
How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
A demo is the first step to transforming your business. Meet with us to develop a plan for attaining your goals.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.

For Business
For Individuals

What is lateral thinking? 7 techniques to encourage creative ideas

Boost your productivity
Maximize your time and productivity with strategies from our expert coaches.

Jump to section
What is lateral thinking?
Why is lateral thinking important, how to improve lateral thinking: 7 techniques, benefits of lateral thinking, challenges of lateral thinking, rethink your problem-solving process.
When you feel comfortable in a routine, you might forget to think outside the box.
Maybe you’ve been communicating with clients the same way for years, or you use the same meeting agenda template for every team. These processes could work, but they could also neglect to make space for innovation and new ideas.
Adjusting your mindset can help you start a more open problem-solving process and drive innovation. This is what lateral thinking proposes.
Lateral thinking means brainstorming creatively to solve problems and generate ideas without the limitations of logic-based critical thinking. Giving your teams the tools to get creative and embrace every new thought, no matter how out there it sounds, can help find inefficiencies and push your business into the future.
Lateral thinking, sometimes called horizontal thinking or divergent thinking, is defined as an approach to problem-solving that strives for creative solutions rather than the most straightforward answer. Through spontaneous, free-flowing brainstorming, lateral thinking disrupts traditional step-by-step thinking patterns to develop as many varied creative ideas as possible.
Psychologist Edward de Bono developed this concept in his 1967 book, The Use of Lateral Thinking. De Bono argued that the human brain has been trained to think “inside the box” and seek typical, predictable solutions, even if those aren’t the best options . He proposed lateral thinking as a new way to move past our cognitive biases and be more inventive.
Vertical thinking, the opposite of lateral thinking according to de Bono, is reason-based. You gather all available data and move sequentially from one step to the next until you reach a logical conclusion. This is what he says the human brain does naturally.
Lateral thinking instead combines imagination and intuition. You consciously try to generate ideas and scenarios that imagine uncertainties outside the information you already have. It places more importance on the ideas themselves and doesn’t dwell on the outcome until later.
Despite their differences, vertical and lateral thinking can work together to make ideas the best they can be. Lateral thinking can stimulate more creative logic in vertical thinking, and vertical thinking fine-tunes lateral thinking’s big ideas.
Lateral thinking can increase adaptability and innovation in people who practice it. With new technologies like AI and shifting demands from the labor force, products, and processes can become outdated quickly, and new ways of thinking offer more ways to overcome potential problems.
According to a McKinsey poll of 200 organizations across several industries, 90% of executives believe that how they do business will fundamentally change between 2020 and 2025 . However, the same study found that only 21% of executives are prepared to create and embrace new growth opportunities .
Lateral thinking offers a framework for innovation that supports growth and change. It helps teams imagine the previously unimaginable and set themselves apart from the competition. Teams that can bring new perspectives to challenges will be more likely to stay with the curve and potentially create disruptive innovation that pushes the curve further ahead.
Lateral thinking might seem abstract and hard to implement. But adding steps to your brainstorming process can help you become more conscious of your th ought patterns, identify gaps, and think of creative ideas . Here are a few lateral thinking techniques to broaden your own and your team’s problem-solving skills.
1. Recognize thought patterns
Humans often get stuck in an anchoring bias : making judgments or decisions based on the first piece of information they receive. Vertical thinking encourages this bias because it builds on what you already have. As new data or ideas arrive, you stack them on top of the existing information instead of innovating.
But lateral thinkers are often more aware of their thought patterns, meaning they can better prevent biases and reorganize information.

You likely accept successful processes and services as unchangeable in your day-to-day professional life. If it’s not broken, why fix it? But asking why and how you use those processes, even when things are going well, is a common creative approach in lateral thinking to challenge ideas and break cognitive biases.
Figuring out why you or your team does something a certain way requires you to deconstruct the process and examine each element. This naturally brings forward new ideas and helps you find barriers you didn’t even know were there.
3. Consider all the alternatives
The logical outcome of problem-solving is to find the most efficient solution. Lateral thinking encourages you to purposefully set aside the “best” answer and brainstorm alternative approaches, regardless of how lofty they seem.
Imagine you’re running into issues with an important spreadsheet. You’re constantly adding new information, the system is slowing down, and it’s harder to find things when you need them. You try adding more sheets and reorganizing the data, but that doesn’t quite work.
Lateral thinking could help you think of an entirely new solution, like switching to project management software instead of relying on one spreadsheet.
4. Invite external stimuli
You may know what work environment best suits your critical thinking and concentration skills . While a steady environment may help your focus, it might also put you in a comfort zone that limits your creativity.
Find new stimuli that encourage lateral thinking, like playing music to concentrate differently, taking breaks in the middle of the day, or soliciting the opinion of a colleague from another department. Not every new method will be successful, but trying is part of innovating.
5. Reframe ideas
During a brainstorming session, you’ll likely come up with good ideas that seem too complicated or hard to implement. Lateral thinking encourages you to take these ideas seriously rather than immediately dismissing them.
If you or your team think of a big idea, dedicate just a few minutes to discussing it. Examine your restrictions and ask what financial, operational, or time constraints create a barrier to entry. With that information, you can try to reformulate the idea from different perspectives until it becomes more viable.

6. Try random entry
When you feel stuck on a certain thinking pattern, random entry can shake things up and stimulate lateral thinking. Random entry introduces a random word or image to a brainstorming session. Even if it seems unrelated, try associating it with the problem at hand. The process of making those connections can help you come up with out-of-the-box ideas.
Imagine you’re a branding agency working on a rebrand for a coffee shop. The client doesn’t want to use the typical insignia like coffee beans or mugs. To provoke a new idea, you randomly select a word from the dictionary: “spine.” You map out different word associations to “spine” and end up creating a new brand based on the idea of coffee as a backbone.
7. Mind mapping
Mind maps are a common brainstorming technique that helps teams visualize problems to find more expansive ideas. You begin with a central problem and break it into smaller pieces until you have a larger document with many ideas in one place.
Seeing everything together fosters more creative connections, and studies have shown that mind mapping helps people retain and develop information more effectively. Lateral thinking also has the potential to become disorganized with so many different ideas at play, and mind maps can avoid that problem by keeping everything in one place.
Lateral thinking skills give you the tools to be more creative and solve problems that you previously thought would stay problems. Here are a few more benefits of lateral thinking:

Offers fresh thoughts: Anything-goes brainstorming sessions have the potential to bring wild new ideas to the table. With lateral thinking, sometimes all it takes is a little refining to bring those unthinkable concepts into exciting solutions.
Challenges assumptions: Lateral thinkers question their thought processes to distance themselves from the biases and linear thinking that limit creativity. Developing self-awareness about your problem-solving unlocks the potential to innovate.
Builds new ways of thinking: Lateral thinking doesn’t just prompt you to seek new solutions. It teaches you that there are other ways to think through problems. Approaching a problem from a creative mindset can apply to other areas of work that require critical thinking, like negotiating a new salary , finding ways to increase employee engagement , or dealing with difficult people .
Widens your focus: Breaking a problem into smaller parts and exploring them laterally helps you spot solutions without distraction. Looking at the whole of a problem can make you waste time jumping around from point to point, and focusing heavily on a single aspect at a time lets you dive deeper.
Presents another way: “This is the way we’ve always done it” doesn’t mean that particular process is the best. Lateral thinking teaches you to challenge that idea and create alternative solutions for everything. The things that work well can work even better if you dissect them and find small ways to improve.
Successful lateral thinking requires effort and experience. Thinking big can break you out of stale habits, but if your team can’t bring those ideas to a realistic action, you could create bigger problems than you started with. Here are some challenges of lateral thinking:

