How to Conduct an Industry Analysis? Steps, Template, Examples
Appinio Research · 16.11.2023 · 39min read

Are you ready to unlock the secrets of Industry Analysis, equipping yourself with the knowledge to navigate markets and make informed strategic decisions? Dive into this guide, where we unravel the significance, objectives, and methods of Industry Analysis.
Whether you're an entrepreneur seeking growth opportunities or a seasoned executive navigating industry shifts, this guide will be your compass in understanding the ever-evolving business terrain.

What is Industry Analysis?
Industry analysis is the process of examining and evaluating the dynamics, trends, and competitive forces within a specific industry or market sector. It involves a comprehensive assessment of the factors that impact the performance and prospects of businesses operating within that industry. Industry analysis serves as a vital tool for businesses and decision-makers to gain a deep understanding of the environment in which they operate.
Key components of industry analysis include:
- Market Size and Growth: Determining the overall size of the market, including factors such as revenue, sales volume, and customer base. Analyzing historical and projected growth rates provides insights into market trends and opportunities.
- Competitive Landscape: Identifying and analyzing competitors within the industry. This includes assessing their market share, strengths, weaknesses, and strategies. Understanding the competitive landscape helps businesses position themselves effectively.
- Customer Behavior and Preferences: Examining consumer behavior , preferences, and purchasing patterns within the industry. This information aids in tailoring products or services to meet customer needs.
- Regulatory and Legal Environment: Assessing the impact of government regulations, policies, and legal requirements on industry operations. Compliance and adaptation to these factors are crucial for business success.
- Technological Trends: Exploring technological advancements and innovations that affect the industry. Staying up-to-date with technology trends can be essential for competitiveness and growth.
- Economic Factors: Considering economic conditions, such as inflation rates, interest rates, and economic cycles, that influence the industry's performance.
- Social and Cultural Trends: Examining societal and cultural shifts, including changing consumer values and lifestyle trends that can impact demand and preferences.
- Environmental and Sustainability Factors: Evaluating environmental concerns and sustainability issues that affect the industry. Industries are increasingly required to address environmental responsibility.
- Supplier and Distribution Networks: Analyzing the availability of suppliers, distribution channels, and supply chain complexities within the industry.
- Risk Factors: Identifying potential risks and uncertainties that could affect industry stability and profitability.
Objectives of Industry Analysis
Industry analysis serves several critical objectives for businesses and decision-makers:
- Understanding Market Dynamics: The primary objective is to gain a comprehensive understanding of the industry's dynamics, including its size, growth prospects, and competitive landscape. This knowledge forms the basis for strategic planning.
- Identifying Growth Opportunities: Industry analysis helps identify growth opportunities within the market. This includes recognizing emerging trends, niche markets, and underserved customer segments.
- Assessing Competitor Strategies: By examining competitors' strengths, weaknesses, and strategies, businesses can formulate effective competitive strategies. This involves positioning the company to capitalize on its strengths and exploit competitors' weaknesses.
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation: Identifying potential risks and vulnerabilities specific to the industry allows businesses to develop risk mitigation strategies and contingency plans. This proactive approach minimizes the impact of adverse events.
- Strategic Decision-Making: Industry analysis provides the data and insights necessary for informed strategic decision-making. It guides decisions related to market entry, product development, pricing strategies, and resource allocation.
- Resource Allocation: By understanding industry dynamics, businesses can allocate resources efficiently. This includes optimizing marketing budgets, supply chain investments, and talent recruitment efforts.
- Innovation and Adaptation: Staying updated on technological trends and shifts in customer preferences enables businesses to innovate and adapt their offerings effectively.
Importance of Industry Analysis in Business
Industry analysis holds immense importance in the business world for several reasons:
- Strategic Planning: It forms the foundation for strategic planning by providing a comprehensive view of the industry's landscape. Businesses can align their goals, objectives, and strategies with industry trends and opportunities.
- Risk Management: Identifying and assessing industry-specific risks allows businesses to manage and mitigate potential threats proactively. This reduces the likelihood of unexpected disruptions.
- Competitive Advantage: In-depth industry analysis helps businesses identify opportunities for gaining a competitive advantage. This could involve product differentiation, cost leadership, or niche market targeting .
- Resource Optimization: Efficient allocation of resources, both financial and human, is possible when businesses have a clear understanding of industry dynamics. It prevents wastage and enhances resource utilization.
- Informed Investment: Industry analysis assists investors in making informed decisions about allocating capital. It provides insights into the growth potential and risk profiles of specific industry sectors.
- Adaptation to Change: As industries evolve, businesses must adapt to changing market conditions. Industry analysis facilitates timely adaptation to new technologies, market shifts, and consumer preferences .
- Market Entry and Expansion: For businesses looking to enter new markets or expand existing operations, industry analysis guides decision-making by evaluating the feasibility and opportunities in target markets.
- Regulatory Compliance: Understanding the regulatory environment is critical for compliance and risk avoidance. Industry analysis helps businesses stay compliant with relevant laws and regulations.
In summary, industry analysis is a fundamental process that empowers businesses to make informed decisions, stay competitive, and navigate the complexities of their respective markets. It is an invaluable tool for strategic planning and long-term success.
How to Prepare for Industry Analysis?
Let's start by going through the crucial preparatory steps for conducting a comprehensive industry analysis.
1. Data Collection and Research
- Primary Research: When embarking on an industry analysis, consider conducting primary research . This involves gathering data directly from industry sources, stakeholders, and potential customers. Methods may include surveys , interviews, focus groups , and observations. Primary research provides firsthand insights and can help validate secondary research findings.
- Secondary Research: Secondary research involves analyzing existing literature, reports, and publications related to your industry. Sources may include academic journals, industry-specific magazines, government publications, and market research reports. Secondary research provides a foundation of knowledge and can help identify gaps in information that require further investigation.
- Data Sources: Explore various data sources to collect valuable industry information. These sources may include industry-specific associations, government agencies, trade publications, and reputable market research firms. Make sure to cross-reference data from multiple sources to ensure accuracy and reliability.
2. Identifying Relevant Industry Metrics
Understanding and identifying the right industry metrics is essential for meaningful analysis. Here, we'll discuss key metrics that can provide valuable insights:
- Market Size: Determining the market's size, whether in terms of revenue, units sold, or customer base, is a fundamental metric. It offers a snapshot of the industry's scale and potential.
- Market Growth Rate: Assessing historical and projected growth rates is crucial for identifying trends and opportunities. Understanding how the market has evolved over time can guide strategic decisions.
- Market Share Analysis: Analyzing market share among industry players can help you identify dominant competitors and their respective positions. This metric also assists in gauging your own company's market presence.
- Market Segmentation : Segmenting the market based on demographics, geography, behavior, or other criteria can provide deeper insights. Understanding the specific needs and preferences of various market segments can inform targeted strategies.
3. Gathering Competitive Intelligence
Competitive intelligence is the cornerstone of effective industry analysis. To gather and utilize information about your competitors:
- Competitor Identification: Begin by creating a comprehensive list of your primary and potential competitors. Consider businesses that offer similar products or services within your target market. It's essential to cast a wide net to capture all relevant competitors.
- SWOT Analysis : Conduct a thorough SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis for each competitor. This analysis helps you identify their internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats they face.
- Market Share Analysis: Determine the market share held by each competitor and how it has evolved over time. Analyzing changes in market share can reveal shifts in competitive dynamics.
- Product and Pricing Analysis: Evaluate your competitors' product offerings and pricing strategies . Identify any unique features or innovations they offer and consider how your own products or services compare.
- Marketing and Branding Strategies: Examine the marketing and branding strategies employed by competitors. This includes their messaging, advertising channels, and customer engagement tactics. Assess how your marketing efforts stack up.
Industry Analysis Frameworks and Models
Now, let's explore essential frameworks and models commonly used in industry analysis, providing you with practical insights and examples to help you effectively apply these tools.
Porter's Five Forces Model
Porter's Five Forces is a powerful framework developed by Michael Porter to assess the competitive forces within an industry. This model helps you understand the industry's attractiveness and competitive dynamics.
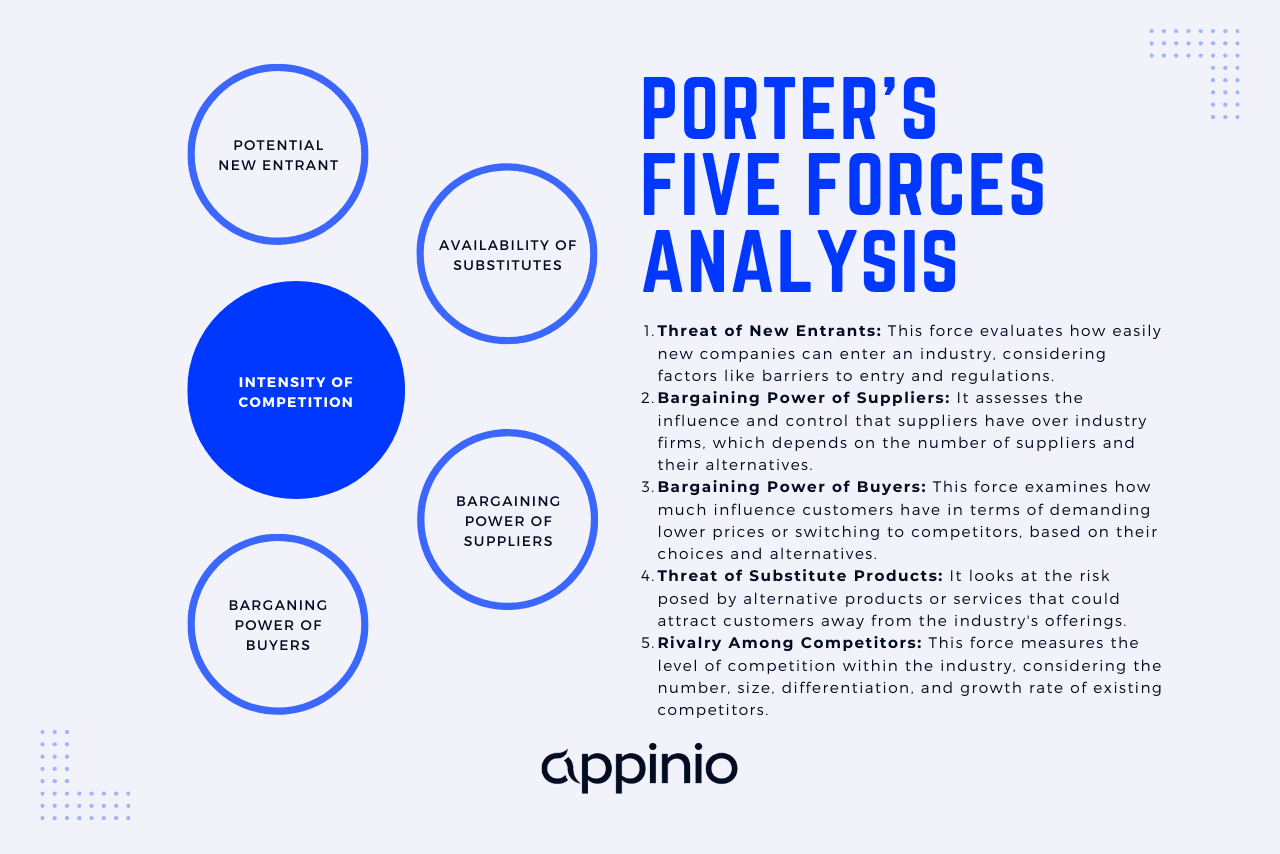
It consists of five key forces:
- Threat of New Entrants: This force evaluates how easy or difficult it is for new companies to enter the industry. Factors that increase barriers to entry include high capital requirements, strong brand loyalty among existing players, and complex regulatory hurdles. For example, the airline industry has significant barriers to entry due to the need for large capital investments in aircraft, airport facilities, and regulatory approvals.
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers: This force examines the influence suppliers have on the industry's profitability. Powerful suppliers can demand higher prices or impose unfavorable terms. For instance, in the automotive industry, suppliers of critical components like microchips can wield significant bargaining power if they are few in number or if their products are highly specialized.
- Bargaining Power of Buyers: The bargaining power of buyers assesses how much influence customers have in negotiating prices and terms. In industries where buyers have many alternatives, such as the smartphone market, they can demand lower prices and better features, putting pressure on manufacturers to innovate and compete.
- Threat of Substitutes: This force considers the availability of substitute products or services that could potentially replace what the industry offers. For example, the rise of electric vehicles represents a significant threat to the traditional gasoline-powered automotive industry as consumers seek eco-friendly alternatives.
- Competitive Rivalry: Competitive rivalry assesses the intensity of competition among existing firms in the industry. A highly competitive industry, such as the smartphone market, often leads to price wars and aggressive marketing strategies as companies vie for market share.
Example: Let's consider the coffee shop industry . New entrants face relatively low barriers, as they can set up a small shop with limited capital. However, the bargaining power of suppliers, such as coffee bean producers, can vary depending on the region and the coffee's rarity. Bargaining power with buyers is moderate, as customers often have several coffee shops to choose from. Threats of substitutes may include energy drinks or homemade coffee, while competitive rivalry is high, with numerous coffee chains and independent cafes competing for customers.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT Analysis is a versatile tool used to assess an organization's internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats. By conducting a SWOT analysis, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of your industry and formulate effective strategies.
- Strengths: These are the internal attributes and capabilities that give your business a competitive advantage. For instance, if you're a tech company, having a talented and innovative team can be considered a strength.
- Weaknesses: Weaknesses are internal factors that hinder your business's performance. For example, a lack of financial resources or outdated technology can be weaknesses that need to be addressed.
- Opportunities: Opportunities are external factors that your business can capitalize on. This could be a growing market segment, emerging technologies, or changing consumer trends.
- Threats: Threats are external factors that can potentially harm your business. Examples of threats might include aggressive competition, economic downturns, or regulatory changes.
Example: Let's say you're analyzing the fast-food industry. Strengths could include a well-established brand, a wide menu variety, and efficient supply chain management. Weaknesses may involve a limited focus on healthy options and potential labor issues. Opportunities could include the growing trend toward healthier eating, while threats might encompass health-conscious consumer preferences and increased competition from delivery apps.
PESTEL Analysis
PESTEL Analysis examines the external macro-environmental factors that can impact your industry. The acronym stands for:
- Political: Political factors encompass government policies, stability, and regulations. For example, changes in tax laws or trade agreements can affect industries like international manufacturing.
- Economic: Economic factors include economic growth, inflation rates, and exchange rates. A fluctuating currency exchange rate can influence export-oriented industries like tourism.
- Social: Social factors encompass demographics, cultural trends, and social attitudes. An aging population can lead to increased demand for healthcare services and products.
- Technological: Technological factors involve advancements and innovations. Industries like telecommunications are highly influenced by technological developments, such as the rollout of 5G networks.
- Environmental: Environmental factors cover sustainability, climate change, and ecological concerns. Industries such as renewable energy are directly impacted by environmental regulations and consumer preferences.
- Legal: Legal factors encompass laws, regulations, and compliance requirements. The pharmaceutical industry, for instance, faces stringent regulatory oversight and patent protection laws.
Example: Consider the automobile manufacturing industry. Political factors may include government incentives for electric vehicles. Economic factors can involve fluctuations in fuel prices affecting consumer preferences for fuel-efficient cars. Social factors might encompass the growing interest in eco-friendly transportation options. Technological factors could relate to advancements in autonomous driving technology. Environmental factors may involve emissions regulations, while legal factors could pertain to safety standards and recalls.
Industry Life Cycle Analysis
Industry Life Cycle Analysis categorizes industries into various stages based on their growth and maturity. Understanding where your industry stands in its life cycle can help shape your strategies.
- Introduction: In the introduction stage, the industry is characterized by slow growth, limited competition, and a focus on product development. New players enter the market, and consumers become aware of the product or service. For instance, electric scooters were introduced as a new mode of transportation in recent years.
- Growth: The growth stage is marked by rapid market expansion, increased competition, and rising demand. Companies focus on gaining market share, and innovation is vital. The ride-sharing industry, exemplified by companies like Uber and Lyft, experienced significant growth in this stage.
- Maturity: In the maturity stage, the market stabilizes, and competition intensifies. Companies strive to maintain market share and differentiate themselves through branding and customer loyalty programs. The smartphone industry reached maturity with multiple established players.
- Decline: In the decline stage, the market saturates, and demand decreases. Companies must adapt or diversify to survive. The decline of traditional print media is a well-known example.
Example: Let's analyze the video streaming industry . The introduction stage saw the emergence of streaming services like Netflix. In the growth stage, more players entered the market, and the industry saw rapid expansion. The industry is currently in the maturity stage, with established platforms like Netflix, Amazon Prime, and Disney+ competing for market share. However, with continued innovation and changing consumer preferences, the decline stage may eventually follow.
Value Chain Analysis
Value Chain Analysis dissects a company's activities into primary and support activities to identify areas of competitive advantage. Primary activities directly contribute to creating and delivering a product or service, while support activities facilitate primary activities.
- Primary Activities: These activities include inbound logistics (receiving and storing materials), operations (manufacturing or service delivery), outbound logistics (distribution), marketing and sales, and customer service.
- Support Activities: Support activities include procurement (acquiring materials and resources), technology development (R&D and innovation), human resource management (recruitment and training), and infrastructure (administrative and support functions).
Example: Let's take the example of a smartphone manufacturer. Inbound logistics involve sourcing components, such as processors and displays. Operations include assembly and quality control. Outbound logistics cover shipping and distribution. Marketing and sales involve advertising and retail partnerships. Customer service handles warranty and support.
Procurement ensures a stable supply chain for components. Technology development focuses on research and development of new features. Human resource management includes hiring and training skilled engineers. Infrastructure supports the company's administrative functions.
By applying these frameworks and models effectively, you can better understand your industry, identify strategic opportunities and threats, and develop a solid foundation for informed decision-making.
Data Interpretation and Analysis
Once you have your data, it's time to start interpreting and analyzing the data you've collected during your industry analysis.
You can unlock the full potential of your data with Appinio 's comprehensive research platform. Beyond aiding in data collection, Appinio simplifies the intricate process of data interpretation and analysis. Our intuitive tools empower you to effortlessly transform raw data into actionable insights, giving you a competitive edge in understanding your industry.
Whether it's assessing market trends, evaluating the competitive landscape, or understanding customer behavior, Appinio offers a holistic solution to uncover valuable findings. With our platform, you can make informed decisions, strategize effectively, and stay ahead of industry shifts.
Experience the ease of data collection and interpretation with Appinio – book a demo today!
Book a Demo
1. Analyze Market Size and Growth
Analyzing the market's size and growth is essential for understanding its dynamics and potential. Here's how to conduct a robust analysis:
- Market Size Calculation: Determine the total market size in terms of revenue, units sold, or the number of customers. This figure serves as a baseline for evaluating the industry's scale.
- Historical Growth Analysis: Examine historical data to identify growth trends. This includes looking at past year-over-year growth rates and understanding the factors that influenced them.
- Projected Growth Assessment: Explore industry forecasts and projections to gain insights into the expected future growth of the market. Consider factors such as emerging technologies, changing consumer preferences, and economic conditions.
- Segmentation Analysis: If applicable, analyze market segmentation data to identify growth opportunities in specific market segments. Understand which segments are experiencing the most significant growth and why.
2. Assess Market Trends
Stay ahead of the curve by closely monitoring and assessing market trends. Here's how to effectively evaluate trends within your industry.
- Consumer Behavior Analysis: Dive into consumer behavior data to uncover shifts in preferences, buying patterns, and shopping habits. Understand how technological advancements and cultural changes influence consumer choices.
- Technological Advancements: Keep a keen eye on technological developments that impact your industry. Assess how innovations such as AI, IoT, blockchain, or automation are changing the competitive landscape.
- Regulatory Changes: Stay informed about regulatory shifts and their potential consequences for your industry. Regulations can significantly affect product development, manufacturing processes, and market entry strategies.
- Sustainability and Environmental Trends: Consider the growing importance of sustainability and environmental concerns. Evaluate how your industry is adapting to eco-friendly practices and how these trends affect consumer choices.
3. Evaluate Competitive Landscape
Understanding the competitive landscape is critical for positioning your business effectively. To perform a comprehensive evaluation:
- Competitive Positioning: Determine where your company stands in comparison to competitors. Identify your unique selling propositions and areas where you excel.
- Market Share Analysis: Continuously monitor market share among industry players. Identify trends in market share shifts and assess the strategies that lead to such changes.
- Competitive Advantages and Weaknesses: Analyze your competitors' strengths and weaknesses. Identify areas where you can capitalize on their weaknesses and where you need to fortify your own strengths.
4. Identify Key Success Factors
Recognizing and prioritizing key success factors is crucial for developing effective strategies. To identify and leverage these factors:
- Customer Satisfaction: Prioritize customer satisfaction as a critical success factor. Satisfied customers are more likely to become loyal advocates and contribute to long-term success.
- Quality and Innovation: Focus on product or service quality and continuous innovation. Meeting and exceeding customer expectations can set your business apart from competitors.
