
002 - Megacity
Geographic knowledge and understanding, the consequences of megacity growth for individuals and societies..
The process of urban growth creates impacts on people and place.
To be able to use one case study of a contemporary megacity experiencing rapid growth to examine the consequences of megacity growth.
One case study of a contemporary megacity experiencing rapid growth.
Key Terminology
Urbanisation
Informal Settlements
Watch the youtube clip below to help you to define the term megacity and use the 'Useful Links' for the other terms.
Useful Links
GCSE Bitesize - Urbanisation
Wikipedia Definition - Metropolis
The Nature of Cities Definition - Informal Settlements
Activity One - Discussion
It is important to discuss the reasons why people migrate to live in urban environments, but what are those reasons. Using the padlet below record your thoughts on what the pull factors are of a city and the push of a more rural area.
Activity Two - Overview of Shanghai
This syllabus point specifically asks you to develop a case study of the growth and impact of one megactiy. Our focus is going to be Shanghai in China. You should already know the location of Shanghai as it was hopefully included on your hand-drawn map from a previous lesson, but just in case you don't there is a map to the side of this text to remind you.
Watch the time-lapse video below to show the colossal growth of Shanghai since 1984.
Now watch the YouYube clip and make notes on the historical growth of the city.
Useful Resources
Image One - Map of China
Growth of Shanghai through time lapse
The Transformation of Shanghai
Activity three - a case study of megacity growth - shanghai.
Your task is to develop a case study of Shanghai . As the guide asks for a case study you could be required to answer a whole essay on this one single topic. Therefore you need detail and data for this syllabus point. You wil need to include the following factors in your notes:
Why has the urban growth occurred?
What has been the impact? - Social, Economic, Environmental
Have any solutions been put in place? Are they working?
arcGIS - The growth of Shanghai and the associated impacts - The essential resource to read.
China Briefing - Shanghai Facts
Slate - China at the Limits of City Growth
BBC - Megacities: China (also environmental)
Global Times - Ageing in Beijing and Shanghai growing at a faster rate and Asia News
Environmental
Environmental Journal - Mitigating the impact of Shanghai's rapid growth
The Guardian - China's radical plan to limit the population of Shanghai
SupChina - Demolition of Laoximen
News in Focus - Shanghai strengthens its services for the elderly population
Extension - Watch
I have used this with my Year 11 classes in the past to show them why megacities should be included in our MYP curriculum in Individuals and Societies. It does discuss well that our megacities help to improve global communication, trade and energy links. In short, megacities are changing the face of the world and could become more powerful than nation-states.
Exam Style Question
Using a named contemporary megacity, examine the geographical consequences of megacity growth [10 marks]
- IB DP Geography concepts
- Geographic themes [Paper 1]
- Core: Global change [Paper 2]
- Higher Level: Global interactions [Paper 3]
- IB DP Geography Key Terms
- IB DP Geography Exam style questions
- IB DP Geography Geographic Skills
- IB DP Geography Visual Stimulus
- IB DP Geography Approaches to learning skills
- IB DP Geography Exam preparation
- IB DP Geography Revision
- IB DP Geography Internal Assessment
- IB DP Geography Extended Essay
- Unit 1: Changing population
- Unit 2: Global climate - vulnerability and resilience
- Unit 3: Global resource consumption and security
- 1.1 Population and economic development patterns
1.2 Changing populations and places
- 1.3 Challenges and opportunities
Unit Contents
- 1.2.1 Population change
- 1.2.2 Megacity growth
- 1.2.3 Migration - knowledge and understanding
- 1.2.4 Forced migrations - detailed examples
- 1.2.1 Population change and Iceland
Geographic inquiry: Processes of population change and their effect on people and places
- Detailed examples of two or more contrasting countries
- One case study of a contemporary megacity experiencing rapid growth
- Detailed examples of two or more forced movements, to include environmental and political push factors, and consequences for people and places

- Comment on Twitter
Introduction: Megacities, Urban Form, and Sustainability
Cite this chapter.

- André Sorensen 4 &
- Junichiro Okata 5
Part of the book series: Library for Sustainable Urban Regeneration ((LSUR,volume 10))
6452 Accesses
3 Citations
Of the many changes to our world wrought during the twentieth century, one of the most profound was the transformation of human settlement systems. A century ago the vast majority of the world’s population was rural, embedded in social and economic systems tied to agricultural production and living in dispersed, small-scale settlements. Now, for the first time in human history, more than half the world’s population is urban, after a century of massive migrations from rural hinterlands to burgeoning cities. In this urban transformation of the globe, one of the most dramatic and momentous developments has been the emergence of giant cities, often referred to as “megacities.”
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Begovic B (1991) The economic approach to optimal city size. Progr Plann 36:93–161
Google Scholar
Benjamin S (2004) Urban land transformation for pro-poor economies. Geoforum 35(2):177–187
Article Google Scholar
Brugmann J (2009) Welcome to the urban revolution: how cities are changing the world. Viking, Canada, Toronto
Campbell S (1996) Green Cities, growing cities, just cities? Urban planning and the contradictions of sustainable development. J Am Plann Assoc 62(3):296–312
Davis M (2006) Planet of slums. Verso, London
Dicken P (1998) Global shift: transforming the world economy. Guilford Press, New York
Dogan, M, Kasarda, JD (eds) (1988) The metropolis era, vol 1. A world of giant cities. Sage, Newbury Park, CA
Fuchs RJ, Brennan E, Chamie J, Uitto J, Lo F-C (eds) (1995) Mega-city growth and the future. United Nations University Press, Tokyo
Gilbert A (ed) (1996) The mega-city in Latin America. United Nations University Press, Tokyo
Graham S, Marvin S (2001) Splintering urbanism: networked infrastructures, technological mobilities and the urban condition. Routledge, London
Book Google Scholar
Haughton G, Hunter C (1994) Sustainable cities. Jessica Kingsley, London
Marcotullio PJ (2007) Variations of urban environmental transitions: the experiences of rapidly developing Asia-Pacific cities. In: Marcotullio PJ, McGranahan G (eds) Scaling urban environmental challenges: from local to global and back. Earthscan, London, pp 45–68
McGee TG, Robinson IM (eds) (1995) The mega-urban regions of Southeast Asia. University of British Columbia Press, Vancouver
McGranahan G, Songsore J, Kjellen M (1999) Sustainability, poverty and urban environmental transitions. In: Satterthwaite D (ed) Sustainable cities. Earthscan, London, pp 107–130
Owens SE (1986) Energy, planning and urban form. Pion, London
Pieterse, EA (2008) City futures: confronting the crisis of urban development. Zed Books, London, New York; UCT Press, Capetown, South Africa
Richardson HW (1973) The economics of urban size. Saxon House, Lexington
Richardson HW (1993) Efficiency and welfare in LDC mega-cities. In: Kasarda JD, Parnell AM (eds) Third world cities: problems, policies and prospects. Sage, Newbury Park, CA, pp 32–57
Roy A (2005) Urban informality: toward an epistemology of planning. J Am Plann Assoc 71(2):147–158
Sassen S (1991) The global city: New York, London, Tokyo. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ
Satterthwaite D (1997) Sustainable cities or cities that contribute to sustainable development? Urban Stud 34(10):1667–1691
Sorensen A, Marcotullio PJ, Grant J (eds) (2004) Towards sustainable cities: East Asian, North American and European perspectives. Ashgate, Aldershot, England
Stren RE, White R, Whitney JB (eds) (1992) Sustainable cities: urbanization and the environment in international perspective. Westview Press, Boulder, CO
UNDESA (2008) World urbanization prospects: the 2007 revision. United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, New York
Ward PM (1990) Mexico City: the production and reproduction of an urban environment. Belhaven Press, London
White R, Whitney JB (1992) Cities and the environment: an overview. In: Stren RE, White R, Whitney JB (eds) Sustainable cities: urbanization and the environment in international perspective. Westview Press, Boulder, CO, pp 8–51
World Congress on Environment and Development (1987) Our common future. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Geography and Programme in Planning, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada
André Sorensen ( Associate Professor )
Department of Urban Engineering School of Engineering, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan
Junichiro Okata ( Professor )
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to André Sorensen .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
University of Toronto Scarborough, Cities Centre 455 Spadina Avenue, Suite 400, Toronto, Ontario, M5S 2G8, Canada
André Sorensen ( Associate Professor ) ( Associate Professor )
Department of Urban Engineering School of Engineering, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, 113-8656, Japan
Junichiro Okata ( Professor ) ( Professor )
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer
About this chapter
Sorensen, A., Okata, J. (2011). Introduction: Megacities, Urban Form, and Sustainability. In: Sorensen, A., Okata, J. (eds) Megacities. Library for Sustainable Urban Regeneration, vol 10. Springer, Tokyo. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-99267-7_1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-99267-7_1
Publisher Name : Springer, Tokyo
Print ISBN : 978-4-431-99266-0
Online ISBN : 978-4-431-99267-7
eBook Packages : Earth and Environmental Science Earth and Environmental Science (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Changing population
Syllabus content:
- Population and economic development patterns
How population varies between places
Physical and human factors affecting population distribution at the global scale
Global patterns and classification of economic development:
- low-income countries
- middle-income countries and emerging economies
- high-income countries
Population distribution and economic development at the national scale, including voluntary internal migration, core-periphery patterns and megacity growth
Two detailed and contrasting examples of uneven population distribution
Synthesis, evaluation and skills opportunities
The relative importance of different influences on where people live and spatial interaction s between places at varying scales
2. Changing populations and places
Processes of population change and their effect on people and places:
Population change and demographic transition over time, including natural increase, fertility rate, life expectancy, population structure and dependency ratios
Detailed examples of two or more contrasting countries
The consequences of megacity growth for individuals and societies
One case study of a contemporary megacity experiencing rapid growth
The causes and consequences of forced migration and internal displacement
Detailed examples of two or more forced movements, to include environmental and political push factors, and consequences for people and places
How the impacts of population change and spatial interactions between places can be categorized and represented graphically.
3. Population possibilities and power over the decision-making process
Population possibilities and power over the decision-making process
Global and regional/continental trends in family size, sex ratios, and ageing/greying
Policies associated with managing population change, focusing on:
- policies related to ageing societies
- pro-natalist or anti-natalist policies
- gender equality policies and anti-trafficking policies
The demographic dividend and the ways in which population could be considered a resource when contemplating possible futures
One case study of a country benefiting from a demographic dividend
How population change may affect the power balance between groups of people at local, national and international scales
Share this:

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
Creator | Martin Roberts | GB |

|Changing Population Lesson's |
|understanding vocab| .

|Content|
|lessons| , |population and economic development |, |lesson 1 course outline | , |lesson 2 physical and human factors affecting population distribution |.

It is important to understand the key command terms found throughout the course. Take some time to study them and understand what each command term means. Also, go through the syllabus to understand what topics and subtopics are part of the course. This will allow for greater synthesis of ideas.
Physical and human factors affecting population distribution at the global scale
Global patterns and classification of economic development:
low-income countries
middle-income countries and emerging economies
high-income countries
Population distribution and economic development at the national scale, including voluntary internal migration, core-periphery patterns and megacity growth
Two detailed and contrasting examples of uneven population distribution
Synthesis, evaluation and skills opportunities
The relative importance of different influences on where people live and spatial interactions between places at varying scales
|Lesson 4 Population Distribution|
|lesson 3 classification of economic development | .
|CASE STUDY|
|Lesson 5 Internal Migration |
|reading/revision & assessment| .
Take some time to look at the data. Make sure to make notes on

|Literature Link|
Make sure to revise the terminology and language needed in your exam.
|Buy Now |
Factfulness allows you to see how data can be used and manipulated. It also allows you to gain a true perception of the level of development for different countries.
|Media in the Classroom|
|understanding population | , |understanding population pyramids| .
|Matthew Connelly is an American professor of international and global history at Columbia University in the city of New York.|
|Academic literature|

|100 people of the World what would society look like?|
|Internal Migration |
|media in the classroom|, |2. changing populations and places| .
Population change and demographic transition over time, including natural increase, fertility rate, life expectancy, population structure and dependency ratios
Detailed examples of two or more contrasting countries
The consequences of megacity growth for individuals and societies
One case study of a contemporary megacity experiencing rapid growth
The causes and consequences of forced migration and internal displacement
Detailed examples of two or more forced movements, to include environmental and political push factors, and consequences for people and places
How the impacts of population change and spatial interactions between places can be categorized and represented graphically
|Lesson 6 DTM & Contrasting Case Study |
|lesson 7 megacity growth |, |lesson 9 mexico city megacity case study |, |lesson 8 migration theories |, |lesson 10 two detailed examples of forced movement |, |lesson 11 mexico migration case study|.
|The century of climate migration: why we need to plan for the great upheaval|
|Migration Has it gone too far?|
|Migration solutions|
|afghanistan forced migration|.

|3. Challenges and opportunities|
Global and regional/continental trends in family size, sex ratios, and ageing/greying
Policies associated with managing population change, focusing on:
policies related to ageing societies
pro-natalist or anti-natalist policies
gender equality policies and anti-trafficking policies
The demographic dividend and the ways in which population could be considered a resource when contemplating possible futures
One case study of a country benefiting from a demographic dividend
How population change may affect the power balance between groups of people at local, national and international scales
|Lesson 13 Ageing Population |
|lesson 14 anti-natalist policy |, |lesson 12 trends in family size/ sex ratio/ageing population |, |lesson 14|, |lesson 14 pro-natalist policy |, |lesson 16 human trafficking |, |lesson 15 demographic dividend |, |lesson 15 gender equality |, |human trafficking | , |ageing population japan| .
|Gender Equality|

|End of Module 1 Revision|
|Case Study Cards|

|Revision Notes|

|Revision:Danny Dorling: Population Growth|
|Danny Dorling is a British social geographer and is the Halford Mackinder Professor of Geography of the School of Geography and the Environment of the University of Oxford |
|Practice Papers|

| | Use the Online Question-bank to answer past paper question. This is important to understand the question formation, command terms and exam structure.|
- Reference Manager
- Simple TEXT file
People also looked at
Original research article, the spatiotemporal characteristics and rationality of emerging megacity urban expansion: a case study of zhengzhou in central china.

