If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.

Digital SAT Math
Course: digital sat math > unit 3, data representations | lesson.
- Key features of graphs — Basic example
- Key features of graphs — Harder example
- Data representations: foundations
What are data representations problems?
- Read types of graphs that commonly appear on the SAT
- Create line graphs based on verbal descriptions
How do I read bar graphs, dot plots, and histograms?
Reading bar graphs, what are bar graphs, dot plots, and histograms.
- Since cereals brands C and D have taller bars than cereal brands A and B, we can immediately tell that cereal brands C and D have more sugar per 100 grams of cereal than cereal brands A and B.
- Cereal brands A and B have close to 10 grams of sugar per 100 grams of cereal, while cereal brands C and D have over 30 grams of sugar per 100 grams of cereal.
- This means cereal brands C and D have over triple the amount of sugar per 100 grams of cereal than cereal brands A and B!
- We can interpret the data as " 250 students take Spanish", "approximately 60 students take French", etc.
- Based on the relative size of the bars, we can tell that Spanish is the most frequently taken foreign language and Latin is the least frequently taken foreign language.
- 3 students take 5 minutes to travel to school, 4 students take 10 minutes to travel to school, etc.
- The most common travel time is 10 minutes.
- The travel times range from 5 to 35 minutes.
- 6 available apartments have areas between 30 and 40 square meters, 4 have areas between 40 and 50 square meters, etc.
- There aren't many larger apartments available.
- Your answer should be
- an integer, like 6
- a simplified proper fraction, like 3 / 5
- a simplified improper fraction, like 7 / 4
- a mixed number, like 1 3 / 4
- an exact decimal, like 0.75
- a multiple of pi, like 12 pi or 2 / 3 pi
How do I read line graphs?
Reading line graphs, what are line graphs.
- Identify values on the graph and use them in calculations
- Determine whether the graph is increasing or decreasing. We may be asked about a specific interval or the whole graph.
- Determine when the rate of change is the highest/lowest. Higher rates of change correspond to steeper sections of the graph, and lower rates of change correspond to shallower sections of the graph.
- The voter turnout in 1992 is approximately 105 million people.
- The difference in voter turnout between 1988 and 2004 is approximately 30 million people.
- From 1980 to 2004 , voter turnout generally increased.
- However, voter turnout decreased between 1984 and 1988 and between 1992 and 1996 .
- The greatest change in voter turnout between consecutive elections occurred between 2000 and 2004 .
- The smallest change in voter turnout between consecutive elections occurred between 1984 and 1988 .
How do I draw line graphs based on verbal descriptions?
Translating a sequence of events to a line graph, what are some key phrases to look out for, let's look at an example.
- (Choice A) Between the 101 st and 102 nd A Between the 101 st and 102 nd
- (Choice B) Between the 102 nd and 103 rd B Between the 102 nd and 103 rd
- (Choice C) Between the 103 rd and 104 th C Between the 103 rd and 104 th
- (Choice D) Between the 104 th and 105 th D Between the 104 th and 105 th
- a proper fraction, like 1 / 2 or 6 / 10
- an improper fraction, like 10 / 7 or 14 / 8
- (Choice A) A
- (Choice B) B
- (Choice C) C
- (Choice D) D
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

- Grade 5 Scholarship |
- O/L Past papers |
- 2024 O/L Model Papers |
- Royal College |
- Western Province |
- Online Book Shop
- Combined Maths
- Agricultural Science
- Business Studies
- Business Statistics
- Christianity
- Buddhist Civilization
- Drama and Theatre
- Political Science
- General English
- Agriculture
- Home Economics
- Indian History
- Sri Lankan History
- Grade 11 Papers
- Grade 10 Papers
- Grade 09 Papers
- Grade 08 Papers
- Grade 07 Papers
- Civic Education
- English Language
- Mathematics
- Second Language
- Sinhala Language
- Tamil Language
- Western Music
- Scholarship Exam Past Papers
- Scholarship Model Papers
- Environment
- Catholicism
- Grade 11 English Medium
- Grade 10 English Medium
- Grade 09 English Medium
- Grade 08 English Medium
- Grade 07 English Medium
- Grade 06 English Medium
- Sinhala Medium
- Sinhala Medium Answers
- English Medium
- English Medium Answers
- Tamil Medium
- Sinhala Medim Papers
- English Medium Papers
- Tamil Medium Papers
- Sinhala Medium Marking
- English Medium Marking
- Tamil Medium Marking
- Western Province
- North Western Province
- Southern Province
- North Central Province
- Central Province
- Sabaragamuwa Province
- Royal College
- Ananda College
- D.S.Senanayake
- Devi Balika
- Nalanda College
- Rathnavali Balika
- Visakha College
- Grade 11 Textbooks
- Grade 10 Textbooks
- Grade 9 Textbooks
- Grade 8 Textbooks
- Grade 7 Textbooks
- Grade 6 Textbooks
- WIKI Forum! Join
DATA REPRESENTATION AND PREDICTION (Daththa Nirupanaya Ha Arthakathanaya) | Grade 11 Maths Textbook Answers
Grade 11 Maths Textbook Answers Lesson 15 - DATA REPRESENTATION AND PREDICTION (Daththa Nirupanaya Ha Arthakathanaya)