Indecision: Weaning down great ideas into a single solution may be difficult and time-consuming. Try including sound market research and other data in your process to find the decision with the biggest impact.
Reckless thinking: Lofty ideas are most helpful when you have the resources to back them up. If you don’t properly check with all stakeholders, you may run into problems along the way that bottleneck development or force you to toss it after dedicating precious time and money.
Too much at once: You may be tempted to tackle too much and burn out your team. Successful change takes time. Roll it out slowly so you have space to review and refine new processes.
Disruption: A culture of experimentation encourages employees to implement ideas that go outside the box. But without clear communication and realistic limitations, you could risk implementing new concepts that do more harm than good. Lateral thinking still requires analysis and planning.
Understanding what lateral thinking is and how to use it can be a challenge. But giving your team the tools and freedom to think outside the box and pursue the roads less traveled will pay off in the end.
Lateral thinking leads to more creative collaboration and greater innovation. You could also uncover inefficiencies in your business you never knew were there.
Madeline Miles
Madeline is a writer, communicator, and storyteller who is passionate about using words to help drive positive change. She holds a bachelor's in English Creative Writing and Communication Studies and lives in Denver, Colorado. In her spare time, she's usually somewhere outside (preferably in the mountains) — and enjoys poetry and fiction.
Learn what process mapping is and how to create one (+ examples)
The only guide you'll need to create effective cascading goals, how to develop critical thinking skills, 9 project management (pm) tools that help you get the job done, make the most of your time with the best time management tools, thinking outside the box: 8 ways to become a creative problem solver, critical thinking is the one skillset you can't afford not to master, how to create a work plan (with template), effective negotiation tactics to level-up your career, similar articles, 8 brainstorming techniques to harness the power of teamwork, what is creative thinking and why does it matter, how to improve your creative skills for effective problem-solving, how divergent thinking can drive your creativity, 8 creative solutions to your most challenging problems, what’s convergent thinking how to be a better problem-solver, improvise, adapt, overcome: your how-to guide for an ever-changing world, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care™
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Life Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences
- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions
Lateral Thinking
What is lateral thinking.
Lateral thinking (horizontal thinking) is a form of ideation where designers approach problems by using reasoning that is disruptive or not immediately obvious. They use indirect and creative methods to think outside the box and see problems from radically new angles, gaining insights to help find innovative solutions.
“You cannot dig a hole in a different place by digging the same hole deeper.” — Dr. Edward de Bono, Brain-training pioneer who devised lateral thinking
See how lateral thinking can stretch towards powerful, “impossible” solutions:
- Transcript loading…
Lateral Thinking helps Break Out of the Box
Many problems (e.g., mathematical ones) require the vertical, analytical, step-by-step approach we’re so familiar with. Called linear thinking , it’s based on logic, existing solutions and experience: You know where to start and what to do to reach a solution, like following a recipe. However, many design problems—particularly, wicked problems —are too complex for this critical path of reasoning. They may have several potential solutions. Also, they won’t offer clues; unless we realize our way of thinking is usually locked into a tight space and we need a completely different approach.
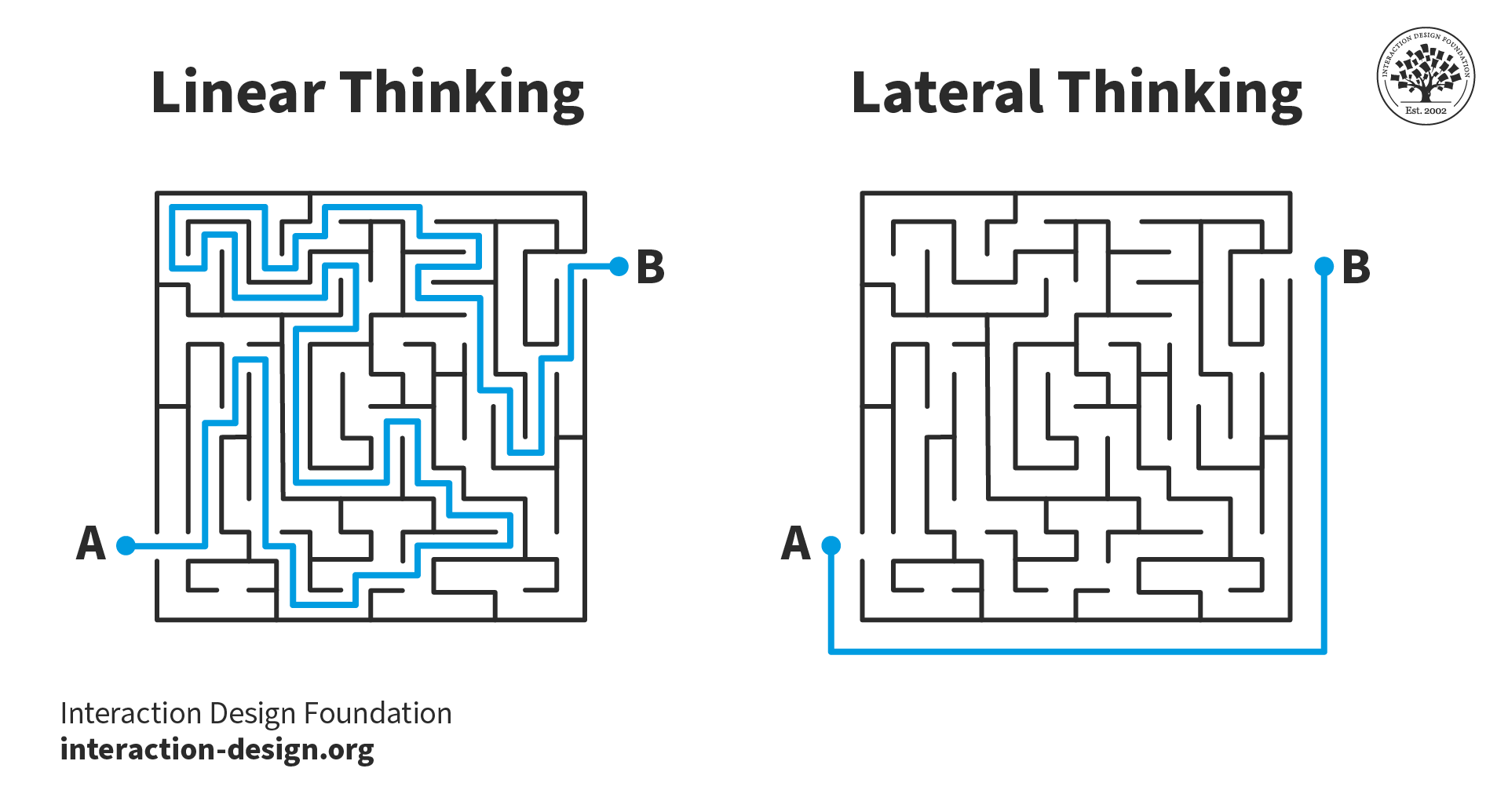
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
That’s where lateral thinking comes in – essentially thinking outside the box. “The box” refers to the apparent constraints of the design space and our limited perspective from habitually meeting problems head-on and linearly. Designers often don’t realize what their limitations are when considering problems – hence why lateral thinking is invaluable in (e.g.) the design thinking process. Rather than be trapped by logic and assumptions, you learn to stand back and use your imagination to see the big picture when you:
Focus on overlooked aspects of a situation/problem .
Challenge assumptions – to break free from traditional ways of understanding a problem/concept/solution.
Seek alternatives – not just alternative potential solutions, but alternative ways of thinking about problems .
When you do this, you tap into disruptive thinking and can turn an existing paradigm on its head. Notable examples include:
The mobile defibrillator and mobile coronary care – Instead of trying to resuscitate heart-attack victims once they’re in hospital, treat them at the scene .
Uber – Instead of investing in a fleet of taxicabs, have drivers use their own cars .
Rather than focus on channeling more resources into established solutions to improve them, these innovators assessed their problems creatively and uncovered game-changing (and life-changing) insights.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 3.0
How to Get Fresh Perspectives with Lateral Thinking
For optimal results, use lateral thinking early in the divergent stages of ideation . You want to reframe the problem and:
Understand what’s constraining you and why .
Find new strategies to solutions and places/angles to start exploring .
Find the apparent edges of your design space and push beyond them – to reveal the bigger picture.
You can use various methods. A main approach is provocations : namely, to make deliberately false statements about an aspect of the problem/situation . This could be to question the norms through contradiction, distortion, reversal (i.e., of assumptions), wishful thinking or escapism , for example:

Here, we see the norm of conventional schooling challenged and some unpredictable (and even outrageous) notions to trigger our thinking. Our example showcases this method:
Bad Ideas – You think up as many bad or crazy ideas as possible, but these might have potentially good aspects (e.g., helping children specialize in desired subjects earlier). You also establish why bad aspects are bad (e.g., inserting biochips would be a gross violation of human rights).
Other helpful methods include:
Random Metaphors
Randomly pick an item near you or word from a dictionary and write down as many aspects/associations about it as possible. E.g., “Exhibition” – “visitors walk around enjoying paintings”; “learn about cultures”; “pleasant environment”.
Pretend some genius in your field told you this item/word is a good metaphor for your project. E.g., you can organize information, tips and images for your travel-related app to also act like an art/museum exhibition, so anyone can enjoy an interesting tour of a given location.
Use the metaphors you think of to improve your design/product. E.g., you create a captivating app which virtual tourists can enjoy with (e.g.) virtual reality features.
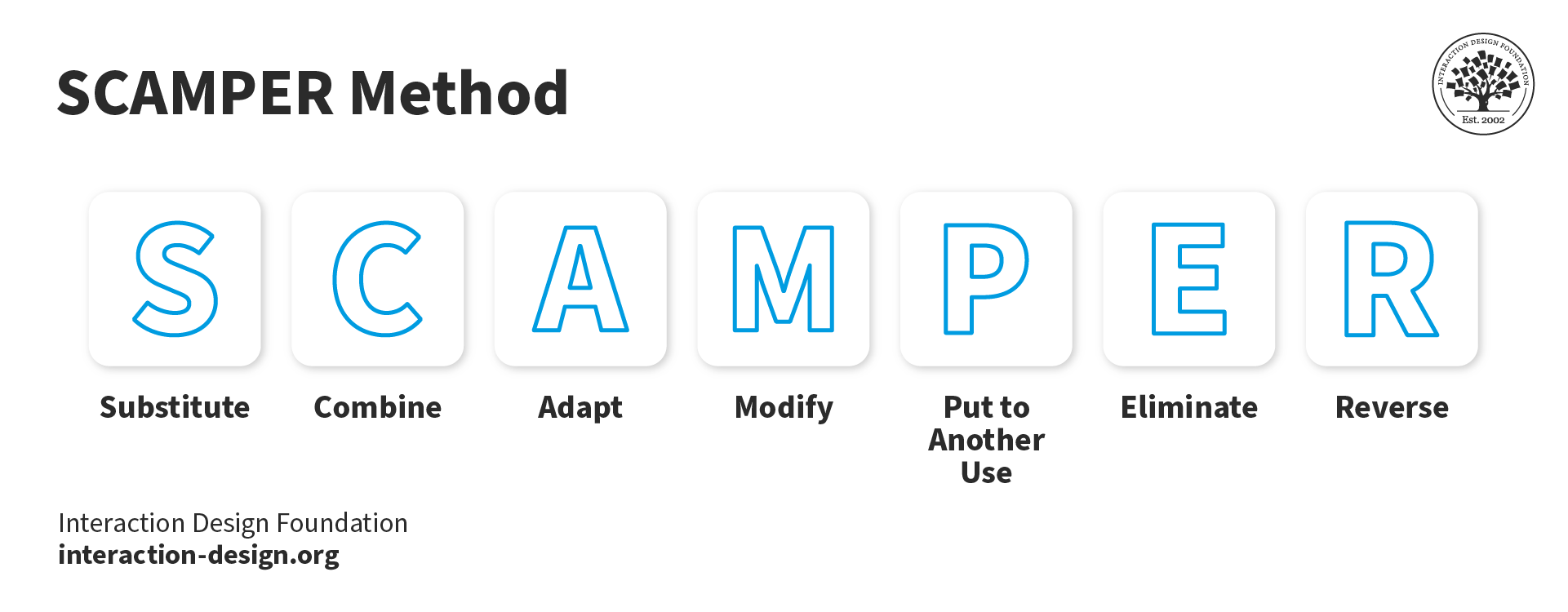
SCAMPER – To help generate ideas for new solutions, ask 7 different types of questions to help understand how you might innovate and improve existing products, services, concepts, etc. SCAMPER is remarkably easy to learn and efficient in ideation sessions.
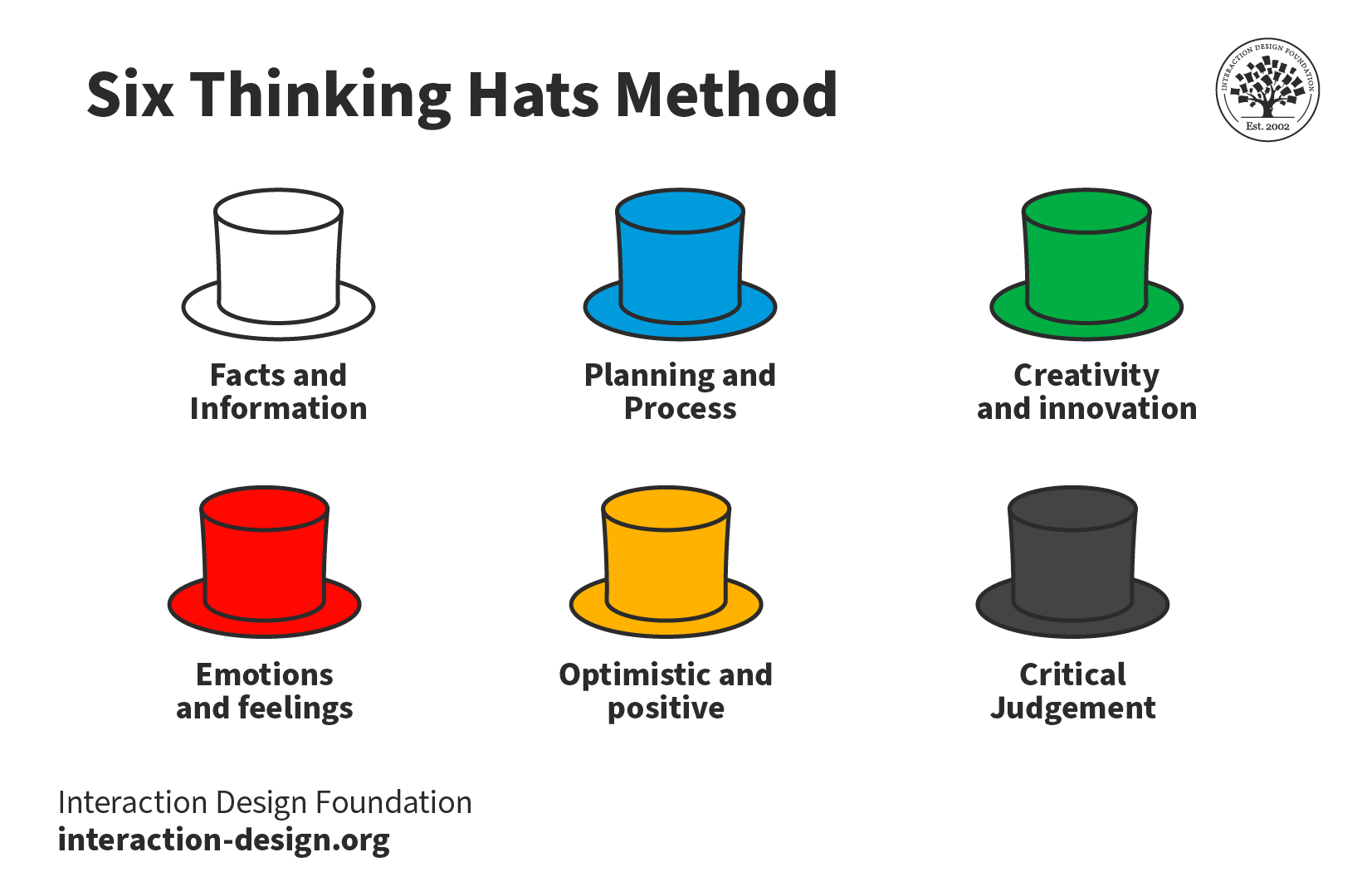
Six Thinking Hats – To reach for alternative viewpoints, you examine problems from 6 perspectives, one at a time (e.g., white hat = focusing on available data; black hat = focusing on potentially negative outcomes).
Overall, it’s important to stay aware of where ideation sessions are going. You may need to pause to redirect the group’s thinking or introduce a new trigger/provocation to help the creative process. Later, you use convergent thinking to isolate optimal solutions.
Learn More about Lateral Thinking
Take our Creativity course , featuring lateral thinking.
This thought-provoking Smashing Magazine blog explores l ateral thinking with more techniques .
Read one design team’s insightful account about lateral thinking .
Questions related to Lateral Thinking
Lateral thinking is changing your approach to solve problems or generate new ideas. Take Edward de Bono’s ‘Six Thinking Hats’ as an example of lateral thinking. It involves adopting different roles to approach problems. This video shows how to break free from your usual thinking patterns.
Imagine a person who is generally optimistic. Using the ' black hat ' approach, they could try looking at things negatively. This might help them find new, innovative solutions that they wouldn't have thought of. They can gain a better understanding of the situation by changing their perspective.
The four lateral thinking techniques are:
Provocation : This involves disrupting conventional thinking patterns with unusual ideas.
Challenge : The challenge is about questioning the status quo. It’s about looking at things as if they might be wrong, even if they seem right. This approach encourages deeper analysis and alternative viewpoints.
Random Entry : This technique generates new ideas using a random word or idea as a starting point. It creates connections that may not be immediately noticeable.
Alternatives : It focuses on shifting thinking patterns by exploring various directions and possibilities.
All these techniques encourage thinking outside the box and fostering creativity.
Lateral thinking and linear thinking are two distinct approaches to problem-solving. Linear thinking is sequential and logical. It follows a straight, step-by-step path that relies on data and analysis. It focuses on following the standard path of reasoning going along, as Alan Dix describes it.
Lateral thinking is non-linear. It involves creativity and looking at problems from various angles. It’s about challenging assumptions and exploring unconventional solutions.
Linear thinking concentrates on details and processes. Whereas lateral thinking emphasizes brainstorming and producing innovative ideas. Both are valuable, but they approach problems from different perspectives.
Yes, lateral thinking is a valuable skill. It's a problem-solving approach that stresses creative thinking. Unlike traditional linear thinking, it's about exploring diverse ideas. You can hone this skill through practice, challenging assumptions, making unexpected connections, and approaching problems from fresh angles.
People skilled in lateral thinking are often adept at generating innovative solutions . Many fields, especially those requiring innovation and creativity, value this skill.
Lateral thinking often aligns with intelligence distinct from traditional measures like IQ. Intelligence manifests in various forms, and lateral thinking showcases creative, problem-solving intelligence. Lateral thinkers view things from unique perspectives. They create innovative ideas and link unrelated concepts. This ability marks an essential aspect of creative intelligence.
This video discusses problem redefinition and negotiation in real-world scenarios. Traditional intelligence focuses on finding a single right solution using given information. But lateral thinking is like solving real-world problems. This approach holds significant value in fields that demand innovation and creative problem-solving. Here, Professor Alan Dix discusses
While different from traditional logical thinking, lateral thinking has its logic. It’s not illogical or random. Instead, it follows a distinct reasoning that prioritizes creativity and innovation. Traditional logic is linear and sequential. It focuses on reaching conclusions based on existing knowledge and facts.