- 1 School of Resources and Environment, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou, China
- 2 College of Forestry, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou, China
Studies on urban expansion in megacities are essential for managing urban sprawl to promote high-quality development. In this study, we have selected the emerging megacity of Zhengzhou as the research area, used the spatial analysis method to quantify the spatiotemporal characteristics of urban expansion from 1990 to 2020, and evaluated the rationality of urban expansion on the basis of the elasticity index and a comparison with other megacities. Results demonstrated that 1) Zhengzhou experienced great urban expansion from 1990 to 2020 and showed a trend of “steady–fast–slow,” with steady expansion from 1990 to 2000, fast expansion from 2000 to 2010, and slow expansion after 2010; 2) Zhengzhou’s urban expansion has obvious imbalance and spatial disorder, mainly concentrated in the urban central area, and is characterized by sprawl or a leap in space; 3) the occupation of cultivated land by urban expansion in Zhengzhou has gradually decreased, but the occupation of ecological land such as water areas has increased significantly, which may lead to a series of negative ecological effects; 4) Zhengzhou’s urban expansion was inefficient, while the utilization intensity and economic benefits of Zhengzhou’s urban construction land have improved, but relatively lower than those of other megacities in China. The findings have important reference that is significant for promoting the sustainable urban expansion of megacities and achieving sustainable regional development.
1 Introduction
Rapid economic and population growth have led to an unprecedented increase in urban construction land, and urban expansion has become a global geographic phenomenon in the process of urbanization ( Schneider and Woodcock, 2014 ; Tayyebi et al., 2014 ). As the carrier of social and economic activities, the expansion of urban construction land not only meets the growing social needs of urban residents but also provides important support for sustainable regional development ( Bagan and Yamagata, 2014 ). However, in recent decades, the rapid urbanization in the world, especially in developing countries, has triggered the disorderly sprawl of urban construction land, which has a profound negative impact on resources ( Hu et al., 2017 ; Lafortezza and Sanesi, 2019 ), the environment ( Hamidi and Ewing, 2014 ), geographic processes ( Liu et al., 2008 ; Xu et al., 2009 ), biodiversity ( Kovács et al., 2019 ), etc. and has become one of the most important factors that hinder sustainable regional and even global development ( He et al., 2018 ). Exploring the mechanism of urban expansion, proposing strategies to prevent urban sprawl, and realizing sustainable development have become core topics of urban research.
In the middle of the twentieth century, many scholars began to conduct systematic research on urban expansion ( Dai et al., 2010 ). A large number of scholars have used spatial analysis tools to conduct quantitative research on urban expansion from a geographic perspective ( Buyantuyev et al., 2015 ; Hecht et al., 2020 ), mainly focusing on measuring urban expansion from the characteristics of land scale and spatial form, and building a series of index models such as expansion intensity index ( Yue et al., 2016 ), expansion steady state index ( Zhao et al., 2017 ), expansion elasticity index ( Rusk, 1993 ), and sprawl index ( Tian et al., 2017 ). With the technological innovation of geographic information systems and spatial statistics, the driving forces, prediction, and simulation of urban expansion have become research hot spots ( Kantakumar et al., 2016 ; Zhang et al., 2018 ; Zhong et al., 2020 ; Liu et al., 2022 ). With the increasing pressure on resources and the environment, the sustainability of urban expansion needs to be discussed, and the rationality of urban expansion has attracted growing interest from urban planners and managers ( Tong, 2020 ). Urban expansion can cause complex changes in regional natural systems. Whether it will lead to ecological degradation ( Chien and Saito, 2021 ), food security issues ( Gren and Andersson, 2018 ), and climate change ( Khamchiangta and Dhakal, 2021 ) has become an important criterion for judging the rationality of urban expansion. Analyzing the coordination between urban expansion, population growth, and economic development by using the decoupling model ( Cai et al., 2020 ) and the elastic coefficient ( Jiao et al., 2016 ) is an important way of evaluating urban expansion. Although previous research generated an impressive body of work, urban expansion research mainly focuses on mature megacities and less on not well-known emerging megacities that have important regional influence and are undergoing rapid socioeconomic transformation. In addition, the urban expansion evaluation is mainly based on the expansion scale and effects of the city itself, and comparative analysis with similar cities is lacking. These comparisons have an important reference for judging the rationality of urban expansion.
Since the implementation of the reform and opening-up policy, China has made world-renowned urban development achievements, and a number of world-influential megacities such as Beijing, Shanghai, and Shenzhen have emerged. The seventh national census in 2020 shows that 21 megacities in China have a population of more than 5 million in central urban areas ( CNBS, 2020 ). These megacities are not only clusters of job creation and population living but also core areas that support economic development and participate in international competition ( Sassen, 1994) . However, under the traditional urban development model oriented by economic growth in the past, Chinese megacities have seen a wave of blind expansion, which has caused problems such as loss of arable land, traffic congestion, skyrocketing land prices, and environmental pollution ( Chen et al., 2013 ; Li et al., 2014 ). Megacities occupy a pivotal position in socioeconomic development, and the resource and environmental problems faced by their urban expansion are more serious than those faced by small- and medium-sized cities. Unlike the urbanization of mature megacities, which has stagnated, the urbanization of emerging megacities is still developing rapidly, and the demand for urban expansion continues to be strong. The expansion of emerging megacities has obvious diversity and differences, and the problems encountered in urban management are more complex ( Yao et al., 2009 ). Therefore, a systematic study needs to be conducted on the characteristics and rationality of urban expansion in China’s emerging megacities, and high-quality and sustainable urban expansion needs to be achieved.
This study takes Zhengzhou, a city in central China, as the research area to study the urban expansion of emerging megacities. The main purposes of this work are 1) to measure the spatiotemporal characteristics of urban expansion from 1990 to 2020; 2) to judge the rationality of urban expansion through the coordination of urban expansion, economy, and population, and a comparison with other megacities; and 3) to propose targeted suggestions for urban expansion management and provide a reference for the development of emerging megacities.
2 Materials and Methods
2.1 study area.
Zhengzhou is the capital of Henan Province in central China (34°16′–34°58′N and 112°42′–114°14′), adjacent to the lower Yellow River in the north. Zhengzhou covers an area of 7446.2 km 2 , of which the central urban area covers 1181.51 km 2 . As the core city of China’s central plains urban agglomeration, one of the eight national central cities and an important national comprehensive transportation hub ( NDRC, 2017 ), Zhengzhou is experiencing rapid economic growth and urbanization. In 2020, the permanent population was 12.6 million, of which the non-agricultural population accounted for 78.4%. Furthermore, its GDP was 1200.3 billion RMB ( Zhengzhou Bureau of Statistics, 2021 ). Zhengzhou had a population of 5.34 million in the central urban area in 2020, becoming one of the 21 cities in China with a population in the central urban area exceeding 5 million, and it is an emerging megacity in China. Zhengzhou has 12 administrative districts, including 6 districts [Jinshui (JS), Zhongyuan (ZY), Erqi (EQ), Guancheng (GC), Huiji (HJ), and Shangjie (SJ)], 5 county-level cities [Xinzheng (XZ), Xinmi (XM), Xingyang (XY), Gongyi (GY), and Dengfeng (DF)], and 1 county [Zhongmo (ZM)] ( Figure 1 ).
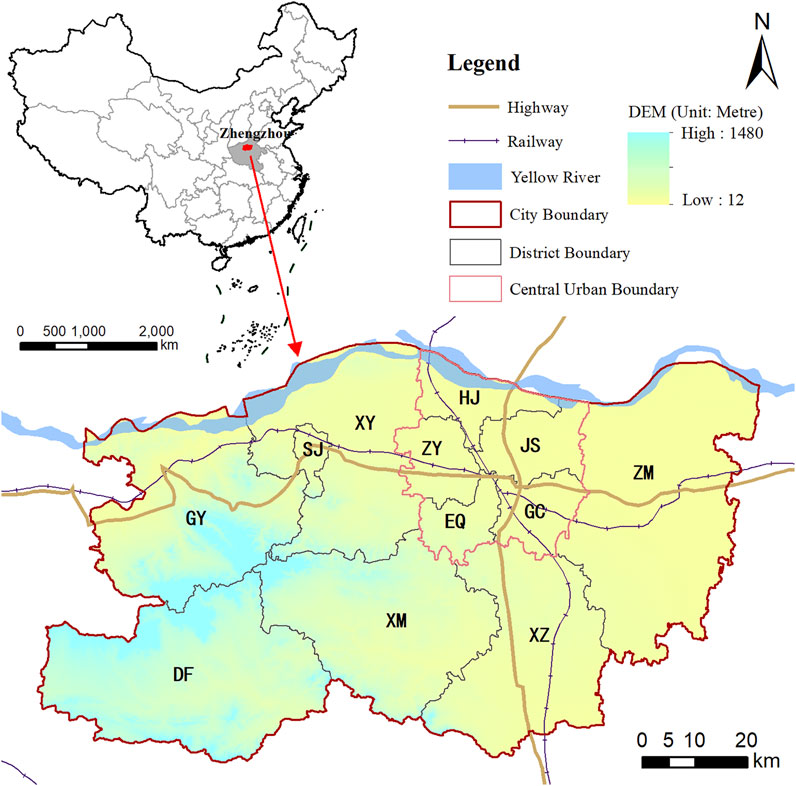
FIGURE 1 . Location and administrative districts of Zhengzhou.
From 1990 to 2020, Zhengzhou’s socioeconomic status experienced rapid development. The urban population and GDP increased significantly. The urban population increased from 2.38 million to 9.89 million, an increase of 3.15 times. Meanwhile, the urbanization rate increased from 42.7 to 78.4%, an increase of 35.7 percentage points. GDP increased from 11.64 billion yuan to 1,200 billion yuan, an increase of 102.12 times ( Figure 2 ). Furthermore, the urban population and GDP growth continue to accelerate, and Zhengzhou’s urbanization is still in the stage of rapid development.
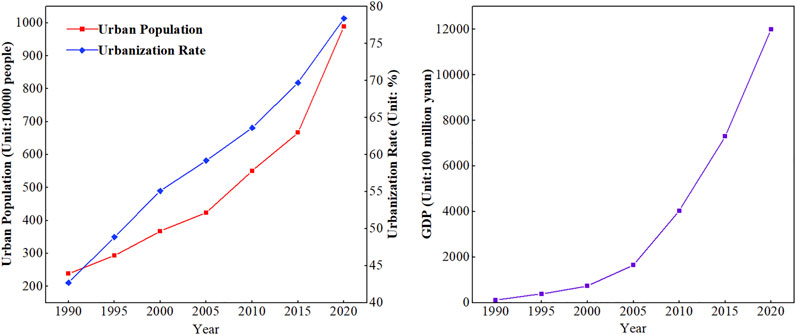
FIGURE 2 . Socioeconomic development of Zhengzhou from 1990 to 2020.
This study collected multi-temporal remote sensing images (Landsat TM/ETM+) and obtained land use and land cover (LUCC) data at the time nodes of 1990, 1995, 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020, with a spatial resolution of 30 m. According to the LUCC classification system proposed by the Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, with the use of supervised classification and human–computer interaction interpretation to extract information, the interpreted land use types were divided into 6 categories and 25 subcategories ( Liu et al., 2003 ). After quality inspection and data integration, the comprehensive evaluation accuracy of land use types reached more than 94.3%. The urban construction land defined by this research refers to the urban land used for construction such as industrial and mining land, residential land, and roads. The urban expansion monitoring process of Zhengzhou was based on LUCC maps from 1990 to 2020 ( Figure 3 ). The socioeconomic data used were mainly derived from the annual socioeconomic statistics published by the official websites of the national-, provincial-, and prefecture-level municipal statistical departments.
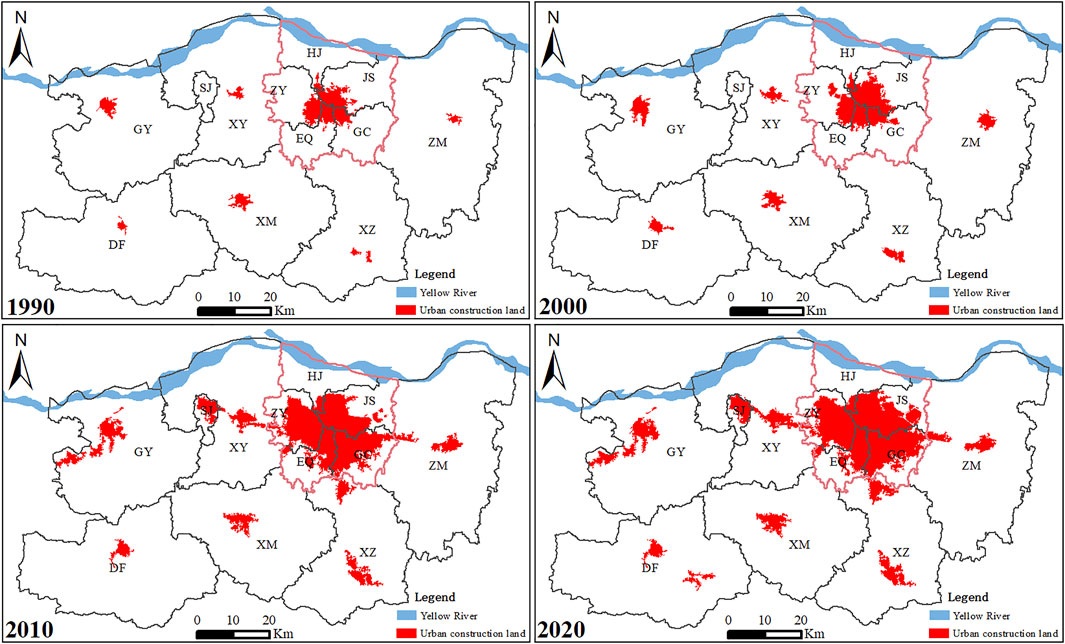
FIGURE 3 . Spatial allocation of urban construction land in 1990, 2000, 2010, and 2020.
2.3 Methods
2.3.1 average annual expansion index.
The urban expansion index refers to the percentage of the growth area of urban construction land in its original urban construction land area within a certain period. A large index value corresponds to fast urban expansion. This study uses the average annual urban expansion index (AAEI) to analyze the characteristics of urban expansion in Zhengzhou. The specific calculation formula is as follows:
where I refers to the AAEI; U i and U j represent the area of urban construction land in the base period and the end period of the study period, respectively; and n is the number of years in the period.
The AAEI was used to analyze the three phases of urban expansion in the various districts of Zhengzhou from 1990 to 2000, 2000 to 2010, and 2010 to 2020. According to the urban expansion characteristics of each district, urban expansion was divided into three types: low-, medium-, and high-speed expansion based on the AAEI value ranges of 0–5, 5–10, and >10, respectively.
2.3.2 Urban Expansion Elasticity Index
The urban expansion elasticity index is mainly divided into the man-land elasticity index and the economic-land elasticity index. Urban construction land is the carrier of urban residents’ life and economic activities. The carrying population and economic scale are important indicators to measure the rationality of urban expansion. The urban expansion man-land elasticity index refers to the ratio of the growth rate of the urban construction land area to the growth rate of the urban population during the study period; the urban expansion economic-land elasticity index refers to the ratio of the regional GDP growth rate to the growth rate of the urban construction land area within the study period. The specific calculation formulas are as follows:
where P EI and G EI refer to the man-land elasticity index and the economic-land elasticity index, respectively; P i and P j are the number of urban permanent residents in the base and end of the study period, respectively; and G i and G j are the GDP in the base and end of the study period, respectively.
2.3.3 Indexes of Urban Expansion Efficiency
The efficiency of urban expansion was mainly analyzed from two aspects: urban construction land intensive use and economic benefits. Per capita urban construction land area and per capita GDP are the most important indicators to measure urban construction land intensive use and economic benefits, respectively, and can also provide an important reference for evaluating whether urban expansion is reasonable. The index’s calculation formulas are as follows:
where PA and PE refer to the per capita urban construction land area and per capita GDP, respectively; UCLA is the urban construction land area; UP is the urban population; and GDP is the gross domestic product.
3.1 Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Urban Expansion
3.1.1 temporal characteristics of urban expansion.
According to the statistical results of land use data from Landsat TM/ETM + image interpretation, from 1990 to 2020, the area of urban construction land in Zhengzhou increased from 168.23 to 751.26 km 2 , with an increase rate of 346.57% and an average annual increase of 19.43 km 2 . During the study period, Zhengzhou’s urban construction land showed a “steady-fast-slow” expansion trend ( Figure 4 ). The growth rate from 1990 to 2000 was relatively stable, with an average annual growth rate of 5.36%; from 2000 to 2010 was a period of rapid growth, with an average annual growth rate of 14.4%; and from 2010 to 2020, the growth rate gradually slowed down, with an average annual growth rate of 1.91%. Especially during 2015–2020, the average annual growth rate is only 0.38%, which was the lowest in 1990–2020.
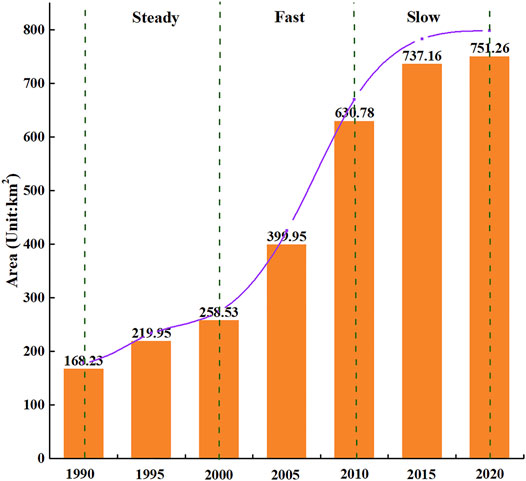
FIGURE 4 . The process of urban construction land expansion from 1990 to 2020.
3.1.2 Spatial Characteristics of Urban Expansion
The data on urban construction land in Zhengzhou in 1990, 2000, 2010, and 2020 were extracted, and the expansion of urban construction land in Zhengzhou from 1990 to 2020 was obtained by the spatial overlay analysis ( Figure 5 ). The urban expansion in Zhengzhou has obvious spatial differences. The urban expansion of the central city was mainly in three directions: east, south, and west, with the east and south having a larger expansion and being the main areas of urban development in Zhengzhou. The urban development space was limited, and the expansion was small during the study period because of the obstruction of the Yellow River in the north. In Xinzheng, Xinmi, Xingyang, and Zhongmu, which are adjacent to the central urban area, the urban expansion direction was mainly toward the central urban area, indicating that the urban development in these areas was obviously driven by the central urban area, and their urban development space was gradually integrated with the central urban area. The urban expansion direction of Gongyi in the outer suburbs was mainly to the west. The urban expansion directions were diverse, and new urban spaces appeared in the later stage of the study because of the influence of the mountains in Dengfeng. The north and southwest of the central urban area were difficult to develop because of the restrictions by geological factors such as the Yellow River basin and the mountainous terrain. Most of the available areas in the central urban area have been developed, and the urban expansion space is faced with a shortage.
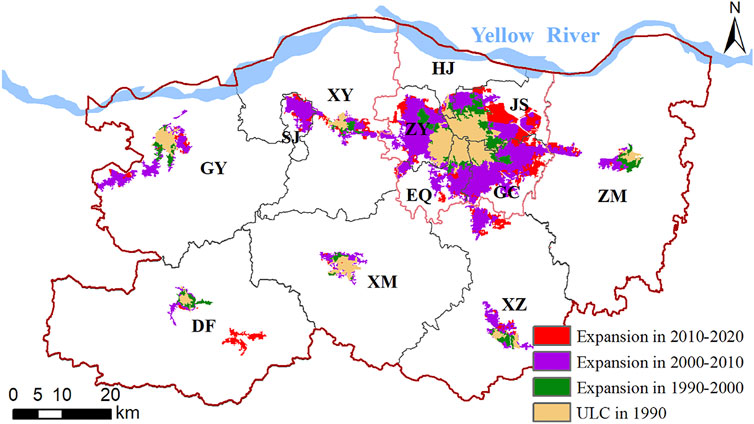
FIGURE 5 . Distribution of urban construction land (UCL) expansion from 1990 to 2020.
From 1990 to 2020, Guancheng and Jinshui had the largest urban expansion areas of 116.57 and 101.29 km 2 , respectively. Except for Shangjie, the largest average annual expansion indexes were those for Xinzheng and Guancheng, reaching 27.96 and 20.44, respectively. Seven high-speed expansion regions, three medium-speed expansion regions, and two low-speed expansion regions were developed during this period ( Table 1 ). The urban expansion rate in the central urban area was generally low, and the areas with a larger expansion rate were mainly in the outer suburbs. Most of the districts experienced rapid urban expansion, among which the central urban area had the largest expansion, and its urban expansion area accounted for 63% of Zhengzhou.
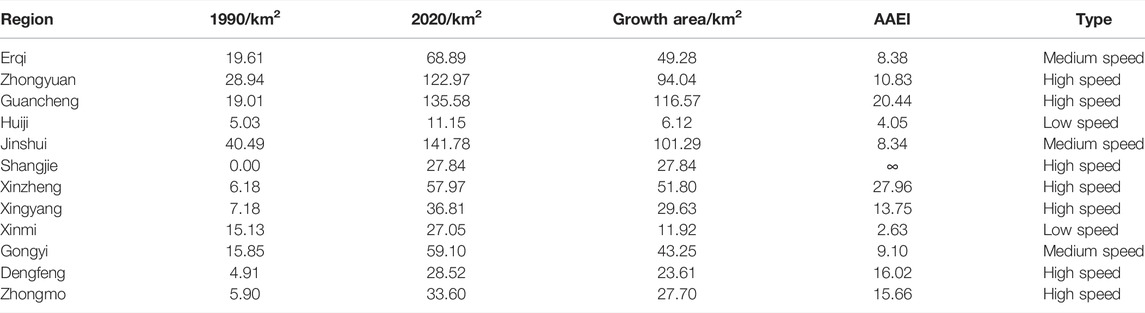
TABLE 1 . Characteristics of urban construction land expansion from 1990 to 2020.
3.1.3 Land Use Effects of Urban Expansion
From 1990 to 2020, the urban expansion area of Zhengzhou was 587.84 km 2 . The land occupied by urban expansion was mainly arable land, with an area of 471.88 km 2 , accounting for 80.27%; followed by construction land with an occupied area of 77.02 km 2 , accounting for 13.1%; and then followed waters, with an occupied area of 20.19 km 2 , accounting for 3.44%. Spatially, in addition to arable land, a large amount of waters (mainly rivers and lakes) in the northeast and west of the central urban area is occupied ( Figure 6 ). The conversion of rural residential land to urban construction land was mainly concentrated in Shangjie and Gongyi.
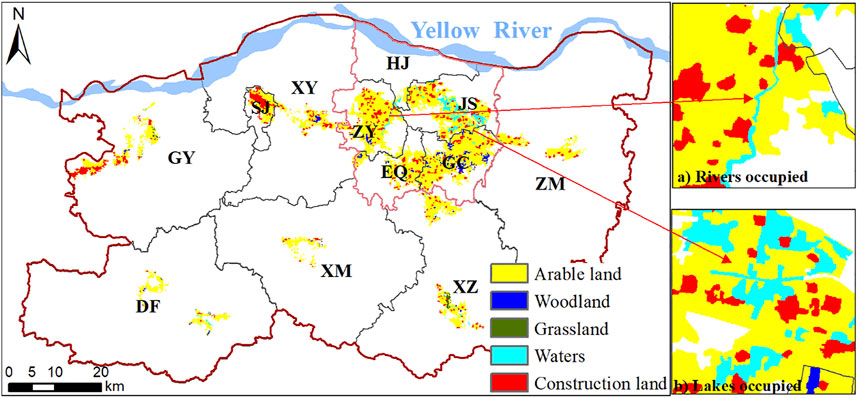
FIGURE 6 . Distribution of the land occupied by urban expansion.
Although arable land was the main type of land occupied by urban expansion, its proportion dropped from 88.89% in 1990–2000 to 69.44% in 2010–2020; the proportion of construction land occupied by urban expansion increased from 10.34% in 1990–2000 to 17.62% in 2010–2020. The proportion of occupied waters grew the fastest, from 0.69% in 1990–2000 to 15.8% in 2010–2020. This finding shows that with the strengthening of cultivated land protection, urban expansion reduces the occupation of cultivated land, and more land is converted from village land to urban land ( Table 2 ). However, the occupation of water bodies has increased rapidly, indicating that the erosion of ecological land by urban expansion has intensified, and caution needs to be taken to avoid damage to the natural ecology, especially water ecology.
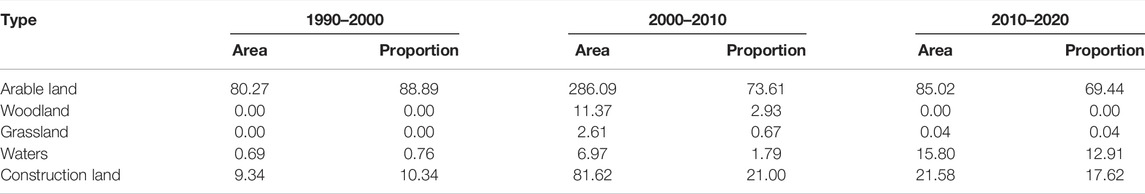
TABLE 2 . Changes in the structure of the urban expansion sources (Units: km 2 , %).
3.2 Rationality of Urban Expansion in Zhengzhou
3.2.1 elasticity indexes of urban expansion.
As shown in Figure 7 , the man-land elasticity index of urban expansion increased from 1.32 to the peak of 3.52 in 2000–2005 and then continued to decrease, indicating that Zhengzhou’s urban expansion was generally too rapid relative to the population growth from 1990 to 2010, and urban land use was relatively extensive. After 2010, the elasticity index was lower than 1 and reached a very low value of 0.04 in 2015–2020. The urban expansion rate began to be lower than the urban population growth rate, the population density of urban land gradually increased, and land use tended to be intensive. The economic land elasticity index of urban expansion showed a “U” shape. During the study period, Zhengzhou’s GDP growth rate was always greater than the urban expansion rate. The elasticity index dropped from 7.55 to 2.34 during 1990–2005 and then began to grow slowly, increasing to 33.54 during 2015–2020. This finding shows that the economic benefits of urban land use continued to improve. Although the rate of improvement declined during 1990–2005, it began to accelerate significantly thereafter, and the economic benefits of urban land use increased significantly in the later period.
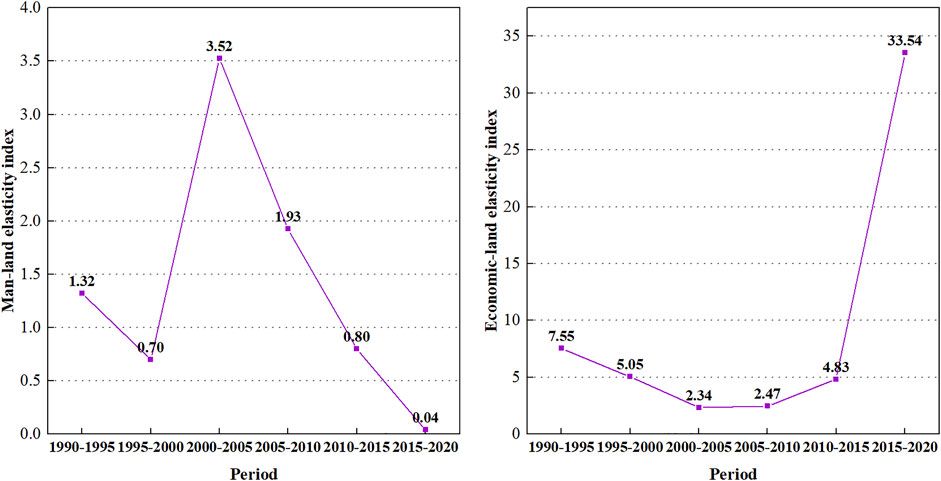
FIGURE 7 . Variation of elastic coefficient of urban expansion from 1990 to 2020.
3.2.2 Comparative Analysis Among Similar Megacities
