.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} Discover how today’s most successful IT leaders stand out from the rest. .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Read the report .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Strategic planning |

Nonprofit business plan template
Success doesn’t just happen—it’s planned. Stay focused on the work that supports your nonprofit’s mission with a business plan template.
Sign up to use this template.
- A library of 70+ templates
- Hundreds of app integrations
- AI features to get more done—faster
Like any business, nonprofits rely on business plans to get funding and stay on mission. But even though they often operate like a traditional for-profit organization, nonprofits need their business plans to highlight slightly different aspects of their organization. Showing cash spend becomes very important when you’re a nonprofit, so donors, board members, and government agencies recognize that you’re putting your money where your mission is. Here, we’ll show you what to include in your own custom nonprofit template, and how to use it to move your mission forward.
![business plan for non profit and government agency [Product ui] Nonprofit business plan project in Asana, spreadsheet-style project view (List)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/dd266e4d-783e-49a4-a61e-12485a66dc0e/TG23-web-hero-027-non-profit-static-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
What is a nonprofit business plan template
A nonprofit business plan template provides a strategic overview of your nonprofit. It’s a breakdown of all higher-level information about your organization, such as the board of directors and your core mission. Use your nonprofit business plan template to give your staff, the board, potential donors, and government funding agencies an overview of your mission and strategies.
Nonprofit business plan vs. strategic plan template
Both business and strategic plan templates share certain sections, such as your core mission. However, your nonprofit business plan template should also include relevant action plans , such as your fundraising plan and marketing strategy. Normally, you share your business plan with internal and partner stakeholders as opposed to the general public. Think of your nonprofit business plan as a roadmap or higher-level operational plan—it tells you what you’re currently doing to pursue your mission, and the steps you’re taking to go even further.
Why nonprofit business plan templates are important
Nonprofits know how to do more with less—a nonprofit business plan template will outline how. There are many benefits to creating your own, including:
Transparency. Visibility is a crucial piece of engaging with donors and board members. Nonprofit business plans showcase the work you’re doing and why others should care.
Reduce work about work . Nonprofits don’t always have the same resources as for-profit companies. As a result, freeing up time for your employees to work on their highest-impact tasks is critical—not just for your bottom line, but for your overall mission.
One source of truth. As a nonprofit, you’re constantly fielding requests for information about your finances, mission, and structure. When compiled with project management software , you can create and share your nonprofit business plan template with anyone who asks, without any additional work on your end.
Save 50% on Asana
Partner with Asana to put more resources toward your mission. The Asana for Nonprofits program helps nonprofits do more mission-critical work. Qualified organizations can save 50% on a one-year subscription, plus get numerous free Asana resources.
How to create your non-profit business plan template
Your nonprofit business plan template should include all relevant information about how your organization operates. If you’re using a digital tool, such as project management software , be sure to attach relevant documents and projects. Your template is essentially your nonprofit business plan outline that you’ll fill in during your planning process.
As you’re going through your nonprofit business plan template, make sure to include the following sections so you can get the most from your template.
Non-profit description
Describe the basics of your organizational structure. Include:
Executive summary
Mission and vision statement
Community benefit
Staff and management team
Board of directors
Partnerships
List any items related to what you do as an organization, including reports that demonstrate results. For example, you can include:
Core problem we solve
Demographics we reach
Past results
Business model
Marketing plan
This is a space for your marketing strategy (the methods you'll use to reach your target audience) and the analyses you used to build that strategy. Here, you can attach:
Target market research
Target audience and social media messaging
Market analysis (including a competitive analysis)
Your positioning (on hot button issues related to your mission)
Outreach plan
Financial plan
Nonprofits need to be very clear with how they spend money. Being transparent with your financial statements restores confidence for potential donors, so you can hit your fundraising goals and boost financial projections. Here’s what to include in this section:
Income statements
Cash flow statements
Grant management plan
Fundraising plan and projections
Integrated features
List View . List View is a grid-style view that makes it easy to see all of your project’s information at a glance. Like a to-do list or a spreadsheet, List View displays all of your tasks at once so you can not only see task titles and due dates, but also view any relevant custom fields like Priority, Status, or more. Unlock effortless collaboration by giving your entire team visibility into who’s doing what by when.
Goals . Goals in Asana directly connect to the work you’re doing to hit them, making it easy for team members to see what they’re working towards. More often than not, our goals live separate from the work that goes into achieving them. By connecting your team and company goals to the work that supports them, team members have real-time insight and clarity into how their work directly contributes to your team—and company—success. As a result, team members can make better decisions. If necessary, they can identify the projects that support the company’s strategy and prioritize work that delivers measurable results.
Milestones . Milestones represent important project checkpoints. By setting milestones throughout your project, you can let your team members and project stakeholders know how you’re pacing towards your goal. Use milestones as a chance to celebrate the little wins on the path towards the big project goal.
Custom fields . Custom fields are the best way to tag, sort, and filter work. Create unique custom fields for any information you need to track—from priority and status to email or phone number. Use custom fields to sort and schedule your to-dos so you know what to work on first. Plus, share custom fields across tasks and projects to ensure consistency across your organization.
Recommended apps
Google Workplace . Attach files directly to tasks in Asana with the Google Workplace file chooser, which is built into the Asana task pane. Easily attach any My Drive file with just a few clicks.
OneDrive . Attach files directly to tasks in Asana with the Microsoft OneDrive file chooser, which is built into the Asana task pane. Easily attach files from Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and more.
Dropbox . Attach files directly to tasks in Asana with the Dropbox file chooser, which is built into the Asana task pane.
Slack . Turn ideas, work requests, and action items from Slack into trackable tasks and comments in Asana. Go from quick questions and action items to tasks with assignees and due dates. Easily capture work so requests and to-dos don’t get lost in Slack.
How do you write a nonprofit business plan template?
First, create your template including sections for your executive summary, mission statement and purpose, marketing plans, and finances. Then when you’re ready to write your nonprofit business plan, fill in the blanks and customize it to fit your organization.
Do nonprofits have business plans?
Yes, nonprofits often have business plans. Nonprofit business plans provide a structured overview of your nonprofit strategies, and can be used to share your accomplishments and goals with stakeholders . You only have to create your nonprofit business plan template once—then you can reuse it every time you need to create a new nonprofit business plan.
How do nonprofit business plans help corporations get involved in nonprofit organizations?
Nonprofit business plans show corporations your organization’s impact, including how you’re spending any potential money they donate to you. Often, corporations want to see the numbers before they decide to invest in a nonprofit, and a nonprofit business plan can help you share that information.
What should be in a nonprofit business plan template?
Include all higher-level summaries of your nonprofit, plus actionable plans like your executive summary, mission and purpose, marketing strategy, and financial plans.
Related templates
Action plan template
Taking action has never been easier. Learn how to create a reusable action plan template in Asana to take the guesswork out of strategic planning.

Marketing strategy
A marketing strategy template is a useful tool that helps your marketing team achieve their goals. Learn how to create your marketing strategy with Asana.

PEST analysis
A PEST analysis template helps compile info on the external environment affecting your business. Learn how to prevent risk with a PEST analysis template.
Objectives and key results (OKR) template
Learn how to create an OKR template in Asana so you can standardize the goal-setting process for everyone.
Cost benefit analysis template
Digital cost benefit analysis templates are a useful framework to see if a new project or idea is viable. Learn how to create your own in a few simple steps, with Asana.
Contingency plan
Using a contingency plan template will help you create well-developed strategies to help you protect your business from potential risk. Learn how Asana can help.

Requirements traceability matrix
A requirements traceability matrix template is a tool to help organize project requirements in a concise manner. Learn how to create one for your team.
Creating a digital punch list template can help streamline the final bits of a project for your team. Here’s how to create one.
Go-to-market strategy template
Simplify your GTM strategy with a go-to-market strategy template that aligns teams and keeps work on track. Learn how in Asana.
Project closure template
Endings are important. Create a project closure template to help your team tie up loose ends and finish their projects with confidence.
Project reporting
Stay on top of your project’s performance. Keep everyone on the same page about what’s been completed and where your project is headed.
![business plan for non profit and government agency [Templates] Product Roadmap (Card image)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/2728edf4-eb35-4dd5-8d03-25ba8cbe5864/TG23-web-thumbnail-028-scrumban-feature-static-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Product roadmap
What if you could create, share, and update your product roadmap in one place? Everyone could see you’re tackling the right priorities. Start planning your product roadmap with this template.

Program roadmap
Create a program roadmap template and know the exact structure of each program, how they operate, and their future plans—company-wide.

Operational plan template
Learn how Asana’s operations team uses standardized processes to streamline strategic planning—no matter how many stakeholders are involved.
Strategic planning template
When you’re launching a new product, team, or even a new business, strategic planning templates keep you laser-focused and on task.

Annual planning template
Set clear goals and streamline your planning process—so every level of your company is aligned on what’s important.
Competitive analysis template
The more you know about your competitors, the better your strategy will be. Competitive analysis templates use a data-driven approach to see exactly how your business, products, and features compare to your competition.

Crisis management plan
Does your team know what to do during a crisis? Using a crisis management plan template can help keep all your employees on the same page.
Business plan
A business plan is the first step to start your business and secure financing. Use our business plan template so you don’t have to start from scratch.
SIPOC template
Use your SIPOC template to ensure that the processes outlined in your SIPOC diagrams are consistent and up to your standards.
Create templates with Asana
Learn how to create a customizable template in Asana. Get started today.
How to Write a Non Profit Business Plan: Step by Step Guide

July 6, 2023
Adam Hoeksema
Does a non profit really need a business plan? Your organization isn’t a “normal” business after all, you are pursuing a mission, so shouldn’t the business plan just be to pursue the mission of the organization?
Also, is there really such a thing as a “non profit business plan”? Non profit organizations are so diverse in their business models. For example, the financial model for a church based on donations is quite different than a non profit healthcare provider financial model based on provided health care services.
Since the only common attribute among non profits is that they are pursuing a mission rather than a profit for shareholders, the size, scope and type of a business plan that your non profit might need can vary dramatically.
In this article I hope to cover the following:
- Why write a business plan for a non-profit?
- What should be included in a non-profit business plan?
- Non-profit business plan outline
- Do non-profits have competitors?
- How to analyze the competition for a non-profit?
- How big is the market for my non-profit?
- How to market a non-profit?
- How to structure a non-profit board?
- How to create financial projections for a non-profit?
- Non-profit business plan example
- Non-profit business plan FAQs
With that in mind as the path forward, let’s dive in.
Why write a business plan for a non profit?
Writing a business plan for a non-profit organization has several important benefits and can serve as a key tool in achieving the organization's goals. Here are a few reasons why writing a business plan for a non-profit is essential:
- Clarity and Direction: A business plan helps define the mission, vision, and values of the organization. It provides a clear roadmap outlining the steps to be taken to achieve these goals, and the strategies and tactics to be used.
- Operational Planning: A business plan includes operational details, including organizational structure, staffing needs, resource allocation, and day-to-day operations. This information is essential for the smooth and efficient running of the organization.
- Financial Planning: Non-profits need financial management and planning as much as for-profit businesses. A business plan outlines the financial needs of the organization, budgeting, funding sources, and expenditure, which helps in ensuring financial sustainability.
- Fundraising Tool: A well-structured business plan can be a crucial tool when seeking funding from donors, grantmakers, or sponsors. It demonstrates to potential funders that the organization is well-organized, has a clear mission, and is likely to be successful in its endeavours.
- Performance Measurement: The business plan sets clear objectives, goals, and milestones that enable the organization to measure its progress. This information can be used to make necessary adjustments to strategies or operations to improve performance.
- Stakeholder Communication: A business plan is a formal document that communicates the organization's purpose, strategies, and financial plans to various stakeholders, including staff, volunteers, board members, donors, and beneficiaries.
What should be included in a non profit business plan?
It is difficult to give you a one size fits all answer for what should be included in a non profit business plan because as we have mentioned every non profit has a different model. So you really need to customize your business plan to your non profit’s unique situation. That being said, we did put together an outline of a generic non profit business plan which should at least give you a good head start.
Non profit business plan outline
1. executive summary.
1.1 Organization Overview
1.2. Objectives
1.3. Mission Statement
2. Organization Description
2.1. Organization History
2.2. Legal Structure
2.3. Unique Value Proposition
2.4. Target Beneficiaries
3. Market Analysis
3.1. industry overview, 3.2. collaborator and competitor identification.
3.3. Target Beneficiaries
Key Point 1
4. marketing and fundraising, 4.1. strategic plan.
4.2. Program or Service Offerings:
4.4. Distribution Channels
4.5. promotions and fundraising, key point 2, 5. organizational structure and management, 5.1. organization’s facility & location, 5.2. staffing plan and volunteer management.
5.3. Governance, Financial Management, and Accountability
Key Point 3
6. financial plan.
6.1. Startup Costs
6.3. Expense Projections
6.4. profit and loss statement, 6.5. cash flow projections, 6.6. break-even analysis, 7. appendix.
7.1. Supporting Documents
7.2. Glossary of Term
7.3. References and Resources
Key Point 5
Do non profits have competitors .
You might be tempted to think that non profit organizations don’t have competition because you are just all out to support the mission. Although you can certainly work toward the same goal, as an organization you still have competition. A non profit church may be competing for church members in a sense, a non profit university is competing for students, and a non profit health care system is competing to recruit the best doctors and employees.
How to analyze the competition for a non profit?
One way to analyze your competition might be to use a tool like Ahrefs.com which allows you to input an organizations website and see roughly how much website traffic they get and what keywords are driving traffic to their website. My alma mater is Taylor University. Ahrefs shows that their website receives roughly 25,000 visitors per month from organic search results.

Furthermore I can do a keyword report and see that they are ranking first for a competitive keyword like “Christian University Indiana” which sends them roughly 34 organic website visitors per month.

How big is the market for my a non profit?
Ahrefs is also a great tool to understand how big the market might be for your particular non profit. For example, we can see that there are only 350 people searching for “Christian colleges in Indiana” per month, so the total market of people searching for an organization like Taylor University is relatively small. If you are starting a church you could run a report for keywords like “church in XYZ city” which would help you understand that number of people searching for a church in your area.
How to market a non profit?
By doing competitor and keyword research for your market on Ahrefs, you should now have a good idea of how your competitors are attracting customers / beneficiaries and you can look for opportunities to compete in that market. You can then advertise for certain keywords, write content or blog posts related to the keywords that your target market is searching for, and you can try to replicate or improve upon strategies that appear to be working for your competitors.
How to structure a non profit board?
Structuring a nonprofit board involves considering a number of elements, including board size, member composition, board officer roles, committees, and member terms. Here are some guidelines for how you can structure a nonprofit board:
- Board Size : The size of a board should be dictated by the needs and capacity of the organization. Smaller nonprofits may only need a board of five to seven people, while larger organizations may require 20 or more. As a general rule, a board should be large enough to carry out its duties, but small enough for effective discussions and decision-making.
- Member Composition : The board should consist of individuals who bring a variety of skills and perspectives to the organization. This can include people with financial, legal, and managerial expertise, as well as those with knowledge of the organization's mission and community. It can also be beneficial to include individuals who reflect the demographics of the community the nonprofit serves.
- Board Officer Roles : Nonprofit boards typically have at least three officers: a Chair, a Secretary, and a Treasurer. The Chair presides over meetings and guides the direction of the board. The Secretary is responsible for keeping records of board actions, and the Treasurer oversees the financial management of the organization. Some boards may also have a Vice Chair to support the Chair in their duties.
- Committees : Committees can be useful for handling specific aspects of board governance. Common nonprofit board committees include the Executive Committee (made up of board officers), the Finance Committee, the Governance or Board Development Committee (which handles board recruitment and training), and the Fundraising or Development Committee. There may also be ad hoc committees set up to handle specific projects or initiatives.
- Member Terms : Board members usually serve for specific terms, which can range from one to four years. Some organizations use staggered terms, where a portion of the board is up for re-election each year, to ensure continuity. There may also be term limits, which can help to ensure fresh perspectives on the board.
- Board Member Roles and Responsibilities : It's important to establish clear roles and responsibilities for board members. This can include setting strategic direction, ensuring financial oversight, hiring and evaluating the executive director, fundraising, and acting as ambassadors for the organization.
- Board Meetings : Regular board meetings are crucial for decision-making and governance. The frequency of these meetings will depend on the organization's needs, but many boards meet quarterly. The board may also meet in special sessions as needed.
- Board Evaluation and Training : Regular evaluations can help ensure that the board is functioning effectively and meeting its responsibilities. This can include individual self-assessments as well as full board evaluations. In addition, ongoing board training can help to ensure that members understand their roles and responsibilities.
Remember, each nonprofit organization is unique and may have different needs and requirements when it comes to board structure. It's important to create a structure that works best for your particular organization, in compliance with any applicable local, state, or national laws.
How to Create Financial Projections for a Nonprofit Business Plan
Just like in any industry, the non-profit sector has its own unique factors that impact financial projections, such as fundraising efforts, grant opportunities, and donor contributions. Utilizing a non-profit financial projection template can simplify the process and boost your confidence. Creating precise financial projections goes beyond demonstrating your organization's ability to secure funding; it's about showcasing the financial path that will enable you to achieve your mission and make a positive impact. To develop accurate projections, consider the following key steps:
- Estimate startup costs for your non-profit, including administrative expenses, program development, and marketing efforts.
- Forecast revenue sources such as grants, donations, fundraising events, and membership fees.
- Project program costs
- Estimate operating expenses like office rent, utilities, insurance, and professional services.
- Calculate the amount of funding needed to launch and sustain your non-profit's activities.
While financial projections are vital for your non-profit business plan, remember to seek guidance from experienced professionals who understand the non-profit landscape. Adapt your projections based on real-world insights and leverage industry resources to refine your financial plan, ensuring you can effectively execute your organization's mission and achieve your desired outcomes.
Example Non Profit Business Plan
Below is the content of our sample non profit business plan . A Google Doc version of this nonprofit business plan template is available here for you to modify and personalize. There's also a video walkthrough available to guide you in tailoring the business plan to your specific nonprofit organization's needs.
Table of Contents
1. organization overview.
Briefly introduce the organization's background, programs, and target market.
- Example: Safe Haven is a non-profit organization based in Minneapolis, Minnesota, dedicated to promoting mental health awareness and providing accessible counseling services to underserved communities
1.2. Objectives
Outlines the organization's short-term and long-term goals.
- Example: Increase the number of counseling sessions offered by 25% within the next six months to meet the growing demand for accessible mental health services in underserved communities.
- Example: Long-term: Establish satellite centers in neighboring cities within three years to expand the reach of Save Haven's mental health programs and services to a wider population.
1.3. Mission Statement
Describes the organization's purpose and core values.
- Example: Empowering underserved communities by promoting mental health awareness and providing accessible counseling services for all.
2.1. Organization History
Provides context on the organization's background and founding story.
- Example: Established in 2010 by Andy Mitchell and a group of passionate professionals and activists, Safe Haven is a mental health organization dedicated to providing accessible counseling services. Through community partnerships and continuous growth, we have made a lasting impact on mental health awareness and support.
2.2. Legal Structure
Describes the organization's legal structure (e.g., sole proprietorship, partnership, LLC, corporation).
- Example: Safe Haven operates as a non-profit organization registered as a 501(c)(3).
2.3. Unique Value Proposition
Emphasizes the organization's competitive advantage or unique values.
- Example: Safe Haven stands out by offering collaborative mental health care, bringing together a multidisciplinary team of professionals who work together to foster holistic well-being and resilience in individuals and communities.
2.4. Target Beneficiaries
Defines the organization's ideal beneficiary base.
- Example: Safe Haven aims to serve underserved communities, including individuals from low-income backgrounds, marginalized groups, and those facing barriers to mental health services.
Presents a general overview of the industry, its trends, and growth potential.
- Example: The mental health industry is experiencing significant growth and increased awareness due to a growing recognition of the importance of mental well-being. Safe Haven aims to leverage this trend and contribute to the industry by providing accessible counseling services and promoting mental health awareness in underserved communities.
Identification of similar non-profit organizations and potential collaborators
- Example: Direct competitors: Compassionate Minds: A non-profit organization providing mental health services and counseling operating in the same region as Safe Haven.
- Example: Indirect competitors: Mental Health Foundation: A national non-profit organization focusing on advocacy and awareness, partnering with various stakeholders to promote mental well-being.
3.3. Target Beneficiaries
Explores the organization's target beneficiaries, demographics, preferences, and pain points.
- Example: Our programs and services primarily target low-income families and individuals residing in Minneapolis, Minnesota, with a focus on marginalized communities, such as homeless individuals, domestic violence survivors, and immigrant populations.

- Example 1: Localized research findings reveal a significant increase in mental health awareness and a growing demand for accessible and affordable mental health services in the community.
- Example 2: Analysis of demographic data indicates a high prevalence of mental health concerns among underserved populations, highlighting the urgent need for targeted intervention programs.
Describes the action plans, timelines, and key milestones for your organization
Describes the organization's programs or services in detail.
- Example: Secure sustainable funding through grant applications, fundraising events, and community partnerships
Key Milestone: Raise a minimum of $100,000 in grant funding within the first year.
- Example: Develop and implement mental health awareness campaigns in collaboration with local community organizations within the first year of operation, starting from Month 1.
Key Milestone: Launch the first mental health awareness campaign within 6 months.
- Example: Recruit and train a team of licensed mental health professionals to offer counseling services within the first year of operation, starting from Month 1.
4.2. Program or Service Offerings:
- Example: Save Haven offers a comprehensive range of services including individual counseling, group therapy, group therapy, crisis intervention, and support groups.
Describes the methods through which the organization will deliver its programs or services to beneficiaries.
- Example: Safe Haven employs a multi-channel distribution approach, utilizing remote counseling, and community partnerships with schools, community centers, and healthcare facilities.
Details of the organization's promotional efforts and advertising strategies.
- Example: Safe Haven employs a comprehensive promotional strategy encompassing online presence through its website and social media platforms, active community outreach at events and health fairs, partnerships with local media outlets, and collaborations with healthcare professionals and community organizations to ensure a continuous flow of individuals seeking mental health support.

