Write a business development plan
Now that you’re in the growth stage of your business, set things in motion with a business development plan.
A business development plan sets goals for growth and explains how you will achieve them. It can have a short-term or long-term focus. Review and revise your plan as often as you can. And keep building on it as your business evolves.

How to write a business development plan
Your business development plan is your roadmap to growth, so make it clear, specific and realistic.
What to include in a business development plan
- Opportunities for growth: Identify where growth will come from – whether it’s in creating new products, adding more services, breaking into new markets, or a combination of these.
- Funding plan: Determine how you’ll fund your business growth. How much capital do you already have? How much more do you need and how will you get it? Check out our guide on financing your business.
- Financial goals: Work out what revenue, costs and profits you’ll have if things stay the same. Use those numbers as a basis for setting new, more ambitious financial goals.
- Operational needs: Identify what things about your business will need to change in order to achieve growth. Will you need extra people, more equipment, or new suppliers?
- Sales and marketing activities: Figure out what sales and marketing efforts will effectively promote growth and how these efforts will change as the business gets bigger and better. Make sure your sales and marketing plan is sturdy enough to support your growing business.
- Team needs: You may need people to take on some of the tasks you’ve been doing. Think about what parts of running the business you enjoy most – and you’re good at – and what parts you might want to delegate to others. And give some thought to the culture you want to develop in your business as it grows. Check out our guide on hiring employees.
A sample business development plan
Avoid these common business development mistakes.
- Thinking short-term instead of long-term
- Underestimating how much money it will take to grow
- Not budgeting enough money to cover the costs of growth
- Focusing on too many growth opportunities: think quality, not quantity
Micro-planning can keep you focused
You may want to create some micro-plans for specific growth projects so their details don’t get overlooked. And you can build in some KPIs to measure your progress and successes. As your business grows, take note of your progress and make periodic adjustments to your business development plan to make sure it’s still relevant.
Support is out there
Remember you’re not the first to go through this. Seek out mentors, advisors or other business owners who can help you with your planning. Your accountant or bookkeeper may also be able to help or point you in the direction of the right people.
Xero does not provide accounting, tax, business or legal advice. This guide has been provided for information purposes only. You should consult your own professional advisors for advice directly relating to your business or before taking action in relation to any of the content provided.
Growing your business
Are you ready to drop the hammer and take your business to the next level? Let’s look at how to grow.
Before you leap into growth, reflect on where you’ve come from. Find out the stage of business growth you’re at.
Understanding your business performance will help you grow. Check out common examples of small business KPIs.
Increasing sales revenue is one obvious way to help grow your business. But how do you sell more?
You can grow your business by selling more things to more people, or fewer things to fewer people. Let’s look at how.
You’re all set to grow your business. But there’s so much to keep track of. Xero’s got resources and solutions to help.
Download the guide to growing your business
Learn how to grow a business, from planning to expansion. Fill out the form to receive this guide as a PDF.
Privacy notice .
Start using Xero for free
Access Xero features for 30 days, then decide which plan best suits your business.
- Included Safe and secure
- Included Cancel any time
- Included 24/7 online support
Or compare all plans
How to Write a Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples

Noah Parsons
24 min. read
Updated March 18, 2024
Writing a business plan doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to write a business plan that’s detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
- The basics of business planning
If you’re reading this guide, then you already know why you need a business plan .
You understand that planning helps you:
- Raise money
- Grow strategically
- Keep your business on the right track
As you start to write your plan, it’s useful to zoom out and remember what a business plan is .
At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow.
A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It’s also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals.
After completing your plan, you can use it as a management tool to track your progress toward your goals. Updating and adjusting your forecasts and budgets as you go is one of the most important steps you can take to run a healthier, smarter business.
We’ll dive into how to use your plan later in this article.
There are many different types of plans , but we’ll go over the most common type here, which includes everything you need for an investor-ready plan. However, if you’re just starting out and are looking for something simpler—I recommend starting with a one-page business plan . It’s faster and easier to create.
It’s also the perfect place to start if you’re just figuring out your idea, or need a simple strategic plan to use inside your business.
Dig deeper : How to write a one-page business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What to include in your business plan
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it’s a summary of the complete business plan.
Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan.
In fact, it’s common for investors to ask only for the executive summary when evaluating your business. If they like what they see in the executive summary, they’ll often follow up with a request for a complete plan, a pitch presentation , or more in-depth financial forecasts .
Your executive summary should include:
- A summary of the problem you are solving
- A description of your product or service
- An overview of your target market
- A brief description of your team
- A summary of your financials
- Your funding requirements (if you are raising money)
Dig Deeper: How to write an effective executive summary
Products and services description
This is where you describe exactly what you’re selling, and how it solves a problem for your target market. The best way to organize this part of your plan is to start by describing the problem that exists for your customers. After that, you can describe how you plan to solve that problem with your product or service.
This is usually called a problem and solution statement .
To truly showcase the value of your products and services, you need to craft a compelling narrative around your offerings. How will your product or service transform your customers’ lives or jobs? A strong narrative will draw in your readers.
This is also the part of the business plan to discuss any competitive advantages you may have, like specific intellectual property or patents that protect your product. If you have any initial sales, contracts, or other evidence that your product or service is likely to sell, include that information as well. It will show that your idea has traction , which can help convince readers that your plan has a high chance of success.
Market analysis
Your target market is a description of the type of people that you plan to sell to. You might even have multiple target markets, depending on your business.
A market analysis is the part of your plan where you bring together all of the information you know about your target market. Basically, it’s a thorough description of who your customers are and why they need what you’re selling. You’ll also include information about the growth of your market and your industry .
Try to be as specific as possible when you describe your market.
Include information such as age, income level, and location—these are what’s called “demographics.” If you can, also describe your market’s interests and habits as they relate to your business—these are “psychographics.”
Related: Target market examples
Essentially, you want to include any knowledge you have about your customers that is relevant to how your product or service is right for them. With a solid target market, it will be easier to create a sales and marketing plan that will reach your customers. That’s because you know who they are, what they like to do, and the best ways to reach them.
Next, provide any additional information you have about your market.
What is the size of your market ? Is the market growing or shrinking? Ideally, you’ll want to demonstrate that your market is growing over time, and also explain how your business is positioned to take advantage of any expected changes in your industry.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write a market analysis
Competitive analysis
Part of defining your business opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage is. To do this effectively, you need to know as much about your competitors as your target customers.
Every business has some form of competition. If you don’t think you have competitors, then explore what alternatives there are in the market for your product or service.
For example: In the early years of cars, their main competition was horses. For social media, the early competition was reading books, watching TV, and talking on the phone.
A good competitive analysis fully lays out the competitive landscape and then explains how your business is different. Maybe your products are better made, or cheaper, or your customer service is superior. Maybe your competitive advantage is your location – a wide variety of factors can ultimately give you an advantage.
Dig Deeper: How to write a competitive analysis for your business plan
Marketing and sales plan
The marketing and sales plan covers how you will position your product or service in the market, the marketing channels and messaging you will use, and your sales tactics.
The best place to start with a marketing plan is with a positioning statement .
This explains how your business fits into the overall market, and how you will explain the advantages of your product or service to customers. You’ll use the information from your competitive analysis to help you with your positioning.
For example: You might position your company as the premium, most expensive but the highest quality option in the market. Or your positioning might focus on being locally owned and that shoppers support the local economy by buying your products.
Once you understand your positioning, you’ll bring this together with the information about your target market to create your marketing strategy .
This is how you plan to communicate your message to potential customers. Depending on who your customers are and how they purchase products like yours, you might use many different strategies, from social media advertising to creating a podcast. Your marketing plan is all about how your customers discover who you are and why they should consider your products and services.
While your marketing plan is about reaching your customers—your sales plan will describe the actual sales process once a customer has decided that they’re interested in what you have to offer.
If your business requires salespeople and a long sales process, describe that in this section. If your customers can “self-serve” and just make purchases quickly on your website, describe that process.
A good sales plan picks up where your marketing plan leaves off. The marketing plan brings customers in the door and the sales plan is how you close the deal.
Together, these specific plans paint a picture of how you will connect with your target audience, and how you will turn them into paying customers.
Dig deeper: What to include in your sales and marketing plan
Business operations
The operations section describes the necessary requirements for your business to run smoothly. It’s where you talk about how your business works and what day-to-day operations look like.
Depending on how your business is structured, your operations plan may include elements of the business like:
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing processes
- Equipment and technology
- Distribution
Some businesses distribute their products and reach their customers through large retailers like Amazon.com, Walmart, Target, and grocery store chains.
These businesses should review how this part of their business works. The plan should discuss the logistics and costs of getting products onto store shelves and any potential hurdles the business may have to overcome.
If your business is much simpler than this, that’s OK. This section of your business plan can be either extremely short or more detailed, depending on the type of business you are building.
For businesses selling services, such as physical therapy or online software, you can use this section to describe the technology you’ll leverage, what goes into your service, and who you will partner with to deliver your services.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write the operations chapter of your plan
Key milestones and metrics
Although it’s not required to complete your business plan, mapping out key business milestones and the metrics can be incredibly useful for measuring your success.
Good milestones clearly lay out the parameters of the task and set expectations for their execution. You’ll want to include:
- A description of each task
- The proposed due date
- Who is responsible for each task
If you have a budget, you can include projected costs to hit each milestone. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section—just list key milestones you want to hit and when you plan to hit them. This is your overall business roadmap.
Possible milestones might be:
- Website launch date
- Store or office opening date
- First significant sales
- Break even date
- Business licenses and approvals
You should also discuss the key numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common metrics worth tracking include:
- Conversion rates
- Customer acquisition costs
- Profit per customer
- Repeat purchases
It’s perfectly fine to start with just a few metrics and grow the number you are tracking over time. You also may find that some metrics simply aren’t relevant to your business and can narrow down what you’re tracking.
Dig Deeper: How to use milestones in your business plan
Organization and management team
Investors don’t just look for great ideas—they want to find great teams. Use this chapter to describe your current team and who you need to hire . You should also provide a quick overview of your location and history if you’re already up and running.
Briefly highlight the relevant experiences of each key team member in the company. It’s important to make the case for why yours is the right team to turn an idea into a reality.
Do they have the right industry experience and background? Have members of the team had entrepreneurial successes before?
If you still need to hire key team members, that’s OK. Just note those gaps in this section.
Your company overview should also include a summary of your company’s current business structure . The most common business structures include:
- Sole proprietor
- Partnership
Be sure to provide an overview of how the business is owned as well. Does each business partner own an equal portion of the business? How is ownership divided?
Potential lenders and investors will want to know the structure of the business before they will consider a loan or investment.
Dig Deeper: How to write about your company structure and team
Financial plan
Last, but certainly not least, is your financial plan chapter.
Entrepreneurs often find this section the most daunting. But, business financials for most startups are less complicated than you think, and a business degree is certainly not required to build a solid financial forecast.
A typical financial forecast in a business plan includes the following:
- Sales forecast : An estimate of the sales expected over a given period. You’ll break down your forecast into the key revenue streams that you expect to have.
- Expense budget : Your planned spending such as personnel costs , marketing expenses, and taxes.
- Profit & Loss : Brings together your sales and expenses and helps you calculate planned profits.
- Cash Flow : Shows how cash moves into and out of your business. It can predict how much cash you’ll have on hand at any given point in the future.
- Balance Sheet : A list of the assets, liabilities, and equity in your company. In short, it provides an overview of the financial health of your business.
A strong business plan will include a description of assumptions about the future, and potential risks that could impact the financial plan. Including those will be especially important if you’re writing a business plan to pursue a loan or other investment.
Dig Deeper: How to create financial forecasts and budgets
This is the place for additional data, charts, or other information that supports your plan.
Including an appendix can significantly enhance the credibility of your plan by showing readers that you’ve thoroughly considered the details of your business idea, and are backing your ideas up with solid data.
Just remember that the information in the appendix is meant to be supplementary. Your business plan should stand on its own, even if the reader skips this section.
Dig Deeper : What to include in your business plan appendix
Optional: Business plan cover page
Adding a business plan cover page can make your plan, and by extension your business, seem more professional in the eyes of potential investors, lenders, and partners. It serves as the introduction to your document and provides necessary contact information for stakeholders to reference.
Your cover page should be simple and include:
- Company logo
- Business name
- Value proposition (optional)
- Business plan title
- Completion and/or update date
- Address and contact information
- Confidentiality statement
Just remember, the cover page is optional. If you decide to include it, keep it very simple and only spend a short amount of time putting it together.
Dig Deeper: How to create a business plan cover page
How to use AI to help write your business plan
Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT can speed up the business plan writing process and help you think through concepts like market segmentation and competition. These tools are especially useful for taking ideas that you provide and converting them into polished text for your business plan.
The best way to use AI for your business plan is to leverage it as a collaborator , not a replacement for human creative thinking and ingenuity.
AI can come up with lots of ideas and act as a brainstorming partner. It’s up to you to filter through those ideas and figure out which ones are realistic enough to resonate with your customers.
There are pros and cons of using AI to help with your business plan . So, spend some time understanding how it can be most helpful before just outsourcing the job to AI.
Learn more: 10 AI prompts you need to write a business plan
- Writing tips and strategies
To help streamline the business plan writing process, here are a few tips and key questions to answer to make sure you get the most out of your plan and avoid common mistakes .
Determine why you are writing a business plan
Knowing why you are writing a business plan will determine your approach to your planning project.
For example: If you are writing a business plan for yourself, or just to use inside your own business , you can probably skip the section about your team and organizational structure.
If you’re raising money, you’ll want to spend more time explaining why you’re looking to raise the funds and exactly how you will use them.
Regardless of how you intend to use your business plan , think about why you are writing and what you’re trying to get out of the process before you begin.
Keep things concise
Probably the most important tip is to keep your business plan short and simple. There are no prizes for long business plans . The longer your plan is, the less likely people are to read it.
So focus on trimming things down to the essentials your readers need to know. Skip the extended, wordy descriptions and instead focus on creating a plan that is easy to read —using bullets and short sentences whenever possible.
Have someone review your business plan
Writing a business plan in a vacuum is never a good idea. Sometimes it’s helpful to zoom out and check if your plan makes sense to someone else. You also want to make sure that it’s easy to read and understand.
Don’t wait until your plan is “done” to get a second look. Start sharing your plan early, and find out from readers what questions your plan leaves unanswered. This early review cycle will help you spot shortcomings in your plan and address them quickly, rather than finding out about them right before you present your plan to a lender or investor.
If you need a more detailed review, you may want to explore hiring a professional plan writer to thoroughly examine it.
Use a free business plan template and business plan examples to get started
Knowing what information you need to cover in a business plan sometimes isn’t quite enough. If you’re struggling to get started or need additional guidance, it may be worth using a business plan template.
If you’re looking for a free downloadable business plan template to get you started, download the template used by more than 1 million businesses.
Or, if you just want to see what a completed business plan looks like, check out our library of over 550 free business plan examples .
We even have a growing list of industry business planning guides with tips for what to focus on depending on your business type.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
It’s easy to make mistakes when you’re writing your business plan. Some entrepreneurs get sucked into the writing and research process, and don’t focus enough on actually getting their business started.
Here are a few common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Not talking to your customers : This is one of the most common mistakes. It’s easy to assume that your product or service is something that people want. Before you invest too much in your business and too much in the planning process, make sure you talk to your prospective customers and have a good understanding of their needs.
- Overly optimistic sales and profit forecasts: By nature, entrepreneurs are optimistic about the future. But it’s good to temper that optimism a little when you’re planning, and make sure your forecasts are grounded in reality.
- Spending too much time planning: Yes, planning is crucial. But you also need to get out and talk to customers, build prototypes of your product and figure out if there’s a market for your idea. Make sure to balance planning with building.
- Not revising the plan: Planning is useful, but nothing ever goes exactly as planned. As you learn more about what’s working and what’s not—revise your plan, your budgets, and your revenue forecast. Doing so will provide a more realistic picture of where your business is going, and what your financial needs will be moving forward.
- Not using the plan to manage your business: A good business plan is a management tool. Don’t just write it and put it on the shelf to collect dust – use it to track your progress and help you reach your goals.
- Presenting your business plan
The planning process forces you to think through every aspect of your business and answer questions that you may not have thought of. That’s the real benefit of writing a business plan – the knowledge you gain about your business that you may not have been able to discover otherwise.
With all of this knowledge, you’re well prepared to convert your business plan into a pitch presentation to present your ideas.
A pitch presentation is a summary of your plan, just hitting the highlights and key points. It’s the best way to present your business plan to investors and team members.
Dig Deeper: Learn what key slides should be included in your pitch deck
Use your business plan to manage your business
One of the biggest benefits of planning is that it gives you a tool to manage your business better. With a revenue forecast, expense budget, and projected cash flow, you know your targets and where you are headed.
And yet, nothing ever goes exactly as planned – it’s the nature of business.
That’s where using your plan as a management tool comes in. The key to leveraging it for your business is to review it periodically and compare your forecasts and projections to your actual results.
Start by setting up a regular time to review the plan – a monthly review is a good starting point. During this review, answer questions like:
- Did you meet your sales goals?
- Is spending following your budget?
- Has anything gone differently than what you expected?
Now that you see whether you’re meeting your goals or are off track, you can make adjustments and set new targets.
Maybe you’re exceeding your sales goals and should set new, more aggressive goals. In that case, maybe you should also explore more spending or hiring more employees.
Or maybe expenses are rising faster than you projected. If that’s the case, you would need to look at where you can cut costs.
A plan, and a method for comparing your plan to your actual results , is the tool you need to steer your business toward success.
Learn More: How to run a regular plan review
Free business plan templates and examples
Kickstart your business plan writing with one of our free business plan templates or recommended tools.

Free business plan template
Download a free SBA-approved business plan template built for small businesses and startups.
Download Template

One-page plan template
Download a free one-page plan template to write a useful business plan in as little as 30-minutes.

Sample business plan library
Explore over 500 real-world business plan examples from a wide variety of industries.
View Sample Plans
How to write a business plan FAQ
What is a business plan?
A document that describes your business , the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy, how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan helps you understand where you want to go with your business and what it will take to get there. It reduces your overall risk, helps you uncover your business’s potential, attracts investors, and identifies areas for growth.
Having a business plan ultimately makes you more confident as a business owner and more likely to succeed for a longer period of time.
What are the 7 steps of a business plan?
The seven steps to writing a business plan include:
- Write a brief executive summary
- Describe your products and services.
- Conduct market research and compile data into a cohesive market analysis.
- Describe your marketing and sales strategy.
- Outline your organizational structure and management team.
- Develop financial projections for sales, revenue, and cash flow.
- Add any additional documents to your appendix.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
There are plenty of mistakes that can be made when writing a business plan. However, these are the 5 most common that you should do your best to avoid:
- 1. Not taking the planning process seriously.
- Having unrealistic financial projections or incomplete financial information.
- Inconsistent information or simple mistakes.
- Failing to establish a sound business model.
- Not having a defined purpose for your business plan.
What questions should be answered in a business plan?
Writing a business plan is all about asking yourself questions about your business and being able to answer them through the planning process. You’ll likely be asking dozens and dozens of questions for each section of your plan.
However, these are the key questions you should ask and answer with your business plan:
- How will your business make money?
- Is there a need for your product or service?
- Who are your customers?
- How are you different from the competition?
- How will you reach your customers?
- How will you measure success?
How long should a business plan be?
The length of your business plan fully depends on what you intend to do with it. From the SBA and traditional lender point of view, a business plan needs to be whatever length necessary to fully explain your business. This means that you prove the viability of your business, show that you understand the market, and have a detailed strategy in place.
If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don’t necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary information in place.
What are the different types of business plans?
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan: The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used when applying for funding or pitching to investors. This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix.
Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
One-page business plan: This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences. It’s most useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Lean Plan: The Lean Plan is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance. It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision.
However, when approached correctly, your business plan can actually function as a strategic plan as well. If kept lean, you can define your business, outline strategic steps, and track ongoing operations all with a single plan.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- Use AI to help write your plan
- Common planning mistakes
- Manage with your business plan
- Templates and examples
Related Articles

5 Min. Read
How To Create a Compelling Message With Your Business Plan to Help Sell Your Idea

7 Min. Read
8 Reasons Business Plans Fail That No One Wants to Talk About

8 Min. Read
How to Write an Auto Repair Shop Business Plan + Free PDF

9 Min. Read
How to Create a Sales Plan for Your Business
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
Tax Season Savings
Get 40% off LivePlan
The #1 rated business plan software
Discover the world’s #1 plan building software


- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.1: Chapter 1 – Developing a Business Plan
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 21274

