- Resume Writing
- Resume Examples
- Cover Letter
- Remote Work
- Famous Resumes
- Try Kickresume

Cover Letter for PhD Application: Guide for Writing One & Example From a Real PhD Student
- Klara Cervenanska ,
- Updated March 27, 2023 9 min read
When applying for a PhD research position, you usually need to submit certain documents, including an academic CV and a cover letter for PhD application .
A PhD cover letter, also referred to as an academic cover letter, should be carefully crafted, well-formatted, and contain specific sections.
We'll show you how to do exactly that, along with a sample of an academic cover letter from a real person admitted to a PhD program at Lyon University in France.
And if you're not sure how to go about writing your PhD CV, check out this article: CV for PhD Application: How to Write One Like a True Scholar (+CV Example) .
Table of Contents
Click on a section to skip
What is an academic cover letter?
What to include in a cover letter for phd application, how to write a cover letter for phd application, how to format an academic cover letter, phd cover letter sample.
An academic cover letter is a document that PhD candidates submit alongside their academic CV when applying for a PhD.
Essentially, it's a cover letter for a PhD application.
It's not exactly the same as your regular business cover letter. Nor is it the same as a personal statement or a motivation letter .
The purpose of a cover letter for PhD application is to explain to the reader, who's likely a researcher or a professor, what you can contribute to their institution and/or field.
Moreover, in a PhD application cover letter, you should explain why you're a good match for the research position on the program.
Differences between academic cover letter and business cover letter
Both these documents serve different purposes and people use them in different settings:
- Academic cover letter is used when applying for positions in academia — most often for a PhD. More emphasis should be on education, research background and scholarly accomplishments. Moreover, it should explain what your contribution to the institution or field could be. It should also point the reader to your academic CV.
- Regular (business) cover letter is normally used when applying for any kind of job . Hence, more emphasis should be on skills and past experience while being tailored to a specific job position. You should also explain why you're a good fit for the position at the given company. It should point the reader to your resume.
There are also other documents people often mistake for an academic cover letter. These include:
- Motivation letter is especially relevant for fresh graduates when applying to a university, a non-profit organization, or voluntary work. A motivation letter focuses more on your interests and motives for applying.
- Personal statement. Also used in an academic setting. It's always written by an applicant, often a prospective student, applying to college, university, or graduate school. You explain why you've chosen a particular course and why you'd be good at it. Other names include a statement of purpose or a letter of intent .
Like every cover letter, an academic one also needs to include specific elements and content sections. These are:
- Header. Here, provide your contact information, such as your name, address, phone number, and email in the header of the document.
- Formal salutation. In an official letter like this one, you should address the reader in a professional and formal way. If you know who'll be reading your cover letter, go with Dear Dr. [Surname] or Dear Professor [Surname] . If you don't, go with Dear Sir/Madam .
- The specific PhD program or position. Clearly state in your letter which research position you're applying for or the name of the PhD program. A cover letter is usually read before a CV, so you need to make sure everything is clear.
- Your motivation. Explain why you're interested in the specific PhD position — it's one of the key elements you should include.
- Your academic background. Now, we don't mean you should list in detail every single university course you ever took. Instead, focus on the most relevant course for the PhD and describe in detail what you learned, any projects you worked on, why it was interesting (and optionally, what knowledge gap you identified). In this way, you also show a certain level of understanding of the field.
- Your ambition. Briefly mention what your ambitions, intentions, and plans are regarding your contribution to the field when securing your PhD position. How is your research going to enrich the field? How will the institution benefit from it?
- Conclusion. Keep the conclusion short. Contrary to a regular cover letter ending , there's no place for reiterating everything here. Simply thank the reader for your consideration and prompt them to read your academic CV.
- Formal sign-off. Just pick from the usual: Sincerely, Respectfully, Regards... Then throw in your full name in the following line.
And that's all you need to include!
Now, let's take a look at how to write your cover letter step-by-step.
Applying for a PhD will be a lot less stressful if you follow these tips on how to write a cover letter for a research position:
Consider researching the background of the organization, department, ongoing research projects, and their past and current projects. All that before you start writing your cover letter. Knowing these things will help you tailor your letter to the specific PhD opening.
Before you actually start writing, try to sit down and take a moment to think first. Assess how your past experiences helped you prepare for the PhD position and scribble down those that are most relevant and significant for the specific program. These include any research experiences, research projects, courses, or internships.
In the first few sentences of your letter, you need to convey some basic information about yourself and what specific position you're applying for. The opening should also state firmly why you're a strong candidate for the position/program, by using a persuasive and convincing wording. Here's an example: "As an MChem Chemistry graduate with a narrow focus on the sustainable synthesis of biologically active molecules from the University of Dundee, I am excited to apply to a "Synthesis Of Small Molecule Inhibitors Using Enzymes" PhD programme at an institution with such a strong foundation and numerous research groups in this field."
This is the place where you may explore more extensively on the educational journey that brought you here. Set the foundation for demonstrating how your Master's degree and research experience seamlessly translate into the next phase — the PhD program. Emphasize how your thesis contributes to the field's body of knowledge. Mention any other publications that support your thesis. And, if you can, identify any knowledge gaps or topics that can be explored further.
This paragraph provides the opportunity to neatly tie in together everything the reader has learned about you so far. You can show how your previous experience, coupled with what you'll learn during the PhD program, will come together to produce something novel to enrich the field. First, identify the courses or topics within the PhD program that interest you the most and how they relate to you developing your research further. Second, introduce your future research aspirations and goals. Third, point out how this future work will enrich the field and what will the intellectual merit be.
When ending your PhD cover letter, briefly refer your reader to your academic CV and encourage them to examine all of the remaining projects, courses, publications, or references . Finally, thank the reader for their time and consideration and let them know you look forward to hearing from them. Sign off.
Put the letter in a drawer and don't think about it for a day or two. Then, when you read it again, you'll have a fresh pair of eyes to see the cover letter in a new light. Maybe you decide some things are redundant, or you think of something that's more relevant. Or you know, find a typo here and there.
Just like an academic cover letter needs to contain certain content components, the formatting should also align with the structural expectations for this type of document.
How long should a cover letter be? How to finish a cover letter? And what about the cover letter font and spacing?
Here's a recommended academic cover letter format:
- Length. While STEM PhD candidates should aim for half a page to one page, humanities candidates can do 1–2 pages.
- Font. Use one of the classics: Times New Roman, Calibri, or Arial. Just no Comic Sans, we beg you. Keep the size between 10–12 points. Also remember to keep the text clean — no underlining, no bolding, and no color. However, you can use italics if appropriate.
- Spacing. Cover letter spacing isn't complicated. Just single-space your text, make sure there's a space between each paragraph, and leave a space between the concluding paragraph and your formal sign-off.
- Margins. The only rule here is that the margins on your cover letter should match those on your CV.
- Consistence with your CV. Your academic cover letter should match your academic CV in all formatting aspects — including the cover letter font and spacing. For example, Kickresume lets you choose a matching template for your CV and your cover letter, so no need to worry about this.
If the institution provided any instructions for formatting your academic cover letter, don’t get creative and follow their guidelines.
Finally, to help you tie everything we talked about together, here's a cover letter sample from a real person admitted to a PhD program at Lyon University in France.
These things ensured Herrera's cover letter was successful:
- She clearly states her motivation in the opening. In the first two paragraphs, Herrera introduces herself and her motivation to apply for the given PhD program.
- She describes educational and research background thoroughly. The main body of the letter is dedicated to describing Herrera's educational background, research projects, internships, and skills acquired throughout the way.
- She presents research aspirations in the letter. Herrera writes: "I have a history of proven results and profound findings. Given opportunity, I’m confident in my abilities to earn similar ground-breaking results while being part of your team."
Even though this example lacks some of the key elements, such as mentioning the specific PhD program or identifying the topics within the PhD program that interest her the most, this PhD cover letter still managed to impress the University of Lyon.
Lyon University PhD Student Cover Letter Sample
Klara graduated from the University of St Andrews in Scotland. After having written resumes for many of her fellow students, she began writing full-time for Kickresume. Klara is our go-to person for all things related to student or 'no experience resumes'. At the same time, she has written some of the most popular resume advice articles on this blog. Her pieces were featured in multiple CNBC articles. When she's not writing, you'll probably find her chasing dogs or people-watching while sipping on a cup of coffee.
Related Posts
How to address a cover letter without a name use these 5 salutations, 10 cover letter samples by people who got hired at volvo, t-mobile or hubspot, share this article, join our newsletter.
Every month, we’ll send you resume advice, job search tips, career hacks and more in pithy, bite-sized chunks. Sounds good?
PHD Application cover letter examples
As the highest postgraduate qualification you can achieve, it’s no wonder that most PhD programs require a cover letter as part of the application process.
So, if you’re hoping to complete your doctorate, you need to brush up on your writing skills and prove why you deserve a place in the program.
To help you do that, we’ve put together this comprehensive guide, complete with PhD cover letter examples to support your application.
CV templates
PHD Application cover letter example 1

PHD Application cover letter example 2

PHD Application cover letter example 3

The example cover letters here should give you a good general idea on how your PHD Application cover letter should be formatted and written.
The rest of this guide gives more specific guidance on how to create your own cover letter in this format, and even includes some templates you can copy and paste.
How to write a PHD Application cover letter
A simple step-by-step guide to writing your very own winning cover letter.
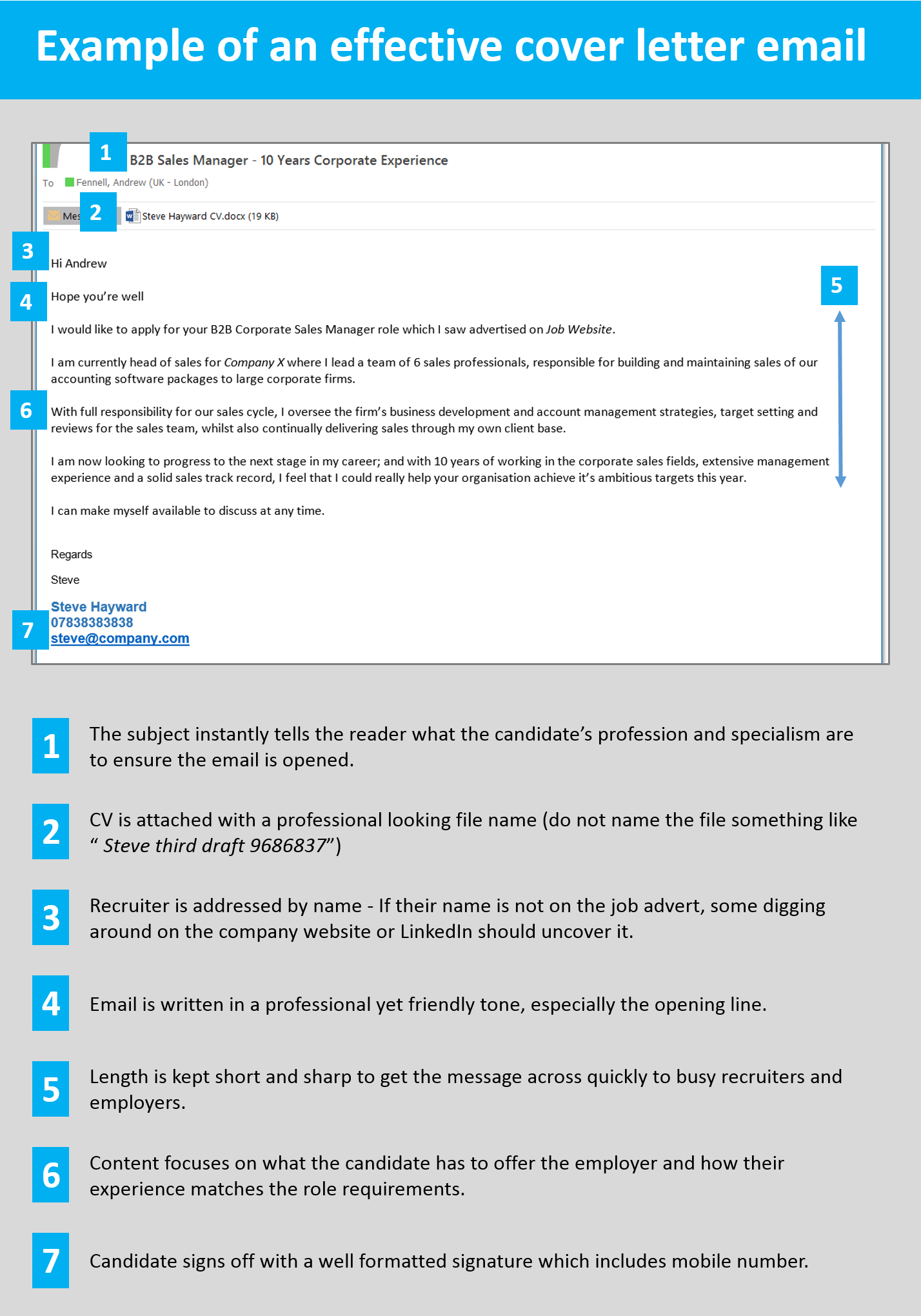
Write your cover letter in the body of an email/message
When writing your PHD Application cover letter, it’s best to type the content into the body of your email (or the job site messaging system) and not to attach the cover letter as a separate document.
This ensures that your cover letter gets seen as soon as a recruiter or employer opens your message.
If you attach the cover letter as a document, you’re making the reader go through an unnecessary step of opening the document before reading it.
If it’s in the body of the message itself, it will be seen instantly, which hugely increases the chances of it being read.
Start with a friendly greeting

Start you cover letter with a greeting that is professional but friendly.
This will build rapport with the recruiter whilst showing your professionalism.
- Hi, hope you’re well
- Hi [insert recruiter name]
- Hi [insert department/team name]
Avoid overly formal greetings like “Dear sir/madam ” unless applying to very traditional companies.
How to find the contact’s name?
Addressing the recruitment contact by name is an excellent way to start building a strong relationship. If it is not listed in the job advert, try these methods to find it.
- Check out the company website and look at their About page. If you see a hiring manager, HR person or internal recruiter, use their name. You could also try to figure out who would be your manager in the role and use their name.
- Head to LinkedIn , search for the company and scan through the list of employees. Most professionals are on LinkedIn these days, so this is a good bet.
Identify the role you are applying for
Once you’ve opened up the cover letter with a warm greeting to start building a relationship, it is time to identify which role you want to apply for.
Recruiters are often managing multiple vacancies, so you need to ensure you apply to the correct one.
Be very specific and use a reference number if you can find one.
- I am interested in applying for the position of *specialist field PHD Applicant* with your company.
- I would like to apply for the role of Sales assistant (Ref: 406f57393)
- I would like to express my interest in the customer service vacancy within your retail department
- I saw your advert for a junior project manager on Reed and would like to apply for the role.
See also: CV examples – how to write a CV – CV profiles
Highlight your suitability
The main purpose of your cover letter is to excite recruiters and make them eager to open your CV. And you achieve this by quickly demonstrating your suitability to the job you are applying for.
Take a look at the job adverts you are applying for, and make note of the most important skills being asked for.
Then, when you write your cover letter, make your suitability the focal point.
Explain how you meet the candidate requirements fully, and why you are so well suited to carry out the job.
This will give recruiters all the encouragement they need to open your CV and consider your application.

