Trending Articles
- Global disparities in surgeons' workloads, academic engagement and rest periods: the on-calL shIft fOr geNEral SurgeonS (LIONESS) study. Podda M, et al. Updates Surg. 2024. PMID: 38684574
- The miR-200 family is increased in dysplastic lesions in ulcerative colitis patients. Lewis A, et al. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28288169 Free PMC article.
- CS incapacitant spray. Southward RD. J Accid Emerg Med. 2000. PMID: 10659007 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
- Left paraduodenal hernia accompanying chylous ascites. Yu DY, et al. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2015. PMID: 26576408 Free PMC article.
- Vitamin D regulates microbiome-dependent cancer immunity. Giampazolias E, et al. Science. 2024. PMID: 38662827

Latest Literature
- Cochrane Database Syst Rev (2)
- J Clin Endocrinol Metab (1)
- J Immunol (3)
- J Neurosci (1)
- Neuron (10)
- Pediatrics (3)
NCBI Literature Resources
MeSH PMC Bookshelf Disclaimer
The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited.

- Career Center
- Research in the Teaching of English
RTE is the flagship research journal of NCTE.
- Current Issue
- Write for Us
- Call for Manuscripts
- Alan C. Purves Award
- Advertise with Us
- Purchase Back Issues (Print)

Research in the Teaching of English ( RTE ) is a broad-based, multidisciplinary journal composed of original research articles and short scholarly essays on a wide range of topics significant to those concerned with the teaching and learning of languages and literacies around the world, both in and beyond schools and universities.
Subscribe Read It!
Editorial Staff
Editors and Editorial Assistants
Mollie Blackburn Ohio State University
David Bloome Ohio State University
Dorian Harrison Ohio State University
Michiko Hikida Ohio State University
Laurie Katz Ohio State University
Stephanie Power-Carter Ohio State University
Director of Publishing
Colin Murcray NCTE
Permissions
RTE Advisory Board for Volumes 58-62 (2023-2028)
Alfredo Artiles, Stanford University; Yona Asfaha, University of Asmara; April Baker-Bell, Michigan State University; Faythe Beauchemin, University of Arkansas; Pietro Boscolo, University of Padova; Maria Botelho, University of Massachusetts, Amherst; Maureen Boyd, University at Buffalo; Ayanna Brown, Elmhurst College; David Bwire, College of New Jersey; Blanca Caldas Chumbes, University of Minnesota; Gerald Campano, University of Pennsylvania; Antonia Candela, Centro de Investigación y Estudios Avanzados; Angela Cannon, Bloomington, IN; Limarys Caraballo, Teachers College, Columbia University; Lucia Cardenas, Michigan State University; Thandeka Chapman, University of California, San Diego; Caroline Clark, The Ohio State University; Catherine Compton-Lilly, University of South Carolina; Jamal Cooks, San Francisco State University; Marcus Croom, Indiana University; Denise Dávila, University of Texas at Austin; Adrienne Dixson, University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign; Leah Durán, University of Arizona; Elizabeth Dutro, University of Colorado, Boulder; Brian Edmiston, The Ohio State University; Patricia Enciso, The Ohio State University; Jeanne Fain, Lipscomb University; Tiffany Flowers, Georgia State University; Brittany Frieson Davis, University of North Texas; Danling Fu, University of Florida; Antero Godina Garcia, Stanford University; James Paul Gee, Arizona State University; Alexandra Georgakopolou, Kings College London; María Paula Ghiso, Teachers College, Columbia University; Susan Goldman, University of Illinois, Chicago; Millie Gort, University of Colorado, Boulder; Steven Graham, Vanderbilt University; Judith Green, University of California, Santa Barbara; David Green, Jr., Howard University; Lydia Haff, Hawaii; Troy Hicks, Central Michigan University; Jim Hoffman, University of North Texas; Huili Hong, Vanderbilt University ; Ana Christina Iddings Da Silva, Vanderbilt University; Vanessa Irvin, University of Hawaii; Hilary Janks, University of Witwatersrand; Korina Jocson, University of Massachusetts Amherst; Lamar Johnson, Michigan State; Latrise Johnson, University of Alabama; Miriam Jorge, University of Missouri-St. Louis; Judith Kalman, Centro de Investigación y Estudios Avanzados; Minjeong Kim, University of Massachusetts, Lowell; Lydiah Kiramba, University of Nebraska; Kafi Kumasi, Wayne State University; Wan Shun Eva Lam, Northwestern University; Kevin Leander, Vanderbilt University; Adam Leftstein, Ben Gurion University of the Negev; Constant Leung, Kings College London; Sarah Levine, Stanford University; Cynthia Lewis, University of California, Santa Cruz; Diana Liu, Columbia University; David Low, California State University, Fresno; Ruth Lowery, University of North Texas; Lian Madsen, University of Copenhagen; Joanne Marciano, Michigan State University; Danny Martinez, University of California, Davis; Ramón Martínez, Stanford University; Wayne Martino, Western University; Stephen May, The University of Auckland; Byeonggon Min, Seoul National University; Nicole Mirra, Rutgers University; Karla Möller, University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign; Briana Morales, St. Louis, MO; Ernest Morrell, Notre Dame University; Luz Murillo, Texas State University; Vanesa Neves, Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais; George Newell, The Ohio State University; Sue Nichols, University of South Australia; Carmen Helena Guerrero-Nieto, Universidad Distrital Francisco José de Caldas ; Silvia Nogueron-Liu, University of Colorado, Boulder; Allison Wynhoff Olsen, Montana State University; Mariana Pacheco, University of Wisconsin; Kate Pahl, Sheffield University; Deborah Palmer, University of Colorado, Boulder; Uta Papen, Lancaster University; Jenell Igeleke Penn, The Ohio State University; Tonya Perry, University of Alabama, Birmingham; Grace Player, University of Connecticut; David Poveda, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid; Detra Price-Dennis, Columbia University; Ben Rampton, Kings College London; Timothy Rasinski, Kent State University; Iliana Reyes, University of Arizona; Ryan Rish, State University of New York, Buffalo; Rebecca Rogers, University of Missouri St Louis; Deborah Rowe, Vanderbilt University; Jennifer Rowsell, University of Bristol; Lee Rutherford, Westerville, Ohio; Ryan Schey, University of Georgia; Yolanda Sealey-Ruiz, Columbia University; Audra Skukauskaite, University of Central Florida; Peter Smagorinsky, University of Georgia; Mandy Smith, Columbus, Ohio; Julia Snell, University of Leeds; Tamara Spencer, St. Mary’s College; Massimiliano Spotti, Tilburg University; Laura Sterponi, University of California, Berkeley; Amy Stornaiuolo, University of Pennsylvania; Laura Taylor, Rhodes College; Ebony Elizabeth Thomas, University of Michigan; K.C. Nat Turner, University of Massachusetts, Amherst; Cynthia Tyson, The Ohio State University; Lalitha Vasudevan, Teachers College, Columbia University; Saba Khan Vlach, University of Iowa; Jon Wargo, Boston College; Autumn West, Illinois State University; Melissa Wetzel, University of Texas, Austin; Jill Williams, Columbus, Ohio; Arlette Willis, University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign; Darius Wimby, Atlanta, GA; Ursula Wingate, Kings College London; Maisha Winn, University of Wisconsin; Karen Wohlwend, Indiana University; Angie Zapata, University of Missouri, Columbia
Annual Annotated Bibliographies
For many years now, RTE has been publishing an Annotated Bibliography of Research in the Teaching of English. Most recently, these bibliographies have been published annually in the February issue since 2018, and they have grown larger every year. Because of their length, the bibliographies are no longer published in their entirety in the print version of the journal; the complete version is to be found only online. They are open and available to all scholars, not just RTE subscribers.
2023 Bibliography
2022 Bibliography
2021 Bibliography
2020 Bibliography
2019 Bibliography
2018 Bibliography
2016 Bibliography
2015 Bibliography
2014 Bibliography
2013 Bibliography
2012 Bibliography
2011 Bibliography
2010 Bibliography
2009 Bibliography
2008 Bibliography
2007 Bibliography
2006 Bibliography
2005 Bibliography
2004 Bibliography
2003 Bibliography
Featured Journals
- Classroom Notes Plus
- College Composition and Communication
- College English
- English Education
- English Journal
- English Leadership Quarterly
- Language Arts
- School Talk
- Talking Points
- Teaching English in the Two-Year College
- Voices from the Middle

English dominates scientific research – here’s how we can fix it, and why it matters
Científica del Instituto de Lengua, Literatura y Antropología (ILLA), del Centro de Ciencias Humanas y Sociales (CCHS) del Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC), Centro de Ciencias Humanas y Sociales (CCHS - CSIC)
Disclosure statement
Elea Giménez Toledo does not receive a salary, nor does she own shares, nor does she receive funding from any company or organisation that might benefit from this article. She is a commissioner of the SEGIB, which implies only unpaid scientific advice to this institution, as part of the scientific activity carried out at the CSIC.
Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas provides funding as a founding partner of The Conversation ES.
View all partners
It is often remarked that Spanish should be more widely spoken or understood in the scientific community given its number of speakers around the world, a figure the Instituto Cervantes places at almost 600 million .
However, millions of speakers do not necessarily grant a language strength in academia. This has to be cultivated on a scientific, political and cultural level, with sustained efforts from many institutions and specialists.
The scientific community should communicate in as many languages as possible
By some estimates, as much as 98% of the world’s scientific research is published in English , while only around 18% of the world’s population speaks it. This makes it essential to publish in other languages if we are to bring scientific research to society at large.
The value of multilingualism in science has been highlighted by numerous high profile organisations, with public declarations and statements on the matter from the European Charter for Researchers , the Helsinki Initiative on Multiligualism , the Unesco Recommendation on Open Science , the OPERAS Multiligualism White Paper , the Latin American Forum on Research Assessment , the COARA Agreement on Reforming Research Assessment , and the Declaration of the 5th Meeting of Minsters and Scientific Authorities of Ibero-American Countries . These organisations all agree on one thing: all languages have value in scientific communication .
As the last of these declarations points out, locally, regionally and nationally relevant research is constantly being published in languages other than English. This research has an economic, social and cultural impact on its surrounding environment, as when scientific knowledge is disseminated it filters through to non-academic professionals, thus creating a broader culture of knowledge sharing.
Greater diversity also enables fluid dialogue among academics who share the same language, or who speak and understand multiple languages. In Ibero-America, for example, Spanish and Portuguese can often be mutually understood by non-native speakers, allowing them to share the scientific stage. The same happens in Spain with the majority of its co-official languages .
Read more: Non-native English speaking scientists work much harder just to keep up, global research reveals
No hierarchies, no categories
Too often, scientific research in any language other than English is automatically seen as second tier, with little consideration for the quality of the work itself.
This harmful prejudice ignores the work of those involved, especially in the humanities and social sciences. It also profoundly undermines the global academic community’s ability to share knowledge with society.
By defending and preserving multilingualism, the scientific community brings research closer to those who need it. Failing to pursue this aim means that academia cannot develop or expand its audience. We have to work carefully, systematically and consistently in every language available to us.
Read more: Prestigious journals make it hard for scientists who don't speak English to get published. And we all lose out
The logistics of strengthening linguistic diversity in science
Making a language stronger in academia is a complex process. It does not happen spontaneously, and requires careful coordination and planning. Efforts have to come from public and private institutions, the media, and other cultural outlets, as well as from politicians, science diplomacy , and researchers themselves.
Many of these elements have to work in harmony, as demonstrated by the Spanish National Research Council’s work in ES CIENCIA , a project which seeks to unite scientific and and political efforts.
Academic publishing and AI models: a new challenge
The global academic environment is changing as a result the digital transition and new models of open access. Research into publishers of scientific content in other languages will be essential to understanding this shift. One thing is clear though: making scientific content produced in a particular language visible and searchable online is crucial to ensuring its strength.
In the case of academic books, the transition to open access has barely begun , especially in the commercial publishing sector, which releases around 80% of scientific books in Spain. As with online publishing, a clear understanding will make it possible to design policies and models that account for the different ways of disseminating scientific research, including those that communicate locally and in other languages. Greater linguistic diversity in book publishing can also allow us to properly recognise the work done by publishers in sharing research among non-English speakers.
Read more: Removing author fees can help open access journals make research available to everyone
Making publications, datasets, and other non-linguistic research results easy to find is another vital element, which requires both scientific and technical support. The same applies to expanding the corpus of scientific literature in Spanish and other languages, especially since this feeds into generative artificial intelligence models.
If linguistically diverse scientific content is not incorporated into AI systems, they will spread information that is incomplete, biased or misleading: a recent Spanish government report on the state of Spanish and co-official languages points out that 90% of the text currently fed into AI is written in English.
Deep study of terminology is essential
Research into terminology is of the utmost importance in preventing the use of improvised, imprecise language or unintelligible jargon. It can also bring huge benefits for the quality of both human and machine translations, specialised language teaching, and the indexing and organisation of large volumes of documents.
Terminology work in Spanish is being carried out today thanks to the processing of large language corpuses by AI and researchers in the TeresIA project, a joint effort coordinated by the Spanish National Research Council. However, 15 years of ups and downs were needed to to get such a project off the ground in Spanish.
The Basque Country, Catalonia and Galicia, on the other hand, have worked intensively and systematically on their respective languages. They have not only tackled terminology as a public language policy issue, but have also been committed to established terminology projects for a long time.
Multiligualism is a global issue
This need for broader diversity also applies to Ibero-America as a whole, where efforts are being coordinated to promote Spanish and Portuguese in academia, notably by the Ibero-American General Secretariat and the Mexican National Council of Humanities, Sciences and Technologies .
While this is sorely needed, we cannot promote the region’s two most widely spoken languages and also ignore its diversity of indigenous and co-official languages. These are also involved in the production of knowledge, and are a vehicle for the transfer of scientific information, as demonstrated by efforts in Spain.
Each country has its own unique role to play in promoting greater linguistic diversity in scientific communication. If this can be achieved, the strength of Iberian languages – and all languages, for that matter – in academia will not be at the mercy of well intentioned but sporadic efforts. It will, instead, be the result of the scientific community’s commitment to a culture of knowledge sharing.
This article was originally published in Spanish
- Scientific publishing
- Multilingualism
- The Conversation Europe