According to China’s urban classification standards, cities with a population of more than 5 million in the central urban area are considered megacities ( SCC, 2014 ). In 2020, China had 21 megacities, which are mainly located in central and eastern China ( Figure 8 ). These megacities account for 7.5% of China’s area, but they carry 20.7% of the population and generate 33.1% of the GDP. These megacities are the core force that supports China’s economic development and participates in international competition.
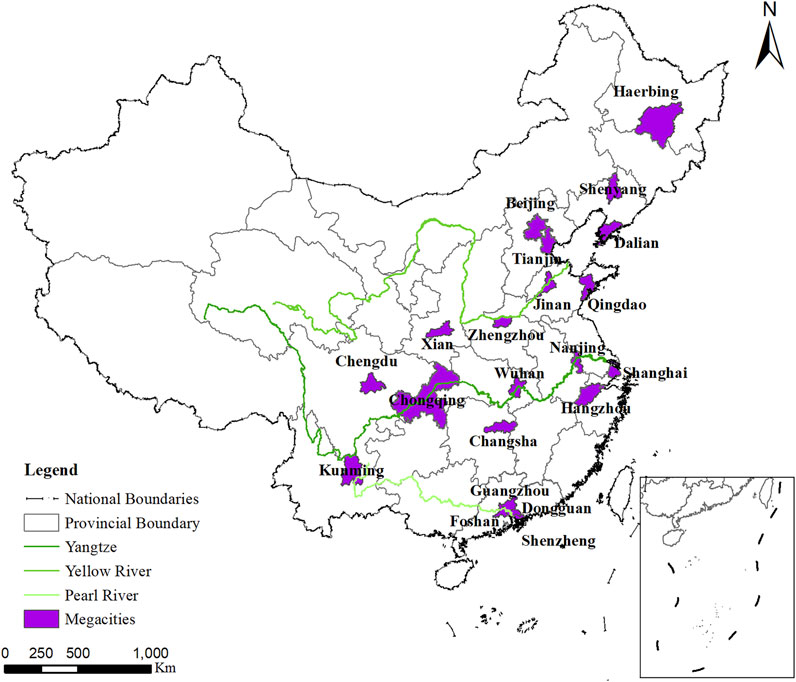
FIGURE 8 . Location of China’s megacities.
3.2.2.1 Area of Urban Construction Land Expansion
From 1990 to 2020, Zhengzhou’s urban construction land area has always been in the middle of 21 megacities, but the ranking continues to increase, from 14th in 1990 to 10th in 2020 ( Figure 9 ). This finding shows that the growth rate of urban construction land in Zhengzhou is higher than the average growth rate of China’s megacities. During the study period, Zhengzhou’s urban construction land area increased by 583.03 km 2 , which was 13% higher than the average growth area of 515.97 km 2 in megacities. The expansion of urban construction land in Zhengzhou was growing rapidly in megacities.
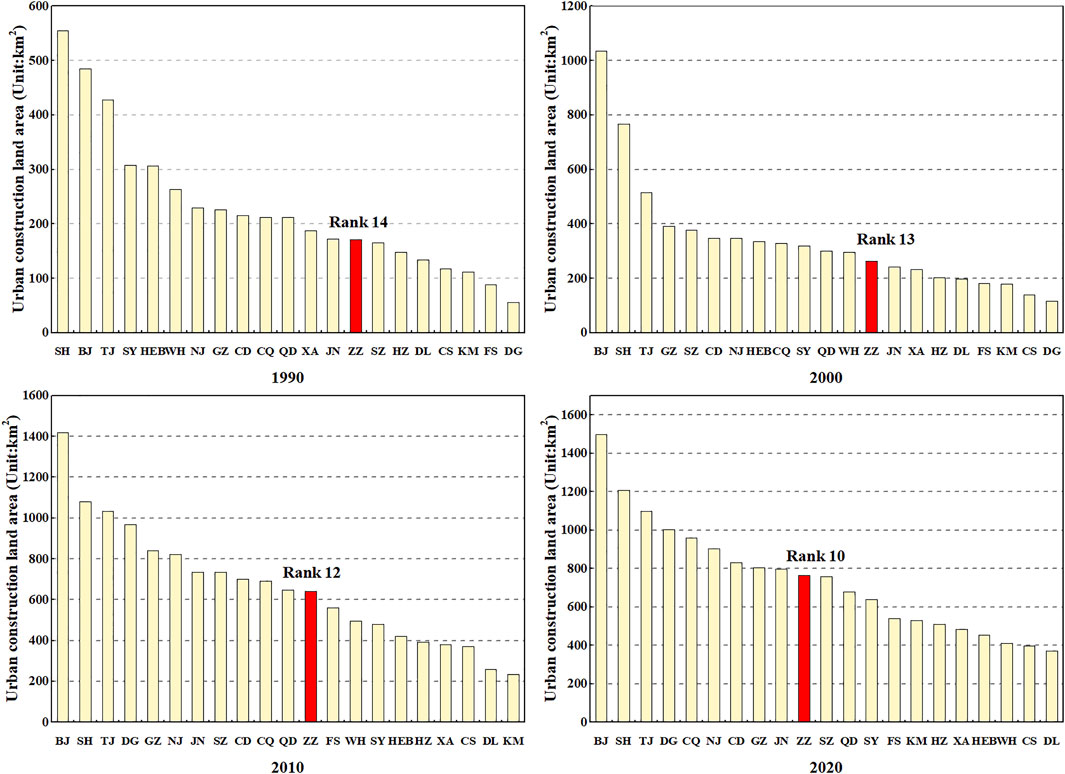
FIGURE 9 . Urban construction land area of China’s megacities from 1990 to 2020. BJ, Beijing; SH, Shanghai; GZ, Guangzhou; SZ, Shenzhen; TJ, Tianjin; DG, Dongguan; NJ, Nanjing; CQ, Chongqing; SY, Shenyang; FS, Foshan; JN, Jinan; CD, Chengdu; ZZ, Zhengzhou; XA, Xian; HZ, Hangzhou; WH, Wuhan; QD, Qingdao; KM, Kunming; HEB, Haerbing; DL, Dalian; CS, Changsha.
3.2.2.2 Efficiency of Urban Construction Land
In 2020, Zhengzhou’s per capita urban construction land area was 77.21 m 2 , and the per capita GDP was 1.574 billion yuan/hm 2 , ranking 13th and 15th among China’s megacities, respectively ( Figure 10 ), which are significantly lower than the ranking of construction land area. Although Zhengzhou has experienced relatively rapid expansion among China’s megacities, its land use efficiency has lagged behind the average level. The intensive use and economic benefits of urban construction land in Zhengzhou reached only 50.97 and 41.22% of the top megacities in China, respectively, indicating that the urban land use efficiency remains unsatisfactory. Under the increasing pressure of land supply and environmental protection faced by urban development, the urban expansion model of Zhengzhou needs to transform from the past spatial sprawl to one with improved land use efficiency.
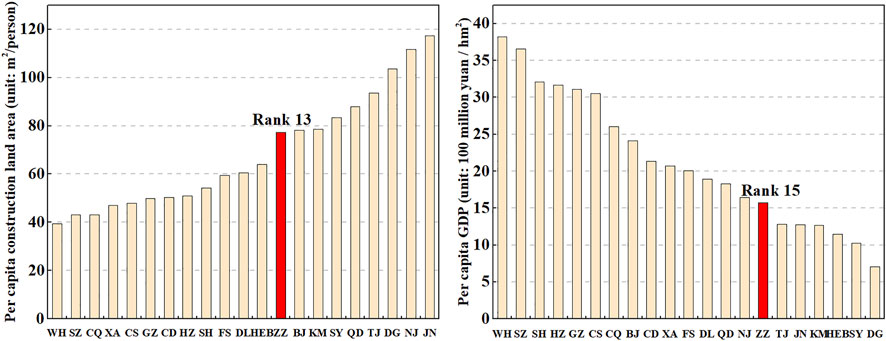
FIGURE 10 . Efficiency of urban construction land of China’s megacities in 2020. BJ, Beijing; SH, Shanghai; GZ, Guangzhou; SZ, Shenzhen; TJ, Tianjin; DG, Dongguan; NJ, Nanjing; CQ, Chongqing; SY, Shenyang; FS, Foshan; JN, Jinan; CD, Chengdu; ZZ, Zhengzhou; XA, Xian; HZ, Hangzhou; WH, Wuhan; QD, Qingdao; KM, Kunming; HEB, Haerbing; DL, Dalian; CS, Changsha.
4 Discussion
4.1 climate effects of urban expansion.
Previous studies on the negative effects of urban expansion mainly focused on the loss of arable land, landscape destruction, and deterioration of human settlements, often ignoring the climatic lag effects of urban expansion ( Camacho-valdez et al., 2014 ). The occupation of arable land by urban expansion has been curbed because of China’s increasingly stringent arable land protection policy. However, wetlands and grasslands were usually regarded as unused land by urban managers without protection and were freely occupied by urban expansion. The spatial analysis of Zhengzhou urban expansion shows that a large number of rivers and lakes in Zhengzhou, especially in the central urban area, have been occupied. The area of waters in the central urban area of Zhengzhou decreased from 95.58 km 2 in 1990 to 66.89 km 2 in 2020, with a reduction rate of 42.89%. The substantial reduction of the water body area has destroyed the urban permeable surface, which not only further aggravates the water shortage in Zhengzhou as a city in arid regions of the northern hemisphere but also weakens the city’s ability to withstand floods.
Zhengzhou experienced a historically rare catastrophic rainstorm and urban waterlogging in the summer of 2021, which brought major property losses and casualties ( Zhang et al., 2021 ). In addition to the natural extreme rainstorm factors, the occupation of rivers and lakes by urban expansion made the rainwater unable to be discharged in time, which may also play an important role in the worsening of this disaster. Emerging megacities are still in the stage of rapid urban development, and the negative climate effects of urban expansion may not yet appear. Research on the prediction of climate disasters that may be caused by improper urban expansion should be carried out to take appropriate countermeasures in advance. The climate effects of urban expansion should also attract the attention of managers and planners of other emerging megacities in the world.
4.2 Urban Expansion Evaluation System
Rapid population and economic growth in emerging megacities have driven urban expansion, while also making urban land use more intensive and efficient. Therefore, if the urban expansion is evaluated based on the city’s conditions only, then the results of urban expansion evaluation are mostly satisfied, and finding the problem of urban expansion is difficult ( Tan et al., 2010 ). As megacities face greater difficulty with land supply and more severe environmental constraints, there should be higher standards for urban land-use. Comparative analysis with similar or higher-level megacities may have different conclusions from the evaluation based on the city’s conditions.
This study adopts an urban expansion evaluation method that combines socioeconomic coupling analysis with a comparison of similar cities. The socioeconomic coupling analysis shows that the economic benefits and intensive utilization of Zhengzhou’s urban land use have improved, and urban land use has developed in a positive direction in the process of urban expansion. However, in comparison with other similar megacities in China, Zhengzhou’s urban expansion was too fast, and its economic benefits and intensive utilization were relatively low. This comprehensive urban expansion evaluation method facilitates the detection of urban expansion problems and avoids the one-sidedness of the evaluation conclusion, which provides important insights into the urban management of emerging megacities.
4.3 Recommendations for Future Study
By analyzing the spatiotemporal characteristics and rationality of urban expansion in Zhengzhou, this study strengthens the cognition of urban expansion in emerging megacities and provides significant reference for cities undergoing rapid development and growth. However, some problems need to be explored in future research. First, systematic research should be conducted on megacity groups, rather than just a single or a few cities. The expansion of megacities at different development stages shows obvious differences, and the study of the urban expansion of megacity groups is helpful for exploring the urban expansion mechanism of megacities. Second, research on the relationship between urban expansion and meteorological disasters should be strengthened. Unreasonable human activities in the process of urban expansion may be the cause of meteorological disasters. Understanding the relationship between the two can help in the implementation of countermeasures.
5 Conclusion
Taking Zhengzhou as an example, this study analyzes the spatiotemporal characteristics of urban expansion in China’s emerging megacities and the rationality for urban expansion on the basis of the man-land elasticity index, the economic-land elasticity index, and a comparison with other megacities. It then summarizes urban expansion problems and presents relevant suggestions. These findings have important reference significance for curbing the disorderly sprawl of megacities, realizing smart management of megacities and promoting regional sustainable development. The main conclusions were as follows:
1) During the study period, the urban expansion of Zhengzhou showed a trend of “steady–fast–slow.” From 1990 to 2000, the urban expansion of Zhengzhou was relatively stable, and from 2000 to 2010, it entered a stage of rapid expansion. After 2010, the urban expansion of Zhengzhou entered a slow stage due to the constraints on the expansion of the central urban area.
2) Zhengzhou urban expansion has obvious imbalance and spatial disorder. The growth area of urban construction land in the central urban area, which accounts for only 13.44% of Zhengzhou, accounts for 63% of the city’s total. The suburban urban expansion was more disorderly, and the central urban area expansion was limited by the Yellow River in the north and the mountainous areas in the southwest. The space for urban development is insufficient. In the future, urban development should transform from single-core development of the central urban area to coordinated development of the central urban area and the suburbs.
3) Urban expansion has gradually increased the occupation of water bodies, and the ecological problems of urban expansion have become prominent. Although the area occupied by waters was relatively small during the urban expansion of Zhengzhou, its proportion has since increased significantly. With Zhengzhou being a rapidly developing emerging megacity with relative water shortage, the occupation of ecological land such as waters may damage the carrying capacity of urban water resources and cause a series of natural ecological problems.
4) Zhengzhou’s urban expansion was inefficient. Although the utilization intensity and economic benefits of Zhengzhou’s urban construction land have continued to improve, compared with other megacities in China, Zhengzhou’s urban expansion was too fast, and the urban construction land utilization intensity and economic benefits were relatively low.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and writing: EC and HH; methodology and software: EC and QB; data acquisition: QB; and analysis and interpretation of data: JL.
This research was funded by the Henan Philosophy and Social Science Planning Project (no. 2019CHH078), Humanities and Social Sciences Research Projects of Higher Education Institutions in Henan Province (no. 2011-ZZJH-157), Zhengzhou Soft Science Research Project (no. 2020RKXF0104), and Major consulting and research projects of institute local cooperation of Chinese Academy of Engineering(no. 2021HENZDA04).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors, and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Bagan, H., and Yamagata, Y. (2014). Land-cover Change Analysis in 50 Global Cities by Using a Combination of Landsat Data and Analysis of Grid Cells. Environ. Res. Lett. 9 (6), 064015. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/9/6/064015
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Buyantuyev, A., Wu, J., and Gries, C. (2015). Multiscale Analysis of the Urbanization Pattern of the Phoenix Metropolitan Landscape of USA: Time, Space and Thematic Resolution. Landscape Urban Plann. 94 (3-4), 206–217. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2009.10.00.5
Cai, E., Liu, Y., Li, J., and Chen, W. (2020). Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Urban-Rural Construction Land Transition and Rural-Urban Migrants in Rapid-Urbanization Areas of Central China. J. Urban Plann. Dev. 146 (1), 05019023. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)UP.1943-5444.0000551
Camacho-Valdez, V., Ruiz-Luna, A., Ghermandi, A., Berlanga-Robles, C. A., and Nunes, P. A. L. D. (2014). Effects of Land Use Changes on the Ecosystem Service Values of Coastal Wetlands. Environ. Manage. 54 (4), 852–864. doi:10.1007/s00267-014-0332-9
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Chen, M., Liu, W., and Tao, X. (2013). Evolution and Assessment on China's Urbanization 1960-2010: Under-urbanization or Over-urbanization? Habitat Int. 38 (4), 25–33. doi:10.1016/j.habitatint.2012.09.007
Chien, H., and Saito, O. (2021). Evaluating Social-Ecological Fit in Urban Stream Management: The Role of Governing Institutions in Sustainable Urban Ecosystem Service Provision. Ecosystem Serv. 49, 101285. doi:10.1016/j.ecoser.2021.101285
China National Bureau of Statistics (CNBS) (2020). Major Figures on 2020 Pupulation Census of China. AvaliableAt: http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/pcsj/rkpc/d7c/202111/P020211126523667366751.pdf (Retreved December 22, 2021).
Google Scholar
Dai, J., Gao, X., and Du, S. (2010). Expansion of Urban Space and Land Use Control in the Process of Urbanization: An Overview. Chin. J. Popul. Resour. Environ. 8 (3), 73–82. doi:10.1080/10042857.2010.10684994
Gren, Å., and Andersson, E. (2018). Being Efficient and green by Rethinking the Urban-Rural divide-Combining Urban Expansion and Food Production by Integrating an Ecosystem Service Perspective into Urban Planning. Sust. Cities Soc. 40, 75–82. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2018.02.031
Hamidi, S., and Ewing, R. (2014). A Longitudinal Study of Changes in Urban Sprawl between 2000 and 2010 in the United States. Landscape Urban Plann. 128, 72–82. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2014.04.021
He, C., Liu, Z., Gou, S., Zhang, Q., Zhang, J., and Xu, L. (2018). Detecting Global Urban Expansion over the Last Three Decades Using a Fully Convolutional Network. Environ. Res. Lett. 14 (3), 034008. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/aaf936
Hecht, R., Behnisch, M., and Herold, H. (2020). Innovative Approaches, Tools and Visualization Techniques for Analysing Land Use Structures and Dynamics of Cities and Regions (Editorial). J. Geovisualization Spat. Anal. 4 (2), 1–4. doi:10.1007/s41651-020-00060-9
Hu, X., Zhou, W., Qian, Y., and Yu, W. (2017). Urban Expansion and Local Land-Cover Change Both Significantly Contribute to Urban Warming, but Their Relative Importance Changes over Time. Landscape Ecol. 32 (4), 763–780. doi:10.1007/s10980-016-0484-5
Jiao, L., Dong, T., and Yanyan, G. U. (2016). The Spatial Resilience of Prefecture-Level Cities in China from 2000 to 2012. Resour. ence 38 (7), 1254–1265. doi:10.18402/resci.2016.07.07
Kantakumar, L. N., Kumar, S., and Schneider, K. (2016). Spatiotemporal Urban Expansion in Pune metropolis, India Using Remote Sensing. Habitat Int. 51, 11–22. doi:10.1016/j.habitatint.2015.10.007
Khamchiangta, D., and Dhakal, S. (2021). Future Urban Expansion and Local Climate Zone Changes in Relation to Land Surface Temperature: Case of Bangkok Metropolitan Administration, Thailand. Urban Clim. 37, 100835. doi:10.1016/j.uclim.2021.100835
Kovács, Z., Farkas, Z. J., Egedy, T., Kondor, A. C., Szabó, B., Lennert, J., et al. (2019). Urban Sprawl and Land Conversion in post-socialist Cities: The Case of Metropolitan Budapest. Cities 92, 71–81. doi:10.1016/j.cities.2019.03.018
Lafortezza, R., and Sanesi, G. (2019). Nature-based Solutions: Settling the Issue of Sustainable Urbanization. Environ. Res. 172, 394–398. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2018.12.063
Li, J., Zhang, W., Sun, T., and Zhang, A. (2014). Characteristics of Clustering and Economic Performance of Urban Agglomerations in China. Acta Geographica Sinica 69 (4), 474–484. doi:10.11821/dlxb201404004
Liu, G., Li, J., and Nie, P. (2022). Tracking the History of Urban Expansion in Guangzhou (China) during 1665-2017: Evidence from Historical Maps and Remote Sensing Images. Land Use Policy 112, 105773. doi:10.1016/j.landusepol.2021.105773
Liu, J., Liu, M., Zhuang, D., Zhang, Z., and Deng, X. (2003). Study on Spatial Pattern of Land-Use Change in China during 1995–2000. Sci. China 46, 374–384. doi:10.1360/03yd9033
Liu, M., Tian, H., Chen, G., Ren, W., Zhang, C., and Liu, J. (2008). Effects of Land-Use and Land-Cover Change on Evapotranspiration and Water Yield in China during 1900-20001. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 44 (5), 1193–1207. doi:10.1111/j.1752-1688.2008.00243.x
Naitonal Development, and Reform Commission (NDRC) (2017). Reply of the National Development and Reform Commission on Supporting Zhengzhou to Build a National central City. AvaliableAt: https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/xwdt/ztzl/xxczhjs/ghzc/201701/t20170125_972047.html?code=&state=123 (Retreved December 23, 2021).
Rusk, D. (1993). Cities without Suburbs . Washington: Woodrow Wilson Center Press .
Sassen, S. (1994). The Urban Complex in a World Economy. Int. Soc. Sci. J. 46 (139), 43–62.
Schneider, A., and Woodcock, C. E. (2014). Compact, Dispersed, Fragmented, Extensive? A Comparison of Urban Growth in Twenty-Five Global Cities Using Remotely Sensed Data, Pattern Metrics and Census Information. Urban Stud. 45 (3), 659. doi:10.1177/0042098007087340
State Council of China (2014). Circular of the State Council on Adjusting the Classification Standards of the City Size. AvaliableAt: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2014-11/20/content_9225.htm (Retreved December 29, 2021).
Tan, K. C., Lim, H. S., MatJafri, M. Z., and Abdullah, K. (2010). Landsat Data to Evaluate Urban Expansion and Determine Land Use/land Cover Changes in Penang Island, Malaysia. Environ. Earth Sci. 60 (7), 1509–1521. doi:10.1007/s12665-009-0286-z
Tayyebi, A., Perry, P. C., and Tayyebi, A. H. (2014). Predicting the Expansion of an Urban Boundary Using Spatial Logistic Regression and Hybrid Raster–Vector Routines with Remote Sensing and GIS. InternationaL J. Geographical Inf. Sci. 28 (3-4), 639–659. doi:10.1080/13658816.2013.845892
Tian, L., Li, Y., Yan, Y., and Wang, B. (2017). Measuring Urban Sprawl and Exploring the Role Planning Plays: A Shanghai Case Study. Land Use Policy 67, 426–435. doi:10.1016/j.landusepol.2017.06.002
Tong, L. (2020). A Review on Definitions and Measurements for Urban Expansion. World Reg. Stud. 29 (4), 762–772. doi:10.17576/geo-2021-1702-10
Xu, H., Ding, F., and Wen, X. (2009). Urban Expansion and Heat Island Dynamics in the Quanzhou Region, China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observations Remote Sensing 2 (2), 74–79. doi:10.1109/JSTARS.2009.2023088
Yao, S., Chen, S., Wu, J., Zhang, Y., and Chan, R. (2009). Spatial Expansion Patterns of Chinese Big Cities the Case of Suzhou. Scientia Geographica Sinica 29 (1), 15–21. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-00205-2_9
Yue, W., Zhang, L., and Liu, Y. (2016). Measuring Sprawl in Large Chinese Cities along the Yangtze River via Combined Single and Multidimensional Metrics. Habitat Int. 57, 43–52. doi:10.1016/j.habitatint.2016.06.009
Zhang, W., Liao, Q., Yang, S., Zhang, X., Zhang, C., Xiang, M., et al. (2021). Thoughts and Inspirations: Urban Flood Risk Management Inferred from Zhengzhou Flood Model. China Flood Drought Manag. 31 (9), 1–4. doi:10.16867/j.issn.1673-9264.2021251
Zhang, Z., Liu, F., Zhao, X., Wang, X., Shi, L., Xu, J., et al. (2018). Urban Expansion in China Based on Remote Sensing Technology: A Review. Chin. Geographical Sci. 28 (05), 727–743. doi:10.1007/s11769-018-0988-9
Zhao, G., Zheng, X., Liu, Y., and Liu, F. (2017). Urban Expansion Steady-State index of Urban Expansion Based on Remote Sensing and GIS and its Applications. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 33 (11), 272–281. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.11.035
Zhengzhou Bureau Of Statistics (2021). Zhengzhou City's Annual Statistics. AvaliableAt: http://tjj.zhengzhou.gov.cn/ndsj/index.jhtml (Retreved December 23, 2021).
Zhong, Y., Lin, A., He, L., Zhou, Z., and Yuan, M. (2020). Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Driving Forces of Urban Land-Use Expansion: A Case Study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Remote Sensing 12 (2), 287. doi:10.3390/rs12020287
Keywords: sustainable development, spatiotemporal characteristics, urban expansion, emerging megacity, Zhengzhou
Citation: Cai E, Bi Q, Lu J and Hou H (2022) The Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Rationality of Emerging Megacity Urban Expansion: A Case Study of Zhengzhou in Central China. Front. Environ. Sci. 10:860814. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2022.860814
Received: 23 January 2022; Accepted: 21 March 2022; Published: 26 April 2022.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2022 Cai, Bi, Lu and Hou. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Heping Hou, [email protected]
This article is part of the Research Topic
Towards Sustainable Urban Development: Use of Geographic Big Data for Spatial Planning
To print the story please do so via the link in the story toolbar.

