- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers


What is a thesis | A Complete Guide with Examples

Table of Contents
A thesis is a comprehensive academic paper based on your original research that presents new findings, arguments, and ideas of your study. It’s typically submitted at the end of your master’s degree or as a capstone of your bachelor’s degree.
However, writing a thesis can be laborious, especially for beginners. From the initial challenge of pinpointing a compelling research topic to organizing and presenting findings, the process is filled with potential pitfalls.
Therefore, to help you, this guide talks about what is a thesis. Additionally, it offers revelations and methodologies to transform it from an overwhelming task to a manageable and rewarding academic milestone.
What is a thesis?
A thesis is an in-depth research study that identifies a particular topic of inquiry and presents a clear argument or perspective about that topic using evidence and logic.
Writing a thesis showcases your ability of critical thinking, gathering evidence, and making a compelling argument. Integral to these competencies is thorough research, which not only fortifies your propositions but also confers credibility to your entire study.
Furthermore, there's another phenomenon you might often confuse with the thesis: the ' working thesis .' However, they aren't similar and shouldn't be used interchangeably.
A working thesis, often referred to as a preliminary or tentative thesis, is an initial version of your thesis statement. It serves as a draft or a starting point that guides your research in its early stages.
As you research more and gather more evidence, your initial thesis (aka working thesis) might change. It's like a starting point that can be adjusted as you learn more. It's normal for your main topic to change a few times before you finalize it.
While a thesis identifies and provides an overarching argument, the key to clearly communicating the central point of that argument lies in writing a strong thesis statement.
What is a thesis statement?
A strong thesis statement (aka thesis sentence) is a concise summary of the main argument or claim of the paper. It serves as a critical anchor in any academic work, succinctly encapsulating the primary argument or main idea of the entire paper.
Typically found within the introductory section, a strong thesis statement acts as a roadmap of your thesis, directing readers through your arguments and findings. By delineating the core focus of your investigation, it offers readers an immediate understanding of the context and the gravity of your study.
Furthermore, an effectively crafted thesis statement can set forth the boundaries of your research, helping readers anticipate the specific areas of inquiry you are addressing.
Different types of thesis statements
A good thesis statement is clear, specific, and arguable. Therefore, it is necessary for you to choose the right type of thesis statement for your academic papers.
Thesis statements can be classified based on their purpose and structure. Here are the primary types of thesis statements:
Argumentative (or Persuasive) thesis statement
Purpose : To convince the reader of a particular stance or point of view by presenting evidence and formulating a compelling argument.
Example : Reducing plastic use in daily life is essential for environmental health.
Analytical thesis statement
Purpose : To break down an idea or issue into its components and evaluate it.
Example : By examining the long-term effects, social implications, and economic impact of climate change, it becomes evident that immediate global action is necessary.
Expository (or Descriptive) thesis statement
Purpose : To explain a topic or subject to the reader.
Example : The Great Depression, spanning the 1930s, was a severe worldwide economic downturn triggered by a stock market crash, bank failures, and reduced consumer spending.
Cause and effect thesis statement
Purpose : To demonstrate a cause and its resulting effect.
Example : Overuse of smartphones can lead to impaired sleep patterns, reduced face-to-face social interactions, and increased levels of anxiety.
Compare and contrast thesis statement
Purpose : To highlight similarities and differences between two subjects.
Example : "While both novels '1984' and 'Brave New World' delve into dystopian futures, they differ in their portrayal of individual freedom, societal control, and the role of technology."
When you write a thesis statement , it's important to ensure clarity and precision, so the reader immediately understands the central focus of your work.
What is the difference between a thesis and a thesis statement?
While both terms are frequently used interchangeably, they have distinct meanings.
A thesis refers to the entire research document, encompassing all its chapters and sections. In contrast, a thesis statement is a brief assertion that encapsulates the central argument of the research.
Here’s an in-depth differentiation table of a thesis and a thesis statement.
Now, to craft a compelling thesis, it's crucial to adhere to a specific structure. Let’s break down these essential components that make up a thesis structure
15 components of a thesis structure
Navigating a thesis can be daunting. However, understanding its structure can make the process more manageable.
Here are the key components or different sections of a thesis structure:
Your thesis begins with the title page. It's not just a formality but the gateway to your research.

Here, you'll prominently display the necessary information about you (the author) and your institutional details.
- Title of your thesis
- Your full name
- Your department
- Your institution and degree program
- Your submission date
- Your Supervisor's name (in some cases)
- Your Department or faculty (in some cases)
- Your University's logo (in some cases)
- Your Student ID (in some cases)
In a concise manner, you'll have to summarize the critical aspects of your research in typically no more than 200-300 words.

This includes the problem statement, methodology, key findings, and conclusions. For many, the abstract will determine if they delve deeper into your work, so ensure it's clear and compelling.
Acknowledgments
Research is rarely a solitary endeavor. In the acknowledgments section, you have the chance to express gratitude to those who've supported your journey.

This might include advisors, peers, institutions, or even personal sources of inspiration and support. It's a personal touch, reflecting the humanity behind the academic rigor.
Table of contents
A roadmap for your readers, the table of contents lists the chapters, sections, and subsections of your thesis.

By providing page numbers, you allow readers to navigate your work easily, jumping to sections that pique their interest.
List of figures and tables
Research often involves data, and presenting this data visually can enhance understanding. This section provides an organized listing of all figures and tables in your thesis.

It's a visual index, ensuring that readers can quickly locate and reference your graphical data.
Introduction
Here's where you introduce your research topic, articulate the research question or objective, and outline the significance of your study.

- Present the research topic : Clearly articulate the central theme or subject of your research.
- Background information : Ground your research topic, providing any necessary context or background information your readers might need to understand the significance of your study.
- Define the scope : Clearly delineate the boundaries of your research, indicating what will and won't be covered.
- Literature review : Introduce any relevant existing research on your topic, situating your work within the broader academic conversation and highlighting where your research fits in.
- State the research Question(s) or objective(s) : Clearly articulate the primary questions or objectives your research aims to address.
- Outline the study's structure : Give a brief overview of how the subsequent sections of your work will unfold, guiding your readers through the journey ahead.
The introduction should captivate your readers, making them eager to delve deeper into your research journey.
Literature review section
Your study correlates with existing research. Therefore, in the literature review section, you'll engage in a dialogue with existing knowledge, highlighting relevant studies, theories, and findings.

It's here that you identify gaps in the current knowledge, positioning your research as a bridge to new insights.
To streamline this process, consider leveraging AI tools. For example, the SciSpace literature review tool enables you to efficiently explore and delve into research papers, simplifying your literature review journey.
Methodology
In the research methodology section, you’ll detail the tools, techniques, and processes you employed to gather and analyze data. This section will inform the readers about how you approached your research questions and ensures the reproducibility of your study.

Here's a breakdown of what it should encompass:
- Research Design : Describe the overall structure and approach of your research. Are you conducting a qualitative study with in-depth interviews? Or is it a quantitative study using statistical analysis? Perhaps it's a mixed-methods approach?
- Data Collection : Detail the methods you used to gather data. This could include surveys, experiments, observations, interviews, archival research, etc. Mention where you sourced your data, the duration of data collection, and any tools or instruments used.
- Sampling : If applicable, explain how you selected participants or data sources for your study. Discuss the size of your sample and the rationale behind choosing it.
- Data Analysis : Describe the techniques and tools you used to process and analyze the data. This could range from statistical tests in quantitative research to thematic analysis in qualitative research.
- Validity and Reliability : Address the steps you took to ensure the validity and reliability of your findings to ensure that your results are both accurate and consistent.
- Ethical Considerations : Highlight any ethical issues related to your research and the measures you took to address them, including — informed consent, confidentiality, and data storage and protection measures.
Moreover, different research questions necessitate different types of methodologies. For instance:
- Experimental methodology : Often used in sciences, this involves a controlled experiment to discern causality.
- Qualitative methodology : Employed when exploring patterns or phenomena without numerical data. Methods can include interviews, focus groups, or content analysis.
- Quantitative methodology : Concerned with measurable data and often involves statistical analysis. Surveys and structured observations are common tools here.
- Mixed methods : As the name implies, this combines both qualitative and quantitative methodologies.
The Methodology section isn’t just about detailing the methods but also justifying why they were chosen. The appropriateness of the methods in addressing your research question can significantly impact the credibility of your findings.
Results (or Findings)
This section presents the outcomes of your research. It's crucial to note that the nature of your results may vary; they could be quantitative, qualitative, or a mix of both.

Quantitative results often present statistical data, showcasing measurable outcomes, and they benefit from tables, graphs, and figures to depict these data points.
Qualitative results , on the other hand, might delve into patterns, themes, or narratives derived from non-numerical data, such as interviews or observations.
Regardless of the nature of your results, clarity is essential. This section is purely about presenting the data without offering interpretations — that comes later in the discussion.
In the discussion section, the raw data transforms into valuable insights.
Start by revisiting your research question and contrast it with the findings. How do your results expand, constrict, or challenge current academic conversations?
Dive into the intricacies of the data, guiding the reader through its implications. Detail potential limitations transparently, signaling your awareness of the research's boundaries. This is where your academic voice should be resonant and confident.
Practical implications (Recommendation) section
Based on the insights derived from your research, this section provides actionable suggestions or proposed solutions.
Whether aimed at industry professionals or the general public, recommendations translate your academic findings into potential real-world actions. They help readers understand the practical implications of your work and how it can be applied to effect change or improvement in a given field.
When crafting recommendations, it's essential to ensure they're feasible and rooted in the evidence provided by your research. They shouldn't merely be aspirational but should offer a clear path forward, grounded in your findings.
The conclusion provides closure to your research narrative.
It's not merely a recap but a synthesis of your main findings and their broader implications. Reconnect with the research questions or hypotheses posited at the beginning, offering clear answers based on your findings.

Reflect on the broader contributions of your study, considering its impact on the academic community and potential real-world applications.
Lastly, the conclusion should leave your readers with a clear understanding of the value and impact of your study.
References (or Bibliography)
Every theory you've expounded upon, every data point you've cited, and every methodological precedent you've followed finds its acknowledgment here.

In references, it's crucial to ensure meticulous consistency in formatting, mirroring the specific guidelines of the chosen citation style .
Proper referencing helps to avoid plagiarism , gives credit to original ideas, and allows readers to explore topics of interest. Moreover, it situates your work within the continuum of academic knowledge.
To properly cite the sources used in the study, you can rely on online citation generator tools to generate accurate citations!
Here’s more on how you can cite your sources.
Often, the depth of research produces a wealth of material that, while crucial, can make the core content of the thesis cumbersome. The appendix is where you mention extra information that supports your research but isn't central to the main text.

Whether it's raw datasets, detailed procedural methodologies, extended case studies, or any other ancillary material, the appendices ensure that these elements are archived for reference without breaking the main narrative's flow.
For thorough researchers and readers keen on meticulous details, the appendices provide a treasure trove of insights.
Glossary (optional)
In academics, specialized terminologies, and jargon are inevitable. However, not every reader is versed in every term.
The glossary, while optional, is a critical tool for accessibility. It's a bridge ensuring that even readers from outside the discipline can access, understand, and appreciate your work.

By defining complex terms and providing context, you're inviting a wider audience to engage with your research, enhancing its reach and impact.
Remember, while these components provide a structured framework, the essence of your thesis lies in the originality of your ideas, the rigor of your research, and the clarity of your presentation.
As you craft each section, keep your readers in mind, ensuring that your passion and dedication shine through every page.
Thesis examples
To further elucidate the concept of a thesis, here are illustrative examples from various fields:
Example 1 (History): Abolition, Africans, and Abstraction: the Influence of the ‘Noble Savage’ on British and French Antislavery Thought, 1787-1807 by Suchait Kahlon.
Example 2 (Climate Dynamics): Influence of external forcings on abrupt millennial-scale climate changes: a statistical modelling study by Takahito Mitsui · Michel Crucifix
Checklist for your thesis evaluation
Evaluating your thesis ensures that your research meets the standards of academia. Here's an elaborate checklist to guide you through this critical process.
Content and structure
- Is the thesis statement clear, concise, and debatable?
- Does the introduction provide sufficient background and context?
- Is the literature review comprehensive, relevant, and well-organized?
- Does the methodology section clearly describe and justify the research methods?
- Are the results/findings presented clearly and logically?
- Does the discussion interpret the results in light of the research question and existing literature?
- Is the conclusion summarizing the research and suggesting future directions or implications?
Clarity and coherence
- Is the writing clear and free of jargon?
- Are ideas and sections logically connected and flowing?
- Is there a clear narrative or argument throughout the thesis?
Research quality
- Is the research question significant and relevant?
- Are the research methods appropriate for the question?
- Is the sample size (if applicable) adequate?
- Are the data analysis techniques appropriate and correctly applied?
- Are potential biases or limitations addressed?
Originality and significance
- Does the thesis contribute new knowledge or insights to the field?
- Is the research grounded in existing literature while offering fresh perspectives?
Formatting and presentation
- Is the thesis formatted according to institutional guidelines?
- Are figures, tables, and charts clear, labeled, and referenced in the text?
- Is the bibliography or reference list complete and consistently formatted?
- Are appendices relevant and appropriately referenced in the main text?
Grammar and language
- Is the thesis free of grammatical and spelling errors?
- Is the language professional, consistent, and appropriate for an academic audience?
- Are quotations and paraphrased material correctly cited?
Feedback and revision
- Have you sought feedback from peers, advisors, or experts in the field?
- Have you addressed the feedback and made the necessary revisions?
Overall assessment
- Does the thesis as a whole feel cohesive and comprehensive?
- Would the thesis be understandable and valuable to someone in your field?
Ensure to use this checklist to leave no ground for doubt or missed information in your thesis.
After writing your thesis, the next step is to discuss and defend your findings verbally in front of a knowledgeable panel. You’ve to be well prepared as your professors may grade your presentation abilities.
Preparing your thesis defense
A thesis defense, also known as "defending the thesis," is the culmination of a scholar's research journey. It's the final frontier, where you’ll present their findings and face scrutiny from a panel of experts.
Typically, the defense involves a public presentation where you’ll have to outline your study, followed by a question-and-answer session with a committee of experts. This committee assesses the validity, originality, and significance of the research.
The defense serves as a rite of passage for scholars. It's an opportunity to showcase expertise, address criticisms, and refine arguments. A successful defense not only validates the research but also establishes your authority as a researcher in your field.
Here’s how you can effectively prepare for your thesis defense .
Now, having touched upon the process of defending a thesis, it's worth noting that scholarly work can take various forms, depending on academic and regional practices.
One such form, often paralleled with the thesis, is the 'dissertation.' But what differentiates the two?
Dissertation vs. Thesis
Often used interchangeably in casual discourse, they refer to distinct research projects undertaken at different levels of higher education.
To the uninitiated, understanding their meaning might be elusive. So, let's demystify these terms and delve into their core differences.
Here's a table differentiating between the two.
Wrapping up
From understanding the foundational concept of a thesis to navigating its various components, differentiating it from a dissertation, and recognizing the importance of proper citation — this guide covers it all.
As scholars and readers, understanding these nuances not only aids in academic pursuits but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the relentless quest for knowledge that drives academia.
It’s important to remember that every thesis is a testament to curiosity, dedication, and the indomitable spirit of discovery.
Good luck with your thesis writing!
Frequently Asked Questions
A thesis typically ranges between 40-80 pages, but its length can vary based on the research topic, institution guidelines, and level of study.
A PhD thesis usually spans 200-300 pages, though this can vary based on the discipline, complexity of the research, and institutional requirements.
To identify a thesis topic, consider current trends in your field, gaps in existing literature, personal interests, and discussions with advisors or mentors. Additionally, reviewing related journals and conference proceedings can provide insights into potential areas of exploration.
The conceptual framework is often situated in the literature review or theoretical framework section of a thesis. It helps set the stage by providing the context, defining key concepts, and explaining the relationships between variables.
A thesis statement should be concise, clear, and specific. It should state the main argument or point of your research. Start by pinpointing the central question or issue your research addresses, then condense that into a single statement, ensuring it reflects the essence of your paper.
You might also like