Assistant Editor - 1 year cadetship

Program Development Officer - Business Processes

Executive Dean, Faculty of Health

Lecturer/Senior Lecturer, Earth System Science (School of Science)

Sydney Horizon Educators (Identified)
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Browse content in Art
- History of Art
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- History by Period
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Regional and National History
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Language Evolution
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Browse content in Religion
- Christianity
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Company and Commercial Law
- Comparative Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Financial Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Society
- Legal System and Practice
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Anaesthetics
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Forensic Medicine
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Medical Skills
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Paediatrics
- Browse content in Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Physical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Browse content in Computing
- Computer Security
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Environmental Sustainability
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Analysis
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Classical Mechanics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Browse content in Psychology
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Health Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Human Evolution
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic History
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Schools Studies
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Environment
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Economic Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- Political Sociology
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Theory
- Public Administration
- Public Policy
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Security Studies
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Research and Information
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Browse content in Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Migration Studies
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Journals A to Z
- Books on Oxford Academic

Most Read in Literature
From Shakespeare's plays to modern literary trends, explore a collection of our most read recent articles and chapters from our literature portfolio. Enhance your knowledge with free access to these highlights from our books and journals until December 2022.
Browse our collections
Browse our journals, browse our books, perilous networks: risk and maritime news in the merchant of venice, manuscript precedents for editorial practices in john benson’s poems: written by wil. shake-speare. gent, the surreal technics of andré breton and gilbert simondon, état présent lgbtq+ studies, humanities in the time of covid: the humanities coronavirus syllabus, li qingzhao and ecofeminism: body and language, intimacy: an alternative model for literary translation, porosity and the transnational: travelling theory between naples and frankfurt (walter benjamin, asja lacis and ernst bloch), encyclopaedic autobiography in roland barthes’s roland barthes (1975) and amy krouse rosenthal’s encyclopedia of an ordinary life (2004), “in de affica soil”: slavery, ethnography, and recovery in zora neale hurston’s barracoon: the story of the “last black cargo”, event, trauma, and ethics in wing tek lum’s the nanjing massacre, aphra behn: portraiture and the biographical account, the style of the old english metrical charms, the luster of studying contemporary publishing, literature and publishing, 1945–2020, ‘surrealism found me’: british surrealism and encounter, anti-narratives of slavery in colson whitehead’s the underground railroad, narratives of displacement: on embodied experience of migration in ulitskaya, lindén, and palei, jennifer egan, new sincerity, and the genre turn in contemporary fiction, mixed feelings, writing white: martha collins’s poetry of collective memory, on the parenthesis in t. s. eliot’s the cultivation of christmas trees, the hawks and the doves: raptors and rapture in the poems of thom gunn and ted hughes, discovery of zobel’s lost wartime short story: ‘bo-bo-bo-o’ or ‘up yours, hitler’, compare and contrast the relationship between voice, space, and forms of intimacy in two or more of the films studied on this unit, an anonymous caesurae uersuum and aldhelm’s de metris : a common source, the etymology of ‘girl’: two more ideas, illuminated caxtons and the trade in printed books, annotated copies of early editions of johnson's dictionary : a preliminary account, affect theory, modern literature, new literatures, women and books in the seventeenth century, oscar wilde’s world literature, transported, what made milton, ‘a profit to people’, introduction: placing early modern criticism, répétition planétaire, introduction: 26 april 1564, a room of one’s own, woolf’s “little book on poetry”, affiliations.
- Copyright © 2024
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
- Systematic Review
- Open access
- Published: 26 April 2024
Systematic review on the frequency and quality of reporting patient and public involvement in patient safety research
- Sahar Hammoud ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4682-9001 1 ,
- Laith Alsabek 1 , 2 ,
- Lisa Rogers 1 &
- Eilish McAuliffe 1
BMC Health Services Research volume 24 , Article number: 532 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
212 Accesses
Metrics details
In recent years, patient and public involvement (PPI) in research has significantly increased; however, the reporting of PPI remains poor. The Guidance for Reporting Involvement of Patients and the Public (GRIPP2) was developed to enhance the quality and consistency of PPI reporting. The objective of this systematic review is to identify the frequency and quality of PPI reporting in patient safety (PS) research using the GRIPP2 checklist.
Searches were performed in Ovid MEDLINE, EMBASE, PsycINFO, and CINAHL from 2018 to December, 2023. Studies on PPI in PS research were included. We included empirical qualitative, quantitative, mixed methods, and case studies. Only articles published in peer-reviewed journals in English were included. The quality of PPI reporting was assessed using the short form of the (GRIPP2-SF) checklist.
A total of 8561 studies were retrieved from database searches, updates, and reference checks, of which 82 met the eligibility criteria and were included in this review. Major PS topics were related to medication safety, general PS, and fall prevention. Patient representatives, advocates, patient advisory groups, patients, service users, and health consumers were the most involved. The main involvement across the studies was in commenting on or developing research materials. Only 6.1% ( n = 5) of the studies reported PPI as per the GRIPP2 checklist. Regarding the quality of reporting following the GRIPP2-SF criteria, our findings show sub-optimal reporting mainly due to failures in: critically reflecting on PPI in the study; reporting the aim of PPI in the study; and reporting the extent to which PPI influenced the study overall.
Conclusions
Our review shows a low frequency of PPI reporting in PS research using the GRIPP2 checklist. Furthermore, it reveals a sub-optimal quality in PPI reporting following GRIPP2-SF items. Researchers, funders, publishers, and journals need to promote consistent and transparent PPI reporting following internationally developed reporting guidelines such as the GRIPP2. Evidence-based guidelines for reporting PPI should be encouraged and supported as it helps future researchers to plan and report PPI more effectively.
Trial registration
The review protocol is registered with PROSPERO (CRD42023450715).
Peer Review reports
Patient safety (PS) is defined as “the absence of preventable harm to a patient and reduction of risk of unnecessary harm associated with healthcare to an acceptable minimum” [ 1 ]. It is estimated that one in 10 patients are harmed in healthcare settings due to unsafe care, resulting in over three million deaths annually [ 2 ]. More than 50% of adverse events are preventable, and half of these events are related to medications [ 3 , 4 ]. There are various types of adverse events that patients can experience such as medication errors, patient falls, healthcare-associated infections, diagnostic errors, pressure ulcers, unsafe surgical procedures, patient misidentification, and others [ 1 ].
Over the last few decades, the approach of PS management has shifted toward actively involving patients and their families in managing PS. This innovative approach has surpassed the traditional model where healthcare providers were the sole managers of PS [ 5 ]. Recent research has shown that patients have a vital role in promoting their safety and decreasing the occurrence of adverse events [ 6 ]. Hence, there is a growing recognition of patient and family involvement as a promising method to enhance PS [ 7 ]. This approach includes involving patients in PS policy development, research, and shared decision making [ 1 ].
In the last decade, research involving patients and the public has significantly increased. In the United Kingdom (U.K), the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) has played a critical role in providing strategic and infrastructure support to integrate Public and Patient Involvement (PPI) throughout publicly funded research [ 8 ]. This has established a context where PPI is recognised as an essential element in research [ 9 ]. In Ireland, the national government agency responsible for the management and delivery of all public health and social services; the National Health Service Executive (HSE) emphasise the importance of PPI in research and provide guidance for researchers on how to involve patients and public in all parts of the research cycle and knowledge translation process [ 10 ]. Similar initiatives are also developing among other European countries, North America, and Australia. However, despite this significant expansion of PPI research, the reporting of PPI in research articles continues to be sub-optimal, inconsistent, and lacks essential information on the context, process, and impact of PPI [ 9 ]. To address this problem, the Guidance for Reporting Involvement of Patients and the Public (GRIPP) was developed in 2011 following the EQUATOR methodology to enhance the quality, consistency, and transparency of PPI reporting. Additionally, to provide guidance for researchers, patients, and the public to advance the quality of the international PPI evidence-base [ 11 ]. The first GRIPP checklist was a significant start in producing higher-quality PPI reporting; however, it was developed following a systematic review, and did not include any input from the international PPI research community. Given the importance of reaching consensus in generating current reporting guidelines, a second version of the GRIPP checklist (GRIPP2) was developed to tackle this problem by involving the international PPI community in its development [ 9 ]. There are two versions of the GRIPP2 checklist, a long form (GRIPP2-LF) for studies with PPI as the primary focus, and a short form (GRIPP2-SF) for studies with PPI as secondary or tertiary focus.
Since the publication of the GRIPP2 checklist, several systematic reviews have been conducted to assess the quality of PPI reporting on various topics. For instance, Bergin et al. in their review to investigate the nature and impact of PPI in cancer research, reported a sub-optimal quality of PPI reporting using the GRIPP2-SF, mainly due to failure to address PPI challenges [ 12 ]. Similarly, Owyang et al. in their systematic review to assess the prevalence, extent, and quality of PPI in orthopaedic practice, described a poor PPI reporting following the GRIPP2-SF checklist criteria [ 13 ]. While a few systematic reviews have been conducted to assess theories, strategies, types of interventions, and barriers and enablers of PPI in PS [ 5 , 14 , 15 , 16 ], no previous review has assessed the quality of PPI reporting in PS research. Thus, our systematic review aims to address this knowledge gap. The objective of this review is to identify the frequency PPI reporting in PS research using the GRIPP2 checklist from 2018 (the year after GRIPP2 was published) and the quality of reporting following the GRIPP2-SF. The GRIPP2 checklist was chosen as the benchmark as it is the first international, evidence-based, community consensus informed guideline for the reporting of PPI in research and more specifically in health and social care research [ 9 ]. Additionally, it is the most recent report-focused framework and the most recommended by several leading journals [ 17 ].
We followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines to plan and report this review [ 18 ]. The review protocol was published on PROSPERO the International Database of Prospectively Registered Systematic Reviews in August 2023 (CRD42023450715).
Search strategy
For this review, we used the PICo framework to define the key elements in our research. These included articles on patients and public (P-Population) involvement (I- phenomenon of Interest) in PS (C-context). Details are presented in Table 1 . Four databases were searched including Ovid MEDLINE, EMBASE, PsycINFO, and CINAHL to identify papers on PPI in PS research. A systematic search strategy was initially developed using MEDLINE. MeSH terms and keywords relevant to specific categories (e.g., patient safety) were combined using the “OR” Boolean term (i.e. patient safety OR adverse event OR medical error OR surgical error) and categories were then combined using the “AND” Boolean term. (i.e. “patient and public involvement” AND “patient safety”). The search strategy was adapted for the other three databases. Full search strategies are provided in Supplementary file 1 . The search was conducted on July 27th, 2023, and was limited to papers published from 2018. As the GRIPP2 tool was published in 2017, this limit ensured the retrieval of relevant studies. An alert system was set on the four databases to receive all new published studies until December 2023, prior to the final analysis. The search was conducted without restrictions on study type, research design, and language. To reduce selection bias, hand searching was carried out on the reference lists of all the eligible articles in the later stages of the review. This was done by the first author. The search strategy was developed by the first author and confirmed by the research team and a Librarian. The database search was conducted by the first author.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Studies on PPI in PS research with a focus on health/healthcare were included in this review. We defined PPI as active involvement which is in line with the NIHR INVOLVE definition as “research being carried out ‘with’ or ‘by’ members of the public rather than ‘to’, ‘about’ or ‘for’ them” [ 19 ]. This includes any PPI including, being a co-applicant on a research project or grant application, identifying research priorities, being a member of an advisory or steering group, participating in developing research materials or giving feedback on them, conducting interviews with study participants, participating in recruitment, data collection, data analysis, drafting manuscripts and/or dissemination of results. Accordingly, we excluded studies where patients or the public were only involved as research participants.
We defined patients and public to include patients, relatives, carers, caregivers and community, which is also in line with the NIHR PPI involvement in National Health Service [ 19 ].
Patient safety included topics on medication safety, adverse events, communication, safety culture, diagnostic errors, and others. A full list of the used terms for PPI and PS is provided in Supplementary file 1 . Regarding the research type and design, we included empirical qualitative, quantitative, mixed methods, and case studies. Only articles published in peer-reviewed journals and in English were included.
Any article that did not meet the inclusion criteria was excluded. Studies not reporting outcomes were excluded. Furthermore, review papers, conference abstracts, letters to editor, commentary, viewpoints, and short communications were excluded. Finally, papers published prior to 2018 were excluded.
Study selection
The selection of eligible studies was done by the first and the second authors independently, starting with title and abstracts screening to eliminate papers that failed to meet our inclusion criteria. Then, full text screening was conducted to decide on the final included papers in this review. Covidence, an online data management system supported the review process, ensuring reviewers were blinded to each other’s decisions. Disagreements between reviewers were discussed first, in cases where the disagreement was not resolved, the fourth author was consulted.
Data extraction and analysis
A data extraction sheet was developed using excel then piloted, discussed with the research team and modified as appropriate. The following data were extracted: citation and year of publication, objective of the study, country, PS topic, design, setting, PPI participants, PPI stages (identifying research priorities, being a member of an advisory or steering group, etc.…), frequency of PPI reporting as per the GRIPP2 checklist, and the availability of a plain language summary. Additionally, data against the five items of GRIPP2-SF (aim of PPI in the study, methods used for PPI, outcomes of PPI including the results and the extent to which PPI influenced the study overall, and reflections on PPI) were extracted. To avoid multiple publication bias and missing outcomes, data extraction was done by the first and the second authors independently and then compared. Disagreements between reviewers were first discussed, and then resolved by the third and fourth authors if needed.
Quality assessment
The quality of PPI reporting was assessed using GRIPP2-SF developed by Staniszewska et al. [ 9 ] as it is developed to improve the quality, consistency, and reporting of PPI in social and healthcare research. Additionally the GRIPP2-SF is suitable for all studies regardless of whether PPI is the primary, secondary, or tertiary focus, whereas the GRIPP2-LF is not suitable for studies where PPI serves as a secondary or tertiary focus. The checklist includes five items (mentioned above) that authors should include in their studies. It is important to mention that Staniszewska et al. noted that “while GRIPP2-SF aims to guide consistent reporting, it is not possible to be prescriptive about the exact content of each item, as the current evidence-base is not advanced enough to make this possible” ([ 9 ] p5). For that reason, we had to develop criteria for scoring the five reporting items. We used three scoring as Yes, No, and partial for each of the five items of the GRIPP2-SF. Yes, was given when authors presented PPI information on the item clearly in the paper. No, when no information was provided, and partial when the information partially met the item requirement. For example, as per GRIPP2-SF authors should provide a clear description of the methods used for PPI in the study. In the example given by Staniszewska et al., information on patient/public partners and how many of them were provided, as well as the stages of the study they were involved in (i.e. refining the focus of the research questions, developing the search strategy, interpreting results). Thus, in our evaluation of the included studies, we gave a yes if information on PPI participants (i.e. patient partners, community partners, or family members etc..) and how many of them were involved was provided, and information on the stages or actions of their involvement in the study was provided. However, we gave a “partial” if information was not fully provided (i.e. information on patient/public partners and how many were involved in the study without describing in what stages or actions they were involved, and vice versa), and a “No” if no information was presented at all.
