a reflective paper is that you need to be more expressive. The more expressive you are, the merrier it will be for your essay. Feel free to talk about life experiences that are valid to your topic. Writing your reflections can actually be a strength in this kind of essay.
If this sounds like something that interests or concerns you, then keep reading! This blog contains every detail necessary to produce an impressive reflective essay.

On this Page
What Is a Reflective Essay?
A reflective essay describes an experience or event and analyzes the meaning of that particular experience and the lessons it delivers. One thing that makes it a reflective essay is that the writer analyzes an event of the past from the present.
When writing a reflective essay, you are required to open up about your emotions and thoughts to paint a clear picture of your personality, history, and individual traits.
It is required that you include a description and a vivid summary of the experience; it will make the reader feel that he has experienced it as well. Moreover, you need to explain your reactions, thoughts, feelings, and emotions.
A good reflective paper should be creative, insightful, and authentic. It needs to express your opinions on a specific topic interestingly so that the reader wants to follow what you're saying without getting bored or leaving it before reading.
Reflective Essay Format
REFLECTIVE ESSAY FORMAT AND TEMPLATE
How to Start a Reflective Essay?
Writing a great reflective essay is a chance to polish your skills of writing and enhance your creativity. However, sometimes, it gets difficult and confusing to write it. There are many high schools as well as college students who get confused thinking where to start.
So, we have compiled some steps that will help you to write a perfect essay.
Let’s discuss them in detail.
1. Choose Your Topic Carefully
If you are given the freedom to choose a topic and don’t have any idea regarding it, the best way is to brainstorm and research some trending and good topic ideas. Unfortunately, a common mistake when writing a reflective essay is to choose a topic that is too broad or too narrow.
2. Research About Your Subject
Make sure you do thorough research on your topic first. Close your eyes and start imagining or remembering. Then, watch, listen, and read the information regarding your topic.
3. Brainstorm
Before you even start writing, brainstorm your ideas first. It is always a wise step to take before writing anything.
4. Choose Reflection Questions
Take a look at the questions below to get a better idea:
- What did I notice?
- What do I feel about it?
- Why am I feeling this way?
5. Answer the Questions You Have Chosen
After selecting your questions, you need to give their answers. Start from one essay question; make sure you answer it properly. After that, head on to the next one.
6. Recognize Your Experience Meaning
Before you even start writing, you need to choose the most significant lesson you have learned from your experience. This “most significant lesson or thing” is going to be the thesis of your essay.
7. Follow the Structure
Like all the other essays, the reflective essay also has the same format, which comprises the introduction, body, and conclusion paragraph.
Therefore, follow these steps and makes your essay writing process easy.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
How to Write a Reflective Essay?
Here are some steps that you should follow when you start writing your reflective paper.
1. Write the Introduction
To understand and know how to start a reflective essay introduction, you must first understand that an introduction is a piece of brief information about the main topic and its background.
In the reflective essay introduction, you will recognize the subject and provide the reader with an overview of the impression you have taken from it. Therefore, the introductory paragraph of your reflective essay needs to include a thesis statement that will act as a focal point of your paper.
2. Body Paragraphs
The first body paragraph should mention the impactful impression your subject has made on you. Then, provide relevant facts to support your thesis statement.
Moreover, the body of your essay will also describe most of the ideas you touched on in your introduction.
3. Write a Conclusion
Restate your thesis statement and summarize all the reasons you have mentioned in the essay’s body paragraphs. After that, sum up your essay with your final thoughts on the subject; close your essay with some reflective thoughts.
4. Proofread and Edit
Never submit your essay without editing or proofreading. Even though you have spent hours of effort and put a lot of hard work in doing your essay, your essay will have no worth if you haven’t proofread and edited it.
Here is the reflective essay outline sample for your ease.
Reflective Essay Outline
REFLECTIVE ESSAY OUTLINE
Reflective Essay Examples
We have compiled some perfect reflective essay examples below to help you get started on your paper.
Personal Reflective Essay Examples
PERSONAL REFLECTIVE ESSAY EXAMPLES
ENGLISH REFLECTIVE ESSAY EXAMPLES
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Reflective Essay Topics
Check out these reflective essay ideas on the most common subjects you can write about:
- Something from your imagination
- Something you have experienced in real
- A special object
- Something you have seen, heard, read, watched, touched, or smelled.
We are sure these subjects must have sparked your imagination, but here are a few essay topics that will help you get the bigger picture. In addition, these topics will help you understand the kind of topics teachers like to assign.
- The desert, mountains, countryside, or beach
- A special room or hideaway
- The house you grew up
- Home of some relative
- A person that taught me how to improve reflective writing skills
- New Experiences
- When your piece of writing published
- Important conversation
- The older man line of thought
- The time you overcame your fears
A list of topics will help you get a picture of what good ideas are like and how to come up with one of your own.
5StarEssays.com is the best essay writing service online with exceptional quality work and insanely affordable rates. In addition, our round-the-clock customer support is ready to help you out with your academic growth.
Your essays are assigned to highly qualified essay writers who have years of experience and education. They make sure to provide you with mind-blowing, error-free, and on-time essays. They don’t just cater to the reflective essay but help with all types of essays.
So, contact us now and get the best write my essay for me? service at affordable rates.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long is a reflective essay.
The reflective essay should be between 300 and 500 words. However, it will vary according to the chosen topic.
What is the purpose of a reflective essay?
A reflective essay is a great opportunity for the author to explore what has happened in their life and show how this specific event may have changed them.

PhD Essay, Literature
John K. is a professional writer and author with many publications to his name. He has a Ph.D. in the field of management sciences, making him an expert on the subject matter. John is highly sought after for his insights and knowledge, and he regularly delivers keynote speeches and conducts workshops on various topics related to writing and publishing. He is also a regular contributor to various online publications.
Was This Blog Helpful?
Keep reading.
- Best Reflective Essay Topics Recommended by Experts

People Also Read
- writing a book review
- writing a book
- speech writing
- compare and contrast essay
- dissertation writing
Burdened With Assignments?