- Example 1: Safe Haven plans to collaborate with local schools to provide mental health education programs and workshops to students, empowering them with essential skills and knowledge for mental well-being.
- Example 2: The organization aims to establish partnerships with community centers and faith-based organizations to create safe spaces for support groups, fostering a sense of belonging and social connection among individuals facing mental health challenges.
- Example 3: Organize a grand opening event offering free washes and dryer credits, attracting over 200 local residents and generating buzz through word-of-mouth referrals.
Specify the organization's premises used to carry out its activities, programs, and services. I
- Example: Save Haven operates from a welcoming and serene facility located in the heart of Minneapolis, Minnesota. The facility comprises modern counseling rooms, a comfortable waiting area, and administrative offices, creating a safe and supportive environment for individuals seeking mental health services.
Involves the systematic approach of recruiting, coordinating, and supporting volunteers and staff
- Example: Safe Haven implements a comprehensive staffing plan that includes recruiting, training, and retaining qualified staff members to ensure the effective delivery of programs and services. Additionally, the organization establishes a volunteer management system to engage and support volunteers in their roles, providing them with meaningful opportunities to contribute to the mission.
5.3. Governance, Financial Management, and Accountability:
Involves the effective and responsible management of financial resources to support the organization's operations
- Example: Safe Haven upholds strong policies and procedures to ensure responsible governance, financial management, and accountability, including clear guidelines for board members, transparent financial reporting, and performance evaluations to continually improve its impact and stakeholder satisfaction.

- The team at Safe Haven comprises licensed mental health professionals with extensive experience in trauma-informed care, ensuring high-quality and compassionate support for individuals affected by adverse life experiences.
- Our board members bring diverse backgrounds in psychology, social work, and public health, offering a comprehensive perspective on addressing mental health disparities and promoting holistic well-being.
All of the unique Non-Profit projections you see here were generated using ProjectionHub’s Non-Profit Financial Projection Template . Use PH20BP to enjoy a 20% discount on the template.
6.1. Startup Costs
Provide a detailed breakdown of the total startup costs requirements, and where you plan for those funds to come from. You will also want to break down how the startup costs will be used including working capital to cover losses before the business breaks even.
- Example: Save Haven's total startup costs are estimated at $150,000. The organization has raised $125,000 through fundraising and donations, and they are seeking an additional $25,000 to cover the remaining expenses.

Watch how to create financial projections for your Non-Profit

6.2. Revenue Projections
Provide an estimate of the organization's future revenue based on market research and assumptions.
- Example: Save Haven projects a steady increase in revenue over the next five years, with anticipated amounts of $509,060 in 2023, in the first year.

Estimates the organization's future expenses, including fixed and variable costs.
- Example: Save Haven has estimated its operating expenses, including direct expenses, fundraising costs, sales and marketing expenses, general and administrative costs, research and development expenses, programming costs, salaries, interest and taxes, loan principal, and leasehold improvements.

Summarizes the organization's financial position and expenses, over a specific period.
- Example: Save Haven anticipates an initial net loss in 2023 due to startup expenses and infrastructure investments. However, the organization projects a positive net income in the following years, demonstrating a consistent and promising financial growth trajectory.

Outlines the organization's projected cash inflows and outflows.
- Example: Save Haven's cash flow projections factor in expected fluctuations in cash inflows and outflows, ensuring effective financial management and stability.

Determines the point at which the organization's revenue equals its expenses.
- Example: Save Haven's break-even analysis indicates that the organization is expected to reach a point of revenue equaling expenses within a relatively short timeframe, highlighting its potential for early profitability.

Key Point 4

- Example 1: Safe Haven's financial projections align with industry benchmarks, with operating costs accounting for a realistic percentage of total revenue based on similar non-profit mental health organizations.
- Example 2: The organization conducts thorough market research to identify potential revenue streams, such as government grants, corporate partnerships, and individual donations, ensuring a diversified and sustainable funding base.
7.1. Supporting Documents
Includes any relevant documentation that supports the information presented in the business plan, such as resumes, financial projections, market research data, and permits or licenses.
7.2. Glossary of Term
Provides definitions for industry-specific terms used throughout the business plan to ensure reader comprehension.
7.3. References and Resources
Lists any sources or resources referenced during the preparation of the business plan, including industry reports, market research data, and relevant publications.

