

Overleaf for LaTeX Theses & Dissertations: Home
- Using Templates on Overleaf
- Reference Managers and Overleaf
- Adding Tables, Images, and Graphs
Tips and tools for writing your LaTeX thesis or dissertation in Overleaf, including templates, managing references , and getting started guides.
Managing References
BibTeX is a file format used for lists of references for LaTeX documents. Many citation management tools support the ability to export and import lists of references in .bib format. Some reference management tools can generate BibTeX files of your library or folders for use in your LaTeX documents.
LaTeX on Wikibooks has a Bibliography Management page.
Find list of BibTeX styles available on Overleaf here
View a video tutorial on how to include a bibliography using BibTeX here
Collaborate with Overleaf
Collaboration tools
- One version of your project accessible to collaborators via a shared link or email invitation
- Easily select the level of access for collaborators (view, edit, or owner access)
- Real-time commenting speeds up the review process
- Tracked changes and full history view help to see contributions from collaborators
- Labels help to organize and compare different versions
- Chat in real time with collaborators right within the project
How to get started writing your thesis in LaTeX
Writing a thesis or dissertation in LaTeX can be challenging, but the end result is well worth it - nothing looks as good as a LaTeX-produced pdf, and for large documents it's a lot easier than fighting with formatting and cross-referencing in MS Word. Review this video from Overleaf to help you get started writing your thesis in LaTeX, using a standard thesis template from the Overleaf Gallery .
You can upload your own thesis template to the Overleaf Gallery if your university provides a set of LaTeX template files or you may find your university's thesis template already in the Overleaf Gallery.
This video assumes you've used LaTeX before and are familiar with the standard commands (see our other tutorial videos if not), and focuses on how to work with a large project split over multiple files.
Add Institutional Library contact info here.
Contact Overleaf or email [email protected]
5-part Guide on How to Write a Thesis in LaTeX
5-part LaTeX Thesis Writing Guide
Part 1: Basic Structure corresponding video
Part 2: Page Layout corresponding video
Part 3: Figures, Subfigures and Tables corresponding video
Part 4: Bibliographies with Biblatex corresponding video
Part 5: Customizing Your Title Page and Abstract corresponding video
ShareLaTeX Joins Overleaf!
Read more about Overleaf and ShareLaTeX joining forces here
Link your ORCiD ID
Link your ORCiD account to your Overleaf account.
See Overleaf news on our blog.
- Next: Using Templates on Overleaf >>
- Last Updated: May 18, 2021 1:57 PM
- URL: https://overleaf.libguides.com/Thesis

Overleaf for Scholarly Writing & Publication: LaTeX Theses and Dissertations
- Reference Managers and Overleaf
- Adding Graphs, Tables, and Images
- Using Templates on Overleaf
- LaTeX Theses and Dissertations
LaTeX Theses and Dissertatons
Tips and tools for writing your LaTeX thesis or dissertation in Overleaf, including templates, managing references , and getting started guides.
Managing References
BibTeX is a file format used for lists of references for LaTeX documents. Many citation management tools support the ability to export and import lists of references in .bib format. Some reference management tools can generate BibTeX files of your library or folders for use in your LaTeX documents.
LaTeX on Wikibooks has a Bibliography Management page.
Find list of BibTeX styles available on Overleaf here
View a video tutorial on how to include a bibliography using BibTeX here
Collaborate with Overleaf
Collaboration tools
Every project you create has a secret link. Just send it to your co-authors, and they can review, comment and edit. Overleaf synchronizes changes from all authors, so everyone always has the latest version. More advanced tools include protected projects and integration with Git.
Collaborate online and offline with Overleaf and Git
Protected projects with Overleaf Pro
Getting Started with Your Thesis or Dissertation
How to get started writing your thesis in LaTeX
Writing a thesis or dissertation in LaTeX can be challenging, but the end result is well worth it - nothing looks as good as a LaTeX-produced pdf, and for large documents it's a lot easier than fighting with formatting and cross-referencing in MS Word. Review this video from Overleaf to help you get started writing your thesis in LaTeX, using a standard thesis template from the Overleaf Gallery .
You can upload your own thesis template to the Overleaf Gallery if your university provides a set of LaTeX template files or you may find your university's thesis template already in the Overleaf Gallery.
This video assumes you've used LaTeX before and are familiar with the standard commands (see our other tutorial videos if not), and focuses on how to work with a large project split over multiple files.
How to Write your Thesis/Dissertation in LaTeX: A Five-Part Guide
Five-Part LaTeX Thesis/Dissertation Writing Guide
Part 1: Basic Structure corresponding video
Part 2: Page Layout corresponding video
Part 3: Figures, Subfigures and Tables corresponding video
Part 4: Bibliographies with Biblatex corresponding video
Part 5: Customizing Your Title Page and Abstract corresponding video
Link Your ORCID
Link yo ur ORCiD account to your Overleaf account via the ORCID @ CMU Portal
Open Knowledge Librarian

- << Previous: Using Templates on Overleaf
- Last Updated: Oct 4, 2023 9:31 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.cmu.edu/overleaf

