Biology Form 2 Questions and Answers End Term 1 Exam Free
Biology form two past paper questions with marking scheme.
1. Identify the discipline of biology that deals with the following.
i) The relationship between organisms and their environment. (1mk)
ii) Study of development of living organisms. (1mk)
iii) Study of body functions of living organisms. (1mk)
iv) Specialization in the study of chemical changes in an organism. (1mk)
v) Study of microscopic organisms. (1mk)
2. Name the organelles that are in abundance in:-
i) White blood cells. (1mk)
ii) Skeletal muscles. (1mk)
iii) Involved in osmoregulation in amoeba. (1mk)
3. (a) Distinguish between diffusion and active transport. (2mks)
(b) State one role that is played by osmosis in:
i) Plants. (1mk)
ii) Animals
4. Classify the following organisms into their kingdoms (4mks)
Organisms Kingdom
a) Maize,Beans
b) Mushrooms,Yeast
c) Protoza, algae
d) Bacteria
5. The diagram below shows a specialized cell from a human being.
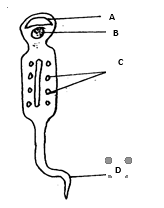
i. Identify the cell. (1mrk)
ii. Name the parts labelled A,B, and C. (3mrks)
A:.
B:.
C:.
iii State the functions of the part labeled D. (1mrk)
6. Study the figure below and answer the questions that follow.
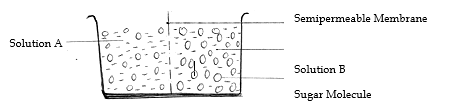
Solution A
Solution B
Sugar Molecule
i. What physiological process was being investigated (1mk)
ii. Which solution has higher concentration of free water molecules? (1mrk)
iii. Which solution is more concentrated? (1mk)
iv. In which direction will osmosis take place? Indicate using the arrow. (1mk)
v. What does semi-permeable membrane represent in an animal cell (1mk)
vi. Name three processes in living organisms that depend on osmosis. (3mks)
7. The table below shows the concentration of some ions in pond water and in the cells sap of an aquatic plant growing in the pond.
a) Name the processes by which the following ions could have been taken up by this plant. (2mks)
i) Sodium ions
ii) Potassium ions
b) For each processes named in (a) (i) and (ii) above, state one condition necessary for the process to take place. (2mks)
(i)
(ii)
8. a) What is meant by the term binomial nomenclature? (1mk)
.
b) Give two reasons why classification is important (2mks)
9. 16. The diameter field of view of a light microscopic is 3.5mm. Plant cells lying of the diameter are 10. Determine the size of one cell microns (1mm = 1000µm) (2mks)
10. Define the following terms in relation to a cell (3mks)
a) Isotonic solution
b) Hypotonic solution
c) Hypertonic solution
11. Explain why plant cells do not burst when immersed in distilled water. (1mk)
12. State the role of light in the process of photosynthesis. (2mks)
13. Name one product of dark reaction in Photosynthesis (1mk)
14. Explain why the following procedures are important when testing a leaf for starch. (3mks)
(a) Boiling the leaf in the water
(b) Boiling the leaf in methylated spirit
(c) Dipping the leaf in hot water after boiling it in alcohol or methylated spirit
15. State three importance of nutrition in living organisms. (3mks)
16. Differentiate between plants and animals in terms of the following characteristics. (2mks)
(i) Gaseous exchange
(ii) Nutrition
17. Two fresh potato cylinders at equal lengths were placed one in distilled water and the other in concentrated sucrose solution.
(a) Account for the change of the length of the cylinder in:
(i) Distilled water (1mk)
(ii) Sucrose solution (1mk)
(b) (i) What would be the result in term of length if a boiled potato was used? (1mk)
(ii)Explain your answer in (b)(i) above. (1mk)
18. The diagram below shows apparatus used in biological study.
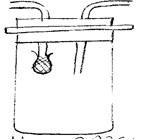
(a) Name the apparatus. (1mk)
(b) State its function. (1mk)
19. Liver damage leads to impaired digestion of fats. Explain the statement. (1mk)
20. In an experiment, a leafy shoot was setup in a photometer and kept in a dark room for two hours. The set up was then transferred to a well lit room for two hours.
(a) What was the aim of the experiment? (1mk)
(b) Explain the results which would be expected in each of the two experiment conditions? (3mks)
21. Name two structures for gaseous exchange in aquatic plants. (2mks)
22. The diagram below represents a model used to demonstrate breathing in mammals.
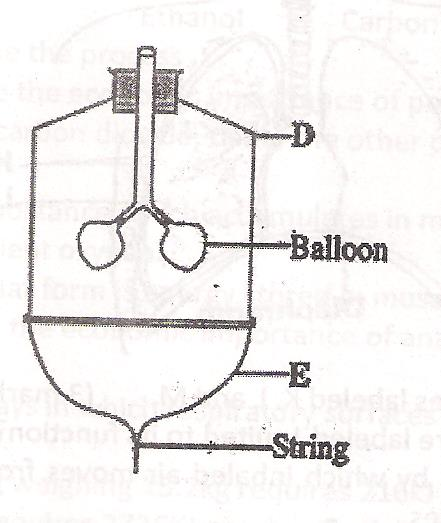
(a) Name the mammalian structure represented by the parts labelled D and E. (2mks)
(b) What is the effect of contraction of the part labelled E during breathing in a mammal? (3mks)
23. The scientific name of a rat is RATTUS NORVEGICUS.
(i) Write thr name correctly. (1mk)
(ii) Identify the genus and species names. (2mks)
e) State two roles of the red blood cells (2mks)
24. The diagram below shows circulation of blood in a mammal.
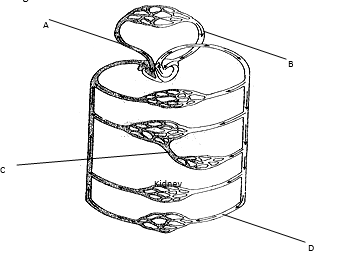
a) Name the type of circulation represented above (1mk)
b) Give reason for your answer (1mk)
c) Name the blood vessel labeled A, B, C ,D (4mks)
d) Name other two types of blood vessels beside capillaries (2mks)
f) Name the three types of immunity (3mks)

Download More Revision Questions and Answers in pdf:
- Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers End Term 1 Exam Free
- Biology Form 4 Paper 2 Questions and Answers End…
- FORM 2 END OF TERM 3 2022 Exam-BIOLOGY Questions And Answers
- FORM 1 END OF TERM 3 2022 Exam-BIOLOGY Questions and Answers
- FORM 3 END OF TERM 3 2022 Exam-BIOLOGY PP2 QUESTIONS…
- FORM 3 END OF TERM 3 2022 Exam-BIOLOGY PP3 QUESTIONS…
OR MPESA BuyGoods Till: 858 39 54
Contact 0726568677 || 0728407013
Clicking "Pay Now" is better and automatic

Biology Form 2 Questions and Answers
Guest account.
Questions Done: 0
Biology Form 2 Revision Questions and Answers
Biology practice questions and answers.

Want to enjoy learning? Try reading without Ads!