Keep it short and sharp
A good cover letter is short and sharp, getting to the point quickly with just enough information to grab the attention of recruiters.
Ideally your cover letter should be around 4-8 sentences long – anything longer will risk losing the attention of time-strapped recruiters and hiring managers .
Essentially you need to include just enough information to persuade the reader to open up your CV, where the in-depth details will sit.
Sign off professionally
To round of your CV, you should sign off with a professional signature.
This will give your cover letter a slick appearance and also give the recruiter all of the necessary contact information they need to get in touch with you.
The information to add should include:
- A friendly sign off – e.g. “Kindest regards”
- Your full name
- Phone number (one you can answer quickly)
- Email address
- Profession title
- Professional social network – e.g. LinkedIn
Here is an example signature;
Warm regards,
Jill North IT Project Manager 078837437373 [email protected] LinkedIn
Quick tip: To save yourself from having to write your signature every time you send a job application, you can save it within your email drafts, or on a separate documents that you could copy in.

What to include in your PHD Application cover letter
Here’s what kind of content you should include in your PHD Application cover letter…
The exact info will obviously depend on your industry and experience level, but these are the essentials.
- Your relevant experience – Where have you worked and what type of jobs have you held?
- Your qualifications – Let recruiters know about your highest level of qualification to show them you have the credentials for the job.
- The impact you have made – Show how your actions have made a positive impact on previous employers; perhaps you’ve saved them money or helped them to acquire new customers?
- Your reasons for moving – Hiring managers will want to know why you are leaving your current or previous role, so give them a brief explanation.
- Your availability – When can you start a new job ? Recruiters will want to know how soon they can get you on board.
Don’t forget to tailor these points to the requirements of the job advert for best results.
PHD Application cover letter templates
Copy and paste these PHD Application cover letter templates to get a head start on your own.
Dear Admissions Committee
I am writing to express my strong interest in the Ph.D. in Physics programme at the University of London. As a highly motivated and dedicated individual with a deep fascination with the fundamental principles of physics, I am eager to contribute my academic background and research experience to your faculty.
I hold an MSc in Physics from the University of Birmingham, where I achieved distinctions for quantum mechanics, thermodynamics, and atomic & molecular physics. During this period, I was involved in evaluating quantum phenomena using computational methods, which honed my analytical skills and provided insights into the intricate nature of quantum systems. My passion for research has also led me to publish two peer-reviewed papers in reputable journals.
I am enthusiastic about continuing my journey in addressing challenges in the field of physics and have previously collaborated with renowned experts in securing £10M in funding to support projects, as well as improving experimental efficiency by 40% through implementing state-of-the-art quantum optics equipment. I have also delivered presentations to share research on condensed matter systems.
I am thrilled at the possibility of joining your institution. Thank you for considering me for the programme.
Kind regards
Matt Turner
I am writing to you concerning the Ph.D. program in Chemical Engineering at the University of Oxford. I possess a profound passion for advanced research and innovation in chemical engineering, with an eagerness to contribute my academic background and problem-solving abilities to your institution.
I hold an MSc in Chemical Engineering from Imperial College London and had the opportunity to delve into cutting-edge projects alongside esteemed experts. We focused on sustainable practices in chemical manufacturing, as well as the efficient production, transformation, and transportation of various products. I helped design and conduct experiments to improve chemical operations and reduce environmental impacts, where my findings were published in two peer-reviewed journals.
Some key accomplishments during master’s studies include, obtaining research funding worth £2M to conduct experiments in catalysis and reaction engineering, and playing a role in improving industrial processes by 50%. In addition, I delivered five oral presentations at international conferences to share information on driving sustainable practices.
Thank you for considering my application, and I am available at your convenience for further discussions.
Sable Norris
Dear Members of the Graduate Admissions Committee
I am writing to express my interest in the Ph.D. programme in Archaeology at the University of Cambridge. I possess a profound fascination for uncovering the mysteries of the past, and I am focused on contributing my academic background, fieldwork experience, and research skills to your institution.
I obtained a master’s degree in Archaeology from the University of Manchester, where I had the privilege of working closely with esteemed faculty and engaged in research that ignited my passion for understanding the Sumerian civilisation.
During my studies I conducted original research on the excavation and analysis of burial sites to shed light on their ancient practices and cultural beliefs, completing 95 excavation seasons, which was 30+ more than any other student, co-authoring two research papers published in reputable journals, and securing £500K from the UK government to conduct a 3-month research trip in the Middle East.
My experience coupled with advanced coursework in archaeological methodologies and artefact analysis have equipped me with the skills to excel in the programme. Thank you for considering my application.
Dominic Ferdinand
Writing an impressive cover letter is a crucial step in landing a place on a PHD, so taking the time to perfect it is well worth while.
By following the tips and examples above you will be able to create an eye-catching cover letter that will wow recruiters and ensure your CV gets read – leading to more job interviews for you.
Good luck with your job search!

What Is a PhD Cover Letter?
What key points should i include within my phd application letter, tips to improve your phd application letter, example phd cover letter, final thoughts, phd cover letters.
Updated October 11, 2023

All products and services featured are independently selected by WikiJob. When you register or purchase through links on this page, we may earn a commission.
A PhD cover letter is an important part of your PhD application. Your cover letter (which may also be referred to as a motivational letter) focuses upon what makes you a great candidate and why you should be invited for interview.
This article will cover what a PhD cover letter is, when it would be used and how you can write a notable cover letter for your PhD application.
Your cover letter is your first opportunity to explain to the committee why you should be selected to study for your postgraduate doctorate. It not only demonstrates your personality, but it can also explain in your own words why the hiring panel should choose you as a PhD student.
Like most cover letters , your PhD application letter should complement, but not repeat, your CV. It should explain and expand on the details referenced within your CV or application form .
You should tailor the content to your chosen PhD topic – this will enable you to focus your specific expertise and academic achievements on your learning capabilities.
It should be noted that when it comes to submitting your application to study for a PhD, you may be required to submit a personal statement as well as a cover letter. Each university will have its own criteria, but note that a cover letter is different from a personal statement.
Your personal statement will focus upon your interests and your ambitions, whilst your PhD cover letter will be looking at your tangible achievements , such as your academic and professional experience.
If you are required to draft both statements, then try to keep this in mind during the writing process.

There are no rules for what to include within your PhD cover letter but, broadly speaking, your submission should include references to the following:
Who you are – what your personality is and what sets you apart from other potential PhD candidates. Your cover letter should be a sales tool that should make any committee want to choose you to join their team.
Your skills and achievements (along with any evidence to substantiate your claims).
Your research into the specific academic institution (why you want to attend that specific school and what makes it a good fit for you).
Your understanding of your research project and what you believe its impact may be upon your sector (this will demonstrate not just your knowledge of the research but will showcase your passion and motivation for the project).
How your specific skills are relevant to the application. Have you undertaken any work experience relevant to that field? Have you been inspired by what previous alumni have achieved?
As with all applications, writing a great cover letter is a skill. It requires you to tread the balance between explaining in detail who you are and why you should be chosen, while remaining concise. It needs to showcase your personality while remaining professional.
It’s a difficult writing skill and one which shouldn’t be rushed. You should take your time to craft your application letter – the more time that is spent on it, the greater your chance of success.
A practical tip is to use the ‘top-down’ approach . This is a writing skill often used by marketers and PR professionals whereby you incorporate the strongest arguments/details at the top and work your way down.
You need to ensure that if a committee member stops reading your cover letter at any point, then they have already noted the most pressing details.
How Do I Write My PhD Cover Letter?
An easy way to focus your thoughts when writing your application letter is to consider it as a way of telling your story, at least in relation to the PhD you are applying for. By this, we mean that your letter should have a clear beginning, middle and end.
Using this format as a guide, here are some examples of how to start writing your PhD cover letter.
Starting Your Cover Letter
As with any form of professional correspondence, do your due diligence and be confident that you know who to send your application to.
As previously mentioned, each school will have its own application criteria – for some, it may need to be addressed to a specific professor, whilst others may direct you to a department or someone responsible for all recruitment.
Make sure you find out their name – along with correct spellings and titles. This is your first chance to make a good impression, so you must pay attention to the details.
Introducing Yourself
A good place to start is to introduce yourself first. Ask yourself, who are you and why should the committee continue to read your application letter?
This is your opportunity to explain what PhD you are applying for and why you want to study further. You may want to start your storytelling in this section.
For example:
I became interested in this subject when I met [name], who is one of your alumni. They inspired me to want to continue my learning and further my knowledge, which has been developed through my professional experience at [company name].
As you can see from this example, the letter is starting to explain why the candidate wants to apply for the application, what inspires them to continue their learning and gives a look into their achievements. The result is that it makes the reader want to continue reading the letter.
Showcasing Your Skills and Achievements
The middle section is where you talk about what you have achieved and how you want to further your development and make an impact on your field of study.
This section should refer to your CV and provide greater insights into what you already know and why you would be a great candidate for the PhD programme.
You could use this section to briefly introduce what topic you believe would make a great research project.
As you can see from my enclosed CV, I have an extensive professional history within my sector. From my experience at [company name], I was able to focus upon my key specialisms, which led me to develop an interest in [project]. I believe that, due to the ever-changing nature of the profession, there is scope to continue the research into [subject] and I’m keen to combine my practical and theoretical knowledge in my research. I believe this is of value to not just myself and my peers but also my wider profession because of [detail].
Again, this is demonstrating a level of professionalism while starting to showcase exactly why you should be chosen to join the PhD programme. It shows that you’re not just thinking of yourself, you’re also considering the wider implications that your research may have upon your field of study.
Ending Your Cover Letter
As you draw towards the end of your cover letter, you may wish to reiterate why you want to study at this specific institution. Showing you have researched the university’s research reputation can go a long way to impressing hiring panels.
It may be globally renowned, or perhaps it’s a good fit for your specific area of interest. Maybe there’s a specific professor you would like to work alongside or maybe you’ve seen the career advancement of previous alumni. If you have a personal reason why you are a good fit for the school, then state it here.
Additionally, we would also recommend explaining what you plan to do with your research upon its completion. Hiring panels will be keen to find out how you plan to use your expertise and what your long term ambitions are.
I am particularly interested in joining the PhD programme at [school] because of your reputation as global research leaders. Throughout my career, I have strived to work alongside the best because I believe in the importance of peer learning. I am keen to work alongside your distinguished professors to carry out my research in [subject]. I believe that I am the right fit for your institution because of [x,y,z] and through my correspondence with [named contact of the previous alumni], I am aware of the help and support that you provide to your PhD applicants. Following on from the completion of my doctorate, I plan to use my knowledge to do [x,y,z].
As you sign off your cover letter, make sure you include a call to action. Encourage the panel to get in touch with you to arrange a formal interview or direct them to your CV so that they can be reminded of your experience.
You need to end the letter with no doubt that you are a good fit for the PhD programme and that you are an ideal candidate that they need to snap up.
I hope that this letter has given you some insight into my dedication to my learning and that you will consider my application. I would like to draw your attention back to my CV which is enclosed with this letter, which demonstrates my professional and academic history. I look forward to hearing from you in due course.
If you have addressed the letter to a named contact, use ‘Yours sincerely’. If you have been directed to address your letter to a general department, then formalities suggest that you should use the sign off ‘Yours faithfully’.
Keep it concise . Where possible, it shouldn’t exceed two pages of A4. They can find out more detail about who you are during the interview stage; this is merely to whet their appetite and excite them to want to find out more about you.
Don’t reiterate what has already been written on your CV . Instead, they want to know how the experience on your CV has made you a more rounded individual. How has it shaped your interest in your chosen study and what is compelling you to continue to further your learning?
Provide evidence . If you are highly regarded within your professional sector, then demonstrate this – are you involved in any sector groups or have you been recognised with any awards? The whole purpose of your potential research project is to provide evidentiary proof of your hypothesis so if you are going to make bold statements about your career history, then the first thing any PhD supervisor will want to know, is 'Where is the evidence?'.
Check for errors . Remember that your letter is a professional representation of who you are. Before submitting your PhD application, make sure that your cover letter is free from grammatical errors and spelling mistakes. It’s a sister document to your CV so try to ensure consistency between the two documents – use similar formatting, a professional font (Ariel or Calibri are good choices) and ensure that your margins are coherent.

Below, is an example of a cover letter for your PhD application. We hope that it inspires you and helps you to understand more about what you should be including when it comes to writing your own letter.
Remember that this is an example only and your cover letter should be tailored to your circumstances.
Recipient Name Recipient Job Title Recipient Address Date Dear [name] Cover letter for application to join the PhD programme at [school]. I am writing to you to showcase my interest in continuing my academic study through the PhD programme in [subject] at [University]. I am keen to join the doctoral programme within your [department] because I believe that its rich history of academic research is a perfect match for my academic aptitude and my extensive career history. I’ve long been interested in [subject] and I recently met with [name], who is one of your alumni. They inspired me to take the leap and submit this application because I’ve long been interested in developing my knowledge honed through my professional experience at [company name]. I studied [subject] at [university] and throughout my academic history and work experience, I’ve developed a strong interest in the niche field of [topic]. My BA thesis was based upon [subject] and since completing my undergraduate studies, I’ve been able to put my theoretical knowledge into practice through my work at [company name]. As you can see from my enclosed CV, I’ve been able to hone my skills into key specialisms which have led me to develop an interest in [project]. I believe that there is scope to continue the research into [subject] due to the ever-changing nature of the profession and I’m keen to combine my practical and theoretical knowledge with my research. I believe this is of value to not just myself and my peers but also my wider profession, since it could help others to understand the importance of [subject]. I wish to continue my academic career by completing my doctorate, which has always been a long-term ambition of mine. I cannot imagine a better place to study than [university]. I have always been inspired by the achievements of this academic institution and I wish to work alongside your teaching staff to research my hypothesis which is [details]. In particular, I would like to work alongside Professor [name], who was highly regarded by our mutual acquaintance [alumni name]. With my theoretical knowledge and my professional expertise, I am confident that I can complete my chosen research project to a high standard. I am a dedicated hard worker and have long been regarded within my sector through my involvement with [professional bodies]. I have also been recognised along with my peers for our work through the achievements of many industry awards including [details]. Following on from the completion of my doctorate, I plan to use my knowledge to help educate fellow professionals, and thus improve awareness and understanding of our sector. I hope that this letter has given you some insight into my dedication to my learning and that you will consider my application. I would like to draw your attention back to my CV which is enclosed with this letter, which will demonstrate my professional and academic history. I look forward to hearing from you in due course. Yours sincerely, [Signature] [Name] Encl. Curriculum Vitae
This article has been designed to give you some insights into what to expect from your PhD application.
To read more about PhDs, we recommend that you read our postgraduate pages , which contain numerous articles about PhDs, MBAs and further study.
You might also be interested in these other Wikijob articles:

Or explore the Postgraduate / PHD sections.

