

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

Essay on Sustainable Development: Samples in 250, 300 and 500 Words
- Updated on
- Nov 18, 2023

On 3rd August 2023, the Indian Government released its Net zero emissions target policy to reduce its carbon footprints. To achieve the sustainable development goals (SDG) , as specified by the UN, India is determined for its long-term low-carbon development strategy. Selfishly pursuing modernization, humans have frequently compromised with the requirements of a more sustainable environment.
As a result, the increased environmental depletion is evident with the prevalence of deforestation, pollution, greenhouse gases, climate change etc. To combat these challenges, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change launched the National Clean Air Programme (NCAP) in 2019. The objective was to improve air quality in 131 cities in 24 States/UTs by engaging multiple stakeholders.
‘Development is not real until and unless it is sustainable development.’ – Ban Ki-Moon
The concept of Sustainable Development in India has even greater relevance due to the controversy surrounding the big dams and mega projects and related long-term growth. Since it is quite a frequently asked topic in school tests as well as competitive exams , we are here to help you understand what this concept means as well as the mantras to drafting a well-written essay on Sustainable Development with format and examples.
What is Sustainable Development?
As the term simply explains, Sustainable Development aims to bring a balance between meeting the requirements of what the present demands while not overlooking the needs of future generations. It acknowledges nature’s requirements along with the human’s aim to work towards the development of different aspects of the world. It aims to efficiently utilise resources while also meticulously planning the accomplishment of immediate as well as long-term goals for human beings, the planet as well and future generations. In the present time, the need for Sustainable Development is not only for the survival of mankind but also for its future protection.
Looking for ideas to incorporate in your Essay on Sustainable Development? Read our blog on Energy Management – Find Your Sustainable Career Path and find out!
250-300 Words Essay on Sustainable Development
To give you an idea of the way to deliver a well-written essay, we have curated a sample on sustainable development below, with 250-300 words:
300 Words Essay on Sustainable Development
To give you an idea of the way to deliver a well-written essay, we have curated a sample on sustainable development below, with 300 + words:

Must Read: Article Writing
500 Words Essay on Sustainable Development
To give you an idea of the way to deliver a well-written essay, we have curated a sample on sustainable development below, with 500 + words:

Essay Format
Before drafting an essay on Sustainable Development, students need to get familiarised with the format of essay writing, to know how to structure the essay on a given topic. Take a look at the following pointers which elaborate upon the format of a 300-350 word essay.
Introduction (50-60 words) In the introduction, students must introduce or provide an overview of the given topic, i.e. highlighting and adding recent instances and questions related to sustainable development. Body of Content (100-150 words) The area of the content after the introduction can be explained in detail about why sustainable development is important, its objectives and highlighting the efforts made by the government and various institutions towards it. Conclusion (30-40 words) In the essay on Sustainable Development, you must add a conclusion wrapping up the content in about 2-3 lines, either with an optimistic touch to it or just summarizing what has been talked about above.
Introduction
How to write the introduction of a sustainable development essay? To begin with your essay on sustainable development, you must mention the following points:
- What is sustainable development?
- What does sustainable development focus on?
- Why is it useful for the environment?
Conclusion of Sustainable Development Essay
How to write the conclusion of a sustainable development essay? To conclude your essay on sustainable development, mention why it has become the need of the hour. Wrap up all the key points you have mentioned in your essay and provide some important suggestions to implement sustainable development.
Importance of Sustainable Development
The importance of sustainable development is that it meets the needs of the present generations without compromising on the needs of the coming future generations. Sustainable development teaches us to use our resources in the correct manner. Listed below are some points which tell us the importance of sustainable development.
- Focuses on Sustainable Agricultural Methods – Sustainable development is important because it takes care of the needs of future generations and makes sure that the increasing population does not put a burden on Mother Earth. It promotes agricultural techniques such as crop rotation and effective seeding techniques.
- Manages Stabilizing the Climate – We are facing the problem of climate change due to the excessive use of fossil fuels and the killing of the natural habitat of animals. Sustainable development plays a major role in preventing climate change by developing practices that are sustainable. It promotes reducing the use of fossil fuels which release greenhouse gases that destroy the atmosphere.
- Provides Important Human Needs – Sustainable development promotes the idea of saving for future generations and making sure that resources are allocated to everybody. It is based on the principle of developing an infrastructure that is can be sustained for a long period of time.
- Sustain Biodiversity – If the process of sustainable development is followed, the home and habitat of all other living animals will not be depleted. As sustainable development focuses on preserving the ecosystem it automatically helps in sustaining and preserving biodiversity.
- Financial Stability – As sustainable development promises steady development the economies of countries can become stronger by using renewable sources of energy as compared to using fossil fuels, of which there is only a particular amount on our planet.
Examples of Sustainable Development
Mentioned below are some important examples of sustainable development. Have a look:
- Wind Energy – Wind energy is an easily available resource. It is also a free resource. It is a renewable source of energy and the energy which can be produced by harnessing the power of wind will be beneficial for everyone. Windmills can produce energy which can be used to our benefit. It can be a helpful source of reducing the cost of grid power and is a fine example of sustainable development.
- Solar Energy – Solar energy is also a source of energy which is readily available and there is no limit to it. Solar energy is being used to replace and do many things which were first being done by using non-renewable sources of energy. Solar water heaters are a good example. It is cost-effective and sustainable at the same time.
- Crop Rotation – To increase the potential of growth of gardening land, crop rotation is an ideal and sustainable way. It is rid of any chemicals and reduces the chances of disease in the soil. This form of sustainable development is beneficial to both commercial farmers and home gardeners.
- Efficient Water Fixtures – The installation of hand and head showers in our toilets which are efficient and do not waste or leak water is a method of conserving water. Water is essential for us and conserving every drop is important. Spending less time under the shower is also a way of sustainable development and conserving water.
- Sustainable Forestry – This is an amazing way of sustainable development where the timber trees that are cut by factories are replaced by another tree. A new tree is planted in place of the one which was cut down. This way, soil erosion is prevented and we have hope of having a better, greener future.
Related Articles
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a set of 17 global goals established by the United Nations in 2015. These include: No Poverty Zero Hunger Good Health and Well-being Quality Education Gender Equality Clean Water and Sanitation Affordable and Clean Energy Decent Work and Economic Growth Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure Reduced Inequality Sustainable Cities and Communities Responsible Consumption and Production Climate Action Life Below Water Life on Land Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions Partnerships for the Goals
The SDGs are designed to address a wide range of global challenges, such as eradicating extreme poverty globally, achieving food security, focusing on promoting good health and well-being, inclusive and equitable quality education, etc.
India is ranked #111 in the Sustainable Development Goal Index 2023 with a score of 63.45.
Hence, we hope that this blog helped you understand the key features of an essay on sustainable development. If you are interested in Environmental studies and planning to pursue sustainable tourism courses , take the assistance of Leverage Edu ’s AI-based tool to browse through a plethora of programs available in this specialised field across the globe and find the best course and university combination that fits your interests, preferences and aspirations. Call us immediately at 1800 57 2000 for a free 30-minute counselling session
Team Leverage Edu
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *
Thanks a lot for this important essay.
NICELY AND WRITTEN WITH CLARITY TO CONCEIVE THE CONCEPTS BEHIND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT IN SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY.
Thankyou so much!