- Lee A. Swanson
- University of Saskatchewan
Learning Objectives
After completing this chapter, you will be able to
- Describe the purposes for business planning
- Describe common business planning principles
- Explain common business plan development guidelines and tools
- List and explain the elements of the business plan development process
- Explain the purposes of each element of the business plan development process
- Explain how applying the business plan development process can aid in developing a business plan that will meet entrepreneurs’ goals
This chapter describes the purposes, principles, and the general concepts and tools for business planning, and the process for developing a business plan.
Purposes for Developing Business Plans
Business plans are developed for both internal and external purposes. Internally, entrepreneurs develop business plans to help put the pieces of their business together. Externally, the most common purpose is to raise capital.
Internal Purposes
As the road map for a business’s development, the business plan
- Defines the vision for the company
- Establishes the company’s strategy
- Describes how the strategy will be implemented
- Provides a framework for analysis of key issues
- Provides a plan for the development of the business
- Helps the entrepreneur develop and measure critical success factors
- Helps the entrepreneur to be realistic and test theories
External Purposes
The business plan provides the most complete source of information for valuation of the business. Thus, it is often the main method of describing a company to external audiences such as potential sources for financing and key personnel being recruited. It should assist outside parties to understand the current status of the company, its opportunities, and its needs for resources such as capital and personnel.
Business Plan Development Principles
Hindle and Mainprize (2006) suggested that business plan writers must strive to effectively communicate their expectations about the nature of an uncertain future and to project credibility. The liabilities of newness make communicating the expected future of new ventures much more difficult than for existing businesses. Consequently, business plan writers should adhere to five specific communication principles .
First, business plans must be written to meet the expectations of targeted readers in terms of what they need to know to support the proposed business. They should also lay out the milestones that investors or other targeted readers need to know. Finally, writers must clearly outline the opportunity , the context within the proposed venture will operate (internal and external environment), and the business model (Hindle & Mainprize, 2006).
There are also five business plan credibility principles that writers should consider. Business plan writers should build and establish their credibility by highlighting important and relevant information about the venture team . Writers need to elaborate on the plans they outline in their document so that targeted readers have the information they need to assess the plan’s credibility. To build and establish credibility, they must integrate scenarios to show that the entrepreneur has made realistic assumptions and has effectively anticipated what the future holds for their proposed venture. Writers need to provide comprehensive and realistic financial links between all relevant components of the plan. Finally, they must outline the deal , or the value that targeted readers should expect to derive from their involvement with the venture (Hindle & Mainprize, 2006).
General Guidelines for Developing Business Plans
Many businesses must have a business plan to achieve their goals. Using a standard format helps the reader understand that the you have thought everything through, and that the returns justify the risk. The following are some basic guidelines for business plan development.
As You Write Your Business Plan
1. If appropriate, include nice, catchy, professional graphics on your title page to make it appealing to targeted readers, but don’t go overboard.
2. Bind your document so readers can go through it easily without it falling apart. You might use a three-ring binder, coil binding, or a similar method. Make sure the binding method you use does not obscure the information next to where it is bound.
3. Make certain all of your pages are ordered and numbered correctly.
4. The usual business plan convention is to number all major sections and subsections within your plan using the format as follows:
1. First main heading
1.1 First subheading under the first main heading
1.1.1. First sub-subheading under the first subheading
2. Second main heading
2.1 First subheading under the second main heading
Use the styles and references features in Word to automatically number and format your section titles and to generate your table of contents. Be sure that the last thing you do before printing your document is update your automatic numbering and automatically generated tables. If you fail to do this, your numbering may be incorrect.
5. Prior to submitting your plan, be 100% certain each of the following requirements are met:
- Everything must be completely integrated. The written part must say exactly the same thing as the financial part.
- All financial statements must be completely linked and valid. Make sure all of your balance sheets balance.
- Everything must be correct. There should be NO spelling, grammar, sentence structure, referencing, or calculation errors.
- Your document must be well organized and formatted. The layout you choose should make the document easy to read and comprehend. All of your diagrams, charts, statements, and other additions should be easy to find and be located in the parts of the plan best suited to them.
- In some cases it can strengthen your business plan to show some information in both text and table or figure formats. You should avoid unnecessary repetition , however, as it is usually unnecessary—and even damaging—to state the same thing more than once.
- You should include all the information necessary for readers to understand everything in your document.
- The terms you use in your plan should be clear and consistent. For example, the following statement in a business plan would leave a reader completely confused: “There is a shortage of 100,000 units with competitors currently producing 25,000. We can help fill this huge gap in demand with our capacity to produce 5,000 units.”
Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Simple Business Plan
By Joe Weller | October 11, 2021
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
A business plan is the cornerstone of any successful company, regardless of size or industry. This step-by-step guide provides information on writing a business plan for organizations at any stage, complete with free templates and expert advice.
Included on this page, you’ll find a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan and a chart to identify which type of business plan you should write . Plus, find information on how a business plan can help grow a business and expert tips on writing one .
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that communicates a company’s goals and ambitions, along with the timeline, finances, and methods needed to achieve them. Additionally, it may include a mission statement and details about the specific products or services offered.
A business plan can highlight varying time periods, depending on the stage of your company and its goals. That said, a typical business plan will include the following benchmarks:
- Product goals and deadlines for each month
- Monthly financials for the first two years
- Profit and loss statements for the first three to five years
- Balance sheet projections for the first three to five years
Startups, entrepreneurs, and small businesses all create business plans to use as a guide as their new company progresses. Larger organizations may also create (and update) a business plan to keep high-level goals, financials, and timelines in check.
While you certainly need to have a formalized outline of your business’s goals and finances, creating a business plan can also help you determine a company’s viability, its profitability (including when it will first turn a profit), and how much money you will need from investors. In turn, a business plan has functional value as well: Not only does outlining goals help keep you accountable on a timeline, it can also attract investors in and of itself and, therefore, act as an effective strategy for growth.
For more information, visit our comprehensive guide to writing a strategic plan or download free strategic plan templates . This page focuses on for-profit business plans, but you can read our article with nonprofit business plan templates .
Business Plan Steps
The specific information in your business plan will vary, depending on the needs and goals of your venture, but a typical plan includes the following ordered elements:
- Executive summary
- Description of business
- Market analysis
- Competitive analysis
- Description of organizational management
- Description of product or services
- Marketing plan
- Sales strategy
- Funding details (or request for funding)
- Financial projections
If your plan is particularly long or complicated, consider adding a table of contents or an appendix for reference. For an in-depth description of each step listed above, read “ How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step ” below.
Broadly speaking, your audience includes anyone with a vested interest in your organization. They can include potential and existing investors, as well as customers, internal team members, suppliers, and vendors.
Do I Need a Simple or Detailed Plan?
Your business’s stage and intended audience dictates the level of detail your plan needs. Corporations require a thorough business plan — up to 100 pages. Small businesses or startups should have a concise plan focusing on financials and strategy.
How to Choose the Right Plan for Your Business
In order to identify which type of business plan you need to create, ask: “What do we want the plan to do?” Identify function first, and form will follow.
Use the chart below as a guide for what type of business plan to create:
Is the Order of Your Business Plan Important?
There is no set order for a business plan, with the exception of the executive summary, which should always come first. Beyond that, simply ensure that you organize the plan in a way that makes sense and flows naturally.
The Difference Between Traditional and Lean Business Plans
A traditional business plan follows the standard structure — because these plans encourage detail, they tend to require more work upfront and can run dozens of pages. A Lean business plan is less common and focuses on summarizing critical points for each section. These plans take much less work and typically run one page in length.
In general, you should use a traditional model for a legacy company, a large company, or any business that does not adhere to Lean (or another Agile method ). Use Lean if you expect the company to pivot quickly or if you already employ a Lean strategy with other business operations. Additionally, a Lean business plan can suffice if the document is for internal use only. Stick to a traditional version for investors, as they may be more sensitive to sudden changes or a high degree of built-in flexibility in the plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step
Writing a strong business plan requires research and attention to detail for each section. Below, you’ll find a 10-step guide to researching and defining each element in the plan.
Step 1: Executive Summary
The executive summary will always be the first section of your business plan. The goal is to answer the following questions:
- What is the vision and mission of the company?
- What are the company’s short- and long-term goals?
See our roundup of executive summary examples and templates for samples. Read our executive summary guide to learn more about writing one.
Step 2: Description of Business
The goal of this section is to define the realm, scope, and intent of your venture. To do so, answer the following questions as clearly and concisely as possible:
- What business are we in?
- What does our business do?
Step 3: Market Analysis
In this section, provide evidence that you have surveyed and understand the current marketplace, and that your product or service satisfies a niche in the market. To do so, answer these questions:
- Who is our customer?
- What does that customer value?
Step 4: Competitive Analysis
In many cases, a business plan proposes not a brand-new (or even market-disrupting) venture, but a more competitive version — whether via features, pricing, integrations, etc. — than what is currently available. In this section, answer the following questions to show that your product or service stands to outpace competitors:
- Who is the competition?
- What do they do best?
- What is our unique value proposition?
Step 5: Description of Organizational Management
In this section, write an overview of the team members and other key personnel who are integral to success. List roles and responsibilities, and if possible, note the hierarchy or team structure.
Step 6: Description of Products or Services
In this section, clearly define your product or service, as well as all the effort and resources that go into producing it. The strength of your product largely defines the success of your business, so it’s imperative that you take time to test and refine the product before launching into marketing, sales, or funding details.
Questions to answer in this section are as follows:
- What is the product or service?
- How do we produce it, and what resources are necessary for production?
Step 7: Marketing Plan
In this section, define the marketing strategy for your product or service. This doesn’t need to be as fleshed out as a full marketing plan , but it should answer basic questions, such as the following:
- Who is the target market (if different from existing customer base)?
- What channels will you use to reach your target market?
- What resources does your marketing strategy require, and do you have access to them?
- If possible, do you have a rough estimate of timeline and budget?
- How will you measure success?
Step 8: Sales Plan
Write an overview of the sales strategy, including the priorities of each cycle, steps to achieve these goals, and metrics for success. For the purposes of a business plan, this section does not need to be a comprehensive, in-depth sales plan , but can simply outline the high-level objectives and strategies of your sales efforts.
Start by answering the following questions:
- What is the sales strategy?
- What are the tools and tactics you will use to achieve your goals?
- What are the potential obstacles, and how will you overcome them?
- What is the timeline for sales and turning a profit?
- What are the metrics of success?
Step 9: Funding Details (or Request for Funding)
This section is one of the most critical parts of your business plan, particularly if you are sharing it with investors. You do not need to provide a full financial plan, but you should be able to answer the following questions:
- How much capital do you currently have? How much capital do you need?
- How will you grow the team (onboarding, team structure, training and development)?
- What are your physical needs and constraints (space, equipment, etc.)?
Step 10: Financial Projections
Apart from the fundraising analysis, investors like to see thought-out financial projections for the future. As discussed earlier, depending on the scope and stage of your business, this could be anywhere from one to five years.
While these projections won’t be exact — and will need to be somewhat flexible — you should be able to gauge the following:
- How and when will the company first generate a profit?
- How will the company maintain profit thereafter?
Business Plan Template

Download Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Smartsheet
This basic business plan template has space for all the traditional elements: an executive summary, product or service details, target audience, marketing and sales strategies, etc. In the finances sections, input your baseline numbers, and the template will automatically calculate projections for sales forecasting, financial statements, and more.
For templates tailored to more specific needs, visit this business plan template roundup or download a fill-in-the-blank business plan template to make things easy.
If you are looking for a particular template by file type, visit our pages dedicated exclusively to Microsoft Excel , Microsoft Word , and Adobe PDF business plan templates.
How to Write a Simple Business Plan
A simple business plan is a streamlined, lightweight version of the large, traditional model. As opposed to a one-page business plan , which communicates high-level information for quick overviews (such as a stakeholder presentation), a simple business plan can exceed one page.
Below are the steps for creating a generic simple business plan, which are reflected in the template below .
- Write the Executive Summary This section is the same as in the traditional business plan — simply offer an overview of what’s in the business plan, the prospect or core offering, and the short- and long-term goals of the company.
- Add a Company Overview Document the larger company mission and vision.
- Provide the Problem and Solution In straightforward terms, define the problem you are attempting to solve with your product or service and how your company will attempt to do it. Think of this section as the gap in the market you are attempting to close.
- Identify the Target Market Who is your company (and its products or services) attempting to reach? If possible, briefly define your buyer personas .
- Write About the Competition In this section, demonstrate your knowledge of the market by listing the current competitors and outlining your competitive advantage.
- Describe Your Product or Service Offerings Get down to brass tacks and define your product or service. What exactly are you selling?
- Outline Your Marketing Tactics Without getting into too much detail, describe your planned marketing initiatives.
- Add a Timeline and the Metrics You Will Use to Measure Success Offer a rough timeline, including milestones and key performance indicators (KPIs) that you will use to measure your progress.
- Include Your Financial Forecasts Write an overview of your financial plan that demonstrates you have done your research and adequate modeling. You can also list key assumptions that go into this forecasting.
- Identify Your Financing Needs This section is where you will make your funding request. Based on everything in the business plan, list your proposed sources of funding, as well as how you will use it.
Simple Business Plan Template

Download Simple Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF | Smartsheet
Use this simple business plan template to outline each aspect of your organization, including information about financing and opportunities to seek out further funding. This template is completely customizable to fit the needs of any business, whether it’s a startup or large company.
Read our article offering free simple business plan templates or free 30-60-90-day business plan templates to find more tailored options. You can also explore our collection of one page business templates .
How to Write a Business Plan for a Lean Startup
A Lean startup business plan is a more Agile approach to a traditional version. The plan focuses more on activities, processes, and relationships (and maintains flexibility in all aspects), rather than on concrete deliverables and timelines.
While there is some overlap between a traditional and a Lean business plan, you can write a Lean plan by following the steps below:
- Add Your Value Proposition Take a streamlined approach to describing your product or service. What is the unique value your startup aims to deliver to customers? Make sure the team is aligned on the core offering and that you can state it in clear, simple language.
- List Your Key Partners List any other businesses you will work with to realize your vision, including external vendors, suppliers, and partners. This section demonstrates that you have thoughtfully considered the resources you can provide internally, identified areas for external assistance, and conducted research to find alternatives.
- Note the Key Activities Describe the key activities of your business, including sourcing, production, marketing, distribution channels, and customer relationships.
- Include Your Key Resources List the critical resources — including personnel, equipment, space, and intellectual property — that will enable you to deliver your unique value.
- Identify Your Customer Relationships and Channels In this section, document how you will reach and build relationships with customers. Provide a high-level map of the customer experience from start to finish, including the spaces in which you will interact with the customer (online, retail, etc.).
- Detail Your Marketing Channels Describe the marketing methods and communication platforms you will use to identify and nurture your relationships with customers. These could be email, advertising, social media, etc.
- Explain the Cost Structure This section is especially necessary in the early stages of a business. Will you prioritize maximizing value or keeping costs low? List the foundational startup costs and how you will move toward profit over time.
- Share Your Revenue Streams Over time, how will the company make money? Include both the direct product or service purchase, as well as secondary sources of revenue, such as subscriptions, selling advertising space, fundraising, etc.
Lean Business Plan Template for Startups