Download Grade 11 Maths textbook answers for DATA REPRESENTATION AND PREDICTION (Daththa Nirupanaya Ha Arthakathanaya), Lesson 15 in Sinhala Medium. DATA REPRESENTATION AND PREDICTION (Daththa Nirupanaya Ha Arthakathanaya) Answers are available in PDF format. Download using the Link Below. It’s free to download.
Grade – Grade 11 Subject – Mathematics Lesson – Lesson no 15 Medium – Sinhala Medium
Download Textbook Answers:

Join our Telegram Group for Daily papers updates:

If you have a problem with this post or PDF File, you can add a comment below or contact us on Facebook . Share this resource with your friends!
Special thanks go to the Kmdc Karunarathna Sir for the development of learning aids to uplift the knowledge of the students. All credit goes to its respective owners. | Visit His Facebook Page – OL Maths | Visit His Website – OL Maths We request you to use it for educational purposes only.
The past paper wiki provides O/L Past Papers, O/L study Materials, and Resources that include syllabus, question papers, Teacher’s resources, Notes, and a lot more. All the content offered here is absolutely free and is provided in the most convenient way to not face any issues.
EQIANGULAR TRIANGLES (Samakoni Thrikona) | Grade 11 Maths Textbook Answers
Geometric progression (gunoththara shreni) | grade 11 maths textbook answers.
Kaushalya Hemamali
https://forum.pastpapers.wiki/

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Buy Books Online

Pastpapers wiki is a free resource site for O/L and A/L Students In Sri Lanka. Past Papers WiKi was founded in October 2019 by Education Resources.lk. The main goal of this site is to provide Past Papers, Marking Schemes, Notes, and other resources that allow students to improve their knowledge.
https://forum.pastpapers.wiki/ Email: [email protected]
Become a Volunteer – Help Others 🙋♂️
We are currently looking for volunteers who are willing to share their expertise and contribute to our community by sharing educational materials in our forum. We’re looking for individuals who can help us create and share educational materials such as articles, videos, and social media posts that will inspire and educate others.
Share Past Papers 📝 | Help Others 🤝 Join With: https://forum.pastpapers.wiki/
Disclaimer of Past Papers WiKi
This website is continued for your personal appreciation or educational purposes only . All Content of this website is published by extracting the information from online sources such as official government websites, social media, other websites, etc. The copyrights of these contents belong to the responsible owners . If a modification will happen in this information, our website does not assume any responsibility. If you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us.
– Mobile No: 071-8540371 – Email: [email protected]
- Science stream
- Commerce stream
- Technology stream
- Arts Stream
- Common Subjects
- WIKI Forum!
Copyright 2019 -2021 © All rights reserved.