Changing Population - Changing Population and Places [2] Challenges and Opportunities [3]
Geographic inquiry: Processes of population change and their effect on people and places
Changing Populations and Places
'Processes of population change and their effect on people and places'
Geographic knowledge and understanding
Population change and demographic transition over time, including:
natural increase,
fertility rate,
life expectancy,
population structure,
dependency ratios
Detailed examples of two or more contrasting countries
The consequences of megacity growth for individuals and societies
One case study of a contemporary megacity experiencing rapid growth
The causes and consequences of forced migration and internal displacement
Detailed examples of two or more forced movements, to include environmental and political push-pull factors , and the consequences for people and places
push factors, and consequences for people and places
Synthesis , evaluation and skills opportunities
How the impacts of population change and spatial interactions between places can be categorized and represented graphically
Challenges and Opportunities
'Population possibilities and power over the decision-making process'
Geographic Knowledge and Understanding
Global and regional/continental trends in family size, sex ratios, and ageing/greying
Policies associated with managing population change, focusing on:
• policies related to ageing societies
• pro-natalist or anti-natalist policies
• gender equality policies and anti-trafficking policies
The demographic dividend and the ways in which population could be considered a resource when contemplating possible futures
• One case study of a country benefiting from a demographic dividend
Synthesis, evaluation and skills opportunities
How population change may affect the power balance between groups of people
at local, national and international scales
This set provides several statistical examples related to challenges and opportunities in population dynamics.
Population change and demographic transition over time
Geographic Knowledge and understanding
How the impacts of population change and spatial interaction between places can be categorized and represented graphically
Access Denied
www.cia.gov
You can find the examples of Bangladesh and Indonesia (specifically Java) here. There are several data sets and researched/well referenced resources here.
13 - September 2023
- Synthesize findings into a structured 800 word comparative essay for paper 1
- Explore population change and demographic transitions
CASE STUDY PROJECT ( Population change and demographic transitions research tasks )
You will compare more than two contracting case studies for these concepts.
1) Create a document entitled Jakarta Case Study. At the top of the page insert a map showing Indonesia, Java and Jakarta's location.
Background: Find the following data for Indonesia using the CIA factbook and add it to the case study document in a table.
Starting point
GDP/capita:
% population working in agriculture:
literacy rate:
Life expectancy in education for Males and Females:
14 September 2023
Investigate how population pyramids can help explain Demographic Transition Models.
Complete draft essays from topic 1
15 September 2023
Patterns in population change and demographic transitions over time (DTM).
Define and apply natural increase, fertility rate, life expectancy, population structure and dependency ratios in relation to DTM.
quizlet.live
enter code: M8H-PHJ
3-5 rounds - note a minimum 5 new terms
WALT/WARMER
Peer editing - Essay 1
Read and apply 'Types and Significance of Population Pyramids'
Links to Indonesian case study data: (Starter kit)
https://www.populationpyrmid.net
https://www.populationpyramid.net/indonesia/2023/
This is the reading guide for your population pyramids and DTM worksheets
Here is a detailed unpacking of an overview of the DTM. He is not everyone's favorite and there is no inbetween with him. You love him or you cannot stand him.
Tuesday 19th September 2023
Interpret DTW stage characteristics and describe examples of each stage.
Compare population dynamics of two contrasting nations and apply it to case study research.
SIT IN TEST ARRANGEMENT to start class
Google classroom quick DTW worksheet (scheduled for 8:52AM Individual task - submit when complete.
You may use 2.3.2 video with the annoying/entertaining guy (depending on if you love or hate the guy in the video to the left) video as guidance, but please use headphones.
Steps - to -Success
- WALT; WARMER
- Google classroom housekeeping
- Case study steps 1-5
- Essay feedback (first batch)