School Base -Online
Biology form 2 topics.
- Classification Of Living Things
- Balance Of Nature
- Transportation Of Materials In Living Things
- Gaseous Exchange And Respiration
Strategies for answering exam and test questions
Click on the accordions below to see more information about how best to tackle the following question types in your exam.
Multi-choice questions
Things to remember about multi-choice questions
- Read through the options and try to eliminate the ones that aren’t right . Multi-choice questions usually have one option that is obviously wrong, and three or four others that are similar. It is important to look carefully at how they are worded in order to select the correct answer.
- Don’t struggle over a question . Do all of the easy questions first and come back to harder ones later to maximise efficient use of test/exam time.
- Answer all the questions . Even if you are not sure, your educated guess may well be correct. It is better to have a go at answering a question than potentially miss out on a mark.
- When you check back through your paper and think an answer is wrong - change the answer . Research indicates that you will probably be correct in doing so.
Short answer questions
Short answer questions range from a sentence or two through to a paragraph in length.
- Keep to the point . Short answers are usually two-three sentences.
- Main ideas . Your answers should incorporate the key points, words, ideas and phrases the marker will be looking for.
- Leave one or two lines after each answer . This is so you can add important points later on.
- Try to answer all the questions . If you don’t know the complete answer, put down what you do know, as this is likely to get you some marks.
Exam essay questions
The advice here is in four parts: Time allocation | Task analysis | Planning | Presentation
Time allocation
- Use the reading time at the start of the exam to choose which essay questions you will answer .
- Check how much time you might have to answer each essay question , and stick to it. You can come back and add more to your answer in your revision time at the end of the exam session.
- If you haven’t finished your answer, jot down the rest in note form . This will show the marker what you know, and you might get some marks for it.
Task analysis
- Read the question carefully .
- Underline or highlight the content words . What is the topic?
- Pick out the instruction words in the question, e.g. identify, describe, compare and contrast, evaluate. What are you being asked to do with the topic?
- Take some time to think and plan your answer . For example: use the reading time to select which essay questions you will answer. Then use the start of the writing time (5-20mins) to make notes of all the points you remember that are relevant to the essay. General guide for timing: for 30 minutes of writing, allow 5-7 minutes for planning .
- Plan out the structure by organising your points into a logical order :e.g. by numbering them according to intended sequence.
- General writing rule for exam essays - one paragraph = one point . Follow standard essay-writing procedure, e.g. start with a topic sentence that contains your key point, and then support this with examples, explanations, and evidence.
Presentation
- Make sure your handwriting is legible . Markers should not have to decipher your handwriting. If your handwriting is illegible, it could compromise your marks.
- Make sure that you can express ideas effectively in terms of sentence structure and word use . Incoherent sentences and incorrect terminology will likely result in the marker not being able to understand your answer properly.
- Don’t worry too much about punctuation, grammar and spelling . Getting your ideas down is more important than ‘perfect’ writing (and markers usually take this into account given that students are writing under pressure in an exam situation). However, you do need a basic level of competency in these areas: an answer that lacks any punctuation and is full of spelling mistakes will probably be incoherent for the marker.
- Don't waffle . Get straight to the point in terms of your answer so that you don’t waste time and word space on unessential or irrelevant detail. Planning your essay beforehand is key to avoiding waffle.
Problem solving questions
Usually these types of questions target formulae, steps in a process, or rules.
- Make sure you write down relevant formulas, equations, and rules . Important: For numerical problems involving computation, make sure you include the appropriate mathematical units in your final answer (e.g. ml, m/sec).
- Clearly show the steps you have taken in working out the answers.
- If necessary, write notes to explain your answers .
- Do the easier answers first , and return to the difficult ones later.

5 comments:

thanks so much, this has been so helpful
yes indeed to me too
Muchas gracias.. I have looking this for long time
thank u so much 4 this program

Biology Essay Questions and Answers PP2 (1,000 Questions and Answers)
Also read...
BIOLOGY FORM ONE SUMMARIZED NOTES
Biology Form one to four exams, notes and revision materials
BIOLOGY FORM FOUR SUMMARIZED NOTES
BIOLOGY FORM TWO SUMMARIZED NOTES
Biology notes form 1-4; Free KCSE downloads
Free Biology notes, revision questions, KCSE past Papers, Exams, Marking Schemes, Topical revision materials, Syllabus and Many more
BIOLOGY FORM ONE NOTES FREE
BIOLOGY FORM THREE SUMMARIZED NOTES
Biology notes (Updated form one to four free notes)
Biology Simplified Notes Form 1 to 4 Free
Biology Free notes and Exams for Form one to Four
BIOLOGY KCSE MARKING AND SETTING TIPS IN LINE WITH EMERGING TRENDS
Biology topical questions and answers
Biology KCSE Past Papers and all marking schemes free downloads
Biology free lesson plans for all topics (Form one to four)
CBC Senior School Subjects (Grade 10, 11, 12)
CRE free lesson plans for all topics (Form one to four)
History and Government free lesson plans for all topics (Form one to four)
Free Secondary School Exams and Marking schemes (Form 1 to 4)
Syllabus For All Secondary Schools Per Subjects (Latest Syllabus)
English free lesson plans for all topics (Form one to four)
Free Physics notes, revision questions, KCSE past Papers, Exams, Marking Schemes, Topical revision materials, Syllabus and Many more
FORM 4 EXAMINATIONS AND MARKING SCHEMES: ALL SUBJECTS FOR KCSE CANDIDATES- OVER 1,000 PAPERS
Form 4 Term 1-3 Free Exams and marking schemes; All subjects downloads
FORM 3 ALL SUBJECTS EXAMS, ASSIGNMENTS: FREE TERM 1-3 EXAMS & ANSWERS
Updated Secondary School Notes form one to four Free Downloads (All subjects Comprehensive Notes)
Physics free lesson plans for all topics (Form one to four)
Posted/ Updated on:
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
TRENDING NOW
- Final TSC Circular On Career Progression Guidelines For Teaching Service
- KCSE 2023-2024 Siaya County Top and Best Performing Schools Nationally
- Updated TSC lists of shortlisted applicants for promotions per County; Interview dates and venues
- Makueni Girls High School’s KCSE Results, KNEC Code, Admissions, Location, Contacts, Fees, Students’ Uniform, History, Directions and KCSE Overall School Grade Count Summary
Search THIS SITE.
Are you a teacher, a student or Parent? Download free Education Resources here .