Data Analysis Class 11 Notes
Teachers and Examiners ( CBSESkillEduction ) collaborated to create the Data Analysis Class 11 Notes . All the important Information are taken from the NCERT Textbook Artificial Intelligence (417) .
Structured Data
Structured data is a standardized format for describing a page’s content and categorizing it. for example, Names, dates, addresses, credit card numbers, stock data, and other everyday items.
It is a clear structure, and is highly organized in a structured repository. In a relational database management system, it can be simply stored and found because it neatly fits into fixed fields and columns (RDBMS).
Common sources of structured data are: a. Excel files b. SQL databases c. Medical devices Logs d. Online Forms
Characteristics of Structured Data a. High organized b. Clearly defined c. Easy to access d. Easy to analyze
Examples of Structured Data a. Name b. Age c. Gender d. Address e. Phone Number f. Currency g. Date h. Billing info
Sources of Structured Data a. SQL database b. Spreadsheet c. Sensors d. Medical Device e. Online Forms f. Point of Sales Systems g. Web and Server Logs
Date and Time Datatype
Date and Time datatypes are used to hold values with both date and time information. Date-time information can be stored in a variety of formats.
String Data Type
An array of bytes (or words) that stores a succession of elements is frequently used to build the structured data type known as a string. A string can contain [A – Z], [as z], [0 -9], and [all special characters], yet they are all treated as though they were text because they can store alphanumeric data. There are also spaces in it. String information has to be enclosed in quotes (“”or”).
Examples: Address = “9th Floor, SAS Tower, Gurgaon” “Hamburger” “I ate 3 hamburgers”.
Categorical Data Types
The term “categorical data” also refers to a collection of information that may be categorised into categories, such as the report cards for all students. Because it may be categorised based on the variables included in the report card, such as class, subjects, sections, school-house, etc., this data is known as categorical data.
There are four different type of Categorical Data Type – a. Nominal b. Continuous c. Ordinal d. Binary
Representation of Data
The study of statistics focuses on gathering, organizing, analyzing, interpreting, and presenting data. The observations are turned into useful knowledge via data science. To complete this work, statisticians condense a lot of data into a format that is manageable and yields useful information.
Data representation techniques are broadly classified in two ways –
Non-Graphical technique – Tabular form and case form Large datasets should not be represented in this outdated format. When our goal is to make decisions after analysing a set of data, non-graphical techniques are less suitable.
Graphical Technique – Pie Chart, Bar graphs, line graphs, etc. The most typical visual representation of statistical data is in the form of points, lines, dots, and other geometric shapes. Due to time restrictions, it would not be feasible to describe the creation techniques for all sorts of diagrams and maps.
for example – a. Line graphs b. Bar diagrams c. Pie diagram d. Scatter Plots
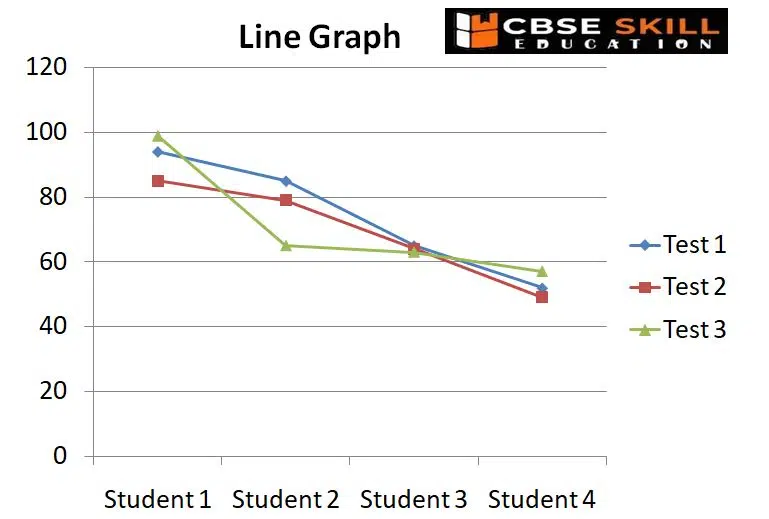
Line Graphs
A line graph, often known as a line chart, is a visual representation of data that is constantly changing over time. A line graph connects the data using points that display a continuous change. Depending on the data points they represent, the lines in a line graph can either ascend or drop.
The advantages of using Line graph is that it is useful for making comparisons between different datasets, it is easy to tell the changes in both long and short term, with even small changes over time.
Bar Diagram
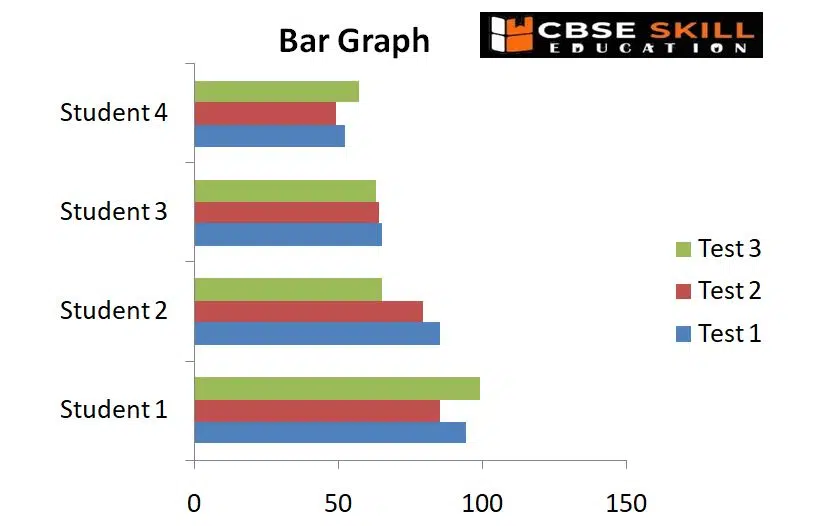
The bars in a bar graph, commonly referred to as a bar chart or bar diagram, are used to compare data between categories. The bar’s length is inversely proportional to the value it stands for. Simply put, the value a bar represents increases with length. The graph’s bars, which can run either horizontally or vertically, are all the same width.
Following rules should be observed while constructing a bar diagram: (a) The width of all the bars or columns should be similar. (b) All the bars should be placed on equal intervals/distance. (c) Bars may be shared with colours or patterns to make them distinct and attractive.
Bar Diagram helpful for comparing data, offer a visual representation for quick comparison of amounts in various categories, and make determining relationships simple. Large changes over time are also depicted in bar graphs.
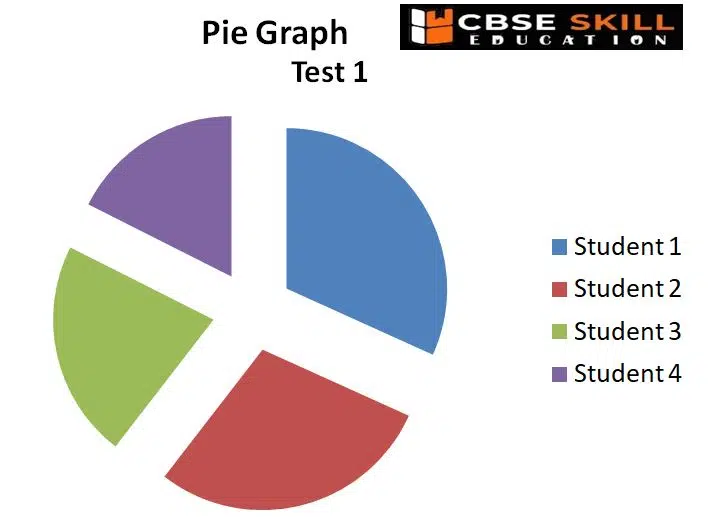
A circular graph with numerous parts or sections is known as a pie chart. Each sector (segment) of the pie represents the relative size, i.e., the percentage or contribution that each category made to the overall pie. Each part of the diagram resembles a slice of a pie, and the whole thing looks like one. Data from a short table can often be visualised using pie charts.
The advantages of a pie chart is that it is simple and easy-to-understand and provides data comparison at a glance.
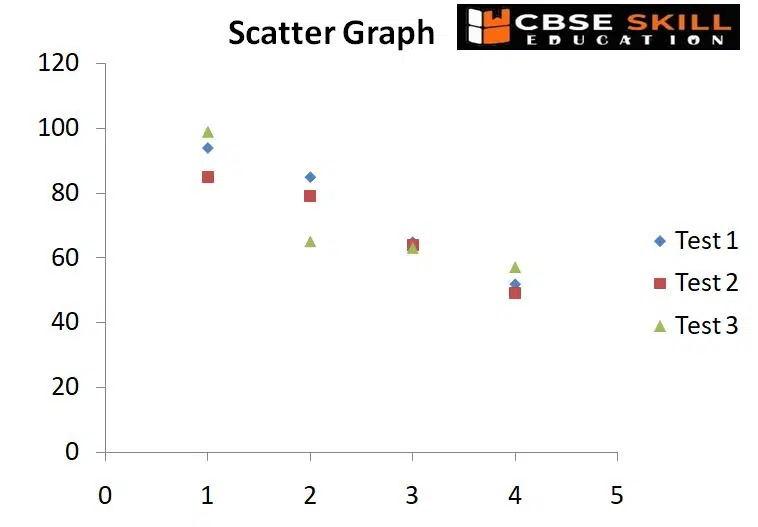
Scatter Plots
Scatter plots are used to show the relationship between two variables (or aspects) for a collection of paired data. They consist of a set of data points plotted along the x and y axes. The various shapes that the data points take tell a tale all their own, most frequently indicating the connection (positive or negative) in a lot of data.
Types of Correlation
The statistical concept of correlation describes how closely two variables move in parallel with one another. Two variables are considered to have a positive correlation if they move in the same direction. They have a negative correlation if they travel in the opposite directions.
Positive Correlation – Both variables are seen to be moving in the same direction. In other words, with the increase in one variable, the other variable also increases.
Negative Correlation – Both the variables are seen to be moving in opposite directions. While one variable increases, the other variable decreases.
Exploring Data
Exploring data entails “getting to know” the data, including its values and their typical, unusual, focused, or extreme characteristics. More significantly, throughout the exploration process, one has the chance to spot and fix any issues with their data that could perhaps influence the findings they come to during analysis. This is the first step in data analysis and involves summarizing the main characteristics of a dataset, such as its size, accuracy, initial patterns in the data and other attributes.
Case, Variables and Levels of Measurement
Cases and variables.
A variable is a quality that may be measured and have several values. Or, anything that varies depending on the circumstance. In contrast, a constant in a research study is the same in every situation. Case a sampling point for an experimental unit.
Cases are nothing more than a collection of objects, a dataset is said to consist of cases.
Levels of Measurement
The level of measurement refers to the method used to determine a set of data. Data cannot be treated equally in all cases. It makes logical to categorise data sets using several standards. Some are qualitative while others are quantitative. There are discrete and continuous data sets. The type of qualitative data can be nominal or ordinal. Additionally, interval and ratio data can be separated into two types.
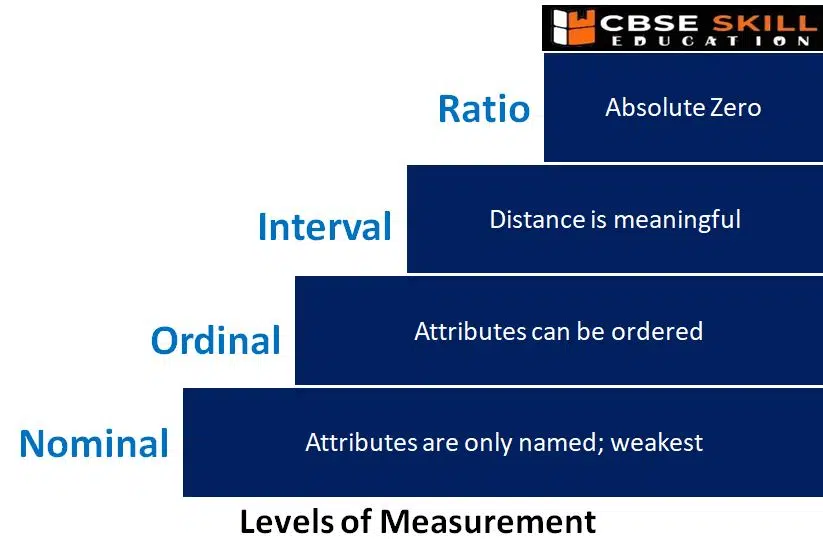
Nominal Level
Nominal-level data are qualitative data. The four seasons of winter, spring, summer, and autumn are examples of nominal variables, as are product categories like Mercedes, BMW, or Audi. Since they are not numbers, they cannot be ranked or utilised in calculations. The easiest or lowest of the four ways to characterise data is the nominal level of measurement.
Ordinal Level
Ordinal data is composed of groups and categories that are arranged in a specific order. For instance, suppose you were asked to give a restaurant meal a rating and you had the choice between unpleasant, unappetizing, just acceptable, tasty, and delicious. Although the restaurant utilised words rather than numbers to judge the quality of its meals, it is obvious that these preferences are ranked from low to high or from negative to positive, making the data qualitative rather than ordinal. The disparity between the data, however, cannot be quantified. Ordinal scale data cannot be used in calculations, much like nominal scale data.