Advertisement
- Homework Services: Essay Topics Generator
© 2024 - All rights reserved

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.18: Reflective Writing
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 58227
- Lumen Learning
Learning Objectives
- Examine the components of reflective writing
Reflective Writing
Reflective writing includes several different components: description, analysis, interpretation, evaluation, and future application. Reflective writers must weave their personal perspectives with evidence of deep, critical thought as they make connections between theory, practice, and learning. The steps below should help you find the appropriate balance among all these factors.
1st Step: Review the assignment
As with any writing situation, the first step in writing a reflective piece is to clarify the task. Reflective assignments can take many forms, so you need to understand exactly what your instructor is asking you to do. Some reflective assignments are short, just a paragraph or two of unpolished writing. Usually the purpose of these reflective pieces is to capture your immediate impressions or perceptions. For example, your instructor might ask you at the end of a class to write quickly about a concept from that day’s lesson. That type of reflection helps you and your instructor gauge your understanding of the concept.
Other reflections are academic essays that can range in length from several paragraphs to several pages. The purpose of these essays is to critically reflect on and support an original claim(s) about a larger experience, such as an event you attended, a project you worked on, or your writing development. These essays require polished writing that conforms to academic conventions, such as articulation of a claim and substantive revision. They might address a larger audience than you and your instructor, including, for example, your classmates, your family, a scholarship committee, etc. It’s important before you begin writing, that you can identify the assignment’s purpose, audience, intended message or content, and requirements.
2nd Step: Generate ideas for content
As you generate ideas for your reflection, you might consider things like:
- Recollections of an experience, assignment, or course
- Ideas or observations made during that event
- Questions, challenges, or areas of doubt
- Strategies employed to solve problems
- A-ha moments linking theory to practice or learning something new
- Connections between this learning and prior learning
- New questions that arise as a result of the learning or experience
- New actions taken as a result of the learning or experience
3rd Step: Organize content
Researchers have developed several different frameworks or models for how reflective writing can be structured. For example, one method has you consider the “What?” “So what?” and “Now what?” of a situation in order to become more reflective. First, you assess what happened and describe the event, then you explain why it was significant, and then you use that information to inform your future practice. [1] [2] Similarly, the DIEP framework can help you consider how to organize your content when writing a reflective piece. Using this method, you describe what happened or what you did, interpret what it means, evaluate its value or impact, and plan steps for improving or changing for the future.
The DIEP Model of reflective writing
The DIEP model (Boud, Keogh & Walker,1985) organizes the reflection into four different components:
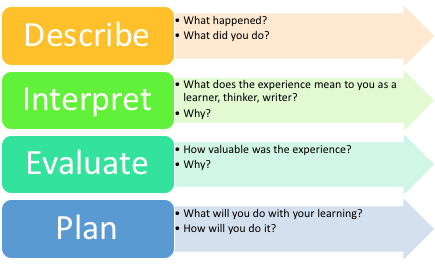
Remember, your goal is to make an interpretive or evaluative claim, or series of claims, that moves beyond obvious statements (such as, “I really enjoyed this project”) and demonstrates you have come to a deeper understanding of what you have learned and how you will use that learning.
In the example below, notice how the writer reflects on her initial ambitions and planning, the a-ha! moment, and then her decision to limit the scope of a project. She was assigned a multimodal (more than just writing) project, in which she made a video, and then reflected on the experience:
Student Example
Keeping a central focus in mind applies to multimodal compositions as well as written essays. A prime example of this was in my remix. When storyboarding for the video, I wanted to appeal to all college students in general. Within my compressed time limit of three minutes, I had planned to showcase numerous large points. It was too much. I decided to limit the scope of the topic to emphasize how digitally “addicted” college students are, and that really changed the project in significant ways.
4th Step: Draft, Revise, Edit, Repeat
A single, unpolished draft may suffice for short, in-the-moment reflections, but you may be asked to produce a longer academic reflection essay, which will require significant drafting, revising, and editing. Whatever the length of the assignment, keep this reflective cycle in mind:
- briefly describe the event or action;
- analyze and interpret events and actions, using evidence for support;
- demonstrate relevance in the present and the future.
The following video, produced by the Hull University Skills Team, provides a great overview of reflective writing. Even if you aren’t assigned a specific reflection writing task in your classes, it’s a good idea to reflect anyway, as reflection results in better learning.
You can view the transcript for “Reflective Writing” here (opens in new window) .
Check your understanding of reflective writing and the things you learned in the video with these quick practice questions:
https://h5p.cwr.olemiss.edu/h5p/embed/60
- Driscoll J (1994) Reflective practice for practise - a framework of structured reflection for clinical areas. Senior Nurse 14 (1):47–50 ↵
- Ash, S.L, Clayton, P.H., & Moses, M.G. (2009). Learning through critical reflection: A tutorial for service-learning students (instructor version). Raleigh, NC. ↵
Contributors and Attributions
- Process of Reflective Writing. Authored by : Karen Forgette. Provided by : University of Mississippi. License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Reflective Writing. Provided by : SkillsTeamHullUni. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QoI67VeE3ds&feature=emb_logo . License : Other . License Terms : Standard YouTube License
- Frameworks for Reflective Writing. Authored by : Karen Forgette. Provided by : University of Mississippi. License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike

- Cambridge Libraries
Study Skills
Reflective practice toolkit, introduction.
- What is reflective practice?
- Everyday reflection
- Models of reflection
- Barriers to reflection
- Free writing
- Reflective writing exercise
- Bibliography

Many people worry that they will be unable to write reflectively but chances are that you do it more than you think! It's a common task during both work and study from appraisal and planning documents to recording observations at the end of a module. The following pages will guide you through some simple techniques for reflective writing as well as how to avoid some of the most common pitfalls.
What is reflective writing?
Writing reflectively involves critically analysing an experience, recording how it has impacted you and what you plan to do with your new knowledge. It can help you to reflect on a deeper level as the act of getting something down on paper often helps people to think an experience through.
The key to reflective writing is to be analytical rather than descriptive. Always ask why rather than just describing what happened during an experience.
Remember...
Reflective writing is...
- Written in the first person
- Free flowing
- A tool to challenge assumptions
- A time investment
Reflective writing isn't...
- Written in the third person
- Descriptive
- What you think you should write
- A tool to ignore assumptions
- A waste of time
Adapted from The Reflective Practice Guide: an Interdisciplinary Approach / Barbara Bassot.
You can learn more about reflective writing in this handy video from Hull University:
Created by SkillsTeamHullUni
- Hull reflective writing video transcript (Word)
- Hull reflective writing video transcript (PDF)
Where might you use reflective writing?
You can use reflective writing in many aspects of your work, study and even everyday life. The activities below all contain some aspect of reflective writing and are common to many people:
1. Job applications
Both preparing for and writing job applications contain elements of reflective writing. You need to think about the experience that makes you suitable for a role and this means reflection on the skills you have developed and how they might relate to the specification. When writing your application you need to expand on what you have done and explain what you have learnt and why this matters - key elements of reflective writing.
2. Appraisals
In a similar way, undertaking an appraisal is a good time to reflect back on a certain period of time in post. You might be asked to record what went well and why as well as identifying areas for improvement.
3. Written feedback
If you have made a purchase recently you are likely to have received a request for feedback. When you leave a review of a product or service online then you need to think about the pros and cons. You may also have gone into detail about why the product was so good or the service was so bad so other people know how to judge it in the future.
4. Blogging
Blogs are a place to offer your own opinion and can be a really good place to do some reflective writing. Blogger often take a view on something and use their site as a way to share it with the world. They will often talk about the reasons why they like/dislike something - classic reflective writing.
5. During the research process
When researchers are working on a project they will often think about they way they are working and how it could be improved as well as considering different approaches to achieve their research goal. They will often record this in some way such as in a lab book and this questioning approach is a form of reflective writing.
6. In academic writing
Many students will be asked to include some form of reflection in an academic assignment, for example when relating a topic to their real life circumstances. They are also often asked to think about their opinion on or reactions to texts and other research and write about this in their own work.
Think about ... When you reflect
Think about all of the activities you do on a daily basis. Do any of these contain elements of reflective writing? Make a list of all the times you have written something reflective over the last month - it will be longer than you think!
Reflective terminology
A common mistake people make when writing reflectively is to focus too much on describing their experience. Think about some of the phrases below and try to use them when writing reflectively to help you avoid this problem:
- The most important thing was...
- At the time I felt...
- This was likely due to...
- After thinking about it...
- I learned that...
- I need to know more about...
- Later I realised...
- This was because...
- This was like...
- I wonder what would happen if...
- I'm still unsure about...
- My next steps are...
Always try and write in the first person when writing reflectively. This will help you to focus on your thoughts/feelings/experiences rather than just a description of the experience.
Using reflective writing in your academic work