- Cost Efficiency: Strive for cost efficiency in your operations. Identifying cost-saving opportunities can lead to improved profitability.
- Marketing and Branding Excellence: Invest in effective marketing and branding strategies to create a strong market presence. Building a recognizable brand can drive customer loyalty and growth.
5. Analyze Customer Behavior and Preferences
Understanding your target audience is central to success. Here's how to analyze customer behavior and preferences:
- Market Segmentation: Use market segmentation to categorize customers based on demographics, psychographics , and behavior. This allows for more personalized marketing and product/service offerings.
- Customer Surveys and Feedback: Gather customer feedback through surveys and feedback mechanisms. Understand their pain points, preferences, and expectations to tailor your offerings.
- Consumer Journey Mapping: Map the customer journey to identify touchpoints where you can improve engagement and satisfaction. Optimize the customer experience to build brand loyalty.
By delving deep into data interpretation and analysis, you can gain valuable insights into your industry, uncover growth opportunities, and refine your strategic approach.
How to Conduct Competitor Analysis?
Competitor analysis is a critical component of industry analysis as it provides valuable insights into your rivals, helping you identify opportunities, threats, and areas for improvement.
1. Identify Competitors
Identifying your competitors is the first step in conducting a thorough competitor analysis. Competitors can be classified into several categories:
- Direct Competitors: These are companies that offer similar products or services to the same target audience. They are your most immediate competitors and often compete directly with you for market share.
- Indirect Competitors: Indirect competitors offer products or services that are related but not identical to yours. They may target a slightly different customer segment or provide an alternative solution to the same problem.
- Potential Competitors: These companies could enter your market in the future. Identifying potential competitors early allows you to anticipate and prepare for new entrants.
- Substitute Products or Services: While not traditional competitors, substitute products or services can fulfill the same customer needs or desires. Understanding these alternatives is crucial to your competitive strategy.
2. Analyze Competitor Strengths and Weaknesses
Once you've identified your competitors, you need to analyze their strengths and weaknesses. This analysis helps you understand how to position your business effectively and identify areas where you can gain a competitive edge.
- Strengths: Consider what your competitors excel at. This could include factors such as brand recognition, innovative products, a large customer base, efficient operations, or strong financial resources.
- Weaknesses: Identify areas where your competitors may be lacking. Weaknesses could involve limited product offerings, poor customer service, outdated technology, or financial instability.
3. Competitive Positioning
Competitive positioning involves defining how you want your business to be perceived relative to your competitors. It's about finding a unique position in the market that sets you apart. Consider the following strategies:
- Cost Leadership: Strive to be the low-cost provider in your industry. This positioning appeals to price-conscious consumers.
- Differentiation: Focus on offering unique features or attributes that make your products or services stand out. This can justify premium pricing.
- Niche Market: Target a specific niche or segment of the market that may be underserved by larger competitors. Tailor your offerings to meet their unique needs.
- Innovation and Technology: Emphasize innovation and technology to position your business as a leader in product or service quality.
- Customer-Centric: Prioritize exceptional customer service and customer experience to build loyalty and a positive reputation.
4. Benchmarking and Gap Analysis
Benchmarking involves comparing your business's performance and practices with those of your competitors or industry leaders. Gap analysis helps identify areas where your business falls short and where improvements are needed.
- Performance Benchmarking: Compare key performance metrics, such as revenue, profitability, market share, and customer satisfaction, with those of your competitors. Identify areas where your performance lags behind or exceeds industry standards.
- Operational Benchmarking: Analyze your operational processes, supply chain, and cost structures compared to your competitors. Look for opportunities to streamline operations and reduce costs.
- Product or Service Benchmarking: Evaluate the features, quality, and pricing of your products or services relative to competitors. Identify gaps and areas for improvement.
- Marketing and Sales Benchmarking: Assess your marketing strategies, customer acquisition costs, and sales effectiveness compared to competitors. Determine whether your marketing efforts are performing at a competitive level.
Market Entry and Expansion Strategies
Market entry and expansion strategies are crucial for businesses looking to enter new markets or expand their presence within existing ones. These strategies can help you effectively target and penetrate your chosen markets.
Market Segmentation and Targeting
- Market Segmentation: Begin by segmenting your target market into distinct groups based on demographics , psychographics, behavior, or other relevant criteria. This helps you understand the diverse needs and preferences of different customer segments.
- Targeting: Once you've segmented the market, select specific target segments that align with your business goals and capabilities. Tailor your marketing and product/service offerings to appeal to these chosen segments.
Market Entry Modes
Selecting the proper market entry mode is crucial for a successful expansion strategy. Entry modes include:
- Exporting: Sell your products or services in international markets through exporting. This is a low-risk approach, but it may limit your market reach.
- Licensing and Franchising: License your brand, technology, or intellectual property to local partners or franchisees. This allows for rapid expansion while sharing the risk and control.
- Joint Ventures and Alliances: Partner with local companies through joint ventures or strategic alliances. This approach leverages local expertise and resources.
- Direct Investment: Establish a physical presence in the target market through subsidiaries, branches, or wholly-owned operations. This offers full control but comes with higher risk and investment.
Competitive Strategy Formulation
Your competitive strategy defines how you will compete effectively in the target market.
- Cost Leadership: Strive to offer products or services at lower prices than competitors while maintaining quality. This strategy appeals to price-sensitive consumers.
- Product Differentiation: Focus on offering unique and innovative products or services that stand out in the market. This strategy justifies premium pricing.
- Market Niche: Target a specific niche or segment within the market that is underserved or has particular needs. Tailor your offerings to meet the unique demands of this niche.
- Market Expansion : Expand your product or service offerings to capture a broader share of the market. This strategy involves diversifying your offerings to appeal to a broader audience.
- Global Expansion: Consider expanding internationally to tap into new markets and diversify your customer base. This strategy involves thorough market research and adaptation to local cultures and regulations.
International Expansion Considerations
If your expansion strategy involves international markets, there are several additional considerations to keep in mind.
- Market Research: Conduct in-depth market research to understand the target country's cultural, economic, and legal differences.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure compliance with international trade regulations, customs, and import/export laws.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Adapt your marketing and business practices to align with the cultural norms and preferences of the target market.
- Localization: Consider adapting your products, services, and marketing materials to cater to local tastes and languages.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluate the political, economic, and legal risks associated with operating in the target country. Develop risk mitigation strategies.
By carefully analyzing your competitors and crafting effective market entry and expansion strategies, you can position your business for success in both domestic and international markets.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Risk assessment and mitigation are crucial aspects of industry analysis and strategic planning. Identifying potential risks, assessing vulnerabilities, and implementing effective risk management strategies are essential for business continuity and success.
1. Identify Industry Risks
- Market Risks: These risks pertain to factors such as changes in market demand, economic downturns, shifts in consumer preferences, and fluctuations in market prices. For example, the hospitality industry faced significant market risks during the COVID-19 pandemic, resulting in decreased travel and tourism .
- Regulatory and Compliance Risks: Regulatory changes, compliance requirements, and government policies can pose risks to businesses. Industries like healthcare are particularly susceptible to regulatory changes that impact operations and reimbursement.
- Technological Risks: Rapid technological advancements can disrupt industries and render existing products or services obsolete. Companies that fail to adapt to technological shifts may face obsolescence.
- Operational Risks: These risks encompass internal factors that can disrupt operations, such as supply chain disruptions, equipment failures, or cybersecurity breaches.
- Financial Risks: Financial risks include factors like liquidity issues, credit risk , and market volatility. Industries with high capital requirements, such as real estate development, are particularly vulnerable to financial risks.
- Competitive Risks: Intense competition and market saturation can pose challenges to businesses. Failing to respond to competitive threats can result in loss of market share.
- Global Risks: Industries with a worldwide presence face geopolitical risks, currency fluctuations, and international trade uncertainties. For instance, the automotive industry is susceptible to trade disputes affecting the supply chain.
2. Assess Business Vulnerabilities
- SWOT Analysis: Revisit your SWOT analysis to identify internal weaknesses and threats. Assess how these weaknesses may exacerbate industry risks.
- Financial Health: Evaluate your company's financial stability, debt levels, and cash flow. Identify vulnerabilities related to financial health that could hinder your ability to withstand industry-specific challenges.
- Operational Resilience: Assess the robustness of your operational processes and supply chain. Identify areas where disruptions could occur and develop mitigation strategies.
- Market Positioning: Analyze your competitive positioning and market share. Recognize vulnerabilities in your market position that could be exploited by competitors.
- Compliance and Regulatory Adherence: Ensure that your business complies with relevant regulations and standards. Identify vulnerabilities related to non-compliance or regulatory changes.
3. Risk Management Strategies
- Risk Avoidance: In some cases, the best strategy is to avoid high-risk ventures or markets altogether. This may involve refraining from entering certain markets or discontinuing products or services with excessive risk.
- Risk Reduction: Implement measures to reduce identified risks. For example, diversifying your product offerings or customer base can reduce dependence on a single revenue source.
- Risk Transfer: Transfer some risks through methods such as insurance or outsourcing. For instance, businesses can mitigate cybersecurity risks by purchasing cyber insurance.
- Risk Acceptance: In cases where risks cannot be entirely mitigated, it may be necessary to accept a certain level of risk and have contingency plans in place to address potential issues.
- Continuous Monitoring: Establish a system for continuous risk monitoring. Regularly assess the changing landscape and adjust risk management strategies accordingly.
4. Contingency Planning
Contingency planning involves developing strategies and action plans to respond effectively to unforeseen events or crises. It ensures that your business can maintain operations and minimize disruptions in the face of adverse circumstances. Key elements of contingency planning include:
- Risk Scenarios: Identify potential risk scenarios specific to your industry and business. These scenarios should encompass a range of possibilities, from minor disruptions to major crises.
- Response Teams: Establish response teams with clearly defined roles and responsibilities. Ensure that team members are trained and ready to act in the event of a crisis.
- Communication Plans: Develop communication plans that outline how you will communicate with employees, customers, suppliers, and other stakeholders during a crisis. Transparency and timely communication are critical.
- Resource Allocation: Determine how resources, including personnel, finances, and equipment, will be allocated in response to various scenarios.
- Testing and Simulation: Regularly conduct tests and simulations of your contingency plans to identify weaknesses and areas for improvement. Ensure your response teams are well-practiced and ready to execute the plans effectively.
- Documentation and Record Keeping: Maintain comprehensive documentation of contingency plans, response procedures, and communication protocols. This documentation should be easily accessible to relevant personnel.
- Review and Update: Continuously review and update your contingency plans to reflect changing industry dynamics and evolving risks. Regularly seek feedback from response teams to make improvements.
By identifying industry risks, assessing vulnerabilities, implementing risk management strategies, and developing robust contingency plans, your business can navigate the complexities of the industry landscape with greater resilience and preparedness.
Industry Analysis Template
When embarking on the journey of Industry Analysis, having a well-structured template is akin to having a reliable map for your exploration. It provides a systematic framework to ensure you cover all essential aspects of the analysis. Here's a breakdown of an industry analysis template with insights into each section.
Industry Overview
- Objective: Provide a broad perspective of the industry.
- Market Definition: Define the scope and boundaries of the industry, including its products, services, and target audience.
- Market Size and Growth: Present current market size, historical growth trends, and future projections.
- Key Players: Identify major competitors and their market share.
- Market Trends: Highlight significant trends impacting the industry.
Competitive Analysis
- Objective: Understand the competitive landscape within the industry.
- Competitor Identification: List direct and indirect competitors.
- Competitor Profiles: Provide detailed profiles of major competitors, including their strengths, weaknesses, strategies, and market positioning.
- SWOT Analysis: Conduct a SWOT analysis for each major competitor.
- Market Share Analysis: Analyze market share distribution among competitors.
Market Analysis
- Objective: Explore the characteristics and dynamics of the market.
- Customer Segmentation: Define customer segments and their demographics, behavior, and preferences.
- Demand Analysis: Examine factors driving demand and customer buying behavior.
- Supply Chain Analysis: Map out the supply chain, identifying key suppliers and distribution channels.
- Regulatory Environment: Discuss relevant regulations, policies, and compliance requirements.
Technological Analysis
- Objective: Evaluate the technological landscape impacting the industry.
- Technological Trends: Identify emerging technologies and innovations relevant to the industry.
- Digital Transformation: Assess the level of digitalization within the industry and its impact on operations and customer engagement.
- Innovation Opportunities: Explore opportunities for leveraging technology to gain a competitive edge.
Financial Analysis
- Objective: Analyze the financial health of the industry and key players.
- Revenue and Profitability: Review industry-wide revenue trends and profitability ratios.
- Financial Stability: Assess financial stability by examining debt levels and cash flow.
- Investment Patterns: Analyze capital expenditure and investment trends within the industry.
Consumer Insights
- Objective: Understand consumer behavior and preferences.
- Consumer Surveys: Conduct surveys or gather data on consumer preferences, buying habits , and satisfaction levels.
- Market Perception: Gauge consumer perception of brands and products in the industry.
- Consumer Feedback: Collect and analyze customer feedback and reviews.
SWOT Analysis for Your Business
- Objective: Assess your own business within the industry context.
- Strengths: Identify internal strengths that give your business a competitive advantage.
- Weaknesses: Recognize internal weaknesses that may hinder your performance.
- Opportunities: Explore external opportunities that your business can capitalize on.
- Threats: Recognize external threats that may impact your business.
Conclusion and Recommendations
- Objective: Summarize key findings and provide actionable recommendations.
- Summary: Recap the most critical insights from the analysis.
- Recommendations: Offer strategic recommendations for your business based on the analysis.
- Future Outlook: Discuss potential future developments in the industry.
While this template provides a structured approach, adapt it to the specific needs and objectives of your Industry Analysis. It serves as your guide, helping you navigate through the complex landscape of your chosen industry, uncovering opportunities, and mitigating risks along the way.
Remember that the depth and complexity of your industry analysis may vary depending on your specific goals and the industry you are assessing. You can adapt this template to focus on the most relevant aspects and conduct thorough research to gather accurate data and insights. Additionally, consider using industry-specific data sources, reports, and expert opinions to enhance the quality of your analysis.
Industry Analysis Examples
To grasp the practical application of industry analysis, let's delve into a few diverse examples across different sectors. These real-world scenarios demonstrate how industry analysis can guide strategic decision-making.
Tech Industry - Smartphone Segment
Scenario: Imagine you are a product manager at a tech company planning to enter the smartphone market. Industry analysis reveals that the market is highly competitive, dominated by established players like Apple and Samsung.
Use of Industry Analysis:
- Competitive Landscape: Analyze the strengths and weaknesses of competitors, identifying areas where they excel (e.g., Apple's brand loyalty ) and where they might have vulnerabilities (e.g., consumer demand for more affordable options).
- Market Trends: Identify trends like the growing demand for sustainable technology and 5G connectivity, guiding product development and marketing strategies.
- Regulatory Factors: Consider regulatory factors related to intellectual property rights, patents, and international trade agreements that can impact market entry and operations.
- Outcome: Armed with insights from industry analysis, you decide to focus on innovation, emphasizing features like eco-friendliness and affordability. This niche approach helps your company gain a foothold in the competitive market.
Healthcare Industry - Telehealth Services
Scenario: You are a healthcare entrepreneur exploring opportunities in the telehealth sector, especially in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. Industry analysis is critical due to rapid market changes.
- Market Size and Growth: Evaluate the growing demand for telehealth services, driven by the need for remote healthcare during the pandemic and convenience factors.
- Regulatory Environment: Understand the evolving regulatory landscape, including changes in telemedicine reimbursement policies and licensing requirements.
- Technological Trends: Explore emerging technologies such as AI-powered diagnosis and remote monitoring that can enhance service offerings.
- Outcome: Industry analysis underscores the potential for telehealth growth. You adapt your business model to align with regulatory changes, invest in cutting-edge technology, and focus on patient-centric care, positioning your telehealth service for success.
Food Industry - Plant-Based Foods
Scenario: As a food industry entrepreneur , you are considering entering the plant-based foods market, driven by increasing consumer interest in health and sustainability.
- Market Trends: Analyze the trend toward plant-based diets and sustainability, reflecting changing consumer preferences.
- Competitive Landscape: Assess the competitive landscape, understanding that established companies and startups are vying for market share.
- Consumer Behavior: Study consumer behavior, recognizing that health-conscious consumers seek plant-based alternatives.
- Outcome: Informed by industry analysis, you launch a line of plant-based products emphasizing both health benefits and sustainability. Effective marketing and product quality gain traction among health-conscious consumers, making your brand a success in the plant-based food industry.
These examples illustrate how industry analysis can guide strategic decisions, whether entering competitive tech markets, navigating dynamic healthcare regulations, or capitalizing on shifting consumer preferences in the food industry. By applying industry analysis effectively, businesses can adapt, innovate, and thrive in their respective sectors.
Industry Analysis is the compass that helps businesses chart their course in the vast sea of markets. By understanding the industry's dynamics, risks, and opportunities, you gain a strategic advantage that can steer your business towards success. From identifying competitors to mitigating risks and formulating competitive strategies, this guide has equipped you with the tools and knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of the business world.
Remember, Industry Analysis is not a one-time task; it's an ongoing journey. Keep monitoring market trends, adapting to changes, and staying ahead of the curve. With a solid foundation in industry analysis, you're well-prepared to tackle challenges, seize opportunities, and make well-informed decisions that drive your business toward prosperity. So, set sail with confidence and let industry analysis be your guiding star on the path to success.
How to Conduct Industry Analysis in Minutes?
Introducing Appinio , the real-time market research platform that transforms how you conduct Industry Analysis. Imagine getting real-time consumer insights in minutes, putting the power of data-driven decision-making at your fingertips. With Appinio, you can:
- Gain insights swiftly: Say goodbye to lengthy research processes. Appinio delivers answers fast, ensuring you stay ahead in the competitive landscape.
- No research degree required: Our intuitive platform is designed for everyone. You don't need a PhD in research to harness its capabilities.
- Global reach, local insights: Define your target group precisely from over 1200 characteristics and access consumer data in over 90 countries.
Join the loop 💌
Be the first to hear about new updates, product news, and data insights. We'll send it all straight to your inbox.
Get the latest market research news straight to your inbox! 💌
Wait, there's more