Interval Level
Because it has a clear ordering, data measured using the interval scale is similar to data recorded using the ordinal scale, but there are some differences as well. Even though the data does not have a starting point, or a zero value, the differences between interval scale data can still be measured.
Ratio Scale Level
Similar to interval scale data, ratio scale data has a 0 point and can be used to calculate ratios. For instance, the results of four multiple-choice questions on the final test in statistics were 80, 68, 20, and 92 (out of a possible 100). The grades are produced by a computer. The numbers 20, 68, 80, and 92 can be arranged from lowest to highest, or vice versa. The variations in the data are significant. The score 92 is 24 points higher than the score 68. One can compute ratios. The lowest score is zero. 20 divided by 4 equals 80. An 80 is four times better than a 20, for example.
Data Matrix and Frequency Tables
What is data matrix.
The Data Matrix is a tabular representation of the cases and variables utilised in your statistical analysis. In a data matrix, each row denotes a case and each column a variable. There could be hundreds, lakhs, or even more examples in a complete data matrix.
Frequency Tables
The number of times a specific data value happens (occurrences) in a given set of data is the frequency of that data value. In cricket, if four players each score 90 runs, the score of 90 is said to occur four times. ‘f’ is frequently used to denote a data value’s frequency.
Graphs and Shapes of Distributions
Statisticians or machine learning engineers often want to summarize the data they have. They can do it by various available methods like data matrix, frequency tables or by graphical representation. When graphed, the data in a set is arranged to show how the points are distributed throughout the set.
Mean, Median and Mode
Imagine yourself returning home with your report card after the announcement of your final grades in class. Your parents will ask, “What is your average score?” regarding your grades and general performance. In actuality, they’re looking for your MEAN score.
The most often used and well-known index of central tendency is the mean (or average). The mean is determined by dividing the total number of values in the data set by the number of values in the data set. The mean in this situation is calculated by adding up all of your marks and dividing them by the number of topics.
M = ∑ fox / n Where M = Mean ∑ = Sum total of the scores f = Frequency of the distribution x = Scores n = Total number of cases
The value of an observation for which half are larger and half are smaller is known as the median. The mean of the two middle points is calculated if the number of data points is even. For the median difference, the median for two samples is calculated, and then their difference is calculated.
For a grouped data, calculation of a median in continuous series involves the following steps: (I) The data arranged in ascending order of their class interval (ii) Frequencies are converted into cumulative frequencies (iii) Median class of the series is identified (iv) Formula used to find actual median value
Another crucial indicator of a tactical series’ primary tendency is its mode. In the data series, it is the value that appears the most frequently. The most frequent score in our data set is the mode. It stands in for the highest bar on a histogram or bar chart. Therefore, you might occasionally think of the mode as the most common choice.
Z – score (For Advance Learners)
The Z-score provides us with a notion of how far our particular data point is from the mean. Technically speaking, it’s a measurement of how far the data point deviates from the population mean by standard deviations. If a value is above the mean, the z-score is positive; if it is below the mean, it is negative.
How do we interpret a z-score?
The value of the z-score tells you how many standard deviations your data point is away from the mean. If a zscore is equal to 0, it is on the mean. A positive z-score indicates the raw score is higher than the mean average. For example, if a z-score is equal to +1, it is 1 standard deviation above the mean. A negative z-score reveals the raw score is below the mean average. For example, if a z-score is equal to -2.
Employability Skills Class 11 Notes
- Unit 1 : Communication Skills – III
- Unit 2 : Self-Management Skills – III
- Unit 3 : Information and Communication Technology Skills – III
- Unit 4 : Entrepreneurial Skills – III
- Unit 5 : Green Skills – III
Employability Skills Class 11 MCQ
Employability skills class 11 questions and answers, subject specific skills notes.
- Unit 1: Introduction To AI
- Unit 2: AI Applications & Methodologie
- Unit 3: Maths For AI
- Unit 4: AI Values (Ethical Decision Making)
- Unit 5: Introduction To Storytelling
- Unit 6: Critical & Creative Thinking
- Unit 7: Data Analysis (Computational Thinking)
- Unit 8: Regression
- Unit 9: Classification & Clustering
- Unit 10: AI Values (Bias Awareness)
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Chapter 11. Interpreting and Explaining Data Representations: A Comparison Across Grades 1-7