How to Write a PhD Motivation Letter
- Applying to a PhD
A PhD motivation letter is a document that describes your personal motivation and competence for a particular research project. It is usually submitted together with your academic CV to provide admissions staff with more information about you as an individual, to help them decide whether or not you are the ideal candidate for a research project.
A motivation letter has many similarities to a cover letter and a personal statement, and institutions will not ask you to submit all of these. However, it is a unique document and you should treat it as such. In the context of supporting a PhD application, the difference is nuanced; all three documents outline your suitability for PhD study. However, compared to a cover letter and personal statement, a motivation letter places more emphasis on your motivation for wanting to pursue the particular PhD position you are applying for.
Academic cover letters are more common in UK universities, while motivation letters are more common abroad.
A motivation letter can play a key part in the application process . It allows the admission committee to review a group of PhD applicants with similar academic backgrounds and select the ideal candidate based on their motivations for applying.
For admission staff, academic qualifications alone are not enough to indicate whether a student will be successful in their doctorate. In this sense, a motivational letter will allow them to judge your passion for the field of study, commitment to research and suitability for the programme, all of which better enables them to evaluate your potential.
How Should I Structure My Motivation Letter?
A strong motivation letter for PhD applications will include:
- A concise introduction stating which programme you are applying for,
- Your academic background and professional work experience,
- Any key skills you possess and what makes you the ideal candidate,
- Your interest and motivation for applying,
- Concluding remarks and thanks.
This is a simplistic breakdown of what can be a very complicated document.
However, writing to the above structure will ensure you keep your letter of motivation concise and relevant to the position you are applying for. Remember, the aim of your letter is to show your enthusiasm and that you’re committed and well suited for the programme.
To help you write a motivation letter for a PhD application, we have outlined what to include in the start, main body, and closing sections.
How to Start a Motivation Letter
Introduction: Start with a brief introduction in which you clearly state your intention to apply for a particular programme. Think of this as describing what the document is to a stranger.
Education: State what you have studied and where. Your higher education will be your most important educational experience, so focus on this. Highlight any relevant modules you undertook as part of your studies that are relevant to the programme you are applying for. You should also mention how your studies have influenced your decision to pursue a PhD project, especially if it is in the same field you are currently applying to.
Work experience: Next summarise your professional work experience. Remember, you will likely be asked to submit your academic CV along with your motivation letter, so keep this section brief to avoid any unnecessary repetition. Include any other relevant experiences, such as teaching roles, non-academic experience, or charity work which demonstrates skills or shows your suitability for the research project and in becoming a PhD student.
Key skills: Outline your key skills. Remember the admissions committee is considering your suitability for the specific programme you are applying for, so mention skills relevant to the PhD course.
Motivation for applying: Show your enthusiasm and passion for the subject, and describe your long-term aspirations. Start with how you first became interested in the field, and how your interest has grown since. You should also mention anything else you have done which helps demonstrate your interest in your proposed research topic, for example:
- Have you attended any workshops or seminars?
- Do you have any research experience?
- Have you taught yourself any aspects of the subject?
- Have you read any literature within the research area?
Finally, describe what has convinced you to dedicate the next 3-4 years (assuming you are to study full time) of your life to research.
How to End a Motivation Letter
Concluding the motivation letter is where most people struggle. Typically, people can easily describe their academic background and why they want to study, but convincing the reader they are the best candidate for the PhD programme is often more challenging.
The concluding remarks of your motivation letter should highlight the impacts of your proposed research, in particular: the new contributions it will make to your field, the benefits it will have on society and how it fits in with your aspirations.
With this, conclude with your career goals. For example, do you want to pursue an academic career or become a researcher for a private organisation? Doing so will show you have put a lot of thought into your decision.
Remember, admissions into a PhD degree is very competitive, and supervisors invest a lot of time into mentoring their students. Therefore, supervisors naturally favour those who show the most dedication. Your conclusion should remind the reader that you are not only passionate about the research project, but that the university will benefit from having you.
Finally, thank the reader for considering your application.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
Motivation Letter Format
There are some basic rules to follow when writing a successful motivation letter. These will mimic the standard format for report writing that the supervisor will be familiar with:
- Use a sans serif font (e.g. Arial or Times New Roman),
- Use a standard font size (e.g. 12pt) and black font colour,
- Keep your writing professional throughout and avoid the use of informal language,
- Write in the first person,
- Address your motivation letter to a named person such as the project supervisor, however, this could also be the person in charge of research admissions,
- Structure your letter into paragraphs using the guidance above, such as introduction, academic history, motivation for research, and concluding remarks.
How Long Should a Motivation Letter Be?
A good rule of thumb for PhD motivation letters is to keep it to around one side of A4. A little longer than one page is acceptable, but two pages is generally considered too long. This equates to approximately 400-600 words.
Things to Avoid when Writing Your Motivational Letter
Your motivational letter will only be one of the several documents you’ll be asked to submit as part of your PhD application. You will almost certainly be asked to submit an Academic CV as well. Therefore, be careful not to duplicate any of the information.
It is acceptable to repeat the key points, such as what and where you have studied. However, while your CV should outline your academic background, your motivation letter should bring context to it by explaining why you have studied what you have, and where you hope to go with it. The simplest way to do this is to refer to the information in your CV and explain how it has led you to become interested in research.
Don’t try to include everything. A motivation letter should be short, so focus on the information most relevant to the programme and which best illustrates your passion for it. Remember, the academic committee will need to be critical in order to do their jobs effectively , so they will likely interpret an unnecessarily long letter as in indication that you have poor written skills and cannot communicate effectively.
You must be able to back up all of your statements with evidence, so don’t fabricate experiences or overstate your skills. This isn’t only unethical but is likely to be picked up by your proposed PhD supervisor or the admissions committee.
Whilst it is good to show you have an understanding of the field, don’t try to impress the reader with excessive use of technical terms or abbreviations.
PhD Motivation Letter Samples – A Word of Caution
There are many templates and samples of motivation letters for PhDs available online. A word of caution regarding these – although they can prove to be a great source of inspiration, you should refrain from using them as a template for your own motivation letter.
While there are no rules against them, supervisors will likely have seen a similar letter submitted to them in the past. This will not only prevent your application from standing out, but it will also reflect poorly on you by suggesting that you have put minimal effort into your application.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
- Extremes and Natural Hazards
- Adaptation Science
- Earth Data Across Scales
- Earth Data Science Education
- Earth Analytics
- Landscape Dynamics
- Partnerships
- Earth Analytics Professional Certificate
- Environmental Data Science Seminar Series
- Post Docs and Graduate Students
- Earth Data Science Corps
- How to Engage
- Learning Portal
How to Write a Good Cover Letter for a Research Position
Writing a cover letter can be intimidating, but it doesn’t have to be!
Some people believe cover letters are a science. Others seem to think they are more akin to black magic. Regardless of how you feel about cover letters, they are one of the most important parts of the job application process. Your resume or CV may get you an interview, but a good cover letter is what ensures that the hiring manager reads your resume in the first place.
Writing a cover letter for any job is important, but the art of writing a good cover letter for a research position can make or break your application. While writing a cover letter for a research position, you have to walk a fine line of proving your expertise and passion while limiting jargon and dense language.
In this post, we will explain cover letter writing basics, and then dive into how to write a research specific cover letter with examples of both good and bad practices.

What Is A Cover Letter and Why Do Cover Letters Matter?
A cover letter is your opportunity to tell a story and connect the dots of your resume. Resumes and curriculum vitae (CVs) are often cold and static—they don’t show any sort of character that will give companies a hint about if you will fit in with their culture.
Your cover letter gives you the chance to demonstrate that you are an interesting, qualified, and intelligent person. Without proving that you are worth the time to interview, a company or research organization will set your application in the rejection pile without giving it a second look.
So, what is a cover letter, exactly? It is an explanation (written out in paragraph form) of what you can bring to the company that goes beyond the information in your resume. Cover letters give a company a glimpse into the qualities that will make you the ideal candidate for their opening.
Note that a cover letter is not the same as a letter of intent. A cover letter is written for a specific job opening. For example, if I got an email saying that the University of Colorado was looking for a tenure track faculty member to teach GEO 1001, and I chose to apply, I would write a cover letter.
A letter of intent, however, is written regardless of the job opening. It is intended to express an interest in working at a particular company or with a particular group. The goal of a letter of intent is to demonstrate your interest in the company (or whatever type of group you are appealing to) and illustrate that you are willing to work with them in whatever capacity they feel is best.
For example, if I loved the clothing company, Patagonia and wanted to work there, I could write a letter of intent. They may have an opening for a sales floor associate, but after reading my application and letter of intent, decide I would be better suited to a design position. Or, they may not have any positions open at all, but choose to keep my resume on hand for the next time they do.
Most organizations want a cover letter, not a letter of intent, so it is important to make sure your cover letter caters to the specifics of the job posting. A cover letter should also demonstrate why you want to work at the company, but it should be primarily focused on why you can do the job better than any of the other applicants.
How to Write a Good Cover Letter: The Basics
Writing a cover letter isn’t hard. Writing a good cover letter, a cover letter that will encourage a hiring manager to look at your application and schedule an interview, is more difficult (but certainly not impossible). Below, we will go over each of the important parts of a cover letter: the salutation, introduction, body, and conclusion, as well as some other best practices.
How to Write a Good Cover Letter Salutation
Don’t start with “Dear Sir/Ma’am” (or any iteration of a vague greeting, including “to whom it may concern”). Avoiding vague greetings is the oldest trick in the book, but it still holds a lot of weight. Starting a cover letter with the above phrase is pretty much stamping “I didn’t bother to research this company at all because I am sending out a million generic cover letters” across your application. It doesn’t look good.
The best practice is to do your research and use your connections to find a name. “Dear Joe McGlinchy” means a lot more than “Dear Hiring Manager.” LinkedIn is a great tool for this—you can look up the company, then look through the employees until you find someone that seems like they hire for the relevant department.
The most important thing about the salutation is to address a real human. By selecting someone in the company, you’ve demonstrated that you’ve done some research and are actually interested in this company specifically. Generic greetings aren’t eye-catching and don’t do well.
How to Write a Good Cover Letter Introduction
Once you’ve addressed your cover letter to a real human being, you need a powerful introduction to prove that this cover letter is worth the time it will take to read. This means that you need a hook.
Your first sentence needs to be a strong starter, something to encourage the hiring manager not only to continue reading the cover letter, but to look at your application as well. If you have a contact in the company, you should mention them in the first sentence. Something along the lines of “my friend, Amanda Rice (UX/UI manager), suggested I apply for the natural language processing expert position after we worked together on a highly successful independent project.”
The example above uses a few techniques. The name drop is good, but that only works if you actually have a connection in the company. Beyond that, this example has two strengths. First, it states the name of the position. This is important because hiring managers can be hiring for several different positions at a time, and by immediately clarifying which position you are applying for, you make their job a little bit easier. Next, this sentence introduces concrete skills that apply to the job. That is a good way to start because it begins leading into the body, where you will go into depth about how exactly your experience and skills make you perfect for the job.
Another technique for a strong lead-in to a cover letter is to begin with an applicable personal experience or anecdote. This attracts more attention than stereotypical intros (like the example above), but you have to be careful to get to the point quickly. Give yourself one or two sentences to tell the story and prove your point before you dive into your skills and the main body of the cover letter.
A more standard technique for introductions is simply expressing excitement. No matter how you choose to start, you want to demonstrate that you are eager about the position, and there is no easier way to do that than just saying it. This could take the form of “When I saw the description for X job on LinkedIn, I was thrilled: it is the perfect job for my Y skills and Z experience.” This option is simple and to-the-point, which can be refreshing for time-crunched hiring managers.
Since we’ve provided a few good examples, we will offer a bad example, so you can compare and contrast. Don’t write anything along the line of: “My name is John Doe, and I am writing to express my interest in the open position at your company.”
There are a few issues here. First, they can probably figure out your name. You don’t need that to be in the first sentence (or any of the sentences—the closing is an obvious enough spot). Next, “the open position” and “your company” are too generic. That sounds like the same cover letter you sent to every single employer in a hundred mile radius. Give the specifics! Finally, try to start with a little more spice. Add in some personality, something to keep the hiring manager reading. If you bore them to death in the first line, they aren’t going to look over your resume and application with the attention they deserve.
How to Write a Good Cover Letter Body
So, you’ve addressed a real human being, and you’ve snagged their attention with a killer opening line. What next? Well, you have to hold on to that attention by writing an engaging and informative cover letter body.
The body of a cover letter is the core of the important information you want to transmit. The introduction’s job was to snag the attention of the hiring manager. The body’s job is to sell them on your skills. There are a few formatting things to be aware of before we start talking about what content belongs in the body of the cover letter. First, keep the company culture and standards in mind when picking a format. For example, if I want to work for a tech startup that is known for its wit and company culture, I can probably get away with using a bulleted list or another informal format. However, if I am applying to a respected research institution, using a standard five paragraph format is best.
In addition, the cover letter should not be longer than a page. Hiring managers are busy people. They may have hundreds of resumes to read, so they don’t need a three page essay per person. A full page is plenty, and many hiring managers report finding three hundred words or less to be the idea length. Just to put that into context, the text from here to the “How to Write a Good Cover Letter Body” header below is about perfect, length-wise.
Now, on to the more important part: the content. A cover letter should work in tandem with a resume. If you have a list of job experiences on your resume, don’t list them again in the cover letter. Use the valuable space in the cover letter to give examples about how you have applied your skills and experience.
For example, if I have worked as a barista, I wouldn’t just say “I have worked as a barista at Generic Cafe.” The hiring manager could learn that from my resume. Instead, I could say “Working as a barista at Generic Cafe taught me to operate under pressure without feeling flustered. Once…” I would go on to recount a short story that illustrated my ability to work well under pressure. It is important that the stories and details you choose to include are directly related to the specific job. Don’t ramble or add anything that isn’t obviously connected. Use the job description as a tool—if it mentions a certain skill a few times, make sure to include it!
If you can match the voice and tone of your cover letter to the voice of the company, that usually earns you extra points. If, in their communications, they use wit, feel free to include it in your letter as well. If they are dry, to the point, and serious, cracking jokes is not the best technique.
A Few Don’ts of Writing a Cover Letter Body
There are a few simple “don’ts” in cover letter writing. Do not:
- Bad: I am smart, dedicated, determined, and funny.
- Better: When I was working at Tech Company, I designed and created an entirely new workflow that cut the product delivery time in half.
- Bad: When I was seven, I really loved the monkeys at the zoo. This demonstrates my fun-loving nature.
- Better: While working for This Company, I realized I was far more productive if I was light-hearted. I became known as the person to turn to in my unit when my coworkers needed a boost, and as my team adopted my ideology, we exceeded our sales goals by 200%.
- Bad: I would love this job because it would propel me to the next stage of my career.
- Better: With my decade of industry experience communicating with engineers and clients, I am the right person to manage X team.
- Bad: I know I’m not the most qualified candidate for this job, but…
- Better: I can apply my years of experience as an X to this position, using my skills in Y and Z to…
- Bad: I am a thirty year old white woman from Denver…
- Better: I have extensive experience managing diverse international teams, as illustrated by the time I…
The most important part of the cover letter is the body. Sell your skills by telling stories, but walk the razor’s edge between saying too much and not enough. When in doubt, lean towards not enough—it is better for the hiring manager to call you in for an interview to learn more than to bore them.
How to Write a Good Cover Letter Conclusion
The last lines of a cover letter are extremely important. Until you can meet in-person for an interview, the conclusion of your cover letter will greatly affect the impression the hiring manager has of you. A good technique for concluding your cover letter is to summarize, in a sentence, what value you can bring to the company and why you are perfect for the position. Sum up the most important points from your cover letter in a short, concise manner.
Write with confidence, but not arrogance. This can be a delicate balance. While some people have gotten away (and sometimes gotten a job) with remarks like, “I’ll be expecting the job offer soon,” most do not. Closing with a courteous statement that showcases your capability and skills is far more effective than arrogance. Try to avoid trite or generic statements in the closing sentence as well. This includes the template, “I am very excited to work for XYZ Company.” Give the hiring manager something to remember and close with what you can offer the company.
The final step in any cover letter is to edit. Re-read your cover letter. Then, set it aside for a few hours (or days, time permitting) and read it again. Give it to a friend to read. Read it aloud. This may seem excessive, but there is nothing more off-putting than a spelling or grammar error in the first few lines of a cover letter. The hiring manager may power through and ignore it, but it will certainly taint their impression.
Once the cover letter is as flawless and compelling as it can be, send it out! If you are super stuck on how to get started, working within a template may help. Microsoft Word has many free templates that are aesthetically appealing and can give you a hint to the length and content. A few good online options live here (free options are at the bottom—there is no reason to pay for a resume template).
How to Write a Cover Letter for a Research Position
Writing a cover letter for a research position is the same as writing any other cover letter. There are, however, a few considerations and additions that are worth pointing out. A job description may not directly ask for a cover letter, but it is good practice to send one unless they specifically say not to. This means that even if a cover letter isn’t mentioned, you should send one—it is best practice and gives you an opportunity to expand on your skills and research in a valuable way.
Format and Writing Style for a Research Position Cover Letter
Research and academics tend to appreciate formality more than start-ups or tech companies, so using the traditional five paragraph format is typically a good idea. The five paragraph format usually includes an introduction, three short examples of skills, and a concluding paragraph. This isn’t set in stone—if you’d rather write two paragraphs about the skills and experience you bring to the company, that is fine.
Keep in mind that concise and to-the-point writing is extremely valuable in research. Anyone who has ever written a project proposal under 300 words knows that every term needs to add value. Proving that you are a skilled writer, starting in your cover letter, will earn you a lot of points. This means that cover letters in research and academia, though you may have more to say, should actually be shorter than others. Think of the hiring manager—they are plowing through a massive stack of verbose, technical, and complex cover letters and CVs. It is refreshing to find an easy to read, short cover letter.
On the “easy to read” point, remember that the hiring manager may not be an expert in your field. Even if they are, you cannot assume that they have the exact same linguistic and educational background as you. For example, if you have dedicated the last five years of your life to studying a certain species of bacteria that lives on Red-Eyed Tree Frogs, all of those technical terms you have learned (and maybe even coined) have no place in your cover letter. Keep jargon to an absolute minimum. Consider using a tool like the Hemingway Editor to identify and eliminate jargon. While you want to reduce jargon, it is still important to prove that you’ve researched their research. Passion about the research topic is one of the most valuable attributes that a new hire can offer.
Use your cover letter to prove that you have done your homework, know exactly what the institution or group is doing, and want to join them. If you have questions about the research or want to learn more, it isn’t a bad idea to get in touch with one of the researchers. You can often use LinkedIn or the group’s staff site to learn who is working on the project and reach out.
What Research Information Should be Included in a Cover Letter
A research position cover letter is not the place for your academic history, dissertation, or publications. While it may be tempting to go into detail about the amazing research you did for your thesis, that belongs in your CV. Details like this will make your cover letter too long. While these are valuable accomplishments, don’t include them unless there is something that pertains to the group’s research, and your CV doesn’t cover it in depth.
If you do choose to write about your research, write about concrete details and skills that aren’t in your CV. For example, if you have spent the last few years working on identifying the effects of a certain gene sequence in bird migration, include information about the lab techniques you used. Also, try to put emphasis on the aspects of your resume and CV that make you stand out from other candidates. It is likely that you will be competing with many similarly qualified candidates, so if you have a unique skill or experience, make sure it doesn’t get lost in the chaos—a cover letter is the perfect place to highlight these sorts of skills.
Industry experience is a great differentiator. If you have relevant industry experience, make sure to include it in your cover letter because it will almost certainly set you apart. Another valuable differentiator is a deep and established research network. If you have been working on research teams for years and have deep connections with other scientists, don’t be afraid to include this information. This makes you a very valuable acquisition for the company because you come with an extensive network
Include Soft Skills in Your Cover Letter
Scientific skills aren’t the only consideration for hiring managers. Experience working with and leading teams is incredibly valuable in the research industry. Even if the job description doesn’t mention teamwork, add a story or description of a time you worked with (or, even better, lead) a successful team. Soft skills like management, customer service, writing, and clear communication are important in research positions. Highlight these abilities and experiences in your cover letter in addition to the hard skills and research-based information.
If you are struggling to edit and polish your letter, give it to both someone within your field and someone who is completely unfamiliar with your research (or, at least, the technical side of it). Once both of those people say that the letter makes sense and is compelling, you should feel confident submitting it.
Cover letters are intended to give hiring managers information beyond what your resume and CV are able to display. Write with a natural but appropriately formal voice, do your research on the position, and cater to the job description. A good cover letter can go a long way to getting you an interview, and with these tips, your cover letters will certainly stand out of the pile.
Related Articles
Lowering barriers to learning and teaching data science.