Download Lean Business Plan Template for Startups
Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF
Startup leaders can use this Lean business plan template to relay the most critical information from a traditional plan. You’ll find all the sections listed above, including spaces for industry and product overviews, cost structure and sources of revenue, and key metrics, and a timeline. The template is completely customizable, so you can edit it to suit the objectives of your Lean startups.
See our wide variety of startup business plan templates for more options.
How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
A business plan for a loan, often called a loan proposal , includes many of the same aspects of a traditional business plan, as well as additional financial documents, such as a credit history, a loan request, and a loan repayment plan.
In addition, you may be asked to include personal and business financial statements, a form of collateral, and equity investment information.
Download free financial templates to support your business plan.
Tips for Writing a Business Plan
Outside of including all the key details in your business plan, you have several options to elevate the document for the highest chance of winning funding and other resources. Follow these tips from experts:.
- Keep It Simple: Avner Brodsky , the Co-Founder and CEO of Lezgo Limited, an online marketing company, uses the acronym KISS (keep it short and simple) as a variation on this idea. “The business plan is not a college thesis,” he says. “Just focus on providing the essential information.”
- Do Adequate Research: Michael Dean, the Co-Founder of Pool Research , encourages business leaders to “invest time in research, both internal and external (market, finance, legal etc.). Avoid being overly ambitious or presumptive. Instead, keep everything objective, balanced, and accurate.” Your plan needs to stand on its own, and you must have the data to back up any claims or forecasting you make. As Brodsky explains, “Your business needs to be grounded on the realities of the market in your chosen location. Get the most recent data from authoritative sources so that the figures are vetted by experts and are reliable.”
- Set Clear Goals: Make sure your plan includes clear, time-based goals. “Short-term goals are key to momentum growth and are especially important to identify for new businesses,” advises Dean.
- Know (and Address) Your Weaknesses: “This awareness sets you up to overcome your weak points much quicker than waiting for them to arise,” shares Dean. Brodsky recommends performing a full SWOT analysis to identify your weaknesses, too. “Your business will fare better with self-knowledge, which will help you better define the mission of your business, as well as the strategies you will choose to achieve your objectives,” he adds.
- Seek Peer or Mentor Review: “Ask for feedback on your drafts and for areas to improve,” advises Brodsky. “When your mind is filled with dreams for your business, sometimes it is an outsider who can tell you what you’re missing and will save your business from being a product of whimsy.”
Outside of these more practical tips, the language you use is also important and may make or break your business plan.
Shaun Heng, VP of Operations at Coin Market Cap , gives the following advice on the writing, “Your business plan is your sales pitch to an investor. And as with any sales pitch, you need to strike the right tone and hit a few emotional chords. This is a little tricky in a business plan, because you also need to be formal and matter-of-fact. But you can still impress by weaving in descriptive language and saying things in a more elegant way.
“A great way to do this is by expanding your vocabulary, avoiding word repetition, and using business language. Instead of saying that something ‘will bring in as many customers as possible,’ try saying ‘will garner the largest possible market segment.’ Elevate your writing with precise descriptive words and you'll impress even the busiest investor.”
Additionally, Dean recommends that you “stay consistent and concise by keeping your tone and style steady throughout, and your language clear and precise. Include only what is 100 percent necessary.”
Resources for Writing a Business Plan
While a template provides a great outline of what to include in a business plan, a live document or more robust program can provide additional functionality, visibility, and real-time updates. The U.S. Small Business Association also curates resources for writing a business plan.
Additionally, you can use business plan software to house data, attach documentation, and share information with stakeholders. Popular options include LivePlan, Enloop, BizPlanner, PlanGuru, and iPlanner.
How a Business Plan Helps to Grow Your Business
A business plan — both the exercise of creating one and the document — can grow your business by helping you to refine your product, target audience, sales plan, identify opportunities, secure funding, and build new partnerships.
Outside of these immediate returns, writing a business plan is a useful exercise in that it forces you to research the market, which prompts you to forge your unique value proposition and identify ways to beat the competition. Doing so will also help you build (and keep you accountable to) attainable financial and product milestones. And down the line, it will serve as a welcome guide as hurdles inevitably arise.
Streamline Your Business Planning Activities with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
How to make a business plan
Table of Contents
How to make a good business plan: step-by-step guide.
A business plan is a strategic roadmap used to navigate the challenging journey of entrepreneurship. It's the foundation upon which you build a successful business.
A well-crafted business plan can help you define your vision, clarify your goals, and identify potential problems before they arise.
But where do you start? How do you create a business plan that sets you up for success?
This article will explore the step-by-step process of creating a comprehensive business plan.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a formal document that outlines a business's objectives, strategies, and operational procedures. It typically includes the following information about a company:
Products or services
Target market
Competitors
Marketing and sales strategies
Financial plan
Management team
A business plan serves as a roadmap for a company's success and provides a blueprint for its growth and development. It helps entrepreneurs and business owners organize their ideas, evaluate the feasibility, and identify potential challenges and opportunities.
As well as serving as a guide for business owners, a business plan can attract investors and secure funding. It demonstrates the company's understanding of the market, its ability to generate revenue and profits, and its strategy for managing risks and achieving success.
Business plan vs. business model canvas
A business plan may seem similar to a business model canvas, but each document serves a different purpose.
A business model canvas is a high-level overview that helps entrepreneurs and business owners quickly test and iterate their ideas. It is often a one-page document that briefly outlines the following:
Key partnerships
Key activities
Key propositions
Customer relationships
Customer segments
Key resources
Cost structure
Revenue streams
On the other hand, a Business Plan Template provides a more in-depth analysis of a company's strategy and operations. It is typically a lengthy document and requires significant time and effort to develop.
A business model shouldn’t replace a business plan, and vice versa. Business owners should lay the foundations and visually capture the most important information with a Business Model Canvas Template . Because this is a fast and efficient way to communicate a business idea, a business model canvas is a good starting point before developing a more comprehensive business plan.
A business plan can aim to secure funding from investors or lenders, while a business model canvas communicates a business idea to potential customers or partners.
Why is a business plan important?
A business plan is crucial for any entrepreneur or business owner wanting to increase their chances of success.
Here are some of the many benefits of having a thorough business plan.
Helps to define the business goals and objectives
A business plan encourages you to think critically about your goals and objectives. Doing so lets you clearly understand what you want to achieve and how you plan to get there.
A well-defined set of goals, objectives, and key results also provides a sense of direction and purpose, which helps keep business owners focused and motivated.
Guides decision-making
A business plan requires you to consider different scenarios and potential problems that may arise in your business. This awareness allows you to devise strategies to deal with these issues and avoid pitfalls.
With a clear plan, entrepreneurs can make informed decisions aligning with their overall business goals and objectives. This helps reduce the risk of making costly mistakes and ensures they make decisions with long-term success in mind.
Attracts investors and secures funding
Investors and lenders often require a business plan before considering investing in your business. A document that outlines the company's goals, objectives, and financial forecasts can help instill confidence in potential investors and lenders.
A well-written business plan demonstrates that you have thoroughly thought through your business idea and have a solid plan for success.
Identifies potential challenges and risks
A business plan requires entrepreneurs to consider potential challenges and risks that could impact their business. For example:
Is there enough demand for my product or service?
Will I have enough capital to start my business?
Is the market oversaturated with too many competitors?
What will happen if my marketing strategy is ineffective?
By identifying these potential challenges, entrepreneurs can develop strategies to mitigate risks and overcome challenges. This can reduce the likelihood of costly mistakes and ensure the business is well-positioned to take on any challenges.
Provides a basis for measuring success
A business plan serves as a framework for measuring success by providing clear goals and financial projections . Entrepreneurs can regularly refer to the original business plan as a benchmark to measure progress. By comparing the current business position to initial forecasts, business owners can answer questions such as:
Are we where we want to be at this point?
Did we achieve our goals?
If not, why not, and what do we need to do?
After assessing whether the business is meeting its objectives or falling short, business owners can adjust their strategies as needed.
How to make a business plan step by step
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include.
1. Create an executive summary
Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
Keep your executive summary concise and clear with the Executive Summary Template . The simple design helps readers understand the crux of your business plan without reading the entire document.
2. Write your company description
Provide a detailed explanation of your company. Include information on what your company does, the mission statement, and your vision for the future.
Provide additional background information on the history of your company, the founders, and any notable achievements or milestones.
3. Conduct a market analysis
Conduct an in-depth analysis of your industry, competitors, and target market. This is best done with a SWOT analysis to identify your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Next, identify your target market's needs, demographics, and behaviors.
Use the Competitive Analysis Template to brainstorm answers to simple questions like:
What does the current market look like?
Who are your competitors?
What are they offering?
What will give you a competitive advantage?
Who is your target market?
What are they looking for and why?
How will your product or service satisfy a need?
These questions should give you valuable insights into the current market and where your business stands.
4. Describe your products and services
Provide detailed information about your products and services. This includes pricing information, product features, and any unique selling points.
Use the Product/Market Fit Template to explain how your products meet the needs of your target market. Describe what sets them apart from the competition.
5. Design a marketing and sales strategy
Outline how you plan to promote and sell your products. Your marketing strategy and sales strategy should include information about your:
Pricing strategy
Advertising and promotional tactics
Sales channels
The Go to Market Strategy Template is a great way to visually map how you plan to launch your product or service in a new or existing market.
6. Determine budget and financial projections
Document detailed information on your business’ finances. Describe the current financial position of the company and how you expect the finances to play out.
Some details to include in this section are:
Startup costs
Revenue projections
Profit and loss statement
Funding you have received or plan to receive
Strategy for raising funds
7. Set the organization and management structure
Define how your company is structured and who will be responsible for each aspect of the business. Use the Business Organizational Chart Template to visually map the company’s teams, roles, and hierarchy.
As well as the organization and management structure, discuss the legal structure of your business. Clarify whether your business is a corporation, partnership, sole proprietorship, or LLC.
8. Make an action plan
At this point in your business plan, you’ve described what you’re aiming for. But how are you going to get there? The Action Plan Template describes the following steps to move your business plan forward. Outline the next steps you plan to take to bring your business plan to fruition.
Types of business plans
Several types of business plans cater to different purposes and stages of a company's lifecycle. Here are some of the most common types of business plans.
Startup business plan
A startup business plan is typically an entrepreneur's first business plan. This document helps entrepreneurs articulate their business idea when starting a new business.
Not sure how to make a business plan for a startup? It’s pretty similar to a regular business plan, except the primary purpose of a startup business plan is to convince investors to provide funding for the business. A startup business plan also outlines the potential target market, product/service offering, marketing plan, and financial projections.
Strategic business plan
A strategic business plan is a long-term plan that outlines a company's overall strategy, objectives, and tactics. This type of strategic plan focuses on the big picture and helps business owners set goals and priorities and measure progress.
The primary purpose of a strategic business plan is to provide direction and guidance to the company's management team and stakeholders. The plan typically covers a period of three to five years.
Operational business plan
An operational business plan is a detailed document that outlines the day-to-day operations of a business. It focuses on the specific activities and processes required to run the business, such as:
Organizational structure
Staffing plan
Production plan
Quality control
Inventory management
Supply chain
The primary purpose of an operational business plan is to ensure that the business runs efficiently and effectively. It helps business owners manage their resources, track their performance, and identify areas for improvement.
Growth-business plan
A growth-business plan is a strategic plan that outlines how a company plans to expand its business. It helps business owners identify new market opportunities and increase revenue and profitability. The primary purpose of a growth-business plan is to provide a roadmap for the company's expansion and growth.
The 3 Horizons of Growth Template is a great tool to identify new areas of growth. This framework categorizes growth opportunities into three categories: Horizon 1 (core business), Horizon 2 (emerging business), and Horizon 3 (potential business).
One-page business plan
A one-page business plan is a condensed version of a full business plan that focuses on the most critical aspects of a business. It’s a great tool for entrepreneurs who want to quickly communicate their business idea to potential investors, partners, or employees.
A one-page business plan typically includes sections such as business concept, value proposition, revenue streams, and cost structure.
Best practices for how to make a good business plan
Here are some additional tips for creating a business plan:
Use a template
A template can help you organize your thoughts and effectively communicate your business ideas and strategies. Starting with a template can also save you time and effort when formatting your plan.
Miro’s extensive library of customizable templates includes all the necessary sections for a comprehensive business plan. With our templates, you can confidently present your business plans to stakeholders and investors.
Be practical
Avoid overestimating revenue projections or underestimating expenses. Your business plan should be grounded in practical realities like your budget, resources, and capabilities.
Be specific
Provide as much detail as possible in your business plan. A specific plan is easier to execute because it provides clear guidance on what needs to be done and how. Without specific details, your plan may be too broad or vague, making it difficult to know where to start or how to measure success.
Be thorough with your research
Conduct thorough research to fully understand the market, your competitors, and your target audience . By conducting thorough research, you can identify potential risks and challenges your business may face and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Get input from others
It can be easy to become overly focused on your vision and ideas, leading to tunnel vision and a lack of objectivity. By seeking input from others, you can identify potential opportunities you may have overlooked.
Review and revise regularly
A business plan is a living document. You should update it regularly to reflect market, industry, and business changes. Set aside time for regular reviews and revisions to ensure your plan remains relevant and effective.
Create a winning business plan to chart your path to success
Starting or growing a business can be challenging, but it doesn't have to be. Whether you're a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting, a well-written business plan can make or break your business’ success.
The purpose of a business plan is more than just to secure funding and attract investors. It also serves as a roadmap for achieving your business goals and realizing your vision. With the right mindset, tools, and strategies, you can develop a visually appealing, persuasive business plan.
Ready to make an effective business plan that works for you? Check out our library of ready-made strategy and planning templates and chart your path to success.
Get on board in seconds
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
Be Stress Free and Tax Ready 🙌 70% Off for 4 Months. BUY NOW & SAVE
70% Off for 4 Months Buy Now & Save
Wow clients with professional invoices that take seconds to create
Quick and easy online, recurring, and invoice-free payment options
Automated, to accurately track time and easily log billable hours
Reports and tools to track money in and out, so you know where you stand
Easily log expenses and receipts to ensure your books are always tax-time ready
Tax time and business health reports keep you informed and tax-time ready
Automatically track your mileage and never miss a mileage deduction again
Time-saving all-in-one bookkeeping that your business can count on
Track project status and collaborate with clients and team members
Organized and professional, helping you stand out and win new clients
Set clear expectations with clients and organize your plans for each project
Client management made easy, with client info all in one place
Pay your employees and keep accurate books with Payroll software integrations
- Team Management
FreshBooks integrates with over 100 partners to help you simplify your workflows
Send invoices, track time, manage payments, and more…from anywhere.
- Freelancers
- Self-Employed Professionals
- Businesses With Employees
- Businesses With Contractors
- Marketing & Agencies
- Construction & Trades
- IT & Technology
- Business & Prof. Services
- Accounting Partner Program
- Collaborative Accounting™
- Accountant Hub
- Reports Library
- FreshBooks vs QuickBooks
- FreshBooks vs HoneyBook
- FreshBooks vs Harvest
- FreshBooks vs Wave
- FreshBooks vs Xero
- Free Invoice Generator
- Invoice Templates
- Accounting Templates
- Business Name Generator
- Estimate Templates
- Help Center
- Business Loan Calculator
- Mark Up Calculator
Call Toll Free: 1.866.303.6061
1-888-674-3175
- All Articles
- Productivity
- Project Management
- Bookkeeping
Resources for Your Growing Business
How to write a business development plan: a step by step guide.

So we’ve already tackled how to write the infamous business plan , but now that you’re in the growth stage of your business – what’s next?
Many business owners will look to write a business development plan with the aim to make their business better. Running a business is never a stationary job, you constantly have to be looking to grow and improve.
But what exactly is a business development plan and how do you write one? Let’s find out.
Here’s What We’ll Cover:
What Is a Business Development Plan?
How to write a business development plan, key takeaways.
A business development plan is a document put together by the business owner with the aim to grow and improve their business. The plan will set goals for growth and explain how you will achieve them.
A business development strategy can have a short-term or long-term focus, or both. They should also be constantly reviewed and revised as things shift and your goals may change.
A health plan is one that builds as your business evolves.

A standard business development strategy can be split up into 6 different sections, each one with a different aim and purpose. These sections are:
You should always be looking to grow your business. In this section, you will identify where growth will come from. For example, whether it’s new product development, adding different services or breaking into new markets. Your main business development goals should always point towards growth.
According to a U.S. Bank study, 82% of small businesses fail because of poor cash flow management and understanding. That’s why it’s vital that you have a constant eye on your funding and your bottom line.
You need to understand how you’ll fund your business development. So in this section, you should lay out your current capital, and how much more you will need to sustain growth.
3. Financial Goals
You should have a good idea of your current revenue, costs and profits. These numbers can then be used as a starting point for setting new, more ambitious revenue goals. This is for when you have expanded and developed your business.
4. Operational Needs
When growing a business, your operational needs will change. For example, what started out as a two-person job can develop into needing a whole team of people. So in this section, you will need to identify what things about your business will need to change to accommodate and promote growth.
5. Sales and Marketing
No business can succeed without a strong and stable sales team and marketing team. As your business grows, so will your sales and marketing needs. So you will need to take the time to figure out your target market and what sales and marketing efforts will promote growth. You should then put all of your focus on those efforts.
It’s vital that your sales process and marketing strategies are strong and sturdy enough to support a growing business.

6. Team Needs
Every strong business needs a strong team around it. When you started your business, it’s likely that you shouldered a lot of the jobs and responsibilities. As your business grows, you’ll soon come to realize that you can no longer do this alone.
So as a business developer, you need to think about what jobs and tasks you are best and most effective at. You should then correctly delegate the other responsibilities to the appropriate team members. This is often a good way to figure out if you have the right team around you. If you dread the thought of offloading tasks to your team, you may not have the trust in your team that you should.
Business development plans may seem like a relatively daunting task. But once you figure out the basics then they can almost write themselves.
You need to have an open mindset, a realistic approach and the ability to accept some potential failures.
Expanding and developing a business is hard work, but with the right plan in place, you are giving yourself the best chance possible.
Are you looking for more business advice on everything from starting a new business to new business practices?
Then check out the FreshBooks Resource Hub .
RELATED ARTICLES

Save Time Billing and Get Paid 2x Faster With FreshBooks
Want More Helpful Articles About Running a Business?
Get more great content in your Inbox.
By subscribing, you agree to receive communications from FreshBooks and acknowledge and agree to FreshBook’s Privacy Policy . You can unsubscribe at any time by contacting us at [email protected].
👋 Welcome to FreshBooks
To see our product designed specifically for your country, please visit the United States site.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is Business Development?
- Understanding the Basics
- Areas of Development
- The Process
- Creating a Plan
- Skills Needed
The Bottom Line
- Small Business
- How to Start a Business
Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
Why more and more companies worldwide are embracing this planning process
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SuzannesHeadshot-3dcd99dc3f2e405e8bd37271894491ac.jpg)
In the simplest terms, business development is a process aimed at growing a company and making it more successful. That can include seeking new business opportunities, building and sustaining connections with existing clients, entering strategic partnerships, and devising other plans to boost profits and market share.
Key Takeaways
- The overarching goal of business development is to make a company more successful.
- It can involve many objectives, such as sales growth, business expansion, the formation of strategic partnerships, and increased profitability.
- The business development process can impact every department within a company, including sales, marketing, manufacturing, human resources, accounting, finance, product development, and vendor management.
- Business development leaders and team members need a wide range of both soft and hard skills.
How Business Development Works Within an Organization
Business development, sometimes abbreviated as BD, strives to increase an organization's capabilities and reach in pursuit of its financial and other goals. In that way, it can impact—and also call upon the specialized skills of—a variety of departments throughout the organization.
As the financial services giant American Express puts it, "When it comes to organizational growth, business development acts as the thread that ties together all of a company's functions or departments, helping a business expand and improve its sales, revenues, product offerings, talent, customer service, and brand awareness."
For example:
Sales and Marketing
Sales personnel frequently focus on a particular market or a particular (set of) client(s), often for a targeted revenue number. A business development team might assess the Brazilian market, for example, and conclude that sales of $1.5 billion can be achieved there in three years. With that as their goal, the sales department targets the customer base in the new market with their sales strategies.
Business development often takes a longer-range perspective in setting goals than many sales departments have in the past. As the Society for Marketing Professional Services puts it, "A traditional view of sales is akin to hunting, but business development is more like farming: it's a longer-term investment of time and energy and not always a quick payoff."
Marketing , which oversees the promotion and advertising of the company's products and services, plays a complementary role to sales in achieving its targets.
A business development leader and their team can help set appropriate budgets based on the opportunities involved. Higher sales and marketing budgets allow for aggressive strategies like cold calling , personal visits, roadshows, and free sample distribution. Lower budgets tend to rely on more passive strategies, such as online, print, and social media ads, as well as billboard advertising.
Legal and Finance
To enter a new market, a business development team must decide whether it will be worth going solo by clearing all the required legal formalities or whether it might be more sensible to form a strategic alliance or partnership with firms already operating in that market. Assisted by legal and finance teams, the business development group weighs the pros and cons of the available options and selects the one that best serves the business.
Finance may also become involved in cost-cutting initiatives. Business development is not just about increasing market reach and sales, but improving the bottom line . An internal assessment revealing high spending on travel , for instance, may lead to travel policy changes, such as hosting video conference calls instead of on-site meetings or opting for less expensive transportation modes. The outsourcing of non-core work, such as billing, technology operations, or customer service, may also be part of the development plan.
Project Management/Business Planning
Does an international business expansion require a new facility in the new market, or will all the products be manufactured in the base country and then imported into the targeted market? Will the latter option require an additional facility in the base country? Such decisions are finalized by the business development team based on their cost- and time-related assessments. Then, the project management /implementation team can swing into action to work toward the desired goal.
Product Management and Manufacturing
Regulatory standards and market requirements can vary across regions and countries. A medicine of a certain composition may be allowed in India but not in the United Kingdom, for example. Does the new market require a customized—or altogether new—version of the product?
These requirements drive the work of product management and manufacturing departments, as determined by the business strategy. Cost considerations, legal approvals, and regulatory adherence are all assessed as a part of the development plan.
Vendor Management
Will the new business need external vendors ? For example, will the shipping of a product require a dedicated courier service? Will the company partner with an established retail chain for retail sales? What are the costs associated with these engagements? The business development team works through these questions with the appropriate internal departments.
10 Potential Areas for Business Development
As noted earlier, business development can require employees throughout an organization to work in tandem to facilitate information, strategically plan future actions, and make smart decisions. Here is a summary list of potential areas that business development may get involved in, depending on the organization.
- Market research and analysis: This information helps identify new market opportunities and develop effective strategies.
- Sales and lead generation: This involves prospecting, qualifying leads, and coordinating with the sales team to convert leads into customers.
- Strategic partnerships and alliances: This includes forming strategic alliances, joint ventures, or collaborations that create mutually beneficial opportunities.
- Product development and innovation: This involves conducting market research, gathering customer feedback, and collaborating with internal teams to drive innovation.
- Customer relationship management: This involves customer retention initiatives, loyalty programs, and gathering customer feedback to enhance customer satisfaction and drive repeat business.
- Strategic planning and business modeling: This includes identifying growth opportunities, setting targets, and implementing strategies to achieve sustainable growth.
- Mergers and acquisitions: This involves evaluating potential synergies, conducting due diligence , and negotiating and executing deals.
- Brand management and marketing: This includes creating effective marketing campaigns, managing online and offline channels, and leveraging digital marketing techniques.
- Financial analysis and funding: This includes exploring funding options, securing investments, or identifying grant opportunities.
- Innovation and emerging technologies: This involves assessing the potential impact of disruptive technologies and integrating them into the organization's growth strategies.
The Business Development Process in Six Steps
While the specific steps in the business development process will depend on the particular company, its needs and capabilities, its leadership, and its available capital, these are some of the more common ones:
Step 1: Market Research/Analysis
Begin by conducting comprehensive market research to gain insights into market trends, customer needs, and the competitive landscape. Analyze data and gather additional information to identify potential growth opportunities and understand the market dynamics.
Step 2: Establish Clear Goals and Objectives
Leveraging that research, define specific objectives and goals for business development efforts. These goals could include revenue targets, market expansion goals, customer acquisition targets, and product/service development objectives. Setting clear goals provides a focus for the business development process.
Step 3: Generate and Qualify Leads
Use various sources, such as industry databases, networking , referrals, or online platforms to generate a pool of potential leads. Identify individuals or companies that fit the target market criteria and have the potential to become customers. Then, evaluate and qualify leads based on predetermined criteria to determine their suitability and potential value.
Step 4: Build Relationships and Present Solutions
Initiate contact with qualified leads and establish relationships through effective communication and engagement. Utilize networking events, industry conferences, personalized emails, or social media interactions to build trust and credibility. As your relationship forms, develop and present tailored solutions that align with the client's needs. Demonstrate the value proposition of the organization's offerings and highlight key benefits and competitive advantages.
Step 5: Negotiate and Expand
Prepare and deliver proposals that outline the scope of work, pricing, deliverables, and timelines. Upon agreement, coordinate with legal and other relevant internal teams to ensure a smooth contract execution process.
Step 6: Continuously Evaluate
Continuously monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of business development efforts. Analyze performance metrics , gather feedback from clients and internal stakeholders, and identify areas for improvement. Regularly refine strategies and processes to adapt to market changes and optimize outcomes.
While it's common for startup companies to seek outside assistance in developing the business, as a company matures, it should aim to build its business development expertise internally.
How to Create a Business Development Plan
To effectively create and implement a business development plan, the team needs to set clear objectives and goals—ones that are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). You can align these objectives with the overall business goals of the company.
Companies often analyze the current state of the organization by evaluating its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats through a SWOT analysis . That can make it easier to identify target markets and customer segments and define their unique value proposition.
A substantial component of a business development plan is the external-facing stages. It should lay out sales and marketing strategies to generate leads and convert them into customers. In addition, it may explore new potential strategic partnerships and alliances to expand your reach, access new markets, or enhance your offerings.
Teams should conduct a financial analysis and do resource planning to determine the resources required for implementing the plan. Once you implement, you should track progress against the key performance indicators (KPIs) you've chosen.
Skills Needed for Business Development Jobs
Business development is a fast-growing field across industries worldwide. It is also one that calls upon a wide range of hard and soft skill sets.
Leaders and other team members benefit from well-honed sales and negotiating skills in order to interact with clients, comprehend their needs, and sway their decisions. They have to be able to establish rapport, cope with challenges, and conclude transactions. They need to be able to communicate clearly, verbally and in writing, to both customers and internal stakeholders.
Business development specialists should have a thorough awareness of the market in which they operate. They should keep up with market dynamics, competition activity, and other industry developments. They should be able to see potential opportunities, make wise judgments, and adjust tactics as necessary. Because many of their decisions will be data-driven, they need good analytical skills.
Internally, business development practitioners need to be able to clarify priorities, establish reasonable deadlines, manage resources wisely, and monitor progress to guarantee timely completion.
Finally, people who work in business development should conduct themselves with the utmost morality and honesty. They must uphold confidentiality, act legally and ethically, and build trust with customers and other stakeholders.
Why Is Business Development Important?
In addition to its benefits to individual companies, business development is important for generating jobs, developing key industries, and keeping the economy moving forward.
What Are the Most Important Skills for Business Development Executives?
Development executives need to have leadership skills, vision, drive, and a willingness to work with a variety of people to get to a common goal.
How Can I Be Successful in Business Development?
Having a vision and putting together a good team are among the factors that help predict success in business development. A successful developer also knows how to write a good business plan, which becomes the blueprint to build from.
What, in Brief, Should a Business Development Plan Include?
A business development plan, or business plan , should describe the organization's objectives and how it intends to achieve them, including financial goals, expected costs, and targeted milestones.
Business development provides a way for companies to rise above their day-to-day challenges and set a course for a successful future. More and more companies, across many different types of industries, are coming to recognize its value and importance.
American Express. " Business Development and Its Importance ."
Society for Marketing Professional Services. " What Is Business Development? "
World Economic Forum. " The Future of Jobs Report 2020 ," Page 30.
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Marketing-Strategy-20dd671d870c4f1db1c9166de9e44e27.png)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
How to Develop a Strategic Plan for Business Development [Free Template]
Published: May 01, 2023
Business development is usually confused with sales , often overlooked, and only sometimes given the strategic focus it deserves. Having a business development strategy, however, is crucial to long-term success. It ensures that everyone in your company is working toward a common goal.