Related Papers
Visual Research Methods in Educational Research
Dawnene Hassett
APPROACHES TO LIFESPAN WRITING RESEARCH
International Journal of …
Kate Wall , Pamela Woolner
Journal of Literacy Research
Peggy Albers
Nicole M Martin
Mohammad Soozandehfar
Following an ethnographic approach, this study was intended to investigate how children transfer meaning in their drawings, as a manifestation of their visual literacy competence. To this end, 32 six- and seven-year-old Iranian male children were observed for six class sessions as they engaged in learning activities that involved drawing. Building upon Kress and Van Leeuwen’s (1996) theoretical framework of Visual Grammar, children’s drawings were analyzed. Field notes were also used to describe experiences and observations the researcher made while participating in the class. Furthermore, children’s descriptions of their own drawings were used as complementary evidence to the analysis. The results of the analyses revealed that drawing upon a variety of visual resources, such as talks, written texts, gestures, and objects, children made ideational, interpersonal and textual meanings in their drawings. Furthermore, although each drawing was uniquely created by different types of inte...
Daniel Lees Fryer
Beth Olshansky
In our rush to push children toward our narrow definition of literacy, we often take away the very tools that could help them the most: pictures. Both evolution and child development speak to the natural place of pictures within human beings' innate drive to make sense of their world and record their experiences. One does not have to be a history buff to have learned that the earliest record of human activity exists in the form of pictures painted on cave walls. Nor does one have to explain to parents of a toddler the innate urge to pick up a marking implement and draw on any available surface. In fact, those seemingly random markings (which we adults label " scribbles ") are often replete with meaning. Recently, I watched my 18-month-old granddaughter draw what appeared to be two random lines as she sat on the deck of our lakeside cabin; she then pointed to her picture and said, " Boat. " Even the youngest children seem to be hard-wired to make sense of the world around them and, without formal instruction, to represent, express, and share their ideas and discoveries using their natural language: pictures. We observe our young explorers of life following predictable developmental patterns as they discover that they can alter a surface by making marks to express and record meaning. Scribbles morph into recognizable shapes and then into identifiable representations. A circle soon becomes a sun with lines radiating from it representing sunbeams, which then evolves into a person with arms and legs emanating from a round head. No one teaches these young recorders of their world the way to do this; they simply know how.
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