- Example 1: The founders of Safe Haven have personally invested their own resources and time into establishing the organization, demonstrating a strong commitment to its mission and the community it serves.
- Example 2: Safe Haven's leadership team actively participates in mental health advocacy initiatives and professional development opportunities, continuously enhancing their expertise and dedication to improving mental health outcomes.
Nonprofit Business Plan FAQs
How do i start a non-profit organization.
To start a non-profit organization, you'll need to define your mission, create a board of directors, file the necessary paperwork with the government, develop a fundraising strategy, and establish policies and procedures for your organization's operations.
How can I fundraise for my non-profit?
You can fundraise for your non-profit by organizing events, applying for grants, seeking corporate sponsorships, launching online crowdfunding campaigns, cultivating individual donor relationships, and exploring partnerships with other organizations.
What are the key elements of a successful non-profit strategic plan?
A successful non-profit strategic plan should include a clear mission and vision, goals and objectives, an analysis of the target community or cause, strategies for fundraising and program implementation, and a monitoring and evaluation framework.
How can I measure the impact of my non-profit's programs?
To measure the impact of your non-profit's programs, establish specific metrics and evaluation methods, conduct surveys or interviews with beneficiaries, track outcomes and outputs, and use data to inform program improvements and report to stakeholders.
What legal requirements do I need to comply with as a non-profit?
Legal requirements for non-profits may include obtaining tax-exempt status, filing annual reports, adhering to accounting and financial regulations, ensuring transparency in governance, and complying with any specific regulations related to your non-profit's activities.
About the Author
Adam is the Co-founder of ProjectionHub which helps entrepreneurs create financial projections for potential investors, lenders and internal business planning. Since 2012, over 50,000 entrepreneurs from around the world have used ProjectionHub to help create financial projections.
Other Stories to Check out
How to finance a small business acquisition.
In this article we are going to walk through how to finance a small business acquisition and answer some key questions related to financing options.
How to Acquire a Business in 11 Steps
Many people don't realize that acquiring a business can be a great way to become a business owner if they prefer not to start one from scratch. But the acquisition process can be a little intimidating so here is a guide helping you through it!
How to Buy a Business with No Money Down
Learn the rare scenarios enabling the purchase of a business with no money down and delve into the complexities of selling via seller notes, highlighting the balance of expanded opportunities and inherent risks in these unique financial transactions.
Have some questions? Let us know and we'll be in touch.
Free Nonprofit Business Plan Templates
By Joe Weller | September 18, 2020
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, we’ve rounded up the most useful list of nonprofit business plan templates, all free to download in Word, PDF, and Excel formats.
Included on this page, you’ll find a one-page nonprofit business plan template , a fill-in-the-blank nonprofit business plan template , a startup nonprofit business planning timeline template , and more. Plus, we provide helpful tips for creating your nonprofit business plan .
Nonprofit Business Plan Template
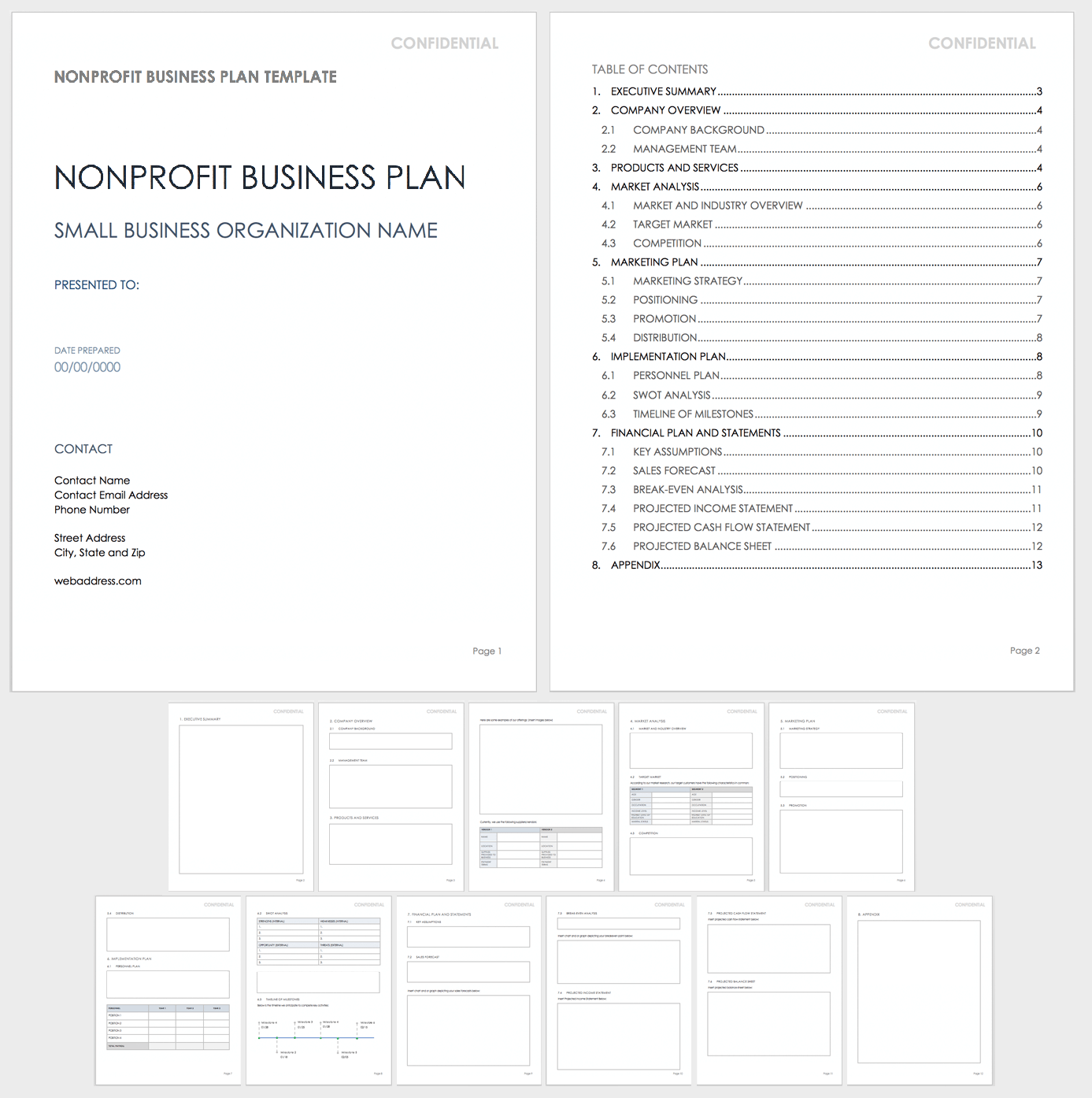
Use this customizable nonprofit business plan template to organize your nonprofit organization’s mission and goals and convey them to stakeholders. This template includes space for information about your nonprofit’s background, objectives, management team, program offerings, market analysis, promotional activities, funding sources, fundraising methods, and much more.
Download Nonprofit Business Plan Template
One-Page Business Plan for Nonprofit Template
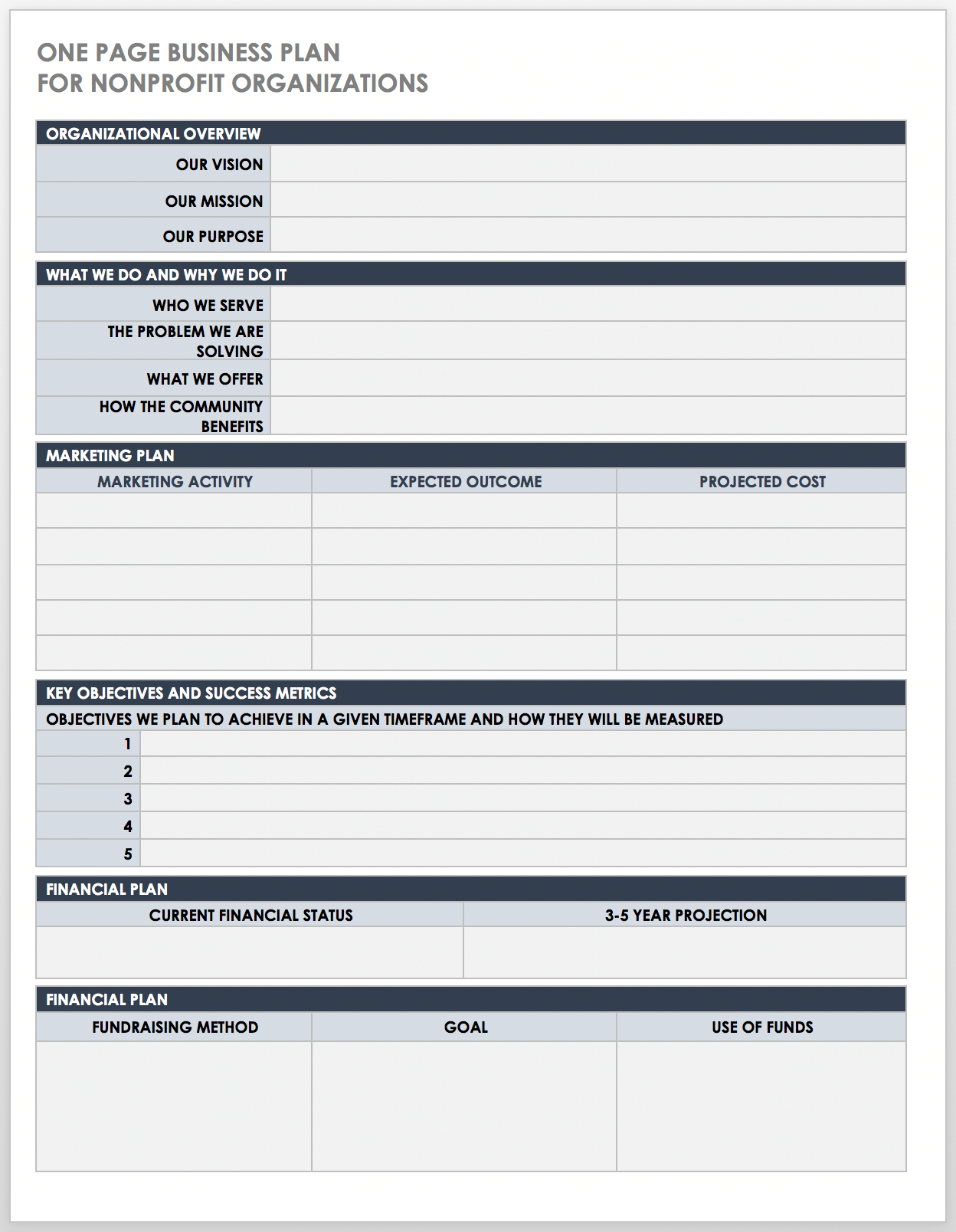
This one-page nonprofit business plan template has a simple and scannable design to outline the key details of your organization’s strategy. This template includes space to detail your mission, vision, and purpose statements, as well as the problems you aim to solve in your community, the people who benefit from your program offerings, your key marketing activities, your financial goals, and more.
Download One-Page Business Plan for Nonprofit Template
Excel | Word | PDF
For additional resources, including an example of a one-page business plan , visit “ One-Page Business Plan Templates with a Quick How-To Guide .”
Fill-In-the-Blank Nonprofit Business Plan Template
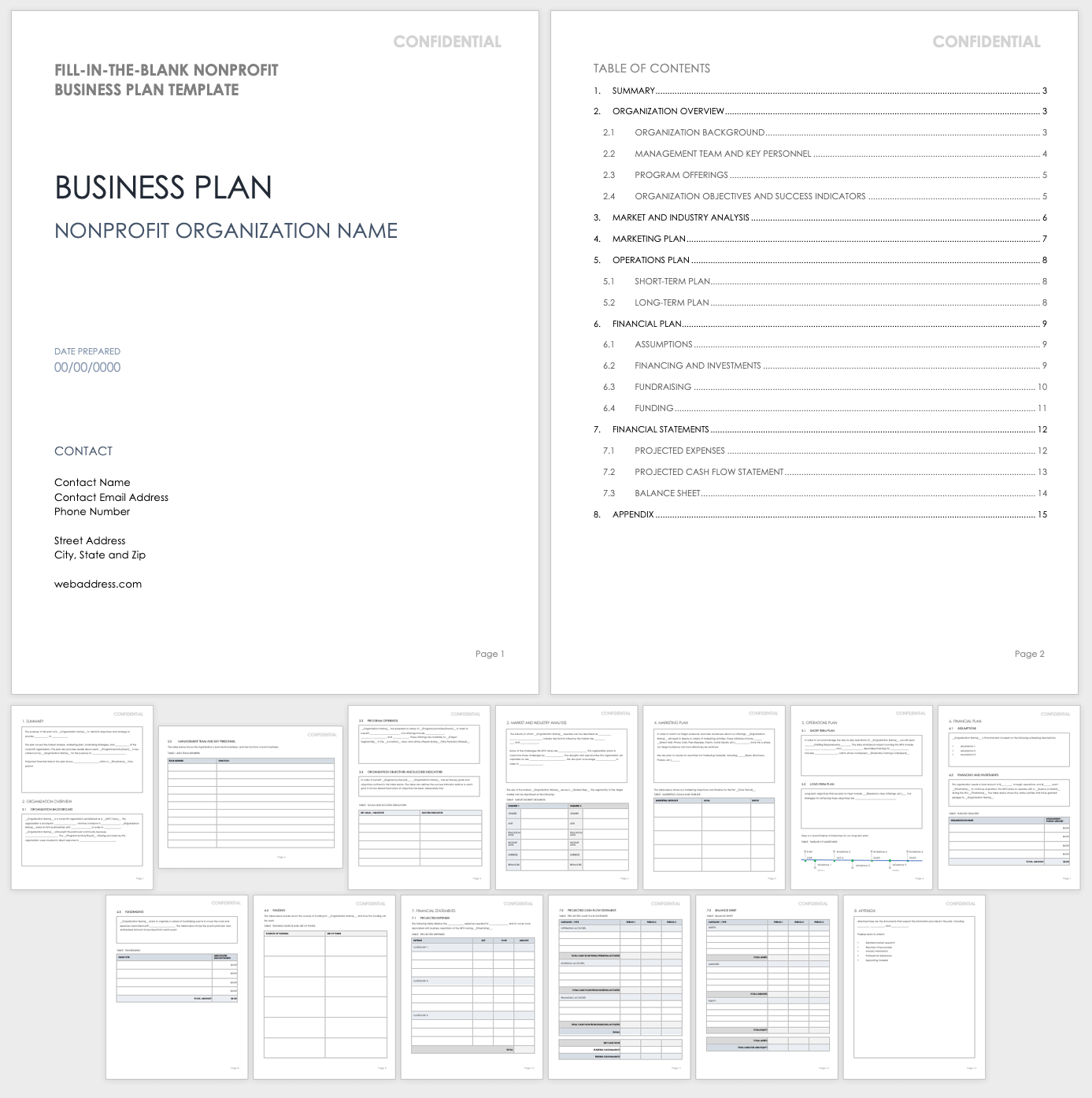
Use this fill-in-the-blank template as the basis for building a thorough business plan for a nonprofit organization. This template includes space to describe your organization’s background, purpose, and main objectives, as well as key personnel, program and service offerings, market analysis, promotional activities, fundraising methods, and more.
Download Fill-In-the-Blank Nonprofit Business Plan Template
For additional resources that cater to a wide variety of organizations, visit “ Free Fill-In-the-Blank Business Plan Templates .”
Startup Nonprofit Business Planning Template with Timeline
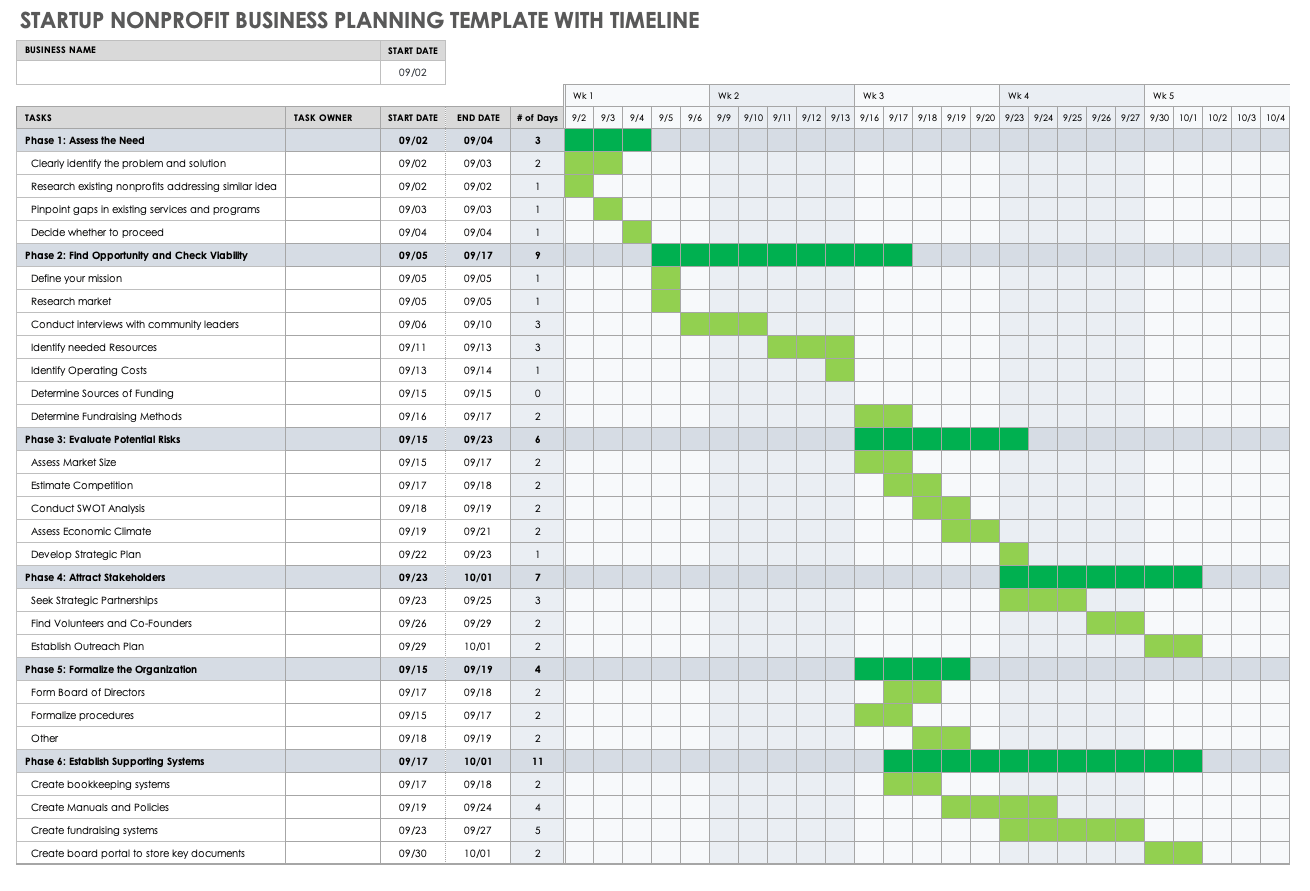
Use this business planning template to organize and schedule key activities for your business. Fill in the cells according to the due dates, and color-code the cells by phase, owner, or category to provide a visual timeline of progress.
Download Startup Nonprofit Business Planning Template with Timeline
Excel | Smartsheet
Nonprofit Business Plan Template for Youth Program
Use this template as a foundation for building a powerful and attractive nonprofit business plan for youth programs and services. This template has all the core components of a nonprofit business plan. It includes room to detail the organization’s background, management team key personnel, current and future youth program offerings, promotional activities, operations plan, financial statements, and much more.
Download Nonprofit Business Plan Template for Youth Program
Word | PDF | Google Doc
Sample Nonprofit Business Plan Outline Template
You can customize this sample nonprofit business plan outline to fit the specific needs of your organization. To ensure that you don’t miss any essential details, use this outline to help you prepare and organize the elements of your plan before filling in each section.
Download Sample Nonprofit Business Plan Outline Template
Nonprofit Startup Business Planning Checklist Template
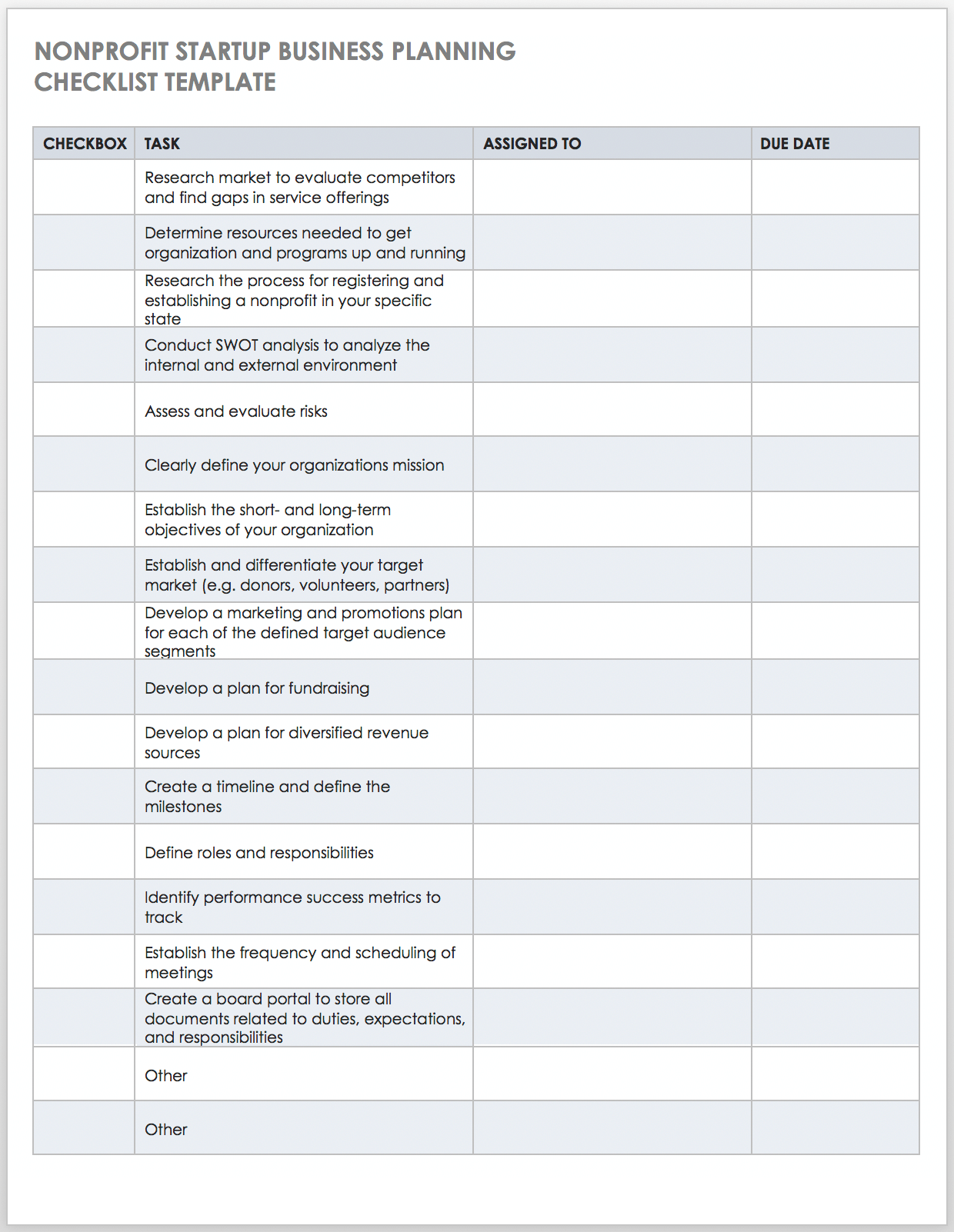
Use this customizable business planning checklist as the basis for outlining the necessary steps to get your nonprofit organization up and running. You can customize this checklist to fit your individual needs. It includes essential steps, such as conducting a SWOT analysis , fulfilling the research requirements specific to your state, conducting a risk assessment , defining roles and responsibilities, creating a portal for board members, and other tasks to keep your plan on track.
Download Nonprofit Startup Business Planning Checklist Template
Tips to Create Your Nonprofit Business Plan
Your nonprofit business plan should provide your donors, volunteers, and other key stakeholders with a clear picture of your overarching mission and objectives. Below, we share our top tips for ensuring that your plan is attractive and thorough.
- Develop a Strategy First: You must aim before you fire if you want to be effective. In other words, develop a strategic plan for your nonprofit in order to provide your team with direction and a roadmap before you build your business plan.
- Save Time with a Template: No need to start from scratch when you can use a customizable nonprofit business plan template to get started. (Download one of the options above.)
- Start with What You Have: With the exception of completing the executive summary, which you must do last, you aren’t obligated to fill in each section of the plan in order. Use the information you have on hand to begin filling in the various parts of your business plan, then conduct additional research to fill in the gaps.
- Ensure Your Information Is Credible: Back up all the details in your plan with reputable sources that stakeholders can easily reference.
- Be Realistic: Use realistic assumptions and numbers in your financial statements and forecasts. Avoid the use of overly lofty or low-lying projections, so stakeholders feel more confident about your plan.
- Strive for Scannability: Keep each section clear and concise. Use bullet points where appropriate, and avoid large walls of text.
- Use Visuals: Add tables, charts, and other graphics to draw the eye and support key points in the plan.
- Be Consistent: Keep the voice and formatting (e.g., font style and size) consistent throughout the plan to maintain a sense of continuity.
- Stay True to Your Brand: Make sure that the tone, colors, and overall style of the business plan are a true reflection of your organization’s brand.
- Proofread Before Distribution: Prior to distributing the plan to stakeholders, have a colleague proofread the rough version to check for errors and ensure that the plan is polished.
- Don’t Set It and Forget It: You should treat your nonprofit business plan as a living document that you need to review and update on a regular basis — as objectives change and your organization grows.
- Use an Effective Collaboration Tool: Use an online tool to accomplish the following: collaborate with key personnel on all components of the business plan; enable version control for all documents; and keep resources in one accessible place.
Improve Your Nonprofit Business Planning Efforts with Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
- Insights & Analysis
- Nonprofit Jobs
Business Planning for Nonprofits
Business planning is a way of systematically answering questions such as, “What problem(s) are we trying to solve?” or “What are we trying to achieve?” and also, “Who will get us there, by when, and how much money and other resources will it take?”
The business planning process takes into account the nonprofit’s mission and vision, the role of the board, and external environmental factors, such as the climate for fundraising.
Ideally, the business planning process also critically examines basic assumptions about the nonprofit’s operating environment. What if the sources of income that exist today change in the future? Is the nonprofit too reliant on one foundation for revenue? What happens if there’s an economic downturn?
A business plan can help the nonprofit and its board be prepared for future risks. What is the likelihood that the planned activities will continue as usual, and that revenue will continue at current levels – and what is Plan B if they don't?
Narrative of a business plan
You can think of a business plan as a narrative or story explaining how the nonprofit will operate given its activities, its sources of revenue, its expenses, and the inevitable changes in its internal and external environments over time. Ideally, your plan will tell the story in a way that will make sense to someone not intimately familiar with the nonprofit’s operations.
According to Propel Nonprofits , business plans usually should have four components that identify revenue sources/mix; operations costs; program costs; and capital structure.
A business plan outlines the expected income sources to support the charitable nonprofit's activities. What types of revenue will the nonprofit rely on to keep its engine running – how much will be earned, how much from government grants or contracts, how much will be contributed? Within each of those broad categories, how much diversification exists, and should they be further diversified? Are there certain factors that need to be in place in order for today’s income streams to continue flowing?
The plan should address the everyday costs needed to operate the organization, as well as costs of specific programs and activities.
The plan may include details about the need for the organization's services (a needs assessment), the likelihood that certain funding will be available (a feasibility study), or changes to the organization's technology or staffing that will be needed in the future.
Another aspect of a business plan could be a "competitive analysis" describing what other entities may be providing similar services in the nonprofit's service and mission areas. What are their sources of revenue and staffing structures? How do their services and capacities differ from those of your nonprofit?
Finally, the business plan should name important assumptions, such as the organization's reserve policies. Do your nonprofit’s policies require it to have at least six months of operating cash on hand? Do you have different types of cash reserves that require different levels of board approval to release?
The idea is to identify the known, and take into consideration the unknown, realities of the nonprofit's operations, and propose how the nonprofit will continue to be financially healthy. If the underlying assumptions or current conditions change, then having a plan can be useful to help identify adjustments that must be made to respond to changes in the nonprofit's operating environment.
Basic format of a business plan
The format may vary depending on the audience. A business plan prepared for a bank to support a loan application may be different than a business plan that board members use as the basis for budgeting. Here is a typical outline of the format for a business plan:
- Table of contents
- Executive summary - Name the problem the nonprofit is trying to solve: its mission, and how it accomplishes its mission.
- People: overview of the nonprofit’s board, staffing, and volunteer structure and who makes what happen
- Market opportunities/competitive analysis
- Programs and services: overview of implementation
- Contingencies: what could change?
- Financial health: what is the current status, and what are the sources of revenue to operate programs and advance the mission over time?
- Assumptions and proposed changes: What needs to be in place for this nonprofit to continue on sound financial footing?
More About Business Planning
Budgeting for Nonprofits
Strategic Planning
Contact your state association of nonprofits for support and resources related to business planning, strategic planning, and other fundamentals of nonprofit leadership.
Additional Resources
- Components of transforming nonprofit business models (Propel Nonprofits)
- The matrix map: a powerful tool for nonprofit sustainability (Nonprofit Quarterly)
- The Nonprofit Business Plan: A Leader's Guide to Creating a Successful Business Model (David La Piana, Heather Gowdy, Lester Olmstead-Rose, and Brent Copen, Turner Publishing)
- Nonprofit Earned Income: Critical Business Model Considerations for Nonprofits (Nonprofit Financial Commons)
- Nonprofit Sustainability: Making Strategic Decisions for Financial Viability (Jan Masaoka, Steve Zimmerman, and Jeanne Bell)
Disclaimer: Information on this website is provided for informational purposes only and is neither intended to be nor should be construed as legal, accounting, tax, investment, or financial advice. Please consult a professional (attorney, accountant, tax advisor) for the latest and most accurate information. The National Council of Nonprofits makes no representations or warranties as to the accuracy or timeliness of the information contained herein.
Nonprofit Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Business Plan Outline
- Nonprofit Business Plan Home
- 1. Executive Summary
- 2. Company Overview
- 3. Industry Analysis
- 4. Customer Analysis
- 5. Competitive Analysis
- 6. Marketing Plan
- 7. Operations Plan
- 8. Management Team
- 9. Financial Plan
You’ve come to the right place to write a nonprofit business plan.
We have helped over 10,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create nonprofit business plans and many have used them to start or grow their nonprofit organizations.
Below are links to the essential sections of our sample nonprofit business plan template to help you with the business planning process for your organization:
- Executive Summary – The Executive Summary of your nonprofit business plan explains your overall strategic plan to achieve success as a nonprofit. It will include your organization’s mission statement, goals, and objectives. This section will also include information on your target market, competition, and marketing strategy.
- Company Overview – Also called the Organization Overview, you will include the mission statement and history of your nonprofit including any significant milestones achieved to date.
- Industry Analysis – Sometimes referred to as the Market Analysis, this section will provide an overview of the nonprofit industry, trends, and the competitive landscape.
- Customer Analysis – The Customer Analysis section details the demographics and psychographics of your target audience and how you plan to reach them.
- Competitive Analysis – In your Competitive Analysis, you will identify and describe the competition, both direct and indirect, including other nonprofits with the same mission. You will also include your strategic plan for competing in the market.
- Marketing Plan – This section of your nonprofit business plan will detail your products, programs and services, your overall marketing strategies and tactics, and how you will measure success. It should include information on your target market, positioning, branding, communications, and lead generation.
- Operations Plan – In the Operations Plan, you will outline your day-to-day operations as well as your long-term business goals and how you will measure success.
- Management Team – In the Management Team section of your business plan, you should include the organizational structure of your nonprofit business as well as bios of your executive team and board members.
- Financial Plan – The Financial Plan is one of the most important sections of your nonprofit business plan. You will establish your financial goals and include financial statements such as the income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statement to show how your nonprofit will be sustainable.
Next Section: Executive Summary >
Nonprofit Business Plan FAQs
What is a non profit business plan.
A nonprofit business plan is a road map to start and/or grow your nonprofit organization. Among other things, it outlines your charitable concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections. Your non profit business plan should be a living document that is updated frequently as your nonprofit grows.
You can easily complete your nonprofit business plan using our Nonprofit Business Plan Template here .
What Are the Main Types of Nonprofit Organizations?
There are many types of nonprofits, but each has a charitable mission to help an underserved segment of society. For example, there are nonprofits that serve the underserved youth, abused or abandoned animals, homeless, veterans and impoverished. There are also many nonprofits that support social awareness and global issues such as the environment, education and equality.
What Are the Main Sources of Revenue and Expenses for a Nonprofit Business?
The primary source of revenue for nonprofit organizations are monetary donations from sponsors, government grants and funding, and tax incentives through 501c3 designations.
The key expenses for a nonprofit business are staffing, supplies, rent, utilities, program costs and working capital to ensure the sustainability of the non profit. Proper strategic planning will help your nonprofit thrive financially.
This differs from a for profit business plan because you do not have to show profitability. Nonprofits focus away from profit and instead center on accountability.
How Do You Secure Funding For Your Nonprofit Organization?
Most nonprofit organizations are likely to receive funding from banks, grants, and donors. As the majority of the funding will come from government grants and funds, grant proposals will need to be compiled and proposed to the necessary funding organization.
A solid business plan is key to showing investors you are well-prepared to start your own business. A nonprofit business plan template is key to proper business planning and getting started quickly.
Where can I download a Nonprofit Business Plan PDF?
You can download our free nonprofit business plan template PDF here . This is a sample nonprofit business plan outline that you can use in PDF format.

Product Overview
- Donor Database Use a CRM built for nonprofits.
- Marketing & Engagement Reach out and grow your donor network.
- Online Giving Enable donors to give from anywhere.
- Reporting & Analytics Easily generate accurate reports.
- Volunteer Management Volunteer experiences that inspire.
- Bloomerang Payments Process payments seamlessly.
- Mobile App Get things done while on the go.
- Data Management Gather and update donor insights.
- Integrations
- Professional Services & Support
- API Documentation
Learn & Connect
- Articles Read the latest from our community of fundraising professionals.
- Guides & Templates Download free guides and templates.
- Webinars & Events Watch informational webinars and attend industry events.
- DEI Resources Get DEI resources from respected and experienced leaders.
- Ask An Expert Real fundraising questions, answered.
- Bloomerang Academy Learn from our team of fundraising and technology experts.
- Consultant Directory
- Comms Audit Tool
- Donor Retention Calculator
- Compare Bloomerang
- Volunteer Management
15 Tips To Create An Effective 2023 Nonprofit Business Plan

