Paragraph on Nelson Mandela | 100, 150, 200, and 400 + Words Amazing Paragraphs


Paragraph on Nelson Mandela – 100 Words
Nelson Mandela was a remarkable leader and an important figure in the history of South Africa. He was imprisoned for 27 years, but he refused to give up his fight for freedom. When he was released in 1990, Mandela became the first black president of South Africa. He served as president until 1994, when he was elected to the parliament of South Africa. Mandela continued to serve in parliament until 1997, when he retired from politics. He died in 2013 at the age of 95. After spending 27 years in prison, he emerged as one of South Africa’s most revered icons and helped to lead the country through its dark days into an era of racial equality and democracy. As one of the architects of freedom in South Africa, his legacy is sure to be remembered for years to come.
Paragraph on Nelson Mandela- 150 Words
Nelson Mandela was a remarkable individual who had a profound impact on both South Africa and the world. He was born in 1918 in Mvezo, Transkei, and became a political activist at a young age. He was imprisoned for years for his beliefs, but eventually became president of South Africa in 1994. Under his leadership, South Africa became a democracy and saw significant economic growth. Mandela passed away in 2013 at the age of 95 after a long and successful career. Nelson Mandela was an icon of human rights and democracy. He fought against apartheid and became the first black president of South Africa in 1994. After his release from prison, he worked tirelessly to promote reconciliation and democracy in his country. Mandela’s tireless work has earned him numerous awards, including the Nobel Peace Prize. His legacy will continue to inspire people around the world to fight for justice and equality.
Paragraph on Nelson Mandela- 200 Words
Nelson Mandela was an influential figure in the fight for democracy and human rights. He was imprisoned for 27 years, but eventually became the president of South Africa. He was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1993 for his work on behalf of the people of South Africa. Mandela is a symbol of hope and resilience, and his legacy will continue to be felt throughout the world. He was an amazing human being who has been credited with helping to bring about change and peace in his country, South Africa. He was also a powerful leader and a prolific writer. He is best known for his role in the struggle against white rule in South Africa and for leading the country to democracy. Mandela was released from prison on February 11, 1990, after serving 27 years of a life sentence for terrorism. Nelson Mandela was a powerful leader and an icon of peace. He fought for human rights and against apartheid, which was a government system that segregated people based on race. He is now considered one of the most influential figures in history. He left an incredible legacy. Mandela was a powerful voice for social justice, fighting for human rights and democracy worldwide. He is considered one of the greatest leaders in history and his influence is still felt today. Read about his amazing life story and see what he accomplished!
Paragraph on Nelson Mandela- 300 Words
Nelson Mandela was a Nobel Prize-winning South African politician and activist who served as President of the country from 1994 to 1999. He played a leading role in the fight against apartheid, and became head of the African National Congress (ANC) in 1961. In 1990, he was elected President of South Africa, becoming the first black leader of a major Western country. He remained president until his death in 2013. During his time as president, Mandela made significant changes to South Africa’s government and society. He abolished apartheid and reorganized the country’s economy into five sectors: public service, private enterprise, agriculture, manufacturing, and tourism. He also created an integrated education system that included both white and black schools. Mandela was a powerful advocate for human rights, and his presidency was marked by significant peace efforts between South Africa and its former enemies. He is often cited as one of the greatest leaders of our time. Nelson Mandela, one of the most iconic and influential leaders in recent history, was born on July 18, 1918. He became president of South Africa in 1994 after years of fighting against white rule. Mandela’s role as president was not without its challenges – he faced many struggles including years of imprisonment on Robben Island – but his legacy is unquestioned. After his presidency ended in 1999, Mandela devoted himself to helping the poor and disadvantaged around the world through his non-profit organization, The Nelson Mandel Foundation. Today, he is widely recognized for his work with democracy and human rights. He played an important role in the fight against apartheid and helped to bring about change for the betterment of all South Africans. His legacy continues to live on through his work and teachings, and we should all be proud of what he has done for our society.
Paragraph on Nelson Mandela in 400 + Words
Introduction
Nelson Mandela was an incredible person who helped to shape the course of history. He is best known for his work as a political activist in South Africa, and later as the first President of South Africa after the country’s liberation from white rule. Mandela was also a deeply spiritual man, and his moral compass helped him navigate through some of the most difficult times in his life. While Mandela’s death at the age of 95 was a great loss to the world, it also opened up space for others to carry on his legacy. In particular, his daughter Zindzi has made it her mission to ensure that her father’s message of forgiveness and reconciliation is heard around the world. Regardless of your political beliefs, be sure to read Zindzi Mandela’s powerful words on her father’s life and death.
Life of Nelson Mandela
Nelson Mandela was born on July 18, 1918 in Mvezo, a small town in the Transkei region of South Africa. After graduating from high school, Mandela enrolled at the University of Fort Hare where he became involved in the African National Congress (ANC). In 1944, he was arrested for his involvement in the ANC and sentenced to five years in prison. While incarcerated, Mandela studied law and developed his political beliefs. Upon his release from prison in 1962, Mandela became the Umkhonto weSizwe ( Spear of the Nation) leader of the ANC and worked to liberate South Africa from white rule. In 1990, after years of campaigning and negotiation, Mandela was elected President of South Africa and served until 1994. Mandela is now retired and resides in Houghton, South Africa.
Nelson Mandela
Nelson Mandela was an incredible figure in the world, and his impact on history is undeniable. He was a leader of the African National Congress during South Africa’s apartheid regime, and after years of fighting and protesting he was eventually imprisoned and released in 1990. Mandela became president of South Africa in 1994, and led the country through a period of significant change and progress. He passed away in 2013, but his legacy will continue to be felt long into the future.
Legacy of Nelson Mandela
Mandela was a global symbol of resistance and reconciliation. He championed the rights of the poor and condemned apartheid as an injustice. Mandela served 27 years in prison before becoming South Africa’s first black president. He passed away in 2013 at the age of 95.
What Nelson Mandela Did
Nelson Mandela was a revolutionary who helped to change South Africa and the world. He was imprisoned for 27 years, but he never gave up hope of one day becoming the president of South Africa. After his release in 1990, Mandela became the first black leader of South Africa. He served as president until 1999, when he was elected as the first black president of the country. Mandela is now retired and lives in Johannesburg.
Mandela’s legacy spans more than sixty years, and his influence is still felt today. He was a powerful symbol of resistance against South Africa’s white minority rule, and his message of Equality, Justice and Peace has inspired millions. Mandela is also credited with helping to revive the African National Congress (ANC) and leading it to victory in the 1990 election. His tireless work for human rights has earned him numerous awards and honors, including the Nobel Peace Prize in 1993.
Background of Nelson Mandela
Nelson Mandela was born on July 18, 1918, in the Transkei region of South Africa. His father, Thembelani Mandela, was a political leader and chief of the Xhosa tribe. Mandela’s mother, Dolly (Dolores) Madikizela, was a teacher. Mandela attended a Christian school and then the University of South Africa where he studied law. He joined the African National Congress (ANC) in 1943 and served as its secretary-general from 1961 to 1989. In 1962, he was arrested and sentenced to life imprisonment on Robben Island for his role in anti-apartheid activities. He was released in 1990 as part of an agreement between the ANC and the government. In 1991, Mandela was elected the first president of South Africa. During his presidency, he led negotiations that led to the dismantling of apartheid and the establishment of a multiracial democracy. Mandela retired from public life in 1999 and died on December 5, 2013.
Achievements of Nelson Mandela
Nelson Mandela is considered one of the most influential and significant political activists of the 20th century. He was a leader in the African National Congress and served 18 years in prison because of his activism. Mandela was released in 1990 after negotiations with the South African government. Mandela has since served as president of South Africa and was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1993. He has made significant contributions to peace and reconciliation, and his work has helped to promote human rights globally.
In the twentieth century, Nelson Mandela was one of the most influential and celebrated leaders in the world. He fought against discrimination and apartheid in South Africa for over twenty-five years, leading to his imprisonment and eventual release. Mandela is now a global symbol of human rights and reconciliation, and his legacy continues to inspire people around the world. Thank you for reading this article on Nelson Mandela, and I hope it has helped you learn more about one of history’s greatest figures.
Related Posts

Short Essay on Nelson Mandela [100, 200, 400 Words] With PDF
Nelson Mandela was a political leader and a former president of South Africa. For his contribution to restoring peace and stability in the region, he is still remembered around the world. In today’s session, you will learn about the life of Nelson Mandela in order to write an essay on this eminent person for your upcoming exam.
Table of Contents
- Short Essay on Nelson Mandela in 100 Words
- Short Essay on Nelson Mandela in 200 Words
- Short Essay on Nelson Mandela in 400 Words

Short Essay on Nelson Mandela in 100 Words
Nelson Mandela was one of the greatest leaders and freedom fighters of South Africa. He was born on 18th July 1918. He studied law and became a successful lawyer. While practising law, he got involved in anti-apartheid, anti-colonial, nationalist movements and soon joined the African National Congress.
South Africa, at that time, was ruled by a white-only government and blacks were discriminated against in their own country. Mandela, along with other revolutionaries, fought against the oppressive rule. Because of their efforts, the white supremacist government was finally overthrown and Nelson Mandela became the first president of a multi-racial democratic South Africa in 1994. He was also the country’s first black president. He died on 5th December 2013, aged 95. He will always be remembered as an icon of democracy and social justice.
Short Essay on Nelson Mandela in 200 Words
Nelson Rolihlahla Mandela was a South African revolutionary leader and freedom fighter who played an important role in ending apartheid in the country. He was born on 18th July 1918 in a village called Mzevo into the Thembu royal family. Although his family was illiterate, he was sent to study in a local school by his mother.
He later studied law and started working as a lawyer in Johannesburg. While he was still studying, he faced racism and saw the terrible political state of his country. Soon, he started getting involved in anti-apartheid, anti-colonial, nationalist movements and joined the African National Congress.
South Africa, at that time, was ruled by a whites-only government, and blacks were discriminated against in their own country. Mandela, along with other revolutionaries, fought against the oppressive rule and was repeatedly arrested and imprisoned. However, even after spending a total of 27 years in jail, Mandela did not give up and continued with his efforts to end apartheid in the country.
Finally, after decades of struggle, South Africa rose as a multi-racial democratic country and Nelson Mandela became its first president in 1994. He was also the country’s first-ever black president. He was an advocate of human rights and brought peace and stability to his country. Nelson Mandela was one of the greatest leaders in the world and he will always be remembered as an icon of democracy and social justice.
Short Essay on Nelson Mandela in 400 Words
Nelson Rolihlahla Mandela was one of the most important leaders in the history of South Africa as well as the world. He was born on 18th July 1918 in a village called Mzevo into the Thembu royal family. Although his family was illiterate, he was sent to study in a local school by his mother.
He later studied law and started working as a lawyer in Johannesburg. While he was still studying, he came face-to-face with racism and saw the terrible political state of his country. Soon, he started getting involved in anti-apartheid, anti-colonial, nationalist movements and joined the African National Congress.
South Africa, at that time, was ruled by a whites-only government, and blacks were discriminated against in their own country. Mandela, along with other revolutionaries like Anton Lembede and Oliver Tambo, fought against the oppressive rule and was repeatedly arrested and imprisoned.
However, even after spending a total of 27 years in jail, Mandela did not give up and continued with his efforts to end apartheid in the country. He led defiance campaigns against the government as well as the mass stay-at-home strikes. He also joined hands with anti-apartheid leaders around the world and trained in guerilla warfare.
Nelson Mandela and his fellow leaders worked hard to end apartheid and bring justice to the millions of black Africans who had been suffering under the white supremacist government. After decades of struggle for freedom and equality, South Africa rose as a multi-racial democratic country in 1994, with the first fully democratic elections held on 27th April 1994.
The African National Congress, under the leadership of Mandela, won the elections by a huge margin and Nelson was sworn as the first president of a democratic South Africa. He held office till 1999 and was focused on national unity and reconciliation.
Nelson Mandela’s government worked a lot for the betterment of society, granting old-age pensions, free healthcare for young children and pregnant women, building houses, providing electricity and connectivity as well as making proper education available for kids. Even after retiring from the political scene, he continued to work towards rural development, school construction and combating HIV/AIDS. He died on 5th December 2013 after suffering from a respiratory infection.
Nelson Mandela was an advocate of human rights and brought peace and stability to his country. He was one of the greatest leaders in the world and he will always be remembered as an icon of democracy and social justice.
That’s all about my presentation on the life of Nelson Mandela. Hopefully, this session has become able to fulfil your requirement. If you have any doubts regarding this session, kindly let me know through the comment section below.
To get the latest updates on our upcoming sessions, please join us on Telegram. Thanks for being with us. All the best.
More from English Compositions
- [FREE PDF] Nelson Mandela MCQs | CBSE Class 10 English Chapter 2 [TERM 1]
- 100, 200, 400 Words Paragraph and Short Essay [With PDF]
- Short Essay on Freedom fighters [100, 200, 400 Words] With PDF
- Short Essay on Jawaharlal Nehru [100, 200, 400 Words] With PDF
- Madhyamik English Writing Suggestion 2022 [With PDF]
- Short Essay on Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel [100, 200, 400 Words] With PDF
- Write a Letter to the Editor about Worsening Law and Order
- Short Essay on Mahatma Gandhi [100, 200, 400 Words] With PDF
- Short Essay on Dr. Rajendra Prasad [100, 200, 400 Words] With PDF
- Short Essay on Leadership [100, 200, 400 Words] With PDF
- Short Essay on Subramania Bharati [100, 200, 400 Words] With PDF
- Paragraph & Short Essay on APJ Abdul Kalam [100, 200, 400 Words] With PDF
Nelson Mandela
Nelson Mandela was the first Black president of South Africa, elected after time in prison for his anti-apartheid work. He won the Nobel Peace Prize in 1993.
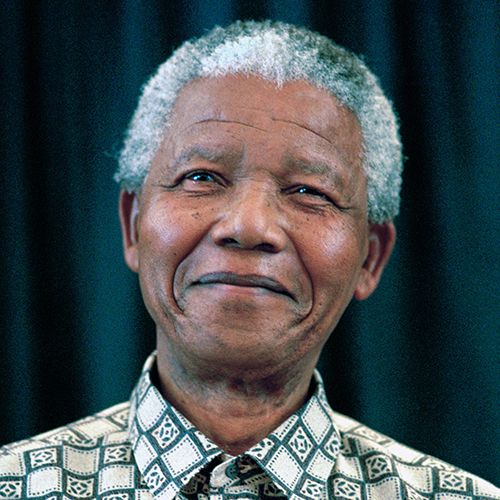

(1918-2013)
Who Was Nelson Mandela?
Beginning in 1962, Mandela spent 27 years in prison for political offenses. In 1993, Mandela and South African President F.W. de Klerk were jointly awarded the Nobel Peace Prize for their efforts to dismantle the country's apartheid system. For generations to come, Mandela will be a source of inspiration for civil rights activists worldwide.
Mandela was born on July 18, 1918, in the tiny village of Mvezo, on the banks of the Mbashe River in Transkei, South Africa.
His birth name was Rolihlahla Mandela. "Rolihlahla" in the Xhosa language literally means "pulling the branch of a tree," but more commonly translates as "troublemaker."
Mandela's father, who was destined to be a chief, served as a counselor to tribal chiefs for several years but lost both his title and fortune over a dispute with the local colonial magistrate.
Mandela was only an infant at the time, and his father's loss of status forced his mother to move the family to Qunu, an even smaller village north of Mvezo. The village was nestled in a narrow grassy valley; there were no roads, only footpaths that linked the pastures where livestock grazed.
The family lived in huts and ate a local harvest of maize, sorghum, pumpkin and beans, which was all they could afford. Water came from springs and streams and cooking was done outdoors.
Mandela played the games of young boys, acting out male right-of-passage scenarios with toys he made from the natural materials available, including tree branches and clay.
At the suggestion of one of his father's friends, Mandela was baptized in the Methodist Church. He went on to become the first in his family to attend school. As was custom at the time, and probably due to the bias of the British educational system in South Africa, Mandela's teacher told him that his new first name would be Nelson.
When Mandela was 12 years old, his father died of lung disease, causing his life to change dramatically. He was adopted by Chief Jongintaba Dalindyebo, the acting regent of the Thembu people — a gesture done as a favor to Mandela's father, who, years earlier, had recommended Jongintaba be made chief.
Mandela subsequently left the carefree life he knew in Qunu, fearing that he would never see his village again. He traveled by motorcar to Mqhekezweni, the provincial capital of Thembuland, to the chief's royal residence. Though he had not forgotten his beloved village of Qunu, he quickly adapted to the new, more sophisticated surroundings of Mqhekezweni.
Mandela was given the same status and responsibilities as the regent's two other children, his son and oldest child, Justice, and daughter Nomafu. Mandela took classes in a one-room school next to the palace, studying English, Xhosa, history and geography.
It was during this period that Mandela developed an interest in African history, from elder chiefs who came to the Great Palace on official business. He learned how the African people had lived in relative peace until the coming of the white people.
According to the elders, the children of South Africa had previously lived as brothers, but white men had shattered this fellowship. While Black men shared their land, air and water with white people, white men took all of these things for themselves.
READ MORE: 14 Inspiring Nelson Mandela Quotes
Political Awakening
When Mandela was 16, it was time for him to partake in the traditional African circumcision ritual to mark his entrance into manhood. The ceremony of circumcision was not just a surgical procedure, but an elaborate ritual in preparation for manhood.
In African tradition, an uncircumcised man cannot inherit his father's wealth, marry or officiate at tribal rituals. Mandela participated in the ceremony with 25 other boys. He welcomed the opportunity to partake in his people's customs and felt ready to make the transition from boyhood to manhood.
His mood shifted during the proceedings, however, when Chief Meligqili, the main speaker at the ceremony, spoke sadly of the young men, explaining that they were enslaved in their own country. Because their land was controlled by white men, they would never have the power to govern themselves, the chief said.
He went on to lament that the promise of the young men would be squandered as they struggled to make a living and perform mindless chores for white men. Mandela would later say that while the chief's words didn't make total sense to him at the time, they would eventually formulate his resolve for an independent South Africa.
DOWNLOAD BIOGRAPHY'S NELSON MANDELA FACT CARD

