- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search


Forms of Energy PowerPoint Presentation
Subject: Physics
Age range: 14-16
Resource type: Worksheet/Activity
Last updated
27 February 2024
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

A fully editable PowerPoint presentation on forms of energy and energy transformations.
The presentation covers the definitions for the different forms of energy and the units used to measure energy. It also provides examples of energy transformations.
Comes with a bonus word search and solutions.
Forms of energy included:
- gravitational potential
- elastic potential
Great accompaniments to this product:
Forms of Energy Cootie Catcher Forms of Energy Task Cards Forms of Energy Card Sort
Clipart by:
Ron Leishman ToonClipart
Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:
FREE K-12 standards-aligned STEM
curriculum for educators everywhere!
Find more at TeachEngineering.org .
- TeachEngineering
- Exploring Energy: What Is Energy?
Lesson Exploring Energy: What Is Energy?
Grade Level: 6 (6-7)
Time Required: 1 hour
Lesson Dependency: None
Subject Areas: Physical Science, Physics, Science and Technology
NGSS Performance Expectations:

- Print lesson and its associated curriculum
Curriculum in this Unit Units serve as guides to a particular content or subject area. Nested under units are lessons (in purple) and hands-on activities (in blue). Note that not all lessons and activities will exist under a unit, and instead may exist as "standalone" curriculum.
- Spool Racer Design & Competition
- Making Moon Craters
- Maximum Mentos Fountain
TE Newsletter
Engineering connection, learning objectives, worksheets and attachments, more curriculum like this, introduction/motivation, associated activities, vocabulary/definitions, user comments & tips.

We are surrounded by and interact with energy every day and thus energy is an important concept across all fields of engineering, including civil, mechanical, electrical and aerospace. Applying an understanding of energy enables the design of products, tools and technologies that require energy use, storage and transformation.
After this lesson, students should be able to:
- Define energy, kinetic energy and potential energy.
- Identify the existence of energy with examples from daily life.
- Explain the concept of energy conversion.
Educational Standards Each TeachEngineering lesson or activity is correlated to one or more K-12 science, technology, engineering or math (STEM) educational standards. All 100,000+ K-12 STEM standards covered in TeachEngineering are collected, maintained and packaged by the Achievement Standards Network (ASN) , a project of D2L (www.achievementstandards.org). In the ASN, standards are hierarchically structured: first by source; e.g. , by state; within source by type; e.g. , science or mathematics; within type by subtype, then by grade, etc .
Ngss: next generation science standards - science, international technology and engineering educators association - technology.
View aligned curriculum
Do you agree with this alignment? Thanks for your feedback!
State Standards
California - science.
Today is the first day of our unit on energy. Energy is evident all around us every day and is a fundamental concept that is used by engineers who design the many products and technologies in our world—such as cars, phones, electronics, appliances, roller coasters, rockets, and more. Let's begin by watching a video. (Show students the four-minute video, MythBusters-Exploding Water Heater , at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jbreKn4PoAc .)
What did you notice? (Have students share their responses.) What questions do you have? (Have students write them down in their notebook.)
What we just saw is an example of a lot of energy being released in a short amount of time. When we get to the end of our lesson on energy, you'll be able to understand what we saw in the video and explain it to your friends.
(Continue by showing the presentation and delivering the content in the Lesson Background section.)
Lesson Background and Concepts for Teachers
Students entering sixth-grade generally have a limited understanding of what energy "is," and sources of energy. This lesson aims to assist students in identifying types of energy, and how energy is used and transferred. Gaining this understanding lays the foundation for further learning during the subsequent lessons of this unit, and gives students the pre-requisite knowledge they need to study more complex concepts related to energy.
Inform students that this lesson is a "keystone" lesson that covers very basic, yet important concepts that will be built upon in subsequent energy-related lessons. Without a basic understanding of what energy is, students may have difficulty grasping more detailed or complicated ideas presented in future lessons.
Teach the lesson using the 13-slide What Is Energy? Presentation , a PowerPoint® file, along with the notes provided below. The presentation is animated, so clicking brings up the next image, text or slide. The presentation contains review questions and activities that ask students to use their new energy knowledge. The associated activity, Spool Racer Design & Competition , also provides opportunities to discuss and review key concepts.
What Is Energy?
(Slide 1) Begin with any engaging demonstration or video related to energy. As one suitable example, the slide provides a link to an exploding water heater clip from MythBusters. Start with the Introduction/Motivation content, explaining that this is the first day of a unit on energy—a fundamental science concept that engineers use to design the products, tools and technologies we depend upon every day, and that by the end of the lesson, students will be able to understand and explain what happened in the demonstration. Then ask the class for answers to the question "what is energy?"
At this point, we do not recommend explaining the details of the video. Students have not yet learned the energy concepts displayed in the video demonstration. By the end of this lesson , expect students to be able to explain that the MythBusters put energy into the water heater by connecting it to the electrical outlet. When the temperature and pressure in the water heater increase, they build up the potential energy. When the water heater explodes, the potential energy is converted to kinetic energy. By the end of this unit , expect students to be able to explain more details of the video, such as the forms of energy present.
For the teacher, the following is a detailed explanation of what happens in the video: The MythBusters put electricity into the water heater. That electricity is transferred to thermal energy by the heating element. Thermal energy builds up in the water heater (potential energy), causing an increase in the temperature of the water and an increase in the pressure inside the water heater. The MythBusters disabled the safety valve that prevents a normal water heater from building up too much pressure. The boiling temperature of water increases as pressure goes up. At atmospheric pressure (14.7 psi), water boils at 100 °C, but at 332 psi, the maximum pressure shown in the video, water remains liquid up to 219 °C. When the water heater bursts and the pressure drops suddenly from 332 psi to 14.7 psi, the water is 119 °C above its boiling point. The superheated water boils suddenly and violently as much of the water is converted to steam. The steam expands out from the water heater (kinetic energy), sending the water heater and pieces of the surrounding shack flying (also kinetic energy). It also creates a loud noise; sound is another form of energy.
(Slide 2) Using the examples shown ask students which of the five pictured items have energy and why they think so.
- Apples: Food must have energy, since we get energy from eating it.
- Violin players: Both the sound of the violins and the motion of the violin players are evidence of energy.
- Fire: The light, heat and sound of a campfire are all evidence of energy.
- Car: In this case, either answer might be correct, depending on how students justify their answers. This car is motionless, so no sign of energy exists in the picture. However, students might correctly note that cars usually have fuel and/or batteries, both of which contain energy.
- Rock: This rock has energy stored due to its height. Even though no motion, heat, light or sound is happening now, it has stored energy that would be released if it tipped over.
Ask students if they can come up with a definition for energy based off of the examples above and what clues exist that indicate the presence of energy. (Have students discuss; get students to say that energy is the ability to make things happen. Motion, heat, light and sound are clues that energy is present.)
(Slide 3) Show students the image of a bow being pulled back. Ask students, does this have energy? Where is the energy?