- Future Students
- Parents and Families
College of Engineering
- Research and Facilities
- Departments
Guide to Writing Your Thesis in LaTeX
The bibliography and list of references.
The Graduate School requires a Bibliography which includes all the literature cited for the complete thesis or dissertation. Quoting from the Graduate School’s Guidelines for the Format of Theses and Dissertations :
“Every thesis in Standard Format must contain a Bibliography which lists all the sources used or consulted in writing the entire thesis and is placed at the very end of the work. The complete citations are arranged alphabetically by last name of the author. Individual citations are not numbered. No abbreviations in titles of published works will be accepted. The full title of a book, journal, website, proceedings, or any other published work must be italicized or underlined. Citations must follow standards set by the style manual that the student is using. The bibliography for URI theses is not broken into categories.”
The List of References is not required by the Graduate School, but is the style commonly used in Engineering, Mathematics, and many of the Sciences. It consists of a numbered list of the sources used or consulted in writing the thesis in the order that they are referenced in the text. There can be either one List of References for the entire thesis, or a List of References at the end of each chapter.
Both the Bibliography and the List of References will be generated by the urithesis LaTeX class. All you need to do is add information about your sources to the references.bib file, which is a database containing all of the necessary information about the references, then cite the reference in your thesis using the \cite{} command.
Generating the Bibliography and References
The bibliography and list of references are generated by running BibTeX. To generate the bibliography, load the file thesisbib.tex into your editor, then run BibTeX on it.
If each chapter has its own list of references, you will need to run BibTeX on each chapter to update its list of references. If there is one list of references for the whole thesis (because you used the oneref option, you will only need to run BibTeX on the top level file thesis.tex .
How to Add a Bibliography Entry
When we want to refer to a source in the thesis, we place an entry for that source in the file references.bib , then cite the source in the thesis with the \cite{LABEL} command. The syntax for an entry in the references.bib file is of the form:
ENTRYTYPE is the type of bibliographic entry such as Book , Article , or TechReport , that this entry describes. At the end of this page is a list of all possible entry types .
LABEL is a unique string that is used to refer to this entry in the body of the thesis when using the \cite{LABEL} command.
The FIELDNAMEn entries are the fields that describe this entry, (ie. author, title, pages, year, etc.). Each entry type has certain required fields and optional fields. See the list of all entry types for a description of the available fields.
As an example, suppose we have a paper from a conference proceedings that we want to cite. First we make an entry in the our references.bib file of the form:
We then cite this source in the text of our thesis with the command \cite{re:toolan:as03} . This will generate a Bibliography entry that looks something like:
and a List of References entry that looks something like:
Types of List of References
The Graduate School requires that the bibliography is always at the end of the thesis and sorted alphabetically by author, therefore there is no options that affect it. The list of references is optional, therefore there are a few different ways that it can created.
By default a separate list of references appears at the end of each chapter, and are sorted by the order that they are cited in that chapter. The option oneref (see options ) will create a single list of references for the whole thesis, which due to the requirements of the Graduate School, will appear after the last chapter and before any appendices.
The option aparefs will cite references using the APA style, which is the last name of the author and year of publication, such as (Toolan, 2006), instead of the default IEEE style, which is a number, such as [1]. This option will also sort the references alphabetically by author, instead of in order of citation. The options oneref and aparefs can be used together to create a single list of references using the APA style.
Supported Bibliography Entry Types
The following is a list of all the entry types that can be used. Click on the desired type to see a detailed description of how to use that type.
- Article – An article from a journal or magazine
- Book – A book with an explicit publisher
- InBook – A part of a book, such as a chapter or selected page(s)
- InCollection – A part of a book having its own title
- Booklet – Printed and bound works that are not formally published
- Manual – Technical documentation
- InProceedings – An article in a conference proceedings
- Proceedings – The entire proceedings of a conference
- MastersThesis – A Master’s thesis
- PhDThesis – A Ph.D. dissertation
- TechReport – A report published by a school or other institution
- Unpublished – A document that has not been formally published
- Electronic – An internet reference like a web page
- Patent – A patent or patent application
- Periodical – A magazine or journal
- Standard – Formally published standard
- Misc – For use when nothing else fits
Articles that have not yet been published can be handled as a misc type with a note. Sometimes it is desirable to put extra information into the month field such as the day, or additional months. This is accomplished by using the BIBTEX concatenation operator “#“:
Example .bib using this type:
Books may have authors, editors or both. Example .bib using this type:
Inbook is used to reference a part of a book, such as a chapter or selected page(s). The type field can be used to override the word chapter (for which IEEE uses the abbreviation “ch.”) when the book uses parts, sections, etc., instead of chapters
Incollection is used to reference part of a book having its own title. Like book , incollection supports the series, chapter and pages fields. Also, the type field can be used to override the word chapter.
Booklet is used for printed and bound works that are not formally published. A primary difference between booklet and unpublished is that the former is/was distributed by some means. Booklet is rarely used in bibliographies.
Technical documentation is handled by the manual entry type.
References of papers in conference proceedings are handled by the inproceedings or conference entry type. These two types are functionally identical and can be used interchangeably. Example .bib using this type:
It is rare to need to reference an entire conference proceedings, but, if necessary, the proceedings entry type can be used to do so.
Master’s (or minor) theses can be handled with the mastersthesis entry type. The optional type field can be used to override the words “Master’s thesis” if a different designation is desired:
The phdthesis entry type is used for Ph.D. dissertations (major theses). Like mastersthesis , the type field can be used to override the default designation. Example .bib using this type:
Techreport is used for technical reports. The optional type field can be used to override the default designation “Tech. Rep.” Example .bib using this type:
The unpublished entry type is used for documents that have not been formally published. IEEE typically just uses “unpublished” for the required note field.
The electronic entry type is for internet references. IEEE formats electronic references differently by not using italics or quotes and separating fields with periods rather than commas. Also, the date is enclosed within parentheses and is placed closer to the title. This is probably done to emphasize that electronic references may not remain valid on the rapidly changing internet. Note also the liberal use of the howpublished field to describe the form or category of the entries. The organization and address fields may also be used. Example .bib using this type:
The nationality field provides a means to handle patents from different countries
The nationality should be capitalized. The assignee and address (of the assignee) fields are not used, however, they are provided. The type field provides a way to override the “patent” description with other patent related descriptions such as “patent application” or “patent request”:
The periodical entry type is used for journals and magazines.
The standard entry type is used for formally published standards. Alternatively, the misc entry type, along with its howpublished field, can be used to create references of standards.
Misc is the most flexible type and can be used when none of the other entry types are applicable. The howpublished field can be used to describe what exactly (or in what form) the reference is (or appears as). Possible applications include technical-report-like entries that lack an institution, white papers and data sheets.
Additional Comments
Because we are effectively creating multiple bibliographies, (one for the actual bibliography, and one for each list of references), the two LATEX commands \bibliographystyle{} and \bibliography{} are not used. They have been redefined to do nothing, and the equivalent of these commands are done automatically when necessary.