- Form 1 Mathematics Notes
- Form 2 Mathematics Notes
- Form 3 Mathematics Notes
- Form 4 Mathematics Notes
- Form 1 Mathematics Topical Questions and Answers
- Form 2 Mathematics Topical Questions and Answers
- Form 3 Mathematics Topical Questions and Answers
- Form 4 Mathematics Topical Questions and Answers
- Form 1 Functional Writing Notes
- Form 2 Functional Writing Notes
- Form 3 Functional Writing Notes
- Form 4 Functional Writing Notes
- Poetry Notes
- Grammar Notes
- Oral Literature Notes
- Oral Skills Notes
- Guide to Blossoms of the Savannah Summarized Notes - Easy Elimu
- A Doll's House
- The Pearl Study Guide
- Memories We Lost and Other Stories Study Guide
- Inheritance Study Guide
- A Silent song and Other Stories Guide
- Fathers of Nations Guide
- An Artist of the Floating World Guide
- The Samaritan Guide
- Sarufi na Matumizi ya Lugha
- Isimu Jamii Notes
- Fasihi Notes
- Ushairi Notes
- Mwongozo wa Kuandika Insha
- Tumbo Lililoshiba na Hadithi Nyingine
- Mwongozo wa Kigogo
- Mwongozo wa Chozi La Heri - Chozi la Heri Notes PDF
- Mwongozo wa Bembea ya Maisha - Bembea ya Maisha Notes PDF
- Mwongozo wa Nguu za Jadi
- Mwongozo wa Mapambazuko ya Machweo na Hadithi Nyingine
- Biology Form 1 Notes
- Biology Form 2 Notes
- Biology Form 3 Notes
- Biology Form 4 Notes
- Biology Essays
- Form 1 Biology Topical Revision Questions and Answers
- Form 2 Biology Topical Revision Questions and Answers
- Form 3 Biology Topical Revision Questions and Answers
- Form 4 Biology Topical Revision Questions and Answers
- Form 1 Chemistry Notes
- Form 2 Chemistry Notes
- Form 3 Chemistry Notes
- Form 4 Chemistry Notes
- All Chemistry Practicals Notes for KCSE and MOCKS
- Form 1 Chemistry Topical Revision Questions and Answers
- Form 2 Chemistry Topical Revision Questions and Answers
- Form 3 Chemistry Topical Revision Questions and Answers
- Form 4 Chemistry Topical Revision Questions and Answers
- IRE Form 1 Notes
- IRE Form 2 Notes
- IRE Form 3 Notes
- IRE Form 4 Notes
- Physics Form 1 Notes
- Physics Form 2 Notes
- Physics Form 3 Notes
- Physics Form 4 Notes
- CRE Form 1 Notes
- CRE Form 2 Notes
- CRE Form 3 Notes
- CRE Form 4 Notes
- Geography Form 1 Notes
- Geography Form 2 Notes
- Geography Form 3 Notes
- Geography Form 4 Notes
- History Form 1 Notes
- History Form 2 Notes
- History Form 3 Notes
- History Form 4 Notes
- Business Studies Form 1 Notes
- Business Studies Form 2 Notes
- Business Studies Form 3 Notes
- Business Studies Form 4 Notes
- Home Science Form 2 Notes
- Home Science Form 3 Notes
- Home Science Form 4 Notes
- Home Science Form 1 Notes
- Agriculture Form 1 Notes
- Agriculture Form 2 Notes
- Agriculture Form 3 Notes
- Agriculture Form 4 Notes
- Agriculture KCSE 2019 Project
- Computer Studies Form 1 Notes
- Computer Studies Form 2 Notes
- Computer Studies Form 3 Notes
- Computer Studies Form 4 Notes
- KCSE 2017 Reports
- 2018 Pre-Mocks
- 2019 Pre-Mocks
- 2022 Pre Mocks
- 2021/2022 Pre-Mock Past Papers
- 2023 Pre Mocks
- 2017 Mock Past Papers
- 2019 Mock Past Papers
- 2020 Mock Past Papers
- Mock Exam Papers 2021/2022 - Easy Elimu
- Mock Exam 2022 Questions and Answers
- Alliance Boys High School
- Maranda High School
- Form 1 Past Papers
- Form 2 Past Papers
- Form 3 Past Papers
- Form 4 Past Papers
- 2019 KCSE Prediction Papers
- 2020 KCSE Prediction Papers
- 2021 KCSE Prediction Papers
- 2022 KCSE Prediction Questions and Answers - EasyElimu
- KCSE Prediction 2023
- 2020 Post Mock Past Papers
- 2021/2022 Post Mocks
- 2023 Post Mocks
- Play Group: Activities, Homework and Syllabus
- 2023 PP1 Exams
- 2023 PP2 Exams
- Grade 1 Notes
- 2023 Grade 1 Exams
- Grade 2 Notes
- 2023 Grade 2 Exams
- Grade 3 Notes
- 2023 Grade 3 Exams
- Grade 4 Notes
- 2023 Grade 4 Exams
- Grade 5 Notes
- 2023 Grade 5 Exams
- Grade 6 Notes
- KPSEA Exams
- 2023 Grade 6 Exams
- Class 6 : Notes, Revision Papers and Syllabus
- Class 7 : Notes, Revision Papers and Syllabus
- Class 8 Notes
- 2023 Class 8 Exams
- 2023 Kcpe Prediction
- Grade 7 Notes
- 2023 Grade 7 Exams
- Pre Mock Exams 2024
- Form 4 Term 2 Opener Exams 2024
- Form 3 Exams 2024
- Form 2 Term 2 Opener Exams 2024
- Form 1 Term 2 Opener Exams 2024
- All Kiswahili setbook guides
- All English setbook guides
- Form 1 - 4 High School Notes
Biology Questions and Answers - Form 2 Term 1 Opener Exams 2021
« Previous Topic Physics Questions and Answers - Form 2 Term 1 Opener Exams 2021
Next Topic » Geography Questions and Answers - Form 2 Term 1 Opener Exams 2021
Answer all the questions in the spaces provided.
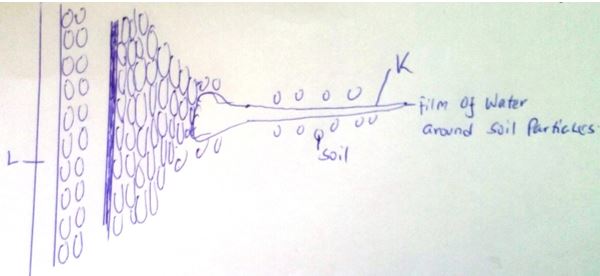
- Name the structures labeled K and L. (2 mks)
- Explain how water from the soil reaches the structure labeled L. (5 mks)
- Name the process by which mineral salts enter into the plant. (1 mk)
- State four ways in which xylem vessels are adapted to their functions. (4 mks)
- Name two processes that bring about the translocation of manufactured food. (2 mks)
- Name three significance of transpiration. (3 mks)
- State three structural factors affection affecting the rate of transpiration in plants. (3 mks)
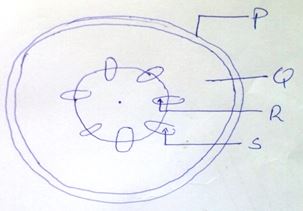
- Identify three parts labeled P, Q, R and S. (4 mks)
- State the functions of the parts labeled R and S. (3 mks)
- What is the function of carnassials teeth. (2 mks)
- Distinguish between the term homodont and heterodont. (3 mks)
- State two functions of bile juice in the digestion of food. (2 mks)
- Plant cell do not burst when immersed in distilled water. Explain. (2 mks)
- Describe what happens during the light stage of photosynthesis. (3 mks)
- State and explain three factors that affect enzymatic activities. (6 mks)
- Ribosomes (1 mk)
- Lysosomes (1 mk)
- Name two dental diseases. (2 mks)
- Give three characteristics of a cell membrane. (3 mks)

Marking Scheme
- K= root hair reject hair root
- L= xylem vessel
- Water moves from the soil into the root hair by osmosis because the concentration of cell sap is higher than the water in the soil. The cell sap in the root hair is diluted thus making it less concentrated than the neighbouring cells. Therefore, water moves into the neighboring cells. It is an actively secreted into structure L.
- Active transport/diffusion
- Lignified thickened to prevent collapsing(acc. Strengthening)
- Narrow to facilitate capillarity and strength
- Hollow for continuous column of water
- Have bordered pits to allow water to move to adjacent vessels
- Active transport
- Cytoplasmic streaming
- Through the process mineral ions and water are transported in the plants
- It serves to cool the plants, especially in hot environments
- It helps in removal of excess water especially in aquatic plants
- It is responsible for turgor in plants
- Leaf size and shape
- Hairy leaves
- P= epidermis
- R- transports water and mineral salts from the roots to all parts of the plant tissues/ cells.
- S- transports dissolved food substances or manufactured food from the leaves to all parts of the plant cell/tissues
- Cutting, chopping, shearing, slicing and crushing
- Homodont- having the same type/kind/ similar teeth
- Heterodont- having different types/kinds of teeth
- Emulsification of fats, breaking into small droplets
- Neutralizing the acidity of chime; provides an alkaline media for enzyme
- Plant cells have a membrane and a cell wall. When a cell is placed in distilled water, the water is absorbed through osmosis. As the cell becomes turgid, the cell creates an inward pressure (e.g. wall pressure) and turgor pressure which prevents the cell from bursting
- Takes place in the grana of the chloroplast. Light is absorbed and used to split water molecules into hydrogen ions and oxygen, photolysis. Energy is formed and stored in form of ATP
- Very low temperatures inactive the enzymes. Very high temperatures denature the enzyme. Therefore optimum temperature should be maintained for maximum enzyme activity.
- Some enzymes act best in acidic or basic medium. Therefore optimum pH should be maintained for maximum enzyme activity.
- When enzyme concentration is increased, the rate of enzyme activity also increases as long as there are enough molecules of the substrate.
- When the substrate concentration is increased, the rate of enzyme activity also increases as long as there are enough molecules of the enzymes. Further increase of the substrate may not increase the rate as all the active sites of the enzymes will be occupied
- They are the non-proteineous substances that activate the enzymes. Most enzymes will not work without co-factors. They are metallic ions.
- They are organic non-protein molecules that work in association with enzymes. They are derived from vitamins.
- They are substances that slow down or stop enzyme activity if present. They fit into the active site of the substrate hence the enzyme has no chance to fit into the active sites.
- Site of protein synthesis
- Destroys old and worn out organelles
- Periodontal diseases
- Dental cavities
- Sensitive to pH
- Highly polarized
- Semi permeability (permeable)