AI for Meta-Analysis — A Comprehensive Guide

How To Write An Argumentative Essay

Beyond Google Scholar: Why SciSpace is the best alternative
Think of yourself as a member of a jury, listening to a lawyer who is presenting an opening argument. You'll want to know very soon whether the lawyer believes the accused to be guilty or not guilty, and how the lawyer plans to convince you. Readers of academic essays are like jury members: before they have read too far, they want to know what the essay argues as well as how the writer plans to make the argument. After reading your thesis statement, the reader should think, "This essay is going to try to convince me of something. I'm not convinced yet, but I'm interested to see how I might be."
An effective thesis cannot be answered with a simple "yes" or "no." A thesis is not a topic; nor is it a fact; nor is it an opinion. "Reasons for the fall of communism" is a topic. "Communism collapsed in Eastern Europe" is a fact known by educated people. "The fall of communism is the best thing that ever happened in Europe" is an opinion. (Superlatives like "the best" almost always lead to trouble. It's impossible to weigh every "thing" that ever happened in Europe. And what about the fall of Hitler? Couldn't that be "the best thing"?)
A good thesis has two parts. It should tell what you plan to argue, and it should "telegraph" how you plan to argue—that is, what particular support for your claim is going where in your essay.
Steps in Constructing a Thesis
First, analyze your primary sources. Look for tension, interest, ambiguity, controversy, and/or complication. Does the author contradict himself or herself? Is a point made and later reversed? What are the deeper implications of the author's argument? Figuring out the why to one or more of these questions, or to related questions, will put you on the path to developing a working thesis. (Without the why, you probably have only come up with an observation—that there are, for instance, many different metaphors in such-and-such a poem—which is not a thesis.)
Once you have a working thesis, write it down. There is nothing as frustrating as hitting on a great idea for a thesis, then forgetting it when you lose concentration. And by writing down your thesis you will be forced to think of it clearly, logically, and concisely. You probably will not be able to write out a final-draft version of your thesis the first time you try, but you'll get yourself on the right track by writing down what you have.
Keep your thesis prominent in your introduction. A good, standard place for your thesis statement is at the end of an introductory paragraph, especially in shorter (5-15 page) essays. Readers are used to finding theses there, so they automatically pay more attention when they read the last sentence of your introduction. Although this is not required in all academic essays, it is a good rule of thumb.
Anticipate the counterarguments. Once you have a working thesis, you should think about what might be said against it. This will help you to refine your thesis, and it will also make you think of the arguments that you'll need to refute later on in your essay. (Every argument has a counterargument. If yours doesn't, then it's not an argument—it may be a fact, or an opinion, but it is not an argument.)
This statement is on its way to being a thesis. However, it is too easy to imagine possible counterarguments. For example, a political observer might believe that Dukakis lost because he suffered from a "soft-on-crime" image. If you complicate your thesis by anticipating the counterargument, you'll strengthen your argument, as shown in the sentence below.
Some Caveats and Some Examples
A thesis is never a question. Readers of academic essays expect to have questions discussed, explored, or even answered. A question ("Why did communism collapse in Eastern Europe?") is not an argument, and without an argument, a thesis is dead in the water.
A thesis is never a list. "For political, economic, social and cultural reasons, communism collapsed in Eastern Europe" does a good job of "telegraphing" the reader what to expect in the essay—a section about political reasons, a section about economic reasons, a section about social reasons, and a section about cultural reasons. However, political, economic, social and cultural reasons are pretty much the only possible reasons why communism could collapse. This sentence lacks tension and doesn't advance an argument. Everyone knows that politics, economics, and culture are important.
A thesis should never be vague, combative or confrontational. An ineffective thesis would be, "Communism collapsed in Eastern Europe because communism is evil." This is hard to argue (evil from whose perspective? what does evil mean?) and it is likely to mark you as moralistic and judgmental rather than rational and thorough. It also may spark a defensive reaction from readers sympathetic to communism. If readers strongly disagree with you right off the bat, they may stop reading.
An effective thesis has a definable, arguable claim. "While cultural forces contributed to the collapse of communism in Eastern Europe, the disintegration of economies played the key role in driving its decline" is an effective thesis sentence that "telegraphs," so that the reader expects the essay to have a section about cultural forces and another about the disintegration of economies. This thesis makes a definite, arguable claim: that the disintegration of economies played a more important role than cultural forces in defeating communism in Eastern Europe. The reader would react to this statement by thinking, "Perhaps what the author says is true, but I am not convinced. I want to read further to see how the author argues this claim."
A thesis should be as clear and specific as possible. Avoid overused, general terms and abstractions. For example, "Communism collapsed in Eastern Europe because of the ruling elite's inability to address the economic concerns of the people" is more powerful than "Communism collapsed due to societal discontent."
Copyright 1999, Maxine Rodburg and The Tutors of the Writing Center at Harvard University
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write a thesis statement + examples

What is a thesis statement?
Is a thesis statement a question, how do you write a good thesis statement, how do i know if my thesis statement is good, examples of thesis statements, helpful resources on how to write a thesis statement, frequently asked questions about writing a thesis statement, related articles.
A thesis statement is the main argument of your paper or thesis.
The thesis statement is one of the most important elements of any piece of academic writing . It is a brief statement of your paper’s main argument. Essentially, you are stating what you will be writing about.
You can see your thesis statement as an answer to a question. While it also contains the question, it should really give an answer to the question with new information and not just restate or reiterate it.
Your thesis statement is part of your introduction. Learn more about how to write a good thesis introduction in our introduction guide .
A thesis statement is not a question. A statement must be arguable and provable through evidence and analysis. While your thesis might stem from a research question, it should be in the form of a statement.
Tip: A thesis statement is typically 1-2 sentences. For a longer project like a thesis, the statement may be several sentences or a paragraph.
A good thesis statement needs to do the following:
- Condense the main idea of your thesis into one or two sentences.
- Answer your project’s main research question.
- Clearly state your position in relation to the topic .
- Make an argument that requires support or evidence.
Once you have written down a thesis statement, check if it fulfills the following criteria:
- Your statement needs to be provable by evidence. As an argument, a thesis statement needs to be debatable.
- Your statement needs to be precise. Do not give away too much information in the thesis statement and do not load it with unnecessary information.
- Your statement cannot say that one solution is simply right or simply wrong as a matter of fact. You should draw upon verified facts to persuade the reader of your solution, but you cannot just declare something as right or wrong.
As previously mentioned, your thesis statement should answer a question.
If the question is:
What do you think the City of New York should do to reduce traffic congestion?
A good thesis statement restates the question and answers it:
In this paper, I will argue that the City of New York should focus on providing exclusive lanes for public transport and adaptive traffic signals to reduce traffic congestion by the year 2035.
Here is another example. If the question is:
How can we end poverty?
A good thesis statement should give more than one solution to the problem in question:
In this paper, I will argue that introducing universal basic income can help reduce poverty and positively impact the way we work.
- The Writing Center of the University of North Carolina has a list of questions to ask to see if your thesis is strong .
A thesis statement is part of the introduction of your paper. It is usually found in the first or second paragraph to let the reader know your research purpose from the beginning.
In general, a thesis statement should have one or two sentences. But the length really depends on the overall length of your project. Take a look at our guide about the length of thesis statements for more insight on this topic.
Here is a list of Thesis Statement Examples that will help you understand better how to write them.
Every good essay should include a thesis statement as part of its introduction, no matter the academic level. Of course, if you are a high school student you are not expected to have the same type of thesis as a PhD student.
Here is a great YouTube tutorial showing How To Write An Essay: Thesis Statements .


- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Writing a Paper: Thesis Statements
Basics of thesis statements.
The thesis statement is the brief articulation of your paper's central argument and purpose. You might hear it referred to as simply a "thesis." Every scholarly paper should have a thesis statement, and strong thesis statements are concise, specific, and arguable. Concise means the thesis is short: perhaps one or two sentences for a shorter paper. Specific means the thesis deals with a narrow and focused topic, appropriate to the paper's length. Arguable means that a scholar in your field could disagree (or perhaps already has!).
Strong thesis statements address specific intellectual questions, have clear positions, and use a structure that reflects the overall structure of the paper. Read on to learn more about constructing a strong thesis statement.
Being Specific
This thesis statement has no specific argument:
Needs Improvement: In this essay, I will examine two scholarly articles to find similarities and differences.
This statement is concise, but it is neither specific nor arguable—a reader might wonder, "Which scholarly articles? What is the topic of this paper? What field is the author writing in?" Additionally, the purpose of the paper—to "examine…to find similarities and differences" is not of a scholarly level. Identifying similarities and differences is a good first step, but strong academic argument goes further, analyzing what those similarities and differences might mean or imply.
Better: In this essay, I will argue that Bowler's (2003) autocratic management style, when coupled with Smith's (2007) theory of social cognition, can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover.
The new revision here is still concise, as well as specific and arguable. We can see that it is specific because the writer is mentioning (a) concrete ideas and (b) exact authors. We can also gather the field (business) and the topic (management and employee turnover). The statement is arguable because the student goes beyond merely comparing; he or she draws conclusions from that comparison ("can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover").
Making a Unique Argument
This thesis draft repeats the language of the writing prompt without making a unique argument:
Needs Improvement: The purpose of this essay is to monitor, assess, and evaluate an educational program for its strengths and weaknesses. Then, I will provide suggestions for improvement.
You can see here that the student has simply stated the paper's assignment, without articulating specifically how he or she will address it. The student can correct this error simply by phrasing the thesis statement as a specific answer to the assignment prompt.
Better: Through a series of student interviews, I found that Kennedy High School's antibullying program was ineffective. In order to address issues of conflict between students, I argue that Kennedy High School should embrace policies outlined by the California Department of Education (2010).
Words like "ineffective" and "argue" show here that the student has clearly thought through the assignment and analyzed the material; he or she is putting forth a specific and debatable position. The concrete information ("student interviews," "antibullying") further prepares the reader for the body of the paper and demonstrates how the student has addressed the assignment prompt without just restating that language.
Creating a Debate
This thesis statement includes only obvious fact or plot summary instead of argument:
Needs Improvement: Leadership is an important quality in nurse educators.
A good strategy to determine if your thesis statement is too broad (and therefore, not arguable) is to ask yourself, "Would a scholar in my field disagree with this point?" Here, we can see easily that no scholar is likely to argue that leadership is an unimportant quality in nurse educators. The student needs to come up with a more arguable claim, and probably a narrower one; remember that a short paper needs a more focused topic than a dissertation.
Better: Roderick's (2009) theory of participatory leadership is particularly appropriate to nurse educators working within the emergency medicine field, where students benefit most from collegial and kinesthetic learning.
Here, the student has identified a particular type of leadership ("participatory leadership"), narrowing the topic, and has made an arguable claim (this type of leadership is "appropriate" to a specific type of nurse educator). Conceivably, a scholar in the nursing field might disagree with this approach. The student's paper can now proceed, providing specific pieces of evidence to support the arguable central claim.
Choosing the Right Words
This thesis statement uses large or scholarly-sounding words that have no real substance:
Needs Improvement: Scholars should work to seize metacognitive outcomes by harnessing discipline-based networks to empower collaborative infrastructures.
There are many words in this sentence that may be buzzwords in the student's field or key terms taken from other texts, but together they do not communicate a clear, specific meaning. Sometimes students think scholarly writing means constructing complex sentences using special language, but actually it's usually a stronger choice to write clear, simple sentences. When in doubt, remember that your ideas should be complex, not your sentence structure.
Better: Ecologists should work to educate the U.S. public on conservation methods by making use of local and national green organizations to create a widespread communication plan.
Notice in the revision that the field is now clear (ecology), and the language has been made much more field-specific ("conservation methods," "green organizations"), so the reader is able to see concretely the ideas the student is communicating.
Leaving Room for Discussion
This thesis statement is not capable of development or advancement in the paper:
Needs Improvement: There are always alternatives to illegal drug use.
This sample thesis statement makes a claim, but it is not a claim that will sustain extended discussion. This claim is the type of claim that might be appropriate for the conclusion of a paper, but in the beginning of the paper, the student is left with nowhere to go. What further points can be made? If there are "always alternatives" to the problem the student is identifying, then why bother developing a paper around that claim? Ideally, a thesis statement should be complex enough to explore over the length of the entire paper.
Better: The most effective treatment plan for methamphetamine addiction may be a combination of pharmacological and cognitive therapy, as argued by Baker (2008), Smith (2009), and Xavier (2011).
In the revised thesis, you can see the student make a specific, debatable claim that has the potential to generate several pages' worth of discussion. When drafting a thesis statement, think about the questions your thesis statement will generate: What follow-up inquiries might a reader have? In the first example, there are almost no additional questions implied, but the revised example allows for a good deal more exploration.
Thesis Mad Libs
If you are having trouble getting started, try using the models below to generate a rough model of a thesis statement! These models are intended for drafting purposes only and should not appear in your final work.
- In this essay, I argue ____, using ______ to assert _____.
- While scholars have often argued ______, I argue______, because_______.
- Through an analysis of ______, I argue ______, which is important because_______.
Words to Avoid and to Embrace
When drafting your thesis statement, avoid words like explore, investigate, learn, compile, summarize , and explain to describe the main purpose of your paper. These words imply a paper that summarizes or "reports," rather than synthesizing and analyzing.
Instead of the terms above, try words like argue, critique, question , and interrogate . These more analytical words may help you begin strongly, by articulating a specific, critical, scholarly position.
Read Kayla's blog post for tips on taking a stand in a well-crafted thesis statement.
Related Resources
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Introductions
- Next Page: Conclusions
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.