- Strategy/Planning

See How Bloomerang Can Have a Bigger Impact on Your Mission!
Creating a nonprofit business plan is an important step for any organization whether you’re about to launch or are well established in your community.
A nonprofit business plan is slightly different to the commercial sector. It’s a strategic plan that outlines the key elements of your organization, including:
- Financial projections
- Strategies for achieving those goals
- Volunteer recruiting
- Record keeping
- Leadership team building
- Board recruiting
- Government funding and donor support
- Long-term term direction of your organization
Why bother if you’re already established?
Regularly outlining the goals and objectives of the organization, as well as the strategies and action plan for achieving them is good practice. It’s like taking your nonprofit into the mechanic to get a check up.
In this article I will go over the fundamental steps to creating an effective nonprofit business plan.
Step 1: Outline the goals and objectives of your organization
- Define the purpose of your organization in one ‘power paragraph!’ Try outlining this core mission in twenty-five words. Clear understanding of this serves as the foundation for all the other elements of your plan. It’s a hard task, but is a great exercise to try.
- Be as specific as possible. This will help you stay focused on your goals and avoid getting sidetracked by other priorities.
- Your mission statement should provide a clear and concise description of your organization’s purpose and its unique value proposition. Try to articulate your organization’s long-term goals and aspirations in high definition.
- These statements will serve as the guiding principles for your business plan and will help to ensure that all of your activities align with your organization’s overall purpose and direction.
Step 2: Conduct Research
Market research is an important step in the planning process . It constructs an understanding of the needs your target audience have and the competition you will face. This information will be crucial in determining the feasibility of your organization’s goals and objectives.
How you undertake this depends greatly on what stage your nonprofit is in. If you’re just starting, then market research could be:
- Research the competition. What other organizations are serving the same audience and how are they doing it? How can your organization differentiate itself from the competition?
- Detailed analysis of the needs your mission seeks to help. This will help you better understand where you can help and how you effectively assist the community.
- Identifying your target audience. Who are the people you are trying to serve? What are their needs and challenges?
- If your organization is already established then feedback from donors and those your mission reaches will inform this stage. Gathering data is of vital importance and in this effort you may also wish to use data management tools available through your donor database.
Analysis of your environment.
- This will involve researching your own current situation, including strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- This SWOT analysis will help you identify the key challenges and opportunities facing your organization, and will serve as the foundation for your business plan.
- When you identify the risks you will face, those who read the plan will feel like you’re including a degree of realism. A business plan which only speaks of clear pathways to success will be less effective than those which speak of challenges which your hard work, team, and supporters seek to overcome through the duration of the plan.
New ideas: innovative strategies that can be used to achieve your organizational goals.
Identify the key areas where your organization can make the greatest impact and brainstorm ideas to address those areas. This may include identifying new sources of funding, developing new programs and services, or expanding your organization’s reach and impact.
1. Detail a budget outline.
In order to create a detailed budget and financial plan, you’ll need to take the following steps:
- Identify your income sources including potential grants, donations, and other funding sources.
- Determine your expenses including any costs associated with your project or organization.
- How much money do you expect to make and spend over a specific period of time? This will help you understand your financial position and determine if you have enough money to cover your expenses.
- Develop a fundraising plan to help you generate additional income. This could include a regimented plan to apply for grants, organize fundraising events, or reach out to potential donors.
- Diversify your fundraising plan by including a variety of income sources. This will help ensure that your organization is not reliant on a single source of funding and can weather any potential setbacks or changes in funding availability.
Sidenote: Monitor your budget and financial plan regularly to ensure that you are staying on track and making progress towards your goals. Make any necessary adjustments to your written plans to keep your finances on track.
2. Identify potential partners and collaborators.
3. develop a strong and experienced board of directors..
There are several potential partners and collaborators for a nonprofit organization. Some possible partners could include other nonprofit organizations that serve similar or complementary missions, businesses that align with the nonprofit’s goals and values, government agencies that support the nonprofit’s work, and foundations or philanthropic organizations that provide funding for similar causes.
4. Build a board of directors.
- It’s important to have a strong and experienced group of individuals who can provide guidance and support for the organization.
- This could include leaders from various sectors such as business, education, healthcare, and social services, as well as individuals with expertise in areas such as finance, fundraising, and legal affairs.
- It’s also important to have diverse perspectives and backgrounds represented on the board to ensure that the nonprofit’s work is reflective of the community it serves.
5. Create a compelling and effective marketing and outreach plan.
- To create a compelling and effective marketing and outreach plan for a nonprofit organization you should start by defining your target audience and identifying the key messages that will resonate with them.
- Next, you should determine the most effective channels for reaching your audience, such as social media, email, or events, and develop a clear call-to-action that encourages them to take a specific action.
- You should also create engaging and visually appealing content that showcases the impact of your organization and its work, and track the results of your outreach efforts to continually improve and refine your plan.
- Get social. Research how social media and effective storytelling is used the world over to create engagement and drive donations.
6. Get SMART! — Create a plan for evaluating the effectiveness of your programs and activities.
- To evaluate the effectiveness of our nonprofit programs and activities, we will first establish specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for each program.
- We will then communicate in the business plan how you will collect data on the progress of these programs. Using methods such as surveys, interviews, and focus groups to gather feedback from participants and stakeholders.
- Indicate you will also track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as program attendance and success rates. This data will be analyzed to assess the extent to which our programs are achieving their goals, and any necessary adjustments will be made to improve their effectiveness. Regular evaluations will be conducted to ensure that our programs continue to meet their objectives and have a positive impact on our target population. Once more data management software will greatly assist in this process.
7. Identify potential challenges for your nonprofit and develop strategies for addressing them.
There are many potential challenges that a nonprofit organization may face. These can include difficulties in:
- Fundraising
- Lack of public awareness
- Support for the organization’s cause
- Competition for donations or volunteers from other similar organizations
In order to address these challenges, a nonprofit can implement a variety of strategies. These can include developing a strong marketing and outreach campaign to increase public awareness, forming partnerships with other organizations to increase visibility and access to resources, and implementing effective fundraising strategies to secure the necessary financial support. Additionally, a nonprofit can focus on building and maintaining strong relationships with donors and volunteers in order to retain their support and engagement over time and the aim is to have each one of these addressed throughout the nonprofit business plan.
8. Develop a plan to build a strong and professional leadership team.
- Recruit diverse and talented individuals who share your organization’s values and goals.
- Provide ongoing training opportunities and support to help your team members develop their leadership skills overtime.
- Encourage open communication, collaboration, and teamwork among your team members.
- Identify the key leadership roles and responsibilities within your organization and then communicate it to your team.
- Hold regular meetings and check-ins to stay informed about your team’s progress and challenges.
- Foster a positive and inclusive work culture that values innovation and creativity.
- Recognize and reward the contributions of your team members, and provide opportunities for growth and development.
9. Create a plan for engaging and retaining volunteers.
- Conduct volunteer recruitment drives with online stories, on the ground leaflets and word of mouth, and clear application to apply on your website.
- Make sure volunteers feel valued and appreciated for their time and efforts by planning to thank them regularly and providing them with opportunities for personal and professional growth.
- Provide volunteers with clear expectations and guidelines for their roles and responsibilities. This will help them feel more confident and comfortable in their roles.
- Engage volunteers in the decision-making process and invite them to provide feedback and suggestions for improving the organization.
- Foster a positive and inclusive work environment that is conducive to collaboration and teamwork. This will help volunteers feel more connected to the organization and their fellow volunteers.
10. Develop a plan for managing and utilizing technology effectively.
This will include building a website. If you’re technologically inclined then there’s plenty of website building sites like WordPress and Squarespace each with their own price plans. You can also hire web designers on Fiverr for every budget.
11. Invest in data management software.
Making sense of your information in the digital age is the difference between success and failure in a lot of professional fields and the nonprofit sector is no different.
Here is a potential plan for effectively managing and utilizing data management software like Bloomerang. Data management is a pretty fundamental element of modern nonprofit management.
- Create a timeline for implementing and using your database. Including training for staff members who will be using the technology.
- Develop clear policies and procedures for using your donor database. Including guidelines for data entry, security, and access.
- Regularly review and assess the effectiveness of your database in achieving the organization’s goals, and make adjustments as needed.
- Stay up to date with new features and capabilities in the platform, and consider incorporating them into the organization’s use of the technology.
- Overall, the key to effectively managing and utilizing technology is to have a clear plan and to regularly review and assess its effectiveness in achieving the organization’s goals.
12. Create a plan for handling financial management and reporting.
To manage the finances for a nonprofit business plan, it’s important to establish a clear budget and regularly track expenses to ensure that the organization is operating within its means. It’s also crucial to maintain accurate financial records and create regular financial reports to provide transparency and accountability to donors and stakeholders. To create a plan for financial management and reporting, the following steps can be taken:
- Establish a budget which outlines the organization’s projected income and expenses.
- Track expenses regularly to ensure that the organization stays within its budget.
- Maintain accurate financial records, including receipts and invoices.
- Create regular financial reports, such as monthly or quarterly statements, to provide transparency and accountability.
- Meet with the organization’s board of directors regularly to review and discuss the financial reports and make any necessary adjustments to the budget.
13. Develop a plan for dealing with legal and compliance issues.
To ensure that your nonprofit organization meets all legal compliances and regulations, you should:
- Research the specific laws and regulations that apply to your organization and its activities.
- Include requirements related to tax exemptions, charitable solicitation, fundraising, governance, and financial reporting.
- Consult with an attorney who is experienced in nonprofit law to help you understand and comply with these requirements.
- Schedule to regularly review and update your policies and procedures to ensure that your organization remains in compliance with all applicable laws and regulations.
14. Identify potential sources of income, such as grants and corporate partnerships and outline how you will do this.
- Research potential grant opportunities from government agencies and private foundations that align with the nonprofit’s mission and goals. This can be done by searching online databases, such as Grants.gov and Foundation Center, and attending grant-related workshops and conferences.
- Reach out to corporations in the community and inquiring about potential partnership opportunities. This can include sponsorships for events, in-kind donations, and cause-related marketing campaigns.
- Develop a list of potential funding sources and carefully review their requirements and application processes. This will help the nonprofit determine which opportunities are the best fit and ensure that all necessary materials are prepared for a successful application.
- Create a calendar of deadlines for grant applications and corporate partnership inquiries, and set aside dedicated time to work on these opportunities. This will help the nonprofit stay organized and ensure that all opportunities are pursued in a timely manner.
- Follow up with potential funding sources after submitting applications or proposals. This can include thanking them for their consideration and providing any additional information they may require. It can also include reaching out to discuss potential opportunities for collaboration or additional funding in the future.
- Monitor the success of the nonprofit’s efforts to secure funding from grants and corporate partnerships, and adjust the plan as needed based on the results. This can include identifying any challenges and implementing strategies to overcome them, as well as celebrating successes and leveraging them to secure additional funding in the future.
15. Develop a plan for continuously improving and adapting to meet the changing needs of your target population over the course of your nonprofit business plan.
To continuously improve and adapt to the changing needs of our nonprofit’s target population, we can implement the following steps:
- Conduct regular needs assessments to identify gaps and areas for improvement in our services. This can involve surveying our target population and gathering feedback from staff and other stakeholders.
- Develop a plan to address identified gaps and prioritize actions based on the needs and priorities of our target population. This can involve implementing new programs and services, as well as making adjustments to existing ones.
- Monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of our programs and services on an ongoing basis, using both qualitative and quantitative data. This can involve collecting feedback from our target population and staff, as well as tracking key performance indicators.
- Engage with our target population and other stakeholders to stay informed about their needs and priorities, and incorporate their feedback into our planning and decision-making processes.
- Collaborate with other organizations and stakeholders to share best practices and resources and identify opportunities for joint initiatives and partnerships.
- Regularly assess and address the needs of the target population, monitoring and evaluating the impact of your programs
- Staying engaged and informed to ensure that your nonprofit is meeting the changing needs of the target population and continuously improving services.
In conclusion
A nonprofit business plan can seem daunting but each part will keep your nonprofit in good shape for 2023.
Clearly defining your mission, fundraising strategies, and funding, while attracting and retaining talented employees, will make a lasting positive impact in this field. Good luck!
Discover How to Maximize the Lifetime Value of Your Donor Database!

Exclusive Resources

Related Articles

Everything that you need to know to start your own business. From business ideas to researching the competition.
Practical and real-world advice on how to run your business — from managing employees to keeping the books.
Our best expert advice on how to grow your business — from attracting new customers to keeping existing customers happy and having the capital to do it.
Entrepreneurs and industry leaders share their best advice on how to take your company to the next level.
- Business Ideas
- Human Resources
- Business Financing
- Growth Studio
- Ask the Board
Looking for your local chamber?
Interested in partnering with us?
Start » strategy, how to write a nonprofit business plan.
A nonprofit business plan ensures your organization’s fundraising and activities align with your core mission.

Every nonprofit needs a mission statement that demonstrates how the organization will support a social cause and provide a public benefit. A nonprofit business plan fleshes out this mission statement in greater detail. These plans include many of the same elements as a for-profit business plan, with a focus on fundraising, creating a board of directors, raising awareness, and staying compliant with IRS regulations. A nonprofit business plan can be instrumental in getting your organization off the ground successfully.
Start with your mission statement
The mission statement is foundational for your nonprofit organization. The IRS will review your mission statement in determining whether to grant you tax-exempt status. This statement also helps you recruit volunteers and staff, fundraise, and plan activities for the year.
[Read more: Writing a Mission Statement: A Step-by-Step Guide ]
Therefore, you should start your business plan with a clear mission statement in the executive summary. The executive summary can also cover, at a high level, the goals, vision, and unique strengths of your nonprofit organization. Keep this section brief, since you will be going into greater detail in later sections.
Identify a board of directors
Many business plans include a section identifying the people behind the operation: your key leaders, volunteers, and full-time employees. For nonprofits, it’s also important to identify your board of directors. The board of directors is ultimately responsible for hiring and managing the CEO of your nonprofit.
“Board members are the fiduciaries who steer the organization towards a sustainable future by adopting sound, ethical, and legal governance and financial management policies, as well as by making sure the nonprofit has adequate resources to advance its mission,” wrote the Council of Nonprofits.
As such, identify members of your board in your business plan to give potential donors confidence in the management of your nonprofit.
Be as realistic as possible about the impact you can make with the funding you hope to gain.
Describe your organization’s activities
In this section, provide more information about what your nonprofit does on a day-to-day basis. What products, training, education, or other services do you provide? What does your organization do to benefit the constituents identified in your mission statement? Here’s an example from the American Red Cross, courtesy of DonorBox :
“The American Red Cross carries out their mission to prevent and relieve suffering with five key services: disaster relief, supporting America’s military families, lifesaving blood, health and safety services, and international service.”
This section should be detailed and get into the operational weeds of how your business delivers on its mission statement. Explain the strategies your team will take to service clients, including outreach and marketing, inventory and equipment needs, a hiring plan, and other key elements.
Write a fundraising plan
This part is the most important element of your business plan. In addition to providing required financial statements (e.g., the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement), identify potential sources of funding for your nonprofit. These may include individual donors, corporate donors, grants, or in-kind support. If you are planning to host a fundraising event, put together a budget for that event and demonstrate the anticipated impact that event will have on your budget.
Create an impact plan
An impact plan ties everything together. It demonstrates how your fundraising and day-to-day activities will further your mission. For potential donors, it can make a very convincing case for why they should invest in your nonprofit.
“This section turns your purpose and motivation into concrete accomplishments your nonprofit wants to make and sets specific goals and objectives,” wrote DonorBox . “These define the real bottom line of your nonprofit, so they’re the key to unlocking support. Funders want to know for whom, in what way, and exactly how you’ll measure your impact.”
Be as realistic as possible about the impact you can make with the funding you hope to gain. Revisit your business plan as your organization grows to make sure the goals you’ve set both align with your mission and continue to be within reach.
[Read more: 8 Signs It's Time to Update Your Business Plan ]
CO— aims to bring you inspiration from leading respected experts. However, before making any business decision, you should consult a professional who can advise you based on your individual situation.
CO—is committed to helping you start, run and grow your small business. Learn more about the benefits of small business membership in the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, here .
Join us for our Small Business Day event!
Join us at our next event on Wednesday, May 1, at 12:00 p.m., where we’ll be kicking off Small Business Month alongside business experts and entrepreneurs. Register to attend in person at our Washington, D.C., headquarters, or join us virtually!
Subscribe to our newsletter, Midnight Oil
Expert business advice, news, and trends, delivered weekly
By signing up you agree to the CO— Privacy Policy. You can opt out anytime.
For more business strategies
How startups contribute to innovation in emerging industries, how entrepreneurs can find a business mentor, 5 business metrics you should analyze every year.
By continuing on our website, you agree to our use of cookies for statistical and personalisation purposes. Know More
Welcome to CO—
Designed for business owners, CO— is a site that connects like minds and delivers actionable insights for next-level growth.
U.S. Chamber of Commerce 1615 H Street, NW Washington, DC 20062
Social links
Looking for local chamber, stay in touch.
How to write an effective non-profit business plan in 10 steps
Nearly 7.5% of the global workforce works in the non-profit sector. To put it simply, the nonprofit sector is huge. While it may seem like a less complicated business model than for-profit entities, running a non-profit organisation is still a business.
And like any business, one of the keys to success is having a well-thought-out business plan.
Of course, if you never wrote a business plan before, the process can be daunting. So we’re here to help with a step-by-step guide on how to write an effective business plan for your non-profit.
Let's take it from the top...

1. Collect the Data
Before you start writing, you must have all your ducks in a row. This means collecting data about your non-profit, such as:
- Financial statements for the past few years
- Programs and services offered
- Audience demographics
- Funding sources
- Income and expenses
If your nonprofit is new, simply compile any projections and assumptions you have at this stage. List secured funding sources or in-kind donations you’ve already received. The goal is to put together a clear picture of where your nonprofit currently stands.
2. Mission Statement
Now that you have all the data in front of you, it’s time to start putting pen to paper - or, more likely, fingers to keyboard. The first step in writing your non-profit business plan is to craft a strong mission statement.
Your mission statement should be clear, concise, and easy to remember. It should also sum up the purpose of your non-profit in one sentence. For inspiration, take a look at some examples of great mission statements:
- Tesla : “To accelerate the world’s transition to renewable energy.”
- Nike : “Bring inspiration and innovation to every athlete* in the world. (*If you have a body, you are an athlete.)”
- Starbucks : “To inspire and nurture the human spirit—one person, one cup, and one neighbourhood at a time.”
After you have your mission statement figured out, it’s time to start working on the meat of your business plan. Begin by outlining the main sections of your document. At a minimum, your nonprofit business plan should include the following:
- An executive summary
- A description of your programs and services
- Your target audience
- A marketing plan
- An operational plan
- An impact plan
- A financial summary
During this phase, you may need some help. A company like Boardroom Advisors has helped many nonprofits and for-profits with their business plans. They can help you get in touch with a finance director who can contribute to your business plan.
4. Programs/Services
Now it’s time to start filling in the outline you created in the previous step. Begin with a description of the programs and services your non-profit offers. Include information on how these programs and services help you achieve your mission.
If you’re having trouble articulating the value of your programs and services, ask yourself the following questions:
- Who are the beneficiaries of our programs and services?
- What needs do our programs and services address?
- What are the outcomes of our programs and services?
Answering these questions will help you paint a picture of the value your nonprofit brings to the table.
5. Marketing Plan
A nonprofit business is still a business. That's why you need a marketing plan.
The first step in creating your marketing plan is identifying your target audience. What people or organisations do you want to reach with your marketing efforts?
Once you know your target audience, you can start thinking about the best way to reach them. Some ideas include:
- Social media
- PR campaigns
- Direct mail
Remember that you don’t have to do all these things. In fact, it’s often better to focus your efforts on one or two channels that will reach your target audience most effectively.
6. Operational Plan
Your operational plan outlines the day-to-day operations of your non-profit. It should feature the following information:
- Your staff and their responsibilities
- Your organisational structure
- Your office space and equipment
- Your policies and procedures
This section of your business plan should be fairly straightforward. Simply describe how your nonprofit runs on a day-to-day basis. And don’t forget to include information on your staff.
The impact section of your non-profit business plan should describe the difference you hope to make in the world. That is your chance to get specific about your goals and objectives.
For example, how many people do you hope to reach if your goal is to reduce poverty in your community? And what difference do you hope to make in their lives?
Social or environmental change can be slow, so it’s important to set realistic goals. But it’s also important to dream big. After all, that’s what nonprofits are all about.
8. Finances
No business plan is complete without a financial summary. The section should include information on your:
- Revenue streams,
- Assets and liabilities
Here's another area where Boardroom Advisors can help. They can connect you with a financial advisor who can help you write your financial summary. Talking to a professional could give you a better understanding of your nonprofit's financial health.
Not to mention help you prevent any legal issues down the road.
9. Executive Summary
Usually written last but placed first in your business plan, the executive summary should introduce your entire business plan. On the first page, you should include:
- The problem your nonprofit is solving
- Your solution
- Your target market
- Your business model
- Your competitive landscape
The executive summary is where you're selling your business and its ideas. Make sure to customise it for each person who reads it.
10. Appendix
The appendix is where you can include any additional information that might be helpful to your reader. This might include:
- Your nonprofit's tax returns
- Your most recent audit
- Articles or press releases about your nonprofit
The appendix is a great place to include any information that doesn't fit neatly into another section of your business plan.
When it comes to writing a non-profit business plan, the process can seem daunting. But it doesn't have to be. By breaking the process down into ten simple steps, you can be sure that you're covering all your bases.
And if you need any inspiration, you can download free business plan templates from HubSpot and Shopify .You ca either follow them closely or use them to guide your writing process.
Stay in the loop. Delivered to your inbox twice a month.

Founder and Chief Executive of BoardroomAdvisors.co, John is a serial entrepreneur, having founded 7 different businesses over 40 years and has been ranked #30 in CityAM’s list of UK Entrepreneurs.

4 marketing tips to promote your nonprofit fundraising event
How to create Facebook Ads to boost donations as a nonprofit

3 Mistakes to avoid when designing your nonprofit website

How to create an effective nonprofit marketing strategy
Stay in the loop..
Delivered to your inbox twice a month.