University Life
Under the guardianship of Regent Jongintaba, Mandela was groomed to assume high office, not as a chief, but a counselor to one. As Thembu royalty, Mandela attended a Wesleyan mission school, the Clarkebury Boarding Institute and Wesleyan College, where, he would later state, he achieved academic success through "plain hard work."
He also excelled at track and boxing. Mandela was initially mocked as a "country boy" by his Wesleyan classmates, but eventually became friends with several students, including Mathona, his first female friend.
In 1939, Mandela enrolled at the University of Fort Hare , the only residential center of higher learning for Black people in South Africa at the time. Fort Hare was considered Africa's equivalent of Harvard , drawing scholars from all parts of sub-Saharan Africa.
In his first year at the university, Mandela took the required courses, but focused on Roman-Dutch law to prepare for a career in civil service as an interpreter or clerk — regarded as the best profession that a Black man could obtain at the time.
In his second year at Fort Hare, Mandela was elected to the Student Representative Council. For some time, students had been dissatisfied with the food and lack of power held by the SRC. During this election, a majority of students voted to boycott unless their demands were met.
Aligning with the student majority, Mandela resigned from his position. Seeing this as an act of insubordination, the university expelled Mandela for the rest of the year and gave him an ultimatum: He could return to the school if he agreed to serve on the SRC. When Mandela returned home, the regent was furious, telling him unequivocally that he would have to recant his decision and go back to school in the fall.
A few weeks after Mandela returned home, Regent Jongintaba announced that he had arranged a marriage for his adopted son. The regent wanted to make sure that Mandela's life was properly planned, and the arrangement was within his right, as tribal custom dictated.
Shocked by the news, feeling trapped and believing that he had no other option than to follow this recent order, Mandela ran away from home. He settled in Johannesburg, where he worked a variety of jobs, including as a guard and a clerk, while completing his bachelor's degree via correspondence courses. He then enrolled at the University of the Witwatersrand in Johannesburg to study law.
Anti-Apartheid Movement
Mandela soon became actively involved in the anti-apartheid movement, joining the African National Congress in 1942. Within the ANC, a small group of young Africans banded together, calling themselves the African National Congress Youth League. Their goal was to transform the ANC into a mass grassroots movement, deriving strength from millions of rural peasants and working people who had no voice under the current regime.
Specifically, the group believed that the ANC's old tactics of polite petitioning were ineffective. In 1949, the ANC officially adopted the Youth League's methods of boycott, strike, civil disobedience and non-cooperation, with policy goals of full citizenship, redistribution of land, trade union rights, and free and compulsory education for all children.
For 20 years, Mandela directed peaceful, nonviolent acts of defiance against the South African government and its racist policies, including the 1952 Defiance Campaign and the 1955 Congress of the People. He founded the law firm Mandela and Tambo, partnering with Oliver Tambo , a brilliant student he'd met while attending Fort Hare. The law firm provided free and low-cost legal counsel to unrepresented Black people.
In 1956, Mandela and 150 others were arrested and charged with treason for their political advocacy (they were eventually acquitted). Meanwhile, the ANC was being challenged by Africanists, a new breed of Black activists who believed that the pacifist method of the ANC was ineffective.
Africanists soon broke away to form the Pan-Africanist Congress, which negatively affected the ANC; by 1959, the movement had lost much of its militant support.
Wife and Children
Mandela was married three times and had six children. He wed his first wife, Evelyn Ntoko Mase, in 1944. The couple had four children together: Madiba Thembekile (d. 1964), Makgatho (d. 2005), Makaziwe (d. 1948 at nine months old) and Maki. The couple divorced in 1957.
In 1958, Mandela wed Winnie Madikizela . The couple had two daughters together, Zenani (Argentina's South African ambassador) and Zindziswa (the South African ambassador to Denmark), before separating in 1996.
Two years later, in 1998, Mandela married Graca Machel, the first Education Minister of Mozambique, with whom he remained until his death in 2013.
Prison Years
Formerly committed to nonviolent protest, Mandela began to believe that armed struggle was the only way to achieve change. In 1961, Mandela co-founded Umkhonto we Sizwe, also known as MK, an armed offshoot of the ANC dedicated to sabotage and use guerilla war tactics to end apartheid.
In 1961, Mandela orchestrated a three-day national workers' strike. He was arrested for leading the strike the following year and was sentenced to five years in prison. In 1963, Mandela was brought to trial again. This time, he and 10 other ANC leaders were sentenced to life imprisonment for political offenses, including sabotage.
Mandela spent 27 years in prison, from November 1962 until February 1990. He was incarcerated on Robben Island for 18 of his 27 years in prison. During this time, he contracted tuberculosis and, as a Black political prisoner, received the lowest level of treatment from prison workers. However, while incarcerated, Mandela was able to earn a Bachelor of Law degree through a University of London correspondence program.
A 1981 memoir by South African intelligence agent Gordon Winter described a plot by the South African government to arrange for Mandela's escape so as to shoot him during the recapture; the plot was foiled by British intelligence.
Mandela continued to be such a potent symbol of Black resistance that a coordinated international campaign for his release was launched, and this international groundswell of support exemplified the power and esteem that Mandela had in the global political community.
In 1982, Mandela and other ANC leaders were moved to Pollsmoor Prison, allegedly to enable contact between them and the South African government. In 1985, President P.W. Botha offered Mandela's release in exchange for renouncing armed struggle; the prisoner flatly rejected the offer.
F. W. de Klerk
With increasing local and international pressure for his release, the government participated in several talks with Mandela over the ensuing years, but no deal was made.
It wasn't until Botha suffered a stroke and was replaced by Frederik Willem de Klerk that Mandela's release was finally announced, on February 11, 1990. De Klerk also lifted the ban on the ANC, removed restrictions on political groups and suspended executions.
Upon his release from prison, Mandela immediately urged foreign powers not to reduce their pressure on the South African government for constitutional reform. While he stated that he was committed to working toward peace, he declared that the ANC's armed struggle would continue until the Black majority received the right to vote.
In 1991, Mandela was elected president of the African National Congress, with lifelong friend and colleague Oliver Tambo serving as national chairperson.
Nobel Peace Prize
In 1993, Mandela and President de Klerk were jointly awarded the Nobel Peace Prize for their work toward dismantling apartheid in South Africa.
After Mandela’s release from prison, he negotiated with President de Klerk toward the country's first multiracial elections. White South Africans were willing to share power, but many Black South Africans wanted a complete transfer of power.
The negotiations were often strained, and news of violent eruptions, including the assassination of ANC leader Chris Hani, continued throughout the country. Mandela had to keep a delicate balance of political pressure and intense negotiations amid the demonstrations and armed resistance.
Due in no small part to the work of Mandela and President de Klerk, negotiations between Black and white South Africans prevailed: On April 27, 1994, South Africa held its first democratic elections. Mandela was inaugurated as the country's first Black president on May 10, 1994, at the age of 77, with de Klerk as his first deputy.
From 1994 until June 1999, President Mandela worked to bring about the transition from minority rule and apartheid to Black majority rule. He used the nation's enthusiasm for sports as a pivot point to promote reconciliation between white and Black people, encouraging Black South Africans to support the once-hated national rugby team.
In 1995, South Africa came to the world stage by hosting the Rugby World Cup, which brought further recognition and prestige to the young republic. That year Mandela was also awarded the Order of Merit.
During his presidency, Mandela also worked to protect South Africa's economy from collapse. Through his Reconstruction and Development Plan, the South African government funded the creation of jobs, housing and basic health care.
In 1996, Mandela signed into law a new constitution for the nation, establishing a strong central government based on majority rule, and guaranteeing both the rights of minorities and the freedom of expression.
Retirement and Later Career
By the 1999 general election, Mandela had retired from active politics. He continued to maintain a busy schedule, however, raising money to build schools and clinics in South Africa's rural heartland through his foundation, and serving as a mediator in Burundi's civil war.
Mandela was diagnosed and treated for prostate cancer in 2001. In June 2004, at the age of 85, he announced his formal retirement from public life and returned to his native village of Qunu.
On July 18, 2007, Mandela and wife Graca Machel co-founded The Elders , a group of world leaders aiming to work both publicly and privately to find solutions to some of the world's toughest issues. The group included Desmond Tutu , Kofi Annan , Ela Bhatt, Gro Harlem Brundtland, Jimmy Carter , Li Zhaoxing, Mary Robinson and Muhammad Yunus.
The Elders' impact has spanned Asia, the Middle East and Africa, and their actions have included promoting peace and women's equality, demanding an end to atrocities, and supporting initiatives to address humanitarian crises and promote democracy.
In addition to advocating for peace and equality on both a national and global scale, in his later years, Mandela remained committed to the fight against AIDS . His son Makgatho died of the disease in 2005.
Relationship With Barack Obama
Mandela made his last public appearance at the final match of the World Cup in South Africa in 2010. He remained largely out of the spotlight in his later years, choosing to spend much of his time in his childhood community of Qunu, south of Johannesburg.
He did, however, visit with U.S. first lady Michelle Obama , wife of President Barack Obama , during her trip to South Africa in 2011. Barack Obama, while a junior senator from Illinois, also met with Mandela during his 2005 trip to the United States.
Mandela died on December 5, 2013, at the age of 95 in his home in Johannesburg, South Africa. After suffering a lung infection in January 2011, Mandela was briefly hospitalized in Johannesburg to undergo surgery for a stomach ailment in early 2012.
He was released after a few days, later returning to Qunu. Mandela would be hospitalized many times over the next several years — in December 2012, March 2013 and June 2013 — for further testing and medical treatment relating to his recurrent lung infection.
Following his June 2013 hospital visit, Machel, canceled a scheduled appearance in London to remain at her husband's side, and his daughter, Zenani Dlamini, flew back from Argentina to South Africa to be with her father.
Jacob Zuma , South Africa's president, issued a statement in response to public concern over Mandela's March 2013 health scare, asking for support in the form of prayer: "We appeal to the people of South Africa and the world to pray for our beloved Madiba and his family and to keep them in their thoughts," Zuma said.
On the day of Mandela’s death, Zuma released a statement speaking to Mandela's legacy: "Wherever we are in the country, wherever we are in the world, let us reaffirm his vision of a society ... in which none is exploited, oppressed or dispossessed by another," he said.
Movie and Books
In 1994, Mandela published his autobiography, Long Walk to Freedom , much of which he had secretly written while in prison. The book inspired the 2013 movie Mandela: Long Walk to Freedom.
He also published a number of books on his life and struggles, among them No Easy Walk to Freedom ; Nelson Mandela: The Struggle Is My Life ; and Nelson Mandela's Favorite African Folktales .
Mandela Day
In 2009, Mandela's birthday (July 18) was declared Mandela Day, an international day to promote global peace and celebrate the South African leader's legacy. According to the Nelson Mandela Foundation , the annual event is meant to encourage citizens worldwide to give back the way that Mandela has throughout his lifetime.
A statement on the Nelson Mandela Foundation's website reads: "Mr. Mandela gave 67 years of his life fighting for the rights of humanity. All we are asking is that everyone gives 67 minutes of their time, whether it’s supporting your chosen charity or serving your local community."
QUICK FACTS
- Name: Nelson Mandela
- Birth Year: 1918
- Birth date: July 18, 1918
- Birth City: Mvezo, Transkei
- Birth Country: South Africa
- Gender: Male
- Best Known For: Nelson Mandela was the first Black president of South Africa, elected after time in prison for his anti-apartheid work. He won the Nobel Peace Prize in 1993.
- Civil Rights
- World Politics
- Astrological Sign: Cancer
- University of Witwatersrand, Johannesburg
- University College of Fort Hare
- Wesleyan College
- University of London
- Clarkebury Boarding Institute
- Nacionalities
- South African
- Interesting Facts
- Mandela's African name "Rolihlahla" means "troublemaker."
- Mandela became the first Black president of South Africa in 1994, serving until 1999.
- Beginning in 1962, Mandela spent 27 years in prison for political offenses.
- Death Year: 2013
- Death date: December 5, 2013
- Death City: Johannesburg
- Death Country: South Africa
We strive for accuracy and fairness.If you see something that doesn't look right, contact us !
CITATION INFORMATION
- Article Title: Nelson Mandela Biography
- Author: Biography.com Editors
- Website Name: The Biography.com website
- Url: https://www.biography.com/political-figures/nelson-mandela
- Access Date:
- Publisher: A&E; Television Networks
- Last Updated: January 7, 2022
- Original Published Date: April 3, 2014
- I hate race discrimination most intensely and in all its manifestations. I have fought it all during my life; I fight it now, and will do so until the end of my days.
- Difficulties break some men but make others. No axe is sharp enough to cut the soul of a sinner who keeps on trying, one armed with the hope that he will rise even in the end.
- Death is something inevitable. When a man has done what he considers to be his duty to his people and his country, he can rest in peace. I believe I have made that effort and that is, therefore, why I will sleep for the eternity.
- Those who conduct themselves with morality, integrity and consistency need not fear the forces of inhumanity and cruelty.
- Everyone can rise above their circumstances and achieve success if they are dedicated to and passionate about what they do.
- Our march to freedom is irreversible. We must not allow fear to stand in our way.
- When a man is denied the right to live the life he believes in, he has no choice but to become an outlaw.
- I learned that courage was not the absence of fear, but the triumph over it....The brave man is not he who does not feel afraid, but he who conquers that fear.
- Prison itself is a tremendous education in the need for patience and perseverance. It is above all a test of one's commitment.
- I can rest only for a moment, for with freedom come responsibilities, and I dare not linger, for my long walk is not yet ended.
- During my lifetime I have dedicated myself to this struggle of the African people. I have fought against white domination, and I have fought against Black domination. I have cherished the ideal of a democratic and free society in which all persons live together in harmony and with equal opportunities. It is an ideal which I hope to live for and to achieve. But if needs be, it is an ideal for which I am prepared to die.
- For to be free is not merely to cast off one's chains, but to live in a way that respects and enhances the freedom of others.
- If you want to make peace with your enemy, you have to work with your enemy. Then he becomes your partner.
- Man's goodness is a flame that can be hidden but never extinguished.
- I was made, by the law, a criminal, not because of what I had done, but because of what I stood for, because of what I thought, because of my conscience.
- The greatest glory in living lies not in never falling, but in rising every time we fall.
- Wherever we are in the country, wherever we are in the world, let us reaffirm his vision of a society ... in which none is exploited, oppressed or dispossessed by another.
Black History

Jesse Owens

Alice Coachman

Wilma Rudolph

Tiger Woods

Deb Haaland

10 Famous Langston Hughes Poems

5 Crowning Achievements of Maya Angelou

Ava DuVernay

Octavia Spencer
Inventor Garrett Morgan’s Lifesaving 1916 Rescue

Get to Know 5 History-Making Black Country Singers
Biography Online

Biography Nelson Mandela

“I learned that courage was not the absence of fear, but the triumph over it. The brave man is not he who does not feel afraid, but he who conquers that fear.”
– Nelson Mandela
Short Bio of Nelson Mandela

A young Nelson Mandela (1938)
Nelson Mandela was born in Transkei, South Africa on July 18, 1918. He was the son of a local tribal leader of the Tembu tribe. As a youngster, Nelson took part in the activities and initiation ceremonies of his local tribe. However, unlike his father Nelson Mandela gained a full education, studying at the University College of Fort Hare and also the University of Witwatersrand. Nelson was a good student and qualified with a law degree in 1942.
During his time at University, Nelson Mandela became increasingly aware of the racial inequality and injustice faced by non-white people. In 1943, he decided to join the ANC and actively take part in the struggle against apartheid.
As one of the few qualified lawyers, Nelson Mandela was in great demand; also his commitment to the cause saw him promoted through the ranks of the ANC. In 1956, Nelson Mandela, along with several other members of the ANC were arrested and charged with treason. After a lengthy and protracted court case, the defendants were finally acquitted in 1961. However, with the ANC now banned, Nelson Mandela suggested an active armed resistance to the apartheid regime. This led to the formation of Umkhonto we Sizwe, which would act as a guerilla resistance movement. Receiving training in other African countries, the Umkhonto we Sizwe took part in active sabotage.
In 1963, Mandela was again arrested and put on trial for treason. This time the State succeeded in convicting Mandela of plotting to overthrow the government. However, the case received considerable international attention and the apartheid regime of South Africa became under the glare of the international community. At the end of his trial, Nelson Mandela made a long speech, in which he was able to affirm his commitment to the ideals of democracy.
“We believe that South Africa belongs to all the people who live in it, and not to one group, be it black or white. We did not want an interracial war, and tried to avoid it to the last minute.”
– Nelson Mandela, Supreme court of South Africa, Pretoria, April 20, 1964
Closing remark at the 1964 trial
“During my lifetime I have dedicated myself to this struggle of the African people. I have fought against white domination, and I have fought against black domination. I have cherished the ideal of a democratic and free society in which all persons live together in harmony and with equal opportunities. It is an ideal which I hope to live for and to achieve. But if needs be, it is an ideal for which I am prepared to die.”
– Nelson Mandela, Supreme court of South Africa, Pretoria, April 20, 1964. (See: full speech )
Time in Prison

F.W.De Klerk and Nelson Mandela at World Economic Forum 1992.
During his time in prison, Mandela became increasingly well known throughout the world. Mandela became the best known black leader and was symbolic of the struggle against the apartheid regime. Largely unbeknown to Mandela, his continued imprisonment led to a world-wide pressure for his release. Many countries implemented sanctions on apartheid South Africa. Due to international pressure, from the mid-1980s, the apartheid regime increasingly began to negotiate with the ANC and Nelson Mandela in particular. On many occasions, Mandela was offered a conditional freedom. However, he always refused to put the political ideals of the ANC above his own freedom.
Freedom and a new Rainbow Nation

Mandela voting in 1994 election. Photo. P.Weinburg
Eventually, Nelson Mandela was released on February 11, 1990. The day was a huge event for South Africa and the world. His release symbolic of the impending end of apartheid. Following his release there followed protracted negotiations to secure a lasting settlement. The negotiations were tense often against the backdrop of tribal violence. However, in April 1994, South Africa had its first full and fair elections. The ANC, with 65% of the vote, were elected and Nelson Mandela became the first President of the new South Africa.
“The time for the healing of the wounds has come. The moment to bridge the chasms that divide us has come. The time to build is upon us.”
As President, he sought to heal the rifts of the past. Despite being mistreated, he was magnanimous in his dealing with his former oppressors. His forgiving and tolerant attitude gained the respect of the whole South African nation and considerably eased the transition to a full democracy.
“If there are dreams about a beautiful South Africa, there are also roads that lead to their goal. Two of these roads could be named goodness and forgiveness.”