Interpreting and Representing Data (Grades 1-2)
Our Interpreting and Representing Data lesson plan for grades 1-2 teaches students how to interpret graphs and why graphs are often used to represent data. Students work with bar charts and learn how bar charts are used to interpret and organize data.
Description
Additional information.
Our Interpreting and Representing Data (Grades 1-2) lesson plan presents graphs and helps students understand why we use them. Organizing data into a graph helps us to see the information quickly and be able to interpret or make predictions about the data. Parts of a graph, including the x- and y-axis, are explained as part of the lesson. During this lesson, students are asked to create several different graphs and answer questions about them in order to demonstrate their understanding of the lesson.
At the end of the lesson, students will be able to organize, represent, and analyze data in a bar chart.
Thank you for submitting a review!
Your input is very much appreciated. Share it with your friends so they can enjoy it too!
Interpreting and Representing Data
Clear and concise!
Good resource for young learners
I like the easy and simple lessons. They cover enough of the basics for grades 3-4. I use these resources frequently for home schooling my kids. Thank you!!
Related products

Read and Write Numbers to 1,000

All about Butterflies

Find the Sum to 20 Using Three Numbers

Picture and Sound Matching
Make your life easier with our lesson plans, stay up-to-date with new lessons.

- Lesson Plans
- For Teachers
© 2024 Learn Bright. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions. Privacy Policy.
- Sign Up for Free
- Mindset Network
- Data Representation I
- Maths Literacy
- Data Handling
- Learn Xtra Lessons
- Numbers and calculations with numbers
- Patterns, relationships and representations
- Measurement (conversions and time)
- Term 1 Revision
- Finance (financial documents and tariff systems)
- Measurement (measuring length, weight, volume, temperature)
- Maps, plans and other representations of the physical world (scale and map work)
- Probability
- Term 2 Revision
- Finance (income, expenditure, profit/loss, income-and-expenditure statements and budgets)
- Measurement (perimeter, area and volume)
- Maps, plans and other representations of the physical world (models and plans)
- Term 3 Revision
- Finance (interest, banking and taxation)
- Term 4 Revision
- Exam Revision
- Numbers and Calculations with Numbers
- Income/expenditure, profit/loss and break-even analysis
- Finance (interest, banking, inflation)
- Finance (taxation)
- Finance (exchange rates)
- Measurement (length, weight, volume, temp, perimeter and area)
- Finance (taxation; exchange rates)
- Maps, plans and other representations of the physical world (scale and plans)
- Maps, plans and other representations of the physical world (models)
Disabled Feature
This functionality is only active if you sign-in with your Google account.
Related Resources