When there is a reference that should be included in the bibliography, but does not need to be explicitly referenced in the thesis, use the \nocite{} command. This command works like the \cite{} command, except it does not put the citation in the list of references, only in the bibliography. The \nocite{} command must appear after the first \newchapter{} command, or it will be ignored.
When using the option aparefs , and a citation does not have an author, (such as often occurs with a web page), the key field can be used to specify what to use in the citation instead of the author’s name.
About the Bibliography Format
The bibliography format used by the urithesis class is based on the IEEE format. See the article “How to Use the IEEEtran BIBTEX Style” by Michael Shell for more details.
Guide to BibTeX Type PhdThesis
BibTeX is a reference management tool that is commonly used in LaTeX documents. The “phdthesis” BibTeX type is used for PhD dissertations or theses. In this guide, we will explain the required and optional fields for the “phdthesis” BibTeX type.
Need a simple solution for managing your BibTeX entries? Explore CiteDrive!
- Web-based, modern reference management
- Collaborate and share with fellow researchers
- Integration with Overleaf
- Comprehensive BibTeX/BibLaTeX support
- Save articles and websites directly from your browser
- Search for new articles from a database of tens of millions of references
Required Fields
The “phdthesis” BibTeX type requires the following fields:
- author : The author of the thesis.
- title : The title of the thesis.
- school : The name of the institution that awarded the degree.
- year : The year the degree was awarded.
Optional Fields
In addition to the required fields, the “phdthesis” BibTeX type also has a number of optional fields that can be used to provide additional information. These fields include:
- type : The type of the thesis, such as “PhD thesis” or “Master’s thesis”.
- address : The location of the institution.
- month : The month the thesis was submitted.
- note : Any additional information about the thesis.
Here is an example of how to use the “phdthesis” BibTeX type:
In this example, the BibTeX entry defines a PhD thesis authored by John Smith titled “An Analysis of Example”. The degree was awarded in 2022 by the University of Example, and the thesis was submitted in June in Example City, CA. The type of the thesis is specified as “PhD thesis”, and a note is included that provides a URL for the thesis.
LaTeX Resources for Graduate Students: Formatting of theses and dissertations
- BibTeX reference format
- BibTeX command
- LaTeX bibliography file
- LaTeX editors and compilers
- Sample LaTeX file with bibliography
- Sample LaTeX file without bibliography
- Formatting of theses and dissertations
Formatting and structure
The Cornell Graduate School has become increasingly flexible about the formatting of theses and dissertations. There now are only seven core requirements . For the structure of theses and dissertations here is a list of required and recommended sections .
Latex template
Among the available thesis and dissertation templates provided by the Graduate School is also a LaTeX template (ZIP archive). This template has been uploaded to Overleaf and placed in the Cornell template directory . This template contains a small fix to avoid an error message about \ifpdf .
- << Previous: Sample LaTeX file without bibliography
- Last Updated: Oct 25, 2022 5:12 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.cornell.edu/latex
- CV & Media Features
- Spaceflight Research
- Aging and Mobility Research
- ADHD Research
- My Teaching Philosophy
- YouTube Channel
- Selected Course Materials
Adding and formatting citations for your UF dissertation (using Overleaf / LaTex)
Picking my format.
First off, forgive me in general if I’m using any of the terms here incorrectly. My only goal in these dissertation posts is to chronicle *one* way that *works* for formatting a University of Florida dissertation using LaTex (instead of Microsoft Word). As described previously , I’m using the UF Overleaf template for formatting my dissertation. In this post, I’ll discuss the way that I formatted my bibliography.
First off, I needed to decide how to format my references. UF requires that you submit a journal article that you used as a model when formatting your references:
So, I used Frontiers formatting as a model for several reasons:
- First, I have several papers in Frontiers journals already, and so I am familiar with their formatting. Also, this means I can just submit one of my previous papers as the ‘model paper’ to UF.
- Second, I plan to submit at least 1-2 of the papers in my dissertation to Frontiers journals, so it’s useful to already have the intended citation formatting going.
- Third, Frontiers has, in my opinion, a nice in-text (author, date) format, and a nice APA-like reference list format.
- Fourth, and most importantly, I knew off-the-bat that Frontiers has LaTex templates . This was critical. This means I didn’t have to do any extra digging to figure out how to set up a Frontiers-style bibliography formatting file. I could just download the relevant Frontiers files from their website. While these did end up needing a tiny bit of tweaking, this was much easier than starting from scratch, or editing other style files more significantly.
So, I decided to use my paper ( Hupfeld et al., 2020; Front. Syst. Neurosc i ) as the model paper. Here are a few example article citations from my paper:
The few big take-aways of this formatting : -Uses et al. if >6 authors -Spells out the word “and” instead of “&” sign for linking the last two authors -Abbreviates journal names -Includes the DOI
Thus, when setting up my LaTex bibliography, I made sure that the resulting formatting identically matched each of these points. You can also see here for more specifics from Frontiers regarding their reference list style.
Inputting references into your LaTex bibliography on Overleaf
Next, I hopped back to my dissertation Overleaf file, and spent a bit of time teasing out the documentation regarding reference lists. I started by understanding which file(s) I would need to input my actual references.
First off, there was a file included in my Overleaf package called bibliography.tex . You can delete this file . This is an old file that does references differently, as explained in the header comment. It is not needed for proceeding. (I verified this by changing its name; my PDF still compiles in the identical way, with no new errors with or without this file.)
Then, head to sample.bib . This is your bibliography file. It already contains some examples of how you should input bibliography information for each reference. Although note that here, I’ve also inputted a DOI line because this will be required for my Frontiers-style formatting.
This is where you’ll continue to add more and more references as you write your dissertation. Note that you don’t need to manually type out these things. If you find a paper on Google Scholar, simply hit the quote button to pull up citation options, followed by the BibTex button .
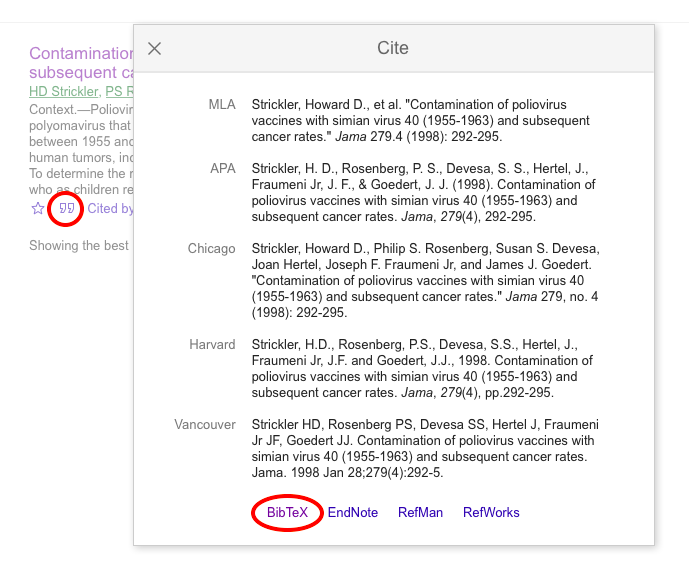
Clicking BibTex will route you to a page with only the relevant information, already formatted as you will need it:
However, do note that this Google Scholar BibTex formatting doesn’t seem to include DOI. Thus, if you’re using a reference style that needs DOI, you may have to grab that on your own, or using a BibTex formatting link from the journal’s website instead of Google Scholar. I’ll update if I find a more efficient way to grab DOIs.
This is essentially it, then, for adding references to your Overleaf file to be able to cite them. Head to sample.bib (though you could rename this file whatever you’d like). Copy-paste in a BibTex-style reference from Google Scholar. Repeat this for all of your citations. Again, will update if I specifically implement a more efficient way to do this (e.g., if you’ve previously worked on a paper in LaTex, you can just copy-paste or copy in that BibTex-style bibliography; there’s also likely ways to export other papers’ bibliographies in BibTex format, though I haven’t played with that yet).
Also, do note that you may want to manually edit several things in your BibTex citations:
- Journal name formatting : you’re probably going to just want to manually edit the journal name if it doesn’t already contain the capitalization you want, or the name abbreviation you want.
- DOI : as stated previously, if using a format with DOI, you’re probably going to need to add that yourself if pulling your BibTex citations from Google Scholar.
Downloading and setting up the *.bst file
Now comes the ‘fun’ part of figuring out how to get your reference list inserted into your Overleaf file properly.
First, you’ll need a reference formatting file, called a *.bst file . The UF Overleaf template already came with a few of these (see the bst folder in your Overleaf project). However, (as described in their comments in the main.tex file), you’ll want one specific to your model journal article.
So, heeding their advice, I headed to the Frontiers website and downloaded their LaTex template folder.
This folder contained exactly what I was looking for — a Frontiers *.bst file . Specifically, I decided to use the frontiersinSCNS_ENG_HUMS.bst to match my model journal article (“ For articles in Science, Engineering and Humanities and Social Sciences domains “).
Next, I simply made a blank file in the bst folder of my Overleaf project, called frontiersinSCNS_ENG_HUMS.bst. In this file, I just copy-pasted in the entirety of the content in the frontiersinSCNS_ENG_HUMS.bst file from the Frontiers LaTex template folder.