(Slide 5) Now show the image of an arrow that has been released. Ask students, what type of energy does the moving arrow have? How is this energy different than when the bow was pulled back?
(Slide 6) Now show the images of kids running on a field as they play soccer and a race car traveling around a track. Ask students, what do they have in common in terms of energy? What type of energy is this? Allow students to share their thoughts. Guide them to understand that all of these are examples of kinetic energy- which is energy of motion. Ask students to come up with other examples of kinetic energy.
(Slide 7) Now ask students how the potential energy from the pulled bow resulted in kinetic energy of the moving arrow? Allow students to share their thoughts. Guide them to understand that the bow and arrow is a classic example of energy transfer. That is, energy can be transferred from one type to another, as with the pulled bow (potential energy) transferred to a moving arrow (kinetic energy).
(Slides 8-12) Numerous examples are provided to help students think intuitively about relative amounts of energy and energy conversion. Objects that look the same represent the same mass. For example, the springs on slide 10 are identical. It is recommended to not identify the particular types of potential energy present in these examples because the types of potential energy are not introduced until the next lesson. However, if desired, explain that energy stored in an object's height is called gravitational potential energy and energy stored in a compressed spring is called elastic potential energy.
(Slide 13) Administer the post-quiz, as described in the Assessment section. Then make a short writing homework assignment, as described on slide 13 (and in the Assessment section).
Watch this activity on YouTube
conservation of energy: A fundamental law in thermodynamics. It states that energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only change from one form to another.
electricity: The flow of electric charge through a conductor. Energy can be transferred from one place to another and from one form to another by electricity.
energy: The ability to make things happen. More advanced definition: The ability to do work.
force: Energy can be transferred from one object to another by a force (by the objects pushing or pulling on each other). A force can also transfer energy from one form to another.
gravitational energy: Energy that is stored in the height of objects. Gravity is the force that pulls things down to Earth. The higher an object, the more gravitational energy it has. Often, gravitational energy (a form of potential energy) is converted to kinetic energy to make things move fast.
kinetic energy: The energy of moving objects. Anything in motion has kinetic energy. The faster an object moves, the more kinetic energy it has.
potential energy: Energy that is stored and can be used when needed. Energy can be stored in chemicals (food, batteries), height (gravitational), elastic stretching, etc.
Pre-Lesson Assessment
Pre-Quiz: Prior to starting the lesson, administer the three-question What Is Energy? Pre-Quiz to assess students' prior knowledge of energy, kinetic energy and potential energy.
Post-Introduction Assessment
Discussion Questions: Use class discussions and student writing assignments to evaluate student knowledge. Throughout the What Is Energy? Presentation are many opportunities for quick assessments of understanding. For example, at slide 8 say, "I want everyone in the class to give me a thumbs-up if you think the ball on the right has more energy, and a thumbs-down if you think the ball on the left has more energy."
Lesson Summary Assessment
Post-Quiz: Administer the five-question What Is Energy? Post-Quiz to assess students' understanding of the concepts presented in the lesson, including energy, kinetic and potential energy and energy conversion. Review their answers to gauge their level of comprehension.
Writing: In addition to the post-quiz, assign students to write short descriptions of what happened in the exploding water heater video using the concepts they learned in the lesson. Assign as either a small group or individual activity. Review students' writing to gauge their depth of comprehension. (Note: Students should be able to explain that the Mythbusters put energy into the water heater by connecting it to the electrical outlet. When the temperature and pressure in the water heater increase, they build up its potential energy. When the water heater explodes, the potential energy is converted to kinetic energy. By the end of the unit, students should be able to explain more details of the video, such as the forms of energy present.)
Students learn more about the concept of energy conversion, and how energy transfers from one form, place or object to another. They learn that energy transfers can take the form of force, electricity, light, heat and sound and are never without some energy "loss" during the process. Two real-world ...