3 Sample Nonprofit Business Plans For Inspiration
Download our Ultimate Nonprofit Business Plan Template here
Below are sample plans to help guide you in writing a nonprofit business plan.
- Example #1 – Kids Are Our First Priority (KAOFP) – a Nonprofit Youth Organization based in Chicago, IL
- Example #2 – Church of the Sacred Heart – a Nonprofit Church based in St. Louis, MO
- Example #3 – Finally Home – a Nonprofit Homeless Shelter in Los Angeles, CA
Sample Nonprofit Business Plan #1 – Kids Are Our First Priority (KAOFP) – a Nonprofit Youth Organization based in Chicago, IL
Executive summary.
Kids Are Our First Priority (KAOFP) is a 501(c)3 nonprofit youth organization that seeks to provide opportunities for students who might otherwise not have access to the arts and humanities. We believe all students should have the opportunity to discover and develop their interests and talents, regardless of socioeconomic status or geographic location. We offer completely free after-school programming in music production, digital photography, creative writing, and leadership development to 12-18-year-olds at risk of dropping out of high school.
Our organization has been active for over five years and has run highly successful programs at two schools in the city of Chicago. We have been awarded an active grant from a local foundation for this coming year, but we will need to cover all costs on our own after that point. Nonprofit administrators have seen a lot of turnovers, leaving the organization without a sustainable plan for reaching its goals.
Organization Overview
The Kids Are Our First Priority (KAOFP) is a 501(c)3 nonprofit youth organization with a mission to provide opportunities for development and self-expression to students who might otherwise not have access. Audiences include at-risk, low-income students from elementary through high school in the Chicago area.
Our programs are built around creative learning with two goals: firstly, creating a space for learning and growth; secondly, encouraging students to share their work with the world.
KAOFP runs three different programs in partnership with closely related nonprofit organizations, providing after-school programming for elementary, middle, and high school-aged children. Programs take place twice a week at different schools around Chicago. While each program is unique in its goals and activities, all programs focus on creative development in the arts and humanities.
Products, Programs, and Services
The three programs offered by KAOFP are Leadership Development (LD), Creative Writing (CW), and Music Production (MP). Students learn in small groups led by skilled instructors. All activities are designed to encourage student engagement, creativity, expression, and community building. Instructors encourage students to share their work with the world through presentations on- and off-site.
Leadership Development (LD)
The Leadership Development program is designed to provide leadership opportunities for high school students who might not otherwise have access to these experiences. Students learn about facilitation, collaboration, communication, and organizational skills as they plan and run projects of their own design. The program’s goal is to provide a structured environment that encourages students to become more confident and comfortable being leaders in their schools, communities, and future careers.
Creative Writing (CW)
Students learn how to use writing creatively as a tool for expression, discovery, and communication. In small groups led by skilled instructors, students write poetry, short stories, and essays of their own design. They also learn about the publishing industry, read each others’ work, and share their writing with the community.
Music Production (MP)
Students learn how to use digital media as a tool for expression, discovery, and communication. In weekly sessions led by skilled instructors, students explore music production through computer software and recording equipment. Students produce their own music and write about their experiences in weekly journals. Industry professionals in the community often volunteer to lead special workshops and seminars.
Industry Analysis
The youth arts and humanities field is extremely competitive. There are many different types of nonprofit organizations doing similar work, but few credible providers with long-term commitments to their communities. KAOFP’s greatest strengths and competitive advantages are our stable and qualified staff, a strong foundation of funding and community support, and a diverse set of programs.
Our biggest competitors include national non-profits with large budgets for advertising and marketing as well as commercial programs that offer music lessons and creative writing courses which may be more cost-effective than our programs. We feel that by focusing on specific areas of creative expression, KAOFP can better serve its communities and differentiate itself from other nonprofit organizations effectively.
Customer Analysis
KAOFP serves elementary, middle, and high school-aged students with programs that include both after-school and summer programming.
Our focus is on low-income neighborhoods with a high population of at-risk youth. In these areas, KAOFP fills a void in the education system by providing opportunities for creative expression and leadership development to students who would not otherwise have access to these resources.
The demographics of our current students are as follows:
- 91% African-American/Black
- 6% Hispanic/Latino
- 5% Multiracial
- 3.9% Low Income
- 4.9% Not Identified
Our main target is low-income African American and Latino youth in Chicago Public Schools. We would like to expand our outreach to include other communities in need of creative enrichment opportunities.
Marketing Plan
KAOFP’s marketing program is designed to support student, parent, and staff recruitment by promoting the organization’s goals and programs. Our main target audience consists of parents seeking after-school enrichment opportunities for their children that emphasize creativity and the arts.
To reach this audience, we advertise in public schools as well as on social networking sites such as Facebook and Twitter. We intend to begin marketing online through a company-sponsored blog, which will feature regular updates about KAOFP events and activities. We also intend to use word of mouth as a form of marketing.
Strategic partnerships with local schools and community centers will provide us with additional exposure as well as additional resources to secure funding.
Operations Plan
KAOFP’s day-to-day operation is structured around its programs on Tuesdays from 4 pm to 8 pm.
Administrative offices are located in the same space as each program, allowing instructors to closely monitor their students and provide support as needed. The administrative offices serve the essential function of fundraising, communications, record-keeping, and volunteer coordination. KAOFP’s Board of Directors meets bi-monthly to provide further leadership, guidance, and oversight to our board members and volunteers.
Customer service is conducted by phone and email during our regular business hours of Monday – Friday 9 am to 12 pm. We are not open on weekends or holidays.
Management Team
KAOFP’s organizational structure includes a Board of Directors, an Executive Director, and Program Directors. The Board of Directors provides guidance and oversight to the organization, while the Executive Director manages day-to-day operations. The Program Directors oversee each of KAOFP’s programs.
KAOFP has a small but dedicated staff that is committed to our students and our mission. Our team has a wide range of experience in the arts, education, and nonprofit sector.
Executive Director
The Executive Director is responsible for the overall management of KAOFP. This includes supervising staff, developing and implementing programs, overseeing finances, and representing the organization to the public.
Our Executive Director, Susie Brown, has been with KAOFP since its inception in 2010. She has a B.A. in Fine Arts from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and an M.F.A. in Creative Writing from Columbia College Chicago. Susie is responsible for the overall management of KAOFP, including supervising staff, developing and implementing programs, overseeing finances, and representing the organization to the public.
Program Directors
Each of KAOFP’s programs is overseen by a Program Director. The Program Directors are responsible for developing and implementing the program curricula, recruiting and training program instructors, and evaluating student progress.
Art Program Director
The Art Program Director, Rachel Smith, has a B.A. in Fine Arts from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. She is responsible for developing and implementing the program curricula, recruiting and training program instructors, and evaluating student progress.
Music Program Director
The Music Program Director, John Jones, has a B.A. in Music Education from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. He is responsible for developing and implementing the program curricula, recruiting and training program instructors, and evaluating student progress.
Theatre Program Director
The Theatre Program Director, Jane Doe, has a B.A. in Theatre Arts from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. She is responsible for developing and implementing the program curricula, recruiting and training program instructors, and evaluating student progress.
Board of Directors
KAOFP’s Board of Directors provides guidance and oversight to the organization. The Board consists of community leaders, educators, artists, and parents. Board members serve three-year terms and can be renewed for one additional term.
Financial Plan
KAOFP’s annual operating budget is approximately $60,000 per year, with an additional one-time cost of about $10,000 for the purchase of equipment and materials. The agency makes very efficient use of its resources by maintaining low overhead costs. Our biggest expense is instructor salaries, which are approximately 75% of total expenses.
Pro Forma Income Statement
Pro forma balance sheet, pro forma cash flow statement, nonprofit business plan example #2 – church of the sacred heart – a nonprofit church based in st. louis, mo.
The Church of Sacred Heart is a nonprofit organization located in St. Louis, Missouri that provides educational opportunities for low-income families. We provide the best quality of education for young children with tuition rates significantly lower than public schools. It has been voted Best Catholic Elementary School by the St Louis Post Dispatch for four years running, and it has maintained consistently high ratings of 4.5 out of 5 stars on Google Reviews since its opening in 1914.
The Church of Sacred Heart strives to build strong relationships with our community by making an impact locally but not forgetting that we operate on global principles. As such, our school commits 10% of its profits to charitable organizations throughout the world every year, while also conducting fundraisers throughout the year to keep tuition rates affordable.
We are currently transitioning from a safe, high-quality learning environment to an even more attractive facility with state-of-the-art technology and modern materials that will appeal to young students and their families. New facilities, such as additional classrooms and teachers’ lounges would allow us not only to accommodate new students but also attract current families by having more places within the school where they can spend time between classes.
By taking full advantage of available opportunities to invest in our teachers, students, and facilities, we will be able to achieve steady revenue growth at 4% per year until 20XX.
The Church of Sacred Heart provides a safe learning environment with an emphasis on strong academics and a nurturing environment that meets the needs of its young students and their families. Investing in new facilities will allow us to provide even better care for our children as we continue to grow as a school.
Mission Statement: “We will strive diligently to create a safe, respectful environment where students are encouraged and inspired to learn through faith.”
Vision Statement: “Sacred Heart believes education gives every child the opportunity to achieve their full potential.”
The Church of the Sacred Heart was built in 1914 and is located in the Old North St. Louis neighborhood, an area with a high concentration of poverty, crime, unemployment, and abandoned buildings.
The church houses the only Catholic school for low-income families in the north city; together they formed Sacred Heart’s educational center (SCE). SCE has strived to provide academic excellence to children from low-income families by providing a small, nurturing environment as well as high academic standards.
The facility is in need of renovations and new equipment to continue its mission.
The Church of the Sacred Heart is a small nonprofit organization that provides a variety of educational and community services.
The services provided by Sacred Heart represent a $5 billion industry, with nonprofit organizations accounting for $258.8 billion of that total.
The health care and social assistance sector is the largest among nonprofits, representing 32 percent of revenues, followed by educational services (18 percent), and human and other social service providers (16 percent).
The key customers for the Church of the Sacred Heart are families in need of affordable education. The number of students in the school has increased from 500 when it opened in 1914 to 1,100 at its peak during 20XX-20XX but has since declined due to various reasons.
The children at Sacred Heart are from low-income families and 91 percent qualify for free or reduced lunches. Most parents work or have a family member who works full-time, while others don’t work due to child care restraints. The number of children enrolled in Sacred Heart is stable at 1,075 students because there is a lack of affordable alternatives to Catholic education in the area.
SCE offers K-5th grade students a unique learning experience in small groups with individualized instruction.
Sacred Heart has an established brand and is well known for its high standards of academic excellence, which include a 100 percent graduation rate.
Sacred Heart attracts prospective students through promotional materials such as weekly bulletins, mailers to homes that are located in the area served, and local churches.
Parents and guardians of children enrolled in Sacred Heart are mainly referrals from current families, word-of-mouth, and parishioners who learn about the school by attending Mass at Sacred Heart.
The Church of Sacred Heart does not currently advertise; however, it is one of the few Catholic schools that serve low-income families in St. Louis, MO, and therefore uses word of mouth to attract new students to its school.
The Church of Sacred Heart has an established brand awareness within the target audience despite not having direct marketing plans or materials.
The operations section for the Church of the Sacred Heart consists of expanding its after-school program as well as revamping its facility to meet the growing demand for affordable educational services.
Sacred Heart is located in an area where more than one-third of children live below the poverty line, which helps Sacred Heart stand out among other schools that are more upscale. Expansion into after-school programs will allow it to capture a larger market share by providing additional services to its target audience.
In order to expand, Sacred Heart will have to hire additional personnel as well as invest in new equipment and supplies for both the school and the after-school program.
The Church of Sacred Heart’s financial plan includes a fundraising plan that would help renovate the building as well as acquire new equipment and supplies for the school.
According to the National Center for Education Statistics, Catholic elementary schools across all grade levels spend an average of $6,910 per pupil on operating expenses. A fundraising initiative would help Sacred Heart acquire additional revenue while expanding its services to low-income families in St Louis, MO.
Financial Overview
The Church of the Sacred Heart expects to generate revenues of about $1.2 million in fiscal year 20XX, representing a growth rate of 2 percent from its 20XX revenue level. For 20XX, the church expects revenues to decrease by 4 percent due to a decline in enrollment and the lack of new students. The Church of Sacred Heart has experienced steady revenue growth since its opening in 1914.
- Revenue stream 1: Tuition – 22%
- Revenue stream 2: Investment income – 1%
Despite being located in a poverty-stricken area, the Church of Sacred Heart has a stable revenue growth at 4 percent per year. Therefore, Sacred Heart should be able to attain its 20XX revenue goal of $1.2 million by investing in new facilities and increasing tuition fees for students enrolled in its after-school program.
Income Statement f or the fiscal year ending December 31, 20XX
Revenue: $1.2 million
Total Expenses: $910,000
Net Income Before Taxes: $302,000
Statement of Financial Position as of December 31, 20XX
Cash and Cash Equivalents: $25,000
Receivables: $335,000
Property and Equipment: $1.2 million
Intangible Assets: $0
Total Assets: $1.5 million
Balance Statement
The board of directors has approved the 20XX fiscal year budget for Sacred Heart Catholic Church, which is estimated at $1.3 million in revenues and $920,000 in expenditures.
Cash Flow Statement f or the Fiscal Year Ending December 31, 20XX
Operating Activities: Income Before Taxes -$302,000
Investing Activities: New equipment and supplies -$100,000
Financing Activities: Fundraising campaign $200,000
Net Change in Cash: $25,000
According to the 20XX fiscal year financial statements for Sacred Heart Catholic Church, it expects its investments to decrease by 4 percent and expects to generate $1.3 million in revenues. Its total assets are valued at $1.5 million, which consists of equipment and property worth approximately 1.2 million dollars.
The Church of Sacred Heart’s financial statements demonstrate its long-term potential for strong revenue growth due to its steady market share held with low-income families in St. Louis, MO.
Nonprofit Business Plan Example #3 – Finally Home – a Nonprofit Homeless Shelter in Los Angeles, CA
Finally Home is a nonprofit organization that aims to provide low-income single-parent families with affordable housing. The management team has a strong background in the social service industry and deep ties in the communities they plan to serve. In addition, Finally Home’s CEO has a background in real estate development, which will help the organization as they begin developing its operations.
Finally Home’s mission is to reinvent affordable housing for low-income single-parent families and make it more sustainable and accessible. They will accomplish this by buying homes from families and renting them out at an affordable price. Finally Home expects its model of affordable housing to become more sustainable and accessible than any other model currently available on the market today. Finally Home’s competitive advantage over similar organizations is that it will purchase land and buildings from which to build affordable housing. This gives them a greater amount of ownership over their communities and the properties in which the homes are located, as well as freedom when financing these projects.
Finally Home plans on accomplishing this by buying real estate in areas with high concentrations of low-income families who are ready to become homeowners. These homes will be used as affordable housing units until they are purchased by Finally Home’s target demographic, at which point the organizations will begin renting them out at a base rate of 30% of the family’s monthly household income.
Finally Home plans on financing its operations through both private donations and contributions from foundations, corporations, and government organizations.
Finally Home’s management team has strong backgrounds in the social service industry, with deep ties to families that will be prepared to take advantage of Finally Home’s affordable housing opportunities. The CEO of Finally Home also brings extensive real estate development experience to the organization, an asset that will be especially helpful as Finally Home begins its operations.
Finally Home is a nonprofit organization, incorporated in the State of California, whose mission is to help homeless families by providing them with housing and support services. The centerpiece of our program, which will be replicated nationwide if successful, is an apartment complex that offers supportive living for single parents and their children.
The apartments are fully furnished, and all utilities are paid.
All the single parents have jobs, but they don’t earn enough to pay market-rate rent while still paying for other necessities such as food and transportation.
The organization was founded in 20XX by Henry Cisneros, a former U.S. Secretary of Housing and Urban Development who served under President Bill Clinton. Cisneros is the chairman of Finally Home’s board of directors, which includes leaders with experience in banking, nonprofit management, and housing professions.
The core values are family unity, compassion for the poor, and respect for our clients. They are the values that guide our employees and volunteers at Finally Home from start to finish.
According to the United States Conference of Mayors’ Task Force on Hunger and Homelessness 20XX Report, “Hunger & Homelessness Survey: A Status Report on Hunger & Homelessness in America’s Cities,” almost half (48%) of all homeless people are members of families with children. Of this number, over one quarter (26%) are under the age of 18.
In 20XX, there were 9.5 million poor adults living in poverty in a family with children and no spouse present. The majority of these families (63%) have only one earner, while 44% have zero earners because the person is not old enough or does not work for other reasons.
The total number of people in poverty in 20XX was 46.5 million, the largest number since Census began publishing these statistics 52 years ago.
Finally Home’s goal is to help single parents escape this cycle of poverty through providing affordable housing and case management services to support them long term.
Unique Market Position
Finally Home creates unique value for its potential customers by creating housing where it does not yet exist.
By helping single parents escape poverty and become self-sufficient, Finally Home will drive demand among low-income families nationwide who are experiencing homelessness. The high level of need among this demographic is significant nationwide. However, there are no other organizations with the same market position as Finally Home.
Finally Home’s target customers are low-income families who are experiencing homelessness in the Los Angeles area. The organization will actively seek out these families through national networks of other social service providers to whom they refer their clients regularly.
Finally Home expects to have a waiting list of families that are interested in the program before they even open their doors.
This customer analysis is based on the assumption that these particular demographic groups are already active users of other social service programs, so referrals will be natural and easy for Finally Home.
Industry Capacity
This information is based on the assumption that these particular demographic groups are already active users of other social service programs, so referrals will be natural and easy for Finally Home.
There is a growing demand for low-income single-parent housing nationwide, yet there is no one organization currently providing these services on a national level like Finally Home.
Thus, Finally Home has a competitive advantage and market niche here because it will be the only nonprofit organization of its kind in the country.
Finally Home’s marketing strategies will focus on attracting potential customers through national networks of other social service providers. They will advertise to their referral sources using materials developed by the organization. Finally Home will also advertise its services online, targeting low-income families using Google AdWords.
Finally Home will be reinventing affordable housing to make it more accessible and sustainable for low-income single parents. In this new model, Finally Home will own the land and buildings on which its housing units are built, as well as the properties in which they are located.
When a family is ready to move into an affordable housing unit, Finally Home will buy the home they currently live in. This way, families can take advantage of homeownership services like property tax assistance and financial literacy courses that help them manage their newfound wealth.
Finally Home has already partnered with local real estate agents to identify properties for purchase. The organization expects this to result in homes that are at least 30% cheaper than market value.
Finally Home will finance its operational plan through the use of private contributions and donations from public and private foundations, as well as corporate sponsorships.
Finally Home’s management team consists of:
- Veronica Jones, CEO, and Founder
- Mark MacDonald, COO
- Scott Bader, CFO
Management Summary
The management team has a strong history of social service advocacy and deep ties in the communities they plan to serve. In addition, the organization’s CEO has a background in real estate development that will be helpful as Finally Home begins operations.
- Year 1: Operation startup costs to launch first five houses ($621,865)
- Year 2: Deliver on market offer and complete first capital raise ($4,753,000)
- Year 3: Deliver on market offer and complete $5 million capital raise ($7,950,000)
- Year 4+: Continue to grow market share with a national network of social services providers ($15,350,000).
This nonprofit business plan will serve as an effective road map for Finally Home in its efforts to create a new model for affordable housing.
Nonprofit Business Plan Example PDF
Download our non-profit business plan pdf here. This is a free nonprofit business plan example to help you get started on your own nonprofit plan.
How to Finish Your Nonprofit Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your nonprofit business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Nonprofit Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Other Helpful Nonprofit Business Planning Articles
- Non-Profit Business Plan
- How to Write a Nonprofit Business Plan
- 10 Tips to Make Your Nonprofit’s Business Plan Stand Out
- How to Write a Mission Statement for Your Nonprofit Organization
- Strategic Planning for a Nonprofit Organization
- How to Write a Marketing Plan for Your Nonprofit Business
- 4 Top Funding Sources for a Nonprofit Organization
- What is a Nonprofit Organization?
- 20 Nonprofit Organization Ideas For Your Community

element—so we can manipulate the *path* fills with CSS --> 501 Commons
- Tools & Best Practices
Starting a Nonprofit & Fiscal Sponsorship
Countless community and global needs have been met by nonprofits. And undoubtedly, new solutions will inspire others to consider this path. Yet critical to success is knowing that not every idea or initiative lends itself to starting a new nonprofit organization . In fact, some ideas are best implemented through alternative methods. Bottom line: pursuing the "right" course requires research, communication, and planning. Please read on.

- Is your idea best suited as a nonprofit or business/for-profit? (Learn about a new for-profit type: social purpose corporation .)
- What other organizations in your community – and beyond – are focused on your interests, and is there an opportunity to work through them (e.g., fiscal sponsorship) or partner in other ways?
- The legal steps to forming a nonprofit
- Nonprofit management obligations
- A checklist for starting a nonprofit
- Online resources and more
Business Planning
Perhaps most important to a group’s potential for success is part four of the Starting a Nonprofit Organization guide. It outlines the steps to developing a business plan. A basic template for creating one – including a staffing plan and budget – can be found at the end of the guide.
The importance of a business plan cannot be overstated . While a nonprofit organization is different in many ways from a business or for-profit from an operations perspective, there are many similarities. In fact, when you think of starting and running a nonprofit, imagine that you are about to start a small business and what that entails. Then add to it nonprofit-specific government requirements.
Ultimately, a well-developed business plan lets you assess if you are ready to start a new organization (e.g., able to meet "staffing" needs) and how sustainable it may be (e.g., you identified research-supported funding streams). It also:
- Becomes an introductory document to share with community leaders and potential board members, staff, donors, and other partners in the venture
- Gives future board, staff, and volunteers of the organization a road map for building a successful organization
- Helps you respond to questions from the state, the IRS, and other government agencies
Legal Support
Getting legal or other professional help when starting a new organization is one way to ensure compliance with state and federal requirements. One organization to note is Communities Rise (formerly Washington Attorneys Assisting Community Organizations). Communities Rise provides pro bono legal assistance to nonprofits so groups can focus on their work in the community with less concern about legal issues. Help with forming a nonprofit is a service Communities Rise and others offer.
Yet here again, having a business plan is an important step. For example, one of Communities Rise’s eligibility requirements for a start-up organization is that it demonstrate that it has such a plan.
Consulting Services & Training
501 Commons and Communities Rise are not the only options for help with starting a new nonprofit. A number of highly skilled consultants are also knowledgeable in this and other areas. Some have experience with particular nonprofit subsectors, like arts and cultural organizations, while others have worked with groups serving diverse communities or specific populations. To find service providers who have been vetted and evaluated by 501 Commons, visit the Nonprofit Resource Directory .
Also, every month and around the Pacific Northwest, there are numerous learning and networking opportunities for current and aspiring nonprofit professionals and volunteers. Take advantage of great trainings offered by service providers in the Resource Directory as well as those put on by 501 Commons . Some events cost a fee, while others are free!
Fiscal Sponsorship & Other Ways to Serve Your Mission
As noted earlier, there may be ways for community-benefiting ideas to become reality other than starting a new organization. The American Bar Association outlines some alternatives to forming a charitable nonprofit . One of these options is fiscal sponsorship (FS).
What is a fiscal sponsorship? According to nonprofit attorney Ellis Carter of Caritas Law Group :
"The term 'fiscal sponsorship' refers to an arrangement by which an established public charity (referred to as the 'Fiscal Sponsor') facilitates fundraising for a charitable project (the 'Sponsored Project') by, among other things, allowing the Sponsored Project to solicit tax-deductible contributions from individuals or grants from private foundations that the Sponsored Project is not itself eligible to receive directly."