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Essay On Sustainable Development
500 words essay on sustainable development.
Sustainable development is basically an action plan which helps us to achieve sustainability in any activity which makes use of the resource. Moreover, it also demands immediate and intergenerational replication. Through essay on sustainable development, we will help you understand the concept and its advantages.
Through sustainable development, we formulate organising principles which help to sustain the limited resources essential to provide for the needs of our future generations. As a result, they will be able to lead a content life on the planet .

What is Sustainable Development?
The World Commission on Environment and Development popularized this concept in 1987. Their report defines the idea as a “development which meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs.”
In other words, they aimed to prevent the stripping the natural world of resources which the future generations will require. As we all know that usually, one particular need drives development. Consequently, the wider future impacts are not considered.
As a result, a lot of damage happens due to this type of approach. Thus, the longer we continue to pursue unsustainable development, the more severe will the consequences be. One of the most common is climate change which is being debated widely worldwide.
In fact, climate change is already wreaking havoc on our surroundings. So, the need of the hour is sustainable development. We must ask ourselves, must we leave a scorched planet with an ailing environment for our future generations?
In order to undo the mess created by us, we must follow sustainable development. This will help us promote a more social, environmental and economical thinking. Most importantly, it is not that difficult to attain this.
We must see that world as a system which connects space, and time. Basically, it helps you understand that water pollution in South Africa will ultimately impact water quality in India. Similarly, it is the case for other things as well.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Measures to Practice Sustainable Development
There are many measures to take up for practising sustainable development. To begin with, it is important to ensure clean and hygienic living and working conditions for the people.
Next, sponsoring research on environmental issues which pertains to regions. Further, ensuring safety against known and proven industrial hazards. It is also important to find economical methods to salvage dangerous industrial wastes.
Most importantly, we must encourage afforestation . Including environmental education as part of the school and college curriculum will also help. Similarly, it is essential to socialize and humanize all environmental issues.
Further, we must encourage uses of non-conventional sources of energy, especially solar energy. Looking for substitutes for proven dangerous materials on the basis of local resources and needs will help. Likewise, we must produce environment-friendly products.
It is also essential to popularize the use of organic fertilizers and other biotechniques. Finally, the key is environmental management which must be monitored and ensure accountability.
Conclusion of Essay on Sustainable Development
To sum it up, sustainable development continuously seeks to achieve social and economic progress in ways which will not exhaust the Earth’s finite natural resources. Thus, we must all develop ways to meet these needs so that our future generations can inherit a healthier and greener planet.
FAQ on Essay on Sustainable Development
Question 1: State two measures we can take for sustainable development.
Answer 1: The first measure we can take is by finding economical methods for salvaging hazardous industrial wastes. Next, we must encourage afforestation.
Question 2: What is the aim of sustainable development?
Answer 2 : The aim of sustainable development is to maximise human well-being or quality of life without having to risk the life support system.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Sustainable Development Goals
The Sustainable Development Goals were adopted by the United Nations in 2015 as a call-to-action for people worldwide to address five critical areas of importance by 2030: people, planet, prosperity, peace, and partnership.
Biology, Health, Conservation, Geography, Human Geography, Social Studies, Civics
Set forward by the United Nations (UN) in 2015, the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) are a collection of 17 global goals aimed at improving the planet and the quality of human life around the world by the year 2030.
Image courtesy of the United Nations

In 2015, the 193 countries that make up the United Nations (UN) agreed to adopt the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. The historic agenda lays out 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and targets for dignity, peace, and prosperity for the planet and humankind, to be completed by the year 2030. The agenda targets multiple areas for action, such as poverty and sanitation , and plans to build up local economies while addressing people's social needs.
In short, the 17 SDGs are:
Goal 1: No Poverty: End poverty in all its forms everywhere.
Goal 2: Zero Hunger: End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture.
Goal 3: Good Health and Well-being: Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages.
Goal 4: Quality Education: Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all.
Goal 5: Gender Equality : Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls.
Goal 6: Clean Water and Sanitation: Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all.
Goal 7: Affordable and Clean Energy: Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all.
Goal 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth: Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all.
Goal 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure: Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization, and foster innovation.
Goal 10: Reduced Inequality : Reduce in equality within and among countries.
Goal 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities: Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable.
Goal 12: Responsible Consumption and Production: Ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns.
Goal 13: Climate Action: Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts.
Goal 14: Life Below Water: Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas, and marine resources for sustainable development.
Goal 15: Life on Land: Protect, restore, and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, sustainably manage forests, combat desertification, and halt and reverse land degradation and halt biodiversity loss.
Goal 16: Peace, Justice , and Strong Institutions: Promote peaceful and inclusive societies for sustainable development, provide access to justice for all and build effective, accountable, and inclusive institutions at all levels.
Goal 17: Partnerships to Achieve the Goal: Strengthen the means of implementation and revitalize the global partnership for sustainable development.
The SDGs build on over a decade of work by participating countries. In essence, the SDGs are a continuation of the eight Millennium Development Goals (MDGs), which began in the year 2000 and ended in 2015. The MDGs helped to lift nearly one billion people out of extreme poverty, combat hunger, and allow more girls to attend school. The MDGs, specifically goal seven, helped to protect the planet by practically eliminating global consumption of ozone-depleting substances; planting trees to offset the loss of forests; and increasing the percent of total land and coastal marine areas worldwide. The SDGs carry on the momentum generated by the MDGs with an ambitious post-2015 development agenda that may cost over $4 trillion each year. The SDGs were a result of the 2012 Rio+20 Earth Summit, which demanded the creation of an open working group to develop a draft agenda for 2015 and onward.
Unlike the MDGs, which relied exclusively on funding from governments and nonprofit organizations, the SDGs also rely on the private business sector to make contributions that change impractical and unsustainable consumption and production patterns. Novozymes, a purported world leader in biological solutions, is just one example of a business that has aligned its goals with the SDGs. Novozymes has prioritized development of technology that reduces the amount of water required for waste treatment. However, the UN must find more ways to meaningfully engage the private sector to reach the goals, and more businesses need to step up to the plate to address these goals.
Overall, limited progress has been made with the SDGs. According to the UN, many people are living healthier lives now compared to the start of the millennium, representing one area of progress made by the MDGs and SDGs. For example, the UN reported that between 2012 and 2017, 80 percent of live births worldwide had assistance from a skilled health professional—an improvement from 62 percent between 2000 and 2005.
While some progress has been made, representatives who attended sustainable development meetings claimed that the SDGs are not being accomplished at the speed, or with the appropriate momentum, needed to meet the 2030 deadline. On some measures of poverty, only slight improvements have been made: The 2018 SDGs Report states that 9.2 percent of the world's workers who live with family members made less than $1.90 per person per day in 2017, representing less than a 1 percent improvement from 2015. Another issue is the recent rise in world hunger. Rates had been steadily declining, but the 2018 SDGs Report stated that over 800 million people were undernourished worldwide in 2016, which is up from 777 million people in 2015.
Another area of the SDGs that lacks progress is gender equality. Multiple news outlets have recently reported that no country is on track to achieve gender equality by 2030 based on the SDG gender index. On a scale of zero to 100, where a score of 100 means equality has been achieved, Denmark was the top performing country out of 129 countries with score slightly under 90. A score of 90 or above means a country is making excellent progress in achieving the goals, and 59 or less is considered poor headway. Countries were scored against SDGs targets that particularly affect women, such as access to safe water or the Internet. The majority of the top 20 countries with a good ranking were European countries, while sub-Saharan Africa had some of the lowest-ranking countries. The overall average score of all countries is a poor score of 65.7.
In fall of 2019, heads of state and government will convene at the United Nations Headquarters in New York to assess the progress in the 17 SDGs. The following year—2020—marks the deadline for 21 of the 169 SDG targets. At this time, UN member states will meet to make a decision to update these targets.
In addition to global efforts to achieve the SDGs, according to the UN, there are ways that an individual can contribute to progress: save on electricity while home by unplugging appliances when not in use; go online and opt in for paperless statements instead of having bills mailed to the house; and report bullying online when seen in a chat room or on social media.
Media Credits
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Production Managers
Program specialists, last updated.
October 19, 2023
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources

Student Resources
Learning about sustainable development from an early age.
The materials available on this page are for adults and youth alike – a fun and engaging way to learn about the Sustainable Development Goals and what you can do to take action to make them a reality. Please download and share with your friends!

The ActNow campaign is the UN’s flagship campaign to inspire action for the Sustainable Development Goals. A gamified mobile app by AWorld continues to engage audiences worldwide. And the Climate Action Superheroes kids’ version of ActNow opened the campaign up to kids and their parents. The campaign provides entry points for individual action for a healthy planet as well as for a better economy , a just society and a world working together .

Teachers Guide on the SDGs
This teaching guide, aimed at grade level K-12, gives an introduction and historical background to the SDGs. Key questions along with primary resources are provided to facilitate comprehension and engage students critically. Through analysis of the Preamble to the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, the connection will be made to the Millenium Development Goals and Human Rights, to demonstrate continuity and evolution of certain principle values held by the international community. Focus then shifts to SDG 4, quality education, so that students can ore clearly analyze the progress that has been made regarding this topic on a micro level.
Download booklet

SDG Book Club
The SDG Book Club aims to use books as a tool to encourage children ages 6-12 to interact with the principles of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) through a curated reading list of books from around the world related to each of the 17 SDGs in all six official UN languages—Arabic, Chinese, English, French, Russian, and Spanish. Find out more!

Storytelling is a powerful communications tool and helps children remember lessons and virtues that they will use in everyday life. The idea behind the production of the story of Frieda was to simplify the lessons of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) so young children can relate to – and better understand – the SDGs. Follow Frieda’s journey through her home in Windhoek, Namibia – read and download the book here to learn about protecting life on land, the importance of water, the environment, and more!

170 Actions to Transform Our World
Get inspired by 170 Actions to Transform Our World ! This book contains 10 daily suggestions for each Goal on how you can make a difference in the world around you. A great tool for parents, teacher and children of all ages.

The Go Goals game is a board game that aims to help teach children around the world about the Sustainable Development Goals in a simple and child-friendly way. You’ll find questions and answers, game rules, dices and rules on how to play by clicking the link!

The Sustainable Development Goals – by YAK
Elyx, the United Nations’ digital ambassador, uses various expressions and actions to help demonstrate the meaning of each Sustainable Development Goal. Created by French artist YAK, Elyx has no race, sex or nationality and is a universal character promoting the importance of the United Nations’ work. Read the book online here .