Nathan A. Quarderer

Ally Faller

Lauren Herwehe
Earth Data Science And The Open Education Movement
Get in touch, certificate form.
Tips for Grads: How to write a good cover letter
By Foram Gathia, PhD student
Writing a compelling cover letter is essential for making a positive impression on potential employers. Here’s a guide to crafting a strong cover letter:
- Start with a Strong Introduction: Address the hiring manager by name if possible and mention the specific position you are applying for. Engage the reader with a captivating opening sentence that highlights your enthusiasm and sets the tone for the letter.
- Highlight Your Relevant Skills and Experience: Tailor your cover letter to the job description by emphasizing the skills and experiences that make you a strong candidate. Provide specific examples of past achievements that demonstrate your qualifications for the role.
- Showcase Your Personality and Passion: Use the cover letter as an opportunity to showcase your personality and passion for the industry or company. Share insights into what motivates you and why you are excited about the opportunity.
- Demonstrate Your Knowledge of the Company: Research the company and mention specific aspects that appeal to you or align with your values. This demonstrates your genuine interest and initiative.
- Close with a Strong Call to Action: End the cover letter with a confident closing statement expressing your eagerness to further discuss your qualifications in an interview. Thank the employer for considering your application and include your contact information.
Remember to keep the cover letter concise, focusing on quality over quantity, and proofread carefully for grammar and spelling errors. A well-crafted cover letter can significantly enhance your job application and increase your chances of landing an interview.
These tips are based on the Beyond Graduate School cover letter webinar as well as the Harvard Business Review article “ How to Write a Cover Letter ”.
Tips for Grads is a professional and academic advice column written by graduate students for graduate students at UW–Madison. It is published in the student newsletter, GradConnections Weekly.
- Facebook Logo
- Twitter Logo
- Linkedin Logo