Lateral thinking involves looking at problems from new angles and making unexpected connections. Lateral thinking is a creative way of problem-solving. It can help you find unique and practical solutions. Lateral thinking is a powerful tool when conventional logic doesn't work. Check out this video to learn about different types of creativity and what can get in the way of being creative.
- Copyright holder: Bengt Oberger. Appearance time: 2:18 - 2:23 Copyright license and terms: CC-BY-SA-4.0 Link: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Margaret_Boden_01.JPG
- Copyright holder: Niklas Morberg. Appearance time: 5:27 - 5:32 Copyright license and terms: CC BY-SA 2.0 Link: https://www.flickr.com/photos/morberg/3231304833
Lateral thinking and brainstorming are similar yet different. Lateral thinking helps solve problems using creative and unconventional approaches. It breaks away from traditional methods.
Brainstorming is a group activity where people contribute ideas without judgment to solve a problem. It generates creative solutions.
Lateral thinking can be a solitary or group activity and it focuses on thinking differently. It's a specific approach to problem-solving that emphasizes creativity.
Lateral thinking is crucial because it fosters creativity and innovation. It allows you to explore new ideas and solutions that conventional, linear thinking might not reveal. Lateral thinking helps adapt to new challenges and situations. It encourages looking at problems from multiple perspectives. This leads to more comprehensive and sometimes unexpected solutions. This type of thinking is crucial in innovative fields like business, technology, and design.
Lateral thinking breaks from traditional thought patterns and contributes to advancements and breakthroughs. It enhances problem-solving skills and promotes a more dynamic approach to challenges.
Yes, lateral thinking is a form of divergent thinking . Divergent thinking is about spontaneously generating diverse ideas or solutions to a problem. Lateral thinking, a term coined by Edward de Bono, is a specific kind of divergent thinking. It looks at problems from new and unusual angles and seeks innovative solutions outside conventions.
Divergent thinking is a broader concept encompassing various methods of generating creative ideas. Lateral thinking focuses more on breaking conventional patterns and thinking beyond the norm. Both are key in creative processes, encouraging broad exploration of possibilities.
You can take the creativity course featuring lateral thinking to learn more about lateral thinking. This course would be a more in-depth and interactive way to learn. The course will also help develop your lateral thinking skills through practical applications.
Literature on Lateral Thinking
Here’s the entire UX literature on Lateral Thinking by the Interaction Design Foundation, collated in one place:
Learn more about Lateral Thinking
Take a deep dive into Lateral Thinking with our course Creativity: Methods to Design Better Products and Services .
The overall goal of this course is to help you design better products, services and experiences by helping you and your team develop innovative and useful solutions. You’ll learn a human-focused, creative design process.
We’re going to show you what creativity is as well as a wealth of ideation methods ―both for generating new ideas and for developing your ideas further. You’ll learn skills and step-by-step methods you can use throughout the entire creative process. We’ll supply you with lots of templates and guides so by the end of the course you’ll have lots of hands-on methods you can use for your and your team’s ideation sessions. You’re also going to learn how to plan and time-manage a creative process effectively.
Most of us need to be creative in our work regardless of if we design user interfaces, write content for a website, work out appropriate workflows for an organization or program new algorithms for system backend. However, we all get those times when the creative step, which we so desperately need, simply does not come. That can seem scary—but trust us when we say that anyone can learn how to be creative on demand . This course will teach you ways to break the impasse of the empty page. We'll teach you methods which will help you find novel and useful solutions to a particular problem, be it in interaction design, graphics, code or something completely different. It’s not a magic creativity machine, but when you learn to put yourself in this creative mental state, new and exciting things will happen.
In the “Build Your Portfolio: Ideation Project” , you’ll find a series of practical exercises which together form a complete ideation project so you can get your hands dirty right away. If you want to complete these optional exercises, you will get hands-on experience with the methods you learn and in the process you’ll create a case study for your portfolio which you can show your future employer or freelance customers.
Your instructor is Alan Dix . He’s a creativity expert, professor and co-author of the most popular and impactful textbook in the field of Human-Computer Interaction. Alan has worked with creativity for the last 30+ years, and he’ll teach you his favorite techniques as well as show you how to make room for creativity in your everyday work and life.
You earn a verifiable and industry-trusted Course Certificate once you’ve completed the course. You can highlight it on your resume , your LinkedIn profile or your website .
All open-source articles on Lateral Thinking
Learn how to use the worst possible idea method.