17.04.2024 | 25min read
Quota Sampling: Definition, Types, Methods, Examples

15.04.2024 | 34min read
What is Market Share? Definition, Formula, Examples

11.04.2024 | 34min read
What is Data Analysis? Definition, Tools, Examples
How to Conduct an Industry Analysis

8 min. read
Updated March 18, 2024
I bet you agree: You need to know the industry you want to start a business in, and the kind of business you want to start, before you can start it.
Industry analysis is part of good management. That’s not just for the business planning, but rather for business survival, beginning to end. Most of the people who successfully start their own business have already had relevant business experience before they start, most often as employees.
But in this article, I focus on how to consolidate and formalize that industry knowledge into a formal business plan .
Although all business owners need to know their industry, the documented details and explanations are mainly for when you’re writing a business plan you need to show to outsiders, like bank lenders or investors . You’ll need to do some industry analysis so you’re able to explain the general state of your industry, its growth potential, and how your business model fits into the landscape.
And if your business plan is more of an internal strategic roadmap, you should still be very sure—whether you have to prove it to others or not—that you know your market, even if you don’t do a formal industry analysis. Whether you’re a service business, manufacturer, retailer, or something else, you want to know your industry inside and out.
- What to cover in your industry analysis
Whether you write it all out in a formal business plan or not, when you’re doing your industry analysis, you’re looking at the following:
- Industry participants
- Distribution patterns
- Competition and buying patterns
Everything in your industry that happens outside of your business will affect your company. The more you know about your industry, the more advantage and protection you will have.
A complete business plan discusses:
- General industry economics
- Participants
- Factors in the competition
- And whatever else describes the nature of your business to outsiders
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
A note on finding industry information
The internet has had an enormous impact on the state of business information. Finding information isn’t really the problem anymore, after the information explosion and the huge growth in the internet beginning in the 1990s and continuing in the 21st century.
Even 10 or 15 years ago, dealing with information was more a problem of sorting through it all than of finding raw data. That generality is truer every day. There are websites for business analysis, financial statistics, demographics, trade associations, and just about everything you’ll need for a complete business plan.
You should know who else sells in your market. You can’t easily describe a type of business without describing the nature of the participants. There is a huge difference, for example, between an industry like broadband television services, in which there are only a few huge companies in any one country, and one like dry cleaning, in which there are tens of thousands of smaller participants.
This can make a big difference to a business and a business plan. The restaurant industry, for example, is what we call “pulverized,” meaning that it, like the dry cleaning industry, is made up of many small participants. The fast-food business, on the other hand, is composed of a few national brands participating in thousands of branded outlets, many of them franchised .
Economists talk of consolidation in an industry as a time when many small participants tend to disappear and a few large players emerge. In accounting, for example, there are a few large international firms whose names are well-known, and tens of thousands of smaller firms. The automobile business is composed of a few national brands participating in thousands of branded dealerships, and in computer manufacturing, for example, there are a few large international firms whose names are well-known, and thousands of smaller firms.
Products and services can follow many paths between suppliers and users.
Explain how distribution works in your industry:
- Is this an industry in which retailers are supported by regional distributors, as is the case for computer products, magazines, or auto parts?
- Does your industry depend on direct sales to large industrial customers?
- Do manufacturers support their own direct sales forces, or do they work with product representatives?
Some products are almost always sold through retail stores to consumers, and sometimes these are distributed by distribution companies that buy from manufacturers. In other cases, the products are sold directly from manufacturers to stores. Some products are sold directly from the manufacturer to the final consumer through mail campaigns, national advertising, or other promotional means.
In many product categories, there are several alternatives, and distribution choices are strategic.
Amazon made direct delivery a huge competitive advantage, especially in its earlier years. Doordash and competitors chose to be intermediaries between restaurants and customers, and several businesses offer prepackaged meal ingredients delivered with instructions for finishing the preparations in the consumers’ kitchens. Now major grocery chains offer grocery delivery. Red Box made a strategy of DVDs in kiosks. An entire industry of food delivery options gives consumers choices like restaurant meals or fresh meals ingredients being delivered. Many products are distributed through direct business-to-business (B2B) sales and in long-term contracts such as the ones between car manufacturers and their suppliers of parts, materials, and components. In some industries, companies use representatives, agents, or commissioned salespeople.
Technology can change the patterns of distribution in an industry or product category. The internet, for example, changed options for software distribution, books, music, and other products. Cable communication first, and more recently streaming, changed the options for distributing video products and video games. Some kinds of specialty items sell best with late-night infomercials on television, but others end up working on the web instead of television.
Distribution patterns may not be as critical to most service companies, because distribution is normally about physical distribution of specific physical products such as a restaurant, graphic artist, professional services practice, or architect.
For a few services, the distribution may still be relevant. A phone service, cable provider, or an internet provider might describe distribution related to physical infrastructure. Some publishers may prefer to treat their business as a service, rather than a manufacturing company, and in that case distribution may also be relevant.
It is essential to understand the nature of competition in your market. This is still in the general area of describing the industry or type of business.
Explain the general nature of competition in this business, and how the customers seem to choose one provider over another:
- What are the keys to success?
- What buying factors make the most difference—is it price? Product features? Service? Support? Training? Software? Delivery dates?
- Are brand names important?
In the computer business, for example, competition might depend on reputation and trends in one part of the market, and on channels of distribution and advertising in another. In many business-to-business industries, the nature of competition depends on direct selling, because channels are impractical.
Price is vital in products competing with each other on retail shelves, but delivery and reliability might be much more important for materials used by manufacturers in volume, for which a shortage can affect an entire production line.
In the restaurant business, for example, competition might depend on reputation and trends in one part of the market, and on location and parking in another.
In many professional service practices, the nature of competition depends on word of mouth, because advertising is not completely accepted. Is there price competition between accountants, doctors, and lawyers? How powerful are the insurance decisions in medicine, like in or out of network? How do people choose travel agencies or florists for weddings? Why does someone hire one landscape architect over another? Why choose Starbucks, a national brand, over the local coffee house? All of this is the nature of competition.
The key to your specific industry analysis is a collection of decisions and educated guesses you’ll probably have to make for yourself. There are few pat answers. Maybe it’s easy parking, a great location, great reviews on Amazon or Yelp, or recommendations on social media. You can’t necessarily look this up. It’s the kind of educated guessing that makes some businesses more successful than others.
- Main competitors
Do a very complete analysis of your main competitors. Make a list, determining who your main competitors are. What are the strengths and weaknesses of each?
Consider your competitors’:
- Financial position
- Channels of distribution
- Brand awareness
- Business development
- Technology, or other factors that you feel are important
- In what segments of the market do they operate? What seems to be their strategy? How much do they impact your products, and what threats and opportunities do they represent?
Finding competitive information
Competitive research starts with a good web search. Look up competitors’ websites and social media, then search for mentions, reviews, announcements, and even vacancies and job search information. An amazing array of competitive information is posted in plain sight, where anybody can find it.
From, there, for a good review of additional sources of information, I suggest Practical Market Research Resources for Entrepreneurs , also here on Bplans.
Competitive matrix
A lot of businesses organize competitive analysis into a competitive matrix. The standard competitive matrix shows how different competitors stack up according to significant factors.
Some people also use a SWOT analysis to think about competition in terms of opportunities and threats, the “OT” of SWOT. Opportunities and threats are generally taken as externals, which would include competition, so it’s valuable to run a SWOT analysis on your business to help figure this out.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.
.png?format=auto)
Table of Contents
Related Articles

3 Min. Read
How to Use TAM, SAM, SOM to Determine Market Size

7 Min. Read
Target Market Examples

9 Min. Read
How to Write a Customer Analysis

4 Min. Read
How to Define Your Target Market
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Market Analysis for a Business Plan

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
A lot of preparation goes into starting a business before you can open your doors to the public or launch your online store. One of your first steps should be to write a business plan . A business plan will serve as your roadmap when building your business.
Within your business plan, there’s an important section you should pay careful attention to: your market analysis. Your market analysis helps you understand your target market and how you can thrive within it.
Simply put, your market analysis shows that you’ve done your research. It also contributes to your marketing strategy by defining your target customer and researching their buying habits. Overall, a market analysis will yield invaluable data if you have limited knowledge about your market, the market has fierce competition, and if you require a business loan. In this guide, we'll explore how to conduct your own market analysis.
How to conduct a market analysis: A step-by-step guide
In your market analysis, you can expect to cover the following:
Industry outlook
Target market
Market value
Competition
Barriers to entry
Let’s dive into an in-depth look into each section:
Step 1: Define your objective
Before you begin your market analysis, it’s important to define your objective for writing a market analysis. Are you writing it for internal purposes or for external purposes?
If you were doing a market analysis for internal purposes, you might be brainstorming new products to launch or adjusting your marketing tactics. An example of an external purpose might be that you need a market analysis to get approved for a business loan .
The comprehensiveness of your market analysis will depend on your objective. If you’re preparing for a new product launch, you might focus more heavily on researching the competition. A market analysis for a loan approval would require heavy data and research into market size and growth, share potential, and pricing.
Step 2: Provide an industry outlook
An industry outlook is a general direction of where your industry is heading. Lenders want to know whether you’re targeting a growing industry or declining industry. For example, if you’re looking to sell VCRs in 2020, it’s unlikely that your business will succeed.
Starting your market analysis with an industry outlook offers a preliminary view of the market and what to expect in your market analysis. When writing this section, you'll want to include:
Market size
Are you chasing big markets or are you targeting very niche markets? If you’re targeting a niche market, are there enough customers to support your business and buy your product?
Product life cycle
If you develop a product, what will its life cycle look like? Lenders want an overview of how your product will come into fruition after it’s developed and launched. In this section, you can discuss your product’s:
Research and development
Projected growth
How do you see your company performing over time? Calculating your year-over-year growth will help you and lenders see how your business has grown thus far. Calculating your projected growth shows how your business will fare in future projected market conditions.
Step 3: Determine your target market
This section of your market analysis is dedicated to your potential customer. Who is your ideal target customer? How can you cater your product to serve them specifically?
Don’t make the mistake of wanting to sell your product to everybody. Your target customer should be specific. For example, if you’re selling mittens, you wouldn’t want to market to warmer climates like Hawaii. You should target customers who live in colder regions. The more nuanced your target market is, the more information you’ll have to inform your business and marketing strategy.
With that in mind, your target market section should include the following points:
Demographics
This is where you leave nothing to mystery about your ideal customer. You want to know every aspect of your customer so you can best serve them. Dedicate time to researching the following demographics:
Income level
Create a customer persona
Creating a customer persona can help you better understand your customer. It can be easier to market to a person than data on paper. You can give this persona a name, background, and job. Mold this persona into your target customer.
What are your customer’s pain points? How do these pain points influence how they buy products? What matters most to them? Why do they choose one brand over another?
Research and supporting material
Information without data are just claims. To add credibility to your market analysis, you need to include data. Some methods for collecting data include:
Target group surveys
Focus groups
Reading reviews
Feedback surveys
You can also consult resources online. For example, the U.S. Census Bureau can help you find demographics in calculating your market share. The U.S. Department of Commerce and the U.S. Small Business Administration also offer general data that can help you research your target industry.
Step 4: Calculate market value
You can use either top-down analysis or bottom-up analysis to calculate an estimate of your market value.
A top-down analysis tends to be the easier option of the two. It requires for you to calculate the entire market and then estimate how much of a share you expect your business to get. For example, let’s assume your target market consists of 100,000 people. If you’re optimistic and manage to get 1% of that market, you can expect to make 1,000 sales.
A bottom-up analysis is more data-driven and requires more research. You calculate the individual factors of your business and then estimate how high you can scale them to arrive at a projected market share. Some factors to consider when doing a bottom-up analysis include:
Where products are sold
Who your competition is
The price per unit
How many consumers you expect to reach
The average amount a customer would buy over time
While a bottom-up analysis requires more data than a top-down analysis, you can usually arrive at a more accurate calculation.
Step 5: Get to know your competition
Before you start a business, you need to research the level of competition within your market. Are there certain companies getting the lion’s share of the market? How can you position yourself to stand out from the competition?
There are two types of competitors that you should be aware of: direct competitors and indirect competitors.
Direct competitors are other businesses who sell the same product as you. If you and the company across town both sell apples, you are direct competitors.
An indirect competitor sells a different but similar product to yours. If that company across town sells oranges instead, they are an indirect competitor. Apples and oranges are different but they still target a similar market: people who eat fruits.
Also, here are some questions you want to answer when writing this section of your market analysis:
What are your competitor’s strengths?
What are your competitor’s weaknesses?
How can you cover your competitor’s weaknesses in your own business?
How can you solve the same problems better or differently than your competitors?
How can you leverage technology to better serve your customers?
How big of a threat are your competitors if you open your business?
Step 6: Identify your barriers
Writing a market analysis can help you identify some glaring barriers to starting your business. Researching these barriers will help you avoid any costly legal or business mistakes down the line. Some entry barriers to address in your marketing analysis include:
Technology: How rapid is technology advancing and can it render your product obsolete within the next five years?
Branding: You need to establish your brand identity to stand out in a saturated market.
Cost of entry: Startup costs, like renting a space and hiring employees, are expensive. Also, specialty equipment often comes with hefty price tags. (Consider researching equipment financing to help finance these purchases.)
Location: You need to secure a prime location if you’re opening a physical store.
Competition: A market with fierce competition can be a steep uphill battle (like attempting to go toe-to-toe with Apple or Amazon).
Step 7: Know the regulations
When starting a business, it’s your responsibility to research governmental and state business regulations within your market. Some regulations to keep in mind include (but aren’t limited to):
Employment and labor laws
Advertising
Environmental regulations
If you’re a newer entrepreneur and this is your first business, this part can be daunting so you might want to consult with a business attorney. A legal professional will help you identify the legal requirements specific to your business. You can also check online legal help sites like LegalZoom or Rocket Lawyer.
Tips when writing your market analysis
We wouldn’t be surprised if you feel overwhelmed by the sheer volume of information needed in a market analysis. Keep in mind, though, this research is key to launching a successful business. You don’t want to cut corners, but here are a few tips to help you out when writing your market analysis:
Use visual aids
Nobody likes 30 pages of nothing but text. Using visual aids can break up those text blocks, making your market analysis more visually appealing. When discussing statistics and metrics, charts and graphs will help you better communicate your data.
Include a summary
If you’ve ever read an article from an academic journal, you’ll notice that writers include an abstract that offers the reader a preview.
Use this same tactic when writing your market analysis. It will prime the reader of your market highlights before they dive into the hard data.
Get to the point
It’s better to keep your market analysis concise than to stuff it with fluff and repetition. You’ll want to present your data, analyze it, and then tie it back into how your business can thrive within your target market.
Revisit your market analysis regularly
Markets are always changing and it's important that your business changes with your target market. Revisiting your market analysis ensures that your business operations align with changing market conditions. The best businesses are the ones that can adapt.
Why should you write a market analysis?
Your market analysis helps you look at factors within your market to determine if it’s a good fit for your business model. A market analysis will help you:
1. Learn how to analyze the market need
Markets are always shifting and it’s a good idea to identify current and projected market conditions. These trends will help you understand the size of your market and whether there are paying customers waiting for you. Doing a market analysis helps you confirm that your target market is a lucrative market.
2. Learn about your customers
The best way to serve your customer is to understand them. A market analysis will examine your customer’s buying habits, pain points, and desires. This information will aid you in developing a business that addresses those points.
3. Get approved for a business loan
Starting a business, especially if it’s your first one, requires startup funding. A good first step is to apply for a business loan with your bank or other financial institution.
A thorough market analysis shows that you’re professional, prepared, and worth the investment from lenders. This preparation inspires confidence within the lender that you can build a business and repay the loan.
4. Beat the competition
Your research will offer valuable insight and certain advantages that the competition might not have. For example, thoroughly understanding your customer’s pain points and desires will help you develop a superior product or service than your competitors. If your business is already up and running, an updated market analysis can upgrade your marketing strategy or help you launch a new product.
Final thoughts
There is a saying that the first step to cutting down a tree is to sharpen an axe. In other words, preparation is the key to success. In business, preparation increases the chances that your business will succeed, even in a competitive market.
The market analysis section of your business plan separates the entrepreneurs who have done their homework from those who haven’t. Now that you’ve learned how to write a market analysis, it’s time for you to sharpen your axe and grow a successful business. And keep in mind, if you need help crafting your business plan, you can always turn to business plan software or a free template to help you stay organized.
This article originally appeared on JustBusiness, a subsidiary of NerdWallet.
On a similar note...


How to Write the Market Analysis Section of a Business Plan
Written by Dave Lavinsky

What is the Market Analysis in a Business Plan?
The market analysis section of your business plan is where you discuss the size of the market in which you’re competing and market trends that might affect your future potential such as economic, political, social and/or technological shifts.
This helps you and readers understand if your market is big enough to support your business’ growth, and whether future conditions will help or hurt your business. For example, stating that your market size is $56 billion, has been growing by 10% for the last 10 years, and that trends are expected to further increase the market size bodes well for your company’s success.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here
What Should a Market Analysis Include?
You’ll want to address these issues in your market analysis:
- Size of Industry – How big is the overall industry?
- Projected Growth Rate of Industry – Is the industry growing or shrinking? How fast?
- Target Market – Who are you targeting with this product or service?
- Competition – How many businesses are currently in the same industry?
Learn how to write the full market analysis below.
How to Write a Market Analysis
Here’s how to write the market analysis section of a business plan.
- Describe each industry that you are competing in or will be targeting.
- Identify direct competition, but don’t forget about indirect competition – this may include companies selling different products to the same potential customer segments.
- Highlight strengths and weaknesses for both direct and indirect competitors, along with how your company stacks up against them based on what makes your company uniquely positioned to succeed.
- Include specific data, statistics, graphs, or charts if possible to make the market analysis more convincing to investors or lenders.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
Industry overview.
In your industry overview, you will define the market in which you are competing (e.g., restaurant, medical devices, etc.).
You will then detail the sub-segment or niche of that market if applicable (e.g., within restaurants there are fast food restaurants, fine dining, etc.).
Next, you will describe the key characteristics of your industry. For example, discuss how big the market is in terms of units and revenues. Let the reader know if the market is growing or declining (and at what rate), and what key industry trends are facing your market.
Use third-party market research as much as possible to validate the discussion of your industry.
Here is a list of additional items you may analyze for a complete industry overview:
- An overview of the current state of the industry . How big is it, how much does it produce or sell? What are its key differentiators from competitors? What is its target customer base like – demographic information and psychographics? How has the industry performed over time (global, domestic)?
- Analyze the macro-economic factors impacting your industry . This includes items such as economic growth opportunities, inflation, exchange rates, interest rates, labor market trends, and technological improvements. You want to make sure that all of these are trending in a positive direction for you while also being realistic about them. For example, if the economy is in shambles you might want to wait before entering the particular market.
- Analyze the political factors impacting your industry . This is an often-overlooked section of any business plan, but it can be important depending on what type of company you are starting. If you’re in a highly regulated industry (such as medical devices), this is something that you’ll want to include.
- Analyze the social factors impacting your industry . This includes analyzing society’s interest in your product or service, historical trends in buying patterns in your industry, and any effects on the industry due to changes in culture. For example, if there is a growing counter-culture trend against big oil companies you might want to position yourself differently than a company in this industry.
- Analyze the technological factors impacting your industry . This includes analyzing new technologies being developed in software, hardware, or applications that can be used to improve your product or service. It also includes emerging consumer trends and will be highly dependent on your business type. In a technology-related venture, you would analyze how these changes are impacting consumers. For an educational-related venture, you would analyze how these changes are impacting students, teachers, and/or administrators.
For each of these items, you want to provide some detail about them including their current state as well as what external factors have played a role in the recent past. You can also include many other important factors if they apply to your business including demographic trends, legal issues, environmental concerns, and sustainability issues.
When you are done analyzing all of these factors, wrap it up by summing them up in a statement that includes your view on the future of the industry. This should be positive to attract investors, potential customers, and partners.
If you’re having trouble thinking about all of these factors then it might be helpful to first develop a SWOT analysis for your business.
Once you have an understanding of the market, you’ll need to think about how you will position yourself within that potential market.
Picking Your Niche
You want to think about how large your market is for this venture. You also want to consider whether you’d like to pick a niche within the overall industry or launch yourself into the mainstream.
If you have an innovative product it can be easier to enter the mainstream market – but at the same time, you might face some additional competition if there are similar products available.
You can choose to specialize in a niche market where you’ll face less competition – but might be able to sell your services at a higher price point (this could make it easier for you to get potential customers).
Of course, if your product or service is unique then there should be no competition. But, what happens if it isn’t unique? Will you be able to differentiate yourself enough to create a competitive advantage or edge?
If you are planning on entering the mainstream market, think about whether there are different sub-niches within your specific market. For example, within the technology industry, you can choose to specialize in laptops or smartphones or tablets, or other categories. While it will be more difficult to be unique in a mainstream market, you will still be able to focus on one type or category of products.
How Will You Stand Out?
Many companies are able to stand out – whether by offering a product that is unique or by marketing their products in a way that consumers notice. For example, Steve Jobs was able to take a business idea like the iPhone and make it into something that people talked about (while competitors struggled to play catch up).
You want your venture to stand out – whether with an innovative product or service or through marketing strategies. This might include a unique brand, name, or logo. It might also include packaging that stands out from competitors.
Write down how you will achieve this goal of standing out in the marketplace. If it’s a product, then what features do you have that other products don’t? If it’s a service, then what is it about this service that will make people want to use your company rather than your competition?
You also need to think about marketing. How are you going to promote yourself or sell your product or service? You’ll need a marketing plan for this – which might include writing copy, creating an advertisement, setting up a website, and several other activities. This should include a description of each of these strategies.
If you’re struggling with the details of any of these sections, it might be helpful to research what other companies in your market are doing and how they’ve been successful. You can use this business information to inform your own strategies and plans.
Relevant Market Size & Competition
In the second stage of your analysis, you must determine the size and competition in your specific market.
Target Market Section
Your company’s relevant market size is the amount of money it could make each year if it owned a complete market share.
It’s simple.
To begin, estimate how many consumers you expect to be interested in purchasing your products or services each year.
To generate a more precise estimate, enter the monetary amount these potential customers may be ready to spend on your goods or services each year.
The size of your market is the product of these two figures. Calculate this market value here so that your readers can see how big your market opportunity is (particularly if you are seeking debt or equity funding).
You’ll also want to include an analysis of your market conditions. Is this a growing or declining market? How fast is it growing (or declining)? What are the general trends in the market? How has your market shifted over time?
Include all of this information in your own business plan to give your readers a clear understanding of the market landscape you’re competing in.
The Competition
Next, you’ll need to create a comprehensive list of the competitors in your market. This competitive analysis includes:
- Direct Competitors – Companies that offer a similar product or service
- Indirect Competitors – Companies that sell products or services that are complementary to yours but not directly related
To show how large each competitor is, you can use metrics such as revenue, employees, number of locations, etc. If you have limited information about the company on hand then you may want to do some additional research or contact them directly for more information. You should also include their website so readers can learn more if they desire (along with social media profiles).
Once you complete this list, take a step back and try to determine how much market share each competitor has. You can use different methods to do this such as market research, surveys, or conduct focus groups or interviews with target customers.
You should also take into account the barriers to entry that exist in your market. What would it take for a new company to enter the market and start competing with you? This could be anything from capital requirements to licensing and permits.
When you have all of this information, you’ll want to create a table like the one below:
Once you have this data, you can start developing strategies to compete with the other companies which will be used again later to help you develop your marketing strategy and plan.
Writing a Market Analysis Tips
- Include an explanation of how you determined the size of the market and how much share competitors have.
- Include tables like the one above that show competitor size, barriers to entry, etc.
- Decide where you’re going to place this section in your business plan – before or after your SWOT analysis. You can use other sections as well such as your company summary or product/service description. Make sure you consider which information should come first for the reader to make the most sense.
- Brainstorm how you’re going to stand out in this competitive market.
Formatting the Market Analysis Section of Your Business Plan
Now that you understand the different components of the market analysis, let’s take a look at how you should structure this section in your business plan.
Your market analysis should be divided into two sections: the industry overview and market size & competition.
Each section should include detailed information about the topic and supporting evidence to back up your claims.
You’ll also want to make sure that all of your data is up-to-date. Be sure to include the date of the analysis in your business plan so readers know when it was conducted and if there have been any major changes since then.
In addition, you should also provide a short summary of what this section covers at the beginning of each paragraph or page. You can do this by using a title such as “Industry Overview” or another descriptive phrase that is easy to follow.
As with all sections in a business plan, make sure your market analysis is concise and includes only the most relevant information to keep your audience engaged until they reach your conclusion.
A strong market analysis can give your company a competitive edge over other businesses in its industry, which is why it’s essential to include this section in your business plan. By providing detailed information about the market you’re competing in, you can show your readers that you understand the industry and know how to capitalize on current and future trends.
Business Plan Market Analysis Examples
The following are examples of how to write the market analysis section of a business plan:
Business Plan Market Analysis Example #1 – Hosmer Sunglasses, a sunglasses manufacturer based in California
According to the Sunglass Association of America, the retail sales volume of Plano (non-prescription) sunglasses, clip-on sunglasses, and children’s sunglasses (hereinafter collectively referred to as “Sunwear”) totaled $2.9 billion last year. Premium-priced sunglasses are driving the Plano Sunwear market. Plano sunglasses priced at $100 or more accounted for more than 49% of all Sunwear sales among independent retail locations last year.
The Sunglass Association of America has projected that the dollar volume for retail sales of Plano Sunwear will grow 1.7% next year. Plano sunglass vendors are also bullish about sales in this year and beyond as a result of the growth of technology, particularly the growth of laser surgery and e-commerce.
Business Plan Market Analysis Example #2 – Nailed It!, a family-owned restaurant in Omaha, NE
According to the Nebraska Restaurant Association, last year total restaurant sales in Nebraska grew by 4.3%, reaching a record high of $2.8 billion. Sales at full-service restaurants were particularly strong, growing 7% over 2012 figures. This steady increase is being driven by population growth throughout the state. The Average Annual Growth Rate (AGR) since 2009 is 2.89%.
This fast growth has also encouraged the opening of new restaurants, with 3,035 operating statewide as of this year. The restaurant industry employs more than 41,000 workers in Nebraska and contributes nearly $3 billion to the state economy every year.
Nebraska’s population continues to increase – reaching 1.9 million in 2012, a 1.5% growth rate. In addition to population, the state has experienced record low unemployment every year since 2009 – with an average of 4.7% in 2013 and 2014.
Business Plan Market Analysis Example #3 – American Insurance Company (AIC), a chain of insurance agencies in Maine
American Insurance Company (AIC) offers high-quality insurance at low prices through its chain of retail outlets in the state of Maine. Since its inception, AIC has created an extensive network of agents and brokers across the country with expanding online, call center and retail business operations.
AIC is entering a market that will more than double in size over the next 50 years according to some industry forecasts. The insurance industry is enjoying low inflation rates, steady income growth, and improving standards of living for most Americans during what has been a difficult period for much of American business. This makes this a good time to enter the insurance industry as it enjoys higher margins because customers are purchasing more coverage due to increased costs from medical care and higher liability claims.
American Insurance Company provides affordable homeowners, auto, and business insurance through high-quality fulfillment centers across America that have earned a reputation for top-notch customer service.
AIC will face significant competition from both direct and indirect competitors. The indirect competition will come from a variety of businesses, including banks, other insurance companies, and online retailers. The direct competition will come from other well-funded start-ups as well as incumbents in the industry. AIC’s competitive advantages include its low prices, high quality, and excellent customer service.
AIC plans to grow at a rate that is above average for the industry as a whole. The company has identified a market that is expected to grow by more than 100% in the next decade. This growth is due to several factors: the increase in the number of two-income households, the aging population, and the impending retirement of many baby boomers will lead to an increase in the number of people who are purchasing insurance.
AIC projects revenues of $20M in year one, which is equivalent to 100% growth over the previous year. AIC forecasts revenue growth of 40%-60% each year on average for 10 years. After that, revenue growth is expected to slow down significantly due to market saturation.
The following table illustrates these projections:
Competitive Landscape
Direct Competition: P&C Insurance Market Leaders
Indirect Competition: Banks, Other Insurance Companies, Retailers
Market Analysis Conclusion
When writing the market analysis section, it is important to provide specific data and forecasts about the industry that your company operates in. This information can help make your business plan more convincing to potential investors.
If it’s helpful, you should also discuss how your company stacks up against its competitors based on what makes it unique. In addition, you can identify any strengths or weaknesses that your company has compared to its competitors.
Based on this data, provide projections for how much revenue your company expects to generate over the next few years. Providing this information early on in the business plan will help convince investors that you know what you are talking about and your company is well-positioned to succeed.
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Other Resources for Writing Your Business Plan
How to Write a Great Business Plan Executive Summary How to Expertly Write the Company Description in Your Business Plan The Customer Analysis Section of Your Business Plan Completing the Competitive Analysis Section of Your Business Plan The Management Team Section of Your Business Plan Financial Assumptions and Your Business Plan How to Create Financial Projections for Your Business Plan Everything You Need to Know about the Business Plan Appendix Best Business Plan Software Business Plan Conclusion: Summary & Recap
Other Helpful Business Planning Articles & Templates