But how do you develop a business development plan? Pull up a chair and stay awhile, I’m diving into that and more below.
.png)
Free Strategic Planning Template
Access a business strategic planning template to grow your business.
- Sales and Revenue Growth
- Growth of Customer Base
- Expansion into New Regions
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Fill out this form to get the strategic growth template.
Business development.
Business development is the practice of identifying, attracting, and acquiring new business to further your company’s revenue and growth goals. How you achieve these goals is sometimes referred to as a business development strategy — and it applies to and benefits everyone at your company.

It’s not unusual to mistake business development with sales, but there’s an important distinction between the two. Business development refers to many activities and functions inside and outside the traditional sales team structure. In some companies, business development is part of the larger sales operations team. In others, it’s part of the marketing team or sits on its own team altogether.
Because business development can look so different among industries and businesses, the strategy behind this function is expansive. Below, we outline each step in the strategy and how to apply it to your business development plan.
Business Development Strategy
- Understand your competitive landscape.
- Choose effective KPIs.
- Develop long-term customer relationships.
- Implement customer feedback.
- Keep your website content and user interface fresh.
- Speed up your response time.
- Leverage a sales plan to identify areas of growth.
- Implement a social listening strategy.
- Sponsor industry organizations, conferences, and events.
1. Understand your competitive landscape.
Before you can develop a strategic plan to drive business growth, you must have a solid understanding of the competitive landscape in your industry. When you know who your ideal customer is and what problem they are looking to solve with your product or service, research who else is providing a viable solution in your industry.
Identify other companies operating in your space. What features do their products have? How competitive is their pricing? Do their systems integrate with other third-party solutions? Get crystal-clear on what the competition is offering so you know how to differentiate your product to your customers.
Featured Resource: 10 Competitive Analysis Templates
2. Choose effective KPIs.
How will you know if your business development efforts are successful? Ensure you can measure your goals with relevant, meaningful key performance indicators (KPIs) that reflect the health of your business. The result of these metrics should give you a strong indication of how effective your business development efforts are.
Featured Resource: Sales Metrics Calculator Dashboard
3. Develop long-term customer relationships.
Do you engage with your customers even after the deal has been closed? If not, it’s time to develop a plan to keep your buyers engaged. Building long-term relationships with your customers pays off. A grand majority of a company's business comes from repeat customers, and returning customers are cheaper to convert. Indeed, it’s famously known that it costs five times more to convert new customers than it does to sell to returning customers.
Not only are repeat customers easier to sell to, they can also provide valuable feedback and insights to help you improve your business. Additionally, customer testimonials can be used for valuable content that can attract your next buyer.
4. Implement customer feedback.
If and when you have customers who are willing to provide feedback on your sales process and offerings, make sure you hear them out and implement it. Your customers offer a unique, valuable perspective because they chose your product over the competition — their insights can help shape your strategy to keep your business ahead of the curve.
5. Keep your website content and user interface fresh.
When was the last time your company had a website refresh? Can you ensure that all links are working, that your site is easy to navigate, and that it is laid out and intuitive for those who want to buy from you?
Keeping your website up-to-date and easy to use can make or break the sale for customers who know they are ready to buy. Don’t make it too difficult for potential customers to get in touch with you or purchase your product directly (if that suits your business model).
6. Speed up your response time.
How fast your sales team responds to your leads can make or break your ability to close the deal. If you notice your sales process has some lag time that prevents you from responding to prospects as soon as possible, these could be areas to prioritize improvement.
7. Leverage a sales plan to identify areas of growth.
No business development strategy is complete without a sales plan . If you’ve already established a plan, make sure to unify it with your business development efforts. Your plan should outline your target audience, identify potential obstacles, provide a “game plan” for sales reps, outline responsibilities for team members, and define market conditions.
While a sales plan primarily affects your sales team, it can inform the activities of your business development reps. A sales plan can help them understand where the business needs growth — whether it’s in a new vertical, a new audience, or a new need that’s recently come to light in the industry.
Not sure how to create a sales plan? Download the following template to get started.
Featured Resource: Sales Plan Template

8. Implement a social listening strategy.
While social listening is mainly used in a marketing and customer service context, it’s also an essential practice for business development. There are more than 4 billion social media users worldwide. Naturally, social media is one of the best places to hear directly from consumers and businesses — without needing to reach out to them first.
In business development, you can use social listening to track what the general public is saying about your brand, industry, product offerings, product category, and more. It can help you identify key weaknesses in the industry, making it a prime opportunity to be the first to address those pitfalls.
Use a social listening tool to pick up on trends before they gain traction.
9. Sponsor industry organizations, conferences, and events.
A key facet of business development is reaching potential customers where they are. One of the easiest ways to do that is by sponsoring industry organizations, conferences, and events. This strategy will guarantee that your business development reps get valuable face-to-face time with your business’ target audience. The additional visibility can also help establish your business as a leader in the field.
Now that you understand what business development entails, it's time to create a plan to set your strategy in motion.
How to Develop a Strategic Plan

When we refer to a business development strategic plan, we’re referring to a roadmap that guides the whole company and requires everyone’s assistance to execute successfully and move your customer through the flywheel . With a plan, you’ll close more deals and quantify success.
Let’s go over the steps you should take to create a strategic plan.
1. Download our strategic plan template .
First, download our free growth strategy template to create a rock-solid strategic plan. With this template, you can map a growth plan for increasing sales, revenue, and customer acquisition rates. You can also create action plans for adding new locations, creating new product lines, and expanding into new regions.
Featured Resource: Strategic Plan Template

2. Craft your elevator pitch.
What is your company’s mission and how do you explain it to potential clients in 30 seconds or less? Keeping your elevator pitch at the forefront of all strategic planning will remind everyone what you’re working toward and why.
Some people believe the best pitch isn’t a pitch at all , but a story. Others have their favorite types of pitches , from a one-word pitch to a Twitter pitch that forces you to boil down your elevator pitch to just 280 characters.
Find the elevator pitch that works best for your reps, company, and offer, and document it in your business development strategy.
3. Include an executive summary.
You’ll share your strategic plan with executives and maybe even board members, so it’s important they have a high-level overview to skim. Pick the most salient points from your strategic plan and list or summarize them here.
You might already have an executive summary for your company if you’ve written a business proposal or value proposition . Use this as a jumping off point but create one that’s unique to your business development goals and priorities.
Once your executives have read your summary, they should have a pretty good idea of your direction for growing the business — without having to read the rest of your strategy.
3. Set SMART goals.
What are your goals for this strategy? If you don’t know, it will be difficult for your company and team to align behind your plan. So, set SMART goals . Remember, SMART stands for:
Featured Resource: SMART Goal Setting Template
Download the template now.
If one of your goals is for 5% of monthly revenue to come from upsells or cross-sells, make this goal specific by identifying what types of clients you’ll target.
Identify how you’ll measure success. Is success when reps conduct upsell outreach to 30 clients every month, or is it when they successfully upsell a customer and close the deal? To make your goal attainable, ensure everyone on your team understands who is responsible for this goal: in this case, sales or business development reps.
This goal is relevant because it will help your company grow, and likely contributes to larger company-wide goals. To make it time-based, set a timeline for success and action. In this case, your sales team must achieve that 5% upsell/cross-sell number by the end of the quarter.

4. Conduct SWOT analysis.
SWOT is a strategic planning technique used to identify a company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Before conducting a SWOT, identify what your goal is. For example, “We’d like to use SWOT to learn how best to conduct outreach to prospective buyers.”
Once you’ve identified what you’re working toward, conduct market research by talking with your staff, business partners, and customers.
Next, identify your business’ strengths. Perhaps you have low employee turnover, a central location that makes it easy to visit with prospects in person, or an in-demand feature your competitors haven’t been able to mimic.
Featured Resource: Market Research Kit with SWOT Analysis Template

Your business’ weaknesses are next. Has your product recently glitched? Have you been unable to successfully build out a customer service team that can meet the demands of your customers?
Then, switch to opportunities. For example, have you made a new business partnership that will transition you into a previously untapped market segment?
What are the threats? Is your physical space getting crowded? What about your market space? Is increasing competition an issue?
Use SWOT results to identify a better way forward for your company.
5. Determine how you’ll measure success.
You’ve identified strengths and weaknesses and set SMART goals , but how will you measure it all ? It’s important for your team to know just how they will be measured, goaled, and rewarded. Common key performance indicators (KPIs) for business development include:
- Company growth
- Lead conversion rate
- Leads generated per month
- Client satisfaction
- Pipeline value
6. Set a budget.
What will your budget be for achieving your goals? Review financial documents, historical budgets, and operational estimates to set a budget that’s realistic.
Once you have a “draft” budget, check it against other businesses in your industry and region to make sure you’re not overlooking or misjudging any numbers. Don’t forget to factor in payroll, facilities costs, insurance, and other operational line items that tend to add up.
7. Identify your target customer.
Who will your business development team pursue? Your target market is the group of customers your product/service was built for. For example, if you sell a suite of products for facilities teams at enterprise-level companies, your target market might be facilities or janitorial coordinators at companies with 1000+ employees. To identify your target market:
- Analyze your product or service
- Check out the competition
- Choose criteria to segment by
- Perform research
Your target customer is the person most likely to buy your product. Do your homework and make sure your business development plan addresses the right people. Only then will you be able to grow your business.
8. Choose an outreach strategy.
What tactics will you use to attract new business for your sales team to close? You might focus on a single tactic or a blend of a few. Once you know who your target market is and where they “hang out,” then you can choose an appropriate outreach strategy.
Will your business development plan rely heavily on thought leadership such as speaking at or attending conferences? Will you host a local meetup for others in your industry? Or will your reps network heavily on LinkedIn and social media?
If referrals will be pivotal to your business’ growth, consider at which stage of the buying process your BDRs will ask for referrals. Will you ask for a referral even if a prospect decides they like your product/service but aren’t a good fit? Or will you wait until a customer has been using your solution for a few months? Define these parameters in your strategy.
Upselling and Cross-Selling
Upselling and cross-selling are a cost-effective way of growing your business. But it’s important that this tactic is used with guardrails. Only upsell clients on features that will benefit them as well as your bottom line. Don’t bloat client accounts with features or services they really don’t need — that’s when turnover and churn start to happen.
Sponsorship and Advertising
Will your BDR work with or be on the marketing team to develop paid advertising campaigns? If so, how will your BDRs support these campaigns? And which channels will your strategy include? If you sell a product, you might want to feature heavily on Instagram or Facebook. If you’re selling a SaaS platform, LinkedIn or Twitter might be more appropriate.
What’s your outreach strategy? Will your BDRs be held to a quota to make 25 calls a week and send 15 emails? Will your outreach strategy be inbound , outbound , or a healthy combination of both? Identify the outreach guardrails that best match your company values for doing business.
Strategic Plan Example
Let’s put all of these moving parts in action with a strategic plan example featuring good ol’ Dunder Mifflin Paper Company.
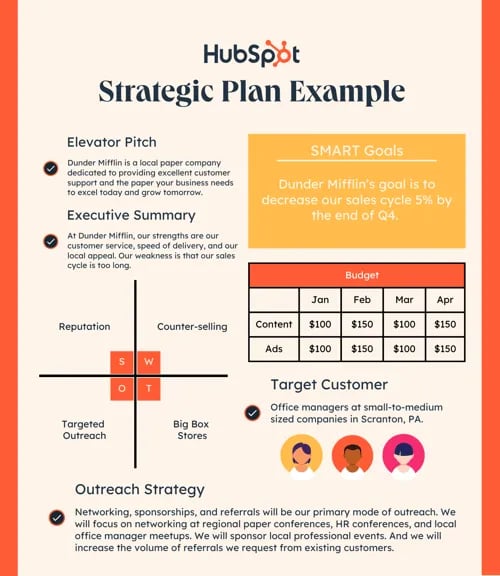
Elevator Pitch Example for Strategic Plan
Dunder Mifflin is a local paper company dedicated to providing excellent customer support and the paper your business needs to excel today and grow tomorrow.
Here are some additional resources for inspiration:
- Elevator Pitch Examples to Inspire Your Own
- Components of an Elevator Pitch
Executive Summary Example for Strategic Plan
At Dunder Mifflin, our strengths are our customer service, speed of delivery, and our local appeal. Our weakness is that our sales cycle is too long.
To shorten the sales cycle 5% by the end of Q4, we need to ask for more referrals (which already enjoy a 15% faster sales cycle), sponsor local professional events, and outreach to big box store customers who suffer from poor customer support and are more likely to exit their contract. These tactics should allow us to meet our goal in the agreed-upon timeline.
- How to Write an Incredibly Well-Written Executive Summary [+ Example]
- Executive Summary Template
SMART Goals Example for Strategic Plan
Dunder Mifflin’s goal is to decrease our sales cycle 5% by the end of Q4. We will do this by more proactively scheduling follow-up meetings, sourcing more qualified, ready-to-buy leads, and asking for 25% more referrals (which have a 15% shorter sales cycle already). We will measure success by looking at the sales pipeline and calculating the average length of time it takes a prospect to become closed won or closed lost.
- 5 Dos and Don'ts When Making a SMART Goal [Examples]
- How to Write a SMART Goal
- SMART Marketing Goals Template
SWOT Analysis Example for Strategic Plan
Strengths: Our strengths are our reputation in the greater Scranton area, our customer service team (led by Kelly Kapoor), and our warehouse team, who ship same-day reams to our customers — something the big box stores cannot offer.
Weaknesses: Our greatest weakness is that our sales team has been unable to successfully counter prospects who choose big box stores for their paper supply. This results in a longer-than-average sales cycle, which costs money and time.
Opportunities: Our greatest business opportunity is to conduct better-targeted outreach to prospects who are ready to buy, ask for more referrals from existing customers, and follow up with closed lost business that’s likely coming up on the end of an annual contract with a big box store.
Threats: Our biggest threat is large box stores offering lower prices to our prospects and customers and a sales cycle that is too long, resulting in low revenue and slow growth.
- How to Conduct Competitive Analysis
- How to Run a SWOT Analysis for Your Business [+ Template]
- SWOT Analysis Template and Market Research Kit
Measurement of Success Example for Strategic Plan
We will measure success by looking at the sales pipeline and calculating the average length of time it takes a prospect to become closed won or closed lost.
Budget Example for Strategic Plan
You've laid out the SMART goals and the way you'll measure for success. The budget section's goal is to estimate how much investment it will take to achieve those goals. This will likely end up being a big-picture overview, broken down into a budget by a program or a summary of key investments. Consider laying it out in a table format like so:
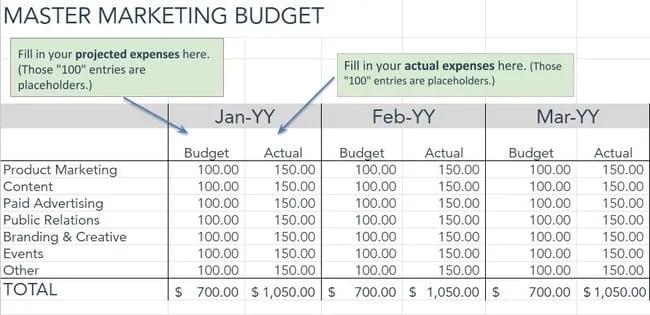
- Budgeting Templates
- How to Write an Incredible Startup Marketing Budget
Target Customer Example for Strategic Plan
Our target customer is office managers at small- to medium-sized companies in the greater Scranton, PA area. They are buying paper for the entire office, primarily for use in office printers, custom letterhead, fax machines. They are busy managing the office and value good customer service and a fast solution for their paper needs.
- How to Create Detailed Buyer Personas for Your Business
- Make My Persona Tool
Outreach Strategy Example for Strategic Plan
Networking, sponsorships, and referrals will be our primary mode of outreach. We will focus on networking at regional paper conferences, HR conferences, and local office manager meetups. We will sponsor local professional events. And we will increase the volume of referrals we request from existing customers.
Create a Strategic Plan for Business Development
Without a strategic plan, you can invest resources, time, and funds into business development initiatives that won't grow your business. A strategic plan is crucial as it aligns your business development and sales teams. With a solid business development strategic plan, everyone will be working toward the greater good of your company.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in January 2020 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

9 Strategic Planning Models and Tools for the Customer-Focused Business

S&OP: A Comprehensive Overview of Sales and Operations Planning

A Straightforward Guide to Qualitative Forecasting

4 Clever and Effective Ways to Simplify Your Sales Process From Seasoned Sales Experts

Lead Distribution Methods and Best Practices

Lead Routing: How to Precisely Implement and Route Key Prospects

The 25 Best Lead Distribution Software in 2022

Return on Sales: How to Calculate It and What You Need to Know

30 Key Interview Questions and Answers for Sales Operations Role

How Using a Document Library Can Improve Your Sales Process
Plan your business's growth strategy with this free template.
Powerful and easy-to-use sales software that drives productivity, enables customer connection, and supports growing sales orgs