Connect with social media
Sign in with your email address.
- Create new account
- Request new password
Mathtastico! 5th Grade Math Bundle Unit 11 DATA REPRESENTATION & INTERPRETATION

Description
5th Grade: Unit 11 (Data Representation And Interpretation)
What makes our products so unique?
Our products are meticulously designed by experts to ensure mastery of the STAAR test, employing a detailed and multifaceted program:
- Math Vocabulary and Guided Questions: Each unit introduces new math vocabulary and guided questions that can serve as the objective of the day or daily goals for teachers. This approach enhances understanding and application of mathematical concepts and terms, facilitating clearer communication and deeper learning.
- Unit Year Planning : Our curriculum breaks down each TEK into manageable segments, scaffolding learning for complete mastery. This methodical approach allows students to fully understand each part of the TEK as it is taught throughout the lessons, making the process more straightforward for educators.
- Daily Spirals : We have structured our math program to ensure continuous review by revisiting all previously taught skills each week, thus ensuring mastery. Normally, by the 7th unit, students are reviewing over 15 skills bi-weekly, covering all material from the first four units. (HIghlight daily spiral by teks.
- Problem Solving Process : Each unit introduces students to a thought-provoking problem-solving process that stirs curiosity and enhances analytical thinking skills.
- Problem Solving Questions : Beyond the daily spirals, each lesson features problem-solving questions, also known as Problem of the Day (P.O.D.) questions, that reinforce the previously taught lesson's skills.
- Vertically Aligned Pre-Assessments : Our approach begins each unit with a succinct pre-assessment that aligns vertically with the new TEKs introduced, enabling focused and effective learning.
- Guided Practice : Every unit includes guided practice sections designed to effectively teach new TEKs/Skills. These can be utilized alongside our engaging animated instructional videos, enhancing the learning experience.
- Skill Building/Independent Practice: Lessons are designed to strengthen students’ math skills and problem-solving abilities through word problems, including STAAR 2.0 questions marked by a small star symbol.
- Homework: We incorporate homework into the lessons to enable students to reinforce the concepts and skills learned in the classroom at home.
- Games: Each unit contains fun and educational games that reinforce the skills learned in each lesson, making learning enjoyable and effective.
- Checkpoints: At the end of each lesson, checkpoints feature a writing exercise and a problem-solving question to assess comprehension and consolidate learning.
- Practice and Unit Assessments : Reflecting the STAAR test's rigor, each unit includes a practice assessment and a comprehensive unit assessment featuring STAAR 2.0 questions.
5.9(A) Represent categorical data with bar graphs or frequency tables and numerical data, including data sets of measurements in fractions or decimals, with dot plots or stem-and-leaf plots.
5.9(B) Represents discrete paired data on a scatterplot.
5.9(C) solve one- and two-step problems using data from a frequency table, dot plot, bar graph, stem-and-leaf plot, or scatterplot.
Save time on planning! This math bundle INCLUDES :
- Unique Design and Content
- Vertically Aligned Pre-Assessments
- Problem-Solving & Daily Spiral Reviews
- TEKS and Other State Standards based
- Formative/Summative Assessments
- Independent and Guided Practice
- Interactive Games and Activities
- Homework Assignments
- Super STAAR 2.0 Questions
- Interactive Activities
Why purchase STEAMspirations Products?
- Created by High Performing teachers that have years of successful classroom experience
- Includes Lessons that are aligned to state standards
- Provides pre-assessments, checkpoints, practice assessments, and assessments that help measure and monitor student growth and progress
- Empower students to monitor their own progress, learn at their own pace, and become self-directed
- Provides students with engaging activities
- Provides at-home support
- Empowers students to use technology as a learning tool
- Helps identify student gaps (pre-assessment) for targeted learning through pre-assessments
- Facilitates planning
- Provide high-quality instructional material for high-impact tutoring
- Prepares students for STAAR 2.0 Questions
- Have a plan in place that supports virtual instruction
If you're looking for a research-based high quality and engaging Math Curriculum, then please check out our Mathtastico! Lite resources. These are custom tailored for the amazing teachers educating the children of tomorrow. Please check out all of our resources and share with your colleagues so that we can continue to create great resources for our teachers.
Questions & Answers
Steamspirations.
- We're hiring
- Help & FAQ
- Privacy policy
- Student privacy
- Terms of service
- Tell us what you think