Population - KS3 Geography - BBC Bitesize
Find out about population and how it is affected by birth rates, death rates and migration with BBC Bitesize Geography. For students aged 11 to 14.
www.bbc.co.uk
Optional revisit

Bangladesh will truly be seen as a developed country when it vanquishes undernutrition
The latest nutrition data out of Bangladesh describe a situation brimming with promise. The Bangladesh Demographic and Health Survey (BDHS) 2017/2018 estimates stunting at 31% and the UNICEF Multiple Indicator Cluster Survey (MICS) 2019 shows an even lower estimate of 28%.
www.gainhealth.org
Just a moment...
www.ohchr.org
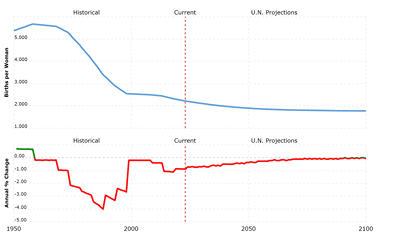
Fertility Rate in Indonesia from 1950 to 2023 data with projections through 2102
Case Study Project Continued ( Population change and demographic transitions research tasks )-
Compare Indonesia/Bangladesh to two other countries considering factors affecting their fertility rates
2) What are the causes for declining fertility rates?
Ensure you transfer this table to your case study research document, this section is on population change .
What issues may arise at each snapshot
3) Describe the population structure using population pyramids for Indonesia (or your chosen example) from the 1950s; 1980s; 2000s; ~2015
Add this data (pyramids with descriptions) to your case study research (if you have chosen Bangladesh or a similar population dynamic that too is fine).
4) Find the projected population pyramid for ~2050 Indonesia and consider the population structure. Then outline the future predicted;
a) Challenges
b) potential benefits
Demographic Dividend in Africa (revisited)
am.afdb.org
The above outlines a panel discussion at a recent African Development Bank(AfDB) annual meeting on 'mobilizing private sector financing for climate and green growth in Africa' in Sharm El Sheikah, Egypt.
The May meeting focuses heavily on population dynamics and effective decision making in light of COP 27. Read more about the 'state of africa' here https://am.afdb.org/en/2023-annual-meetings/about-2023-annual-meetings
How does this relate to your reading on Kenya?
What is AfDB doing
Above is what you provided as the barriers to tapping into the demographic dividend in Africa as per the ted talk above. We did this in class towards the end of quarter 1. It is important to connect this with the overall population changes we have studied and how this dividend requires and is directly related to education, empowerment and employment
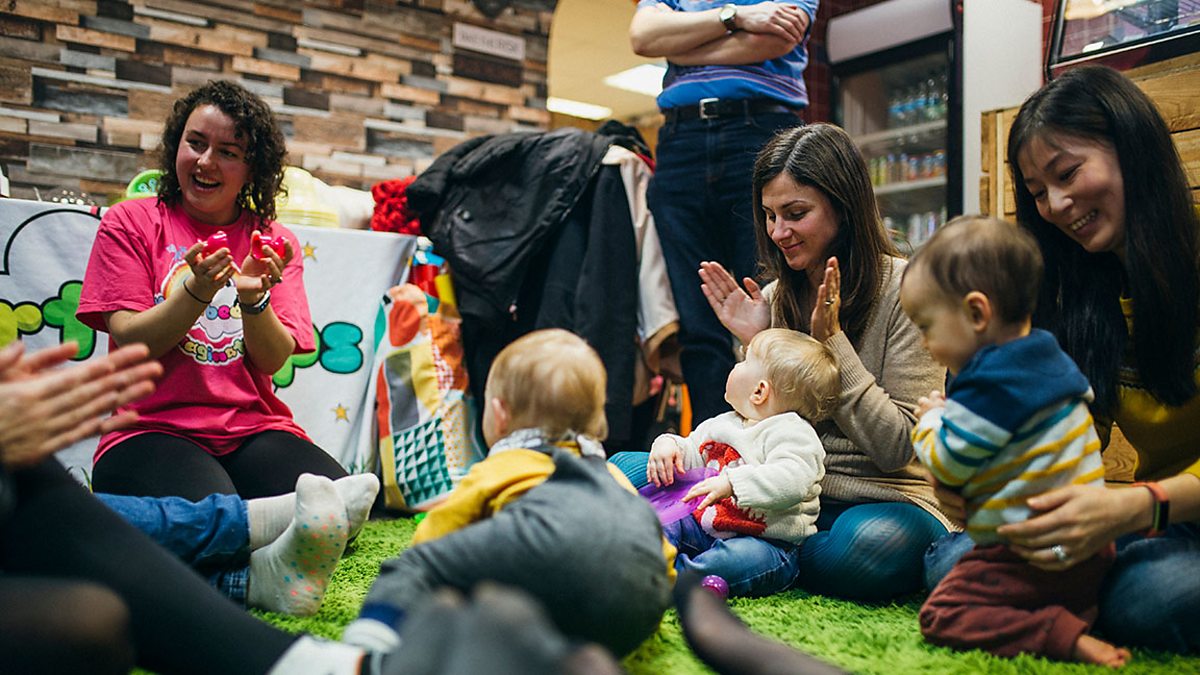
Megacity and Rapid Growth

