Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates

How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on October 12, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on November 21, 2023.

A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organized and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research proposals.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: “A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management”
- Example research proposal #2: “Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use”
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesize prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasize again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement .
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is relevant and worthy of being conducted.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, November 21). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 10, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-proposal/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Academic Proposals

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This resource introduces the genre of academic proposals and provides strategies for developing effective graduate-level proposals across multiple contexts.
Introduction
An important part of the work completed in academia is sharing our scholarship with others. Such communication takes place when we present at scholarly conferences, publish in peer-reviewed journals, and publish in books. This OWL resource addresses the steps in writing for a variety of academic proposals.
For samples of academic proposals, click here .
Important considerations for the writing process
First and foremost, you need to consider your future audience carefully in order to determine both how specific your topic can be and how much background information you need to provide in your proposal. While some conferences and journals may be subject-specific, most will require you to address an audience that does not conduct research on the same topics as you. Conference proposal reviewers are often drawn from professional organization members or other attendees, while journal proposals are typically reviewed by the editorial staff, so you need to ensure that your proposal is geared toward the knowledge base and expectations of whichever audience will read your work.
Along those lines, you might want to check whether you are basing your research on specific prior research and terminology that requires further explanation. As a rule, always phrase your proposal clearly and specifically, avoid over-the-top phrasing and jargon, but do not negate your own personal writing style in the process.
If you would like to add a quotation to your proposal, you are not required to provide a citation or footnote of the source, although it is generally preferred to mention the author’s name. Always put quotes in quotation marks and take care to limit yourself to at most one or two quotations in the entire proposal text. Furthermore, you should always proofread your proposal carefully and check whether you have integrated details, such as author’s name, the correct number of words, year of publication, etc. correctly.
Methodology is often a key factor in the evaluation of proposals for any academic genre — but most proposals have such a small word limit that writers find it difficult to adequately include methods while also discussing their argument, background for the study, results, and contributions to knowledge. It's important to make sure that you include some information about the methods used in your study, even if it's just a line or two; if your proposal isn't experimental in nature, this space should instead describe the theory, lens, or approach you are taking to arrive at your conclusions.
Reasons proposals fail/common pitfalls
There are common pitfalls that you might need to improve on for future proposals.
The proposal does not reflect your enthusiasm and persuasiveness, which usually goes hand in hand with hastily written, simply worded proposals. Generally, the better your research has been, the more familiar you are with the subject and the more smoothly your proposal will come together.
Similarly, proposing a topic that is too broad can harm your chances of being accepted to a conference. Be sure to have a clear focus in your proposal. Usually, this can be avoided by more advanced research to determine what has already been done, especially if the proposal is judged by an important scholar in the field. Check the names of keynote speakers and other attendees of note to avoid repeating known information or not focusing your proposal.
Your paper might simply have lacked the clear language that proposals should contain. On this linguistic level, your proposal might have sounded repetitious, have had boring wording, or simply displayed carelessness and a lack of proofreading, all of which can be remedied by more revisions. One key tactic for ensuring you have clear language in your proposal is signposting — you can pick up key phrases from the CFP, as well as use language that indicates different sections in academic work (as in IMRAD sections from the organization and structure page in this resource). This way, reviewers can easily follow your proposal and identify its relatedness to work in the field and the CFP.
Conference proposals
Conference proposals are a common genre in graduate school that invite several considerations for writing depending on the conference and requirements of the call for papers.
Beginning the process
Make sure you read the call for papers carefully to consider the deadline and orient your topic of presentation around the buzzwords and themes listed in the document. You should take special note of the deadline and submit prior to that date, as most conferences use online submission systems that will close on a deadline and will not accept further submissions.
If you have previously spoken on or submitted a proposal on the same topic, you should carefully adjust it specifically for this conference or even completely rewrite the proposal based on your changing and evolving research.
The topic you are proposing should be one that you can cover easily within a time frame of approximately fifteen to twenty minutes. You should stick to the required word limit of the conference call. The organizers have to read a large number of proposals, especially in the case of an international or interdisciplinary conference, and will appreciate your brevity.
Structure and components
Conference proposals differ widely across fields and even among individual conferences in a field. Some just request an abstract, which is written similarly to any other abstract you'd write for a journal article or other publication. Some may request abstracts or full papers that fit into pre-existing sessions created by conference organizers. Some request both an abstract and a further description or proposal, usually in cases where the abstract will be published in the conference program and the proposal helps organizers decide which papers they will accept.
If the conference you are submitting to requires a proposal or description, there are some common elements you'll usually need to include. These are a statement of the problem or topic, a discussion of your approach to the problem/topic, a discussion of findings or expected findings, and a discussion of key takeaways or relevance to audience members. These elements are typically given in this order and loosely follow the IMRAD structure discussed in the organization and structure page in this resource.
The proportional size of each of these elements in relation to one another tends to vary by the stage of your research and the relationship of your topic to the field of the conference. If your research is very early on, you may spend almost no time on findings, because you don't have them yet. Similarly, if your topic is a regular feature at conferences in your field, you may not need to spend as much time introducing it or explaining its relevance to the field; however, if you are working on a newer topic or bringing in a topic or problem from another discipline, you may need to spend slightly more space explaining it to reviewers. These decisions should usually be based on an analysis of your audience — what information can reviewers be reasonably expected to know, and what will you have to tell them?
Journal Proposals
Most of the time, when you submit an article to a journal for publication, you'll submit a finished manuscript which contains an abstract, the text of the article, the bibliography, any appendices, and author bios. These can be on any topic that relates to the journal's scope of interest, and they are accepted year-round.
Special issues , however, are planned issues of a journal that center around a specific theme, usually a "hot topic" in the field. The editor or guest editors for the special issue will often solicit proposals with a call for papers (CFP) first, accept a certain number of proposals for further development into article manuscripts, and then accept the final articles for the special issue from that smaller pool. Special issues are typically the only time when you will need to submit a proposal to write a journal article, rather than submitting a completed manuscript.
Journal proposals share many qualities with conference proposals: you need to write for your audience, convey the significance of your work, and condense the various sections of a full study into a small word or page limit. In general, the necessary components of a proposal include:
- Problem or topic statement that defines the subject of your work (often includes research questions)
- Background information (think literature review) that indicates the topic's importance in your field as well as indicates that your research adds something to the scholarship on this topic
- Methodology and methods used in the study (and an indication of why these methods are the correct ones for your research questions)
- Results or findings (which can be tentative or preliminary, if the study has not yet been completed)
- Significance and implications of the study (what will readers learn? why should they care?)
This order is a common one because it loosely follows the IMRAD (introduction, methods, results and discussion) structure often used in academic writing; however, it is not the only possible structure or even always the best structure. You may need to move these elements around depending on the expectations in your field, the word or page limit, or the instructions given in the CFP.
Some of the unique considerations of journal proposals are:
- The CFP may ask you for an abstract, a proposal, or both. If you need to write an abstract, look for more information on the abstract page. If you need to write both an abstract and a proposal, make sure to clarify for yourself what the difference is. Usually the proposal needs to include more information about the significance, methods, and/or background of the study than will fit in the abstract, but often the CFP itself will give you some instructions as to what information the editors are wanting in each piece of writing.
- Journal special issue CFPs, like conference CFPs, often include a list of topics or questions that describe the scope of the special issue. These questions or topics are a good starting place for generating a proposal or tying in your research; ensuring that your work is a good fit for the special issue and articulating why that is in the proposal increases your chances of being accepted.
- Special issues are not less valuable or important than regularly scheduled issues; therefore, your proposal needs to show that your work fits and could readily be accepted in any other issue of the journal. This means following some of the same practices you would if you were preparing to submit a manuscript to a journal: reading the journal's author submission guidelines; reading the last several years of the journal to understand the usual topics, organization, and methods; citing pieces from this journal and other closely related journals in your research.
Book Proposals
While the requirements are very similar to those of conference proposals, proposals for a book ought to address a few other issues.
General considerations
Since these proposals are of greater length, the publisher will require you to delve into greater detail as well—for instance, regarding the organization of the proposed book or article.
Publishers generally require a clear outline of the chapters you are proposing and an explication of their content, which can be several pages long in its entirety.
You will need to incorporate knowledge of relevant literature, use headings and sub-headings that you should not use in conference proposals. Be sure to know who wrote what about your topic and area of interest, even if you are proposing a less scholarly project.
Publishers prefer depth rather than width when it comes to your topic, so you should be as focused as possible and further outline your intended audience.
You should always include information regarding your proposed deadlines for the project and how you will execute this plan, especially in the sciences. Potential investors or publishers need to know that you have a clear and efficient plan to accomplish your proposed goals. Depending on the subject area, this information can also include a proposed budget, materials or machines required to execute this project, and information about its industrial application.
Pre-writing strategies
As John Boswell (cited in: Larsen, Michael. How to Write a Book Proposal. Writers Digest Books , 2004. p. 1) explains, “today fully 90 percent of all nonfiction books sold to trade publishers are acquired on the basis of a proposal alone.” Therefore, editors and agents generally do not accept completed manuscripts for publication, as these “cannot (be) put into the usual channels for making a sale”, since they “lack answers to questions of marketing, competition, and production.” (Lyon, Elizabeth. Nonfiction Book Proposals Anybody Can Write . Perigee Trade, 2002. pp. 6-7.)
In contrast to conference or, to a lesser degree, chapter proposals, a book proposal introduces your qualifications for writing it and compares your work to what others have done or failed to address in the past.
As a result, you should test the idea with your networks and, if possible, acquire other people’s proposals that discuss similar issues or have a similar format before submitting your proposal. Prior to your submission, it is recommended that you write at least part of the manuscript in addition to checking the competition and reading all about the topic.
The following is a list of questions to ask yourself before committing to a book project, but should in no way deter you from taking on a challenging project (adapted from Lyon 27). Depending on your field of study, some of these might be more relevant to you than others, but nonetheless useful to reiterate and pose to yourself.
- Do you have sufficient enthusiasm for a project that may span years?
- Will publication of your book satisfy your long-term career goals?
- Do you have enough material for such a long project and do you have the background knowledge and qualifications required for it?
- Is your book idea better than or different from other books on the subject? Does the idea spark enthusiasm not just in yourself but others in your field, friends, or prospective readers?
- Are you willing to acquire any lacking skills, such as, writing style, specific terminology and knowledge on that field for this project? Will it fit into your career and life at the time or will you not have the time to engage in such extensive research?
Essential elements of a book proposal
Your book proposal should include the following elements:
- Your proposal requires the consideration of the timing and potential for sale as well as its potential for subsidiary rights.
- It needs to include an outline of approximately one paragraph to one page of prose (Larsen 6) as well as one sample chapter to showcase the style and quality of your writing.
- You should also include the resources you need for the completion of the book and a biographical statement (“About the Author”).
- Your proposal must contain your credentials and expertise, preferably from previous publications on similar issues.
- A book proposal also provides you with the opportunity to include information such as a mission statement, a foreword by another authority, or special features—for instance, humor, anecdotes, illustrations, sidebars, etc.
- You must assess your ability to promote the book and know the market that you target in all its statistics.
The following proposal structure, as outlined by Peter E. Dunn for thesis and fellowship proposals, provides a useful guide to composing such a long proposal (Dunn, Peter E. “Proposal Writing.” Center for Instructional Excellence, Purdue University, 2007):
- Literature Review
- Identification of Problem
- Statement of Objectives
- Rationale and Significance
- Methods and Timeline
- Literature Cited
Most proposals for manuscripts range from thirty to fifty pages and, apart from the subject hook, book information (length, title, selling handle), markets for your book, and the section about the author, all the other sections are optional. Always anticipate and answer as many questions by editors as possible, however.
Finally, include the best chapter possible to represent your book's focus and style. Until an agent or editor advises you to do otherwise, follow your book proposal exactly without including something that you might not want to be part of the book or improvise on possible expected recommendations.
Publishers expect to acquire the book's primary rights, so that they can sell it in an adapted or condensed form as well. Mentioning any subsidiary rights, such as translation opportunities, performance and merchandising rights, or first-serial rights, will add to the editor's interest in buying your book. It is enticing to publishers to mention your manuscript's potential to turn into a series of books, although they might still hesitate to buy it right away—at least until the first one has been a successful endeavor.
The sample chapter
Since editors generally expect to see about one-tenth of a book, your sample chapter's length should reflect that in these building blocks of your book. The chapter should reflect your excitement and the freshness of the idea as well as surprise editors, but do not submit part of one or more chapters. Always send a chapter unless your credentials are impeccable due to prior publications on the subject. Do not repeat information in the sample chapter that will be covered by preceding or following ones, as the outline should be designed in such a way as to enable editors to understand the context already.
How to make your proposal stand out
Depending on the subject of your book, it is advisable to include illustrations that exemplify your vision of the book and can be included in the sample chapter. While these can make the book more expensive, it also increases the salability of the project. Further, you might consider including outstanding samples of your published work, such as clips from periodicals, if they are well-respected in the field. Thirdly, cover art can give your potential publisher a feel for your book and its marketability, especially if your topic is creative or related to the arts.
In addition, professionally formatting your materials will give you an edge over sloppy proposals. Proofread the materials carefully, use consistent and carefully organized fonts, spacing, etc., and submit your proposal without staples; rather, submit it in a neat portfolio that allows easy access and reassembling. However, check the submission guidelines first, as most proposals are submitted digitally. Finally, you should try to surprise editors and attract their attention. Your hook, however, should be imaginative but inexpensive (you do not want to bribe them, after all). Make sure your hook draws the editors to your book proposal immediately (Adapted from Larsen 154-60).
How To Write A Research Proposal
A Straightforward How-To Guide (With Examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | August 2019 (Updated April 2023)
Writing up a strong research proposal for a dissertation or thesis is much like a marriage proposal. It’s a task that calls on you to win somebody over and persuade them that what you’re planning is a great idea. An idea they’re happy to say ‘yes’ to. This means that your dissertation proposal needs to be persuasive , attractive and well-planned. In this post, I’ll show you how to write a winning dissertation proposal, from scratch.
Before you start:
– Understand exactly what a research proposal is – Ask yourself these 4 questions
The 5 essential ingredients:
- The title/topic
- The introduction chapter
- The scope/delimitations
- Preliminary literature review
- Design/ methodology
- Practical considerations and risks
What Is A Research Proposal?
The research proposal is literally that: a written document that communicates what you propose to research, in a concise format. It’s where you put all that stuff that’s spinning around in your head down on to paper, in a logical, convincing fashion.
Convincing is the keyword here, as your research proposal needs to convince the assessor that your research is clearly articulated (i.e., a clear research question) , worth doing (i.e., is unique and valuable enough to justify the effort), and doable within the restrictions you’ll face (time limits, budget, skill limits, etc.). If your proposal does not address these three criteria, your research won’t be approved, no matter how “exciting” the research idea might be.
PS – if you’re completely new to proposal writing, we’ve got a detailed walkthrough video covering two successful research proposals here .