Students makes sense of kinetic and potential energy, including various types of potential energy: chemical, gravitational, elastic and thermal energy. They identify everyday examples of these energy types, as well as the mechanism of corresponding energy transfers.

Students learn about the definition of heat as a form of energy and how it exists in everyday life. They learn about the three types of heat transfer—conduction, convection and radiation—as well as the connection between heat and insulation.

Students are introduced to the concepts of force, inertia and Newton's first law of motion: objects at rest stay at rest and objects in motion stay in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Students learn the difference between speed, velocity and acceleration, and come to see that the cha...

Contributors
Supporting program, acknowledgements.
The contents of this digital library curriculum were developed by the Renewable Energy Systems Opportunity for Unified Research Collaboration and Education (RESOURCE) project in the College of Engineering under National Science Foundation GK-12 grant no. DGE 0948021. However, these contents do not necessarily represent the policies of the National Science Foundation, and you should not assume endorsement by the federal government.
Last modified: May 5, 2021
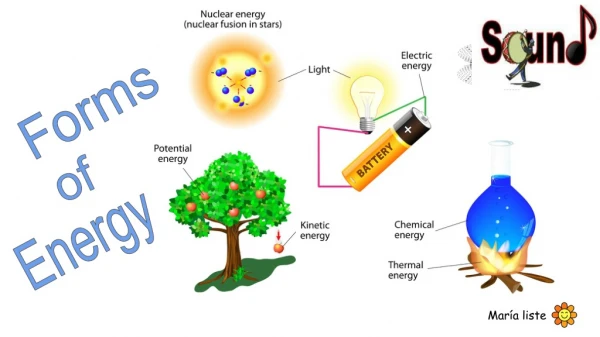
10 Types of Energy With Examples
- Chemical Laws
- Periodic Table
- Projects & Experiments
- Scientific Method
- Biochemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Medical Chemistry
- Chemistry In Everyday Life
- Famous Chemists
- Activities for Kids
- Abbreviations & Acronyms
- Weather & Climate
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
Energy is defined as the ability to do work . Energy comes in various forms—from sonic and gravitational to nuclear and thermal. Understanding these diverse forms of energy helps us comprehend the forces that fuel our natural world and day-to-day activities, from charging our cell phones to powering our homes.
Here are ten common types of energy and examples of each.
Mechanical Energy
Mechanical energy is energy that results from either the movement or location of an object. Mechanical energy is the sum of kinetic energy and potential energy .
Examples: An object possessing mechanical energy has both kinetic and potential energy , although the energy of one of the forms may be equal to zero. A moving car has kinetic energy. If you move the car up a mountain, it has kinetic and potential energy. A book sitting on a table has potential energy.
Thermal Energy
Thermal energy or heat energy reflects the temperature difference between two systems.
Example: A cup of hot coffee has thermal energy. Additionally, you produce heat and possess thermal energy in relation to your surroundings.
Nuclear Energy
Nuclear energy is energy resulting from nuclear reactions or changes in the atomic nuclei.
Example: Nuclear fission , nuclear fusion, and nuclear decay are examples of nuclear energy. An atomic detonation or power from a nuclear plant are also examples of this type of energy.
Chemical Energy
Chemical energy results from chemical reactions between atoms or molecules. There are different types of chemical energy , such as electrochemical energy and chemiluminescence.
Example: A good example of chemical energy is an electrochemical cell or battery.
Electromagnetic Energy
Electromagnetic energy (or radiant energy) is energy from light or electromagnetic waves.
Example: Any form of light has electromagnetic energy , including parts of the spectrum we can't see. Radio, gamma rays , x-rays, microwaves, and ultraviolet light are some examples of electromagnetic energy.
Sonic Energy
Sonic energy is the energy of sound waves. Sound waves travel through mediums, such as the air or water, carrying sonic energy with them.
Example : A sonic boom, a song played on a stereo, your voice.