The quality of PPI reporting was done by the first and the second authors independently and then compared. Disagreements between reviewers were first discussed, and then resolved by the third and fourth author when needed.
Assessing the quality or risk of bias of the included studies was omitted, as the focus in this review was on appraising the quality of PPI reporting rather than assessing the quality of each research article.
Data synthesis
After data extraction, a table summarising the included studies was developed. Studies were compared according to the main outcomes of the review; frequency of PPI reporting following the GRIPP2 checklist and the quality of reporting as per GRIPP2-SF five items, and the availability of a plain language summary.
Search results and study selection
The database searches yielded a total of 8491 studies. First, 2496 were removed as duplicates. Then, after title and abstract screening, 5785 articles were excluded leaving 210 articles eligible for the full text review. After a careful examination, 68 of these studies were included in this review. A further 38 studies were identified from the alert system that was set on the four databases and 32 studies from the reference check of the included studies. Of these 70 articles, 56 were further excluded and 14 were added to the previous 68 included studies. Thus, 82 studies met the inclusion criteria and were included in this review. A summary of the database search results and the study selection process are presented in Fig. 1 .
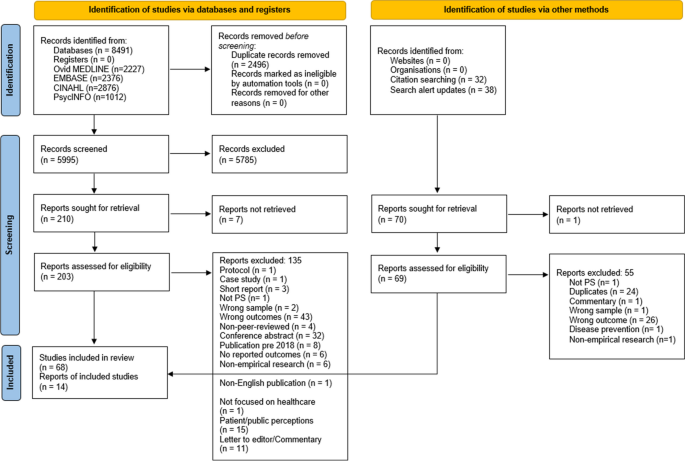
PRISMA flow diagram of the study selection process. The PRISMA flow diagram details the review search results and selection process
Overview of included studies
Details of the study characteristics including first author and year of publication, objective, country, study design, setting, PS topic, PPI participants and involvement stages are presented in Supplementary file 2 . The majority of the studies were conducted in the U.K ( n = 24) and the United States of America ( n = 18), with the remaining 39 conducted in other high income countries, the exception being one study in Haiti. A range of study designs were identified, the most common being qualitative ( n = 31), mixed methods ( n = 13), interventional ( n = 5), and quality improvement projects ( n = 4). Most PS topics concerned medication safety ( n = 17), PS in general (e.g., developing a PS survey or PS management application) ( n = 14), fall prevention ( n = 13), communication ( n = 11), and adverse events ( n = 10), with the remaining PS topics listed in Supplementary file 2 .
Patient representatives, advocates, and patient advisory groups ( n = 33) and patients, service users, and health consumers ( n = 32) were the main groups involved. The remaining, included community members/ organisations. Concerning PPI stages, the main involvement across the studies was in commenting on or developing research materials ( n = 74) including, patient leaflets, interventional tools, mobile applications, and survey instruments. Following this stage, involvement in data analysis, drafting manuscripts, and disseminating results ( n = 30), and being a member of a project advisory or steering group ( n = 18) were the most common PPI evident in included studies. Whereas the least involvement was in identifying research priorities ( n = 5), and being a co-applicant on a research project or grant application ( n = 6).
Regarding plain language summary, only one out of the 82 studies (1.22%) provided a plain language summary in their paper [ 20 ].
Frequency and quality of PPI reporting
The frequency of PPI reporting following the GRIPP2 checklist was 6.1%, where only five of the 82 included studies reported PPI in their papers following the GRIPP2 checklist. The quality of PPI reporting in those studies is presented in Table 2 . Of these five studies, one study (20%) did not report the aim of PPI in the study and one (20%) did not comment on the extent to which PPI influenced the study overall.
The quality of PPI reporting of the remaining 77 studies is presented in Table 3 . The aim of PPI in the study was reported in 62.3% of articles ( n = 48), while 3.9% ( n = 3) partially reported this. A clear description of the methods used for PPI in the study was reported in 79.2% of papers ( n = 61) and partially in 20.8% ( n = 16). Concerning the outcomes, 81.8% of papers ( n = 63) reported the results of PPI in the study, while 10.4% ( n = 8) partially did. Of the 77 studies, 68.8% ( n = 53) reported the extent to which PPI influenced the study overall and 3.9% ( n = 3) partially reported this. Finally, 57.1% ( n = 44) of papers critically reflected on the things that went well and those that did not and 2.6% ( n = 2) partially reflected on this.
Summary of main findings
This systematic review assessed the frequency of reporting PPI in PS research using the GRIPP2 checklist and quality of reporting using the GRIPP2-SF. In total, 82 studies were included in this review. Major PS topics were related to medication safety, general PS, and fall prevention. Patient representatives, advocates, patient advisory groups, patients, service users, and health consumers were the most involved. The main involvement across the studies was in commenting on or developing research materials such as educational and interventional tools, survey instruments, and applications while the least was in identifying research priorities and being a co-applicant on a research project or grant application. Thus, significant effort is still needed to involve patients and the public in the earlier stages of the research process given the fundamental impact of PS on their lives.
Overall completeness and applicability of evidence
A low frequency of reporting PPI in PS research following the GRIPP2 guidelines was revealed in this review, where only five of the 82 studies included mentioned that PPI was reported as per the GRIPP2 checklist. This is despite it being the most recent report-focused framework and the most recommended by several leading journals [ 17 ]. This was not surprising as similar results were reported in recent reviews in other healthcare topics. For instance, Musbahi et al. in their systematic review on PPI reporting in bariatric research reported that none of the 90 papers identified in their review mentioned or utilised the GRIPP2 checklist [ 102 ]. Similarly, a study on PPI in orthodontic research found that none of the 363 included articles reported PPI against the GRIPP2 checklist [ 103 ].
In relation to the quality of reporting following the GRIPP2-SF criteria, our findings show sub-optimal reporting within the 77 studies that did not use GRIPP2 as a guide/checklist to report their PPI. Similarly, Bergin et al. in their systematic review to investigate the nature and impact of PPI in cancer research concluded that substandard reporting was evident [ 12 ]. In our review, this was mainly due to failure to meet three criteria. First, the lowest percentage of reporting (57.1%, n = 44) was related to critical reflection on PPI in the study (i.e., what went well and what did not). In total, 31 studies (42.9%) did not provide any information on this, and two studies were scored as partial. The first study mentioned that only involving one patient was a limitation [ 27 ] and the other stated that including three patients in the design of the tool was a strength [ 83 ]. Both studies did not critically comment or reflect on these points so that future researchers are able to avoid such problems and enhance PPI opportunities. For instance, providing the reasons/challenges behind the exclusive inclusion of a single patient and explaining how this limits the study findings and conclusion would help future researchers to address these challenges. Likewise, commenting on why incorporating three patients in the design of the study tool could be seen as a strength would have been beneficial. This could be, fostering diverse perspectives and generating novel ideas for developing the tool. Similar to our findings, Bergin et al. in their systematic review reported that 40% of the studies failed to meet this criterion [ 12 ].
Second, only 48 out of 77 articles (62.3%) reported the aim of PPI in their study, which is unlike the results of Bergin et al. where most of the studies (93.1%) in their review met this criterion [ 12 ]. Of the 29 studies which did not meet this criterion in our review, few mentioned in their objective developing a consensus-based instrument [ 41 ], reaching a consensus on the patient-reported outcomes [ 32 ], obtaining international consensus on a set of core outcome measures [ 98 ], and facilitating a multi-stakeholder dialogue [ 71 ] yet, without indicating anything in relation to patients, patient representatives, community members, or any other PPI participants. Thus, the lack of reporting the aim of PPI was clearly evident in this review. Reporting the aim of PPI in the study is crucial for promoting transparency, methodological rigor, reproducibility, and impact assessment of the PPI.
Third, 68.8% ( n = 53) of the studies reported the extent to which PPI influenced the study overall including positive and negative effects if any. This was again similar to the findings of Bergin et al., where 38% of the studies did not meet this criterion mainly due to a failure to address PPI challenges in their respective studies [ 12 ]. Additionally, Owyang et al. in their review on the extent, and quality of PPI in orthopaedic practice, also described a poor reporting of PPI impact on research [ 13 ]. As per the GRIPP2 guidelines, both positive and negative effects of PPI on the study should be reported when applicable. Providing such information is essential as it enhances future research on PPI in terms of both practice and reporting.
Reporting a clear description of the methods used for PPI in the study was acceptable, with 79.2% of the papers meeting this criterion. Most studies provided information in the methods section of their papers on the PPI participants, their number, stages of their involvement and how they were involved. Providing clear information on the methods used for PPI is vital to give the reader a clear understanding of the steps taken to involve patients, and for other researchers to replicate these methods in future research. Additionally, reporting the results of PPI in the study was also acceptable with 81.8% of the papers reporting the outcomes of PPI in the results section. Reporting the results of PPI is important for enhancing methodological transparency, providing a more accurate interpretation for the study findings, contributing to the overall accountability and credibility of the research, and informing decision making.
Out of the 82 studies included in this review, only one study provided a plain language summary. We understand that PS research or health and medical research in general is difficult for patients and the public to understand given their diverse health literacy and educational backgrounds. However, if we expect patients and the public to be involved in research then, it is crucial to translate this research that has a huge impact on their lives into an easily accessible format. Failing to translate the benefits that such research may have on patient and public lives may result in them underestimating the value of this research and losing interest in being involved in the planning or implementation of future research [ 103 ]. Thus, providing a plain language summary for research is one way to tackle this problem. To our knowledge, only a few health and social care journals (i.e. Cochrane and BMC Research Involvement and Engagement) necessitate a plain language summary as a submission requirement. Having this as a requirement for submission is crucial in bringing the importance of this issue to researchers’ attention.
Research from recent years suggests that poor PPI reporting in articles relates to a lack of submission requirements for PPI reporting in journals and difficulties with word limits for submitted manuscripts [ 13 ]. Price et al. assessed the frequency of PPI reporting in published papers before and after the introduction of PPI reporting obligations by the British Medical Journal (BMJ) [ 104 ]. The authors identified an increase in PPI reporting in papers published by BMJ from 0.5% to 11% between the periods of 2013–2014 and 2015–2016. The study findings demonstrate the impact of journal guidelines in shaping higher quality research outputs [ 13 ]. In our review, we found a low frequency of PPI reporting in PS research using the GRIPP2 checklist, alongside sub-optimal quality of reporting following GRIPP2-SF. This could potentially be attributed to the absence of submission requirements for PPI reporting in journals following the GRIPP2 checklist, as well as challenges posed by word limits.
Strengths and limitations
This systematic review presents an overview on the frequency of PPI reporting in PS research using the GRIPP2 checklist, as well as an evaluation of the quality of reporting following the GRIPP2-SF. As the first review to focus on PS research, it provides useful knowledge on the status of PPI reporting in this field, and the extent to which researchers are adopting and adhering to PPI reporting guidelines. Despite these strengths, our review has some limitations that should be mentioned. First, only English language papers were included in this review due to being the main language of the researchers. Thus, there is a possibility that relevant articles on PPI in PS research may have been omitted. Another limitation is related to our search which was limited to papers published starting 2018 as the GRIPP2 guidelines were published in 2017. Thus it is probable that the protocols of some of these studies were developed earlier than the publication of the GRIPP2 checklist, meaning that PPI reporting following GRIPP2 was not common practice and thus not adopted by these studies. This might limit the conclusions we can draw from this review. Finally, the use of GRIPP2 to assess the quality of PPI reporting might be a limitation as usability testing has not yet been conducted to understand how the checklist works in practice with various types of research designs. However, the GRIPP2 is the first international, evidence-based, community consensus informed guideline for the reporting of PPI in health and social care research. Reflections and comments from researchers using the GRIPP2 will help improve its use in future studies.
Implications for research and practice
Lack of PPI reporting not only affects the quality of research but also implies that others cannot learn from previous research experience. Additionally, without consistent and transparent reporting it is difficult to evaluate the impact of various PPI in research [ 9 ]: “if it is not reported it cannot be assessed” ([ 105 ] p19). Enhanced PPI reporting will result in a wider range and richer high-quality evidence-based PPI research, leading to a better understanding of PPI use and effectiveness [ 103 ]. GRIPP2 reporting guidelines were developed to provide guidance for researchers, patients, and the public to enhance the quality of PPI reporting and improve the quality of the international PPI evidence-base. The guidance can be used prospectively to plan PPI or retrospectively to guide the structure or PPI reporting in research [ 9 ]. To enhance PPI reporting, we recommend the following;
Publishers and journals
First, we encourage publishers and journals to require researchers to report PPI following the GRIPP2 checklist. Utilising the short or the long version should depend on the primary focus of the study (i.e., if PPI is within the primary focus of the research then the GRIPP2-LF is recommended). Second, we recommend that journals and editorial members advise reviewers to evaluate PPI reporting within research articles following the GRIPP2 tool and make suggestions accordingly. Finally, we encourage journals to add a plain language summary as a submission requirement to increase research dissemination and improve the accessibility of research for patients and the public.
Researchers
Though there is greater evidence of PPI in research, it is still primarily the researchers that are setting the research agenda and deciding on the research questions to be addressed. Thus, significant effort is still needed to involve patients and the public in the earlier stages of the research process given the fundamental impact of PS on their lives. To enhance future PPI reporting, perhaps adding a criterion following the GRIPP2 tool to existing EQUATOR checklists for reporting research papers such as STROBE, PRISMA, CONSORT, may support higher quality research. Additionally, currently, there is no detailed explanation paper for the GRIPP2 where each criterion is explained in detail with examples. Addressing this gap would be of great benefit to guide the structure of PPI reporting and to explore the applicability of each criterion in relation to different stages of PPI in research. For instance, having a detailed explanation for each criterion across different research studies having various PPI stages would be of high value to improve future PPI reporting given the growing interest in PPI research in recent years and the relatively small PPI evidence base in health and medical research.
Funding bodies can also enhance PPI reporting by adding a requirement for researchers to report PPI following the GRIPP2 checklist. In Ireland, the National HSE has already initiated this by requiring all PPI in HSE research in Ireland to be reported following the GRIPP2 guidelines [ 10 ].
This study represents the first systematic review on the frequency and quality of PPI reporting in PS research using the GRIPP2 checklist. Most PS topics were related to medication safety, general PS, and fall prevention. The main involvement across the studies was in commenting on or developing research materials. Thus, efforts are still needed to involve patients and the public across all aspects of the research process, especially earlier stages of the research cycle. The frequency of PPI reporting following the GRIPP2 guidelines was low, and the quality of reporting following the GRIPP2-SF criteria was sub-optimal. The lowest percentages of reporting were on critically reflecting on PPI in the study so future research can learn from this experience and work to improve it, reporting the aim of the PPI in the study, and reporting the extent to which PPI influenced the study overall including positive and negative effects. Researchers, funders, publishers, journals, editorial members and reviewers have a responsibility to promote consistent and transparent PPI reporting following internationally developed reporting guidelines such as the GRIPP2. Evidence-based guidelines for reporting PPI should be supported to help future researchers plan and report PPI more effectively, which may ultimately improve the quality and relevance of research.

Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and its Supplementary information files.
Abbreviations
- Patient safety
United Kingdom
National Institute for Health Research
Public and Patient Involvement
Health Service Executive
Guidance for Reporting Involvement of Patients and the Public
Second version of the GRIPP checklist
Long form of GRIPP2
Short form of GRIPP2
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
The International Database of Prospectively Registered Systematic Reviews
British Medical Journal
Patient saftey: World Health Organisation. 2023. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/patient-safety . Updated 11 Sept 2023.
Slawomirski L, Klazinga N. The economics of patient safety: from analysis to action. Paris: Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development; 2020.
Google Scholar
Panagioti M, Khan K, Keers RN, Abuzour A, Phipps D, Kontopantelis E, et al. Prevalence, severity, and nature of preventable patient harm across medical care settings: systematic review and meta-analysis. Bmj-Brit Med J. 2019;366:l4185.
Article Google Scholar
Hodkinson A, Tyler N, Ashcroft DM, Keers RN, Khan K, Phipps D, et al. Preventable medication harm across health care settings: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Bmc Medicine. 2020;18(1):313.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Park M, Giap TTT. Patient and family engagement as a potential approach for improving patient safety: A systematic review. J Adv Nurs. 2020;76(1):62–80.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Chegini Z, Janati A, Bababie J, Pouraghaei M. The role of patients in the delivery of safe care in hospital: Study protocol. J Adv Nurs. 2019;75(9):2015–23.
Chegini Z, Arab-Zozani M, Islam SMS, Tobiano G, Rahimi SA. Barriers and facilitators to patient engagement in patient safety from patients and healthcare professionals’ perspectives: A systematic review and meta-synthesis. Nurs Forum. 2021;56(4):938–49.
Going the extra mile: improving the nation’s health and wellbeing through public involvement in research. London: National Institute for Health; 2015.
Staniszewska S, Brett J, Simera I, Seers K, Mockford C, Goodlad S, et al. GRIPP2 reporting checklists: tools to improve reporting of patient and public involvement in research. Bmj-Brit Med J. 2017;358:j3453.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Minogue V. Knowledge translation, dissemination, and impact: a practical guide for researchers. Guide No 8: patient and public involvement in HSE research. Ireland: Health Service Executive Research and Development; 2021.
Staniszewska S, Brett J, Mockford C, Barber R. The GRIPP checklist: Strengthening the quality of patient and public involvement reporting in research. Int J Technol Assess Health Care. 2011;27(4):391–9.
Bergin RJ, Short CE, Davis N, Marker J, Dawson MT, Milton S, et al. The nature and impact of patient and public involvement in cancer prevention, screening and early detection research: A systematic review. Prev Med. 2023;167:107412.
Owyang D, Bakhsh A, Brewer D, Boughton OR, Cobb JP. Patient and public involvement within orthopaedic research a systematic review. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2021;103(13):e51.
Busch IM, Saxena A, Wu AW. Putting the patient in patient safety investigations: barriers and strategies for involvement. J Patient Saf. 2021;17(5):358–62.
Lee M, Lee NJ, Seo HJ, Jang H, Kim SM. Interventions to engage patients and families in patient safety: a systematic review. West J Nurs Res. 2021;43(10):972–83.
Ocloo J, Garfield S, Franklin BD, Dawson S. Exploring the theory, barriers and enablers for patient and public involvement across health, social care and patient safety: a systematic review of reviews. Health Res Policy Syst. 2021;19(1):8.
Greenhalgh T, Hinton L, Finlay T, Macfarlane A, Fahy N, Clyde B, et al. Frameworks for supporting patient and public involvement in research: Systematic review and co-design pilot. Health Expect. 2019;22(4):785–801.
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Plos Medicine. 2021;18(3):372.
INVOLVE. What is public involvement in research? NIHR; 2019. Available from: https://www.invo.org.uk/find-out-more/what-is-public-involvement-in-research-2/ .
Shahid A, Sept B, Kupsch S, Brundin-Mather R, Piskulic D, Soo A, et al. Development and pilot implementation of a patient-oriented discharge summary for critically Ill patients. World J Crit Care Med. 2022;11(4):255–68.
Bisset CN, Dames N, Oliphant R, Alasadi A, Anderson D, Parson S, et al. Exploring shared surgical decision-making from the patient’s perspective: is the personality of the surgeon important? Colorectal Dis. 2020;22(12):2214–21.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Morris RL, Ruddock A, Gallacher K, Rolfe C, Giles S, Campbell S. Developing a patient safety guide for primary care: A co-design approach involving patients, carers and clinicians. Health Expect. 2021;24(1):42–52.
Tobiano G, Marshall AP, Gardiner T, Jenkinson K, Shapiro M, Ireland M. Development and psychometric testing of the patient participation in bedside handover survey. Health Expect. 2022;25(5):2492–502.
Francis-Coad J, Farlie MK, Haines T, Black L, Weselman T, Cummings P, et al. Revising and evaluating falls prevention education for older adults in hospital. Health Educ J. 2023;82(8):878–91.
Troya MI, Chew-Graham CA, Babatunde O, Bartlam B, Higginbottom A, Dikomitis L. Patient and public involvement and engagement in a doctoral research project exploring self-harm in older adults. Health Expect. 2019;22(4):617–31.
Aharaz A, Kejser CL, Poulsen MW, Jeftic S, Ulstrup-Hansen AI, Jorgensen LM, et al. Optimization of the Danish National Electronic Prescribing System to improve patient safety: Development of a user-friendly prototype of the digital platform shared medication record. Pharmacy (Basel, Switzerland). 2023;11(2):41.
PubMed Google Scholar
Aho-Glele U, Bouabida K, Kooijman A, Popescu IC, Pomey MP, Hawthornthwaite L, et al. Developing the first pan-Canadian survey on patient engagement in patient safety. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021;21(1):1099.
Albutt A, O’Hara J, Conner M, Lawton R. Involving patients in recognising clinical deterioration in hospital using the patient wellness questionnaire: A mixed-methods study. J Res Nurs. 2020;25(1):68–86.
Bell SK, Bourgeois F, DesRoches CM, Dong J, Harcourt K, Liu SK, et al. Filling a gap in safety metrics: development of a patient-centred framework to identify and categorise patient-reported breakdowns related to the diagnostic process in ambulatory care. BMJ Qual Saf. 2022;31(7):526–40.
Boet S, Etherington N, Lam S, Lê M, Proulx L, Britton M, et al. Implementation of the Operating Room Black Box research program at the Ottawa Hospital through patient, clinical, and organizational engagement: Case study. J Med Internet Res. 2021;23(3):e15443.
Carter J, Tribe RM, Shennan AH, Sandall J. Threatened preterm labour: Women’s experiences of risk and care management: A qualitative study. Midwifery. 2018;64:85–92.
Da Silva Lopes AM, Colomer-Lahiguera S, Mederos Alfonso N, Aedo-Lopez V, Spurrier-Bernard G, Tolstrup LK, et al. Patient-reported outcomes for monitoring symptomatic toxicities in cancer patients treated with immune-checkpoint inhibitors: A Delphi study. Eur J Cancer. 2021;157:225–37.
de Jong LD, Lavender AP, Wortham C, Skelton DA, Haines TP, Hill AM. Exploring purpose-designed audio-visual falls prevention messages on older people’s capability and motivation to prevent falls. Health Soc Care Community. 2019;27(4):e471–82.
Doucette L, Kiely BT, Gierisch JM, Marion E, Nadler L, Heflin MT, et al. Participatory research to improve medication reconciliation for older adults in the community. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2023;71(2):620–31.
Elrod CS, Pappa ST, Heyn PC, Wong RA. Using an academic-community partnership model to deliver evidence-based falls prevention programs in a metropolitan setting: A community case study. Front Public Health. 2023;11:1073520.
Feldman E, Pos FJ, Smeenk RJ, van der Poel H, van Leeuwen P, de Feijter JM, et al. Selecting a PRO-CTCAE-based subset for patient-reported symptom monitoring in prostate cancer patients: a modified Delphi procedure. ESMO Open. 2023;8(1):100775.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Francis-Coad J, Watts T, Bulsara C, Hill A-M. Designing and evaluating falls prevention education with residents and staff in aged care homes: a feasibility study. Health Educ (0965-4283). 2022;122(5):546–63.
Fuller TE, Pong DD, Piniella N, Pardo M, Bessa N, Yoon C, et al. Interactive digital health tools to engage patients and caregivers in discharge preparation: implementation study. J Med Internet Res. 2020;22(4):e15573.
Gibson B, Butler J, Schnock K, Bates D, Classen D. Design of a safety dashboard for patients. Patient Educ Couns. 2020;103(4):741–7.
Giles SJ, Lewis PJ, Phipps DL, Mann F, Avery AJ, Ashcroft DM. Capturing patients’ perspectives on medication safety: the development of a patient-centered medication safety framework. J Patient Saf. 2020;16(4):e324–39.
Gnagi R, Zuniga F, Brunkert T, Meyer-Massetti C. Development of a medication literacy assessment instrument (MELIA) for older people receiving home care. J Adv Nurs. 2022;78(12):4210–20.
Goodsmith N, Zhang L, Ong MK, Ngo VK, Miranda J, Hirsch S, et al. Implementation of a community-partnered research suicide-risk management protocol: case study from community partners in care. Psychiatr Serv (Washington, DC). 2021;72(3):281–7.
Gorman LS, Littlewood DL, Quinlivan L, Monaghan E, Smith J, Barlow S, et al. Family involvement, patient safety and suicide prevention in mental healthcare: ethnographic study. BJPsych open. 2023;9(2):e54.
Green MM, Meyer C, Hutchinson AM, Sutherland F, Lowthian JA. Co‐designing being your best program—a holistic approach to frailty in older community dwelling australians. Health Soc Care Community. 2021;30(5):e2022–32.
Guo X, Wang Y, Wang L, Yang X, Yang W, Lu Z, et al. Effect of a fall prevention strategy for the older patients: A quasi-experimental study. Nurs Open. 2023;10(2):1116–24.
Hahn-Goldberg S, Chaput A, Rosenberg-Yunger Z, Lunsky Y, Okrainec K, Guilcher S, et al. Tool development to improve medication information transfer to patients during transitions of care: A participatory action research and design thinking methodology approach. Res Social Adm Pharm. 2022;18(1):2170–7.
Harrington A, Darke H, Ennis G, Sundram S. Evaluation of an alternative model for the management of clinical risk in an adult acute psychiatric inpatient unit. Int J Ment Health Nurs. 2019;28(5):1099–109.
Harris K, Softeland E, Moi AL, Harthug S, Ravnoy M, Storesund A, et al. Development and validation of patients’ surgical safety checklist. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022;22(1):259.
Hawley-Hague H, Tacconi C, Mellone S, Martinez E, Ford C, Chiari L, et al. Smartphone apps to support falls rehabilitation exercise: app development and usability and acceptability study. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020;8(9):e15460.
Holmqvist M, Ros A, Lindenfalk B, Thor J, Johansson L. How older persons and health care professionals co-designed a medication plan prototype remotely to promote patient safety: case study. JMIR aging. 2023;6:e41950.
Jayesinghe R, Moriarty F, Khatter A, Durbaba S, Ashworth M, Redmond P. Cost outcomes of potentially inappropriate prescribing in middle-aged adults: A Delphi consensus and cross-sectional study. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2022;88(7):3404–20.
Johannessen T, Ree E, Stromme T, Aase I, Bal R, Wiig S. Designing and pilot testing of a leadership intervention to improve quality and safety in nursing homes and home care (the SAFE-LEAD intervention). BMJ Open. 2019;9(6):e027790.
Joseph K, Newman B, Manias E, Walpola R, Seale H, Walton M, et al. Engaging with ethnic minority consumers to improve safety in cancer services: A national stakeholder analysis. Patient Educ Couns. 2022;105(8):2778–84.
Khan A, Spector ND, Baird JD, Ashland M, Starmer AJ, Rosenbluth G, et al. Patient safety after implementation of a coproduced family centered communication programme: multicenter before and after intervention study. BMJ. 2018;363:k4764.
Khazen M, Mirica M, Carlile N, Groisser A, Schiff GD. Developing a framework and electronic tool for communicating diagnostic uncertainty in primary care: a qualitative study. JAMA Network Open. 2023;6(3):e232218-e.
Knight SW, Trinkle J, Tschannen D. Hospital-to-homecare videoconference handoff: improved communication, coordination of care, and patient/family engagement. Home Healthc Now. 2019;37(4):198–207.
Lawrence V, Kimona K, Howard RJ, Serfaty MA, Wetherell JL, Livingston G, et al. Optimising the acceptability and feasibility of acceptance and commitment therapy for treatment-resistant generalised anxiety disorder in older adults. Age Ageing. 2019;48(5):741–50.
Louch G, Reynolds C, Moore S, Marsh C, Heyhoe J, Albutt A, et al. Validation of revised patient measures of safety: PMOS-30 and PMOS-10. BMJ Open. 2019;9(11):e031355.
MacDonald T, Jackson S, Charles M-C, Periel M, Jean-Baptiste M-V, Salomon A, et al. The fourth delay and community-driven solutions to reduce maternal mortality in rural Haiti: a community-based action research study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2018;18(1):254.
Mackintosh N, Sandall J, Collison C, Carter W, Harris J. Employing the arts for knowledge production and translation: Visualizing new possibilities for women speaking up about safety concerns in maternity. Health Expect. 2018;21(3):647–58.
Marchand K, Turuba R, Katan C, Brasset C, Fogarty O, Tallon C, et al. Becoming our young people’s case managers: caregivers’ experiences, needs, and ideas for improving opioid use treatments for young people using opioids. Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2022;17(1):1–15.
Mazuz K, Biswas S. Co-designing technology and aging in a service setting: Developing an interpretive framework of how to interact with older age users. Gerontechnology. 2022;21(1):1–13.
McCahon D, Duncan P, Payne R, Horwood J. Patient perceptions and experiences of medication review: qualitative study in general practice. BMC Prim Care. 2022;23(1):293.
McMullen S, Panagioti M, Planner C, Giles S, Angelakis I, Keers RN, et al. Supporting carers to improve patient safety and maintain their well-being in transitions from mental health hospitals to the community: A prioritisation nominal group technique. Health Expect. 2023;26(5):2064–74.
Morris RL, Giles S, Campbell S. Involving patients and carers in patient safety in primary care: A qualitative study of a co-designed patient safety guide. Health Expect. 2023;26(2):630–9.
Morris RL, Stocks SJ, Alam R, Taylor S, Rolfe C, Glover SW, et al. Identifying primary care patient safety research priorities in the UK: a James Lind Alliance Priority Setting Partnership. BMJ Open. 2018;8(2):e020870.
Nether KG, Thomas EJ, Khan A, Ottosen MJ, Yager L. Implementing a robust process improvement program in the neonatal intensive care unit to reduce harm. J Healthc Qual. 2022;44(1):23–30.
Powell C, Ismail H, Cleverley R, Taylor A, Breen L, Fylan B, et al. Patients as qualitative data analysts: Developing a method for a process evaluation of the “Improving the Safety and Continuity of Medicines management at care Transitions” (ISCOMAT) cluster randomised control trial. Health Expect. 2021;24(4):1254–62.
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
Powell C, Ismail H, Davis M, Taylor A, Breen L, Fylan B, et al. Experiences of patients with heart failure with medicines at transition intervention: Findings from the process evaluation of the Improving the Safety and Continuity of Medicines management at Transitions of care (ISCOMAT) programme. Health Expect. 2022;25(5):2503–14.
Radecki B, Keen A, Miller J, McClure JK, Kara A. Innovating fall safety: engaging patients as experts. J Nurs Care Qual. 2020;35(3):220–6.
Rosgen BK, Plotnikoff KM, Krewulak KD, Shahid A, Hernandez L, Sept BG, et al. Co-development of a transitions in care bundle for patient transitions from the intensive care unit: a mixed-methods analysis of a stakeholder consensus meeting. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022;22(1):10.
Schenk EC, Bryant RA, Van Son CR, Odom-Maryon T. Developing an intervention to reduce harm in hospitalized patients: patients and families in research. J Nurs Care Qual. 2019;34(3):273–8.
Spazzapan M, Vijayakumar B, Stewart CE. A bit about me: Bedside boards to create a culture of patient-centered care in pediatric intensive care units (PICUs). J Healthc Risk Manag. 2020;39(3):11–9.
Stoll JA, Ranahan M, Richbart MT, Brennan-Taylor MK, Taylor JS, Brady L, et al. Development of video animations to encourage patient-driven deprescribing: A team alice study. Patient Educ Couns. 2021;104(11):2716–23.
Subbe CP, Tomos H, Jones GM, Barach P. Express check-in: developing a personal health record for patients admitted to hospital with medical emergencies: a mixed-method feasibility study. Int J Qual Health Care. 2021;33(3):121.
Tai D, Li E, Liu-Ambrose T, Bansback N, Sadatsafavi M, Davis JC. Patient-Reported Outcome Measures (PROMs) to support adherence to falls prevention clinic recommendations: a qualitative study. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2020;14:2105–21.
Thakur T, Chewning B, Zetes N, Lee JTY. Involving caregivers in design and assessment of opioid risk and safety communication intervention in children. Patient Educ Couns. 2021;104(10):2432–6.
Thomas J, Dahm MR, Li J, Georgiou A. Can patients contribute to enhancing the safety and effectiveness of test-result follow-up? Qualitative outcomes from a health consumer workshop. Health Expect. 2021;24(2):222–33.
Tremblay MC, Bradette-Laplante M, Witteman HO, Dogba MJ, Breault P, Paquette JS, et al. Providing culturally safe care to indigenous people living with diabetes: Identifying barriers and enablers from different perspectives. Health Expect. 2021;24(2):296–306.
Troya MI, Dikomitis L, Babatunde OO, Bartlam B, Chew-Graham CA. Understanding self-harm in older adults: A qualitative study. EClinicalMedicine. 2019;12:52–61.
Tyler N, Giles S, Daker-White G, McManus BC, Panagioti M. A patient and public involvement workshop using visual art and priority setting to provide patients with a voice to describe quality and safety concerns: Vitamin B12 deficiency and pernicious anaemia. Health Expect. 2021;24(1):87–94.
Tyler N, Planner C, Shears B, Hernan A, Panagioti M, Giles S. Developing the Resident Measure of Safety in Care Homes (RMOS): A Delphi and think aloud study. Health Expect. 2023;26(3):1149–58.
Van den Bulck SA, Vankrunkelsven P, Goderis G, Van Pottelbergh G, Swerts J, Panis K, et al. Developing quality indicators for Chronic Kidney Disease in primary care, extractable from the Electronic Medical Record. A Rand-modified Delphi method. BMC Nephrol. 2020;21(1):161.
Van Strien-Knippenberg IS, Boshuizen MCS, Determann D, de Boer JH, Damman OC. Cocreation with Dutch patients of decision-relevant information to support shared decision-making about adjuvant treatment in breast cancer care. Health Expect. 2022;25(4):1664–77.
Wilson NA, Reich AJ, Graham J, Bhatt DL, Nguyen LL, Weissman JS. Patient perspectives on the need for implanted device information: Implications for a post-procedural communication framework. Health Expect. 2021;24(4):1391–402.
Winterberg AV, Lane B, Hill LM, Varughese AM. Optimizing Pediatric Induction Experiences Using Human-centered Design. J Perianesth Nurs. 2022;37(1):48–52.
Yang R, Donaldson GW, Edelman LS, Cloyes KG, Sanders NA, Pepper GA. Fear of older adult falling questionnaire for caregivers (FOAFQ-CG): Evidence from content validity and item-response theory graded-response modelling. J Adv Nurs. 2020;76(10):2768–80.
Young A, Menon D, Street J, Al-Hertani W, Stafinski T. A checklist for managed access programmes for reimbursement co-designed by Canadian patients and caregivers. Health Expect. 2018;21(6):973–80.
Yuen EYN, Street M, Abdelrazek M, Blencowe P, Etienne G, Liskaser R, et al. Evaluating the efficacy of a digital App to enhance patient-centred nursing handover: A simulation study. J Clin Nurs. 2023;32(19–20):7626–37.
Jo S, Nabatchi T. Coproducing healthcare: individual-level impacts of engaging citizens to develop recommendations for reducing diagnostic error. Public Manag Rev. 2019;21(3):354–75.
O’Hara JK, Reynolds C, Moore S, Armitage G, Sheard L, Marsh C, et al. What can patients tell us about the quality and safety of hospital care? Findings from a UK multicentre survey study. BMJ Qual Saf. 2018;27(9):673–82.
de Jong LD, Francis-Coad J, Wortham C, Haines TP, Skelton DA, Weselman T, et al. Evaluating audio-visual falls prevention messages with community-dwelling older people using a World Cafe forum approach. BMC Geriatrics. 2019;19(1):345.
O’Donnell D, Shé ÉN, McCarthy M, Thornton S, Doran T, Smith F, et al. Enabling public, patient and practitioner involvement in co-designing frailty pathways in the acute care setting. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019;19(1):797.
Russ S, Latif Z, Hazell A, Ogunmuyiwa H, Tapper J, Wachuku-King S, et al. A Smartphone app designed to empower patients to contribute toward safer surgical care: community-based evaluation using a participatory approach. Jmir Mhealth Uhealth. 2020;8(1):e12859.
Mazuz K, Biswas S, Lindner U. Developing self-management application of fall prevention among older adults: a content and usability evaluation. Front Digital Health. 2020;2:11.
Hjelmfors L, Strömberg A, Friedrichsen M, Sandgren A, Mårtensson J, Jaarsma T. Using co-design to develop an intervention to improve communication about the heart failure trajectory and end-of-life care. Bmc Palliat Care. 2018;17:17.
Horgan S, Hegarty J, Andrews E, Hooton C, Drennan J. Impact of a quality improvement intervention on the incidence of surgical site infection in patients undergoing colorectal surgery: Pre-test-post-test design. J Clin Nurs. 2023;32(15–16):4932–46.
Tyler N, Wright N, Grundy A, Waring J. Developing a core outcome set for interventions to improve discharge from mental health inpatient services: a survey, Delphi and consensus meeting with key stakeholder groups. BMJ Open. 2020;10(5):e034215.
Ward ME, De Brún A, Beirne D, Conway C, Cunningham U, English A, et al. Using Co-Design to Develop a Collective Leadership Intervention for Healthcare Teams to Improve Safety Culture. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018;15(6):1182.
Berthelsen DB, Simon LS, Ioannidis JPA, Voshaar M, Richards P, Goel N, et al. Stakeholder endorsement advancing the implementation of a patient-reported domain for harms in rheumatology clinical trials: outcome of the OMERACT safety working group. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2023;63:152288.
Okkenhaug A, Tritter JQ, Landstad BJ. Developing a research tool to detect iatrogenic adverse events in psychiatric health care by involving service users and health professionals. J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2023;00:1–12.
Musbahi A, Clyde D, Small P, Courtney M, Mahawar K, Lamb PJ, et al. A systematic review of patient and public involvement (PPI) in bariatric research trials: the need for more work. Obes Surg. 2022;32(11):3740–51.
Patel VA, Shelswell J, Hillyard N, Pavitt S, Barber SK. A study of the reporting of patient and public involvement and engagement (PPIE) in orthodontic research. J Orthod. 2021;48(1):42–51.
Price A, Schroter S, Snow R, Hicks M, Harmston R, Staniszewska S, et al. Frequency of reporting on patient and public involvement (PPI) in research studies published in a general medical journal: a descriptive study. BMJ Open. 2018;8:e020452.
Amadea T, Anne-Marie B, Louise L. A researcher’s guide to patient and public involvement. 2017.
Download references
Acknowledgements
This research is funded as part of the Collective Leadership and Safety Cultures (Co-Lead) research programme which is funded by the Irish Health Research Board, grant reference number RL-2015–1588 and the Health Service Executive. The funders had no role in the study conceptualisation, design, data collection, analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
UCD Centre for Interdisciplinary Research, Education and Innovation in Health Systems (UCD IRIS), School of Nursing, Midwifery and Health Systems, Health Sciences Centre, University College Dublin, Dublin, Ireland
Sahar Hammoud, Laith Alsabek, Lisa Rogers & Eilish McAuliffe
Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, University Hospital Galway, Galway, Ireland
Laith Alsabek
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
S.H and E.M.A designed the study. S.H developed the search strategies with feedback from L.A, L.R, and E.M.A. S.H conducted all searches. S.H and L.A screened the studies, extracted the data, and assessed the quality of PPI reporting. S.H analysed the data with feedback from E.M.A. S.H drafted the manuscript. All authors revised and approved the submitted manuscript. All authors agreed to be personally accountable for the author's own contributions and to ensure that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Authors’ information
Corresponding author.
Correspondence to Sahar Hammoud .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1., supplementary material 2., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Hammoud, S., Alsabek, L., Rogers, L. et al. Systematic review on the frequency and quality of reporting patient and public involvement in patient safety research. BMC Health Serv Res 24 , 532 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-11021-z
Download citation
Received : 10 January 2024
Accepted : 21 April 2024
Published : 26 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-11021-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Patient and public involvement
- Patient participation
- Research reporting
- Research involvement
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
A Peek Inside the Brains of ‘Super-Agers’
New research explores why some octogenarians have exceptional memories.