How do I know I’m ready?
Before starting the writing process, you need to ask yourself 4 important questions . If you can’t answer them succinctly and confidently, you’re not ready – you need to go back and think more deeply about your dissertation topic .
You should be able to answer the following 4 questions before starting your dissertation or thesis research proposal:
- WHAT is my main research question? (the topic)
- WHO cares and why is this important? (the justification)
- WHAT data would I need to answer this question, and how will I analyse it? (the research design)
- HOW will I manage the completion of this research, within the given timelines? (project and risk management)
If you can’t answer these questions clearly and concisely, you’re not yet ready to write your research proposal – revisit our post on choosing a topic .
If you can, that’s great – it’s time to start writing up your dissertation proposal. Next, I’ll discuss what needs to go into your research proposal, and how to structure it all into an intuitive, convincing document with a linear narrative.
The 5 Essential Ingredients
Research proposals can vary in style between institutions and disciplines, but here I’ll share with you a handy 5-section structure you can use. These 5 sections directly address the core questions we spoke about earlier, ensuring that you present a convincing proposal. If your institution already provides a proposal template, there will likely be substantial overlap with this, so you’ll still get value from reading on.
For each section discussed below, make sure you use headers and sub-headers (ideally, numbered headers) to help the reader navigate through your document, and to support them when they need to revisit a previous section. Don’t just present an endless wall of text, paragraph after paragraph after paragraph…
Top Tip: Use MS Word Styles to format headings. This will allow you to be clear about whether a sub-heading is level 2, 3, or 4. Additionally, you can view your document in ‘outline view’ which will show you only your headings. This makes it much easier to check your structure, shift things around and make decisions about where a section needs to sit. You can also generate a 100% accurate table of contents using Word’s automatic functionality.

Ingredient #1 – Topic/Title Header
Your research proposal’s title should be your main research question in its simplest form, possibly with a sub-heading providing basic details on the specifics of the study. For example:
“Compliance with equality legislation in the charity sector: a study of the ‘reasonable adjustments’ made in three London care homes”
As you can see, this title provides a clear indication of what the research is about, in broad terms. It paints a high-level picture for the first-time reader, which gives them a taste of what to expect. Always aim for a clear, concise title . Don’t feel the need to capture every detail of your research in your title – your proposal will fill in the gaps.
Need a helping hand?
Ingredient #2 – Introduction
In this section of your research proposal, you’ll expand on what you’ve communicated in the title, by providing a few paragraphs which offer more detail about your research topic. Importantly, the focus here is the topic – what will you research and why is that worth researching? This is not the place to discuss methodology, practicalities, etc. – you’ll do that later.
You should cover the following:
- An overview of the broad area you’ll be researching – introduce the reader to key concepts and language
- An explanation of the specific (narrower) area you’ll be focusing, and why you’ll be focusing there
- Your research aims and objectives
- Your research question (s) and sub-questions (if applicable)
Importantly, you should aim to use short sentences and plain language – don’t babble on with extensive jargon, acronyms and complex language. Assume that the reader is an intelligent layman – not a subject area specialist (even if they are). Remember that the best writing is writing that can be easily understood and digested. Keep it simple.

Note that some universities may want some extra bits and pieces in your introduction section. For example, personal development objectives, a structural outline, etc. Check your brief to see if there are any other details they expect in your proposal, and make sure you find a place for these.
Ingredient #3 – Scope
Next, you’ll need to specify what the scope of your research will be – this is also known as the delimitations . In other words, you need to make it clear what you will be covering and, more importantly, what you won’t be covering in your research. Simply put, this is about ring fencing your research topic so that you have a laser-sharp focus.
All too often, students feel the need to go broad and try to address as many issues as possible, in the interest of producing comprehensive research. Whilst this is admirable, it’s a mistake. By tightly refining your scope, you’ll enable yourself to go deep with your research, which is what you need to earn good marks. If your scope is too broad, you’re likely going to land up with superficial research (which won’t earn marks), so don’t be afraid to narrow things down.
Ingredient #4 – Literature Review
In this section of your research proposal, you need to provide a (relatively) brief discussion of the existing literature. Naturally, this will not be as comprehensive as the literature review in your actual dissertation, but it will lay the foundation for that. In fact, if you put in the effort at this stage, you’ll make your life a lot easier when it’s time to write your actual literature review chapter.
There are a few things you need to achieve in this section:
- Demonstrate that you’ve done your reading and are familiar with the current state of the research in your topic area.
- Show that there’s a clear gap for your specific research – i.e., show that your topic is sufficiently unique and will add value to the existing research.
- Show how the existing research has shaped your thinking regarding research design . For example, you might use scales or questionnaires from previous studies.
When you write up your literature review, keep these three objectives front of mind, especially number two (revealing the gap in the literature), so that your literature review has a clear purpose and direction . Everything you write should be contributing towards one (or more) of these objectives in some way. If it doesn’t, you need to ask yourself whether it’s truly needed.
Top Tip: Don’t fall into the trap of just describing the main pieces of literature, for example, “A says this, B says that, C also says that…” and so on. Merely describing the literature provides no value. Instead, you need to synthesise it, and use it to address the three objectives above.