Many courses will also expect you to reflect on your own learning as you progress through a particular programme. You may be asked to keep some type of reflective journal or diary. Depending on the needs of your course this may or may not be assessed but if you are using one it's important to write reflectively. This can help you to look back and see how your thinking has evolved over time - something useful for job applications in the future. Students at all levels may also be asked to reflect on the work of others, either as part of a group project or through peer review of their work. This requires a slightly different approach to reflection as you are not focused on your own work but again this is a useful skill to develop for the workplace.
You can see some useful examples of reflective writing in academia from Monash University , UNSW (the University of New South Wales) and Sage . Several of these examples also include feedback from tutors which you can use to inform your own work.
Laptop/computer/broswer/research by StockSnap via Pixabay licenced under CC0.
Now that you have a better idea of what reflective writing is and how it can be used it's time to practice some techniques.
This page has given you an understanding of what reflective writing is and where it can be used in both work and study. Now that you have a better idea of how reflective writing works the next two pages will guide you through some activities you can use to get started.
- << Previous: Barriers to reflection
- Next: Free writing >>
- Last Updated: Jun 21, 2023 3:24 PM
- URL: https://libguides.cam.ac.uk/reflectivepracticetoolkit
© Cambridge University Libraries | Accessibility | Privacy policy | Log into LibApps
Reflective Essay Writing
Reflective Essay: Step-by-Step Guide with Examples & Tips