Thesis Statements
What this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can craft or refine one for your draft.
Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence near the beginning of your paper (most often, at the end of the first paragraph) that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I create a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis” that presents a basic or main idea and an argument that you think you can support with evidence. Both the argument and your thesis are likely to need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following :
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question. If the prompt isn’t phrased as a question, try to rephrase it. For example, “Discuss the effect of X on Y” can be rephrased as “What is the effect of X on Y?”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is likely to be “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s okay to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on contemporary communication, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: “Discuss the impact of social media on public awareness.” Looking back at your notes, you might start with this working thesis:
Social media impacts public awareness in both positive and negative ways.
You can use the questions above to help you revise this general statement into a stronger thesis.
- Do I answer the question? You can analyze this if you rephrase “discuss the impact” as “what is the impact?” This way, you can see that you’ve answered the question only very generally with the vague “positive and negative ways.”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not likely. Only people who maintain that social media has a solely positive or solely negative impact could disagree.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? No. What are the positive effects? What are the negative effects?
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? No. Why are they positive? How are they positive? What are their causes? Why are they negative? How are they negative? What are their causes?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? No. Why should anyone care about the positive and/or negative impact of social media?
After thinking about your answers to these questions, you decide to focus on the one impact you feel strongly about and have strong evidence for:
Because not every voice on social media is reliable, people have become much more critical consumers of information, and thus, more informed voters.
This version is a much stronger thesis! It answers the question, takes a specific position that others can challenge, and it gives a sense of why it matters.
Let’s try another. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
You begin to analyze your thesis:
- Do I answer the question? No. The prompt asks you to analyze some aspect of the novel. Your working thesis is a statement of general appreciation for the entire novel.
Think about aspects of the novel that are important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
- Do I answer the question? Yes!
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not really. This contrast is well-known and accepted.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? It’s getting there–you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation. However, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? Not yet. Compare scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions and anything else that seems interesting.
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?”
After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A. 2015. The St. Martin’s Handbook , 8th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Ramage, John D., John C. Bean, and June Johnson. 2018. The Allyn & Bacon Guide to Writing , 8th ed. New York: Pearson.
Ruszkiewicz, John J., Christy Friend, Daniel Seward, and Maxine Hairston. 2010. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers , 9th ed. Boston: Pearson Education.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write a Thesis Statement for a Research Paper

4-minute read
- 26th July 2023
A strong thesis statement is the foundation of a successful research paper . The thesis gives focus to your ideas, engages readers, and sets the tone for the rest of the paper. You’ve spent substantial time and effort to craft a well-written and effective study , so you want your thesis statement to accurately reflect the impact of your work.
However, writing a thesis is often easier said than done. So if you’ve already got the arguments, the data, and the conclusions, keep scrolling for our straightforward guide on how to write a thesis statement for a research paper.
What Is a Thesis Statement?
A thesis statement is a clear and succinct assertion that presents the main argument or central idea of a research paper or other academic work. You usually find the thesis, which serves as a road map for the entire piece of writing, at the end of the introductory paragraph. The thesis also highlights the importance and relevance of the research topic , explaining why it’s worth studying and what impact it may have.
A good thesis statement also invites critical discussion and debate. Although your statement should provide a compelling argument , it should also inspire readers to engage with your ideas and potentially challenge or explore alternative viewpoints.
How to Write a Thesis Statement
Your thesis statement should outline the scope and boundaries of the paper and indicate what aspects of the topic you’ll cover. But now that you know what a good thesis statement entails, where should you start? Check out our series of steps below for help on writing an impactful thesis statement that accurately summarizes your research and arguments.
Understand the Purpose of Your Research
Before you can write a thesis statement, you need to understand the purpose and scope of your research. Pinpoint the specific topic or issue you’ll be exploring and the main objective of your paper. You should also familiarize yourself with the existing literature and research related to your topic because these will help you refine your focus and identify gaps in the existing knowledge that your research can address.
Consider the Impact of Your Research
Your thesis statement should answer the question, What is the relevance? – meaning it should tell the reader what the practical implications of your research are, why the research is significant, and what it adds to the broader academic landscape.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Make a Concise Claim or Argument
Your statement should be clear, specific, and concise, conveying the main point of your research in one or two sentences. It should present a claim or argument that you’ll go on to support and defend in your paper, so avoid purely factual or self-evident statements. Be precise in your wording and tailor your thesis statement to the scope of your research – don’t introduce a new or unrelated topic that you don’t expressly address in your paper. The thesis statement is meant to indicate what the reader can expect to find in your paper, and you must support the thesis with evidence throughout.
Revise and Refine the Statement
Crafting a strong thesis statement may require multiple attempts, so take the time to revise and edit it until you’re satisfied that it meets your requirements.
Example Thesis Statement
Below is an example of a strong thesis statement that clearly emphasizes the main points of a research topic:
In this example, the thesis statement clearly identifies the main topic (technology’s impact on education) and presents a strong argument about technology’s positive effects. The thesis conveys the essential message of the research concisely in one sentence, leaving no doubt about the position of the author and what they’ll address in the paper.
Expert Editing Services
Ensure your research paper makes an impact by having our expert editors proofread it professionally. Our team has experience proofreading a variety of academic work, from research papers to dissertations to journal articles. Get started today by submitting your free sample of 500 words or less.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
3-minute read
What Is a Content Editor?
Are you interested in learning more about the role of a content editor and the...
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
2-minute read
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...
8 Press Release Distribution Services for Your Business
In a world where you need to stand out, press releases are key to being...
How to Get a Patent
In the United States, the US Patent and Trademarks Office issues patents. In the United...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This resource provides tips for creating a thesis statement and examples of different types of thesis statements.
Tips for Writing Your Thesis Statement
1. Determine what kind of paper you are writing:
- An analytical paper breaks down an issue or an idea into its component parts, evaluates the issue or idea, and presents this breakdown and evaluation to the audience.
- An expository (explanatory) paper explains something to the audience.
- An argumentative paper makes a claim about a topic and justifies this claim with specific evidence. The claim could be an opinion, a policy proposal, an evaluation, a cause-and-effect statement, or an interpretation. The goal of the argumentative paper is to convince the audience that the claim is true based on the evidence provided.
If you are writing a text that does not fall under these three categories (e.g., a narrative), a thesis statement somewhere in the first paragraph could still be helpful to your reader.
2. Your thesis statement should be specific—it should cover only what you will discuss in your paper and should be supported with specific evidence.
3. The thesis statement usually appears at the end of the first paragraph of a paper.
4. Your topic may change as you write, so you may need to revise your thesis statement to reflect exactly what you have discussed in the paper.
Thesis Statement Examples
Example of an analytical thesis statement:
The paper that follows should:
- Explain the analysis of the college admission process
- Explain the challenge facing admissions counselors
Example of an expository (explanatory) thesis statement:
- Explain how students spend their time studying, attending class, and socializing with peers
Example of an argumentative thesis statement:
- Present an argument and give evidence to support the claim that students should pursue community projects before entering college
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Paper
Definition:
Research Paper is a written document that presents the author’s original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue.
It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new knowledge or insights to a particular field of study, and to demonstrate the author’s understanding of the existing literature and theories related to the topic.
Structure of Research Paper
The structure of a research paper typically follows a standard format, consisting of several sections that convey specific information about the research study. The following is a detailed explanation of the structure of a research paper:
The title page contains the title of the paper, the name(s) of the author(s), and the affiliation(s) of the author(s). It also includes the date of submission and possibly, the name of the journal or conference where the paper is to be published.
The abstract is a brief summary of the research paper, typically ranging from 100 to 250 words. It should include the research question, the methods used, the key findings, and the implications of the results. The abstract should be written in a concise and clear manner to allow readers to quickly grasp the essence of the research.
Introduction
The introduction section of a research paper provides background information about the research problem, the research question, and the research objectives. It also outlines the significance of the research, the research gap that it aims to fill, and the approach taken to address the research question. Finally, the introduction section ends with a clear statement of the research hypothesis or research question.
Literature Review
The literature review section of a research paper provides an overview of the existing literature on the topic of study. It includes a critical analysis and synthesis of the literature, highlighting the key concepts, themes, and debates. The literature review should also demonstrate the research gap and how the current study seeks to address it.
The methods section of a research paper describes the research design, the sample selection, the data collection and analysis procedures, and the statistical methods used to analyze the data. This section should provide sufficient detail for other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the research, using tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate the data. The findings should be presented in a clear and concise manner, with reference to the research question and hypothesis.
The discussion section of a research paper interprets the findings and discusses their implications for the research question, the literature review, and the field of study. It should also address the limitations of the study and suggest future research directions.
The conclusion section summarizes the main findings of the study, restates the research question and hypothesis, and provides a final reflection on the significance of the research.
The references section provides a list of all the sources cited in the paper, following a specific citation style such as APA, MLA or Chicago.
How to Write Research Paper
You can write Research Paper by the following guide:
- Choose a Topic: The first step is to select a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. Brainstorm ideas and narrow down to a research question that is specific and researchable.
- Conduct a Literature Review: The literature review helps you identify the gap in the existing research and provides a basis for your research question. It also helps you to develop a theoretical framework and research hypothesis.
- Develop a Thesis Statement : The thesis statement is the main argument of your research paper. It should be clear, concise and specific to your research question.
- Plan your Research: Develop a research plan that outlines the methods, data sources, and data analysis procedures. This will help you to collect and analyze data effectively.
- Collect and Analyze Data: Collect data using various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments. Analyze data using statistical tools or other qualitative methods.
- Organize your Paper : Organize your paper into sections such as Introduction, Literature Review, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion. Ensure that each section is coherent and follows a logical flow.
- Write your Paper : Start by writing the introduction, followed by the literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and follows the required formatting and citation styles.
- Edit and Proofread your Paper: Review your paper for grammar and spelling errors, and ensure that it is well-structured and easy to read. Ask someone else to review your paper to get feedback and suggestions for improvement.
- Cite your Sources: Ensure that you properly cite all sources used in your research paper. This is essential for giving credit to the original authors and avoiding plagiarism.
Research Paper Example
Note : The below example research paper is for illustrative purposes only and is not an actual research paper. Actual research papers may have different structures, contents, and formats depending on the field of study, research question, data collection and analysis methods, and other factors. Students should always consult with their professors or supervisors for specific guidelines and expectations for their research papers.
Research Paper Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health among Young Adults
Abstract: This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults. A literature review was conducted to examine the existing research on the topic. A survey was then administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Introduction: Social media has become an integral part of modern life, particularly among young adults. While social media has many benefits, including increased communication and social connectivity, it has also been associated with negative outcomes, such as addiction, cyberbullying, and mental health problems. This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults.
Literature Review: The literature review highlights the existing research on the impact of social media use on mental health. The review shows that social media use is associated with depression, anxiety, stress, and other mental health problems. The review also identifies the factors that contribute to the negative impact of social media, including social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Methods : A survey was administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The survey included questions on social media use, mental health status (measured using the DASS-21), and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis.
Results : The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Discussion : The study’s findings suggest that social media use has a negative impact on the mental health of young adults. The study highlights the need for interventions that address the factors contributing to the negative impact of social media, such as social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Conclusion : In conclusion, social media use has a significant impact on the mental health of young adults. The study’s findings underscore the need for interventions that promote healthy social media use and address the negative outcomes associated with social media use. Future research can explore the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health. Additionally, longitudinal studies can investigate the long-term effects of social media use on mental health.
Limitations : The study has some limitations, including the use of self-report measures and a cross-sectional design. The use of self-report measures may result in biased responses, and a cross-sectional design limits the ability to establish causality.
Implications: The study’s findings have implications for mental health professionals, educators, and policymakers. Mental health professionals can use the findings to develop interventions that address the negative impact of social media use on mental health. Educators can incorporate social media literacy into their curriculum to promote healthy social media use among young adults. Policymakers can use the findings to develop policies that protect young adults from the negative outcomes associated with social media use.
References :
- Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2019). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study. Preventive medicine reports, 15, 100918.
- Primack, B. A., Shensa, A., Escobar-Viera, C. G., Barrett, E. L., Sidani, J. E., Colditz, J. B., … & James, A. E. (2017). Use of multiple social media platforms and symptoms of depression and anxiety: A nationally-representative study among US young adults. Computers in Human Behavior, 69, 1-9.
- Van der Meer, T. G., & Verhoeven, J. W. (2017). Social media and its impact on academic performance of students. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 16, 383-398.
Appendix : The survey used in this study is provided below.
Social Media and Mental Health Survey
- How often do you use social media per day?
- Less than 30 minutes
- 30 minutes to 1 hour
- 1 to 2 hours
- 2 to 4 hours
- More than 4 hours
- Which social media platforms do you use?
- Others (Please specify)
- How often do you experience the following on social media?
- Social comparison (comparing yourself to others)
- Cyberbullying
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
- Have you ever experienced any of the following mental health problems in the past month?
- Do you think social media use has a positive or negative impact on your mental health?
- Very positive
- Somewhat positive
- Somewhat negative
- Very negative
- In your opinion, which factors contribute to the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Social comparison
- In your opinion, what interventions could be effective in reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Education on healthy social media use
- Counseling for mental health problems caused by social media
- Social media detox programs
- Regulation of social media use
Thank you for your participation!
Applications of Research Paper
Research papers have several applications in various fields, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Research papers contribute to the advancement of knowledge by generating new insights, theories, and findings that can inform future research and practice. They help to answer important questions, clarify existing knowledge, and identify areas that require further investigation.
- Informing policy: Research papers can inform policy decisions by providing evidence-based recommendations for policymakers. They can help to identify gaps in current policies, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and inform the development of new policies and regulations.
- Improving practice: Research papers can improve practice by providing evidence-based guidance for professionals in various fields, including medicine, education, business, and psychology. They can inform the development of best practices, guidelines, and standards of care that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- Educating students : Research papers are often used as teaching tools in universities and colleges to educate students about research methods, data analysis, and academic writing. They help students to develop critical thinking skills, research skills, and communication skills that are essential for success in many careers.
- Fostering collaboration: Research papers can foster collaboration among researchers, practitioners, and policymakers by providing a platform for sharing knowledge and ideas. They can facilitate interdisciplinary collaborations and partnerships that can lead to innovative solutions to complex problems.
When to Write Research Paper
Research papers are typically written when a person has completed a research project or when they have conducted a study and have obtained data or findings that they want to share with the academic or professional community. Research papers are usually written in academic settings, such as universities, but they can also be written in professional settings, such as research organizations, government agencies, or private companies.
Here are some common situations where a person might need to write a research paper:
- For academic purposes: Students in universities and colleges are often required to write research papers as part of their coursework, particularly in the social sciences, natural sciences, and humanities. Writing research papers helps students to develop research skills, critical thinking skills, and academic writing skills.
- For publication: Researchers often write research papers to publish their findings in academic journals or to present their work at academic conferences. Publishing research papers is an important way to disseminate research findings to the academic community and to establish oneself as an expert in a particular field.
- To inform policy or practice : Researchers may write research papers to inform policy decisions or to improve practice in various fields. Research findings can be used to inform the development of policies, guidelines, and best practices that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- To share new insights or ideas: Researchers may write research papers to share new insights or ideas with the academic or professional community. They may present new theories, propose new research methods, or challenge existing paradigms in their field.
Purpose of Research Paper
The purpose of a research paper is to present the results of a study or investigation in a clear, concise, and structured manner. Research papers are written to communicate new knowledge, ideas, or findings to a specific audience, such as researchers, scholars, practitioners, or policymakers. The primary purposes of a research paper are:
- To contribute to the body of knowledge : Research papers aim to add new knowledge or insights to a particular field or discipline. They do this by reporting the results of empirical studies, reviewing and synthesizing existing literature, proposing new theories, or providing new perspectives on a topic.
- To inform or persuade: Research papers are written to inform or persuade the reader about a particular issue, topic, or phenomenon. They present evidence and arguments to support their claims and seek to persuade the reader of the validity of their findings or recommendations.
- To advance the field: Research papers seek to advance the field or discipline by identifying gaps in knowledge, proposing new research questions or approaches, or challenging existing assumptions or paradigms. They aim to contribute to ongoing debates and discussions within a field and to stimulate further research and inquiry.
- To demonstrate research skills: Research papers demonstrate the author’s research skills, including their ability to design and conduct a study, collect and analyze data, and interpret and communicate findings. They also demonstrate the author’s ability to critically evaluate existing literature, synthesize information from multiple sources, and write in a clear and structured manner.
Characteristics of Research Paper
Research papers have several characteristics that distinguish them from other forms of academic or professional writing. Here are some common characteristics of research papers:
- Evidence-based: Research papers are based on empirical evidence, which is collected through rigorous research methods such as experiments, surveys, observations, or interviews. They rely on objective data and facts to support their claims and conclusions.
- Structured and organized: Research papers have a clear and logical structure, with sections such as introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. They are organized in a way that helps the reader to follow the argument and understand the findings.
- Formal and objective: Research papers are written in a formal and objective tone, with an emphasis on clarity, precision, and accuracy. They avoid subjective language or personal opinions and instead rely on objective data and analysis to support their arguments.
- Citations and references: Research papers include citations and references to acknowledge the sources of information and ideas used in the paper. They use a specific citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Peer-reviewed: Research papers are often peer-reviewed, which means they are evaluated by other experts in the field before they are published. Peer-review ensures that the research is of high quality, meets ethical standards, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
- Objective and unbiased: Research papers strive to be objective and unbiased in their presentation of the findings. They avoid personal biases or preconceptions and instead rely on the data and analysis to draw conclusions.
Advantages of Research Paper
Research papers have many advantages, both for the individual researcher and for the broader academic and professional community. Here are some advantages of research papers:
- Contribution to knowledge: Research papers contribute to the body of knowledge in a particular field or discipline. They add new information, insights, and perspectives to existing literature and help advance the understanding of a particular phenomenon or issue.
- Opportunity for intellectual growth: Research papers provide an opportunity for intellectual growth for the researcher. They require critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, which can help develop the researcher’s skills and knowledge.
- Career advancement: Research papers can help advance the researcher’s career by demonstrating their expertise and contributions to the field. They can also lead to new research opportunities, collaborations, and funding.
- Academic recognition: Research papers can lead to academic recognition in the form of awards, grants, or invitations to speak at conferences or events. They can also contribute to the researcher’s reputation and standing in the field.
- Impact on policy and practice: Research papers can have a significant impact on policy and practice. They can inform policy decisions, guide practice, and lead to changes in laws, regulations, or procedures.
- Advancement of society: Research papers can contribute to the advancement of society by addressing important issues, identifying solutions to problems, and promoting social justice and equality.
Limitations of Research Paper
Research papers also have some limitations that should be considered when interpreting their findings or implications. Here are some common limitations of research papers:
- Limited generalizability: Research findings may not be generalizable to other populations, settings, or contexts. Studies often use specific samples or conditions that may not reflect the broader population or real-world situations.
- Potential for bias : Research papers may be biased due to factors such as sample selection, measurement errors, or researcher biases. It is important to evaluate the quality of the research design and methods used to ensure that the findings are valid and reliable.
- Ethical concerns: Research papers may raise ethical concerns, such as the use of vulnerable populations or invasive procedures. Researchers must adhere to ethical guidelines and obtain informed consent from participants to ensure that the research is conducted in a responsible and respectful manner.
- Limitations of methodology: Research papers may be limited by the methodology used to collect and analyze data. For example, certain research methods may not capture the complexity or nuance of a particular phenomenon, or may not be appropriate for certain research questions.
- Publication bias: Research papers may be subject to publication bias, where positive or significant findings are more likely to be published than negative or non-significant findings. This can skew the overall findings of a particular area of research.
- Time and resource constraints: Research papers may be limited by time and resource constraints, which can affect the quality and scope of the research. Researchers may not have access to certain data or resources, or may be unable to conduct long-term studies due to practical limitations.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
How To Write A Research Paper
Research Paper Thesis