Gravitational Energy
Energy associated with gravity involves the attraction between two objects based on their mass . It can serve as a basis for mechanical energy, such as the potential energy of an object placed on a shelf or the kinetic energy of the Moon in orbit around the Earth.
Example : Gravitational energy holds the atmosphere to the Earth.
Kinetic Energy
Kinetic energy is the energy of a body's motion. It ranges from 0 to a positive value.
Example : An example is a child swinging on a swing. No matter whether the swing is moving forward or backward, the value of the kinetic energy is never negative.
Potential Energy
Potential energy is the energy of an object's position.
Example : When a child swinging on a swing reaches the top of the arc, she has maximum potential energy. When she is closest to the ground, her potential energy is at its minimum (0). Another example is throwing a ball into the air. At the highest point, the potential energy is greatest. As the ball rises or falls it has a combination of potential and kinetic energy.
Ionization Energy
Ionization energy is the form of energy that binds electrons to the nucleus of an atom, ion, or molecule.
Example : The first ionization energy of an atom is the energy needed to remove one electron completely. The second ionization energy is energy to remove a second electron and is greater than that required to remove the first electron.
How Different Types of Energy Work Together
Though many different types of energy exist, you can classify the different forms as either potential or kinetic, and it's common for objects to typically exhibit multiple types of energy at the same time. For example, a car in motion exhibits kinetic energy, and its engine converts chemical energy from fuel into mechanical energy to propel it forward. Additionally, the car's headlights emit light energy, and its exhaust system releases thermal energy.
U.S. Energy Information Administration. " What is energy? "
- The 2 Main Forms of Energy
- Energy: A Scientific Definition
- Why Are Light and Heat Not Matter?
- How Does Electrical Energy Work?
- Potential Energy Definition and Formula
- 12 Examples of Chemical Energy
- Oscillation and Periodic Motion in Physics
- Radiation in Space Gives Clues about the Universe
- A Scientific Way to Define Heat Energy
- Definition and Examples of Latent Heat
- Comparing the Hydrogen Bomb and the Atomic Bomb
- Sources of Power Production
- FAQ: What is Electricity?
- Ionization Energy of the Elements
- What Is Natural Frequency?
- A to Z Chemistry Dictionary

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Types and Forms of Energy
Published by Sylvia Geraldine Lawrence Modified over 6 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Types and Forms of Energy"— Presentation transcript:

What is energy?.

Energy Forms.

Types of Energy and Forms of Energy

Types of Energy and Forms of Energy EPIT C. Ned Rogers.

As a group… How could you prove something is matter? How could we test something like air to prove it is or is not matter?

Nature of Energy EEEEnergy is all around you! YYYYou can hear energy as sound. YYYYou can see energy as light. AAAAnd you can feel it.

Chapter 9 Preview Section 1 What Is Energy?

Energy: its forms and uses

Finish the following sentence: “Energy is the ability to ____.”

The rapper who is Smac-full of energy!. Energy is the ability to do WORK. WORK is to make something MOVE by applying FORCE to it. There are 9 Forms of.

Sun Source of almost all the energy is the… Wood, coal, petroleum and natural gas come from the sun. The USA gets 90% of its energy from fossil fuel.

Chapter 9 Types of Energy and Forms of Energy. Energy Energy is defined as the ability to do work (product of force applied over a distance) Energy exists.

How do you describe the relationship between potential and kinetic energy? S8P2b.

Energy Systems. Energy Energy is the ability to do work Two main forms of energy Kinetic – The energy of motion Kinetic – The energy of motion Potential.

Chapter 3 Energy 3.1 Energy exists in different forms.

Learning Objectives I can explain some of the different forms of energy. I can identify situations when energy is transformed from one form to another.

What is Energy and forms of energy

Energy Types and Transformation

Energy Transformation
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
- Preferences

Forms of Energy - PowerPoint PPT Presentation

Forms of Energy
What is energy includes definitions of the different types of energy. that is electromagnetic energy, mechanical energy, chemical energy, thermal energy, electrical energy. – powerpoint ppt presentation.
- Physicists, who are scientists who study force, motion and energy, say that energy is the ability to do work, and work is moving something against a force, like gravity.
- In physics, energy is the ability to do work, or the ability to move or elicit change in matter. In effect, the amount of energy something has refers to its capacity to cause things to happen.
- Measure of the ability of a body or system to do work or produce a change, expressed usually in joules or kilowatt hours (kWh).
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics , the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.

