Read our research on: Gun Policy | International Conflict | Election 2024

Regions & Countries
1. americans’ views on whether, and in what circumstances, abortion should be legal.
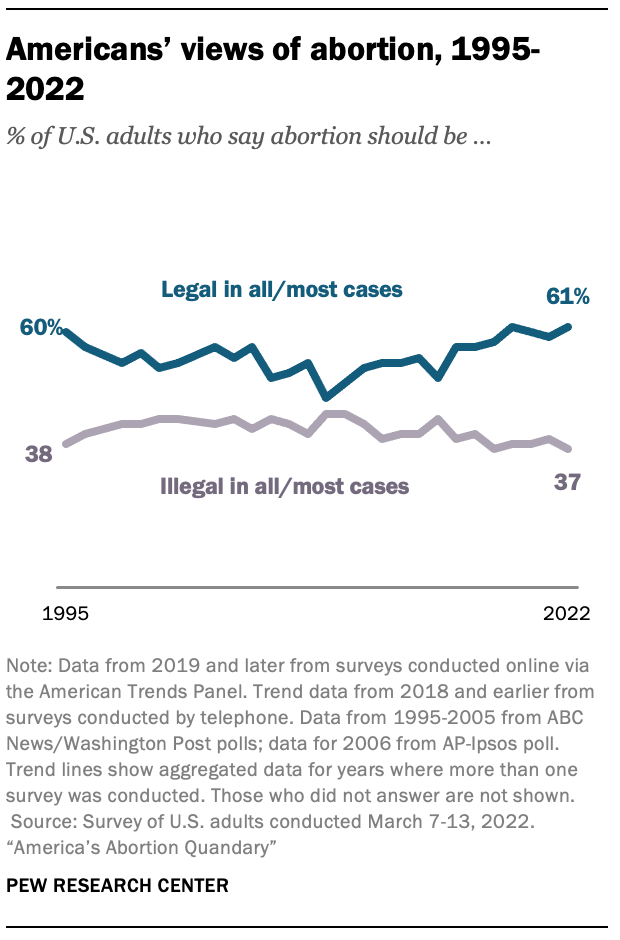
As the long-running debate over abortion reaches another key moment at the Supreme Court and in state legislatures across the country , a majority of U.S. adults continue to say that abortion should be legal in all or most cases. About six-in-ten Americans (61%) say abortion should be legal in “all” or “most” cases, while 37% think abortion should be illegal in all or most cases. These views have changed little over the past several years: In 2019, for example, 61% of adults said abortion should be legal in all or most cases, while 38% said it should be illegal in all or most cases. Most respondents in the new survey took one of the middle options when first asked about their views on abortion, saying either that abortion should be legal in most cases (36%) or illegal in most cases (27%).
Respondents who said abortion should either be legal in all cases or illegal in all cases received a follow-up question asking whether there should be any exceptions to such laws. Overall, 25% of adults initially said abortion should be legal in all cases, but about a quarter of this group (6% of all U.S. adults) went on to say that there should be some exceptions when abortion should be against the law.
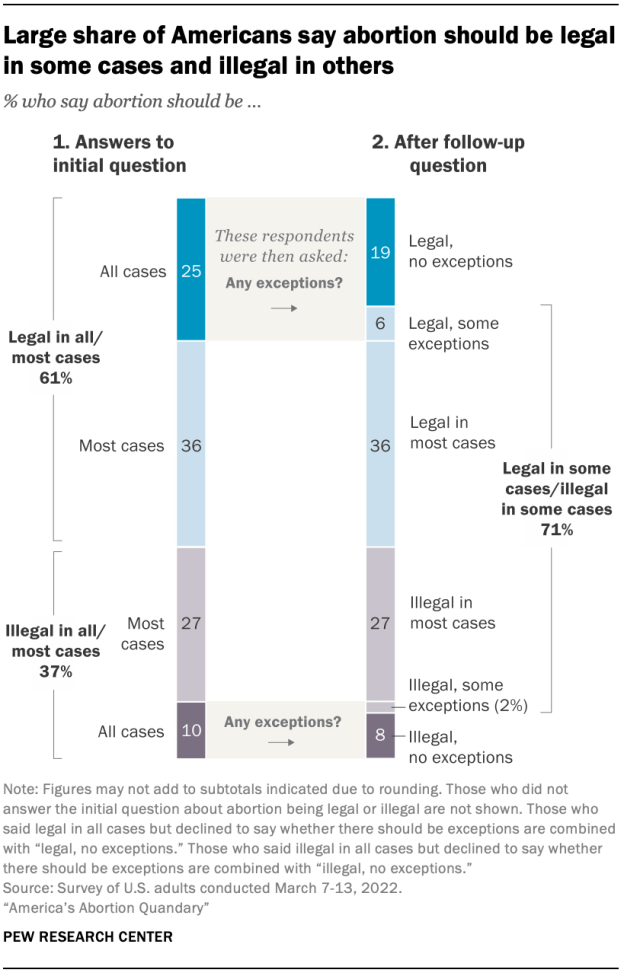
One-in-ten adults initially answered that abortion should be illegal in all cases, but about one-in-five of these respondents (2% of all U.S. adults) followed up by saying that there are some exceptions when abortion should be permitted.
Altogether, seven-in-ten Americans say abortion should be legal in some cases and illegal in others, including 42% who say abortion should be generally legal, but with some exceptions, and 29% who say it should be generally illegal, except in certain cases. Much smaller shares take absolutist views when it comes to the legality of abortion in the U.S., maintaining that abortion should be legal in all cases with no exceptions (19%) or illegal in all circumstances (8%).
There is a modest gender gap in views of whether abortion should be legal, with women slightly more likely than men to say abortion should be legal in all cases or in all cases but with some exceptions (63% vs. 58%).
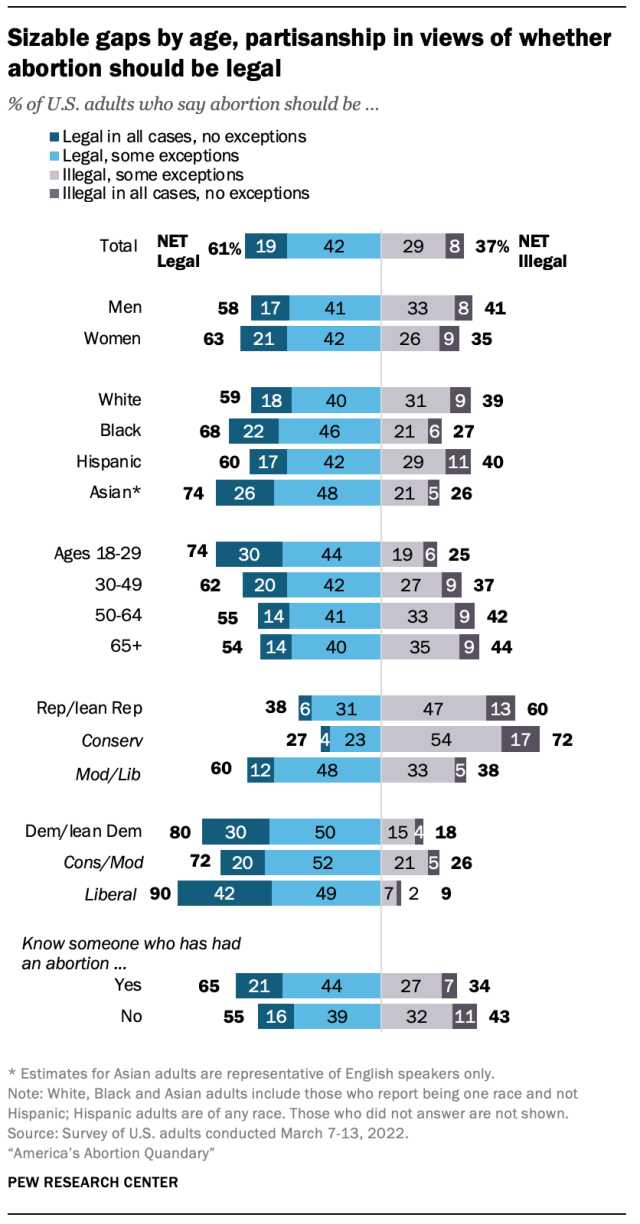
Younger adults are considerably more likely than older adults to say abortion should be legal: Three-quarters of adults under 30 (74%) say abortion should be generally legal, including 30% who say it should be legal in all cases without exception.
But there is an even larger gap in views toward abortion by partisanship: 80% of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents say abortion should be legal in all or most cases, compared with 38% of Republicans and GOP leaners. Previous Center research has shown this gap widening over the past 15 years.
Still, while partisans diverge in views of whether abortion should mostly be legal or illegal, most Democrats and Republicans do not view abortion in absolutist terms. Just 13% of Republicans say abortion should be against the law in all cases without exception; 47% say it should be illegal with some exceptions. And while three-in-ten Democrats say abortion should be permitted in all circumstances, half say it should mostly be legal – but with some exceptions.
There also are sizable divisions within both partisan coalitions by ideology. For instance, while a majority of moderate and liberal Republicans say abortion should mostly be legal (60%), just 27% of conservative Republicans say the same. Among Democrats, self-described liberals are twice as apt as moderates and conservatives to say abortion should be legal in all cases without exception (42% vs. 20%).
Regardless of partisan affiliation, adults who say they personally know someone who has had an abortion – such as a friend, relative or themselves – are more likely to say abortion should be legal than those who say they do not know anyone who had an abortion.
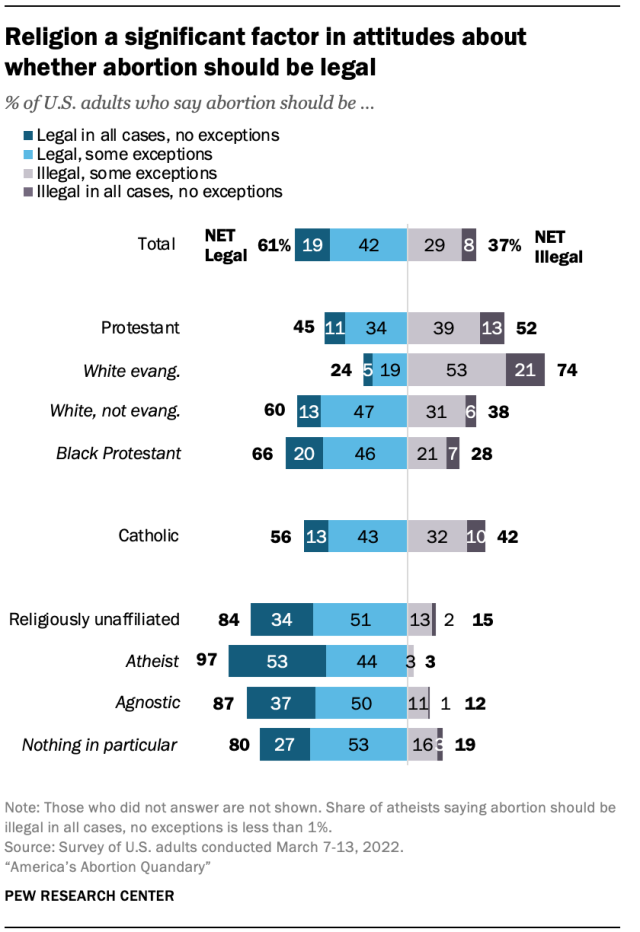
Views toward abortion also vary considerably by religious affiliation – specifically among large Christian subgroups and religiously unaffiliated Americans.
For example, roughly three-quarters of White evangelical Protestants say abortion should be illegal in all or most cases. This is far higher than the share of White non-evangelical Protestants (38%) or Black Protestants (28%) who say the same.
Despite Catholic teaching on abortion , a slim majority of U.S. Catholics (56%) say abortion should be legal. This includes 13% who say it should be legal in all cases without exception, and 43% who say it should be legal, but with some exceptions.
Compared with Christians, religiously unaffiliated adults are far more likely to say abortion should be legal overall – and significantly more inclined to say it should be legal in all cases without exception. Within this group, atheists stand out: 97% say abortion should be legal, including 53% who say it should be legal in all cases without exception. Agnostics and those who describe their religion as “nothing in particular” also overwhelmingly say that abortion should be legal, but they are more likely than atheists to say there are some circumstances when abortion should be against the law.
Although the survey was conducted among Americans of many religious backgrounds, including Jews, Muslims, Buddhists and Hindus, it did not obtain enough respondents from non-Christian groups to report separately on their responses.
Abortion at various stages of pregnancy
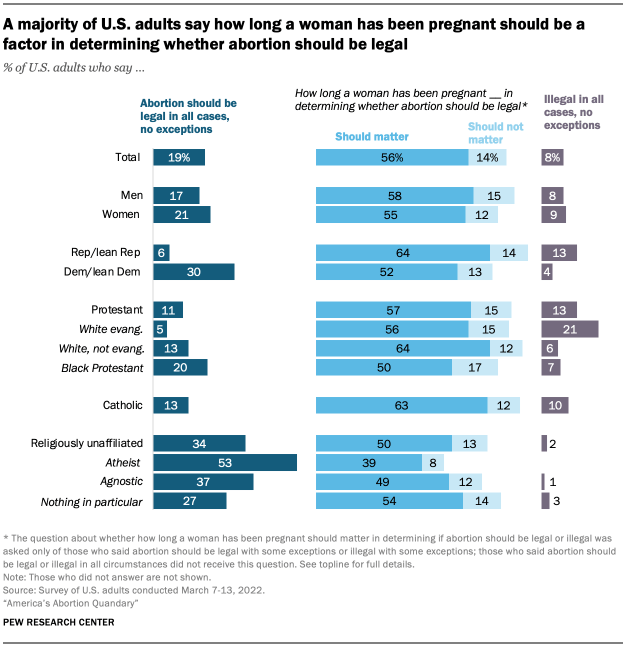
As a growing number of states debate legislation to restrict abortion – often after a certain stage of pregnancy – Americans express complex views about when abortion should generally be legal and when it should be against the law. Overall, a majority of adults (56%) say that how long a woman has been pregnant should matter in determining when abortion should be legal, while far fewer (14%) say that this should not be a factor. An additional one-quarter of the public says that abortion should either be legal (19%) or illegal (8%) in all circumstances without exception; these respondents did not receive this question.
Among men and women, Republicans and Democrats, and Christians and religious “nones” who do not take absolutist positions about abortion on either side of the debate, the prevailing view is that the stage of the pregnancy should be a factor in determining whether abortion should be legal.
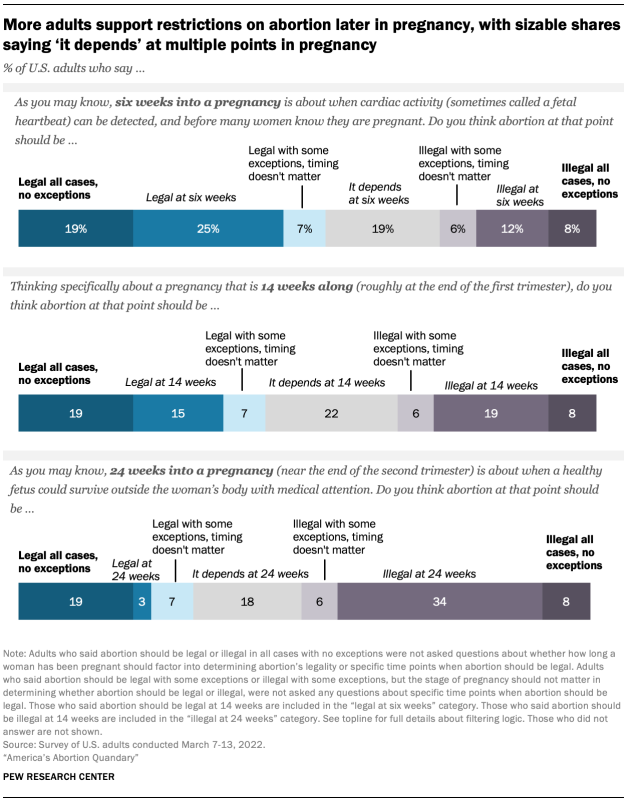
Americans broadly are more likely to favor restrictions on abortion later in pregnancy than earlier in pregnancy. Many adults also say the legality of abortion depends on other factors at every stage of pregnancy.
One-in-five Americans (21%) say abortion should be illegal at six weeks. This includes 8% of adults who say abortion should be illegal in all cases without exception as well as 12% of adults who say that abortion should be illegal at this point. Additionally, 6% say abortion should be illegal in most cases and how long a woman has been pregnant should not matter in determining abortion’s legality. Nearly one-in-five respondents, when asked whether abortion should be legal six weeks into a pregnancy, say “it depends.”
Americans are more divided about what should be permitted 14 weeks into a pregnancy – roughly at the end of the first trimester – although still, more people say abortion should be legal at this stage (34%) than illegal (27%), and about one-in-five say “it depends.”
Fewer adults say abortion should be legal 24 weeks into a pregnancy – about when a healthy fetus could survive outside the womb with medical care. At this stage, 22% of adults say abortion should be legal, while nearly twice as many (43%) say it should be illegal . Again, about one-in-five adults (18%) say whether abortion should be legal at 24 weeks depends on other factors.
Respondents who said that abortion should be illegal 24 weeks into a pregnancy or that “it depends” were asked a follow-up question about whether abortion at that point should be legal if the pregnant woman’s life is in danger or the baby would be born with severe disabilities. Most who received this question say abortion in these circumstances should be legal (54%) or that it depends on other factors (40%). Just 4% of this group maintained that abortion should be illegal in this case.
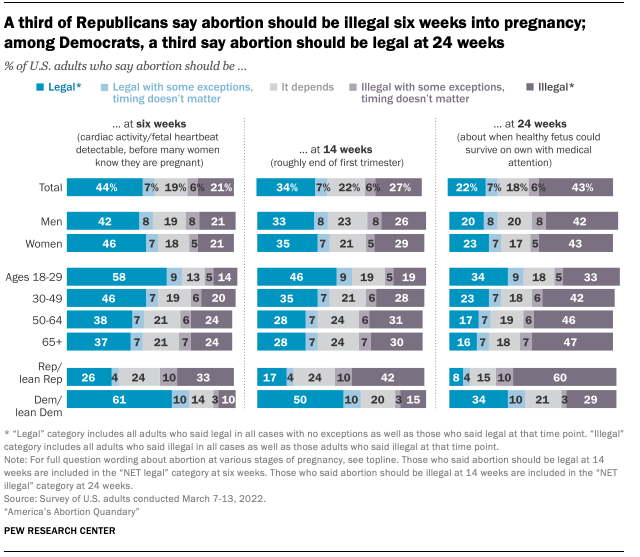
This pattern in views of abortion – whereby more favor greater restrictions on abortion as a pregnancy progresses – is evident across a variety of demographic and political groups.
Democrats are far more likely than Republicans to say that abortion should be legal at each of the three stages of pregnancy asked about on the survey. For example, while 26% of Republicans say abortion should be legal at six weeks of pregnancy, more than twice as many Democrats say the same (61%). Similarly, while about a third of Democrats say abortion should be legal at 24 weeks of pregnancy, just 8% of Republicans say the same.
However, neither Republicans nor Democrats uniformly express absolutist views about abortion throughout a pregnancy. Republicans are divided on abortion at six weeks: Roughly a quarter say it should be legal (26%), while a similar share say it depends (24%). A third say it should be illegal.
Democrats are divided about whether abortion should be legal or illegal at 24 weeks, with 34% saying it should be legal, 29% saying it should be illegal, and 21% saying it depends.
There also is considerable division among each partisan group by ideology. At six weeks of pregnancy, just one-in-five conservative Republicans (19%) say that abortion should be legal; moderate and liberal Republicans are twice as likely as their conservative counterparts to say this (39%).
At the same time, about half of liberal Democrats (48%) say abortion at 24 weeks should be legal, while 17% say it should be illegal. Among conservative and moderate Democrats, the pattern is reversed: A plurality (39%) say abortion at this stage should be illegal, while 24% say it should be legal.
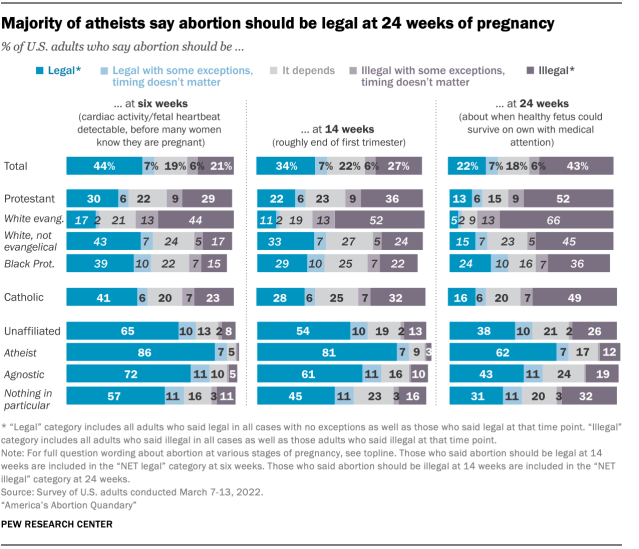
Christian adults are far less likely than religiously unaffiliated Americans to say abortion should be legal at each stage of pregnancy.
Among Protestants, White evangelicals stand out for their opposition to abortion. At six weeks of pregnancy, for example, 44% say abortion should be illegal, compared with 17% of White non-evangelical Protestants and 15% of Black Protestants. This pattern also is evident at 14 and 24 weeks of pregnancy, when half or more of White evangelicals say abortion should be illegal.