Ingredient #5 – Research Methodology
Now that you’ve clearly explained both your intended research topic (in the introduction) and the existing research it will draw on (in the literature review section), it’s time to get practical and explain exactly how you’ll be carrying out your own research. In other words, your research methodology.
In this section, you’ll need to answer two critical questions :
- How will you design your research? I.e., what research methodology will you adopt, what will your sample be, how will you collect data, etc.
- Why have you chosen this design? I.e., why does this approach suit your specific research aims, objectives and questions?
In other words, this is not just about explaining WHAT you’ll be doing, it’s also about explaining WHY. In fact, the justification is the most important part , because that justification is how you demonstrate a good understanding of research design (which is what assessors want to see).
Some essential design choices you need to cover in your research proposal include:
- Your intended research philosophy (e.g., positivism, interpretivism or pragmatism )
- What methodological approach you’ll be taking (e.g., qualitative , quantitative or mixed )
- The details of your sample (e.g., sample size, who they are, who they represent, etc.)
- What data you plan to collect (i.e. data about what, in what form?)
- How you plan to collect it (e.g., surveys , interviews , focus groups, etc.)
- How you plan to analyse it (e.g., regression analysis, thematic analysis , etc.)
- Ethical adherence (i.e., does this research satisfy all ethical requirements of your institution, or does it need further approval?)
This list is not exhaustive – these are just some core attributes of research design. Check with your institution what level of detail they expect. The “ research onion ” by Saunders et al (2009) provides a good summary of the various design choices you ultimately need to make – you can read more about that here .
Don’t forget the practicalities…
In addition to the technical aspects, you will need to address the practical side of the project. In other words, you need to explain what resources you’ll need (e.g., time, money, access to equipment or software, etc.) and how you intend to secure these resources. You need to show that your project is feasible, so any “make or break” type resources need to already be secured. The success or failure of your project cannot depend on some resource which you’re not yet sure you have access to.
Another part of the practicalities discussion is project and risk management . In other words, you need to show that you have a clear project plan to tackle your research with. Some key questions to address:
- What are the timelines for each phase of your project?
- Are the time allocations reasonable?
- What happens if something takes longer than anticipated (risk management)?
- What happens if you don’t get the response rate you expect?
A good way to demonstrate that you’ve thought this through is to include a Gantt chart and a risk register (in the appendix if word count is a problem). With these two tools, you can show that you’ve got a clear, feasible plan, and you’ve thought about and accounted for the potential risks.
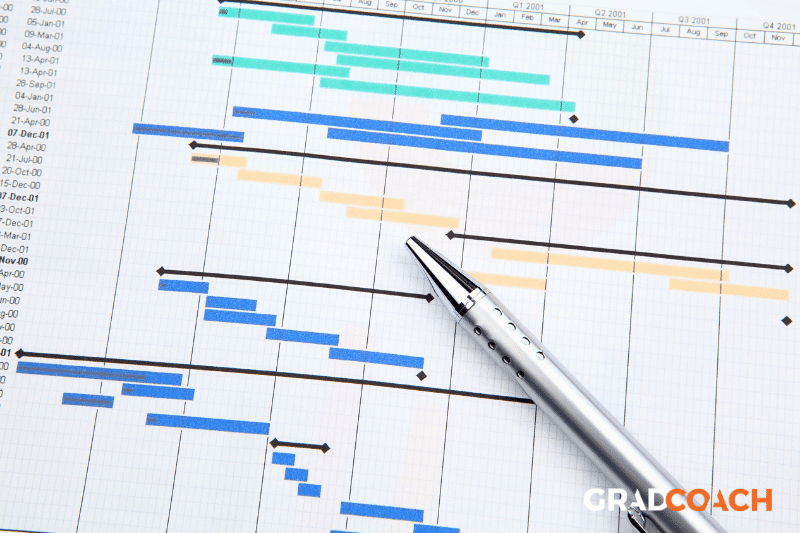
Tip – Be honest about the potential difficulties – but show that you are anticipating solutions and workarounds. This is much more impressive to an assessor than an unrealistically optimistic proposal which does not anticipate any challenges whatsoever.
Final Touches: Read And Simplify
The final step is to edit and proofread your proposal – very carefully. It sounds obvious, but all too often poor editing and proofreading ruin a good proposal. Nothing is more off-putting for an assessor than a poorly edited, typo-strewn document. It sends the message that you either do not pay attention to detail, or just don’t care. Neither of these are good messages. Put the effort into editing and proofreading your proposal (or pay someone to do it for you) – it will pay dividends.
When you’re editing, watch out for ‘academese’. Many students can speak simply, passionately and clearly about their dissertation topic – but become incomprehensible the moment they turn the laptop on. You are not required to write in any kind of special, formal, complex language when you write academic work. Sure, there may be technical terms, jargon specific to your discipline, shorthand terms and so on. But, apart from those, keep your written language very close to natural spoken language – just as you would speak in the classroom. Imagine that you are explaining your project plans to your classmates or a family member. Remember, write for the intelligent layman, not the subject matter experts. Plain-language, concise writing is what wins hearts and minds – and marks!
Let’s Recap: Research Proposal 101
And there you have it – how to write your dissertation or thesis research proposal, from the title page to the final proof. Here’s a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- The purpose of the research proposal is to convince – therefore, you need to make a clear, concise argument of why your research is both worth doing and doable.
- Make sure you can ask the critical what, who, and how questions of your research before you put pen to paper.
- Title – provides the first taste of your research, in broad terms
- Introduction – explains what you’ll be researching in more detail
- Scope – explains the boundaries of your research
- Literature review – explains how your research fits into the existing research and why it’s unique and valuable
- Research methodology – explains and justifies how you will carry out your own research
Hopefully, this post has helped you better understand how to write up a winning research proposal. If you enjoyed it, be sure to check out the rest of the Grad Coach Blog . If your university doesn’t provide any template for your proposal, you might want to try out our free research proposal template .

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling Udemy Course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

30 Comments
Thank you so much for the valuable insight that you have given, especially on the research proposal. That is what I have managed to cover. I still need to go back to the other parts as I got disturbed while still listening to Derek’s audio on you-tube. I am inspired. I will definitely continue with Grad-coach guidance on You-tube.
Thanks for the kind words :). All the best with your proposal.
First of all, thanks a lot for making such a wonderful presentation. The video was really useful and gave me a very clear insight of how a research proposal has to be written. I shall try implementing these ideas in my RP.
Once again, I thank you for this content.
I found reading your outline on writing research proposal very beneficial. I wish there was a way of submitting my draft proposal to you guys for critiquing before I submit to the institution.
Hi Bonginkosi
Thank you for the kind words. Yes, we do provide a review service. The best starting point is to have a chat with one of our coaches here: https://gradcoach.com/book/new/ .
Hello team GRADCOACH, may God bless you so much. I was totally green in research. Am so happy for your free superb tutorials and resources. Once again thank you so much Derek and his team.
You’re welcome, Erick. Good luck with your research proposal 🙂
thank you for the information. its precise and on point.
Really a remarkable piece of writing and great source of guidance for the researchers. GOD BLESS YOU for your guidance. Regards
Thanks so much for your guidance. It is easy and comprehensive the way you explain the steps for a winning research proposal.
Thank you guys so much for the rich post. I enjoyed and learn from every word in it. My problem now is how to get into your platform wherein I can always seek help on things related to my research work ? Secondly, I wish to find out if there is a way I can send my tentative proposal to you guys for examination before I take to my supervisor Once again thanks very much for the insights
Thanks for your kind words, Desire.
If you are based in a country where Grad Coach’s paid services are available, you can book a consultation by clicking the “Book” button in the top right.
Best of luck with your studies.
May God bless you team for the wonderful work you are doing,
If I have a topic, Can I submit it to you so that you can draft a proposal for me?? As I am expecting to go for masters degree in the near future.
Thanks for your comment. We definitely cannot draft a proposal for you, as that would constitute academic misconduct. The proposal needs to be your own work. We can coach you through the process, but it needs to be your own work and your own writing.
Best of luck with your research!
I found a lot of many essential concepts from your material. it is real a road map to write a research proposal. so thanks a lot. If there is any update material on your hand on MBA please forward to me.
GradCoach is a professional website that presents support and helps for MBA student like me through the useful online information on the page and with my 1-on-1 online coaching with the amazing and professional PhD Kerryen.
Thank you Kerryen so much for the support and help 🙂
I really recommend dealing with such a reliable services provider like Gradcoah and a coach like Kerryen.
Hi, Am happy for your service and effort to help students and researchers, Please, i have been given an assignment on research for strategic development, the task one is to formulate a research proposal to support the strategic development of a business area, my issue here is how to go about it, especially the topic or title and introduction. Please, i would like to know if you could help me and how much is the charge.
This content is practical, valuable, and just great!
Thank you very much!
Hi Derek, Thank you for the valuable presentation. It is very helpful especially for beginners like me. I am just starting my PhD.
This is quite instructive and research proposal made simple. Can I have a research proposal template?
Great! Thanks for rescuing me, because I had no former knowledge in this topic. But with this piece of information, I am now secured. Thank you once more.
I enjoyed listening to your video on how to write a proposal. I think I will be able to write a winning proposal with your advice. I wish you were to be my supervisor.
Dear Derek Jansen,
Thank you for your great content. I couldn’t learn these topics in MBA, but now I learned from GradCoach. Really appreciate your efforts….
From Afghanistan!
I have got very essential inputs for startup of my dissertation proposal. Well organized properly communicated with video presentation. Thank you for the presentation.
Wow, this is absolutely amazing guys. Thank you so much for the fruitful presentation, you’ve made my research much easier.
this helps me a lot. thank you all so much for impacting in us. may god richly bless you all
How I wish I’d learn about Grad Coach earlier. I’ve been stumbling around writing and rewriting! Now I have concise clear directions on how to put this thing together. Thank you!
Fantastic!! Thank You for this very concise yet comprehensive guidance.
Even if I am poor in English I would like to thank you very much.
Thank you very much, this is very insightful.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Postgraduate
Research degrees
- Examples of Research proposals
- Apply for 2024
- Find a course
- Accessibility
Examples of research proposals
How to write your research proposal, with examples of good proposals.
Research proposals
Your research proposal is a key part of your application. It tells us about the question you want to answer through your research. It is a chance for you to show your knowledge of the subject area and tell us about the methods you want to use.
We use your research proposal to match you with a supervisor or team of supervisors.
In your proposal, please tell us if you have an interest in the work of a specific academic at York St John. You can get in touch with this academic to discuss your proposal. You can also speak to one of our Research Leads. There is a list of our Research Leads on the Apply page.
When you write your proposal you need to:
- Highlight how it is original or significant
- Explain how it will develop or challenge current knowledge of your subject
- Identify the importance of your research
- Show why you are the right person to do this research
- Research Proposal Example 1 (DOC, 49kB)
- Research Proposal Example 2 (DOC, 0.9MB)
- Research Proposal Example 3 (DOC, 55.5kB)
- Research Proposal Example 4 (DOC, 49.5kB)
Subject specific guidance
- Writing a Humanities PhD Proposal (PDF, 0.1MB)
- Writing a Creative Writing PhD Proposal (PDF, 0.1MB)
- About the University
- Our culture and values
- Academic schools
- Academic dates
- Press office
Our wider work
- Business support
- Work in the community
- Donate or support
Connect with us
York St John University
Lord Mayor’s Walk
01904 624 624
York St John London Campus
6th Floor Export Building
1 Clove Crescent
01904 876 944
- Policies and documents
- Module documents
- Programme specifications
- Quality gateway
- Admissions documents
- Access and Participation Plan
- Freedom of information
- Accessibility statement
- Modern slavery and human trafficking statement
© York St John University 2024
Colour Picker
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Dui id ornare arcu odio.
Felis bibendum ut tristique et egestas quis ipsum. Et netus et malesuada fames ac turpis egestas. Faucibus pulvinar elementum integer enim neque volutpat ac. Hac habitasse platea dictumst vestibulum rhoncus.
Nec ullamcorper sit amet risus nullam eget felis eget. Eget felis eget nunc lobortis mattis aliquam faucibus purus.