Photo: Governor-General of Australia
In 1995, the Rugby World Cup was held in South Africa. Nelson Mandela was instrumental in encouraging black South Africans to support the ‘Springboks’ – The Springboks were previously reviled for being a symbol of white supremacy. Mandela surprised many by meeting the Springbok captain, Francois Pienaar, before the World Cup to wish the team well. After an epic final, in which South Africa beat New Zealand, Mandela, wearing a Springbok jersey, presented the trophy to the winning South Africa team. De Klerk later stated Mandela successfully won the hearts of a million white rugby fans.
Nelson Mandela also oversaw the formation of the Truth and Reconciliation Committee in which former crimes of apartheid were investigated, but stressing individual forgiveness and helping the nation to look forward. The Committee was chaired by Desmond Tutu , and Mandela later praised its work.
Nelson Mandela retired from the Presidency in 1999, to be succeeded by Thabo Mbeki. In Mandela’s later years, ill health curtailed his public life. However, he did speak out on certain issues. He was very critical of the US-led invasion of Iraq during 2003. Speaking in a Newsweek interview in 2002, he expressed concern at American actions, he said:
“I really wanted to retire and rest and spend more time with my children, my grandchildren and of course with my wife. But the problems are such that for anybody with a conscience who can use whatever influence he may have to try to bring about peace, it’s difficult to say no.” (10 September 2002)
He has also campaigned to highlight the issue of HIV / AIDS in South Africa.
Mandela was married three times, fathered six children, and had 17 grandchildren. His first wife was Evelyn Ntoko Mase. His second wife was Winnie Madikizela-Mandela, they split after an acrimonious dispute. Winnie was alleged to have an involvement in human rights abuses. Mandela married for a third time on his 80th birthday to Graça Machel.

Graça Michel, Sri Chinmoy and Nelson Mandela holding Peace Torch. Source
Nelson Mandela was often referred to as Madiba – his Xhosa clan name.
Nelson Mandela died on 5 December 2013 after a long illness with his family at his side. He was 95.
At his memorial, Barack Obama, the President of the US said:
“We will not likely see the likes of Nelson Mandela ever again, so it falls to us, as best we can, to carry forward the example that he set. He no longer belongs to us; he belongs to the ages.”
Citation: Pettinger, Tejvan . “Biography of Nelson Mandela”, Oxford, UK. www.biographyonline.net. Published: 7th December 2013. Last updated 13th February 2018.
Nelson Mandela – In His Own Words

Nelson Mandela – In His Own Words at Amazon
Mandela – The Authorised Portrait

Mandela – The Authorised Portrait at Amazon
Related Pages

- Nelson Mandela Quotes
- Inspirational People
- People who fought for human rights
- Nelson Mandela.org
- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
Nelson Mandela
By: History.com Editors
Updated: March 29, 2023 | Original: November 9, 2009

The South African activist and former president Nelson Mandela (1918-2013) helped bring an end to apartheid and has been a global advocate for human rights. A member of the African National Congress party beginning in the 1940s, he was a leader of both peaceful protests and armed resistance against the white minority’s oppressive regime in a racially divided South Africa. His actions landed him in prison for nearly three decades and made him the face of the antiapartheid movement both within his country and internationally. Released in 1990, he participated in the eradication of apartheid and in 1994 became the first Black president of South Africa, forming a multiethnic government to oversee the country’s transition. After retiring from politics in 1999, he remained a devoted champion for peace and social justice in his own nation and around the world until his death in 2013 at the age of 95.
Nelson Mandela’s Childhood and Education
Nelson Mandela was born on July 18, 1918, into a royal family of the Xhosa-speaking Thembu tribe in the South African village of Mvezo, where his father, Gadla Henry Mphakanyiswa (c. 1880-1928), served as chief. His mother, Nosekeni Fanny, was the third of Mphakanyiswa’s four wives, who together bore him nine daughters and four sons. After the death of his father in 1927, 9-year-old Mandela—then known by his birth name, Rolihlahla—was adopted by Jongintaba Dalindyebo, a high-ranking Thembu regent who began grooming his young ward for a role within the tribal leadership.
Did you know? As a sign of respect, many South Africans referred to Nelson Mandela as Madiba, his Xhosa clan name.
The first in his family to receive a formal education, Mandela completed his primary studies at a local missionary school. There, a teacher dubbed him Nelson as part of a common practice of giving African students English names. He went on to attend the Clarkebury Boarding Institute and Healdtown, a Methodist secondary school, where he excelled in boxing and track as well as academics. In 1939 Mandela entered the elite University of Fort Hare, the only Western-style higher learning institute for Black South Africans at the time. The following year, he and several other students, including his friend and future business partner Oliver Tambo (1917-1993), were sent home for participating in a boycott against university policies.
After learning that his guardian had arranged a marriage for him, Mandela fled to Johannesburg and worked first as a night watchman and then as a law clerk while completing his bachelor’s degree by correspondence. He studied law at the University of Witwatersrand, where he became involved in the movement against racial discrimination and forged key relationships with Black and white activists. In 1944, Mandela joined the African National Congress (ANC) and worked with fellow party members, including Oliver Tambo, to establish its youth league, the ANCYL. That same year, he met and married his first wife, Evelyn Ntoko Mase (1922-2004), with whom he had four children before their divorce in 1957.
Nelson Mandela and the African National Congress
Nelson Mandela’s commitment to politics and the ANC grew stronger after the 1948 election victory of the Afrikaner-dominated National Party, which introduced a formal system of racial classification and segregation—apartheid—that restricted nonwhites’ basic rights and barred them from government while maintaining white minority rule. The following year, the ANC adopted the ANCYL’s plan to achieve full citizenship for all South Africans through boycotts, strikes, civil disobedience and other nonviolent methods. Mandela helped lead the ANC’s 1952 Campaign for the Defiance of Unjust Laws, traveling across the country to organize protests against discriminatory policies, and promoted the manifesto known as the Freedom Charter, ratified by the Congress of the People in 1955. Also in 1952, Mandela and Tambo opened South Africa’s first Black law firm, which offered free or low-cost legal counsel to those affected by apartheid legislation.
On December 5, 1956, Mandela and 155 other activists were arrested and went on trial for treason. All of the defendants were acquitted in 1961, but in the meantime tensions within the ANC escalated, with a militant faction splitting off in 1959 to form the Pan Africanist Congress (PAC). The next year, police opened fire on peaceful Black protesters in the township of Sharpeville, killing 69 people; as panic, anger and riots swept the country in the massacre’s aftermath, the apartheid government banned both the ANC and the PAC. Forced to go underground and wear disguises to evade detection, Mandela decided that the time had come for a more radical approach than passive resistance.

Nelson Mandela and the Armed Resistance Movement
In 1961, Nelson Mandela co-founded and became the first leader of Umkhonto we Sizwe (“Spear of the Nation”), also known as MK, a new armed wing of the ANC. Several years later, during the trial that would put him behind bars for nearly three decades, he described the reasoning for this radical departure from his party’s original tenets: “[I]t would be wrong and unrealistic for African leaders to continue preaching peace and nonviolence at a time when the government met our peaceful demands with force. It was only when all else had failed, when all channels of peaceful protest had been barred to us, that the decision was made to embark on violent forms of political struggle.”
Under Mandela’s leadership, MK launched a sabotage campaign against the government, which had recently declared South Africa a republic and withdrawn from the British Commonwealth. In January 1962, Mandela traveled abroad illegally to attend a conference of African nationalist leaders in Ethiopia, visit the exiled Oliver Tambo in London and undergo guerilla training in Algeria. On August 5, shortly after his return, he was arrested and subsequently sentenced to five years in prison for leaving the country and inciting a 1961 workers’ strike. The following July, police raided an ANC hideout in Rivonia, a suburb on the outskirts of Johannesburg, and arrested a racially diverse group of MK leaders who had gathered to debate the merits of a guerilla insurgency. Evidence was found implicating Mandela and other activists, who were brought to stand trial for sabotage, treason and violent conspiracy alongside their associates.
Mandela and seven other defendants narrowly escaped the gallows and were instead sentenced to life imprisonment during the so-called Rivonia Trial, which lasted eight months and attracted substantial international attention. In a stirring opening statement that sealed his iconic status around the world, Mandela admitted to some of the charges against him while defending the ANC’s actions and denouncing the injustices of apartheid. He ended with the following words: “I have cherished the ideal of a democratic and free society in which all persons live together in harmony and with equal opportunities. It is an ideal which I hope to live for and to achieve. But if needs be, it is an ideal for which I am prepared to die.”
Nelson Mandela’s Years Behind Bars
Nelson Mandela spent the first 18 of his 27 years in jail at the brutal Robben Island Prison, a former leper colony off the coast of Cape Town, where he was confined to a small cell without a bed or plumbing and compelled to do hard labor in a lime quarry. As a Black political prisoner, he received scantier rations and fewer privileges than other inmates. He was only allowed to see his wife, Winnie Madikizela-Mandela (1936-), who he had married in 1958 and was the mother of his two young daughters, once every six months. Mandela and his fellow prisoners were routinely subjected to inhumane punishments for the slightest of offenses; among other atrocities, there were reports of guards burying inmates in the ground up to their necks and urinating on them.
These restrictions and conditions notwithstanding, while in confinement Mandela earned a bachelor of law degree from the University of London and served as a mentor to his fellow prisoners, encouraging them to seek better treatment through nonviolent resistance. He also smuggled out political statements and a draft of his autobiography, “Long Walk to Freedom,” published five years after his release.
Despite his forced retreat from the spotlight, Mandela remained the symbolic leader of the antiapartheid movement. In 1980 Oliver Tambo introduced a “Free Nelson Mandela” campaign that made the jailed leader a household name and fueled the growing international outcry against South Africa’s racist regime. As pressure mounted, the government offered Mandela his freedom in exchange for various political compromises, including the renouncement of violence and recognition of the “independent” Transkei Bantustan, but he categorically rejected these deals.
In 1982 Mandela was moved to Pollsmoor Prison on the mainland, and in 1988 he was placed under house arrest on the grounds of a minimum-security correctional facility. The following year, newly elected president F. W. de Klerk (1936-) lifted the ban on the ANC and called for a nonracist South Africa, breaking with the conservatives in his party. On February 11, 1990, he ordered Mandela’s release.
Nelson Mandela as President of South Africa
After attaining his freedom, Nelson Mandela led the ANC in its negotiations with the governing National Party and various other South African political organizations for an end to apartheid and the establishment of a multiracial government. Though fraught with tension and conducted against a backdrop of political instability, the talks earned Mandela and de Klerk the Nobel Peace Prize in December 1993. On April 26, 1994, more than 22 million South Africans turned out to cast ballots in the country’s first multiracial parliamentary elections in history. An overwhelming majority chose the ANC to lead the country, and on May 10 Mandela was sworn in as the first Black president of South Africa, with de Klerk serving as his first deputy.
As president, Mandela established the Truth and Reconciliation Commission to investigate human rights and political violations committed by both supporters and opponents of apartheid between 1960 and 1994. He also introduced numerous social and economic programs designed to improve the living standards of South Africa’s Black population. In 1996 Mandela presided over the enactment of a new South African constitution, which established a strong central government based on majority rule and prohibited discrimination against minorities, including whites.
Improving race relations, discouraging Blacks from retaliating against the white minority and building a new international image of a united South Africa were central to President Mandela’s agenda. To these ends, he formed a multiracial “Government of National Unity” and proclaimed the country a “rainbow nation at peace with itself and the world.” In a gesture seen as a major step toward reconciliation, he encouraged Blacks and whites alike to rally around the predominantly Afrikaner national rugby team when South Africa hosted the 1995 Rugby World Cup.
On his 80th birthday in 1998, Mandela wed the politician and humanitarian Graça Machel (1945-), widow of the former president of Mozambique. (His marriage to Winnie had ended in divorce in 1992.) The following year, he retired from politics at the end of his first term as president and was succeeded by his deputy, Thabo Mbeki (1942-) of the ANC.
Nelson Mandela’s Later Years and Legacy
After leaving office, Nelson Mandela remained a devoted champion for peace and social justice in his own country and around the world. He established a number of organizations, including the influential Nelson Mandela Foundation and The Elders, an independent group of public figures committed to addressing global problems and easing human suffering. In 2002, Mandela became a vocal advocate of AIDS awareness and treatment programs in a culture where the epidemic had been cloaked in stigma and ignorance. The disease later claimed the life of his son Makgatho (1950-2005) and is believed to affect more people in South Africa than in any other country.
Treated for prostate cancer in 2001 and weakened by other health issues, Mandela grew increasingly frail in his later years and scaled back his schedule of public appearances. In 2009, the United Nations declared July 18 “Nelson Mandela International Day” in recognition of the South African leader’s contributions to democracy, freedom, peace and human rights around the world. Nelson Mandela died on December 5, 2013 from a recurring lung infection.

HISTORY Vault: Black History
Watch acclaimed Black History documentaries on HISTORY Vault.