Academic Cover Letters
What is this handout about.
The long list of application materials required for many academic teaching jobs can be daunting. This handout will help you tackle one of the most important components: the cover letter or letter of interest. Here you will learn about writing and revising cover letters for academic teaching jobs in the United States of America.
What is an academic cover letter?
An academic cover letter describes your experiences and interest as a candidate for a specific position. It introduces you to the hiring committee and demonstrates how your academic background fits with the description of the position.
What do cover letters for academic teaching jobs typically contain?
At their most basic level, academic cover letters accomplish three things: one, they express your interest in the job; two, they provide a brief synopsis of your research and teaching; and three, they summarize your past experiences and achievements to illustrate your competence for the job. For early-career scholars, cover letters are typically no more than two pages (up to four pages for senior scholars). Occasionally, a third page may make sense for an early-career scholar if the application does not require a separate teaching statement and/or research statement. Digital versions of cover letters often contain hyperlinks to your CV or portfolio page. For some fields, cover letters may also include examples of your work, including music, popular articles, and other multimedia related to your research, service, or teaching available online. Typically, letters appear on departmental or university letterhead and include your signature. Above all, a strong cover letter presents your accomplishments and your familiarity with the institution and with the position.
How should I prepare to write my academic cover letter?
Like all writing, composing a cover letter is a process. The process may be as short as a few hours or as long as several weeks, but at the end the letter should present you as a strong candidate for the job. The following section has tips and questions for thinking through each stage of this writing process. You don’t need to answer all of these questions to write the letter; they are meant to help you brainstorm ideas.
Before you begin writing your cover letter, consider researching the institution, the department, and the student population. Incorporating all three aspects in your letter will help convey your interest in the position.
Get to know the institution. When crafting your cover letter, be aware of the type of institution to which you are applying. Knowing how the institution presents itself can help you tailor your letter and make it more specific.
- Where is the institution located?
- Is it on a quarter-system or semester-system?
- What type of institution is it? Is it an R1? Is it an R2? Is it a liberal arts college? Is it an HBCU? Is it a community college? A private high school?
- What is the institution’s culture? Is it teaching-focused or research-focused? Does it privilege experiential learning? Does it value faculty involvement outside the classroom? Is it affiliated with a specific religious tradition?
- Does it have any specific institutional commitments?
- How does the institution advocate for involvement in its local community?
- What are the professional development opportunities for new and junior faculty?
Learn about the department. Knowing the specific culture and needs of the department can help you reach your audience: the department members who will be reading your documents and vetting you as a candidate.
- Who is on the search committee? Who is the search committee chair?
- What is the official name of the department?
- Which different subfields make up the department?
- Is it a dual appointment or a position in a dual department?
- How does the department participate in specific types of student outreach?
- Does the department have graduate students? Does it offer a terminal Master’s degree, Ph.D., or both? How large are the cohorts? How are they funded?
- Does the department encourage or engage in interdisciplinary work?
- Does the majority of the department favor certain theoretical or methodological approaches?
- Does the department have partnerships with local institutions? If so, which ones?
- Is the department attempting to fill a specific vacancy, or is it an entirely new position?
- What are the typical course offerings in the department? Which courses might you be expected to teach? What courses might you be able to provide that are not currently available?
Consider the students. The search committee will often consider how you approach instructing and mentoring the student body. Sometimes committees will even reserve a position for a student or solicit student feedback on a candidate:
- What populations constitute the majority of the undergraduate population?
- Have there been any shifts in the student population recently?
- Do students largely come from in-state or out-of-state?
- Is there an international student population? If so, from which countries?
- Is the university recruiting students from traditionally underrepresented populations?
- Are students particularly active on campus? If so, how?
Many answers to these questions can be found both in the job description and on the institution’s website. If possible, consider contacting someone you know at the institution to ask about the culture directly. You can also use the institution’s course catalog, recruitment materials, alumni magazine, and other materials to get answers to these questions. The key is to understand the sort of institution to which you are applying, its immediate needs, and its future trajectory.
Remember, there is a resource that can help you with all three aspects—people. Reach out to your advisor, committee members, faculty mentors, and other contacts for insight into the prospective department’s culture and faculty. They might even help you revise your letter based on their expertise. Think of your job search as an opportunity to cultivate these relationships.
After you have done some initial research, think about how your experiences have prepared you for the job and identify the ones that seem the most relevant. Consider your previous research, internships, graduate teaching, and summer experiences. Here are some topics and questions to get you started thinking about what you might include.
Research Experiences. Consider how your research has prepared you for an academic career. Since the letter is a relatively short document, select examples of your research that really highlight who you are as a scholar, the direction you see your work going, and how your scholarship will contribute to the institution’s research community.
- What are your current research interests?
- What topics would you like to examine in the future?
- How have you pursued those research interests?
- Have you traveled for your research?
- Have you published any of your research? Have you presented it at a conference, symposium, or elsewhere?
- Have you worked or collaborated with scholars at different institutions on projects? If so, what did these collaborations produce?
- Have you made your research accessible to your local community?
- Have you received funding or merit-based fellowships for your research?
- What other research contributions have you made? This may include opinion articles, book chapters, or participating as a journal reviewer.
- How do your research interests relate to those of other faculty in the department or fill a gap?
Teaching Experience. Think about any teaching experience you may have. Perhaps you led recitations as a teaching assistant, taught your own course, or guest lectured. Pick a few experiences to discuss in your letter that demonstrate something about your teaching style or your interest in teaching.
- What courses are you interested in teaching for the department? What courses have you taught that discussed similar topics or themes?
- What new courses can you imagine offering the department that align with their aim and mission?
- Have you used specific strategies that were helpful in your instruction?
- What sort of resources do you typically use in the classroom?
- Do you have anecdotes that demonstrate your teaching style?
- What is your teaching philosophy?
- When have you successfully navigated a difficult concept or topic in the classroom, and what did you learn?
- What other opportunities could you provide to students?
Internships/Summer/Other Experiences. Brainstorm a list of any conferences, colloquiums, and workshops you have attended, as well as any ways you have served your department, university, or local community. This section will highlight how you participate in your university and scholarly community. Here are some examples of things you might discuss:
- Professional development opportunities you may have pursued over the summer or during your studies
- International travel for research or presentations
- Any research you’ve done in a non-academic setting
- Presentations at conferences
- Participation in symposia, reading groups, working groups, etc.
- Internships in which you may have implemented your research or practical skills related to your discipline
- Participation in community engagement projects
- Participation in or leadership of any scholarly and/or university organizations
In answering these questions, create a list of the experiences that you think best reflect you as a scholar and teacher. In choosing which experiences to highlight, consider your audience and what they would find valuable or relevant. Taking the time to really think about your reader will help you present yourself as an applicant well-qualified for the position.
Writing a draft
Remember that the job letter is an opportunity to introduce yourself and your accomplishments and to communicate why you would be a good fit for the position. Typically, search committees will want to know whether you are a capable job candidate, familiar with the institution, and a great future addition to the department’s faculty. As such, be aware of how the letter’s structure and content reflect your preparedness for the position.
The structure of your cover letter should reflect the typical standards for letter writing in the country in which the position is located (the list below reflects the standards for US letter writing). This usually includes a salutation, body, and closing, as well as proper contact information. If you are affiliated with a department, institution, or organization, the letter should be on letterhead.
- Use a simple, readable font in a standard size, such as 10-12pt. Some examples of fonts that may be conventional in your field include Arial, Garamond, Times New Roman, and Verdana, among other similar fonts.
- Do not indent paragraphs.
- Separate all paragraphs by a line and justify them to the left.
- Make sure that any included hyperlinks work.
- Include your signature in the closing.
Before you send in your letter, make sure you proofread and look for formatting mistakes. You’ll read more about proofreading and revising later in this handout!
The second most important aspect of your letter is its content. Since the letter is the first chance to provide an in-depth introduction, it should expand on who you are as a scholar and possible faculty member. Below are some elements to consider including when composing your letter.
Identify the position you are applying to and introduce yourself. Traditionally, the first sentence of a job letter includes the full name of the position and where you discovered the job posting. This is also the place to introduce yourself and describe why you are applying for this position. Since the goal of a job letter is to persuade the search committee to include you on the list of candidates for further review, you may want to include an initial claim as to why you are a strong candidate for the position. Some questions you might consider:
- What is your current status (ABD, assistant professor, post-doc, etc.)?
- If you are ABD, have you defended your dissertation? If not, when will you defend?
- Why are you interested in this position?
- Why are you a strong candidate for this position?
Describe your research experience and interests. For research-centered positions, such as positions at R1 or other types of research-centered universities, include information about your research experience and current work early in the letter. For many applicants, current work will be the dissertation project. If this is the case, some suggest calling your “dissertation research” your “current project” or “work,” as this may help you present yourself as an emerging scholar rather than a graduate student. Some questions about your research that you might consider:
- What research experiences have you had?
- What does your current project investigate?
- What are some of the important methods you applied?
- Have you collaborated with others in your research?
- Have you acquired specific skills that will be useful for the future?
- Have you received special funding? If so, what kind?
- Has your research received any accolades or rewards?
- What does your current project contribute to the field?
- Where have you presented your research?
- Have you published your research? If so, where? Or are you working on publishing your work?
- How does your current project fit the job description?
Present your plans for future research. This section presents your research agenda and usually includes a description of your plans for future projects and research publications. Detailing your future research demonstrates to the search committee that you’ve thought about a research trajectory and can work independently. If you are applying to a teaching-intensive position, you may want to minimize this section and/or consider including a sentence or two on how this research connects to undergraduate and/or graduate research opportunities. Some questions to get you started:
- What is your next research project/s?
- How does this connect to your current and past work?
- What major theories/methods will you use?
- How will this project contribute to the field?
- Where do you see your specialty area or subfield going in the next ten years and how does your research contribute to or reflect this?
- Will you be collaborating with anyone? If so, with whom?
- How will this future project encourage academic discourse?
- Do you already have funding? If so, from whom? If not, what plans do you have for obtaining funding?
- How does your future research expand upon the department’s strengths while simultaneously diversifying the university’s research portfolio? (For example, does your future research involve emerging research fields, state-of-the-art technologies, or novel applications?)
Describe your teaching experience and highlight teaching strategies. This section allows you to describe your teaching philosophy and how you apply this philosophy in your classroom. Start by briefly addressing your teaching goals and values. Here, you can provide specific examples of your teaching methods by describing activities and projects you assign students. Try to link your teaching and research together. For example, if you research the rise of feminism in the 19th century, consider how you bring either the methodology or the content of your research into the classroom. For a teaching-centered institution, such as a small liberal arts college or community college, you may want to emphasize your teaching more than your research. If you do not have any teaching experience, you could describe a training, mentoring, or coaching situation that was similar to teaching and how you would apply what you learned in a classroom.
- What is your teaching philosophy? How is your philosophy a good fit for the department in which you are applying to work?
- What sort of teaching strategies do you use in the classroom?
- What is your teaching style? Do you lecture? Do you emphasize discussion? Do you use specific forms of interactive learning?
- What courses have you taught?
- What departmental courses are you prepared to teach?
- Will you be able to fill in any gaps in the departmental course offerings?
- What important teaching and/or mentoring experiences have you had?
- How would you describe yourself in the classroom?
- What type of feedback have you gotten from students?
- Have you received any awards or recognition for your teaching?
Talk about your service work. Service is often an important component of an academic job description. This can include things like serving on committees or funding panels, providing reviews, and doing community outreach. The cover letter gives you an opportunity to explain how you have involved yourself in university life outside the classroom. For instance, you could include descriptions of volunteer work, participation in initiatives, or your role in professional organizations. This section should demonstrate ways in which you have served your department, university, and/or scholarly community. Here are some additional examples you could discuss:
- Participating in graduate student or junior faculty governance
- Sitting on committees, departmental or university-wide
- Partnerships with other university offices or departments
- Participating in community-partnerships
- Participating in public scholarship initiatives
- Founding or participating in any university initiatives or programs
- Creating extra-curricular resources or presentations
Present yourself as a future faculty member. This section demonstrates who you will be as a colleague. It gives you the opportunity to explain how you will collaborate with faculty members with similar interests; take part in departmental and/or institution wide initiatives or centers; and participate in departmental service. This shows your familiarity with the role of faculty outside the classroom and your ability to add to the departmental and/or institutional strengths or fill in any gaps.
- What excites you about this job?
- What faculty would you like to collaborate with and why? (This answer may be slightly tricky. See the section on name dropping below.)
- Are there any partnerships in the university or outside of it that you wish to participate in?
- Are there any centers associated with the university or in the community that you want to be involved in?
- Are there faculty initiatives that you are passionate about?
- Do you have experience collaborating across various departments or within your own department?
- In what areas will you be able to contribute?
- Why would you make an excellent addition to the faculty at this institution?
Compose a strong closing. This short section should acknowledge that you have sent in all other application documents and include a brief thank you for the reader’s time and/or consideration. It should also state your willingness to forward additional materials and indicate what you would like to see as next steps (e.g., a statement that you look forward to speaking with the search committee). End with a professional closing such as “Sincerely” or “Kind Regards” followed by your full name.
If you are finding it difficult to write the different sections of your cover letter, consider composing the other academic job application documents (the research statement, teaching philosophy, and diversity statement) first and then summarizing them in your job letter.
Different kinds of letters may be required for different types of jobs. For example, some jobs may focus on research. In this case, emphasize your research experiences and current project/s. Other jobs may be more focused on teaching. In this case, highlight your teaching background and skills. Below are two models for how you could change your letter’s organization based on the job description and the institution. The models offer a guide for you to consider how changing the order of information and the amount of space dedicated to a particular topic changes the emphasis of the letter.
Research-Based Position Job Letter Example:
Teaching-based position job letter example:.
Remember your first draft does not have to be your last. Try to get feedback from different readers, especially if it is one of your first applications. It is not uncommon to go through several stages of revisions. Check out the Writing Center’s handout on editing and proofreading and video on proofreading to help with this last stage of writing.
Potential pitfalls
Using the word dissertation. Some search committee members may see the word “dissertation” as a red flag that an applicant is too focused on their role as a graduate student rather than as a prospective faculty member. It may be advantageous, then, to describe your dissertation as current research, a current research project, current work, or some other phrase that demonstrates you are aware that your dissertation is the beginning of a larger scholarly career.
Too much jargon. While you may be writing to a specific department, people on the search committee might be unfamiliar with the details of your subfield. In fact, many committees have at least one member from outside their department. Use terminology that can easily be understood by non-experts. If you want to use a specific term that is crucial to your research, then you should define it. Aim for clarity for your reader, which may mean simplification in lieu of complete precision.
Overselling yourself. While your job letter should sell you as a great candidate, saying so (e.g., “I’m the ideal candidate”) in your letter may come off to some search committee members as presumptuous. Remember that although you have an idea about the type of colleague a department is searching for, ultimately you do not know exactly what they want. Try to avoid phrases or sentences where you state you are the ideal or the only candidate right for the position.
Paying too much attention to the job description. Job descriptions are the result of a lot of debate and compromise. If you have skills or research interests outside the job description, consider including them in your letter. It may be that your extra research interests; your outside skills; and/or your extracurricular involvements make you an attractive candidate. For example, if you are a Latin Americanist who also happens to be well-versed in the Spanish Revolution, it could be worth mentioning the expanse of your research interests because a department might find you could fill in other gaps in the curriculum or add an additional or complementary perspective to the department.
Improper sendoff. The closing of your letter is just as important as the beginning. The end of the letter should reflect the professionalism of the document. There should be a thank-you and the word sincerely or a formal equivalent. Remember, it is the very last place in your letter where you present yourself as a capable future colleague.
Small oversights. Make sure to proofread your letter not just for grammar but also for content. For example, if you use material from another letter, make sure you do not include the names of another school, department, or unassociated faculty! Or, if the school is in Chicago, make sure you do not accidentally reference it as located in the Twin Cities.
Name dropping. You rarely know the internal politics of the department or institution to which you are applying. So be cautious about the names you insert in your cover letters. You do not want to unintentionally insert yourself into a departmental squabble or add fire to an interdepartmental conflict. Instead, focus on the actions you will undertake and the initiatives you are passionate about.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Ball, Cheryl E. 2013. “Understanding Cover Letters.” Inside Higher Ed , November 3, 2013. https://www.insidehighered.com/advice/2013/11/04/essay-cover-letter-academic-jobs .
Borchardt, John. 2014. “Writing a Winning Cover Letter.” Science Magazine , August 6, 2014. https://www.sciencemag.org/careers/2014/08/writing-winning-cover-letter# .
Helmreich, William. 2013. “Your First Academic Job.” Inside Higher Ed , June 17, 2013. https://www.insidehighered.com/advice/2013/06/17/essay-how-land-first-academic-job .
Kelsky, Karen. 2013. “How To Write a Journal Article Submission Cover Letter.” The Professor Is In (blog), April 26, 2013. https://theprofessorisin.com/2013/04/26/how-to-write-a-journal-article-submission-cover-letter/ .
Tomaska, Lubomir, and Josef Nosek. 2008. “Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Cover Letter to Accompany a Job Application for an Academic Position.” PLoS Computational Biology 14(5). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006132 .
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
404 Not found
- Virtual Experiences
- In-Person Experiences
- Hybrid Experiences
- Social Calendar [New]
- Experience FAQ
- Features & Benefits
- How Pricing Works
- Client Testimonials
- Happiness Guarantee
- Blog Articles
- Video Library
- View 48 Experiences
25 Tips on How to Write a Cover Letter with Examples
You found our guide on how to write a cover letter with examples .
These tips provide step-by-step instructions on creating an effective cover letter. For example, steps can include understanding the purpose and identifying the target audience. The purpose of these guidelines is to help job seekers create attention-grabbing letters. These guidelines are also known as “best cover letter examples” and “writing a cover letter.”
These tips on how to write a cover letter with examples are similar to preparing for an interview , writing work emails , and business writing books .
This list includes:
- writing a cover letter
- steps for writing a cover letter
- cover letter templates
- cover letter tips
- cover letter guidelines
Let’s get to it!
Tips on how to structure a cover letter
Formatting a cover letter makes it easier to read, so it is important to refine your structure. Here are some cover letter guidelines to consider.
1. Cover Letter Format
The cover letter format should be professional, clear, and concise. The formatting should match your resume for a clean and consistent look. You should use the same font, font size, and header style. These simple tips help you look organized and composed.
2. Header and Contact Details
When creating a cover letter, the header is the first item potential employers see. This section contains your contact information and the date. Your name, address, phone number, email address, and professional social media links are crucial parts of the header.
It is important to ensure that all information is accurate and current. The date should align with your contact details on either side of the page. A properly designed header establishes a professional first impression. Further, employers can readily contact you for additional communication.
Get our free team building toolbox
- icebreaker games
- bingo cards