- Schools & departments

Writing your PhD research proposal
Find guidance on how to write your PhD research proposal and a template form for you to use to submit your research proposal.
By asking you for an outline research proposal we hope to get a good picture of your research interests and your understanding of what such research is likely to entail.
The University's application form is designed to enable you to give an overview of your academic experience and qualifications for study at postgraduate level. Your outline research proposal then gives us an idea of the kind of research you want to undertake. This, together with information from your referees, will help us assess whether the Moray House School of Education and Sport would be the appropriate place for you to pursue your research interests.
At the application stage you are unlikely to be in a position to provide a comprehensive research proposal; the detailed shaping up of a research plan would be done in conjunction with your supervisors(s). But it is important for us to appreciate what you are hoping to investigate, how you envisage carrying out the research, and what the results might be expected to contribute to current knowledge and understanding in the relevant academic field(s) of study. In writing your proposal, please indicate any prior academic or employment experience relevant to your planned research.
In your research proposal, please also ensure that you clearly identify the Moray House research cluster your proposal falls under, as well as two to three staff members with expertise in this area. We also encourage you to contact potential supervisors within your area of proposed research prior to submitting your application in order to gauge their interest and availability.
How to write your research proposal
The description of your proposed research should consist of 4-5 typed A4 sheets. It can take whatever form seems best, but should include some information about the following:
- The general area within which you wish to conduct research, and why (you might find it helpful to explain what stimulated your interest in your chosen research field, and any study or research in the area that you have already undertaken)
- The kind of research questions that you would hope to address, and why (in explaining what is likely to be the main focus of your research, it may be helpful to indicate, for example, why these issues are of particular concern and the way in which they relate to existing literature)
- The sources of information and type of research methods you plan to use (for example, how you plan to collect your data, which sources you will be targeting and how you will access these data sources).
In addition to the above, please include any comments you are able to make concerning:
- The approach that you will take to analysing your research data
- The general timetable you would follow for carrying out and writing up your research
- Any plans you may have for undertaking fieldwork away from Edinburgh
- Any problems that might be anticipated in carrying out your proposed research
Please note: This guidance applies to all candidates, except those applying to conduct PhD research as part of a larger, already established research project (for example, in the Institute for Sport, Physical Education & Health Sciences).
In this case, you should provide a two- to three-page description of a research project that you have already undertaken, as a means of complementing information given in the application form. If you are in any doubt as to what is appropriate please contact us:
Contact us by email: Education@[email protected]
All doctoral proposals submitted as part of an application will be run through plagiarism detection software.

Template form for your research proposal
All applicants for a PhD or MSc by Research are required to submit a research proposal as part of their application. Applicants must use the template form below for their research proposal. This research proposal should then be submitted online as part of your application. Please use Calibri size 11 font size and do not change the paragraph spacing (single, with 6pt after each paragraph) or the page margins.

How to write a research proposal that stands out

Stand out from the competition
Take the next steps towards your PhD
Writing your research proposal
When you apply for a research degree at the University of Portsmouth, you may have to submit a research proposal that outlines, among many other things, the nature of your research, and why it's important.
To help make yours as compelling as possible, read our helpful hints for creating a clear, concise and engaging research proposal.
Prospective supervisors will not be expecting you to have all the answers at this stage; if accepted onto a research degree, your ideas will develop throughout the course of your studies.
What should a research proposal contain?
Title and abstract.
- Your title should be clear and easy-to-understand.
- The abstract is a concise and engaging summary of your research question and approach (around 300 words). It should be written as a standalone piece so that any prospective supervisor can understand what you plan to do, and why, from the abstract alone.
Introduction, background and rationale
- This section should provide a background to your research - what you want to investigate and why the research is important/needed.
Research aims, questions or hypothesis
- You should clearly communicate the research question(s) you would seek to answer in your intended research proposal. Depending on your chosen subject area you may also wish to specify some aims, objectives and hypotheses. If you are not sure whether this is necessary, discuss this with your potential supervisor.
Literature review
- In this section you will need to demonstrate your understanding of the key literature that relates to your research question(s), and outline your critical understanding of what previous research has found. You may also have identified any gaps in the current knowledge related to your area of research, and you can highlight these here.
Methodology
- A rationale and description of the approach you would intend to take to answer your research question(s). You should discuss the general approach you would take to answering your research question(s) e.g. in a Social Science PhD, whether you’d take a qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods approach, as well as considering the more specific issues e.g. would you use interviews or focus groups.
- Clearly outline any separate studies you expect to conduct and how they link or relate to each other. As a rule of thumb, most Science, Social Science and Engineering PhDs research proposals would be expected to contain 3-4 separate studies, each approximately equivalent to a Masters thesis project in size.
- What ethical considerations do you anticipate within your research, and how might you approach these?
Dissemination and impact
- Sharing the findings of your research is a fundamental part of being a researcher, and prospective supervisors will be interested to know how you anticipate disseminating your research findings.
- A research degree can take between 3-6 years to complete, so a timeline of the key stages of your research should be included.
Referencing
- Don't forget to include your references
How long should my research proposal be?
Most proposals are between 1,500-4,000 words, but the exact length will vary depending on which research area you're applying to join.
Your potential supervisor can let you know any specific requirements for the area you’re applying to.
You are strongly encouraged to work with your potential supervisor to refine your proposal before you make a formal application. This way, you can make sure the project is a good fit with their interests and expertise.
Do your homework - make sure your problem hasn't already been solved.
Engage the reader - you don't want the reader to switch off!
Be realistic - especially about timescales and accessing data
Take your time - it's important not to rush writing your research proposal
Seek feedback - it's always a good idea to get others to read your research proposal
Prepare to be flexible, your project can evolve or change

Important do’s and don’ts
- Write your research proposal in your own words.
- Acknowledge any sources you used for information or ideas presented in your research proposal.
- Make sure the research proposal you are about to submit looks fantastic - f irst impressions count!
Don’t:
- Copy and paste text directly from sources such as journal articles without acknowledging them in the text. Some universities use plagiarism checking software on the research proposals submitted to them.
- Use AI or similar tools to produce your finished proposal.
My PhD supervisor supported my career ambitions and has been crucial in getting me where I am today.
Robert Lawerence, PhD Molecular Microbiology

Postgraduate Research Proposal Guide
Learn more about research proposals and the process involved in creating the perfect application.
Follow our step by step guide