Then, I uncommented this *.bst file in my main.tex file, to let my project know that I wanted to use this formatting, instead of the other available formatting options.
Calling your reference list in your dissertation file
Now, the test! We have the reference list (*.bib) and formatting (*.bst) all set up — but we still need to integrate this all into the actual dissertation file, so that both the in-text references and the reference list show up as we expect.
First, call your *.bib file in main.tex . I renamed sample.bib to ref_list.bib, so I need to call ref_list in my main.tex file.
This should now populate a reference list at the end of your document. In my case, I still had the template’s introduction, which contains a few references, so these now populate — in Frontiers format — in my reference list at the end of my document.
To add new citations in-text, see your *.bst file. (At least this was the case for the file I downloaded from Frontiers — they spelled out everything very nicely for me within the *.bst file.)
After reviewing it, for me, I’ll probably primarily use two of these options for calling my references in-text: \citep and \citet. For example:
This yields the intended output:

Note as well the ‘key’ you need to call the article. This is the first line of your BibTex file (e.g., strickler1998contamination). I think of this as a nickname for each article. You can change them to be whatever you’d like after you grab the BibTex citation for each reference. I’m calling each reference something that makes sense to me personally, which makes for super easy citing as I work through all of my writing.
Finally, if you want to cite more than one article , you just need a comma between the calls for the 2+ citations:
Tweaking your *.bst formatting
Lastly, in checking how my reference list matched up with my model article, I noticed two (small) differences I wanted to fix.

First, my model article has a space between the colon following ‘doi’ and the start of the doi. My outputted reference did not. Second, for some reason the doi was written in a different font than the rest of the citation, which looked sloppy.
Both of these were easy fixes after I probed a little. I went into my *.bst file to the doi formatting lines, which start at line 1538 in my file. To fix the first issue, I just added a space between doi: and \discretionary…, as shown below.
To fix the second issue, I had to play a bit more. Ultimately what worked was described in this tex Stack Exchange post . I just had to change \urlstyle{rm} to \urlstyle{sf} in line 1541. Thus, my updated *.bst file code looked like this:
And my fixed citation in my reference list looked like this:

This reference now nicely matches those examples at the top of the page from my Frontiers paper; for instance, here is a screenshot of a reference from my model paper:
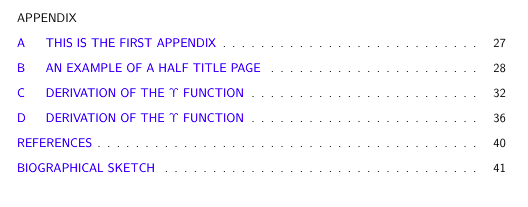
Adding your reference list to the table of contents
In my version of the UF LaTex dissertation template, their call to add ‘references’ to the table of contents didn’t appear to work. At least when I compile their template, the reference list (which comes after everything else, but before the biosketch) is not listed:

Exploring the *.cls file, they tried to add the reference list to the TOC, but this approach does not work for the BibTex reference list (whereas this line does work for other ‘extra chapter’ sections like the biosketch, where we want them in the TOC, but we don’t want to assign them a chapter number). My guess is that this did work for the previous iteration of the template where they note that BibTex wasn’t used, and they do note that BibTex integration isn’t complete in this template, so that’s fair that it’s not working at 100% here. Here’s how they tried to pipe in the reference list to the TOC as an extra chapter:
This took a decent bit of Googling and playing around, but here’s a fix that worked for me. No promises that this is the “most correct” fix, but it worked, which was my sole goal. In main.tex , I added the following two lines before the bibliography call:
I also commented out the above line in the *.cls file, although this doesn’t seem to make a difference in the compiled file. Note that this only worked when I put these two lines in the main.tex file, but not if I added them into the *.cls file instead. Also note that I edited the StackExchange code to say ‘extrachapter’ instead of ‘chapter’ because I didn’t want the reference list to be a numbered chapter.
That’s all for now! Will update if any other tips or fixes I encounter as I continue working on my dissertation.
Categories:
- Dissertation Writing
- Fellowships
- Google Apps
- Manuscript Prep
- Neuroimaging
- NIH F99/K00

Overleaf - LaTeX: Bibliographies and Citing
- Getting Started
- Creating a LaTeX Document in Overleaf
- Structuring and Formatting
- Lists, Tables, Images, and Labelling
- Mathematics in LaTeX
- Bibliographies and Citing
- Books and Dissertations
- Submitting from Overleaf
Bibliographies in LaTeX
In order to cite references, you first need to create a separate bibliography file ending with a .bib extension within your LaTeX project. You can do that by clicking on the New File icon on the upper-left corner of the screen.