See the caption for more. This is a visual thinking activity
Advantages of Mega-Cities
- A source of innovation and entrepreneurial activity
- Employment opportunities: the increase in the population creates a skilled workforce that attracts transnational corporations, thus creating jobs
- Transportation: megacities usually have good transportation routes due to where they are sited which allows for transportation services to be developed
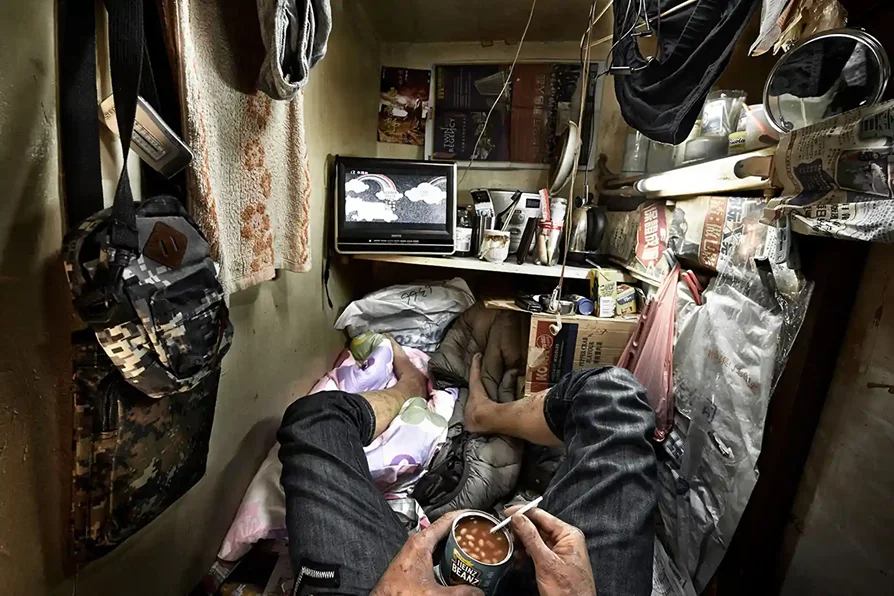
Disadvantages of Mega Cities:
- Slum development: this can occur because of housing shortages due to large numbers of people living in the area
- Air pollution: Megacity growth can lead to an increase of traffic congestion, which can lead to air pollution
- Crime: this occurs due to growing inequalities amongst people
- Unemployment: due to the large numbers of people, finding employment would be difficult
- Rising cost of living
- Overcrowding
The case study of the Indonesian capital city of Jakarta
In this section we examine the case study of Jakarta as one case study of contemporary megacity experiencing rapid growth (Jakarta)

Indonesia: crime rate | Statista
In 2022, Indonesia's crime rate was at 137 per one hundred thousand resident population.
www.statista.com
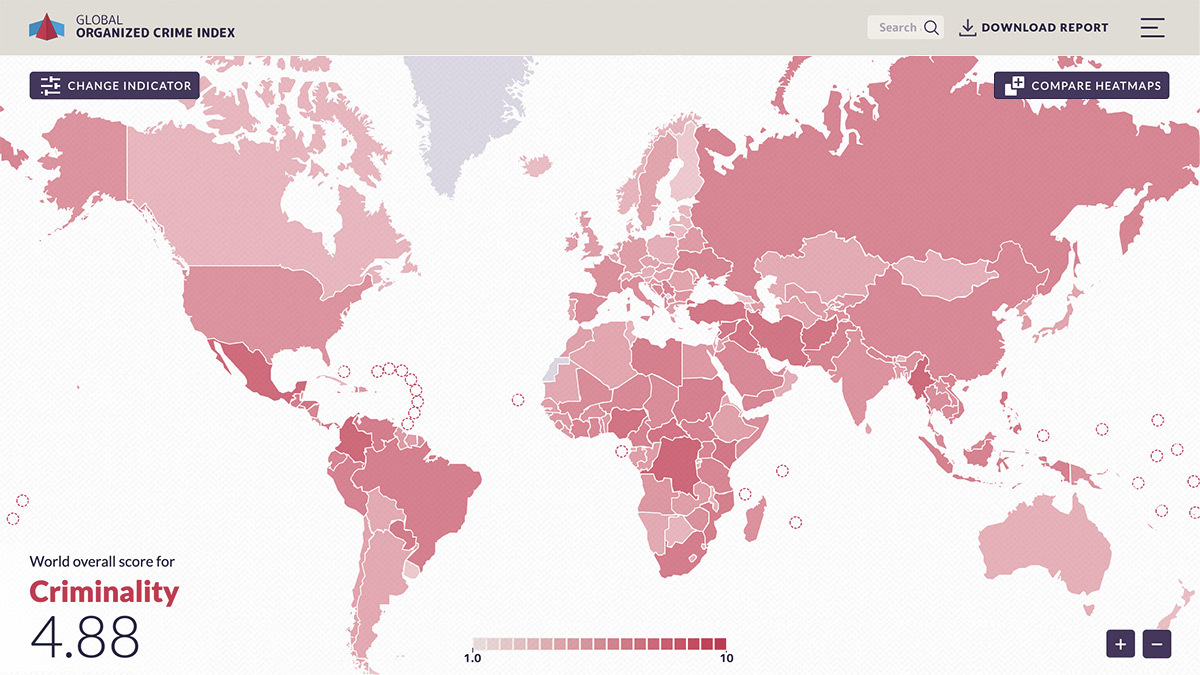
Criminality in Indonesia - The Organized Crime Index
Based on the 2019 ENACT Organised Crime Index for Africa, the Global Organized Crime Index is a key flagship project of the Global Initiative Against Transnational Organized Crime.
ocindex.net

Consequences in View - The Move to Move the Capital
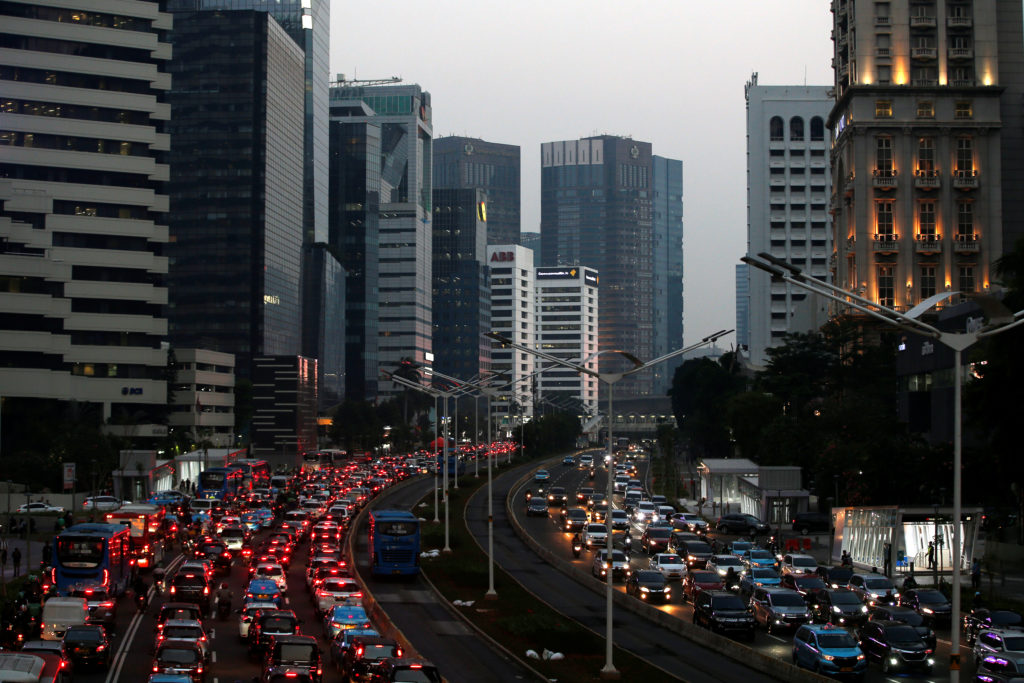

Why Indonesia is moving its capital from Jakarta to Borneo
Indonesian government authorities unveiled the site of the country's new capital this week, showing a preview of what progress has been made on the city's construction.
www.pbs.org
ERROR: The request could not be satisfied
www.travelandleisureasia.com
This TDC documentary follows a journalist around the issues surrounding Jakarta's consequences of extremely rapid mega city growth.
Reflection:
Using the vocabulary from the unit, summarize the drivers for moving the capital.
Reflect on the pros and cons, what is the benefit, what is the impact/harm?
Do you agree? Justify your response (reflections for our return from break, due Wednesday 18th October) .
Switzerland, Sweden and Japan - Contrasting the Population Dynamics in Bangladesh and Indonesia
Case study continued.
( Population change and demographic transitions research task )
Switzerland (or country of choice)
Switzerland
i) Open a second and shared google doc with the title, “Swiss Case Study.”
ii) Insert a map showing the location of Switzerland.
iii) Use the articles and videos below to outline the factors affecting Switzerland's fertility rates.
CIA Factbook - Swiss profile -

Population growth pushes births to 24-year record - SWI swissinfo.ch
The number of births has been steadily increasing since 2005. In 2014, it was 2,600 more than the previous year – an increase of 3.1%. Such demographic growth is currently unique in Europe, the statistical office said, pointing out that the birth rate has collapsed in southern Europe in particular as a result of the…
www.swissinfo.ch
Switzerland has fewest young mothers in Europe - SWI swissinfo.ch
An international comparison by the EURO-PERISTAT project published on Monday found that the health of mothers and newborns, as well as the medical management of birth, varied greatly from one country to another. For most of the indicators, Switzerland falls within the European average. However, in addition to the lowest proportion of young mothers, Switzerland…
Swiss birth rate hits all-time low - SWI swissinfo.ch
Fertility rate has fallen to an all-time low in Switzerland with 1.39 children per woman in 2022.
Causes and Consequences of Involuntary Migration and Internal Displacement
In your tables choose a region of the world to use for a case study which will be guided research for understanding forced movements.
Refugee movements and forced migration are geographically brutal at times and you are forewarned that these may be very personal and difficult topics to discuss, read, observe and critically analyse.
In your case study, you should consider:
- Environmental push factors
- Political push factors
- Consequences for people
- Consequences for places

Pre-Questions and Reflection Questions:
- What are examples of economic push factors
Are these voluntary or involuntary?
2. Examples of environmental push factors
Are these voluntary or involuntary?
3. Examples of political push factors
Are these voluntary or involuntary?
At what point do push-pull factors become human trafficking? Who is responsible for this?

UNHCR, the UN Refugee Agency
UNHCR, the UN Refugee Agency, is a global organisation dedicated to saving lives and protecting the rights of refugees, forcibly displaced communities and stateless people.
www.unhcr.org
Tentative plan for late October field trip to the UNHCR partner organizational office in Arusha. Here is a snapshot from the UN Refugee Agency
www.state.gov
- Last activity of the unit - Human trafficking - Q2 W1 deadline
I nvestigate policy at different scales on gender equality and people trafficking
Steps to success:
PART A - Blue
Complete the warmer worksheet on your community, compare with your table partner
This survey serves as your first step in the assignment, produce a brief infographic representing your findings.
PART B - Yellow
Complete the following statistics from the BBC video shown during class (this video is seemingly blocked on campus)
12 countries
40% of countries, task b: group work - [up to 4/group].
Part 1 - Thursday
Investigate policies focused on gender equality and human trafficking.
You have 4 members in your groups, identify as such:
Than move onto the reading and make evaluative comments as outlined below
Sorry, this embed is not embeddable or has been removed from its original source.
This page provides a broad range of strategies that develop policies in a LIC context .
This page provides a broad range of strategies that develop policies in both a HIC context .
This page provides a wide range of examples and strategies targeting the prevention of human trafficking.
TASK 1 (PART 1 Thursday)
This page (chapter 3f) provides a wide range of examples and strategies targeting the prevention of human trafficking., the un and sustainable development goal s and un sdgs (all group members should know this well), a country with a high level of gender equality such as iceland (group member a), a country focused on preventing trafficking from their country (group member b), a country focused on preventing trafficking into their country. (group member c), an ngo that integrates gender equality into its projects (group member d), an ngo focused solely on human trafficking (group member d or e), for each example you should should include evaluative comments..
Role Play - THIS IS PART 2
Separate into 4 groups focused on each specialism [members A-D].
Each table should produce a briefing on a policy and on the scale of the problem [Human Trafficking] and how to manage it.
The policies are shared on the links below and are available via organizations and state authorities.
The final outcome should be two collaborative policies, one on gender equality, the second on human trafficking
Your group should be prepared to add value to the meeting and should be confident about contributing to the wider policies on gender equality and the prevention of human trafficking.
Each group should be able to:
- Describe their role and outline their key focus
- Outline the situation and context of the problem that they encounter
- Outline the policy recommendation towards gender equality or human trafficking
Further Resources
- Modern Slavery Act 2015 -UK (use webpage)
- Scottish Police - Recognizing the signs of human trafficking brochure (police policy)
- Human Trafficking - Scotland (printed)
- Polaris - USA
- US Department of Justice
- European Commission
- EU Infographic
Rollplay Feedback sheet - HT
Sheet1 Rollplay Feedback sheet,Group A,Group B,Group C,Group D,provide feeback for each group (including your own),Name: Quality of presented research Depth of knowledge in intial policy Verbal communication of key elements of the policy Quality of communication in collaborative phase Contribut...
docs.google.com
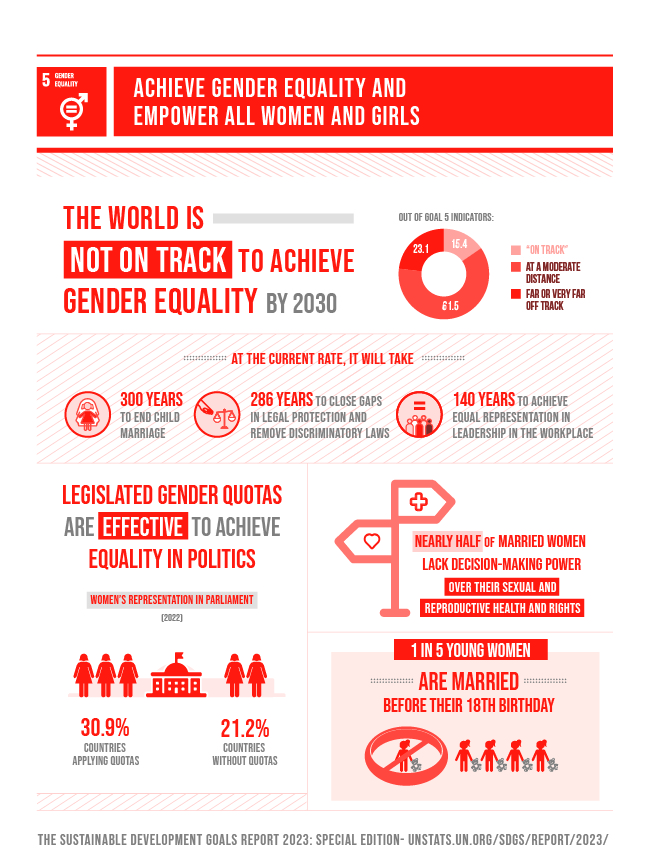
Goal 5 | Department of Economic and Social Affairs
Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls
sdgs.un.org
Human trafficking
Our policy on human trafficking in Scotland.
www.gov.scot
Policy from Scotland
Modern Slavery Act 2015
8.Human Trafficking and Exploitation (Criminal Justice and Support for Victims) Act (Northern Ireland) 2015 (c. 2 (N.I.))
www.legislation.gov.uk
Policy from the United Kingdom

Policy & Legislation
Congress has built on the TVPA, honing and expanding the U.S. strategy to combat sex trafficking and labor trafficking through a holistic, multi-agency approach.
polarisproject.org
The Polaris Project - Formulating priorities and reflecting congressional influences

A Whole-of-Government Approach
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
www.justice.gov