How To Write a Thesis For a Research Paper Step by Step
12 min read
Published on: Mar 6, 2024
Last updated on: Mar 5, 2024

People also read
How to Write a Research Paper Step by Step
How to Write a Proposal For a Research Paper in 10 Steps
A Comprehensive Guide to Creating a Research Paper Outline
Types of Research - Methodologies and Characteristics
300+ Engaging Research Paper Topics to Get You Started
Interesting Psychology Research Topics & Ideas
Qualitative Research - Types, Methods & Examples
Understanding Quantitative Research - Definition, Types, Examples, And More
Research Paper Example - Examples for Different Formats
How To Start A Research Paper - Steps With Examples
How to Write an Abstract That Captivates Your Readers
How To Write a Literature Review for a Research Paper | Steps & Examples
Types of Qualitative Research Methods - An Overview
Understanding Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research - A Complete Guide
How to Cite a Research Paper in Different Citation Styles
Easy Sociology Research Topics for Your Next Project
200+ Outstanding History Research Paper Topics With Expert Tips
How To Write a Hypothesis in a Research Paper | Steps & Examples
How to Write an Introduction for a Research Paper - A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Write a Good Research Paper Title
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper in 3 Simple Steps
How to Write an Abstract For a Research Paper with Examples
How to Write a Discussion For a Research Paper | Objectives, Steps & Examples
How to Write the Results Section of a Research Paper - Structure and Tips
How to Write a Problem Statement for a Research Paper in 6 Steps
How To Write The Methods Section of a Research Paper Step-by-Step
How to Find Sources For a Research Paper | A Guide
Share this article
Creating a strong thesis for a research paper can be tough for researchers and scholars. Despite their expertise, condensing complex ideas into a clear thesis statement is a common struggle.
This concise element encapsulates the core arguments or points of the piece. Notably, a thesis statement serves various roles, prominently addressing the research question.
This guide offers a step-by-step approach for researchers and scholars to learn thesis writing. From choosing a solid topic to balancing academic standards, each step aims to empower you in creating a thesis that meets scholarly criteria and resonates widely.
This guide ensures you develop a strong thesis, making your research paper stand out in academic circles.
On This Page On This Page -->
What is a Thesis Statement?
A thesis statement is a concise sentence that presents the main point or argument of a research paper or an essay.
According to the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill's Writing Center , a thesis statement is defined as, "a concise, declarative statement that encapsulates the central argument or main point of an academic paper or essay. It serves as a guidepost for the reader, outlining the focus and direction of the piece"
In a standard academic essay writing or research paper , the thesis statement is typically placed at the end of the introduction. It serves as a roadmap for the reader, providing a concise summary of the main point or argument that the paper will explore.
The structure of an introduction often follows a general pattern:
- Hook/Attention Grabber
- Background Information/Context
- Thesis Statement
There is no strict rule regarding the length of a thesis statement, as it can vary depending on the complexity of the topic and the scope of the paper. However, as a general guideline, a thesis statement is typically one or two sentences long.
Qualities of a Good Thesis Statement
A strong thesis statement possesses several key qualities that contribute to its effectiveness:
- Clarity and Precision : Clearly conveys the main idea without unnecessary complexity, avoiding vague language.
- Debatable and Focused : Presents a claim open to interpretation, requiring support and evidence, and maintains a narrow focus.
- Assertive and Defensible: Takes a clear position, avoiding indecisiveness, and is defensible through logical reasoning and evidence.
- Relevance to the Topic : Directly relates to the subject matter, avoiding irrelevant or off-topic statements.
- Scope Limitation : Defines the paper's scope, avoiding broad, sweeping statements to maintain focus.
- Analytical and Thought-Provoking : Goes beyond stating facts, presenting an argument that requires analysis and thought, encouraging consideration of multiple perspectives.
- Coherent and Well-Structured : Well-crafted with a logical structure, serving as a roadmap to guide the reader through the main points of the research paper.
How To Write a Thesis Statement in 5 Steps
Writing a thesis statement involves several key steps to ensure that it is clear, concise, and effectively conveys the main idea of your essay or research paper. Here's a guide with steps and examples:
Step 1. Understand the Assignment
Before diving into writing a thesis statement, thoroughly understand the assignment's requirements, including the topic, length, and specific guidelines provided by your instructor or the prompt.
Step 2. Narrow Down Your Topic
Choose a specific aspect or angle within your broader topic that you can effectively address in your paper. This helps in focusing your research and drafting a more precise thesis.
Example : If your original topic is "Global warming," narrow it down to "The impact of deforestation on global warming."
Step 3. Conduct Research
Gather relevant information and evidence from reputable sources to support your thesis. A well-researched thesis is more likely to be compelling and convincing.
Example : Find studies, scientific articles, or statistics that demonstrate the connection between deforestation and increased carbon emissions.
Step 4. Identify Your Position or Claim
Determine your stance on the narrowed topic. What is the main argument or point you want to make?
Example : Decide that your position is that "Deforestation contributes significantly to the acceleration of global warming."

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Step 5. Craft a Concise Thesis Statement
Summarize your main argument in a clear, specific, and concise sentence. This will be the central point around which your entire paper revolves.
Example : "The rampant deforestation observed globally is a primary driver of increased carbon emissions, leading to a substantial acceleration of global warming."
Step 6. Make It Arguable
Ensure that your thesis statement is debatable. Avoid stating facts that everyone would agree with; instead, present a claim that invites discussion.
Example : "While some argue that deforestation has minimal impact on global warming, the overwhelming evidence supports the assertion that it plays a significant role."
Step 7. Consider Counterarguments
Anticipate potential counterarguments and address them within your thesis. This shows that you've considered different perspectives and strengthens your overall position.
Example : "While some contend that other factors contribute to global warming, the undeniable link between deforestation and increased carbon emissions cannot be ignored."
Step 8. Ensure Clarity and Specificity
Avoid vague language and make sure your thesis clearly communicates the main point of your paper. Provide enough detail to guide your reader.
Example : "Deforestation's impact on global warming is a complex issue that demands immediate attention."
Step 9. Review and Revise
Critically evaluate your thesis for clarity, relevance, and strength. Revise as needed to ensure it encapsulates your main argument effectively.
The final Thesis Statement may look like this:
Types of Thesis Statements
Thesis statements serve as the core of a research paper, providing the main argument or purpose of the work. Here are a few types of thesis statements with examples:
Argumentative Thesis Statement
Argumentative thesis statements assert a specific stance on an issue and provide reasons or evidence to support that viewpoint. They aim to persuade the reader of a particular perspective.
Here is a thesis statement example for argumentative essay :
Analytical Thesis Statement
Analytical thesis statements break down a topic into its constituent parts, examining it critically to understand its components or significance. They don't argue a point but rather analyze and interpret.
Expository Thesis Statement
Expository thesis statements present factual information or explain a topic without expressing opinions or arguments. They aim to inform and elucidate.
Comparative Thesis Statement
Comparative thesis statements highlight similarities and differences between two or more subjects, offering an evaluation or analysis of their relationship.
Cause and Effect Thesis Statement
Cause and effect thesis statements outline the relationship between events or phenomena, indicating how one factor influences another and the resulting consequences.
Research Paper Thesis Template
A useful guideline for creating a thesis statement is to follow a three-part structure that includes the topic, the main point or claim, and the supporting reasons or evidence. This formula can be expressed as:
Topic + Claim + Reasons/Evidence
Here's a breakdown of each component:
Follow the steps above and use this research paper thesis statement template to develop a useful thesis.
Thesis For a Research Paper Examples
Here are a few thesis statement examples for research papers:
Research Paper Thesis Examples
Thesis For a Research Paper Middle School
College thesis statement examples, thesis for a research report, thesis statement for a research paper in apa format.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Thesis For a History Research Paper
Thesis statements for personal essays, examples of weak and strong thesis statements.
Here's a table with examples of weak and strong thesis statements across three different subjects:

Tips for Writing Strong Thesis Statements
Here are some tips for developing strong thesis statements:
- Challenge conventional wisdom or commonly held beliefs in your thesis.
- Use powerful and vivid words to evoke emotions or curiosity in your thesis.
- Introduce a fresh perspective or angle that hasn't been widely discussed.
- Offer a glimpse into potential solutions or broader implications of your thesis.
- Pose a thought-provoking question or a startling fact to engage the reader.
- Highlight the contemporary relevance or timeliness of your thesis statement.
- Appeal to the reader's emotions or personal experiences to make a connection.
- Emphasize the importance of exploring contradictions or complexities in your topic.
- Encourage the reader to contemplate the deeper implications of your thesis.
- Highlight how your thesis reflects personal growth or a change in perspective over time.
Thesis Statement Assessment Checklist
So, you may be wondering, how do I know if my thesis is strong? Use the checklist below to assess the strength of your thesis statement:
Summit it Up!
Crafting a strong thesis for a research paper involves precision, specificity, and a clear position. Remember to regularly revisit and refine your thesis as you progress through the writing process.
If you find yourself struggling to formulate the perfect thesis statement, worry not! The professionals at CollegeEssay.org are here to provide expert assistance.
Our professional writing service can guide you through the process, ensuring a compelling and impactful thesis statement.
Get custom research paper today and elevate the quality of your academic work.
Commonly Asked Questions
How does a research hypothesis differ from a thesis statement.
A research hypothesis is a specific, testable prediction about the outcome of a research study. On the other hand, a thesis statement is a broader statement summarizing the main argument of a paper.
Can a thesis statement change during the research process?
Yes, as you conduct research and refine your understanding of the topic, it's common for your thesis statement to evolve or be adjusted.
How does the thesis statement relate to the research methodology?
The thesis statement may hint at the research approach but focuses more on the main argument. The methodology is detailed separately in the research paper to explain how the study was conducted.
How do I choose the right tone for my thesis statement?
Tailor the tone to match the nature of your research. It can be analytical, argumentative, or explanatory, depending on the purpose and style of your paper.
Cathy A. (Marketing, Literature)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
Research Paper Writing Guides
Research Paper Thesis
Last updated on: Mar 27, 2024
How to Write a Research Paper Thesis: A Detailed Guide
By: Donna C.
20 min read
Reviewed By: Jared P.
Published on: Jan 6, 2024

Have you ever had trouble making a thesis for your research paper? It's a common challenge, often leaving writers uncertain about where to begin and how to structure their thoughts.
A thesis statement is what your research paper revolves around. The argument, evidence, and facts stated in the thesis are carried out throughout the research paper .
Having said that, the importance of creating a thesis statement that stands out, cannot be denied. But, not everyone is competent enough to craft effective thesis statements.
Fear not!
We've streamlined the process for you, breaking it down into manageable steps. From brainstorming your topic to crafting a clear thesis, we’ll help you write the optimal thesis.
Let’s get going!

On this Page

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
What is a Research Paper Thesis?
To understand the question, “What is a thesis for a research paper?” we’ll look at the standard definition :
“A thesis statement is a declarative sentence that asserts the position a paper will be taking. This statement should be both specific and arguable. Generally, the thesis statement will be placed at the end of the first paragraph of your paper. The remainder of your paper will support this thesis.”
Think of it as the roadmap for your readers that guides them throughout the entire research paper.
Usually, thesis statements consist of one or, at most, two sentences . A good thesis isn't just about summarizing; it's about making a clear point and an arguable claim.
The thesis takes place in the research paper introduction. It is a good practice to include the thesis at the end of the introduction paragraph.
For example, If you're exploring how technology affects learning, a strong thesis statement could be:
Now that you know what a research paper thesis is, let’s discuss some characteristics of a good thesis statement in the context of research.
Elements of a Good Research Paper Thesis
A solid research paper thesis is like a well-built foundation for your research work. Here are the key elements that make it strong:
A good thesis is crystal clear, leaving no room for confusion. It conveys the main point clearly and makes sure that the readers grasp the essence of the argument.
Specificity
It goes beyond generalities, providing specific aspects about the focus of the paper. Specificity adds depth and helps in guiding the research process.
Arguability
A strong thesis statement takes a stance on an issue and presents an arguable claim. It sparks curiosity and encourages discussion rather than stating an obvious fact.
Conciseness
Keeping it short and to the point is key. A good thesis doesn’t go off-track—it gets straight to the heart of your message in a sentence or two.
Alignment with Paper Content
A good thesis aligns seamlessly with the content, reflecting the direction and purpose of the research.
Incorporation of Main Ideas
It serves as a preview of the main ideas in the research. A good thesis introduces the key concepts that will be explored and substantiated throughout the research.
A relevant thesis statement connects directly to the research and questions that the author aims to answer. It avoids unnecessary information that might divert from the main focus.
Guidance for Research
An effective thesis summarizes the point and provides a roadmap for your research. It outlines the direction of the research and sets expectations for the reader.
Adaptability
A good thesis remains flexible. As the research progresses, it can be refined to accommodate new insights or changes in the direction of the paper.
Now, let’s see what are the different types of research paper theses.
Different Research Paper Thesis Types
Depending on different types of research papers, the thesis can take any of the following forms:
Argumentative Thesis
An argumentative thesis takes a firm stance on a controversial issue and aims to persuade the reader to adopt the same position on the topic. Your goal is not just to present information but to convince others that your perspective is valid.
Including supporting evidence and well-structured arguments play an important role in an argumentative thesis.
Analytical Thesis
An analytical thesis approaches a complex topic by breaking it down into its fundamental components. It aims to understand how these parts interact and contribute to the overall understanding of the subject.
Explanatory Thesis
An explanatory thesis aims to clarify a concept, process, or phenomenon by offering detailed information. It helps explain a topic without picking sides or breaking it into pieces.
These are the most common types of research paper theses. Although there are some other types as well.
- Comparative Thesis: Examines similarities and differences between two or more subjects, presenting an analysis of their relationships.
- Cause and Effect Thesis: Identifies a relationship between events, asserting that one event leads to another and explaining the consequences.
- Descriptive Thesis: Paints a vivid picture of a subject, providing detailed information to create a clear and rich understanding.
- Problem-Solution Thesis: Highlights an issue and proposes specific solutions to address the identified problem.
- Exploratory Thesis: Explores a subject with an open mind, aiming to understand different aspects and perspectives without necessarily forming a definite conclusion.
Now that you have a better understanding of what a research paper thesis is, we’ll get straight to the writing steps.