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
2 Developing a Business Plan
Learning Objectives
After completing this chapter, you will be able to
- Describe the purposes for business planning
- Describe common business planning principles
- Explain common business plan development guidelines and tools
- List and explain the elements of the business plan development process
- Explain the purposes of each element of the business plan development process
- Explain how applying the business plan development process can aid in developing a business plan that will meet entrepreneurs’ goals
This chapter describes the purposes, principles, and the general concepts and tools for business planning, and the process for developing a business plan.
Purposes for Developing Business Plans
Business plans are developed for both internal and external purposes. Internally, entrepreneurs develop business plans to help put the pieces of their business together. Externally, the most common purpose is to raise capital.
Internal Purposes
As the road map for a business’s development, the business plan
- Defines the vision for the company
- Establishes the company’s strategy
- Describes how the strategy will be implemented
- Provides a framework for analysis of key issues
- Provides a plan for the development of the business
- Helps the entrepreneur develop and measure critical success factors
- Helps the entrepreneur to be realistic and test theories
External Purposes
The business plan provides the most complete source of information for valuation of the business. Thus, it is often the main method of describing a company to external audiences such as potential sources for financing and key personnel being recruited. It should assist outside parties to understand the current status of the company, its opportunities, and its needs for resources such as capital and personnel.
Business Plan Development Principles [1]
Hindle and Mainprize suggested that business plan writers must strive to effectively communicate their expectations about the nature of an uncertain future and to project credibility. The liabilities of newness make communicating the expected future of new ventures much more difficult than for existing businesses. Consequently, business plan writers should adhere to five specific communication principles .
First, business plans must be written to meet the expectations of targeted readers in terms of what they need to know to support the proposed business. They should also lay out the milestones that investors or other targeted readers need to know. Finally, writers must clearly outline the opportunity , the context within the proposed venture will operate (internal and external environment), and the business model.
There are also five business plan credibility principles that writers should consider. Business plan writers should build and establish their credibility by highlighting important and relevant information about the venture team . Writers need to elaborate on the plans they outline in their document so that targeted readers have the information they need to assess the plan’s credibility. To build and establish credibility, they must integrate scenarios to show that the entrepreneur has made realistic assumptions and has effectively anticipated what the future holds for their proposed venture. Writers need to provide comprehensive and realistic financial links between all relevant components of the plan. Finally, they must outline the deal , or the value that targeted readers should expect to derive from their involvement with the venture. [2]
General Guidelines for Developing Business Plans
Many businesses must have a business plan to achieve their goals. Using a standard format helps the reader understand that the you have thought everything through, and that the returns justify the risk. The following are some basic guidelines for business plan development.
As You Write Your Business Plan
- If appropriate, include nice, catchy, professional graphics on your title page to make it appealing to targeted readers, but don’t go overboard.
- Bind your document so readers can go through it easily without it falling apart. You might use a three-ring binder, coil binding, or a similar method. Make sure the binding method you use does not obscure the information next to where it is bound.
- Make certain all of your pages are ordered and numbered correctly.
- The usual business plan convention is to number all major sections and subsections within your plan using the format as follows:
1. First main heading
1.1 First subheading under the first main heading
1.1.1. First sub-subheading under the first subheading
2. Second main heading
2.1 First subheading under the second main heading
Use the styles and references features in Word to automatically number and format your section titles and to generate your table of contents. Be sure that the last thing you do before printing your document is update your automatic numbering and automatically generated tables. If you fail to do this, your numbering may be incorrect.
5. Prior to submitting your plan, be 100% certain each of the following requirements are met:
- Everything must be completely integrated. The written part must say exactly the same thing as the financial part.
- All financial statements must be completely linked and valid. Make sure all of your balance sheets balance.
- Everything must be correct. There should be NO spelling, grammar, sentence structure, referencing, or calculation errors.
- Your document must be well organized and formatted. The layout you choose should make the document easy to read and comprehend. All of your diagrams, charts, statements, and other additions should be easy to find and be located in the parts of the plan best suited to them.
- In some cases it can strengthen your business plan to show some information in both text and table or figure formats. You should avoid unnecessary repetition , however, as it is usually unnecessary—and even damaging—to state the same thing more than once.
- You should include all the information necessary for readers to understand everything in your document.
- The terms you use in your plan should be clear and consistent. For example, the following statement in a business plan would leave a reader completely confused: “There is a shortage of 100,000 units with competitors currently producing 25,000. We can help fill this huge gap in demand with our capacity to produce 5,000 units.” This statement might mean there is a total shortage of 100,000 units, but competitors are filling this gap by producing 25,000 per year; in which case there will only be a shortage for four years. However, it could mean that the annual shortage is 100,000 units and only 25,000 are produced each year, in which case the total shortage is very high and is growing each year.
- You must always provide the complete perspective by indicating the appropriate time frame, currency, size, or other measurement.
- If you use a percentage figure, you must indicate to what it refers—otherwise the number is meaningless to a reader.
- If your plan includes an international element, you must indicate in which currency or currencies the costs, revenues, prices, or other values are quoted. This can be solved by indicating up-front in the document in which currency all values will be quoted. Another option is to indicate each time which currency is being used, and sometimes you might want to indicate the value in more than one currency. Of course, you will need to assess the exchange rate risk to which you will be exposed and describe this in your document.
6. Ensure credibility is both established and maintained. [3]
- If a statement presents something as a fact when this fact is not generally known, always indicate the source. Unsupported statements damage credibility.
- Be specific. A business plan is simply not of value if it uses vague references to high demand, carefully set prices, and other weak phrasing. It must show hard numbers (properly referenced, of course), actual prices, and real data acquired through proper research. This is the only way to ensure your plan is considered credible.
- Your strategies must be integrated. For example, your pricing strategy must complement and mesh perfectly with your product/service strategy, distribution strategy, and promotions strategy. For example, you probably shouldn’t promote your product as a premium product if you plan to charge lower-than-market prices for it.
7. Before finalizing your business plan, re-read each section to evaluate whether it will appeal to your targeted readers.
Useful Resources for Business Planning
- Financial Performance Data : Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada
- BizPal for accessing licensing and other needs
- Canada Revenue Agency for CRA asset classifications
- Canadian Company Capabilities database to use to find suppliers and buyers
- Merx for finding possible Canadian Government contracts
- The Conference Board of Canada
- Bank of Canada
- Scotia Bank
- Bank of Montreal
- Business Loan Calculator
Library Resources
NSCC Library – Business Databases [journals and other resources]
Employee compensation calculators
- Salary Data & Career Research Center – Canada
Existing business plans
The Word and Excel templates in this book
- Business Plan Template (Word)
- Business Plan Template (Excel)
Business Plan Development Tools
Credibility and communication.
According to Hindle and Mainprize, strong business plans effectively communicate the necessary information to the targeted readers while also establishing the credibility of the plan and the entrepreneur. [4] The Credibility and Communication Meter icon is used throughout this book to highlight where and how business plan writers can improve the quality of the information and enhance their and their plan’s credibility.
Use the following tools to improve the information in and credibility of your plans:
The Ratchet Effect
A ratchet is a tool that most of us are familiar with. It is useful because it helps its user accomplish something with each effort expended while guarding against losing past advancements.
With each word, sentence, paragraph, heading, chart, figure, and table you include in your final business plan, the ratchet should move ahead a notch because you achieve two important things.
First, only needed and relevant information is included.
Second, your additions build credibility in a relevant way.
Apply the ratchet effect by making sure that each and every sentence and paragraph conveys needed and relevant information that adds to your and your plan’s credibility. Use the following principles: Rarely—and only if it truly needs to be said again—repeat something that you have already said in your plan.
Avoid using killer phrases, like “there is no competition for our product” or “our product will sell itself, so we will not need to advertise it.” Any savvy reader will understand that these kinds of statements are naive and demonstrate a lack of understanding about how the market and other real-life factors actually work.
Avoid contradicting yourself. Make sure that what is said in the written part of your plan completely syncs with what is said in the other parts of your plan. Likewise, ensure that what you include in the financial parts of your plan is completely in sync with what is said the written part.
The Magic Formula
Apply the following magic formula throughout your write your plan.
- …consideration X affects my business because…
- …consideration X is subject to this trend into the future…
- …which means that we have decided to do this…(or) will implement this strategy…in response to how the expected trends for consideration X will affect my business
Here is an example of how you can use the magic formula to develop part of the pricing strategy in the marketing plan part of your business plan: We expect that our expenses to run our business will rise with the rate of inflation, which means that we must plan to increase the prices on our products to establish and maintain our profitability. The Bank of Canada (201x) has projected that the general inflation rate in <the city in which my business will operate> will be 3.0% in 201x, 3.5% in 201y, and 4.0% in 201z. In our projected financial statements, therefore, we have inflated both our expenses and our prices by those rates in those years.
Context and Framing
You must provide the right context when you describe situations, strategies, and other components of your plan. Business plan readers should never be left to guess why you indicate in a business plan that you will do something. Proper context is needed to help you frame the information you present.
When you frame the stories you tell correctly, the ratchet effect will happen and your plan will be stronger. One example of effective framing is when you, as the writer of the plan and the entrepreneur, clearly indicate how your education, expertise, relevant experiences, and network of contacts will make up for any lack of direct experience you have in running this particular kind of business. An example of ineffective framing is when you indicate that you lack experience with this type of business, or when you fail to specify how and why your levels of experience will affect the business’s development.
Prioritizing Problems
Don’t get hung up on something that doesn’t need an immediate solution. Instead, flag it for future consideration and move on. When you return to re-address the issue, it might no longer be a problem or you might have by then figured out a solution.
Process for Developing Business Plans
The business plan development process described next has been extensively tested with entrepreneurship students and has proven to provide the guidance entrepreneurs need to develop a business plan appropriate for their needs: a high power business plan .
Developing a high power business plan has six stages, which can be compared to a process for hosting a dinner for a few friends. A host hoping to make a good impression with their anticipated guests might analyze the situation at multiple levels to collect data on new alternatives for healthy ingredients, what ingredients have the best prices and are most readily available at certain times of year, the new trends in party appetizers, what food allergies the expected guests might have, possible party themes, and so on. This analysis is the Essential Initial Research stage.
In the Business Model stage, the host might construct a menu of items to include with the meal along with a list of decorations to order, music to play, and costume themes to suggest to the guests. The mix of these kinds of elements chosen by the host will aid in the success of the party.
The Initial Business Plan Draft stage is where the host rolls up their sleeves and begins to make some of the food items, puts up some of the decorations, and generally gets everything started for the party.
During this stage, the host will begin to realize that some plans are not feasible and that changes are needed. The required changes might be substantial, like the need to postpone the entire party and ultimately start over in a few months, and others might be less drastic, like the need to change the menu when an invited guest indicates that they can’t eat food containing gluten. These changes are incorporated into the plan during the Making the Business Plan Realistic stage to make it realistic and feasible.
The Making the Plan Appeal to Stakeholders and Desirable to the Entrepreneur stage involves further changes to the party plan to make it more appealing to both the invited guests and to make it a fun experience for the host. For example, the host might learn that some of the single guests would like to bring dates and others might need to be able to bring their children to be able to attend. The host might be able to accommodate those desires or needs in ways that will also make the party more fun for them—maybe by accepting some guests’ offers to bring food or games, or maybe hiring a babysitter to entertain and look after the children.
The final stage— Finishing the Business Plan— involves the host putting all of the final touches in place for the party in preparation for the arrival of the guests.
Essential Initial Research
A business plan writer should analyze the environment in which they anticipate operating at each of the levels of analysis: Societal , Industry , Market , and Firm . This stage of planning is called the Essential Initial Research stage, and it is a necessary first step to better understand the trends that will affect their business and the decisions they must make to lay the groundwork for, which will improve their potential for success.
In some cases, much of this research should be included in the developing business plan as its own separate section to help show readers that there is a market need for the business being considered and that it stands a good chance of being successful.
In other cases, a business plan will be stronger when the components of the research are distributed throughout the business plan to provide support for the outlined plans and strategies outlined. For example, the industry- or market-level research might outline the pricing strategies used by identified competitors, which might be best placed in the Pricing Strategy part of the business plan to support the decision made to employ a particular pricing strategy.
Business Model
Inherent in any business plan is a description of the Business Model chosen by the entrepreneur as the one that they feel will best ensure success. Based upon their analysis from the Essential Initial Research stage, an entrepreneur should determine how each element of their business model—including their revenue streams, cost structure, customer segments, value propositions, key activities, key partners, and so on—might fit together to improve the potential success of their business venture (see Chapter 3 – Business Models ).
For some types of ventures, at this stage an entrepreneur might launch a lean start-up (see the “Lean Start-up” section in Chapter 2 – Essential Initial Research ) and grow their business by continually pivoting, or constantly adjusting their business model in response to the real-time signals they get from the markets’ reactions to their business operations. In many cases, however, an entrepreneur will require a business plan. In those cases, their initial business model will provide the basis for that plan.
Of course, throughout this and all of the stages in this process, the entrepreneur should seek to continually gather information and adjust the plans in response to the new knowledge they gather. As shown in Figure 1 by its enclosure in the Progressive Research box, the business plan developer might need to conduct further research before finishing the business model and moving on to the initial business plan draft.
Initial Business Plan Draft
The Initial Business Plan Draft stage involves taking the knowledge and ideas developed during the first two stages and organizing them into a business plan format. Many entrepreneurs prefer to create a full draft of the business plan with all of the sections, including the front part with the business description, vision, mission, values, value proposition statement, preliminary set of goals, and possibly even a table of contents and lists of tables and figures all set up using the software features enabling their automatic generation. Writing all of the operations, human resources, marketing, and financial plans as part of the first draft ensures that all of these parts can be appropriately and necessarily integrated. The business plan will tell the story of a planned business startup in two ways: 1) by using primarily words along with some charts and graphs in the operations, human resources, and marketing plans and 2) through the financial plan. Both must tell the same story.
The feedback loop shown in Figure 1 demonstrates that the business developer may need to review the business model. Additionally, as shown by its enclosure in the Progressive Research box, the business plan developer might need to conduct further research before finishing the Initial Business Plan Draft stage and moving on to the Making Business Plan Realistic stage.
Making Business Plan Realistic
The first draft of a business plan will almost never be realistic. As the entrepreneur writes the plan, it will necessarily change as new information is gathered. Another factor that usually renders the first draft unrealistic is the difficulty in making certain that the written part—in the front part of the plan along with the operations, human resources, and marketing plans—tells the exact same story as the financial part does. This stage of work involves making the necessary adjustments to the plan to make it as realistic as possible.
The Making Business Plan Realistic stage has two possible feedback loops. The first means going back to the Initial Business Plan Draft stage if the initial business plan needs to be significantly changed before it is possible to adjust it so that it is realistic. The second feedback loop circles back to the Business Model stage if the business developer needs to rethink the business model. As shown in Figure 1 by its enclosure in the Progressive Research box, the business plan developer might need to conduct further research before finishing the Making Business Plan Realistic stage and moving on to the Making Plan Appeal to Stakeholders stage.
Making Plan Appeal to Stakeholders and Desirable to the Entrepreneur
A business plan can be realistic without appealing to potential investors and other external stakeholders, like employees, suppliers, and needed business partners. It might also be realistic (and possibly appealing to stakeholders) without being desirable to the entrepreneur. During this stage, the entrepreneur will keep the business plan realistic as they adjust plans to appeal to potential investors, stakeholders, and themselves.
If, for example, investors will be required to finance the business’s start, some adjustments might need to be relatively extensive to appeal to potential investors’ needs for an exit strategy from the business, to accommodate the rate of return they expect from their investments, and to convince them that the entrepreneur can accomplish all that is promised in the plan. In this case, and in others, the entrepreneur will also need to get what they want out of the business to make it worthwhile for them to start and run it. So, this stage of adjustments to the developing business plan might be fairly extensive, and they must be informed by a superior knowledge of what targeted investors need from a business proposal before they will invest. They also need to be informed by a clear set of goals that will make the venture worthwhile for the entrepreneur to pursue.
The caution with this stage is to balance the need to make realistic plans with the desire to meet the entrepreneur’s goals while avoiding becoming discouraged enough to drop the idea of pursuing the business idea . If an entrepreneur is convinced that the proposed venture will satisfy a valid market need, there is often a way to assemble the financing required to start and operate the business while also meeting the entrepreneur’s most important goals. To do so, however, might require significant changes to the business model.
One of the feedback loops shown in Figure 1 indicates that the business plan writer might need to adjust the draft business plan while ensuring that it is still realistic before it can be made appealing to the targeted stakeholders and desirable to the entrepreneur. The second feedback loop indicates that it might be necessary to go all the way back to the Business Model stage to re-establish the framework and plans needed to develop a realistic, appealing, and desirable business plan. Additionally, this stage’s enclosure in the Progressive Research box suggests that the business plan developer might need to conduct further research.
Finishing the Business Plan
The final stage involves putting the important finishing touches on the business plan so that it will present well to potential investors and others. This involves making sure that the math and links between the written and financial parts are accurate. It involves ensuring that all the needed corrections are made to the spelling, grammar, and formatting. The final set of goals should be written to appeal to the target readers and to reflect what the business plan says. An executive summary should be written and included as a final step.
Chapter Summary
This chapter described the internal and external purposes for business planning. It also explained how business plans must effectively communicate while establishing and building credibility for both the entrepreneur and the venture. The general guidelines for business planning were covered as were some important business planning tools. The chapter concluded with descriptions of the stages of the business development process for effective business planning.
- Hindle, K., & Mainprize, B. (2006). A systematic approach to writing and rating entrepreneurial business plans. The Journal of Private Equity, 9(3), 7-23. ↵
- Ibid. ↵
Business Plan Development Guide Copyright © 2023 by Lee A. Swanson is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Business Plan Development Guide
(6 reviews)
Lee Swanson, University of Saskatchewan
Copyright Year: 2017
Publisher: OPENPRESS.USASK.CA
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Kevin Heupel, Affiliate Faculty, Metropolitan State University of Denver on 3/4/20
The text does a good job of providing a general outline about writing and developing a written business plan. All of the important steps and components are included. However, the text is light on details, examples, and rationale for each element... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 3 see less
The text does a good job of providing a general outline about writing and developing a written business plan. All of the important steps and components are included. However, the text is light on details, examples, and rationale for each element of the business plan. Some examples from actual business plans would be helpful.
Content Accuracy rating: 4
For the most part, the content is accurate. The content covers all important aspects of drafting a business plan. I thought the industry analysis could use more information about collecting primary and secondary sources; instead, this information was referenced in the marketing plan section.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
Most of the content relies on cites as far back as 2006; however, when it comes to developing and writing a business plan nothing has changed. Thus, the content is current and there is no concern about it becoming obsolete in the near future.
Clarity rating: 4
The text is clear. There are no difficult terms used and the writing is simple. The text uses a lot of bullet points though, which gets tedious to read for a few pages.
Consistency rating: 5
The text does a good job of maintaining consistency in terms of framework and terminology. The text is organized where it's easy to find the information you want in a quick manner.
Modularity rating: 3
The text has a lot of bullet points and the paragraphs are dense. However, the use of subheading is excellent.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
The book is organized as if you're writing a business plan from start to finish, which is helpful as a practical guide.
Interface rating: 5
There are no navigation problems, distortion of images/charts, or any other display features that may distract or confuse the reader.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
The text is free of grammatical errors. The sentence structure is simple with many bullet points, which helps to avoid any grammatical issues.
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
This book was written by a Canadian professor and provides references to Canadian sources. However, the information in this text can be used for U.S. schools.
This book is very short and provides a good, general overview about the process of creating and writing a business plan. It won't help a reader if he/she is confused about a certain part of the business plan. The reader will have to find another source, such as "Preparing Effective Business Plans" by Bruce Barringer, Ph.D. The book provides links to good resources and a finished business plan that the reader can reference. I would recommend the book for undergraduate courses.
Reviewed by Kenneth Lacho, Professor of Management, The University of New Orleans on 6/19/18
1. Text is relevant to Canada. Not the United States 2. Needs to cover resources available to entrepreneur, e.g., federal government agencies, trade associations, chambers of commerce, economic development agencies. 3. Discuss local economy or... read more
1. Text is relevant to Canada. Not the United States 2. Needs to cover resources available to entrepreneur, e.g., federal government agencies, trade associations, chambers of commerce, economic development agencies. 3. Discuss local economy or economic area relevant to this proposed business. 4. Business model ok as a guide. 5. Suggested mission statement to cover: product/business, target customer, geographical area covered. 6. Need detailed promotion plan, e.g., personal selling, advertising, sales promotion, networking publicity, and social media. 7. How do you find the target market? 8. Chapter 6 too much detail on debt and equity financing. 9. Discuss how to find sources of financing, e.g., angels. 10. Expand coverage of bootstring, crowdfunding. 11. Chapter 4 – good checklist. 12. Chapter 3 - overlaps. 13. Chapter 7 – 3 pages of executive summary – double or single spaced typing. Number all tables, graphs. 14. Some references out-of-date, mostly academic. Bring in trade magazines such as Entrepreneur.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
In my opinion, the content is accurate and error free.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 4
The material is relevant to writing a business plan. I wonder if the Porter, SWOT VRIO, etc. material is too high level for students who may not be seniors or have non-business degrees (e.g., liberal arts). Porter has been around for a while and does have longevity. The author has to be more alert to changes in promotion, e.g., social media and sources of financing, e.g., crowdfunding.
Clarity rating: 3
As noted in No. 9, the tone of the writing is too academic, thus making the material difficult to understand. Paragraphs are too long. Need to define: Porter, TOWS Matrix, VRIO, PESTEL. A student less from a senior or a non-business major would not be familiar with these terms.
Consistency rating: 4
The text is internally consistent. The model approach helps keep the process consistent.
Modularity rating: 4
The process of developing a business plan is divided into blocks which are parts of the business plan. Paragraphs tend to be too long in some spots.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 4
The topics are presented in a logical step-wise flow. The language style is too academic in parts, paragraphs too long. Leaves out the citations. Provides excellent check lists.
There are no display features which confuse the reader.
Grammatical Errors rating: 4
The text has no grammatical errors. On the other hand, I found the writing to be too academic in nature. Some paragraphs are too long. The material is more like an academic conference paper or journal submission. Academic citations references are not needed. The material is not exciting to read.
The text is culturally neutral. There are no examples which are inclusive of a variety of races, ethnicities, and backgrounds.
This book best for a graduate class.
Reviewed by Louis Bruneau, Part Time Faculty, Portland Community College on 6/19/18
The text provides appropriate discussion and illustration of all major concepts and useful references to source and resource materials. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
The text provides appropriate discussion and illustration of all major concepts and useful references to source and resource materials.
Contents of the book were accurate, although it could have benefited from editing/proofreading; there was no evidence of bias. As to editing/proofreading, a couple of examples: A. “Figure 1 – Business Plan… “ is shown at the top of the page following the diagram vs. the bottom of the page the diagram is on. (There are other problems with what is placed on each page.) B. First paragraph under heading “Essential Initial Research” there is reference to pages 21 to 30 though page numbering is missing from the book. (Page numbers are used in the Table of Contents.)
The book is current in that business planning has been stable for sometime. The references and resources will age in time, but are limited and look easy to update.
Clarity rating: 5
The book is written in a straightforward way, technical terms that needed explanations got them, jargon was avoided and generally it was an easy read.
The text is internally consistent in terms of terminology and framework.
Modularity rating: 5
The book lends itself to a multi-week course. A chapter could be presented and students could work on that stage of Plan development. It could also be pre-meeting reading for a workshop presentation. Reorganizing the book would be inappropriate.
The topics in the text are presented in a logical, clear fashion.
Generally, the book is free of interface problems. The financial tables in the Sample Plan were turned 90° to maintain legibility. One potential problem was with Figure 6 – Business Model Canvas. The print within the cells was too small to read; the author mitigated the problem by presenting the information, following Figure 6, in the type font of the text.
I found no grammatical errors.
The text is not culturally insensitive or offensive in any way.
I require a business plan in a course I teach; for most of the students the assignment is a course project that they do not intend to pursue in real life. I shared the book with five students that intended to develop an actual start-up business; three of them found it helpful while the other two decided not to do that much work on their plans. If I were planning a start-up, I would use/follow the book.
Reviewed by Todd Johnson, Faculty of Business, North Hennepin Community College on 5/21/18
The text is a thorough overview of all elements of a business plan. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
The text is a thorough overview of all elements of a business plan.
The content is accurate and seems to lack bias.
Content seems relevant and useful . It does not help an entrepreneur generate ideas, and is very light on crowdfunding and other novel funding source content. It is more traditional. This can be easily updated in future versions, however. "Social Media" appears once in the book, as does "Crowd Funding".
The book is comprehensive, but perhaps not written in the most lucid, accessible prose. I am not sure any college student could pick this up and just read and learn. It would be best used as a "teach along guide" for students to process with an instructor.
The text seems consistent. The author does a nice job of consistently staying on task and using bullets and brevity.
Here I am not so certain. The table of contents is not a good guide for this book. It does make the book look nicely laid out, but there is a lot of complexity within these sections. I read it uncertain that it was well organized. Yes there are many good bits of information, however it is not as if I could spend time on one swathe of text at a time. I would need to go back and forth throughout the text.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 2
Similar to the above. I did not like the flow and organization of this. An editor would help things be in a more logical order.
Interface rating: 2
The interface is just OK. It is not an attractice interface, as it presents text in a very dense manner. The images and charts are hard to follow.
I did not find any grammatical errors.
Cultural Relevance rating: 4
I a not certain of the origins of Saskatchewan, but I do feel this is a different read. It is more formal and dense than it has to be. This would be a difficult read for my students. I do not feel it is insensitive in any way, or offensive in any way.
I would not adopt this book if given the chance. It is too dense, and not organized very well, even though the information is very good. The density and lack of modularity are barriers to understanding what is obviously very good information.
Reviewed by Mariana Mitova, Lecturer, Bowling Green State University on 2/1/18
Though this textbook has a prescriptive nature, it is quite comprehensive. The author strikes a good balance between presenting concepts in a concise way and providing enough information to explain them. Many every-day examples and live links to... read more
Though this textbook has a prescriptive nature, it is quite comprehensive. The author strikes a good balance between presenting concepts in a concise way and providing enough information to explain them. Many every-day examples and live links to other resources add to the completeness of the textbook.
Content seems accurate.
Since the content is somewhat conceptual, the text will not become obsolete quickly. In addition, the author seems to be updating and editing content often hence the relevance to current developments is on target.
The text is very clear, written in clear and straight-to-the point language.
The organization of content is consistent throughout the entire text.
The textbook is organized by chapters, beginning with overview of the model used and followed by chapters for each concept within the model. Nicely done.
The flow is clear, logical and easy to follow.
Overall, images, links, and text are well organized. Some headlines were misaligned but still easy to follow.
No concerns for grammar.
No concerns for cultural irrelevance.
Reviewed by Darlene Weibye, Cosmetology Instructor, Minnesota State Community and Technical College on 2/1/18
The text is comprehensive and covers the information needed to develop a business plan. The book provides all the means necessary in business planning. read more
The text is comprehensive and covers the information needed to develop a business plan. The book provides all the means necessary in business planning.
The text was accurate, and error-free. I did not find the book to be biased.
The content is up-to-date. I am reviewing the book in 2017, the same year the book was published.
The content was very clear. A business plan sample included operation timelines, start up costs, and all relevant material in starting a business.
The book is very consistent and is well organized.
The book has a table of contents and is broken down into specific chapters. The chapters are not divided into sub topics. I do not feel it is necessary for sub topics because the chapters are brief and to the point.
There is a great flow from chapter to chapter. One topic clearly leads into the next without repeating.
The table of contents has direct links to each chapter. The appearance of the chapters are easy to read and the charts are very beneficial.
Does not appear to have any grammatical errors.
The text is not culturally insensitive or offensive.
I am incorporating some of the text into the salon business course. Very well written book.
Table of Contents
Introduction
- Chapter 1 – Developing a Business Plan
- Chapter 2 – Essential Initial Research
- Chapter 3 – Business Models
- Chapter 4 – Initial Business Plan Draft
- Chapter 5 – Making the Business Plan Realistic
- Chapter 6 – Making the Plan Appeal to Stakeholders and Desirable to the Entrepreneur
- Chapter 7 – Finishing the Business Plan
- Chapter 8 – Business Plan Pitches
References Appendix A – Business Plan Development Checklist and Project Planner Appendix B – Fashion Importers Inc. Business Plan Business Plan Excel Template
Ancillary Material
About the book.
This textbook and its accompanying spreadsheet templates were designed with and for students wanting a practical and easy-to-follow guide for developing a business plan. It follows a unique format that both explains what to do and demonstrates how to do it.
About the Contributors
Dr. Lee Swanson is an Associate Professor of Management and Marketing at the Edwards School of Business at the University of Saskatchewan. His research focuses on entrepreneurship, social entrepreneurship, Aboriginal entrepreneurship, community capacity-building through entrepreneurship, and institutional-stakeholder engagement. Dr. Swanson’s current research is funded through a Social Sciences Humanities Research Council grant and focuses on social and economic capacity building in Northern Saskatchewan and Northern Scandinavia. He is also actively studying Aboriginal community partnerships with resource based companies, entrepreneurship centres at universities, community-based entrepreneurship, and entrepreneurial attitudes and intentions. He teaches upper-year and MBA entrepreneurship classes and conducts seminars on business planning and business development.
Contribute to this Page
🔔 Important Update: on February 12th we will implement a price increase on all the courses. Supercharge your career with our Business Development Courses at current rates.
- Train your team
- Log in Find courses
Business development plan: A step-by-step approach