500+ business plans and financial models
How to Conduct an Industry Analysis
- March 21, 2024
- Business Plan , How to Write

An industry analysis is a fundamental component of any business plan, offering insights into the market dynamics, competitive landscape , and future market trends . This analysis helps businesses understand their industry’s environment, make informed strategic decisions, and identify potential opportunities and threats.
This guide will walk you through the steps of conducting a thorough industry analysis, using examples to illustrate key points.
Identify Your Industry
Before diving into the analysis, it’s crucial to clearly identify and define your industry. This involves outlining the scope in terms of products, services, and geographic reach.
Understanding the industry’s value chain and how your business fits within this ecosystem is essential. Consider the broader market forces at play, the typical customer base, and the regulatory landscape that shapes your industry’s boundaries.
- Example for a Hair Salon : If you’re opening a hair salon, your industry encompasses beauty and personal care services focused on hair treatment and styling.
Gather Information
The foundation of a solid industry analysis is robust data collection.
Utilize a variety of sources to gather information about your industry, including industry reports online, government publications, academic journals, and news articles. Attend industry conferences or trade shows and engage with other professionals on social media or industry forums to gain firsthand insights.
- Example for a Hair Salon : For a hair salon, look into beauty industry trends, salon service pricing strategies , and consumer spending habits in personal care services.
Analyze Market Trends
Identifying and understanding current market trends that affect your industry is vital.
Look for patterns in technological advancements, consumer behavior changes, regulatory developments, and economic factors. Projecting these trends into the future can help predict shifts in the industry landscape, allowing your business to adapt and innovate proactively.
- Example for a Hair Salon : An increasing preference for organic and eco-friendly hair care products is a significant trend in the hair salon industry.
Assess the Competitive Landscape
Analyze who your direct and indirect competitors are, what strategies they employ, their strengths and weaknesses, and their market positioning.
Tools like SWOT analyses analysis can help assess the competitive intensity and the profitability potential within the industry. This analysis also identifies potential barriers to entry and the threat of substitute products or services.
- Example for a Hair Salon : Examine other salons in your area, noting services offered, pricing levels, customer reviews, and marketing tactics.
Determine Market Entry Barriers
Barriers to entry can vary significantly across industries and affect your strategy for market entry and growth.
[link to Market Entry Barriers]
High capital requirements, strict regulatory standards, established brand loyalty, and access to distribution channels are common barriers. Identifying these early on helps in formulating strategies to overcome them, whether through innovation, strategic partnerships, or niche targeting.
- Example for a Hair Salon : For a hair salon, barriers might include the cost of acquiring a prime location, compliance with health and safety regulations, and establishing a brand in a competitive market.
Predict Future Industry Changes
Leveraging the information gathered, anticipate potential changes in the industry. This could involve innovations that disrupt traditional business models, regulatory changes, or shifts in consumer preferences. Understanding these potential changes allows businesses to be agile and adapt their strategies accordingly.
- Example for a Hair Salon : Anticipate how the growing use of online booking platforms and social media marketing could transform customer engagement strategies in the hair salon industry.
Identify Opportunities and Threats
Synthesize your findings to pinpoint opportunities for your business to exploit and threats you may need to mitigate. This SWOT analysis will be crucial for your strategic planning.
[link to SWOT]
- Example for a Hair Salon : Opportunities might include a gap in the market for salons specializing in sustainable practices. A threat could be the rising cost of eco-friendly products.
Privacy Overview
What Is an Industry Analysis and Trends Business Plan?
An industry analysis and trends business plan is a component of a business plan that provides a comprehensive insight into industry conditions and trends. 3 min read updated on February 01, 2023
An industry analysis and trends business plan is a component of a business plan that provides a comprehensive insight into industry conditions and trends that can impact a company's success and growth. A thorough analysis of your industry and its trends can give you and other people a clearer idea of the feasibility and relevance of your business idea or goals.
Elements of a Business Plan
There are many different types of business plans. When you are creating your business plan, the information you choose to include will depend on your audience and personal preferences, as well as the questions you wish to answer and problems you seek to solve. While business plans may vary greatly, most of them contain the following elements:
- Executive summary
- Business description
- Analysis of business environment analysis
- Industry analysis
- Market analysis
- Competitive analysis
- Marketing plan
- Management plan
- Operations plan
- Financial projections
- What Is an Industry Analysis?
An industry analysis enables you to gain a better understanding of the industry and market in which you will be conducting business. By conducting an industry analysis before you start writing your business plan , you will be able to:
- Identify industry trends, such as potentially problematic aspects of the industry
- Identify trends and opportunities in products and services
- Calculate capital requirements
- Determine business risks and find ways to reduce them
An industry analysis must be specific to the industry in which you are conducting or are planning to conduct business. With the information you obtain from the analysis, you can devise a long-term strategy to mitigate risks and take full advantage of growth opportunities.
It is important not to confuse an industry analysis with a competitor or market analysis. An industry analysis seeks to describe the products or services offered in a specific industry and the boundaries of the marketplace in relation to economic, political, and regulatory issues. In other words, it defines the scope of the marketplace. A market analysis , on the other hand, helps you determine whether or not a market within your industry will be profitable for your products or services.
Conducting an Industry Analysis
The most widely used method for evaluating any industry was devised by Michael E. Porter from Harvard University. This method can help you create an effective strategy for competing in your industry. According to Porter, all industries and markets are influenced by five forces, which include:
- Ease of entry — Companies that are already operating in an industry will enjoy a competitive advantage over newcomers. However, their profits will be reduced unless they find a way to slow down or block the new entries. As for new businesses, they will face a variety of barriers, including government regulations, patents and copyrights, and customer loyalty.
- Suppliers' power — Suppliers of materials, products, or services can have a significant impact on a business' ability to compete. In the event that there are few suppliers offering the products or materials or few alternative products, the suppliers have the power to dictate quantities, prices, and delivery times for companies that have no choice but to buy from them.
- Buyers' power — In an industry where buyers can choose from many competing products, consumers will have strong bargaining power. This can affect the ability of a company to price its products or services without being afraid of losing customers.
- Availability of alternative products — In the situation where two businesses with similar products are competing within an industry, both of them will benefit as their marketing efforts will generally increase demand for their products. However, their market share will be reduced if there is another company selling a different kind of products that can serve as a substitute for theirs.
- Competitive rivalry — Competitive rivalry takes into account the number of competitors present in a particular industry, as well as their relative strength. In an industry where many companies are selling similar products, there is little opportunity for one company to control consumers' or suppliers' tendency to go elsewhere.
There are many free industry analysis tools and resources available to business owners who are preparing to create a business plan, such as:
- Securities and Exchange Commission
- U.S. Census Bureau
- Hoover's Online
- Thomas Register
- Library of Congress Legislative Information
- Websites of trade associations and companies
If you need help creating an industry analysis and trends business plan, you can post your legal need on UpCounsel's marketplace. UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees
Content Approved by UpCounsel
- Business Plan Outline: Everything You Need To Know
- How to Make a Business Plan Format
- Parts of Business Plan and Definition
- Business Description Outline
- Market Analysis: Everything You Need To Know
- Service Business Plan
- IT Company Business Plan
- Clothing Boutique Business Plan Outline
- Business Plan for Existing Company
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
How to Write The Industry Section of a Business Plan
Writing a Business Plan: Section 2
Susan Ward wrote about small businesses for The Balance for 18 years. She has run an IT consulting firm and designed and presented courses on how to promote small businesses.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SusanWardLaptop2crop1-57aa62eb5f9b58974a12bac9.jpg)
Geber86 / Getty Images
When writing a business plan, the Industry section is best organized as two parts: an overview of the industry and a summary of your business's position within the overall industry.
Before writing this section of the business plan, use these questions to focus your research:
- What is the size of your industry?
- What sectors does this industry include?
- Who are the major players in this industry?
- What are the markets and customers for this industry?
- What are the industry's estimated sales this year? Last year? The year before?
- What national and economic trends have affected this industry and how?
- What national and economic trends might affect it in the future and how?
- What is the long-term outlook for this industry?
- What products or services will your business be selling?
- What is your Unique Selling Proposition? (What is it about your business that makes it unique and sets it apart from competitors?)
- What are the barriers to entry in your industry?
- How will you overcome these barriers?
- Who are your competitors?
- What is the market share of your competitors?
- What is your business's competitive advantage (i.e., your market niche or estimated market share)?
- What is your target market?
- How are you protecting your product or process (i.e., patents, copyrights, trademarks, franchise rights that you either hold or plan to acquire)?
Once you have all this information, you'll write this section of the business plan in the form of several short paragraphs. (Remember, each of these paragraphs is a summary, not a detailed point-by-point explanation.) Use appropriate headings for each paragraph.
Finding Information on Your Industry
But where do you find the information that you need for writing the Industry Overview section of your business plan?
United States Research
In the United States, you may want to start your research by reviewing information from the U.S. Census Bureau, Industry Statistics Portal. This site provides data for selected industries separated into categories using the North American Industry Classification System (NAICS). The Bureau of Labor Statistics also offers a large selection of information grouped by NAICS industry.
There are also other sources of information—some free and some paid sources—including IBIS World, Select USA, and the U.S. the Department of Commerce Bureau of Economic Analysis.
Canadian Research
When you're writing a business plan and looking for information on Canadian industries, Industry Canada is your logical first stop. Their Find Statistics by Industry page lets you see key economic indicators for different sectors of the Canadian economy, access industry profiles, and analysis and research small businesses in Canada generally.
Another primary source for industry and economic information that you can easily access online when you're writing a business plan is Statistics Canada. From this homepage you can find a wealth of free statistical information; use this page, to search for Statistics Canada publications back to 1980.
There are also provincial statistics websites where you'll be able to find more economic, social, and demographic statistics relating to your industry and the business environment.
The Canada Business Service Centres located in each province also offer excellent collections of resources online, and telephone and email information services. You'll find a list of links to the Canada Business Service Centre in each province in my Provincial Programs and Services Resources.
The business sections of national newspapers and business magazines will also be helpful; these often carry features on the past and future business trends.
And don't forget your local sources of business information when you're researching your business plans, such as your Economic Development Centre, Chamber of Commerce, or Women's Enterprise Centre, or the business section of the local library.
Doing Business Plan Research
If your business is related to manufacturing when you're writing a business plan begin by determining the NAICS of your particular industry, and the sector and sub-sector if applicable. It will make it easier for you to find statistical information relating to your industry. If your business is a service, begin with Industry Canada's service industry profiles.
Refer to the list of questions earlier in this article on how to write a business plan as a research guide. Whenever you find a piece of information that you want:
- Check its date and determine whether or not the information is current enough to be valid;
- Write down the date and source of the information, as you'll need to cite your information sources in the business plan.
When you're writing a business plan, you want your research information to be as up-to-date as possible. After all, there's no point in starting a business if you don't want it to succeed.
Analyze your market like a pro with this step-by-step guide + insider tips
Don’t fall into the trap of assuming that you already know enough about your market.
No matter how fantastic your product or service is, your business cannot succeed without sufficient market demand .
You need a clear understanding of who will buy your product or service and why .
You want to know if there is a clear market gap and a market large enough to support the survival and growth of your business.
Industry research and market analysis will help make sure that you are on the right track .
It takes time , but it is time well spent . Thank me later.
WHAT is Market Analysis?
The Market Analysis section of a business plan is also sometimes called:
- Market Demand, Market Trends, Target Market, The Market
- Industry Analysis & Trends, Industry & Market Analysis, Industry and Market Research
WHY Should You Do Market Analysis?
First and foremost, you need to demonstrate beyond any reasonable doubt that there is real need and sufficient demand for your product or service in the market, now and going forward.
- What makes you think that people will buy your products or services?
- Can you prove it?
Your due diligence on the market opportunity and validating the problem and solution described in the Product and Service section of your business plan are crucial for the success of your venture.
Also, no company operates in a vacuum. Every business is part of a larger overall industry, the forces that affect your industry as a whole will inevitably affect your business as well.
Evaluating your industry and market increases your own knowledge of the factors that contribute to your company’s success and shows the readers of your business plan that you understand the external business conditions.
External Support
In fact, if you are seeking outside financing, potential backers will most definitely be interested in industry and market conditions and trends.
You will make a positive impression and have a better chance of getting their support if you show market analysis that strengthens your business case, combining relevant and reliable data with sound judgement.
Let’s break down how to do exactly that, step by step:
HOW To Do Market Analysis: Step-by-Step
So, let’s break up how market analysis is done into three steps:
- Industry: the total market
- Target Market: specific segments of the industry that you will target
- Target Customer: characteristics of the customers that you will focus on
Step 1: Industry Analysis
How do you define an industry.
For example, the fashion industry includes fabric suppliers, designers, companies making finished clothing, distributors, sales representatives, trade publications, retail outlets online and on the high street.
How Do You Analyze an Industry?
Briefly describe your industry, including the following considerations:
1.1. Economic Conditions
Outline the current and projected economic conditions that influence the industry your business operates in, such as:
- Official economic indicators like GDP or inflation
- Labour market statistics
- Foreign trade (e.g., import and export statistics)
1.2. Industry Description
Highlight the distinct characteristic of your industry, including:
- Market leaders , major customer groups and customer loyalty
- Supply chain and distribution channels
- Profitability (e.g., pricing, cost structure, margins), financials
- Key success factors
- Barriers to entry preventing new companies from competing in the industry
1.3. Industry Size and Growth
Estimate the size of your industry and analyze how industry growth affects your company’s prospects:
- Current size (e.g., revenues, units sold, employment)
- Historic and projected industry growth rate (low/medium/high)
- Life-cycle stage /maturity (emerging/expanding/ mature/declining)
1.4. Industry Trends
- Industry Trends: Describe the key industry trends and evaluate the potential impact of PESTEL (political / economic / social / technological / environmental / legal) changes on the industry, including the level of sensitivity to:
- Seasonality
- Economic cycles
- Government regulation (e.g. environment, health and safety, international trade, performance standards, licensing/certification/fair trade/deregulation, product claims) Technological change
- Global Trends: Outline global trends affecting your industry
- Identify global industry concerns and opportunities
- International markets that could help to grow your business
- Strategic Opportunity: Highlight the strategic opportunities that exist in your industry
Step 2: Target Customer Identification
Who is a target customer.
One business can have–and often does have–more than one target customer group.
The success of your business depends on your ability to meet the needs and wants of your customers. So, in a business plan, your aim is to assure readers that:
- Your customers actually exist
- You know exactly who they are and what they want
- They are ready for what you have to offer and are likely to actually buy
How Do You Identify an Ideal Target Customer?
2.1. target customer.
- Identify the customer, remembering that the decision-maker who makes the purchase can be a different person or entity than the end-user.
2.2. Demographics
- For consumers ( demographics ): Age, gender, income, occupation, education, family status, home ownership, lifestyle (e.g., work and leisure activities)
- For businesses ( firmographic ): Industry, sector, years in business, ownership, size (e.g., sales, revenues, budget, employees, branches, sq footage)
2.3. Geographic Location
- Where are your customers based, where do they buy their products/services and where do they actually use them
2.4 Purchasing Patterns
- Identify customer behaviors, i.e., what actions they take
- how frequently
- and how quickly they buy
2.5. Psychographics
- Identify customer attitudes, i.e., how they think or feel
- Urgency, price, quality, reputation, image, convenience, availability, features, brand, customer service, return policy, sustainability, eco-friendliness, supporting local business
- Necessity/luxury, high involvement bit ticket item / low involvement consumable
Step 3: Target Market Analysis
What is a target market.
Target market, or 'target audience', is a group of people that a business has identified as the most likely to purchase its offering, defined by demographic, psychographic, geographic and other characteristics. Target market may be broken down to target customers to customize marketing efforts.
How Do You Analyze a Target Market?
So, how many people are likely to become your customers?
To get an answer to this questions, narrow the industry into your target market with a manageable size, and identify its key characteristics, size and trends:
3.1. Target Market Description
Define your target market by:
- Type: B2C, B2B, government, non-profits
- Geographic reach: Specify the geographic location and reach of your target market