People also read
How to Create a Reflective Essay Outline | Easy Guide with Examples
Good Reflective Essay Topics For Your Paper
Thought and reflection are a major part of our inner lives. Whenever we engage with art and literature or experience anything novel, we tend to reflect on it later.
What if we write our reflections down in a structured way? That is a reflective essay.
Among various types of essays , reflective essays stand out for being the most personal form of writing. Reflective writing lets you explore your thoughts and experiences about something and gain profound insights into yourself and the world around you.
So how can you write a great reflective essay? Read on to understand reflective essays better with examples and get useful tips.
- 1. What is a Reflective Essay?
- 2. How to Write a Reflective Essay?
- 3. Reflective Essay Structure
- 4. Reflective Essay Examples
- 5. Tips for Writing Better Reflective Essays
- 6. Reflective Essay Topics
What is a Reflective Essay?
A reflective essay is a type of writing where a writer explores their thoughts, feelings, and observations about a personal experience. These essays are deeply subjective, personal, and introspective.
At its core, a reflective essay prompts you to answer the question: "How did a particular experience impact me?" Unlike narrative or descriptive writing, reflective essays are not just about recounting events. The goal is to analyze and interpret the event with your unique perspective and insights.
In addition, reflective essays do not require you to provide external evidence or validation, nor do you have to argue or prove something. However, it's important to follow a structured approach that allows you to organize your thoughts and engage your readers.
So what is that structured approach to writing a reflective essay? Read below.
How to Write a Reflective Essay?
Writing a reflective essay can become a lot easier if you follow a structured writing process. It allows you to effectively communicate your insights to your audience.
Here is a step-by-step process to start a reflective essay:
Step 1: Brainstorm and Choose a Topic
Begin by brainstorming a specific event, experience, or topic to reflect upon. It could be a personal experience, a book you've read, a class you've taken, or a significant life event.
Here are some helpful tips for choosing a topic:
- Think about your personal experiences and select a topic that resonates with you and offers room for reflection.
- Consider which one is most relevant to the purpose of your reflective essay.
- Choose a topic that holds personal significance and allows you to explore and convey meaningful insights.
Step 2: Reflect Deeply & Gather Your Thoughts
Unlike other types of academic essays, reflection papers do not demand research or gathering sources. The source material for the essay can be found in your own thoughts.
You can write down your thoughts in the form of a bulleted list, mind mapping, or other forms of note-taking. Take time to immerse yourself in the experience and consider its various aspects, including:
- Specific details, emotions, and observations from the event or experience.
- Your initial reactions and thoughts at the time. Recall how the experience affected you and what you learned.
You don’t have to write down complete sentences yet, you can simply note down keywords and phrases.
Step 3: Organize Your Thoughts
To ensure a coherent and logical essay, organize the points you’ve gathered in an outline. The outline should clarify these aspects:
- A clear thesis statement that indicates the main idea of the essay.
- Body paragraphs that explore different aspects of your reflection, organized in a logical sequence.
- Key points, experiences, and insights you want to include in each paragraph.
This is the last step of your pre-writing preparation. With an organized outline for your essay, you have everything you need to start writing.
Learn more about crafting efficient outlines in our reflective essay outline guide
Step 4: Write Your First Draft
With your outline in hand, start writing your first draft. Follow your organizational structure and express your thoughts and experiences clearly and concisely. As you write:
- Maintain a reflective and personal tone, as this is a chance to express your thoughts and emotions.
- Use specific examples, anecdotes, and details to illustrate your points.
- Ensure that each paragraph flows logically to the next, creating a smooth reading experience.
Don't worry too much about perfection at this stage; the first draft is about getting your thoughts on paper.
Step 5: Proofread and Revise
After completing your first draft, take a break before revising. Returning to your essay with fresh eyes will help you identify areas for improvement. During the revision process:
- Check for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors.
- Ensure clarity and coherence in your writing.
- Review the flow of your essay to ensure that it logically progresses from introduction to conclusion. Paragraphs should be connected to each other through transition phrases.
- Trim unnecessary or repetitive content and add details or insights where needed.
By following these five steps, you'll be well on your way to crafting a well-organized and impactful reflective essay.
Reflective Essay Structure
A reflective essay typically follows a standard structure that includes an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Let’s delve into each of these parts here.
Reflective Essay Introduction
The introduction aims to draw the reader in by catching their interest and providing some context to the topic. A good introduction clearly indicates the subject and type of essay and tells the readers what to expect ahead.
Follow the tips below to craft an engaging introduction.
- Start with a hook or an intriguing opening sentence to pique the reader's interest. For example, you might begin with a thought-provoking quote, a relevant anecdote, or a rhetorical question.
- Provide context by briefly introducing the topic or the experience you will reflect upon. Mention any necessary background information to help the reader understand the context.
- End your introduction with a thesis statement . The thesis statement for a reflective essay can be flexible and can be more than one sentence long. It states the main point you want to convey, such as what you learned, gained, or how were you changed by the experience.
Reflective Essay Body Paragraphs
The body paragraphs of your essay are the heart of your reflection, where you dive deep into the experience and explore it from multiple angles. It's essential to organize your body paragraphs logically to maintain a coherent flow.
Here is how body paragraphs are organized in this type of paper:
First Body Paragraph
Provide a clear and detailed description of the experience or event you are reflecting upon. Set the stage by answering the basic questions: What, when, where, and who?
Share the most significant aspects of the experience. Consider the sensory details, the environment, the people involved, and other aspects. This will help your readers immerse themselves in the situation.
Second Body Paragraph
Once you’ve described the structure of your experience in detail, now is the time to move on to your thoughts, experiences, and observations.
Reflect on your immediate feelings and initial thoughts. Were you excited, anxious, or confused?
What did you notice about the people or surroundings? This section allows the reader to connect with your emotional journey, helping them understand the initial impact of the experience.
Third & Fourth Body Paragraphs
In the subsequent paragraphs, delve into in-depth reflection and analysis of your experience.
This is where you critically examine the experience, asking yourself why it was significant and how it impacted you. Consider the implications and connections to your personal growth, beliefs, or values and analyze the experience in the context of your life, education, or career.
You should also engage in critical reflection. For instance,
- What did you learn from the experience?
- How did it challenge or reinforce your existing beliefs?
- Did it change your perspective on certain issues?
Feel free to use multiple paragraphs for this reflection if needed. Each paragraph can explore different facets of your experience and offer a more comprehensive analysis.
Reflective Essay Conclusion
The conclusion of your reflective essay brings your reflection to a meaningful closure. It ties together the entire essay and aims to leave the reader with a lasting impression.
Here are some tips for writing a good conclusion:
- Summarize the key points you discussed in the body paragraphs without introducing new information. Reinforce the main message of your essay.
- Present the significance of the experience and its impact on your personal growth, beliefs, or understanding.
- Consider ending with a thought-provoking statement or a powerful insight to make it more impactful for the reader.
Reflective Essay Examples
Although you now know how to write a reflective essay, you should read some examples before you start writing. Reading the reflective essay samples below will help you get a feel of this type of writing.
Reflective Essay Sample - Reflections on Reading a Book
Reflective Essay Example - A Visit to a Historical Place
Tips for Writing Better Reflective Essays
Only following the writing steps can help you write a good essay. But to make it even better, you should do something extra. Here are some writing tips that can help you polish your reflective writing.
- Be Genuine and Authentic: Reflective essays thrive on authenticity. Share your true thoughts and feelings without embellishment or pretense. Readers appreciate sincerity and honesty in your reflections.
- Show, Don't Just Tell: Instead of merely stating your emotions or thoughts, demonstrate them through concrete examples and anecdotes. Let readers experience your reflection alongside you.
- Be Concise and Focused: Avoid unnecessary tangents or excessive details that may distract from your main reflection. Keep your essay focused on the central experience and its significance.
- Engage the Reader's Emotions: Touch on universal emotions and experiences that resonate with readers. Connecting on an emotional level can make your reflective essay more relatable and memorable.
- Seek Feedback: Don't hesitate to share your reflective essay with peers, mentors, or writing tutors. Their feedback can offer valuable insights and help you refine your writing.
- Reflect on Your Reflection: After completing your reflective essay, take a moment to reflect on your own reflection process. Consider what you've learned about yourself and your writing style. Use this insight to improve future reflective essays.
Reflective Essay Topics
Reflective essays can be written on a variety of topics. Here are some ideas you can write about:
- Engaging with Art: Reflect on your experience of reading a book, watching a documentary etc.
- A Life-Changing Journey: Reflect lessons learned from a trip or adventure.
- Mentorship and Learning: Reflect on the influence of a particular teacher, mentor, or role model on your life.
- Overcoming a Challenge: Write about a challenging experience or obstacle you've faced
- Life Milestones: Write about a major life event, such as graduating from school, getting married, or becoming a parent, etc.
- Career Transitions: Share your reflections on transitioning between careers or jobs.
- A Turning Point: Reflect on a specific moment or decision in your life that marked a turning point.
- Relationships: Explore the dynamics of a significant friendship or relationship.
- Ethical Dilemmas: Discuss a moral or ethical dilemma you faced and how you navigated it.
- Volunteer or Community Service: Share your experiences with community service.
These are just a few general ideas. With the help of these topics, you can ignite your creativity and choose the most meaningful topic for yourself.
Need more ideas to find a great topic for your reflective paper? Here are 100+ engaging reflective essay topics for your help!
Reflective essays serve as powerful instruments for self-discovery. It allows you to delve into your thoughts and experiences and share them with others in a meaningful way.
By following the steps, tips, and, examples above, you can explore the richness of your own experiences and engage others along the way. Trying to write a reflective essay can even become another one of your amazing experiences! So, embrace authenticity, engage your readers, and inspire those who read your words.
Need help writing a reflective essay? Don’t worry!
We understand the significance of these reflective journeys, and we've expert writers to assist you. At our reflective essay writing service , our team of writing professionals is dedicated to helping you craft insightful and impactful essays that meet your custom requirements.
So contact our paper writer service now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Can you say i in a reflective essay.
Yes! First-person pronouns are a great way to give the reader insight into your life and thoughts. I, me, we - these words all have personal meaning. So, they should be used in a reflective essay.
What person is a reflective essay?
A reflective essay is a type of academic writing that can take on many different forms. You might be asked to write it in the first person or third person, and there's no one correct way to do so!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Caleb S. has been providing writing services for over five years and has a Masters degree from Oxford University. He is an expert in his craft and takes great pride in helping students achieve their academic goals. Caleb is a dedicated professional who always puts his clients first.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