We also recommend the following to learn more about fiscal sponsorship, access agreement templates, and research potential fiscal sponsors:
Fiscal Sponsorship Summary
Sample fiscal sponsorship agreement (direct project model), sample fiscal sponsorship agreement (re-grant model).
- Guide to Fiscal Sponsorship
- Fiscal Sponsor Directory
- National Network of Fiscal Sponsors
Starting a Nonprofit Resources
Remember: starting a new nonprofit organization begins as a question, not a conclusion. Take time to read what is involved in running a nonprofit and talk with others who are already in the sector – especially those working on the issue(s) in which you are interested – before jumping in! The following documents will help you reach an informed decision.
- Starting a Nonprofit Organization guide by 501 Commons (includes a customizable business plan template)
- The Nonprofit Association of Washington's Starting a Nonprofit toolkit
- For information on applying to the IRS for 501(c)(3) and 501(c)(4) status, including sample forms, policies, and agreements, visit Bolder Advocacy - Establishing Your Organization
- The National Council of Nonprofits website provides diverse resources with easily searchable categories
- The Balance discusses How Much Does It Cost to Start a Nonprofit Organization?
- GrantSpace offers a free online course, Establishing a Nonprofit , which outlines the 12 tasks you need to accomplish to start a nonprofit organization.
Other printed materials we like include:
- The Nonprofit Handbook by Gary M. Grobman
- Starting and Building a Nonprofit: A Practical Guide by Peri H. Pakaroo
- How to Form a Nonprofit Corporation by Anthony Mancuso
- What Does Tax Exempt Mean? by Tricia Delles, CPA
Applying for 501(c)(3) Tax-Exempt Status
If you want to file for federal tax-exempt status , visit Tax Information for Charities & Other Non-Profits or contact the IRS at 1-877-829-5500. Ask about the following free items:
- SS-4 - Employer Identification Number
- Form 1023 - Application for Recognition of Tax-Exemption (i.e., 501(c)(3) status)
- Publication 557 - Tax-Exempt Status for Your Organization
Note: When you file the Form 1023 or other IRS tax-exemption application form, you will need to pay the IRS a filing fee .
You may also need to file an annual information return (Form 990) with the IRS sooner than you think. According to the IRS's website, "An organization should file a Form 990-series return if it claims exempt status but hasn’t applied for it, or if it has applied but not yet received an IRS letter recognizing tax-exempt status.
"For recognition of exemption from the date of formation, organizations requesting recognition generally must apply within 27 months after legal formation of the organization. Organizations apply for exemption by filing Forms 1023 , 1023-EZ , 1024 or 1024-A ." Learn more about this IRS filing responsibility, including when to submit your information return and which type to submit, at an IRS page titled " Many tax-exempt organizations must file annual returns in May ."
Finally, to help the application process go smoothly, read the IRS' top ten tips to shorten the tax-exempt application review process .
Social Purpose Corporation
A social purpose corporation (SPC) is a type of for-profit corporation in Washington State and some other US states. For would-be organizations, this style of corporation may be preferred over a nonprofit one. Think of a social purpose corporation as a hybrid between a traditional for-profit company and a nonprofit. Directors of a for-profit corporation have a duty to act in the best interest of the corporation. This duty has been interpreted as a responsibility to maximize the financial returns for shareholders. Conversely, nonprofit organizations seek out charitable and social purposes, and they are legally prohibited from distributing profits to members, officers, and others.
Social purpose corporations, on the other hand, can pursue both social and financial goals in the for-profit context. A state-registered SPC operates its business “in a manner intended to promote positive short-term or long-term effects of, or minimize adverse short-term or long-term effects of, the corporation’s activities upon any or all of (1) the corporation’s employees, suppliers or customers; (2) the local, state, national or world community; or (3) the environment.” But, it is not be eligible for federal 501(c)(3) status. Consider the comparisons in the table and downloadable chart below when deciding which organizational type best suits your situation:
For a more detailed comparison between a traditional business corporation, social purpose corporation, and nonprofit corporation (i.e., 501(c)(3)), see this Business Entity Comparison Chart from Apex Law Group, LLP.
Social Purpose Corporation vs. Benefit Corporation vs. B Corporation
A social purpose corporation is not the same as a benefit corporation , which is the “formalized legal entity” in some other US states. Note: Washington State SPCs have less stringent requirements than benefit corporations elsewhere. For example, “SPCs are not obligated to consider social purposes in their decision-making – rather, they ‘may’ do so.” These two designations are different still than a B Corporation , which is a third-party certified company but not a legal entity (like a SPC or benefit corporation). Read more about these corporations on the UpCounsel website .
Researched content contributed – in part – by: Yoshihiro Fumoto, 501 Commons intern
Business Entity Comparison Chart

Fiscal Sponsorship Infographic
Starting a Nonprofit Organization - 2017
What does tax exempt mean.
Business Plan Template for Government Agencies
- Great for beginners
- Ready-to-use, fully customizable Subcategory
- Get started in seconds

Creating a solid business plan is essential for any organization, including government agencies. It's not just about setting goals and objectives, but also about efficiently utilizing resources and showcasing transparency. That's why ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Government Agencies is here to help!
With this template, government agencies can:
- Clearly define their strategic goals and objectives for maximum impact
- Develop actionable plans to allocate resources effectively and drive performance
- Demonstrate accountability to stakeholders and the public through transparent reporting
Whether you're a local council or a federal agency, ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Government Agencies empowers you to create a comprehensive and compelling roadmap for success—all in one centralized location. Start planning for a better future today!
Business Plan Template for Government Agencies Benefits
A business plan template for government agencies offers numerous benefits, including:
- Streamlining the strategic planning process and ensuring alignment with organizational goals and objectives
- Facilitating effective resource allocation and budget management to maximize efficiency and productivity
- Providing a clear roadmap for action, enabling agencies to prioritize initiatives and track progress
- Enhancing transparency and accountability by clearly communicating the agency's mission, vision, and performance metrics to stakeholders
- Enabling agencies to adapt and respond to changing priorities and external factors, ensuring long-term success and sustainability.
Main Elements of Government Agencies Business Plan Template
ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Government Agencies is designed to help government agencies effectively outline and manage their strategic goals, objectives, and action plans. Here are the main elements of this template:
- Custom Statuses: Easily track progress with four custom statuses - Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do - to ensure that all tasks and sections of the business plan are properly managed and updated.
- Custom Fields: Use three custom fields - Reference, Approved, and Section - to add vital information and metadata to each task, allowing for easy organization and filtering of business plan sections.
- Custom Views: Utilize five different views, including Topics, Status, Timeline, Business Plan, and Getting Started Guide, to gain different perspectives on your business plan, track progress, and ensure alignment with strategic objectives.
- Collaboration and Accountability: Enhance collaboration and accountability by utilizing features such as task comments, mentions, file attachments, and assigning responsibilities to team members.
- Reporting and Analytics: Leverage ClickUp's reporting and analytics features to gain insights into progress, performance, and resource allocation, enabling effective decision-making and demonstrating accountability to stakeholders and the public.
How To Use Business Plan Template for Government Agencies
If you're a government agency looking to create a comprehensive business plan, follow these steps to make the process easier using the Business Plan Template in ClickUp:
1. Define your mission and objectives
Start by clearly defining the mission and objectives of your government agency. What is the purpose of your agency and what do you hope to achieve? This step is crucial as it sets the foundation for the rest of your business plan.
Use the Goals feature in ClickUp to create and track your agency's mission and objectives.
2. Assess your current situation
Take a deep dive into your agency's current situation. Analyze your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT analysis). This will help you identify areas of improvement and potential challenges that need to be addressed in your business plan.
Use the Table view in ClickUp to create a SWOT analysis and track your agency's current situation.
3. Develop your strategies and action plans
Based on your mission, objectives, and SWOT analysis, develop strategies and action plans to achieve your goals. Outline the specific steps you will take to address the challenges identified and leverage your agency's strengths.
Use tasks in ClickUp to create action plans and assign responsibilities to team members.
4. Monitor and review
Once your business plan is in place, it's important to regularly monitor and review your progress. Keep track of key performance indicators (KPIs) and milestones to measure the success of your strategies and action plans. Make adjustments as needed to stay on track and ensure the continued success of your government agency.
Use Dashboards in ClickUp to visualize and monitor your KPIs and milestones.
By following these steps and utilizing the features in ClickUp's Business Plan Template, your government agency can create a well-structured and effective business plan to guide your operations and achieve your objectives.
Get Started with ClickUp’s Business Plan Template for Government Agencies
Government agencies can use the Business Plan Template for Government Agencies in ClickUp to streamline their strategic planning process and ensure alignment with organizational goals and objectives.
To get started, hit "Add Template" to sign up for ClickUp and add the template to your Workspace. Make sure you designate which Space or location in your Workspace you'd like this template applied.
Next, invite relevant members or guests to your Workspace to start collaborating.
Now you can take advantage of the full potential of this template to create a comprehensive business plan:
- Use the Topics View to outline and organize key sections and topics of your business plan
- The Status View will help you track the progress of each section, with statuses such as Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do
- Utilize the Timeline View to set deadlines and visualize the timeline of your business plan
- The Business Plan View provides a holistic overview of your entire plan, allowing you to easily navigate between sections
- The Getting Started Guide View offers step-by-step instructions and guidance to help you kickstart your business plan creation process
Additionally, customize your business plan template with the following custom fields:
- Reference: Add references or sources to support your business plan
- Approved: Indicate whether each section has been approved or not
- Section: Categorize each section of your business plan for easy organization and filtering
With this template, government agencies can efficiently create, manage, and update their business plans, ensuring transparency, accountability, and successful execution of strategic initiatives.
- Business Plan Template for Hoteliers
- Business Plan Template for Stationery Suppliers
- Business Plan Template for Ulta Beauty
- Business Plan Template for Interns
- Business Plan Template for Political Scientists
Template details
Free forever with 100mb storage.
Free training & 24-hours support
Serious about security & privacy
Highest levels of uptime the last 12 months
- Product Roadmap
- Affiliate & Referrals
- On-Demand Demo
- Integrations
- Consultants
- Gantt Chart
- Native Time Tracking
- Automations
- Kanban Board
- vs Airtable
- vs Basecamp
- vs MS Project
- vs Smartsheet
- Software Team Hub
- PM Software Guide
Don't bother with copy and paste.
Get this complete sample business plan as a free text document.
Government Services Business Plan
Start your own government services business plan
ASTI - Advanced Science and Technology Institute
Executive summary executive summary is a brief introduction to your business plan. it describes your business, the problem that it solves, your target market, and financial highlights.">.
The Advanced Science and Technology Institute (ASTI) supports research faculty and staff at **State University, University of AnyState, AnyState Health Sciences University and AnyCity State University in its management of new discoveries. This support includes the management of new discoveries having commercial applications, as well as the management of corporate research agreements leading to new discovery.
**(Editor’s Note: Names disguised for confidentiality.)
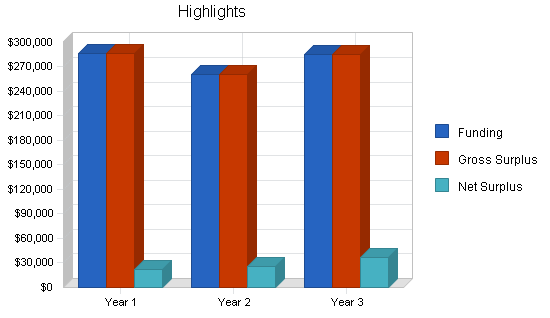
1.1 Keys to Success
- Building a strong support base with the private sector within State and the Northwest.
- Creating an effective network between researchers to facilitate cross-disciplinary contact.
- Raising the viability of ASTI as the one-stop resource for all transferable technology that is being developed on the campuses of State’s four largest universities.
1.2 Mission
The mission of the ASTI is to bring technologies from **State University, University of AnyState, AnyState Health Sciences University and AnyCity State University into public use; thereby providing economic development assistance to state and federal agencies and companies to benefit State constituents, providing service to the technology transfer staff of each institution by assisting in identifying, protecting, developing and transferring technology to the private sector and generating income. ASTI’s unique perspective is in its ability to link researchers from various institutions to create new technologies that can then be marketed to the private sector.
Historically, State has received less attention from companies that develop long-term relationships with the university research community. With SouthernState universities to the south and the University of AnyState to the north, State has had a difficult time reaching the level of viability necessary to draw the interest of companies outside the state.
It is a problem of economy of scale. Currently, State University, University of AnyState, AnyState Health Sciences University and AnyCity State University have 128 technologies available for licensing. One university in SouthernState, The University of Southern State (USS), has over 200 technologies available for licensing. In addition, USS has received $20 million in corporate research funding last year. This far exceeds the total for all corporate research funding for the four State schools ($3 million) during the same period. In State, the State Technology Center has secured $91 million in private funding for technology transfer from the University of State. It is critical that the four major universities in State pool its resources in order to be competitive in drawing corporate attention to the excellent researchers working within their institutions.
It is ASTI’s mission to create a resource for the private sector that rivals USC by providing an aggressive one-stop center for all the pivotal research that is occuring in State.
1.3 Objectives
- Establish a 42-member corporate research support council and increase corporate membership in ASTI’s Technology Development Council by 20% each year.
- Facilitate two new industry sponsored research agreements the first year and increase the number of agreements each year.
- Create new research linkages between the four campuses and develop new collaborative relationships between researchers.
- Develop a cross-disciplinary research database that will link researchers throughout the state.
Organization Summary organization overview ) is an overview of the most important points about your company—your history, management team, location, mission statement and legal structure.">
ASTI is a focused program that offers a powerful resource to researchers who are seeking corporate support for research and corporations seeking new technologies. The program also seeks linkages between the four campus researchers in developing new partnerships that will generate additional corporate interest.
2.1 Legal Entity
State University, University of AnyState, AnyState Health Sciences University, and AnyCity State University are all share holders in ASTI.
2.2 Start-up Summary
Start-up costs and initial financing are shown on the following table. Each institution will contribute $40,000 to ASTI’s operating budget.

2.3 Program Location
ASTI will be located in AnyCity, AnyState. This is a good central location for a state-wide program. AnyCity State University is located in AnyCity. AnyState Health Sciences University and State University are located in NewTown 60 miles to the north. The University of State is located in OldTown which is 40 miles south of AnyCity.
ASTI’s services include:
New Technology Assist in identifying new invention disclosures for new discoveries and evaluation of these new discoveries to determine commercial potential. A research database will be created and maintained by ASTI in order to respond quickly to requests for information from the private sector, especially when it links researchers on multiple campuses. Companies will have a quick and accessible resource that will identify researchers that match their interest areas. ASTI will also assist in the establishment of new businesses to develop emerging technologies.
Research Collaborations ASTI will actively seek cross-disciplinary collaboration opportunities between researchers on the four member campuses.
Technology Conferences ASTI will sponsor two conferences in Portland each year focusing on the areas of Biotechnology, Material Science, Computer Science, and Medical Technology.
Newsletter and Promotional Publications ASTI will produce a monthly newsletter and quarterly promotional publications directed toward the private sector which will focus on current research on the four campuses and researcher profiles. This material will also highlight researchers seeking corporate support.
Market Analysis Summary how to do a market analysis for your business plan.">
The research enterprise at State University, University of AnyState, AnyState Health Sciences University and AnyCity State University is remarkably broad, deep and diverse, spanning activities in twenty-two academic colleges and more than 40 multidisciplinary programs, centers, programs, and institutes.
ASTI will first focus on creating the information base necessary to satisfy high-technology corporations that are currently prospecting for new technologies. These are mostly larger companies, but also include medium- to small-sized companies.
Our most important group of potential customers are the researchers in these companies. They do not want to waste their time or resources looking for a needle in a haystack. It is critical that they find ASTI an excellent tool in quickly identifying technologies and researchers that will lead to profitable products.
ASTI will provide a two-tier service that will correspond to a company’s membership in ASTI’s Technology Development Council. There will be both a full and associate membership option in the Technology Development Council. We anticipate that larger companies will select the full membership option because it will offer additional research services. An associate membership is tailored for the medium- to small-sized companies whose contacts will be less frequent.
4.1 Market Segmentation
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
Medium to Small Companies: These companies are critical to the growth of ASTI because they represent the state’s developing high-tech industries. Their focus in not only on a specific technology that is being developed at one of the member campuses but also on the graduate students that are working on the research. As associate members of the Technology Development Council, these companies will gain greater access to all the research opportunities that will meet their technology and staff needs.
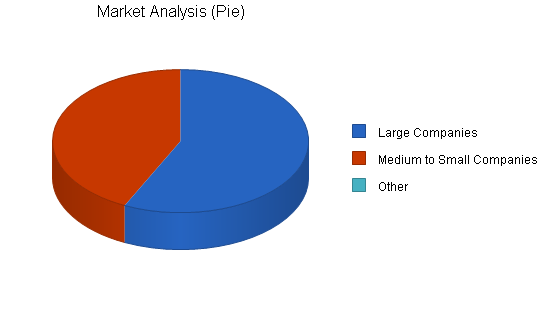
4.2 Target Market Segment Strategy
As indicated by the previous table, we must first focus on all companies that have current relationships with researchers on the member campuses.
4.3 Service Providers Analysis
The private sector’s access to researchers at the member campuses range from excellent in selected disciplines, to completely chaotic and frustrating in most others areas.
ASTI’s goal is to assure access to all critical research through a streamlined process that leaves the company both satisfied with the results as well as the time invested in the search.
Strategy and Implementation Summary
The initial funding from the four member institutions will provide the foundation for launching ASTI. Its survival will depend on the program’s ability to grow a membership base to its Technology Development Council. The program will not survive if it is unable to meet its goal of increasing membership in the Council by 20% each year.
ASTI’s information products and services will add real value to the companies search for emerging technology. As stated before, our most important group of potential customers are the researchers in these companies. Their input into the kind of services they want will be critical to the evolution of ASTI. Our focus will be to add value in everything connected with ASTI.
5.1 Competitive Edge
ASTI’s competitive advantage is their comprehensive approach to providing unequalled access to researchers. ASTI’s focus is to support the companies in their successful pursuit of emerging technologies. The most critical component is the responsiveness of the program to company inquiries into selected research areas.
The best scenario is the company responding to research highlights provided by ASTI before initial inquires are made. ASTI will strive to open doors for companies so that long-term relationships will develop and companies will become members of the Technology Development Council.
The approach is decidedly sales-oriented in focus. This is a critical advantage when in competition with universities in SouthernState and NorthernState. Companies will find State research viable and easy to access.
Yet the key to ASTI’s success will be in how the program evolves in response to companies demands. ASTI’s Technology Development Council was a vehicle for that evolution. The Council will provide companies with the access to fine-tune services to improve the program’s ability to meet industry demands.
5.2 Marketing Strategy
ASTI’s marketing strategy will be to build the Technology Development Council as a base of support for technology transfer. The plan is to use existing members of the Council as lead contact for other companies. The best description of the strategy is the ever-widening ripples when a stone is thrown in a pond. The first step is to capture all the companies the are currently quite aware of the excellent researchers at the four member institutions. From that base, begin to recruit new companies that current members will invite into the Council.
Though it is possible that fresh contacts to ASTI, from inquiries about technology highlighted in promotional material, can lead to companies joining the Council, it will be the membership of the Council that will drive the success of the program.
5.3 Fundraising Strategy
The fund raising strategy will be the payment of annual membership fees in the Technology Development Council. A full membership will be $3,000 a year. An associate membership will be $1,000.
5.3.1 Funding Forecast
During the first year, ASTI will recruit 20 full members and 21 associate members to the Technology Development Council.

5.4 Milestones
ASTI’s milestones are as follows:
- Within the first six months of operation to assemble the Technology Development Council membership.
- Publish the first ASTI monthly newsletter in December.
- Stage high tech conferences in AnyCity during the month of March and September in 2002.
- Achieve two new industry sponsored research agreements with researchers at the member institutions during the first year of operation.
Management Summary management summary will include information about who's on your team and why they're the right people for the job, as well as your future hiring plans.">
ASTI’s director is John Doe. He is excited about the state’s vision of establishing a technology transfer consortium involving the state’s strongest corporate citizens. “These are ideas that many people have shared and promoted,” Doe said. “I’m hoping to work with units around the state to implement these and other ideas related to research agreements with industry.” Doe understands the need for State to strengthen connections with the private sector.
He joins ASTI from Pacific Northwest National Laboratory in MoneyCity, State, where he worked as technology transfer manager in the Environmental Technology Division. He has a Ph.D. in low-temperature geochemistry from The Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, Md., and a post-doctoral fellow from Yale University.
He believes the technology transfer consortium is a natural mechanism to allow large and small enterprises to make use of the expertise at the member institutions and allow faculty to participate in entrepreneurial pursuits. “I will promote ideas such as an entrepreneurial sabbatical for faculty where they could pursue business start-ups and the universities will receive some benefit in return,” Doe said. “I’m excited about the opportunities and look forward to working with the Technology Development Council and promoting the critical research efforts occuring at the institutions that ASTI represents.”
6.1 Personnel Plan
ASTI’s director position is full-time. In addition, ASTI will also have three full-time employees; a research associate that will be responsible for research data collection, a communication associate who will be responsible for the program’s publications, and a full-time administrative assistant.
Financial Plan investor-ready personnel plan .">
The following sections will outline important financial information.
7.1 Break-even Analysis
The following table shows what our break-even point will be to cover our montuhly costs.