At six weeks, a plurality of Catholics (41%) say abortion should be legal, while smaller shares say it depends or it should be illegal. But by 24 weeks, about half of Catholics (49%) say abortion should be illegal.
Among adults who are religiously unaffiliated, atheists stand out for their views. They are the only group in which a sizable majority says abortion should be legal at each point in a pregnancy. Even at 24 weeks, 62% of self-described atheists say abortion should be legal, compared with smaller shares of agnostics (43%) and those who say their religion is “nothing in particular” (31%).
As is the case with adults overall, most religiously affiliated and religiously unaffiliated adults who originally say that abortion should be illegal or “it depends” at 24 weeks go on to say either it should be legal or it depends if the pregnant woman’s life is in danger or the baby would be born with severe disabilities. Few (4% and 5%, respectively) say abortion should be illegal at 24 weeks in these situations.
Abortion and circumstances of pregnancy
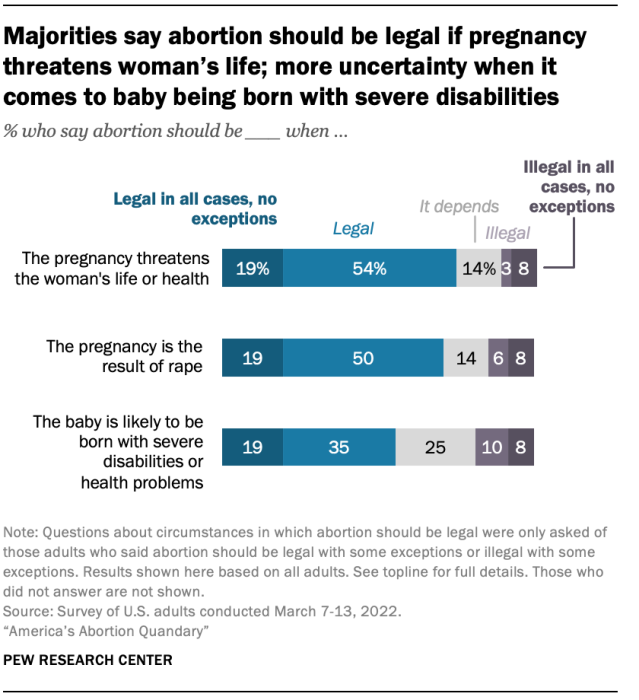
The stage of the pregnancy is not the only factor that shapes people’s views of when abortion should be legal. Sizable majorities of U.S. adults say that abortion should be legal if the pregnancy threatens the life or health of the pregnant woman (73%) or if pregnancy is the result of rape (69%).
There is less consensus when it comes to circumstances in which a baby may be born with severe disabilities or health problems: 53% of Americans overall say abortion should be legal in such circumstances, including 19% who say abortion should be legal in all cases and 35% who say there are some situations where abortions should be illegal, but that it should be legal in this specific type of case. A quarter of adults say “it depends” in this situation, and about one-in-five say it should be illegal (10% who say illegal in this specific circumstance and 8% who say illegal in all circumstances).
There are sizable divides between and among partisans when it comes to views of abortion in these situations. Overall, Republicans are less likely than Democrats to say abortion should be legal in each of the three circumstances outlined in the survey. However, both partisan groups are less likely to say abortion should be legal when the baby may be born with severe disabilities or health problems than when the woman’s life is in danger or the pregnancy is the result of rape.
Just as there are wide gaps among Republicans by ideology on whether how long a woman has been pregnant should be a factor in determining abortion’s legality, there are large gaps when it comes to circumstances in which abortions should be legal. For example, while a clear majority of moderate and liberal Republicans (71%) say abortion should be permitted when the pregnancy is the result of rape, conservative Republicans are more divided. About half (48%) say it should be legal in this situation, while 29% say it should be illegal and 21% say it depends.
The ideological gaps among Democrats are slightly less pronounced. Most Democrats say abortion should be legal in each of the three circumstances – just to varying degrees. While 77% of liberal Democrats say abortion should be legal if a baby will be born with severe disabilities or health problems, for example, a smaller majority of conservative and moderate Democrats (60%) say the same.
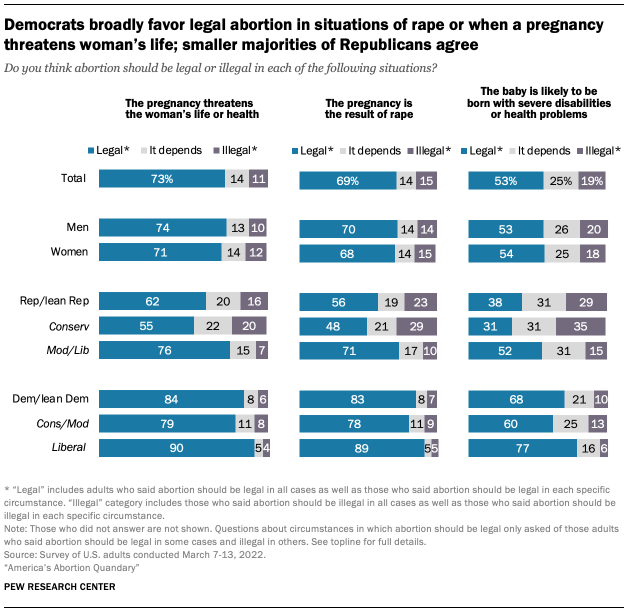
White evangelical Protestants again stand out for their views on abortion in various circumstances; they are far less likely than White non-evangelical or Black Protestants to say abortion should be legal across each of the three circumstances described in the survey.
While about half of White evangelical Protestants (51%) say abortion should be legal if a pregnancy threatens the woman’s life or health, clear majorities of other Protestant groups and Catholics say this should be the case. The same pattern holds in views of whether abortion should be legal if the pregnancy is the result of rape. Most White non-evangelical Protestants (75%), Black Protestants (71%) and Catholics (66%) say abortion should be permitted in this instance, while White evangelicals are more divided: 40% say it should be legal, while 34% say it should be illegal and about a quarter say it depends.
Mirroring the pattern seen among adults overall, opinions are more varied about a situation where a baby might be born with severe disabilities or health issues. For instance, half of Catholics say abortion should be legal in such cases, while 21% say it should be illegal and 27% say it depends on the situation.
Most religiously unaffiliated adults – including overwhelming majorities of self-described atheists – say abortion should be legal in each of the three circumstances.
Parental notification for minors seeking abortion
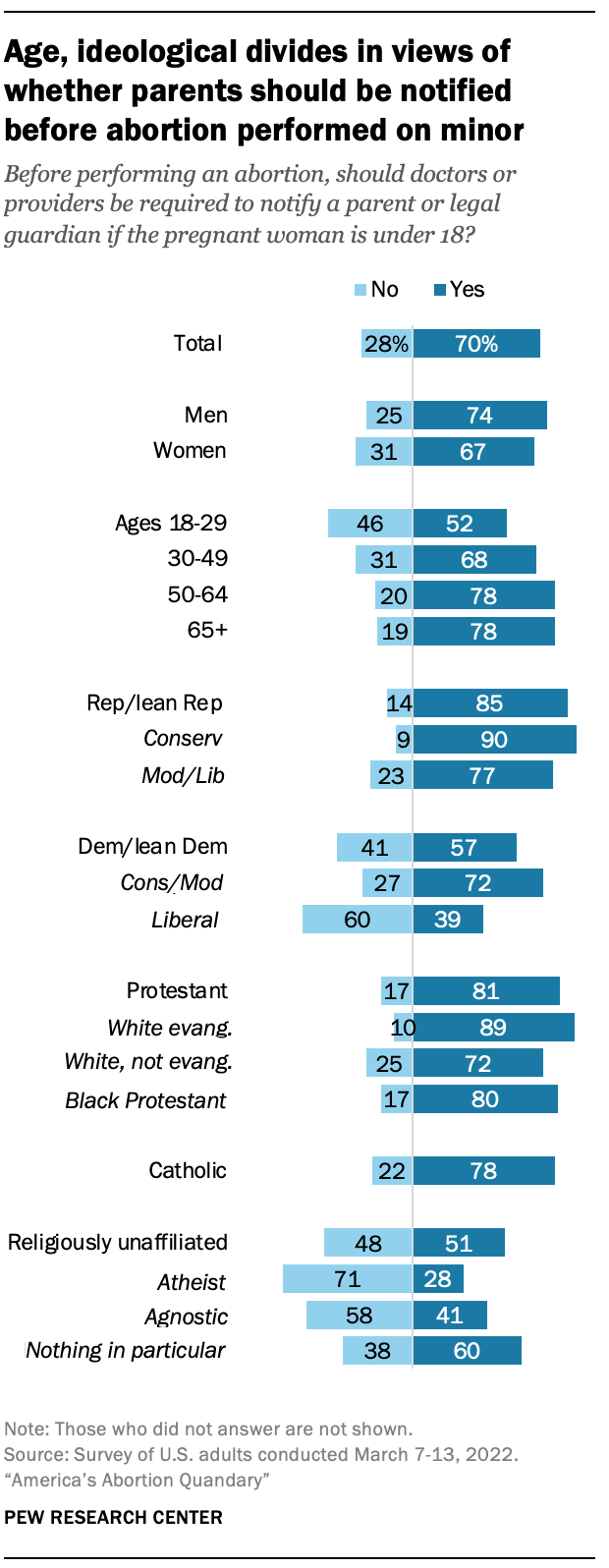
Seven-in-ten U.S. adults say that doctors or other health care providers should be required to notify a parent or legal guardian if the pregnant woman seeking an abortion is under 18, while 28% say they should not be required to do so.
Women are slightly less likely than men to say this should be a requirement (67% vs. 74%). And younger adults are far less likely than those who are older to say a parent or guardian should be notified before a doctor performs an abortion on a pregnant woman who is under 18. In fact, about half of adults ages 18 to 24 (53%) say a doctor should not be required to notify a parent. By contrast, 64% of adults ages 25 to 29 say doctors should be required to notify parents of minors seeking an abortion, as do 68% of adults ages 30 to 49 and 78% of those 50 and older.
A large majority of Republicans (85%) say that a doctor should be required to notify the parents of a minor before an abortion, though conservative Republicans are somewhat more likely than moderate and liberal Republicans to take this position (90% vs. 77%).
The ideological divide is even more pronounced among Democrats. Overall, a slim majority of Democrats (57%) say a parent should be notified in this circumstance, but while 72% of conservative and moderate Democrats hold this view, just 39% of liberal Democrats agree.
By and large, most Protestant (81%) and Catholic (78%) adults say doctors should be required to notify parents of minors before an abortion. But religiously unaffiliated Americans are more divided. Majorities of both atheists (71%) and agnostics (58%) say doctors should not be required to notify parents of minors seeking an abortion, while six-in-ten of those who describe their religion as “nothing in particular” say such notification should be required.
Penalties for abortions performed illegally
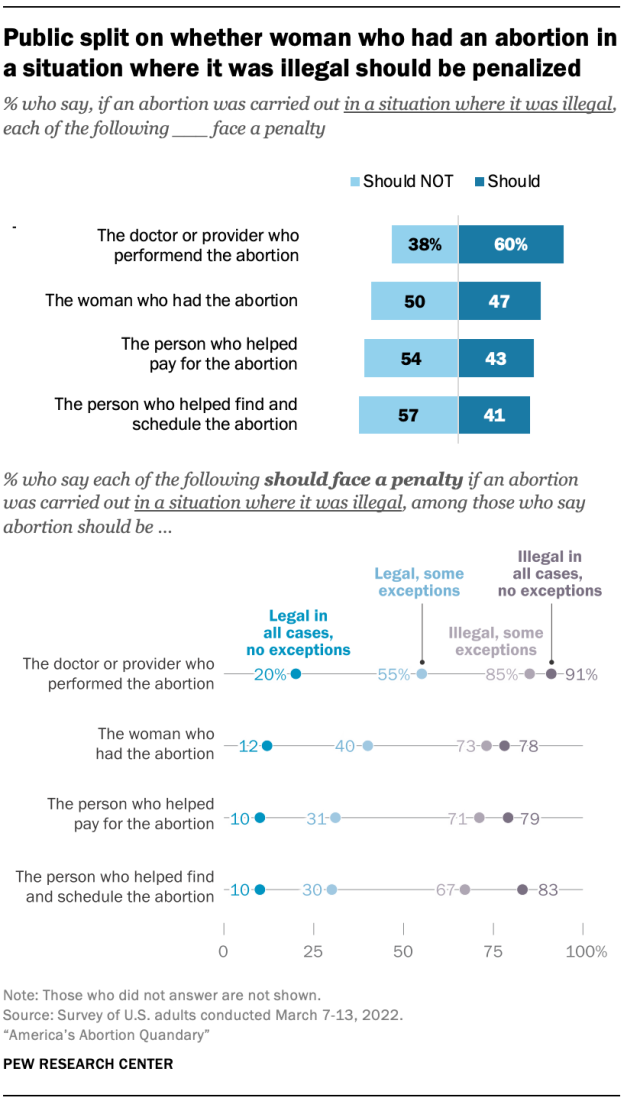
Americans are divided over who should be penalized – and what that penalty should be – in a situation where an abortion occurs illegally.
Overall, a 60% majority of adults say that if a doctor or provider performs an abortion in a situation where it is illegal, they should face a penalty. But there is less agreement when it comes to others who may have been involved in the procedure.
While about half of the public (47%) says a woman who has an illegal abortion should face a penalty, a nearly identical share (50%) says she should not. And adults are more likely to say people who help find and schedule or pay for an abortion in a situation where it is illegal should not face a penalty than they are to say they should.
Views about penalties are closely correlated with overall attitudes about whether abortion should be legal or illegal. For example, just 20% of adults who say abortion should be legal in all cases without exception think doctors or providers should face a penalty if an abortion were carried out in a situation where it was illegal. This compares with 91% of those who think abortion should be illegal in all cases without exceptions. Still, regardless of how they feel about whether abortion should be legal or not, Americans are more likely to say a doctor or provider should face a penalty compared with others involved in the procedure.
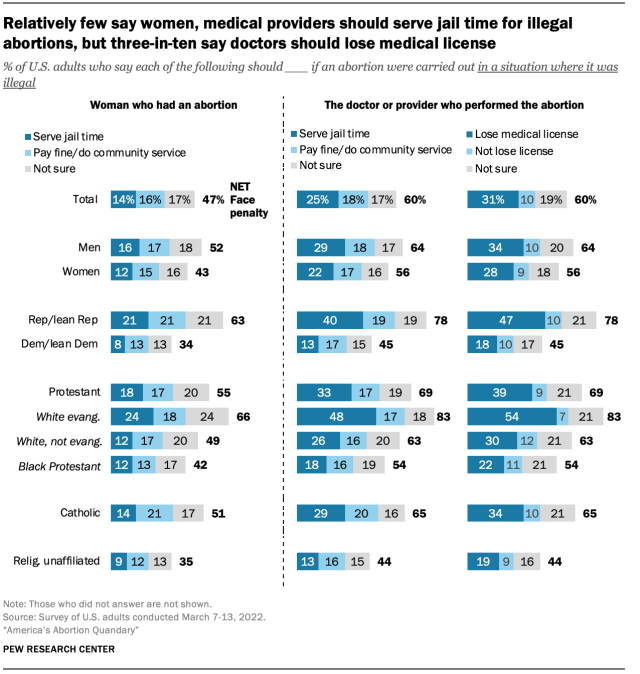
Among those who say medical providers and/or women should face penalties for illegal abortions, there is no consensus about whether they should get jail time or a less severe punishment. Among U.S. adults overall, 14% say women should serve jail time if they have an abortion in a situation where it is illegal, while 16% say they should receive a fine or community service and 17% say they are not sure what the penalty should be.
A somewhat larger share of Americans (25%) say doctors or other medical providers should face jail time for providing illegal abortion services, while 18% say they should face fines or community service and 17% are not sure. About three-in-ten U.S. adults (31%) say doctors should lose their medical license if they perform an abortion in a situation where it is illegal.
Men are more likely than women to favor penalties for the woman or doctor in situations where abortion is illegal. About half of men (52%) say women should face a penalty, while just 43% of women say the same. Similarly, about two-thirds of men (64%) say a doctor should face a penalty, while 56% of women agree.
Republicans are considerably more likely than Democrats to say both women and doctors should face penalties – including jail time. For example, 21% of Republicans say the woman who had the abortion should face jail time, and 40% say this about the doctor who performed the abortion. Among Democrats, far smaller shares say the woman (8%) or doctor (13%) should serve jail time.
White evangelical Protestants are more likely than other Protestant groups to favor penalties for abortions in situations where they are illegal. Fully 24% say the woman who had the abortion should serve time in jail, compared with just 12% of White non-evangelical Protestants or Black Protestants. And while about half of White evangelicals (48%) say doctors who perform illegal abortions should serve jail time, just 26% of White non-evangelical Protestants and 18% of Black Protestants share this view.
- Only respondents who said that abortion should be legal in some cases but not others and that how long a woman has been pregnant should matter in determining whether abortion should be legal received questions about abortion’s legality at specific points in the pregnancy. ↩
Sign up for our Religion newsletter
Sent weekly on Wednesday
Report Materials
Table of contents, majority of public disapproves of supreme court’s decision to overturn roe v. wade, wide partisan gaps in abortion attitudes, but opinions in both parties are complicated, key facts about the abortion debate in america, about six-in-ten americans say abortion should be legal in all or most cases, fact sheet: public opinion on abortion, most popular.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .

Princeton Legal Journal

The First Amendment and the Abortion Rights Debate
Sofia Cipriano
Following Dobbs v. Jackson ’s (2022) reversal of Roe v. Wade (1973) — and the subsequent revocation of federal abortion protection — activists and scholars have begun to reconsider how to best ground abortion rights in the Constitution. In the past year, numerous Jewish rights groups have attempted to overturn state abortion bans by arguing that abortion rights are protected by various state constitutions’ free exercise clauses — and, by extension, the First Amendment of the U.S. Constitution. While reframing the abortion rights debate as a question of religious freedom is undoubtedly strategic, the Free Exercise Clause is not the only place to locate abortion rights: the Establishment Clause also warrants further investigation.
Roe anchored abortion rights in the right to privacy — an unenumerated right with a long history of legal recognition. In various cases spanning the past two centuries, t he Supreme Court located the right to privacy in the First, Fourth, Fifth, Ninth, and Fourteenth Amendments . Roe classified abortion as a fundamental right protected by strict scrutiny, meaning that states could only regulate abortion in the face of a “compelling government interest” and must narrowly tailor legislation to that end. As such, Roe ’s trimester framework prevented states from placing burdens on abortion access in the first few months of pregnancy. After the fetus crosses the viability line — the point at which the fetus can survive outside the womb — states could pass laws regulating abortion, as the Court found that “the potentiality of human life” constitutes a “compelling” interest. Planned Parenthood of Southeastern Pennsylvania v. Casey (1992) later replaced strict scrutiny with the weaker “undue burden” standard, giving states greater leeway to restrict abortion access. Dobbs v. Jackson overturned both Roe and Casey , leaving abortion regulations up to individual states.
While Roe constituted an essential step forward in terms of abortion rights, weaknesses in its argumentation made it more susceptible to attacks by skeptics of substantive due process. Roe argues that the unenumerated right to abortion is implied by the unenumerated right to privacy — a chain of logic which twice removes abortion rights from the Constitution’s language. Moreover, Roe’s trimester framework was unclear and flawed from the beginning, lacking substantial scientific rationale. As medicine becomes more and more advanced, the arbitrariness of the viability line has grown increasingly apparent.
As abortion rights supporters have looked for alternative constitutional justifications for abortion rights, the First Amendment has become increasingly more visible. Certain religious groups — particularly Jewish groups — have argued that they have a right to abortion care. In Generation to Generation Inc v. Florida , a religious rights group argued that Florida’s abortion ban (HB 5) constituted a violation of the Florida State Constitution: “In Jewish law, abortion is required if necessary to protect the health, mental or physical well-being of the woman, or for many other reasons not permitted under the Act. As such, the Act prohibits Jewish women from practicing their faith free of government intrusion and thus violates their privacy rights and religious freedom.” Similar cases have arisen in Indiana and Texas. Absent constitutional protection of abortion rights, the Christian religious majorities in many states may unjustly impose their moral and ethical code on other groups, implying an unconstitutional religious hierarchy.
Cases like Generation to Generation Inc v. Florida may also trigger heightened scrutiny status in higher courts; The Religious Freedom Restoration Act (1993) places strict scrutiny on cases which “burden any aspect of religious observance or practice.”
But framing the issue as one of Free Exercise does not interact with major objections to abortion rights. Anti-abortion advocates contend that abortion is tantamount to murder. An anti-abortion advocate may argue that just as religious rituals involving human sacrifice are illegal, so abortion ought to be illegal. Anti-abortion advocates may be able to argue that abortion bans hold up against strict scrutiny since “preserving potential life” constitutes a “compelling interest.”
The question of when life begins—which is fundamentally a moral and religious question—is both essential to the abortion debate and often ignored by left-leaning activists. For select Christian advocacy groups (as well as other anti-abortion groups) who believe that life begins at conception, abortion bans are a deeply moral issue. Abortion bans which operate under the logic that abortion is murder essentially legislate a definition of when life begins, which is problematic from a First Amendment perspective; the Establishment Clause of the First Amendment prevents the government from intervening in religious debates. While numerous legal thinkers have associated the abortion debate with the First Amendment, this argument has not been fully litigated. As an amicus brief filed in Dobbs by the Freedom From Religion Foundation, Center for Inquiry, and American Atheists points out, anti-abortion rhetoric is explicitly religious: “There is hardly a secular veil to the religious intent and positions of individuals, churches, and state actors in their attempts to limit access to abortion.” Justice Stevens located a similar issue with anti-abortion rhetoric in his concurring opinion in Webster v. Reproductive Health Services (1989) , stating: “I am persuaded that the absence of any secular purpose for the legislative declarations that life begins at conception and that conception occurs at fertilization makes the relevant portion of the preamble invalid under the Establishment Clause of the First Amendment to the Federal Constitution.” Judges who justify their judicial decisions on abortion using similar rhetoric blur the line between church and state.
Framing the abortion debate around religious freedom would thus address the two main categories of arguments made by anti-abortion activists: arguments centered around issues with substantive due process and moral objections to abortion.
Conservatives may maintain, however, that legalizing abortion on the federal level is an Establishment Clause violation to begin with, since the government would essentially be imposing a federal position on abortion. Many anti-abortion advocates favor leaving abortion rights up to individual states. However, in the absence of recognized federal, constitutional protection of abortion rights, states will ban abortion. Protecting religious freedom of the individual is of the utmost importance — the United States government must actively intervene in order to uphold the line between church and state. Protecting abortion rights would allow everyone in the United States to act in accordance with their own moral and religious perspectives on abortion.
Reframing the abortion rights debate as a question of religious freedom is the most viable path forward. Anchoring abortion rights in the Establishment Clause would ensure Americans have the right to maintain their own personal and religious beliefs regarding the question of when life begins. In the short term, however, litigants could take advantage of Establishment Clauses in state constitutions. Yet, given the swing of the Court towards expanding religious freedom protections at the time of writing, Free Exercise arguments may prove better at securing citizens a right to an abortion.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
Find anything you save across the site in your account
How the Right to Legal Abortion Changed the Arc of All Women’s Lives
By Katha Pollitt

I’ve never had an abortion. In this, I am like most American women. A frequently quoted statistic from a recent study by the Guttmacher Institute, which reports that one in four women will have an abortion before the age of forty-five, may strike you as high, but it means that a large majority of women never need to end a pregnancy. (Indeed, the abortion rate has been declining for decades, although it’s disputed how much of that decrease is due to better birth control, and wider use of it, and how much to restrictions that have made abortions much harder to get.) Now that the Supreme Court seems likely to overturn Roe v. Wade sometime in the next few years—Alabama has passed a near-total ban on abortion, and Ohio, Georgia, Kentucky, Mississippi, and Missouri have passed “heartbeat” bills that, in effect, ban abortion later than six weeks of pregnancy, and any of these laws, or similar ones, could prove the catalyst—I wonder if women who have never needed to undergo the procedure, and perhaps believe that they never will, realize the many ways that the legal right to abortion has undergirded their lives.
Legal abortion means that the law recognizes a woman as a person. It says that she belongs to herself. Most obviously, it means that a woman has a safe recourse if she becomes pregnant as a result of being raped. (Believe it or not, in some states, the law allows a rapist to sue for custody or visitation rights.) It means that doctors no longer need to deny treatment to pregnant women with certain serious conditions—cancer, heart disease, kidney disease—until after they’ve given birth, by which time their health may have deteriorated irretrievably. And it means that non-Catholic hospitals can treat a woman promptly if she is having a miscarriage. (If she goes to a Catholic hospital, she may have to wait until the embryo or fetus dies. In one hospital, in Ireland, such a delay led to the death of a woman named Savita Halappanavar, who contracted septicemia. Her case spurred a movement to repeal that country’s constitutional amendment banning abortion.)
The legalization of abortion, though, has had broader and more subtle effects than limiting damage in these grave but relatively uncommon scenarios. The revolutionary advances made in the social status of American women during the nineteen-seventies are generally attributed to the availability of oral contraception, which came on the market in 1960. But, according to a 2017 study by the economist Caitlin Knowles Myers, “The Power of Abortion Policy: Re-Examining the Effects of Young Women’s Access to Reproductive Control,” published in the Journal of Political Economy , the effects of the Pill were offset by the fact that more teens and women were having sex, and so birth-control failure affected more people. Complicating the conventional wisdom that oral contraception made sex risk-free for all, the Pill was also not easy for many women to get. Restrictive laws in some states barred it for unmarried women and for women under the age of twenty-one. The Roe decision, in 1973, afforded thousands upon thousands of teen-agers a chance to avoid early marriage and motherhood. Myers writes, “Policies governing access to the pill had little if any effect on the average probabilities of marrying and giving birth at a young age. In contrast, policy environments in which abortion was legal and readily accessible by young women are estimated to have caused a 34 percent reduction in first births, a 19 percent reduction in first marriages, and a 63 percent reduction in ‘shotgun marriages’ prior to age 19.”
Access to legal abortion, whether as a backup to birth control or not, meant that women, like men, could have a sexual life without risking their future. A woman could plan her life without having to consider that it could be derailed by a single sperm. She could dream bigger dreams. Under the old rules, inculcated from girlhood, if a woman got pregnant at a young age, she married her boyfriend; and, expecting early marriage and kids, she wouldn’t have invested too heavily in her education in any case, and she would have chosen work that she could drop in and out of as family demands required.
In 1970, the average age of first-time American mothers was younger than twenty-two. Today, more women postpone marriage until they are ready for it. (Early marriages are notoriously unstable, so, if you’re glad that the divorce rate is down, you can, in part, thank Roe.) Women can also postpone childbearing until they are prepared for it, which takes some serious doing in a country that lacks paid parental leave and affordable childcare, and where discrimination against pregnant women and mothers is still widespread. For all the hand-wringing about lower birth rates, most women— eighty-six per cent of them —still become mothers. They just do it later, and have fewer children.
Most women don’t enter fields that require years of graduate-school education, but all women have benefitted from having larger numbers of women in those fields. It was female lawyers, for example, who brought cases that opened up good blue-collar jobs to women. Without more women obtaining law degrees, would men still be shaping all our legislation? Without the large numbers of women who have entered the medical professions, would psychiatrists still be telling women that they suffered from penis envy and were masochistic by nature? Would women still routinely undergo unnecessary hysterectomies? Without increased numbers of women in academia, and without the new field of women’s studies, would children still be taught, as I was, that, a hundred years ago this month, Woodrow Wilson “gave” women the vote? There has been a revolution in every field, and the women in those fields have led it.
It is frequently pointed out that the states passing abortion restrictions and bans are states where women’s status remains particularly low. Take Alabama. According to one study , by almost every index—pay, workforce participation, percentage of single mothers living in poverty, mortality due to conditions such as heart disease and stroke—the state scores among the worst for women. Children don’t fare much better: according to U.S. News rankings , Alabama is the worst state for education. It also has one of the nation’s highest rates of infant mortality (only half the counties have even one ob-gyn), and it has refused to expand Medicaid, either through the Affordable Care Act or on its own. Only four women sit in Alabama’s thirty-five-member State Senate, and none of them voted for the ban. Maybe that’s why an amendment to the bill proposed by State Senator Linda Coleman-Madison was voted down. It would have provided prenatal care and medical care for a woman and child in cases where the new law prevents the woman from obtaining an abortion. Interestingly, the law allows in-vitro fertilization, a procedure that often results in the discarding of fertilized eggs. As Clyde Chambliss, the bill’s chief sponsor in the state senate, put it, “The egg in the lab doesn’t apply. It’s not in a woman. She’s not pregnant.” In other words, life only begins at conception if there’s a woman’s body to control.
Indifference to women and children isn’t an oversight. This is why calls for better sex education and wider access to birth control are non-starters, even though they have helped lower the rate of unwanted pregnancies, which is the cause of abortion. The point isn’t to prevent unwanted pregnancy. (States with strong anti-abortion laws have some of the highest rates of teen pregnancy in the country; Alabama is among them.) The point is to roll back modernity for women.
So, if women who have never had an abortion, and don’t expect to, think that the new restrictions and bans won’t affect them, they are wrong. The new laws will fall most heavily on poor women, disproportionately on women of color, who have the highest abortion rates and will be hard-pressed to travel to distant clinics.
But without legal, accessible abortion, the assumptions that have shaped all women’s lives in the past few decades—including that they, not a torn condom or a missed pill or a rapist, will decide what happens to their bodies and their futures—will change. Women and their daughters will have a harder time, and there will be plenty of people who will say that they were foolish to think that it could be otherwise.
By signing up, you agree to our User Agreement and Privacy Policy & Cookie Statement . This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
By Jia Tolentino

By Isaac Chotiner

By Stephania Taladrid
There Are More Than Two Sides to the Abortion Debate
Readers share their perspectives.