By Dana G. Smith
When it comes to aging, we tend to assume that cognition gets worse as we get older. Our thoughts may slow down or become confused, or we may start to forget things, like the name of our high school English teacher or what we meant to buy at the grocery store.
But that’s not the case for everyone.
For a little over a decade, scientists have been studying a subset of people they call “super-agers.” These individuals are age 80 and up, but they have the memory ability of a person 20 to 30 years younger.
Most research on aging and memory focuses on the other side of the equation — people who develop dementia in their later years. But, “if we’re constantly talking about what’s going wrong in aging, it’s not capturing the full spectrum of what’s happening in the older adult population,” said Emily Rogalski, a professor of neurology at the University of Chicago, who published one of the first studies on super-agers in 2012.
A paper published Monday in the Journal of Neuroscience helps shed light on what’s so special about the brains of super-agers. The biggest takeaway, in combination with a companion study that came out last year on the same group of individuals, is that their brains have less atrophy than their peers’ do.
The research was conducted on 119 octogenarians from Spain: 64 super-agers and 55 older adults with normal memory abilities for their age. The participants completed multiple tests assessing their memory, motor and verbal skills; underwent brain scans and blood draws; and answered questions about their lifestyle and behaviors.
The scientists found that the super-agers had more volume in areas of the brain important for memory, most notably the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex. They also had better preserved connectivity between regions in the front of the brain that are involved in cognition. Both the super-agers and the control group showed minimal signs of Alzheimer’s disease in their brains.
“By having two groups that have low levels of Alzheimer’s markers, but striking cognitive differences and striking differences in their brain, then we’re really speaking to a resistance to age-related decline,” said Dr. Bryan Strange, a professor of clinical neuroscience at the Polytechnic University of Madrid, who led the studies.
These findings are backed up by Dr. Rogalski’s research , initially conducted when she was at Northwestern University, which showed that super-agers’ brains looked more like 50- or 60-year-olds’ brains than their 80-year-old peers. When followed over several years, the super-agers’ brains atrophied at a slower rate than average.
No precise numbers exist on how many super-agers there are among us, but Dr. Rogalski said they’re “relatively rare,” noting that “far less than 10 percent” of the people she sees end up meeting the criteria.
But when you meet a super-ager, you know it, Dr. Strange said. “They are really quite energetic people, you can see. Motivated, on the ball, elderly individuals.”
Experts don’t know how someone becomes a super-ager, though there were a few differences in health and lifestyle behaviors between the two groups in the Spanish study. Most notably, the super-agers had slightly better physical health, both in terms of blood pressure and glucose metabolism, and they performed better on a test of mobility . The super-agers didn’t report doing more exercise at their current age than the typical older adults, but they were more active in middle age. They also reported better mental health .
But overall, Dr. Strange said, there were a lot of similarities between the super-agers and the regular agers. “There are a lot of things that are not particularly striking about them,” he said. And, he added, “we see some surprising omissions, things that you would expect to be associated with super-agers that weren’t really there.” For example, there were no differences between the groups in terms of their diets, the amount of sleep they got, their professional backgrounds or their alcohol and tobacco use.
The behaviors of some of the Chicago super-agers were similarly a surprise. Some exercised regularly, but some never had; some stuck to a Mediterranean diet, others subsisted off TV dinners; and a few of them still smoked cigarettes. However, one consistency among the group was that they tended to have strong social relationships , Dr. Rogalski said.
“In an ideal world, you’d find out that, like, all the super-agers, you know, ate six tomatoes every day and that was the key,” said Tessa Harrison, an assistant project scientist at the University of California, Berkeley, who collaborated with Dr. Rogalski on the first Chicago super-ager study.
Instead, Dr. Harrison continued, super-agers probably have “some sort of lucky predisposition or some resistance mechanism in the brain that’s on the molecular level that we don’t understand yet,” possibly related to their genes.
While there isn’t a recipe for becoming a super-ager, scientists do know that, in general , eating healthily, staying physically active, getting enough sleep and maintaining social connections are important for healthy brain aging.
Dana G. Smith is a Times reporter covering personal health, particularly aging and brain health. More about Dana G. Smith
A Guide to Aging Well
Looking to grow old gracefully we can help..
The “car key conversation,” when it’s time for an aging driver to hit the brakes, can be painful for families to navigate . Experts say there are ways to have it with empathy and care.
Calorie restriction and intermittent fasting both increase longevity in animals, aging experts say. Here’s what that means for you .
Researchers are investigating how our biology changes as we grow older — and whether there are ways to stop it .
You need more than strength to age well — you also need power. Here’s how to measure how much power you have and here’s how to increase yours .
Ignore the hyperbaric chambers and infrared light: These are the evidence-backed secrets to aging well .
Your body’s need for fuel shifts as you get older. Your eating habits should shift , too.
People who think positively about getting older often live longer, healthier lives. These tips can help you reconsider your perspective .
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- 29 April 2024
How reliable is this research? Tool flags papers discussed on PubPeer
- Dalmeet Singh Chawla
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar

RedacTek’s tool alerts users to PubPeer discussions, and indicates when a study, or the papers that it cites, has been retracted. Credit: deepblue4you/Getty
A free online tool released earlier this month alerts researchers if a paper cites studies that are mentioned on the website PubPeer , a forum scientists often use to raise integrity concerns surrounding published papers.
Studies are usually flagged on PubPeer when readers have suspicions, for example about image manipulation , plagiarism , data fabrication or artificial intelligence (AI)-generated text . PubPeer already offers its own browser plug-in that alerts users if a study that they are reading has been posted on the site. The new tool, a plug-in released on 13 April by RedacTek , based in Oakland, California, goes further — it searches through reference lists for papers that have been flagged. The software pulls information from many sources, including PubPeer’s database; data from the digital-infrastructure organization Crossref, which assigns digital object identifiers to articles; and OpenAlex , a free index of hundreds of millions of scientific documents.
It’s important to track mentions of referenced articles on PubPeer, says Jodi Schneider, an information scientist at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, who has tried out the RedacTek plug-in. “Not every single reference that’s in the bibliography matters, but some of them do,” she adds. “When you see a large number of problems in somebody’s bibliography, that just calls everything into question.”
The aim of the tool is to flag potential problems with studies to researchers early on, to reduce the circulation of poor-quality science, says RedacTek founder Rick Meyler, who is based in Emeryville, California. Future versions might also use AI to automatically clarify whether the PubPeer comments on a paper are positive or negative, he adds.
Third-generation retractions
As well as flagging PubPeer discussions, the plug-in alerts users if a study, or a paper that it cites, has been retracted. There are existing tools that alert academics about retracted citations ; some can do this during the writing process, so that researchers are aware of the publication status of studies when constructing bibliographies. But with the new tool, users can opt in to receive notifications about further ‘generations’ of retractions — alerts cover not only the study that they are reading, but also the papers it cites, articles cited by those references and even papers cited by the secondary references.
The software also calculates a ‘retraction association value’ for studies, a metric that measures the extent to which the paper is associated with science that has been withdrawn from the literature. As well as informing individual researchers, the plug-in could help scholarly publishers to keep tabs on their own journals, Meyler says, because it allows users to filter by publication.
In its ‘paper scorecard’, the tool also flags any papers in the three generations of referenced studies in which more than 25% of papers in the bibliography are self-citations — references by authors to their previous works.
Future versions could highlight whether papers cited retracted studies before or after the retraction was issued, notes Meyler, or whether mentions of such studies acknowledge the retraction. That would be useful, says Schneider, who co-authored a 2020 analysis that found that as little as 4% of citations to retracted studies note that the referenced paper has been retracted 1 .
Meyler says that RedacTek is currently in talks with the scholarly-services firm Cabell’s International in Beaumont, Texas, which maintains pay-to-view lists of suspected predatory journals . These publish articles without running proper quality checks for issues such as plagiarism, but still collect authors’ fees. The plan is to use these lists to improve the tool so that it can also automatically flag any cited papers that are published in such journals.
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-024-01247-6
Schneider, J., Ye, D., Hill, A. M. & Whitehorn, A. S. Scientometrics 125 , 2877–2913 (2020).
Article Google Scholar
Download references
Reprints and permissions
Related Articles