3.2. Market Size and Share
Estimate how large is the market for your product or service (e.g., number of customers, annual purchases in sales units and $ revenues). Explain the logic behind your calculation:
- TAM (Total Available/Addressable/Attainable Market) is the total maximum demand for a product or service that could theoretically be generated by selling to everyone in the world who could possibly buy from you, regardless of competition and any other considerations and restrictions.
- SAM (Serviceable Available Market) is the portion of the TAM that you could potentially address in a specific market. For example, if your product/service is only available in one country or language.
- SOM (Service Obtainable Market / Share of Market) is the share of the SAM that you can realistically carve out for your product or service. This the target market that you will be going after and can reasonably expect to convert into a customer base.
3.3. Market Trends
Illustrate the most important themes, changes and developments happening in your market. Explain the reasons behind these trends and how they will favor your business.
3.4. Demand Growth Opportunity
Estimate future demand for your offering by translating past, current and future market demand trends and drivers into forecasts:
- Historic growth: Check how your target market has grown in the past.
- Drivers past: Identify what has been driving that growth in the past.
- Drivers future: Assess whether there will be any change in influence of these and other drivers in the future.
How Big Should My Target Market Be?
Well, if the market opportunity is small, it will limit how big and successful your business can become. In fact, it may even be too small to support a successful business at all.
On the other hand, many businesses make the mistake of trying to appeal to too many target markets, which also limits their success by distracting their focus.
What If My Stats Look Bad?
Large and growing market suggests promising demand for your offering now and into the future. Nevertheless, your business can still thrive in a smaller or contracting market.
Instead of hiding from unfavorable stats, acknowledge that you are swimming against the tide and devise strategies to cope with whatever lies ahead.
Step 4: Industry and Market Analysis Research
The market analysis section of your business plan should illustrate your own industry and market knowledge as well as the key findings and conclusions from your research.
Back up your findings with external research sources (= secondary research) and results of internal market research and testing (= primary research).
What is Primary and Secondary Market Research?
Yes, there are two main types of market research – primary and secondary – and you should do both to adequately cover the market analysis section of your business plan:
- Primary market research is original data you gather yourself, for example in the form of active fieldwork collecting specific information in your market.
- Secondary market research involves collating information from existing data, which has been researched and shared by reliable outside sources . This is essentially passive desk research of information already published .
Unless you are working for a corporation, this exercise is not about your ability to do professional-level market research.
Instead, you just need to demonstrate fundamental understanding of your business environment and where you fit in within the market and broader industry.
Why Do You Need To Do Primary & Secondary Market Research?
There are countless ways you could go collecting industry and market research data, depending on the type of your business, what your business plan is for, and what your needs, resources and circumstances are.
For tried and tested tips on how to properly conduct your market research, read the next section of this guide that is dedicated to primary and secondary market research methods.
In any case, tell the reader how you carried out your market research. Prove what the facts are and where you got your data. Be as specific as possible. Provide statistics, numbers, and sources.
When doing secondary research, always make sure that all stats, facts and figures are from reputable sources and properly referenced in both the main text and the Appendix of your business plan. This gives more credibility to your business case as the reader has more confidence in the information provided.
Go to the Primary and Secondary Market Research post for my best tips on industry, market and competitor research.
7 TOP TIPS For Writing Market Analysis
1. realistic projections.
Above all, make sure that you are realistic in your projections about how your product or service is going to be accepted in the market, otherwise you are going to seriously undermine the credibility of your entire business case.
2. Laser Focus
Discuss only characteristic of your target market and customers that are observable, factual and meaningful, i.e. directly relate to your customers’ decision to purchase.
Always relate the data back to your business. Market statistics are meaningless until you explain where and how your company fits in.
For example, as you write about the market gap and the needs of your target customers, highlight how you are uniquely positioned to fill them.
In other words, your goal is to:
- Present your data
- Analyze the data
- Tie the data back to how your business can thrive within your target market
3. Target Audience
On a similar note, tailor the market analysis to your target audience and the specific purpose at hand.
For example, if your business plan is for internal use, you may not have to go into as much detail about the market as you would have for external financiers, since your team is likely already very familiar with the business environment your company operates in.
4. Story Time
Make sure that there is a compelling storyline and logical flow to the market information presented.
The saying “a picture is worth a thousand words” certainly applies here. Industry and market statistics are easier to understand and more impactful if presented as a chart or graph.
6. Information Overload
Keep your market analysis concise by only including pertinent information. No fluff, no repetition, no drowning the reader in a sea of redundant facts.
While you should not assume that the reader knows anything about your market, do not elaborate on unnecessary basic facts either.
Do not overload the reader in the main body of the business plan. Move everything that is not essential to telling the story into the Appendix. For example, summarize the results of market testing survey in the main body of the business plan document, but move the list of the actual survey questions into the appendix.
7. Marketing Plan
Note that market analysis and marketing plan are two different things, with two distinct chapters in a business plan.
As the name suggests, market analysis examines where you fit in within your desired industry and market. As you work thorugh this section, jot down your ideas for the marketing and strategy section of your business plan.
Final Thoughts
Remember that the very act of doing the research and analysis is a great opportunity to learn things that affect your business that you did not know before, so take your time doing the work.
Related Questions
What is the purpose of industry & market research and analysis.
The purpose of industry and market research and analysis is to qualitatively and quantitatively assess the environment of a business and to confirm that the market opportunity is sufficient for sustainable success of that business.
Why are Industry & Market Research and Analysis IMPORTANT?
Industry and market research and analysis are important because they allow you to gain knowledge of the industry, the target market you are planning to sell to, and your competition, so you can make informed strategic decisions on how to make your business succeed.
How Can Industry & Market Research and Analysis BENEFIT a Business?
Industry and market research and analysis benefit a business by uncovering opportunities and threats within its environment, including attainable market size, ideal target customers, competition and any potential difficulties on the company’s journey to success.
Sign up for our Newsletter
Get more articles just like this straight into your mailbox.
Related Posts
Recent Posts
Industry Analysis – Definition, Types, Examples & How-to Guide
Studying the market trends and the competition level is important for businesses because it helps them to lay out their future strategies. Therefore, they use various tools and methods to achieve their goals. Industry analysis is the same process. Today, we’ll discuss industry analysis, its types, examples, and guide.
Table of Contents
What is Industry Analysis?
Industry analysis is a market evaluation tool that businesses and companies use to comprehend and analyze the degree of competition in a certain industry. It helps you to understand the market position of the industry. Like the external factors impacting the industry, credit system, technological changes and how shaping the future, other competitive developing industries, competition level within the industry, and statistics of supply and demand.
Industry analysis helps an entrepreneur or a startup company to comprehend the position of a business relevant to the other competitive businesses in the industry. Most importantly, it helps you to recognize the upcoming threats and opportunities and how you can handle them with your strong points. The only way to survive in today’s business environment is to distinguish yourself from the competitors within the industry.
Types of Industry Analysis
Businesses and companies use three main tools and methods to perform industry analysis, and they’re as follows;
Competitive Force Model (Porter’s Five Forces)
Michael Porter introduced this model in the 1980s and it goes by the name of Porter’s 5 Forces. It analyzes the five forces impacting the industry. They are as follows;
- The intensity of Industry Rivals. The businesses operating in the same industry and their market share makes them industry rivals. Some of the factors that make the competition intense are; increasing fixed cost, lower differentiation, and high exit cost.
- The threat of Potential Entrants. The entrance of the new business in the industry makes the business environment competitive. If the entrance is easier, then it makes the business environment risky. If the entrance is difficult, then they could enjoy benefits for a long time.
- Bargaining Power of Supplier. If a business depends on the supplies of suppliers, then they would have a significant influence over your businesses. It could directly impact the price and quality of your product.
- Bargaining Power of Buyer. Here the customers have more negotiating power over the business. They would demand discounts, better quality, and economical price. It usually happens when there are more competitors in the industry.
- Threats of Substitute Products. It’s when competitive businesses are offering similar substitute products of the other industry. A business usually has to face competitors from various industries and they impact your revenue stream. However, the substitute’s products are of two types; same product features with the higher price and same product features with lower price.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis comprises strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, and its analysis studies the impact on the business. It further consists of two parts;
- Internal Factors. The strengths and weaknesses fall under the category of internal factors. They exist within any business and continue to play their role.
- External Factors. The opportunities and threats are the external factors. They tell us the impact of potential happenings and how the company should react. Now it depends on the management whether it has the ability to exploit the opportunities and ignore threats.
PESTLE Analysis
PESTLE analysis comprises six macro-environmental factors like political, economical, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors.
- Political. Political factors mean government regulations, trade policies, tariffs, and the country’s overall stable environment.
- Economical. Economical factors include revenue, GDP, net income, import and exports, taxation, unemployment, growth rate, interest rate, and many other factors.
- Social. The social factor comprises fashion, trends, shopping, attitude and behavior, demography, healthy standards, and cultures.
- Technological. Technological factors consist of research and development, latest innovation and creativity, internet, and digital tech trends.
- Legal. Legal factors comprise labor laws, regulations, minimum wage, employment contracts, paychecks, leaves, and other issues.
- Environmental. The environmental factor comprises environmental issues like deforestation, pollution, carbon emission, soil degradation, and others.
Reasons to Perform an Industry Analysis
Industry analysis allows you to have an insight into the competitive business environment. The weaknesses of your competitors would be your strong suits. You can integrate such information to make the marketing plan to grow your business.
The result of industry analysis provides you an insight into the future growth of your business. If the report tells you upcoming threats, then you can take preventive measures to avoid them.
The analysis confirms and ensures the credibility of your business, and it would help you attract investors. It means that you’re familiar with competitors and knows what your customers want.
How to Perform Industry Analysis Effectively
Review available documented/reports.
You should take some time to find and study already published reports relevant to your industry. You would probably find a well-detailed report, and studying it would answer your questions. It doesn’t mean that you should completely rely on such published reports.
Therefore, you should choose the most report of your industry. It’s because trends and statistics change over time. If you rely on the old report, it won’t give you conclusive results.
Carefully Choose the Industry You Analyze
You must select the most relevant industry for your business. It’s because every industry has got many sub-categories. For instance, a chemical industry would have sub-categories of pesticides, organic, inorganic, and so on.
Come up with the Supply and Demand of Industry
Supply and demand play a significant role in controlling the market. You should study the past trends and product and product scenarios, and the findings would help you to predict the future.
Know Your Competitors
You should consider studying your competitors and their expectations and plans from the market. Porter’s 5 forces model would help you in this regard.
Follow Recent Developments in the Industry
Most importantly, you should study the macro-environmental factors that could impact your industry. Like the technological development, the latest tech trends, and technology innovation would impact many businesses worldwide.
Focus on dynamics of the Industry
The industry analysis should focus on the particular industry in question and understand the various dynamics of the industry. It should be direct, to the point, and in-depth. For instance, if your focus industry is aluminum, then you should be aware of the per capita consumption within the industry along with production and total consumption.
Examples and Templates of Industry Analysis
If you want to study the industry analysis of other businesses relevant to the industry as an example, it’s because it helps business owners to understand the position of their business. It answers them that how they can get a competitive edge over competitors.
- Industry Analysis Example, Templates, and Reports
Advantages of Industry Analysis
- It helps you to touch the unexplored opportunities
- It helps startup companies to know the position of their business relevant to the competitors
- Its focus is to point out the opportunities and threats
- It helps you to find out those points that could provide you the best results
- It helps you to develop a competitive strategy that would defend you in the competition
- It helps you to evaluate the profitability of the relevant industries
Disadvantages of Industry Analysis
- Misinterpretation of the statistics and data could lead you to make the wrong decision
- It’s a one-sided approach and it doesn’t guarantee success
- If inflation decreases the sale and company’s revenue stream, it would badly impact the report
- Season factors usually have a good and bad impact on the business, if the interpreter doesn’t consider these factors, it would impact the conclusions.
About The Author
Ahsan Ali Shaw
Industry Analysis
What is an industry analysis.
An industry analysis is a marketing process that provides statistics about the market potential of your business products and services. This section of your plan needs to have specific information about the current state of the industry, and its target markets. An industry analysis may contain reference materials such as spreadsheets, pie charts, and bar graphs in order to represent the data.
Navigation:
Step-by-step checklist.
- Library Business Research Resources
- Government Websites, Including Labour Market Information Sources
Identify your industry and provide a brief overview. You may need to explore your industry on a local, regional, provincial, national, and/or global level. Be sure to define relevant industry codes. Provide statistics and historical data about the nature of the industry and growth potential for your business, based on economic factors and conditions.
Summarize the nature of the industry. Include specific information about growth patterns, fluctuations related to the economy, and income projections. Be sure to document recent developments, news, and innovations. Also, discuss marketing strategies, and the industry's prevalent operational and management trends.
Provide a forecast for your industry. Compile economic data and industry predictions at different time intervals (5, 10, 20 years). Be sure to cite sources. Note: the type and size of the industry will determine how much information you will be able to find about a particular industry. Define if it is new and emerging, growing, maturing or declining.
Identify government regulations that affect the industry. Include any recent laws pertaining to your industry, and any licenses or authorizations you would need to conduct business in your target market. This section may include information about fees and costs involved.
Explain your unique position within the industry. Once you have completed your Competitive Analysis (in the next section) you can list the leading companies in the industry, and compile an overview of data of your direct and indirect competition. This will help you communicate your unique value proposition.
List potential limitations and risks. Write about factors that might negatively impact your business and what you foresee in the short-term and long-term future. Outline what you know about the driving forces: new regulations, technology, globalization, competitors, changing customer needs.
Talk to people! Go to tradeshows, do cold calls, talk to people in relevant associations and go to business events.
Tip: How to generate keywords to search databases
Before you access the resources and databases below, it is best practice to consider the key words you can use as search terms to find information about your industry. Follow the steps below:
- Pinpoint the main words/phrases that describe your industry. (i.e. "bar")
- Brainstorm several alternative words/phrases that will bring you additional search results. These may be direct synonyms, or tangentially related. (i.e. "pub," "nightclub," "drinking place," "tavern," "restaurant.")
Tip: How to use NAICS codes
At the start of your research, it may not be clear what specific industry you should be examining. A good strategy is to find out if your business idea is classified in an industrial classification system. These systems organize industries by assigning them a numeric code. The most commonly used system is the North American Industry Classification System (NAICS). Once you know your Industry Classification Code you can use this number to :
- Find industry-specific statistics on government websites or in library databases
- Generate lists of competitors in company directories
Another common classification system is the Standard Industry Code (SIC). NAICS have most replaced the SIC, but the SIC is still used by some commercial databases. Finding and using these classification systems to effectively search can be tricky, so don't hesitate to ask a librarian for help.
You can keyword search for your industry NAICS code here:
Search or browse all NAICS or SIC codes on the NAICS Association website . Some NAICS codes are different in Canada — you can search by keyword or browse Canadian NAICS codes at Statistics Canada or Canadian Industry Statistics. To search for a SIC code using a NAICS code and vice versa, use the NAICS & SIC Crosswalks.
For more information about planning your industry research, including identifying your industry codes, check out the video tutorial for Module 3: Planning Your Industry Research .
Don't forget to take a look at our Industry Guides for detailed industry-specific market research resources!
Library Business Research Resources:
Business resources at academic libraries .
Colleges and Universities with business programs will have useful business collections you may be able to get access to through their academic library. Often these academic libraries can provide the general public with access to their collections, which include electronic resources like databases and e-books. For example, they could have alumni or community cards, and can provide temporary "guest" passes in certain situations. Contact your local college or university library to see what they can provide. Please note: you probably will not get access to their electronic resources with remote access.
UBC Library Business Databases
How to access: If you are a UBC student, staff, faculty or in-person library visitor you may have access to business databases through the David Lam Management Research Library and Canaccord Learning Commons through the links below.
Full Listing By Title or Full Listing By Subject
There are two different ways to identify databases: Use "by title" if you already know the name; otherwise you can search the list "by subject" to find starting places for undertaking market research, finding articles or researching companies. To learn more about how you can access library resources if you are a community user or temporary visitor, check out the UBC Library Community Users & Visitors Guide . Community users and temporary visitors may have additional access restrictions to specific databases because of license agreements.
Discovering where you can access the information you need to complete your research can be tricky. Below, we have a few examples of potential sources that collect the type of information you will need.
Ibis World Industry Reports
Business Source Complete
Canadian Business and Current Affairs
Canadian Newsstream
Trade Publications, Journals, and Magazines:
Industry and trade associations work to keep people within an industry informed about the industry through newsletters, magazines, and trade fairs. The information can range from a detailed focus on a specific product line, to general coverage of an industry or key business risk and trends. Industry and professional association websites can be excellent sources of free information whether or not you are a member of that organization. In addition, you can find news about industries via government websites, news databases, as well as news directories and search engines.
Ulrichsweb Provides publisher information on more than 300,000 periodicals of all types. Use this to create a list of relevant ones to check out in your industry. Search by keyword, publisher or geographic location.
Trade Associations:
Trade associations often publish free industry newsletters that are excellent sources of information for your business plan. Such newsletters often have articles that cover in-depth topics on business management, manufacturing practices, how-tos, current industry news and much more. One good reason to create a list of relevant associations is to see if any of them publish a monthly industry newsletter on their website.
ASAE Gateway to Associations Directory Use this directory to search for an association by name, interest area, or international geographic location (including Canada and BC). You can also search using a combination of various fields.
Associations Canada This library database covers Canadian, as well as some international, industry, professional or special interest associations. Searchable by type or keyword. You can use this to identify key associations' websites and search for freely available newsletters, blogs or reports they they may publish on your industry. Please contact your local public or research library for access. Use of your library card may be required for online access to this resource. Print copies may also be available for in-person users.
Web searching tip: Use Google or another search engine to search for industry associations relevant to your industry in your location. If you don't find a relevant industry association, try broadening your geographic area (e.g. from Vancouver to British Columbia, or from Canada to the U.S. or international). If your industry is very specialized or new, look for associations for broader or similar industries.
Government Websites, Including Labour Market Information Sources:
BC Stats | Current reports and statistics from British Columbia's central statistical agency including labour market information, economic statistics and bankruptcies. Start by searching their Industry section and narrowing by industry type or go to the Business, Industry & Trade page to skim all the different business-related topics.
WorkBC | Find current employment outlooks, labour market information, relevant links, and a geographic representation of the BC workforce. Start by searching your Industry Profile .
Innovation, Science, and Economic Development Canada Provides market research, industry statistics, licensing information for intellectual property, and information about doing business internationally. The Industry Canada site features interactive applications such as customizable trade reports, cost calculators, and online business planning guides. You can also search broad Canadian industry statistics .
Entrepreneurship Indicators Database This database is intended to provide comprehensive business demography statistics and performance indicators for enterprises in Canada. This information is available upon request.
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
First Steps: Writing the Industry Section of Your Business Plan This quick guide offers tips that will help you create the industry section for your business plan.
By The Staff of Entrepreneur Media, Inc. • Jan 4, 2015
In their book Write Your Business Plan , the staff of Entrepreneur Media, Inc. offer an in-depth understanding of what's essential to any business plan, what's appropriate for your venture, and what it takes to ensure success. In this edited excerpt, the authors outline what type of details you should include in the industry section of your business plan.
It isn't enough to just work hard. If you're in the wrong industry at the wrong time, making your business grow is going to be difficult. The investment community tends to believe that any business can be buoyed by an industry on the rise and that the opposite is true in an industry whose tide is ebbing. This means it's important for you to include an industry analysis in your business plan.
Readers of your business plan may want to see an industry on a fast-growth track with few established competitors and great potential. Or they may be more interested in a big, if somewhat slower-growing, market with competitors who have lost touch with the market, leaving the door open for rivals.
Whatever the facts are, you'll need to support them with a snapshot analysis of the state of your industry and any trends taking place. This can't be mere off-the-cuff thinking. You need to support your opinions with market research that identifies specific competitors and outlines their weaknesses and strengths and any barriers to entry into the market. You need to describe why your industry is valuable and how it will continue to be important. Finally, and perhaps most important, you'll have to convincingly describe what makes you better and destined to succeed.
When preparing the state of the industry section, instead of looking at your business as a self-contained system, you'll describe the whole industry in which you operate and point to your position in that universe. You then zero in on your country, your state and your local community, deepening on how far your business stretches.
This part of your plan may take a little more legwork than other sections because you'll be drawing together information from a number of outside sources. You may also be reporting on or even conducting your own original research into industry affairs.
To start preparing your industry analysis and outlook, dig up the following facts about your field:
1. What is your total industry-wide sales volume? In dollars? In units?
2. What are the trends in sales volumes within your industry?
3. Who are the major players and your key competitors? What are they like?
4. What does it take to compete? What are the barriers to entry?
5. What technological trends affect your industry?
6. What are the main modes of marketing?
7. How does government regulation affect the industry?
8. In what ways are changing consumer tastes affecting your industry?
9. Identify recent demographic trends affecting the industry.
10. How sensitive is the industry to seasons and economic cycles?
11. What are key financial measures in your industry (average profit margins, sales commissions, etc.)?
If your business addresses a trend before it's been widely recognized, you need to include this information in your business plan. Providing some statistics in the trends section of your plan can make it more convincing.
Barriers to Entry
If you want to become a semiconductor manufacturer, you'll need a billion-dollar factory or two. If you want to have a TV network, you'll need programming and cable carriage in the major markets. These problems are called barriers to entry, and they exist to some extent in all industries. The barriers may be monetary, technological, distribution or market-related, or they may simply be a matter of ownership of prime real estate.
An important part of analyzing your market is determining what the barriers to entry are and how high they stretch. If the barriers are high, as is the case with automobile manufacturing, you can be assured new competitors are likely to be slow in springing up. If the barriers are low, such as opening a nail salon, which doesn't have a huge overhead, you have more opportunity to get into the game.
Be alert for innovative competitors when writing the section of your plan in which you analyze barriers to entry. Clearly some markets are also more saturated than others, and today some are dominated by the McDonald's of their industry. For example, it's hard to open a bookstore today with Amazon changing the way people buy books. In that industry, you need to be creative and explore entry into specialty books, mystery books or another niche within the larger market. Exploring entry points in the marketplace carefully will save you from a disastrous error and will certainly demonstrate to investors that you've thought your plan through and aren't jumping to conclusions.
Identifying Competitors
You're not alone, even if you have a one-person business. You also have your competition to worry about, and your backers will worry about competition, too. Even if you're truly in the rare position of addressing a brand-new market where no competition exists, most experienced people reading your plan will have questions about companies they suspect may be competitors. For these reasons, you should devote a special section of your plan to identifying competitors.
If you had to name two competitors in the athletic shoe market, you'd quickly come up with Nike and Reebok. But these by far aren't the only competitors in the sneaker business. They're just two of the main ones, and depending on the business you're in, the other ones may be more important. If you sell soccer shoes, for instance, Adidas is a bigger player than either of the two American firms. And smaller firms such as Etonic, New Balance and Saucony also have niches where they are comparatively powerful.
You can develop a list of competitors by talking to customers and suppliers, checking with industry groups, and reading trade journals. But it's not enough to simply name your competitors. You need to know their manner of operation, how they compete.
Does a competitor stress a selective, low-volume, high-margin business, or does she emphasize sales growth at any cost, taking every job that comes along, whether or not it fits any coherent scheme or offers an attractive profit? Knowing this kind of information about competitors can help you identify their weaknesses as well as their names.
Entrepreneur Staff
Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- James Clear Explains Why the 'Two Minute Rule' Is the Key to Long-Term Habit Building
- They Designed One Simple Product With a 'Focus on Human Health' — and Made $40 Million Last Year
- Lock Younger Americans Don't Necessarily Want to Retire in Florida — and the 2 Affordable States at the Top of Their List Might Surprise You
- I Tried Airchat , the Hottest New Social Media App in Silicon Valley — Here's How It Works
- Lock This Side Hustle Is Helping Farmers Earn Up to $60,000 a Year While Connecting Outdoor Lovers With Untouched Wilderness
- Are Franchises in the Clear After the Expanded Joint Employer Rule Was Struck Down? Industry Experts Answer 2 Critical Questions About What's Next.
Most Popular Red Arrow
Most people have no business starting a business. here's what to consider before you become an entrepreneur.
You need to find the right business opportunity at the right time and take the right steps to beat the odds.
AI vs. Humanity — Why Humans Will Always Win in Content Creation
With the proliferation and integration of AI across organizations and business units, PR and marketing professionals may be tempted to lean into this new technology more than recommended.
Passengers Are Now Entitled to a Full Cash Refund for Canceled Flights, 'Significant' Delays
The U.S. Department of Transportation announced new rules for commercial passengers on Wednesday.
Who You Hire Matters — Here's How to Form a Team That's Built to Last
Among the many challenges related to managing a small business, hiring a quality team of employees is one of the most important. Check out this list of tips and best practices to find the best people for your business.
Franchising Is Not For Everyone. Explore These Lucrative Alternatives to Expand Your Business.
Not every business can be franchised, nor should it. While franchising can be the right growth vehicle for someone with an established brand and proven concept that's ripe for growth, there are other options available for business owners.
7 Ways You Can Use AI to 10x Your Leadership Skills
While technology can boost individual efficiency and effectiveness, it's essential to balance their use with human intuition and creativity to avoid losing personal connection and to optimize workplace satisfaction.
Successfully copied link
ZenBusinessPlans
Home » Business Plans
How to Write a Business Plan Industry Analysis
How do you conduct industry analysis for a business plan? Do you need help conducting market research and industry analysis for your business plan? Then I advice you read on. So you have a great business idea, you have refined and fine-tuned it, and you are ready to launch. You are going to offer a product or service with a clearly defined customer base, and you are confident that you will be successful in the long term.
Well, if the above applies perfectly to you, then you have not completed your assignment. What happens when you enter an examination hall without having studied for the exam at all? You’d spend all your time in the hall blaming yourself for being silly, right? Now, starting a business is even much more important because there’s a lot more at stake than passing or failing a grade. So, you must not leave out any aspect of research undone.
In this section of your business plan, you will demonstrate that the industry’s market size is worth going after, who your main competitors will be if you decide to take a plunge, and how you will be able to carve out a niche for yourself and give your competitors a run for their money. Planning a business goes beyond analyzing the potential of your offer. You must analyze the following three factors as well:
- The strengths and weaknesses of your business
- The competition
- Who your customers are, what they want, and how they want it
These are the major components of a business plan’s market or industrial analysis and it is also known as a SWOT (Strength, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats) analysis. This section of your business plan reveals the chances of your business to achieve success with its offers. And that’s why the industry analysis is a very important section of your business plan, which must be carefully conducted and documented.
So in this article, we will be looking at how to conduct industry analysis for a business plan. If you are a budding entrepreneur, or you are planning to start a new business; then below are the exact steps to follow when conducting an industry analysis for a new business:
How to Conduct Industry Analysis for a Business Plan
1. analyze the competition.
Of the three factors listed above, the competition may prove the most difficult to analyze, especially if you are new to the industry. But there are ways to simplify the task. You can start by looking at your direct competitors. If you are planning to start a new restaurant in an area, your direct competitors are other restaurants within that locality, while your indirect competitors are those that are slightly remote but still around.
Now, you are not just counting the number of rivals you have. You are trying to see how you can push ahead of them by filling a loophole they never noticed all these while. Some people find it hard to leave their workplace for the restaurant at lunchtime, but it’s either they do it or go hungry. You can disrupt the market’s status quo by offering to deliver lunch to people right in their workplaces. Filling loopholes like this one should be your goal.
If you don’t device strategies for pushing ahead of the competition, you will just enter the industry and join the survival race that you may never win. So, you need to introduce an innovation that will threaten your rivals. Remember, it’s either you differentiate or you fizzle out fast!
2. Assess the industry / market size
After analyzing your direct and indirect competitors, you will need to analyze your chances of standing firm even in the face of stiffer competition. Your first step in market research is to get an idea of how big the opportunity is and why it’s worth going after.
This means finding out how many customers you are catering to and much revenue you are likely to make. This is a convincing first step to lure in whoever is reading your business plan to become intrigued and dig further into your findings. Here are some factors you should consider:
- The individual strengths and weaknesses of your competitors.
- The rate at which new competitors enter the market or the rate at which old competitors are leaving the market.
- The products or services that fetch most revenue for your competitors.
- How you will overcome the threat of substitute goods.
You can get lots of helpful information about your market from government sources, trade associations, financial services firms, online data providers, and free resources on the web.
3. Analyze industry forces and trends
You will need to outline what’s happening in the industry from many perspectives that would help the reader get the full gist on whether the market is lucrative or not. A great general-purpose tool for doing just that is the PEST Analysis. Here’s what it stands for and what you should consider:
- P – Political factors ( the role government plays in your industry )
- E – Economic factors ( the state of the economy on both local and national level )
- S – Social factors ( relevant changes in matters like lifestyle trends, demographics, consumer attitudes, buying patterns and opinions )
- T – Technological factors ( the impact of changing technological trends on your industry )
4. Develop your marketing plan
Developing your marketing plan entails answering the following questions:
- What products or services are you offering?
- How much will you charge for your offers?
- Where will you sell your product, and who are your target customers?
- What special incentives would you use to encourage customers to buy your product?
In short, this section of your industry analysis outlines how you will deliver your product to the customers and how you will win customers to your side.
5. Craft your growth plan
While some entrepreneurs are of the opinion that this step should come only after you have established your business, crafting your market development plan helps you envision your company growing in a few years. Your growth plan should address the following questions:
- According to recent data, is the market for your product growing or dwindling?
- Do you plan to introduce new products or line extensions in the next few years?
- If you plan to introduce new offers, would they be closely related to your current offers or within another niche entirely?
- Are there strategies for giving your business the competitive advantage in the industry?
- Are there plans to handle increasing demand?
6. Fine-tune your analysis
After the steps discussed above, cross check your analyses to ensure that your findings are factual and your figures are accurate. Another handy tool to have in your arsenal when conducting industry research is the almighty Porter’s 5 Forces Analysis . ( Don’t worry if you’ve never attended a business strategy class in your life, it’s actually quite straightforward ). Here’s the breakdown:
Threat of new entrants
How difficult ( or easy ) is it for someone to enter your specific vertical? If it’s very easy then most likely the space will be crowded with competitors fighting for margins. Conversely, if it’s very difficult, that that in itself can become a competitive advantage.
Threat of substitute products or services
How likely is it that another product or service could decrease demand or displace you and potentially the entire industry all together?
Bargaining power of customers
When it comes to pricing and terms, how much power does your customer have? Are they organized enough to exercise their purchase power, or is there so much competition that they have their pick resulting in pricing wars amongst providers?
Bargaining power of suppliers
This refers to how dependent you are on a given supplier to operate your business. If it’s difficult or near impossible for you to switch, that means they have the upper hand, whereas, if the switching costs are low, you can negotiate better terms for yourself.
Competitive rivalry of the market
Factoring in the first four forces, you can arrive at a good understanding of the playing field and whether it’s in your favor if you enter it, how long you’ll be able to last, through what means you’ll carve a space for yourself, and what you’re up against.
As a final note, you must never forget that the industry analysis is a vital part of your business plan and it will probably be the most extensive portion of it. So, take your time to conduct extensive research on your competitors and market trends over the recent years.
- Go to Chapter 9 Part B: Writing a Business Plan Competitive Market Analysis
- Go Back to Chapter 8: Writing your Company’s Profile
- Go Back to Introduction and Table of Content
More on Business Plans
Just in Time for Spring 🌻 50% Off for 3 Months. BUY NOW & SAVE
50% Off for 3 Months Buy Now & Save
Wow clients with professional invoices that take seconds to create
Quick and easy online, recurring, and invoice-free payment options
Automated, to accurately track time and easily log billable hours
Reports and tools to track money in and out, so you know where you stand
Easily log expenses and receipts to ensure your books are always tax-time ready
Tax time and business health reports keep you informed and tax-time ready
Automatically track your mileage and never miss a mileage deduction again
Time-saving all-in-one bookkeeping that your business can count on
Track project status and collaborate with clients and team members
Organized and professional, helping you stand out and win new clients
Set clear expectations with clients and organize your plans for each project
Client management made easy, with client info all in one place
Pay your employees and keep accurate books with Payroll software integrations
- Team Management
FreshBooks integrates with over 100 partners to help you simplify your workflows
Send invoices, track time, manage payments, and more…from anywhere.
- Freelancers
- Self-Employed Professionals
- Businesses With Employees
- Businesses With Contractors
- Marketing & Agencies
- Construction & Trades
- IT & Technology
- Business & Prof. Services
- Accounting Partner Program
- Collaborative Accounting™
- Accountant Hub
- Reports Library
- FreshBooks vs QuickBooks
- FreshBooks vs HoneyBook
- FreshBooks vs Harvest
- FreshBooks vs Wave
- FreshBooks vs Xero
- Free Invoice Generator
- Invoice Templates
- Accounting Templates
- Business Name Generator
- Estimate Templates
- Help Center
- Business Loan Calculator
- Mark Up Calculator
Call Toll Free: 1.866.303.6061
1-888-674-3175
- All Articles
- Productivity
- Project Management
- Bookkeeping
Resources for Your Growing Business
Industry analysis: why it’s important & how to analyze an industry.