Sign up for Conor’s newsletter here.
Earlier this week I curated some nuanced commentary on abortion and solicited your thoughts on the same subject. What follows includes perspectives from several different sides of the debate. I hope each one informs your thinking, even if only about how some other people think.
We begin with a personal reflection.
Cheryl was 16 when New York State passed a statute legalizing abortion and 19 when Roe v. Wade was decided in 1973. At the time she was opposed to the change, because “it just felt wrong.” Less than a year later, her mother got pregnant and announced she was getting an abortion.
She recalled:
My parents were still married to each other, and we were financially stable. Nonetheless, my mother’s announcement immediately made me a supporter of the legal right to abortion. My mother never loved me. My father was physically abusive and both parents were emotionally and psychologically abusive on a virtually daily basis. My home life was hellish. When my mother told me about the intended abortion, my first thought was, “Thank God that they won’t be given another life to destroy.” I don’t deny that there are reasons to oppose abortion. As a feminist and a lawyer, I can now articulate several reasons for my support of legal abortion: a woman’s right to privacy and autonomy and to the equal protection of the laws are near the top of the list. (I agree with Ruth Bader Ginsburg that equal protection is a better legal rationale for the right to abortion than privacy.) But my emotional reaction from 1971 still resonates with me. Most people who comment on the issue, on both sides, do not understand what it is to go through childhood unloved. It is horrific beyond my powers of description. To me, there is nothing more immoral than forcing that kind of life on any child. Anti-abortion activists often like to ask supporters of abortion rights: “Well, what if your mother had decided to abort you?” All I can say is that I have spent a great portion of my life wishing that my mother had done exactly that.
Steven had related thoughts:
I have respect for the idea that there should be some restrictions on abortion. But the most fundamental, and I believe flawed, unstated assumptions of the anti-choice are that A) they are acting on behalf of the fetus, and more importantly B) they know what the fetus would want. I would rather not have been born than to have been born to a mother who did not want me. All children should be wanted children—for the sake of all concerned. You can say that different fetuses would “want” different things—though it’s hard to say a clump of cells “wants” anything. How would we know? The argument lands, as it does generally, with the question of who should be making that decision. Who best speaks in the fetus’s interests? Who is better positioned morally or practically than the expectant mother?
Geoff self-describes as “pro-life” and guilty of some hypocrisy. He writes:
I’m pro-life because I have a hard time with the dehumanization that comes with the extremes of abortion on demand … Should it be okay to get an abortion when you find your child has Down syndrome? What of another abnormality? Or just that you didn’t want a girl? Any argument that these are legitimate reasons is disturbing. But so many of the pro-life just don’t seem to care about life unless it’s a fetus they can force a woman to carry. The hypocrisy is real. While you can argue that someone on death row made a choice that got them to that point, whereas a fetus had no say, I find it still hard to swallow that you can claim one life must be protected and the other must be taken. Life should be life. At least in the Catholic Church this is more consistent. I myself am guilty of a degree of hypocrisy. My wife and I used IVF to have our twins. There were other embryos created and not inserted. They were eventually destroyed. So did I support killing a life? Maybe? I didn’t want to donate them for someone else to give birth to—it felt wrong to think my twins may have brothers or sisters in the world they would never know about. Yet does that mean I was more willing to kill my embryos than to have them adopted? Sure seems like it. So I made a morality deal with myself and moved the goal post—the embryos were not yet in a womb and were so early in development that they couldn’t be considered fully human life. They were still potential life.
Colleen, a mother of three, describes why she ended her fourth pregnancy:
I was young when I first engaged this debate. Raised Catholic, anti-choice, and so committed to my position that I broke my parents’ hearts by giving birth during my junior year of college. At that time, my sense of my own rights in the matter was almost irrelevant. I was enslaved by my body. One husband and two babies later I heard a remarkable Jesuit theologian (I wish I could remember his name) speak on the matter and he, a Catholic priest, framed it most directly. We prioritize one life over another all the time. Most obviously, we justify the taking of life in war with all kinds of arguments that often turn out to be untrue. We also do so as we decide who merits access to health care or income support or other life-sustaining things. So the question of abortion then boils down to: Who gets to decide? Who gets to decide that the life of a human in gestation is actually more valuable than the life of the woman who serves as host—or vice versa? Who gets to decide when the load a woman is being asked to carry is more than she can bear? The state? Looking back over history, he argued that he certainly had more faith in the person most involved to make the best decision than in any formalized structure—church or state—created by men. Every form of birth control available failed me at one point or another, so when yet a 4th pregnancy threatened to interrupt the education I had finally been able to resume, I said “Enough.” And as I cried and struggled to come to that position, the question that haunted me was “Doesn’t MY life count?” And I decided it did.
Florence articulates what it would take to make her anti-abortion:
What people seem to miss is that depriving a woman of bodily autonomy is slavery. A person who does not control his/her own body is—what? A slave. At its simplest, this is the issue. I will be anti-abortion when men and women are equal in all facets of life—wages, chores, child-rearing responsibilities, registering for the draft, to name a few obvious ones. When there is birth control that is effective, where women do not bear most of the responsibility. We need to raise boys who are respectful to girls, who do not think that they are entitled to coerce a girl into having sex that she doesn’t really want or is unprepared for. We need for sex education to be provided in schools so young couples know what they are getting into when they have sex. Especially the repercussions of pregnancy. We need to raise girls who are confident and secure, who don’t believe they need a male to “complete” them. Who have enough agency to say “no” and to know why. We have to make abortion unnecessary … We have so far to go. If abortion is ruled illegal, or otherwise curtailed, we will never know if the solutions to women’s second-class status will work. We will be set back to the 50s or worse. I don’t want to go back. Women have fought from the beginning of time to own their bodies and their lives. To deprive us of all of the amazing strides forward will affect all future generations.
Similarly, Ben agrees that in our current environment, abortion is often the only way women can retain equal citizenship and participation in society, but also agrees with pro-lifers who critique the status quo, writing that he doesn’t want a world where a daughter’s equality depends on her right “to perform an act of violence on their potential descendents.” Here’s how he resolves his conflictedness:
Conservatives arguing for a more family-centered society, in which abortion is unnecessary to protect the equal rights of women, are like liberals who argue for defunding the police and relying on addiction, counselling, and other services, in that they argue for removing what offends them without clear, credible plans to replace the functions it serves. I sincerely hope we can move towards a world in which armed police are less necessary. But before we can remove the guardrails of the police, we need to make the rest of the changes so that the world works without them. Once liberal cities that have shown interest in defunding the police can prove that they can fund alternatives, and that those alternatives work, then I will throw my support behind defunding the police. Similarly, once conservative politicians demonstrate a credible commitment to an alternative vision of society in which women are supported, families are not taken for granted, and careers and short-term productivity are not the golden calves they are today, I will be willing to support further restrictions on abortion. But until I trust that they are interested in solving the underlying problem (not merely eliminating an aspect they find offensive), I will defend abortion, as terrible as it is, within reasonable legal limits.
Two readers objected to foregrounding gender equality. One emailed anonymously, writing in part:
A fetus either is or isn’t a person. The reason I’m pro-life is that I’ve never heard a coherent defense of the proposition that a fetus is not a person, and I’m not sure one can be made. I’ve read plenty of progressive commentary, and when it bothers to make an argument for abortion “rights” at all, it talks about “the importance of women’s healthcare” or something as if that were the issue.
Christopher expanded on that last argument:
Of the many competing ethical concerns, the one that trumps them all is the status of the fetus. It is the only organism that gets destroyed by the procedure. Whether that is permissible trumps all other concerns. Otherwise important ethical claims related to a woman’s bodily autonomy, less relevant social disparities caused by the differences in men’s and women’s reproductive functions, and even less relevant differences in partisan commitments to welfare that would make abortion less appealing––all of that is secondary. The relentless strategy by the pro-choice to sidestep this question and pretend that a woman’s right to bodily autonomy is the primary ethical concern is, to me, somewhere between shibboleth and mass delusion. We should spend more time, even if it’s unproductive, arguing about the status of the fetus, because that is the question, and we should spend less time indulging this assault-on-women’s-rights narrative pushed by the Left.
Jean is critical of the pro-life movement:
Long-acting reversible contraceptives, robust, science-based sex education for teens, and a stronger social safety net would all go a remarkable way toward decreasing the number of abortions sought. Yet all the emphasis seems to be on simply making abortion illegal. For many, overturning Roe v. Wade is not about reducing abortions so much as signalling that abortion is wrong. If so-called pro-lifers were as concerned about abortion as they seem to be, they would spend more time, effort, and money supporting efforts to reduce the need for abortion—not simply trying to make it illegal without addressing why women seek it out. Imagine, in other words, a world where women hardly needed to rely on abortion for their well-being and ability to thrive. Imagine a world where almost any woman who got pregnant had planned to do so, or was capable of caring for that child. What is the anti-abortion movement doing to promote that world?
Destiny has one relevant answer. She writes:
I run a pro-life feminist group and we often say that our goal is not to make abortion illegal, but rather unnecessary and unthinkable by supporting women and humanizing the unborn child so well.
Robert suggests a different focus:
Any well-reasoned discussion of abortion policy must include contraception because abortion is about unwanted children brought on by poorly reasoned choices about sex. Such choices will always be more emotional than rational. Leaving out contraception makes it an unrealistic, airy discussion of moral philosophy. In particular, we need to consider government-funded programs of long-acting reversible contraception which enable reasoned choices outside the emotional circumstances of having sexual intercourse.
Last but not least, if anyone can unite the pro-life and pro-choice movements, it’s Errol, whose thoughts would rankle majorities in both factions as well as a majority of Americans. He writes:
The decision to keep the child should not be left up solely to the woman. Yes, it is her body that the child grows in, however once that child is birthed it is now two people’s responsibility. That’s entirely unfair to the father when he desired the abortion but the mother couldn’t find it in her heart to do it. If a woman wants to abort and the man wants to keep it, she should abort. However I feel the same way if a man wants to abort. The next 18+ years of your life are on the line. I view that as a trade-off that warrants the male’s input. Abortion is a conversation that needs to be had by two people, because those two will be directly tied to the result for a majority of their life. No one else should be involved with that decision, but it should not be solely hers, either.
Thanks to all who contributed answers to this week’s question, whether or not they were among the ones published. What subjects would you like to see fellow readers address in future installments? Email [email protected].
By submitting an email, you’ve agreed to let us use it—in part or in full—in this newsletter and on our website. Published feedback includes a writer’s full name, city, and state, unless otherwise requested in your initial note.
The independent source for health policy research, polling, and news.
Women’s Views of Abortion Access and Policies in the Dobbs Era: Insights From the KFF Health Tracking Poll
Audrey Kearney , Ashley Kirzinger , Liz Hamel , and Alina Salganicoff Published: Apr 05, 2024
- Methodology
Nearly two years after the Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization Supreme Court ruling overturned Roe v. Wade , eliminating federal constitutional protections for abortion, abortion is banned in 14 states and limited by gestational limits in 11 others. The latest polling from KFF finds that women in states where abortion is banned are more likely to report personal connections to people who have had difficulty accessing abortion services since the overturn of Roe . Recent research has documented that many women who live in states where abortion is banned have traveled to other states to secure abortions. This can be costly and require them to take time off from work, find childcare, and in some cases make multiple visits to get abortion services. There have also been reports of women who have been denied abortions even though they meet the state standards for exemptions. Previous reporting from the KFF Health Tracking Poll examines women’s views on abortion policy including by partisanship, which is one of the strongest predictors of these views. This analysis examines women’s views by geography—specifically whether they live in a state where abortion is currently banned, limited, or legal.
One in Seven Women in States With Abortion Bans Say They or Someone They Know Has Had Difficulty Accessing an Abortion
Eight percent of women overall, rising to one in seven (14%) women of reproductive age (ages 18 to 49), say they or someone they know has had difficulty accessing an abortion due to restrictions in their state since Roe was overturned. Women living in states where abortion is banned are twice as likely to report knowing someone who had difficulty accessing an abortion compared to women living in states where abortion is limited or legal. One in seven (14%) women living in states where abortion is banned say they or someone they know has struggled to access an abortion due to restrictions on abortions in their state, including one in five (21%) women ages 18-49 living in these states. Fewer women in states where abortion is limited by gestational periods (6%) or in states where abortion is legal past 22 weeks of gestation (7%) say they or someone they know has experienced such difficulties.
A Majority of Women Living in States Where Abortion Is Banned Want Abortion To Be Legal, Support Laws Protecting Abortion Access
While there are some small differences in levels of support for abortion restrictions between women living in states where abortion is banned and those living in other states, majorities of women across states—including in those with abortion bans—think abortion should be legal in all or most cases and support a range of policies that protect abortion access.
Regardless of whether abortion in their state is banned, restricted, or legal, a majority of women think abortion should be legal in all or most cases, including two-thirds (67%) of women in states where abortion is banned and seven in ten (71%) in states where abortion is limited by gestational limits. A larger majority (81%) of women in states where abortion is currently legal say abortion should be legal in all or most cases. One in four women living in states where abortion is banned think abortion should be “illegal in most cases,” as do one in five women living in states where abortion is limited by gestational limits (19%) and women living in states where abortion is legal (17%). A small share of women, regardless of their state’s laws, say abortion should be “illegal in all cases” (8% of women living in states where abortion is banned, 10% in states with limited abortion access, 2% in states with legal abortions available).
A majority of women, regardless of the abortion laws in their state, support laws such as protecting abortion access for women experiencing pregnancy-related emergencies such as miscarriages, protecting the right to travel to get an abortion, and guaranteeing a federal right to abortion.
Regardless of the type of abortion restrictions in their state, fewer than half of women support laws that restrict or criminalize abortion access, though there are some variations in the level of support for different policies. Among women living in states where abortion is banned, just under half support establishing a federal 16-week ban on abortions (45%), and four in ten support prohibiting clinics that receive federal funding from providing abortions or referring patients to abortion providers (40%) or making it a crime for health care providers to mail abortion pills to state with abortion bans (38%). One-third support a national ban on mifepristone, the abortion medication (33%).
Fewer women in states where abortion is legal support establishing a federal ban on abortion at 16 weeks (33% vs. 45% among women in states where abortion is banned), likely reflecting underlying political differences between women who live in these types of states. In fact, four in ten (38%) women living in states where abortion is banned or limited either are or lean Republican, compared to about three in ten (28%) women living in states where abortion is legal. The largest predictor of support for these policies is political partisanship, even among women. For a further exploration on these partisanship differences, see previous reporting on this survey .
The issue of abortion access is likely to emerge in multiple forms in the November 2024 election. A number of states are moving forward with ballot initiatives to protect abortion rights at the state level. In addition, KFF polling shows that one in eight voters (12%) say abortion is the most important issue to their vote, largely comprised of adults who say abortion should be legal and support protections for abortion access. Notably, one in five women of reproductive age in states where abortion is banned say that either they or someone they personally know has had difficulty obtaining an abortion. Support for abortion protections including a federal guarantee to the right to abortion is robust among women, regardless of where they reside. While substantial minorities of women in states with abortion bans support some restrictions on abortion access, two-thirds of women living in these states think abortion should be legal in all or most cases, suggesting a disconnect between what women in these states support and the policies their state lawmakers have enacted.
- Women's Health Policy
- Reproductive Health
- Tracking Poll
- TOPLINE & METHODOLOGY
news release
- One in Five Women of Reproductive Age in States with Abortion Bans Say They or Someone They Know Has Had Difficulty Accessing an Abortion Since Dobbs
Also of Interest
- KFF Health Tracking Poll March 2024: Abortion in the 2024 Election and Beyond
- KFF Health Tracking Poll: The Public’s Views on the ACA
- KFF Health Tracking Poll: Early 2023 Update On Public Awareness On Abortion and Emergency Contraception
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
What the current landscape of abortion rights looks like going into 2024