Contact Postgraduate Admissions
Speak to one of our friendly team and ask us anything about your postgraduate study options.
Get in touch
Main navigation
- Graduate Students
- Faculty & Staff
- Dean's Welcome
- Graduate Education Statistics
- Registration and degree progress
- Writing research proposals
- Comprehensive Exams
- Policies and Guidelines
- Joint PhD/Cotutelles
- Supporting Graduate student well-being
- Graduate Research Trainee
Ten tips for writing your research proposal
1. follow the instructions.
Read and conform to all instructions found on the council website. Make sure that your proposal fits the criteria of the competition.
2. Break down your proposal into point form before writing your first draft.
Based on the total length of the proposal, decide whether you will have headings/subheadings and what they will be (e.g., Introduction, Background Material, Methodology, and so on). These headings can be selected based on the advice given in the specific award instructions. For each section, lay out in point form what you will discuss.
3. Know your audience.
- Describe your research proposal in non-technical terms. Use clear, plain language and avoid jargon.
- Make sure your proposal is free of typographic and grammatical errors.
- Remember that, at every level, adjudication committees are multi-disciplinary and will include researchers in fields other than your own.
- Therefore, follow the KIS principle – K eep I t S imple! Reviewers like it that way.
4. Make an impact in the first few sentences.
Reviewers are very busy people. You must grab their attention and excite them about your project from the very beginning. Make it easy for them to understand (and thus fund) your proposal. Show how your research is innovative and valuable. Remember, too, to show your enthusiasm for your project—enthusiasm is contagious!
Organize your proposal so that it is tight, well-integrated, and makes a point, focused on a central question (e.g., “I am looking at this to show...”). Depending on the discipline, a tight proposal is often best achieved by having a clear hypothesis or research objective and by structuring the research proposal in terms of an important problem to be solved or fascinating question to be answered. Make sure to include the ways in which you intend to approach the solution.
5. Have a clear title.
It is important that the title of your project is understandable to the general public, reflects the goal of the study, and attracts interest.
6. Emphasize multidisciplinary aspects of the proposal, if applicable.
7. show that your research is feasible..
Demonstrate that you are competent to conduct the research and have chosen the best research or scholarly environment in which to achieve your goals.
8. Clearly indicate how your research or scholarship will make a “contribution to knowledge” or address an important question in your field.
9. get the proposal reviewed and commented on by others..
Get feedback and edit. Then edit some more. And get more feedback. The more diverse opinion and criticism you receive on your proposal the better suited it will be for a multi-disciplinary audience.
10. Remember that nothing is set in stone.
Your research proposal is not a binding document; it is a proposal . It is well understood by all concerned that the research you end up pursuing may be different from that in your proposal. Instead of treating your proposal as a final, binding document, think of it as a flexible way to plan an exciting (but feasible) project that you would like to pursue.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International License . Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies, McGill University .
Department and University Information
Graduate and postdoctoral studies.
17 Research Proposal Examples

A research proposal systematically and transparently outlines a proposed research project.
The purpose of a research proposal is to demonstrate a project’s viability and the researcher’s preparedness to conduct an academic study. It serves as a roadmap for the researcher.
The process holds value both externally (for accountability purposes and often as a requirement for a grant application) and intrinsic value (for helping the researcher to clarify the mechanics, purpose, and potential signficance of the study).
Key sections of a research proposal include: the title, abstract, introduction, literature review, research design and methods, timeline, budget, outcomes and implications, references, and appendix. Each is briefly explained below.
Watch my Guide: How to Write a Research Proposal
Get your Template for Writing your Research Proposal Here (With AI Prompts!)
Research Proposal Sample Structure
Title: The title should present a concise and descriptive statement that clearly conveys the core idea of the research projects. Make it as specific as possible. The reader should immediately be able to grasp the core idea of the intended research project. Often, the title is left too vague and does not help give an understanding of what exactly the study looks at.
Abstract: Abstracts are usually around 250-300 words and provide an overview of what is to follow – including the research problem , objectives, methods, expected outcomes, and significance of the study. Use it as a roadmap and ensure that, if the abstract is the only thing someone reads, they’ll get a good fly-by of what will be discussed in the peice.
Introduction: Introductions are all about contextualization. They often set the background information with a statement of the problem. At the end of the introduction, the reader should understand what the rationale for the study truly is. I like to see the research questions or hypotheses included in the introduction and I like to get a good understanding of what the significance of the research will be. It’s often easiest to write the introduction last
Literature Review: The literature review dives deep into the existing literature on the topic, demosntrating your thorough understanding of the existing literature including themes, strengths, weaknesses, and gaps in the literature. It serves both to demonstrate your knowledge of the field and, to demonstrate how the proposed study will fit alongside the literature on the topic. A good literature review concludes by clearly demonstrating how your research will contribute something new and innovative to the conversation in the literature.
Research Design and Methods: This section needs to clearly demonstrate how the data will be gathered and analyzed in a systematic and academically sound manner. Here, you need to demonstrate that the conclusions of your research will be both valid and reliable. Common points discussed in the research design and methods section include highlighting the research paradigm, methodologies, intended population or sample to be studied, data collection techniques, and data analysis procedures . Toward the end of this section, you are encouraged to also address ethical considerations and limitations of the research process , but also to explain why you chose your research design and how you are mitigating the identified risks and limitations.
Timeline: Provide an outline of the anticipated timeline for the study. Break it down into its various stages (including data collection, data analysis, and report writing). The goal of this section is firstly to establish a reasonable breakdown of steps for you to follow and secondly to demonstrate to the assessors that your project is practicable and feasible.
Budget: Estimate the costs associated with the research project and include evidence for your estimations. Typical costs include staffing costs, equipment, travel, and data collection tools. When applying for a scholarship, the budget should demonstrate that you are being responsible with your expensive and that your funding application is reasonable.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: A discussion of the anticipated findings or results of the research, as well as the potential contributions to the existing knowledge, theory, or practice in the field. This section should also address the potential impact of the research on relevant stakeholders and any broader implications for policy or practice.
References: A complete list of all the sources cited in the research proposal, formatted according to the required citation style. This demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the relevant literature and ensures proper attribution of ideas and information.
Appendices (if applicable): Any additional materials, such as questionnaires, interview guides, or consent forms, that provide further information or support for the research proposal. These materials should be included as appendices at the end of the document.
Research Proposal Examples
Research proposals often extend anywhere between 2,000 and 15,000 words in length. The following snippets are samples designed to briefly demonstrate what might be discussed in each section.
1. Education Studies Research Proposals
See some real sample pieces:
- Assessment of the perceptions of teachers towards a new grading system
- Does ICT use in secondary classrooms help or hinder student learning?
- Digital technologies in focus project
- Urban Middle School Teachers’ Experiences of the Implementation of
- Restorative Justice Practices
- Experiences of students of color in service learning
Consider this hypothetical education research proposal:
The Impact of Game-Based Learning on Student Engagement and Academic Performance in Middle School Mathematics
Abstract: The proposed study will explore multiplayer game-based learning techniques in middle school mathematics curricula and their effects on student engagement. The study aims to contribute to the current literature on game-based learning by examining the effects of multiplayer gaming in learning.
Introduction: Digital game-based learning has long been shunned within mathematics education for fears that it may distract students or lower the academic integrity of the classrooms. However, there is emerging evidence that digital games in math have emerging benefits not only for engagement but also academic skill development. Contributing to this discourse, this study seeks to explore the potential benefits of multiplayer digital game-based learning by examining its impact on middle school students’ engagement and academic performance in a mathematics class.
Literature Review: The literature review has identified gaps in the current knowledge, namely, while game-based learning has been extensively explored, the role of multiplayer games in supporting learning has not been studied.
Research Design and Methods: This study will employ a mixed-methods research design based upon action research in the classroom. A quasi-experimental pre-test/post-test control group design will first be used to compare the academic performance and engagement of middle school students exposed to game-based learning techniques with those in a control group receiving instruction without the aid of technology. Students will also be observed and interviewed in regard to the effect of communication and collaboration during gameplay on their learning.
Timeline: The study will take place across the second term of the school year with a pre-test taking place on the first day of the term and the post-test taking place on Wednesday in Week 10.
Budget: The key budgetary requirements will be the technologies required, including the subscription cost for the identified games and computers.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: It is expected that the findings will contribute to the current literature on game-based learning and inform educational practices, providing educators and policymakers with insights into how to better support student achievement in mathematics.
2. Psychology Research Proposals
See some real examples:
- A situational analysis of shared leadership in a self-managing team
- The effect of musical preference on running performance
- Relationship between self-esteem and disordered eating amongst adolescent females
Consider this hypothetical psychology research proposal:
The Effects of Mindfulness-Based Interventions on Stress Reduction in College Students
Abstract: This research proposal examines the impact of mindfulness-based interventions on stress reduction among college students, using a pre-test/post-test experimental design with both quantitative and qualitative data collection methods .
Introduction: College students face heightened stress levels during exam weeks. This can affect both mental health and test performance. This study explores the potential benefits of mindfulness-based interventions such as meditation as a way to mediate stress levels in the weeks leading up to exam time.
Literature Review: Existing research on mindfulness-based meditation has shown the ability for mindfulness to increase metacognition, decrease anxiety levels, and decrease stress. Existing literature has looked at workplace, high school and general college-level applications. This study will contribute to the corpus of literature by exploring the effects of mindfulness directly in the context of exam weeks.
Research Design and Methods: Participants ( n= 234 ) will be randomly assigned to either an experimental group, receiving 5 days per week of 10-minute mindfulness-based interventions, or a control group, receiving no intervention. Data will be collected through self-report questionnaires, measuring stress levels, semi-structured interviews exploring participants’ experiences, and students’ test scores.
Timeline: The study will begin three weeks before the students’ exam week and conclude after each student’s final exam. Data collection will occur at the beginning (pre-test of self-reported stress levels) and end (post-test) of the three weeks.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: The study aims to provide evidence supporting the effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions in reducing stress among college students in the lead up to exams, with potential implications for mental health support and stress management programs on college campuses.
3. Sociology Research Proposals
- Understanding emerging social movements: A case study of ‘Jersey in Transition’
- The interaction of health, education and employment in Western China
- Can we preserve lower-income affordable neighbourhoods in the face of rising costs?
Consider this hypothetical sociology research proposal:
The Impact of Social Media Usage on Interpersonal Relationships among Young Adults
Abstract: This research proposal investigates the effects of social media usage on interpersonal relationships among young adults, using a longitudinal mixed-methods approach with ongoing semi-structured interviews to collect qualitative data.
Introduction: Social media platforms have become a key medium for the development of interpersonal relationships, particularly for young adults. This study examines the potential positive and negative effects of social media usage on young adults’ relationships and development over time.
Literature Review: A preliminary review of relevant literature has demonstrated that social media usage is central to development of a personal identity and relationships with others with similar subcultural interests. However, it has also been accompanied by data on mental health deline and deteriorating off-screen relationships. The literature is to-date lacking important longitudinal data on these topics.
Research Design and Methods: Participants ( n = 454 ) will be young adults aged 18-24. Ongoing self-report surveys will assess participants’ social media usage, relationship satisfaction, and communication patterns. A subset of participants will be selected for longitudinal in-depth interviews starting at age 18 and continuing for 5 years.
Timeline: The study will be conducted over a period of five years, including recruitment, data collection, analysis, and report writing.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: This study aims to provide insights into the complex relationship between social media usage and interpersonal relationships among young adults, potentially informing social policies and mental health support related to social media use.
4. Nursing Research Proposals
- Does Orthopaedic Pre-assessment clinic prepare the patient for admission to hospital?
- Nurses’ perceptions and experiences of providing psychological care to burns patients
- Registered psychiatric nurse’s practice with mentally ill parents and their children
Consider this hypothetical nursing research proposal:
The Influence of Nurse-Patient Communication on Patient Satisfaction and Health Outcomes following Emergency Cesarians
Abstract: This research will examines the impact of effective nurse-patient communication on patient satisfaction and health outcomes for women following c-sections, utilizing a mixed-methods approach with patient surveys and semi-structured interviews.
Introduction: It has long been known that effective communication between nurses and patients is crucial for quality care. However, additional complications arise following emergency c-sections due to the interaction between new mother’s changing roles and recovery from surgery.
Literature Review: A review of the literature demonstrates the importance of nurse-patient communication, its impact on patient satisfaction, and potential links to health outcomes. However, communication between nurses and new mothers is less examined, and the specific experiences of those who have given birth via emergency c-section are to date unexamined.
Research Design and Methods: Participants will be patients in a hospital setting who have recently had an emergency c-section. A self-report survey will assess their satisfaction with nurse-patient communication and perceived health outcomes. A subset of participants will be selected for in-depth interviews to explore their experiences and perceptions of the communication with their nurses.
Timeline: The study will be conducted over a period of six months, including rolling recruitment, data collection, analysis, and report writing within the hospital.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: This study aims to provide evidence for the significance of nurse-patient communication in supporting new mothers who have had an emergency c-section. Recommendations will be presented for supporting nurses and midwives in improving outcomes for new mothers who had complications during birth.
5. Social Work Research Proposals
- Experiences of negotiating employment and caring responsibilities of fathers post-divorce
- Exploring kinship care in the north region of British Columbia
Consider this hypothetical social work research proposal:
The Role of a Family-Centered Intervention in Preventing Homelessness Among At-Risk Youthin a working-class town in Northern England
Abstract: This research proposal investigates the effectiveness of a family-centered intervention provided by a local council area in preventing homelessness among at-risk youth. This case study will use a mixed-methods approach with program evaluation data and semi-structured interviews to collect quantitative and qualitative data .
Introduction: Homelessness among youth remains a significant social issue. This study aims to assess the effectiveness of family-centered interventions in addressing this problem and identify factors that contribute to successful prevention strategies.
Literature Review: A review of the literature has demonstrated several key factors contributing to youth homelessness including lack of parental support, lack of social support, and low levels of family involvement. It also demonstrates the important role of family-centered interventions in addressing this issue. Drawing on current evidence, this study explores the effectiveness of one such intervention in preventing homelessness among at-risk youth in a working-class town in Northern England.
Research Design and Methods: The study will evaluate a new family-centered intervention program targeting at-risk youth and their families. Quantitative data on program outcomes, including housing stability and family functioning, will be collected through program records and evaluation reports. Semi-structured interviews with program staff, participants, and relevant stakeholders will provide qualitative insights into the factors contributing to program success or failure.
Timeline: The study will be conducted over a period of six months, including recruitment, data collection, analysis, and report writing.
Budget: Expenses include access to program evaluation data, interview materials, data analysis software, and any related travel costs for in-person interviews.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: This study aims to provide evidence for the effectiveness of family-centered interventions in preventing youth homelessness, potentially informing the expansion of or necessary changes to social work practices in Northern England.
Research Proposal Template
Get your Detailed Template for Writing your Research Proposal Here (With AI Prompts!)
This is a template for a 2500-word research proposal. You may find it difficult to squeeze everything into this wordcount, but it’s a common wordcount for Honors and MA-level dissertations.
Your research proposal is where you really get going with your study. I’d strongly recommend working closely with your teacher in developing a research proposal that’s consistent with the requirements and culture of your institution, as in my experience it varies considerably. The above template is from my own courses that walk students through research proposals in a British School of Education.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
8 thoughts on “17 Research Proposal Examples”
Very excellent research proposals
very helpful
Very helpful
Dear Sir, I need some help to write an educational research proposal. Thank you.