Understand the Elements and Thinking Modes that Create Fruitful Ideation Sessions
- 3 years ago
Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this page , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share the knowledge!
Share this content on:
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this page.
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!

Critical, Lateral, & Creative Thinking
Lateral & creative thinking, introduction.
Lateral and creative thinking work hand-in-hand with critical thinking as we solve problems. Lateral thinking offers a somewhat structured way to generate new ideas, while creative thinking opens the door to all possibilities. While critical thinking is needed in identifying and starting to solve problems, lateral and creative thinking help generate multiple, different, and often unexpected solutions.
Lateral Thinking
One way to deal with assumptions and problem-solving is to develop your lateral thinking skills. Lateral thinking includes a conscious generation of alternative solutions, and a conscious questioning of assumptions.
Read the article on Lateral Thinking Skills and watch the following video on lateral thinking.
How can we think laterally, when our brains are programmed to think in terms of patterns and linear movement from point A to point B? Play on that proclivity for patterns and apply a pattern to help you think outside of the box.
- On a sheet of paper, make three columns. Title the first “positives,” the second “negatives,” and the third “interesting.”
- List out the positives, the negatives, and what’s interesting about the following situation: What if all cars were painted yellow? What would be positive, negative and interesting about this situation?
Critical and Lateral Thinking are about being proactive in identifying assumptions and biases, and about using reasoning and your own insights to make decisions. Lateral thinking actually bridges critical and creative thinking, and provides an additional way in which we can consider information.
What is a problem that you have in your life right now that you can use lateral thinking to solve? Create a chart with the positives, negatives and interesting points for yourself.
Creative Thinking
Creative thinking helps you solve problems in unexpected or new ways.
Read the article on What is Creative Thinking? and view the videos below for a fuller definition of creative thinking.
One really interesting example of creative thinking deals with a solution to dementia and Alzheimer’s patients wandering off. You can listen to a podcast explaining this creative solution, or read the text of the podcast on the page entitled The Bus Stop . Then read a reflection on this solution from a medical student in the blog post, A Wait for the Bus .
initial activity
Apply lateral and creative thinking to the scenario in the following video:
Training Video: When the Phone Rings. (Example of poor receptionist skills.)
After viewing the video, apply lateral and creative thinking skills to the situation. Put yourself in the role of supervisor of this employee, the woman who left at the start of the video. The boss mentioned to you the assistant’s lack of appropriate protocol in taking messages and his need to apologize to the client. You need to relay the information to the assistant so that it does not happen again. Instead of simply focusing on the negative and giving her a rebuke, consider the positive and interesting aspects of this employee and the situation (you’ve already identified the negative). How can you use the positive and interesting aspects of the employee’s behavior to help her develop into a stronger administrative professional? More generally, what creative actions can you take to train newer employees and ensure that a situation like this does not happen again?
Write a brief analysis (3-4 pages) applying lateral and creative thinking skills to this situation.
Submit: analysis
in-depth activity
Choose one of the following options.
Read the article “ Your Brain on Creativity ” from Psychology Today .
Apply lateral and creative thinking concepts to consider how the information in this article might be presented in an alternative, perhaps divergent way. Then create that presentation, to represent the main ideas from the article in another way.
Submit: the presentation
Identify a problem at work or with a community group. Apply concepts and strategies of lateral and creative thinking, and generate at least 4 potential alternative solutions to the problem, solutions that are not the obvious ones, solutions that are “outside the box.”
Submit: a written proposal offering these solutions. Include the following sections in the proposal:
- statement of problem
- discussion of why the obvious solution is not the best
- presentation of alternative solutions with reasons why they are better than the obvious solution
interested in learning more about creative thinking?
You may want to read a relatively short book chapter on Creative Approaches to Problem Solving .
You may want to consider taking courses in:
- Creativity Across the Disciplines
- Creativity in the World Around Us
- Psychology of Creativity
Related college Learning Goals
Communication: Express and receive ideas effectively, in multiple contexts and through multiple strategies.
Critical Thinking and Problem Solving: Evaluate, analyze, synthesize and critique key concepts and experiences, and apply diverse perspectives to find creative solutions to problems concerning human behavior, society and the natural world.
For more information, see the College Learning Goals Policy .
- Lateral & Creative Thinking. Authored by : Susan Oaks; adapted from team work by Nan Travers (lead), Cathy Davison, Elaine Handley, Linda Jones, Jessica Kindred, Gohar Marikyan, Lynette Nickleberry, Susan Oaks, Eileen O'Connor. Project : Educational Planning. License : CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial
- video Lateral Thinking: Generate Brilliant Ideas. Authored by : Blahzinga. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CxbB0DAlx7c . License : Other . License Terms : YouTube video
- video Trick Your Mind into Being Creative. Authored by : Aadil Vora. Provided by : Farquhar College of Arts and Sciences. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1xWa3Ok2e94 . Project : TEDx Talks. License : Other . License Terms : YouTube video
- video Tina Seelig: Challenge Assumptions. Authored by : Tina Seelig. Provided by : Stanford eCorner, Stanford Technology Ventures Program. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mp-Jj6BBkzM . Project : TEDx Talks. License : Other . License Terms : YouTube video
Rick Pastoor
- Side projects
Analytical, lateral and critical thinking
Aug 3, 2016
In my Strategic Thinking Week , some time ago, one of the posts was titled be hypercritical . Still interesting, in case you missed it. In today’s post I want to look at a three step approach to thinking, which builds towards being hypercritical: analytical, lateral and strategic thinking.
Analytical thinking focuses on facts and evidence. In order to solve problems, one should have the strength and ability to pull apart data and break down facts. Another big part of analytical thinking involves systematic rejection of unacceptable alternatives.
Lateral thinking is a more creative approach, where one needs to have the ability to think outside the box and come up with solutions that do not follow a step by step plan. Where an analytical approach is looking at what’s there, the lateral approach focusses on what’s not there.
Critical thinking is giving weight at everything that’s discovered in the steps above. It is about weighing all the options and forming a solid opinion. Critical thinking is always putting all the given data to the test in order to check if it is current and accurate.
These three have a lot in common, but their approach is very different at the same time. In order to solve complex questions, follow the three steps: analyze the data available, try to look at what is not there and finally form your own sound opinion by looking critically at everything you have.
Matthew Kenney
Small Business | Workplace Law
Critical and Lateral Thinking
Posted on: 07.07.16 | by Matthew Kenney
A common frustration of new business school students is that professors are trying to teach them “ what to think ” about business. There are certainly some instructors who make this mistake, but this is not the objective of faculty. Rather, the goal is to help students develop critical thinking skills, and lateral thinking skills.
- Critical thinking is established when we use a criteria for making decisions and analysis (the words critical and criteria both derive from the Greek word kritērion , defined as a means of judging).
- Lateral thinking is the process of problem solving through creativity and non-traditional approaches. Imagination and possibilities are emphasized over step-by-step approaches.
Most people will have a natural inclination towards one of these approaches. Therefore, when instructed in a style using the opposite approach it might feel as if they are being taught what to think . In reality, they are being taught how to think critically and laterally. The ability to blend critical and lateral thinking is essential to career success, since it is a key element in seeing things from different perspectives.
Leave a Comment Cancel
Social media.