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
Nelson Rolihlahla Mandela became known and respected all over the world as a symbol of the struggle against apartheid and all forms of racism; the icon and the hero of African liberation.
Mandela or Madiba, as he was affectionately known, has been called a freedom fighter, a great man, South Africa's Favourite Son, a global icon and a living legend, among countless other names. He has been an activist, a political prisoner, South Africa's first democratically elected president, an international peacemaker and statesman, and a Nobel Peace Prize winner.
As a husband and a father, Mandela sacrificed the joys of family life and of seeing his children grow up. As a young man, he missed out on a normal life spent with family and friends and pursuing a career of his choice, to fight for the cause he unshakably stood for.
Most ordinary South Africans knew little about Mandela during his prison years, as the apartheid government suppressed information, and what was released was biased. Limited information about Mandela was available from the international press, anti-apartheid activist groups and the Free Nelson Mandela campaign.
But prison bars could not prevent him from continuing to inspire his people to struggle and sacrifice for their liberation. Public opinion polls repeatedly showed that he was the most popular leader the country has ever had. As the Commonwealth Eminent Persons Group observed in 1986, he had become "a living legend", galvanising the resistance in his country.
He is the most honoured political prisoner in history. He has received prestigious international awards, the freedom of many cities and honorary degrees from several universities.
Musicians have been inspired to compose songs and music in his honour. Major international art exhibits have been dedicated to him and some of the most prominent writers have contributed to books for him and about him. Even an atomic particle has been named after him.
Mandela is a universal symbol of freedom and reconciliation, an icon representing the triumph of the human spirit. During his lifetime he not only dedicated himself to the struggle of the African people, but with his humility, and his spirit of forgiveness, he captured hearts and inspired people all over the world. As South Africans, we owe it to this great champion of our nation to continue to live by his example.
The early years
Rolihlahla Nelson Mandela was born in Mvezo, a village near Mthatha in the Transkei, on 18 July 1918, to Nongaphi Nosekeni and Gadla Henry Mandela. His father was the key counsellor/adviser to the Thembu royal house. His Xhosa name Rolihlahla literally means "pulling the branch of a tree". After his father's death in 1927, the young Rolihlahla became the ward of Chief Jongintaba Dalindyebo, the acting regent of the Thembu nation. It was at the Thembu royal homestead that his personality, values and political views were shaped. Hearing the elders' stories of his ancestors' valour during the wars of resistance to colonialism, he dreamed also of making his own contribution to the freedom struggle of his people.
After receiving his primary education at a local mission school, where he was given the name Nelson, he was sent to the Clarkebury Boarding Institute for his Junior Certificate and then to Healdtown, a reputable Wesleyan secondary school, where he matriculated. He then enrolled at the University College of Fort Hare for a Bachelor of Arts (BA) Degree where he was elected onto the Students' Representative Council. He was suspended from college for joining a protest boycott, along with Oliver Tambo.
Shortly after his return to the royal homestead, he and his cousin, Justice, ran away to Johannesburg to avoid arranged marriages and for a short period he worked as a mine policeman. Mandela was introduced to Walter Sisulu in 1941 and it was Sisulu who arranged for him to serve his articles at Lazar Sidelsky's law firm. Completing his BA through the University of South Africa (Unisa) in 1942, he commenced study for his Bachelor of Laws Degree shortly afterwards (though he left the University of the Witwatersrand without graduating in 1948). He entered politics in earnest while studying, and joined the African National Congress (ANC) in 1943.
At the height of the Second World War in 1944, a small group of young Africans who were members of the ANC, banded together under the leadership of Anton Lembede. Among them were William Nkomo, Sisulu, Oliver R Tambo, Ashby P Mda and Mandela. Starting out with 60 members, all of whom were residing around the Witwatersrand, these young people set themselves the formidable task of transforming the ANC into a more radical mass movement.
In September 1944, they came together to found the African National Congress Youth League (ANCYL).
Mandela soon impressed his peers by his disciplined work and consistent effort and was elected as the league's national secretary in 1948. Through painstaking work, campaigning at the grass-roots and through its mouthpiece Inyaniso ("Truth"), the ANCYL was able to canvass support for its policies among the ANC membership.
The political journey
Spurred on by the victory of the National Party, which won the 1948 all-white elections on the platform of apartheid, at the 1949 Annual Conference, the Programme of Action, inspired by the Youth League, which advocated the weapons of boycott, strike, civil disobedience and non-cooperation, was accepted as official ANC policy.
In December, Mandela was elected to the National Executive Committee at the National Conference.
When the ANC launched its Campaign for the Defiance of Unjust Laws in 1952, Mandela, by then president of the Youth League, was elected national volunteer-in-chief. The Defiance Campaign was conceived as a mass civil disobedience campaign that would snowball from a core of selected volunteers to involve more and more ordinary people, culminating in mass defiance. Fulfilling his responsibility as volunteer-in-chief, Mandela travelled the country, organising resistance to discriminatory legislation. Charged, with Moroka, Sisulu and 17 others, and brought to trial for his role in the campaign, the court found that Mandela and his co-accused had consistently advised their followers to adopt a peaceful course of action and to avoid all violence.
For his part in the Defiance Campaign, Mandela was convicted of contravening the Suppression of Communism Act and given a suspended prison sentence. Shortly after the campaign ended, he was also prohibited from attending gatherings and confined to Johannesburg for six months.
In December 1952, in partnership with Tambo, Mandela opened South Africa's first black law firm in central Johannesburg.
In 1953, Mandela was given the responsibility to prepare a plan that would enable the leadership of the movement to maintain dynamic contact with its membership without recourse to public meetings. The objective was to prepare for the possibility that the ANC would, like the Communist Party, be declared illegal and to ensure that the organisation would be able to operate from underground. This was the M-Plan, named after him.
During the early 1950s, Mandela played an important part in leading the resistance to the Western Areas removals, and to the introduction of Bantu Education. He also played a significant role in popularising the Freedom Charter, adopted by the Congress of the People in 1955.
During the whole of the 1950s, Mandela was the victim of various forms of repression. He was banned, arrested and imprisoned. A five-year banning order was enforced against him in March 1956.
The prison years
For much of the latter half of the 1950s, Mandela was one of the 156 accused in the mammoth Treason Trial. After the Sharpeville Massacre on 21 March 1960, the ANC was outlawed, and Mandela, still on trial, was detained, along with hundreds of others.
The Treason Trial collapsed in 1961 as South Africa was being steered towards the adoption of a republic. With the ANC now illegal, the leadership picked up the threads from its underground headquarters and Nelson Mandela emerged as the leading figure in this new phase of struggle.
Forced to live apart from his family, moving from place to place to evade detection by the Government's ubiquitous informers and police spies, Mandela had to adopt a number of disguises. Sometimes dressed as a labourer, Politicsat other times as a chauffeur, his successful evasion of the police earned him the title of the Black Pimpernel.
It was during this time that he, together with other leaders of the ANC, constituted a new section of the liberation movement, Umkhonto we Sizwe (MK), as an armed nucleus with a view to preparing for armed struggle, with Mandela as its commander-in-chief.
In 1962, Mandela left the country as "David Motsamayi", and travelled abroad for several months. In Ethiopia, he addressed the Conference of the Pan-African Freedom Movement of East and Central Africa, and was warmly received by senior political leaders in several countries, including the then Tanganyika, Senegal, Ghana and Sierra Leone. He also spent time in London. During this trip, Mandela met with the first group of 21 MK recruits on their way to Addis Ababa for guerrilla training.
Not long after his return to South Africa, Mandela was arrested, on 5 August, and charged with illegal exit from the country, and incitement to strike.
Mandela was convicted and sentenced to five years imprisonment. He was transferred to Robben Island in May 1963 only to be brought back to Pretoria again in July.
Not long afterwards, he encountered Thomas Mashifane, the foreman from Liliesleaf Farm in Rivonia where MK had set up their headquarters. He knew then that their hide-out had been discovered. A few days later, he and 10 others were charged with sabotage.
The Rivonia Trial, as it came to be known, lasted eight months.
Mandela's statement in court during the trial is a classic in the history of the resistance to apartheid, and has been an inspiration to all who have opposed it. He ended with these words: "I have fought against white domination, and I have fought against black domination. I have cherished the ideal of a democratic and free society in which all persons live together in harmony and with equal opportunities. It is an ideal which I hope to live for and to achieve. But if needs be, it is an ideal for which I am prepared to die."
All but two of the accused were found guilty and sentenced to life imprisonment on 12 June 1964. The black prisoners were flown secretly to Robben Island immediately after the trial was over to begin serving their sentences.
In March 1982, after 18 years, he was transferred to Pollsmoor Prison in Cape Town (with Sisulu, Raymond Mhlaba and Andrew Mlangeni) and in December 1988, he was moved to the Victor Verster Prison near Paarl, from where he was eventually released. While in prison, Mandela flatly rejected offers made by his jailers for remission of sentence in exchange for accepting the bantustan policy by recognising the independence of the Transkei and agreeing to settle there. Again in the 1980s, Mandela and others rejected an offer of release on condition that he renounce violence.
Nevertheless, Mandela did initiate talks with the apartheid regime in 1985, when he wrote to then Minister of Justice, Kobie Coetsee. They first met later that year when Mandela was hospitalised for prostate surgery. Shortly after this, he was moved to a single cell at Pollsmoor and this gave Mandela the chance to start a dialogue with the Government – which took the form of "talks about talks". Throughout this process, he was adamant that negotiations could only be carried out by the full ANC leadership.
Released on 11 February 1990, Mandela plunged wholeheartedly into his life's work, striving to attain the goals he and others had set out almost four decades earlier. In 1991, at the first national conference of the ANC held inside South Africa after being banned for decades, Nelson Mandela was elected president of the ANC while his lifelong friend and colleague, Oliver Tambo, became the organisation's national chairperson.
The era of apartheid formally came to an end on 27 April 1994, when Nelson Mandela voted for the first time in his life – along with his people. However, long before that date, it had become clear, even before the start of the Convention for a Democratic South Africa (Codesa) negotiations at the World Trade Centre in Kempton Park, that the ANC was increasingly charting the future of South Africa.
Rolihlahla Nelson Dalibunga Mandela was inaugurated as President of a democratic South Africa on 10 May 1994. In his inauguration speech, he said: "We dedicate this day to all the heroes and heroines in this country and the rest of the world who sacrificed in many ways and surrendered their lives so that we could be free. Their dreams have become reality. Freedom is their reward. We are both humbled and elevated by the honour and privilege that you, the people of South Africa, have bestowed on us, as the first President of a united, democratic, non-racial and non-sexist government."
In June 1999, Nelson Mandela retired from the Presidency of South Africa. But although he retired as President of South Africa, he worked tirelessly, campaigning globally for peace, children and the fight against HIV/Aids in particular.
Shortly before his 86th birthday in June 2004, Mandela officially retired from public life. However, he did not retreat from working for the good of the world – as a testimony to his sharp political intellect, wisdom and unrelenting commitment to make the world a better place, Mandela formed the prestigious group of Elders, an independent group of eminent global leaders, who offer their collective influence and experience to support peace-building, help address major causes oh human suffering and promote the shared interest of humanity.
General enquiries
Frequently asked questions
Tel: 012 473 0114 or 012 473 0389 E-mail: [email protected]
A Brief History of Nelson Mandela's Life
The key moments of an extraordinary life.
By The Nelson Mandela Foundation
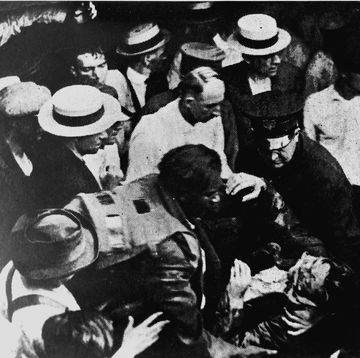
Nelson Mandela walks out of the gates of Victor Verster prison (1990-02-11) by Gideon Mendel The Nelson Mandela Foundation
Madiba's journey
Known and loved around the world for his commitment to peace, negotiation and reconciliation, Nelson Rolihlahla Mandela was South Africa's first democratically elected president (1994-1999). Mandela was an anti-apartheid revolutionary and political leader, as well as a philanthropist with an abiding love for children. Mandela was born into the Xhosa royal family on 18 July 1918 and died on 5 December 2013.
Mvezo rondavels v2 (2007-04-16) The Nelson Mandela Foundation
The early years
Rolihlahla Mandela was born into the Madiba clan in the village of Mvezo, in the Eastern Cape, on 18 July 1918. His mother was Nonqaphi Nosekeni and his father was Nkosi Mphakanyiswa Gadla Mandela, principal counsellor to the Acting King of the Thembu people, Jongintaba Dalindyebo. In 1930, when he was 12 years old, his father died and the young Rolihlahla became a ward of Jongintaba at the Great Place in Mqhekezweni. Hearing the elders’ stories of his ancestors’ valour during the wars of resistance, he dreamed also of making his own contribution to the freedom struggle of his people.
Childhood (2010/2010) The Nelson Mandela Foundation
Gilbert Nzimeni Collection Healdtown photograph (front) The Nelson Mandela Foundation
Education He attended primary school in Qunu where his teacher, Miss Mdingane, gave him the name Nelson, in accordance with the custom of giving all schoolchildren “Christian” names. He completed his Junior Certificate at Clarkebury Boarding Institute and went on to Healdtown, a Wesleyan secondary school of some repute, where he matriculated. Mandela began his studies for a Bachelor of Arts degree at the University College of Fort Hare but did not complete the degree there as he was expelled for joining in a student protest. On his return to the Great Place at Mqhekezweni the King was furious and said if he didn’t return to Fort Hare he would arrange wives for him and his cousin Justice. They ran away to Johannesburg instead, arriving there in 1941. There he worked as a mine security officer and after meeting Walter Sisulu, an estate agent, he was introduced to Lazer Sidelsky. He then did his articles through a firm of attorneys – Witkin, Eidelman and Sidelsky. He completed his BA through the University of South Africa and went back to Fort Hare for his graduation in 1943.
Mandela with his law class at the University of the Witwatersrand (1944) by WITS University archive The Nelson Mandela Foundation
University Meanwhile, he began studying for an LLB at the University of the Witwatersrand. By his own admission he was a poor student and left the university in 1952 without graduating. He only started studying again through the University of London after his imprisonment in 1962 but also did not complete that degree. In 1989, while in the last months of his imprisonment, he obtained an LLB through the University of South Africa. He graduated in absentia at a ceremony in Cape Town.
The Big City (2010/2010) The Nelson Mandela Foundation
NRM and Bikitsha (1941/1941) The Nelson Mandela Foundation
Entering politics
Mandela, while increasingly politically involved from 1942, only joined the African National Congress in 1944 when he helped to form the ANC Youth League (ANCYL).In 1944 he married Walter Sisulu’s cousin, Evelyn Mase, a nurse. They had two sons, Madiba Thembekile "Thembi" and Makgatho, and two daughters both called Makaziwe, the first of whom died in infancy. He and his wife divorced in 1958.Mandela rose through the ranks of the ANCYL and through its efforts, the ANC adopted a more radical mass-based policy, the Programme of Action, in 1949.
scan0003 The Nelson Mandela Foundation
National Volunteer-in-Chief In 1952 he was chosen as the National Volunteer-in-Chief of the Defiance Campaign with Maulvi Cachalia as his deputy. This campaign of civil disobedience against six unjust laws was a joint programme between the ANC and the South African Indian Congress. He and 19 others were charged under the Suppression of Communism Act for their part in the campaign and sentenced to nine months of hard labour, suspended for two years.
Nelson Mandela and Jerry Moloi sparring by Bob Gosani/ BAHA The Nelson Mandela Foundation
Mandela and Tambo A two-year diploma in law on top of his BA allowed Mandela to practise law, and in August 1952 he and Oliver Tambo established a law firm called Mandela & Tambo. At the end of 1952 he was banned for the first time. As a restricted person he was only permitted to watch in secret as the Freedom Charter was adopted in Kliptown on 26 June 1955.
Treason Trial, Unthreading Mandela (2018-11-07) by Nelson Mandela Foundation The Nelson Mandela Foundation
The Treason Trial
Mandela was arrested in a countrywide police swoop on 5 December 1956, which led to the 1956 Treason Trial. Men and women of all races found themselves in the dock in the marathon trial that only ended when the last 28 accused, including Mandela, were acquitted on 29 March 1961.
The Prisoner (2010/2010) The Nelson Mandela Foundation
Nelson Mandela with his dog Gompo by Alf Khumalo The Nelson Mandela Foundation
State of emergency On 21 March 1960 police killed 69 unarmed people in a protest in Sharpeville against the pass laws. This led to the country’s first state of emergency and the banning of the ANC and the Pan Africanist Congress (PAC) on 8 April. Mandela and his colleagues in the Treason Trial were among thousands detained during the state of emergency.
Amy Thornton-Reitstein (1994-01-01) Original Source: To download a photograph click here
Spear of the Nation Days before the end of the Treason Trial, Mandela travelled to Pietermaritzburg to speak at the All-in Africa Conference, which resolved that he should write to Prime Minister Verwoerd requesting a national convention on a non-racial constitution, and to warn that should he not agree there would be a national strike against South Africa becoming a republic. After he and his colleagues were acquitted in the Treason Trial, Mandela went underground and began planning a national strike for 29, 30 and 31 March. In the face of massive mobilisation of state security the strike was called off early. In June 1961 he was asked to lead the armed struggle and helped to establish Umkhonto weSizwe (Spear of the Nation), which launched on 16 December 1961 with a series of explosions.
Winni and Mandela getting married (1958-06) by UWC, Robben Island , Mayibuye archives / Eli Weinberg The Nelson Mandela Foundation
Marriage During the trial Mandela married a social worker, Winnie Madikizela, on 14 June 1958. They had two daughters, Zenani and Zindziswa. The couple divorced in 1996.
AT040-13 Mandela Algeria (1962) by UWC, Robben Island , Mayibuye archives The Nelson Mandela Foundation
Undercover On 11 January 1962, using the adopted name David Motsamayi, Mandela secretly left South Africa. He travelled around Africa and visited England to gain support for the armed struggle. He received military training in Morocco and Ethiopia and returned to South Africa in July 1962. He was arrested in a police roadblock outside Howick on 5 August while returning from KwaZulu-Natal, where he had briefed ANC President Chief Albert Luthuli about his trip.
Nelson Mandela and Walter Sisulu by Unknown Robben Island Museum
Sentenced to 5 years in prison He was charged with leaving the country without a permit and inciting workers to strike. He was convicted and sentenced to five years' imprisonment, which he began serving at the Pretoria Local Prison. On 27 May 1963 he was transferred to Robben Island and returned to Pretoria on 12 June. Within a month police raided Liliesleaf, a secret hideout in Rivonia, Johannesburg, used by ANC and Communist Party activists, and several of his comrades were arrested.
8 Rivonia Trialists (1964) by Unknown Robben Island Museum
The Rivonia Trial On 9 October 1963 Mandela joined 10 others on trial for sabotage in what became known as the Rivonia Trial. While facing the death penalty his words to the court at the end of his famous "Speech from the Dock" on 20 April 1964 became immortalised: “During my lifetime I have dedicated my life to this struggle of the African people. I have fought against white domination, and I have fought against black domination. I have cherished the ideal of a democratic and free society in which all persons will live together in harmony and with equal opportunities. It is an ideal for which I hope to live for and to see realised. But, My Lord, if it needs be, it is an ideal for which I am prepared to die.” Speech from the Dock quote by Nelson Mandela on 20 April 1964
Robben Island group of prisoners (1977-04-25) The Nelson Mandela Foundation
Robben Island On 11 June 1964 Mandela and seven other accused, Walter Sisulu, Ahmed Kathrada, Govan Mbeki, Raymond Mhlaba, Denis Goldberg, Elias Motsoaledi and Andrew Mlangeni, were convicted and the next day were sentenced to life imprisonment. Goldberg was sent to Pretoria Prison because he was white, while the others went to Robben Island.
Life in prison Mandela’s mother died in 1968 and his eldest son, Thembi, in 1969. He was not allowed to attend their funerals.
Release Mandela Original Source: Graeme Williams / South Photos
From freedom to liberation On 31 March 1982 Mandela was transferred to Pollsmoor Prison in Cape Town with Sisulu, Mhlaba and Mlangeni. Kathrada joined them in October. When he returned to the prison in November 1985 after prostate surgery, Mandela was held alone. Justice Minister Kobie Coetsee visited him in hospital. Later Mandela initiated talks about an ultimate meeting between the apartheid government and the ANC.
Release from prison
On 12 August 1988 he was taken to hospital where he was diagnosed with tuberculosis. After more than three months in two hospitals he was transferred on 7 December 1988 to a house at Victor Verster Prison near Paarl where he spent his last 14 months of imprisonment. He was released from its gates on Sunday 11 February 1990, nine days after the unbanning of the ANC and the PAC and nearly four months after the release of his remaining Rivonia comrades. Throughout his imprisonment he had rejected at least three conditional offers of release.
Inauguration of President Nelson Mandela (1994-05-10) Original Source: Guy Stubbs
Nobel Peace Prize Mandela immersed himself in official talks to end white minority rule and in 1991 was elected ANC President to replace his ailing friend, Oliver Tambo. In 1993 he and President FW de Klerk jointly won the Nobel Peace Prize and on 27 April 1994 he voted for the first time in his life.
Nelson Mandela signing the 'President's Bible' (1994-05-10) The Nelson Mandela Foundation
On 10 May 1994 he was inaugurated as South Africa’s first democratically elected President. On his 80th birthday in 1998 he married Graça Machel, his third wife.
The Statesman (2010/2010) The Nelson Mandela Foundation
Retiring from Retirement (2007-06/2007-06) The Nelson Mandela Foundation
Retirement True to his promise, Mandela stepped down in 1999 after one term as President. He continued to work with the Nelson Mandela Children’s Fund he set up in 1995 and established the Nelson Mandela Foundation and The Mandela Rhodes Foundation.
Madiba at Home - Mvezo (2005-07-18/2005-07-18) The Nelson Mandela Foundation
Mvezo and Mandla Mandela In April 2007 his grandson, Mandla Mandela, was installed as head of the Mvezo Traditional Council at a ceremony at the Mvezo Great Place.
Mandela's body being transported (2013-12-14) by Gallo images /Foto24/ Deaan Vivier The Nelson Mandela Foundation
Mandela's legacy Nelson Mandela died at his home in Johannesburg on 5 December 2013.
Mandela at 92 (2010-07-17) The Nelson Mandela Foundation
Nelson Mandela never wavered in his devotion to democracy, equality and learning. Despite terrible provocation, he never answered racism with racism. His life is an inspiration to all who are oppressed and deprived; and to all who are opposed to oppression and deprivation.
Robben Island Prison Tour
Robben island museum, 11 february 1990: mandela's release from prison, africa media online, nelson mandela's fight to empower the next generation, the nelson mandela foundation, in their own words: recollections of former political prisoners, what happened at the treason trial, a virtual exhibition on the life and times of nelson mandela, poster power: protest art from south africa, 9 august 1956: the women's anti-pass march, what happened when nelson mandela previewed his prison archive, a timeline of robben island from 700,000 bce to 1845 ce, the signs that defined the apartheid.
- CBSE Class 10th
- CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore
Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Main Question Paper
- JEE Main Cutoff
- JEE Main Answer Key
- SRMJEEE Result
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- JEE Advanced Registration
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2023
- CAT 2023 College Predictor
- CMAT 2024 Registration
- TS ICET 2024 Registration
- CMAT Exam Date 2024
- MAH MBA CET Cutoff 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- DNB CET College Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Admit Card 2024
- NEET PG Application Form 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- LSAT India 2024
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top Law Collages in Indore
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- AIBE 18 Result 2023
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Predictors & Articles
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- NID DAT Syllabus 2025
- NID DAT 2025
- Design Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Interior Design Colleges in India
- Top Graphic Designing Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Fashion Design Colleges in Bangalore
- Top Interior Design Colleges in Bangalore
- NIFT Result 2024
- NIFT Fees Structure
- NIFT Syllabus 2025
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission 2024
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- LPU NEST 2024
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET Exam City Intimation Slip 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET Mock Test 2024
- CUET Admit card 2024
- CUET PG Syllabus 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Syllabus 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- IGNOU Result
- CUET Courses List 2024
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses

Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Nelson Mandela Essay
Nelson Mandela was a statesman and black nationalist leader in South Africa who was born on July 18, 1918, in Umtata, Cape of Good Hope. He passed away on December 5, 2013, in Johannesburg. Mandela, a law student at the University of Witwatersrand and the son of a Xhosa chief, joined the African National Congress(ANC) in 1944. Here are a few sample essays on Nelson Mandela.

100 Words Essay On Nelson Mandela
Nelson Mandela was an outstanding leader of African nationalism and a professional lawyer born on July 18, 1918, in South Africa. He eventually gave up on that, and in 1944 joined the African National Congress. In South Africa, he spearheaded the nonviolent resistance against racial inequality.
He was one of South Africa's finest leaders and independence fighters. Mandela battled against the repressive regime alongside the revolutionaries. Nelson Mandela became the nation's first black president, ultimately leading to the overthrow of the white supremacist administration. He will always be seen as a symbol of social justice and equality. At age 95, he passed away on December 5th, 2013.
200 Words Essay On Nelson Mandela
Nelson Mandela was born on July 18, 1918. He was a native of a little South African community called Umtata. His entire life represents a struggle in South Africa against ingrained racism. He was one of those who were burdened by the impartial system. Thus it wasn't simple for him to fight against the current circumstances.
Nelson Mandela’s Contributions
Nelson Mandela lived through years of being a colonised person before becoming actively involved in the anti-apartheid movement. Mandela endured suffering as an African boy who fell victim to the European expatriate effort that involved 'civilising' local people. Nelson Mandela was imprisoned in the 1960s for opposing the government's racial restrictions. He spent around three decades behind bars, yet he never wavered in his quest for justice and equality for all people.
Nelson Mandela was regarded as a man of strength, integrity, and ideals and a strong, unyielding leader. He was the only person to lead the country in 1994 in the fight to eradicate racial discrimination. In South Africa, he received the first-ever nomination for president of a race. Between 1994 and 1999, he presided over South Africa for five years.
Nelson Mandela symbolised the aspirations for a just and free world even after he left public life.
500 Words Essay On Nelson Mandela
Henry Mandela, the chief of the Tembu tribe, gave birth to Nelson Mandela in 1918. He married Evelyn Ntoko Mase, a nurse, in the year 1944. His twelve fruitful years of marriage ended in divorce. After two years, in 1958, he wed Nomzamo Winnie Madikileza, a political activist and social worker. In 1998, after divorcing her, he married Graca Machel, a lawyer. He had two daughters from his second marriage and three kids from his first marriage.
Nelson Mandela’s Academics
Speaking of his schooling, Nelson Mandela completed his bachelor's degree through distance learning at South Africa University in 1941. He earned a law degree from Witwatersrand University in 1942. He began working as a lawyer in South Africa in 1948.
Nelson Mandela’s Life As A Prisoner
He experienced repeated police harassment between the 1940s and the 1950s, including harassment, banishment, and detention. In 1960, he formed a military wing and went into hiding. Nelson Mandela was imprisoned for five years in 1962 due to his illegal international travel. This act angered South Africans, and a strike was called. He was held for two years before being accused of disloyalty, which resulted in a life sentence for him.
His 4-and-a-half-hour lecture, which criticised racial prejudice, is still remembered today. Mandela served nearly 27 years of a life sentence in prison. His detention improved his political standing, which sparked a global effort to have his sentence commuted.
Mandela spent all of these twenty-seven years behind bars. He was kept out of sight and concealed from everyone as he dug limestone and grew seaweed. Nelson Mandela was hospitalised for TB in 1988. After he had healed, he was sent back to prison under less stringent circumstances. He was fully discharged in 1990, allowing him to watch happy celebration scenes at home and abroad.
His Life As A Politician
Mandela's involvement in politics began after he enrolled in college. He worked hard to earn a Bachelor of "Fine Arts" degree. He received a nomination from a student political organisation to serve on the Representative Council while he was a student. He was following his debarment due to his participation in a campus protest. As a result, he travelled to Johannesburg to complete his BA. When World War II broke out, Nelson Mandela joined forces with the ANC's "African National Congress" after receiving his degree in 1942.
Together with the other ANC members, Nelson Mandela formed a group. This group's main goal was to make the ANC a widespread movement. Mandela was a key figure in several racial activities and political campaigns that relied on nonviolent tactics, including strikes, boycotts, and acts of civil disobedience.
He passed away in December 2013. At the time, he was 95 years old. Nelson Mandela received more than 250 honours and distinctions, including the Medal of Freedom, the Bharat Ratna, and the "1993 Nobel Peace" Prize.
He was a great inspiration for me. I used to study the biography of the legend Nelson Mandela. He is known for saying, "A Winner is a Dreamer who Never Gives Up."
Applications for Admissions are open.

JEE Main Important Physics formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Physics formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

UPES School of Liberal Studies
Ranked #52 Among Universities in India by NIRF | Up to 30% Merit-based Scholarships | Lifetime placement assistance

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

PACE IIT & Medical, Financial District, Hyd
Enrol in PACE IIT & Medical, Financial District, Hyd for JEE/NEET preparation

ALLEN JEE Exam Prep
Start your JEE preparation with ALLEN
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Certifications
We Appeared in
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Nelson Mandela: His Life In His Words And The Words Of Others
Joe Richman
In April 1994, the world watched as millions of South Africans, most of them jubilant but many wary, cast their ballots in that nation's first multiracial election. Ten years later, NPR broadcast "Mandela: An Audio History," by producers Joe Richman and Sue Johnson of Radio Diaries. The radio documentary tells the story of Nobel Peace Prize-winner Nelson Mandela through the leader's own words, the voices those who fought with him, as well as those who fought against him. You can listen to a segment of the documentary by clicking play on the audio above, or you can listen to the full hour-long documentary, and read a timeline of his life, here .
Copyright © 2013 NPR. All rights reserved. Visit our website terms of use and permissions pages at www.npr.org for further information.
NPR transcripts are created on a rush deadline by an NPR contractor. This text may not be in its final form and may be updated or revised in the future. Accuracy and availability may vary. The authoritative record of NPR’s programming is the audio record.
Connect with us

- STUDY @ MANDELA
- LEARNING AND TEACHING
- RESEARCH, INNOVATION AND INTERNATIONALISATION
- ENGAGEMENT AND TRANSFORMATION
- LEADERSHIP AND GOVERNANCE
- FACULTIES AND SCHOOLS
- NEWS AND EVENTS
- STAKEHOLDERS AND SUPPLIERS
- A man named Mandela
- A glimpse of Madiba's life
- Thoughts about Madiba
- Madiba Diaries

Born on 18 July 1918 at Mvezo, near Qunu in the former Transkei, Nelson Rolihlahla Mandela spent much of his childhood being groomed to become a chief. He matriculated at Healdtown Methodist Boarding School and went on to study at Fort Hare University College where he met Oliver Tambo. Here he became involved in student politics and was expelled in 1940 as a result of participating in a student protest. On moving to Johannesburg, he was employed as a mine policeman where he met Walter Sisulu who assisted him in obtaining articles with a legal firm. Completing a BA degree by correspondence in 1941, he then began studying for a law degree which he did not complete. In December 1952, Mandela and Tambo opened the first African legal partnership in the country. Together with Sisulu and Tambo, Mandela participated in the founding of the African National Congress Youth League in 1944, serving as National Secretary in 1948, becoming National President in 1950.
In October 1952, as President of the ANC in the Transvaal, he became one of four Deputy Presidents of the organisation. Later that year, Mandela and 19 others were arrested and charged under the Suppression of Communism Act for their participation in the Defiance Campaign. They were sentenced to nine months imprisonment with hard labour, suspended for two years. In 1956, he was one of the 156 political activists arrested and charged with high treason for the campaign leading to the adoption of the Freedom Charter the previous year. The trial lasted four and a half years (during which time charges against many of the accused were dropped) and ended in March 1961, when Mandela and 29 others were found not guilty. In 1961 Umkhonto we Sizwe was formed with Mandela as its Commander-in-Chief. Nelson Mandela was instrumental in a number of protest actions and campaigns, including the anti-pass law campaigns. He addressed international audiences and travelled widely to gain support for the struggle against apartheid. He returned to South Africa in July 1962, and on 5 August was captured near Howick, Natal. He was tried and sentenced to five years imprisonment for incitement to strike and for illegally leaving the country. While Mandela was in prison, police raided the underground headquarters of the African National Congress at Lilliesleaf Farm, Rivonia and arrested central ANC leaders. The Rivonia trial commenced in October 1963 and Mandela joined the other accused being tried for sabotage and conspiracy to overthrow the government by revolution. His statement from the dock received worldwide publicity. On 12 June 1964, all eight of the accused, including Mandela, were sentenced to life imprisonment. Whilst incarcerated on Robben Island, Mandela (who was kept in isolation cells along with other senior leaders) continued to exercise leadership in the education of fellow prisoners and attending to political questions facing the organisation. Whilst in exile, her maintained contact with the leadership of the ANC. In 1988, Mandela was diagnosed with tuberculosis and was transferred to a house on the grounds of the Victor Verster Prison, near Paarl. In the late eighties, he initiated contact with government representatives, which eventually led to his meeting with State President PW Botha in July 1989 at Tuynhuys. In December 1989 he met the new State President, FW de Klerk. On 2 February 1990, the ANC, the South African Communist Party, the PAC and other anti-apartheid organisations were unbanned and Nelson Mandela was released from jail on Sunday, 11 February 1990. Upon his release, he reassumed his leadership role in the ANC and the National Executive Committee appointed him Deputy President. He undertook a tour of the country, addressing the biggest rallies ever seen in the country’s history and helped re-establish the ANC as a legal organisation. He led the ANC in negotiations with the South African government which culminated in the adoption of the interim constitution in November 1993. Mandela led the ANC campaign in the 1994 elections, in which the ANC won with a 62% majority. On Monday, 9 May 1994, Mandela was elected President of the Republic of South Africa by the National Assembly in Cape Town and sworn in the following day. In June of that year, he undertook to donate one-third of his annual salary (R150 000) to The Nelson Mandela Children’s Fund which was established to address the needs of marginalised youths.
In 1997 he retired as the President of the ANC and in July 1998, married Graca Machel, the widow of former Mozambiquan President, Samora Machel. The following year he stepped down as President of South Africa
In the year 2000 he was appointed as mediator in the civil war in Burundi and in 2002, discovered new talents when he started his training as an artist.
In June 2004, he announced that he would be stepping down from public life, however, in 2010 – the year that South Africa hosted the FIFA World Cup, he was formally presented with the Web Ellis Trophy before it embarked on a tour of the country. He late made a surprise appearance at the final of the massive world sporting event held in Soweto in June.
In 2010 his second book Conversations with Myself was published and in 2011, his third book - Nelson Mandela By Himself: The Authorised Book of Quotations.
On 5 December 2013, Nelson Rolihlahla Mandela passed away at his home in Johannesburg, aged 95.
He was awarded numerous honours and many honorary degrees during his lifetime and was a recipient of the Nobel Peace Prize, which he shared with Executive Deputy President Frederick W de Klerk, who was State President when the award was given.