Hi Levi, use the site search bar to ask a question and I’ll likely have a guide already written for your specific question. Thanks for reading!
very good research proposal
Thank you so much sir! ❤️
Very helpful 👌
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Writing your research proposal
The purpose of the research proposal is to demonstrate that the research you wish to undertake is significant, necessary and feasible, that you will be able to make an original contribution to the field, and that the project can be completed within the normal time period. Some general guidelines and advice on structuring your proposal are provided below. Research proposals should be between 1,000 and 3,000 words depending on the programme (excluding the reference list/bibliography).
Title sheet
Topic statement, research aims, review of the literature, study design / theoretical orientation, research methods, tentative chapter outline, references/bibliography.

Applying for a research degree
/images/cornell/logo35pt_cornell_white.svg" alt="graduate school research proposal sample"> Cornell University --> Graduate School
Writing your research statement, set yourself apart.
Most reviewers volunteer their time. Faced with a huge pile of applications, they’ll move quickly and won’t take time to search out hidden answers.
In reviewing your application, the reader will scan for clear answers to three questions:
- What new knowledge will be generated for the discipline?
- Why is it valuable?
- How can they be assured the conclusions will be valid?
You want to make sure that the reviewer will be left with something to remember: a message that will remain after reading many other proposals. Make sure your proposal is clear and has a strong opening paragraph that will grab the reader’s attention. Your statement should tell a compelling story with a beginning, a middle, and an end.
Avoid jargon
Always keep in mind that reviewers may not be experts in your particular research area. It is essential that you couch your proposal in language and a narrative that will be accessible to an intelligent but non-specialized reviewer. In particular, don’t use jargon. Eliminate any theoretical discourse that is only accessible to those trained in your area.
Keep the spotlight on ideas
Start with a subject that interests you – a research proposal or a question – and develop a good proposal around it. Don’t worry if your proposed research project isn’t the “hot” topic in the field right now. In fact, an off-the-beaten-path project may stand out among all the other applications.
Show the reviewer that you are ready to take on the challenge of independent research; that you have not only a strong foundation for research as evidenced by a knowledge of the core scholarly publications in your discipline, but also that you possess the creativity, passion, and drive that will take you from more passive learning to active invention and hypothesis. Be clear about how you will undertake the research and how you will analyze the results. Argue why you think this is the best approach to the problem.
Explain which approaches are standard and which are innovative. The way you formulate your questions and describe how you will address them will reveal a lot to the review committee about your thought processes.
Your proposal is not the same as a final plan
If you’re a first-year student, remember that you’re writing a proposal: you are not committed to following the exact path you establish in your proposal. Most funding agencies expect that your project will change as you get underway. The important thing is to show that you’ll be capable of carrying out research in the discipline area proposed given the resources available to you.
Applying for dissertation-year fellowships
If you’re applying for a dissertation-year fellowship, the bar has been raised. Given your breadth of experience, the reviewers will expect to see more from you than they will from a first-year student. Reviewers will want to see that you’ve taken an interest in your professional development by presenting at national conferences and by having publications accepted to peer-review journals or in process, so be sure to address those issues.
Discuss your research proposal with your special committee chair, your director of graduate studies, faculty in your field, and other students. If you can identify students who have had successful proposals or faculty who have served as adjudicators, ask them. It’s okay to tailor your research statement to present the version most likely to win the fellowship. Focus on the aspects of your project that are the best fit with the sponsoring agency’s stated goals for the fellowship program. If you need inspiration, check out the reference notebooks of successful applications available in 350 Caldwell Hall.
Details matter, so sweat them
Your bibliography is important. This is where you will show experts in your field that you know the discipline and that you’ve done your homework. Make sure you cover the key papers in your discipline, but don’t make the bibliography too long. Reviewers want to see that you can distinguish between the most important contributions and secondary papers. A good bibliography shows you know enough about the discipline to avoid duplicating other work.
Proof your work
Make sure that there are no typographical or grammatical errors and follow the guidelines carefully. Your statements reflect on the level of professionalism you will bring to your research. When the competition is extreme, reviewers look for clues that differentiate one application from another. Typographical errors, grammatical errors, and inattention to guidelines will create suspicion over your attention to detail and will probably result in your application being passed over.
Allow enough time
You need to be exceptional in an excellent group of applicants. A good proposal may take up to three months to develop. Write a draft, seek input from others, revise, set it aside, come back to it, revise again, seek input again. Keep working until you have a polished product. If you put in the time to make your proposal as good as it can be, it will show in the end result and your application will be more competitive.
The Heller School Recognized as a Top 10 Graduate School
U.S. News & World Report ranks Heller #9 for social policy, and #13 for health policy and management: “Brandeis University graduate program earned ‘Best’ status as a result of its high ranking”
April 09, 2024
For its 2025 rankings, U.S. News & World Report ranked the Heller School for Social Policy and Management among the top public affairs graduate schools in two specialty categories: social policy (where Heller has been top-ranked for over a decade) and health policy and management.
This year, Heller rose from #14 to #9 for social policy , ranking in the prestigious top 10 of its category, and ranked #13 for health policy and management .
Social policy and health policy and management are specialty areas within the public affairs category, where Heller ranks in the top 21% of graduate schools in the U.S. U.S. News & World Report rankings are based on a survey of deans, directors, and department chairs at 271 graduate schools of public affairs across the country.
“Heller’s legacy is one of innovation and dedication to making the world a more equitable place. As we continue to make profound contributions to the fields of social policy and health policy and management, we are cognizant of the changes that need to be made and how we can make them,” says Interim Dean Maria Madison . “Every day, our faculty and researchers commit themselves to improving health care access, promoting racial and economic equity, and advocating for improvements in disability rights, child poverty, and workforce and labor market conditions. It’s an honor to be recognized by our peer institutions for these efforts that impact meaningful change in our world.”
Led by the motto “knowledge advancing social justice,” Heller is a nationally-recognized research and educational institution at Brandeis University. The school, celebrating its 65th anniversary year in 2024, has expanded from a single doctoral program to include several master’s degrees spanning global and domestic social policy. Heller is also home to nine research centers and institutes renowned for conducting applied interdisciplinary research and active public engagement.
School of Environmental and Forest Sciences
- College of the Environment
- University of Washington
SEFS Students win big at 2024 Alaska Airlines Environmental Innovation Challenge
Photos | Courtesy of Charles Trillingham
Students competing in this year’s Alaska Airlines Environmental Innovation Challenge showed up in a big way. Taking home the $15,000 Grand Prize was AgroFilms, a team of graduate and undergraduate students from the UW School of Environmental and Forest Sciences Bioresource Science and Engineering program as well as a technology management MBA student. The team’s mulch film, both innovative and low-cost, has the potential to keep plastic waste out of farms, landfills and oceans.