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Introduction of Sustainability, Sustainable Development, and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
What is sustainability.
Sustainability is a well-known and frequently used term of the 21st century. How often do you see or hear the word? Have you ever stopped to really think about what exactly does sustainability mean and where did the term originate from?
A quick Google search for ‘what is sustainability’ yields over 1.9 billion results. Sustainability is widely defined as ‘the ability to be maintained at a certain rate or level’. Embedded in most definitions of sustainability are concerns for the environment, social equity, and economic prosperity(1). Most definitions look to avoid the depletion of natural resources to maintain an ecological balance. Sustainability in the context of the environment looks at the activities required to balance social, economic, and environmental needs to maintain ecosystem services at a suitable level. It is generally accepted, the goals of sustainability are related to the need for the conservation of natural capital and ecosystem services, with a shift to a less resource-intensive future [1] .
While to most, the concept of sustainability is a relatively new idea, sustainability has a long history of use and meaning. The practice of sustainability has been utilized by various cultures for thousands of years, with the term sustainability first used in the 1700’s. Sustainability comes from the practice of nachhaltigkeit , translated to mean ‘sustained yield’ in English, a term coined in 1713 by German foresters [2] . Sustained yield refers to the practice of taking only enough trees to allow forests to naturally regenerate well into the future. The concept of sustained yield broadened to include the conservation of plants, animals, and other food necessities, eventually moving beyond the forestry discourse but still mainly confined to research and science.
It was not until the 1970’s that the concept of sustainability became more widely used. In January 1972, the journal the Ecologist published the Blueprint for Survival , a series of science papers calling for better management of natural resources and modification of consumptive lifestyles of western civilizations. That same year, a global think-tank published the report Limits to Growth , where a definition was given to the term sustainable. For the first time in the literature, sustainable was defined to mean without sudden and uncontrolled collapse and capable of satisfying the basic material requirements of all its people (2). Then later that year the United Nations (UN) world conference on human environment was held Stockholm, Sweden to address the global the growing environmental crisis. The term sustainable development was introduced into the discourse. As evidenced at the UN Conference, the environment was being neglected and not in balance with economic development.
Through the 1980’s, the concept of sustainability became more mainstream. In 1987, former Norwegian Prime Minister Gro Harlem Brundtland, as chairwoman of what was then the World Commission on Environment and Development (WCED) released a Report, widely known as the Brundtland’s Commission, Our Common Future . The report emphasized the importance that development should consider social, environmental, and economic aspects to ensure the sustainability of all human societies. Her main concern was that development had to meet “the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs” [3] . This concept went on to become the most widely used definition of sustainability although in the context of sustainable development.
Although sustainability and sustainable development both consider the environment, society, and economies with a future timeframe, the two terms have very different meanings and should not be used interchangeably. Sustainability looks at the activities required to protect the environment as our base for survival while balancing social, cultural, and economic needs. It is generally accepted that the goals of sustainability are related to the need to conserve our natural world with a shift away from the resource-intensive current way of living 1 .
What is Sustainable Development?
We learned that sustainability is the process of living within the limits of available physical, natural, and social resources in ways that allow all living things, not only humans to thrive well into the future.
Sustainable development is a process that creates growth and progress through the addition of physical, economic, environmental, and social components to improve quality of life without damaging the resources of the environment. Simply put, sustainable development is a way for people to use resources without the resources running out 3 .
As previously discussed, the concept of sustainable development arrived in 1987 by the Brundtland Commission “Our Common Future”, the document that defined sustainable development as an approach designed to meet the needs of the present [generation] without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs 3 . This definition incorporated the understanding that economic growth is required to provide societies with the necessities of life such as clean water and food, while acknowledging the dilemma of environmental degradation that often coincides with economic development.
In 1992 the UN conference on the environment and development, informally known as the Earth Summit, or the Rio Conference took place in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. The conference promoted the idea of ecological sustainable development and in order to achieve it you had to consider social development (communities). From the mid 1990’s, different strategies were developed to try to work out what sustainability means in practice, how do we get that middle area where the environment, economics, and social development are achieved at the same time. Governments alone can not achieve sustainable development. Governments can set regulations and determine infrastructure needs but they don’t tend to have long-term goals in mind, they tend to focus on election cycles which are typically about 4 to 8 years. The market economies (goods and services) timeframe is usually only about 4 months to a year. Sustainability is about long-term solutions. The market economies and governments can not effectively do this. If the community is not driving the will for a better more sustainable future, sustainable development will be difficult to achieve. As we previously discussed, the Brundtland Commission’s definition has become a widely used definition for sustainable development and sustainability and has therefore come with many challenges, including confusion over meaning, interpretations, and misinformation.
Recognizing some of the key challenges with the implementation of sustainable development and the quest for achieving a balance between the environment and economies, the role of people and societies were formally added into the equation for sustainable development in 2005 at the UN World Summit on Social Development. The three pillars of sustainability became widely known and currently used today:
(Click on the “?” icons below for more information):
This updated model for sustainable development recognizes that in order to meet the needs of current and future generations you have to consider the three pillars or the 3P’s (people, planet, prosperity), and they all need to be working together at the same. The key being all at the same time, or simultaneously.
Integrating the short-term and long-term needs with a focus on future generations, will require social development, environmental protection, and economic prosperity working in unison. Being able to incorporate sustainability into your day to day activities, this is what will create change.
The United Nations and the Path to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
History of the un.
Direct Source
The United Nations is an international organization founded in 1945 after the Second World War by 51 countries committed to maintaining international peace and security, developing friendly relations among nations, and promoting social progress, better living standards and human rights.
Due to its unique international character, and the powers vested in its founding Charter, the Organization can take action on a wide range of issues and provide a forum for its 193 Member States to express their views, through the General Assembly, the Security Council, the Economic and Social Council and other bodies and committees.
The work of the United Nations reaches every corner of the globe. Although best known for peacekeeping, peace-building, conflict prevention and humanitarian assistance, there are many other ways the United Nations and its System (specialized agencies, funds, and programmes) affect our lives and make the world a better place. The Organization works on a broad range of fundamental issues, from sustainable development, environment and refugees protection, disaster relief, counter terrorism, disarmament and non-proliferation, to promoting democracy, human rights, gender equality and the advancement of women, governance, economic and social development and international health, clearing landmines, expanding food production, and more, in order to achieve its goals and coordinate efforts for a safer world for this and future generations.
The UN has 4 main purposes:
- To keep peace throughout the world;
- To develop friendly relations among nations;
- To help nations work together to improve the lives of poor people, to conquer hunger, disease, and illiteracy, and to encourage respect for each other’s rights and freedoms;
- To be a centre for harmonizing the actions of nations to achieve these goals

Pathway to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
In 2015, the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development was adopted by 193 United Nations (UN) Member States. The 2030 Agenda is centered on the 17 SDGs which are underpinned by the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs). The MDGs were developed in 2000 to end poverty and hunger, fight inequality and injustice, advance climate change action, create sustainable consumption and production, and promote peace and prosperity for all. One major change between the MDGs versus the SDGs is that for the SDGs, all countries are now involved. The MDGs only applied to developing countries. Another difference is that each country has set their own goals and priorities for achieving the SDGs. International collaboration to advance the SDG Agenda remains a critical component. The 17 SD goals, with their 169 targets, and over 230 indicators work together at the local and international level to help promote a shared global framework to achieve a fair, equitable, and sustainable future for all. Currently, all countries and international organizations are working on the achievement of the UN 2030 Agenda serving as the basis for better economic development that is environmentally low impact, socially just, and economically efficient and fair.
Pathway to the SDGs
Comprehension Questions
Recommended reading.
- Sustainable Development Solutions Network. (2021). Sustainable Development Report 2021: The Decade of Action for the Sustainable Development Goals .
Additional Readings
- Brundtland G, Khalid M. 1987. UN Brundtland commission report. Our Common Future . 41-59.
- Kidd C. V. 1992. The evolution of sustainability . Journal of Agricultural and Environmental Ethics , 5(1), 1-26.
- Baker, J., Dupont, D., & Vasseur, L. (2021). Exploring Canadian Ramsar Sites Ecosystem Governance and Sustainability. Wetlands, 41(1), 1-11. ↵
- Grober, U. (2007). Deep roots-a conceptual history of sustainable development (Nachhaltigkeit) . ↵
- United Nations. (2021). 1987 Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development: Our Common Future (page 41) . ↵
Introduction to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Copyright © by Jocelyn Baker is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Development Class 10 Notes CBSE Economics Chapter 1 (Free PDF Download)
- Revision Notes

Development Class 10 Notes Economics Chapter 1 - PDF Download
In Class 10 SST Economics Chapter 1, we’ll study the basic concept of development like What development is? Is it the same for everyone? How do we compare development? How to measure it? What does sustainable development mean? and many other things. In higher classes, we study this concept very deeply because it is very important for the economy to develop continuously. Here, we’ll be covering the various topics of CBSE Class 10 Social Science Economics Chapter 1, Development.