Then, enter your file name. Note that the default file extension in LaTeX is .tex. Your bibliography file must end in .bib. Once you create your file, you can add references to it in the BibTeX format.
Exporting references from ProQuest RefWorks
If you use RefWorks to manage your references, you can export your references from RefWorks into the BibTeX format. To export your references from RefWorks, click on the Share tab. Then, click on Export References and select the BibTeX option. You can import the references you exported from RefWorks into LaTeX as a .bib file.
To learn more about RefWorks, visit the RefWorks e-course module .
Exporting references from a database or Google Scholar
The easiest way to add references to your .bib file, other than exporting them from RefWorks, is to import or copy them directly from Google Scholar or from a database. To cite from Google Scholar, click on the cite icon underneath the article, which is represented with a quotation sign. Select the option BibTeX at the bottom of the pop-up screen. You will be directed to another page where you can copy the reference in the BibTeX format. Make sure to check that the relevant fields are entered correctly before copying the reference into your .bib file.
Note that Google Scholar does not include a DOI, which is often needed as part of your reference.
Some databases also provide the option to export a reference in the BibTeX format. The way to export a reference from a database can vary depending on the database being used.
Note: Not all databases allow you to export citation information in the BibTeX format. To work around this, use RefWorks to manage your references which you can then export in the BibTeX format.
Entering references manually
When entering a reference to BibTeX, the fields that are required to be filled in for each citation will vary depending on the type of the work you are citing. The reference type is specified by using the @ symbol followed by the type. Regardless of the reference type, the first field to be entered in the reference is the label that you want to give to a particular reference. You will later be able to use this label to cite the reference in the main text of the document.
Below is an example of the fields you are required to enter for articles.
Here's another example illustrating the fields required for a Ph.D. thesis.
Visit the page on standard templates for BibTeX to see how other types of works can be included.

Citing in LaTeX
To begin citing sources within your LaTeX document, you can use the biblatex package. Add \usepackage { biblatex } to your preamble. Note that there are other packages that you could use for this, including the natbib package, which is also a popular option.
There are a number of specifications you can enter to the \usepackage { biblatex } command. The first specification you should add within the square brackets of the command is backend = biber . Biber provides the relevant information needed to implement the biblatex package.
You can also specify the style of your bibliography by using the style parameter. For instance, style=authoryear will print your references in the author-year format. Another common variant is style=authoryear-comp , which will only print the author's last name once, and not for the subsequent references. Visit the page on biblatex's citation styles for a full list.
Using biblatex, you can also determine what criteria should be used to sort your bibliography by specifying the sorting parameter. For instance, sorting=nyt will sort your bibliography by name, title, and year. The end result of specifying these parameters may look something like this:
To be able to cite the references from your bibliography, you will need to implement a command mapping your BibTeX file to your document. To do that, you can use the \addbibresource {..} command and add your file name in between the curly brackets.
There are many options to call and format your in-text citations in LaTeX. Below is a list of common commands you can use with the corresponding output. For instance, the command \parencite {JonesandSmith1997} will result in (Jones and Smith 1997) in the pdf.
Adding the \printbibliography command at the end of the document will instruct LaTeX to print your references.
- << Previous: Mathematics in LaTeX
- Next: Books and Dissertations >>
- Last Updated: Mar 14, 2022 9:28 AM
- URL: https://libguides.eur.nl/overleaf
Keine Suchergebnisse
How to Write a Thesis in LaTeX (Part 4): Bibliographies with BibLaTeX
Part 1 | Part 2 | Part 3 | Part 4 | Part 5
Author: Josh Cassidy (August 2013)
This five-part series of articles uses a combination of video and textual descriptions to teach the basics of writing a thesis using LaTeX. These tutorials were first published on the original ShareLateX blog site during August 2013; consequently, today's editor interface (Overleaf) has changed considerably due to the development of ShareLaTeX and the subsequent merger of ShareLaTeX and Overleaf. However, much of the content is still relevant and teaches you some basic LaTeX—skills and expertise that will apply across all platforms.
In the previous post we looked at using images and tables in our thesis. In this post we are going to look at adding a bibliography to our thesis. To do this we are going to use the biblatex package . This involves creating a list of sources in a separate file called a .bib file.
The Bib File
When we create this file we need to choose a name for it and save it as a .bib file rather than a .tex file.

Now every time we need to reference a source we can cite it in the text and then fill in the source details in the .bib file. First we'll look at filling in our .bib file and then we'll move on to discussing citations. To add a new entry to our .bib file we need to first tell BibLaTeX what type of source we are referencing. We do this using an @ symbol followed immediately by the source type.
Then comes an opening curly bracket and a citation key of our choice followed by a comma. We then need to tell it all the details it wants for that particular type of source. We do this using a list of keywords each followed by an equals sign and the corresponding information in curly brackets. Items in the list are separated by commas. Each recognised source type has a list of required details which we must provide. But we'll often want to give more details. For example, for an article entry we need to use the author , title , journaltitle and year or date keywords. For an online source we need to use the author or editor , title , year or date and url keywords, and finally for a book it's the author , title and year or date keywords. Here's an example of what they might look like filled-in:
All of the information about the recognised source types and all the keywords you can use can be found in the biblatex documentation .
Now let's return to the main .tex file. To set it up for a bibliography we need to load up the biblatex package using the \usepackage command. Also in the preamble we need to specify which .bib files we want to use by calling the \addbibresource command and entering the file name in the curly brackets including the .bib extension.
Now let's look at citations. To cite a source in the text we use one of the biblatex citation commands. The simplest is the \cite command which prints the citation without any brackets unless you are using the numeric or alphabetic styles. We'll discuss styles a little later on. For example we may cite a source in the text like this:
Another one is the \parencite command which prints citations in parentheses except when using the numeric or alphabetic styles when it uses square brackets. There are more citation commands available to you which again can be found in the biblatex documentation .
The citation commands in biblatex also give us the option of adding a prenote and postnote in as arguments:
- a prenote is a word or phrase like "see" that is inserted at the start of the citation;
- a postnote is text you want inserted at the end of the citation.
To add these notes in you uses two sets of square brackets in the citation command. If you only open one set of square brackets it will assume the contents of the brackets is a postnote , so if you only want a prenote make sure you still open the second set of square brackets and then just leave them empty. Here are some examples:
Now to actually get the bibliography printed in our thesis we use the \printbibliography command at the end of the document. By default the bibliography and citations use the numeric style which looks like this:

To change the style we pass more arguments into the \usepackage command in square brackets. For example this specifies the alphabetic style:
Which looks like this:

And this is the authoryear style:

Another thing we can change here is the way the bibliography is ordered. For example this sorts entries by year , name , title :
While this doesn't sort them at all but displays them in the order they are cited.
More information about the numerous styles and sorting options available can be found in the biblatex documentation . This concludes our discussion on adding a bibliography. In the final post of this series we'll look at customising some of the opening pages.
All articles in this series
- Part 1: Basic Structure ;
- Part 2: Page Layout ;
- Part 3: Figures, Subfigures and Tables ;
- Part 4: Bibliographies with BibLaTeX ;
- Part 5: Customising Your Title Page and Abstract .
- Documentation Home
- Learn LaTeX in 30 minutes
Overleaf guides
- Creating a document in Overleaf
- Uploading a project
- Copying a project
- Creating a project from a template
- Using the Overleaf project menu
- Including images in Overleaf
- Exporting your work from Overleaf
- Working offline in Overleaf
- Using Track Changes in Overleaf
- Using bibliographies in Overleaf
- Sharing your work with others
- Using the History feature
- Debugging Compilation timeout errors
- How-to guides
- Guide to Overleaf’s premium features
LaTeX Basics
- Creating your first LaTeX document
- Choosing a LaTeX Compiler
- Paragraphs and new lines
- Bold, italics and underlining
Mathematics
- Mathematical expressions
- Subscripts and superscripts
- Brackets and Parentheses
- Fractions and Binomials
- Aligning equations
- Spacing in math mode
- Integrals, sums and limits
- Display style in math mode
- List of Greek letters and math symbols
- Mathematical fonts
- Using the Symbol Palette in Overleaf
Figures and tables
- Inserting Images
- Positioning Images and Tables
- Lists of Tables and Figures
- Drawing Diagrams Directly in LaTeX
- TikZ package
References and Citations
- Bibliography management with bibtex
- Bibliography management with natbib
- Bibliography management with biblatex
- Bibtex bibliography styles
- Natbib bibliography styles
- Natbib citation styles
- Biblatex bibliography styles
- Biblatex citation styles
- Multilingual typesetting on Overleaf using polyglossia and fontspec
- Multilingual typesetting on Overleaf using babel and fontspec
- International language support
- Quotations and quotation marks
Document structure
- Sections and chapters
- Table of contents
- Cross referencing sections, equations and floats
- Nomenclatures
- Management in a large project
- Multi-file LaTeX projects
- Lengths in L a T e X
- Headers and footers
- Page numbering
- Paragraph formatting
- Line breaks and blank spaces
- Text alignment
- Page size and margins
- Single sided and double sided documents
- Multiple columns
- Code listing
- Code Highlighting with minted
- Using colours in LaTeX
- Margin notes
- Font sizes, families, and styles
- Font typefaces
- Supporting modern fonts with X Ǝ L a T e X
Presentations
- Environments
Field specific
- Theorems and proofs
- Chemistry formulae
- Feynman diagrams
- Molecular orbital diagrams
- Chess notation
- Knitting patterns
- CircuiTikz package
- Pgfplots package
- Typesetting exams in LaTeX
- Attribute Value Matrices
Class files
- Understanding packages and class files
- List of packages and class files
- Writing your own package
- Writing your own class
Advanced TeX/LaTeX
- In-depth technical articles on TeX/LaTeX
Kontaktiere uns
Hast du dir schon Wissensdatenbank angeschaut?
Anforderung gesendet, danke.
No Search Results
How to Write a Thesis in LaTeX (Part 1): Basic Structure
Part 1 | Part 2 | Part 3 | Part 4 | Part 5
Author: Josh Cassidy (August 2013)
This five-part series of articles uses a combination of video and textual descriptions to teach the basics of writing a thesis using LaTeX. These tutorials were first published on the original ShareLateX blog site during August 2013; consequently, today's editor interface (Overleaf) has changed considerably due to the development of ShareLaTeX and the subsequent merger of ShareLaTeX and Overleaf. However, much of the content is still relevant and teaches you some basic LaTeX—skills and expertise that will apply across all platforms.
Your thesis could be the longest and most complicated document you'll ever write, which is why it's such a good idea to use L a T e X instead of a common word processor. L a T e X makes tasks that are difficult and awkward in word processors, far simpler.
When writing something like a thesis its worth splitting up the document into multiple .tex files. It's also wise to organise the project using folders; therefore, we'll create two new folders, one for all the images used in the project and one for all the .tex files making up the main body of the thesis.