Forms of Energy
Jul 27, 2014
1.25k likes | 2.56k Views
5.6A SW explore the uses of energy, including mechanical, light, thermal, electrical and sound energy. Forms of Energy -Wind is moving air. We can use the energy in wind to do work. The energy in wind comes from the sun.
Share Presentation
- electrical energy travels
- potential energy
- physical state
- thermal energy everyday

Presentation Transcript
5.6A SW explore the uses of energy, including mechanical, light, thermal, electrical and sound energy.
Forms of Energy -Wind is moving air. We can use the energy in wind to do work. The energy in wind comes from the sun. -When the wind blows, it pushes against the blades of the wind turbines. -The blades spin around and turn a generator that makes electricity. -This electrical energy travels to your house. Wind energy only makes a little bit of the electricity we use in the U.S.
Heat Energy -Heat is a form of energy. Heat energy depends on the temperature of matter. As matter heats up its molecules vibrate faster. A thermometer measures heat energy. -We use heat, called thermal energy everyday. There is a rule of heat flow—Heat always moves from a hotter object to a cooler object. -Energy cannot be created or destroyed. The same amount of energy exists before and after it changes form. EX: Wind Mechanical Electrical Heat Iron clothes
Sound Energy • -Sound is a form of energy created when an object vibrates. • A tuning fork emits sound when it vibrates. • -When a drummer plays a drum, the drumhead vibrates and creates sound waves.
-Sound waves cannot exist in outer space. They must pass through a medium. A medium is a solid, liquid or gas. -Sound waves travel faster through a solid than a liquid. It travels faster through a liquid than through a gas. Sound travels the slowest through air.
-Sound energy helps us communicate with our friends, listen to music, and watch television.
Light Energy -Light is a form of energy that travels in waves.
Light travels in straight lines unless it hits another object.
-Light is produced when one form of energy is changed to light energy. -The source might be a candle, a light bulb, a fire, or the sun.
Mechanical Energy -There are two forms of mechanical energy: Kinetic energy-the energy of motion Potential energy-stored energy -A roller coaster at the top of the hill has potential energy. -As the car moves downhill, potential energy changes to kinetic energy.
Electrical Energy-Circuits 5.6B SW demonstrate that the flow of electricity in circuits requires a complete path through which an electric current can pass and can produce light, heat an sound -Electricity-is a form of energy that is produced when electrons move from one place to another -The constant flow of electrons is called an electric current.
-Materials that allow electricity to move through them easily are called Conductors. -Copper is a very good conductor of electricity. That’s why electrical wires are made of copper. -Materials that resist the flow of electricity are called insulators. -Rubber and plastic resist the flow of electricity. That makes them good insulators.
Electric circuit-is a pathway that electrons flow through. Electric circuits allow electrical energy to be changed into other forms of energy.
Closed circuit-the switch is in the ON position. Think of the switch as a drawbridge. When it is in the down position, electrons can flow across the bridge from one wire to the other wire. The bulb lights.
Open circuit-the switch is in the OFF position. Electrons can’t flow from one wire to the other wire . The bulb turns off.
Light Energy-Reflection and Refraction 5.6C SW demonstrate that light travels in a straight line until it strikes an object or travels through one medium to another and demonstrate that light can be reflected such as the use of mirrors or other shiny surfaces and refracted such as the appearance of an object when observed through water Light Energy is a form of energy that travels in waves. It can come from a light bulb, the sun, or a computer screen. No matter what the source it is, light travels in a straight line.
Light Energy Terms Reflection-The bouncing of light from a surface. Light travels in straight lines unless it hits another surface. Then it reflects in angles.
Refraction-the bending of light as it moves from one material into another.
Convex lens- a lens that is thicker in the center and thinner at the edges. This shape bends light rays inward. Concave lens-is a lens that is thinner in the center and thicker at the edges. This shape bends light outward.
Transmit-means that light passes through an object. Light can pass through a transparent window or something that is translucent.
Transparent-allows light to be transmitted or to pass through Translucent- allows some light to be transmitted or to pass through Opaque-does not allow any light to be transmitted or to pass through Absorb- means the light is taken in by the object
Matter and Energy 5.5A,B.C,D Classify matter based on physical properties, including mass, magnetism, physical state, relative density (sinking and floating), solubility in water, and the ability to conduct or insulate thermal energy or electric energy. Identify the boiling, freezing, and melting points of water on the Celsius scale ,demonstrate that some mixtures maintain their physical properties and identify changes that occur in the physical properties of solutions such as dissolving salt in water or adding lemon juice to water
- More by User
308 views • 19 slides

Forms of Energy. `. All Forms of energy can be put into two categories: Potential energy or kinetic energy. Each of the following Forms of energy can be either potential or kinetic energy There are 6 Common Forms of Energy. Can you give an example of each form of energy below? Mechanical
288 views • 10 slides

Forms of Energy. Unit 5 . Energy. Is the ability to cause changes in matter. Energy can transform, or change, from one form into another. Energy is never used up. Potential Energy. The energy an object has because of its position or condition. Kinetic Energy.
331 views • 15 slides
Forms of Energy. M – Mechanical E - Electrical L - Light T - Thermal S - Sound. Mechanical Energy. Energy that is produced by some force of motion, such as water power (hydroelectric), wind power, gas power, or human power. . Mechanical Energy.
2.09k views • 7 slides