Related Chapters
Access Class 10 Social Science (Economics) Chapter 1- Development Notes
1. Introduction
Developmental goals of any particular idea vary from person to person.
Apart from personal development, we should definitely think of a country's development.
Development is defined as the people’s economic growth, along with the growth of their basic needs like education, health, lifestyle, etc.
The main aim of development is to update as per the demand of time.
For example: to generate electricity, a dam is constructed over a river where nearby mass is considered for construction resulting in the development of society and country.
It causes destruction for farmers and the lives of people living nearby.
2. Income and other goals
Money is considered to be the basic need of people and to fulfill their daily requirements making money or income is very important.
Money is required to buy materialistic things as well as freedom, security, treatment, respect to maintain a quality lifestyle.
Hence, developmental goals are necessary to get a better income and other things in life.
3. National Development
It is defined as a country’s ability to enhance the living standards of its residents.
For people, belief in nations' development is different.
Improvement in people’s living standards, providing basic things to citizens like food, education, social service, medical aid, etc, and increase in per capita income, is referred to as National development.
4. How can you differentiate different countries or states?
Income is a key feature to compare countries.
Countries that have higher income are called developed countries and vice versa.
The income of a country is about the income of the citizens of that country.
National income: it is the sum of the total value of the country’s goods and services produced in a year. As every country has a different population rate, so National income cannot be considered to compare between different countries.
Per capita income: it is also called average income, defined as a country's total earnings divided by the whole population. It shows the living standard of the citizens of the country.
The average income of the country is the ratio of the overall income of the country to the overall population of the country.
5. Income and other criteria
To achieve a goal, people earn more and want respect from others, the security of their lives, and freedom.
If we consider per capita in the country’s development, then Goa is the most developed and Bihar is the least developed state in India.
Net attendance ratio: defined as the total number of children, the age group from 14 years attending the school from the total percentage of children in the same age group.
Literacy rate: it is the total number of people above 7 years who can write, read and understand. If the literacy rate is high, then the state is considered to be developed. Kerala has the highest literacy rate of 96.2% and Andhra Pradesh has the lowest literacy rate of 66.4%.
Infant mortality rate: it is the total number of children that die in one year of age as a proportion of 1000 births in a year. It shows how efficient health facilities are in any country. Kerala has the lowest infant mortality rate, that is deaths per 1000 live births and Madhya Pradesh has the highest mortality rate that is 48 per 1000 live births in India.
6. Human Development Index
The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) prepares this index, in which an annual report of human development is published every year.
The major parameters include per capita income, literacy rate, and durability of a person’s life, which measure the countries’ development.
Countries are marked as very high, high, medium, and low developed countries respectively.
Apart from infant mortality rate, literacy rate, net attendance ratio; the BMI index also plays an important role.
7. Body mass index (BMI) is measured to measure the adults who are undernourished by calculating the weight of the person (kg) divided by the square of the height. If the value is less than 18.5, the person is undernourished and if it is more than 25, then the person is highly obese.
8. Public Facilities
Public facilities play a major role in the development of the country.
These are the facilities provided by the government like schools, transportation, electricity, hospitals, residences, community halls, etc.
These facilities are important as we cannot purchase every major facility.
9. Sustainable Development
It is the development that meets all needs of today’s generation.
It is the development of a nation without affecting the environment.
To achieve sustainable development, we should use non-renewable resources such as carbon-based fuel wisely.
Frequently Asked Questions and Answers
1. Write down the features of a developed country? Name the countries having the highest and lowest per capita income in 2019 (US Dollars).
Any country whose literacy rate, per capita income, and service rate is high, those countries are called a developed country.
The per capita income of a country is a measure of its number of people’s economic output.
Countries with per capita income having to be $128000 per annum are called developed countries. Example – Qatar.
Countries with a per capita income of $800 or less are known as developing countries. Example: Central African Republic.
2. What is IMR and why is it important? Which state has a high and low infant mortality rate?
IMR is the total number of children that die within 1 year of age as a proportion of 1000 births in a year.
This shows the efficiency of health facilities in a country.
Madhya Pradesh has a high infant mortality rate of 48 deaths per 1000 live births and Nagaland has a low infant mortality rate of 4 deaths per 1000 live births.
3. What is India’s per capita income in 2020? Which is the richest state of India? And which state of India makes more income?
As per the world development indicators, India has $7680 per capita income.
Maharashtra is the richest state in India with a nominal GDP of 28.78 lakh crore.
Sikkim has the lowest GDP of 0.287 lakh crore.
Goa has the highest per capita income of $6698 (Rs. 4,30,081)
4. Other than income, what are the other factors that are important for our lives?
Ans: Important factors for our lives are:
Safe environment for women at their workplace.
Freedom, respect, treatment, and security.
Pollution-free environment.
Political rights
5. What do you mean by development? Write down the aspect of development.
Ans: Development is the improvement of citizens' lives in terms of income, lifestyle, etc.
Major aspects of development are:
Development for anyone can be destructive for others.
Different people have different goals in life.
6. Why is average income an essential criterion for development?
Average income is the basic criteria because it shows the earning of a person, it also gives a clear idea about the standard of living. The average income will be less if the number of people who are not working is less.
7. Which neighboring country of India has better performance in terms of Human development?
Sri Lanka performed better in terms of human development than India.
It’s per capita income is $4390, 91% literacy rate, 93 HDI rank, 74 life expectancy at birth which is better than India and other neighboring countries that are Myanmar, Pakistan, Bhutan, Nepal, and Bangladesh.
8. Why do we use averages and what are their limitations? Provide some examples where the word “average” is used to compare situations.
Averages are used to compare different parameters of the same category, not people.
Averages do not provide information about the distribution of a particular thing between people.
Example: where the word average is used for comparing situations are:
To find out the literacy rates in the country.
Height and weight of students in a class with a total number of students.
To find the average income of people in the state.
9. “A development for one individual can be destructive for others”. Explain this statement with two examples.
Ans: Here are two examples are:
A businessman hires workers, those who are providing them more wages which is a development for workers, but on the other hand, it gives a loss for a businessman as he could have hired 2 or more workers at the same price.
Industrialists construct apartments and buildings for his/her personal development and for the nation. These apartments are destructive for farmers as they could have used this land for irrigation.
Class 10 Social Science Economics Chapter 1 Development Revision Notes
Class 10 sst economics chapter 1.
The topics covered in this chapter are discussed in brief below.
What Development Promises? - Different People, Different Goals
Society is a mixture of different people and different people have different goals and aspirations. This table shows that not all people have the same desires or goals. Buying a tractor can be said development for a farmer but not for a student or an employee. Thus, Different people can have different developmental goals.
Income & Other Goals
The aspirations or goals of a person can not only be just related to monetary aspects. Income is the most vital part to fulfill our goals and aspirations but people do have some non-material desires as well.
For example, You've got a job offer in company A and also in company B. A Provides a higher salary but no growth opportunities or a healthy job environment whereas B provides less pay with good working conditions and growth opportunities.
There are a lot of things that matter a lot but can't be measured. Thus, People also seek such non-material things besides seeking more income. Similarly, development is also a mixture of different sets of goals or desires.
National Development
As People have different goals, their notions of development will also be different. What should a country do for development? National development talks about this only.
(Image will be uploaded soon)
Class 10 social science economics chapter 1 does not talk about development in terms of individual or personal growth. It talks about Economic development and National Development.
How to Compare Different Countries?
Income is the most appropriate and important attribute to Compare different countries or states. The income of all the residents of the country is called the income of the country.
Different countries have different sizes of the population. Therefore, they can't be compared in terms of their total income.
Thus, Average income is used to compare the countries which are calculated by dividing the total population by the total income. It is also called Per Capita Income.
This criterion is also used for classifying countries as per World Development Reports of the World Bank.
Countries having a per capita income of US$ 12,056 p.a. and above in 2017 are classified as rich countries.
Countries having a per capita income of US$ 955 or less are classified as low-income countries.
Other Criteria Besides Income
While taking two countries or regions into consideration, not only average income is important but also public facilities do matter.
What are Public Facilities
The facilities provided by the government are called public facilities. These are provided for the welfare of the society and the development of the country.
For example Health & educational facilities, Infrastructure, sanitation, etc.
Kerala achieved a low infant mortality rate because of its adequate health & educational facilities.
In Some states, the Public Distribution System ( PDS ) works well.
Sustainability of Development
Sustainable Development means the development of the present without compromising future generations. Scientists are warning the world that present practices are not sustainable in nature. For example:
Exhaustion of Natural resources like Forests & Groundwater.
Exhaustion of Non-renewable resources like Coal, Petroleum, and natural gas.
Did You Know?
There are also Middle-Income Countries ( MICs ) which are having per capita between $ 1,036 and $ 12,535 and India lies in Low MICs having a per capita income of$1820 in 2017.