Selena Simmons-Duffin

Sarah McCammon
There have been wins and losses since the overturning of Roe v. Wade . The women fighting against abortion restriction laws have impacted laws, policies and court cases – all ahead of an election year.
JUANA SUMMERS, HOST:
When it comes to reproductive rights, 2023 is ending in much the same way it began - with confusion, lawsuits and the stories of women in the midst of health crises unable to access abortion care because of a host of restrictive abortion laws across the country. The most recent example of this is Kate Cox, a 31-year-old mother of two in Texas. That state has some of the most restrictive abortion laws in the country.
ARI SHAPIRO, HOST:
At around 20 weeks, Cox learned the fetus she was carrying had trisomy 18, a condition where the fetus often dies before birth or just after. Cox was having complications with the pregnancy, and continuing to carry the fetus could jeopardize her future fertility. Along with the Center for Reproductive Rights, Cox petitioned a Texas court for a medical exception for an abortion. The request was granted but later overturned when the state's attorney general, Ken Paxton, appealed the ruling to the state Supreme Court.
SUMMERS: With time running out, Cox left Texas to seek an abortion in another state. While this past year saw a number of states move to protect abortion rights, Cox's story is far from unique. We're going to talk through the state of reproductive rights in this country with NPR national political correspondent Sarah McCammon and NPR health policy reporter Selena Simmons-Duffin. And, Sarah, I want to start with you here and a big-picture look. What has been happening this year in terms of the legal landscape?
SARAH MCCAMMON, BYLINE: Well, you know, this was the first full year without Roe v. Wade after the Dobbs decision was issued in June of 2022. And since then, we've seen continued fights in state legislatures, in courtrooms and at the ballot box over abortion rights and abortion policy. So currently, according to the Guttmacher Institute, which supports abortion rights, 14 states have total or near-total abortion bans. Seven more prohibit abortions sometime before 18 weeks. And at the same time, 22 states and the District of Columbia have passed protections this year for abortion access. So there's really been an intensification of this divide we see where access depends on where you live. Also, more patients have been coming forward with stories about being turned away for emergency abortion care. Some of them are fighting back by filing lawsuits. And because of all this, we're seeing continued political fallout.
SUMMERS: Selena, to you, we know that people are still getting abortions, and there is data that suggests that the number of abortions actually rose in 2023. Explain how that could be the case when so many states have moved to limit access.
SELENA SIMMONS-DUFFIN, BYLINE: Yeah, it's a really surprising finding. There are some theories as to why. So there may be an increased demand for abortion because of the economy. It could be because of reduced stigma as more people talk about their experiences with miscarriage and abortion. There's also way more information out there about what state laws are and different options for ending a pregnancy. So in states with bans, people who are seeking abortions and have the money to do this are just traveling to states where it's legal. One study found that birth rates increased in states with abortion bans since these new laws took effect.
SUMMERS: Selena, remind us who's being impacted the most by all this.
SIMMONS-DUFFIN: The real demographic differences in terms of access are financial - who can afford to travel and who can't. And because of the racial wealth differentials in the U.S., that means low-income people of color are the most likely to be stuck. As an example, I spoke with Samantha Casiano last spring. She didn't have the money to leave the state of Texas when she was pregnant with a fetus that had anencephaly. That's a condition where the brain and skull do not fully form. It's always fatal. She had to carry that pregnancy to term and give birth, and her baby died soon after that. She's now a plaintiff in a lawsuit arguing that the Texas abortion ban exception for medical reasons is too narrow and that that harmed her.
SUMMERS: Sarah, to you, what has the response to these stories been like?
MCCAMMON: You know, it's important to understand that poll after poll suggests that most Americans support at least some legal access to abortion, particularly in situations like the ones we've been talking about where there's an emergency medical crisis and an abortion is the recommended standard of care. So abortion rights opponents who have supported these laws have had varying responses. You know, some have suggested that Kate Cox, who we heard about earlier, should carry the pregnancy to term and give birth regardless of how it might affect her future fertility. There are activists who are committed to that idea. But just as often, if not more often, I've heard Republican politicians downplay the idea that these laws are meant to prevent abortions in these cases.
Earlier this year, I interviewed the architect of one of these laws, Texas law SB 8, which first took effect in September 2021. This is the one that allows civil lawsuits against anyone believed to have been involved in providing or helping someone get an illegal abortion, and it banned most abortions after about six weeks. So Jonathan Mitchell is a lawyer based in Austin who helped Republican lawmakers draft that legislation. I asked him about one specific case in Texas involving a woman named Anna Zargarian. She's one of the plaintiffs in the Center for Reproductive Rights case that we've been talking about. She had to fly to Colorado for an emergency abortion after her water broke prematurely. So I asked Jonathan Mitchell, the architect of this law, what he thought about that.
JONATHAN MITCHELL: I do have a hard time understanding why SB 8 would have stopped medically necessary abortions because the statute specifically allows them at any point in the pregnancy, and it specifically exempts those abortions from any type of liability, civil or criminal.
MCCAMMON: Does it concern you that this happens?
MITCHELL: It concerns me, yeah, because the statute was never intended to restrict access to medically necessary abortions. Only the purely elective abortions are unlawful under SB 8.
MCCAMMON: But as we've heard, that is not what's happening. Many doctors have told both Selena and me that they don't feel like they're able to terminate pregnancies even when there's an emergency and the standard of care established by the medical community would suggest that they should. They're worried about prosecution and other repercussions.
SUMMERS: Selena, what else have you been hearing from doctors?
SIMMONS-DUFFIN: Well, they really feel like they're in an impossible situation, especially when it comes to complications. So you have the threat of prosecution by the state if you provide an abortion that someone deems doesn't fall into the medical exception. You also have the threat of malpractice suits if you deny an abortion and someone gets really sick or dies as a result.
SUMMERS: Sarah, how has the overturning of Roe reshaped political conversations about abortion?
MCCAMMON: Well, we've now had two elections in 2022 and '23 where voters have had a chance to weigh in since the Dobbs decision. Several states had ballot initiatives that spoke to questions related to abortion rights. And in every case where the question was put directly to voters, voters supported abortion rights in one way or another.
SUMMERS: So, Sarah, we have, at this point, been talking about elections in the past, but we are headed into a monumental election year in 2024. The primary is already underway. What are you seeing and hearing?
MCCAMMON: You know, Republicans are looking at these election results and seeing voters appear to push back against abortion restrictions, often even in pretty red states. So this is a challenge for - particularly for Republican presidential hopefuls who are trying to navigate that. They're trying to appeal to a base that's strongly anti-abortion. But also, they have to be mindful of what they're saying and not turn off general election voters. So we've seen them try to sort of walk that line. Several of them have told personal stories about experiences in their families with miscarriages or difficulty conceiving. What that seems like is an effort by the candidates to humanize themselves and seem more relatable on this issue. All of these candidates generally support the overturning of Roe v. Wade. The question is, just how restrictive should laws be, and should they support a national abortion ban if, hypothetically - and it's very hypothetical - Republicans would ever get enough votes in Congress to do that?
SUMMERS: Selena, the other big thing that we're watching next year on this front is that the Supreme Court has agreed to take up another case about abortion, this one involving the abortion pill.
SIMMONS-DUFFIN: Right. So this is a case brought by doctors who oppose abortion rights, who say the FDA didn't use the right procedures when it loosened access to a drug called mifepristone. And the shakiest part of this case is whether they have the right to sue. But even so, many academics believe that this impact of this decision could be really, really, really big. And that's because most of the abortions in the U.S. happen as medication abortions, which involve mifepristone and another drug called misoprostol. So a decision that limits access to mifepristone could have national impact, including for people living in New York and California and Colorado and other states that have positioned themselves as bastions of reproductive rights. We haven't heard oral arguments. We don't know what the justices are thinking. But this is the same court that overturned Roe v. Wade, and the decision could come just months before the election. So it's going to be a huge story in the coming year.
SUMMERS: NPR's Selena Simmons-Duffin and Sarah McCammon. Thanks to both of you.
SIMMONS-DUFFIN: You're welcome.
MCCAMMON: Thank you.
Copyright © 2023 NPR. All rights reserved. Visit our website terms of use and permissions pages at www.npr.org for further information.
NPR transcripts are created on a rush deadline by an NPR contractor. This text may not be in its final form and may be updated or revised in the future. Accuracy and availability may vary. The authoritative record of NPR’s programming is the audio record.
- Newsletters
Site search
- Israel-Hamas war
- 2024 election
- Solar eclipse
- Supreme Court
- All explainers
- Future Perfect
Filed under:
- Health Care
The Supreme Court will decide if states can ban lifesaving abortions
A federal law requires hospitals to provide abortions when necessary to prevent serious health consequences. The justices could neutralize that law.
Share this story
- Share this on Facebook
- Share this on Twitter
- Share this on Reddit
- Share All sharing options
Share All sharing options for: The Supreme Court will decide if states can ban lifesaving abortions
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/73265790/2115237711.0.jpg)
Moyle v. United States should have been a very easy case.
A federal law, the Emergency Medical Treatment and Labor Act (EMTALA), requires nearly all hospitals to provide “such treatment as may be required to stabilize the medical condition” of “any individual” who arrives at the hospital’s ER with an “emergency medical condition.” Though the law does not specifically mention abortions, EMTALA is written in capacious terms — requiring covered hospitals to perform an emergency abortion when that is the appropriate treatment to resolve a patient’s medical emergency.
And yet, last January, the Supreme Court effectively nullified EMTALA , at least for patients who require abortion . Moyle , which the Court will hear the last full week of April, asks whether this nullification should be made permanent.
The case involves a conflict between the federal law and Idaho’s unusually restrictive anti-abortion statute, which permits physicians to perform an abortion when “ necessary to prevent the death of the pregnant woman ,” but not when a patient’s pregnancy only threatens to disable or seriously harm them.
EMTALA, meanwhile, requires most hospitals to provide whatever care is necessary to stabilize a patient who is at risk of “serious impairment to bodily functions,” “serious dysfunction of any bodily organ or part,” or other nonfatal consequences that are defined as medical emergencies by EMTALA . So, for example, if a patient’s uterus could be destroyed, but she is likely to survive if untreated, EMTALA requires hospitals to perform an abortion if terminating the pregnancy would stabilize the patient’s medical condition.
When federal law conflicts with a state’s law, the Constitution provides that the federal law “ shall be the supreme Law of the Land” — and thus the state law is “preempted.” EMTALA also contains a provision stating that state and local laws must give way “ to the extent that the [state law] directly conflicts with a requirement of this section .”
So, again, Moyle should be an easy case, and a federal district court ruled in 2022 that Idaho’s abortion ban must give way to EMTALA when a pregnant patient has a medical emergency that must be treated with an abortion.
Last January, however, the Supreme Court temporarily blocked this district court’s order, reinstating Idaho’s sweeping abortion ban while the justices ponder the Moyle case. That’s a strong sign that, despite EMTALA’s clear text, the justices could permanently neutralize the federal law’s protections for people who must have an abortion to avoid catastrophic medical consequences. (No justice publicly dissented from this temporary order, but justices sometimes disagree with the Court’s orders but do not note their dissent.)
Moyle is a test of whether these justices will follow the text of a clearly drafted law
EMTALA is a reasonably straightforward statute. It only applies to hospitals with emergency rooms, and only to those hospitals that accept Medicare funds. That’s most hospitals because Medicare provides health coverage to Americans over the age of 65.
The primary purpose of this law is to ensure that hospitals provide emergency medical care to patients who may not be able to pay for it . But the law is also written in expansive terms. It states that “if any individual ... comes to a hospital and the hospital determines that the individual has an emergency medical condition,” the hospital typically must “stabilize the medical condition.” (In limited circumstances, the hospital may transfer the patient to another facility.)
EMTALA also defines the term “emergency medical condition” to include not just life-threatening medical conditions , but also conditions that place a patient’s health in “serious jeopardy” or that threatens serious harm to a patient’s “bodily functions” or “any bodily organ or part.”
Faced with this fairly explicit text, Idaho’s lawyers (and a separate team of lawyers representing the state’s GOP legislature ) offer several arguments to justify leaving its broad abortion ban in place.
One of their main arguments is that EMTALA should be read only to prohibit “ turning away indigent patients with serious medical conditions .” The Justice Department agrees that preventing hospitals from turning away such patients was Congress ’s prime motive when it enacted EMTALA in 1986. But the text of the statute does not support such a narrow reading of its effects.
Both the state’s brief and the state legislature’s brief also lean heavily into a provision of federal Medicare law which provides that EMTALA should not be read “to authorize any Federal officer or employee to exercise any supervision or control over the practice of medicine or the manner in which medical services are provided.” They claim that this provision prevents EMTALA from being read to alter which medical procedures can legally be performed in Idaho.
But this argument also conflicts with the text of federal law. Even if the Court agrees that requiring doctors to perform medically necessary abortions constitutes “supervision or control over the practice of medicine,” the statutory provision Idaho points to only prohibits “any Federal officer or employee” from exercising such supervision.
No federal officer or employee — meaning, a member of the federal executive branch — has decreed that Idaho hospitals must provide emergency abortions. Rather, the Biden administration argues that Congress made this determination when it enacted EMTALA.
The anti-abortion briefs also point to several provisions of the EMTALA statute which require hospitals to offer stabilizing care to a pregnant patient’s “unborn child” if a medical emergency endangers the fetus’s life. They claim that reading the federal law to require emergency abortions would “put it at war with” its provisions protecting fetal life.
But this argument is also at odds with EMTALA’s text. The federal statute provides that a hospital meets its obligations under EMTALA if it “ offers ” a patient medically stabilizing treatment and “informs the individual (or a person acting on the individual’s behalf) of the risks and benefits” of that treatment.
Thus, when a pregnant patient faces a medical emergency that endangers both the patient and their fetus, the hospital’s obligation is to offer treatment that will stabilize both patients. And, in the tragic case where a patient is forced to choose between an abortion, which would stabilize their own condition, or a treatment which would save the fetus but leave the mother at risk, EMTALA requires the hospital to offer both treatments, and inform the patient of the terrible choice they must make.
And then the hospital must honor the patient’s choice, even if the state does not approve of it.
Idaho also wants the Supreme Court to fundamentally alter the balance of power between Congress and the states
Idaho’s two legal teams also make a pair of arguments that seek to weaken Congress in fundamental ways and to place novel new limits on the federal government’s ability to preempt state laws.
The first of these arguments is that EMTALA — or, at least, the Biden administration’s textualist reading of EMTALA — violates something called the “major questions doctrine.”
The major questions doctrine claims that Congress must “speak clearly” if it wishes to give a federal agency the power to decide a question of “vast ‘economic and political significance.’” This doctrine is not mentioned in the Constitution or in any federal law , and appears to have been made up entirely by Republican appointees to the Supreme Court.
Even if you accept this made-up doctrine as legitimate, however, it is not at all clear why it is relevant to the Moyle case. By its own terms, the major questions doctrine only applies when a federal agency claims the authority to decide an important policy question. But no federal agency — meaning, an agency within the Executive Branch — has made any policymaking decision of any kind in Moyle . Rather, the question is whether a law enacted by Congress requires Idaho hospitals to perform emergency abortions.
Idaho, in other words, is arguing that a made-up legal doctrine, which appears in no legal text and that was fabricated entirely by judges, should be read to limit Congress’s ability to decide important policy questions. If the Court agrees, that would be an extraordinary transfer of power from an elected Congress to an unelected judiciary.
The state’s strongest legal argument, meanwhile, turns on the fact that EMTALA’s obligations only apply to hospitals that accept federal Medicare funds.
The Supreme Court has long held that, when Congress spends money, it may impose conditions on the recipients of that money — including on state governments. So, for example, the Court held in South Dakota v. Dole (1987) that Congress may require states that accept federal highway funds to raise their drinking age to 21 (Congress thought that the roads would be safer if there were less underage drinking and driving).
In Moyle, however, the question is whether private hospitals that accept Medicare funds must perform emergency abortions. Idaho claims that, because it has not weighed in on whether to accept that funding, it has not consented to having its own state law overridden by EMTALA. And it argues that such consent is necessary for a federal spending program to override a state law.
Idaho actually does have some legal support for this argument. In Pennhurst State School & Hospital v. Halderman (1981), the Supreme Court said that a state’s decision to accept federal funds is “much in the nature of a contract: in return for federal funds, the States agree to comply with federally imposed conditions.” So that does suggest that a state need not comply with “federally imposed conditions” if it did not “agree to comply” with them.
But the Justice Department also cites many Supreme Court cases holding that Congress preempted a state law when it enacted a federal spending program that does not provide grants to states. Thus, in Coventry Health Care v. Nevils (2017), the Court held that the federal government’s decision to offer its own employees health plans that violate Missouri law preempts that state law. And in Bennett v. Arkansas (1988), the Court held that federal Social Security law overrides an Arkansas law that allowed the state to seize an incarcerated person’s Social Security benefits.
Indeed, as recently as last year, the Court held in Health and Hospital Corporation v. Talevski (2023) that private plaintiffs may sue to enforce provisions of federal Medicaid law that impose obligations on institutions that accept Medicaid funds. Talevski rested on the proposition that conditions attached to federal grant programs are “laws” just like any other federal law, and thus can be enforced using the same mechanism individuals would use to enforce a different law.
So, while Pennhurst offers some legal support for Idaho’s claim that EMTALA cannot modify a state law without the state’s consent, there are myriad cases supporting the opposing proposition. A justice who is determined to deny emergency abortions to patients who need them could rely on Pennhurst to achieve that result, but such a decision risks undermining countless other acts of Congress that override state laws.
The Court’s decision in Moyle is likely to determine whether some women live or die
Theoretically, Idaho’s law permits abortions when necessary to save a patient’s life. Many other states with abortion bans have broader exemptions on the books, which theoretically permit an abortion when a patient faces serious health consequences that may not be life-threatening.
In practice, however, women in many states with strict abortion bans have struggled to obtain lifesaving or otherwise medically necessary care . In one case, a Texas woman with a nonviable pregnancy was told she had to wait to receive an abortion even though her body was discharging blood clots and a strange-smelling yellow liquid , Her doctors eventually agreed to induce labor after her vagina started to emit a dark, foul-smelling fluid.
This happened, moreover, despite the fact that Texas law permits abortions when a patient “has a life-threatening physical condition” or faces a “serious risk of substantial impairment of a major bodily function” that relates to their pregnancy.
Incidents like this are common because many state legal provisions permitting emergency abortions have never been interpreted by any court, or have been interpreted largely by Republican judges who are hostile to abortion. So hospital lawyers often cannot know in advance when their state’s courts will allow doctors to perform an abortion, and doctors who guess wrong risk very serious criminal charges.
If the Supreme Court reads EMTALA to say what it actually says in Moyle , that would relieve some of this uncertainty. It would mean that doctors or patients who cannot obtain a state court order permitting an emergency abortion could also seek such an order from federal court. It would also mean that, over time, a body of case law would develop establishing when federal law entitles someone experiencing a medical emergency to an abortion.
But all of that depends on whether these justices, a majority of whom voted to overrule Roe v. Wade , will set aside their personal opposition to abortion and read EMTALA to do what it actually says.
Will you support Vox today?
We believe that everyone deserves to understand the world that they live in. That kind of knowledge helps create better citizens, neighbors, friends, parents, and stewards of this planet. Producing deeply researched, explanatory journalism takes resources. You can support this mission by making a financial gift to Vox today. Will you join us?
We accept credit card, Apple Pay, and Google Pay. You can also contribute via
Next Up In Supreme Court
Sign up for the newsletter today, explained.
Understand the world with a daily explainer plus the most compelling stories of the day.
Thanks for signing up!
Check your inbox for a welcome email.
Oops. Something went wrong. Please enter a valid email and try again.
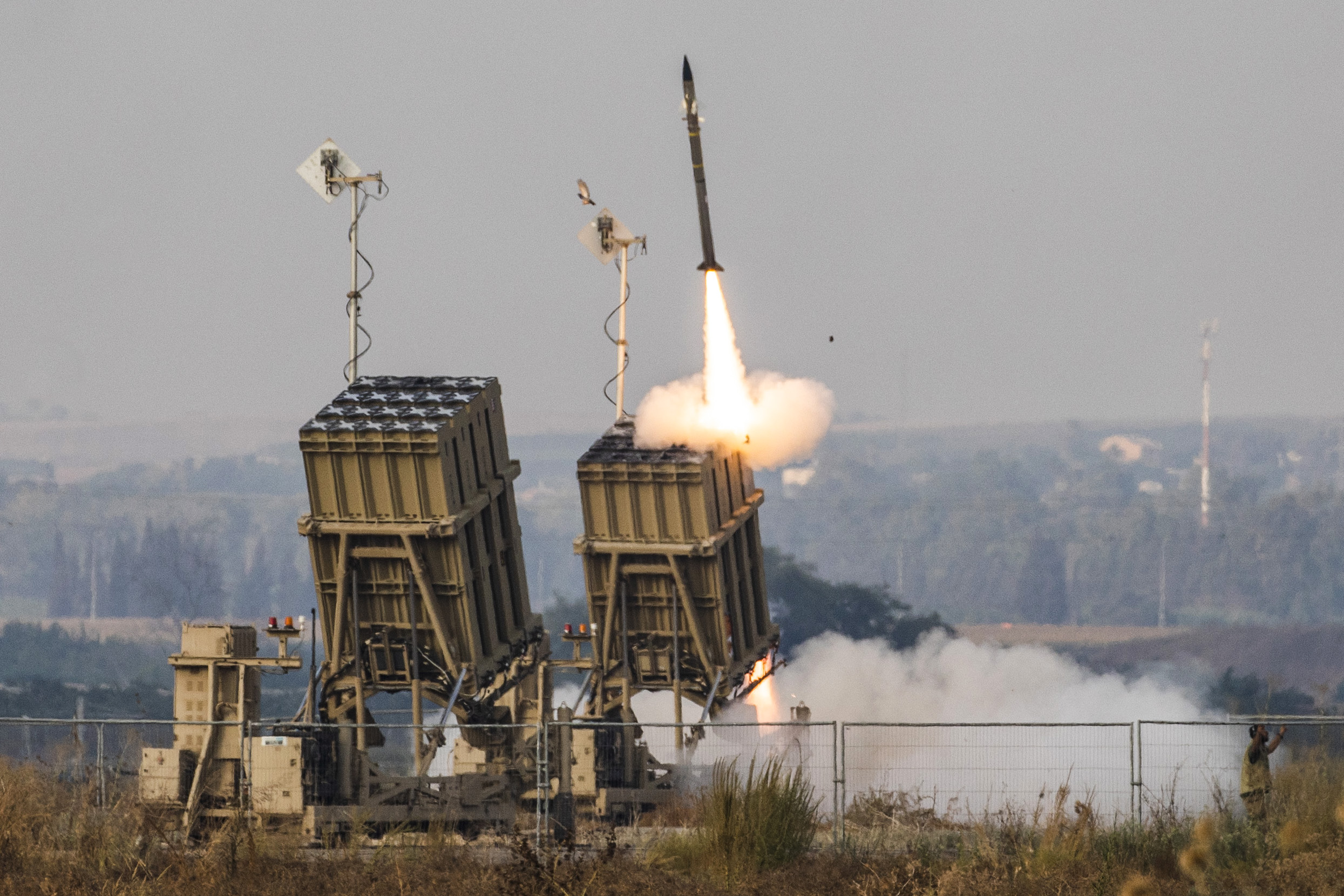

Iran’s retaliatory attack against Israel, briefly explained

Life is hard. Can philosophy help?


Don’t sneer at white rural voters — or delude yourself about their politics
You probably shouldn’t panic about measles — yet

Biden’s student loan forgiveness plan, explained

A hack nearly gained access to millions of computers. Here’s what we should learn from this.
Home — Essay Samples — Social Issues — Abortion — Why Abortion Should Be Legal
Why Abortion Should Be Legal
- Categories: Abortion Women in Business
About this sample

Words: 476 |
Published: Mar 20, 2024
Words: 476 | Page: 1 | 3 min read
Table of contents
Reproductive rights, health and safety, right to choose.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof. Kifaru
Verified writer
- Expert in: Social Issues Business

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 1067 words
4 pages / 1770 words
2 pages / 728 words
1 pages / 584 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Abortion
Abortion is a highly controversial topic that has sparked intense debate and divided public opinion for decades. While some argue that it is a woman's right to choose, others believe that it is morally and ethically wrong. In [...]
Medically ending a pregnancy before it has the chance to result in the birth of a baby is abortion (Izugbara, Otsola, & Ezeh, 2009). Abortion is yet to be legalized in Kenya due to pro-life and pro-choice squabbles. Pro-life [...]
The debate surrounding abortion has long been a contentious and deeply divided issue in society. This essay will provide an argumentative analysis of the pros and cons of abortion to society, addressing both the ethical and [...]
Abortion has been a subject of intense debate and controversy, with impassioned arguments from both sides. However, amidst the fervent discourse, it is crucial to recognize the multifaceted impact of legalizing abortion. The [...]
Abortion has been a major conflict in society. It puts a tremendous amount of pressure on women who are debating whether to change their lives dramatically by having a baby. Abortion terminates fetuses in the womb and that is [...]
Throughout the United States, there are many life issues, such as euthanasia, capital punishment, economic rights, war and the list goes on and on. But one of the biggest issue is abortion. There tends to be a rift between [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
I Hope to Repeal an Arcane Law That Could Be Misused to Ban Abortion Nationwide