Forms of Energy. Mechanical Focus for now May be kinetic (associated with motion) or potential (associated with position) Chemical Electromagnetic Nuclear. Some Energy Considerations. Energy can be transformed from one form to another
603 views • 31 slides

Forms of Energy. Science 10. Topics covered today. Outline of today’s lesson: What is Energy? Heat and Energy Different forms of energy Chemical Electrical and Magnetic Nuclear and Solar What is Potential and Kinetic Energy?. What is Energy?. What do you think Energy can do ?.
881 views • 35 slides

Samuel DuPont 2009. Forms of Energy. Samuel DuPont 2009. What is Energy?. Energy is.. The ability to do work. Two Types of Energy. Potential Kinetic. Potential Energy. Potential Energy: Stored Energy. Can you think of any other forms of potential energy?. Kinetic Energy.
529 views • 13 slides

Forms of Energy. Add these notes to your graphic organizer. Refer to textbook chapter 9, section 1 for additional information. What do we need to know?. S8P2. Students will be familiar with the forms and transformations of energy. .
388 views • 24 slides
Forms of Energy. Forms of Energy. Mechanical Thermal Chemical. Electrical Electromagnetic Nuclear. Energy can be transferred, or converted, from one form to another!. Mechanical Energy. Energy associated with the motion of an object. Chewing Sound Frog Dancing. Thermal Energy.
266 views • 8 slides

FORMS OF ENERGY
FORMS OF ENERGY. BY: Krystal A. Jack 5B. What is ENERGY???. NON-RENEWABLE -Oil (petroleum) -Natural gas -coal -uranium (nuclear). RENEWABLE -solar -wind -geothermal -biomass -hydro -ocean. Sources of ENERGY. What is ENERGY??.
413 views • 22 slides

Forms of Energy. Electrical energy is changed to. Mechanical energy and then to…. Heat energy. What type of energy is being released ?. Sound energy. What forms of energy were needed to bake these cookies?. Electrical. Thermal. What forms of energy are being produced?.
555 views • 10 slides

Forms of Energy. 1. All energy falls into two categories: Potential: stored energy and energy of position Kinetic: motion of waves , electrons, atoms , molecules and substances. 2. What Forms of Energy Are There?. How will we ever remember these?!.
732 views • 12 slides

Forms of Energy. What is energy?. Ability to do work or cause change Produces Warmth Produces Light Produces Sound Produces Movement Produces Growth Powers Technology. Classes of Energy. POTENTIAL. KINETIC. Stored energy or energy of position. Energy of motion.
335 views • 19 slides

Forms of Energy. Remember… all forms of energy are either kinetic or potential. Kinetic Energy. Energy of motion. Potential. Stored energy Positional energy PE=heightXmassXgravity. Thermal Energy. Definition : Hea t . Vibration and movement of the particles in a substance
628 views • 16 slides

Forms of Energy. Chapter F3. Kinetic and Potential Energy #1 (F62). ___________ is the ability to cause changes in matter _________, which is a form of energy, can change solid ice into liquid There are two basic kind of energy-the energy of __________ and the energy of ____________
330 views • 23 slides

Mr. Dunnum Physical Science. Forms of Energy. Law of Conservation. According to the law law of conservationlawla of energy, energy is never created or destroyed. The only thing that changes is the form in which energy appears. What is Energy?.
247 views • 17 slides
Forms of Energy. Forms of Energy. Electrical Radiation/Electromagnetic Nuclear Sound. Gravitational Mechanical Thermal Chemical. Energy can be transferred, or converted, from one form to another!. Mechanical Energy. Energy stored in the tension of an object. Chewing
336 views • 10 slides

what is energy? Includes definitions of the different types of energy. That is electromagnetic energy, Mechanical energy, Chemical energy, Thermal energy, Electrical energy. For more vist http://energy.wesrch.com/
459 views • 10 slides
Energy. Forms of Energy
772 views • 43 slides

Forms of Energy. Mechanical Chemical Electrical. Forms of Energy. Mechanical - the energy an object has from its motion or its potential . a. kinetic - an object in motion b. potential - a result of position or ability to perform work. Forms of Energy.
601 views • 57 slides

Forms of Energy. Kinetic Energy – due to the movement of an object. As the blocks move they lose potential energy but it is converted to kinetic
134 views • 10 slides

Forms of Energy. States of Energy. What is Energy ? Energy is the ability to cause a change or do work There are 2 states and 6 forms of energy.
209 views • 19 slides