FAQs on Development Class 10 Notes CBSE Economics Chapter 1 (Free PDF Download)
1. How Countries or States are Compared? And Why?
The income of all the residents of the country is called the income of the country. States and countries cannot be compared by the total income of the country because different countries and states have different sizes of the population. Therefore, Countries or states are always compared by using the Average Income of both.
Average income is calculated by :
= Total income / Total population
This criterion is also used as per World Development Reports by the World Bank for classifying countries into various categories like rich countries or low-level income countries etc.
2. Write the Difference Between:
Development and Growth.
Development and Sustainable Development.
Thus, from Class 10 Social Science Economics Chapter 1 Development, we can conclude that development not only means having maximum per capita income but also means improving the quality and standard of living. The goals and desires of different people are different. Hence, their ways of seeing development will also be different. We’ve also learned about how to measure and compare different countries or states. It is always done to check and analyze where we’re lacking In the end, we also solved some questions. We hope this will help in understanding the whole SST Economics Class 10 Chapter 1.
3. What is sustainable development according to Chapter 1 of Class 10 Economics?
Sustainable development is the approach of economic development of the future generations without compromising and trading off the environment. This approach is developed and applied because it is often seen that for the sake of economic development, one has to often look over the damage that the environment has to go through in the form of air and water pollution, soil erosion, land degradation, deforestation etc. Therefore, with sustainable development, one aims at promoting development that minimises environmental damage.
4. What is sustainable management of natural resources according to the Notes of Chapter 1 of Class 10 Economics?
Due to the gradual increase in the population that results in the increase in demands, it is the need of the hour to ensure sustainable management of the resources for future generations, as the resources are seen to be depleting at an alarming rate. In order to achieve this, one can practice the 3 Rs.
Reduce: This aims to suggest the reduction in the use of the resources unnecessarily. For example, turning the switches off when not in need to save electricity, and turning the taps off to save water.
Reuse: This aims at suggesting the reusing of things and materials as much as they can be used. For instance, reusing plastic bottles instead of just throwing them away.
Recycle: In this process, the products such as plastic, metal or glass can be recycled and manufactured instead of developing from the start.
5. Are the NCERT Solutions provided by Vedantu for Chapter 1 of Class 10 Social Science useful?
Yes, the NCERT Solutions for Chapter 1 of Class 10 are extremely useful because they give deep insight and understanding of the chapters for the students. These solutions are particularly made to meet the demands of the students. Every exercise has with them solved answers that will help the student clear their doubts. These exercises are exam based, so the student will be able to practise how to answer any question asked in the exam. Thus, getting a copy of each NCERT solution for every subject will definitely lead the student in the right direction and help them score more than 90 percent in their exams.
6. How to prepare for Chapter 1 of Class 10 Social Science Economics?
It is undoubtedly important that the student should be thorough with all the concepts that are taught to them to be able to score desirable grades in their exams. To achieve this, they have to devote a good amount of time to read the chapter thoroughly. Along with this they also need to mark the important portion, for instance studying the goals that the people desire while doing work, the national development, the comparison between different countries and states and other such topics and revise them regularly to be able to retain the concepts. It is also advisable that they write down all the doubts that might arise while reading, and clear those doubts in the classroom. Referring to the Vedantu NCERT solutions available free of cost will help them immensely.
7. Is Chapter 1 of Class 10 Social Studies Economics scoring?
Yes, undoubtedly the Class 10 Social Studies Economics is easily scoring. But to be able to score well, it is important that the student is thorough with the topics. Without any understanding of what is being taught, even the easiest concepts become hard to write in the exams. For a subject such as social studies, the students need to take organized notes. They need to write down what they have understood in their own words under the various subheadings. This will help in sharpening their memory. Apart from this, they can also refer to the NCERT solutions available on the Vedantu website and app, which will prove to be a great source of guidance to them. These solutions for Economics Chapter 1 have exercises with solved solutions that will make the learning process easier for the students. The students will also be able to develop an idea of how the questions are set in the examination.
- CBSE Notes For Class 10
- Class 10 Science Notes
- Chapter 16: Sustainable Management Of Natural Resource
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 16 Sustainable Management of Natural Resources Notes
According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been removed from NCERT Class 10 Science textbook .
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 16 Sustainable Management Of Natural Resource Notes
Introduction.
Natural resources are substances obtained from the planet that is used to sustain life and provide for human needs. A natural resource is something that comes from nature that humans use. Natural resources include things like stone, sand, metals, oil, coal, and natural gas. Air, sunlight, soil, and water are other natural resources.
The well-being of people depends on natural resources. We cannot survive without the freshwater we drink, the plants we consume, or the pure air we breathe. To build roofs over our heads and heat our homes, we require natural resources.
Pollution in Ganga
- The river Ganga is used as a sewage dump for more than 100 cities stretching across Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and West Bengal.
- Dumping of untreated sewage, excreta and chemicals from industries increase the toxicity of the water.
- This makes it inhabitable for flora and fauna in the river system.
- In 1985 the GAP (Ganga Action Plan) project was initialised to curb the poor quality of the water of the river Ganges.
Reduce, Recycle and Reuse
The 3 Rs to save the environment can be performed by each individual in our society:
- Reduce: Reducing our usage and wasteful habits. E.g. not wasting food, turning off the switches to save electricity, repairing leaky taps, reducing the amount of water used for bathing, etc.
- Reuse: Using things again instead of discarding them. For example, reusing plastic utensils and bottles. Many things cannot be recycled or require a lot of energy; instead, we can utilize them for other purposes.
- Recycle: Collecting discarded paper, plastic, glass or metal objects to manufacture different products rather than synthesizing them from scratch. It must have a mechanism to segregate and dispose of each type of waste separately.
To know more about Saving the Environment from Pollution, visit here .
Why Do We Need to Manage Our Resources?
Need to manage natural resources.
- Due to the ever-increasing population and rising demands of changing lifestyles, natural resources are being depleted at an alarming rate. To ensure sustainable, equal distribution of resources and reduction of damage to the environment, management of resources must be an integral part of our society.
- We must ensure judicious use of our natural resources as it is not unlimited, and management of such requires long-term planning in order to last generations.
Increase in Demand for Natural Resources
- The increasing population is increasing the demand for more resources that are getting depleted at an exponential rate.
- Changing lifestyles and advancements in technology are compelling industries to exploit our natural reserves to meet the demands.
To know more about the Management of Natural Resources, visit here .
Forests and Wildlife
- Forests are termed biodiversity hotspots.
- Biodiversity is the variety and range of plant and animal life in a particular habitat.
- Loss of biodiversity may result in loss of ecological balance and damage to the ecosystem.
To know more about the Conservation of Forests and Wildlife, visit here .
Stakeholders of Forests
When we consider the conservation of forests, we must consider the following stakeholders:
- People who habituate around forests are dependent on forest produce.
- The Forest Department of Government owns the land and resources.
- Industrialists: who use the forest to produce certain products, e.g. leaves of Tendu for bidis and paper mills.
- Conservationists and wildlife enthusiasts who want to conserve nature in its pristine form.
To know more about the Stakeholders of a forest, visit here .
Monoculture
- Monoculture is the cultivation of a single crop in a given area.
- Excessive monoculture destroys the biodiversity of the area.
- Various needs of the people local to forest areas are neglected, such as leaves for fodder, herbs and fruits for consumption.
Industrialist’s Mentality and Influence
- Industrialists consider forests as a source of raw materials.
- Industries have more political power than the locals and only bother about meeting their demands. They do not care about sustainability and will move on from one habitat to another in search of raw materials.
People’s Intervention in Forests
- Human intervention is a necessity in the management of forest resources and landscapes.
- Resources must be utilised to ensure development while preserving the environment.
- Benefits must go to the local people to ensure economic growth and conservation takes place simultaneously.
- Examples: Bishnoi community in Rajasthan for saving Khejri trees in Jodhpur Rajasthan.
Damage to Forests and Wildlife
- Excessive and lawless utilisation of forests will deplete the resources quicker than they can be restored.
- Destroys the ecological balance and may damage the habitats of various species of flora and fauna.
Sustainable Development
- Sustainable development needs all stakeholders of forest resources to be satisfied.
- In reality, industries use forests at rates far below the market rates, which causes conflict between local dwellers and industrialists.
- West Bengal’s Arabari forests are well-known for being protected areas. This forest gained notoriety as a result of the participation of locals who established a community and worked with village police and forest officials to ensure that there was no significant deforestation, land poaching, or illegal wildlife hunting there.
Chipko Movement