Download Biology Questions and Answers - Form 2 Term 1 Opener Exams 2021 .
Why download.
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
Related items
- CRE Questions and Answers - Form 3 Term 1 Opener Exams 2024
- Mathematics Questions and Answers - Form 3 Term 1 Opener Exams 2024
- Electricity Paper 2 Questions and Answers - KCSE 2021 Past Papers
- Biology Paper 3 Questions - Kapsabet Boys Post Mock 2023 Exams
- Biology Paper 2 Questions - Kapsabet Boys Post Mock 2023 Exams
access all the content at an affordable rate or Buy any individual paper or notes as a pdf via MPESA and get it sent to you via WhatsApp
What does our community say about us?
Join our community on:.

- KCSE Revision Questions
- Privacy Policy
- Mobile App Privacy Policy
- High Schools in Kenya
- Teacher Resources
- Questions and Answers
- Online Tuition and Classes in Kenya
Copyright © 2022 EasyElimu
Biology Questions and Answers Form 2 - Biology Form Two Notes
Click here - free kcse past papers » knec past exams » free downloads » kcse papers & marking schemes.
Please insert your question in the form below. Check and ensure that your question has not been asked and answered in the enquiries appearing beneath the form.
Enter the title of your question.
Author Information (optional)
To receive credit as the author, enter your information below.
Submit Your Contribution
- Check box to agree to these submission guidelines .
- I am at least 16 years of age.
- I understand and accept the privacy policy .
- I understand that you will display my submission on your website.
(You can preview and edit on the next page)
Biology Notes Questions and Answers
Click below to see contributions from other visitors to this page...
Click here to write your own.
Biology Questions and Answers Form 2 - Biology Questions and Answers Form 2 - Biology Questions and Answers Form 2
- NGOs Grants
- Current Scholarships
- Jobs in Africa
- Link to Us!
- Site Search
- What is New?
- Volunteer in Africa
- Volunteer in Kenya
- Medical Electives
- Submit Article
- Internships
- Scholarships Grants
- Undergraduate Scholarships
- Call for Proposals
- Study Abroad
- KCSE Past Papers
- Research Grants
- Entrepreneur Grants
- Journalist Grants