“The students did a great job in translating a material we are developing, nanocellulose, into a product (biodegradable agricultural mulch film) that can address a major environmental problem, ocean plastic pollution,” said Rick Gustafson , a UW professor in Bioresource Science and Engineering.
This year marked the competition’s 16th year, hosted by UW Foster School’s Buerk Center for Entrepreneurship. The competition draws students in from Washington, Oregon, Idaho, Alaska and British Columbia, including students from 10 regional colleges and universities this year. Tens of thousands of dollars were on the table in prize money and, in years past, success at this event has been a stepping stone toward acceptance into accelerator programs like the Jones + Foster Accelerator Program as well as seed and grant money to further research.
Of the 42 teams that applied to compete, 22 were selected as finalists. The teams were tasked with bringing forward innovative solutions to today’s environmental problems. Finalists included students from across the College of the Environment in both SEFS and the School of Oceanography .
Another team of finalists, including a Ph.D. student from SEFS Hema Velappan, pitched TimberTwin to a panel of 100 cleantech entrepreneurs, innovators and investors who served as this year’s judges. TimberTwin, using blockchain-based technology, traces timber from the point of harvest to processing, offering the wood supply chain a more transparent and accurate tracking system.
Velappan sees challenges like these advancing ecological literacy by giving those in academia a platform to communicate science to the general public. She said, “Competitions like EIC provide an excellent platform to showcase science and communicate it to a crowd with a diverse background. We are living in a time where research is becoming more multidisciplinary and challenges like EIC underscore this trend and bring together students from multiple research backgrounds.”
Student finalists from the School of Oceanography pitched SEAPEN, which won the competition’s $2,500 Leo Cup Innovation in Oceanography Prize. Their technology uses oceanographic computer vision tools that enable effective analysis of marine data that will help to address critical environmental challenges faced by our oceans.
Participation in the Environmental Innovation Challenge gives students access to invaluable feedback from the judges on avenues for advancing their innovations. Learn more about competition success stories here .
We asked this year’s Grand Prize winners what advice they have for students considering competing next year. “Find ways to make an impression! Be enthusiastic about your product and bring in product samples if you can,” said BSE undergraduate Lexi Escure. Hussain Aladwan emphasized, “Be clear – it should be easy to tell what problem you’re trying to solve and how you’re solving it.”
Are you interested in entering the competition or looking for members to join your team? The UW Foster School of Business suggests attending a team formation event through UW Startup Tree , a Team Tuesday Meetup or reaching out directly to Lauren Brohawn at [email protected] .
We asked 6,000 New Englanders: Is a college degree still worth the cost?
Emerson college polling and the globe magazine partnered on a sweeping survey of adults around new england. here’s what they had to say..