MAIL AND PORTALS
- Student Portal
- Staff Portal
- Student Mail
- Publications
- Report a Security Breach
- Ethics Hotline
- University social media
WORK@MANDELA
- Work environment
- +27 (0) 41 504 1111
- [email protected]
- PO Box 77000 Nelson Mandela University Gqeberha, 6031 South Africa
© 2023 Nelson Mandela University Privacy Statement / BEE & Tax Certificate / PAIA / ISPA / FAQ / Sitemap / --> Directory / WCMS
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Nelson Mandela Biography

The first President of South Africa to be elected in entirely representative democratic elections was Nelson Mandela. He was a prominent anti-apartheid radical and leader of the African National Congress before his presidency, who spent 27 years in jail for his participation in the activities of clandestine armed resistance and sabotage.
About Nelson Mandela
Full Name - Nelson Rolihlahla Mandela
Date of Birth - July 18, 1918
Date of Death - December 5, 2013
Cause of Death - Prolonged respiratory infection
Age - 95 years
Nelson Mandela spouse(s) -
Evelyn Ntoko Mase (m. 1944; div. 1958)
Winnie Madikizela (m. 1958; div. 1996)
Graça Machel (m. 1998)
Who is Nelson Mandela?
Nelson Mandela belonged to the Thembu Dynasty cadet branch which reigned (nominally) in the Transkeian Territories of the Cape Province Union of South Africa. He was born in the small village of Qunu in the Mthatha district, the capital of the Transkei. Ngubengcuka (died 1830), the Inkosi Enkulu or King of the Thembu people, was his great-grandfather and was ultimately subjected to British colonial rule. One of the king's sons, named Mandela, became Nelson's grandfather and the source of his surname.
His father, Gadla Henry Mphakanyiswa (1880-1928) was appointed chief of the village of Mvezo. However, he was stripped of his position after alienating the colonial authorities and he moved his family to Qunu. Gadla, however, remained a member of the Privy Council of Inkosi and was instrumental in the ascension of Jongintaba Dalindyebo to the Thembu throne, who would later return this favor by informally adopting Mandela upon the death of Gadla.
Mandela's father had four wives, with whom he fathered a total of 13 children (four boys and nine girls). Nosekeni Fanny, daughter of Nkedama of the Mpemvu Xhosa tribe, in whose homestead Mandela spent most of his childhood, was born to Gadla's third wife ('third' by a complex royal ranking system). His given name, Rolihlahla, means "one who brings trouble upon himself."
Nelson Mandela Education
Rolihlahla Mandela became the first member of his family to attend a school at the age of seven, where a Methodist teacher gave him the name 'Nelson,' after the British admiral Horatio Nelson. When Rolihlahla was nine, his father died of tuberculosis, and the Regent, Jongintaba, became his guardian. Mandela was attending a Wesleyan mission school next door to the Regent's palace. He was initiated at age 16, adopting Thembu tradition, and attended Clarkebury Boarding Institute, learning about Western culture. Instead of the standard three, he completed his Junior Certificate in two years.
In 1937, Mandela moved to Healdtown, the Wesleyan college in Fort Beaufort, which was attended by most Thembu royalty, as he was supposed to inherit the place of his father as a private counselor. He took an interest in boxing and running at the age of nineteen. After registering, he began studying for a B.A. and met Oliver Tambo at Fort Hare University, where the two became lifelong friends and colleagues. He became active in a protest by the Students' Representative Council against university policies at the end of his first year and was forced to leave Fort Hare.
Mandela initially found employment as a guard at a mine upon his arrival in Johannesburg. This was quickly terminated, however, after the employer learned that Mandela was the runaway adopted son of the Regent. Thanks to connections with his friend and fellow lawyer Walter Sisulu, he then managed to find work as a clerk at a law firm. He completed his degree at the University of South Africa (UNISA) through correspondence while working, after which he began his law studies at the University of Witwatersrand. Mandela lived in a township called Alexandra during that time.
About Nelson Mandela Marriage and Family
Nelson Mandela married thrice and had fathered six children, 20 grandchildren, and an increasing number of great-grandchildren. His first marriage was to Evelyn Ntoko Mase, who, like Mandela, was also from what later became South Africa's Transkei region. They first met in Johannesburg. The couple had two sons, Madiba Thembekile (born 1946) and Makgatho (born 1950), and two daughters, both named Makaziwe (known as Maki; born 1947 and 1953).
Nelson Mandela’s second wife, Winnie Madikizela-Mandela, was also from the Transkei region, even though they also met in Johannesburg, where she was the first black social worker in the city. The marriage bore two daughters, Zenani (Zeni), born on February 4, 1958, and Zindziswa (Zindzi), born in 1960. The union, fuelled by political estrangement, ended in separation (April 1992) and divorce (March 1996).
In 1998, on his 80th birthday, Mandela married Graça Machel, née Simbine, the widow of Samora Machel, a former Mozambican president and an ANC ally killed 12 years earlier in an air crash. His traditional sovereign, King Buyelekhaya Zwelibanzi Dalindyebo, born in 1964, carried out the wedding on Mandela's behalf (which followed months of international negotiations to fix the unparalleled bride price sent to her clan). Ironically, it was the grandfather of this paramount leader, the Regent, whose selection of a bride for him compelled Mandela to flee as a young man to Johannesburg.
About Nelson Mandela Political Activity
Nelson Mandela was influential in the ANC's 1952 Defiance Movement and the 1955 People's Congress. They adopted the Freedom Charter which provided the basic program of the anti-apartheid cause, after the 1948 election victory of the Afrikaner-dominated National Party with its apartheid racial segregation policy. Nelson Mandela and fellow lawyer Oliver Tambo ran the Mandela and Tambo law firm during this period, offering free or low-cost legal advice to many blacks who would otherwise have been without legal representation.
Initially influenced by Mahatma Gandhi and devoted to non-violent mass struggle, on December 5, 1956, Mandela was arrested and charged with treason along with 150 others. The 1956-1961 marathon Treason Trial followed, and all were acquitted. As a new class of black activists (Africanists) emerged in the townships seeking more drastic action against the National Party government, the ANC witnessed disruption from 1952-1959. Albert Luthuli, Oliver Tambo, and Walter Sisulu's ANC leadership thought not only that events were moving too rapidly, but also that their leadership was being questioned.
The ANC lost its most militant support in 1959 when, under Robert Sobukwe and Potlako Leballo, most of the Africanists, with financial support from Ghana and major political support from the Transvaal-based Basotho, split away to form the Pan Africanist Congress (PAC).
Arrest and Imprisonment
In 1961, Nelson Mandela became the chief of Umkhonto we Sizwe (Spear of the Nation, also abbreviated as MK), the armed wing of the ANC, which he co-founded. He coordinated a campaign of sabotage against military and government objectives and if sabotage failed to end apartheid, made preparations for a future guerrilla war. MK did indeed wage a guerrilla war against the regime a few decades later, especially during the 1980s, in which many civilians were killed. Mandela also collected funds and organized paramilitary training for MK overseas, visiting different African governments.
He was captured after living on the run for 17 months on August 5, 1962, and imprisoned in the Johannesburg Fort. Three days later, at a court appearance, the charges of leading workers to a strike in 1961 and leaving the country illegally were read to him. Mandela was sentenced to five years in prison on October 25, 1962.
On June 11th, 1964, two years later, a verdict was reached concerning his prior participation in the African National Congress (ANC). Nelson Mandela was incarcerated on Robben Island for the next 18 of his 27 years in prison. It was there that he wrote the bulk of his 'Long Walk to Freedom' autobiography. Mandela did not disclose anything in that book about the suspected involvement of President F. W. De Klerk, or the role of his ex-wife Winnie Mandela in the brutality of the 1980s and early 1990s. In Mandela: The Authorized Biography, however, he later cooperated with his friend, journalist Anthony Sampson, who addressed these issues.
Mandela remained in jail rejecting an offer of conditional release in exchange for renouncing armed struggle in February 1985 until concerted ANC and international activism came up with the resounding slogan “Free Nelson Mandela!”. President de Klerk simultaneously ordered the release of Mandela in February 1990 and the revocation of the ANC ban.
Post-apartheid
On April 27, 1994, South Africa's first democratic elections were held in which full enfranchisement was given. In the election, the ANC won the vote, and Nelson Mandela, as ANC leader, was inaugurated as the country's first black president, with de Klerk of the National Party as his deputy president in the National Unity Government.
As South Africa hosted the 1995 Rugby World Cup, Nelson Mandela urged black South Africans to get behind the previously despised Springboks (the South African national rugby team). Nelson Mandela, wearing a Springbok jersey, presented the trophy to captain Francois Pienaar, an Afrikaner after the Springboks had secured an epic final over New Zealand. This has been widely seen as a significant step in white and black South Africans' reconciliation.
It was also during his administration when, with the launch of the SUNSAT satellite in February 1999, South Africa entered the space age. It was developed by Stellenbosch University students and was used primarily to photograph land related to vegetation and forestry issues in South Africa.
Nelson Mandela Awards
Nelson Mandela has received many South African, foreign, and international awards, including the 1993 Nobel Peace Prize, Queen Elizabeth II's Order of Merit and the Order of St. John, and George W. Bush's Presidential Medal of Freedom. In July 2004, during a ceremony in Orlando, Soweto, the city of Johannesburg, South Africa, conferred its highest honor on Mandela by granting him the freedom of the city.
As an indication of his popular international recognition, he had a speaking engagement at the SkyDome in the city of Toronto during his tour of Canada in 1998, where 45,000 school children welcomed him with intense adulation.
He was the first living person to be named an honorary Canadian citizen in 2001.
In 1992, Turkey awarded him the Ataturk Peace Prize. He declined the award, alleging abuses of human rights committed during that period by Turkey, but later accepted the award in 1999. He has also received the Ambassador of Conscience Award from Amnesty International (2006).
Retirement and Death
Nelson Mandela was diagnosed and treated for prostate cancer in the summer of 2001. Mandela declared in June 2004, at the age of 85, that he would retire from public life. His health had been deteriorating, and he and his family decided to spend more time.
He passed away on December 5, 2013, at the age of 95, after suffering from a prolonged respiratory infection. He died, surrounded by his relatives, at his home in Houghton, Johannesburg.
Some facts about Nelson Mandela
From 1994 until 1999, Nelson Mandela served as President of South Africa. He was South Africa's first black president and the first to be elected in a fully representative election.
The leadership of Nelson Mandela concentrated on overthrowing the country's Apartheid government, which had enforced racial segregation through the law.
Nelson Mandela studied law at school and then went on to become one of South Africa's first black lawyers.
He was chosen leader of the African National Congress (ANC) liberation movement's youth section in the 1950s.
Mandela established a hidden military movement after the government banned the ANC for racial reasons. He had previously participated in nonviolent protests, but as the government responded with brutality, he moved on to promote an anti-government movement.

‘I am prepared to die’: Mandela’s speech which shook apartheid
Sixty years ago during the Rivonia Trial in South Africa, Nelson Mandela delivered one of the most famous speeches of the 20th century. He expected to be sentenced to death but instead lived to see his dream ‘of a democratic and free society’ realised.
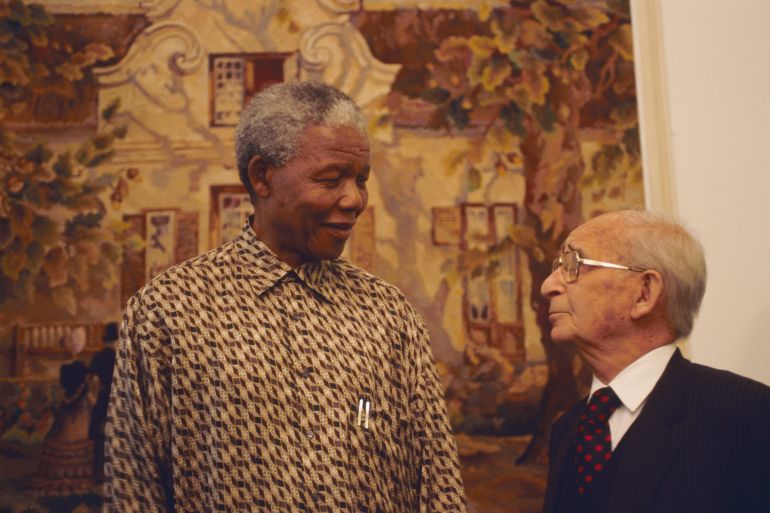

“Accused number one” had been speaking from the dock for almost three hours by the time he uttered the words that would ultimately change South Africa. The racially segregated Pretoria courtroom listened in silence as Nelson Mandela’s account of his lifelong struggle against white minority rule reached its conclusion. Judge Quintus de Wet managed not to look at Mandela for the majority of his address. But before accused number one delivered his final lines, defence lawyer Joel Joffe remembered, “Mandela paused for a long time and looked squarely at the judge” before saying:
“During my lifetime, I have dedicated my life to this struggle of the African people. I have fought against white domination, and I have fought against Black domination. I have cherished the ideal of a democratic and free society in which all persons will live together in harmony and with equal opportunities. It is an ideal for which I hope to live for and to see realised. But, my Lord, if it needs be, it is an ideal for which I am prepared to die.”
Keep reading
Ramaphosa hails anc record as south africa marks 30 years of democracy, ‘free at last’: when south africa voted in democracy, kicked out apartheid, april 27, 1994: what has changed in south africa 30 years after apartheid, south africa seeks to stop auction of historic nelson mandela artefacts.
After he spoke that last sentence, novelist and activist Nadine Gordimer, who was in the courtroom on April 20, 1964, said, “The strangest and most moving sound I have ever heard from human throats came from the Black side of the court audience. It was short, sharp and terrible: something between a sigh and a groan.”
This was because there was a very good chance that Mandela and his co-accused would be sentenced to death for their opposition to the apartheid government. His lawyers had actually tried to talk him out of including the “I am prepared to die” line because they thought it might be seen as a provocation. But as Mandela later wrote in his autobiography, “I felt we were likely to hang no matter what we said, so we might as well say what we truly believed.”

‘The trial that changed South Africa’
The Rivonia Trial – in which Mandela, Walter Sisulu, Govan Mbeki and seven other anti-apartheid activists were charged with sabotage – was the third and final time Mandela would stand accused in an apartheid court. From 1956 to 1961, he had been involved in the Treason Trial, a long-running embarrassment for the apartheid government, which would ultimately see all 156 of the accused acquitted because the state failed to prove they had committed treason.
And in 1962, he had been charged with leaving the country illegally and leading Black workers in a strike. He knew he was guilty on both counts, so he decided to put the apartheid government on trial. On the first day of the case, Mandela, known for his natty Western dress, arrived in traditional Xhosa attire to the shock of all present. He led his own defence and did not call any witnesses. Instead, he gave what has been remembered as the “Black man in a white court” speech, during which he asserted that “posterity will pronounce that I was innocent and that the criminals that should have been brought before this court are the members of the Verwoerd government,” a reference to Prime Minister Hendrik Verwoerd.
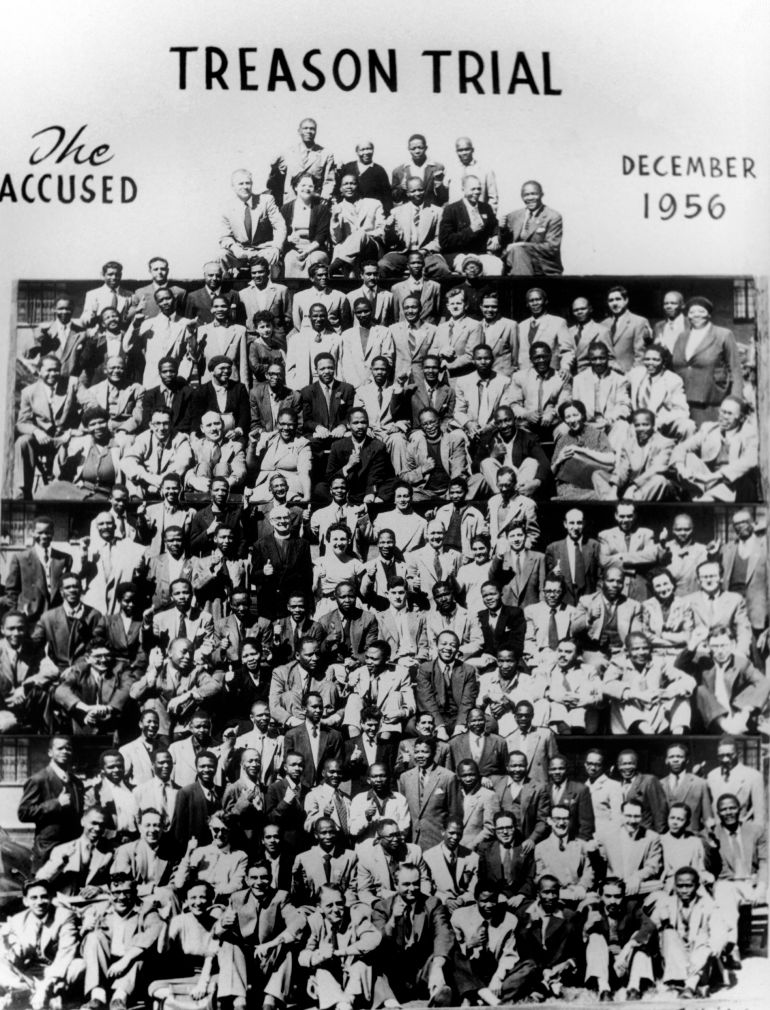

The Rivonia Trial, which kicked off in October 1963, was named after the Johannesburg suburb where Liliesleaf Farm was located. From 1961 to 1963, the Liliesleaf museum website notes, the farm served “as the secret headquarters and nerve centre” of the African National Congress (ANC), the South African Communist Party (SACP) and Umkhonto we Sizwe (MK, the military wing of the ANC). On July 11, 1963, acting on a tip-off, the police raided Liliesleaf, seizing many incriminating documents and arresting the core leadership of the underground liberation movement. Mandela, who was serving a five-year sentence on Robben Island from his conviction in the 1962 trial, was flown to Pretoria to take his place as accused number one.