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
How to Write a Thesis for a Research Paper?
Follow these steps, and you’ll be writing compelling research thesis statements in no time.
Step 1. Brainstorm Your Topic
If you haven’t yet decided on the research paper topic , the first step is to brainstorm ideas.
- Start with identifying your key research areas and interests.
- Once you pick a general idea, dig deeper.
- Think about what makes you curious about the topic.
For example, if you’ve chosen climate change, your brainstorming might lead you to questions like:
- How does climate change affect wildlife in specific regions?
- What are the human activities contributing to climate change?
Topic brainstorming helps you create a roadmap and aids you in pinpointing areas within the broader topic that you’re most interested in.
Step 2. Conduct Preliminary Research
After brainstorming, the next step is to conduct research and explore what others have discovered about your topic.
You can read books, articles, and reliable sources. Gather information to understand the current state of knowledge on your topic.
Doing preliminary research helps build the foundation of your research thesis. You’ll have a better insight and understanding of your topic if you know it’s background.
Step 3. Choose a Clear Research Question
Now, it's time to narrow down your focus to a specific and well-defined research problem .
Make sure your question is relevant and it aligns with your interests and the assignment.
Here’s how you should narrow down your research questions:
- Get Specific
After looking at the overall topic, narrow it down to a specific aspect.
For example, Instead of saying “climate change,” think about something like “How does cutting down trees (deforestation) add to climate change?” It's like getting focused on one part of the bigger picture.
- Make it Matter
Your question should be important. Ask yourself why it's a big deal to you and why it matters for your assignment.
For example, instead of just wondering about technology and people, ask, “How do smartphones affect our work every day?” This makes your question relevant and calculated.
Be clear about your question and try not to make it confusing. Craft a question that's easy to understand. If your assignment doesn't come with a set question, make one up.
Ask yourself, “What do I want to find out about my topic?” Your self-made question becomes your guide for exploring.
Step 4. Answer the Research Question
After you’ve crafted your research question, comes the time to compose your answer. What you need to do is to think about why this is your response and how you will convince readers.
- First Answer, or Working Thesis:
This is your starting answer, kind of like a rough draft.
For example, If your question is “How does cutting down trees affect climate change?” your first answer could be something like:
- Get Your Direction:
Think of this answer as a compass. It helps you know where you're going in your research project. It's the beginning of your thesis statement, which is the big idea that leads your whole research paper.
Remember, it's okay if this answer changes later as you learn more. It's like starting with a map and adjusting your path as you find new stuff. The point is to start with a thoughtful and informed beginning for your research project.
Step 5. Include Evidence and Reasoning
After making your first educated guess (working thesis), it's time to collect evidence that supports your idea. This is like finding puzzle pieces that fit with your initial thoughts.
If your working thesis is “ Cutting down trees lets out carbon, adding to the warming of the Earth ,” find data that shows how deforestation releases carbon. This data is like your evidence that makes your thesis more convincing.
Use real-life examples and expert opinions to strengthen your thesis.
For instance, if case studies show the environmental impact of deforestation or if reputable scientists have published articles supporting your point, include them.
- Include data showing the correlation between deforestation rates and increased carbon emissions.
- Provide examples of regions where deforestation has led to changes in climate patterns.
- Reference scholarly articles written by environmental experts that discuss the impact of deforestation on global warming.
This step elevates your working thesis to a solid thesis statement by grounding it in concrete evidence and expert perspectives. It transforms your idea into a well-supported argument that has the potential to engage readers from the get-go.
Step 6. Refine Your Answer
Now that you've presented your initial answer backed by evidence and reasoning, it's time to fine-tune it.
- Take a step back and look at your initial answer or working thesis . Does it still hold up in light of the evidence you've gathered? Consider if any adjustments or clarifications are needed.
- Also, try to look at your answer from different angles and perspectives . Acknowledge alternative perspectives and see if there are valid counterarguments. This step adds depth and meaning to your thesis.
- Refine your answer to capture the complexity of your topic. Your thesis should not oversimplify; it should reflect the richness of your research project.
- Make sure that your thesis remains well-supported by the evidence you've gathered.
For example, if your working thesis is “Cutting down trees lets out carbon, adding to the warming of the Earth,” after evaluating, you might refine it to:
Step 7. Finalize Your Thesis Statement
Now comes the final step of the thesis writing process. In the last stage, summarize your refined answer into a powerful single sentence or, if required, two sentences.
It should capture the main point of your research project and set the tone for your entire paper.
The final version of the refined answer we discussed would look something like this in the form of a final thesis statement .
One thing to note here is that you shouldn’t exceed the number of sentences used to more than 2.
Comparing a Strong and a Weak Thesis Statement
Some thesis statements are strong, precise, and accurately address the scope of the research study. On the other hand, some statements lack these aspects in one way or the other.
It could be beneficial for you to look at some examples of strong and weak thesis statements for an even better understanding. Take a look at the comparison table below:
By now, you should have a clear idea about what elements are required to craft a strong and adequate thesis statement.
Research Paper Thesis - Examples
Here are some great research paper thesis statement examples for you. Go through them, and you’ll have a practical understanding of what makes a perfect research paper thesis.
Research Paper Thesis Example
See this effective research paper thesis example that brilliantly addresses the argument and the research direction.
Research Paper Thesis Template
Here is a good research paper thesis template that you can follow:
Thesis Statement Outline PDF
How to Write Thesis for a Research Paper APA Format - Example
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to write a thesis statement for a research paper in APA format:
Middle School Research Paper Thesis
Research report thesis , history research paper thesis, thesis statement for a psychology research paper, thesis paragraph for a research paper.
Having read these examples, you should be able to give your research paper an edge with compelling thesis statements.
Thesis Statement vs. Research Question vs. Hypothesis
It is vital to understand the difference between your thesis, research question, and the hypothesis of the research paper . Look at the table below to know the key differences between them.
Things to Avoid in a Research Paper Thesis
There are some things that you avoid performing at all costs for a great thesis.
So, for an effective research paper thesis, you should avoid
- vague or overly broad statements.
- making statements without proper evidence
- ambiguous and complex language that might confuse your readers.
- using a personal bias to overshadow your thesis
- overly simplistic statements
- stating the obvious without adding any fresh perspective
To sum it up,
Learning how to create a thesis for a research paper can take some time. But, after a bit of research and getting help from experts, you can engage readers will well-written statements.
With our comprehensive and step-by-step guide, we aim to help you understand everything about creating a thesis statement. From the initial topic brainstorming to the final statement, we’ve covered every writing step in detail.However, if you’re still stuck somewhere, and you’re unsure how to move forward, don’t worry; we have a solution for that as well.
Our paper writing service online has a pool of experienced writing specialists who can take your research paper worries away in a breeze. Experts at our service are up for any challenge you throw at them.
Just visit our website, let us know what you require, and we’ll solve your writing-related woes at the best and most affordable rates!

Donna writes on a broad range of topics, but she is mostly passionate about social issues, current events, and human-interest stories. She has received high praise for her writing from both colleagues and readers alike. Donna is known in her field for creating content that is not only professional but also captivating.
Was This Blog Helpful?
Keep reading.
- Learning How to Write a Research Paper: Step-by-Step Guide

- Best 300+ Ideas For Research Paper Topics in 2024

- A Complete Guide to Help You Write a Research Proposal

- The Definitive Guide on How to Start a Research Paper
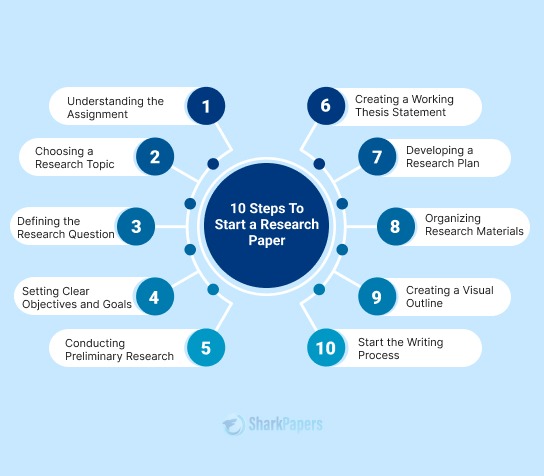
- How To Write An Introduction For A Research Paper - A Complete Guide
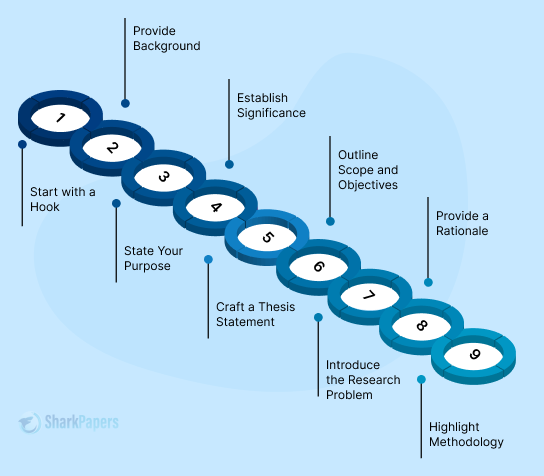
- Learn How To Write An Abstract For A Research Paper with Examples and Tips

- How to Write a Literature Review for a Research Paper | A Complete Guide

- How To Write The Methods Section of A Research Paper

- How to Write a Research Paper Title That Stands Out

- A Detailed Guide on How To Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper

- How To Write The Results Section of A Research Paper | Steps & Tips

- How to Problem Statement for a Research Paper: An Easy Guide

- How to Find Credible Sources for a Research Paper

- A Detailed Guide: How to Write a Discussion for a Research Paper
)
- How To Write A Hypothesis In A Research Paper - A Simple Guide

- Learn How To Cite A Research Paper in Different Formats: The Basics

- The Ultimate List of Ethical Research Paper Topics in 2024
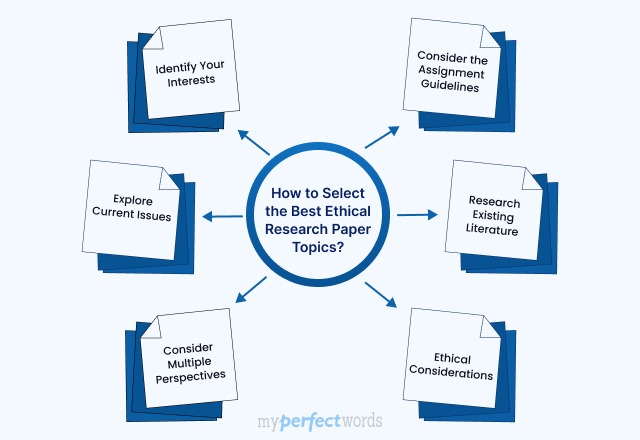
- 150+ Controversial Research Paper Topics to Get You Started

- How to Edit Research Papers With Precision: A Detailed Guide

- A Comprehensive List of Argumentative Research Paper Topics
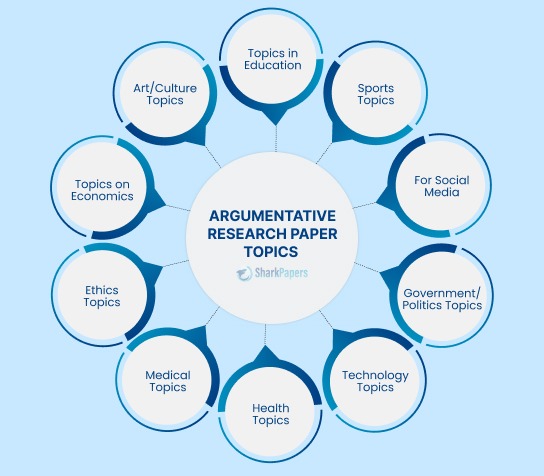
- A Detailed List of Amazing Art Research Paper Topics

- Diverse Biology Research Paper Topics for Students: A Comprehensive List

- 230 Interesting and Unique History Research Paper Topics
- 190 Best Business Research Paper Topics
- 200+ Engaging and Novel Literature Research Paper Topics
- A Guide on How to Write a Social Science Research
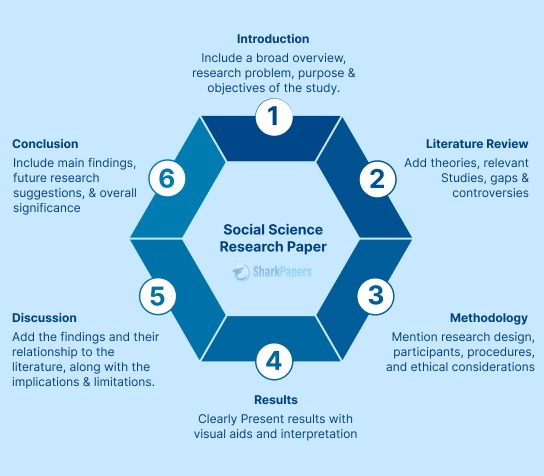
- Sociology Research Papers: Format, Outline, and Topics
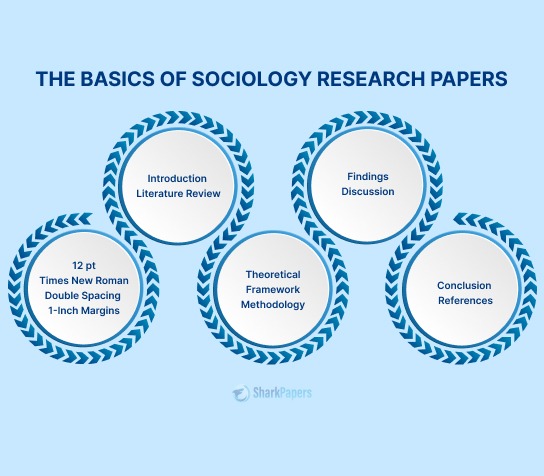
- Understanding the Basics of Biology Research Papers
- How to Write a Psychology Research Paper: Guide with Easy Steps
- Exploring the Different Types of Research Papers: A Guide

People Also Read
- opinion essay
- how to write an essay
- autobiography vs biography
- scholarship essay
- personal statement
Burdened With Assignments?

Advertisement
© 2024 - All rights reserved
2000+ SATISFIED STUDENTS
95% Satisfaction RATE
30 Days Money Back GUARANTEE
95% Success RATE
Privacy Policy | Terms & Conditions | Contact Us
© 2021 SharkPapers.com(Powered By sharkpapers.com). All rights reserved.
© 2022 Sharkpapers.com. All rights reserved.
LOGIN TO YOUR ACCOUNT
SIGN UP TO YOUR ACCOUNT
- Your phone no.
- Confirm Password
- I have read Privacy Policy and agree to the Terms and Conditions .
FORGOT PASSWORD
- SEND PASSWORD
Thesis and Purpose Statements
Use the guidelines below to learn the differences between thesis and purpose statements.
In the first stages of writing, thesis or purpose statements are usually rough or ill-formed and are useful primarily as planning tools.
A thesis statement or purpose statement will emerge as you think and write about a topic. The statement can be restricted or clarified and eventually worked into an introduction.
As you revise your paper, try to phrase your thesis or purpose statement in a precise way so that it matches the content and organization of your paper.
Thesis statements
A thesis statement is a sentence that makes an assertion about a topic and predicts how the topic will be developed. It does not simply announce a topic: it says something about the topic.
Good: X has made a significant impact on the teenage population due to its . . . Bad: In this paper, I will discuss X.
A thesis statement makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of the paper. It summarizes the conclusions that the writer has reached about the topic.
A thesis statement is generally located near the end of the introduction. Sometimes in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or an entire paragraph.
A thesis statement is focused and specific enough to be proven within the boundaries of the paper. Key words (nouns and verbs) should be specific, accurate, and indicative of the range of research, thrust of the argument or analysis, and the organization of supporting information.
Purpose statements
A purpose statement announces the purpose, scope, and direction of the paper. It tells the reader what to expect in a paper and what the specific focus will be.
Common beginnings include:
“This paper examines . . .,” “The aim of this paper is to . . .,” and “The purpose of this essay is to . . .”
A purpose statement makes a promise to the reader about the development of the argument but does not preview the particular conclusions that the writer has drawn.
A purpose statement usually appears toward the end of the introduction. The purpose statement may be expressed in several sentences or even an entire paragraph.
A purpose statement is specific enough to satisfy the requirements of the assignment. Purpose statements are common in research papers in some academic disciplines, while in other disciplines they are considered too blunt or direct. If you are unsure about using a purpose statement, ask your instructor.
This paper will examine the ecological destruction of the Sahel preceding the drought and the causes of this disintegration of the land. The focus will be on the economic, political, and social relationships which brought about the environmental problems in the Sahel.
Sample purpose and thesis statements
The following example combines a purpose statement and a thesis statement (bold).
The goal of this paper is to examine the effects of Chile’s agrarian reform on the lives of rural peasants. The nature of the topic dictates the use of both a chronological and a comparative analysis of peasant lives at various points during the reform period. . . The Chilean reform example provides evidence that land distribution is an essential component of both the improvement of peasant conditions and the development of a democratic society. More extensive and enduring reforms would likely have allowed Chile the opportunity to further expand these horizons.
For more tips about writing thesis statements, take a look at our new handout on Developing a Thesis Statement.