Scholarship 2024/25

KCSE 2023 Biology Essay Questions and Answers (KCSE 2023 Prediction Questions)
Here are KCSES 2022/2023 Biology Essay Questions and Answers (KCSE 2022 Prediction Questions). Content: 31 pages with 60 questions and answers.
BIOLOGY (231/2) Revision Questions (Essays): Expected Responses
Q1. Explain the various ways in which a typical cell is adapted to its functions
Has a cell membrane; with pores; that regulates substances entering and leaving the cell; cytoplasm; contain sugars and salts; for maintaining its osmotic pressure; also has a liquid medium; for all biochemical reactions; nucleus; contain chromosomes having hereditary material; and controls all the activities of the cell; ribosomes; are sites for protein synthesis; golgi bodies/apparatus; for secretion of hormones and enzymes; formation of lysosomes; lysosomes; contain lytic enzymes for breaking down worn-out organelles; secretory vesicles; formed from golgi apparatus for secreting substances; smooth endoplasmic reticulum; synthesizes and transports lipids; rough endoplasmic reticulum; transport proteins; nucleolus; controls the activities of the nucleus; produces ribosomes; mitochondria; form sites for energy production; centrioles; formation of cilia and flagella; forms spindle fibres used in cell division; plant sap vacuoles; store salts and other dissolved substances; controls osmotic pressure and turgidity of cells; food vacuoles involved in digestion of engulfed food; chloroplasts; form sites for photosynthesis in plant cells; Max. 20 mks
Q2. Explain how the various specialized cells are modified to carry out their functions in plants and animals
Animal cells: Sperm cell; has acrosome containing lytic enzymes; that digest the egg membranes for penetration during fertilization; has a long tail; containing numerous mitochondria; to generate maximum energy for propulsion/swimming in the vaginal fluid after ejaculation; Red blood cells; are flattened, circular/spherical biconcave in shape; to increase the surface area for packaging of haemoglobin; has haemoglobin; that combines with respiratory gases; for transport to and from body tissues; White blood cells; are amoeboid in shape hence able to change shape; to engulf pathogens through phagocytosis; lymphocytes produce antibodies to fight pathogens; Nerve cell; has extensions/dentrites; to receive and send information for sensation; Ciliated epithelial cells; have cilia for propulsion of mucus that traps dust and micro-organisms in the respiratory tract; Muscle cells; elongated, striated and contractile; to bring about movement; Plant cells: Guard cells; bean-shaped; to regulate the size of the stomata allowing gaseous exchange; and control water loss; has chloroplasts with chlorophyll; for photosynthesis; Root hair cell; elongated; thin-walled; with dense cytoplasm for absorption of water and mineral salts; Epidermal cell; thin; for protection of inner tissues from mechanical and micro-organism attack; Palisade cell; contains numerous chloroplasts with chlorophyll; for photosynthesis; elongated; to increase surface area for trapping maximum amounts of light energy; Meristematic cell; thin-walled; with dense cytoplasm; for primary and secondary growth; Max. 20 mks
Q3. Describe how the mammalian body protects itself against infections
Pathogenic microbes are found on the skin, respiratory tract, mouth, vagina and the intestinal tract; the skin; has a keratinised and waterproof cornified outer layer; that provides a mechanical barrier to microbes/prevents entry of microbes; sebaceous gland; produces sebum; which has antiseptic properties; the respiratory tract; produce mucus secretions that trap dust; cilia sweep/waft/propel the microbes to the pharynx for swallowing or to be coughed out; reflex actions of coughing/sneezing/vomiting help remove foreign materials from the respiratory tract/digestive tract; lysozymes/enzymes in saliva/nasal secretions/tears; digest walls of bacteria destroying them; gastric secretions such as hydrochloric acid lowers the pH in the stomach killing micro-organisms; clotting of blood; prevents entry of microbes after damage of blood vessels; phagocytosis; by phagocytes engulf and destroy microbes and other foreign bodies; lymphocytes are stimulated to produce antibodies; by proteins present in microbes protecting the body; antibodies destroy/kill micro-organisms through various ways: agglutinins; bind to pathogens making them clump together; killing them; Lysins; bind to pathogens and make them burst or disintegrate; opsonins; bind to pathogens making them easily recognized hence be engulfed/destroyed by other lymphocytes; anti-toxins; bind and neutralize toxins produced by micro-organisms; vagina is acidic; hence making it not conducive for growth and reproduction of micro-organisms; Max: 20 mks
Q4. How are the leaves of higher plants adapted to their functions?
Broad and flattened lamina; to increase surface area; for absorption of light; thin blade; to reduce distance for diffusion of gases and penetration of light waves; transparent epidermis and cuticle; to allow light to penetrate to tissues; cuticle layer absent on stomata; to allow for gaseous exchange; one-cell thick epidermal layer; to reduce the distance over which sunlight penetrates; palisade cells have numerous chloroplasts containing chlorophyll; to trap maximum amounts of light energy; have stomata on the epidermis; to allow for gaseous exchange; and control of water loss through transpiration; palisade layer have elongated cells located at right angles to the leaf surface; for maximum absorption of light energy; spongy mesophyll; consists of spherical and loosely-packed cells; to create air spaces; which communicate with the atmosphere through stomata; for purposes of gaseous exchange and control of water loss; veins have conducting tissues: xylem; for movement of water and dissolved mineral salts; phloem; for translocation of manufactured food; Max. 20 mks
Q5. Explain how the various teeth adapt mammals for nutrition
Incisor; sharp; chisel-shaped; for biting; and cutting food; one root for support in the jaw bone; Canines; long; sharp; pointed; for holding prey; piercing; and tearing flesh from prey; single root; for support in the jaw bone; Premolars; large/wide; to increase surface area for grinding food; highly cusped; to increase surface area for grinding food; two roots; for firm support/anchorage in the jaw bone; molars; large/wide; to increase surface area for grinding food; highly cusped; to increase surface area for grinding food; Max. 20 mks
Q6. Describe what happens to a meal of oily beans and maize from the time of ingestion up to the time of absorption
In the mouth; starch in maize; is digested by salivary amylase/ptyalin/diastase into maltose; food is chewed and mixed by teeth and the tongue; rolled into boluses by peristalsis; it enters into the stomach via the cardiac sphincter; in the stomach, gastric juice containing pepsinogen that is activated to pepsin; digests proteins in the beans; into shorter peptides; food is churned and allowed into the duodenum; via the pyloric sphincter muscle; in the duodenum; bile juice secreted by the gall bladder; emulsifies the oils in the beans into tiny oil droplets; pancreatic juice; secreted by the pancrease; contains pancreatic amylase; that digests starch to maltose; pancreatic lipase; that digests the oil in the beans to fatty acids and glycerol; trypsin; digests proteins into shorter peptides; food enters into the ileum; where succus entericus is secreted; it contains maltase enzyme; that digests the maltose into glucose; that is absorbed; peptidase; digests peptides into amino acids; lipase digests the remaining lipids (oil) into fatty acids and glycerol; which is absorbed through the lacteals of the villi; Max. 20 mks
Q7. How are the small intestines in mammals adapted to their functions?
Small intestines consists of the duodenum and the ileum; most digestion of food occurs in the duodenum; bile from the gall bladder of the liver is secreted through the bile ducts; and it is used to emulsify fats/break fat particles into tiny droplets; to increase the surface area for enzyme action; the pancreas secretes pancreatic juice to the duodenum; the juice contains pancreatic amylase; that helps to breakdown the remaining starch into maltose; trypsin; (that is secreted in its inactive form, trypsinogen , and activated by enterokinase enzyme); hydrolyses proteins into shorter peptides; pancreatic lipase; converts lipids into fatty acids and glycerol; sodium hydrogen carbonate is also produced; to neutralize the acidic chyme from the stomach; and provide a suitable alkaline medium for pancreatic and other intestinal enzymes; the ileum is long; and narrow; to increase the surface area for complete digestion of food; and maximum absorption of digested food; highly-coiled; to reduce speed of food flow; for maximum digestion; and absorption; presence of villi; and microvilli; to increase surface area; for maximum absorption; dense network of capillaries; to transport blood; for efficient transport of absorbed food; presence of lacteals in the villi; for absorption of fatty acids and glycerol molecules; presence of enzymes: Lipase; for digestion of lipids into fatty acids and glycerol; maltase; for digestion of maltose to glucose molecules; peptidase; for breakdown of peptides into amino acids; sucrase; for digestion of sucrose into glucose and fructose; lactase; for digestion of lactose into glucose and galactose; goblet cells; produce mucus; to lubricate the walls of the ileum; for smooth flow of food; coats the walls of ileum to prevent digestion by peptidase enzyme; Max. 20 mks
Q8. Outline and explain the various homeostatic functions of the liver in mammals
Deamination; process of removal of an amino group from an amino acid molecule; the process gets rid of excess amino acids in the body; as the body is not able to store them; the amino group enters the ornithine cycle; where it is combined with carbon (IV) oxideto form urea; which is excreted in urine through the kidney; Heat production; many metabolic activities take place in the liver; releasing heat energy; that is distributed by the blood to other parts of the body; this helps in thermoregulation; Storage of vitamins and mineral salts; Vitamins A, B, D, E and K; are stored in the liver; worn-out red blood cells, are broken down to yield iron; which is stored in the liver in form of ferritin; this is used later in case of shortage; Formation of red blood cells; occurs in the liver of the foetus; the liver also breaks down old/exhausted red blood cells; leading to formation of more in the bone marrow to replace the worn-out cells; to enhance oxygen and carbon (IV) oxide distribution; Regulation of blood sugar level; liver cells convert excess glucose into glycogen and fats under the influence of insulin hormone; the stored glycogen is however converted back to glucose; when glucose levels are low; by the liver cells; under the influence of glucagon hormone; Regulation of plasma proteins; plasma proteins such as prothrombin and fibrinogen are manufactured in the liver using the amino acids found in the liver; they play a major role in blood clotting; that prevents excessive blood loss and infection at the injured area; other plasma proteins produced by the liver such as serum and albumen; contribute to the maintenance of osmotic pressure in the body; non-essential amino acids are also synthesized by the liver; for use by the body; Storage of blood; the liver is highly vascularised; hence it is capable of holding a large volume of blood when the blood vessels dilate during hot conditions; when the temperatures are low, the blood vessels constrict under the influence of the endocrine and nervous systems; hence less blood is stored in the liver; this contributes to thermoregulation; Detoxification; this is the process where harmful compounds such as drugs and poisons; are converted to less toxic compounds in the liver; toxicity is caused by medication, drugs and microorganisms; the toxic compounds are later excreted in urine; detoxification prevents the accumulation of toxins in body cells; which could lead to death or malfunctioning of the body cells; Max. 20 mks
Q9. Explain why the following conditions are necessary for photosynthesis
- Carbon (IV) Oxide
Required in the dark stage of photosynthesis; it combines with the hydrogen ion from the light stage; to form glucose, proteins and lipids; low concentrations reduces the rate of production of energy and food; while high concentrations leads to an increase in the amount of energy and food formed;
It is used to break down water molecules (through photolysis); into hydrogen ions, oxygen and energy; the energy and hydrogen ions formed are used in the dark stage;
- Chlorophyll
Green pigment that traps light energy from the sun; that is used in photolysis of water molecules;
- Suitable temperature and pH
Temperature affects the enzymes involved in photosynthesis; suitable/optimum temperatures activate enzymes; for maximum production of food; while extremely low temperatures inactivate enzymes; leading to less or no production of food; high temperatures denature enzymes; stopping the process of photosynthesis; photosynthetic enzymes work well in low pH; so the rate is high; while higher pH reduces enzyme activity; lowering the rate of photosynthesis;
Forms a medium for the chemical reactions; it is split to yield hydrogen ions, oxygen and energy for use in the dark stage; solvent for the materials used in photosynthesis; Max. 20 mks
Q10. How is the ileum adapted to its functions?
Long; and narrow; to increase the surface area for complete digestion of food; and maximum absorption of digested food; highly-coiled; to reduce speed of food flow; for maximum digestion; and absorption; presence of villi; and microvilli; to increase surface area; for maximum absorption; dense network of capillaries; to transport blood; for efficient transport of absorbed food; presence of lacteals; for absorption of fatty acids and glycerol molecules; presence of enzymes: Lipase; for digestion of lipids into fatty acids and glycerol; maltase; for digestion of maltose to glucose molecules; peptidase; for breakdown of peptides into amino acids; sucrase; for digestion of sucrose into glucose and fructose; lactase; for digestion of lactose into glucose and galactose; goblet cells; produce mucus; to lubricate the walls of the ileum; for smooth flow of food; coats the walls of ileum to prevent digestion by peptidase enzyme; Max. 20 mks
Q11. a) What is homeostasis?
(Mechanisms of) control and maintenance of a constant internal environment regardless of the external conditions; 2 mks
- b) Name any three factors that must be maintained constant in mammalian bodies
Temperature; Water; Salt or ion content; Carbon (IV) oxide; Glucose; amino acids; Max. 3 mks
- c) Explain how endotherms respond to heat and cold conditions in their environment
Heat/hot conditions: Increased sweating; to lose heat through latent heat of vaporization; dilation of arterioles under the skin; to bring more blood to the skin surface to lose heat to the atmosphere; decreased body metabolism; to reduce heat generation; erector pili muscles relax; making hair follicles to relax hence hair lies flat on skin, no air is trapped; to lose heat; slow/reduced muscular activity due to slow metabolism; to reduce heat production; panting to expose tongue and mouth; to release heat; moving to shades to avoid direct heat; aestivation; to escape the extreme heat; flapping of ears to create currents to carry away heat; Cold conditions: stamping of feet; to generate heat; basking in the sun to gain heat directly; less production of sweat; to reduce water loss through latent heat of vaporization; vasoconstriction of arterioles; hence less blood flow to the skin surface to reduce heat loss; increased metabolism through release of more thyroxine hormone; to generate heat; erector pili muscles contract; pulling hair follicles hence hair is raised; to trap a layer of moist air; to prevent heat loss; shivering/rapid contraction of muscles; to yield heat to warm body; Max. 15 mks
Q12. Describe the route taken by water from the soil up to the evaporating surface of a plant
Water is drawn into the root hair cells by osmosis; due to the presence of dissolved substances in the cell sap of root hairs, the concentration of cell sap is greater than that of the surrounding solution in the soil/concentration gradient; this exerts a higher osmotic pressure, thus drawing the water molecules across the cell wall and cell membrane into the root hair cells; more water drawn into the root hair cells dilutes the cell sap; making it less concentrated than that in the adjacent cortex cell of the root; due to osmotic gradient, water moves from the adjacent cells to the next by osmosis; until it enters the xylem vessels located in the center of the root; the xylem vessels of the root then conduct the water up into the xylem vessels in the stem into the leaves; there is a force in the roots which pushes water up the stem; this force is known as root pressure; and can be considerably high in some plants; energy from the endodermal cells of the root is responsible for driving this force; in the xylem vessels, water would rise up by capillarity; to some extent because the vessels are narrower and there is a high attractive force between the water molecules and the cell walls; the cohesive; and adhesive forces are important in the maintenance of a continuous and uninterrupted water column in the xylem vessels up the tree to the leaves; water vaporizes from the spongy mesophyll cells; their cell sap becomes concentrated than the adjacent cells. This increases the osmotic pressure of the spongy mesophyll cells; as a result of this, water flows into the cell from other surrounding cell, which in turn takes in water from xylem vessels within the leaf veins; this creates a pull/suction force that pulls a stream of water from xylem vessels in the stem and roots. This force, known as transpiration pull; helps in maintaining a continuous column of water from the roots to the leaves; water flows from the midrib into leaf veins from where it enters leaf cells; from the mesophyll cells, it enters the airspaces; then the substomatal air chambers; from where it evaporates through the stomata; to the atmosphere; Max. 20 mks
Q13. How is the mammalian heart adapted to its functions?
Heart is enclosed in a pericardial membrane/pericardium; that produces a fluid; to lubricate it; the membrane also keeps the heart in position; It is covered in a fatty layer; that acts as a shock absorber; made up of cardiac muscles; which are interconnected/interacted hence contract and relax without fatigue or nervous stimulation/myogenic; for continuous pumping of blood throughout the lifespan of the animal; the muscles are supplied by nutrients and oxygen; by the coronary arteries; and the coronary veins take away wastes and carbon (IV) oxide; heart is divided into 4 chambers; for efficient double circulation/ avoid mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood/carry large volume of blood; has interventricular septum; to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood; ventricles are thick/muscular; to generate high pressure to pump blood out of the heart; left ventricle has thick muscles/more muscular; to pump blood to all body tissues; heart has bicuspid; and tricuspid valves; to prevent back flow of blood to left auricle; and right auricle respectively; valves have tendinous cords/valve tendons; to prevent them from turning inside out; semi lunar valves located at the beginning of major arteries; prevent backflow of blood into the ventricles; has sino-artrio node located in the muscles of the right auricle; to initiate heart beat/contractions of heart muscles/cardiac muscles, rate of heart beat is controlled by nerves; vagus nerve; slows down heartbeat; while sympathetic nerve; speeds up the heartbeat; has aorta; to transport oxygenated blood to all body parts; has pulmonary artery; that transports deoxygenated blood from right ventricles to lungs for oxygenation; has pulmonary vein; that transports oxygenated blood from lungs to the left ventricles; for distribution to all body parts; has the venacava; that receives deoxygenated blood from all body parts to right ventricles; Max. 20 mks
Q14. Describe double circulation in mammals
Deoxygenated blood from body tissues (except lungs); enters the heart via the right auricle; through the venacava; it flows to the right ventricle; via the tricuspid valve; the right ventricle contracts; pumping blood; via the semi lunar valves; through the pulmonary artery; to the lungs for oxygenation; the oxygenated blood from the lungs; flow through the pulmonary vein; to the left auricle; via the bicuspid valve; to the left ventricle; the left ventricle contracts; pumping blood via the semi lunar valves; through the aorta; to the rest of the body tissues; Max. 20 mks
Q15. Describe the process of urine formation in the mammalian kidneys
The afferent arteriole which is a branch of the renal artery supplies blood to the glomerulus; the afferent arteriole has a wider lumen/diameter than the efferent arteriole; which takes away blood from the glomerulus; the differences in the diameter of the afferent and the afferent vessels causes high pressure; leading to ultrafiltration of blood; the walls of the blood capillaries are one-cell thick; hence glucose, amino acids, vitamins, hormones, salts, creatine, urea and water filter into the Bowmans capsule; to form glomerular filtrate; white blood cells, red blood cells, plasma proteins such as globulin and platelets are too large to pass through the capillary wall; hence remain in the blood capillaries; useful substances in the human body are selectively reabsorbed; back into the blood stream at the proximal convoluted tubule; the tubule is highly coiled; to increase the surface area for reabsorption of the substances; the useful substances include amino acids, glucose, vitamins, hormones, sodium chloride and water; many mitochondria found at the proximal convoluted tubule; provide energy for reabsorption of these substances against a concentration gradient; the glomerular filtrate flows into the descending and the ascending limb of the loop of Henle; blood in the capillaries and the glomerular filtrate in the loop of Henle move in opposite directions/counter-current flow; this provides a steep concentration gradient that leads to maximum absorption of water through osmosis; sodium chloride is actively absorbed from the ascending limb into the blood capillaries; under the influence of aldosterone hormone; the glomerular filtrate flows into the collecting tubule from where, more water is reabsorbed into the blood stream; antidiuretic hormone influences the amount of water to be reabsorbed depending on the osmotic pressure of the blood; the glomerular filtrate from several collecting tubules now referred to as urine; is emptied into the collecting duct; the urine passes through pyramid, pelvis and ureter into the bladder; where it is stored for some time. The sphincter on the urethra relaxes to allow urine to be released from the body; Max. 20 mks
Q16. Explain the role of the following hormones during homeostasis
- Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
Secreted by the (posterior lobe/end) pituitary gland; in response to an increase in the osmotic pressure of blood; the hormone stimulates the distal convoluted tubules and the collecting ducts; to increase their permeability to water; this increases the reabsorption of water into the bloodstream; concentrated and less urine is excreted; when the osmotic pressure decreases, less or no hormone is produced; hence the tubules become impermeable to water; less water is reabsorbed into the bloodstream; hence more dilute urine is excreted; fluctuations in the osmotic pressure is detected by the hypothalamus;
Secreted by the pancrease; in response to a rise in blood sugar level; it stimulates liver cells to convert the excess glucose into glycogen and fats for storage in the liver and muscle cells; increases the oxidation of glucose in respiration to yield water energy and carbon (IV) oxide/increases metabolism in the body; this leads to a fall in blood glucose to normal level;
Secreted by the pancrease; in response to a decline in blood glucose level; it stimulates liver cells to convert the stored glycogen and fats back to glucose; stimulates the conversion of amino acids to glucose; and stops the oxidation of glucose in the body cells; the glucose formed is released to the bloodsteream causing a rise of blood glucose level to normal; Max. 20 mks
Q17. a) Distinguish between Diabetes mellitus and Diabetes insipidus
Diabetes mellitus is a condition/disease caused by failure of the pancrease to produce adequate insulin hormone; leading to excess glucose levels in the body some of which is released in urine while diabetes insipidus is a condition caused by failure/inability of the kidney tubules to control the amount of water in urine as a result of a defect in production of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) leading to production of more dilute urine; Max. 2 mks
Request to download full notes.
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Fee Structure for Secondary Schools in Kenya 2023-2024
Icm past papers 2023/2024 with answers download free (march 2023), kmtc fees structure of 2023/2024 download and print.
I will realy want to study and become a doctor
Thanks for the same. Contact me @ 0795409452
i love this
- Advertise With Us
Why is writing essays so hard?
Patterns and boring topics imposed by schools and universities are not very conducive to creativity and human development. Such essays are very difficult to write, because many are not interested in this and do not see the meaning of the text. There are a number of criteria that make it impossible to write essays:
- Boring and incomprehensible topics. Many topics could be more interesting, but teachers formulate them in a way that makes you want to yawn.
- Templates. 90% do not know how to make an essay interesting, how to turn this detailed answer to a question into a living story.
- Fear of not living up to expectations. It seems to many that the essay is stupid and that they simply did not understand the question. There is a fear of getting a bad mark and disappointing the professor, parents and classmates. There is a fear of looking stupid and embarrassing in front of the team.
- Lack of experience. People don't know what and how to write about. In order to make a good essay, you need to have a perfect understanding of the topic and have the skills of a writer.
That is why the company EssaysWriting provides its services. We remove the responsibility for the result from the clients and do everything to ensure that the scientific work is recognized.
Can you write my essay fast?
Our company has been among the leaders for a long time, therefore, it modernizes its services every day. This applies to all points of cooperation, but we pay special attention to the speed of writing an essay.
Of course, our specialists who have extensive experience can write the text quickly without losing quality. The minimum lead time is three hours. During this time, the author will find the necessary information, competently divide the text into several parts so that it is easy to read and removes unnecessary things. We do not accept those customers who ask to do the work in half an hour or an hour just because we care about our reputation and clients, so we want your essay to be the best. Without the necessary preparation time, specialists will not be able to achieve an excellent result, and the user will remain dissatisfied. For the longest time, we write scientific papers that require exploratory research. This type of work takes up to fourteen days.
We will consider any offers from customers and advise the ideal option, with the help of which we will competently organize the work and get the final result even better than we expected.
Customer Reviews
If you can’t write your essay, then the best solution is to hire an essay helper. Since you need a 100% original paper to hand in without a hitch, then a copy-pasted stuff from the internet won’t cut it. To get a top score and avoid trouble, it’s necessary to submit a fully authentic essay. Can you do it on your own? No, I don’t have time and intention to write my essay now! In such a case, step on a straight road of becoming a customer of our academic helping platform where every student can count on efficient, timely, and cheap assistance with your research papers, namely the essays.
Courtney Lees
The experts well detail out the effect relationship between the two given subjects and underline the importance of such a relationship in your writing. Our cheap essay writer service is a lot helpful in making such a write-up a brilliant one.
Finished Papers
Finished Papers
Who are your essay writers?
Earl M. Kinkade
Testimonials
Business Enquiries
Who can help me write my essay.
At the end of the school year, students have no energy left to complete difficult homework assignments. In addition, inspiration is also lacking, so there are only a few options:
- do not write a scientific work;
- write it badly;
- delegate these responsibilities to other people.
Most often, people choose the latter option, which is why companies have appeared on the Internet offering to take full responsibility.
When you visit the site, the managers clarify all the details in order to correctly design the article. They select a person who is well versed in the topic of the report and give him your task.
You will not be able to personally communicate with the writer who will do your work. This is done to ensure that all your personal data is confidential. The client, of course, can make edits, follow the writing of each section and take part in the correction, but it is impossible to communicate with the team.
Do not worry that you will not meet personally with the site team, because throughout the entire cooperation our managers will keep in touch with each client.