Press corner
Highlights, press releases and speeches
ec.europa.eu

Together Against Trafficking in Human Beings
Protecting our societies from organised crime, including tackling trafficking in human beings, is a priority under the new EU Security Union Strategy. Trafficking in human beings is a highly profitable crime that brings enormous profit to criminals while incurring a tremendous cost to society.
home-affairs.ec.europa.eu

ChildSafe - Together, protecting children
ChildSafe is a global movement empowering people to protect children.
thinkchildsafe.org
Paper 2 [Global Change] - assessment
Friday you will have a chance to sort an example essay relevant to your assessment (paper 2) upcoming in Q2 Week 1.
Understanding text in exam questions:
- Referring to : using, mentioning explicitly
- Outcome : consequence, result
- Benefits/costs : positive/negative outcomes
- Pressures/conflicts : undesirable competition
- Challenges : difficulties which may be overcome
- Social : relates to human welfare (e.g. housing, health)
- Cultural : relates to languages, customs, religions, moral codes
- Political : relates to government actions
- Demographic : relates to populations (e.g. fertility)
- Environmental : relates to the physical environment
- Issues : important and controversial results
- Trend : change over time (usually on a graph)
- Pattern : distribution in space (IE: can be mapped)
- Process : actions or changes which occur between two parts/stages
- Relationship : two-way interactions
- Global scale : the entire world
- Regional scale : large regions (e.g. Europe, Asia Pacific)
- National scale : within one country
- Local scale : immediate district or state
This section is for preparation for the E Assessment. You work on skills throughout year 1 so that you are capable of interpreting information graphically and extrapolate from text. Do save yourself time by using the guided materials or case studies you have already engaged with.
1 hour 15 minutes
Section A - Answer all questions
Section A includes shorter answers, ranging from 1 - 6 marks; often a 6 or mark question is broken down as follows (3 + 3) or (2 + 2). There will be graphics within the questions or resource booklet
The topics in this section include:
- Changing Population (10 marks)
- Global Climate - Vulnerability and Resilience (10 marks)
- Global Resource Consumption and Security (10 marks)
Section B - Answer all questions
Section B includes shorter answers, ranging from 1 - 6 marks; often a 6 or mark question is broken down as follows (3 + 3) or (2 + 2).
The questions are based around an infographic found in the resource booklet. The infographic will based on any topic assesses in Section A (10 marks)
Section C Answer one question
Section C includes two 10 mark essay questions from which students must choose one.
Students should where relevant, refer to case studies or examples, and where appropriate include well-draw geographically accurate and annotated maps or diagrams
Answers are written inside the booklet and there is an additional resource booklet to accompany the examination
Marking scheme

The response has some relevant knowledge and understanding but it remains too general and is listed and poorly structured with a lack of critical comment

The response addresses the question but with a narrow argument and limited evaluation and conclusions

The response addresses the question and the analysis is evaluated and the conclusion is relevant but biased
The response is in-depth and question specific (topic and command word). The analysis and conclusion is justified through well -developed evaluation and critical examination of different perspectives
catamaran tour

Icacos Snorkeling & Beach Tour
Prices per person, children under 12:.
* Plus taxes 11.5% & DRNA fees $3.00 p/p
QUICK DETAILS
- Duration: 6 hours
- Check-in time: 45 minutes prior to departure
- Location: Marina Puerto Del Rey, Fajardo
- Ages: No age restriction. Family friendly tour
Transportation Available
Roundtrip transportation is available for an additional fee from most hotel/locations in San Juan, Condado, and Isla Verde. For Puerto Rico’s northeast coast, Rio Grande, Rio Mar, Luquillo, Fajardo, and Palmas del Mar in Humacao, please call for minimum and pricing.
ASK US ABOUT OUR PRIVATE CHARTER OPTIONS
Boat Options: *East Wind Sailing Catamaran or for private option on *Eco Isleño Power Catamaran up to 15 passengers and *Zatara sailing catamaran up to 12 passengers
More Information
Experience Fajardo’s #1 top-rated snorkeling excursion aboard the largest sailing catamaran “East Wind” .
Get to know the enchanted cays of the east coast of Puerto Rico and enjoy the views of our natural treasures beginning with the El Yunque National Forest and all of its wonders while also admiring the intricate and quiet beauty of the east coast of this amazing island. On the vessel, have fun on the waterslide which delights kids of all ages or have a peek out of the 8′ underwater windows below deck so you can see the underwater beauties without having to get wet thoroughly enjoyed by our non-swimmers and first-timers alike.
What's included in the Price?
Your icacos snorkeling tour includes:.

- Deli-style Lunch buffet
- Beverages, including rum drinks
- Floating devices
- Snorkeling Equipment & swimming fins
- Swim platforms where our guests have easy access to the water
- Snorkeling instruction if needed
- Spacious shaded cabin
Lunch Buffet & Drinks
Tour lunch and beverages includes:.
- Lunch buffet includes a variety of cold cuts, cheeses, fresh bread, pasta salad, bean salad, and chicken salad.
- Snacks – chips and fresh fruit
- Rum drinks – Piña Colada & Rum punch
- Assorted regular and diet sodas
- Juices & water
- Any guest that needs any special dietary needs can bring their own lunch or contact 787-860-3434 for details.
What to Bring?
What to bring aboard icacos snorkeling tour:, recommendations:.

When sailing the waters of Fajardo aboard the East Wind Catamaran you will enjoy warm temperatures along with spectacular views of El Yunque Rainforest and the Fajardo Cays, if you take a sunset trip you will enjoy beautiful landscapes never seen before.
That’s why we recommend bringing on board:
- Waterproof Photo Camera, GoPro Camera or Cell Phone with a waterproof cover with a good amount of battery to take pictures aboard.
- Sunblock: We are in the Caribbean and with the Warm Temperatures year-round it’s always good to be protected against the Sun.
- Sunglasses and/or Hat
- Comfortable Shoes and swim suite under light beach clothing
- Personal Towel
- Get seasick, take an over-the-counter remedy with food at least 1 hour before the trip
- We include the use of the snorkeling equipment during the tour but, you may also bring your own if preferred, or purchase new equipment at our East Island Excursions Store.
Please read our Restrictions and Cancellation Policy!
Cancellation policy, individual reservations:.
10:00 am the day before the scheduled trip, the reservation can be canceled for 1-9 passengers, 10 + passengers 2 days prior with No penalty. The full payment is required upon booking with any major credit card to confirm the reservations.
“NO SHOW” or if you don’t arrive on time, the ticket is NOT REFUNDABLE and NOT REUSABLE unless (and only if) we have space available to reschedule on a future date. Reschedule must be made on the day of the original trip, based on availability and a rescheduling fee of $25+ tax per person will be applied.
*All marine activities are subject to water conditions please call the prior day for an update, cancellations or change of destination due to water conditions is at the Captain’s discretion. These decisions can be informed upon check-in.
Departure Site Information
This tour departs from Marina Puerto del Rey in Fajardo , Puerto Rico, please be on site by 45- 30 minutes prior your departure time for check-in Process. The marina offers parking at no extra charge. If you have any questions about the boarding process or regarding your reservation please contact us at +1 (787) 860-3434 . or text us at 787-409-2485


We were a group of 8 adults and 2 small children ( ages 4 and 1 ) and this was the perfect trip. The entire crew was excellent! The sailing was steady, the views beautiful, the lunch and drinks delicious, and the swimming and snorkeling in crystal clear turquoise waters amazing! There was plenty of time to enjoy each part of the trip, very fun and relaxing!
Sailing, swimming, and snorkeling fun!
One of the best day’s in Puerto Rico, ever! This excursion is affordable, fun and it was an amazing experience! Went to Icacos Island and snorkeling nearby. The staff was awesome and it felt safe and fun at the same time. (open bar and buffet) was awesome. I definitely high recommend!!
Excellent Excursion
This catamaran trip was AWESOME! One of the best things I’ve experienced vacationing in Puerto Rico. First of all I want to thank Jorge one of the crew members for making this trip a great experience, he made sure my family and I had food, drinks and was very informative on the sights. Thank you for helping make great memories!
catamaran trip was AWESOME!
This was my second excursion with East Island Excursions and they did it again! We were a family of four (with a 5 yr old). Fun was had by all…I could not keep my 5 year old off the water-slide 🙂 Food was great and a great atmosphere.
Did it again!
Took the Icacos Island tour with East Island Excursions. Loved every bit of the tour. Truly professional, friendly and helpful crew. The places we were taken to were exotic and I just loved it . My phone which had most of the pics and memories got drenched in the sea water and died and Levi one of the member of the crew member truly felt our anxiety took pictures for us and sent it later . Wonderful guy. I am not a swimmer but took the plunge with the help of Moises from the crew team . I would recommend East Island Excursions and Levi to anyone visiting Puerto Rico and taking the Island tours
Loved the Icacos Island tour with East Island Excursions
Loved our visit to Icacos with East Island Excursions. Originally we had booked for Vieques, but due to weather, we could not go there. East Island was very prompt in calling us every day and giving us an update. In the end, they even offered to shift us to Icacos on priority and refunded the balance amount. Their boats are amazing and look luxurious. The staff is insanely friendly, offer great food and drinks and snorkeling tips. Had a lovely time with East Island. Will definitely try Vieques tour with them next time I am in San Juan.
Great tour company, especially for Snorkelling
This was a family trip that we all enjoyed, but must of all, I loved the crew, excellent customer service…. constantly taking care of every customer…. Thanks so much from the family Quijada-Morales to: Alexandra, Ismael, Moises & I cant remember the name of the 4th crew member… you all were great & made our experience unforgettable….excellent service…. Keep up with the great service guys, & definitely we will return back to one of your trips on our next vacation to Puerto Rico…. we are from Atlanta, GA…..sm
Unforgettable Trip to Icacos
This is my second time in two years traveling with East Island Excursions – and they really do a great job! You will NOT be disappointed. They are very easy to make reservations with and they call with reminders, The staff is extremely friendly, the boat clean and the overall experience is amazing. There are two stops – one at Icacos Island and another at another site where the coral is. You will see a bunch of beautiful things! And the water is amazingly crystal blue . You’ll arrive around 9am to check in, leave at 9:30am and be back at the dock around 3:30 pm. A great activity for all ages – my family thoroughly enjoyed. They serve you food and rum drinks too! Just an overall great time!

We took 2 tours with East Island–snorkeling and the Amazing Grace. Highly recommend this company. Classy. Everything done well.

Visiting from Chicago. By all means the highlight of our Vacation. Wow, we had the best time. We booked a snorkeling trip to the Island of Icacos Catamaran Full Day trip. The boat was beautiful, the crew was so friendly and helpful! The captain “William” mingled with everyone and took time to make sure everyone was having a great time. The bartender/cook/organizer Chris was very informative and kept everyone’s attention with important information so as to keep everyone safe and having a great time. The food was a delightful surprise. These guys have it down to a science, Excellent food music and ambiance. This is a must do for the entire family. Will definitely do this again! Love these guys!
2017 Puerto Rico Vacay
Amazing trip to the Icacos island. Even thou it was raining we were still able to enjoy the crystal blue water. The captain and crew are really organized and always on the look out for the well being of the people. Thank you to Capt. William, Daniel, Christian, Neftali and others for your excellent customer service. Thanks to your professionalism during the trip me, my best friend and the kids had a superb experience at Icacos.
Trip to Icacos
I was so glad we got to experience snorkeling like this when we were in Puerto Rico. East lsland excursions was a great company to book with. It was an all day adventure and they provide lunch and service unlimited alcoholic drinks. The crew on the boat was great very friendly and knowledge. Our captain was Ty and he did an amazing job informing us about the water, different sea animals and islands that we past. The gear that they provided was clean and looked new, the boat was kept clean as well. I definitely recommend booking a tour through them for a great experience just remember to bring your sunblock and keep reapplying because we got sun burnt.
Snorkeling fun
Great time at Cayo Icacos. Willy was the best snorkeling guide I’ve ever had and I’ve been to every reef in DR. Great job Willy & Carlos. you guys are awesome.

Cayo Icacos
This is by far the most fulfilling activity I did while in PR. This excursion handles everything you need from food, to drinks and location. First stop is snorkeling and the crew were helpful in explaining all safety concerns, for us and the environment. They served us an incredible lunch complete with pina coladas to refresh from the heat. The 2nd stop was a relaxing beach and they gave us ample time to really enjoy the water and take pictures. I would without a doubt book this trip again and can’t wait to visit 🙂

Tour Duration
Minimun Age
Food Aboard
Launch Site
Transportation
- 1113 Shares
- 293122 Views
Thanks for sharing this, you are awesome !

Get Ready to
and enjoy a 'day off on your vacation'
The best Catamaran Private Charter to Isla Mujeres
We're more than your average tour operator. Our distinction lies in our owner, a seasoned French sailor and chef with over 35 years of navigating the Mexican Caribbean. With this wealth of experience, your catamaran adventure becomes unique and guided by a true expert. Our state-of-the-art catamaran offers the ultimate blend of luxury and adventure, ensuring your voyage is nothing short of extraordinary. Be it adventure, relaxation, or exquisite cuisine, our host's expertise guarantees an unforgettable experience. Choose us for a voyage filled with years of dedicated exploration, where you can snorkel in sunken ships, swim in Isla Mujeres' world-famous beaches, paddleboard on crystal-clear waters, or simply enjoy cold drinks on the sun deck. Book your catamaran private charter today and enjoy A DAY OFF ON YOUR VACATION!
Say goodbye to crowded tours and ferry rides – step into a world of exclusivity.
Your own private sailing yacht to isla mujeres.

Our catamarans offer spacious deck areas for you to unwind, sunbathe, or simply enjoy the stunning views. Revel in the elegance of formal interior and exterior dining tables with fine cutlery, ensuring your dining experience is as exceptional as the scenery.
Need a break from the sun? Retreat to the air-conditioned cabin , where you can relax in style. With us, every moment is tailored to your desires, creating memories of a lifetime. Discover the true meaning of a customized, luxurious sailing experience.

Take advantage of our included activities and elevate your Isla Mujeres getaway! Enjoy stand-up paddleboarding, snorkeling at a sunken ship and vibrant coral reefs with complimentary top-tier equipment. Dive into the crystal-clear waters and swim at the world-famous beaches of Isla Mujeres.
Not feeling adventurous? No problem. Stay onboard the catamaran, soak up the sun on the front deck, and savor a cold drink while grooving to your favorite tunes through our all-around Bluetooth sound system. It's the ultimate relaxation—a day off in your vacation.

Premium Meal Plans
Top-notch Snorkeling Gear

Included Paddle Board
Spacious luxury boat.
"I have the simplest of tastes. I am always satisfied with the best"
- Oscar Wilde-
How long is the tour?
The initial fee includes a 4-hour tour. If you wish, you have the option to add extra hours during the checkout process and include them in your total payment.
What to do during the tour?
You'll have a great time sailing through the beautiful blue waters of the Caribbean. You can go snorkeling at a shipwreck, take a swim at the famous Playa Norte beach on Isla Mujeres, and savor a delicious meal with cold drinks on the boat while listening to your favorite music.
What's Included?
- Safety Equipment
- Full Snorkeling Gear
- Stand Up Paddle Boards
- Air Conditioning
- Bluetooth Sound System
- 1 Bottle of Tequila
- 48 Bottles of Beer
- 24 Soft Drinks
- 24 Bottles of Water
- Ceviche or Grilled Fajitas Prepared Fresh
*Upgrade your meal plan to Lobster and wine during check out. (optional)

Check availability and BOOK NOW!