Writing Process and Structure
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Getting Started with Your Paper
Interpreting Writing Assignments from Your Courses
Generating Ideas for Your Paper
Creating an Argument
Thesis vs. Purpose Statements
Developing a Thesis Statement
Architecture of Arguments
Working with Sources
Quoting and Paraphrasing Sources
Using Literary Quotations
Citing Sources in Your Paper
Drafting Your Paper
Introductions
Paragraphing
Developing Strategic Transitions
Conclusions
Revising Your Paper
Peer Reviews
Reverse Outlines
Revising an Argumentative Paper
Revision Strategies for Longer Projects
Finishing Your Paper
Twelve Common Errors: An Editing Checklist
How to Proofread your Paper
Writing Collaboratively
Collaborative and Group Writing

The Quintessence of Basic and Clinical Research and Scientific Publishing pp 769–781 Cite as
Writing a Postgraduate or Doctoral Thesis: A Step-by-Step Approach
- Usha Y. Nayak 4 ,
- Praveen Hoogar 5 ,
- Srinivas Mutalik 4 &
- N. Udupa 6
- First Online: 01 October 2023
662 Accesses
1 Citations
A key characteristic looked after by postgraduate or doctoral students is how they communicate and defend their knowledge. Many candidates believe that there is insufficient instruction on constructing strong arguments. The thesis writing procedure must be meticulously followed to achieve outstanding results. It should be well organized, simple to read, and provide detailed explanations of the core research concepts. Each section in a thesis should be carefully written to make sure that it transitions logically from one to the next in a smooth way and is free of any unclear, cluttered, or redundant elements that make it difficult for the reader to understand what is being tried to convey. In this regard, students must acquire the information and skills to successfully create a strong and effective thesis. A step-by-step description of the thesis/dissertation writing process is provided in this chapter.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Carter S, Guerin C, Aitchison C (2020) Doctoral writing: practices, processes and pleasures. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-1808-9
Book Google Scholar
Odena O, Burgess H (2017) How doctoral students and graduates describe facilitating experiences and strategies for their thesis writing learning process: a qualitative approach. Stud High Educ 42:572–590. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075079.2015.1063598
Article Google Scholar
Stefan R (2022) How to write a good PhD thesis and survive the viva, pp 1–33. http://people.kmi.open.ac.uk/stefan/thesis-writing.pdf
Google Scholar
Barrett D, Rodriguez A, Smith J (2021) Producing a successful PhD thesis. Evid Based Nurs 24:1–2. https://doi.org/10.1136/ebnurs-2020-103376
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Murray R, Newton M (2009) Writing retreat as structured intervention: margin or mainstream? High Educ Res Dev 28:541–553. https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360903154126
Thompson P (2012) Thesis and dissertation writing. In: Paltridge B, Starfield S (eds) The handbook of english for specific purposes. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, Hoboken, NJ, pp 283–299. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118339855.ch15
Chapter Google Scholar
Faryadi Q (2018) PhD thesis writing process: a systematic approach—how to write your introduction. Creat Educ 09:2534–2545. https://doi.org/10.4236/ce.2018.915192
Faryadi Q (2019) PhD thesis writing process: a systematic approach—how to write your methodology, results and conclusion. Creat Educ 10:766–783. https://doi.org/10.4236/ce.2019.104057
Fisher CM, Colin M, Buglear J (2010) Researching and writing a dissertation: an essential guide for business students, 3rd edn. Financial Times/Prentice Hall, Harlow, pp 133–164
Ahmad HR (2016) How to write a doctoral thesis. Pak J Med Sci 32:270–273. https://doi.org/10.12669/pjms.322.10181
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Gosling P, Noordam LD (2011) Mastering your PhD, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 12–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15847-6
Cunningham SJ (2004) How to write a thesis. J Orthod 31:144–148. https://doi.org/10.1179/146531204225020445
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Azadeh F, Vaez R (2013) The accuracy of references in PhD theses: a case study. Health Info Libr J 30:232–240. https://doi.org/10.1111/hir.12026
Williams RB (2011) Citation systems in the biosciences: a history, classification and descriptive terminology. J Doc 67:995–1014. https://doi.org/10.1108/00220411111183564
Bahadoran Z, Mirmiran P, Kashfi K, Ghasemi A (2020) The principles of biomedical scientific writing: citation. Int J Endocrinol Metab 18:e102622. https://doi.org/10.5812/ijem.102622
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Yaseen NY, Salman HD (2013) Writing scientific thesis/dissertation in biology field: knowledge in reference style writing. Iraqi J Cancer Med Genet 6:5–12
Gorraiz J, Melero-Fuentes D, Gumpenberger C, Valderrama-Zurián J-C (2016) Availability of digital object identifiers (DOIs) in web of science and scopus. J Informet 10:98–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2015.11.008
Khedmatgozar HR, Alipour-Hafezi M, Hanafizadeh P (2015) Digital identifier systems: comparative evaluation. Iran J Inf Process Manag 30:529–552
Kaur S, Dhindsa KS (2017) Comparative study of citation and reference management tools: mendeley, zotero and read cube. In: Sheikh R, Mishra DKJS (eds) Proceeding of 2016 International conference on ICT in business industry & government (ICTBIG). Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Piscataway, NJ. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICTBIG.2016.7892715
Kratochvíl J (2017) Comparison of the accuracy of bibliographical references generated for medical citation styles by endnote, mendeley, refworks and zotero. J Acad Librariansh 43:57–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acalib.2016.09.001
Zhang Y (2012) Comparison of select reference management tools. Med Ref Serv Q 31:45–60. https://doi.org/10.1080/02763869.2012.641841
Hupe M (2019) EndNote X9. J Electron Resour Med Libr 16:117–119. https://doi.org/10.1080/15424065.2019.1691963
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Pharmaceutics, Manipal College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, Karnataka, India
Usha Y. Nayak & Srinivas Mutalik
Centre for Bio Cultural Studies, Directorate of Research, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, Karnataka, India
Praveen Hoogar
Shri Dharmasthala Manjunatheshwara University, Dharwad, Karnataka, India
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to N. Udupa .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Retired Senior Expert Pharmacologist at the Office of Cardiology, Hematology, Endocrinology, and Nephrology, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, US Food and Drug Administration, Silver Spring, MD, USA
Gowraganahalli Jagadeesh
Professor & Director, Research Training and Publications, The Office of Research and Development, Periyar Maniammai Institute of Science & Technology (Deemed to be University), Vallam, Tamil Nadu, India
Pitchai Balakumar
Division Cardiology & Nephrology, Office of Cardiology, Hematology, Endocrinology and Nephrology, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, US Food and Drug Administration, Silver Spring, MD, USA
Fortunato Senatore
Ethics declarations
No conflict of interest exists.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter.
Nayak, U.Y., Hoogar, P., Mutalik, S., Udupa, N. (2023). Writing a Postgraduate or Doctoral Thesis: A Step-by-Step Approach. In: Jagadeesh, G., Balakumar, P., Senatore, F. (eds) The Quintessence of Basic and Clinical Research and Scientific Publishing. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1284-1_48
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1284-1_48
Published : 01 October 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-99-1283-4
Online ISBN : 978-981-99-1284-1
eBook Packages : Biomedical and Life Sciences Biomedical and Life Sciences (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Home » Education » What is the Difference Between Thesis and Research Paper
What is the Difference Between Thesis and Research Paper
The main difference between thesis and research paper is that thesis is a long academic paper that typically serves as the final project for a university degree, while research paper is a piece of academic writing on a particular topic.
In brief, both thesis and research paper are types of academic writing students need to complete in their academic life. While there are many similarities between the two, including the use of academic writing and structure, they are not the same.
Key Areas Covered
1. What is a Thesis – Definition, Features 2. What is a Research Paper – Definition, Features 3. Difference Between Thesis and Research Paper – Comparison of Key Differences

What is a Thesis
A thesis is a long paper that typically serves as the final project for a university degree. Submitting a thesis is generally required for completing undergraduate honours, masters , and doctoral degrees . The theses are very long and may contain hundreds of pages. They are also scholarly in nature and allows students to contribute valuable research in their field of study.
Moreover, a major part of a thesis work involves research and writing. It generally has advanced research design and analysis. When writing a thesis, the students will have to prove or disapprove a hypothesis , and their conclusions have to be backed by extensive research and an insightful, learned description of how they got to that conclusion. In some degree programs, students also have to perform an oral defence of the thesis paper in front of a panel of experts.
Components of a Thesis
These are the components you will usually find in a thesis paper.
- Title Page
- Abstract
- Table of Contents
- List of Figures
- List of Tables
- Introduction
- Methods
- Discussion
- Conclusions
- Recommendations
- Acknowledgements
- References
What is a Research Paper
A research paper is a type of academic writing that involves research, source evaluation, critical thinking, organization, and composition. Moreover, through a research paper, students can explore, interpret, and evaluate sources related to a particular topic. In fact, primary and secondary sources are very important components of a research paper. But it’s important to note that a research paper is not just a summary of a topic using primary and secondary sources. It’s not just an opinion essay or an expository essay that contains the writer’s opinions and views, either. A research paper is a type of writing that requires evaluating different sources and interpreting the information of these sources through one’s own lens. Furthermore, the main purpose of this type of writing is to offer a unique perspective on a topic analyzing and evaluating what others have already said about it.

In addition, there are different types of research papers. Argumentative research papers and analytical research papers are two of the main types of research papers.
Difference Between Thesis and Research Paper
A thesis or dissertation is a long academic paper that typically serves as the final project for a university degree while a research paper is a type of academic writing that involves research, source evaluation, critical thinking, organization, and composition.
In an Academic Context
In an academic context, students may be required to write research papers for assignments and homework, but a thesis is usually the final project.
A thesis tends to be longer than a research paper; in fact, a thesis can take many months, sometimes years, to complete.
Supervision
The thesis is written under the supervision of one or more academic supervisors whereas research papers usually do not have supervisors.
Students have to complete a thesis in order to complete their degree, whereas students write research papers to expand their knowledge.
In brief, the main difference between thesis and research paper is that thesis is a long research paper that typically serves as the final project for a university degree, while a research paper is a piece of academic writing on a particular topic. Moreover, in an academic context, students may be required to write research papers for assignments and homework. But the thesis is usually the final project.
1. Stute, Martin. “ How to Write Your Thesis .” Columbia University. 2. “ Genre and the Research Paper .” Purdue Writing Lab.
Image Courtesy:
1. “ Research Paper ” (CC BY-SA 3.0) By Nick Youngson via Alpha Stock Images
About the Author: Hasa
Hasanthi is a seasoned content writer and editor with over 8 years of experience. Armed with a BA degree in English and a knack for digital marketing, she explores her passions for literature, history, culture, and food through her engaging and informative writing.
You May Also Like These
Leave a reply cancel reply.
- Key Differences
Know the Differences & Comparisons
Difference Between Thesis and Research Paper
On the other hand, a research paper is analytical, argumentative and interpretative in nature. It involves the pursuit of knowledge and intelligent analysis of the information collected. It contains the idea of the author, often supported by expert opinions, research and information available in this regard.
Whether you are writing a thesis or research paper, they are equally challenging and take a lot of time to prepare. In this post, we will update you on all the points of difference between thesis and research paper.
Content: Thesis Vs Research Paper
- Key Elements
- Thesis Statement
How to start a research paper?
Comparison chart, what is thesis.
The thesis is a document containing the research and findings that students submit to get the professional qualification or degree . It has to be argumentative, which proposes a debatable point with which people could either agree or disagree. In short, it is a research report in writing that contains a problem which is yet to be dealt with.
In a thesis, the researcher puts forth his/her conclusion. The researcher also gives evidence in support of the conclusion.
Submission of the thesis is a mandatory requirement of a postgraduate course and PhD degree. In this, the primary focus is on the novelty of research along with the research methodology.
It is all about possibilities, by introducing several anti-thesis. Also, it ends up all the possibilities by nullifying all these anti-thesis.
Key Elements of Thesis
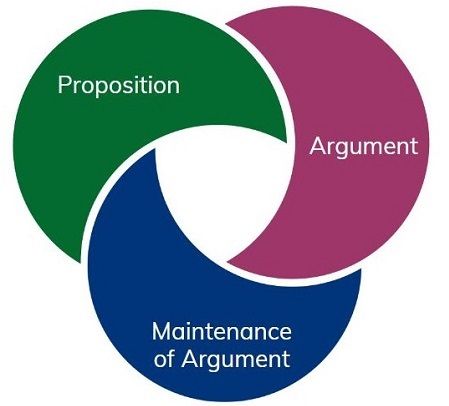
- Proposition : The thesis propagates an idea, hypothesis or recommendation.
- Argument : Gives reasons for accepting the proposition instead of just asserting a point of view.
- Maintenance of argument : The argument should be made cogent enough by providing suitable logic and adequate evidence.
Features of An Ideal Thesis
- An Ideal thesis is expected to add fresh knowledge to the existing theory.
- It communicates the central idea of the research in a clear and concise manner.
- An effective thesis is more than a simple statement, fact or question.
- It answers why and how questions concerned with the topic.
- To avoid confusion, it is worded carefully.
- It outlines the direction and scope of your essay.
- It gives reasons to the reader to continue reading.
Also Read : Difference Between Thesis and Dissertation
What is Thesis Statement?
A thesis statement is a sentence of one line, usually written at the end of your first paragraph. It presents the argument to the reader.
It is a blueprint of your thesis that directs the writer while writing the thesis and guides the reader through it.
What is Research Paper?
Research Paper is a form of academic writing. It is prepared on the basis of the original research conducted by the author on a specific topic, along with its analysis and interpretation of the findings.
An author generally starts writing a research paper on the basis of what he knows about the topic and seeks to find out what experts know. Further, it involves thorough and systematic research on a particular subject to extract the maximum information.
In short, a research paper is a written and published report containing the results of scientific research or a review of published scientific papers. Here, the scientific research is the primary research article, while the review of a published scientific paper is the review article.
In case of the primary research article, the author of the research paper provides important information about the research. This enables the scientific community members to:
- Evaluate it
- Reproduce the experiments
- Assess the reasoning and conclusions drawn
On the other hand, a review article is written to analyze, summarize and synthesize the research carried out previously.
When a research work is published in a scientific journal, it conveys the knowledge to a larger group of people and also makes people aware of the scientific work. Research work published as a research paper passes on knowledge and information to many people. The research paper provides relevant information about the disease and the treatment options at hand .
To start writing a research paper, one should always go for a topic that is interesting and a bit challenging too. Here, the key to choosing the topic is to pick the one that you can manage. So, you could avoid such topics which are very technical or specialized and also those topics for which data is not easily available. Also, do not go for any controversial topic.
The researcher’s approach and attitude towards the topic will decide the amount of effort and enthusiasm.
Steps for writing Research Paper
The total number of pages included in a Research Paper relies upon the research topic. It may include 8 to 10 pages, which are:
- Introduction
- Review of Literature
- Methodology
- Research Analysis
- Recommendations
Also Read : Difference Between Research Proposal and Research Report
Key Differences Between Thesis and Research Paper
- A thesis implies an original, plagiarism-free, written academic document that acts as a final project for a university degree of a higher level. But, Research Paper is a novel, plagiarism-free long essay. It portrays the interpretation, evaluation or argument submitted by a researcher.
- The thesis acts as a final project. Whereas a research paper is a kind of research manual of journals.
- The length of the thesis is around 20,000 to 80,000 words. On the contrary, the length of the research paper is relative to the study.
- The thesis focuses on the central question or statement of an intellectual argument that entails further research. On the contrary, the research paper is concerned with proving the central argument.
- The purpose of submitting the thesis is to get the degree or professional qualification. It also presents the knowledge of the candidate in the respective field. Conversely, the aim of publishing research papers is to prove credibility and contribute knowledge in the respective field.
- While the student submits the thesis to the educational committee or panel of professors who review it. In contrast, scientists and other researchers read and review the research paper.
- Preparation and completion of thesis is always under the guidance of a supervisor. For submission of the thesis, the university assigns a supervisor to each student, under whose guidance the thesis must be completed. As against, no supervisor is appointed as a guide in case of a research paper.
- The thesis contains a broader description of the subject matter. In contrast, the research paper contains a narrow description of the subject matter.
Once the research paper is published, it increases the fellowship and job opportunities for new researchers. On the other hand, thesis writing will enable the students to get the desired degree at the end of the course they have opted.
You Might Also Like:

Dr. Owenga says
February 23, 2023 at 2:38 pm
So good and informative. These are quite beneficial insights. Thanks
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
How to Use AI to Enhance Your College Essays and Thesis

With the integration of AI, the academic trends are gradually starting to leverage the AI tools to enhance the quality and efficiency of their work. From grammar correction to content generation, these digital assistants AI-powered tools have revolutionized the writing process by providing language editing, paraphrasing, and structural guidance to students navigating the complexities of scholarly writing.
Amidst this technological revolution, Paperpal stands out as the go-to academic writing assistant—equipped with intuitive interface and comprehensive suite of advanced features like language suggestions to built-in templates, tailored specifically for academic writing. Paperpal streamlines the writing process, enabling students to produce high-quality, consistent, and academically sound documents with ease.
Table of Contents
Language suggestions and consistency check (edit), paraphrase and contextual synonyms (rewrite), built-in academic writing prompts (templates).
- Why should students use Paperpal to enhance their essays and thesis?
How to Use Paperpal to Improve Your Essays and Thesis?
Paperpal’s Language and Consistency Check feature is invaluable for maintaining uniformity and professionalism in your academic writing, whether it involves tables, figures, equation labels, word forms, data formats, or variations between US and UK English. By using advanced NLP algorithms, Paperpal streamlines the proofreading process, sparing researchers from manual effort and ensuring consistent styling throughout the document. This feature swiftly detects errors, preserving coherence and professionalism in your essays and thesis writing for research.
Here’s a a step-by-step guide to enhance your essay and thesis writing for research with Paperpal:
- Sign up or log in to Paperpal and open a new or existing document.
- Go to the Edit section on the right sidebar and choose the first tab for Language or the second tab for Consistency .
- Paperpal will generate suggestions and reviews for improvement based on the provided content, helping you refine your writing effortlessly.
This feature enables users to enhance the clarity and academic tone of their writing by offering alternative word choices. By utilizing Paperpal’s paraphrasing tool, students can maintain the originality of their writing while enhancing its readability and effectiveness.
Here’s how to use it:
- Sign up or log in to your Paperpal account. Open a new document or access an existing one.
- Navigate to the Rewrite section on the right-hand pane and choose Paraphrase or Synonyms based on your needs.
- Select the content you wish to paraphrase, then click on Generate to allow Paperpal to produce an improved version of the provided information.
Similarly, for synonyms, select a specific word for which you want alternatives. Paperpal will generate suggestions that closely match the given context and adhere to academic writing norms.
Paperpal’s Templates feature includes built-in academic writing prompts, offering students a starting point for their writing tasks. These prompts cover various academic genres such as academic journals, essays, and theses writing for research, providing students with structured guidelines to follow. By leveraging these templates, students can streamline their writing process and ensure that their documents adhere to academic standards.
Here’s how to access this feature:
- Sign up or log in to your Paperpal account and open a new document or access an existing one.
- Navigate to the right sidebar and select Templates . From the list of options, choose the built-in prompts that best suit your requirements.
Why should students use Paperpal to enhance their essays and thesis?
In academic writing, precision, clarity, and adherence to norms are crucial. Paperpal stands out in this category, with a range of advanced capabilities designed exclusively for scholarly writing. Here’s why students should use Paperpal to improve their essays and theses:
Writing Quality: With advanced grammar and vocabulary correction, precise rephrase suggestions, adherence to academic writing conventions, meticulous consistency checks, and invaluable writing tips, Paperpal ensures that your academic work reflects the highest standard of clarity and professionalism.
Consistency and Accuracy: Ensures consistency throughout the document. Paperpal identifies spelling errors, verb tense issues, and offers rephrasing options. This feature acts as a virtual writing assistant, helping students produce error-free and polished documents.
No Prompt Writing: Paperpal’s in-built academic writing prompts embedded with templates eliminates the need to write lengthy prompts to get academically aligned results. Students can use this time organize their thoughts and ideas more effectively.
Consistent Learning: Paperpal’s suggestions come with in-depth reasoning that allows students to learn their mistakes and not repeat them. Instead of bulk correcting all errors in a go, Paperpal empowers students to achieve academic writing perfection over time.
Paperpal has helped 750,000 students and researchers ace their essays, thesis, research papers, and more. Before submitting your essay, thesis, or an any other academic work, give Paperpal a try !
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- What are Journal Guidelines on Using Generative AI Tools
- How to Use Paperpal to Generate Emails & Cover Letters?
- What are the Benefits of Generative AI for Academic Writing?
- Webinar: How to Use Generative AI Tools Ethically in Your Academic Writing
AI + Human Expertise – A Paradigm Shift In Safeguarding Research Integrity
What is hedging in academic writing , you may also like, how to use paperpal to generate emails &..., ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., do plagiarism checkers detect ai content, word choice problems: how to use the right..., how to avoid plagiarism when using generative ai..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai..., types of plagiarism and 6 tips to avoid..., how to write an essay introduction (with examples)....
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
Writing a Research Paper Introduction | Step-by-Step Guide
Published on September 24, 2022 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on March 27, 2023.

The introduction to a research paper is where you set up your topic and approach for the reader. It has several key goals:
- Present your topic and get the reader interested
- Provide background or summarize existing research
- Position your own approach
- Detail your specific research problem and problem statement
- Give an overview of the paper’s structure
The introduction looks slightly different depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or constructs an argument by engaging with a variety of sources.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: introduce your topic, step 2: describe the background, step 3: establish your research problem, step 4: specify your objective(s), step 5: map out your paper, research paper introduction examples, frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
The first job of the introduction is to tell the reader what your topic is and why it’s interesting or important. This is generally accomplished with a strong opening hook.
The hook is a striking opening sentence that clearly conveys the relevance of your topic. Think of an interesting fact or statistic, a strong statement, a question, or a brief anecdote that will get the reader wondering about your topic.
For example, the following could be an effective hook for an argumentative paper about the environmental impact of cattle farming:
A more empirical paper investigating the relationship of Instagram use with body image issues in adolescent girls might use the following hook:
Don’t feel that your hook necessarily has to be deeply impressive or creative. Clarity and relevance are still more important than catchiness. The key thing is to guide the reader into your topic and situate your ideas.
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries

This part of the introduction differs depending on what approach your paper is taking.
In a more argumentative paper, you’ll explore some general background here. In a more empirical paper, this is the place to review previous research and establish how yours fits in.
Argumentative paper: Background information
After you’ve caught your reader’s attention, specify a bit more, providing context and narrowing down your topic.
Provide only the most relevant background information. The introduction isn’t the place to get too in-depth; if more background is essential to your paper, it can appear in the body .
Empirical paper: Describing previous research
For a paper describing original research, you’ll instead provide an overview of the most relevant research that has already been conducted. This is a sort of miniature literature review —a sketch of the current state of research into your topic, boiled down to a few sentences.
This should be informed by genuine engagement with the literature. Your search can be less extensive than in a full literature review, but a clear sense of the relevant research is crucial to inform your own work.
Begin by establishing the kinds of research that have been done, and end with limitations or gaps in the research that you intend to respond to.
The next step is to clarify how your own research fits in and what problem it addresses.
Argumentative paper: Emphasize importance
In an argumentative research paper, you can simply state the problem you intend to discuss, and what is original or important about your argument.
Empirical paper: Relate to the literature
In an empirical research paper, try to lead into the problem on the basis of your discussion of the literature. Think in terms of these questions:
- What research gap is your work intended to fill?
- What limitations in previous work does it address?
- What contribution to knowledge does it make?
You can make the connection between your problem and the existing research using phrases like the following.
Now you’ll get into the specifics of what you intend to find out or express in your research paper.
The way you frame your research objectives varies. An argumentative paper presents a thesis statement, while an empirical paper generally poses a research question (sometimes with a hypothesis as to the answer).
Argumentative paper: Thesis statement
The thesis statement expresses the position that the rest of the paper will present evidence and arguments for. It can be presented in one or two sentences, and should state your position clearly and directly, without providing specific arguments for it at this point.
Empirical paper: Research question and hypothesis
The research question is the question you want to answer in an empirical research paper.
Present your research question clearly and directly, with a minimum of discussion at this point. The rest of the paper will be taken up with discussing and investigating this question; here you just need to express it.
A research question can be framed either directly or indirectly.
- This study set out to answer the following question: What effects does daily use of Instagram have on the prevalence of body image issues among adolescent girls?
- We investigated the effects of daily Instagram use on the prevalence of body image issues among adolescent girls.
If your research involved testing hypotheses , these should be stated along with your research question. They are usually presented in the past tense, since the hypothesis will already have been tested by the time you are writing up your paper.
For example, the following hypothesis might respond to the research question above:
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The final part of the introduction is often dedicated to a brief overview of the rest of the paper.
In a paper structured using the standard scientific “introduction, methods, results, discussion” format, this isn’t always necessary. But if your paper is structured in a less predictable way, it’s important to describe the shape of it for the reader.
If included, the overview should be concise, direct, and written in the present tense.
- This paper will first discuss several examples of survey-based research into adolescent social media use, then will go on to …
- This paper first discusses several examples of survey-based research into adolescent social media use, then goes on to …
Full examples of research paper introductions are shown in the tabs below: one for an argumentative paper, the other for an empirical paper.
- Argumentative paper
- Empirical paper
Are cows responsible for climate change? A recent study (RIVM, 2019) shows that cattle farmers account for two thirds of agricultural nitrogen emissions in the Netherlands. These emissions result from nitrogen in manure, which can degrade into ammonia and enter the atmosphere. The study’s calculations show that agriculture is the main source of nitrogen pollution, accounting for 46% of the country’s total emissions. By comparison, road traffic and households are responsible for 6.1% each, the industrial sector for 1%. While efforts are being made to mitigate these emissions, policymakers are reluctant to reckon with the scale of the problem. The approach presented here is a radical one, but commensurate with the issue. This paper argues that the Dutch government must stimulate and subsidize livestock farmers, especially cattle farmers, to transition to sustainable vegetable farming. It first establishes the inadequacy of current mitigation measures, then discusses the various advantages of the results proposed, and finally addresses potential objections to the plan on economic grounds.
The rise of social media has been accompanied by a sharp increase in the prevalence of body image issues among women and girls. This correlation has received significant academic attention: Various empirical studies have been conducted into Facebook usage among adolescent girls (Tiggermann & Slater, 2013; Meier & Gray, 2014). These studies have consistently found that the visual and interactive aspects of the platform have the greatest influence on body image issues. Despite this, highly visual social media (HVSM) such as Instagram have yet to be robustly researched. This paper sets out to address this research gap. We investigated the effects of daily Instagram use on the prevalence of body image issues among adolescent girls. It was hypothesized that daily Instagram use would be associated with an increase in body image concerns and a decrease in self-esteem ratings.
The introduction of a research paper includes several key elements:
- A hook to catch the reader’s interest
- Relevant background on the topic
- Details of your research problem
and your problem statement
- A thesis statement or research question
- Sometimes an overview of the paper
Don’t feel that you have to write the introduction first. The introduction is often one of the last parts of the research paper you’ll write, along with the conclusion.
This is because it can be easier to introduce your paper once you’ve already written the body ; you may not have the clearest idea of your arguments until you’ve written them, and things can change during the writing process .
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis —a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, March 27). Writing a Research Paper Introduction | Step-by-Step Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved April 15, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-paper/research-paper-introduction/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, writing a research paper conclusion | step-by-step guide, research paper format | apa, mla, & chicago templates, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Research Objectives: The Compass of Your Study
Table of contents
- 1 Definition and Purpose of Setting Clear Research Objectives
- 2 How Research Objectives Fit into the Overall Research Framework
- 3 Types of Research Objectives
- 4 Aligning Objectives with Research Questions and Hypotheses
- 5 Role of Research Objectives in Various Research Phases
- 6.1 Key characteristics of well-defined research objectives
- 6.2 Step-by-Step Guide on How to Formulate Both General and Specific Research Objectives
- 6.3 How to Know When Your Objectives Need Refinement
- 7 Research Objectives Examples in Different Fields
- 8 Conclusion
Embarking on a research journey without clear objectives is like navigating the sea without a compass. This article delves into the essence of establishing precise research objectives, serving as the guiding star for your scholarly exploration.
We will unfold the layers of how the objective of study not only defines the scope of your research but also directs every phase of the research process, from formulating research questions to interpreting research findings. By bridging theory with practical examples, we aim to illuminate the path to crafting effective research objectives that are both ambitious and attainable. Let’s chart the course to a successful research voyage, exploring the significance, types, and formulation of research paper objectives.
Definition and Purpose of Setting Clear Research Objectives
Defining the research objectives includes which two tasks? Research objectives are clear and concise statements that outline what you aim to achieve through your study. They are the foundation for determining your research scope, guiding your data collection methods, and shaping your analysis. The purpose of research proposal and setting clear objectives in it is to ensure that your research efforts are focused and efficient, and to provide a roadmap that keeps your study aligned with its intended outcomes.
To define the research objective at the outset, researchers can avoid the pitfalls of scope creep, where the study’s focus gradually broadens beyond its initial boundaries, leading to wasted resources and time. Clear objectives facilitate communication with stakeholders, such as funding bodies, academic supervisors, and the broader academic community, by succinctly conveying the study’s goals and significance. Furthermore, they help in the formulation of precise research questions and hypotheses, making the research process more systematic and organized. Yet, it is not always easy. For this reason, PapersOwl is always ready to help. Lastly, clear research objectives enable the researcher to critically assess the study’s progress and outcomes against predefined benchmarks, ensuring the research stays on track and delivers meaningful results.
How Research Objectives Fit into the Overall Research Framework
Research objectives are integral to the research framework as the nexus between the research problem, questions, and hypotheses. They translate the broad goals of your study into actionable steps, ensuring every aspect of your research is purposefully aligned towards addressing the research problem. This alignment helps in structuring the research design and methodology, ensuring that each component of the study is geared towards answering the core questions derived from the objectives. Creating such a difficult piece may take a lot of time. If you need it to be accurate yet fast delivered, consider getting professional research paper writing help whenever the time comes. It also aids in the identification and justification of the research methods and tools used for data collection and analysis, aligning them with the objectives to enhance the validity and reliability of the findings.
Furthermore, by setting clear objectives, researchers can more effectively evaluate the impact and significance of their work in contributing to existing knowledge. Additionally, research objectives guide literature review, enabling researchers to focus their examination on relevant studies and theoretical frameworks that directly inform their research goals.
Types of Research Objectives
In the landscape of research, setting objectives is akin to laying down the tracks for a train’s journey, guiding it towards its destination. Constructing these tracks involves defining two main types of objectives: general and specific. Each serves a unique purpose in guiding the research towards its ultimate goals, with general objectives providing the broad vision and specific objectives outlining the concrete steps needed to fulfill that vision. Together, they form a cohesive blueprint that directs the focus of the study, ensuring that every effort contributes meaningfully to the overarching research aims.
- General objectives articulate the overarching goals of your study. They are broad, setting the direction for your research without delving into specifics. These objectives capture what you wish to explore or contribute to existing knowledge.
- Specific objectives break down the general objectives into measurable outcomes. They are precise, detailing the steps needed to achieve the broader goals of your study. They often correspond to different aspects of your research question , ensuring a comprehensive approach to your study.
To illustrate, consider a research project on the impact of digital marketing on consumer behavior. A general objective might be “to explore the influence of digital marketing on consumer purchasing decisions.” Specific objectives could include “to assess the effectiveness of social media advertising in enhancing brand awareness” and “to evaluate the impact of email marketing on customer loyalty.”
Aligning Objectives with Research Questions and Hypotheses
The harmony between what research objectives should be, questions, and hypotheses is critical. Objectives define what you aim to achieve; research questions specify what you seek to understand, and hypotheses predict the expected outcomes.
This alignment ensures a coherent and focused research endeavor. Achieving it necessitates a thoughtful consideration of how each component interrelates, ensuring that the objectives are not only ambitious but also directly answerable through the research questions and testable via the hypotheses. This interconnectedness facilitates a streamlined approach to the research process, enabling researchers to systematically address each aspect of their study in a logical sequence. Moreover, it enhances the clarity and precision of the research, making it easier for peers and stakeholders to grasp the study’s direction and potential contributions.
Role of Research Objectives in Various Research Phases
Throughout the research process, objectives guide your choices and strategies – from selecting the appropriate research design and methods to analyzing data and interpreting results. They are the criteria against which you measure the success of your study. In the initial stages, research objectives inform the selection of a topic, helping to narrow down a broad area of interest into a focused question that can be explored in depth. During the methodology phase, they dictate the type of data needed and the best methods for obtaining that data, ensuring that every step taken is purposeful and aligned with the study’s goals. As the research progresses, objectives provide a framework for analyzing the collected data, guiding the researcher in identifying patterns, drawing conclusions, and making informed decisions.
Crafting Effective Research Objectives