The Peak Performance Center
The pursuit of performance excellence, critical thinking vs. creative thinking.
Creative thinking is a way of looking at problems or situations from a fresh perspective to conceive of something new or original.
Critical thinking is the logical, sequential disciplined process of rationalizing, analyzing, evaluating, and interpreting information to make informed judgments and/or decisions.
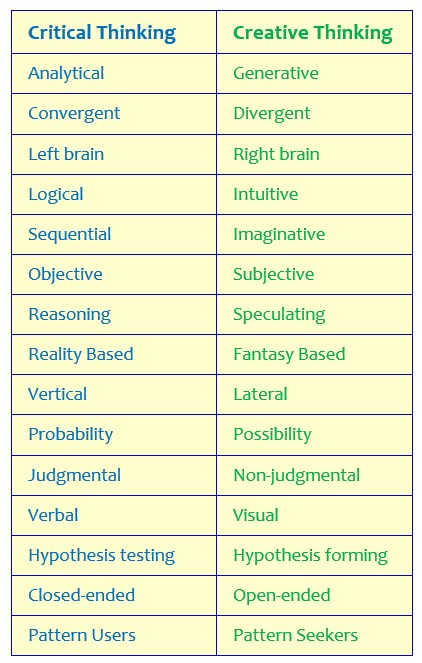
Critical Thinking vs. Creative Thinking – Key Differences
- Creative thinking tries to create something new, while critical thinking seeks to assess worth or validity of something that already exists.
- Creative thinking is generative, while critical thinking is analytical.
- Creative thinking is divergent, while critical thinking is convergent.
- Creative thinking is focused on possibilities, while critical thinking is focused on probability.
- Creative thinking is accomplished by disregarding accepted principles, while critical thinking is accomplished by applying accepted principles.
About Creative Thinking
Creative thinking is a process utilized to generate lists of new, varied and unique ideas or possibilities. Creative thinking brings a fresh perspective and sometimes unconventional solution to solve a problem or address a challenge. When you are thinking creatively, you are focused on exploring ideas, generating possibilities, and/or developing various theories.
Creative thinking can be performed both by an unstructured process such as brainstorming, or by a structured process such as lateral thinking.
Brainstorming is the process for generating unique ideas and solutions through spontaneous and freewheeling group discussion. Participants are encouraged to think aloud and suggest as many ideas as they can, no matter how outlandish it may seem.
Lateral thinking uses a systematic process that leads to logical conclusions. However, it involves changing a standard thinking sequence and arriving at a solution from completely different angles.
No matter what process you chose, the ultimate goal is to generate ideas that are unique, useful and worthy of further elaboration. Often times, critical thinking is performed after creative thinking has generated various possibilities. Critical thinking is used to vet those ideas to determine if they are practical.
Creative Thinking Skills
- Open-mindedness
- Flexibility
- Imagination
- Adaptability
- Risk-taking
- Originality
- Elaboration
- Brainstorming

About Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is the process of actively analyzing, interpreting, synthesizing, evaluating information gathered from observation, experience, or communication. It is thinking in a clear, logical, reasoned, and reflective manner to make informed judgments and/or decisions.
Critical thinking involves the ability to:
- remain objective
In general, critical thinking is used to make logical well-formed decisions after analyzing and evaluating information and/or an array of ideas.
On a daily basis, it can be used for a variety of reasons including:
- to form an argument
- to articulate and justify a position or point of view
- to reduce possibilities to convergent toward a single answer
- to vet creative ideas to determine if they are practical
- to judge an assumption
- to solve a problem
- to reach a conclusion
Critical Thinking Skills
- Interpreting
- Integrating
- Contrasting
- Classifying
- Forecasting
- Hypothesizing

Copyright © 2024 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes

- Search Search Search …
- Search Search …
Lateral Thinking and Logical Reasoning