FERC Unanimously Approves Backstop Transmission Siting Procedures
Item E-2 | Presentation
FERC today unanimously approved a rule outlining how it plans to implement its limited authority over siting electricity transmission lines, as amended by Congress in 2021.
Today’s new rule, Order No. 1977, updates the process to be used in the limited circumstances when the Commission is called upon to exercise its siting authority. Order No. 1977 includes a Landowner Bill of Rights, codifies an Applicant Code of Conduct as one way for applicants to demonstrate good-faith efforts to engage with landowners in the permitting process, and directs applicants to develop engagement plans for outreach to environmental justice communities and Tribes. The rule does not adopt the proposal to allow simultaneous processing of state and FERC siting applications.
“As a former state regulator, I recognize the primary role of the states in siting transmission within their borders,” FERC Chairman Willie Phillips said. “This rule today follows the action of Congress in the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act of 2021 by updating the deliberative process for FERC in the event the Commission needs to act on a transmission siting request.”
The Landowner Bill of Rights notifies landowners who would be affected by a proposed transmission line of their right to intervene in any open Commission proceeding. A transmission line applicant must include a copy of the Landowner Bill of Rights with the pre-filing notification mailed to affected landowners.
Order No. 1977 also requires applicants to produce Tribal Resources Reports, which consolidate existing requirements for information describing effects on Tribes, Tribal lands and Tribal resources. Applicants must identify potentially affected Tribes and describe the impacts of project construction, operation and maintenance on Tribes and Tribal interests. Additionally, they must develop Tribal Engagement Plans that describe outreach activities that may affect Tribes.
The new rule requires applicants to develop Environmental Justice Public Engagement Plans describing outreach activities targeted at potentially affected environmental justice communities. This information will inform the new Environmental Justice Resource Reports that identify potentially affected environmental justice communities and describe the effects of project construction, operation and maintenance on those communities, including whether any impacts would be disproportionate and adverse.
Order No. 1977 will take effect 60 days after publication in the Federal Register .
Latest News
Innovations and efficiencies in generator interconnection workshop, staff presentation | building for the future through electric regional transmission planning and cost allocation, ferc takes on long-term planning with historic transmission rule.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
What is energy? 3 Energy exists in different forms, but they are all grouped into two main "states": potential and kinetic. Potential energy is stored energy and the energy of position. Kinetic energy is the energy of motion — of waves, electrons, atoms, molecules, substances, and objects. States of energy 4 Potential energy can be thought of ...
7. electromagnetic energy Energy from a magnetic field that is produced by the motion of electric charges such as electric current. Electromagnetic radiation exists in the form of particles called photons. Each particle or photon is an extremely small grain of energy - an energy packet. Electromagnetic energy is said to be the type of energy which comes from electromagnetic waves.
It defines energy as the ability to do work. There are two main types of energy: kinetic energy, which is the energy of motion, and potential energy, which is stored energy. The document then describes five specific forms of energy - radiant or light, sound, heat/thermal, electrical, and mechanical. For each form, it provides a definition and ...
Energy Transformations occur when one form of energy is changed into a different form of energy. We can diagram how this energy is transformed at each stage. Ex: In a microwave oven, the following energy transformation takes place: Electrical energy → Radiant energy → Thermal energy.
Oct 25, 2016 • Download as PPTX, PDF •. 7 likes • 8,764 views. B. bassantnour. Forms of energy. Education. 1 of 20. Download now. Forms of energy explain powerpoint - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
Energy: The ability to cause change, or to do work. All objects have energy, but we usually only notice when a change takes place. There are 5 different forms of energy. MOST of Earth's energy comes from the Sun. Mechanical Energy: Energy due to the motion or position of an object. There are two types of mechanical energy: Potential and Kinetic.
An editable PowerPoint to use when teaching about the different forms of energy. Use this teaching presentation when teaching your students about the different forms of energy. This PowerPoint goes into depth when explaining each form of energy, making it the perfect presentation to use with your students. It incorporates excellent visuals and ...
Chemical energy fuels automobiles and airplanes. Electrical energy drives many small machines and keeps lights glowing. Almost every form of energy can be converted into other forms. But whatever form it is in, energy is essentially the capacity for making something happen or, as engineers and scientists say, "doing work." Figure 1.
ppt, 2.14 MB. Forms of Energy PowerPoint. 7 basic forms of energy. Defines what energy is, and explains the different types of energy including Mechanical energy, Thermal energy, Chemical Energy,Electrical Energy, Electromagnetic or Radiant Energy, Sound Energy, and Nuclear Energy. Animated clips make it fun! 24 slides.
A fully editable PowerPoint presentation on forms of energy and energy transformations. The presentation covers the definitions for the different forms of energy and the units used to measure energy. It also provides examples of energy transformations. Comes with a bonus word search and solutions. Forms of energy included: sound. heat. electrical.