By Tina Smith
Ms. Smith is a Democratic senator from Minnesota and a former Planned Parenthood executive.
A long discredited, arcane 150-year-old law is back in the news in 2024, and that should terrify anyone who supports reproductive freedom. Last week at the Supreme Court, the Comstock Act of 1873 was referenced on three separate occasions during oral arguments in a case dealing with access to mifepristone, one of two drugs typically used in medication abortions.
Anti-abortion activists like to bring up the Comstock Act because one of its clauses prohibits sending through the mail “every article, instrument, substance, drug, medicine or thing” that could possibly lead to an abortion. Even if the Supreme Court doesn’t take the bait, a newly re-elected President Trump could order his Department of Justice to start interpreting that line to mean that it is illegal to mail mifepristone — a safe, effective, Food and Drug Administration-approved drug — to doctors and pharmacies, as well as to patients directly. The same could go for medical supplies that are used in performing surgical abortions. That could effectively make abortion impossible to access even in places like Minnesota, which has affirmatively protected a woman’s right to choose by passing reproductive freedom laws.
In response, I’m prepared to fight back — including by introducing legislation to take away the Comstock Act as a tool to limit reproductive freedom.
Let me take a step back and explain how ridiculous it is that we’re even talking about this legislative relic today. The Comstock Act hasn’t been broadly enforced since the 1930s. The Biden administration considers it utterly irrelevant. Many legal experts consider it dead letter law. And once you know its back story, it becomes clear why no one has paid much attention to it in nearly a century.
Back in the 1860s, a former Civil War soldier from rural Connecticut named Anthony Comstock moved to New York City for work. He was shocked and appalled by what he found. Advertisements for contraception! Open discussions of sexual health! It all struck Comstock as terribly lewd and anti-Christian.
So he made it his mission to clean up society, creating the loftily named New York Society for the Suppression of Vice and gathering evidence for police raids on places that distributed material he thought was obscene or promoted indecent living. In the early 1870s he took his crusade to Washington, lobbying for federal legislation that would empower the post office to search for and seize anything in the mail that met Comstock’s criteria for being “obscene,” “lewd” or just plain “filthy.” Morality, as determined by Comstock, would be the law of the land, and Comstock himself would be its enforcer, appointed by Congress as a special agent of the post office.
In a fit of Victorian puritanism, Congress passed the Comstock Act into law. But it quickly became apparent that Comstock’s criteria were unworkably vague. In its broad wording, the law not only made it illegal to send pornography through the mail, it also outlawed the sending of medical textbooks for their depictions of the human body, personal love letters that hinted at physical as well as romantic relationships, and even news stories.
The whole thing was very silly and impracticable, and that’s why the Comstock Act was relegated to the dustbin of history.
But conservative activists recently revived it from obscurity as part of their playbook for a potential second Trump term: The 887-page plan nicknamed Project 2025 being promoted by groups like the Heritage Foundation explicitly calls for a newly elected second-term President Trump to use this zombie law to severely ratchet back abortion access in America without congressional action.
Legislation to repeal Comstock could take many forms, and we need to do it the right way. That’s why I’ve begun reaching out to my colleagues in the House of Representatives and the Senate to build support and see what legislation to repeal the Comstock Act might look like. Anti-abortion extremists will continue to exploit any avenue they can find to get the national ban they champion, and I want to make sure my bill shuts down every one of those avenues. Once the Supreme Court has had its say (and many legal analysts speculate that the mifepristone case heard last week should be thrown out on procedural grounds, and may well be), I’ll be ready to have mine.
Here’s the bottom line: We can’t let anyone — not the Supreme Court, not Donald Trump and certainly not a random busybody from the 19th century — take away Americans’ right to access medication abortion. We must protect the ability of doctors, pharmacies and patients to receive in the mail the supplies they need to exercise their right to reproductive care.
As the only former Planned Parenthood executive serving in the Senate, I feel I have a special responsibility to protect not just abortion rights but also abortion access.
Very few Republicans will admit to wanting to see a total, no-exceptions ban on abortion in all 50 states, but the Comstock Act could allow them to achieve that in effect, if not in so many words.
Americans deserve better. The Constitution demands better. And common sense dictates that we stop this outrageous backdoor ploy to eliminate abortion access in its tracks.
Tina Smith is a Democratic senator from Minnesota and a former Planned Parenthood executive.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
- Newsletters
- Account Activating this button will toggle the display of additional content Account Sign out
Arizona’s Zombie Abortion Ban Is Back. It’s Every State’s Future If Trump Wins.
On Tuesday, the Arizona Supreme Court ruled that its total abortion ban, a seemingly dead law dating back to 1864, is once again enforceable, despite more recent legislation that seemed to supercede it. The zombie ban makes virtually all abortions a felony, imposing a prison sentence of two to five years for any provider. There is no exception for rape or incest. The law was enacted before women could vote, and was long presumed to be permanently unenforceable. But the Arizona Supreme Court’s conservative majority, by a 4–2 margin, has now revived it. Republican governors appointed all seven justices on the bench, and the GOP recently expanded the court to entrench this far-right majority—which had no trouble finding that a ban enacted in an era in which women were chattel remains good law in 2024. As a result of this ruling, in 14 days almost every abortion in Arizona will be a crime, and nearly every clinic will close its doors. For all intents and purposes, it’s 1864 again for pregnant people in Arizona.
The decision should serve as a warning for the rest of the country, in light of ongoing efforts to revive the Comstock Act: In the hands of a far-right court, a dead, openly misogynistic, wildly unpopular abortion ban can spring back to life with a vengeance.
This zombie law was passed in 1864, long before Arizona was a state, and was codified in 1901, at which point it included a narrow exception to save the patient’s life. Much more recently, Arizona has passed less restrictive abortion laws, including a 15-week ban that appeared to wipe out more severe bans that preceded it. In late 2022, after the Supreme Court overturned Roe v. Wade, the Arizona Court of Appeals ruled that the two conflicting abortion laws in the state had to be reconciled, or “harmonized.” It maintained that abortion would remain legal through 15 weeks when provided by licensed physicians in compliance with the state’s other laws.
But on Tuesday, the Arizona Supreme Court, tasked with finally “harmonizing” Arizona’s 15-week abortion ban with the total ban dating back to hoop skirts, ruled that in the aftermath of Roe ’s reversal in Dobbs, the total ban takes precedence: The more recent 15-week restriction, wrote the majority, “does not create a right to, or otherwise provide independent statutory authority for, an abortion that repeals or restricts” the 1864 law, “but rather is predicated entirely on the existence of a federal constitutional right to an abortion since disclaimed” by Dobbs. In other words, in “harmonizing” the two laws, the harsher one wins out—even though, as the dissenters noted, the Legislature seemed to override this absolute ban when passing the recent 15-week limit. And so, starting in two weeks, even rape victims at the earliest stage of pregnancy may not obtain a legal abortion in Arizona.
Since Dobbs, nearly two dozen states have banned or limited access to the procedure. Arizona now joins those states with almost no exceptions , according to the Guttmacher Institute. As was the case with the far-right Florida Supreme Court’s interpretation of that state’s constitution last week , the majority simply ignored any evidence that the original meaning and text of the recent law provided greater protections for reproductive freedom. Instead, the majority rejected the Legislature’s evident intent to supplant the Civil War–era law with a more lenient ban. As a consolation, it gestured toward the fact that Arizona voters will likely have an opportunity to enact a ballot initiative restoring reproductive rights. So Arizona now joins Florida as a state in which the high court takes away reproductive freedom with one hand while allowing it to go to a popular vote with the other. Abortion-rights groups say they have enough signatures to put the abortion amendment on the November ballot, creating a fundamental right to receive abortion care until viability. Unlike Florida, where amendments need 60 percent approval to pass, Arizona allows amendments to take effect with simple majority support. (Note, as well, that two justices in the majority on Tuesday have retention elections in November; if ousted, Democratic Gov. Katie Hobbs can replace them with progressives.)
In an election year in which winning the state of Arizona is an absolutely essential factor for the GOP, the abortion dog continues to catch the electoral car in ways that can only hurt Donald Trump and the GOP extremists who seek to harm women’s health and equality. So long as voters are aware of the game as it’s being played and what the stakes will be, Republicans faces the potential for heaving losses. So these efforts to do that which is extraordinarily unpopular must happen via subterfuge, wink-wink nudge-nudge public statements about states’ rights and not taking a national position on abortion, while the courts and would-be Trump administration functionaries do all the quiet dirty work. The self-evident tension between the massive public rebuke of Dobbs —in the form of state ballot initiatives and referenda , local special elections , and state Supreme Court races —and the unabating efforts by rogue legislatures and fringe Supreme Courts to roll back abortion rights, was in evidence with Donald Trump’s refusal to state a coherent position on abortion on Monday : Turning back the clock for women is a demonstrably losing issue at the ballot box. And when candidate Trump says he wants to return the issue of abortion to the states, what he is really saying is that Arizona is free to return the issue to the time before doctors understood the value of hand-washing . (Also, why would anyone take his word on anything, ever?)
What happened in Alabama in February , in Florida last week, and in Arizona on Tuesday makes it clear that returning the reproductive freedom landscape to the Victorian age requires subverting whatever happens in elections. That’s why this massive rollback will be achieved by antidemocratic measures, including promises to breathe new life into the Comstock Act, and revanchist theocratic decisions from courts attempting to do away with IVF and rape exceptions in the name of fetal and embryonic personhood .
Comstock, in particular, is an instructive comparison here. That 1873 law, read expansively, bans all abortions , including both medication and in-clinic procedures. Indeed, far-right lawyers are at the Supreme Court trying to weaponize it against abortion pills right now. Trump’s top lawyers, including Jonathan Mitchell, have said that they plan to use Comstock as a nationwide ban on abortion if Trump regains office. They tell us that they intend to stay quiet about this scheme until after the election, at which point they will prepare for an executive order accompanied by prosecutions and regulations that make abortion a federal felony in all 50 states. The plot is similar to what just happened in Arizona: Republicans enacted a seemingly moderate 15-week ban, only to stand by and watch as their colleagues on a GOP-packed court resuscitated a total ban passed during the Civil War. Democratic Attorney General Kris Mayes—who beat her anti-abortion opponent in 2022 by 280 votes—has said she won’t prosecute violations of the law. But GOP county attorneys have rejected Mayes’ efforts to shield doctors and may well seek to charge any providers that stay open, throwing access into immediate jeopardy.
The next time someone tells you they really worry about abortion rights, but that President Biden is just too old , please gently remind them that Joe Biden is not, in fact 160. That is the age of the law that will soon be sending abortion providers to prison in Arizona if they attempt to assist a victim of rape or incest. If edgy modernity is truly your thing, be afraid of Republican judges who are at war with modernity itself; they will gladly welcome the assistance of pro-choice voters whose apathy facilitates the rollback of women’s equal citizenship. And it’s now abundantly clear that we’re not rolling back the tape to the 1970s or to the 1920s. The project is to set your clocks back to the time when women didn’t even matter enough to have a vote.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Rom J Morphol Embryol
- v.61(1); Jan-Mar 2020

A research on abortion: ethics, legislation and socio-medical outcomes. Case study: Romania
Andreea mihaela niţă.
1 Faculty of Social Sciences, University of Craiova, Romania
Cristina Ilie Goga
This article presents a research study on abortion from a theoretical and empirical point of view. The theoretical part is based on the method of social documents analysis, and presents a complex perspective on abortion, highlighting items of medical, ethical, moral, religious, social, economic and legal elements. The empirical part presents the results of a sociological survey, based on the opinion survey method through the application of the enquiry technique, conducted in Romania, on a sample of 1260 women. The purpose of the survey is to identify Romanians perception on the decision to voluntary interrupt pregnancy, and to determine the core reasons in carrying out an abortion.
The analysis of abortion by means of medical and social documents
Abortion means a pregnancy interruption “before the fetus is viable” [ 1 ] or “before the fetus is able to live independently in the extrauterine environment, usually before the 20 th week of pregnancy” [ 2 ]. “Clinical miscarriage is both a common and distressing complication of early pregnancy with many etiological factors like genetic factors, immune factors, infection factors but also psychological factors” [ 3 ]. Induced abortion is a practice found in all countries, but the decision to interrupt the pregnancy involves a multitude of aspects of medical, ethical, moral, religious, social, economic, and legal order.
In a more simplistic manner, Winston Nagan has classified opinions which have as central element “abortion”, in two major categories: the opinion that the priority element is represented by fetus and his entitlement to life and the second opinion, which focuses around women’s rights [ 4 ].
From the medical point of view, since ancient times there have been four moments, generally accepted, which determine the embryo’s life: ( i ) conception; ( ii ) period of formation; ( iii ) detection moment of fetal movement; ( iv ) time of birth [ 5 ]. Contemporary medicine found the following moments in the evolution of intrauterine fetal: “ 1 . At 18 days of pregnancy, the fetal heartbeat can be perceived and it starts running the circulatory system; 2 . At 5 weeks, they become more clear: the nose, cheeks and fingers of the fetus; 3 . At 6 weeks, they start to function: the nervous system, stomach, kidneys and liver of the fetus, and its skeleton is clearly distinguished; 4 . At 7 weeks (50 days), brain waves are felt. The fetus has all the internal and external organs definitively outlined. 5 . At 10 weeks (70 days), the unborn child has all the features clearly defined as a child after birth (9 months); 6 . At 12 weeks (92 days, 3 months), the fetus has all organs definitely shaped, managing to move, lacking only the breath” [ 6 ]. Even if most of the laws that allow abortion consider the period up to 12 weeks acceptable for such an intervention, according to the above-mentioned steps, there can be defined different moments, which can represent the beginning of life. Nowadays, “abortion is one of the most common gynecological experiences and perhaps the majority of women will undergo an abortion in their lifetimes” [ 7 ]. “Safe abortions carry few health risks, but « every year, close to 20 million women risk their lives and health by undergoing unsafe abortions » and 25% will face a complication with permanent consequences” [ 8 , 9 ].
From the ethical point of view, most of the times, the interruption of pregnancy is on the border between woman’s right over her own body and the child’s (fetus) entitlement to life. Judith Jarvis Thomson supported the supremacy of woman’s right over her own body as a premise of freedom, arguing that we cannot force a person to bear in her womb and give birth to an unwanted child, if for different circumstances, she does not want to do this [ 10 ]. To support his position, the author uses an imaginary experiment, that of a violinist to which we are connected for nine months, in order to save his life. However, Thomson debates the problem of the differentiation between the fetus and the human being, by carrying out a debate on the timing which makes this difference (period of conception, 10 weeks of pregnancy, etc.) and highlighting that for people who support abortion, the fetus is not an alive human being [ 10 ].
Carol Gilligan noted that women undergo a true “moral dilemma”, a “moral conflict” with regards to voluntary interruption of pregnancy, such a decision often takes into account the human relationships, the possibility of not hurting the others, the responsibility towards others [ 11 ]. Gilligan applied qualitative interviews to a number of 29 women from different social classes, which were put in a position to decide whether or not to commit abortion. The interview focused on the woman’s choice, on alternative options, on individuals and existing conflicts. The conclusion was that the central moral issue was the conflict between the self (the pregnant woman) and others who may be hurt as a result of the potential pregnancy [ 12 ].
From the religious point of view, abortion is unacceptable for all religions and a small number of abortions can be seen in deeply religious societies and families. Christianity considers the beginning of human life from conception, and abortion is considered to be a form of homicide [ 13 ]. For Christians, “at the same time, abortion is giving up their faith”, riot and murder, which means that by an abortion we attack Jesus Christ himself and God [ 14 ]. Islam does not approve abortion, relying on the sacral life belief as specified in Chapter 6, Verse 151 of the Koran: “Do not kill a soul which Allah has made sacred (inviolable)” [ 15 ]. Buddhism considers abortion as a negative act, but nevertheless supports for medical reasons [ 16 ]. Judaism disapproves abortion, Tanah considering it to be a mortal sin. Hinduism considers abortion as a crime and also the greatest sin [ 17 ].
From the socio-economic point of view, the decision to carry out an abortion is many times determined by the relations within the social, family or financial frame. Moreover, studies have been conducted, which have linked the legalization of abortions and the decrease of the crime rate: “legalized abortion may lead to reduced crime either through reductions in cohort sizes or through lower per capita offending rates for affected cohorts” [ 18 ].
Legal regulation on abortion establishes conditions of the abortion in every state. In Europe and America, only in the XVIIth century abortion was incriminated and was considered an insignificant misdemeanor or a felony, depending on when was happening. Due to the large number of illegal abortions and deaths, two centuries later, many states have changed legislation within the meaning of legalizing voluntary interruption of pregnancy [ 6 ]. In contemporary society, international organizations like the United Nations or the European Union consider sexual and reproductive rights as fundamental rights [ 19 , 20 ], and promotes the acceptance of abortion as part of those rights. However, not all states have developed permissive legislation in the field of voluntary interruption of pregnancy.
Currently, at national level were established four categories of legislation on pregnancy interruption area:
( i ) Prohibitive legislations , ones that do not allow abortion, most often outlining exceptions in abortion in cases where the pregnant woman’s life is endangered. In some countries, there is a prohibition of abortion in all circumstances, however, resorting to an abortion in the case of an imminent threat to the mother’s life. Same regulation is also found in some countries where abortion is allowed in cases like rape, incest, fetal problems, etc. In this category are 66 states, with 25.5% of world population [ 21 ].
( ii ) Restrictive legislation that allow abortion in cases of health preservation . Loosely, the term “health” should be interpreted according to the World Health Organization (WHO) definition as: “health is a state of complete physical, mental and social wellbeing and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity” [ 22 ]. This type of legislation is adopted in 59 states populated by 13.8% of the world population [ 21 ].
( iii ) Legislation allowing abortion on a socio-economic motivation . This category includes items such as the woman’s age or ability to care for a child, fetal problems, cases of rape or incest, etc. In this category are 13 countries, where we have 21.3% of the world population [ 21 ].
( iv ) Legislation which do not impose restrictions on abortion . In the case of this legislation, abortion is permitted for any reason up to 12 weeks of pregnancy, with some exceptions (Romania – 14 weeks, Slovenia – 10 weeks, Sweden – 18 weeks), the interruption of pregnancy after this period has some restrictions. This type of legislation is adopted in 61 countries with 39.5% of the world population [21].
The Centre for Reproductive Rights has carried out from 1998 a map of the world’s states, based on the legislation typology of each country (Figure (Figure1 1 ).