There are a myriad of ways to solve problems in our world, and as humans, there are a lot of different methods we can use to generate ideas and find the best ways of addressing those problems. Two of these methods are lateral thinking and logical reasoning. Here are the differences between lateral thinking and logical reasoning.
Lateral thinking is a method of problem solving that emphasizes the generation of ideas in an indirect way. In contrast, logical reasoning is much more vertical in nature, beginning with the problem at hand and following a logical thought pattern to see it to its conclusion.
There are a number of differences between lateral and logical thinking, and both can be used effectively in different circumstances. Lateral thinking is generally considered to be more creative, demonstrating its value in artistic fields, while logical thinking is a good problem-solving tool.
The rest of this article will define lateral and logical thinking, discuss the differences between the two, provide examples on how they are used.
Lateral Thinking Explained
At its heart, lateral thinking is an indirect though process. It is, by definition, thinking outside the box. To think laterally, you must put aside any perceived conditions, restrictions, and patterns associated with a problem in order to look at it in a unique and creative way.
One of the oldest examples of this type of thinking is demonstrated by King Solomon, who solved a dispute over a child’s parentage by suggesting that the child be cut in half. He then based his judgement on the reactions of the two women.
While there are certainly some more traditional and logical recourses to discern who the real mother was, this method of problem-solving enabled King Solomon to frame the problem in an entirely different light and still solve it all the same.
The History of Lateral Thinking
Lateral thinking is a term coined by the Maltese psychologist Edward De Bono, who saw lateral thinking as a way of thinking outside the box. Traditionally, marketing strategies involved a very formula-oriented approach: evaluate the consumer’s need based on market trend and create a new product to fill those needs.
De Bono argued and observed that this rigid approach would inevitably lead to market fragmentation and pin the company into a niche market such that they would, over time, be unable to turn a profit.
Lateral Thinking and Business
One of the most prominent fields where lateral thinking thrives is in entrepreneurships and businesses as a whole. Companies and individual entrepreneurs need to avail lateral thinking to create new solutions to problems, all tying back to the simple question: what does the customer want?
Removing the formulaic way of thinking allows marketing strategists and creatively minded individuals to develop new methods of creative thinking, therefore discovering previously unknown ways to solve a “problem” that the consumer is facing.
After all, many businesses thrive on the simple capability to meet a consumer’s need and solve a problem; moreover, companies excel by figuring out how to better meet those needs. It’s not enough to use lateral thinking to develop a unique solution to a consumer problem.
To stay ahead of the curve, companies must continue to develop that product using lateral thinking to preempt future problems that consumers might have, whether it be creative improvements to the product or similar products serving similar purposes.
Perhaps the best part of lateral thinking is that it allows for ridiculous, nonsensical, and just plain old silly ideas to be put on the table. If nothing else, these thought exercises can encourage people in any field to consider nontraditional approaches to their careers.
Logical Reasoning Explained
In contrast to lateral thinking, logical reasoning is a method of problem solving that evaluates the rules of a scenario and evaluates the logical conclusion. As a base example, consider this thought exercise: you have a carton of 12 eggs and 12 people.
Each person receives an egg, but the carton isn’t empty. Why? Logically, this seems nonsensical since, by observation, if each person took one egg, then the carton would be empty. Lateral thinking might eventually help you realize that there is a way that the carton remains unemptied—because the last person took the carton and the egg.
It’s easy to see from this example how quickly our minds utilize logical reasoning to find solutions to problems. In this example, logical thinking constrains your understanding of the question until you think outside the box.
That’s not to say that logical thinking is an inferior method, just that logical thinking tends to be more ordered and result in a more common solution.
The Three Types of Logical Thinking
Logical thinking is a broad term for three more specific approaches to problem solving. First, deductive reasoning starts by establishing a premise and taking specific information relating to the problem to draw a conclusion.
Example: All dogs have four legs. Teddy is a dog. Therefore, Teddy has four legs.
Inductive reasoning works backwards and uses observations to draw conclusions about the world at large. In this example, you might start with the observation that Teddy is a dog and has four legs.
When this phenomenon is observed at large, given that by their biological nature, dogs always have four legs, it’s safe to assume that all dogs have four legs.
Lastly, abductive reasoning is predictive in that it takes an observation similar to deductive reasoning and considers the most likely outcome of that scenario.
For example, if we’ve already deduced that all dogs have four legs, then it’s quite possible that Teddy, who meets those criteria, is a dog. Of course, Teddy could be a cat in this scenario, which is why abductive reasoning can be inaccurate and open to interpretation.
Final Thoughts
There are a number of differences between lateral thinking and logical reasoning , and both have their uses in the modern world. Logical thinking helps establish the most likely outcome of a problem, while lateral thinking is designed to generate ideas and inspire people to think differently.
https://study.com/academy/lesson/what-is-lateral-thinking-definition-theory-examples.html
https://www.practiceaptitudetests.com/what-is-logical-reasoning/
What Is Lateral Thinking And Why It Matters In Entrepreneurship
You may also like

Lateral Thinking vs Creative Thinking: Understanding Different Problem-Solving Approaches
Lateral thinking and creative thinking are often used interchangeably, signaling a departure from conventional logic to generate innovative solutions and ideas. Lateral […]

Lateral Thinking for Management
Lateral thinking has the potential to totally transform businesses from top to bottom, especially when the charges led by great leaders (and […]

Top 5 Lateral Thinking Puzzles (Tips and Answers Included)
One of the best ways to improve at lateral thinking is to practice with lateral thinking puzzles. Even if you do not […]

Best Books on Lateral Thinking: Expand Your Problem-Solving Skills
Lateral thinking is a valuable skill that can help individuals solve problems and approach challenges in new ways. Whether you’re looking to […]
- Organizations
- Planning & Activities
- Product & Services
- Structure & Systems
- Career & Education
- Entertainment
- Fashion & Beauty
- Political Institutions
- SmartPhones
- Protocols & Formats
- Communication
- Web Applications
- Household Equipments
- Career and Certifications
- Diet & Fitness
- Mathematics & Statistics
- Processed Foods
- Vegetables & Fruits
Difference Between Thinking and Critical Thinking
• Categorized under Nature | Difference Between Thinking and Critical Thinking

Thinking vs. Critical Thinking
The Two Think Tanks: Thinking and Critical Thinking
Every human being is capable of thinking, but some say that few are able to practice critical thinking. What’s the difference?
Thinking is the mental process, the act and the ability to produce thoughts. People think about almost everything and anything. They often think of people, things, places, and anything without a reason or as a result of a trigger of a stimulus. Meanwhile, critical thinking often means “thinking about thinking.” In a sense, it is a deeper form of thinking about a particular issue or situation before actually deciding and acting.
In any given situation, thinking is an action that requires the person to form a thought about that situation. Any thought can be formed, even without facts or evidence. When critical thinking is applied, the mind is open to all considerations, assumptions, and details before actually forming a thought or an opinion. A person who is a critical thinker regards the subject itself and all its aspects, like the methods of collecting facts or the motivation behind said facts. A person who employs critical thinking often adds the question “why” to “who, what, where, and when” in a particular situation.
To illustrate, imagine a person at a bookstore. This person can pick out a book and think that the book is good upon first impression. A critical thinking person would open the book, read some passages, and read about the author before actually deciding whether to buy the book or not. The customer might often wonder about the title or why the author chose to write this particular piece of literature.
A thinker may accept facts or realities based on faith alone and without examination and analysis of the issue. These facts or realities are often perceived as “truth” and cannot be criticized or modified. In this situation, there is no need for evidence or the effort to produce it and its examination.
Critical thinking is the opposite of all of this. It often requires a lot of time, questions, and considerations. It also involves a longer process before arriving at a conclusion or decision.
Individuals who apply critical thinking are often open-minded and mindful of alternatives. They try to be well informed and do not jump to conclusions. Critical thinkers know and identify conclusions, reasons, and assumptions. They use clarifying and probing questions in order to formulate their reasonable situations and arguments. They often try to integrate all items in the situation and then draw conclusions with reason and caution. They also have good judgment on the credibility of sources and the quality of an argument, aside from developing and defending their stand. If asked, these people can clearly articulate their argument with all its strengths and weaknesses.
Critical thinking is an on-going process and activity. This skill is learned through active practice and constant use. Exposure to controversial issues and thought-provoking situations stimulates the mind to utilize this skill, which is then applied upon careful examination of an issue or situation. Meanwhile, thinking can be done in an instant without any given proof and/or justification.
Critical thinking requires logic and accuracy, while thinking sometimes occurs in the form of faith and personal opinion. The former requires evidence and further actions of examination and analysis, while the latter does not. It’s up to you to think and decide.
- Both thinking and critical thinking are mental processes.
- Thinking can be classified as an action, while critical thinking can be said to be a skill.
- Critical thinking is used with caution, while thinking can be spontaneous.
- A critical thinker is able to identify the main contention in an issue, look for evidence that supports or opposes that contention, and assess the strength of the reasoning, while a thinker may base their belief solely on faith or personal opinion.
- Recent Posts
- Differences Between Fraternity And Sorority - January 8, 2014
- Differences Between Lucite and Plastic - January 7, 2014
- Differences Between Oil and Butter - January 6, 2014
Sharing is caring!
- Pinterest 7
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
- Difference Between Concrete and Abstract Thinking
- Difference Between Fact and Opinion
- Difference between Argument and Debate
- Difference Between Facts and Opinions
- Difference Between Argument and Persuasion
Cite APA 7 Franscisco, . (2017, June 30). Difference Between Thinking and Critical Thinking. Difference Between Similar Terms and Objects. http://www.differencebetween.net/science/nature/difference-between-thinking-and-critical-thinking/. MLA 8 Franscisco, . "Difference Between Thinking and Critical Thinking." Difference Between Similar Terms and Objects, 30 June, 2017, http://www.differencebetween.net/science/nature/difference-between-thinking-and-critical-thinking/.
Thank you very, much, this was a discussion question and the information was too closly related to find a significant difference.
As I was reading this article I kind of think I’m a critical thinker. When my boyfriend tells me thing about his day I’m not going to lie I try and ask why did that happen. Or I say strange that happened in order to get him to tell me more things. Just the other day we were out with our friends and Jose one of our friends was telling us how one of there friend is different ever since he got his promotion at work and Jose was like that foo needs to chill I’m not going talk about our wild nights and I was like oh yeah like which ones. I was trying to get him to talk but then our other friend pointed it out and was like umm look at Brenda thinking we really do have wild nights. I tend to always ask why is it done that way or could it have ever crossed there mind that they can do it this way.
Thx for the article,it’s very easy to understand
Leave a Response
Name ( required )
Email ( required )
Please note: comment moderation is enabled and may delay your comment. There is no need to resubmit your comment.
Notify me of followup comments via e-mail
References :
Advertisments, more in 'nature'.
- Difference Between Climate Change and Global Warming
- Difference Between Crohn’s and Colitis
- Difference Between African and Asian Elephants
- Difference Between Zebra And Horse
- Difference Between Squid and Octopus
Top Difference Betweens
Get new comparisons in your inbox:, most emailed comparisons, editor's picks.
- Difference Between MAC and IP Address
- Difference Between Platinum and White Gold
- Difference Between Civil and Criminal Law
- Difference Between GRE and GMAT
- Difference Between Immigrants and Refugees
- Difference Between DNS and DHCP
- Difference Between Computer Engineering and Computer Science
- Difference Between Men and Women
- Difference Between Book value and Market value
- Difference Between Red and White wine
- Difference Between Depreciation and Amortization
- Difference Between Bank and Credit Union
- Difference Between White Eggs and Brown Eggs