The effective objective of research is pivotal in laying the groundwork for a successful investigation. These objectives clarify the focus of your study and determine its direction and scope. Ensuring that your objectives are well-defined and aligned with the SMART criteria is crucial for setting a strong foundation for your research.
Key characteristics of well-defined research objectives
Well-defined research objectives are characterized by the SMART criteria – Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. Specific objectives clearly define what you plan to achieve, eliminating any ambiguity. Measurable objectives allow you to track progress and assess the outcome. Achievable objectives are realistic, considering the research sources and time available. Relevant objectives align with the broader goals of your field or research question. Finally, Time-bound objectives have a clear timeline for completion, adding urgency and a schedule to your work.
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Formulate Both General and Specific Research Objectives
So lets get to the part, how to write research objectives properly?
- Understand the issue or gap in existing knowledge your study aims to address.
- Gain insights into how similar challenges have been approached to refine your objectives.
- Articulate the broad goal of research based on your understanding of the problem.
- Detail the specific aspects of your research, ensuring they are actionable and measurable.
How to Know When Your Objectives Need Refinement
Your objectives of research may require refinement if they lack clarity, feasibility, or alignment with the research problem. If you find yourself struggling to design experiments or methods that directly address your objectives, or if the objectives seem too broad or not directly related to your research question, it’s likely time for refinement. Additionally, objectives in research proposal that do not facilitate a clear measurement of success indicate a need for a more precise definition. Refinement involves ensuring that each objective is specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound, enhancing your research’s overall focus and impact.
Research Objectives Examples in Different Fields
The application of research objectives spans various academic disciplines, each with its unique focus and methodologies. To illustrate how the objectives of the study guide a research paper across different fields, here are some research objective examples:
- In Health Sciences , a research aim may be to “determine the efficacy of a new vaccine in reducing the incidence of a specific disease among a target population within one year.” This objective is specific (efficacy of a new vaccine), measurable (reduction in disease incidence), achievable (with the right study design and sample size), relevant (to public health), and time-bound (within one year).
- In Environmental Studies , the study objectives could be “to assess the impact of air pollution on urban biodiversity over a decade.” This reflects a commitment to understanding the long-term effects of human activities on urban ecosystems, emphasizing the need for sustainable urban planning.
- In Economics , an example objective of a study might be “to analyze the relationship between fiscal policies and unemployment rates in developing countries over the past twenty years.” This seeks to explore macroeconomic trends and inform policymaking, highlighting the role of economic research study in societal development.
These examples of research objectives describe the versatility and significance of research objectives in guiding scholarly inquiry across different domains. By setting clear, well-defined objectives, researchers can ensure their studies are focused and impactful and contribute valuable knowledge to their respective fields.
Defining research studies objectives and problem statement is not just a preliminary step, but a continuous guiding force throughout the research journey. These goals of research illuminate the path forward and ensure that every stride taken is meaningful and aligned with the ultimate goals of the inquiry. Whether through the meticulous application of the SMART criteria or the strategic alignment with research questions and hypotheses, the rigor in crafting and refining these objectives underscores the integrity and relevance of the research. As scholars venture into the vast terrains of knowledge, the clarity, and precision of their objectives serve as beacons of light, steering their explorations toward discoveries that advance academic discourse and resonate with the broader societal needs.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
To revisit this article, visit My Profile, then View saved stories .
- Backchannel
- Newsletters
- WIRED Insider
- WIRED Consulting
Amanda Hoover
Students Are Likely Writing Millions of Papers With AI
Students have submitted more than 22 million papers that may have used generative AI in the past year, new data released by plagiarism detection company Turnitin shows.
A year ago, Turnitin rolled out an AI writing detection tool that was trained on its trove of papers written by students as well as other AI-generated texts. Since then, more than 200 million papers have been reviewed by the detector, predominantly written by high school and college students. Turnitin found that 11 percent may contain AI-written language in 20 percent of its content, with 3 percent of the total papers reviewed getting flagged for having 80 percent or more AI writing. (Turnitin is owned by Advance, which also owns Condé Nast, publisher of WIRED.) Turnitin says its detector has a false positive rate of less than 1 percent when analyzing full documents.
ChatGPT’s launch was met with knee-jerk fears that the English class essay would die . The chatbot can synthesize information and distill it near-instantly—but that doesn’t mean it always gets it right. Generative AI has been known to hallucinate , creating its own facts and citing academic references that don’t actually exist. Generative AI chatbots have also been caught spitting out biased text on gender and race . Despite those flaws, students have used chatbots for research, organizing ideas, and as a ghostwriter . Traces of chatbots have even been found in peer-reviewed, published academic writing .
Teachers understandably want to hold students accountable for using generative AI without permission or disclosure. But that requires a reliable way to prove AI was used in a given assignment. Instructors have tried at times to find their own solutions to detecting AI in writing, using messy, untested methods to enforce rules , and distressing students. Further complicating the issue, some teachers are even using generative AI in their grading processes.
Detecting the use of gen AI is tricky. It’s not as easy as flagging plagiarism, because generated text is still original text. Plus, there’s nuance to how students use gen AI; some may ask chatbots to write their papers for them in large chunks or in full, while others may use the tools as an aid or a brainstorm partner.
Students also aren't tempted by only ChatGPT and similar large language models. So-called word spinners are another type of AI software that rewrites text, and may make it less obvious to a teacher that work was plagiarized or generated by AI. Turnitin’s AI detector has also been updated to detect word spinners, says Annie Chechitelli, the company’s chief product officer. It can also flag work that was rewritten by services like spell checker Grammarly, which now has its own generative AI tool . As familiar software increasingly adds generative AI components, what students can and can’t use becomes more muddled.
Detection tools themselves have a risk of bias. English language learners may be more likely to set them off; a 2023 study found a 61.3 percent false positive rate when evaluating Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL) exams with seven different AI detectors. The study did not examine Turnitin’s version. The company says it has trained its detector on writing from English language learners as well as native English speakers. A study published in October found that Turnitin was among the most accurate of 16 AI language detectors in a test that had the tool examine undergraduate papers and AI-generated papers.
Charlie Wood

Eric Ravenscraft

Caitlin Kelly
Schools that use Turnitin had access to the AI detection software for a free pilot period, which ended at the start of this year. Chechitelli says a majority of the service’s clients have opted to purchase the AI detection. But the risks of false positives and bias against English learners have led some universities to ditch the tools for now. Montclair State University in New Jersey announced in November that it would pause use of Turnitin’s AI detector. Vanderbilt University and Northwestern University did the same last summer.
“This is hard. I understand why people want a tool,” says Emily Isaacs, executive director of the Office of Faculty Excellence at Montclair State. But Isaacs says the university is concerned about potentially biased results from AI detectors, as well as the fact that the tools can’t provide confirmation the way they can with plagiarism. Plus, Montclair State doesn’t want to put a blanket ban on AI, which will have some place in academia. With time and more trust in the tools, the policies could change. “It’s not a forever decision, it’s a now decision,” Isaacs says.
Chechitelli says the Turnitin tool shouldn’t be the only consideration in passing or failing a student. Instead, it’s a chance for teachers to start conversations with students that touch on all of the nuance in using generative AI. “People don’t really know where that line should be,” she says.
You Might Also Like …
In your inbox: The best and weirdest stories from WIRED’s archive
Jeffrey Epstein’s island visitors exposed by data broker
8 Google employees invented modern AI. Here’s the inside story
The crypto fraud kingpin who almost got away
It's shadow time! How to view the solar eclipse, online and in person

Steven Levy

Will Knight

Lauren Goode

Matt Burgess
Benj Edwards, Ars Technica

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A thesis is an in-depth research study that identifies a particular topic of inquiry and presents a clear argument or perspective about that topic using evidence and logic. Writing a thesis showcases your ability of critical thinking, gathering evidence, and making a compelling argument. Integral to these competencies is thorough research ...
A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
Thesis. Your thesis is the central claim in your essay—your main insight or idea about your source or topic. Your thesis should appear early in an academic essay, followed by a logically constructed argument that supports this central claim. A strong thesis is arguable, which means a thoughtful reader could disagree with it and therefore ...
Keep these guidelines in mind when writing your research paper thesis: 1 It should be clear and concise: A research paper thesis statement should use plain language and explain the topic briefly, without going into too much detail. 2 It's a single sentence: A thesis statement is generally only one sentence, which helps keep the topic simple ...
A good thesis has two parts. It should tell what you plan to argue, and it should "telegraph" how you plan to argue—that is, what particular support for your claim is going where in your essay. Steps in Constructing a Thesis. First, analyze your primary sources. Look for tension, interest, ambiguity, controversy, and/or complication.
It is a brief statement of your paper's main argument. Essentially, you are stating what you will be writing about. Organize your papers in one place. Try Paperpile. No credit card needed. Get 30 days free. You can see your thesis statement as an answer to a question. While it also contains the question, it should really give an answer to the ...
When drafting your thesis statement, avoid words like explore, investigate, learn, compile, summarize, and explain to describe the main purpose of your paper. These words imply a paper that summarizes or "reports," rather than synthesizing and analyzing. Instead of the terms above, try words like argue, critique, question, and interrogate.
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
A thesis statement is a clear and succinct assertion that presents the main argument or central idea of a research paper or other academic work. You usually find the thesis, which serves as a road map for the entire piece of writing, at the end of the introductory paragraph.
Thesis. Definition: Thesis is a scholarly document that presents a student's original research and findings on a particular topic or question. It is usually written as a requirement for a graduate degree program and is intended to demonstrate the student's mastery of the subject matter and their ability to conduct independent research.
Choose a research paper topic. Conduct preliminary research. Develop a thesis statement. Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft.
Analytical An analytical thesis statement is used for essays, research papers, and other pieces of writing that seek to analyze, interpret, or evaluate a topic's various aspects. Analytical thesis statements typically map out key points of the analysis and include the resulting conclusions (McCombes, 2020).
Tips for Writing Your Thesis Statement. 1. Determine what kind of paper you are writing: An analytical paper breaks down an issue or an idea into its component parts, evaluates the issue or idea, and presents this breakdown and evaluation to the audience.; An expository (explanatory) paper explains something to the audience.; An argumentative paper makes a claim about a topic and justifies ...
A thesis statement is a sentence in a paper or essay (in the opening paragraph) that introduces the main topic to the reader. As one of the first things your reader sees, your thesis statement is one of the most important sentences in your entire paper—but also one of the hardest to write! In this article, we explain how to write a thesis ...
A research paper is a piece of academic writing that provides analysis, interpretation, and argument based on in-depth independent research. About us; Disclaimer; ... It also helps you to develop a theoretical framework and research hypothesis. Develop a Thesis Statement: The thesis statement is the main argument of your research paper. It ...
Here's a guide with steps and examples: Step 1. Understand the Assignment. Before diving into writing a thesis statement, thoroughly understand the assignment's requirements, including the topic, length, and specific guidelines provided by your instructor or the prompt. Step 2.
Step 7. Finalize Your Thesis Statement. Now comes the final step of the thesis writing process. In the last stage, summarize your refined answer into a powerful single sentence or, if required, two sentences. It should capture the main point of your research project and set the tone for your entire paper.
A thesis statement makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of the paper. It summarizes the conclusions that the writer has reached about the topic. A thesis statement is generally located near the end of the introduction. Sometimes in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or an entire ...
The foundation of the entire postgraduate or doctoral research program is disciplinary knowledge. At most universities, one of the main requirements is that the research introduces or expands a novelty that contributes to the advancement of the subject [].Even though the writing is a clear component of higher-level coursework and is frequently acknowledged as a source of significant concern ...
Conclusion. In brief, the main difference between thesis and research paper is that thesis is a long research paper that typically serves as the final project for a university degree, while a research paper is a piece of academic writing on a particular topic. Moreover, in an academic context, students may be required to write research papers ...
thesis writing to guide the PhD candidate so that the task of PhD thesis writ-ing becomes manageable and less daunting. This research is a useful roadmap especially for students of the social sciences studies. Further, in this paper, research procedure and thesis writing strategies are explained in a simple manner.
But, Research Paper is a novel, plagiarism-free long essay. It portrays the interpretation, evaluation or argument submitted by a researcher. The thesis acts as a final project. Whereas a research paper is a kind of research manual of journals. The length of the thesis is around 20,000 to 80,000 words.
This paragraph should both attract the reader's attention and give them the necessary information about the paper. In any academic paper, the introduction paragraph constitutes 10% of the paper's total word count. For example, if you are preparing a 3,000-word paper, your introduction paragraph should consist of approximately 300 words.
Table of contents. 1 The importance of Clearly Defining the Scope of the Study for Guiding Research Focus. 1.1 Examples of Elements Included in the Scope; 2 Role of Delimitations in Qualitative Research. 2.1 Examples of Delimitations in Research; 3 Determining the Scope and Delimitation; 4 Writing the Scope and Delimitations Section; 5 Conclusion
Paperpal has helped 750,000 students and researchers ace their essays, thesis, research papers, and more. Before submitting your essay, thesis, or an any other academic work, give Paperpal a try! Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time.
An argumentative paper presents a thesis statement, while an empirical paper generally poses a research question (sometimes with a hypothesis as to the answer). Argumentative paper: Thesis statement The thesis statement expresses the position that the rest of the paper will present evidence and arguments for.
Well-defined research objectives are characterized by the SMART criteria - Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. Specific objectives clearly define what you plan to achieve, eliminating any ambiguity. Measurable objectives allow you to track progress and assess the outcome.
Research papers rely on other people's writing as a foundation to create new ideas, but you can't just use someone else's words. That's why paraphrasing is an essential writing technique for academic writing.. Paraphrasing rewrites another person's ideas, evidence, or opinions in your own words.With proper attribution, paraphrasing helps you expand on another's work and back up ...
A year ago, Turnitin rolled out an AI writing detection tool that was trained on its trove of papers written by students as well as other AI-generated texts. Since then, more than 200 million ...