7.2 Projected Surplus or Deficit
The following table will indicate projected surplus and deficit.

7.3 Projected Cash Flow
The following table and chart illustrate the projected cash flow.

7.4 Standard Ratios
The following table compares our standard ratios with the Standard Industry Code #8748, Other Management Consulting Services.

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Business Plan for Investors
- Bank/SBA Business Plan
- Operational/Strategic Planning Services
- L1 Visa Business Plan
- E1 Treaty Trader Visa Business Plan
- E2 Treaty Investor Visa Business Plan
- EB-1 Business Plan
- EB-2 NIW Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- Innovator Founder Visa Business Plan
- Start-Up Visa Business Plan
- Expansion Worker Visa Business Plan
- Manitoba MPNP Visa Business Plan
- Nova Scotia NSNP Visa Business Plan
- British Columbia BC PNP Visa Business Plan
- Self-Employed Visa Business Plan
- OINP Entrepreneur Stream Business Plan
- LMIA Owner Operator Business Plan
- ICT Work Permit Business Plan
- LMIA Mobility Program – C11 Entrepreneur Business Plan
- USMCA (ex-NAFTA) Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Landlord business plan
- Nonprofit Start-Up Business Plan
- USDA Business Plan
- Cannabis business plan
- Ecommerce business plan
- Online boutique business plan
- Mobile application business plan
- Daycare business plan
- Restaurant business plan
- Food delivery business plan
- Real estate business plan
- Business Continuity Plan
- Pitch Deck Consulting Services
- Financial Due Diligence Services
- ICO whitepaper
- ICO consulting services
- Confidential Information Memorandum
- Private Placement Memorandum
- Feasibility study
- Fractional CFO
- How it works
- Business Plan Examples
Creating a Winning Business Plan for Social Entrepreneurs
MAY.23, 2023

1. What is a Social Entrepreneur Business Plan?
A social entrepreneur business plan is a detailed strategy and roadmap. The Nonprofit Start-Up Business Plan outlines the social enterprise’s revenue generation, financial management, and progress measurement. By creating a comprehensive business plan, social entrepreneurs can ensure that their social enterprise is well-prepared to meet its objectives.
2. Why do we need a social entrepreneur business plan?
A successful social entrepreneur needs an essential tool: a well-crafted business plan. This plan serves multiple purposes. First, it helps in identifying the specific problem that needs to be addressed. Second, it sets clear goals and defines the target audience. Third, it devises strategies for achieving these objectives. Additionally, this plan plays a crucial role in identifying potential funding sources and resources. It also maps out a timeline for goal attainment.
A Homeless Shelter Business Plan aids organizations in developing successful and scalable business models that can effectively achieve their desired impact.
3. Sources of funding for social enterprise businesses
Grants are one of the sources for funding social enterprise businesses. Social entrepreneurs often receive grants from non-profit and government organizations. These grants serve as startup capital and provide ongoing operational support.
Links to funds for non-profit organizations: Newprofit: https://www.newprofit.org/ Ashoka: https://www.ashoka.org/en-us MassChallenge: https://masschallenge.org/
In addition to traditional funding sources like crowdfunding, angel investors, and venture capital firms, social enterprises can also explore loan programs provided by the Small Business Administration. Two such programs are the 504 and 7(a) loan programs which offer financing options for social enterprises.
Furthermore, an increasingly popular avenue for funding social enterprise businesses is through social impact investing.
4. How to write a social enterprise business plan
- Start by Defining Your Social Mission: Before diving into writing your business plan, it is essential to have a clear understanding of your organization’s purpose, values, and desired social outcomes.
- Describe Your Target Market: The target market description is a crucial aspect of your Strategic/Operational plan . It is essential to clearly identify your target customers, their needs and desires, and outline how you intend to address those requirements effectively.
- Outline Your Business Model: Then comes outlining your business model. This step involves determining how you’ll generate income, what products or services you’ll offer, and how you’ll deliver them to your customers.
- Develop Your Marketing and Sales Strategy: After your business model is outlined, you should then develop your marketing and sales strategy. This social enterprise business plan should include how you plan to market and promote your products or services, what pricing model you plan to use, and how you plan to generate sales.
- Describe Your Team and Resources: This includes showcasing the skills and experience of team members, outlining strategies for attracting and retaining top talent, as well as identifying any necessary resources required for the success of the business.
- Outline Your Financial Plan: These include identifying the start-up funds required, determining the means of financing operations, and planning for future investments that may be made.
5. Executive summary
Our social enterprise, JYC, has a mission to empower vulnerable communities in developing countries. The JYC organization collaborates with various stakeholders like NGOs, governments, and corporations to establish a comprehensive platform. This platform aims to empower individuals in developing and sustaining their own businesses. Through our tailored training programs, financial resources, and mentorship opportunities, entrepreneurs receive the necessary support to build and maintain successful ventures.
6. Company (Institutional) analysis
The social entrepreneurship business plan aims to establish a sustainable, equitable, and responsible economy. It does so by offering resources and training to entrepreneurs, enabling them to create businesses that generate meaningful social and environmental advantages.
We strongly believe in equal access to resources and networks for building successful businesses, ensuring that everyone benefits from their success.
7. Structure and Background
JYC, a social entrepreneurship company founded in 2020, is dedicated to tackling social and environmental challenges through the implementation of innovative and sustainable business models. Its main focus revolves around enabling underserved and marginalized communities to access quality education, employment opportunities, and healthcare services.
Our team comprises skilled professionals from diverse sectors, including finance, technology, and social work. Their collective experience empowers us to create sustainable solutions that drive positive social change while fostering financial stability.

8. Market (Industry) analysis
The social entrepreneurship market is growing rapidly in the United States of America; estimated that 22% have over $2 million in revenue, 89% were created since 2006, and 90% focus on solving problems at home (2012).
https://www.socialchangecentral.com/social-enterprise-statistics-from-around-the-world/
JYC’s social entrepreneurship business plan will focus on providing innovative solutions to social issues and problems that have not been solved traditionally.
9. Competitor analysis
Our social entrepreneur business plan template competitors are:
- Social Impact Exchange – a global platform that helps social entrepreneurs connect with investors to fund their projects
- UnLtd – a social enterprise accelerator that provides support for early-stage social entrepreneurs
- GlobalGiving – a crowdfunding platform that helps social entrepreneurs and non-profits raise funds for their projects
- Ashoka – a global network of social entrepreneurs providing mentorship and resources to empower the social enterprise sector
- Social Enterprise UK – a membership organization that supports and promotes social enterprises in the UK.
10. Services and Products
Our components of a business plan social enterprise include services and products which are:
- Consulting services for small businesses and start-ups
- Advisory services for nonprofits
- Educational programs for children in underserved communities
- Professional development programs for adults
- Impact investing services
- Training and development programs for entrepreneurs
- Community outreach programs
- Corporate social responsibility programs
- Social enterprise incubator services
11. Sales and Marketing Plan
In order to ensure the success of a social entrepreneurship company, an effective sales and marketing plan should incorporate the following key elements:
The business aims to develop a mission and vision statement that effectively outlines its goals and objectives. This statement serves as a guiding framework for the organization’s future
In order to set the company apart from competitors and establish a unique selling proposition, an innovative social enterprise app is being created.
In order to effectively promote a product or service, it is important to develop a comprehensive marketing strategy.
12. Operational plan
Our hybrid social enterprise operational plan’s format focuses on serving our community, creating jobs, and reducing our carbon footprint.
- Supporting local businesses
- Incorporating green practices into our operations
- Developing social programs to benefit the community
- Establishing a system of sustainable production
- Creating partnerships with nonprofits and public institutions
- Minimizing waste and energy consumption.
13. Evaluation/assessment
- Analyzing the mission statement and goals of the social entrepreneurship company.
- Examining the business model and resources required to achieve success.
- Assessing the impact of the company on the community.
- Examining the company’s financial health and sustainability.
- Evaluating the management team and their ability to execute the plan.
- Analyzing the marketing strategy and its effectiveness.
- Evaluating the potential for growth and scalability.
- Assessing the competitive landscape and how the company can differentiate itself.
14. Management team
Executive Team:
- Chief Operating Officer
- Chief Financial Officer
- Chief Technology Officer
- Head of Human Resources
Advisory Board:
- Business Development Advisor
- Legal Advisor
- Marketing Advisor
- Technology Advisor
15. Projection and Financial Planning
The social enterprise group aims to raise $1 million in capital over the next five years. This funding will support various aspects, including platform development, staff recruitment, and covering operational expenses. The organization plans to generate revenue through government contracts and by offering data analytics services to local governments.
Startup Costs
The initial startup costs for this business will be $200,000.
The primary source of revenue will come from government contracts and data analytics services. Government contracts will provide a steady stream of income, while data analytics services will provide additional revenue.
Financial Highlights
The projected financial highlights for the business are as follows:
- Revenue: $1.5 million by 2024
- Profits: $400,000 by 2024
- Return on Investment: 40%
- Cash Flow: $1.2 million by 2024
- Break-even Point: 12 months
16. Discover the Power of Social Entrepreneurship with OGS Capital
Highly efficient service.
Highly Efficient Service! I am incredibly happy with the outcome; Alex and his team are highly efficient professionals with a diverse bank of knowledge.
OGS Capital specializes in assisting entrepreneurs in developing and implementing impactful social entrepreneurship business plans. Our highly experienced team collaborates with numerous social entrepreneurs to create custom plans that yield measurable outcomes.
Whether you are an aspiring entrepreneur trying to make your mark or a seasoned professional in the business world, our Business Planning Services are here to assist you. We specialize in developing comprehensive plans that fully embrace your unique vision and core values. Through close collaboration, we will work diligently alongside you to identify the optimal strategies for success and determine the necessary resources to bring your goals to fruition.
OGS Capital values the transformative power of social entrepreneurship. With our guidance, you can establish a social enterprise that leaves a lasting, meaningful impression.
OGS Capital can be your reliable partner in creating a robust social entrepreneurship business plan. Feel free to reach out to us today for assistance.
Q. What are examples of social entrepreneurship businesses?
1. Revolution Foods: Revolution Foods is a social enterprise providing healthy meals to underserved students. https://www.revolutionfoods.com/
2. Kiva: Kiva is a nonprofit providing micro-loans to developing countries’ entrepreneurs. https://www.kiva.org/
3. Ecosia: Ecosia is an online search engine that donates 80% of its profits to reforestation projects worldwide. https://www.ecosia.org/
4. Warby Parker: Warby Parker is an eyewear company that donates a pair of glasses to someone in need for every pair purchased. https://www.warbyparker.com/
5. Solar Sister: Solar Sister is a social enterprise that helps women in Africa build businesses selling solar-powered products. https://solarsister.org/
Q. How do you write a social enterprise business plan?
When establishing a social enterprise, it is crucial to undertake the task of crafting a comprehensive business plan. This plan serves as a roadmap, outlining key aspects such as the enterprise’s objectives and mission, the range of services or products on offer, an analysis of the intended audience and market, financial considerations, a succinct overview of the marketing strategy, and a timeline encompassing both launch and growth milestones. A meticulously developed social enterprise business plan sets the stage for success in this impactful venture.
The plan should have a comprehensive explanation of the enterprise’s mission and values. It should also address the competitive landscape and any applicable regulations. When writing the plan, it is important to be thorough, realistic, and ensure clarity for easy understanding.
Download Social entrepreneur business plan Template in PDF
OGSCapital’s team has assisted thousands of entrepreneurs with top-rate business plan development, consultancy and analysis. They’ve helped thousands of SME owners secure more than $1.5 billion in funding, and they can do the same for you.

Add comment
E-mail is already registered on the site. Please use the Login form or enter another .
You entered an incorrect username or password
Comments (0)
mentioned in the press:
Search the site:
OGScapital website is not supported for your current browser. Please use:


Build plans, manage results, & achieve more
Learn about the AchieveIt Difference vs other similar tools
We're more than just a software, we're a true partner
- Strategic Planning
- Business Transformation
- Enterprise PMO
- Project + Program Management
- Operational Planning + Execution
- Integrated Plan Management
- Federal Government
- State + Local Government
- Banks + Credit Unions
- Manufacturing
Best practices on strategy, planning, & execution
Real-world examples of organizations that have trusted AchieveIt
Ready-to-use templates to take planning to the next level
Research-driven guides to help your strategy excel
Pre-recorded & upcoming webinars on everything strategy & planning
- *NEW!* Podcast 🎙️
How to Create a Strategic Plan for Your Government Department or Agency

RELATED TAGS:
blog , government , Strategic Planning
Budgets and deadlines are two of the most crucial elements when it comes to getting things done in a local government. To be as efficient as possible, you’ll need a robust strategic plan for your government department that outlines how you’ll spend your provincial budget and how you and your subcontractors will achieve public project deadlines. Building a long-term and multiyear strategic plan with goals and objectives can be challenging. We also understand how complicated it is to transform your ideas into tangible results for your community, and we’re here to help.
In This Article
Why Government Departments and Agencies Need Strategic Plans
Why current government strategic processes and tools fall short, conduct internal and external analysis, consider the vision and mission , perform a holistic risk-assessment , list the focus areas , develop strategic objectives, set up an actionable game plan , utilize measurable kpis , put the plan into action , evaluate the results , transform government strategic planning and execution with achieveit, ready to accelerate your planning and execution efforts let’s actually do this..
Why should the state and municipal governments consider strategic planning? Isn’t having a yearly budget sufficient? After all, things may change when heavy rains overflow the city sewers or roadway repairs exceed the budget. What difference does additional planning make? What exactly is department strategic planning?
A department strategic plan is a comprehensive and systematic management tool that assists governmental departments, agencies and organizations in assessing their current environment, anticipating changes and responding appropriately to issues. Strategic planning involves envisioning the future, improving effectiveness, developing commitment to the department’s mission and reaching a consensus on strategies and objectives for achieving that mission. It involves influencing the future rather than merely preparing for or responding to it.
While combining community vision with available resources is critical, the resources should not stifle the vision. The objectives of a departmental strategic plan will involve identifying how the resources available may be linked to future ambitions. A long-term financial plan, created with the department strategy plan, is crucial to the departmental strategic planning process. A government should have an established financial planning mechanism that evaluates the long-term economic consequences of current and planned policies and programs. A financial plan depicts the expected financial repercussions of certain activities.
Regarding strategic planning in government positions, the notion is that leaders must be good strategists if their departments and agencies are to achieve their goals, accomplish their mandates and, most importantly, satisfy their communities in the coming years. The strategic planning department must lay out effective strategies to deal with changing conditions and governmental leaders must create a cohesive and defensible framework for their judgments. Ultimately, a department strategy provides a big-picture document that directs resources and activities toward a well-defined vision.
A state department strategic plan is a long-term commitment to various governmental objectives. Selecting the correct solutions to support the department’s strategic plan is critical to attaining them. The strategic planning department requires integrated and holistic systems and tools to increase productivity and improve the overall management of the various objectives while keeping operations running smoothly. An adequate system also keeps communication channels open between different departments.
Many procedures and systems on the market can help manage a department’s strategic plan but mainly focuses on short-term success. Business intelligence, project management, strategy development tools and other mainstream options focus on something other than integrated plans that span departments and locations. Each focuses on a specific function of planning, developing, executing or reporting strategies, so finding a single system that keeps everything in one secure place is challenging.

Taking an analytical look into these traditional options, we can see some pros to utilizing them. Still, some cons can lead to your government’s strategic processes falling short:
- Business intelligence tools: Although business intelligence tools provide visual dashboards, reports and a data-driven understanding of how the government is performing, they miss the “why” behind the strategic plan — the vision and future forecasts.
- Project management tools: These tools are excellent for providing detailed project statuses but lack the big-picture view and are typically challenging to use and connect with other projects.
- Strategy management tools: Strategy development tools can most certainly help organize plans and foster project alignment. However, these tools are less proficient at enabling the effective execution of these plans. They have limited flexibility and make it difficult to manage multiple plans across the agency.
- Mainstream tools: You might recognize mainstream and user-friendly tools like PowerPoint and Excel. Despite being customizable, these tools lack format and version control.
Strategic planning in government can be challenging. You must include stakeholder input, ensure that your department’s strategy is consistent across all municipal agencies, connect capital projects to multiple plans and ensure that everyone engaged is on board with the strategy. The good news is that it’s possible and the approach may be more straightforward than you think.
Follow these tips for creating your government agency’s strategic plan:

Conduct an environmental scan, where the local government can investigate and assess the current and developing factors within their own area’s internal and external environments. The internal and external analysis provides detailed information on the government’s existing conditions, including prospective opportunities, strengths, threats and weaknesses to control or prevent.
An internal analysis looks at the government’s internal environment to analyze its abilities, resources and competitive advantages. An internal analysis helps you identify strengths and weaknesses and the opportunities and threats that government departments or agencies face. This information assists government officials in making strategic decisions as they carry out the strategy development and implementation process. In a nutshell, the following topics should be included in your internal analysis:
- SWOT Analysis: Conducting a SWOT analysis can help you comprehensively understand your area’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats.
- Strategy analysis: This analysis assists you in evaluating how well you performed against your current department strategy plan, what you can improve on and where you can focus your efforts.
- Internal stakeholder analysis: This analysis enables you to gain insight into the issues and perspectives of your area’s internal stakeholders and their influence.
- VRIO Analysis: A VRIO analysis can assist you in identifying any competitive advantages you may have and how to convert them into long-term competitive advantages.
An external analysis investigates and evaluates the government’s external environment to understand possibilities and risks in its area. Forces outside a local government’s immediate control affect them, and they need to be able to plan accordingly. For example, changes in legislation and policies, demographic shifts or climate concerns can influence a government’s decisions. An external analysis should usually consider the following:
- PESTEL analysis: Conducting a PESTEL analysis can help you discover the many scopes that may influence an area.
- External stakeholder analysis: This analysis enables you to gain insight into the issues and perspectives of your local government’s external stakeholders and their influence.
The government’s vision statement defines where they want to go — it’s the anchor that keeps them from being stranded at sea. A clear vision statement will aid in directing the strategic plan toward the best results for the community. Everything written into the plan will eventually help the government department or agency get closer to its vision. Additionally, your local government should base its department’s strategic plan on its mission statement. Consider asking the following questions to articulate the critical components of the strategy:
- What are the top concerns that your government must address?
- Which forthcoming public projects are most important to your constituents?
Every government has risks that require attention through policy and infrastructure developments. A comprehensive assessment of the different risks to your community may include the following:
- National issues: At the federal level, social and economic concerns arise and citizens on both sides may be dissatisfied with their government’s shortcomings. Considering which issues are most essential at the national level can enable your community to make localized efforts to address them.
- Constituent dissatisfaction: Angry constituents equals a poor reelection campaign. To avoid unfavorable government-constituent relations, your local government should examine which topics are most beneficial to your community and analyze these concerns.
- Economic hardship: Local governments must examine the impact of inflation on local companies, citizens and budgets.
- Natural disasters: Which natural disasters are the greatest threat to your area? What steps have been taken or are being made to address these events, reduce risks and communicate with the public?
- Cybercrime: Cybercriminals have been creating data breaches in municipal governments for years, and attacks are increasing daily. Have your local government invested in cyber-safe technologies and backed up its data?
- International challenges: Do you need help attracting new government employees due to intergovernmental challenges? Do your internal procedures need to be more effective and costly? Do you have an up-to-date information technology strategy? One of the leading reasons for inefficient bureaucracy is a failure to recognize and handle such difficulties.
- Public policies: Which national and state legislation are the most important for your municipality to handle in the near future in terms of public policy? What consequences will you face if you do not address these policies?
After reviewing all the significant risks, it’s time to prioritize the most critical ones and develop a strategy to manage them. List the top focus areas that are crucial to your citizens or represent significant risks to your community’s health, safety, quality and economy. Your focus areas should also align with the local government’s and community’s future aspirations. Although it would be ideal to address all areas immediately, it could be more realistic. Try to prioritize a few critical issues.
Strategic objectives indicate what your city genuinely wants to achieve — they’re quite high-priority and should have a date attached. Your strategic goals should align with one or more of your focus areas and provide some tangibility to how you envision attaining your focus areas. Similar to selecting a few focus areas at a time, you can develop a few realistic and achievable strategic objectives. An example of a strategic objective can be to “improve the community’s safety by implementing a new reporting system by June 30, 2023.”
Now that you’ve decided on the primary focus areas and objectives, it’s time to consider how to execute them. A game plan defines what the government will need to do to achieve its goals. An actionable game plan assists in breaking down the bigger picture into smaller, more attainable results and activities. At this phase in your strategic planning process, you will begin to define the steps you will take to attain specific goals and the talents, expertise and resources required.