I s college still worth it?
At universities today, it’s a nearly $125,000 question — that’s how much students on campus for four years can expect to rack up in school bills, on average, according to federal data.
And here in New England, it’s a $22 billion question — that’s how much our roughly 250 colleges and universities contributed to the regional economy in 2022 alone, according to the New England Board of Higher Education.
For generations, college students have invested money — plus years of time and effort — in hopes of emerging from schools as well-rounded critical thinkers with job skills that would get them hired in a flash. And for many decades, a college degree seemed as safe a bet as you could find for a bright future. But now campuses (and college presidents) are in the crosshairs of ideological fights, overall student debt stands at a near-record $1.72 trillion , and new graduates fear AI will snatch away jobs before the ink is even dry on their diplomas.
So, back to that question: Is college still worth it?
Advertisement
To find what New Englanders think right now, the Globe Magazine partnered with Emerson College Polling, a nonpartisan, nationally-ranked polling center based in Boston, to survey 6,000 adults across all six states in this region. In February, we cast a wide net for respondents, including adults of any age and education status; those currently in school and people long graduated; those working or unemployed, homemaking, or retired.
For many, their reply to the question was a resounding Yes. In New England, our survey revealed, folks who show notable support for the idea that a college degree is worth the expense includes students who are working full time (71 percent agree), current students who aren’t working (64 percent), Hispanic/Latino people (58 percent), Asian people (56 percent), Democrats (56 percent), people with advanced degrees (55 percent), and 18- to 24-year-olds (51 percent). Even respondents who didn’t finish high school are pro-college (53 percent).
However, when you look at answers for all 6,000 New England adults combined, opinions are split nearly down the middle. While 46 percent agree that a four-year college degree is worth the expense, 44 percent disagree and 10 percent neither agree nor disagree. Groups with particularly high levels of disagreement include vocational and technical school grads (63 percent disagree), people with an associate’s degree (51 percent), and Republicans (51 percent).
There are doubts about college in our region, to be sure, but higher education here doesn’t have the thoroughly chilly reception it has earned nationally. A March 2023 Wall Street Journal -NORC survey of 1,019 US adults found that 56 percent said a college degree isn’t worth the cost. More than 60 percent of 18- to 34-year-olds in that survey had also lost faith in the value of a degree — a notable difference from ours, which shows young New Englanders still supporting it.
At the state level, our survey found Connecticut residents have the highest support for college, at 49 percent, followed by Rhode Island, at 48 percent. Opinions are mixed in Massachusetts and Vermont. And in New Hampshire and Maine, the largest share of respondents who weighed in say college isn’t worth it.
As for how most New Englanders define “worth it,” respondents overwhelmingly drew a direct line between college and career. Forty percent of respondents said the main reason to attend college was to get a good job (followed by “to make more money,” at 24 percent). This was the top reported answer for every state, age, education level, race/ethnicity, and political leaning.
Equally striking, our survey revealed that 56 percent of New England adults believe that a college degree is essential for landing a good job. While this shows an overwhelming belief in the promise of college, that support suggests a sharp drop from 13 years ago, when a Gallup-Lumina survey found that 69 percent of respondents nationwide said a degree is essential.
Other Gallup surveys found the portion of US adults ages 18 to 29 saying a college degree is “very important” plunged from 74 percent in 2013 to 41 percent in 2019.
“A college education is worth it, no question,” says Lawrence Schall, president of the New England Commission of Higher Education, an accrediting agency for colleges and universities in the region and beyond. He points to the long-term earning power of a degree, known as the college wage premium, compared with not having one. “With the return on investment, over a lifetime of work, how do those rates progress? That premium [with a degree] almost doubles.”
But studies show that historic economic advantage has been eroding for recent graduates as loans and other debts have skyrocketed. And amid these higher-than-ever stakes of making the wrong choice, the cost-benefit analysis undertaken by prospective students and their families has gotten far more complicated.
Things are different now than when Lisa Cornelio, a 58-year-old survey respondent from Connecticut, and her siblings went to college. “I grew up in an old New England mill town, so most folks were blue collar,” she says. “For whatever reason, my mom was able to encourage my dad to send all of us to great institutions, and he had the resources to do that.” Cornelio was also able to work jobs while attending Princeton, and didn’t need to take out loans.
Now, however, Cornelio works as a social worker and college consultant, and sees the different kinds of struggles her students go through. “It’s not even the top-tier institutions that are expensive, but community colleges, too,” she says. She asks her students a core question, one she didn’t necessarily need to ask herself in school: “You have to do a real inventory: What are you doing this for?”
Julie Reuben, a historian at the Harvard Graduate School of Education, has seen the risks when students start school but don’t finish. “Going into higher education is very expensive,” she says, “and what is particularly expensive is not finishing.” Almost a third of the 2.4 million students who started college in 2017 have since left without earning a degree , according to the National Student Clearinghouse Research Center. “These students take on loans but do not get the economic benefit of a four-year degree.”
The risks didn’t used to be this high. Adjusted for inflation, students at four-year colleges face tuition costs that have more than tripled in the past six decades . “Generationally, it was [once]much easier to get a college degree, affordable enough to work your way through,” Reuben says. “Students could go without gaining a lot of debt. That’s the reality they knew.” But today, she continues, “To graduate without significant debt, you have to come from a well-resourced family or go to a school with financial aid.”
In the Globe Magazine -Emerson College Polling survey, 52 percent of New England adults said their college degrees were not worth the loans they needed to get them, and now regret taking on that debt. A similar portion of respondents — 53 percent — support using government funds to reduce or forgive student loans, though the Republican and age 60-plus segments show strong opposition.
People such as Michael Poliakoff believe it’s not just the cost of college that is draining support: What is taught is inadequate to prepare students for many jobs. Moreover, colleges have become an “echo chamber” of ideas, he says. “It used to be a diploma from a four-year college would get you a good job,” says Poliakoff, president of the Washington, D.C.-based nonprofit American Council of Trustees and Alumni. “So many employers are not confident in newly hired four-year college graduates.”
The concept of free speech on campuses is hotly contested. When our survey asked respondents to choose which was the bigger problem for colleges, 52 percent reported it’s people being allowed to say harmful or misleading things, while the rest believe it’s people being prevented from saying what they want.
“Take these findings as a wake-up call,” says Poliakoff, whose organization advocates for the free exchange of ideas on campus. “College should be a place where you think the unthinkable and challenge the unchallengeable. . . . It should be an opportunity for everyone to come out with greater strength for career and citizenry.”
Lisa Cornelio, the social worker and college counselor from Connecticut, tries to remind her students that “there are a lot of options for greatness.” For some, that’s going from high school to college. “A good education can expand your mind,” she says, “bring you the confidence to go after things that, without that degree, you may hold yourself back from.”
But for others, success is ignoring the drumbeat (and peer pressure) that a four-year degree is the only path. “If you have a dream and a vision, then you can get going on it,” she says. “I think vocational schools and training can do wonders, and people end up living great lives because they’re out doing what they love every day, and it didn’t involve going to a four-year institution.”
According to the Globe Magazine -Emerson College Polling survey, New England adults seem to agree with Cornelio about options. When asked what a high schooler should do after graduation — assuming no obstacles stood in the way — 39 percent say attend a four-year college. But the next highest answer — at 23 percent — was to enter a non-college training program. (For 18- to 24-year-olds surveyed, the second choice is to enter the workforce.)
Lawrence Schall’s accreditation agency, the New England Commission of Higher Education, recently announced it would consider accreditation proposals from colleges looking to offer bachelor’s degrees in fewer than the traditional 120 credits, which could mean going for three years rather than four. The idea is to get people out of the classroom and into the job market sooner and less burdened by debt (Merrimack College and New England College have both expressed interest).
“The power of American education is in the diversity of institutions,” Schall says. “All with different admissions, price points, outcomes — the information is out there for people to find their place.” The Harvards and MITs represent only a sliver of New England institutions, he points out, adding there is a huge number of smaller colleges here where an “extraordinary education” is available at an affordable price.
“People think of college as one thing,” Schall says, “but it is nowhere near one thing.”
Survey methodology: The Boston Globe Magazine-Emerson College Polling survey of New England adults was conducted February 2-7, 2024. The study interviewed 6,000 adults (n=1,000 residents per New England state), with a credibility interval, similar to a poll's margin of error, per state of +/-3%. The overall New England sample was weighted proportionately for n=2,167 with a credibility interval of +/-2%. Data was collected by contacting cellphones via MMS-to-web, landlines via Interactive Voice Response, email, and an online panel.
Laurie Hilburn is pursuing her master’s degree in publishing and writing at Emerson College. Send comments to [email protected] . Contributors: This project was produced in collaboration with an Emerson College writing course led by associate professor Susanne Althoff, a former editor of the Globe Magazine. The undergraduate and graduate students who contributed are Libby Bancroft, Nicole Belcastro, Joei Chan, Julia DaSilva-Novotny, Gianna Di Cristo, Laurie Hilburn, Lauren Hunt, Angelina Parrillo, Audrey Silalahi, Lauren Smith, Gabel Strickland, and Rachel Tarby.
Read more from College & Careers:
- Is a college degree needed for a great job? The answer is surprising.
- How conservatives lost their trust in the value of college
- College debt is higher than ever. One in 2 grads with loans have regrets.
- The FAFSA aid debacle is like trying to get Taylor Swift tickets. My kid can’t go to college until it’s fixed.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research Proposal Example/Sample. Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template. If you're getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals, you've come to the right place. In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals, one for a Master's-level ...
semesters (a proposal will be submitted to the Purdue Graduate School for this option.). Citizens with advanced degrees earn higher salaries and contribute more to local and regional economic prosperity. The 4 + 1 option is more affordable, increases programmatic productivity and provides incentives to students to achieve completion.
Research and Citation. Overview; Conducting Research; Using Research; APA Style (7th Edition) ... Reading for Graduate School; Sample Academic Proposals; Suggested Resources ... Select the Sample Academic Proposals PDF in the Media box above to download this file and read examples of proposals for conferences, journals, and book chapters. ...
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management" Example research proposal #2: "Medical Students as Mediators of ...
An important part of the work completed in academia is sharing our scholarship with others. Such communication takes place when we present at scholarly conferences, publish in peer-reviewed journals, and publish in books. This OWL resource addresses the steps in writing for a variety of academic proposals. For samples of academic proposals ...
In the humanities, these sections may include scholarly research, archival research, theoretical orientation, etc. • Cite sources in your methods section. Ex: Critical Race Theory (Ladson-Billings) • Acknowledge problems with your research design • Provide support for your chosen approach by showing
institution you are applying to. However, if you are not given any guidelines on how to format your research proposal, you could adopt the suggested structure below. This is also relevant if you are applying for external funding or asking your employer to sponsor you to undertake a research degree. Suggested structure for a research proposal:
Make sure you can ask the critical what, who, and how questions of your research before you put pen to paper. Your research proposal should include (at least) 5 essential components : Title - provides the first taste of your research, in broad terms. Introduction - explains what you'll be researching in more detail.
Research proposals. Your research proposal is a key part of your application. It tells us about the question you want to answer through your research. It is a chance for you to show your knowledge of the subject area and tell us about the methods you want to use. We use your research proposal to match you with a supervisor or team of supervisors.
Most good research proposals are usually between 2000 and 4000 words in length. A strong research proposal can and should make a positive first impression about your potential to become a good researcher. It should show those reading it that your ideas are focused, interesting and realistic. Although you should write the proposal yourself, it ...
All applicants for a PhD or MSc by Research are required to submit a research proposal as part of their application. Applicants must use the template form below for their research proposal. This research proposal should then be submitted online as part of your application. Please use Calibri size 11 font size and do not change the paragraph ...
1.Choose a research topic and develop a working title. Having a strong interest in your research topic will certainly help you to keep going when the journey becomes more challenging. The research topic is the subject of your research, which is a part of a broader field of study.
Write your research proposal in your own words. Acknowledge any sources you used for information or ideas presented in your research proposal. Make sure the research proposal you are about to submit looks fantastic - first impressions count! Copy and paste text directly from sources such as journal articles without acknowledging them in the text.
1 of 5. Research Proposals. Writing a research proposal is the first step for a research project. Before you can work on your research, it must be approved, whether that is by a professor, thesis advisor, or supervisor. It is essential to make your proposal as strong as possible; if your proposal is denied, you may not get the funding you need ...
A Sample Research Proposal with Comments A research project or thesis will take at least two semesters to complete. Prior to starting a research, i.e. enrolling in the first semester research course, students must go through the proposal stage, during which students will develop their proposal and have it reviewed by his/her research advisor. ...
1. Follow the instructions! Read and conform to all instructions found on the council website. Make sure that your proposal fits the criteria of the competition. 2. Break down your proposal into point form before writing your first draft. Based on the total length of the proposal, decide whether you will have headings/subheadings and what they will be (e.g., Introduction, Background Material ...
Graduate School Writing Samples Bernhard Nickel · [email protected] July 10, 2022 ... • Your writing sample should not talk about your plans, in the way that a research proposal does. You can talk about your plans for the future in your personal statement. The writing sample is supposed
Research Proposal Examples. Research proposals often extend anywhere between 2,000 and 15,000 words in length. The following snippets are samples designed to briefly demonstrate what might be discussed in each section. 1. Education Studies Research Proposals.
Graduate School. The Graduate School exists to provide a stimulating and enriching environment for postgraduate students. Postgraduate course search. Professional. ... The purpose of the research proposal is to demonstrate that the research you wish to undertake is significant, necessary and feasible, that you will be able to make an original ...
Seek input. Discuss your research proposal with your special committee chair, your director of graduate studies, faculty in your field, and other students. If you can identify students who have had successful proposals or faculty who have served as adjudicators, ask them. It's okay to tailor your research statement to present the version most ...
To submit the research proposal, the following conditions must be met: Have an approved degree plan; Have no open requests in DPSS; ... Contact the Graduate and Professional School: Email: [email protected]; Phone: 979.845.3631; Fax: 979.862.1692; 204 Nagle Hall 1113 TAMU College Station, TX 77843
For its 2025 rankings, U.S. News & World Report ranked the Heller School for Social Policy and Management among the top public affairs graduate schools in two specialty categories: social policy (where Heller has been top-ranked for over a decade) and health policy and management. This year, Heller rose from #14 to #9 for social policy, ranking in the prestigious top 10 of its category, and ...
We are living in a time where research is becoming more multidisciplinary and challenges like EIC underscore this trend and bring together students from multiple research backgrounds." Student finalists from the School of Oceanography pitched SEAPEN, which won the competition's $2,500 Leo Cup Innovation in Oceanography Prize.
However, when you look at answers for all 6,000 New England adults combined, opinions are split nearly down the middle. While 46 percent agree that a four-year college degree is worth the expense ...