Instead of charging the men with high treason, State Prosecutor Percy Yutar opted for the easier-to-prove crime of sabotage – the definition of which was so broad that it included misdemeanours such as trespassing – and which had recently been made a capital offence by the government. Thanks to the evidence seized from Liliesleaf, which included several documents handwritten by Mandela and the testimony of Bruno Mtolo (referred to as Mr X throughout the trial), a regional commander of MK who had turned state witness, Yutar was virtually assured of convictions for the main accused.
In his autobiography, Mandela explains their defence strategy: “Right from the start we had made it clear that we intended to use the trial not as a test of the law but as a platform for our beliefs. We would not deny, for example, that we had been responsible for acts of sabotage. We would not deny that a group of us had turned away from non-violence. We were not concerned with getting off or lessening our punishment, but with making the trial strengthen the cause for which we were struggling – at whatever cost to ourselves. We would not defend ourselves in a legal sense so much as in a moral sense.”
The accused and their lawyers decided that Mandela would open the defence case not as a witness – who would be subject to cross-examination – but with a statement from the dock. This format would allow him to speak uninterrupted, but it carried less legal weight.

Mandela writes that he spent “about a fortnight drafting [his] address, working mainly in my cell in the evenings”. He first read it to his co-accused, who approved the text with a few tweaks, before passing it to lead defence lawyer Bram Fischer. Fischer was concerned that the final paragraph might be taken the wrong way by the judge, so he got another member of the defence team, Hal Hanson, to read it. Hanson was unequivocal: “If Mandela reads this in court, they will take him straight to the back of the courthouse and string him up.”
“Nelson remained adamant” that the line should stay, wrote George Bizos, another member of the defence team. Bizos eventually persuaded Mandela to tweak his wording: “I proposed that Nelson say he hoped to live for and achieve his ideals but if needs be was prepared to die.”
On the evening of April 19, Bizos got Mandela’s permission to take a copy of his statement to Gordimer. The respected British journalist Anthony Sampson, who knew Mandela well, happened to be staying with her and he retired to Gordimer’s study with the text. “What seemed like hours” later, Bizos wrote, Sampson “eventually returned, obviously moved by what he had read”. Sampson made no major changes to the text, but he did advise moving some of the paragraphs because he felt journalists were likely to read the beginning and the end properly and skim over the rest.
Gordimer does not seem to have suggested changes to the address, but she did see several drafts. She, too, was happy with the final version.

The statement from the dock
Yutar, who had been hoodwinked by the defence team’s constant requests for court transcripts into spending weeks preparing to cross-examine Mandela, was visibly shocked when Fischer announced that Mandela would instead be making a statement from the dock. He even tried to get the judge to explain to Mandela that he was committing a legal error. But the usually stone-faced judge laughed as he dismissed the request. Mandela, himself a lawyer, was represented by some of the country’s finest legal minds. He knew exactly what he was doing.
“My Lord, I am the first accused,” Mandela said. “I admit immediately that I was one of the persons who helped to form Umkhonto we Sizwe and that I played a prominent role in its affairs until I was arrested in August 1962.” Thanks to the recent recovery of the original recordings of Mandela’s statement, we now know that he spoke for 176 minutes , not the four and a half hours regularly cited.
As Martha Evans, author of Speeches That Shaped South Africa, explained, Mandela “candidly confessed some of the crimes levelled against him before giving a cogent and detailed account of the conditions and events that had led to the establishment of MK and the adoption of the armed struggle”.
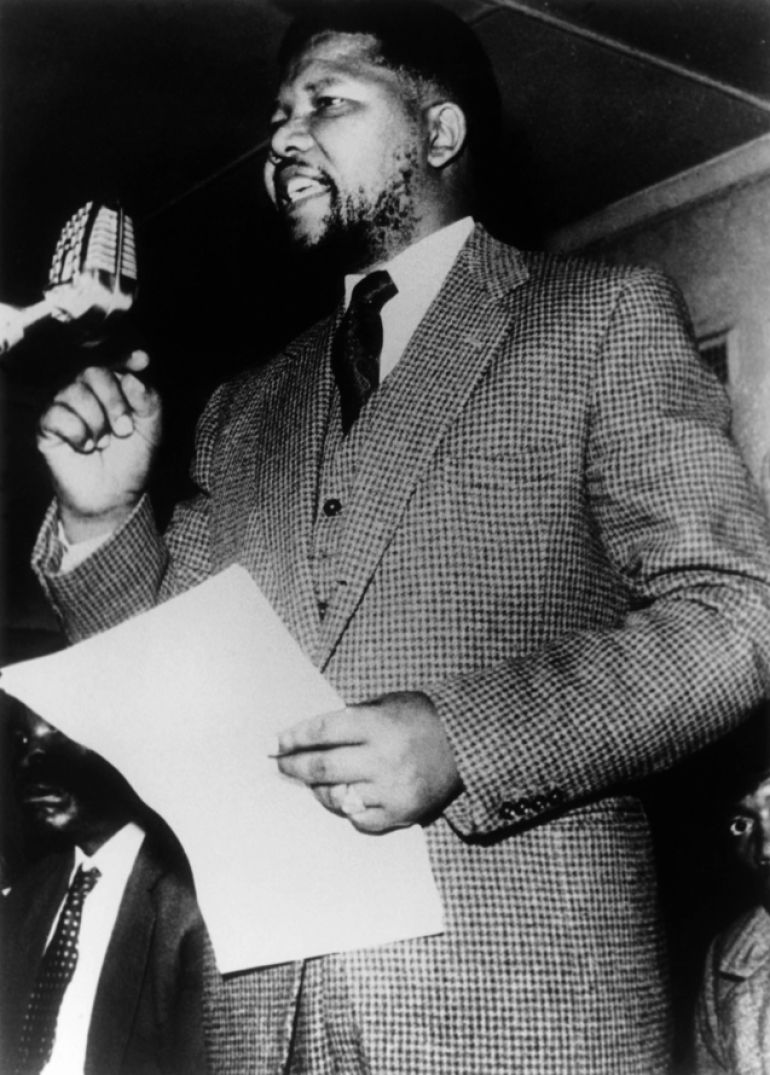

He spoke at length of the ANC’s tradition of nonviolence and explained why he had planned sabotage: “I did not plan it in a spirit of recklessness nor because I have any love for violence. I planned it as a result of a calm and sober assessment of the political situation that had arisen after many years of tyranny, exploitation and oppression of my people by the whites.”
The final section of the address focused on inequality in South Africa and humanised Black South Africans in ways that Mandela argued the country’s white population rarely acknowledged:
“Whites tend to regard Africans as a separate breed. They do not look upon them as people with families of their own. They do not realise that we have emotions, that we fall in love like white people do, that we want to be with our wives and children like white people want to be with theirs, that we want to earn money, enough money to support our families properly.”
And: “Above all, my Lord, we want equal political rights because without them our disabilities will be permanent. I know this sounds revolutionary to the whites in this country because the majority of voters will be Africans. This makes the white man fear democracy. But this fear cannot be allowed to stand in the way of the only solution which will guarantee racial harmony and freedom for all.”
Interestingly, Gordimer noted that the speech “read much better than it was spoken. Mandela’s delivery was very disappointing indeed, hesitant, parsonical (if there is such a word), boring. Only at the end did the man come through.”

Hanging by a thread
After Mandela’s address, several of the accused subjected themselves to cross-examination. Gordimer was particularly impressed by Walter Sisulu: “Sisulu was splendid. What a paradox – he is almost uneducated while [Mandela] has a law degree! He was lucid and to the point – and never missed a point in his replies to Yutar.”
The defence team enjoyed a number of minor victories with Judge de Wet fairly regularly telling the court that Yutar had failed to prove one point or another. After final arguments were heard in mid-May, court was adjourned for three weeks for the judge to consider his verdict.
For the main accused, that verdict was always going to be guilty. Avoiding the noose became the defence team’s number one priority. In the courtroom, this entailed asking Alan Paton, a world famous novelist who was leader of the vehemently anti-apartheid Liberal Party, to give evidence in mitigation of sentence.
But the real action happened outside the court, Sampson wrote in his authorised biography of Mandela: “The accused had been buoyed up by the growing support from abroad, not only from many African countries but also, more to Mandela’s surprise, from Britain. … On May 7, 1964, the British Prime Minister, Alec Douglas-Home, offered to send a private message to Verwoerd about the trial. But Sir Hugh Stephenson [Britain’s ambassador to South Africa] recommended that ‘no more pressure should be exerted’ and, contrary to some published reports, there is no evidence the message was sent. When the South African Ambassador called on the Foreign Office that month, he was told that the government was now under less pressure to take a stronger line against South Africa, though death sentences would bring the matter to a head again.”

A week before the verdicts, Bizos visited British Consul-General Leslie Minford at his Pretoria home. “As I was leaving, Leslie put his arm around my shoulders and said, ‘George, there won’t be a death sentence.’ I did not ask him how he knew. For one thing, he had downed a number of whiskies. Certainly, I felt I could not rely on the information nor could I tell the team or our anxious clients.”
Upping the stakes further was the decision by Mandela, Sisulu and Mbeki to not appeal their sentence – even if it were death. As he listened to sentencing arguments, Mandela clutched a handwritten note that concluded with the words: “If I must die, let me declare for all to know that I will meet my fate as a man.”
Paton and Hanson spoke in mitigation of sentence on the morning of June 12, 1964. Bizos noted, “Judge de Wet not only took no note of what was being said but he appeared not to be listening.” He had already made his mind up, and when the formalities were over, he announced: “I have decided not to impose the supreme penalty, which in a case like this would usually be the penalty for such a crime. But consistent with my duty, that is the only leniency which I can show. The sentence in the case of all the accused will be one of life imprisonment.”
Professor Thula Simpson, the leading historian of MK, told Al Jazeera, “There is no evidence that De Wet was leaned on by the state. I don’t believe there’s any evidence for this being a political rather than a judicial judgement.”
Professor Roger Southall, author of dozens of books on Southern African politics, agreed. “At the time, there was a lot of speculation about whether there was pressure on the SA government to ensure that capital punishment was not imposed,” he told Al Jazeera. “But there is also no proof that the SA government intervened. That remains an unanswered question. We have to presume that the judge knew the international and local climate.”

Business as usual?
“Rivonia got a lot of global publicity,” Southall said. “But once the trial ended, it seemed like Mandela had been forgotten.” Mandela and other senior ANC figures were either locked up on Robben Island or were living in relative obscurity in exile. “Capital came pouring into South Africa at a rate that’s never been equalled since,” Southall continued. “The apartheid government seemed totally in control. The resistance was dead. It was a thoroughly grim period for the ANC.”
This only started to change in 1973, Southall said, “with the Durban strikes and the revival of the trade union movement”, which had been battered into submission. The rebirth of the Black trade union movement signalled the beginning of a new phase of opposition politics. Things ratcheted up several notches on June 16, 1976, when apartheid policemen opened fire on a peaceful protest of schoolchildren in the Black township of Soweto, killing 15 people. In the eight months that followed, violence spread across South Africa, killing about 700 people.
The resuscitation of Black opposition to apartheid under a new band of leaders coincided with the decline of the economy. After the Soweto uprising, foreign investors fled South Africa in their droves, laying bare the fundamental flaws of the apartheid government’s dependence on cheap labour and mining and its point-blank refusal to meaningfully educate people of colour. The apartheid government spent about 12 times more per child on white schoolchildren than it did on Black ones.

By the 1980s, even the apartheid government could see something had to change, and in 1983, Prime Minister PW Botha announced plans to include multiracial and Indian South Africans, but not Black South Africans, in a new “tricameral” parliament. His plan backfired spectacularly, uniting the opposition like never before under the newly formed United Democratic Front (UDF). One of the UDF’s key demands was the unconditional release of all political prisoners, especially Mandela. Soon after its launch in August 1983, the UDF numbered almost 1,000 different organisations from all segments of South African society. Botha didn’t know what had hit him.
When, in 1984, Oliver Tambo, the ANC’s exiled leader, asked his supporters to “make South Africa ungovernable”, the townships rose up. Things got so bad in 1985 that Botha declared a state of emergency – but this was also the year in which tentative secret talks with Mandela began.
An icon re-emerges
“In the late 1970s, you started getting occasional demands that Mandela be released,” Southall said. By the mid-1980s, “Free Nelson Mandela” became a constant and global refrain with the “I am prepared to die” statement being quoted at rallies and emblazoned on T-shirts. “On one level, the ANC ‘invented’ this version of Mandela,” Southall said. “Until 1976, the apartheid government had done a very good job of erasing him from public memory.”
What might have happened if Mandela had been sentenced to death at Rivonia? One does not need to look far for a possible answer. The other poster boy of the global anti-apartheid movement in the 1980s was Steve Biko (subject of the Peter Gabriel hit song), the young leader of the Black Consciousness movement, who had been tortured to death by apartheid police in 1977. “You can also have myths develop when you execute people,” Simpson said. “If they had executed Mandela, he would have been a different icon in a different struggle.”

A dream realised
On February 11, 1990, Mandela was released from prison. From the balcony of Cape Town City Hall, he addressed his supporters for the first time since Rivonia. He opened his speech by saying: “I stand here before you not as a prophet but as a humble servant of you, the people. Your tireless and heroic sacrifices have made it possible for me to be here today. I, therefore, place the remaining years of my life in your hands.”
He ended by quoting the final lines of his 1964 statement from the dock, explaining that “they are true today as they were then.” Over the course of the next decade, as Mandela first navigated the treacherous path to democracy and then served as the country’s first democratically elected president, he lived out his vision of a “democratic and free society in which all persons live together in harmony and with equal opportunities”.
When the ANC’s Chris Hani was assassinated by an apartheid supporter in 1993, Mandela assumed the moral leadership of the country by urging his incensed supporters not to derail the peace process. After becoming president, he engaged in numerous public shows of reconciliation: He went for tea with the widow of slain apartheid Prime Minister Verwoerd, and he donned the Springbok rugby jersey (for many, a symbol of white supremacy) when he presented the almost entirely white South African team with the World Cup trophy in 1995.

When Mandela died in 2013, US President Barack Obama spoke at his memorial, famously – and predictably – quoting the final paragraph of the statement from the dock at Rivonia. By that stage, there were already some in South Africa who felt that Mandela was a “sellout” because he had been too forgiving of whites during the transition.
Now, more than a decade later as inequality continues to plague the country and South Africa stands on the cusp of its most competitive general election in 30 years of democracy, it is common to hear young Black South Africans accuse Mandela of selling out . Southall does not take such claims too seriously: “People who say he’s a sellout are either too young or too forgetful to appreciate how close we came to civil war. Mandela played a huge role in pulling off the peaceful transition.”
“Now, after 30 years of democracy, there is still a tension between white domination and Black domination,” Simpson said. “South Africa is not what Mandela dreamed of. He might be turning in his grave, but we can’t forget that many of the policies that have gone wrong were introduced by him. He might have turned things around, but he might have not.”
“You can’t blame Mandela for where we are now,” Southall said. “There are individual things he got wrong. But he also got a lot of things right.”
Mandela’s is one of the 12 remarkable lives covered in Nick Dall’s recent book, Legends: People Who Changed South Africa for the Better, co-written with Matthew Blackman.
Nelson Mandela Foundation
- Mandela Day
Advanced search
Learners' biography
Rolihlahla Mandela was born into the Madiba clan in Mvezo, Transkei, on 18 July 1918.
His mother was Nonqaphi Nosekeni and his father, Nkosi Mphakanyiswa Gadla Mandela, was the main advisor to the Acting King of the Thembu people, Jongintaba Dalindyebo.
He received the name "Nelson" on his first day in primary school from his teacher Miss Mdingane. When he was 12 his father died and he was raised by the Regent at the Great Place in Mqhekezweni. He was sent to the best schools available and began studying a BA at Fort Hare University.

When he was expelled for joining a student protest, the Regent told him to return or get married. So he ran away to Johannesburg with his cousin Justice. His first job in 1941 was as a security guard on a gold mine and then as a legal clerk in the law firm Witkin, Edelman and Sidelsky. At the same time he completed his BA through Unisa.
In 1943 he enrolled for an LLB at Wits University. He was a poor student and became more involved in politics from 1944 after he helped to start the ANC Youth League. He married in the same year and needed money to support his family.
By mid-1952 when the university asked him to pay the 27 pounds he owed or leave, he already had three children. He only started studying again in 1962 in prison. He finally graduated with an LLB through Unisa 27 years later.
Later in 1952 he became the National Volunteer-in-Chief of the Defiance Campaign against apartheid laws. He and 19 others were later charged and sentenced to nine months, suspended for two years. In August he and Oliver Tambo started South Africa’s first black law firm, Mandela & Tambo.

In those days one could practise as an attorney with a two-year diploma. Later that year he was banned for the first time – he had to ask the government for permission whenever he needed to leave Johannesburg. After the adoption of the Freedom Charter in 1955, 156 people were arrested and charged with treason. The trial lasted four-and-a-half years until 29 March 1961 by which time all were acquitted. The ANC and PAC were banned after the 21 March 1961 killing by police of 69 unarmed protesters in Sharpeville.
Mandela called on the government not to turn South Africa into a republic on 31 May 1961 but to discuss a non-racial constitution. He was ignored so he called for a strike on 29, 30 and 31 March.
In June 1961 he was asked to lead the ANC’s armed wing, Umkhonto weSizwe and it launched on 16 December that year. On 11 January 1962, Mandela secretly left South Africa to undergo military training and to get support from African countries for the armed struggle.
He was arrested on 5 August and charged with leaving the country illegally and encouraging the strike. He was convicted and sentenced on 7 November 1962 to five years in prison.
On 11 July 1963, a secret hideout he once used was raided by police. On 9 October 1963 he joined 10 others on trial for sabotage in the Rivonia Trial.