KPIs track progress toward your strategic goals. KPIs are quantitative metrics that demonstrate your government’s progress toward essential strategic objectives. KPIs tell you whether or not you have met your strategic target. Once KPIs have been determined, describe who is responsible for what and give them a job using your local government management tool to keep everyone organized and accountable.
Following your department’s strategy’s completion and policymakers’ approval of budgets and deadlines for major projects, it’s time to begin implementing your government initiatives. File requests for proposals (RFPs) for private-sector partnerships, fill out the necessary documentation and clarify who is doing what and when.
Taking strategic action to address concerns entails some risk in and of itself. You’ll need to pay close attention to your KPIs and adjust if problems with fulfilling timelines and budgets develop. If such problems arise, you must assess whether parts of the process may be expedited using government technology. Automation will save you time and money while increasing the likelihood of project success in your management planning.
A government strategic plan is the first vital step toward achieving governmental goals. The execution of these plans also plays a pivotal role in the goals’ success. A government runs high-level plans that cascade down and across multiple departments — which can make managing the execution of strategic plans more challenging. This is because different departments work with tools that support their specific work and role. As a result, information is stockpiled across these departments, making planning and organization a manual process.
Transform your strategic planning and execution process with strategic planning software built for your organization. AchieveIt is a FedRAMP-authorized cloud-based platform that connects, manages and executes mission-critical plans and activities for federal government agencies. AchieveIt is a platform that easily tracks the performance of all your integrated plans while automating time-consuming update collection. Managing all these moving parts goes from multiple spreadsheets to a single, easy-to-use platform.
By utilizing AchieveIt, federal government agencies can:
- Establish uniformity in data collection and reporting.
- Create visibility across plans and initiatives to know what needs attention.
- Promote accountability for mission execution.
- Make informed decisions with real-time data and proper context.
- Monitor the performance of long-term initiatives with dashboards and reports.
- Connect all its plans and strategies in one single place.

Do you need help developing and aligning your plans? Since planning and executing is more than just software, AcieveIt’s expert team will partner with you. Our strategy experts can ensure you stay on track and offer advice on how other federal agencies approach planning and execution. Allow AchieveIt to make your agency more efficient, so you can better serve the public while focusing on achieving mission-critical objectives. Request a demo or give us a call at 1-800-535-1559 today.
Related Posts

Four Stages for Successful Cultural Transformation in Organizations

Measuring Progress: KPIs for Tracking Strategy Implementation

How to Leverage Strategic Leadership in Turbulent Times
Hear directly from our awesome customers
See first-hand why the world's best leaders use AchieveIt
See AchieveIt in action
Stay in the know. Join our community of subscribers.
Subscribe for plan execution content sent directly to your inbox.
Mobile Menu Overlay
The White House 1600 Pennsylvania Ave NW Washington, DC 20500
FACT SHEET: Companies, Non-Profits, Government Agencies Answer Biden- Harris Call: Make Combined Commitment to Alert Tens of Millions of Americans to Emergency Rental Assistance
Major companies, non-profits, and government agencies from the Social Security Administration to the Department of Veterans Affairs, to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have answered the Biden-Harris Administration’s Call to Action to spread the word and alert Americans that emergency rental assistance is available. The combined commitments announced today – part of an ongoing all-out push to make sure tenants and landlords take advantage of federal rental assistance to help cover rent, utilities, and other housing costs and keep people in their homes – could reach tens of millions of Americans.
The continued call to action coincides with the launch of a new rental assistance finder produced by the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB). Americans who may be behind on rent can go to ConsumerFinance.gov/RentHelp and input information on their location to find local rental assistance programs in their area and apply for assistance.
Thanks to the American Rescue Plan, billions of dollars in federal rental assistance is available to renters who are behind on housing costs, as well as landlords who have struggled during the pandemic. The Administration is building on a whole-of-government effort and engaging a wide variety of stakeholders to spread awareness of the CFPB’s new tool, as well as the resources available to assist tenants and landlords.
Emergency rental assistance is available to tenants in all 50 states, Washington, D.C., territories, and in Tribal areas, and will continue to be available after the expiration of the CDC eviction moratorium on August 1, 2021. The continued Call to Action builds on the groundwork laid over the past several months by the Administration to engage renters and landlords, including hosting two virtual convenings with thousands of participants to share best practices on eviction prevention and build local plans of action, streamline guidance for the rental assistance program to make it easier and more efficient, and engage agencies across the federal government to help get the word out to households in need.
For more general information about the Emergency Rental Assistance program, visit the unified federal housing assistance portal hosted by the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau .
Agencies across the federal government, non-profit groups, faith-based organizations, and private sector companies are responding to the Biden-Harris Administration’s call to action to raise awareness. We expect that these efforts will reach tens of millions of Americans.
Private sector and non-profit commitments include:
- PayPal , where many pay their rent and monthly bills, will include messaging on emergency rental assistance and a link to the CFPB look-up tool in their PayPal and Venmo apps and on paypal.com.
- Square, Inc. will provide information about the CFPB tool and emergency rental assistance on Cash App – a popular place to pay rent and bills that as of December 2020 had more than 36 million monthly transacting active customers – and on their Square Seller Community platform.
- GoFundMe will send direct emails to roughly 20,000 people who have recently started fundraising campaigns in the “food, rent, or monthly bills” category on the GoFundMe site.
- Lyft will spread the word about emergency rental assistance and the new CFPB tool via a blog post for the Lyft Community.
- Avail , a property management application that touches landlords and renters, will send emails directly to their users and will post a banner on their website with an anticipated reach of at least 21,000 people per week.
- Propel, a mission-driven financial technology company, will connect more than 5 million low-income families to resources to help them receive emergency rental assistance.
- National Apartment Association will send an alert to their 90,000 members nationwide.
- National Multifamily Housing Coalition will share the CFPB tool with their 10,000 members through emails and a newsletter.
- The National Low Income Housing Coalition will include a link to the CFPB tool on their website, place an article about the tool and emergency rental assistance in their newsletter which is distributed to 135,000 people, and will brief stakeholders on their weekly call.
- United Way will raise awareness through their state associations and by sharing the information with the United Way Financial Stability Cohort.
- The Arc , a non-profit dedicated to promoting and protecting human rights of people with intellectual and developmental disabilities, will send an email with the information to their 600 national chapters.
- Children’s Defense Fund will share the information with their state offices and will publish a blog post promoting the CFPB tool.
- Operation HOPE , a non-profit organization dedicated to poverty alleviation and financial inclusion for low and moderate-income youth and adults, will share the CFPB tool and information on emergency rental assistance with a network of over 180 community-based financial coaches and will include the information in their weekly news briefing which reaches over 60,000 people.
- Bread for the World , a faith-based organization dedicated to poverty and hunger alleviation, will host regional events throughout the country with local faith leaders and churches to educate them about emergency rental assistance.
This Call to Action remains open to everyone – other companies, non-profits, faith-based organizations, and more can answer the Call to Action by leveraging their own communications channels to spread the word.
Commitments from the Administration include:
- The Department of Veterans Affairs is sharing the information in a newsletter that reaches 12 million veterans.
- The Social Security Administration is creating a new, special web page in both English and Spanish dedicated to emergency rental assistance and linking to the CFPB tool.
- The U.S. Department of Agriculture is building off of previous outreach efforts by sending letters to 65,000 people who live in USDA multi-family properties who are not receiving rental assistance; sharing information with Food Nutrition Service Regional Leads who will then share information with State Departments of Social Services that work with SNAP recipients; and holding a webinar in the coming weeks to provide background on emergency rental assistance.
- The Administration for Community Living (ACL) is sharing the information about emergency rental assistance with 200,000 community-based organizations that serve people with disabilities and older adults, many of whom are low income and at higher risk for eviction.
- The Administration for Children and Families (ACF) is amplifying the existence of emergency rental assistance and the new CFPB tool with program grantees who can pass along information in the communities they serve.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is sharing the information about emergency rental assistance with healthcare providers and local health departments, and is putting the information on the CDC’s COVID-19 website.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) is incorporating messaging around the CFPB tool and emergency rental assistance into call center scripts and will share with partners via their listserv.
- Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) is promoting the CFPB tool and emergency rental assistance via the Maternal and Child Health Bureau and the Federal Office of Rural Policy.
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) is sending emergency rental assistance information to state offices of mental health and homelessness coordinators throughout the country that work with the Projects for Assistance in Transition for Homelessness (PATH) program. The PATH program provides support to individuals with serious mental illness who are experiencing homelessness.
- The Department of the Treasury is sharing the CFPB tool with state and local governments and tribes who are administering emergency rental assistance programs.
- The Department of Housing and Urban Development is hosting webinars for non-profit groups and faith-based organizations and is developing their own website to distribute information on emergency rental assistance.
- The U.S. Interagency Council on Homelessness is distributing information about emergency rental assistance through a newsletter that reaches over 34,000 people.
- The Census Bureau will share the CFPB tool and information on emergency rental assistance with members of their Census Counts and States Count lists. The Census Counts list includes over 60 national organizations with a deep investment in meeting the needs of marginalized communities and the States Count list includes partners in all 50 states plus the District of Columbia.
Stay Connected
We'll be in touch with the latest information on how President Biden and his administration are working for the American people, as well as ways you can get involved and help our country build back better.
Opt in to send and receive text messages from President Biden.
2024 federal budget's key takeaways: Housing and carbon rebates, students and sin taxes
Budget sees nearly $53b in new spending over the next 5 years.

What's in the new federal budget?
Social sharing.
Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland today tabled a 400-page-plus budget her government is pitching as a balm for anxious millennials and Generation Z.
The budget proposes $52.9 billion in new spending over five years, including $8.5 billion in new spending for housing. To offset some of that new spending, Ottawa is pitching policy changes to bring in new revenue.
Here are some of the notable funding initiatives and legislative commitments in budget 2024.
Ottawa unloading unused offices to meet housing targets
One of the biggest pillars of the budget is its housing commitments. Before releasing the budget, the government laid out what it's calling Canada's Housing Plan — a pledge to "unlock" nearly 3.9 million homes by 2031.

The government says two million of those would be net new homes and it believes it can contribute to more than half of them.
It plans to do that by:
- Converting underused federal offices into homes. The budget promises $1.1 billion over ten years to transform 50 per cent of the federal office portfolio into housing.
- Building homes on Canada Post properties. The government says the 1,700-plus Canada Post offices across the country can be used to build new homes while maintaining postal services. The federal government says it's assessing six Canada Post properties in Quebec, Alberta and British Columbia for development potential "as a start."
- Rethinking National Defence properties. The government is promising to look at redeveloping properties and buildings on National Defence lands for military and civilian use.
- Building apartments. Ottawa is pledging a $15 billion top-up to the Apartment Construction Loan Program, which says it will build 30,000 new homes across Canada.
Taxing vacant land?
As part of its push on housing, the federal government also says it's looking at vacant land that could be used to build homes.
It's not yet committing to new measures but the budget says the government will consider introducing a new tax on residentially zoned vacant land.
- Freeland's new federal budget hikes taxes on the rich to cover billions in new spending
- Are you renting with no plans to buy? Here's what the federal budget has for you
The government said it plans to launch consultations on the measure later this year.
Help for students
There's also something in the budget for students hunting for housing.

The government says it will update the formula used by the Canada Student Financial Assistance Program to calculate housing costs when determining financial need, to better reflect the cost of housing in the current climate.
The government estimates this could deliver more aid for rent to approximately 79,000 students each year, at an estimated cost of $154.6 million over five years.
- Updated Federal budget's funding boost for defence spread out over multiple years
- Liberals pledge $9B in new money for Indigenous communities in 2024 budget
The government is also promising to extend increased student grants and interest-free loans, at an estimated total cost of $1.1 billion this year.
Increase in taxes on capital gains
To help cover some of its multi-billion dollar commitments, the government is proposing a tax hike on capital gains — the profit individuals make when assets like stocks and second properties are sold.
The government is proposing an increase in the taxable portion of capital gains, up from the current 50 per cent to two thirds for annual capital gains over $250,000.
New investment to lead 'housing revolution in Canada,' Freeland says
Freeland said the change would impact the wealthiest 0.1 per cent.
There's still some protection for small businesses. There's been a lifetime capital gains exemption which allows Canadians to exempt up to $1,016,836 in capital gains tax-free on the sale of small business shares and farming and fishing property. This June the tax-free limit will be increased to $1.25 million and will continue to be indexed to inflation thereafter, according to the budget.
The federal government estimates this could bring in more than $19 billion over five years, although some analysts are not convinced.
Disability benefit amounts to $200 per month
Parliament last year passed the Canada Disability Benefit Act, which promised to send a direct benefit to low-income, working-age people with disabilities.
Budget 2024 proposes funding of $6.1 billion over six years, beginning this fiscal year, and $1.4 billion per year ongoing, for a new Canada Disability Benefit.
Advocates had been hoping for something along the lines of $1,000 per month per person . They'll be disappointed.
According to the budget document, the maximum benefit will amount to $2,400 per year for low income individuals with disabilities between the ages of 18 and 64 — about $200 a month.
- Federal government plans to lease public lands for construction through new housing strategy
- Alberta premier says she's prepared to take Ottawa to court over housing deals
The government said it plans for the Canada Disability Benefit Act to come into force in June 2024 and for payments to start in July 2025.
Carbon rebate for small businesses coming
The federal government has heard an earful from small business advocates who accuse it of reneging on a promise to return a portion of carbon pricing revenues to small businesses to mitigate the tax's economic costs.
- What's behind the carbon tax, and does it work?
- Federal government scales back carbon tax rebates for small businesses
The budget proposes to return fuel charge proceeds from 2019-20 through 2023-24 to an estimated 600,000 businesses with 499 or fewer employees through a new refundable tax credit.
The government said this would deliver $2.5 billion directly to Canada's small- and medium-sized businesses.
Darts and vape pods will cost more
Pitching it as a measure to cut the number of people smoking and vaping, the Liberals are promising to raise revenues on tobacco and smoking products.
- Just Asking wants to know: What questions do you have about quitting smoking or vaping? Do you think sin taxes will encourage smoking cessation? Fill out the details on this form and send us your questions ahead of our show on April 20.
Starting Wednesday, the total tobacco excise duty will be $5.49 per carton. The government estimates this could increase federal revenue by $1.36 billion over five years starting in 2024-25.

The budget also proposes to increase the vaping excise duty rates by 12 per cent effective July 1. That means an increase of 12 to 24 cents per pod, depending on where you live.
- 'Stay the hell away from our kids': Health minister vows to restrict nicotine pouches — but how?
Ottawa hopes this increase in sin taxes will bring in $310 million over five years, starting in 2024-25.
More money for CBC
Heritage Minister Pascale St-Onge has mused about redefining the role of the public broadcaster before the next federal election . But before that happens, CBC/Radio-Canada is getting a top-up this year.

The budget promises $42 million more in 2024-25 for CBC/Radio-Canada for "news and entertainment programming." CBC/Radio-Canada received about $1.3 billion in total federal funding last year.
The government says it's doing this to ensure that Canadians across the country, including rural, remote, Indigenous and minority language communities, have access to independent journalism and entertainment.
Last year, the CBC announced a financial shortfall, cut 141 employees and eliminated 205 vacant positions. In a statement issued Tuesday, CBC spokesperson Leon Mar said the new funding means the corporation can balance its budget "without significant additional reductions this year."
Boost for Canada's spy agency

As the government takes heat over how it has handled the threat of foreign election interference, it's promising more money to bolster its spy service.
The Canadian Security Intelligence Service is in line to receive $655.7 million over eight years, starting this fiscal year, to enhance its intelligence capabilities and its presence in Toronto.
- CSIS chief defends his spies' work after PM casts doubt on reliability of agency's reports
- Trudeau says it's his job to question CSIS intelligence, call out 'contradictions'
The budget also promises to guarantee up to $5 billion in loans for Indigenous communities to participate in natural resource development and energy projects in their territories.
These loans would be provided by financial institutions or other lenders and guaranteed by the federal government, meaning Indigenous borrowers who opt in could benefit from lower interest rates, the budget says.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

Catharine Tunney is a reporter with CBC's Parliament Hill bureau, where she covers national security and the RCMP. She worked previously for CBC in Nova Scotia. You can reach her at [email protected]
- Follow Cat on Twitter
Add some “good” to your morning and evening.
Your weekly guide to what you need to know about federal politics and the minority Liberal government. Get the latest news and sharp analysis delivered to your inbox every Sunday morning.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Develop a strategic plan with clear goals and objectives. Choose a suitable legal structure for your non-profit organization. Establish a dedicated board of directors for guidance and governance. Create a strong fundraising strategy to secure funds. Build partnerships for collaboration and extra support.
A nonprofit business plan template provides a strategic overview of your nonprofit. It's a breakdown of all higher-level information about your organization, such as the board of directors and your core mission. Use your nonprofit business plan template to give your staff, the board, potential donors, and government funding agencies an ...
To develop accurate projections, consider the following key steps: Estimate startup costs for your non-profit, including administrative expenses, program development, and marketing efforts. Forecast revenue sources such as grants, donations, fundraising events, and membership fees. Project program costs.
This template has all the core components of a nonprofit business plan. It includes room to detail the organization's background, management team key personnel, current and future youth program offerings, promotional activities, operations plan, financial statements, and much more. Download Nonprofit Business Plan Template for Youth Program.
According to Propel Nonprofits, business plans usually should have four components that identify revenue sources/mix; operations costs; program costs; and capital structure. A business plan outlines the expected income sources to support the charitable nonprofit's activities. What types of revenue will the nonprofit rely on to keep its engine ...
Step 3: Outline. Create an outline of your nonprofit business plan. Write out everything you want your plan to include (e.g. sections such as marketing, fundraising, human resources, and budgets). An outline helps you focus your attention. It gives you a roadmap from the start, through the middle, and to the end.
Here are the essential components: Executive Summary - This is a summary of your entire business plan, and should include a brief description of your nonprofit organization, its mission and goals, the problem you are trying to solve, your proposed solutions, and an overview of your financial projections. Organization Overview - This section ...
Marketing Plan - This section of your nonprofit business plan will detail your products, programs and services, your overall marketing strategies and tactics, and how you will measure success. It should include information on your target market, positioning, branding, communications, and lead generation. Operations Plan - In the Operations ...
A non-profit business plan is simply a roadmap for a non-profit organization, one which outlines the organization's goals and objectives, and how it plans to attain them. A non-profit is a business entity that is started for any specified purpose other than making a profit. The most common reason for a non-profit organization is charity work.
Some possible partners could include other nonprofit organizations that serve similar or complementary missions, businesses that align with the nonprofit's goals and values, government agencies that support the nonprofit's work, and foundations or philanthropic organizations that provide funding for similar causes. 4. Build a board of ...
Write a fundraising plan. This part is the most important element of your business plan. In addition to providing required financial statements (e.g., the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement), identify potential sources of funding for your nonprofit. These may include individual donors, corporate donors, grants, or in-kind ...
We've put together this sample nonprofit business plan to show you what you should include when you write your business plan. Routing Number: 263181384 . Quick Links ... The National Credit Union Administration (NCUA) is a U.S. Government Agency. Traditional and Roth IRAs (Individual Retirement Accounts) are insured to $250,000 by the NCUA. ...
Simply describe how your nonprofit runs on a day-to-day basis. And don't forget to include information on your staff. 7. Impact. The impact section of your non-profit business plan should describe the difference you hope to make in the world. That is your chance to get specific about your goals and objectives.
Outline the financial plan. 1. Create an executive summary. The first section of nonprofit business plans is the executive summary. The executive summary should describe your organization and the contents of your nonprofit business plan. This section should be no more than a page, briefly covering the following:
Download our Ultimate Nonprofit Business Plan Template here. Below are sample plans to help guide you in writing a nonprofit business plan. Example #1 - Kids Are Our First Priority (KAOFP) - a Nonprofit Youth Organization based in Chicago, IL. Example #2 - Church of the Sacred Heart - a Nonprofit Church based in St. Louis, MO.
Sources Used for This Article. [1] We use the term "business planning" to refer to the process of developing a comprehensive document that sets forth what an organization is working to accomplish and how it intends to succeed. Others use the term "strategic planning" to encompass the same set of activities.
Applying for 501 (c) (3) Tax-Exempt Status. If you want to file for federal tax-exempt status, visit Tax Information for Charities & Other Non-Profits or contact the IRS at 1-877-829-5500. Ask about the following free items: SS-4 - Employer Identification Number.
ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Government Agencies is designed to help government agencies effectively outline and manage their strategic goals, objectives, and action plans. Here are the main elements of this template: Custom Statuses: Easily track progress with four custom statuses - Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do - to ...
Total Capital and Liabilities. $154,200. Total Funding. $160,000. Need real financials. We recommend using LivePlan as the easiest way to create automatic financials for your own business plan. Create your own business plan.
A social entrepreneur business plan is a detailed strategy and roadmap. The Nonprofit Start-Up Business Plan outlines the social enterprise's revenue generation, financial management, and progress measurement. By creating a comprehensive business plan, social entrepreneurs can ensure that their social enterprise is well ...
How to Create a Strategic Plan for Your Government Department or Agency. Conduct Internal and External Analysis. Consider the Vision and Mission. Perform a Holistic Risk-Assessment. List the Focus Areas. Develop Strategic Objectives. Set up an Actionable Game Plan. Utilize Measurable KPIs. Put the Plan Into Action.
Agencies across the federal government, non-profit groups, faith-based organizations, and private sector companies are responding to the Biden-Harris Administration's call to action to raise ...
For individuals without a line provided by an agency, our best discount for first responders and their families is our Go5G First Responder plan. Go5G First Responder plan gives first responders and their families 40% off lines 2-6 vs. Go5G with AutoPay discount using eligible payment method, without Autopay, $5 more/line/mo; debit or bank acct ...
Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland today tabled a 400-page-plus budget her government is pitching as a balm for anxious millennials and Generation Z. The budget proposes $52.9 billion in new ...
The Biden administration released the draft text of its revised student loan forgiveness plan. Here's what to know.