The analysis of states according to the legislation regarding abortion. Source: Centre for Reproductive Rights. The World’s Abortion Laws, 2018 [ 23 ]
An unplanned pregnancy, socio-economic context or various medical problems [ 24 ], lead many times to the decision of interrupting pregnancy, regardless the legislative restrictions. In the study “Unsafe abortion: global and regional estimates of the incidence of unsafe abortion and associated mortality in 2008” issued in 2011 by the WHO , it was determined that within the states with restrictive legislation on abortion, we may also encounter a large number of illegal abortions. The illegal abortions may also be resulting in an increased risk of woman’s health and life considering that most of the times inappropriate techniques are being used, the hygienic conditions are precarious and the medical treatments are incorrectly administered [ 25 ]. Although abortions done according to medical guidelines carry very low risk of complications, 1–3 unsafe abortions contribute substantially to maternal morbidity and death worldwide [ 26 ].
WHO has estimated for the year 2008, the fact that worldwide women between the ages of 15 and 44 years carried out 21.6 million “unsafe” abortions, which involved a high degree of risk and were distributed as follows: 0.4 million in the developed regions and a number of 21.2 million in the states in course of development [ 25 ].
Case study: Romania
Legal perspective on abortion
In Romania, abortion was brought under regulation by the first Criminal Code of the United Principalities, from 1864.
The Criminal Code from 1864, provided the abortion infringement in Article 246, on which was regulated as follows: “Any person, who, using means such as food, drinks, pills or any other means, which will consciously help a pregnant woman to commit abortion, will be punished to a minimum reclusion (three years).
The woman who by herself shall use the means of abortion, or would accept to use means of abortion which were shown or given to her for this purpose, will be punished with imprisonment from six months to two years, if the result would be an abortion. In a situation where abortion was carried out on an illegitimate baby by his mother, the punishment will be imprisonment from six months to one year.
Doctors, surgeons, health officers, pharmacists (apothecary) and midwives who will indicate, will give or will facilitate these means, shall be punished with reclusion of at least four years, if the abortion took place. If abortion will cause the death of the mother, the punishment will be much austere of four years” (Art. 246) [ 27 ].
The Criminal Code from 1864, reissued in 1912, amended in part the Article 246 for the purposes of eliminating the abortion of an illegitimate baby case. Furthermore, it was no longer specified the minimum of four years of reclusion, in case of abortion carried out with the help of the medical staff, leaving the punishment to the discretion of the Court (Art. 246) [ 28 ].
The Criminal Code from 1936 regulated abortion in the Articles 482–485. Abortion was defined as an interruption of the normal course of pregnancy, being punished as follows:
“ 1 . When the crime is committed without the consent of the pregnant woman, the punishment was reformatory imprisonment from 2 to 5 years. If it caused the pregnant woman any health injury or a serious infirmity, the punishment was reformatory imprisonment from 3 to 6 years, and if it has caused her death, reformatory imprisonment from 7 to 10 years;
2 . When the crime was committed by the unmarried pregnant woman by herself, or when she agreed that someone else should provoke the abortion, the punishment is reformatory imprisonment from 3 to 6 months, and if the woman is married, the punishment is reformatory imprisonment from 6 months to one year. Same penalty applies also to the person who commits the crime with the woman’s consent. If abortion was committed for the purpose of obtaining a benefit, the punishment increases with another 2 years of reformatory imprisonment.
If it caused the pregnant woman any health injuries or a severe disablement, the punishment will be reformatory imprisonment from one to 3 years, and if it has caused her death, the punishment is reformatory imprisonment from 3 to 5 years” (Art. 482) [ 29 ].
The criminal legislation from 1936 specifies that it is not considered as an abortion the interruption from the normal course of pregnancy, if it was carried out by a doctor “when woman’s life was in imminent danger or when the pregnancy aggravates a woman’s disease, putting her life in danger, which could not be removed by other means and it is obvious that the intervention wasn’t performed with another purpose than that of saving the woman’s life” and “when one of the parents has reached a permanent alienation and it is certain that the child will bear serious mental flaws” (Art. 484, Par. 1 and Par. 2) [ 29 ].
In the event of an imminent danger, the doctor was obliged to notify prosecutor’s office in writing, within 48 hours after the intervention, on the performance of the abortion. “In the other cases, the doctor was able to intervene only with the authorization of the prosecutor’s office, given on the basis of a medical certificate from hospital or a notice given as a result of a consultation between the doctor who will intervene and at least a professor doctor in the disease which caused the intervention. General’s Office Prosecutor, in all cases provided by this Article, shall be obliged to maintain the confidentiality of all communications or authorizations, up to the intercession of any possible complaints” (Art. 484) [ 29 ].
The legislation of 1936 provided a reformatory injunction from one to three years for the abortions committed by doctors, sanitary agents, pharmacists, apothecary or midwives (Art. 485) [ 29 ].
Abortion on demand has been legalized for the first time in Romania in the year 1957 by the Decree No. 463, under the condition that it had to be carried out in a hospital and to be carried out in the first quarter of the pregnancy [ 30 ]. In the year 1966, demographic policy of Romania has dramatically changed by introducing the Decree No. 770 from September 29 th , which prohibited abortion. Thus, the voluntary interruption of pregnancy became a crime, with certain exceptions, namely: endangering the mother’s life, physical or mental serious disability; serious or heritable illness, mother’s age over 45 years, if the pregnancy was a result of rape or incest or if the woman gave birth to at least four children who were still in her care (Art. 2) [ 31 ].
In the Criminal Code from 1968, the abortion crime was governed by Articles 185–188.
The Article 185, “the illegal induced abortion”, stipulated that “the interruption of pregnancy by any means, outside the conditions permitted by law, with the consent of the pregnant woman will be punished with imprisonment from one to 3 years”. The act referred to above, without the prior consent from the pregnant woman, was punished with prison from two to five years. If the abortion carried out with the consent of the pregnant woman caused any serious body injury, the punishment was imprisonment from two to five years, and when it caused the death of the woman, the prison sentence was from five to 10 years. When abortion was carried out without the prior consent of the woman, if it caused her a serious physical injury, the punishment was imprisonment from three to six years, and if it caused the woman’s death, the punishment was imprisonment from seven to 12 years (Art. 185) [ 32 ].
“When abortion was carried out in order to obtain a material benefit, the maximum punishment was increased by two years, and if the abortion was made by a doctor, in addition to the prison punishment could also be applied the prohibition to no longer practice the profession of doctor”.
Article 186, “abortion caused by the woman”, stipulated that “the interruption of the pregnancy course, committed by the pregnant woman, was punished with imprisonment from 6 months to 2 years”, quoting the fact that by the same punishment was also sanctioned “the pregnant woman’s act to consent in interrupting the pregnancy course made out by another person” (Art. 186) [ 26 ].
The Regulations of the Criminal Code in 1968, also provided the crime of “ownership of tools or materials that can cause abortion”, the conditions of this holding being met when these types of instruments were held outside the hospital’s specialized institutions, the infringement shall be punished with imprisonment from three months to one year (Art. 187) [ 32 ].
Furthermore, the doctors who performed an abortion in the event of extreme urgency, without prior legal authorization and if they did not announce the competent authority within the legal deadline, they were punished by imprisonment from one month to three months (Art. 188) [ 32 ].
In the year 1985, it has been issued the Decree No. 411 of December 26 th , by which the conditions imposed by the Decree No. 770 of 1966 have been hardened, meaning that it has increased the number of children, that a woman could have in order to request an abortion, from four to five children [ 33 ].
The Articles 185–188 of the Criminal Code and the Decree No. 770/1966 on the interruption of the pregnancy course have been abrogated by Decree-Law No. 1 from December 26 th , 1989, which was published in the Official Gazette No. 4 of December 27 th , 1989 (Par. 8 and Par. 12) [ 34 ].
The Criminal Code from 1968, reissued in 1997, maintained Article 185 about “the illegal induced abortion”, but drastically modified. Thus, in this case of the Criminal Code, we identify abortion as “the interruption of pregnancy course, by any means, committed in any of the following circumstances: ( a ) outside medical institutions or authorized medical practices for this purpose; ( b ) by a person who does not have the capacity of specialized doctor; ( c ) if age pregnancy has exceeded 14 weeks”, the punishment laid down was the imprisonment from 6 months to 3 years” (Art. 185, Par. 1) [ 35 ]. For the abortion committed without the prior consent of the pregnant woman, the punishment consisted in strict prison conditions from two to seven years and with the prohibition of certain rights (Art. 185, Par. 2) [ 35 ].
For the situation of causing serious physical injury to the pregnant woman, the punishment was strict prison from three to 10 years and the removal of certain rights, and if it had as a result the death of the pregnant woman, the punishment was strict prison from five to 15 years and the prohibition of certain rights (Art. 185, Par. 3) [ 35 ].
The attempt was punished for the crimes specified in the various cases of abortion.
Consideration should also be given in the Criminal Code reissued in 1997 for not punishing the interruption of the pregnancy course carried out by the doctor, if this interruption “was necessary to save the life, health or the physical integrity of the pregnant woman from a grave and imminent danger and that it could not be removed otherwise; in the case of a over fourteen weeks pregnancy, when the interruption of the pregnancy course should take place from therapeutic reasons” and even in a situation of a woman’s lack of consent, when it has not been given the opportunity to express her will, and abortion “was imposed by therapeutic reasons” (Art. 185, Par. 4) [ 35 ].
Criminal Code from 2004 covers abortion in Article 190, defined in the same way as in the prior Criminal Code, with the difference that it affects the limits of the punishment. So, in the event of pregnancy interruption, in accordance with the conditions specified in Paragraph 1, “the penalty provided was prison time from 6 months to one year or days-fine” (Art. 190, Par. 1) [ 36 ].
Nowadays, in Romania, abortion is governed by the criminal law of 2009, which entered into force in 2014, by the section called “aggression against an unborn child”. It should be specified that current criminal law does not punish the woman responsible for carrying out abortion, but only the person who is involved in carrying out the abortion. There is no punishment for the pregnant woman who injures her fetus during pregnancy.
In Article 201, we can find the details on the pregnancy interruption infringement. Thus, the pregnancy interruption can be performed in one of the following circumstances: “outside of medical institutions or medical practices authorized for this purpose; by a person who does not have the capacity of specialist doctor in Obstetrics and Gynecology and the right of free medical practice in this specialty; if gestational age has exceeded 14 weeks”, the punishment is the imprisonment for six months to three years, or fine and the prohibition to exercise certain rights (Art. 201, Par. 1) [ 37 ].
Article 201, Paragraph 2 specifies that “the interruption of the pregnancy committed under any circumstances, without the prior consent of the pregnant woman, can be punished with imprisonment from 2 to 7 years and with the prohibition to exercise some rights” (Art. 201, Par. 1) [ 37 ].
If by facts referred to above (Art. 201, Par. 1 and Par. 2) [ 37 ] “it has caused the pregnant woman’s physical injury, the punishment is the imprisonment from 3 to 10 years and the prohibition to exercise some rights, and if it has had as a result the pregnant woman’s death, the punishment is the imprisonment from 6 to 12 years and the prohibition to exercise some rights” (Art. 201, Par. 3) [ 37 ]. When the facts have been committed by a doctor, “in addition to the imprisonment punishment, it will also be applied the prohibition to exercise the profession of doctor (Art. 201, Par. 4) [ 37 ].
Criminal legislation specifies that “the interruption of pregnancy does not constitute an infringement with the purpose of a treatment carried out by a specialist doctor in Obstetrics and Gynecology, until the pregnancy age of twenty-four weeks is reached, or the subsequent pregnancy interruption, for the purpose of treatment, is in the interests of the mother or the fetus” (Art. 201, Par. 6) [ 37 ]. However, it can all be found in the phrases “therapeutic purposes” and “the interest of the mother and of the unborn child”, which predisposes the text of law to an interpretation, finally the doctors are the only ones in the position to decide what should be done in such cases, assuming direct responsibility [ 38 ].
Article 202 of the Criminal Code defines the crime of harming an unborn child, pointing out the punishments for the various types of injuries that can occur during pregnancy or in the childbirth period and which can be caused by the mother or by the persons who assist the birth, with the specification that the mother who harms her fetus during pregnancy is not punished and does not constitute an infringement if the injury has been committed during pregnancy or during childbirth period if the facts have been “committed by a doctor or by an authorized person to assist the birth or to follow the pregnancy, if they have been committed in the course of the medical act, complying with the specific provisions of his profession and have been made in the interest of the pregnant woman or fetus, as a result of the exercise of an inherent risk in the medical act” (Art. 202, Par. 6) [ 37 ].
The fact situation in Romania
During the period 1948–1955, called “the small baby boom” [ 39 ], Romania registered an average fertility rate of 3.23 children for a woman. Between 1955 and 1962, the fertility rate has been less than three children for a woman, and in 1962, fertility has reached an average of two children for a woman. This phenomenon occurred because of the Decree No. 463/1957 on liberalization of abortion. After the liberalization from 1957, the abortion rate has increased from 220 abortions per 100 born-alive children in the year 1960, to 400 abortions per 100 born-alive children, in the year 1965 [ 40 ].
The application of provisions of Decrees No. 770 of 1966 and No. 411 of 1985 has led to an increase of the birth rate in the first three years (an average of 3.7 children in 1967, and 3.6 children in 1968), followed by a regression until 1989, when it was recorded an average of 2.2 children, but also a maternal death rate caused by illegal abortions, raising up to 85 deaths of 100 000 births in the year of 1965, and 170 deaths in 1983. It was estimated that more than 80% of maternal deaths between 1980–1989 was caused by legal constraints [ 30 ].
After the Romanian Revolution in December 1989 and after the communism fall, with the abrogation of Articles 185–188 of the Criminal Code and of the Decree No. 770/1966, by the Decree of Law No. 1 of December 26 th , 1989, abortion has become legal in Romania and so, in the following years, it has reached the highest rate of abortion in Europe. Subsequently, the number of abortion has dropped gradually, with increasing use of birth control [ 41 ].
Statistical data issued by the Ministry of Health and by the National Institute of Statistics (INS) in Romania show corresponding figures to a legally carried out abortion. The abortion number is much higher, if it would take into account the number of illegal abortion, especially those carried out before 1989, and those carried out in private clinics, after the year 1990. Summing the declared abortions in the period 1958–2014, it is to be noted the number of them, 22 037 747 exceeds the current Romanian population. A detailed statistical research of abortion rate, in terms of years we have exposed in Table Table1 1 .
The number of abortions declared in Romania in the period 1958–2016
Source: Pro Vita Association (Bucharest, Romania), National Institute of Statistics (INS – Romania), EUROSTAT [ 42 , 43 , 44 ]
Data issued by the United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund (UNICEF) in June 2016, for the period 1989–2014, in matters of reproductive behavior, indicates a fertility rate for Romania with a continuous decrease, in proportion to the decrease of the number of births, but also a lower number of abortion rate reported to 100 deliveries (Table (Table2 2 ).
Reproductive behavior in Romania in 1989–2014
Source: United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund (UNICEF), Transformative Monitoring for Enhanced Equity (TransMonEE) Data. Country profiles: Romania, 1989–2015 [ 45 ].
By analyzing data issued for the period 1990–2015 by the International Organization of Health , UNICEF , United Nations Fund for Population Activity (UNFPA), The World Bank and the United Nations Population Division, it is noticed that maternal mortality rate has currently dropped as compared with 1990 (Table (Table3 3 ).
Maternal mortality estimation in Romania in 1990–2015
Source: World Health Organization (WHO), Global Health Observatory Data. Maternal mortality country profiles: Romania, 2015 [ 46 ].
Opinion survey: women’s opinion on abortion
Argument for choosing the research theme
Although the problematic on abortion in Romania has been extensively investigated and debated, it has not been carried out in an ample sociological study, covering Romanian women’s perception on abortion. We have assumed making a study at national level, in order to identify the opinion on abortion, on the motivation to carry out an abortion, and to identify the correlation between religious convictions and the attitude toward abortion.
Examining the literature field of study
In the conceptual register of the research, we have highlighted items, such as the specialized literature, legislation, statistical documents.
Formulation of hypotheses and objectives
The first hypothesis was that Romanian women accept abortion, having an open attitude towards this act. Thus, the first objective of the research was to identify Romanian women’s attitude towards abortion.
The second hypothesis, from which we started, was that high religious beliefs generate a lower tolerance towards abortion. Thus, the second objective of our research has been to identify the correlation between the religious beliefs and the attitude towards abortion.
The third hypothesis of the survey was that, the main motivation in carrying out an abortion is the fact that a woman does not want a baby, and the main motivation for keeping the pregnancy is that the person wants a baby. In this context, the third objective of the research was to identify main motivation in carrying out an abortion and in maintaining a pregnancy.
Another hypothesis was that modern Romanian legislation on the abortion is considered fair. Based on this hypothesis, we have assumed the fourth objective, which is to identify the degree of satisfaction towards the current regulatory provisions governing the abortion.
Research methodology
The research method is that of a sociological survey by the application of the questionnaire technique. We used the sampling by age and residence looking at representative numbers of population from more developed as well as underdeveloped areas.
Determination of the sample to be studied
Because abortion is a typical women’s experience, we have chosen to make the quantitative research only among women. We have constructed the sample by selecting a number of 1260 women between the ages of 15 and 44 years (the most frequently encountered age among women who give birth to a child). We also used the quota sampling techniques, taking into account the following variables: age group and the residence (urban/rural), so that the persons included in the sample could retain characteristic of the general population.
By the sample of 1260 women, we have made a percentage of investigation of 0.03% of the total population.
The Questionnaires number applied was distributed as follows (Table (Table4 4 ).
The sampling rates based on the age, and the region of residence
Source: Sample built, based on the population data issued by the National Institute of Statistics (INS – Romania) based on population census conducted in 2011 [ 47 ].
Data collection
Data collection was carried out by questionnaires administered by 32 field operators between May 1 st –May 31 st , 2018.
The analysis of the research results
In the next section, we will present the main results of the quantitative research carried out at national level.
Almost three-quarters of women included in the sample agree with carrying out an abortion in certain circumstances (70%) and only 24% have chosen to support the answer “ No, never ”. In modern contemporary society, abortion is the first solution of women for which a pregnancy is not desired. Even if advanced medical techniques are a lot safer, an abortion still carries a health risk. However, 6% of respondents agree with carrying out abortion regardless of circumstances (Table (Table5 5 ).
Opinion on the possibility of carrying out an abortion
Although abortions carried out after 14 weeks are illegal, except for medical reasons, more than half of the surveyed women stated they would agree with abortion in certain circumstances. At the opposite pole, 31% have mentioned they would never agree on abortions after 14 weeks. Five percent were totally accepting the idea of abortion made to a pregnancy that has exceeded 14 weeks (Table (Table6 6 ).
Opinion on the possibility of carrying out an abortion after the period of 14 weeks of pregnancy
For 53% of respondents, abortion is considered a crime as well as the right of a women. On the other hand, 28% of the women considered abortion as a crime and 16% associate abortion with a woman’s right (Table (Table7 7 ).
Opinion on abortion: at the border between crime and a woman’s right
Opinions on what women abort at the time of the voluntary pregnancy interruption are split in two: 59% consider that it depends on the time of the abortion, and more specifically on the pregnancy development stage, 24% consider that regardless of the period in which it is carried out, women abort a child, and 14% have opted a fetus (Table (Table8 8 ).
Abortion of a child vs. abortion of a fetus
Among respondents who consider that women abort a child or a fetus related to the time of abortion, 37.5% have considered that the difference between a baby and a fetus appears after 14 weeks of pregnancy (the period legally accepted for abortion). Thirty-three percent of them have mentioned that the distinction should be performed at the first few heartbeats; 18.1% think it is about when the child has all the features definitively outlined and can move by himself; 2.8% consider that the difference appears when the first encephalopathy traces are being felt and the child has formed all internal and external organs. A percentage of 1.7% of respondents consider that this difference occurs at the beginning of the central nervous system, and 1.4% when the unborn child has all the features that we can clearly see to a newborn child (Table (Table9 9 ).
The opinion on the moment that makes the difference between a fetus and a child
We noticed that highly religious people make a clear association between abortion and crime. They also consider that at the time of pregnancy interruption it is aborted a child and not a fetus. However, unexpectedly, we noticed that 27% of the women, who declare themselves to be very religious, have also stated that they see abortion as a crime but also as a woman’s right. Thirty-one percent of the women, who also claimed profound religious beliefs, consider that abortion may be associated with the abortion of a child but also of a fetus, this depending on the time of abortion (Tables (Tables10 10 and and11 11 ).
The correlation between the level of religious beliefs and the perspective on abortion seen as a crime or a right
The correlation between the level of religious beliefs and the perspective on abortion procedure conducted on a fetus or a child
More than half of the respondents have opted for the main reason for abortion the appearance of medical problems to the child. Baby’s health represents the main concern of future mothers, and of each parent, and the birth of a child with serious health issues, is a factor which frightens any future parent, being many times, at least theoretically, one good reason for opting for abortion. At the opposite side, 12% of respondents would not choose abortion under any circumstances. Other reasons for which women would opt for an abortion are: if the woman would have a medical problem (22%) or would not want the child (10%) (Table (Table12 12 ).
Potential reasons for carrying out an abortion
Most of the women want to give birth to a child, 56% of the respondents, representing also the reason that would determine them to keep the child. Morality (26%), faith (10%) or legal restrictions (4%), are the three other reasons for which women would not interrupt a pregnancy. Only 2% of the respondents have mentioned other reasons such as health or age.
A percentage of 23% of the surveyed people said that they have done an abortion so far, and 77% did not opted for a surgical intervention either because there was no need, or because they have kept the pregnancy (Table (Table13 13 ).
Rate of abortion among women in the sample
Most respondents, 87% specified that they have carried out an abortion during the first 14 weeks – legally accepted limit for abortion: 43.6% have made abortion in the first four weeks, 39.1% between weeks 4–8, and 4.3% between weeks 8–14. It should be noted that 8.7% could not appreciate the pregnancy period in which they carried out abortion, by opting to answer with the option “ I don’t know ”, and a percentage of 4.3% refused to answer to this question.
Performing an abortion is based on many reasons, but the fact that the women have not wanted a child is the main reason mentioned by 47.8% of people surveyed, who have done minimum an abortion so far. Among the reasons for the interruption of pregnancy, it is also included: women with medical problems (13.3%), not the right time to be a mother (10.7%), age motivation (8.7%), due to medical problems of the child (4.3%), the lack of money (4.3%), family pressure (4.3%), partner/spouse did not wanted. A percentage of 3.3% of women had different reasons for abortion, as follows: age difference too large between children, career, marital status, etc. Asked later whether they regretted the abortion, a rate of 69.6% of women who said they had at least one abortion regret it (34.8% opted for “ Yes ”, and 34.8% said “ Yes, partially ”). 26.1% of surveyed women do not regret the choice to interrupted the pregnancy, and 4.3% chose to not answer this question. We noted that, for women who have already experienced abortion, the causes were more diverse than the grounds on which the previous question was asked: “What are the reasons that determined you to have an abortion?” (Table (Table14 14 ).
The reasons that led the women in the sample to have an abortion
The majority of the respondents (37.5%) considered that “nervous depression” is the main consequence of abortion, followed by “insomnia and nightmares” (24.6%), “disorders in alimentation” and “affective disorders” (each for 7.7% of respondents), “deterioration of interpersonal relationships” and “the feeling of guilt”(for 6.3% of the respondents), “sexual disorders” and “panic attacks” (for 6.3% of the respondents) (Table (Table15 15 ).
Opinion on the consequences of abortion
Over half of the respondents believe that abortion should be legal in certain circumstances, as currently provided by law, 39% say it should be always legal, and only 6% opted for the illegal option (Table (Table16 16 ).
Opinion on the legal regulation of abortion
Although the current legislation does not punish pregnant women who interrupt pregnancy or intentionally injured their fetus, survey results indicate that 61% of women surveyed believe that the national law should punish the woman and only 28% agree with the current legislation (Table (Table17 17 ).
Opinion on the possibility of punishing the woman who interrupts the course of pregnancy or injures the fetus
For the majority of the respondents (40.6%), the penalty provided by the current legislation, the imprisonment between six months and three years or a fine and deprivation of certain rights for the illegal abortion is considered fair, for a percentage of 39.6% the punishment is too small for 9.5% of the respondents is too high. Imprisonment between two and seven years and deprivation of certain rights for an abortion performed without the consent of the pregnant woman is considered too small for 65% of interviewees. Fourteen percent of them think it is fair and only 19% of respondents consider that Romanian legislation is too severe with people who commit such an act considering the punishment as too much. The imprisonment from three to 10 years and deprivation of certain rights for the facts described above, if an injury was caused to the woman, is considered to be too small for more than half of those included in the survey, 64% and almost 22% for nearly a quarter of them. Only 9% of the respondents mentioned that this legislative measure is too severe for such actions (Table (Table18 18 ).
Opinion on the regulation of abortion of the Romanian Criminal Code (Art. 201)
Conclusions
After analyzing the results of the sociological research regarding abortion undertaken at national level, we see that 76% of the Romanian women accept abortion, indicating that the majority accepts only certain circumstances (a certain period after conception, for medical reasons, etc.). A percentage of 64% of the respondents indicated that they accept the idea of abortion after 14 weeks of pregnancy (for solid reasons or regardless the reason). This study shows that over 50% of Romanian women see abortion as a right of women but also a woman’s crime and believe that in the moment of interruption of a pregnancy, a fetus is aborted. Mostly, the association of abortion with crime and with the idea that a child is aborted is frequently found within very religious people. The main motivation for Romanian women in taking the decision not to perform an abortion is that they would want the child, and the main reason to perform an abortion is the child’s medical problems. However, it is noted that, in real situations, in which women have already done at least one abortion, most women resort to abortion because they did not want the child towards the hypothetical situation in which women felt that the main reason of abortion is a medical problem. Regarding the satisfaction with the current national legislation of the abortion, the situation is rather surprising. A significant percentage (61%) of respondents felt as necessary to punish the woman who performs an illegal abortion, although the legislation does not provide a punishment. On the other hand, satisfaction level to the penalties provided by law for various violations of the legal conditions for conducting abortion is low, on average only 25.5% of respondents are being satisfied with these, the majority (average 56.2%) considering the penalties as unsatisfactory. Understood as a social phenomenon, intensified by human vulnerabilities, of which the most obvious is accepting the comfort [ 48 ], abortion today is no longer, in Romanian society, from a legal or religious perspective, a problem. Perceptions on the legislative sanction, moral and religious will perpetual vary depending on beliefs, environment, education, etc. The only and the biggest social problem of Romania is truly represented by the steadily falling birth rate.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
The Arizona Supreme Court upheld an 1864 law on abortion: Read the full text and ruling