On 12 June 1964 he and seven others were sentenced to life imprisonment. While he was in prison his mother and his eldest son died. He was not allowed to attend their funerals.
He spent 18 years on Robben Island, and while at Pollsmoor Prison in Cape Town in 1985 he had to go to hospital. When Justice Minister Kobie Coetsee visited him, he had an idea: to see if the government wanted to talk about one day meeting with the ANC.
In 1988 he was taken to hospital for tuberculosis. Three months later he was moved to Victor Verster Prison where he spent his last 14 months in prison. He was released on Sunday 11 February 1990, nine days after the unbanning of the ANC and the PAC.
Other political prisoners were freed and exiles returned. The ANC began talking to the government about South Africa’s future. For this work he and President FW de Klerk won the Nobel Peace Prize in 1993, and on 27 April 1994, Mandela voted in South Africa’s first democratic elections.
On 10 May 1994, he was inaugurated as South Africa’s first democratically elected President and stepped down after one term. In his retirement he worked on building schools and clinics, highlighting HIV, children and leadership. He died at his home in Johannesburg on 5 December 2013.

Nelson Mandela Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on nelson mandela.
Nelson Rolihlahla Mandela was born on 18 July 1918 in the Transkei village close Umtata. Nelson Mandela was sent to Healdtown, a Wesleyan secondary school with some reputation where he enrolled after getting a primary education at a local mission school. He then registered for the Bachelor of Arts degree at Fort Hare University College where he was appointed to the Representative Council of the Student. Also, he was suspended for joining a protest boycott from college. He went to Johannesburg where, by correspondence, he finished his BA, took clerkship papers and began studying for his LLB . The Nelson Mandela essay is an insight into the life and works of the great man.

The greatest pleasure of Nelson Mandela, his most private moment, is to watch the sunset playing with the music of Händel or Tchaikovsky.
During daylight hours locked up in his cell, deprived of music, he was denied these two simple pleasures for centuries. Concerts were organized with his fellow inmates as far as possible, especially at Christmas time, where they would sing.
Nelson Mandela finds music very uplifting and is interested in European classical music as well as African choral music and the many talents in South African music. But above all, one voice stands out – Paul Robeson’s, whom he defines as our hero.
The years in prison strengthened already engraved practices: athlete’s disciplined eating system started in the 1940s, as did the early morning practice. Nelson Mandela is still up by 4.30am today, regardless of how late he worked last night.
He started his exercise routine by 5 am, which lasts for at least an hour. Breakfast is at 6.30 when newspapers are read during the days. With a normal working day of at nearly 12 hours, time management is critical and Nelson Mandela is highly impatient with impunctuality, considering it to be insulting to those with whom you deal.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Life of Nelson Mandela
He has conducted comprehensive traveling since his release from prison when he spoke. Nelson Mandela claims: “The biography of Pandit Nehru helped me prepare for my discharge. Who wrote about what’s going on when you leave prison.
My daughter Zinzi claims she grew up without a dad who became the nation’s dad when he came back. This has put on my shoulders a huge burden.
And wherever I travel, I instantly start missing the familiar–the mine dumps, the uniquely South African color and smell, and especially the individuals. I don’t like being away for a long moment. There’s no place like home for me.
Mandela accepted the Nobel Peace Prize as a tribute to all those who worked for peace and opposed racism. This individual has been awarded as much as it has been to the ANC and all the individuals of South Africa.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


How the Mandela myth helped win the battle for democracy in South Africa
Senior lecturer in African Studies, Yale University
Disclosure statement
Jonny Steinberg does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
View all partners
Political history scholar Jonny Steinberg’s 2023 book Winnie & Nelson: Portrait of a Marriage is a double biography of South Africa’s most famous political figures – Nelson Mandela and Winnie Madikizela Mandela – and their role in the country’s struggle for democracy. It’s also a book that shatters countless myths about the couple and the liberation struggle that have been formed in popular culture and even academic tellings of history. As South Africa commemorates 30 years of democracy, we asked Steinberg for his views on how and why these historical myths are formed.
How did Winnie and Nelson become so mythologised?
It may be best to start with a working definition of myth. I don’t take myth to mean fiction; to mythologise isn’t necessarily to make things up that are not true. To say that a person is mythologised means that their personal story is told in a way that exemplifies something bigger, generally a lesson, like how the oppressed should respond to their own suffering, or how oppressive systems of rule should end.
To begin with, Winnie and Nelson mythologised themselves. Both intuitively understood that their greatest talent lay in public performance. Not just any public performance, but the sort that is exemplary, that embodies a collective spirit, a set of yearnings.
When Nelson went underground to start the military wing of the African National Congress (ANC) liberation movement Umkhonto we Sizwe he understood not just that he must wage an armed struggle, but that people must see what a black man who chooses to fight looks like.
Same with Winnie. When she appeared in court in Johannesburg when Nelson was arrested in 1962, she brought two pairs of clothes: a traditional Thembu outfit for the courtroom to match the jackal-skin kaross she knew he would be wearing, and a business suit for the illegal march that would commence in the street after the hearing. She understood that for a black woman to confront the enemy in style was not a trivial matter or a mere detail. They both knew that wars were won and lost by the power of the myths one’s appearance tells.
But while Nelson and Winnie were responsible for the beginning of their mythologisation, others came on board later. In the late 1970s, ANC leader Oliver Tambo was approached with the idea of celebrating Mandela’s 60th birthday. He understood immediately that he’d been presented with the opportunity of crafting a hero figure to embody the struggle for freedom. He did not consult with the ANC executive because he knew they’d shout it down, warning of personality cults and so forth.
And so he gave the ANC the most powerful weapon imaginable, a simple story about a good man and a good woman who loved one another and had been torn asunder by an evil regime. Stories like that are worth their weight in gold. Imagine if the Palestinians had a story like that at their disposal now in their fight against Israeli occupation.
How does this play into the broader popular narrative about liberation?
Well, it meant that the very idea of freedom was embodied in a person, Nelson Mandela, which is an extraordinary thing, when you think about it. Would South Africa have been torn apart by civil war without the myth of Nelson Mandela? It’s a counterfactual question, the answer to which we’ll never know. But it’s certainly plausible to argue that we could not have crossed the bridge from apartheid to democracy without a blinding myth to mesmerise us all, so that we could walk together into the unknown.
That’s the positive side of the story. The negative side is that myths conceal a great deal. Tambo told colleagues quite bluntly that he promoted the myth of Mandela because Mandela was ANC and if the myth worked, rivals like the Pan Africanist Congress and the Black Consciousness Movement would lose. And so leaders of those movements like Robert Sobukwe and Steve Biko faded. ANC partisan history became hegemonic history. Vital, uncomfortable questions were suppressed. Like what it meant to be black and to reconcile with whites and on what terms such reconciliation was acceptable.
How did you arrive at a different telling of their stories?
I think that the Mandelas really did embody the story of their people’s struggle for freedom, but not in ways that they could control. I was so moved to discover that Nelson thought his life tragic in much the same way that the lives of so many black men under apartheid were tragic. He was a patriarch, and he was robbed of the means to protect his family. This humiliated and embittered him. It’s a quintessential South African story. Winnie, too. The insurrectionary violence of the 1980s was so scarring. So many people lost control over the violence they wielded. She was one of those people.
Winnie and Nelson’s story exemplifies all the pain and damage this country went through. They arrived at their freedom, but, just like their people, they did so battered and bruised. That they both had the strength to conceal the extent to which they were damaged seems heroic to me. They understood that they carried the myth of their people on their shoulders, and that if they broke, so would their people.
Is South Africa ready to view this struggle history through a clear lens?
If you’re asking whether there can ever be a single, objective way of understanding the past, one that we can all agree on, the answer is surely no. There is far too much of the past in the present for it ever to become uncontentious. But I do think that it is both possible and very important to fight against the falsification of the past.
Read more: Winnie and Nelson: new book paints a deeply human portrait of the Mandela marriage and South Africa's struggle
There’s a big difference between mythologisation and falsification. The former is about fashioning the facts of the past to tell a value-laden story, which is fine. The latter is to make up facts about the past, which is truly scary.
When people say that Winnie didn’t hurt anyone in the late 1980s, that it was all fabricated by a shadowy enemy , they are doing harm. Similarly, when people say that Nelson did not beat his first wife, Evelyn Mase, when there is plain evidence that he did, they are doing harm. It is possible both to mythologise the past and to be brave enough to confront what actually happened there.
- Nelson Mandela
- African history
- South African history
- Robert Sobukwe
- Oliver Tambo
- Women and girls
- Winnie Mandela
- Liberation struggle
- Winnie Madikizela Mandela
- African National Congress (ANC)
- South Africa democracy 30

Assistant Editor - 1 year cadetship

Program Development Officer - Business Processes

Executive Dean, Faculty of Health

Lecturer/Senior Lecturer, Earth System Science (School of Science)

Sydney Horizon Educators (Identified)
Pen2Print Services
Get Pen2Print services from our Educational Platform for scholars.
- _Published Books
- Conferences
- Conference Proceedings
- Edited Books
- Cover Design
Search more articles
Short biography of 'nelson mandela' (294 words).

Featured post
How to write effective literature review.
A literature review is an essential component of any research project or academic paper. It involves identifying, evaluating, and summarizin...

- Book Chapters
- IS TEXTING THE NEXT BIG THING IN RECRUITING? At first glance texting and interviewing candidates seems to go together as well as ketchup and lobster. But if you think about it just a mi...

Services Tags
- Audio Books
- Book Chapter Publication
- Book Chapters Publication
- Book Publication
- Book Publishing
- Book review
- Book Series
- Book-Chapters
- Book-Cover-Design
- Call for Book Chapters
Call for Papers
- Conference-Proceedings
- Content Writing
- Copywriting
- Creative Writing
- Edited-Books
- Pen2Print Publication
- Pen2print Services
- Physical Educational Books
- Publications
- Research Papers
- Research Publication
- Website Development
- Writing Services
Readers of the Forum
Search this website.
Our YouTube channel crossed 10k subs!
- Publication
Popular Posts
- IS TEXTING THE NEXT BIG THING IN RECRUITING?

Get More Services
Welcome to Books and Book Chapters, if you wish to get your scholarly books and book chapters published then you are at the right place.

Send mail to [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Nelson Mandela (born July 18, 1918, Mvezo, South Africa—died December 5, 2013, Johannesburg) was a Black nationalist and the first Black president of South Africa (1994-99). His negotiations in the early 1990s with South African Pres. F.W. de Klerk helped end the country's apartheid system of racial segregation and ushered in a peaceful ...
Paragraph on Nelson Mandela- 200 Words. Nelson Mandela was an influential figure in the fight for democracy and human rights. He was imprisoned for 27 years, but eventually became the president of South Africa. He was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1993 for his work on behalf of the people of South Africa. Mandela is a symbol of hope and ...
Biography of Nelson Mandela. Rolihlahla Mandela was born into the Madiba clan in the village of Mvezo, in the Eastern Cape, on 18 July 1918. His mother was Nonqaphi Nosekeni and his father was Nkosi Mphakanyiswa Gadla Mandela, principal counsellor to the Acting King of the Thembu people, Jongintaba Dalindyebo. In 1930, when he was 12 years old ...
Short Essay on Nelson Mandela in 100 Words. Nelson Mandela was one of the greatest leaders and freedom fighters of South Africa. He was born on 18th July 1918. He studied law and became a successful lawyer. While practising law, he got involved in anti-apartheid, anti-colonial, nationalist movements and soon joined the African National Congress.
Mandela's African name "Rolihlahla" means "troublemaker." Mandela became the first Black president of South Africa in 1994, serving until 1999. Beginning in 1962, Mandela spent 27 years in prison ...
Nelson Rolihlahla Mandela (/ m æ n ˈ d ɛ l ə / man-DEH-lə; Xhosa: [xolíɬaɬa mandɛ̂ːla]; born Rolihlahla Mandela; 18 July 1918 - 5 December 2013) was a South African anti-apartheid activist, politician, and statesman who served as the first president of South Africa from 1994 to 1999. He was the country's first black head of state and the first elected in a fully representative ...
A young Nelson Mandela (1938) Nelson Mandela was born in Transkei, South Africa on July 18, 1918. He was the son of a local tribal leader of the Tembu tribe. As a youngster, Nelson took part in the activities and initiation ceremonies of his local tribe. However, unlike his father Nelson Mandela gained a full education, studying at the ...
Nelson Mandela was born on July 18, 1918, into a royal family of the Xhosa-speaking Thembu tribe in the South African village of Mvezo, where his father, Gadla Henry Mphakanyiswa (c. 1880-1928 ...
Nelson Rolihlahla Mandela became known and respected all over the world as a symbol of the struggle against apartheid and all forms of racism; the icon and the hero of African liberation. Mandela or Madiba, as he was affectionately known, has been called a freedom fighter, a great man, South Africa's Favourite Son, a global icon and a living ...
Madiba's journey. Known and loved around the world for his commitment to peace, negotiation and reconciliation, Nelson Rolihlahla Mandela was South Africa's first democratically elected president (1994-1999). Mandela was an anti-apartheid revolutionary and political leader, as well as a philanthropist with an abiding love for children.
500 Words Essay On Nelson Mandela. Henry Mandela, the chief of the Tembu tribe, gave birth to Nelson Mandela in 1918. He married Evelyn Ntoko Mase, a nurse, in the year 1944. His twelve fruitful years of marriage ended in divorce. After two years, in 1958, he wed Nomzamo Winnie Madikileza, a political activist and social worker.
Biography & Timeline. Rolihlahla Mandela was born into the Madiba clan in the village of Mvezo, in the Eastern Cape. His mother was Nonqaphi Nosekeni and his father was Nkosi Mphakanyiswa Gadla Mandela. Our archivists and researchers have compiled a chronology of important events in Nelson Mandela's life. Nelson Mandela was arrested on several ...
Contents Acknowledgements xi Abbreviations xv List of illustrations xvii Map of South Africa during apartheid xix 1 Mandela: story and symbol 1 2 Scripting a life: the early years 17 3 Growth of a national icon: later years 51 4 Infl uences and interactions 82 5 Sophiatown sophisticate 110 6 Masculine performer 123 7 Spectres in the prison garden 149 8 Mandela's ethical legacy 170
Nelson Mandela was one of thousands of black South Africans who flocked to Johannesburg in the 1940s in search of work. By 1948, he was a young lawyer and activist, when a new political party came ...
Nelson Mandela and his colleagues in the Treason Trial were among the thousands detained during the state of emergency. During the trial on 14 June 1958 Nelson Mandela married a social worker Winnie Madikizela. They had two daughters Zenani and Zindziswa. The couple divorced in 1996. Days before the end of the Treason Trial Nelson Mandela ...
Monday, 9 May 1994, Mandela was elected President of the Republic of South Africa by the National Assembly in Cape Town and sworn in the following day. In June of that year, he undertook to donate one-third of his annual salary (R150 000) to The Nelson Mandela Children's Fund which was established to address the needs of marginalised youths.
Nelson Mandela studied law at school and then went on to become one of South Africa's first black lawyers. He was chosen leader of the African National Congress (ANC) liberation movement's youth section in the 1950s. Mandela established a hidden military movement after the government banned the ANC for racial reasons.
Widely considered to be the most important biography of Nelson Mandela, Antony Sampson's remarkable book has been updated with an afterword by acclaimed South African journalist, John Battersby. Long after his presidency of South Africa, Nelson Mandela remained an inspirational figure to millions - both in his homeland and far beyond. He has been, without doubt, one of the most important ...
A 1995 photograph of President Nelson Mandela, left, with Percy Yutar, the prosecutor in the 1963-1964 Rivonia treason trial, in which Mandela was sentenced to life in prison [File: Louise Gubb ...
Learners' biography. Rolihlahla Mandela was born into the Madiba clan in Mvezo, Transkei, on 18 July 1918. His mother was Nonqaphi Nosekeni and his father, Nkosi Mphakanyiswa Gadla Mandela, was the main advisor to the Acting King of the Thembu people, Jongintaba Dalindyebo. He received the name "Nelson" on his first day in primary school from ...
500+ Words Essay on Nelson Mandela. Nelson Rolihlahla Mandela was born on 18 July 1918 in the Transkei village close Umtata.Nelson Mandela was sent to Healdtown, a Wesleyan secondary school with some reputation where he enrolled after getting a primary education at a local mission school. He then registered for the Bachelor of Arts degree at Fort Hare University College where he was appointed ...
Political history scholar Jonny Steinberg's 2023 book Winnie & Nelson: Portrait of a Marriage is a double biography of South Africa's most famous political figures - Nelson Mandela and ...
He served as President of South Africa from 1994 to 1999. After he retired from public life, Mandela continued to embody the hopes and dreams of a free and equal world. He died on December 5th, 2013 at the age of 95 at Johannesburg, South Africa. Nelson Mandela received more than 250 honours, including the 1993 Nobel Peace Prize, the US ...
Nelson Mandela had to his credit more than two hundred and fifty awards and honors that included the "1993 Nobel Peace" Prize, the Medal of Freedom, and the Bharat Ratna. 500 Words Essay on Nelson Mandela. All About The Life Of Nelson Mandela Nelson Mandela was born to Henry Mandela, Tembu' tribal chief in the year 1918.