Susan Devlin
1(888)499-5521
1(888)814-4206
Once I Hire a Writer to Write My Essay, Is It Possible for Me to Monitor Their Progress?
Absolutely! Make an order to write my essay for me, and we will get an experienced paper writer to take on your task. When you set a deadline, some people choose to simply wait until the task is complete, but others choose a more hands-on process, utilizing the encrypted chat to contact their writer and ask for a draft or a progress update. On some occasions, your writer will be in contact with you if a detail from your order needs to be clarified. Good communication and monitoring is the key to making sure your work is as you expected, so don't be afraid to use the chat when you get someone to write my essay!
Customer Reviews
You may be worried that your teacher will know that you took an expert's assistance to write my essay for me, but we assure you that nothing like that will happen with our write essay service. Taking assistance to write from PenMyPaper is both safe and private. We respect your privacy and thus do not ask for credentials like your name, college, location, or your phone number. To pay for the essay writing, you can either use your debit or credit cards to pay via PayPal or use your wallet balance from our website. All we would need is your card details and your email-id. This is our responsibility that your information will be kept all safe. This is what makes our service the best essay writing service to write with.
Margurite J. Perez
10 question spreadsheets are priced at just .39! Along with your finished paper, our essay writers provide detailed calculations or reasoning behind the answers so that you can attempt the task yourself in the future.