3. Salutation
Your cover letter opener should include a professional greeting addressed directly to the hiring manager. If possible, research the manager’s name for personalized engagement. For example, “Dear Mr. Smith” stands out. If you do not know the hiring manager, then default to a general “Dear Hiring Manager.” This opener shows respect and formality.
4. Opening Paragraph
When writing a cover letter, the first paragraph introduces you to a potential employer. It is important to begin clearly stating the specific position you are applying for and how you found out about the job opportunity. You can also touch on your relevant experience or skills that show why you are a good fit for the role. However, remember that you do not need to repeat your entire resume on the cover letter.
This paragraph establishes the tone for the rest of your letter and encourages the reader to continue learning about you. Creating an interesting opening paragraph can grab the attention of hiring managers. By showing your enthusiasm and skills, you make a positive initial impression.
5. Body Paragraph
In the body paragraph, you should write details that support the main points of your cover letter. This section should expand on your qualifications, experiences, and achievements. This info can highlight specific examples demonstrating why you are the ideal fit for the position. Each sentence should add value and relevance to your application, showcasing your skills. Writing a strong body paragraph can greatly enhance the overall impact of your cover letter.
Readability is an important factor in your letter. Try to avoid walls of text. Many recruiters skim cover letters, so perhaps line breaks and bullet points to make the letter easier to scan. Be sure to incorporate plenty of white space. Also, consider placing your most important achievements and information strategically in highly visible spots, such as the start of a line or a paragraph, to increase the likelihood of a reader noticing them. Incorporating keywords from the job posting is another smart move.
When writing your cover letter, avoid replicating your resume. The cover letter is a chance for you to provide additional information that might not be evident in your resume or CV, such as your motivation to work for the company or individual achievements or experiences that make you desirable for the role. Be sure also to use action language and mention accomplishments and results instead of simply stating duties.
6. Closing Paragraph
To close a cover letter, express gratitude for the reader’s time and consideration. This section should also reiterate your interest and invite further contact. For example, “Thank you for considering my application. I look forward to the possibility of discussing my qualifications further. Feel free to contact me at your earliest convenience.” Overall, showing gratitude and offering a call to action helps close out your writing.
7. Signature
A signature provides a personal touch and enhances the document’s professionalism. First, start by choosing a closing salutation. Friendly and professional phrases work best, such as “All the best” or even “Sincerely.”
Your signature should be at the end of your document. This signature must be clear and contain your full name. If you are submitting a cover letter online, then consider using a digital signature. Another option is to sign your name using a program like Procreate and insert the signature in the document as an image. Taking this extra step can differentiate you from other applicants.
Tips on what to include in a cover letter
There are several steps for writing a cover letter. Here are a few tips to get you started.
Understanding the purpose of a cover letter helps you write a successful document. The letter highlights your skills and experiences, showing why you are the ideal candidate for a specific job. With a cover letter, you can introduce yourself to potential employers. This document highlights relevant experiences, skills, and accomplishments. Be sure to tailor this info to the job you are applying for.
Additionally, the letter shows your enthusiasm for the position while addressing job requirements. Finally, you can provide context for parts of your resume and showcase your communication skills. Overall, a well-crafted cover letter offers interviewers a personalized introduction.
2. Audience
To craft an effective cover letter, it is important to identify your audience. You should research the firm and role to find out who the hiring manager is. Letters should address this individual directly. Further, be sure to find out more about the company itself. With this information, you can tailor your skills and experiences to meet the expectations of the potential employer. Understanding your audience provides direction for your content and tone.
3. Professional Tone
Throughout your cover letter, maintain a professional tone. To show respect toward the receiver, avoid inappropriate or casual language. Be sure to always address the reader formally unless they have indicated otherwise. This style demonstrates your professionalism and maturity. Writing well sets a positive impression even before managers read your qualifications.
4. Relevant Keywords
Knowing the right keywords is one of the top cover letter tips. Recruiters commonly use screening software to assess cover letters. These keywords often match the job description. For example, if you are applying for a sales role, terms like “performance targets” or “customer acquisition” might be relevant. Tailoring your cover letter with such keywords can showcase your understanding and fit for the role.
5. Measurable Achievements
Measurable accomplishments are crucial in a cover letter. This information offers solid proof of your skills. When describing measurable accomplishments, emphasize specific numbers or percentages to highlight your achievements. For instance, mention increasing sales by a certain percentage or reducing costs by a particular amount. By showcasing measurable achievements, you effectively prove your worth to potential employers.
6. Soft Skills Highlight
To complement your technical abilities, highlight your soft skills within your cover letter. Leadership, communication, teamwork, critical thinking, and flexibility are attractive traits in potential candidates. You can demonstrate these skills through practical examples and professional experiences. When writing, show what you achieved and how you accomplished it.
7. Hard Skills Highlight
A cover letter should focus on hard skills, highlighting expertise and qualifications that are applicable to the job. Hard skills include skills like technical knowledge, data analysis, or language proficiency. Adding these specifics to a cover letter can capture the employer’s interest. For example, referencing software proficiencies can showcase your suitability for the position. By effectively showcasing hard skills, you can position yourself as a qualified candidate.
8. Company-Specific Content
When writing a cover letter, it is crucial to include content specific to the company. Customizing your letter for the company you are applying to demonstrates genuine interest and effort. Referencing the company’s particular projects or values shows that you have done your research. By showing how your skills fit the company’s requirements, you can set yourself apart as a strong candidate. This individualized approach can make a lasting impression on hiring managers.
9. Proofreading
Proofreading your cover letter ensures it is free of errors and maintains a professional tone. Once you have written your cover letter, make sure to carefully reread it for any spelling or grammar errors. Reading the letter out loud can help you find any awkward phrasing or unclear sentences. Further, ask for feedback from a friend or colleague before sending out your cover letter. A proofread cover letter can leave a favorable impact on prospective employers.
10. Application Follow Up
After submitting a job application, it is important to follow up. This step shows your interest and enthusiasm for the position. You can send a courteous email one week after applying, stating your continued interest in the role. The email should be brief and professional, thanking the hiring manager for reviewing your application. Be sure to specify why you are excited about the opportunity and briefly reiterate your relevant skills. Following up on job applications is a crucial part of the application process.

Tips for writing cover letters
Crafting cover letters can be a time-intensive process. Here are helpful tips to make writing cover letters easier.
1. Make a Master Cover Letter
Instead of starting each letter from scratch, make a master cover letter with all of your experiences and achievements. When starting a new application, you can copy and paste the relevant information from the template into your company cover letter.
Using AI can speed up the process of crafting your letter and help you tailor and personalize the letter to specific companies, positions, and job postings. Software like Grammarly and Teal have AI Cover Letter Generators that can help.
3. Start with a Hook
Like any good piece of writing, a strong start entices readers to continue. Try to include a compelling hook in your first sentence or first paragraph to catch the recruiter’s attention, demonstrate your personality and unique value as a candidate, and make your application more memorable.
4. Label Your File
When submitting a cover letter as an attachment, it is wise to name your file practically. For Example [YOUR NAME][COMPANY] [POSITION] [MONTH] [YEAR]. This simple step demonstrates your professionalism and attention to detail, and also makes it easier for the recruiter to keep track of your cover letter. Not to mention, good organization can help you keep track of your submission materials and prevent you from sending the wrong letter to a company.
5. Do one last check before you hit send
It is wise to review your cover letter one final time before you hit send. Be sure to do a thorough spelling and grammar check, and make sure the formatting is clear, consistent, and that converting the document to a new file format does not affect your layout. Most importantly, double check that the hiring manager, company name, and position are correct, especially if you copy and paste the same letter into new applications.
Cover letter templates
Below are a few cover letter examples to help you start your writing journey.
1. Standard Cover Letter
[Your Name]
[Your Address]
[City, State, Zip Code]
[Your Email Address]
[Your Phone Number]
[Today’s Date]
[Hiring Manager’s Name]
[Company Name]
[Company Address]
Dear [Hiring Manager’s Name],
I am writing to express my strong interest in the [Job Title] position at [Company Name], as advertised on [where you found the job posting]. With a [mention years of experience or relevant background] in [relevant field or industry], I am excited about the opportunity to contribute to [Company Name] and further develop my skills in [mention specific area or skill related to the job].
During my time at [Previous Company/Organization], I [describe relevant achievement or responsibility that showcases your skills]. Additionally, my experience with [mention relevant software, tools, or techniques] has equipped me with the ability to [highlight a skill or capability relevant to the job description]. I am confident that my background in [specific area] aligns well with the requirements of the [Job Title] position.
I am particularly drawn to [Company Name]’s commitment to [mention a specific aspect of the company’s mission, values, or projects]. I am eager to bring my [specific skill or expertise] to your team and contribute to [mention a goal or project relevant to the company].
Thank you for considering my application. I am enthusiastic about the opportunity to discuss how my background, skills, and enthusiasm can benefit [Company Name]. Please find my resume attached for your review. I am available for an interview at your earliest convenience and can be reached at [Your Phone Number] or via email at [Your Email Address].
2. Entry-Level Cover Letter
I am writing to express my interest in the [Job Title] position at [Company Name], as advertised on [where you found the job posting]. As a recent graduate with a [mention your degree or educational background] from [University/College Name], I am excited about the opportunity to begin my career journey and contribute to [Company Name].
While I may be new to the industry, I have gained valuable skills and experiences through internships, coursework, and extracurricular activities. For instance, during my internship at [Previous Company/Organization], I developed proficiency in [mention a relevant skill or task]. Additionally, my coursework in [mention relevant subject areas] has given me a strong foundation in [mention a relevant area of knowledge].
I am particularly impressed by [Company Name]’s commitment to [mention a specific aspect of the company’s mission, values, or projects]. I am eager to bring my enthusiasm, fresh perspective, and willingness to learn to your team. I am confident that my combination of academic achievements, internship experiences, and passion for [mention a relevant industry or field] make me a strong candidate for the [Job Title] position.
Thank you for considering my application. I am enthusiastic about the opportunity to discuss how my skills and eagerness to contribute can benefit [Company Name]. Please find my resume attached for your review. I am available for an interview at your earliest convenience and can be reached at [Your Phone Number] or via email at [Your Email Address].
3. Career Change Cover Letter
I am writing to express my interest in the [Job Title] position at [Company Name]. As someone with a diverse background in [mention your current or previous industry], I am eager to use my skills in [transferable skills] to make a successful transition into [new industry or field].
Throughout my career, I have developed strong skills in [mention relevant skills or experiences from your previous career]. While my background may seem unconventional for the [new industry], I am confident that my abilities in [mention transferable skills] are directly applicable to the requirements of the [Job Title] role at [Company Name].
I am particularly drawn to [Company Name]’s [mention a specific aspect of the company’s mission, values, or projects]. I am excited about the opportunity to bring my unique perspective, adaptability, and passion for learning to your team. I am committed to making a meaningful contribution to [Company Name] and am eager to embark on this new career path.
Thank you for considering my application. I am enthusiastic about the opportunity to discuss how my skills and experiences can benefit [Company Name] in the [new industry or field]. Please find my resume attached for your review. I am available for an interview at your earliest convenience and can be reached at [Your Phone Number] or via email at [Your Email Address].
Final Thoughts
Mastering cover letter writing can significantly increase your chances of landing your dream job. This document allows you to showcase your skills, qualifications, and passion in a way that your resume cannot. Be sure to tailor each cover letter for every job application and include specific examples where possible. Further, proofread your work before sending it off because first impressions matter!
Next, check out our posts on virtual interview tips , steps on writing a job posting , company culture fit , and communication books.
Book wildly fun team building events with expert hosts

FAQ: How to write a cover letter with examples
Here are frequently asked questions about how to write a cover letter with examples.
What are the key elements of a cover letter?
There are several key elements of a good cover letter.
Here are a few examples:
- understanding its purpose
- identifying your audience
- writing compelling opening and closing paragraphs
- highlighting hard and soft skills
- showcasing quantifiable achievements
- tailoring content for each company you apply to
These tips will help you create an eye-catching cover letter.
What should the tone of a cover letter be?
The tone of a cover letter should be professional yet approachable. It is important to convey your qualifications while also showing some personality.
How do I tailor my cover letter to a specific company?
To tailor your cover letter for a specific company, research the company’s values, culture, products, or services. Then, highlight how your skills and experiences align with the company’s needs.
What are some common mistakes in a cover letter?
Cover letters are notoriously difficult to write.
Here are a few common mistakes to avoid:
- being too generic
- focusing too much on yourself instead of how you can contribute to the company
- including irrelevant information
- making the letter too long or too short
- having grammatical errors
By avoiding these issues, you can ensure your cover letter stands out.
How do I follow up after sending my cover letter?
After sending your cover letter, wait about a week before sending a polite follow-up email. If you still do not hear back after another week, then it is okay to send one more follow-up.
Author: Michael Alexis
CEO at teambuilding.com. I write about my experience working with and leading remote teams since 2010.
We lead wildly fun experiences for teams with 1,000,000+ players to date.

4.96 / 5.0 rating on
50,225 Google Reviews
Create your Europass Cover Letter
Europass helps you to develop a structured, consistent and professional cover letter guiding you through each step. You can create new cover letters or edit existing ones using the Europass tool to create and edit cover letters.
How does Europass help?
Europass will guide you step by step through the process to help you create a good cover letter with all the essential information. You can create, store and share cover letters in 31 languages , choose from different templates to customise your application and share them easily from your Europass Library .
Create your Europass
How to write a good cover letter
A cover letter should highlight your motivation to apply for a specific job or opportunity, and demonstrate why you consider yourself to be the best candidate. Your cover letter should refer to particular examples in your CV and describe why these are relevant for the job vacancy you are applying for.
Read carefully
Read the vacancy notice carefully and highlight the skills that relate to the requirements of the position in your cover letter.
Use keywords
Use the keywords when you list your soft skills as mentioned on the vacancy notice (punctual, organised, team-player and so on).
Have short and clear paragraphs that show different aspects clearly.
Get to know the employer
Take time to research the employer to gain valuable insights into the culture of their organisation and make references in your cover letter to one or two key points.
Keep it short
You cover letter should not be longer than one page.
- First paragraph - why you are motivated to apply for the position,
- Second paragraph - how you are the most suitable candidate for the position, and
- Third Paragraph - why the company is a good match for you.
Use formal tone
Use a formal, polite tone and make sure there are no spelling mistakes.
Use simple fonts
Use simple non-decorative font styles, normal font-sizes (11-12) and optimal spacing (1 or 1.5).
Helpful EU services
Eures - the european job mobility portal.
Find jobs from all over Europe
Working abroad in other EU countries
Information, help and advice on EU rights related to work
Education and training in other EU countries
Information, help and advice on EU rights related to learning
You may be interested to read

Create your Europass CV

Europass and data privacy
Plan your career with Europass
Share this page.

Our Recommendations
- Best Small Business Loans for 2024
- Businessloans.com Review
- Biz2Credit Review
- SBG Funding Review
- Rapid Finance Review
- 26 Great Business Ideas for Entrepreneurs
- Startup Costs: How Much Cash Will You Need?
- How to Get a Bank Loan for Your Small Business
- Articles of Incorporation: What New Business Owners Should Know
- How to Choose the Best Legal Structure for Your Business
Small Business Resources
- Business Ideas
- Business Plans
- Startup Basics
- Startup Funding
- Franchising
- Success Stories
- Entrepreneurs
- The Best Credit Card Processors of 2024
- Clover Credit Card Processing Review
- Merchant One Review
- Stax Review
- How to Conduct a Market Analysis for Your Business
- Local Marketing Strategies for Success
- Tips for Hiring a Marketing Company
- Benefits of CRM Systems
- 10 Employee Recruitment Strategies for Success
- Sales & Marketing
- Social Media
- Best Business Phone Systems of 2024
- The Best PEOs of 2024
- RingCentral Review
- Nextiva Review
- Ooma Review
- Guide to Developing a Training Program for New Employees
- How Does 401(k) Matching Work for Employers?
- Why You Need to Create a Fantastic Workplace Culture
- 16 Cool Job Perks That Keep Employees Happy
- 7 Project Management Styles
- Women in Business
- Personal Growth
- Best Accounting Software and Invoice Generators of 2024
- Best Payroll Services for 2024
- Best POS Systems for 2024
- Best CRM Software of 2024
- Best Call Centers and Answering Services for Busineses for 2024
- Salesforce vs. HubSpot: Which CRM Is Right for Your Business?
- Rippling vs Gusto: An In-Depth Comparison
- RingCentral vs. Ooma Comparison
- Choosing a Business Phone System: A Buyer’s Guide
- Equipment Leasing: A Guide for Business Owners
- HR Solutions
- Financial Solutions
- Marketing Solutions
- Security Solutions
- Retail Solutions
- SMB Solutions

Online only.