Conducting an industry analysis is the best way to understand your competition and any opportunities in the market.
Think about a time when you put all your energy and effort into something, only for someone else to do it better or do it first. It’s discouraging, isn’t it? You then think back through your process to identify where you went wrong.
Did you overlook some external factors? Were you not up-to-date with industry trends? The degree of competition is important to recognize when developing a competitive strategy.
It’s always easier to look back and see what went wrong. You could have missed technological factors or competitive factors. Or your business plan and competitive analysis might not have taken into account the market size.
So how do you figure out the degree of competition and use that information to set your business apart? You perform an industry analysis! Here’s everything you need to know.
Here’s What We’ll Cover:
What Is an Industry Analysis?
The importance of analyzing an industry in business, what you need for industry analysis , different methods to perform industry analysis, key takeaways .
There’s no difference if you have been in business for decades or you’re new to the market. Performing an industry analysis is important to better understand your niche. Essentially, industry analysis is a look into your market to see how your business compares to your competition.
An industry analysis looks into every element of your business and how it lines up with others. It’s important to fully understand your strengths and weaknesses to identify any opportunities or threats. When you know your market conditions and any financial factors, you get ahead of your competition.

By taking a look into what makes your industry tick you get a better sense of your company’s position. Industry analysis can assess demand and supply and technological changes. It can also find external factors that influence the competition.
You’re able to better forecast your growth rate and plan for evolving industry dynamics. The result is the best possible strategy to increase your market power. If you don’t take the steps to understand how you stack up compared to your competition and gain a competitive edge, they definitely will.
Conducting an industry analysis requires more than doing a simple search. You need to find and understand any competitive advantages, and there are a few different ways you can do it.
Some businesses hire outside firms to use mathematical forecasting for quantitative analysis. Others use qualitative analysis to come to make business decisions based on the information they gather. Whatever route you go, it will include specific market research and competitive analysis.
Here is everything you need to know to conduct your own in-depth industry analysis and get ahead of the competition!
Understand the competition:
- When you know your competitor’s products and services, you know how you can differentiate
- Are you targeting similar audiences?
- What products and services are your competition offering?
Use market research:
- Look into the demand of your market, the market size, and any economic indicators
- Where do your customers live? How saturated is the market? What do your customers usually pay for similar products and services?
Analyze the data that you have collected:
- Knowing your own strengths and weaknesses is important. But knowing the strengths and weaknesses of your competition is equally as important
- Assess what your competition offers and compare it against your own
- Are the features and benefits that you offer meeting the demands and needs of your consumer base?
Evaluate your position in the market:
- What’s your market share compared to your competitors?
- Understand if you need to adjust the price of your product or service
- Find any advantages that you have and identify possible threats in the future
- Similarly, find any weaknesses your company has and address how you can turn them into advantages
When you compile all of this information into an industry analysis, you can make better business decisions moving forward. You can identify any gaps in the market and how you can fill them. Plus, knowing what your competition is doing is the best way to know how to beat them.
The points outlined above are an excellent starting block to understand your business and where it stands in the market. But there are some industry research and analysis models designed to take it even further.
Competitive Forces Model (Porter’s 5 Forces)
The main purpose of using this model is to formulate a strategy and understand the competitive landscape. It consists of the Five Forces of Analysis.
- Industry rivalry and the amount of competition in the market
- The threat of new products or services entering the market
- The bargaining power of buyers and how they can influence pricing
- The bargaining power of suppliers and how they can limit your profit
- The threat of new competition potentially entering the market

SWOT Analysis
The SWOT Analysis is commonly used across many different industries. It represents identifying and understanding any strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- Identify the strengths of your business and what currently sets up apart from the competition
- Recognize the weaknesses that may be present and where you have any disadvantages compared to your competitors
- Find the opportunities that are available in the market and how you can develop a strategy to increase profitability
- Determine any threats to your business, both internal and external. How could they affect the way you operate, your profits, or overall integrity?
It’s one thing to find information and conduct an industry analysis, but it’s another thing to understand the data you collect. Markets are constantly fluctuating and can change at the snap of a finger. It can be overwhelming!
But the power and influence that you can generate from understanding how your industry and competition work can set you apart. You will be more knowledgeable and better prepared to leverage opportunities and stop any threats in their tracks.
Find more relevant articles for your small business on our resource guide .
RELATED ARTICLES

Save Time Billing and Get Paid 2x Faster With FreshBooks
Want More Helpful Articles About Running a Business?
Get more great content in your Inbox.
By subscribing, you agree to receive communications from FreshBooks and acknowledge and agree to FreshBook’s Privacy Policy . You can unsubscribe at any time by contacting us at [email protected].
👋 Welcome to FreshBooks
To see our product designed specifically for your country, please visit the United States site.
Small Business Trends
How to create a business plan: examples & free template.
This is the ultimate guide to creating a comprehensive and effective plan to start a business . In today’s dynamic business landscape, having a well-crafted business plan is an important first step to securing funding, attracting partners, and navigating the challenges of entrepreneurship.
This guide has been designed to help you create a winning plan that stands out in the ever-evolving marketplace. U sing real-world examples and a free downloadable template, it will walk you through each step of the process.
Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or launching your very first startup, the guide will give you the insights, tools, and confidence you need to create a solid foundation for your business.
Table of Contents
How to Write a Business Plan
Embarking on the journey of creating a successful business requires a solid foundation, and a well-crafted business plan is the cornerstone. Here is the process of writing a comprehensive business plan and the main parts of a winning business plan . From setting objectives to conducting market research, this guide will have everything you need.
Executive Summary

The Executive Summary serves as the gateway to your business plan, offering a snapshot of your venture’s core aspects. This section should captivate and inform, succinctly summarizing the essence of your plan.
It’s crucial to include a clear mission statement, a brief description of your primary products or services, an overview of your target market, and key financial projections or achievements.
Think of it as an elevator pitch in written form: it should be compelling enough to engage potential investors or stakeholders and provide them with a clear understanding of what your business is about, its goals, and why it’s a promising investment.
Example: EcoTech is a technology company specializing in eco-friendly and sustainable products designed to reduce energy consumption and minimize waste. Our mission is to create innovative solutions that contribute to a cleaner, greener environment.
Our target market includes environmentally conscious consumers and businesses seeking to reduce their carbon footprint. We project a 200% increase in revenue within the first three years of operation.
Overview and Business Objectives

In the Overview and Business Objectives section, outline your business’s core goals and the strategic approaches you plan to use to achieve them. This section should set forth clear, specific objectives that are attainable and time-bound, providing a roadmap for your business’s growth and success.
It’s important to detail how these objectives align with your company’s overall mission and vision. Discuss the milestones you aim to achieve and the timeframe you’ve set for these accomplishments.
This part of the plan demonstrates to investors and stakeholders your vision for growth and the practical steps you’ll take to get there.
Example: EcoTech’s primary objective is to become a market leader in sustainable technology products within the next five years. Our key objectives include:
- Introducing three new products within the first two years of operation.
- Achieving annual revenue growth of 30%.
- Expanding our customer base to over 10,000 clients by the end of the third year.
Company Description

The Company Description section is your opportunity to delve into the details of your business. Provide a comprehensive overview that includes your company’s history, its mission statement, and its vision for the future.
Highlight your unique selling proposition (USP) – what makes your business stand out in the market. Explain the problems your company solves and how it benefits your customers.
Include information about the company’s founders, their expertise, and why they are suited to lead the business to success. This section should paint a vivid picture of your business, its values, and its place in the industry.
Example: EcoTech is committed to developing cutting-edge sustainable technology products that benefit both the environment and our customers. Our unique combination of innovative solutions and eco-friendly design sets us apart from the competition. We envision a future where technology and sustainability go hand in hand, leading to a greener planet.
Define Your Target Market

Defining Your Target Market is critical for tailoring your business strategy effectively. This section should describe your ideal customer base in detail, including demographic information (such as age, gender, income level, and location) and psychographic data (like interests, values, and lifestyle).
Elucidate on the specific needs or pain points of your target audience and how your product or service addresses these. This information will help you know your target market and develop targeted marketing strategies.
Example: Our target market comprises environmentally conscious consumers and businesses looking for innovative solutions to reduce their carbon footprint. Our ideal customers are those who prioritize sustainability and are willing to invest in eco-friendly products.
Market Analysis

The Market Analysis section requires thorough research and a keen understanding of the industry. It involves examining the current trends within your industry, understanding the needs and preferences of your customers, and analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors.
This analysis will enable you to spot market opportunities and anticipate potential challenges. Include data and statistics to back up your claims, and use graphs or charts to illustrate market trends.
This section should demonstrate that you have a deep understanding of the market in which you operate and that your business is well-positioned to capitalize on its opportunities.
Example: The market for eco-friendly technology products has experienced significant growth in recent years, with an estimated annual growth rate of 10%. As consumers become increasingly aware of environmental issues, the demand for sustainable solutions continues to rise.
Our research indicates a gap in the market for high-quality, innovative eco-friendly technology products that cater to both individual and business clients.
SWOT Analysis

A SWOT analysis in your business plan offers a comprehensive examination of your company’s internal and external factors. By assessing Strengths, you showcase what your business does best and where your capabilities lie.
Weaknesses involve an honest introspection of areas where your business may be lacking or could improve. Opportunities can be external factors that your business could capitalize on, such as market gaps or emerging trends.
Threats include external challenges your business may face, like competition or market changes. This analysis is crucial for strategic planning, as it helps in recognizing and leveraging your strengths, addressing weaknesses, seizing opportunities, and preparing for potential threats.
Including a SWOT analysis demonstrates to stakeholders that you have a balanced and realistic understanding of your business in its operational context.
- Innovative and eco-friendly product offerings.
- Strong commitment to sustainability and environmental responsibility.
- Skilled and experienced team with expertise in technology and sustainability.
Weaknesses:
- Limited brand recognition compared to established competitors.
- Reliance on third-party manufacturers for product development.
Opportunities:
- Growing consumer interest in sustainable products.
- Partnerships with environmentally-focused organizations and influencers.
- Expansion into international markets.
- Intense competition from established technology companies.
- Regulatory changes could impact the sustainable technology market.
Competitive Analysis

In this section, you’ll analyze your competitors in-depth, examining their products, services, market positioning, and pricing strategies. Understanding your competition allows you to identify gaps in the market and tailor your offerings to outperform them.
By conducting a thorough competitive analysis, you can gain insights into your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses, enabling you to develop strategies to differentiate your business and gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Example: Key competitors include:
GreenTech: A well-known brand offering eco-friendly technology products, but with a narrower focus on energy-saving devices.
EarthSolutions: A direct competitor specializing in sustainable technology, but with a limited product range and higher prices.
By offering a diverse product portfolio, competitive pricing, and continuous innovation, we believe we can capture a significant share of the growing sustainable technology market.
Organization and Management Team