- Originated in Reni Garhwal, high up in the Himalayas.

- The movement quickly gained popularity and media attention and forced the government to rethink the management of forest resources.
- The involvement of local people is equally important in the management of forest resources.
Water for All
- Water is a necessity for all terrestrial forms of life.
- In India, places having water scarcity are also places experiencing acute poverty.
- Despite the monsoon, there exists a failure to retain groundwater due to the loss of vegetation and the release of effluents from industries.
- Decrease in fresh usable water due to the destruction of the water table and disruption in the water cycle.
To know more about Water, visit here .
Rains and Irrigation Practices
- Intervention of the government to pursue mega projects neglected the local irrigation methods.
- Strict regulations on the usage of stored water and building tanks, dams and canals
- Optimum cropping patterns must be followed based on water availability.
Involvement of Local People (ex: kulhs)
- Himachal Pradesh had a canal irrigation system called kulhs where flowing stream water was diverted to man-made channels, which took it to villages down the hillside.
- The water was used first by the village farthest from the origin of the kulh. This helped water percolate in the soil.
- It was made defunct after the government irrigation system took over.
- Dams can store large amounts of water and generate electricity.
- Mismanagement of dams causes exploitation, and there is no equitable distribution of this resource.
- Criticism about large dams addresses: (i) Displacement of tribals without compensation (ii) Corruption and consumption of money without generation of benefits (iii) Environmental problems like deforestation.
- For irrigation, water from dams is used.
- Dam water is purified and made available for drinking in neighbouring towns and cities.
- Hydroelectric power is produced by dams and utilised to produce electricity.
- Dams stop flooding from taking lives and property.
Coal and Petroleum
Water harvesting.
- Water harvesting encourages soil and water conservation in order to sustain and increase biomass.
- Increases income for the local community but also alleviates floods and droughts.
- Examples: Rajasthan’s tanks, Khadins, and Nadis; Maharashtra’s Tals and Bandharas; Madhya Pradesh’s and Uttar Pradesh’s Bundhis; Bihar’s Pynes and Ahars; Himachal Pradesh’s Kulhs; Kattas in Karnataka; ponds in the Kandi belt of Jammu region; Eris (tanks) in Tamil Nadu and Kerala’s Surangams.
- Water harvesting constructions are crescent-shaped earthen embankments/concrete check dams built in areas that are seasonally flooded.
- The main purpose is to recharge groundwater.
The following is a list of the advantages of a rainwater harvesting system.
- Decreases the demand for water imports.
- Encourages energy and water conservation.
- Increases groundwater availability and quality.
- Does not need a filtering system for irrigation in gardens.
- This technology is comparatively straightforward and simple to install and use.
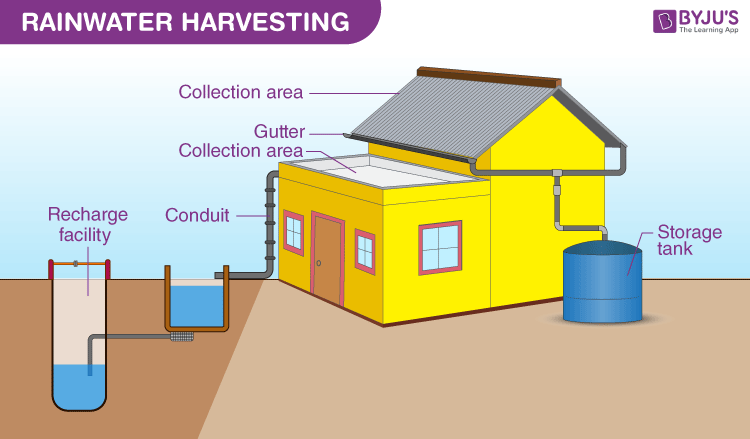
Groundwater
Advantages:
- does not evaporate
- recharges wells
- when flowing does not allow mosquitoes to breed
- does not come in contact with human contamination
To know more about Groundwater, visit here .
- Coal and petroleum are derived from fossil fuels, which are non-renewable. They will get depleted in due time. Hence, proper management of the consumption of fossil fuels is important.
- Their combustion pollutes our environment due to the production of oxides of carbon, sulfur and nitrogen. Therefore, we need to use these resources judiciously.
To know more about Coal and Petroleum, visit here .
Why Should Fossil Fuels Be Used Judiciously?
- Fossil fuels are formed over millions of years of degrading biomass and have a huge amount of carbon.
- When combusted in a limited supply of oxygen, they form harmful gases that pollute the atmosphere, which leads to global warming.
- Judicious use of fossil fuels addresses the efficiency of our machines and ensures the sustainability of our resources for the future.
Choices that Can Make a Difference in Energy Consumption
- Put your computer to sleep.
- Unplug any gadgets and equipment you are not using.
- Shower for fewer minutes.
- Set the refrigerator to 37–40 degrees F.
- Reduce your plug load by using a power strip.
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 16 Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
- Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 16 – Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
- NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Solutions for Chapter 16 – Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
- Maths Notes For Class 10
- CBSE Class 10 Social Science Notes
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 16 Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
What is sustainable development.
Sustainable development is defined as an approach to developing or growing by using resources in a way that allows them to renew or continue to exist for others.
What are the types of natural resources?
Natural resources include oil, coal, natural gas, metals, stone and sand. Air, sunlight, soil and water are other natural resources.
What are the main reasons for water pollution?
1. Rapid urban development 2. Improper sewage disposal 3. Oil spills 4. Chemical waste dumping 5. Radioactive waste discharge
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