6 Things You Should Never Put in Your Cover Letter
Table of contents.
When submitting a job application, your resume can only go so far. Resumes tell prospective employers about your experience and education, but they’re essentially fact sheets. A cover letter gives applicants the opportunity to share more detailed information on why they’d be a good fit for a particular role at a specific company.
We’ll outline some common cover letter mistakes to avoid and share tips and best practices for cover letters that show you in the best possible light.
Cover letter mistakes to avoid
A cover letter can show a hiring manager why you’re the best fit for a position, so getting it right is worth your time and effort. However, crafting an effective cover letter can be challenging. You must showcase your skills without appearing self-important or succumbing to cliches.
Here are six cover letter mistakes to avoid at all costs.
1. Highlighting where you lack specific skills
It’s easy to feel vulnerable when applying for a job, especially if you have limited work experience or few required skills. However, starting a cover letter by underselling yourself or drawing attention to the skills or knowledge you lack is never advisable.
Author and career development professional Lavie Margolin says cover letters aren’t the place to list your weaknesses. “I have seen one too many cover letters with the following phrase: ‘Although I do not yet have,'” Margolin noted. “If you do not have something, why are you emphasizing it?”
Instead, Margolin says job seekers should focus on existing in-demand career skills , experiences and talents that will interest the potential employer.
“If you are looking for a job, then you are in the sales business. What you write in your cover letter should most effectively sell the skills, experience and abilities that you do have, as opposed to emphasizing those things that are lacking,” Margolin advised. “Emphasizing a weakness on your cover letter may be costing you the job.”
2. Not proofreading for typos and cliches
Sometimes, job seekers get so caught up in finding the best way to express their ideas that they forget to pay close attention to their cover letter’s details. Typos, using the wrong company information and cliches are common mistakes to look for in your proofreading efforts.
- Look for cover letter typos. According to Joe Weinlick, COO of Catalyst Experiential, cover letter typos are an egregious yet common mistake. Rigorously proofreading your cover letter will allow your content to shine. “Spell-check is your friend. Use it, but don’t rely on it,” Weinlick advised. “Print out your cover letter, read it from start to finish and make sure there aren’t any typos before sending it out. Your cover letter is the first impression you make on a hiring manager – make sure it’s a good one.”
- Ensure you use the correct company information. You may be tempted to reuse parts of your cover letter when applying for similar positions with different companies. However, failing to update the company information for each letter is an unforgivable offense. Double-check that you have the correct details for the company, including the specific position for which you are applying and the name of the hiring manager, if possible.
- Watch for cliches and buzzwords. When proofreading your cover letter, look for and eliminate cliches and overused buzzwords . Instead of using vague words to describe your work ethic or experience (“I’m a motivated self-starter”), provide specific examples that demonstrate the qualities you’d like to highlight. “Don’t use buzzwords,” warned Bob Kovalsky, vice president of Volt Workforce Solutions. “Including descriptors such as ‘detail-oriented,’ ‘hardworking,’ ‘team player’ and ‘proactive’ doesn’t tell HR managers anything about your experience.”
Watch for cliches and worthless words in your LinkedIn profile . Overused buzzwords won’t convey your unique qualifications and personality.
3. Remaining stuck in the past
Maybe you were let go from your last job, or maybe you’re looking for new opportunities. Regardless of the reason for your job search , don’t spend your cover letter’s limited space focusing on your past.
“The worst thing a potential employee can do [in a cover letter] is to explain why they left their current or former position,” shared Kim Kaupe, co-founder of Bright Ideas Only. “It’s like starting out a first date by talking about your ex! I don’t want to hear about your past; I want to hear about your now and future and how you are going to become an asset to my company.”
Steering clear of the past is especially important if you had a contentious relationship with an employer. “Saying that you’re looking for a new opportunity because your previous employer was unfair or you had an incompetent boss will only make you look bad,” warned Tracy Russell, a talent acquisition coordinator at Intuit. “Oftentimes, if this type of negative information is in the cover letter, recruiters won’t even look at the resume.”
4. Talking about money too soon
There’s a time and place to discuss salary during the hiring process , but your cover letter isn’t it. Lisa Benson, president and CEO of Mary Kraft HR, advises against providing any unsolicited salary information in the cover letter “unless [you] are specifically asked to do so, particularly if there is a disparity between what is advertised or indicated in the ad [you] are responding to. No prospective employer wants to hire someone who is only about the money.”
5. Making it all about you
Another common mistake applicants make is using their cover letter to boast about their talents without acknowledging how they will use them to benefit a prospective employer.
“The worst thing a candidate can do in their cover letter is make it all about themselves and what they’re looking for,” said Ian Yates, senior director of corporate accounts at Thermo Fisher Scientific. “The best thing to do is focus on why they’ll be a great fit, how they’ll make a contribution, and what they’ve done, or will do, to support [the organization].”
“It is a fine line between confident and arrogant,” added Sue Hardek, managing director at ZRG Partners. Hardek noted that candidates should avoid overselling themselves and being boastful about accomplishments and strengths.
Job candidates should also steer clear of oversharing personal history or exaggerating or lying on their resume or cover letter.
6. Letting AI do the heavy lifting
Many generative AI companies boast that their AI tools can save time by drafting perfect cover letters. While AI is transforming business , including the job search process, you must be especially careful when using it for your cover letter.
Opinions about using AI in the workplace are mixed. You don’t want to risk coming across a hiring manager who suspects an AI-generated cover letter and immediately tosses your application. Worse, AI might utilize copied text or provide other job seekers with the same phrasing, leading hiring managers to suspect you of plagiarism.
AI can be a good place to start, but you should never rely on it for a final product. AI can help you generate ideas, synthesize your experience with the history and needs of the company, or assist with general editing. But when it comes to the final product, you want your voice to shine through, so ensure the writing is your own – even if you’ve had some help.
What is a cover letter?
A cover letter is a company’s first introduction to who you are as a person. Your resume will explain your previous work experience and skills, but your cover letter is an opportunity to show recruiters your personal side. It’s also a chance to demonstrate why you stand out from the crowd. Employers get many applications, many of which display similar backgrounds and experience. A cover letter helps narrow down their talent pool.
Cover letters are typically written in a three-paragraph format and should be no more than 300 words.
The benefits of a cover letter
Some job listings require the candidate to submit a cover letter, while others make it optional. However, applicants should always take the time to write a cover letter to express their interest in the company and flesh out their professional experience.
A cover letter brings the following advantages:
1. Cover letters personalize your application.
Even great resumes don’t allow applicants to show off their writing skills. A cover letter can help candidates sell themselves by letting their personalities shine. Recruiters get a sense of who the candidate is beyond their work experience and education. Cover letters also allow candidates to discuss parts of their background that may not be explicitly stated on a resume but are relevant to the job they’re applying for.
2. Cover letters showcase your interest in the position and company.
Many candidates blindly shoot off job applications, believing in quantity over quality. To be as efficient as possible, they’ll either send a generic cover letter or fail to send one. However, this is a missed opportunity.
A cover letter with specific details about why you’d be a great fit for the company shows you’ve done your research and are interested in working for that organization. Employers will notice candidates who researched the business and its company culture . These candidates show they want to be there specifically – they don’t just want a job.
3. Cover letters demonstrate your hard work.
Taking the time to draft a well-researched cover letter shows employers you’re self-motivated and passionate about the position. The skills of researching, writing and submitting clean copy before the deadline demonstrate your ability to work and follow directions.
In addition to crafting an excellent cover letter, job candidates should prepare for the interview process and send a thank-you letter to follow up.
How to write a good cover letter
Hiring managers may receive hundreds of cover letters and resumes for a single job post. Potential employees have only a few seconds to make a good first impression, and a boring cover letter could land them straight in the “no” pile.
Follow these eight tips from hiring experts to write a cover letter that will land you an interview:
1. Be yourself in your cover letter.
You don’t want to sound like everyone else. Give hiring managers a sense of your personality traits and how you might fit into the company.
“One key thing we look for is whether they’ve incorporated aspects of their personality into examples of how they would succeed in this position,” shared Margaret Freel, digital marketing specialist at No Dirty Earth and a former corporate recruiter.
Mentioning experiences that qualify you for a particular position is one way to personalize your letter. “Candidates should be concise and self-aware enough to know how their track record of results makes them unique and [be] able to relate that back to the position,” Freel advised.
2. Do your research and customize your cover letter.
Like your resume, your cover letter should be tailored to each position and company. Instead of a template-style cover letter, use industry-specific language referencing points from the job description and company website.
In your research, determine the hiring manager’s name, if possible. Addressing the hiring manager sets you apart. If you’re unsure who the hiring manager is, use a generic salutation – but only as a last resort.
“Address the cover letter to a specific person within the company, not the general – and much-hated – ‘dear sir or madam,'” advised Alina Cincan, managing director and co-founder of Inbox Translation. “This shows the candidate has done some research and is truly interested in working with that company, not just any company.”
Christa Shapiro, a director at the staffing firm Yoh, said one thing that always draws attention to a cover letter is mentioning why you want to be a part of a particular organization. Show a passion for the organization and industry. Employers don’t want to hire someone who won’t care about their work.
Getting a feel for the company will also prepare you for the types of interview questions the hiring manager will likely ask.
3. Be creative in your cover letter.
Hiring managers won’t finish reading your cover letter if they’re bored after the first line. A strong intro should find a unique way to highlight experiences or something specific from the job posting.
Grabbing their attention is key; hiring managers review tons of cover letters for each position. Find a creative way to stand out so the hiring manager notices you and moves on to your resume.
A creative cover letter moves beyond stiff cover letter templates and stock phrases. A great way to make your cover letter pop is to include a brief story that connects you to the company through its mission or product. “This exercise will undoubtedly separate you from the majority of other candidates,” advised Kenneth Johnson, founder and president of East Coast Executives.
4. Mention referrals in your cover letter.
If you were introduced or connected to a hiring manager via an employee referral or mutual industry contact, include that person’s name in your cover letter (with their permission).
“Candidates can include referrals in a cover letter to make them stand out,” said Bill Peppler, COO of staffing firm Kavaliro. “They should always gain permission for this before they name-drop, but the cover letter gives a great opportunity to include the name of someone that can vouch for your skills.”
5. Address potential resume concerns in your cover letter.
A well-crafted cover letter does more than explain why you’re the right person for the job. It also gives you a chance to explain items on your resume that might otherwise be considered red flags.
“Address any issues that may give a hiring manager pause, such as gaps in employment,” advised Diane Domeyer Kock, senior vice president and managing director at Robert Half.
Unfortunately, studies have shown that an unemployment bias exists, as some companies are reluctant to hire out-of-work people. However, the cover letter allows you to reclaim the narrative and demonstrate that you are an ideal candidate despite your employment history.
6. Don’t just repeat your resume in your cover letter.
While your cover letter should reference material from your resume, it shouldn’t simply be a word-for-word repeat. According to Jane Trnka, a career coach with Rady School of Management at UC San Diego, job candidates can use their cover letter to expand where necessary and discuss their listed experiences from a different angle.
“Craft the letter to acknowledge the requirements of the role and culture of the organization while highlighting the skills and experiences that align with the job description,” Trnka advised.
A cover letter is a great place to discuss any volunteer work or side projects that may not be on your resume but are relevant to the job you’re applying for.
7. Proofread and fact-check your resume.
As mentioned earlier, it’s imperative to check and double-check your cover letter for any grammatical or factual errors. Even the smallest mistake can make a bad impression on the person reading your letter.
“If there are errors of any kind, it’s a huge red flag,” warned Guryan Tighe, leadership coach and founder of Fourage. “This is your one opportunity to impress [the hiring manager] and show who you are. If there are typos, misspellings or formatting issues, it’s generally an automatic out.”
8. Keep your cover letter brief.
Hiring managers are busy and usually have many applications to review. Keeping your cover letter concise and to the point will improve the chances of it being read. It also makes the hiring manager’s job easier – which is always a good thing.
“The best cover letters can [be] concise, friendly and transparent,” explained Chris Wood, managing partner of Paige Technologies. “The best cover letters get right to the heart of why we are a great fit for them and why they are the best fit for us.”
Get your foot in the door
Perfecting your cover letter is an essential step in the job search process. You must spend time researching the company and crafting a creative, personalized letter that shows hiring managers you’ll be a valuable addition. Your cover letter should be unique to you and unique to each company you apply for.
But a great cover letter only gets your foot in the door. If you want to secure the job, you must carefully prepare for each part of the job search process. Whether it’s the cover letter or the interview, each step is a chance to show why you and the company you want to work for are a perfect fit.
Tom Anziano and Sean Peek contributed to this article. Source interviews were conducted for a previous version of this article.

Building Better Businesses
Insights on business strategy and culture, right to your inbox. Part of the business.com network.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CORRESPONDENCE
- 02 April 2024
How can we make PhD training fit for the modern world? Broaden its philosophical foundations
- Ganesh Alagarasan 0
Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Tirupati, India.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
You have highlighted how PhD training assessment has stagnated, despite evolving educational methodologies (see Nature 613 , 414 (2023) and Nature 627 , 244; 2024 ). In particular, you note the mismatch between the current PhD journey and the multifaceted demands of modern research and societal challenges.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Nature 628 , 36 (2024)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-024-00969-x
Competing Interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Related Articles
See more letters to the editor
- Research management
- Scientific community

Ready or not, AI is coming to science education — and students have opinions
Career Feature 08 APR 24

After the genocide: what scientists are learning from Rwanda
News Feature 05 APR 24

The neuroscientist formerly known as Prince’s audio engineer
Career Feature 14 MAR 24
Brazil’s postgraduate funding model is about rectifying past inequalities
Correspondence 09 APR 24
Declining postdoc numbers threaten the future of US life science

How we landed job interviews for professorships straight out of our PhD programmes
Career Column 08 APR 24

How two PhD students overcame the odds to snag tenure-track jobs
Adopt universal standards for study adaptation to boost health, education and social-science research
Correspondence 02 APR 24
Equipment Service Technician
Memphis, Tennessee
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital (St. Jude)
Supv-Environmental Services
Biomedical technician, maintenance assistant - liquid nitrogen handling, building automation systems engineer (hvac and lighting).
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

I write like I mean it!
4/10/2024 By | Paige Chung
Cornell Writes! Tips from our community of writers is a digital newsletter sponsored by the Knight Institute for Writing in the Disciplines and the Cornell University Graduate School .
Each week, a member of our writing community – a Graduate Writing Service , English Language Support Office , or Cornell Writing Centers tutor; a writing specialist from the Knight Institute; a writing instructor from our First-Year Writing Seminars or Writing in the Majors programs; maybe YOU – will share a writing strategy from their own writer’s toolkit. #writelikeabear
Contact Tracy Hamler Carrick with questions and ideas.
Sign up to receive weekly emails
Submit a writing tip
Meet Paige Chung
Paige Chung is a writer and DJ. They currently research hip-hop and DJ turntablism. They write poetry, plays, and essays. Born x Raised in Los Angeles but they roll everywhere. They currently train in DJ turntablism at the Beat Junkies Institute of Sound and study Performing and Media Arts at Cornell University.
Here is this week’s Writing Tip!
Sometimes I get anxious or nervous when I am about to start writing. Stress to do well and impress the audience or the professor. Doubts of whether I am a good enough writer to pull off an idea I want to execute. Regardless, when I get a bit emotional, I take a deep breath and I approach the page with three strategies.
- Write like my best friend is listening to my latest tea and wants to know every word. What were they wearing? Who is that again, the one from your math class? How dare she!!! Sounds silly, but whenever I am talking to my best friend, I am welcomed with love, curiosity, and a genuine desire to know every detail of my story. So when I am stuck, I write like she is listening. This can apply to any kind of writing, I am a scholar like you writing papers for my professors too.
- Breakdown what I need to write like instructions to build a shelf. 1-2 sentences describing the performance. 3 sentences about the theoretical framework and why it is related to this performance. 6 sentences about the musical structure of the party. 4 sentences about the……….I don't always know exactly what I need to write next, which is sometimes where the anxiety rolls in. However, planning this way anticipates what I might need to say and how much. It's an art not a science, so it is only an approximation. But when I can see an outline like this, I think I only need to write one sentence at a time. Then I build and build and build. This structure can always change later.
- Cut with a knife. My mentor Dr. G gave me this one. When you are editing, NOT WRITING, cut with a knife meaning go through each of your sentences and cut any words that you do not need to make the point you need to make. If you already made the point, why make it again? We are going for expansion, concision, potency: expand the idea from another perspective, say it simple and say it clean. No need for repetitiveness, unless that's what you're going for, in that case you know what you are doing. Cue O.T. Genasis: Cut it, cut it, cut it -- you need to cuuuuuuut it.
Now, get to it.
Paige Chung
Graduate Student, Performing and Media Arts, Cornell University
More Cornell Writes! Tips from our community of writers

Filing Academic Concern Letters: What you might not know, or might not have thought about

My Writing Space
Submit your writing tip for a chance to win, it's a good time to collect midterm feedback.