Provide an overview of your company’s organizational structure, including key roles and responsibilities. Introduce your management team, highlighting their expertise and experience to demonstrate that your team is capable of executing the business plan successfully.
Showcasing your team’s background, skills, and accomplishments instills confidence in investors and other stakeholders, proving that your business has the leadership and talent necessary to achieve its objectives and manage growth effectively.
Example: EcoTech’s organizational structure comprises the following key roles: CEO, CTO, CFO, Sales Director, Marketing Director, and R&D Manager. Our management team has extensive experience in technology, sustainability, and business development, ensuring that we are well-equipped to execute our business plan successfully.
Products and Services Offered

Describe the products or services your business offers, focusing on their unique features and benefits. Explain how your offerings solve customer pain points and why they will choose your products or services over the competition.
This section should emphasize the value you provide to customers, demonstrating that your business has a deep understanding of customer needs and is well-positioned to deliver innovative solutions that address those needs and set your company apart from competitors.
Example: EcoTech offers a range of eco-friendly technology products, including energy-efficient lighting solutions, solar chargers, and smart home devices that optimize energy usage. Our products are designed to help customers reduce energy consumption, minimize waste, and contribute to a cleaner environment.
Marketing and Sales Strategy

In this section, articulate your comprehensive strategy for reaching your target market and driving sales. Detail the specific marketing channels you plan to use, such as social media, email marketing, SEO, or traditional advertising.
Describe the nature of your advertising campaigns and promotional activities, explaining how they will capture the attention of your target audience and convey the value of your products or services. Outline your sales strategy, including your sales process, team structure, and sales targets.
Discuss how these marketing and sales efforts will work together to attract and retain customers, generate leads, and ultimately contribute to achieving your business’s revenue goals.
This section is critical to convey to investors and stakeholders that you have a well-thought-out approach to market your business effectively and drive sales growth.
Example: Our marketing strategy includes digital advertising, content marketing, social media promotion, and influencer partnerships. We will also attend trade shows and conferences to showcase our products and connect with potential clients. Our sales strategy involves both direct sales and partnerships with retail stores, as well as online sales through our website and e-commerce platforms.
Logistics and Operations Plan

The Logistics and Operations Plan is a critical component that outlines the inner workings of your business. It encompasses the management of your supply chain, detailing how you acquire raw materials and manage vendor relationships.
Inventory control is another crucial aspect, where you explain strategies for inventory management to ensure efficiency and reduce wastage. The section should also describe your production processes, emphasizing scalability and adaptability to meet changing market demands.
Quality control measures are essential to maintain product standards and customer satisfaction. This plan assures investors and stakeholders of your operational competency and readiness to meet business demands.
Highlighting your commitment to operational efficiency and customer satisfaction underlines your business’s capability to maintain smooth, effective operations even as it scales.
Example: EcoTech partners with reliable third-party manufacturers to produce our eco-friendly technology products. Our operations involve maintaining strong relationships with suppliers, ensuring quality control, and managing inventory.
We also prioritize efficient distribution through various channels, including online platforms and retail partners, to deliver products to our customers in a timely manner.
Financial Projections Plan

In the Financial Projections Plan, lay out a clear and realistic financial future for your business. This should include detailed projections for revenue, costs, and profitability over the next three to five years.
Ground these projections in solid assumptions based on your market analysis, industry benchmarks, and realistic growth scenarios. Break down revenue streams and include an analysis of the cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and potential investments.
This section should also discuss your break-even analysis, cash flow projections, and any assumptions about external funding requirements.
By presenting a thorough and data-backed financial forecast, you instill confidence in potential investors and lenders, showcasing your business’s potential for profitability and financial stability.
This forward-looking financial plan is crucial for demonstrating that you have a firm grasp of the financial nuances of your business and are prepared to manage its financial health effectively.
Example: Over the next three years, we expect to see significant growth in revenue, driven by new product launches and market expansion. Our financial projections include:
- Year 1: $1.5 million in revenue, with a net profit of $200,000.
- Year 2: $3 million in revenue, with a net profit of $500,000.
- Year 3: $4.5 million in revenue, with a net profit of $1 million.
These projections are based on realistic market analysis, growth rates, and product pricing.
Income Statement

The income statement , also known as the profit and loss statement, provides a summary of your company’s revenues and expenses over a specified period. It helps you track your business’s financial performance and identify trends, ensuring you stay on track to achieve your financial goals.
Regularly reviewing and analyzing your income statement allows you to monitor the health of your business, evaluate the effectiveness of your strategies, and make data-driven decisions to optimize profitability and growth.
Example: The income statement for EcoTech’s first year of operation is as follows:
- Revenue: $1,500,000
- Cost of Goods Sold: $800,000
- Gross Profit: $700,000
- Operating Expenses: $450,000
- Net Income: $250,000
This statement highlights our company’s profitability and overall financial health during the first year of operation.
Cash Flow Statement

A cash flow statement is a crucial part of a financial business plan that shows the inflows and outflows of cash within your business. It helps you monitor your company’s liquidity, ensuring you have enough cash on hand to cover operating expenses, pay debts, and invest in growth opportunities.
By including a cash flow statement in your business plan, you demonstrate your ability to manage your company’s finances effectively.
Example: The cash flow statement for EcoTech’s first year of operation is as follows:
Operating Activities:
- Depreciation: $10,000
- Changes in Working Capital: -$50,000
- Net Cash from Operating Activities: $210,000
Investing Activities:
- Capital Expenditures: -$100,000
- Net Cash from Investing Activities: -$100,000
Financing Activities:
- Proceeds from Loans: $150,000
- Loan Repayments: -$50,000
- Net Cash from Financing Activities: $100,000
- Net Increase in Cash: $210,000
This statement demonstrates EcoTech’s ability to generate positive cash flow from operations, maintain sufficient liquidity, and invest in growth opportunities.
Tips on Writing a Business Plan

1. Be clear and concise: Keep your language simple and straightforward. Avoid jargon and overly technical terms. A clear and concise business plan is easier for investors and stakeholders to understand and demonstrates your ability to communicate effectively.
2. Conduct thorough research: Before writing your business plan, gather as much information as possible about your industry, competitors, and target market. Use reliable sources and industry reports to inform your analysis and make data-driven decisions.
3. Set realistic goals: Your business plan should outline achievable objectives that are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Setting realistic goals demonstrates your understanding of the market and increases the likelihood of success.
4. Focus on your unique selling proposition (USP): Clearly articulate what sets your business apart from the competition. Emphasize your USP throughout your business plan to showcase your company’s value and potential for success.
5. Be flexible and adaptable: A business plan is a living document that should evolve as your business grows and changes. Be prepared to update and revise your plan as you gather new information and learn from your experiences.
6. Use visuals to enhance understanding: Include charts, graphs, and other visuals to help convey complex data and ideas. Visuals can make your business plan more engaging and easier to digest, especially for those who prefer visual learning.
7. Seek feedback from trusted sources: Share your business plan with mentors, industry experts, or colleagues and ask for their feedback. Their insights can help you identify areas for improvement and strengthen your plan before presenting it to potential investors or partners.
FREE Business Plan Template
To help you get started on your business plan, we have created a template that includes all the essential components discussed in the “How to Write a Business Plan” section. This easy-to-use template will guide you through each step of the process, ensuring you don’t miss any critical details.
The template is divided into the following sections:
- Mission statement
- Business Overview
- Key products or services
- Target market
- Financial highlights
- Company goals
- Strategies to achieve goals
- Measurable, time-bound objectives
- Company History
- Mission and vision
- Unique selling proposition
- Demographics
- Psychographics
- Pain points
- Industry trends
- Customer needs
- Competitor strengths and weaknesses
- Opportunities
- Competitor products and services
- Market positioning
- Pricing strategies
- Organizational structure
- Key roles and responsibilities
- Management team backgrounds
- Product or service features
- Competitive advantages
- Marketing channels
- Advertising campaigns
- Promotional activities
- Sales strategies
- Supply chain management
- Inventory control
- Production processes
- Quality control measures
- Projected revenue
- Assumptions
- Cash inflows
- Cash outflows
- Net cash flow
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a strategic document that outlines an organization’s goals, objectives, and the steps required to achieve them. It serves as a roadmap as you start a business , guiding the company’s direction and growth while identifying potential obstacles and opportunities.
Typically, a business plan covers areas such as market analysis, financial projections, marketing strategies, and organizational structure. It not only helps in securing funding from investors and lenders but also provides clarity and focus to the management team.
A well-crafted business plan is a very important part of your business startup checklist because it fosters informed decision-making and long-term success.

Why You Should Write a Business Plan
Understanding the importance of a business plan in today’s competitive environment is crucial for entrepreneurs and business owners. Here are five compelling reasons to write a business plan:
- Attract Investors and Secure Funding : A well-written business plan demonstrates your venture’s potential and profitability, making it easier to attract investors and secure the necessary funding for growth and development. It provides a detailed overview of your business model, target market, financial projections, and growth strategies, instilling confidence in potential investors and lenders that your company is a worthy investment.
- Clarify Business Objectives and Strategies : Crafting a business plan forces you to think critically about your goals and the strategies you’ll employ to achieve them, providing a clear roadmap for success. This process helps you refine your vision and prioritize the most critical objectives, ensuring that your efforts are focused on achieving the desired results.
- Identify Potential Risks and Opportunities : Analyzing the market, competition, and industry trends within your business plan helps identify potential risks and uncover untapped opportunities for growth and expansion. This insight enables you to develop proactive strategies to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities, positioning your business for long-term success.
- Improve Decision-Making : A business plan serves as a reference point so you can make informed decisions that align with your company’s overall objectives and long-term vision. By consistently referring to your plan and adjusting it as needed, you can ensure that your business remains on track and adapts to changes in the market, industry, or internal operations.
- Foster Team Alignment and Communication : A shared business plan helps ensure that all team members are on the same page, promoting clear communication, collaboration, and a unified approach to achieving the company’s goals. By involving your team in the planning process and regularly reviewing the plan together, you can foster a sense of ownership, commitment, and accountability that drives success.
What are the Different Types of Business Plans?
In today’s fast-paced business world, having a well-structured roadmap is more important than ever. A traditional business plan provides a comprehensive overview of your company’s goals and strategies, helping you make informed decisions and achieve long-term success. There are various types of business plans, each designed to suit different needs and purposes. Let’s explore the main types:
- Startup Business Plan: Tailored for new ventures, a startup business plan outlines the company’s mission, objectives, target market, competition, marketing strategies, and financial projections. It helps entrepreneurs clarify their vision, secure funding from investors, and create a roadmap for their business’s future. Additionally, this plan identifies potential challenges and opportunities, which are crucial for making informed decisions and adapting to changing market conditions.
- Internal Business Plan: This type of plan is intended for internal use, focusing on strategies, milestones, deadlines, and resource allocation. It serves as a management tool for guiding the company’s growth, evaluating its progress, and ensuring that all departments are aligned with the overall vision. The internal business plan also helps identify areas of improvement, fosters collaboration among team members, and provides a reference point for measuring performance.
- Strategic Business Plan: A strategic business plan outlines long-term goals and the steps to achieve them, providing a clear roadmap for the company’s direction. It typically includes a SWOT analysis, market research, and competitive analysis. This plan allows businesses to align their resources with their objectives, anticipate changes in the market, and develop contingency plans. By focusing on the big picture, a strategic business plan fosters long-term success and stability.
- Feasibility Business Plan: This plan is designed to assess the viability of a business idea, examining factors such as market demand, competition, and financial projections. It is often used to decide whether or not to pursue a particular venture. By conducting a thorough feasibility analysis, entrepreneurs can avoid investing time and resources into an unviable business concept. This plan also helps refine the business idea, identify potential obstacles, and determine the necessary resources for success.
- Growth Business Plan: Also known as an expansion plan, a growth business plan focuses on strategies for scaling up an existing business. It includes market analysis, new product or service offerings, and financial projections to support expansion plans. This type of plan is essential for businesses looking to enter new markets, increase their customer base, or launch new products or services. By outlining clear growth strategies, the plan helps ensure that expansion efforts are well-coordinated and sustainable.
- Operational Business Plan: This type of plan outlines the company’s day-to-day operations, detailing the processes, procedures, and organizational structure. It is an essential tool for managing resources, streamlining workflows, and ensuring smooth operations. The operational business plan also helps identify inefficiencies, implement best practices, and establish a strong foundation for future growth. By providing a clear understanding of daily operations, this plan enables businesses to optimize their resources and enhance productivity.
- Lean Business Plan: A lean business plan is a simplified, agile version of a traditional plan, focusing on key elements such as value proposition, customer segments, revenue streams, and cost structure. It is perfect for startups looking for a flexible, adaptable planning approach. The lean business plan allows for rapid iteration and continuous improvement, enabling businesses to pivot and adapt to changing market conditions. This streamlined approach is particularly beneficial for businesses in fast-paced or uncertain industries.
- One-Page Business Plan: As the name suggests, a one-page business plan is a concise summary of your company’s key objectives, strategies, and milestones. It serves as a quick reference guide and is ideal for pitching to potential investors or partners. This plan helps keep teams focused on essential goals and priorities, fosters clear communication, and provides a snapshot of the company’s progress. While not as comprehensive as other plans, a one-page business plan is an effective tool for maintaining clarity and direction.
- Nonprofit Business Plan: Specifically designed for nonprofit organizations, this plan outlines the mission, goals, target audience, fundraising strategies, and budget allocation. It helps secure grants and donations while ensuring the organization stays on track with its objectives. The nonprofit business plan also helps attract volunteers, board members, and community support. By demonstrating the organization’s impact and plans for the future, this plan is essential for maintaining transparency, accountability, and long-term sustainability within the nonprofit sector.
- Franchise Business Plan: For entrepreneurs seeking to open a franchise, this type of plan focuses on the franchisor’s requirements, as well as the franchisee’s goals, strategies, and financial projections. It is crucial for securing a franchise agreement and ensuring the business’s success within the franchise system. This plan outlines the franchisee’s commitment to brand standards, marketing efforts, and operational procedures, while also addressing local market conditions and opportunities. By creating a solid franchise business plan, entrepreneurs can demonstrate their ability to effectively manage and grow their franchise, increasing the likelihood of a successful partnership with the franchisor.
Using Business Plan Software

Creating a comprehensive business plan can be intimidating, but business plan software can streamline the process and help you produce a professional document. These tools offer a number of benefits, including guided step-by-step instructions, financial projections, and industry-specific templates. Here are the top 5 business plan software options available to help you craft a great business plan.
1. LivePlan
LivePlan is a popular choice for its user-friendly interface and comprehensive features. It offers over 500 sample plans, financial forecasting tools, and the ability to track your progress against key performance indicators. With LivePlan, you can create visually appealing, professional business plans that will impress investors and stakeholders.
2. Upmetrics
Upmetrics provides a simple and intuitive platform for creating a well-structured business plan. It features customizable templates, financial forecasting tools, and collaboration capabilities, allowing you to work with team members and advisors. Upmetrics also offers a library of resources to guide you through the business planning process.
Bizplan is designed to simplify the business planning process with a drag-and-drop builder and modular sections. It offers financial forecasting tools, progress tracking, and a visually appealing interface. With Bizplan, you can create a business plan that is both easy to understand and visually engaging.
Enloop is a robust business plan software that automatically generates a tailored plan based on your inputs. It provides industry-specific templates, financial forecasting, and a unique performance score that updates as you make changes to your plan. Enloop also offers a free version, making it accessible for businesses on a budget.
5. Tarkenton GoSmallBiz
Developed by NFL Hall of Famer Fran Tarkenton, GoSmallBiz is tailored for small businesses and startups. It features a guided business plan builder, customizable templates, and financial projection tools. GoSmallBiz also offers additional resources, such as CRM tools and legal document templates, to support your business beyond the planning stage.
Business Plan FAQs
What is a good business plan.
A good business plan is a well-researched, clear, and concise document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies, target market, competitive advantages, and financial projections. It should be adaptable to change and provide a roadmap for achieving success.
What are the 3 main purposes of a business plan?
The three main purposes of a business plan are to guide the company’s strategy, attract investment, and evaluate performance against objectives. Here’s a closer look at each of these:
- It outlines the company’s purpose and core values to ensure that all activities align with its mission and vision.
- It provides an in-depth analysis of the market, including trends, customer needs, and competition, helping the company tailor its products and services to meet market demands.
- It defines the company’s marketing and sales strategies, guiding how the company will attract and retain customers.
- It describes the company’s organizational structure and management team, outlining roles and responsibilities to ensure effective operation and leadership.
- It sets measurable, time-bound objectives, allowing the company to plan its activities effectively and make strategic decisions to achieve these goals.
- It provides a comprehensive overview of the company and its business model, demonstrating its uniqueness and potential for success.
- It presents the company’s financial projections, showing its potential for profitability and return on investment.
- It demonstrates the company’s understanding of the market, including its target customers and competition, convincing investors that the company is capable of gaining a significant market share.
- It showcases the management team’s expertise and experience, instilling confidence in investors that the team is capable of executing the business plan successfully.
- It establishes clear, measurable objectives that serve as performance benchmarks.
- It provides a basis for regular performance reviews, allowing the company to monitor its progress and identify areas for improvement.
- It enables the company to assess the effectiveness of its strategies and make adjustments as needed to achieve its objectives.
- It helps the company identify potential risks and challenges, enabling it to develop contingency plans and manage risks effectively.
- It provides a mechanism for evaluating the company’s financial performance, including revenue, expenses, profitability, and cash flow.
Can I write a business plan by myself?
Yes, you can write a business plan by yourself, but it can be helpful to consult with mentors, colleagues, or industry experts to gather feedback and insights. There are also many creative business plan templates and business plan examples available online, including those above.
We also have examples for specific industries, including a using food truck business plan , salon business plan , farm business plan , daycare business plan , and restaurant business plan .
Is it possible to create a one-page business plan?
Yes, a one-page business plan is a condensed version that highlights the most essential elements, including the company’s mission, target market, unique selling proposition, and financial goals.
How long should a business plan be?
A typical business plan ranges from 20 to 50 pages, but the length may vary depending on the complexity and needs of the business.
What is a business plan outline?
A business plan outline is a structured framework that organizes the content of a business plan into sections, such as the executive summary, company description, market analysis, and financial projections.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
The five most common business plan mistakes include inadequate research, unrealistic financial projections, lack of focus on the unique selling proposition, poor organization and structure, and failure to update the plan as circumstances change.
What questions should be asked in a business plan?
A business plan should address questions such as: What problem does the business solve? Who is the specific target market ? What is the unique selling proposition? What are the company’s objectives? How will it achieve those objectives?
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan focuses on the overall vision, goals, and tactics of a company, while a strategic plan outlines the specific strategies, action steps, and performance measures necessary to achieve the company’s objectives.
How is business planning for a nonprofit different?
Nonprofit business planning focuses on the organization’s mission, social impact, and resource management, rather than profit generation. The financial section typically includes funding sources, expenses, and projected budgets for programs and operations.
Image: Envato Elements

Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
© Copyright 2003 - 2024, Small Business Trends LLC. All rights reserved. "Small Business Trends" is a registered trademark.
Bakery Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Business Plan Outline
- Bakery Business Plan Home
- 1. Executive Summary
- 2. Company Overview
- 3. Industry Analysis
- 4. Customer Analysis
- 5. Competitive Analysis
- 6. Marketing Plan
- 7. Operations Plan
- 8. Management Team
- 9. Financial Plan
Bakery Industry Analysis
The Bakery industry is expected to grow to over $46 billion in the next five years.
Consumers are increasingly demanding healthier ingredients in bread and desserts. Successful operators will, therefore, need to offer a greater variety of whole-grain, all-natural or gluten-free products in order to capitalize on these trends. Moreover, changing preferences and increasing disposable income levels are encouraging consumers to choose more premium and specialty varieties over conventional private-label products.
Bakery items tend to be discretionary purchases so the revenues will also benefit from rising per capita disposable income and consumer confidence, both of which are anticipated to continue to grow over the next five years.
- Online Degree Explore Bachelor’s & Master’s degrees
- MasterTrack™ Earn credit towards a Master’s degree
- University Certificates Advance your career with graduate-level learning
- Top Courses
- Join for Free
Business Plan: What It Is + How to Write One
Discover what a business plan includes and how writing one can foster your business’s development.
![industry analysis in a business plan [Featured image] Woman showing a business plan to a man at a desk.](https://d3njjcbhbojbot.cloudfront.net/api/utilities/v1/imageproxy/https://images.ctfassets.net/wp1lcwdav1p1/3GxwyORRIvag1Dj3jnHuiZ/a23bcf202d72e7074fd83a5222a1de79/GettyImages-1127726432__1_.jpg?w=1500&h=680&q=60&fit=fill&f=faces&fm=jpg&fl=progressive&auto=format%2Ccompress&dpr=1&w=1000)
What is a business plan?
Think of a business plan as a document that guides the journey to start-up and beyond. Business plans are written documents that define your business goals and the strategies you’ll use to achieve those goals. In addition to exploring the competitive environment in which the business will operate, a business plan also analyses a market and different customer segments, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines financial planning.
How to write a business plan
In the sections below, you’ll build the following components of your business plan:
Executive summary
Business description
Products and services
Competitor analysis
Marketing plan and sales strategies
Brand strategy
Financial planning
Explore each section to bring fresh inspiration and reveal new possibilities for developing your business. Depending on your format, you may adapt the sections, skip over some, or go deeper into others. Consider your first draft a foundation for your efforts and one you can revise, as needed, to account for changes in any area of your business.
1. Executive summary
This short section introduces the business plan as a whole to the people who will be reading it, including investors, lenders, or other members of your team. Start with a sentence or two about your business, development goals, and why it will succeed. If you are seeking funding, summarise the basics of the financial plan.
2. Business description
You can use this section to provide detailed information about your company and how it will operate in the marketplace.
Mission statement: What drives your desire to start a business? What purpose are you serving? What do you hope to achieve for your business, the team, and your customers?
Revenue streams: From what sources will your business generate revenue? Examples include product sales, service fees, subscriptions, rental fees, licence fees, and more.
Leadership: Describe the leaders in your business, their roles and responsibilities, and your vision for building teams to perform various functions, such as graphic design, product development, or sales.
Legal structure: If you’ve incorporated your business, include the legal structure here and the rationale behind this choice.
3. Competitor analysis
This section will assess potential competitors, their offers, and marketing and sales efforts. For each competitor, explore the following:
Value proposition: What outcome or experience does this brand promise?
Products and services: How does each solve customer pain points and fulfill desires? What are the price points?
Marketing: Which channels do competitors use to promote? What kind of content does this brand publish on these channels? What messaging does this brand use to communicate value to customers?
Sales: What sales process or buyer’s journey does this brand lead customers through?
4. Products and services
Use this section to describe everything your business offers to its target market. For every product and service, list the following:
The value proposition or promise to customers, in terms of how they will experience it
How the product serves customers, addresses their pain points, satisfies their desires, and improves their lives
The features or outcomes that make the product better than those of competitors
Your price points and how these compare to competitors
5. Marketing plan and sales strategies
In this section, you’ll draw from thorough market research to describe your target market and how you will reach it.
Who are your ideal customers?
How can you describe this segment according to their demographics (age, ethnicity, income, location, etc.) and psychographics (beliefs, values, aspirations, lifestyle, etc.)?
What are their daily lives like?
What problems and challenges do they experience?
What words, phrases, ideas, and concepts do consumers in your target market use to describe these problems when posting on social media or engaging with your competitors?
What messaging will present your products as the best on the market? How will you differentiate messaging from competitors?
On what marketing channels will you position your products and services?
How will you design a customer journey that delivers a positive experience at every touchpoint and leads customers to a purchase decision?
6. Brand strategy
In this section, you will describe your business’s design, personality, values, voice, and other details that go into delivering a consistent brand experience.
What are the values that define your brand?
What visual elements give your brand a distinctive look and feel?
How will your marketing messaging reflect a distinctive brand voice, including tone, diction, and sentence-level stylistic choices?
How will your brand look and sound throughout the customer journey?
Define your brand positioning statement. What will inspire your audience to choose your brand over others? What experiences and outcomes will your audience associate with your brand?
7. Financial planning
In this section, you will explore your business’s financial future. Suppose you are writing a traditional business plan to seek funding. In that case, this section is critical for demonstrating to lenders or investors you have a strategy for turning your business ideas into profit. For a lean start-up business plan, this section can provide a valuable exercise for planning how to invest resources and generate revenue [ 1 ].
Use past financials and other sections of this business plan to begin your financial planning, such as your price points or sales strategies.
How many individual products or service packages do you plan to sell over a specific period?
List your business expenses, such as subscribing to software or other services, hiring contractors or employees, purchasing physical supplies or equipment, etc.
What is your break-even point or the amount you must sell to cover all expenses?
Create a sales forecast for the next three to five years: (No. of units to sell X price for each unit) – (cost per unit X No. of units) = sales forecast
Quantify how much capital you have on hand.
When writing a traditional business plan to secure funding, you may append supporting documents, such as licences, permits, patents, letters of reference, resumes, product blueprints, brand guidelines, the industry awards you’ve received, and media mentions and appearances.
Business plan key takeaways and best practices
Remember: Creating a business plan is crucial when starting a business. You can use this document to guide your decisions and actions and even seek funding from lenders and investors.
Keep these best practices in mind:
Your business plan should evolve as your business grows. Return to it periodically, such as quarterly or annually, to update individual sections or explore new directions your business can take.
Make sure everyone on your team has a copy of the business plan, and welcome their input as they perform their roles.
Ask fellow entrepreneurs for feedback on your business plan and look for opportunities to strengthen it, from conducting more market and competitor research to implementing new strategies for success.
Start your business with Coursera
Ready to start your business? Watch this video on the Lean approach from the Entrepreneurship Specialisation on Coursera:
Article sources
Inc. “ How to Write the Financial Section of a Business Plan , https://www.inc.com/guides/business-plan-financial-section.html.” Accessed April 15, 2024.
Keep reading
Coursera staff.
Editorial Team
Coursera’s editorial team is comprised of highly experienced professional editors, writers, and fact...
This content has been made available for informational purposes only. Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet their personal, professional, and financial goals.
The Business of Fashion
Agenda-setting intelligence, analysis and advice for the global fashion community.
News & Analysis
- Professional Exclusives
- The News in Brief
- Sustainability
- Direct-to-Consumer
- Global Markets
- Fashion Week
- Workplace & Talent
- Entrepreneurship
- Financial Markets
- Newsletters
- Case Studies
- Masterclasses
- Special Editions
- The State of Fashion
- Read Careers Advice
- BoF Professional
- BoF Careers
- BoF Insights
- Our Journalism
- Work With Us
- Read daily fashion news
- Download special reports
- Sign up for essential email briefings
- Follow topics of interest
- Receive event invitations
- Create job alerts
JW Pei’s Bags Are a Hit With Celebrities. Can They Catch on With Everyone Else?

A year after launching accessories label JW Pei, husband and wife duo Yang Pei and Stephanie Li were faced with a choice: Go up or down.
When the two launched their brand, which sells bags, shoes and other accessories, in 2018, it sat squarely within the accessible luxury category, selling bags like its now discontinued Fiona Bag for $300. But after launch, it had found only “lukewarm success,” Pei said, as the contemporary sector, which sits in the often-tough middle between luxury and fast fashion, was becoming increasingly saturated, with labels like Staud, Danse Lente and Rouje.
To differentiate, contemporary brands like Isabel Marant hiked their prices so they could sell to higher-earning customers who are usually less vulnerable to economic downturns. JW Pei, however, did the opposite.
The accessories label’s hero product, the Gabbi handbag, which features a ruched shoulder strap and hobo shape, is priced at $89.
ADVERTISEMENT
“We can keep prices low because we function like a tech company,” said Pei, the label’s chief executive. “We only make what the data tells us will sell.”
In deciding what bags to produce, JW Pei looks at what bags are added to cart and which “eventually turn into a sale,” Pei said, and orders product accordingly to eliminate excess inventory. Plus, the brand owns its entire supply chain – pillars which Pei says have allowed the brand to grow profitably. Last year, the brand grew sales 50 percent over 2022 to $50 million.
More than just profitable growth, the brand has earned a crop of high-profile fans. Stars including Gigi Hadid, Megan Fox and Emily Ratajkowski have been spotted carrying JW Pei bags. The label’s bags have also made it onto the red carpet, with actress Selena Gomez wearing a sparkly Gabbi bag to this year’s Golden Globes.
To drive further growth, JW Pei wants to use artificial intelligence to speed up its design process and expand its geographic footprint with new store openings. Meanwhile, its parent company, PL Brands Group, is acquiring its competitors, like Danse Lente, betting that it can build a network of affordable bags that feel a bit more luxe than fast fashion.
“Consumers are feeling pressure across their entire wallet,” said Kristen Classi-Zummo, industry analyst for apparel at Circana. “Consumers are trading down to fast fashion or to dupes. For those trading up, their ceiling is much lower and has landed in contemporary fashion.”
Generating Buzz
For consumers like New York City-based writer Jacquelyne Germain, who owns three JW Pei bags, the brand feels like “a step-up from Zara” with a price tag much easier to swallow than a designer label.
According to Pei, that mix of “high quality materials” with trendy design details has been instrumental to the brand’s growth.
“We had quietly built a community on Instagram where our products really shine,” said Li, the brand’s creative director. “The buzz had been organic largely because I believe we’re fun and playful, but also, the bags can be worn over and over and in different situations.”
Another boost to that buzz has been the brand’s circle of celebrity fans. Former first daughter Ivanka Trump was one of the first known names to place an order on the brand’s site, prompting Pei and Li to begin sending their bags to celebrity stylists, eventually landing on the arms of Hadid, Hailey Bieber and more. Since then, Pei says, the brand’s growth has been exponential.
“Any $600 bag or a Birkin can be seen on a model, but the press, paparazzi and social media pay attention when the bag is less than $100,” said Pei. “It’s a win-win for us and the stylists.”
Celebrity placement remains its primary tool for driving conversation online, and the brand is exclusively looking to connect with massive names like Hadid and Bieber.
“We’re a little-known brand, but everyone in the world would instantly know who Gigi Hadid is,” Pei said. “That is our leverage when we enter new markets like Japan and Korea or work with new retailers. Working with local celebrities would not be as effective.”
What’s Next
Relying on a data-driven product strategy and celebrity endorsements has gotten the brand this far, but JW Pei is looking beyond those tactics in 2024.
This year, the company will launch a ready-to-wear line and begin experimenting with artificial intelligence in the design process. JW Pei will use generative AI programme Midjourney to assist in fashion design research — so it can more quickly identify emerging trends and silhouettes — as well as sketching the designs. The label’s human designers, led by Li, will use the research to inform new colourways, material selection and produce collections.
The goal is to shorten production times to get trendy items to consumers faster, Li added.

Later this year, the brand — which sells via its own e-commerce platform and wholesale partners like Nordstrom and Selfridges — is set to open its first brick-and-mortar shop in New York’s SoHo neighbourhood in the autumn. The store’s stock will be determined by data: Prior to opening the shop, JW Pei will launch an online marketing campaign designed to determine which products and styles New York consumers want to buy. Only those products will be sold in store.
The plan is to repeat this process in other locations, and open 20 stores in the US as well as locations in London, Dubai and Hong Kong in the next three to five years.
But perhaps JW Pei’s greatest ambition is to expand the reach of its parent PL Brands Group, which is owned by Pei and Li.
The company acquired Danse Lente, a London-based accessories label and one of JW Pei’s competitors, in December 2023, and wants to apply the same approach it took with JW Pei to the label: Expanding into new categories, entering wholesale and of course, lowering prices. Because it also owns China-based manufacturing and distribution firm Lo Monte International, it controls the supply chain for both brands, giving the company more control over pricing, materials and labour costs.
“Danse Lente has great brand value but their prices are too high,” said Pei. “With our factories, we’ll be able to drive the prices down, test new styles online and ensure the brand keeps growing.”
This year, it hopes to add three new brands to its arsenal, whether through an internal launch or acquisition. In keeping the strategies that have proved fruitful so far at the heart of their business, Pei believes it can keep expanding.
“Everybody has the capability to design bags, have beautiful images and strong marketing, which is why the $300 price point or the contemporary market is a dead zone,” said Pei. “In a few years, the biggest differentiator will be the supply chain and how well a company is situated to get the consumer’s attention in new ways.”

Yola Mzizi is the Editorial Apprentice at The Business of Fashion (BoF). She is based in New York and provides operational support to the New York team and writes features for BoF and The Business of Beauty.
- Danse Lente
- Mergers & Acquisitions
- Artificial Intelligence
© 2024 The Business of Fashion. All rights reserved. For more information read our Terms & Conditions

New York Says Goodbye to Downtown Darling Puppets and Puppets
Designer Carly Mark sparked conversation about what it takes to make it as an emerging designer in New York when she announced she was shutting her ready-to-wear line and moving to London. On Thursday she held her last sample sale.

The Emerging Brand Survival Plan: Bags, Basics and Beyoncé
To stabilise their businesses brands are honing in on what their particular consumer wants to buy, introducing new categories and starting conversations.

Now, Anyone Can Be a Sneaker Designer
That’s the promise of Zellerfeld, a 3D-printing partner to Louis Vuitton and Moncler that’s becoming a platform for emerging designers to easily make and sell footwear of their own.

Inside Soeur’s Plans to Go From French Girl Favourite to Global Powerhouse
With a new heavyweight backer in Italian firm Style Capital — which helped Zimmermann secure a billion dollar valuation — the French contemporary womenswear brand has ambitions to go global. But it sits in a competitive and hard-to-crack category.
Subscribe to the BoF Daily Digest
The essential daily round-up of fashion news, analysis, and breaking news alerts.
Our newsletters may include 3rd-party advertising, by subscribing you agree to the Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
Our Products
- BoF Insights Opens in new window

- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Share of electricity generated by fossil fuels in Great Britain drops to record low
Gas and coal accounted for just 2.4% of power generation for an hour last week, data shows, amid ‘zero-carbon grid’ plans
The share of Great Britain’s electricity generated by burning fossil fuels plummeted to unprecedented lows this month, ahead of plans to begin running a “zero-carbon grid” for short periods from next year.
Electricity generated by burning gas and coal fell to a record low of just 2.4% for an hour at lunchtime on Monday 15 April, according to an analysis of data from National Grid’s electricity system operator (ESO).
The same data has revealed that earlier this month the share of fossil fuels in the generation mix taken over an entire day fell to a record low of 6.4%, on 5 April.
The findings lend support to the aims of the ESO to begin the “groundbreaking and world-leading” step of running a zero-carbon electricity grid for Great Britain for short periods from next year.
Craig Dyke, the director of system operations at the ESO, said Britain had made “excellent progress” towards this goal and there had already been periods when the grid had run safely on more than 90% zero-carbon power.
The new records mark a dramatic shift from 15 years ago, when gas and coal power plants made up 75% of the electricity mix , while renewables accounted for only 2%. Last year only a third of Great Britain’s electricity came from fossil fuels, compared with 40% from renewables.
The research, undertaken by Carbon Brief , found a dramatic increase in the frequency of short periods when fossil fuels made up less than 5% of Great Britain’s electricity generation in recent months.
There have been 75 half-hour periods in the year to date when fossil fuels have accounted for less than 5% of the country’s electricity needs, more than four times the number recorded last year. Just five ultra-low carbon half hours were recorded in 2022, the analysis said.
The new record low took place amid a glut of renewable energy, according to the ESO. At the time, wind power made up about half of electricity generation while solar power accounted for just over 30%. Britain’s nuclear reactors generated more than 13%.
after newsletter promotion
The low-carbon generation squeezed gas-fired power to just 1.8% of Great Britain’s electricity generation while the country’s last remaining coal power plant, at Ratcliffe-on-Soar in Nottinghamshire, generated 0.6%. The plant is due to close in September .
Dyke said: “This is a culmination of a significant amount of effort over a number of years. It’s not just about technologies, it’s about hearts and minds and processes and systems and people working together across the industry, the energy regulator and government.
“Getting to the 2025 ambition has been a significant engineering challenge, which we are solving.”
- Energy industry
- Fossil fuels
- Energy efficiency
- Green economy
- National Grid

England could produce 13 times more renewable energy, using less than 3% of land – analysis

Scottish Power to pay out £1.5m after overcharging 1,700 households

World’s largest solar manufacturer to cut one-third of workforce

Only 1,500 people compensated so far over prepayment meters, Ofgem says

New blow to British smart meter rollout as number of faulty machines leaps to 4m

African leaders call for equity over minerals used for clean energy

EU countries already hitting some of their sustainable energy targets for 2030

UK government accused of trying to ‘stoke culture war on climate issues’

What does Sunak’s plan for new gas plants mean for UK climate targets?

Danish windfarm firm Ørsted to axe up to 800 jobs and pause dividend
Most viewed.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
An example of the industry analysis in a business plan of an Indian soap company: Market overview: The market is estimated to be at INR 195 billion in 2020 and is expected to grow at 7% annually ...
Here's how to conduct a robust analysis: Market Size Calculation: Determine the total market size in terms of revenue, units sold, or the number of customers. This figure serves as a baseline for evaluating the industry's scale. Historical Growth Analysis: Examine historical data to identify growth trends.
Whether you write it all out in a formal business plan or not, when you're doing your industry analysis, you're looking at the following: Industry participants. Distribution patterns. Competition and buying patterns. Everything in your industry that happens outside of your business will affect your company.
Industry analysis is a market assessment tool used by businesses and analysts to understand the competitive dynamics of an industry. ... It is very important when planning a small business. Analysis helps to identify which stage an industry is currently in; whether it is still growing and there is scope to reap benefits or has reached its ...
Step 4: Calculate market value. You can use either top-down analysis or bottom-up analysis to calculate an estimate of your market value. A top-down analysis tends to be the easier option of the ...
Writing a Market Analysis Tips. Include an explanation of how you determined the size of the market and how much share competitors have. Include tables like the one above that show competitor size, barriers to entry, etc. Decide where you're going to place this section in your business plan - before or after your SWOT analysis.
An industry analysis is a fundamental component of any business plan, offering insights into the market dynamics, competitive landscape, and future market trends.This analysis helps businesses understand their industry's environment, make informed strategic decisions, and identify potential opportunities and threats.
Industry Analysis Explained. The term industry analysis in strategic management explains the procedure followed to evaluate or analyse the general market environment in which the business is operating. It is necessary for every business to understand the industry dynamics by studying the trends, level of competition, potential growth opportunities and resistances that it may face during ...
An industry analysis enables you to gain a better understanding of the industry and market in which you will be conducting business. By conducting an industry analysis before you start writing your business plan, you will be able to: Identify industry trends, such as potentially problematic aspects of the industry.
Industry analysis. The industry analysis is the section of your business plan where you demonstrate your knowledge about the general characteristics of the type of business you're in. You should be able to present statistics about the size of the industry, such as total U.S. sales in the last year and industry growth rate over the last few years.
When you're writing a business plan and looking for information on Canadian industries, Industry Canada is your logical first stop. Their Find Statistics by Industry page lets you see key economic indicators for different sectors of the Canadian economy, access industry profiles, and analysis and research small businesses in Canada generally.
Note that market analysis and marketing plan are two different things, with two distinct chapters in a business plan. As the name suggests, market analysis examines where you fit in within your desired industry and market. As you work thorugh this section, jot down your ideas for the marketing and strategy section of your business plan.
Industry analysis in a business plan is a tool that enables a company to understand its position relative to other companies that produce similar products or services like it. While considering the strategic planning process, a company must understand the overall industry's forces. Thus, industry analysis techniques in a business plan enable ...
Reasons to Perform an Industry Analysis. Industry analysis allows you to have an insight into the competitive business environment. The weaknesses of your competitors would be your strong suits. You can integrate such information to make the marketing plan to grow your business. The result of industry analysis provides you an insight into the ...
What is an Industry Analysis? An industry analysis is a marketing process that provides statistics about the market potential of your business products and services. This section of your plan needs to have specific information about the current state of the industry, and its target markets. An industry analysis may contain reference materials such as spreadsheets, pie charts, and bar graphs in ...
An industry analysis can tell you a lot about how your company fits into the broader industry. ... it's time to educate potential investors on the industry. This part of your business plan will be ...
By The Staff of Entrepreneur Media, Inc. • Jan 4, 2015. In their book Write Your Business Plan, the staff of Entrepreneur Media, Inc. offer an in-depth understanding of what's essential to any ...
How to Conduct Industry Analysis for a Business Plan. 1. Analyze the competition. Of the three factors listed above, the competition may prove the most difficult to analyze, especially if you are new to the industry. But there are ways to simplify the task. You can start by looking at your direct competitors.
Performing an industry analysis is important to better understand your niche. Essentially, industry analysis is a look into your market to see how your business compares to your competition. An industry analysis looks into every element of your business and how it lines up with others. It's important to fully understand your strengths and ...
Use the following steps to learn how to do an industry analysis for your business or potential company: 1. Conduct background research. Conduct detailed background research on your industry and competitors to understand your market. Choose if you want to research your entire industry or look at a specific subsection.
In this video, I describe why we need to conduct an an industry analysis. This is an overview of industry analysis. More in depth industry and market analy...
U.S. Small Business Administration: The Small Business Administration provides detailed information on planning your business, including preparing a business plan, completing a market analysis ...
A SWOT analysis in your business plan offers a comprehensive examination of your company's internal and external factors. By assessing Strengths, you showcase what your business does best and where your capabilities lie. ... Seek feedback from trusted sources: Share your business plan with mentors, industry experts, or colleagues and ask for ...
Bakery Industry Analysis. The Bakery industry is expected to grow to over $46 billion in the next five years. Consumers are increasingly demanding healthier ingredients in bread and desserts. Successful operators will, therefore, need to offer a greater variety of whole-grain, all-natural or gluten-free products in order to capitalize on these ...
Competitor analysis Marketing plan and sales strategies ... letters of reference, resumes, product blueprints, brand guidelines, the industry awards you've received, and media mentions and appearances. Business plan key takeaways and best practices. Remember: Creating a business plan is crucial when starting a business. You can use this ...
The Los Angeles-based accessories label has been a well-kept secret in the industry, but founders Yang Pei and Stephanie Li are hoping to change that through new acquisitions, opening brick-and-mortar stores and using AI to speed up the design and production process. ... The Business of Fashion. Agenda-setting intelligence, analysis and advice ...
How to Conduct Industry Analysis for a Business Plan. 1. Analyze the competition. Of the three factors listed above, the competition may prove the most difficult to analyze, especially if you are new to the industry. But there are ways to simplify the task. You can start by looking at your direct competitors.
Gas and coal accounted for just 2.4% of power generation for an hour last week, data shows, amid 'zero-carbon grid' plans The share of Great Britain's electricity generated by burning fossil ...