The Arizona Supreme Court ruled Tuesday to uphold an 1864 abortion law , making the procedure illegal in nearly all instances.
The 160-year-old law had an injunction placed on it when the U.S. Supreme Court issued its Roe v. Wade decision in 1973. But activists began petitioning to have the injunction removed when the U.S. Supreme Court overturned the right to an abortion in 2022.
Enforcement could take place as soon as 60 days from now, and the law mandates a two-to-five years prison sentence for those who aid in an abortion, except when it is necessary to save the life of the mother.
Here is more about the law, which was passed in 1864 before Arizona was a state, and Tuesday's ruling:
More: Donald Trump says states should decide abortion policy, avoids talk of a national ban
Read the 1864 abortion law text
This text was part of the first package of laws passed by the territorial Legislature in 1864: "A person who provides, supplies or administers to a pregnant woman, or procures such woman to take any medicine, drugs or substance, or uses or employs any instrument or other means whatever, with intent thereby to procure the miscarriage of such woman, unless it is necessary to save her life, shall be punished by imprisonment in the state prison for not less than two years nor more than five years."
A companion law requiring a minimum one-year sentence for a woman seeking an abortion sentence was repealed in 2021 .
See the Arizona Supreme Court abortion ruling opinion
In the opinion, the high court argued that the legislature never faltered from its 1864 intent to ban abortions.
Four justices voted in favor, two dissented and one recused himself from the case .
Here is the full opinion:
Contributing: Ray Stern, Shelby Slade, Jimmy Jenkins, Mary Jo Pitzl, Stephanie Innes, Sasha Hupkam Stacey Barchenger; USA TODAY Network
Abortion should be Legal
This essay about the legalization of abortion argues for women’s rights and bodily autonomy. It highlights the dangers of illegal abortions and emphasizes the importance of ensuring safe medical procedures. Additionally, it addresses the complex moral and ethical considerations surrounding abortion, stressing the need to respect individual circumstances. Furthermore, the essay discusses how legalizing abortion promotes social and economic equity by empowering women to pursue their goals without the burden of unplanned pregnancies. Overall, it asserts that legalizing abortion is essential for creating a society founded on justice, autonomy, and compassion.
How it works
Abortion remains a deeply divisive issue that ignites fervent debates across societies worldwide. Amidst the ethical, moral, and legal complexities surrounding this topic, one resounding argument persists: abortion should be legal. As a conscientious student, I aim to delineate a unique perspective, weaving together diverse strands of thought to elucidate the imperative of legalizing abortion.
First and foremost, the legalization of abortion is paramount for the preservation of women’s rights and bodily autonomy. Central to the ethos of gender equality is a woman’s inherent right to make decisions concerning her body without external coercion.
Denying women access to safe and legal abortion services not only undermines this fundamental principle but also shackles them to a fate dictated by others. By legalizing abortion, society unequivocally affirms its commitment to upholding women’s agency, granting them the freedom to navigate their reproductive destinies with autonomy and dignity.
Moreover, the criminalization of abortion engenders perilous consequences, imperiling the health and well-being of women. History bears witness to the harrowing reality of illegal abortions conducted in clandestine settings, often resulting in grievous harm or even death. Legalizing abortion obviates this grave public health risk by ensuring that procedures are performed under regulated conditions by competent medical professionals. In so doing, society fulfills its obligation to safeguard the lives and health of women, sparing them from the perils of unsafe practices.
Furthermore, the legalization of abortion is not tantamount to an endorsement of its morality but rather an acknowledgment of its inevitability within the fabric of human existence. Every pregnancy unfolds within a unique tapestry of circumstances, beset by myriad complexities and nuances. Legalizing abortion affords due recognition to this multifaceted reality, affording women the latitude to navigate their reproductive choices in consonance with their individual contexts and convictions.
Additionally, the legalization of abortion serves as a potent catalyst for social and economic equity, emancipating women from the shackles of unwanted pregnancies that could otherwise derail their aspirations. Access to safe and legal abortion services confers upon women the liberty to pursue educational, professional, and personal endeavors unencumbered by the specter of unplanned motherhood. By affording women the agency to exercise control over their reproductive destinies, society fosters a more equitable landscape wherein women can actualize their fullest potential unhindered by the exigencies of biology.
In conclusion, the legalization of abortion represents a pivotal step towards fostering a society founded upon principles of justice, autonomy, and compassion. By upholding women’s rights, protecting public health, acknowledging the complexities of individual circumstances, and fostering social and economic equity, the legalization of abortion stands as a beacon of progress in the annals of human civilization. As conscientious stewards of societal welfare, it behooves us to advocate fervently for the legalization of abortion, ensuring that women are empowered to chart their destinies with autonomy, dignity, and respect.
Cite this page
Abortion Should Be Legal. (2024, Apr 07). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/abortion-should-be-legal/
"Abortion Should Be Legal." PapersOwl.com , 7 Apr 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/abortion-should-be-legal/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Abortion Should Be Legal . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/abortion-should-be-legal/ [Accessed: 14 Apr. 2024]
"Abortion Should Be Legal." PapersOwl.com, Apr 07, 2024. Accessed April 14, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/abortion-should-be-legal/
"Abortion Should Be Legal," PapersOwl.com , 07-Apr-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/abortion-should-be-legal/. [Accessed: 14-Apr-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Abortion Should Be Legal . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/abortion-should-be-legal/ [Accessed: 14-Apr-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers

- Rebuilding of Moscow
Texts Images Visual Essays Video Music Other Resources
Subject essay: Lewis Siegelbaum
The capital city of both the RSFSR and the USSR, Moscow also served under Stalin as a beacon for world socialism. But Moscow was a nearly 800-year old city, with dozens of churches and residential structures dating from the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries, many narrow twisting lanes, and in a preponderance of wooden, brick, and stone buildings from the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. The “Master Plan for the Reconstruction of the City of Moscow,” devised by a commission under Lazar Kaganovich and co-signed by Stalin and Viacheslav Molotov on July 10, 1935, was intended as an “offensive against the old Moscow” that would utterly transform the city. Four years in the making, the plan called for the expansion of the city’s area from 285 to 600 square kilometers that would take in mostly farmland to the south and west beyond the Lenin (a.k.a. Sparrow) Hills. It involved sixteen major highway projects, the construction of “several monumental buildings of state-wide significance,” and fifteen million square meters of new housing to accommodate a total population of approximately five million. Surrounding the city would be a green belt up to a width of ten kilometers.
Even while the master plan was being drawn up, old Moscow was giving way to the new. One of the showpieces of the new Moscow was to be the Moscow Metro[politen] which broke ground in March 1932 and went into service on May 14, 1935. A second project begun in the early 1930s was the Moscow-Volga Canal, built by an army of prison laborers numbering 200,000 and opened in July 1937. Yet another project, for a monumental Palace of Soviets capable of hosting meetings of up to 15,000 people, was the subject of an architectural competition held in 1931. Entries were received from 160 Soviet and foreign architects including Walter Gropius and Le Corbusier. In June 1933, the jury headed by Molotov awarded the project to the Soviet architect, Boris Iofan. His terraced, colonnaded palace was to be the tallest building in the world, soaring eight meters above the recently completed Empire State Building. It was to be crowned with a massive, 90-meter-tall statue of Lenin.
The site selected for the colossus was, symbolically enough, the ground on which the Cathedral of Christ the Redeemer had stood before its demolition in 1931. This was one of many churches and religious abbeys destroyed in the frenzy to make over the capital. Work on the Palace of Soviets commenced in 1935 and continued until the Nazi invasion. In 1960 a giant outdoor heated swimming pool, the biggest in the Soviet Union (and reputedly, the world), opened on the site. It, in turn, gave way in the 1990s to a replica of the cathedral which was constructed under the auspices of Moscow’s flamboyant mayor, Iurii Luzhkov.
Comments are closed.
- Abolition of Legal Abortion
- Childhood under Stalin
- Creation of the Ethnic Republics
- The Great Terror
- Pilots and Explorers
- Popular Front
- Rehabilitation of Cossack Divisions
- Second Kolkhoz Charter
- Stalin Constitution
- Upheaval in the Opera
- Year of the Stakhanovite
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Slovenščina
- Science & Tech
- Russian Kitchen
Moscow city administration launches English-language website

The building of the Moscow City Government.
The Moscow city administration has launched the English version of its website for tourists and expats. It is available on Mos.ru beginning today. Guests of Russia’s capital will find an adapted newsfeed, calendar of events and other information relevant for foreign citizens. In particular, there are step-by-step instructions on the portal about how to get medical assistance, book a hotel and use public transport.
“Moscow’s website will also suggest how foreigners can reach the embassy or the consulate of their country and where it’s possible to exchange their currency into Russian rubles,” writes the city’s press center .
According to reports the English version of the site will not be a mirror of the main portal but instead will become an independent resource, with plans for the content to be adapted for foreign audiences.
Read more: 5 easy ways to learn Russian>>>
Subscribe to get the hand picked best stories every week.
All rights reserved by Rossiyskaya Gazeta.
to our newsletter!
Get the week's best stories straight to your inbox
This website uses cookies. Click here to find out more.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
As the long-running debate over abortion reaches another key moment at the Supreme Court and in state legislatures across the country, a majority of U.S. adults continue to say that abortion should be legal in all or most cases.About six-in-ten Americans (61%) say abortion should be legal in "all" or "most" cases, while 37% think abortion should be illegal in all or most cases.
Lack of access to safe, legal abortion can result in forced pregnancy, including among girls. Your tax deductible gift can help stop human rights violations and save lives around the world. $50.
While numerous legal thinkers have associated the abortion debate with the First Amendment, this argument has not been fully litigated. As an amicus brief filed in Dobbs by the Freedom From Religion Foundation, Center for Inquiry, and American Atheists points out, anti-abortion rhetoric is explicitly religious: "There is hardly a secular veil ...
The Case Against Abortion. Nov. 30, 2021. Crosses representing abortions in Lindale, Tex. Tamir Kalifa for The New York Times. Share full article. 3367. By Ross Douthat. Opinion Columnist. A ...
By David Leonhardt. May 19, 2021. For nearly 50 years, public opinion has had only a limited effect on abortion policy. The Roe v. Wade decision, which the Supreme Court issued in 1973 ...
State laws also limit abortion access; 43 states prohibit abortions after a specified point in pregnancy, and 36 states require some degree of parental involvement in a minor's decision to have an abortion. 18 Seventeen states have mandatory waiting periods between initial counseling, completion of consent forms, and the abortion. 18 Waiting ...
The bill would legalize abortion during the first 14 weeks of pregnancy—and later, if the pregnancy resulted from rape or threatened the person's life or health, exceptions currently allowed ...
In contrast, policy environments in which abortion was legal and readily accessible by young women are estimated to have caused a 34 percent reduction in first births, a 19 percent reduction in ...
The future of abortion, always a contentious issue, is up at the Supreme Court on Dec. 1. Arguments are planned challenging Roe v. Wade and Planned Parenthood v. Casey, the court's major decisions ...
Where safe and legal abortion services are unreasonably restricted or not fully available, many other internationally protected human rights may be at risk, including rights to nondiscrimination ...
The decision to keep the child should not be left up solely to the woman. Yes, it is her body that the child grows in, however once that child is birthed it is now two people's responsibility ...
Fewer women in states where abortion is legal support establishing a federal ban on abortion at 16 weeks (33% vs. 45% among women in states where abortion is banned), likely reflecting underlying ...
Legal abortion promotes a culture in which life is disposable. Increased access to birth control, health insurance, and sexual education would make abortion unnecessary. This article was published on June 24, 2022, at Britannica's ProCon.org, a nonpartisan issue-information source. Some argue that believe abortion is a safe medical procedure ...
The women fighting against abortion restriction laws have impacted laws, policies and court cases - all ahead of an election year. Law What the current landscape of abortion rights looks like ...
1. Questions about the moral status of abortion, and debates about whether. abortion should be legal have occupied a central and highly contentious place in. public discourse and philosophical writing for more than four decades.1 These. debates are highly polarized: debaters rarely agree on shared assumptions or.
The case involves a conflict between the federal law and Idaho's unusually restrictive anti-abortion statute, which permits physicians to perform an abortion when "necessary to prevent the ...
1962: Thalidomide. In the late 1950s and early '60s, thousands of pregnant women took a drug called thalidomide to ease pregnancy symptoms. The problem: It was found to cause severe birth defects. In 1962, a pregnant TV host who ingested thalidomide could not obtain a legal abortion in the United States.
Legalizing abortion acknowledges and respects women's autonomy, allowing them to make choices that align with their personal circumstances, values, and beliefs. Whether it is due to health concerns, financial constraints, or personal reasons, women should have the freedom to choose whether to continue a pregnancy or seek an abortion.
Ms. Smith is a Democratic senator from Minnesota and a former Planned Parenthood executive. A long discredited, arcane 150-year-old law is back in the news in 2024, and that should terrify anyone ...
On Tuesday, the Arizona Supreme Court ruled that its total abortion ban, a seemingly dead law dating back to 1864, is once again enforceable. On Tuesday, the Arizona Supreme Court ruled that its ...
Abstract. This article presents a research study on abortion from a theoretical and empirical point of view. The theoretical part is based on the method of social documents analysis, and presents a complex perspective on abortion, highlighting items of medical, ethical, moral, religious, social, economic and legal elements.
The Arizona Supreme Court ruled Tuesday to uphold an 1864 abortion law, making the procedure illegal in nearly all instances. The 160-year-old law had an injunction placed on it when the U.S ...
Essay Example: Abortion remains a deeply divisive issue that ignites fervent debates across societies worldwide. Amidst the ethical, moral, and legal complexities surrounding this topic, one resounding argument persists: abortion should be legal. As a conscientious student, I aim to delineate
One of the showpieces of the new Moscow was to be the Moscow Metro [politen] which broke ground in March 1932 and went into service on May 14, 1935. A second project begun in the early 1930s was the Moscow-Volga Canal, built by an army of prison laborers numbering 200,000 and opened in July 1937. Yet another project, for a monumental Palace of ...
By April 20, of these 24, fourteen were sentenced on assault charges to 2 to 3.5 years in prison. One of them, Pavel Ustinov, was released from jail on his own recognizance on September 20 ...
GENEVA (27 January 2023) - UN experts* today expressed alarm over the escalating crackdown against civil society by Russian authorities after the decision by the Moscow city court this week to liquidate Moscow Helsinki Group, a prominent human rights organisation. "The authorities must immediately halt all acts of repression, judicial harassment and intimidation against civil society ...
City administration introduces an English version of their site filled with useful information.