Predatory-journal papers have little scientific impact
Pioneer behind controversial PubPeer site reveals his identity
- Scientific community

Hunger on campus: why US PhD students are fighting over food
Career Feature 03 MAY 24

France’s research mega-campus faces leadership crisis
News 03 MAY 24

Mount Etna’s spectacular smoke rings and more — April’s best science images

Plagiarism in peer-review reports could be the ‘tip of the iceberg’
Nature Index 01 MAY 24

Algorithm ranks peer reviewers by reputation — but critics warn of bias
Nature Index 25 APR 24
Assistant, Associate, or Full Professor
Athens, Georgia
University of Georgia
Associate Professor - Synthetic Biology
Position Summary We seek an Associate Professor in the department of Synthetic Biology (jcvi.org/research/synthetic-biology). We invite applicatio...
Rockville, Maryland
J. Craig Venter Institute
Associate or Senior Editor (microbial genetics, evolution, and epidemiology) Nature Communications
Job Title: Associate or Senior Editor (microbial genetics, evolution, and epidemiology), Nature Communications Locations: London, New York, Philade...
New York (US)
Springer Nature Ltd
Postdoctoral Research Fellow
Two postdoctoral positions offered at HMS to study the role hypothalamic leptin resistance in control of neuron activity
Boston, Massachusetts (US)
Boston Children’s Hospital-Ozcan Lab
Two Junior Research Group Leaders (f/d/m) for Photonics
Friedrich Schiller University is a traditional University with a strong research profile based in the heart of Germany. As a University covering al...
07743, Jena (DE)
Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Suggestions or feedback?
MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Machine learning
- Social justice
- Black holes
- Classes and programs
Departments
- Aeronautics and Astronautics
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Architecture
- Political Science
- Mechanical Engineering
Centers, Labs, & Programs
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Lincoln Laboratory
- School of Architecture + Planning
- School of Engineering
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing
Francis Fan Lee, former professor and interdisciplinary speech processing inventor, dies
Press contact :.