How to Write a Cover Letter That Will Get You a Job
I ’ve read thousands, maybe tens of thousands, of cover letters in my career. If you’re thinking that sounds like really boring reading, you’re right. What I can tell you from enduring that experience is that most cover letters are terrible — and not only that, but squandered opportunities. When a cover letter is done well, it can significantly increase your chances of getting an interview, but the vast majority fail that test.
So let’s talk about how to do cover letters right.
First, understand the point of a cover letter.
The whole idea of a cover letter is that it can help the employer see you as more than just your résumé. Managers generally aren’t hiring based solely on your work history; your experience is crucial, yes, but they’re also looking for someone who will be easy to work with, shows good judgment, communicates well, possesses strong critical thinking skills and a drive to get things done, complements their current team, and all the other things you yourself probably want from your co-workers. It’s tough to learn much about those things from job history alone, and that’s where your cover letter comes in.
Because of that …
Whatever you do, don’t just summarize your résumé.
The No. 1 mistake people make with cover letters is that they simply use them to summarize their résumé. This makes no sense — hiring managers don’t need a summary of your résumé! It’s on the very next page! They’re about to see it as soon as they scroll down. And if you think about it, your entire application is only a few pages (in most cases, a one- or two-page résumé and a one-page cover letter) — why would you squander one of those pages by repeating the content of the others? And yet, probably 95 percent of the cover letters I see don’t add anything new beyond the résumé itself (and that’s a conservative estimate).
Instead, your cover letter should go beyond your work history to talk about things that make you especially well-suited for the job. For example, if you’re applying for an assistant job that requires being highly organized and you neurotically track your household finances in a detailed, color-coded spreadsheet, most hiring managers would love to know that because it says something about the kind of attention to detail you’d bring to the job. That’s not something you could put on your résumé, but it can go in your cover letter.
Or maybe your last boss told you that you were the most accurate data processor she’d ever seen, or came to rely on you as her go-to person whenever a lightning-fast rewrite was needed. Maybe your co-workers called you “the client whisperer” because of your skill in calming upset clients. Maybe you’re regularly sought out by more senior staff to help problem-solve, or you find immense satisfaction in bringing order to chaos. Those sorts of details illustrate what you bring to the job in a different way than your résumé does, and they belong in your cover letter.
If you’re still stumped, pretend you’re writing an email to a friend about why you’d be great at the job. You probably wouldn’t do that by stiffly reciting your work history, right? You’d talk about what you’re good at and how you’d approach the work. That’s what you want here.
You don’t need a creative opening line.
If you think you need to open the letter with something creative or catchy, I am here to tell you that you don’t. Just be simple and straightforward:
• “I’m writing to apply for your X position.”
• “I’d love to be considered for your X position.”
• “I’m interested in your X position because …”
• “I’m excited to apply for your X position.”
That’s it! Straightforward is fine — better, even, if the alternative is sounding like an aggressive salesperson.
Show, don’t tell.
A lot of cover letters assert that the person who wrote it would excel at the job or announce that the applicant is a skillful engineer or a great communicator or all sorts of other subjective superlatives. That’s wasted space — the hiring manager has no reason to believe it, and so many candidates claim those things about themselves that most managers ignore that sort of self-assessment entirely. So instead of simply declaring that you’re great at X (whatever X is), your letter should demonstrate that. And the way you do that is by describing accomplishments and experiences that illustrate it.
Here’s a concrete example taken from one extraordinarily effective cover-letter makeover that I saw. The candidate had originally written, “I offer exceptional attention to detail, highly developed communication skills, and a talent for managing complex projects with a demonstrated ability to prioritize and multitask.” That’s pretty boring and not especially convincing, right? (This is also exactly how most people’s cover letters read.)
In her revised version, she wrote this instead:
“In addition to being flexible and responsive, I’m also a fanatic for details — particularly when it comes to presentation. One of my recent projects involved coordinating a 200-page grant proposal: I proofed and edited the narratives provided by the division head, formatted spreadsheets, and generally made sure that every line was letter-perfect and that the entire finished product conformed to the specific guidelines of the RFP. (The result? A five-year, $1.5 million grant award.) I believe in applying this same level of attention to detail to tasks as visible as prepping the materials for a top-level meeting and as mundane as making sure the copier never runs out of paper.”
That second version is so much more compelling and interesting — and makes me believe that she really is great with details.
If there’s anything unusual or confusing about your candidacy, address it in the letter.
Your cover letter is your chance to provide context for things that otherwise might seem confusing or less than ideal to a hiring manager. For example, if you’re overqualified for the position but are excited about it anyway, or if you’re a bit underqualified but have reason to think you could excel at the job, address that up front. Or if your background is in a different field but you’re actively working to move into this one, say so, talk about why, and explain how your experience will translate. Or if you’re applying for a job across the country from where you live because you’re hoping to relocate to be closer to your family, let them know that.
If you don’t provide that kind of context, it’s too easy for a hiring manager to decide you’re the wrong fit or applying to everything you see or don’t understand the job description and put you in the “no” pile. A cover letter gives you a chance to say, “No, wait — here’s why this could be a good match.”
Keep the tone warm and conversational.
While there are some industries that prize formal-sounding cover letters — like law — in most fields, yours will stand out if it’s warm and conversational. Aim for the tone you’d use if you were writing to a co-worker whom you liked a lot but didn’t know especially well. It’s okay to show some personality or even use humor; as long as you don’t go overboard, your letter will be stronger for it.
Don’t use a form letter.
You don’t need to write every cover letter completely from scratch, but if you’re not customizing it to each job, you’re doing it wrong. Form letters tend to read like form letters, and they waste the chance to speak to the specifics of what this employer is looking for and what it will take to thrive in this particular job.
If you’re applying for a lot of similar jobs, of course you’ll end up reusing language from one letter to the next. But you shouldn’t have a single cover letter that you wrote once and then use every time you apply; whatever you send should sound like you wrote it with the nuances of this one job in mind.
A good litmus test is this: Could you imagine other applicants for this job sending in the same letter? If so, that’s a sign that you haven’t made it individualized enough to you and are probably leaning too heavily on reciting your work history.
No, you don’t need to hunt down the hiring manager’s name.
If you read much job-search advice, at some point you’ll come across the idea that you need to do Woodward and Bernstein–level research to hunt down the hiring manager’s name in order to open your letter with “Dear Matilda Jones.” You don’t need to do this; no reasonable hiring manager will care. If the name is easily available, by all means, feel free to use it, but otherwise “Dear Hiring Manager” is absolutely fine. Take the hour you just freed up and do something more enjoyable with it.
Keep it under one page.
If your cover letters are longer than a page, you’re writing too much, and you risk annoying hiring managers who are likely sifting through hundreds of applications and don’t have time to read lengthy tomes. On the other hand, if you only write one paragraph, it’s unlikely that you’re making a compelling case for yourself as a candidate — not impossible, but unlikely. For most people, something close to a page is about right.
Don’t agonize over the small details.
What matters most about your cover letter is its content. You should of course ensure that it’s well-written and thoroughly proofread, but many job seekers agonize over elements of the letter that really don’t matter. I get tons of questions from job seekers about whether they should attach their cover letter or put it in the body of the email (answer: No one cares, but attaching it makes it easier to share and will preserve your formatting), or what to name the file (again, no one really cares as long as it’s reasonably professional, but when people are dealing with hundreds of files named “resume,” it’s courteous to name it with your full name).
Approaching your cover letter like this can make a huge difference in your job search. It can be the thing that moves your application from the “maybe” pile (or even the “no” pile) to the “yes” pile. Of course, writing cover letters like this will take more time than sending out the same templated letter summarizing your résumé — but 10 personalized, compelling cover letters are likely to get you more interview invitations than 50 generic ones will.
- ‘I Had a Great Job Interview — Why Haven’t I Heard Back?’
- How to Answer ‘Tell Me About Yourself’ in a Job Interview


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
How to write a cover letter for your Ph.D. application. Follow these steps to write your academic cover letter: 1. Review the program and organization information. Before crafting your academic cover letter, review the information you have about the program you're applying for. Avoid using the same cover letter for each organization, as they ...
A cover letter should be addressed to a named person i.e. "Dear Professor Smith". For a PhD application, this will usually be the PhD supervisor, but may be a specific person in charge of recruitment. If you are still unsure who to address the cover letter to, it should be directed to the Head of Department.
Formal salutation. In an official letter like this one, you should address the reader in a professional and formal way. If you know who'll be reading your cover letter, go with Dear Dr. [Surname] or Dear Professor [Surname]. If you don't, go with Dear Sir/Madam. The specific PhD program or position.
This will give your cover letter a slick appearance and also give the recruiter all of the necessary contact information they need to get in touch with you. The information to add should include: A friendly sign off - e.g. "Kindest regards". Your full name. Phone number (one you can answer quickly)
Try to match the font size, type, line spacing and margin size to your academic CV for neat and consistent presentation. Your cover letter should be addressed to the PhD supervisor, starting with a "Dear [academic title] [surname]", for example, "Dear Professor Williams". Tip: Make sure to get the title of the supervisor correct.
It's best to address your PhD cover letter to a specific person, such as the head of the department or the admission team. 2. Body paragraphs. The body paragraphs of your PhD cover letter should include some key information about your academic history and motivation. Use these prompts to help you write the body of your PhD cover letter.
Formal Closing: Opt for a formal and universally accepted closing such as Sincerely, Kind regards, or Best regards. Name and Title: Under the closing, type your full name. It's also a good practice to include your current academic title or designation, adding to the clarity and formality. PhD Cover Letter Example.
As with all applications, writing a great cover letter is a skill. It requires you to tread the balance between explaining in detail who you are and why you should be chosen, while remaining concise. It needs to showcase your personality while remaining professional. It's a difficult writing skill and one which shouldn't be rushed.
Choose the name of your profession and the company to which you're applying, and the builder will automatically adapt the content for you. Create a cover letter faster than you ever thought possible and apply for the job in record time. Create your cover letter now. 2. Open the PhD cover letter with your motivation.
A strong motivation letter for PhD applications will include: A concise introduction stating which programme you are applying for, Your academic background and professional work experience, Any key skills you possess and what makes you the ideal candidate, Your interest and motivation for applying, Concluding remarks and thanks.
Although a PhD cover letter has a more academic focus, it is as much of a sales pitch as any other cover letter. Here is what we cover in the PhD cover letter example and writing guide: Understanding how to structure your cover letter, with each part serving a purpose: header, greeting, introduction, body and conclusion.
A good technique for concluding your cover letter is to summarize, in a sentence, what value you can bring to the company and why you are perfect for the position. Sum up the most important points from your cover letter in a short, concise manner. Write with confidence, but not arrogance.
STEM letters should not exceed one page. Humanities and social sciences letters may extend up to two pages. Check with faculty in your department. Address to the individual named in the job posting, or with "Dear Members of the Search Committee." The cover letter is a writing sample. It must be good. Proofread and spell check! TIPS
By Foram Gathia, PhD student. Writing a compelling cover letter is essential for making a positive impression on potential employers. Here's a guide to crafting a strong cover letter: Start with a Strong Introduction: Address the hiring manager by name if possible and mention the specific position you are applying for. Engage the reader with ...
Make your cover letter personal, remarkable (i.e., stands out from other cover letters), specific to you and specific to the position at hand. Be enthusiastic. Be specific. Show that you've put thought into the position and why you are applying. Relate your specific skill sets and previous experience to the programme you are applying for.
At their most basic level, academic cover letters accomplish three things: one, they express your interest in the job; two, they provide a brief synopsis of your research and teaching; and three, they summarize your past experiences and achievements to illustrate your competence for the job. For early-career scholars, cover letters are ...
A PhD cover letter, also referred to as certain academic cover letter, should be carefully crafted, well-formatted, and contain specific sections. We'll how you how toward do exactly that, ahead includes a sample are an university cover letter from adenine real person admitted toward ampere PhD scheme at Lyon University in Toulouse.
Avoid addressing the recipient with "Dear Sir or Madam," which is outdated and impersonal. It's always best to address them by their title and name. For example: Good cover letter greeting examples: "Dear hiring manager,". "Dear [XYZ Company] team,". "Dear Customer Acquisition Hiring Manager,". Weak cover letter greeting examples:
The formatting should match your resume for a clean and consistent look. You should use the same font, font size, and header style. These simple tips help you look organized and composed. 2. Header and Contact Details. When creating a cover letter, the header is the first item potential employers see.
Europass will guide you step by step through the process to help you create a good cover letter with all the essential information. You can create, store and share cover letters in 31 languages, choose from different templates to customise your application and share them easily from your Europass Library . Create your Europass.
3. Remaining stuck in the past. Maybe you were let go from your last job, or maybe you're looking for new opportunities. Regardless of the reason for your job search, don't spend your cover ...
02 April 2024. How can we make PhD training fit for the modern world? Broaden its philosophical foundations. By. Ganesh Alagarasan. You have highlighted how PhD training assessment has stagnated ...
Paige Chung is a writer and DJ. They currently research hip-hop and DJ turntablism. They write poetry, plays, and essays. Born x Raised in Los Angeles but they roll everywhere. They currently train in DJ turntablism at the Beat Junkies Institute of Sound and study Performing and Media Arts at Cornell University. Here is this week's Writing Tip!
You don't need a creative opening line. , If you think you need to open the letter with something creative or catchy, I am here to tell you that you don't. Just be simple and straightforward ...