- Food & Dining
- Coronavirus
- Real Estate
- Seattle History
- PNW Politics
The Differences Between a Reflective & Narrative Essay
Related articles, from which point of view is "the tell-tale heart" written, how to write an essay that stands out, how to write a college narrative essay.
- Analysis of Voice in a Narrative
- What Is the Difference Between a Memoir and Personal Narrative?
One of the best way for somebody to get to know you is for them to learn about your life and experiences from your writing. This is often the case for colleges, universities, and employers that are attempting to find an applicant that meets their unique needs. The most efficient way for them to do this is to require that you submit either a narrative or a reflective essay. Both will give them information about you as a person, but there are some subtle differences in the guidelines.
Reflective Essay
A reflective essay is generally done along with some type of personal development portfolio. Many schools, such as Bridgewater College and DePaul University, require a reflective essay that documents your growth at the school. A reflective essay gives the reader a reflection of you, the writer, that tells them what kind of person you are. It should relate to your experience, but more importantly, it should focus on your personal change -- your attitude -- due to those experiences.
Narrative Essay
As opposed to the reflective essay, a narrative essay focuses on a specific event or a short sequence of events. Generally, this event would precipitate a change in belief or attitude in the writer. However, the emphasis is on the story itself. Purdue OWL recommends including all elements of a story, such as introduction, characters, plot, setting, climax and resolution. Telling a good story is important, but don't get sidetracked from incorporating your strengths, which is what the reader is ultimately interested in.
Elements in Both
Regardless of the type of essay you are writing, both share common elements. Both need a clear purpose and a narrator or central character. There should be a concise organizational structure, such as an orderly sequence of events. Either essay can be written from the first person, but it is not necessary. Both essays will consider the writer's emotional responses to the situation. The difference only shows in the focus of the essay; is it on the event itself, with accompanying emotional shift, or is it on the emotional shift, as a result of an event?
Other Types of Essays
Purdue OWL also lists three other common types of essay: expository, descriptive and argumentative. An expository essay involves investigating a topic, evaluating evidence and presenting a concise analysis. A descriptive essay describes a noun, verb or just about anything else, in intense detail. An argumentative essay is very similar to an expository essay, with the writer gathering more evidence to support a specific position regarding the topic and then presenting the argument in support of that position.
- DePaul College: University Center for Writing-based Learning
- Purdue University: Purdue OWL: Essay Writing
- Monash University: Essay writing
Michael Mason has a Bachelor of Science in psychology and a Master of Education in education. He has taught high school language arts and adult-level GED classes. He currently teaches adult basic education classes in a medium security detention facility. Prior to his career in education, he was a manager for a successful hotel company and a 911 dispatcher.
Explanation on Theme in Literature for Students
How to write a concept essay for college english, differences in narrative vs. exposition in a story, what are the differences between an autobiographical narrative & a biography, what stage of the plot comes after conflict, what are the similarities of persuasive and narrative essays, how to write an in-class essay, how to find the main idea of a narrative, lyrical poems vs. ballads, most popular.
- 1 Explanation on Theme in Literature for Students
- 2 How to Write a Concept Essay for College English
- 3 Differences in Narrative vs. Exposition in a Story
- 4 What Are the Differences Between an Autobiographical Narrative & a Biography?
- FRONT MATTER
- TABLE OF CONTENTS
Defining the Personal Statement
Because a personal statement is unlike other documents you write in college, many students struggle with understanding the fundamentals of its definition. First off, don’t let the term itself confuse you—some application materials will use other terms such as “personal essay,” “reflective essay,” “statement of purpose,” or “narrative.” Regardless of the term used, such essays are defined by their comment elements, as detailed below.
One of the best extended definitions of the personal statement I’ve seen appears on a website from the Fellowships Office at Bryn Mawr (see the article "Advice from Fellowship Foundations "). Below I offer a condensed version adapted from that website.
A personal statement is:
- A picture . Provide a snapshot of who you are as a person.
- An invitation . Your job is to “bridge the assumed distance of strangers.” Invite your reader to get to know you.
- An indication of your priorities and judgment . Your selection of material reveals your priorities and ability to discern effectively.
- A story, or more precisely, your story . The personal statement allows you room for creative, meaningful self-reflection.
A personal statement is not:
- An academic paper with you as the subject. The objective distance of academic writing disengages the reader from you in a personal statement.
- A resume in narrative form . Other parts of your application, which might include a resume, already tell readers about your accomplishments. A personal statement must reveal and interpret well beyond a resume.
- A journal entry . A common mistake is allowing your personal statement to read like a diary. Share only relevant material selectively, in a voice that remains both individual and professional.
- A plea or justification . Don’t beg and don’t defend the (incorrect) assertion that you are more worthy than other candidates—it only backfires.
Of course, nuances to this definition may be added based on the circumstances. For instance, at times an application might require three different essays with highly specific parameters, and perhaps one of these essays involves a personal narrative while another poses you a philosophical question to answer. Always look to the application itself to determine the degree to which the definitions above apply, and know that when there is a series of questions in an application at least one of them is usually designed to elicit a personal essay from you.
To further help you in defining the basics of the personal statement, I recommend these two sites:
“Instructions for Completing a Personal Statement Worksheet” (automatic download) from Bryn Mawr College
“Definition of a Personal Statement” from the Deputy Executive Secretary of the Truman Scholarship Foundation

- Schools & departments

Structure of academic reflections
Guidance on the structure of academic reflections.
Academic reflections or reflective writing completed for assessment often require a clear structure. Contrary to some people’s belief, reflection is not just a personal diary talking about your day and your feelings.
Both the language and the structure are important for academic reflective writing. For the structure you want to mirror an academic essay closely. You want an introduction, a main body, and a conclusion.
Academic reflection will require you to both describe the context, analyse it, and make conclusions. However, there is not one set of rules for the proportion of your reflection that should be spent describing the context, and what proportion should be spent on analysing and concluding. That being said, as learning tends to happen when analysing and synthesising rather than describing, a good rule of thumb is to describe just enough such that the reader understands your context.
Example structure for academic reflections
Below is an example of how you might structure an academic reflection if you were given no other guidance and what each section might contain. Remember this is only a suggestion and you must consider what is appropriate for the task at hand and for you yourself.
Introduction
Identifies and introduces your experience or learning
- This can be a critical incident
- This can be the reflective prompt you were given
- A particular learning you have gained
When structuring your academic reflections it might make sense to start with what you have learned and then use the main body to evidence that learning, using specific experiences and events. Alternatively, start with the event and build up your argument. This is a question of personal preference – if you aren’t given explicit guidance you can ask the assessor if they have a preference, however both can work.
Highlights why it was important
- This can be suggesting why this event was important for the learning you gained
- This can be why the learning you gained will benefit you or why you appreciate it in your context
You might find that it is not natural to highlight the importance of an event before you have developed your argument for what you gained from it. It can be okay not to explicitly state the importance in the introduction, but leave it to develop throughout your reflection.
Outline key themes that will appear in the reflection (optional – but particularly relevant when answering a reflective prompt or essay)
- This can be an introduction to your argument, introducing the elements that you will explore, or that builds to the learning you have already gained.
This might not make sense if you are reflecting on a particular experience, but is extremely valuable if you are answering a reflective prompt or writing an essay that includes multiple learning points. A type of prompt or question that could particularly benefit from this would be ‘Reflect on how the skills and theory within this course have helped you meet the benchmark statements of your degree’
It can be helpful to explore one theme/learning per paragraph.
Explore experiences
- You should highlight and explore the experience you introduced in the introduction
- If you are building toward answering a reflective prompt, explore each relevant experience.
As reflection is centred around an individual’s personal experience, it is very important to make experiences a main component of reflection. This does not mean that the majority of the reflective piece should be on describing an event – in fact you should only describe enough such that the reader can follow your analysis.
Analyse and synthesise
- You should analyse each of your experiences and from them synthesise new learning
Depending on the requirements of the assessment, you may need to use theoretical literature in your analysis. Theoretical literature is a part of perspective taking which is relevant for reflection, and will happen as a part of your analysis.
Restate or state your learning
- Make a conclusion based on your analysis and synthesis.
- If you have many themes in your reflection, it can be helpful to restate them here.
Plan for the future
- Highlight and discuss how your new-found learnings will influence your future practice
Answer the question or prompt (if applicable)
- If you are answering an essay question or reflective prompt, make sure that your conclusion provides a succinct response using your main body as evidence.
Using a reflective model to structure academic reflections
You might recognise that most reflective models mirror this structure; that is why a lot of the reflective models can be really useful to structure reflective assignments. Models are naturally structured to focus on a single experience – if the assignment requires you to focus on multiple experiences, it can be helpful to simply repeat each step of a model for each experience.
One difference between the structure of reflective writing and the structure of models is that sometimes you may choose to present your learning in the introduction of a piece of writing, whereas models (given that they support working through the reflective process) will have learning appearing at later stages.
However, generally structuring a piece of academic writing around a reflective model will ensure that it involves the correct components, reads coherently and logically, as well as having an appropriate structure.
Reflective journals/diaries/blogs and other pieces of assessed reflection
The example structure above works particularly well for formal assignments such as reflective essays and reports. Reflective journal/blogs and other pieces of assessed reflections tend to be less formal both in language and structure, however you can easily adapt the structure for journals and other reflective assignments if you find that helpful.
That is, if you are asked to produce a reflective journal with multiple entries it will most often (always check with the person who issued the assignment) be a successful journal if each entry mirrors the structure above and the language highlighted in the section on academic language. However, often you can be less concerned with form when producing reflective journals/diaries.
When producing reflective journals, it is often okay to include your original reflection as long as you are comfortable with sharing the content with others, and that the information included is not too personal for an assessor to read.
Developed from:
Ryan, M., 2011. Improving reflective writing in higher education: a social semiotic perspective. Teaching in Higher Education, 16(1), 99-111.
University of Portsmouth, Department for Curriculum and Quality Enhancement (date unavailable). Reflective Writing: a basic introduction [online]. Portsmouth: University of Portsmouth.
Queen Margaret University, Effective Learning Service (date unavailable). Reflection. [online]. Edinburgh: Queen Margaret University.