What is a good essay writing service?
Oddly enough, but many people still have not come across a quality service. A large number of users fall for deceivers who take their money without doing their job. And some still fulfill the agreements, but very badly.
A good essay writing service should first of all provide guarantees:
- confidentiality of personal information;
- for the terms of work;
- for the timely transfer of the text to the customer;
- for the previously agreed amount of money.
The company must have a polite support service that will competently advise the client, answer all questions and support until the end of the cooperation. Also, the team must get out of conflict situations correctly.
It is necessary to have several payment methods on the site to make it easier for the client to transfer money.
And of course, only highly qualified writers with a philological education should be present in the team, who will not make spelling and punctuation errors in the text, checking all the information and not stealing it from extraneous sites.
Compare Properties
Can i pay after you write my essay for me.
Essays service custom writing company - The key to success
Quality is the most important aspect in our work! 96% Return clients; 4,8 out of 5 average quality score; strong quality assurance - double order checking and plagiarism checking.

I work with the same writer every time. He knows my preferences and always delivers as promised. It’s like having a 24/7 tutor who is willing to help you no matter what. My grades improved thanks to him. That’s the story.
The writers of PenMyPaper establish the importance of reflective writing by explaining its pros and cons precisely to the readers. They tend to ‘do my essay’ by adding value to both you (enhancing your knowledge) and your paper.
Ask the experts to write an essay for me!
Our writers will be by your side throughout the entire process of essay writing. After you have made the payment, the essay writer for me will take over ‘my assignment’ and start working on it, with commitment. We assure you to deliver the order before the deadline, without compromising on any facet of your draft. You can easily ask us for free revisions, in case you want to add up some information. The assurance that we provide you is genuine and thus get your original draft done competently.