Students are introduced to the definition of energy and the concepts of kinetic energy, potential energy, and energy transfer. This lesson is a broad overview of concepts that are taught in more detail in subsequent lessons and activities in this curricular unit. A PowerPoint® presentation and pre/post quizzes are provided.
7 Radiant (EM) 8 Electrical (KE) Electrical energy is the movement of electrons in matter to create electricity. Electrons are found on the energy levels of an atom and they have a negative charge. 9 Thermal (KE) Thermal energy -the vibration and movement of atoms and molecules within substance. Thermal energy is related to temperature.
Examples: An object possessing mechanical energy has both kinetic and potential energy, although the energy of one of the forms may be equal to zero. A moving car has kinetic energy. If you move the car up a mountain, it has kinetic and potential energy. A book sitting on a table has potential energy.
During download, if you can't get a presentation, the file might be deleted by the publisher. E N D . Presentation Transcript. Forms of Energy M - Mechanical E - Electrical L - Light T ... All Forms of energy can be put into two categories: Potential energy or kinetic energy. Each of the following Forms of energy can be either potential or ...
9 Types and Forms of Energy PLTW Gateway Unit 3- Lesson 3.1- Investigating Energy Nuclear Energy Energy contained in the nucleus of an atom Example Nuclear energy is released when nuclei are split apart into several pieces, or when they are combined to form a single, larger nucleus An atom's nucleus can be split apart. When this is done, a tremendous amount of energy is released.
The energy acquired by the objects upon which. work is done is known as mechanical energy. 6. Electrical Energy. A form of energy that is produced when electrons. move from one place to another place. Electrical. energy is the energy newly derived from electric. potential energy.
Energy resources are the different ways of supplying a particular form of energy. For example: Chemical energy is a form of energy. Food, oil, coal, gas, petrol, turf and wood are some of the ...
Make your energy presentations come alive with this energy PowerPoint template. Whether you're a professor, student, or energy specialist, these templates will help you share your message with clarity and style. With a range of customizable slides, you can easily manage your lessons and workshops, and make learning interactive and engaging.
kinetic- an object in motion • b. potential- a result of position or ability to perform work. Forms of Energy • Chemical- released in a chemical reaction, often forms heat • Batteries • Biomass • Petroleum • Explosives • Food. Forms of Energy • Electrical- energy made available by the flow of electric charge through a conductor ...
Energy can be neither created nor destroyed but only changed from one form to another. This principle is known as the conservation of energy or the first law of thermodynamics.For example, when a box slides down a hill, the potential energy that the box has from being located high up on the slope is converted to kinetic energy, energy of motion. As the box slows to a stop through friction, the ...
Presentation Transcript. 5.6A SW explore the uses of energy, including mechanical, light, thermal, electrical and sound energy. Forms of Energy -Wind is moving air. We can use the energy in wind to do work. The energy in wind comes from the sun. -When the wind blows, it pushes against the blades of the wind turbines.
Electrical Energy SC Standard 6-5.1 - Electrical energy is the energy flowing in an electric circuit. circuit - Sources of electrical energy include: i. Stored chemical energy in batteries ii. Solar energy in solar cells iii.Fuel or hydroelectric energy in generators.
Department of Energy Philippines. Philippine Standard Time: Thursday, May 16, 2024, 7:01:08 AM. Private Sector - Initiated Power Projects as of March 31, 2024. Published on Wednesday, 15 May 2024. List of Existing Power Plants as of March 2024. Published on Wednesday, 15 May 2024. Prior Notice on Price Adjustments as of May 13-15, 2024 [For Fuels]
Research will Focus on Microelectronics for Energy Efficiency and Extreme Environments WASHINGTON, D.C.. - Today, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced $160 million to advance President Biden's vision to secure the future of American leadership in semiconductor innovation by implementing a key provision in the historic CHIPS and Science Act of 2022 (42 U.S.C. §19331 ...
Item E-1 | Presentation | Fact Sheet FERC acted today to ensure the transmission grid can meet the nation's growing demand for reliable electricity with a new rule that outlines how to plan and pay for facilities that regions of the country will need to keep the lights on and power the American economy through the 21st
WORLD OIL PRICES (May 6-10, 2024, trading days) The week-on-week price of Dubai crude has decreased by almost $2.50 per barrel. The international price of gasoline, diesel and kerosene have also decreased per barrel week-on-week by about $5.90, $1.50 and$ 1.50, respectively.
Item E-1 | News Release | Presentation FERC's new Grid Expansion Rule continues the essential work of the Commission - ensuring a reliable grid - by requiring the nation's transmission providers to plan for the transmission we know we will need in the future.
Item E-2 | Presentation FERC today unanimously approved a rule outlining how it plans to implement its limited authority over siting electricity transmission lines, as amended by Congress in 2021. Today's new rule, Order No. 1977, updates the process to be used in the limited circumstances when the Commission is called upon to exercise its ...
Nov 17, 2008 • Download as PPT, PDF •. 187 likes • 217,075 views. Pinaki Bhadury. A presentation on types of Energy meant for school going children between standard 3 to 5 (Class or Grade 3 to 5) Technology Business. 1 of 21. Download now. Energy - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
But mandatory energy codes do not allow for such discretion. Eight states currently mandate no energy code at all, and only Nevada and New Jersey have fully adopted the 2021 code statewide for ...