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Critical thinking is about taking a step back without emotion to judge and evaluate an issue or problem, while Lateral thinking is all about using emotion and creative thinking to understand a problem. Being distant vs being personal, the two, at first, appear to be like fire and water. Two different elements, two different ways of thinking.
To make the most of both skills, use critical thinking to define the problem, gather information, evaluate options, and refine your ideas. Meanwhile, use lateral thinking to generate ideas ...
Here are a few lateral thinking techniques to broaden your own and your team's problem-solving skills. 1. Recognize thought patterns. Humans often get stuck in an anchoring bias: making judgments or decisions based on the first piece of information they receive.
Critical thinking is primarily concerned with judging the truth value of statements and seeking errors. Lateral thinking is more concerned with the "movement value" of statements and ideas. A person uses lateral thinking to move from one known idea to creating new ideas.'. 3 Modes Of Thinking: Lateral, Divergent & Convergent Thought.
Analytical thinking is a thinking process or skill in which an individual has the ability to scrutinize and break down facts and thoughts into their strengths and weaknesses. It involves thinking in thoughtful, discerning ways, in order to solve problems, analyze data, and recall and use information. It involves the following main activities:
Analytical thinking is a thinking process or skill in which an individual has the ability to scrutinize and break down facts and thoughts into their strengths and weaknesses. It involves thinking ...
Lateral thinking helps solve problems using creative and unconventional approaches. It breaks away from traditional methods. Brainstorming is a group activity where people contribute ideas without judgment to solve a problem. It generates creative solutions. Lateral thinking can be a solitary or group activity and it focuses on thinking ...
Lateral thinking is a manner of solving problems using an indirect and creative approach via reasoning that ... Critical thinking is primarily concerned with judging the true value of statements and seeking errors whereas lateral thinking focuses more on the "movement value" of statements and ideas. A person uses lateral thinking to move from ...
Lateral thinking offers a somewhat structured way to generate new ideas, while creative thinking opens the door to all possibilities. While critical thinking is needed in identifying and starting to solve problems, lateral and creative thinking help generate multiple, different, and often unexpected solutions.
Lateral thinking is a more creative approach, where one needs to have the ability to think outside the box and come up with solutions that do not follow a step by step plan. Where an analytical approach is looking at what's there, the lateral approach focusses on what's not there. Critical thinking is giving weight at everything that's ...
Lateral vs. Vertical Thinking. Vertical thinking uses the processes of logic. Vertical thinking is analytical, sequenced, deliberate, and precise. It involves taking the data from a problem and analyzing it with defined methodologies to find logical solutions. Lateral thinking involves using reasoning that is not straightforward and obvious.
Lateral thinking is the essence of creativity. In times of crisis, much gets written about the importance of leaders not "losing their heads.". But, while remaining calm is a pre-requisite of ...
Critical thinking is established when we use a criteria for making decisions and analysis (the words critical and criteria both derive from the Greek word kritērion, defined as a means of judging). Lateral thinking is the process of problem solving through creativity and non-traditional approaches. Imagination and possibilities are emphasized ...
Here are three key differences between analytical thinking and critical thinking: Gathering information and making conclusions To apply analytical thinking skills, you can gather and process information from complex sources, such as theories or situations, break them down into more manageable parts, or study them together to draw a logical ...
Lateral Thinking: Definition. is a form of thinking that uses many different perspectives to solve problems. It is often associated with brainstorming and can be applied in many different fields ...
Critical Thinking vs. Creative Thinking Creative thinking is a way of looking at problems or situations from a fresh perspective to conceive of something new or original. Critical thinking is the logical, sequential disciplined process of rationalizing, analyzing, evaluating, and interpreting information to make informed judgments and/or decisions.
A leader has to have critical thinking abilities, but lateral thinking abilities can be found across levels. Sunil Kumar, CHRO, PVR, says, "For certain routine functions, it is better to have lateral thinkers on board, but for role-specific functions, it is advisable to hire critical thinkers.". "There are certain leaders - given the ...
Lateral thinking is generally considered to be more creative, demonstrating its value in artistic fields, while logical thinking is a good problem-solving tool. The rest of this article will define lateral and logical thinking, discuss the differences between the two, provide examples on how they are used. Contents.
The term Lateral Thinking was invented by Dr. Edward de Bono in 1967 and is defined by the Oxford English Dictionary as " a way of thinking which seeks the solution to problems through unorthodox methods, or elements which would normally be ignored by logical thinking" All of the lateral thinking techniques have been designed to make an ...
Thinking can be classified as an action, while critical thinking can be said to be a skill. Critical thinking is used with caution, while thinking can be spontaneous. A critical thinker is able to identify the main contention in an issue, look for evidence that supports or opposes that contention, and assess the strength of the reasoning, while ...
summarizes the differences between vertical and lateral thinking approaches along various dimensions. Table 2. clearly indicates that lateral thinking is quite different from traditional vertical ...