Finished Papers
Margurite J. Perez
- Human Resource
- Business Strategy
- Operations Management
- Project Management
- Business Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Scholarship Essay
- Narrative Essay
- Descriptive Essay
- Buy Essay Online
- College Essay Help
- Help To Write Essay Online
Who will write my essay?
On the website are presented exclusively professionals in their field. If a competent and experienced author worked on the creation of the text, the result is high-quality material with high uniqueness in all respects. When we are looking for a person to work, we pay attention to special parameters:
- work experience. The longer a person works in this area, the better he understands the intricacies of writing a good essay;
- work examples. The team of the company necessarily reviews the texts created by a specific author. According to them, we understand how professionally a person works.
- awareness of a specific topic. It is not necessary to write a text about thrombosis for a person with a medical education, but it is worth finding out how well the performer is versed in a certain area;
- terms of work. So that we immediately understand whether a writer can cover large volumes of orders.
Only after a detailed interview, we take people to the team. Employees will carefully select information, conduct search studies and check each proposal for errors. Clients pass anti-plagiarism quickly and get the best marks in schools and universities.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
KCSE BIOLOGY BIOLOGY ESSAY QUESTIONS WITH MARK SCHEMES 1. Explain the various ways in which a typical cell is adapted to its functions ... chloroplasts; form sites for photosynthesis in plant cells; Max. 20 mks ... grinding food; highly cusped; to increase surface area for grinding food; two roots; for firm support/anchorage in the jaw bone ...
BIOLOGY Form 2 Term 2 Joint Exam 2022 Questions.docx: Zeraki - Biology Form 2 - Marking Scheme.docx: Join Our WhatsApp Group: Download CBC Resources App: Download Highschool Resources App: Download a Guide for All Highschool SetBooks: Zeraki - Biology Form 2 - Question Paper.docx: 231 Form 2 End Term 1 Exams BIOLOGY Questions.doc: 2020_T1_BIO ...
Attempt Form 2 Biology questions on Transportation in Plants, Transportation in Animals, Gaseous Exchange in Plants, Gaseous Exchange in Animals (respiration), Excretion, Homeostasis. Attempt Form 3 Biology revision questions on Classification II, Ecology, Adaptation of Plants, Pollution, Reproduction, External and internal fertilization in ...
Back to TOPICAL QUESTIONS & ANSWERS menu Updated on 6/12/2023. Join Kenya's Largest Teachers Telegram Group with Over 80K Teachers FORM 1-4 CLASS 7-8 GRADE 1-6 PP1-PP2 KASNEB PTE. Biology Topic By Topic Questions and Answers for All Topics in Form 1, Form 2, Form 3 and Form 4 for Kenya Secondary Schools in preparation for KCSE .
18 exams and past papers. Get access to thousands of educational resources. Form 2 Biology End of Term 2 Examination 2023. Form 2 Biology Mid Term 1 Examination 2023. Form 2 Biology End of Term 3 Examination 2022. Form 2 Biology End of Term 2 Examination 2022. Form 2 Biology End of Term 3 Examination 2021. Form 2 Biology End Term 2 Exams 2021.
a). Describe the role of hormones in the growth and development of plants (20 marks; KCSE 2002) a). Name three types of skeletons found in multicellular animals ( KCSE2002) b). Describe how the cervical, lumbar and sacral vertebrae are suited to their functions. BIOLOGY FORM ONE SUMMARIZED NOTES.
Download. Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers. This document contains Biology Questions and Answers Form 2 Brief Overview: a) i) Define transport • Movement of substances from one part of the body to another ii) Explain the necessity of... Price: KES : 150.
Answers should be written in the spaces provided. Define the following terms. (2mks) Taxon. Taxonomy. A donkey and a horse can breed and produce a young one called a mule. Explain why they do not belong to the same species. (2mks) Give one reason for each of the following operations in microscopy work. (3mks)
Biology Form 2 Revision Questions and Answers: Form Two Biology, Secondary School. Back to Revision Questions. Change Revision Questions Class Form 1 Questions Form 2 Questions Form 3 Questions Form 4 Questions. [email protected]. Esoma-KE. Esoma-KE HOME; PP1 - GRADE 3. PP1; PP2; GRADE 1; GRADE 2; GRADE 3; GRADE 4 - GRADE 7. GRADE 4; GRADE 5;
Short answer questions. Short answer questions range from a sentence or two through to a paragraph in length. Keep to the point. Short answers are usually two-three sentences. Main ideas. Your answers should incorporate the key points, words, ideas and phrases the marker will be looking for. Leave one or two lines after each answer.
Biology Simplified Notes Form 1 to 4 Free. See also Free Physics notes, revision questions, KCSE past Papers, Exams, Marking Schemes, Topical revision materials, Syllabus and Many more. Biology Free notes and Exams for Form one to Four. BIOLOGY KCSE MARKING AND SETTING TIPS IN LINE WITH EMERGING TRENDS. Biology topical questions and answers.
State the functions of the parts labeled R and S. (3 mks) What is the function of carnassials teeth. (2 mks) Distinguish between the term homodont and heterodont. (3 mks) State two functions of bile juice in the digestion of food. (2 mks) Plant cell do not burst when immersed in distilled water. Explain. (2 mks)
Biology Notes Form 2. 1. a) i) Define transport. Movement of substances from one pan of the body to another. ii) Explain the necessity of transport in plants and animals. make nutrients move from one point to another. movement of respiratory gases i.e. oxygen and carbon IV oxide. elimination of metabolic wastes.
BIOLOGY (231/2) Revision Questions (Essays): Expected Responses. Q1. Explain the various ways in which a typical cell is adapted to its functions. Has a cell membrane; with pores; that regulates substances entering and leaving the cell; cytoplasm; contain sugars and salts; for maintaining its osmotic pressure; also has a liquid medium; for all ...
Grab these brilliant features with the best essay writing service of PenMyPaper. With our service, not the quality but the quantity of the draft will be thoroughly under check, and you will be able to get hold of good grades effortlessly. So, hurry up and connect with the essay writer for me now to write. For expository writing, our writers ...
5 Signs of a quality essay writer service. Level: College, High School, University, Undergraduate, Master's. Liberal Arts and Humanities. Urgency. I work with the same writer every time. He knows my preferences and always delivers as promised. It's like having a 24/7 tutor who is willing to help you no matter what.
Professional Essay Writer at Your Disposal! Quality over quantity is a motto we at Essay Service support. We might not have as many paper writers as any other legitimate essay writer service, but our team is the cream-of-the-crop. On top of that, we hire writers based on their degrees, allowing us to expand the overall field speciality depth!
Form Two Biology Essay Questions. 989 Orders prepared. Order now Login. As we have previously mentioned, we value our writers' time and hard work and therefore require our clients to put some funds on their account balance. The money will be there until you confirm that you are fully satisfied with our work and are ready to pay your paper writer.
Customer Reviews. Biology Essay Questions And Answers Form 2. Medicine and Health. 1084Orders prepared. REVIEWSHIRE. ID 2644. 4.9/5. 100%Success rate. A certified document that proves 100% content originality.
On some occasions, your writer will be in contact with you if a detail from your order needs to be clarified. Good communication and monitoring is the key to making sure your work is as you expected, so don't be afraid to use the chat when you get someone to write my essay! $ 4.90. Niamh Chamberlain.
Form Two Biology Essay Questions - 1811 Orders prepared. 10 Customer reviews. We Make It Better. Kaylin G. 535 . Finished Papers. Form Two Biology Essay Questions: 4.8/5. 100% Success rate Level: College, High School, University, Master's, PHD, Undergraduate. Sign up for free. Order now Login. Your order is written Before ...
Besides, there is an option to get help with your homework assignments. We help complete tasks on Biology, Chemistry, Engineering, Geography, Maths, Physics, and other disciplines. Our authors produce all types of papers for all degree levels. Essay. (415) 520-5258.
Form Two Biology Essay Questions: Prices than inspire from. 1349 . Finished Papers. ID 4595967. Finished paper. 1770 . Finished Papers. Total orders: 5897. Jan 19, 2021. Perfect Essay #5 in Global Rating 2640 Orders prepared. John N. Williams ...