CRAFT: What’s the Difference Between Memoir and Personal Essay? by Suzanne Farrell Smith
January 11, 2022.

It’s the most common question my creative nonfiction students ask. We know memoir and personal essay overlap. Both tell true stories from the author’s life with intimacy and honesty. And both are crafted with literary devices: scene, dialogue, sensory detail… That’s what makes creative nonfiction compelling. We love true stories and we love to be entertained.
So where do they differ? To answer, I draw from several resources on writing creative nonfiction and illustrate with two Hippocampus pieces. By my measure, memoir and personal essay differ along four lines: focus, mining, voice, and sense.
- Focus on Self vs. Focus on Relating
The memoirist focuses on the self and what has changed over time. Readers may identify— I went through something similar or I changed in the same way —but the memoirist’s driving force is self-exploration.
In the memoir essay “Fits and Starts,” Matthew Zanoni Müller tells a short, significant story about an afternoon in childhood as a relatively new immigrant to the United States. Müller’s friend, David, coaxes him out of the house and into the world. While Müller’s descriptions of David and others are important to the story, we really only know Müller. We are inside his child mind, being pushed, gently, along with him, step by step.
The personal essayist focuses on the self, too, but seeks to relate. Where, in culture, place, and time, does her story fit in? Which of her questions do others ask? Accordingly, we talk about personal essay’s “universal theme.” The writer paints herself against the backdrop of humanity.
Linda Anne Silver announces the universal with her title, “The Capacity of a Human.” In the wake of her daughter’s death, Silver searches for a new normal that incorporates profound grief. With her husband, she travels around Lake Superior, and along the way gains insight from novelists, fellow travelers, parents of children who’ve died in mass tragedies, and the lake itself.
- Memory Mining vs. Experiential Mining
My boys love the game Minecraft, gathering materials to build underwater palaces and schools in the sky. Where you mine determines what you find. The same goes for writing. The memoirist “relies almost solely on memory,” writes Sue William Silverman in “The Meandering River.” He mines his mind, perhaps consults artifacts from his past.
In Müller’s memoir, all the important details, the who-and-what and beginning-middle-end, come from the author’s memory. “Mostly we’d play with cars,” he recalls, “arranging them in a long line and driving them slowly down the hallway toward the bedroom, moving each one forward an inch at a time.” Müller remembers how playtime mirrored the halting way he adapted to the U.S. “ Autoschlange , I called it, and my friend understood what it meant, because his father was German too.”
The personal essayist mines her memory, too, but also mines the landscape of her evolving life. She collects data and processes in-the-moment interactions.
Silver writes, “I examine things and snap photos, acting as a tourist.” We understand she is not just examining flora, fauna, and food, but also the circumstances, the places hope might surface. She draws from the novel Grief is the Thing with Feathers to understand “the crow of grief had moved in with us when Allison was first diagnosed.” She sets herself apart from “[t]he parents of Newtown or Manchester or Aleppo” while associating with all parents who’ve lost a child. She even researches on the page: “I try Googling, ‘Ontario stone piles,’ on my phone, but there’s no signal here.”
- Voices vs. Voice
Memoir contains multiple voices, including, at minimum, the voices of the past self and present self (what Sue William Silverman calls “song of innocence” and “song of experience”). Voices speak to readers, who reply. Someone who knows a memoirist might say, I had no idea that happened to you .
Müller’s memoir is entirely from his young self’s point of view. That big world he was persuaded to explore? A car, a grocery store, David’s house… places that, to a child in a new country, loomed large. “I was happy,” Müller’s child-voice writes, “because I knew that … soon we’d come back down and around the block and I’d be home again.” Moments later, as his child voice considers turning back, his adult voice offers meaning: “I didn’t want to compromise the heroic feelings I had just earned.”
In personal essay, one voice dominates. The narrator is a current version of the author who opines, worries, delights, fears. Friends might listen and say, I had no idea you felt that way .
Silver wrestles with herself. “Our daughter’s death feels like a failure,” she admits, “as if we weren’t paying attention when danger stalked.” She notices beauty for the first time since the death, then wonders how she’ll ever find it again. She questions, doubts, and guesses, seemingly in real time. There’s no divide between innocence and experience: the song is both.
- Past Sense vs. Present Sense
Memoir conveys a sense of the past, even if the events happened recently. The author has emerged and looks back to articulate meaning. Whether written in past or present tense, what’s palpable is the past sense . The author asks, what happened?
Müller signals the past sense with his opening line: “The first couple years we were in America…” It’s a before-time story, one that proved pivotal in some way. The author can examine the past because his life is different now. To underscore, Müller uses the past real conditional tense: “We’d play under the shadows of the cherry trees.” Memoirists use this tense to convey the general past in a way that feels both fresh and wistful.
In personal essay, there’s a sense things aren’t buttoned up. The author writes not to articulate meaning, but to find meaning in the first place. Personal essay feels open, like a thought experiment. The author asks, what is happening?
Silver’s first paragraph lists inspirations for her trip, ending with, “the need comes after our fifty-year-old daughter dies on a midsummer’s morning and we are numb: wanting to flee the sadness, not knowing how to move forward.” She’s in limbo: “I don’t know the answer, don’t know how I should grieve.” She repeatedly questions. About a missed chance to see the northern lights, she wonders, “Had we seen them, I might have latched on to the experience as a sign of—what? Hope? Resolution? Transformation?”
It’s true that memoir and personal essay often blend. New, hybrid forms emerge. Undefinable forms. So why draw lines between them?
I tell my students that understanding is power; when you get into your writing workshop, sharpen your tools, practice your craft moves, shape your piece . If we know what makes a memoir, we can push that much deeper into our past, search for the particular nerve that will animate our past selves, give us ah-ha insights. And if we know what makes a personal essay, we can reach that much wider into the tangle of free-floating human stories, search for, maybe even find, connections that change everything.
References and Resources:
- Faulkner, Sandra L., and Sheila Squillante. Writing the Personal: Getting Your Stories onto the Page . Rotterdam, The Netherlands: Brill | Sense, 2016.
- Miller, Brenda, and Suzanne Paola. Tell It Slant: Writing and Shaping Creative Nonfiction. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2005.
- Müller, Matthew Zanoni. “ Fits and Starts .” Hippocampus Magazine (December 2013).
- Silver, Linda Anne. “ The Capacity of a Human .” Hippocampus Magazine (May 2020).
- Silverman, Sue William. “The Meandering River.” The Writer’s Chronicle (September 2008).
Meet the Contributor