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Read line plots (data with fractions) Get 3 of 4 questions to level up! Quiz 3. Level up on the above skills and collect up to 240 Mastery points Start quiz. Up next for you: Unit test. Level up on all the skills in this unit and collect up to 900 Mastery points! Start Unit test.
=====Lesson15-Data representation and Interpretation=====Part 011.1 Introduction ⏩00:00:001.2 Data ⏩00:00:271...
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday Ticket Press Copyright ...
Grade 11 - Data Representation and Interpretation (Part 1) | ජාල රේඛය සහ සංඛ්යාත බහු-අස්රය | 11 ශ්රේණිය - දත්ත ...
Data representation and interpretation. Maths Literacy. Grade 11. Data Handling. Learn Xtra Live 2012. Data representation and interpretation.
Aside from tables, the two most common data representation types on the SAT are bar graphs and line graphs. Example bar graph. Example line graph. In this lesson, we'll learn to: Read types of graphs that commonly appear on the SAT. Create line graphs based on verbal descriptions. You can learn anything.
Create a free account to gain full access to the website. Save & Organize Resources. See State Standards. Manage Classes & Assignments. Sync with Google Classroom. Create Lessons. Customized Dashboard. Find lessons on Representing and Interpreting Data for all grades. Free interactive resources and activities for the classroom and home.
Download Grade 11 Maths textbook answers for DATA REPRESENTATION AND PREDICTION (Daththa Nirupanaya Ha Arthakathanaya), Lesson 15 in Sinhala Medium. DATA REPRESENTATION AND PREDICTION (Daththa Nirupanaya Ha Arthakathanaya) Answers are available in PDF format. Download using the Link Below. It's free to download. Grade - Grade 11 Subject - Mathematics Lesson - Lesson no 15 Medium - Sinhala Medium
Objectives. The lesson focuses on representation, analysis, and interpretation of data. Students will: create and analyze representations, including the following: line graph, circle graph, bar graph, histogram, double-line graph, and double-bar graph. determine appropriate representations for various situations.
Data Analysis Class 11 Notes. Representation of Data. The study of statistics focuses on gathering, organizing, analyzing, interpreting, and presenting data. The observations are turned into useful knowledge via data science. To complete this work, statisticians condense a lot of data into a format that is manageable and yields useful ...
Grade 11. Numbers and Calculations with Numbers; Patterns, relationships and representations; Measurement (conversions and time) ... Data representation and interpretation II. Grade 11 | Learn Xtra Live 2012. 46 | 0 | 0. 49:5. Revision Video . Summarising and display of data. Grade 11 | Learn Xtra Live 2012. 45 | 0 | 1.
Grade 11 - Data Representation and Interpretation (Part 2) | චතුර්ථක සහ සමුච්චිත සංඛ්යාත වක්රය | 11 ශ්රේණිය ...
The format is two related experiments with line graphs, which would be a Data Representation format. The 11 questions cover all three ACT Science subtypes: interpretation of data, scientific investigation, and evaluation. A key with detailed answer explanations is included.
Data Handling; Term 4 Revision; Exam Revision; Grade 11. Numbers and Calculations with Numbers; Patterns, relationships and representations; Measurement (conversions and time) Income/expenditure, profit/loss and break-even analysis; Term 1 Revision; Finance (interest, banking, inflation) Measurement (measuring length, weight, volume, temperature)
Figure 11.2 represents the varied complexity of the selected DRs. 182 Interpreting and Explaining Data Representations Figure 11.2. Images of two selected DRs. ... from the first and second graders while the interpretation of the third-grade students captured the key point (spending habits of children). The following exchange between a first ...
The mean is calculated by adding all the values in the data set together and then dividing by the number of values in the data set. Example: Calculate the mean of 4, 7, 15, 8, 9, 7, 13 4+7+15+8+9+7+13 = 63 ÷ 7 = 9. The Median The median is the value that literally lies in the middle of all the values. You must first order the data before being ...
Reviews. Our Interpreting and Representing Data (Grades 1-2) lesson plan presents graphs and helps students understand why we use them. Organizing data into a graph helps us to see the information quickly and be able to interpret or make predictions about the data. Parts of a graph, including the x- and y-axis, are explained as part of the lesson.
Dislike. Xtra Gr 11 Maths Literacy: In this lesson on Data Representation we introduce data representation as well as discuss organising the data and displaying data. Revision Video. Maths Literacy / Grade 11 / Data Handling. Maths Literacy / Grade 11 / Patterns, relationships and representations.
=====Lesson 11. Data Representation=====Part 011.1 Introduction⏩00:00:001.2 Examples⏩00:02:441.3 Pie charts⏩00:...
5.9 (B) Represents discrete paired data on a scatterplot. 5.9 (C) solve one- and two-step problems using data from a frequency table, dot plot, bar graph, stem-and-leaf plot, or scatterplot. Save time on planning! This math bundle INCLUDES: Unique Design and Content. Vertically Aligned Pre-Assessments.
This video is about data Representation and Interpretation in grade 11 You can get more marks for o/l exam from this video. So let'swatch this video. First o...
#HexPowerTutor #Grade11Maths #dataInterpretationThis video is about data Representation and Interpretation in grade 11 You can get more marks for the o/l exa...