COMMENTS
Essay on Sustainable Development: Samples in 250, 300 and 500 Words. On 3rd August 2023, the Indian Government released its Net zero emissions target policy to reduce its carbon footprints. To achieve the sustainable development goals (SDG), as specified by the UN, India is determined for its long-term low-carbon development strategy.
FAQ on Essay on Sustainable Development. Question 1: State two measures we can take for sustainable development. Answer 1: The first measure we can take is by finding economical methods for salvaging hazardous industrial wastes. Next, we must encourage afforestation.
The term "Sustainable Development" is defined as the development that meets the needs of the present generation without excessive use or abuse of natural resources so that they can be preserved for the next generation. There are three aims of sustainable development; first, the "Economic" which will help to attain balanced growth ...
Khejri Tree. 16.2.2 Management of forest. We need to consider if the goals of all the above stakeholders with regard to the management of the forests are the same. Forest resources are often made available for industrial use at rates far below the market value while these are denied to the local people.
The key principle of sustainable development underlying all others is the integration of environmental, social, and economic concerns into all aspects of decision making. All other principles in the SD framework have integrated decision making at their core (Dernbach J. C., 2003; Stoddart, 2011).
In short, the 17 SDGs are: Goal 1: No Poverty: End poverty in all its forms everywhere. Goal 2: Zero Hunger: End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture. Goal 3: Good Health and Well-being: Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages.
Class 10 - Social Science (Geography) Chapter 1 - Resources and Development ... Agenda 21 for achieving Sustainable Development in the 21st century. It aimed at achieving global sustainable development. It is an agenda which aims at combating environmental damage, poverty, disease through global co-operation on common interests, ...
Sustainable development objectives have been widely defined along three dimensions: "economic, environmental and social" or "ecology, economy and equity". The origins of the concept of sustainable development The concept of sustainable development has a very long history in science. For example, in 1713 Hans Carl von Carlowitz referred
The SDG Book Club aims to use books as a tool to encourage children ages 6-12 to interact with the principles of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) through a curated reading list of books ...
Sustainable development is. . . Considering that the concept of sustainable development is now enshrined on the masthead of Environment magazine, featured on 8,720,000 Web pages,1 and enmeshed in the aspirations of countless programs, places, and institutions, it should be easy to complete the sentence.2 But the most widely accepted definition
Sustainable development is a process that creates growth and progress through the addition of physical, economic, environmental, and social components to improve quality of life without damaging the resources of the environment. Simply put, sustainable development is a way for people to use resources without the resources running out 3.
Three core elements of sustainable development are economic growth, social inclusion and environmental protection. It is crucial to harmonize them. Sustainable economic growth, achieving sustainable livelihood, living in harmony with nature and appropriate technology are important for sustainable development.
Access Class 10 Science Chapter 16 - Management of Natural Resources. Natural resources are naturally occurring assets that are used to sustain life and meet our daily needs. It includes forests, water, coal, natural gases, and petroleum reserves. Depletion i.e., reduction in number or quality of natural resources is increasing at an alarming rate.
The students will also be able to develop an idea of how the questions are set in the examination. Share this with your friends. Download PDF. Download Development CBSE Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 notes PDF for free. Secure good marks by referring NCERT Class 10 Development revision notes prepared by Vedantu experts.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Selected Online Resources On 25 September 2015, a new set of global goals to end poverty, protect the planet, and ... to-Deliver-Agenda-2030.pdf • Bringing Data to Life: SDG human impact stories from across the globe (1 August 2022):
In 2015, the United Nations General Assembly adopted the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. 193 member countries, including India, got committed to the 17 Sustainable Development Goals that require efforts to end all forms of poverty, fight inequalities and tackle climate change while ensuring that no one was left behind.
while sustainable development refers to the many processes and pathways to achieve it (e.g. sustainable agriculture and forestry, sustainable production and consumption, good government, research and technology transfer, education and training, etc.). Principles of Sustainable Development All sustainable development programmes must consider the
Sustainable Development Index (SDI), 2019. It is released by the Sustainable Development Solutions Network (SDSN). The SDI seeks to help countries identify gaps that must be closed in order to achieve SDGs by 2030 and to identify priorities for early action. India ranked 115 out of 162 countries.
Sustainable development requires six central capacities. Sustainable development is an organizing principle that aims to meet human development goals while also enabling natural systems to provide necessary natural resources and ecosystem services to humans. The desired result is a society where living conditions and resources meet human needs without undermining the planetary integrity and ...
Target 6.5 "By 2030, implement integrated water resources management at all levels, including through transboundary cooperation as appropriate". • "Integrated water resources management (IWRM)" is a process to manage water resources in a comprehensive, participatory and coordinate manner by incorporating relevant sectors, stakeholders ...
It is important to preserve them in order to maintain ecological balance. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 16 Sustainable Management of Natural Resources are provided here to help the students clear their doubts and perform well in their exams. Visit now to download 2023-24 NCERT Class 10 Science Solutions PDF for free.
In this chapter, students will understand the various aspects of development that a country needs. The NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics Chapter 1 - Development contain the answers to the exercises given at the end of the book of Chapter 1. These solutions will help students to write their answers in an effective way during the CBSE exams.
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 16 Sustainable Management Of Natural Resource Notes. Download PDF. The management of human and natural landscape interactions is referred to as "natural resource management" (NRM). It combines land use planning, biodiversity preservation, water management, and the long-term viability of many enterprises ...