- 1 The preamble
- 2 The frontmatter
- 3 The main body
- 4 The endmatter
- 5 All articles in this series
The preamble
In this example, the main.tex file is the root document and is the .tex file that will draw the whole document together. The first thing we need to choose is a document class. The article class isn't designed for writing long documents (such as a thesis) so we'll choose the report class, but we could also choose the book class.
We can also change the font size by adding square brackets into the \documentclass command and specifying the size—we'll choose 12pt. Let's also prepare the document for images by loading the graphicx package. We'll also need to tell L a T e X where to look for the images using the \graphicspath command, as we're storing them in a separate folder.
The start of our preamble now looks like this:
Now we can finish off the preamble by filling in the title, author and date information. To create the simplest title page we can add the thesis title, institution name and institution logo all into the \title command; for example:
This isn't the best way to alter the title page so we'll look at more elaborate ways of customising title pages later on in the series, but this will suffice for now.
This is what the \maketitle command now produces for us:

The frontmatter
After the title page we need to add in an abstract, dedication, declaration and acknowledgements section. We can add each of these in on separate pages using unnumbered chapters. To do this we use the \chapter command and add an asterisk. After these sections we'll add a table of contents using the \tableofcontents command:
The main body
Now for the main body of the document. In this example we will add-in five chapters, one of which will be an introduction and another will be a conclusion. However, instead of just composing these chapters in the main .tex file, we'll create a separate .tex file for each chapter in the chapters folder. We can then fill in these chapters with text remembering to split them up into sections and subsections.

Then to add these chapters into the document, we use the \input command in the root document. Remember to add in chapters/ before the file name so that L a T e X knows where to find it.
The endmatter
We will now add in an appendix at the end of the document. To do this we use the \appendix command to tell L a T e X that what follows are appendices. Again We'll write the appendix in a separate file and then input it.
If we now compile the document, all our chapters will be added to the document and the table of contents will be automatically generated.

Now we have a basic structure for a thesis set up. In the next post I will show you how to change the page layout and add headers.
All articles in this series
- Part 1: Basic Structure ;
- Part 2: Page Layout ;
- Part 3: Figures, Subfigures and Tables ;
- Part 4: Bibliographies with BibLaTeX ;
- Part 5: Customising Your Title Page and Abstract .
- Documentation Home
- Learn LaTeX in 30 minutes
Overleaf guides
- Creating a document in Overleaf
- Uploading a project
- Copying a project
- Creating a project from a template
- Using the Overleaf project menu
- Including images in Overleaf
- Exporting your work from Overleaf
- Working offline in Overleaf
- Using Track Changes in Overleaf
- Using bibliographies in Overleaf
- Sharing your work with others
- Using the History feature
- Debugging Compilation timeout errors
- How-to guides
- Guide to Overleaf’s premium features
LaTeX Basics
- Creating your first LaTeX document
- Choosing a LaTeX Compiler
- Paragraphs and new lines
- Bold, italics and underlining
Mathematics
- Mathematical expressions
- Subscripts and superscripts
- Brackets and Parentheses
- Fractions and Binomials
- Aligning equations
- Spacing in math mode
- Integrals, sums and limits
- Display style in math mode
- List of Greek letters and math symbols
- Mathematical fonts
- Using the Symbol Palette in Overleaf
Figures and tables
- Inserting Images
- Positioning Images and Tables
- Lists of Tables and Figures
- Drawing Diagrams Directly in LaTeX
- TikZ package
References and Citations
- Bibliography management with bibtex
- Bibliography management with natbib
- Bibliography management with biblatex
- Bibtex bibliography styles
- Natbib bibliography styles
- Natbib citation styles
- Biblatex bibliography styles
- Biblatex citation styles
- Multilingual typesetting on Overleaf using polyglossia and fontspec
- Multilingual typesetting on Overleaf using babel and fontspec
- International language support
- Quotations and quotation marks
Document structure
- Sections and chapters
- Table of contents
- Cross referencing sections, equations and floats
- Nomenclatures
- Management in a large project
- Multi-file LaTeX projects
- Lengths in L a T e X
- Headers and footers
- Page numbering
- Paragraph formatting
- Line breaks and blank spaces
- Text alignment
- Page size and margins
- Single sided and double sided documents
- Multiple columns
- Code listing
- Code Highlighting with minted
- Using colours in LaTeX
- Margin notes
- Font sizes, families, and styles
- Font typefaces
- Supporting modern fonts with X Ǝ L a T e X
Presentations
- Environments
Field specific
- Theorems and proofs
- Chemistry formulae
- Feynman diagrams
- Molecular orbital diagrams
- Chess notation
- Knitting patterns
- CircuiTikz package
- Pgfplots package
- Typesetting exams in LaTeX
- Attribute Value Matrices
Class files
- Understanding packages and class files
- List of packages and class files
- Writing your own package
- Writing your own class
Advanced TeX/LaTeX
- In-depth technical articles on TeX/LaTeX
Have you checked our knowledge base ?
Message sent! Our team will review it and reply by email.
- Entertainment
Applying the mathematical principles of Pareto to Mario Kart 8
In this thesis, i....
By Emilia David , a reporter who covers AI. Prior to joining The Verge, she covered the intersection between technology, finance, and the economy.
Share this story
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25385148/Mario_Kart_8_Deluxe_Booster_Course_Pass.jpg)
If you’re the kind of Mario Kart 8 player who cares about winning and not just playing their favorite characters (Daisy and Peach supremacy), choosing the best combination of driver, vehicle, and wheels gets tricky.
Luckily, thanks to data science and 19th-century Italian economist Vilfredo Pareto, there’s a way to figure that out. Data scientist Antoine Mayerowitz applies one of Pareto’s principles, the Pareto front, to plot the best combination among the 703,560 possible decisions players must make in Mario Kart. Eurogamer helpfully explains that a Pareto front finds the best possible solution to a problem with different objectives.
In a cool piece of data visualization you should definitely check out, Mayerowitz narrows down the possible choices to 25,704. From here, Mayerowitz plots the potential builds on a chart. Starting with the speed factor, the fastest characters are technically Bowser and Wario, but the story is different after adding acceleration to the mix. Some characters are dominated by just speed or just acceleration, but those that aren’t form a curve that’s called the Pareto front, the drivers most optimal if you want to prioritize those two factors. Cat Peach is in the middle of the Pareto front for speed and acceleration.
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25409134/Screen_Shot_2024_04_19_at_16.34.38_PM.png)
Next, consider the vehicle build. There are around 585 combinations of karts, wheels, and gliders. Mayerowitz applies the Pareto front concept to this factor and ends up with 14 choices. The best choice from these 14 options depends on which factor the player wants to prioritize.
However, if, like Mayerowitz, you prioritize speed and acceleration, then the best build is Peach on the Teddy Buggy with roller tires and the Cloud Glider.
See, Princess Peach supremacy. Huh, I guess my method of just playing my favorite character works.
Tesla recalls all 3,878 Cybertrucks over faulty accelerator pedal
The invisible seafaring industry that keeps the internet afloat, airplay turns the delta emulator into a full-on retro console, emulators are taking over the app store, how phish turned las vegas’ sphere into the ultimate music visualizer.
More from Gaming
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25409026/H2_Wallpaper_Melinoe_4k_01.png)
The Hades 2 technical test is a trial in self-control
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25404717/delta_app_store.png)
Razer’s Kishi Ultra gaming controller brings haptics to your USB-C phone, PC, or tablet
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/21869417/akrales_200904_4160_0216.0.jpg)
The Meta Quest 2 gets a permanent price cut to $199