- This is some text inside of a div block.
A good business development plan can set you up for success. Learn how to create your own from scratch with zero experience!
If you’re just starting with business development , chances are that you’re a little confused about how you should do it. I got lost many times during my entrepreneurial journey. One of those moments was when I had to write a business development plan for the first time.
Now, the main problem was that I didn’t have a clue about what a business development plan was to start with. And of course, when I started digging, I got even more confused. I found a lot of information online, but nothing that would tell me how to do it step-by-step.
So after some years of trying and failing, I finally found my way to deal with it and build my own business development plan.
Below I’ll explain how to write a business development plan and what information you should include in practical terms. But first, let’s define what a business development plan is.
What is a business development plan?
A business development plan is a document that helps you implement your business development strategy in a step-by-step method. It involves a lot of research on the market and customers. But also, other aspects such as your competitors and buyer persona.
So, a business development plan is a detailed summary of important steps you’re going to take to grow your business. One key aspect to remember is that a business development plan is a LIVING document. This means that you have to update your plan continuously based on new information about your ecosystem.
This helps you strategize better but also ensures that it’s a document of quality insights.
A business development plan is divided into two main parts:
- Research: in the research phase, you learn more about your market, customers, and competitors.
- Action: you use your research and put it into action. Specifically, this translates into creating a value proposition, and content, and experimenting with ideas.
You can download our template for free at this link .

Step 1: Organize your business development plan
I’m a fan of organizing information in a structured, intuitive, and efficient way. Although it may sound basic, the first thing you should think about is to have a proper file you can consult on a daily basis.
It doesn’t have to contain every piece of information. Keep it simple by including only essential and key facts that will help you build an effective business development machine. Your business development plan needs to be easily accessible and quick to consult.
In this sense, you don’t need to get fancy and start looking for the latest software that promises you great time savings. Stick to something basic yet powerful. Google Sheets is your best ally when it comes to your business development plan.
So, the main goal of a business development plan is to keep information structured so that you can spot growth opportunities easier.
You can download our template for free at this link and start your business development plan.
Step 2: Market research
Market research is a stepping stone in a business development plan. It’s an activity to gather more information about customers’ preferences and needs. Many companies overlook this step thinking that their intuition will guide them through their challenges. Intuition can be helpful, but it’s still essential to know your customers better using research and data.
After all, most ideas start off from intuition. However, basing an entire plan on assumptions is never a smart strategy to use in business development. So, do your homework and make sure you always take educated guesses before starting to work on your business development plan.
Market research takes into account 3 variables . These will tell you the realistic size of the market you’re trying to target.
1 – Total Addressable Market or Total Available Market (TAM)
The TAM takes into account the entire market you’re operating in and basically tells you how much annual revenue there is available for your product or service.
Now, finding this information can be the first bummer. To me at least, it sounded quite impossible to find out. Later, I figured that there are many people out there that dedicate their life only to market research.
You can use Google to find out this information. But of course, you first need to know what you’re looking for. The information you need, in this case, is basically knowing how many companies or people would benefit from your product or service.
You also want to know how many companies operate in your exact space both in terms of services and geography. To get relevant market news, try Googling “your industry market trends”, “your market report”, or “your industry report”.
Many big consultancy groups and governmental institutions dedicate a lot of time to this type of research. It’s a good and reliable starting point.
PRO TIP: Choose your sources very carefully. You’ll find a lot of random information, learn to filter out what you’re reading.
2 – Total Served Market (TSM)
Once you know how big your market is, you need to check how much of it is already served by your competitors.
In this case, the information you’re looking for is all about your competition. You should ask yourself first how many of them you have.
Then you need to find out how well they’re doing and start hunting for as much intelligence as possible.
The info you need to look for is how many clients your competitors claim to have, what revenue they generate, and where they are present.
First, Google keywords to identify your competitors. Right after that, you can start digging deeper into their websites and find detailed info.
Bigger competitors will most likely have good press coverage. Read these articles to gather more insight.
Last, don’t overlook the importance of customer review websites. Customers can uncover many relevant details that your competitors don’t want to reveal. And of course, make use of technology to make the most out of your research.
3 – Serviceable Obtainable Market (SOM)
The last step in your market research is to quantify how much you can realistically obtain with your business development effort.
Your SOM is your share in the market. So, to put it simply, it’s not possible to have an entire market buy only your products and services. There is a specific customer base that will buy from your company . So, your SOM refers to your market share and the people that can become your customers if they see a benefit from your products or services.
SOM takes into account your brand awareness, market insights, but also competition. It helps you forecast potential earnings and also gain customers. Based on the research, you become aware of what your competitors are offering to the market. Moreover, you will be able to tailor your products and services to meet the needs and preferences of your customers.

Step 3: Competitor analysis
The third step to do when creating your business development plan is to do a competitor analysis . So far, I discussed market research and how it helps you get to know the preferences of your target audience better. But, to grow your business sustainably and profitably, it’s vital that you analyze your competitors as well.
First, figure out who your direct and indirect competitors are. So, in a Google search, we try to identify or find the ID of each company that competes in your market. This can be found in the website’s ‘About us’ section. Then, the aim is to find key personalities such as managers and executives, and so on.
Once you have this information, you can move on to products and services. You can find this on your competitor’s website as well. This specific section defines what the company specializes in. You can use this information to compare your products to those of your competitors and try to find ways to improve them.
Continue by checking their clients, and the pricing they offer for their products and services.
PRO TIP: Read the customer reviews of your competitors to spot their strengths and weaknesses. Use the insights to improve your offer.

Step 4: Customer research
After identifying your market share, you can start thinking of what kind of customers within this segment, you are trying to sell your products and services to.
The best way to tackle this is by running proper customer research that will provide you with your Ideal Customer Profile and Buyer Persona.
This is the part I like the most because it really helps you understand who you’re talking to. But how do you do it? First, if you already have some customers, start analyzing them. You want to gather more information on who they are, what they do, and their habitual traits.
For example:
- What job titles do these people have?
- How old are they?
- What communication tools do they use?
- Where do they hang out?
- What are their personalities like?
- What are their challenges?
- What do they do in their daily lives?
You can find all this info by simply checking social media profiles. Really, just by observing their social media platforms, you can get to know them in-depth! Take some time to check a few ones (at least 10) and you’re going to start seeing patterns.
Then, check some job descriptions about the people you’re targeting. This will highlight what are their professional responsibilities and how your product or service can help them. Last, it’s always advisable to run a survey.
Step 5: Build your Buyer Persona
Right after having run your customer research, you can now create your buyer persona.
The buyer persona is a semi-fictional representation of your ideal customers based on data and research,
In your buyer persona, you need to include all the relevant information you found through your customer research. It should look like something below:

Step 6: Value Propositions
The customer research concludes the research part of your business development plan. Now it’s time to put your insights into action and start building your business development strategy .
The first valuable asset you need to build is a value proposition.
A value proposition is the value your customers get should they choose to buy your products and services
The value proposition helps you communicate your value as a company and you can use it on your website, sales calls, social media posts, etc. Having a clear value proposition will help you attract the right audience and persuade potential customers to work with you.
Of course, a good value proposition is based on that, and if you followed all the steps, you should have all the insights you need.
To build a value proposition we will use the Job-To-Be-Done framework. This helps you identify what are the responsibilities of your buyer persona when they’re doing their job.
For example, a typical responsibility for a recruiter is to find the right talent .

Second, consider the pains and gains of your customers. Customers’ emotions are usually the reason behind their buying decisions. They influence their preferences, frequency of buying, and also which companies they buy from.
Especially the challenges are a crucial element in your value proposition because you can immediately link your solution to a concrete pain that your customers are facing.
For example, let’s go back to the example of the recruiter. We know that one main responsibility of a recruiter is to find talent. One major challenge for recruiters is to have enough time to process all the CVs they receive daily.
Now, let’s assume you work for a company that provides recruitment software that can automate CV screening.
A good value proposition, in this case, would sound like this:
Save 70% of your CV screening time using our recruitment software

Step 7: Content plan
Once you have your value proposition, the next step is to share it with your target audience. That’s when having a content plan becomes a must.
A content plan helps you strategize the type of information you want to feed your audience. It also helps you select the channels on which you should build your presence.
For content to be effective, you need to have a clear idea of your target audience when you write posts/emails, or articles. So, always consult your buyer persona before creating content.
Just like the value propositions, effective content revolves around the pain point you identified earlier. Use them to get the attention of your audience and provide valuable information that helps them alleviate these pains.
This will help you establish yourself as a valuable resource and when they will want to solve their issues, you’ll be the first to pop into their minds.
Step 8: Experiments
The last step in your business development plan is all about creativity and finding opportunities. This is the moment in which we create experiments to validate some of our business assumptions. Your experiment should be ideas that you think will bring sustainable growth to your company.
Once you identify some ideas, define some goals and set up the methodology you will follow to run this experiment. For example, if you heard of a new social media and you think your audience might be on it, build an experiment to validate if this is true and if it can bring you results.
Attach a goal to this idea, for example, generating 10 qualified leads on this new channel.
Then decide for how long you will run the experiment – ideally a couple of weeks. Once the experiment is over analyze what happened. If the experiment was successful, you need to scale this activity. If not, take the learnings for further improvements.
Read this article with 10 business development examples to have some ideas on how to implement your strategy.
The business development plan is a key document that helps you map your ecosystem and strategize your business development efforts .
It consists of a research part and an action part. In the first part, you analyze your market, competitors, and customers. In the second, you use your insights to build value propositions, content plans, and experiments.
The business development plan is a live document, so you have to update it every time you have new insights. Of course, you have to use it in your daily operations to make sure you’re on the right track.
The business development plan is one of the assets you will build during our training. Would you like to shake up your business development career and work in a more structured way? Then join our next cohort .
Last, if you are a company wanting to train your business development team, our custom training solutions are the best way to take your team to the next level.

Want to stay informed?
Explore our related blog posts.

+10 Best Business Development Training & Courses in 2024 - with Certification
Expand your business skills with our selection of the top 10 business development courses and certifications in 2024.

10 Business Development Examples
Business development examples to show you different applications of business development. All the examples are based on real-life cases.

10 Common business development activities
Common business development activities you should be doing. Check this shortlist to organize your work, improve productivity and get results.

How to Create a Business Development Plan (Insights From a Six-Figure Business)
I’ve grown three successful businesses in the last decade. A large part of my success is down to planning. This is certainly the case with Launch Space, where I offer SaaS consulting services.
Having a business development plan has helped me avoid a lot of silly rookie mistakes. It also kept me focused, which is important for business owners. In this guide, you will learn how to create an actionable business development plan you can apply to your business.
What is a Business Development Plan
A business development plan is a document that outlines the steps you will take to get your company off the ground. It’s a roadmap of sorts, but it also serves as a marketing tool and sales pitch for your product or service.
The business development plan should include everything from where you are now to where you want to be in the future. This can help you determine what kind of strategy needs to be implemented to achieve your goals. Having a plan in place should help you better assign your resources and set relevant Key Performance Indicators to track your progress.
How to Create a Business Development Plan
One of the first things I did before setting up Launch Space was design a business development plan to outline my goals. The following paragraphs will walk you through a tried and tested formula I used that you can follow. Let’s jump right in.
1. Analyze The Competition
Every great business plan is based on research. Well, most great plans are based on research. Ice cream at midnight is rarely planned, but it’s pretty great 😀
The first thing I do when creating a business development strategy is to review the company and consider the target market. You need to understand the strengths and weaknesses of your company. It’s important to also review your competition, customer (creating a customer persona is handy), and review market trends.
Let me use Launch Space as my example. During my review of the competitive landscape for this business, I discovered some of the following:
- There are only a few agencies that provide specialized services for SaaS firms. Most agencies don’t have a clear target audience.
- Most SEO agencies lock clients into a 6 or 12-month contract. A long contract is a big commitment for a company. For example, $4k a month is a $48k contract.
- Many clients don’t see a return on investment from working with an agency. Trust in the agency is a big issue for clients.
- Most SEO agencies don’t promote their services through guest posting on authority sites.
You will gain many useful insights by researching your niche and conducting competitive intelligence before you make a plan. The research is a chance to test your assumptions, and gain insights.
2. Identify Your Business Opportunities
At the end of the research phase of your business development plan, you need to review the information you gathered about your company, the target market, and your customer base. Spend time analyzing all the data. You will use these insights to create your business development plan.
For Launch Space, my goal was to find ways to do things that are disruptive and help me stand out. I created a table. On one side I listed my insights. On the other side, I listed the opportunities for my business.
Your research helps you understand the market. You can then use those insights to identify business opportunities and define your competitive advantages.
For example, through my research, I learned that one of the biggest issues agencies have is trust. They naturally don’t trust an agency they have never met. Skipping a contract would allow me to differentiate myself from the competition. In fact, I made the fact you don’t need to sign a contract key part of my sales copy . You can see this on the homepage I created with a landing page builder .

When I made my business plan, I didn’t have a company. If I had a company with lots of customers, I’d still do the same type of research. However, I’d spend more time reviewing company operations. I’d look at what are the main drivers of growth for the company. I’d also consider what are the company’s biggest problems.
3. How to Set Your Business Development Goals
The next stage of business development is to set targets. Your targets help you understand what you want to achieve and measure your success. You should make sure your goals are SMART – Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Time Based.
When I created my business plan for Launch Space, I set a single company goal. The goal was ambitious and easy to understand.

I then created sub-goals for the different parts of your business. So for example, for my website, I started with the following goal.
- Generate $10k in monthly recurring revenue
That’s a pretty easy goal to understand. I then thought about how to achieve that target. My sub-goals look like this.
- Sales Goal: Secure 1 new client each month from cold outreach
- Delivery: Every two months get 1 client to increase their order
- Human Resources: Hire 1 full-time member of staff
I then looked at the things I would need to do to achieve each sub-goal.
For example, if I was to get one new client a month I would need to meet with five potential clients. I estimated that to secure those meetings I would need to cold email 200 businesses a week. Those were my activities for that goal.
Those activities are quantifiable. I can tell you if I sent 200 emails in a month. Businesses like Google have these sorts of systems in place to measure targets. It helps keep people accountable and provides management with a way to check progress.
Setting my goals helped me develop a strategic plan. That company target is the common goal. You can use this goal to align the operations of your sales team, operations team, and marketing team.
4. Create Standard Operating Procedures
After you have finished strategizing you need to implement your business development goals. There are too many variables in place for me to provide you with many useful insights for this part of the process.
However, there is one business development tip I can share…
As you work on tasks, create Standard Operating Procedures (SOP). Standard Operating Procedures are a set of rules for how the company operates.
Your SOP should build on your business development plan. For example, I have created a whole set of SOP for things like candidate sourcing and sales outreach.
I started by setting sales targets for the company with SMART goals . I then looked at how I’d achieve those goals. Then, I tested my approach. Once I found a system that worked, I broke the job down into chunks.

I listed out all of the things I needed to do to complete the task. I then gave this information to an employee. They did the work.
Systemizing your business in this way has multiple benefits. It helps you:
- Reduce the amount of time it takes to complete a task
- Keep information when a person leaves the company, which speeds up the transition. Role-based access in product management tools and maintains institutional knowledge.
- Ensure vital tasks get completed every month
Keep in mind that your business strategy is not fixed. As a business developer, make sure to periodically review your business development strategy. Analyze what is working and what is not, then adapt your strategy.
5. Review Your Progress
The final stage of your business development strategy is the review stage. This is where you put a date in the diary and say, “in three months’ time we should be…”
Then, you can review progress against your goals.
The purpose of these reviews is to see how you’ve done against your business goals. Just as importantly, a review is a chance to adjust your business plan to make sure that it aligns with what you’re trying to accomplish.
You can incorporate things like a SWOT analysis in your quarterly or annual review. Periodic reviews help you assess your progress, identify weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.

During a review, you should assess the validity of your business goals. Make sure they are still relevant to your company. If they are, great. If not, change your business development goals.
Look at the activities in your business that make the most money. For example, at Launch Space I’m making around:
- SEO Consulting work = $20k+
- Private training = $3k
- Affiliate marketing = $0.5k
It’s easy to see what makes the company the most money.
I then look at how I can maximize growth through my SEO consulting work over a quarter. Periodic reviews help me ensure my business development strategy aligns with the drivers of company growth.
You should also review the problems the company is facing. For example, as Launch Space grows I often find myself spending a lot of time doing a job that doesn’t help the company scale.
I don’t want to get stuck managing the day-to-day tasks that don’t add value to my business. It’s a pain point.
When I get stuck in a task, I try to find a way to free up my time. Normally that involves, creating SOP and then outsourcing the work.
In this guide, I provided you with an example of my business development strategy. I showed you how I put together a business strategy that allowed me to scale a marketing agency from a side hustle to a six-figure business in less than 12 months.
I hope you’ve found this article interesting. If you have any questions, hit me up in the comments below.
About the author
Nicholas Prins
I'm the founder of Launch Space. We work with global companies helping them scale lead generation through SEO and content marketing. Head over to the homepage to find out more.