2 comments for “ CRAFT: What’s the Difference Between Memoir and Personal Essay? by Suzanne Farrell Smith ”
This was so helpful, I even took notes! Thank you for writing this.
As fabulous as ever, Suzanne. Love, Aunt Mary
Share a Comment Cancel reply
Contributor updates.

Alumni & Contributor Updates: Early 2024
Contributor Updates: Fall 2023
Contributor & Alumni Updates: Spring 2023
Contributor Updates: Spring 2022

The Difference between an Essay and a Reflection
If you're writing an essay, there are certain structures and guideline requirements to follow. If you're writing a reflection, the only guide is your emotions and your memories, and the only requirement is to be honest about what you think and how you feel.
Essay Guidelines and Structures

An essay is a short, informative piece of writing. It includes an introductory paragraph with a clear thesis statement, a body of at least three more paragraphs that relate back to the thesis statement, and a conclusion that sums up the writer's points and makes inferences about them.
The four main types of essays (persuasive, expository, descriptive, and narrative) each have their own guidelines to follow, and it's important to understand what is expected before outlining your essay and trying to organize your thoughts.
Reflection: Anything Goes
If you've been assigned a writing piece that is strictly a piece of reflective writing, you will most likely be given guidelines to follow that were chosen by the teacher or professor giving the assignment. However, there are no strict guidelines to follow in writing a traditional reflective piece and you don't have to wait for one to be assigned to practice and benefit from them. Think of it as being similar to writing in your diary or journal but with an attempt to explore why the experience you're writing made you feel the way you did and why you reacted to it in the way you did.
Reflective writing helps to capture your thoughts and feelings on an event, a current news story, a memory, or any other experience. Reflections can help you discover lessons you learned from that experience, develop your writing skills, and make sense of things that happen around you. The only real requirement is that you explore your own mind through your writing. You won't be just recounting a story or summarizing things that happened, reflection goes deeper into the writer's response to the subject being reflected upon.
The most important thing to remember about a reflection is that there is no correct or incorrect way to respond to any experience, so your reflection is not a judgment of your reactions. It is simply an exploration of them; therefore, exploring why you had that reaction and what past experiences you've had that caused you to react or feel the way you did is key to writing a good reflection.
- Synthesis essays
- GED essay ideas
- Descriptive essays about a place
- Winning IB extended essay samples
- Quality essay writing help
- Paper custom writing
- Custom paper online: no plagiarism
- A high-qualified paper writer
- College classification paper ideas
- Getting paper samples
- Custom paper writing services
- Finding paper writing help
- Quality paper writing agencies
- Compare & contrast paper tips
- Free 5 paragraph paper samples
- Getting I Have A Dream paper samples
- Finding a problem solution paper
- Picking up topics on social issues
- 500-word essay on youth violence
- Creating a business evaluation essay
- Writing a strong definition paper
- Extended response essay
- Product evaluation paper sample
- Essay about university and college
- Synthesis essay introduction
- Literary evaluation writing secrets
- Where to buy a cheap essay
- Visual media analysis paper
- College application topic ideas
- Picking up a trusted writing service
- Getting a Chicago style sample essay
- Writing about family education
- Nursing academic paper outline
- Creating an essay on sports clubs
- How to find an MLA style essay
- Definition paper about family
- Expository essay introduction
- Writing a paper on Romeo & Juliet
- Oprah Winfrey
- Irish War of Independence
- Socialization
- African American Women
- Igor Sikorsky
- Social Media
- The Scarlet Letter
- Nikola Tesla
- Alternative medicine
- Slavery in India
- Tourism in Thailand
- My future career
- Kodak & Fujifilm
- Johnny Depp
- The New York Times
- Johann Wolfgang Von Goethe
- Table Tennis
- Traditional VS Online Homework
- Kids are smarter due to the Internet
- Goals of the Civil War
- Same-sex marriage
- Political system of Cuba
- Habeas Corpus
- Boston Marathon bombing
- Substance abuse
- Critical analysis
- The Arabian Gulf and pollution
- The American Revolution
- Multi-cultural workforce
- Media and body image
- Paper quotes
poppies bookstore
writing ideas
- Search Here:
- Write my essay
- Freelance writing jobs
- Dissertation writing
- Looking for an experienced writer
- Biology argumentative paper ideas
- Writing about baseball
- Topics on pros & cons of uniforms
- Plastic surgery paper template
- Pope John Paul 2 essay example
- Guide to crafting a reflective essay
- Creating great paper topic ideas
- Discursive writing fundamentals
- Ideas for your profile paper writing
- Narrative essay VS reflective essay
- A descriptive paper about a picture
- Neanderthals paper sample
- Rhetorical evaluation writing basics
- Compare & contrast paper subjects
- Exploratory paper templates online
- Creating a paper on environment
- UFO essay sample
- Toyota essay template
- Dividing Korea essay template
- Writing a definition paper on values
- Good informative paper topics
- Opinion paper topics for 5th grade
What Is The Difference Between A Narrative And A Reflective Essay: Basic Tips
When you instructor says he wants a reflective essay written on a given topic, he’s probably assuming you know what “reflective means. He is probably assuming you know the difference between a narrative paper and a reflective one. Where does that leave you if his assumption is incorrect? What do you do if you are clueless as to the difference between narrative and reflective writing?
First of all, don’t panic. The difference between the two is not difficult to grasp. Simply put, a narrative essay is one that uses a story to teach a specific point or to offer an opinion on a certain matter. A narrative paper can use a story simply to entertain. A reflective essay has a specific purpose, such as demonstrating how you’ve overcome some obstacle in your life or how you made sense of a particular event or series of events. A reflective writing can use the same story as a narrative, but the reflective would show how the experience molded your view of the world around you or your perception of things to come.
A narrative tells the story; a reflective explains the story.
There are a few tips and tricks to getting the perfect writing on paper, whether you’re going for narrative or reflective:
- Go for clarity: Using complex words and intricate syntax may look impressive but it doesn’t add a lot to the overall clarity of your writing.
- Narrative essay: distribute the information between sentences and paragraphs to guide the reader through the sequence of events.
- Reflective essay: relate the event that is the subject of your paper in clear terms, remembering that your focus is not on the event itself but your response to that event.
- Keep it simple. You don’t have to describe each and every one of your movements or reactions.
- Pay attention to the tense of your writing. Avoid writing in second-person narrative. Writing in the present tense, first person point of view is acceptable for either a narrative or reflective essay.
- Choose your words wisely. Whether you’re writing narrative or reflective, your goal should be to engage your reader. Word choice is important because that is what will hold or lose your reader’s attention. Don’t be dry and clinical; but don’t get carried away with slang and “texting” language.
- Limit the number of references. Explain what you mean in your writing without referring your reader back to source material over and over.
Need help with essay or term paper? Go to https://mypaperdone.com to buy custom papers.
2024 © PoppiesBookstore.com | Great Ideas To Use When Writing An Essay