A five-star experience, I must say! Captain Bertrand was an incredible host, a true bon vivant, and an absolute master in the kitchen. We snorkeled, paddleboarded, and swam in stunning locations, far from the crowds. We were even fortunate enough to encounter some tortues sauvages along the way. The boat is in excellent condition, and the crew members are exceptionally accommodating. I highly recommend it if you are seeking a private charter with great value. C'est magnifique!

Our catamaran charter to Isla Mujeres was AWESOME! The boat was big, comfy, and clean. The host was nice and very fun. He took us to beautiful places and let us swim. The food was yummy. I loved it! 5 stars!
Jennifer Reagan
Palm Desert

I recently embarked on a catamaran charter to Isla Mujeres with Captain Bertrand, and I can't say enough about the incredible experience! Celebrating my 60th birthday with friends couldn't have been better. Bertrand's expertise and warm personality made the journey truly memorable. The catamaran was spacious and comfortable, and we enjoyed some fantastic drinks on board. The scenery along the way was breathtaking. I give it a perfect 10/10 and would absolutely recommend this charter to anyone looking for a fantastic adventure. Thanks, Captain Bertrand!
CONTACT INFO
+52 9982421619, [email protected] , useful links.
Catamaran Cancun Tour

Cancun Hotel Zone

- 10:00 hrs
Who is this tour for? Take this tour if…
- You travel with or without minors, families that travel with or without minors
- You travel alone or as a couple and you like to explore and enjoy the beach
- The 10am schedule is perfect for travelers who like to take advantage of the day
- The 10am schedule, you want to return to your hotel before sunset
- The 12pm schedule is perfect for travelers who enjoy sunsets
- The 12pm schedule is perfect for travelers who might want to party or stayed late a night prior
Catamaran Tour Cancun Highlights
- Experience the beauty of the Caribbean Sea on our catamaran sailing tour.
- Easy Check-In: Hassle-free check-in process for a stress-free experience.
- Amenities: Enjoy access to the private Isla Mujeres beach club at Playa Lancheros, featuring showers and lounge chairs.
- Infants under 4 years old ride free
Discover the best of Isla Mujeres as you embark on this memorable sailing journey. Your adventure begins at "El Meco," where you'll snorkel in the crystal clear waters between Isla Mujeres and Cancun. After some time in the Sea, head out to our Beach Club, and enjoy your time here for about 3 hours. If it’s of your interest, you can rent a Golf Cart and enjoy a quick trip through Isla Mujeres
Embark on an epic adventure with our Cancun Catamaran Tour Prepare for a day of sun, sea, and excitement as you immerse yourself in the perfect paradise of the Mexican Caribbean.
Boat Departure
- From Marina Albatros Km 3.5 Hotel Zone next to Hotel Temptation (Our Transportation will take you to this meeting point)
- 10:00 - 11:00 - Departure to Isla Mujeres
- 11:00 - 11:45 - Snorkel Activity at the coral reef
- 12:00 - 13:00 - Downtown sightseeing in Isla Mujeres
- 13:00 - 15:00 - Beach Club and Lunch
- 15:15 - 16: 30 - Sailing back to Cancún and Spinnaker
- 16:30 - 17:00 - Arrival at Marina
- 12:00 - 13:00 - Departure to Isla Mujeres
- 12:00 - 13:45 - Snorkel Activity at the coral reef
- 14:00 - 15:00 - Downtown sightseeing in Isla Mujeres
- 17:15 - 18:30 - Sailing back to Cancún and Spinnaker
- 18:30 - 19:00 - Arrival at Marina
- Open bar on board and beach bar (Rum, Vodka, Tequila, beer, soda, juice, water)
- Lunch buffet. Salad bar, fish ceviche, pasta, soup, pizza, chicken, fish, pork, and dessert
- Spinnaker Activity
- Downtown visit of Isla Mujeres
Not Included
- Dock fee of $20 USD per person What is this?
- Golf car rental
What we recommend you to bring for an exceptional day trip
- Bring flip flops
- Bring your personal towel
- Biodegradable Sun Block
- Credit card is accepted but we recommend some cash to be brought
- Sun glasses
Additional Information
- For greater convenience you can add the transportation service that will pick you up from your hotel and take you to the meeting point and back for $20 (To the Tulum area)
- Please note that this tour is operated by an affiliate partner of Happy Catamarans Cancun.
- Snorkeling and spinnaker activities are subject to weather conditions.
- For the snorkeling activity, guests should know how to swim
- There are no lockers or anywhere in the Catamaran or Beach Club
- Golf cart rental is $35 USD, a drivers license is needed which has to be 18 years old
- Check-in is 45 min before departure time, meeting point is Mini Market & Deli at km 3.5 of Blvd. Kukulkan (hotel zone)
- Vegetarian options are available, please select the option at checkout
- If you require special attention for individuals with reduced mobility please let us know on the checkout form too
Does it includes transportation from my hotel?
No, transportation is not included. You can add transportation from your hotel to the departure point, by easily selecting any of the prompt options to “Add Transportation to Tour” throughout the purchase process. We highly recommend selecting this option as the van pick you at your hotel lobby and transfer you directly to the boat departure point.
Are there any vegetarian options?
The buffet we offer has salads, vegetables, and fruits available. At the moment we do not offer a full vegan or vegetarian menu, but please write down in the comment section if you are vegan, vegetarian, or allergic to any ingredients.
What happens if there is bad weather the day of the tour?
Rain does not affect the tour, all tours will continue as scheduled, however, due to safety issues, the snorkeling activity will be canceled if the weather is too rough to swim. But, If port authorities close the boat's navigation due to strong wind predictions, the tour can be rescheduled or canceled. If canceled due to the port authorities' instructions, customers will be entitled to a full refund.
Do they have a vegan menu at the buffet?
Choose date and passengers
- Adults 12 < Age $85.00 USD 1
- Children 4-11 Age $49.00 USD 0
Still not sure to book your Catamaran Cancun Tour? See what our customers are saying... 5 stars of 5, based on 5 reviews
Jack Wier 5 months ago
This was the best tour during my vacation! Snorkeling coral reefs, exploring Isla Mujeres, and relaxing on the catamaran. Recommend!
Arles Rivera 5 months ago
Stress-free pick-up and return from Cancun made our day trip to Isla Mujeres even better
Geremias Ferreto 1 year ago
The helpful crew ensured a safe and enjoyable catamaran trip to Isla Mujeres. Top-notch service!
Francis Prisse 1 year ago
Right from the start, Happy Catamarans provided exceptional customer service. Our Isla Mujeres trip was truly unforgettable!
Cinthia Humite 10 months ago
Kids loved it! Patient crew, perfect snorkeling & beach fun! ️Memories that will last a lifetime!
- Adults 12 < Age $85.00 USD 0

- Worry-free comfort: By hiring our transportation service, you free yourself from the stress of driving and navigation, allowing you to relax and fully enjoy the tour.
- Take advantage of every moment: Dedicated transportation ensures you arrive at each destination on time, maximizing the time you spend enjoying attractions instead of worrying about logistical details.
- Seamless connection: Avoid the hassle of switching between different modes of public transportation. Our service takes you directly from your location to the tour location, and vice versa, without interruptions.
- Information and personalized guide: Our drivers are familiar with the area and can provide additional information about places of interest, offering a more enriching experience during the journey.
- Security and peace of mind: By relying on our transportation service, you can feel safe and relaxed, knowing that you have a reliable option to get you safely from one place to another.
- Avoid parking problems: Forget about searching for parking and paying expensive fees. With our service, we drop you off and pick up right at your door, eliminating the hassle of finding a parking spot.

IBDP Geography
Website by Paul Christmas
Updated 6 May 2024
InThinking Subject Sites
Subscription websites for IB teachers & their classes
Find out more
- thinkib.net
- IBDP Biology
- IBDP Business Management
- IBDP Chemistry
- IBDP Economics
- IBDP English A Literature
- IBDP English A: Language & Literature
- IBDP English B
- IBDP Environmental Systems & Societies
- IBDP French B
- IBDP German A: Language & Literature
- IBDP History
- IBDP Maths: Analysis & Approaches
- IBDP Maths: Applications & Interpretation
- IBDP Physics
- IBDP Psychology
- IBDP Spanish A
- IBDP Spanish Ab Initio
- IBDP Spanish B
- IBDP Visual Arts
- IBMYP English Language & Literature
- IBMYP Resources
- IBMYP Spanish Language Acquisition
- IB Career-related Programme
- IB School Leadership
Disclaimer : InThinking subject sites are neither endorsed by nor connected with the International Baccalaureate Organisation.
InThinking Subject Sites for IB Teachers and their Classes
Supporting ib educators.
- Comprehensive help & advice on teaching the IB diploma.
- Written by experts with vast subject knowledge.
- Innovative ideas on ATL & pedagogy.
- Detailed guidance on all aspects of assessment.
Developing great materials
- More than 14 million words across 24 sites.
- Masses of ready-to-go resources for the classroom.
- Dynamic links to current affairs & real world issues.
- Updates every week 52 weeks a year.
Integrating student access
- Give your students direct access to relevant site pages.
- Single student login for all of your school’s subscriptions.
- Create reading, writing, discussion, and quiz tasks.
- Monitor student progress & collate in online gradebook.
Meeting schools' needs
- Global reach with more than 200,000 users worldwide.
- Use our materials to create compelling unit plans.
- Save time & effort which you can reinvest elsewhere.
- Consistently good feedback from subscribers.
For information about pricing, click here
Download brochure
See what users are saying about our Subject Sites:
Find out more about our Student Access feature:
- Changing Populations and Places
- P2 SL/HL Core
- Changing Population
This is a link page to sub-pages that provided detailed lesson plans and learning activities that cover everything in the IB guide for this topic. Lesson plans include resources to use on an interactive whiteboard and worksheets to print. The pages have full student access to give maximum flexibility to the teacher and the student. There are theoretical notes for extended reading and teacher notes at the top that provide...
To access the entire contents of this site, you need to log in or subscribe to it.
Alternatively, you can request a one month free trial .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
To be able to use one case study of a contemporary megacity experiencing rapid growth to examine the consequences of megacity growth. Case Study. ... This syllabus point specifically asks you to develop a case study of the growth and impact of one megactiy. Our focus is going to be Shanghai in China.
One case study of a contemporary mega-city experiencing rapid growth. A. Definitions. Urbanisation ... that Jakarta is a megacity experiencing rapid urban growth; that urban sprawl is an issue in Jakarta; This time series of images shows the growth of the city between 1976, when the population was 6 million, and 1989, when the population was 9 ...
possibilities for the successful transition of a megacity towards a Smart City. What future lies ahead for megacities in Europe is discussed lastly in this part by Jerzy Kleer and Katarzyna A. Nawrot. The third part of the volume serves as a diverse set of selected megacity Case Studies. They examine Tokyo — the biggest megacity to date, with
One case study of a contemporary megacity experiencing rapid growth Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free. ... One case study of a contemporary megacity experiencing rapid growth. Share. Terms in this set (6) Background Information
The consequences of megacity growth for individuals and societies. One case study of a contemporary megacity experiencing rapid growth; The causes and consequences of forced migration and internal displacement. Detailed examples of two or more forced movements, to include environmental and political push factors, and consequences for people and ...
Shanghai - a case study of a contemporary megacity experiencing rapid growthby Shukri Abdiker. 1. The consequences of megacity growth for individuals and societies. 1.1. Social. 1.1.1. shortage of public services, including education and medical care. 1.1.2. overcrowded. 1.1.2.1. removals of "urban villages" - low-cost housing generally ...
Interestingly, Tokyo as the world's largest megacity had. a population of nearly 37.4 million in 2020 and was 8.8 million bigger than in 1980. The growth of Tokyo accounted for 34% of total urban population growth. The pace of the growth of megacities is striking with reference to national population growth.
Meanwhile, the physical growth of urban land occurs at an accelerating rate. It represents the megacity growth in China and can be typically used to analyze the response of megacity growth to economic transition. The primary of this paper was to examine the megacity growth in response to economic transition, with a case of Shanghai.
Through 15 in-depth case studies by researchers around the world, this ... discuss, debate, and share ideas about contemporary megacity challenges. Participants were asked to examine contemporary issues at the intersec- ... rapid urbanization in poor countries has meant that key ele-ments of infrastructure, such as water supply, waste removal ...
The consequences of megacity growth for individuals and societies. One case study of a contemporary megacity experiencing rapid growth . The causes and consequences of forced migration and internal displacement. Detailed examples of two or more forced movements, to include environmental and political push factors, and consequences for people ...
The consequences of megacity growth for individuals and societies. One case study of a contemporary megacity experiencing rapid growth. The causes and consequences of forced migration and internal displacement. Detailed examples of two or more forced movements, to include environmental and political push factors, and consequences for people and ...
Studies on urban expansion in megacities are essential for managing urban sprawl to promote high-quality development. In this study, we have selected the emerging megacity of Zhengzhou as the research area, used the spatial analysis method to quantify the spatiotemporal characteristics of urban expansion from 1990 to 2020, and evaluated the rationality of urban expansion on the basis of the ...
The consequences of megacity growth for individuals and societies • One. case study of a contemporary megacity experiencing rapid growth . The causes and consequences of forced migration and internal displacement • Detailed examples of two or more forced movements, to include environmental and political push factors, and consequences for ...
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Two detailed and contrasting examples of uneven population distribution, One case study of a contemporary megacity experiencing rapid growth, Detailed examples of two or more forced movements, to include environmental and political push factors, and consequences for people and places and more.
One case study of a contemporary megacity experiencing rapid growth The causes and consequences of forced migration and internal displacement Detailed examples of two or more forced movements, to include environmental and political push-pull factors , and the consequences for people and places
High natural... that Jakarta is a megacity experiencing rapid urban growth; that urban sprawl is an... The consequences of megacity growth for individuals and societies · One case study of a contemporary megacity experiencing rapid growth · The... Case Study. One case study of a contemporary megacity experiencing rapid growth. Key Terminology.
• One case study of a contemporary megacity experiencing rapid growth "The greatest global demographic challenge is the growth of overpopulated megacities."
Shanghai - A Mega City Case Study Syllabus Link: One case study of a contemporary mega-city experiencing rapid growth Use the handout and resources on to do a case study analysis of the growth of Shanghai: What? give an overview of the case study (discuss Shanghai as a megacity)and it's growth Where? give a specific relative location of Shanghai and show why this has helped it grow When?
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Two detailed and contrasting examples of uneven population distribution, Detailed examples of two or more contrasting countries, One case study of a contemporary megacity experiencing rapid growth and more.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Two detailed and contrasting examples of uneven population distribution., Detailed examples of two or more contrasting countries, One case study of a contemporary megacity experiencing rapid growth and more.
Changing Population. Changing Populations and Places. This is a link page to sub-pages that provided detailed lesson plans and learning activities that cover everything in the IB guide for this topic. Lesson plans include resources to use on an interactive whiteboard and worksheets to print. The pages have full student access to give maximum ...
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Two detailed and contrasting examples of uneven population distribution, One case study of a contemporary megacity experiencing rapid growth, Detailed examples of two or more forced movements, to include environmental and political push factors, and consequences for people and places and more.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like two detailed and contrasting examples of uneven population distribution, detailed examples of 2 or more contrasting countries (demographic transition stages), one case study of a contemporary megacity experiencing rapid growth and more.