How to Start a Cleaning Business

How to Start a Cybersecurity Business
Guest Post Guidelines
Business Blog Content Marketing Blog Entrepreneurship Blog General Blog
Software Review Software Comparison Lifetime Software Deals
9 steps for writing a strategic business development plan
Updated 04 October 2023 • 7 min read
Developing a business plan can mark the start of an exciting phase, as you start charting future growth. This document serves as the roadmap for your business development strategy as you take your business to new heights.
Creating an effective business development plan can be a tough task. It requires you to think through several aspects of your business that you may not consider on a day-to-day basis.
Don’t worry — we’re here to help. This article will walk you through how to write a business development plan, so you can grow your business in the most effective way possible.
What is a business development plan?
A business development plan is the growth roadmap for your business. It’s a strategy document that lays out where you want to take your business and how you intend to get there.
A thorough and carefully crafted business development plan lays out your growth targets, financial projections and the tools and resources your company needs. It may also define your marketing and efforts that support your goals.
A business development plan provides clarity and helps you keep your objectives in focus during the day-to-day grind. It also provides a strong foundation for making business decisions — if you’re not sure whether a move makes sense, you can always consult your plan.
Why do you need a business development plan?
Creating a proper business development strategy can be a lot of work. But it pays dividends by providing clarity and focus. It also helps when trying to secure funding, as it shows you've thought through all the possibilities.
A business development plan helps you:
Get clarity
A strong business development plan helps you get clear about priorities during the hectic launch phase of your business. It helps you define your goals and objectives, as well as chart out how you’ll reach them.
Stay focused
As you dive into the day-to-day running of your business, it can be easy to get bogged down in details and lose sight of your larger goals. Your business plan provides an anchor that keeps you in place. And if you’re already in business, it can help you take a step back and refocus on the fundamentals.
Secure funding
A detailed business plan is one of the most effective ways to show investors that you can be trusted. This is especially important when you’re just starting out and have no track record of performance. Your business plan shows that you’ve thought about how your business will fare in the long run, not just in the short term.
Achieve growth
A proper business development plan should include a roadmap. This is your high-level strategy document that serves as the map to your company’s growth. It lays out how you’ll measure success, provides targets to aim for and defines your plans for hitting them.
How to write a business development plan
If you’re convinced that you need to write your own business development plan (or update the one you have), you might be wondering where to start. Let’s walk through the process.
1. Set clear financial goals
Your business development strategy should include clear financial goals. For example, every business wants to increase sales; however, that’s not a specific goal. Instead, set a target for your sales figures within a certain timeframe, and keep it realistic by using your current numbers as a baseline.
To do this, project your revenue, profit and expenses if business were to stay the same. Then consider what a realistic target might be and include that. This number may be lower than you'd expect, but it’s more important that it’s actually achievable.
2. Refine customer profiles
Detailed customer and audience profiles help your business effectively target its marketing efforts. Your business might already have customer profiles — updating your business plan is a perfect time to update these profiles, as well. And if you don’t have profiles yet, there’s no time like the present.
You can start refining your customer profiles by examining your current customer base. Look at their demographics and habits. Then use a similar strategy to create profiles of your ideal customers.
3. Identify key growth opportunities
Next, identify your key growth opportunities. These could be new products or services, an expansion into a new market, or even a complete rebuild of your current offerings.
Whatever these opportunities are, include them in your business development plan. Articulate how and why these opportunities will help grow the business.
4. List funding sources
Your plan should include not just the amount of funding you’ll need, but how you plan to get it — loans , equity investors or crowdfunding , for example. Now is the time to come up with an in-depth funding strategy. Doing this legwork on the front end, while developing your plan, makes it easier to focus on execution when stress inevitably creeps in.
This part of your plan should include the sources you’ve secured, as well as those you’d like to seek funds from. It should also include how much you’ll seek from each source, what form those funds will take, and any obstacles you might encounter.
5. Determine operational needs
You’ve laid out your goals, growth opportunities and potential funding sources. Now, look over these items and determine how to make all this happen.
Be aware that as your operational needs expand, your business expenses will also increase. For example, you may require additional equipment, a new warehouse to enable expanded logistics, or more employees to help serve customers. Whatever it is, build it into your business development plan.
6. Develop a sales and marketing strategy
Your business development plan is the perfect place to include sales and marketing strategies. Ultimately, these will be some of the key drivers for leveraging your growth opportunities and hitting your financial goals.
As you draft these ideas, run them through this simple test: Will they still hold up if you reach your growth targets, or will you need to rework them? Ideally, you want sales and marketing strategies that can grow along with your business.
7. Create your elevator pitch
Your elevator pitch is the short-and-sweet version of your company’s mission. The premise is simple: If you were to meet someone on an elevator and only had that brief ride to pitch your company, what would you say?
Some people adopt arbitrary rules on their elevator pitch, such as limiting it to a Twitter-length 280 characters. While this limitation isn’t necessary, it should give you a good idea of the brevity of an elevator pitch and the impact you’ll need to make.
8. Identify your resource needs
You’ve identified your broad operational needs — equipment, facilities and employees. You’ll also want to identify your resource needs. These include how you might manage your technology and team members in a more specific way.
For example, if your marketing plan involves creating video content, you’ll need the proper equipment and software to create it. Your sales strategy might involve retooling your CRM or migrating to a new system. Or, your growth targets might mean that you need to move to a new accounting platform .
9. Determine how you'll measure success
Last, but certainly not least, you’ll need to decide how you’ll measure progress towards your goals. How will you know when you’ve hit that ambitious sales target or grown your business in that new market?
You need to be able to measure your business performance and progress. Setting targets and KPIs for your employees may be good ways to keep things on track.
Business Development Plan Template
If you need a business development plan example, we’ve put together this template . It’ll help you shape your own business plan and outline the key sections.
Stay productive and profitable with MYOB
A strong business development plan is a powerful asset for driving growth. It helps you outline your plans and stay on course, even when you’re overwhelmed with day-to-day tasks.
Achieving your business goals is much easier when you have help — and that doesn’t mean you need to hire more people. MYOB accounting software automates business operations like invoicing, payroll, and tax reporting, so you can spend more time focusing on strategic growth.
Related Guides
How to get a business loan arrow right, how to find investors: a guide for startups arrow right.
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
Developing a Business Plan

An important task in starting a new venture is to develop a business plan. As the phrase suggests, a business plan is a "road map" to guide the future of the business or venture. The elements of the business plan will impact the daily decisions of the business and provide direction for expansion, diversification, and future evaluation of the business.
This publication will assist in drafting your own business plan. It includes a discussion of the makeup of the plan and the information needed to develop a business plan. Business plans are traditionally developed and written by the owner with input from family members and the members of the business team. Business plans are "living" documents that should be reviewed and updated every year or if an opportunity for change presents itself. Reviews reinforce the thoughts and plans of the owner and the business and are a key item in the evaluation process. For an established venture, evaluation determines if the business is in need of change or if it is meeting the expectations of the owners.
Using the Proper Format
The format and appearance of the plan should be as professional as possible to portray your business in a positive manner. When dealing with a lender or possible investor, the plan will be reviewed for accuracy and suggestions for changes to the plan may be offered. The decision to recommend a loan for approval will be largely based on your business plan. Often loan officers will not know a great deal about the proposed venture, but they will know the correct structure of a business plan.
Investors will make their decision based on the plan and the integrity of the owner. For this reason, it is necessary to use a professional format. After loan officers complete their evaluations, the loan committee will further review the business plan and make a decision. The committee members often spend limited time reviewing the document, focusing on the message of the executive summary and financial statements to make their determination. They will refer to other sections of the plan for details and clarification. Because of this, these portions need to be the strongest parts of the plan and based on sound in-depth research and analysis.
Sections of the Business Plan
A business plan should be structured like a book with the title or cover page, followed by a table of contents. Following these two pages, the body of the plan normally appears in this order: executive summary, business mission statement, goals and objectives, background information, organizational matters, marketing plan, and financial plan.
Executive Summary
The executive summary is placed at the front of the business plan, but it should be the last part written. The summary should identify the type of business and describe the proposed business, or changes to the existing business. Research findings and recommendations should be summarized concisely to provide the reader with the information required to make any decisions. The summary outlines the direction and future plans or goals of the business, as well as the methods that will be used to achieve these goals. The summary should include adequate background information to support these recommendations.
The final financial analysis and the assumptions used are also a part of the executive summary. The analysis should show how proposed changes will ensure the sustainability of the current or proposed business. All challenges facing the existing business or proposed venture should be discussed in this section. Identifying such challenges shows the reader that all possibilities have been explored and taken into account during the research process.
Overview, Mission, and Goals and Objectives
This section has three separate portions. It begins with a brief overview that includes a general description of the existing or planned business. The overview is followed by the mission statement of the business. You should try to limit the mission statement to three sentences if possible and include only the key ideas about why the business exists. An example of a mission statement for a produce farm might be: The mission of XYZ Produce is to provide fresh, healthy produce to our customers, and to provide a safe, friendly working environment for our employees. If you have more than three sentences, you should be as concise as possible.
The final portion sets the business's goals and objectives. There are at least two schools of thought about goals and objectives. Goals and objectives should show the reader what the business wishes to accomplish, and the steps needed to obtain the desired results. Conducting a SWOT analysis will assist your team when developing goals and objectives. SWOT in an acronym for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats and is covered more in-depth later in the publication. You may want to include marketing topics in the SWOT or conduct two SWOT analyses, one for the entire business and one for the marketing plan.
Goals should follow the acronym DRIVE, which stands for D irectional, R easonable, I nspiring, V isible, and E ventual. The definitions of DRIVE are:
- Directional: It should guide you to follow your vision.
- Reasonable: You should be able to reach the goal, and it should be related to your business.
- Inspiring: Make sure the goal is positive but should challenge the business to grow into the goal.
- Visible: You and your employees should be able to easily recognize the goal. Goals should be posted where everyone sees them every day.
- Eventual: The goals should focus on the future and be structured to provide motivation to all to strive towards the goals.
Objectives should follow the acronym SMART, which stands for S pecific, M easurable, A ttainable, R ewarding, and T imed. Objectives are the building blocks to achieve the goals and stand for:
- Specific: Each objective should focus on one building block to reach the goal.
- Measurable: You should be able to determine if your progress is going in the right direction.
- Attainable: You should be able to complete the objective with an appropriate amount of work.
- Rewarding: Reaching the objective should be something to celebrate and provide positive reinforcement to the business.
- Timed: You must have a deadline for the objective to be achieved. You do not want to have the objectives linger for too long. Not reaching the objectives delays reaching the goals. Not achieving goals is detrimental to the morale of the business.
Goals and objectives should follow these formats to allow for evaluation of the entire process and provide valuable feedback along the way. The business owner should continually evaluate the outcomes of decisions and practices to determine if the goals or objectives are being met and make modifications when needed.
Background Information
Background information should come from the research conducted during the writing process. This portion should include information regarding the history of the industry, the current state of the industry, and information from reputable sources concerning the future of the industry.
This portion of the business plan requires the most investment of time by the writer, with information gathered from multiple sources to prevent bias or undue optimism. The writer should take all aspects of the industry (past, present, and future) and business into account. If there are concerns or questions about the viability of the industry or business, these must be addressed. In writing this portion of the plan, information may be obtained from your local public library, periodicals, industry personnel, trusted sources on the Internet, and publications such as the Penn State Extension Agricultural Alternatives series . Industry periodicals are another excellent source of up-to-date information. The more varied the sources, the better the evaluation of the industry and the business, and the greater the opportunity to have a viable plan.
The business owner must first choose an appropriate legal structure for the business. The business structure will have an impact on the future, including potential expansion and exit from the business. If the proper legal structure is not chosen, the business may be negatively impacted down the road. Only after the decision is made about the type of business can the detailed planning begin.
Organizational Matters
This section of the plan describes the current or planned business structure, the management team, and risk-management strategies. There are several forms of business structure to choose from, including sole proprietorship, partnership, corporations (subchapter S or subchapter C), cooperative, and limited liability corporation or partnership (LLC or LLP). These business structures are discussed in Agricultural Alternatives: Starting or Diversifying an Agricultural Business .
The type of business structure is an important decision and often requires the advice of an attorney (and an accountant). The business structure should fit the management skills and style(s) of the owner(s) and take into account the risk management needs (both liability and financial) of the business. For example, if there is more than one owner (or multiple investors), a sole proprietorship is not an option because more than one person has invested time and/or money into the business. In this case a partnership, cooperative, corporation, LLC, or LLP would be the proper choice.
Another consideration for the type of business structure is the transfer of the business to the next generation or the dissolution of the business. There are benefits and drawbacks for each type of structure covering the transition of ownership. If the business has a high exposure to risk or liability, then an LLC might be preferred over a partnership or sole proprietorship.
If the business is not a sole proprietorship, the management team should be described in the business plan. The management team should consist of all parties involved in the decisions and activities of the business. The strengths and backgrounds of the management team members should be discussed to highlight the positive aspects of the team. Even if the business is a sole proprietorship, usually more than one person (often a spouse, child, relative, or other trusted person) will have input into the decisions, and so should be included as team members.
Regardless of the business structure, all businesses should also have an external management support team. This external management support team should consist of the business's lawyer, accountant, insurance agent or broker, and possibly a mentor. These external members are an integral part of the management team. Many large businesses have these experts on staff or on retainer. For small businesses, the external management team replaces full-time experts; the business owner(s) should consult with this external team on a regular basis (at least once a year) to determine if the business is complying with all rules and regulations. Listing the management team in the business plan allows the reader to know that the business owner has developed a network of experts to provide advice.
The risk-management portion of the business plan provides a description of how the business will handle unexpected or unusual events. For example, if the business engages in agricultural production, will the business purchase crop insurance? Does the business have adequate liability insurance? Is the business diversified to protect against the unexpected, rather than "putting all its eggs in one basket"? If the business has employees, does the business carry adequate workers' compensation insurance? All of these questions should be answered in the risk-management portion of the business plan. More information on how liability can affect your business and on the use of insurance as a risk-management tool can be found in Agricultural Alternatives: Agricultural Business Insurance and Agricultural Alternatives: Understanding Agricultural Liability . The business structure will also determine a portion of the risk-management strategy because the way that a business is structured carries varying levels of risk to the owner and/or owners. All opportunities carry a degree of risk that must be evaluated, and mitigation strategies should be included in this portion of the plan.
Marketing Plan
Every purchase decision that a consumer makes is influenced by the marketing strategy or plan of the company selling the product or service. Products are usually purchased based on consumer preferences, including brand name, price, and perceived quality attributes. Consumer preferences develop (and change) over time and an effective marketing plan takes these preferences into account. This makes the marketing plan an important part of the overall business plan.
In order to be viable, the marketing plan must coincide with the production activities. The marketing plan must address consumer desires and needs. For example, if a perishable or seasonal crop (such as strawberries) will be produced, the marketing plan should not include sales of locally grown berries in January if the business is in northeastern United States. If the business plans to purchase berries in the off-season from other sources to market, this information needs to be included. In this way, the marketing plan must fit the production capabilities (or the capability to obtain products from other sources).
A complete marketing plan should identify target customers, including where they live, work, and purchase the product or service you are providing. This portion of the plan contains a description of the characteristics and advantages of your product or service. Identifying a "niche" market will be of great value to your business.
Products may be sold directly to the consumer (retail) or through another business (wholesale) or a combination of both. Whichever marketing avenue you choose, if you are starting a new enterprise or expanding an existing one, you will need to decide if the market can bear more of what you plan to produce. Your industry research will assist in this determination. The plan must also address the challenges of the proposed marketing strategy.
Other variables to consider are sales location, market location, promotion, advertising, pricing, staffing, and the costs associated with all of these. All of these aspects of the marketing plan will take time to develop and should not be taken lightly. Further discussion on marketing fruits and vegetables can be found in Agricultural Alternatives: Fruit and Vegetable Marketing for Small-Scale and Part-Time Growers .
SWOT Analysis
An adequate way of determining the answers to business and marketing issues is to conduct a SWOT analysis. The acronym SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. Strengths represent internal attributes and may include aspects like previous experience in the business. Experience in sales or marketing would be an area of strength for a retail farm market. Weaknesses are also internal and may include aspects such as the time, cost, and effort needed to introduce a new product or service to the marketplace.
Opportunities are external aspects that will help your business to take off and be sustained. If no one is offering identical products or services in your immediate area, you may have the opportunity to capture the market. Threats are external and may include aspects like other businesses offering the same product in close proximity to your business or government regulations impacting business practices and cost.
Financial Plan
The financial plan and assumptions are crucial to the success of the business and should be included in the business plan. One of the foremost reasons new businesses fail is because they do not have enough start-up capital to cover all expenses to make a profit. The scope of your business will be determined by the financial resources you can acquire. Because of this, you will need to develop a financial plan and create the supporting documents to substantiate it.
The financial plan has its basis in historical data (if you are an existing business) or from projections (for a proposed business). The first issue to address is recordkeeping. You should indicate who will keep the necessary records and how these records will be used. Internal controls, such as who will sign checks and handle any funds, should also be addressed. A good rule to follow for businesses that are not sole proprietorships is having at least two people sign all checks.
The next portion of the financial plan should detail where funding will come from. This includes if (and when) the business will need additional capital, how much capital will be needed, and how these funds will be obtained. If start-up capital is needed, this information should be included in this portion. Personal contributions should be included, along with other funding sources. The amount of money and repayment terms should be listed. One common mistake affecting many new businesses is under-funding at start-up. Many start-up businesses do not evaluate all areas of expense and underestimate the amount of capital needed to see a new business through the development stages (including personal living expenses, if off-farm income is not available).
Typically, a balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement, and partial budget or enterprise budgets are included in a business plan. More information on agricultural budgets can be found in Agricultural Alternatives: Budgeting for Agricultural Decision Making . These documents will display the financial information in a form that lending institutions are used to seeing. If these are not prepared by an accountant, having one review them will ensure that the proper format has been used.
Financial projections should be completed for at least two years and, ideally, for five years. In agricultural businesses, five-year projections are sometimes difficult to make because of variability in prices, weather, and other aspects affecting production. One way to illustrate these risks is to develop several projection scenarios covering a range of production assumptions. This attention to detail will often result in a positive experience with lenders because they realize that the plan covers several possible circumstances and provides insight into how the business plans to manage risk. More information on financing agricultural businesses can be found in the publication Agricultural Alternatives: Financing Small-Scale and Part-Time Farms .
Financial Statements
To keep personal assets and liabilities separate from business assets and liabilities, it is beneficial to create both business and personal financial statements. A lender will need to see both, but the separation will show how the business will support the family or how the off-farm income will support the business.
Cash Flow Statement
A cash flow statement is the predicted flow of cash into and out of a business over a year. Cash flow statements are prepared by showing the total amounts predicted for each item of income or expense. This total is then broken down by month to show when surpluses and shortfalls in cash will occur. In this way, the cash flow statement can be used to predict when additional cash is needed and when the business will have a surplus to pay back any debt. This monthly prediction allows the owner(s) to better evaluate the cash needs of the business, taking out applicable loans and repaying outstanding debts. The cash flow statement often uses the same categories as the income statement plus additional categories to cover debt payments and borrowing.
After these financial statements are completed, the business plan writer will have an accurate picture of how the business has performed and can project how the business will perform in the coming year(s). With such information, the owner—and any readers of the business plan—will be able to evaluate the viability of the business and will have an accurate understanding of actions and activities that will contribute to its sustainability. This understanding will enable them to make better informed decisions regarding loans or investments in the business.
Income Statement
The income statement is a summary of the income (revenue) and expenses for a given accounting cycle. If the balance sheet is a "snapshot" of the financial health of the business, the income statement is a "motion picture" of the financial health of the business over a specific time period. An income statement is constructed by listing the income (or revenue) at the top of the page and the expenses (and the resulting profit or loss) at the bottom of the page.
Revenue is any income realized by the sale of crops or livestock, government payments, and any other income the business may have (including such items as fuel tax refunds, patronage dividends, and custom work). Other items impacting revenues are changes in inventory and accounts receivable between the start of the time period and the end—even if these changes are negative.
Expenses include any expense the business has incurred from the production of the products sold. Examples of expenses include feed, fertilizer, pesticides, fuel, labor, maintenance, repairs, insurance, taxes, utilities, and any changes in accounts payable. Depreciation, which is the calculated wear and tear on assets (excluding land), is included as an expense for accounting purposes. Interest is considered an expense, but any principal payments related to loans are not an expense. Repayment of principal is recorded on the balance sheet under "Loans Payable."
As the income statement is created, the desired outcome is to have more income than expenses, so the income statement shows a profit. If not, the final number is shown in parentheses (signifying a negative number). Another name for this financial record is a Profit and Loss Statement. Income statements are one way to clearly show how the farm is making progress from one year to the next and may show a much more optimistic view of sustainability than can be seen by looking at a single year's balance sheet.
Balance Sheet
A balance sheet is a snapshot of a business’s assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity at a specific point in time. A balance sheet can be prepared at any time, but is usually done at the end of the fiscal year (for many businesses, this is the end of the calendar year). Evaluating the business by using the balance sheet requires several years of balance sheets to tell the true story of the business’s progress over time. A balance sheet is typically constructed by listing assets on the left and liabilities and owner’s equity on the right. The difference between the assets and liabilities of the business is called the "owner's equity" and provides an estimate of how much of the business is owned outright.
Assets are anything owned by, or owed to, the business. These include cash (and checking account balances), accounts receivable (money owed to the business), inventory (any crops or supplies that the business has stored on farm), land, equipment, and buildings. This may also include machinery, breeding stock, small-fruit bushes or canes, and fruit trees. Sometimes assets are listed as current (those easily converted to cash) and fixed (those that are required for the business to continue). Assets are basically anything of value to the business. Some valuations of assets are not easily determined for items such as breeding stock, small-fruit bushes or canes, and fruit trees and may require the use of a certified appraiser familiar with the items.
Balance sheets may use a market-basis or a cost-basis to calculate the value of assets. A market-basis balance sheet better reflects the current economic conditions because it relies on current or market value for the assets, rather than what those assets originally cost. Market values are more difficult to obtain because of the difficulty in finding accurate current prices of assets and often results in the inflation of the value of assets. Cost-basis balance sheets are more conservative because the values are often from prior years. For example, a cost-basis balance sheet would use the original purchase price of land, rather than what selling that land would bring today. Because purchase records are easily obtained, constructing a cost-basis balance sheet is easier. Depreciable assets such as buildings, tractors, and equipment are listed on the cost-basis balance sheet at purchase price less accumulated depreciation. Most accountants use the cost-basis balance sheet method. Whether you choose to use market-basis or cost-basis, it is critical that you remain consistent over the years to allow for accurate comparison.
Liabilities are what the business owes on the date the balance sheet is prepared. Liabilities include both current liabilities (accounts payable, any account the business has with a supplier, short-term notes, operating loans, and the current portion of long-term debt), which are payable within the current year, and noncurrent liabilities (mortgages and loans with a term that extends over one year).
Owner's equity is what remains after all liabilities have been subtracted from all assets. It represents money that the owner(s) have invested in the business, profits that are retained in the business, and changes caused by fluctuating market values (on a market-basis balance sheet). Owner’s equity will be affected whenever there are changes in capital contributed to the business or retained earnings, so if your practice is to use all earnings as your "paycheck," rather than reinvesting them in the business, your owner's equity will be impacted. On the balance sheet, owner’s equity plus liabilities equals assets. Or stated another way, all of the assets less the amount owed (liabilities) equals the owner’s equity (sometimes referred to as "net worth"). Owner's equity provides the "balance" in a balance sheet.
Putting It All Together
After the mission, background information, organization, and marketing and financial plans are complete, an executive summary can then be prepared. Armed with the research results and information in the other sections, the business will come alive through this section. Research results can be included in an appendix if desired. The next step is to share this plan with others whose opinions you respect. Have them ask you the hard questions—make you defend an opinion you have expressed or challenge you to describe what you plan to do in more detail. Often, people are hesitant to share what they have written with their families or friends because they fear the plan will not be taken seriously. However, it is much better to receive constructive criticism from family and friends (and gain the opportunity to strengthen your plan) than it is to take it immediately to the lender, only to have any problems pointed out and receive a rejection.
Once all parts of the business plan have been written, you will have a document that will enable you to analyze your business and determine which, if any, changes need to be made. Changes on paper take time and effort but are not as expensive as changing a business practice only to find that the chosen method is not viable. For a proposed venture, if the written plan points to the business not being viable, large sums of money have not been invested and possibly lost. In short, challenges are better faced on paper than with investment capital.
Remember, a business plan is a "road map" that will guide the future of the business. The best business plan is a document in continual change, reacting to the influence of the outside world on the business. Having the basis of a written plan will give you the confidence to consider changes in the business to remain competitive. Once the plan is in place, the business will have a better chance of future success.
For More Information
Publications.
Abrams, R. The Successful Business Plan: Secrets and Strategies (Successful Business Plan Secrets and Strategies) . Palo Alto, Calif.: Planning Shop, 2014.
Becker, J. C., L. F. Kime, J. K. Harper, and R. Pifer. Agricultural Alternatives: Understanding Agricultural Liability . University Park: Penn State Extension, 2011.
Dethomas, A., and L. and S. Derammelaere. Writing a Convincing Business Plan (Barron's Business Library) . Hauppauge, N.Y.: Barron's Educational Series. 2015.
Dunn, J., J. K. Harper, and L. F. Kime. Agricultural Alternatives: Fruit and Vegetable Marketing for Small-scale and Part-time Growers . University Park: Penn State Extension, 2009.
Grant, W. How to Write a Winning Business Plan: A Step-by-Step Guide for Startup Entrepreneurs to Build a Solid Foundation, Attract Investors and Achieve Success with a Bulletproof Business Plan (Business 101). Independently published. 2020.
Harper, J. K., S. Cornelisse, L. F. Kime, and J. Hyde. Agricultural Alternatives: Budgeting for Agricultural Decision Making . University Park: Penn State Extension, 2019.
Kime, L. F., J. A. Adamik, E. E. Gantz, and J. K. Harper. Agricultural Alternatives: Agricultural Business Insurance . University Park: Penn State Extension, 2019.
Kime, L. F., S. Cornelisse, and J. K. Harper. Agricultural Alternatives: Starting or Diversifying an Agricultural Business . University Park: Penn State Extension, 2018.
Lesonsky, R. Start Your Own Business Fifth Edition: The Only Start-Up Book You'll Ever Need. Irvine, Calif.: Entrepreneur Media Inc., 2010.
Shelton, H. The Secrets to Writing a Successful Business Plan: A Pro Shares a Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Plan That Gets Results. Rockville, Md.: Summit Valley Press, 2017.
Stokes, J. S., G. D. Hanson, J. K. Harper, and L. F. Kime. Agricultural Alternatives: Financing Small-scale and Part-time Farms . University Park: Penn State Extension, 2005.
Online Course
Starting a Farm: Business Planning
Periodicals
- American Agriculturist Magazine Farm Progress Companies Inc. 5482 Wilshire Blvd, Suite 260 Los Angeles, CA 90036
- Businessweek Magazine
- Fortune Magazine
- Kiplinger's Personal Finance
- Money Magazine
- BizPlanit - Virtual Business Plan
- PA Business One-Stop Shop
- Small Business Administration
- SCORE—volunteer business assistance
- The Pennsylvania Department of Revenue Starting a Business in Pennsylvania—A Guide to Pennsylvania Taxes
- The Pennsylvania State University Agricultural Alternative Tools
- The Pennsylvania State University Conducting a SWOT Analysis
- The Pennsylvania State University Happy Valley Launch Box
Prepared by Lynn F. Kime, senior extension associate; Linda Falcone, extension educator in Wyoming County, Jayson K. Harper, professor of agricultural economics; and Winifred W. McGee, retired extension educator in Dauphin County
Additional financial support for this publication was provided by the Risk Management Agency of the United States Department of Agriculture and the Pennsylvania Department of Agriculture.
This publication was developed by the Small-scale and Part-time Farming Project at Penn State with support from the U.S. Department of Agriculture-Extension Service.
You may also be interested in ...