Previous image Next image
Francis Fan Lee ’50, SM ’51, PhD ’66, a former professor of MIT’s Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, died on Jan. 12. He was approximately 97.
Born in 1927 in Nanjing, China, to professors Li Rumian and Zhou Huizhan, Lee learned English from his father, a faculty member in the Department of English at the University of Wuhan. Lee’s mastery of the language led to an interpreter position at the U.S. Office of Strategic Services, and eventually a passport and permission from the Chinese government to study in the United States.
Lee left China via steamship in 1948 to pursue his undergraduate education at MIT. He earned his bachelor’s and master’s degrees in electrical engineering in 1950 and 1951, respectively, before going into industry. Around this time, he became reacquainted with a friend he’d known in China, who had since emigrated; he married Teresa Jen Lee, and the two welcomed children Franklin, Elizabeth, Gloria, and Roberta over the next decade.
During his 10-year industrial career, Lee distinguished himself in roles at Ultrasonic (where he worked on instrument type servomechanisms, circuit design, and a missile simulator), RCA Camden (where he worked on an experimental time-shared digital processor for department store point-of-sale interactions), and UNIVAC Corp. (where he held a variety of roles, culminating in a stint in Philadelphia, planning next-generation computing systems.)
Lee returned to MIT to earn his PhD in 1966, after which he joined the then-Department of Electrical Engineering as an associate professor with tenure, affiliated with the Research Laboratory of Electronics (RLE). There, he pursued the subject of his doctoral research: the development of a machine that would read printed text out loud — a tremendously ambitious and complex goal for the time.
Work on the “RLE reading machine,” as it was called, was inherently interdisciplinary, and Lee drew upon the influences of multiple contemporaries, including linguists Morris Halle and Noam Chomsky, and engineer Kenneth Stevens , whose quantal theory of speech production and recognition broke down human speech into discrete, and limited, combinations of sound. One of Lee’s greatest contributions to the machine, which he co-built with Donald Troxel , was a clever and efficient storage system that used root words, prefixes, and suffixes to make the real-time synthesis of half-a-million English words possible, while only requiring about 32,000 words’ worth of storage. The solution was emblematic of Lee’s creative approach to solving complex research problems, an approach which earned him respect and admiration from his colleagues and contemporaries.
In reflection of Lee’s remarkable accomplishments in both industry and building the reading machine, he was promoted to full professor in 1969, just three years after he earned his PhD. Many awards and other recognition followed, including the IEEE Fellowship in 1971 and the Audio Engineering Society Best Paper Award in 1972. Additionally, Lee occupied several important roles within the department, including over a decade spent as the undergraduate advisor. He consistently supported and advocated for more funding to go to ongoing professional education for faculty members, especially those who were no longer junior faculty, identifying ongoing development as an important, but often-overlooked, priority.
Lee’s research work continued to straddle both novel inquiry and practical, commercial application — in 1969, together with Charles Bagnaschi, he founded American Data Sciences, later changing the company’s name to Lexicon Inc. The company specialized in producing devices that expanded on Lee’s work in digital signal compression and expansion: for example, the first commercially available speech compressor and pitch shifter, which was marketed as an educational tool for blind students and those with speech processing disorders. The device, called Varispeech, allowed students to speed up written material without losing pitch — much as modern audiobook listeners speed up their chapters to absorb books at their preferred rate. Later innovations of Lee’s included the Time Compressor Model 1200, which added a film and video component to the speeding-up process, allowing television producers to subtly speed up a movie, sitcom, or advertisement to precisely fill a limited time slot without having to resort to making cuts. For this work, he received an Emmy Award for technical contributions to editing.
In the mid-to-late 1980s, Lee’s influential academic career was brought to a close by a series of deeply personal tragedies, including the 1984 murder of his daughter Roberta, and the subsequent and sudden deaths of his wife, Theresa, and his son, Franklin. Reeling from his losses, Lee ultimately decided to take an early retirement, dedicating his energy to healing. For the next two decades, he would explore the world extensively, a nomadic second chapter that included multiple road trips across the United States in a Volkswagen camper van. He eventually settled in California, where he met his last wife, Ellen, and where his lively intellectual life persisted despite diagnoses of deafness and dementia; as his family recalled, he enjoyed playing games of Scrabble until his final weeks.
He is survived by his wife Ellen Li; his daughters Elizabeth Lee (David Goya) and Gloria Lee (Matthew Lynaugh); his grandsons Alex, Benjamin, Mason, and Sam; his sister Li Zhong (Lei Tongshen); and family friend Angelique Agbigay. His family have asked that gifts honoring Francis Fan Lee’s life be directed to the Hertz Foundation .
Share this news article on:
Related links.
- Francis Lee: A Lifetime of Innovation
- Research Laboratory of Electronics
- Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
Related Topics
- Electrical Engineering & Computer Science (eecs)
Related Articles

Donald Troxel, longtime EECS professor, dies at 76

Kenneth Stevens, professor emeritus in EECS, dies at 89
Previous item Next item
More MIT News

Creating bespoke programming languages for efficient visual AI systems
Read full story →

HPI-MIT design research collaboration creates powerful teams

MIT conductive concrete consortium cements five-year research agreement with Japanese industry

One of MIT’s best-kept secrets lives in the Institute’s basement

Exploring frontiers of mechanical engineering

President Mokgweetsi Masisi of Botswana visits the Legatum Center at MIT
- More news on MIT News homepage →
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Map (opens in new window)
- Events (opens in new window)
- People (opens in new window)
- Careers (opens in new window)
- Accessibility
- Social Media Hub
- MIT on Facebook
- MIT on YouTube
- MIT on Instagram

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions.
Unveiling allelopathic dynamics and impacts of invasive Erigeron bonariensis and Bidens pilosa on plant communities and soil parameters. Mohamed A. Balah. Abeer Al-Andal. Abd ElRaheim M. Donia ...
PubMed is a comprehensive database of biomedical literature from various sources, including MEDLINE, life science journals, and online books. You can search for citations, access full text content, and explore topics related to health, medicine, and biology. PubMed also provides advanced search options and tools for researchers and clinicians.
The New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) is a weekly general medical journal that publishes new medical research and review articles, and editorial opinion on a wide variety of topics of ...
research articles. Research articles. Filter By: Article Type. All. All; Appointments Vacant (974) Article (23103) Brief Communication (1079) Brief Communications Arising (580) British Association ...
Harness the power of visual materials—explore more than 3 million images now on JSTOR. Enhance your scholarly research with underground newspapers, magazines, and journals. Explore collections in the arts, sciences, and literature from the world's leading museums, archives, and scholars. JSTOR is a digital library of academic journals ...
Find the research you need | With 160+ million publications, 1+ million questions, and 25+ million researchers, this is where everyone can access science
English Language and Linguistics, published four times a year, is an international journal which focuses on the description of the English language within the framework of contemporary linguistics.The journal is concerned equally with the synchronic and the diachronic aspects of English language studies and publishes articles of the highest quality which make a substantial contribution to our ...
The Journal of English Linguistics is your premier resource for original linguistic research based on data drawn from the English language, encompassing a broad theoretical and methodological scope. Highlighting theoretically and technologically innovative scholarship, the Journal provides in-depth research and analysis in a variety of areas, including history of English, English grammar ...
3.3 million articles on ScienceDirect are open access. Articles published open access are peer-reviewed and made freely available for everyone to read, download and reuse in line with the user license displayed on the article. ScienceDirect is the world's leading source for scientific, technical, and medical research.
Call for Submissions . English: Journal of the English Association publishes scholarship on a wide range of authors and literary texts, and particularly encourages submissions which speak to the discipline as a whole. Our readership comprises schoolteachers as well as academics, so we provide a platform for scholars and educators to reflect on the key questions facing our discipline.
Discussion. The purpose of this meta-analysis was to explore the effects of reading interventions for ELLs and to identify research-based characteristics of effective reading interventions for enhancing their reading ability. To achieve this goal, this study tried to determine the answers to two research questions.
Research in the Teaching of English is a multidisciplinary journal composed of original research and scholarly essays on the relationships between language teaching and learning at all levels, preschool through adult. Articles reflect a variety of methodologies and address issues of pedagogical relevance related to the content, context, process, and evaluation of language learning.
Prof. V. Chandra Sekhar Rao. 1. The Use of English Language in Research. Prof. V. Chandra Sekhar Ra o ([email protected]) Professor in English, SITECH, Hyderabad, India. Abstract. English as the ...
English in Education publishes research-based articles and short creative pieces that provide informed reflection on the teaching of English within the school, college and higher education curriculum. Most our readers live and work in countries where English is the main language of communication. We regard English as a dynamic, creative and ...
However, available research affirms that emergent bilinguals who achieve reading proficiency in their first language perform equal to, or better than, their peers in English-only programs (August & Shanahan, Citation 2006). Moreover, reading proficiency in L1 supports development of reading skills in English because many L1 skills transfer to L2.
Writing the self: Black queer youth challenge heteronormative ways of being in an after-school writing club. Research in the Teaching of English, 52 (1), 13-33. Johnson, L. P., & Sullivan, H. (2020). Revealing the human and the writer: The promise of a humanizing writing pedagogy for black students.
Introduction. This paper reports an exercise in agenda setting for the next 10 years of research in English education. We defined English education as education in literature or language in a first language context, that is, in countries where English is the main language. It therefore included the teaching of students who have English as an ...
Explore the latest full-text research PDFs, articles, conference papers, preprints and more on ENGLISH LITERATURE. Find methods information, sources, references or conduct a literature review on ...
Research in the Teaching of English. Research in the Teaching of English (RTE) is a broad-based, multidisciplinary journal composed of original research articles and short scholarly essays on a wide range of topics significant to those concerned with the teaching and learning of languages and literacies around the world, both in and beyond schools and universities.
The scientific community should communicate in as many languages as possible. By some estimates, as much as 98% of the world's scientific research is published in English, while only around 18% ...
This article investigated the English research article (RA) titles across different disciplines and cultures. To this end, 600 RA titles in the Chinese context and 600 RA titles in the international context were collected from six disciplines, which are grouped as social and natural sciences. The frequency of title types, their subtypes, and ...
Most Read in Literature. From Shakespeare's plays to modern literary trends, explore a collection of our most read recent articles and chapters from our literature portfolio. Enhance your knowledge with free access to these highlights from our books and journals until December 2022.
Regarding the research type and design, we included empirical qualitative, quantitative, mixed methods, and case studies. Only articles published in peer-reviewed journals and in English were included. Any article that did not meet the inclusion criteria was excluded. Studies not reporting outcomes were excluded.
The research was conducted on 119 octogenarians from Spain: 64 super-agers and 55 older adults with normal memory abilities for their age. The participants completed multiple tests assessing their ...
The mRNA technology enables quick and flexible responses to new variants of pathogens and rapid scale-up in production, said one researcher.
Related Articles. More than 10,000 research papers were retracted in 2023 — a new record US project seeks standard way to communicate research retractions
Lee helped to develop a machine that read English text out loud and won an Emmy for his work on subtly speeding up film and audio without a noticeable loss of pitch. ... Lee's research work continued to straddle both novel inquiry and practical, commercial application — in 1969, together with Charles Bagnaschi, he founded American Data ...
Academic deans showed me critiques of research papers that ignored the scientific merits and attacked the country's military actions.