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Make a copy of this file and call it plain-diss.bst (or some other name). Save this in the same folder as your document, or put it in your local texmf folder in texmf/bibtex/bst/. Edit the file and search for "thesis". You will find the following function: FUNCTION {phdthesis} { output.bibitem.
All of the information about the recognised source types and all the keywords you can use can be found in the biblatex documentation.. Now let's return to the main .tex file. To set it up for a bibliography we need to load up the biblatex package using the \usepackage command. Also in the preamble we need to specify which .bib files we want to use by calling the \addbibresource command and ...
Introduction. When it comes to bibliography-management packages, there are three main options in LaTeX: bibtex, natbib and biblatex. This article explains how to use the biblatex package, to manage and format the bibliography in a LaTeX document.biblatex is a modern option for processing bibliography information, provides an easier and more flexible interface and a better language localization ...
BibTeX is a file format used for lists of references for LaTeX documents. Many citation management tools support the ability to export and import lists of references in .bib format. Some reference management tools can generate BibTeX files of your library or folders for use in your LaTeX documents. LaTeX on Wikibooks has a Bibliography ...
Writing a thesis or dissertation in LaTeX can be challenging, but the end result is well worth it - nothing looks as good as a LaTeX-produced pdf, and for large documents it's a lot easier than fighting with formatting and cross-referencing in MS Word. Review this video from Overleaf to help you get started writing your thesis in LaTeX, using a ...
How to Add a Bibliography Entry. When we want to refer to a source in the thesis, we place an entry for that source in the file references.bib, then cite the source in the thesis with the \cite{LABEL} command. The syntax for an entry in the references.bib file is of the form: @ ENTRYTYPE { LABEL,
verbose Citation style that prints a full citation when the entry is cited for the first time and a short version afterwards. reading Citation style that goes with the bibliography style by the same name. Loads the authortitle style. There are other non-standard citation styles popular in different journals and thesis In Sciences:
BibTeX is a reference management tool that is commonly used in LaTeX documents. The "phdthesis" BibTeX type is used for PhD dissertations or theses. In this guide, we will explain the required and optional fields for the "phdthesis" BibTeX type.
BibTeX reference format; BibTeX command; LaTeX bibliography file; LaTeX editors and compilers; Sample LaTeX file with bibliography; ... For the structure of theses and dissertations here is a list of required and recommended sections. Latex template.
Adding your reference list to the table of contents . In my version of the UF LaTex dissertation template, their call to add 'references' to the table of contents didn't appear to work. At least when I compile their template, the reference list (which comes after everything else, but before the biosketch) is not listed:
5-part Guide on How to Write a Thesis in LaTeX. 5-part LaTeX Thesis Writing Guide. Part 1: Basic Structure corresponding video. Part 2: Page Layout corresponding video. Part 3: Figures, Subfigures and Tables corresponding video. Part 4: Bibliographies with Biblatex corresponding video. Part 5: Customizing Your Title Page and Abstract ...
together with the thebibliography block from before, this is what gets rendered into your PDF when you run a \(\mathrm{\LaTeX}\) processor (i.e. any of latex, pdflatex, xelatex or lualatex) on your source file:. Figure 1: Citing entries from a thebibliography list. Notice how each \bibitem is automatically numbered, and how \cite then inserts the corresponding numerical label.
How to Write a Doctoral Dissertation with LATEX A DISSERTATION ... Run LATEX on your main le, say foo.tex: latex foo. This generates an aux-iliary le foo.aux with a list of \cite references. 30 (4) Run BiBTEX on your le: bibtex foo. BiBTEX reads the auxiliary le, looks
In order to cite references, you first need to create a separate bibliography file ending with a .bib extension within your LaTeX project. You can do that by clicking on the New File icon on the upper-left corner of the screen. Then, enter your file name. Note that the default file extension in LaTeX is .tex. Your bibliography file must end in ...
Writing a thesis or dissertation in LaTeX can be challenging, but the end result is well worth it - nothing looks as good as a LaTeX-produced pdf, and for large documents it's a lot easier than fighting with formatting and cross-referencing in MS Word. Review this video from Overleaf to help you get started writing your thesis in LaTeX, using a ...
The citation commands in biblatex also give us the option of adding a prenote and postnote in as arguments: a prenote is a word or phrase like "see" that is inserted at the start of the citation; a postnote is text you want inserted at the end of the citation. To add these notes in you uses two sets of square brackets in the citation command.
In biblatex @phdthesis is an alias for @thesis with field type= {phdthesis} by default. See biblatex manual: "@phdthesis: Similar to @thesis except that the type field is optional and defaults to the localised term 'PhD thesis'. You may still use the type field to override that." 2.
The preamble. In this example, the main.tex file is the root document and is the .tex file that will draw the whole document together. The first thing we need to choose is a document class. The article class isn't designed for writing long documents (such as a thesis) so we'll choose the report class, but we could also choose the book class.. We can also change the font size by adding square ...
23. Use @master s thesis (with an s after master) instead of @masterthesis (which doesn't exist and probably defaults to some other type), then school will appear. The entry type @unpublished doesn't support school, so I'd suggest using note instead, as is recommended in the biblatex documentation:
The most optimal Mario Kart 8 characters, based on speed and acceleration using the Pareto front. Next, consider the vehicle build. There are around 585 combinations of karts, wheels, and gliders ...
I cite it using the example format. "This is my manuscript \cite {bibtex_key}." then it returns me an output as. "This is my manuscript. [1]" whereas I need it to be like. "This is my manuscript [1]." Below is the working example, you can compile and see that the reference 1 comes after the full stop which should not be as I cited it before the ...