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here's a recap of the contents of this article, which also serves as a way to create a mind map: 1. Identify the topic you will be writing on. 2. Note down any ideas that are related to the topic and if you want to, try drawing a diagram to link together any topics, theories, and ideas. 3.
4. Writing the Body. Write the body of your essay, which should include the personal reflection, description of the experience, analysis of the experience, evaluation of the experience, identification of key learning, and planning for future action. Make sure to use specific examples and details to support your reflection. 5.
Reflective writing is a personal exploration of experiences, analyzing thoughts, feelings, and learnings to gain insights. It involves critical thinking, deep analysis, and focuses on personal growth through structured reflection on past events. In this guide, you'll learn everything you need to know about reflective writing — with lots of ...
The language of reflective writing. Reflective academic writing is: almost always written in the first person. evaluative - you are judging something. partly personal, partly based on criteria. analytical - you are usually categorising actions and events. formal - it is for an academic audience. carefully constructed.
Reflective essays are essays in which the writer looks back on, or reflects upon, his or her experiences and how they caused personal change. Reflective essays involve self-reflection. Reflective ...
Reflective Essay in MLA Format. Times New Roman 12pt font double spaced; 1" margins; The top right includes the last name and page number on every page; Titles are centered; The header should include your name, your professor's name, course number, and the date (dd/mm/yy); The last page includes a Works Cited.
A reflection is an essay, so provide full, thoughtful responses to the questions in your instructor's prompt. The style and tone of your reflective essay should match the purpose of the overall assignment. This is a personal essay meant to showcase what you learned from the text, event, or experience that you are writing about.
What Is a Reflective Essay: Definition. A good question to start with is, "What is a reflective essay?" A reflective essay is a type of academic writing, in which the student has to test personal life experience/position towards a particular topic. Unlike in argumentative writing, the student does not have to defend the personal position.
1. Choose Your Topic Carefully. If you are given the freedom to choose a topic and don't have any idea regarding it, the best way is to brainstorm and research some trending and good topic ideas. Unfortunately, a common mistake when writing a reflective essay is to choose a topic that is too broad or too narrow. 2.
4th Step: Draft, Revise, Edit, Repeat. A single, unpolished draft may suffice for short, in-the-moment reflections, but you may be asked to produce a longer academic reflection essay, which will require significant drafting, revising, and editing. Whatever the length of the assignment, keep this reflective cycle in mind:
Generally you will have two choices: Write about a topic chosen for you, also known as the essay prompt. Write about any topic you choose that is related to course content. To choose the best topic for your reflective essay, think about all you have gone over in your class. Brainstorming ideas can also help.
1. Job applications. Both preparing for and writing job applications contain elements of reflective writing. You need to think about the experience that makes you suitable for a role and this means reflection on the skills you have developed and how they might relate to the specification.
Step 1: Brainstorm and Choose a Topic. Begin by brainstorming a specific event, experience, or topic to reflect upon. It could be a personal experience, a book you've read, a class you've taken, or a significant life event. Here are some helpful tips for choosing a topic: Think about your personal experiences and select a topic that resonates ...
Narrative Essay. As opposed to the reflective essay, a narrative essay focuses on a specific event or a short sequence of events. Generally, this event would precipitate a change in belief or attitude in the writer. However, the emphasis is on the story itself. Purdue OWL recommends including all elements of a story, such as introduction ...
Reflective writing is an activity in which the writer chooses a memory, event, interaction, or scene, describes it, and includes a personal reflection. Such writing is valuable in the way it helps the writer thoroughly examine their thoughts and emotions and come up with a comprehensive conclusion as to what occurred in the past, how it ...
Because a personal statement is unlike other documents you write in college, many students struggle with understanding the fundamentals of its definition. First off, don't let the term itself confuse you—some application materials will use other terms such as "personal essay," "reflective essay," "statement of purpose," or ...
A typical academic essay is always informed by sound research, is written in the third person and has a clear structure formed around a thesis statement. However, in a reflective essay you are encouraged to: Also use first person: for example: I, me, he, orshe. Only use second person who you are quoting someone who has used the word "you ...
Both the language and the structure are important for academic reflective writing. For the structure you want to mirror an academic essay closely. You want an introduction, a main body, and a conclusion. Academic reflection will require you to both describe the context, analyse it, and make conclusions. However, there is not one set of rules ...
By my measure, memoir and personal essay differ along four lines: focus, mining, voice, and sense. Focus on Self vs. Focus on Relating. The memoirist focuses on the self and what has changed over time. Readers may identify— I went through something similar or I changed in the same way —but the memoirist's driving force is self-exploration.
A reflective essay is a type of written work which reflects your own self. Since it's about yourself, you already have a topic to write about. For reflective essay examples, readers expect you to evaluate a specific part of your life. To do this, you may reflect on emotions, memories, and feelings you've experienced at that time.
Reflective writing helps to capture your thoughts and feelings on an event, a current news story, a memory, or any other experience. Reflections can help you discover lessons you learned from that experience, develop your writing skills, and make sense of things that happen around you. The only real requirement is that you explore your own mind ...
Simply put, a narrative essay is one that uses a story to teach a specific point or to offer an opinion on a certain matter. A narrative paper can use a story simply to entertain. A reflective essay has a specific purpose, such as demonstrating how you've overcome some obstacle in your life or how you made sense of a particular event or ...