A Guide to Farming in Pennsylvania: Planning

Starting a New Agricultural Business

Starting or Diversifying an Agricultural Business

Conducting a SWOT Analysis

Choosing a Legal Structure for Your Agriculture Business

Cooperatives

Example Business Plan

Obtaining a Loan - The C's of Credit

Opportunities for Veterans in Pennsylvania Agriculture

Milk Production Records for Management Control
Personalize your experience with penn state extension and stay informed of the latest in agriculture..
- Credit Cards
- Making & Saving
Join Our Newsletter!
Daily inspiration, tips, and coaching to reach your financial goals
How to Create the Right Business Development Plan

Key Highlights
- A business development plan is a strategic roadmap that outlines the steps and strategies needed to achieve specific business goals, such as identifying new opportunities, expanding into new markets, forging partnerships, and improving overall performance.
- A well-crafted business development plan provides clear direction, allocates resources efficiently, aligns teams, and allows for tracking progress and measuring success.
- Key components of a business development plan include setting goals, understanding target audiences, analyzing the competition, creating marketing and sales strategies, and implementing action plans.
- Startups should focus on high-impact growth opportunities, maximize their marketing budget, build strategic partnerships, and prioritize teamwork. Large organizations should invest in long-term strategic initiatives, diversify their business development efforts, leverage their resources and expertise, and establish talent development programs.
Whether steering a fresh-faced startup or commanding a massive corporate ship, mastering the art of crafting a robust business development plan is your secret weapon for success.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll take you through the process and strategies of creating a robust business development plan. Whether it’s leveraging market research to identify new opportunities or utilizing the power of partnerships to accelerate growth, these strategies will equip you with the tools to navigate the dynamic business landscape confidently.
- What is a Business Development Plan?
A business development plan is a strategic roadmap that helps a company grow and succeed. It outlines the steps and strategies needed to achieve specific business goals. These goals may include identifying new opportunities, expanding into new markets, forging partnerships, and improving overall performance.
Now, you might be wondering why you need a business development plan. First, it provides a clear direction for your company’s growth, ensuring your efforts are focused and targeted. For example, if your goal is to enter a new market, the plan will outline the necessary research , partnerships, and marketing efforts required to achieve that goal.
But that’s not all. A well-crafted business development plan also helps you allocate resources more efficiently , preventing wasted time and money. By outlining priorities and setting realistic timelines, you can ensure that every aspect of your business gets the attention it deserves.
Moreover, a business development plan can be one of the most powerful tools for team alignment . When everyone on your team understands the company’s objectives and strategies, they are more likely to work together seamlessly, improving overall productivity and efficiency.
A solid plan also allows you to track progress and measure success. By setting specific targets and monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs), you can quickly identify areas that need improvement and adjust your strategies accordingly.
In short, a business development plan is your company’s GPS, guiding you toward growth and success. By creating a comprehensive and actionable plan, you can ensure that your business is always moving forward, ready to seize new opportunities and overcome challenges along the way.
- Key Components of a Business Development Plan
A comprehensive business development plan should include several key components to guide your organization’s growth efforts. These components provide a structured framework for identifying, evaluating, and pursuing growth opportunities.

Here’s a detailed look at each element:
- Goals : Clearly defined objectives and measurable targets guide your business development efforts. These goals should align with your overall business objectives and include short-term and long-term targets. When setting goals, consider using the SMART criteria (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) to ensure they are clear and actionable.
- Target audience : A thorough understanding of your ideal customers contributes to crafting a more effective business development plan. This includes identifying their needs, preferences, and behaviors. In addition, understanding your target audience can tailor your marketing and sales strategies to reach and engage them more effectively. To identify your target audience, consider conducting market research through surveys, interviews, and focus groups, analyzing demographic data, and studying your competitors’ customer base.
- Competition analysis : A detailed examination of your competitors is necessary to identify their strengths and weaknesses and potential opportunities for differentiation. This analysis should include data on market share, product offerings, pricing strategies, marketing tactics, and customer experience. By understanding your competition, you can develop a unique value proposition that sets your organization apart and attracts your target audience.
- Marketing and sales strategies : A well-integrated strategy to engage your target audience, advertise your products or services, and produce leads significantly contributes to effective business development. Your marketing and sales strategies should be tailored to your target audience’s preferences and behaviors, using the most effective channels and tactics for reaching them. This may include content marketing, social media advertising, email campaigns, events, and other promotional activities.
- Action plans : A clear, step-by-step guide that lists the tasks, duties, and deadlines needed to reach your business development objectives is valuable for maintaining focus on your progress. This action plan should include short-term tasks, such as launching marketing campaigns or attending networking events, and long-term initiatives, like developing new products or entering new markets. Regularly reviewing and updating your action plan will ensure that your business development efforts remain focused and aligned with your objectives.
- Business Development Process
The business development process is a series of steps to identify, evaluate, and pursue growth opportunities. While the exact process may vary between organizations, it typically includes the following stages:
- Market research and analysis: In this stage, you’ll gather information about your target market, including customer demographics, preferences, and pain points. This research will help you identify potential opportunities and understand the competitive landscape better. Techniques for market research include surveys, interviews, focus groups, and analysis of existing data sources. For example, a software company looking to expand its product offerings might conduct surveys to determine which features are most desired by potential customers, helping them tailor their new product to meet market gaps.
- Identifying potential opportunities: Based on your market research, you’ll identify growth opportunities that align with your organization’s strengths and capabilities. This may include entering new markets, developing new products or services, targeting new customer segments, or forging strategic partnerships. For instance, a small e-commerce business might realize that its products appeal to a specific age group and decide to target this demographic more aggressively with marketing campaigns.
- Evaluating the feasibility of each opportunity : Once you’ve identified potential growth opportunities, assess their practicality. This involves analyzing the potential benefits, risks, and resources required for each option. You’ll want to consider factors such as market size, competition, barriers to entry, and the potential return on investment (ROI) . For example, a manufacturing company considering expanding its production capacity might delve into specifics such as the costs of acquiring new machinery, hiring and training additional staff, potential supply chain complexities, and the projected increase in revenue from enhanced production capacity.
- Developing a business development strategy : After evaluating the feasibility of each opportunity, you’ll create a strategic plan to pursue the most promising ones. This plan should outline your objectives, target markets, value proposition, and the specific tactics you’ll use to reach your goals. Your strategy may also include a timeline for implementation and key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure progress. For example, a health and wellness company might enter a new market by launching a line of supplements. Its strategy could involve targeted marketing campaigns, influencer partnerships, and social media marketing.
- Implementing the strategy and measuring results: In this final stage, you’ll implement your business development plan. This involves executing the tactics outlined in your strategy, such as launching marketing campaigns, developing new products, or establishing partnerships. Throughout the implementation process, ensure you monitor your results using the KPIs established earlier. Regularly measuring your progress will help you identify areas for improvement and make any necessary adjustments to your strategy. For instance, a B2B service provider might track the number of new clients acquired, revenue growth, and customer satisfaction scores to gauge the effectiveness of their business development efforts and make data-driven decisions to optimize their approach.
- Creating a Business Development Plan
Let’s consider a hypothetical example of a software company aiming to expand into the healthcare industry to demonstrate how a business development plan can be created.

- Step 1: Set Clear Goals and Objectives
The company sets a specific goal: “Increase our market share in the healthcare industry by 15% within the next two years.” This goal is SMART, as it is specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
- Step 2: Conduct Market Research and Identify Your Target Audience
The company conducts market research to understand the healthcare industry’s needs, preferences, and pain points. They gather information through surveys, interviews, and focus groups with healthcare professionals and analyze existing data sources such as industry reports, whitepapers, and case studies.
- Step 3: Analyze Your Competition
The software company identifies its key competitors in the healthcare market, analyzing its product offerings, market share, pricing strategies, marketing tactics, and customer experience to understand its strengths and weaknesses and find potential areas for differentiation.
Step 4: Develop Marketing and Sales Strategies Based on market research and competitor analysis insights, the company tailors its marketing and sales strategies to the healthcare industry. They develop targeted content marketing campaigns, engage healthcare influencers, attend industry events, and create healthcare-specific case studies to showcase their software solutions’ value.
- Step 5: Create an Action Plan
The company outlines specific steps, responsibilities, and deadlines to expand into the healthcare market. They assign tasks to team members, establish clear communication channels for progress tracking, and ensure everyone is working towards the same objective.
- Step 6: Monitor and Measure Results
The company tracks the performance of its business development activities using key performance indicators (KPIs), such as the number of healthcare leads generated, conversion rates, and revenue growth in the healthcare sector. They regularly review these results to make informed decisions about adjusting strategies and allocating resources more effectively.
- How to Customize a Plan for Startups vs. Large Organizations
The development of a business, whether a startup or a large organization, requires a thorough understanding of its unique needs and opportunities. Nonetheless, creating a business development plan might vary between startups and large organizations. Startups often have limited resources and focus on immediate growth opportunities.
In contrast, large organizations may allocate more resources to long-term strategic initiatives. Regardless of your organization’s size, tailoring your business development plan to meet your unique needs and goals is valuable.
- For Startups
- Identify high-impact growth opportunities : When creating an action plan for business development, startups might consider focusing on options that offer quick wins. For example, a startup could target a niche market segment with unmet needs or provide a unique solution to an existing problem. Airbnb, a startup in its early days, tapped into the unmet demand for affordable accommodations by allowing homeowners to rent out their spaces to travelers.
- Maximize your startup marketing budget : Startups frequently work with restricted budgets, making it necessary to utilize economical business development and marketing channels that deliver the most significant ROI. For instance, content marketing, social media, and email marketing can be powerful tools for startups to build brand awareness and engage with their target audience without breaking the bank. In addition, consider prioritizing essential expenses, seeking strategic partnerships, and exploring innovative ways to reduce costs and increase efficiency throughout your business operations.
- Build a strong network of strategic partners : Partnerships can help startups access new customers, resources, and expertise. For example, a startup could partner with complementary businesses to offer bundled services, co-host events, or cross-promote products. Dropbox, for instance, partnered with Samsung to provide pre-installed Dropbox storage on Samsung devices , significantly increasing their user base. To connect with larger companies for potential partnerships, attend industry events, conferences, and trade shows, and leverage social media platforms like LinkedIn to identify and engage with key decision-makers. Establishing relationships with industry leaders can open doors for collaboration.
- Prioritize teamwork and collaboration : Startups often feature smaller teams, so establishing a teamwork-driven atmosphere that bolsters productivity and capitalizes on resource allocation proves beneficial. Encourage open communication, delegate responsibilities, and set clear expectations to ensure your team works efficiently and effectively towards your business development goals.
- For Large Organizations
- Invest in long-term strategic initiatives : Large organizations can benefit from focusing on strategic business development initiatives that capitalize on their established market presence and resources. For example, large businesses can diversify their business development activities to mitigate risks and capitalize on growth opportunities. This may involve exploring new customer segments, entering different industries, or adopting new technologies. Google’s diversified portfolio, including investments in artificial intelligence, self-driving cars, and renewable energy, demonstrates this approach.
- Diversify your business development efforts : Large organizations can explore opportunities in new markets and industries to drive innovation and growth beyond their core business. This can include investing in research and development (R&D) to create innovative products or forming strategic partnerships with companies from other sectors. Amazon’s continuous expansion into new industries, such as healthcare and grocery, exemplifies this approach. By broadening their scope, large organizations can capitalize on emerging trends and stay ahead of the competition.
- Leverage your organization’s resources and expertise : Large organizations have a wealth of resources and expertise at their disposal. They can develop innovative solutions and strategies to drive business growth by tapping into this knowledge. Take IBM, for example. This tech giant leverages its profound technological know-how and data analysis expertise to develop ground-breaking solutions, like their AI platform, Watson. Watson has revolutionized industries ranging from healthcare, where it aids in diagnosing diseases and suggesting treatments, to finance, where it helps banks in risk assessment and fraud detection. The key here is leveraging what you have to create solutions that drive growth and add value for your clients’ businesses.
- Establish robust talent development programs : One unique strength of large organizations is their capacity to develop and nurture talent within their ranks. These businesses can continuously enhance their workforce skills by investing in comprehensive training and development programs, fueling innovation and growth. This approach also helps to retain top performers, reducing turnover and promoting a high-performance culture. For instance, consider the case of General Electric. GE’s renowned leadership development programs have been instrumental in grooming a cadre of leaders who have gone on to hold top positions within GE and other major corporations. Large organizations can foster a culture of excellence, innovation, and continuous improvement by focusing on talent development.
- Strategies for Generating Creative Business Development Ideas
Don’t be afraid to challenge conventional wisdom and explore alternative business development models that deliver value to your customers. Innovation contributes to business growth and helps maintain a competitive edge.

Here are some tips and examples to help you develop innovative business development ideas:
- Encourage a culture of innovation : Foster an environment where employees feel empowered to share their ideas, experiment, and take risks. Promote open communication and collaboration and recognize and reward innovative thinking. Google’s “20% time” policy, which allows employees to dedicate 20% of their working hours to passion projects, has resulted in successful products like Gmail and Google Maps.
- Monitor industry trends and technological advancements : Stay informed about the latest developments in your industry and related technology sectors. This can help you identify new opportunities for growth and stay ahead of the competition. For instance, consider the rapidly advancing field of AI in healthcare. Companies like Zebra Medical Vision leverage AI for early disease detection , using sophisticated algorithms to analyze medical imaging data and detect anomalies that could indicate conditions like cancer, liver disease, or cardiovascular issues. This use of AI improves diagnostic accuracy and significantly accelerates the process, potentially saving lives by enabling earlier intervention.
- Leverage internal expertise and resources : Tap into your organization’s wealth of knowledge and resources to identify innovative solutions to business challenges. For example, Google’s Project Aristotle analyzed data from hundreds of teams within the company to identify the key factors that made teams effective. By leveraging its internal expertise in data analysis and organizational behavior, Google was able to implement new strategies and foster a more collaborative work environment, ultimately driving innovation and growth.
- Explore strategic partnerships and collaborations : Collaborate with external partners, such as complementary businesses, suppliers, or research institutions, to access new ideas, resources, and expertise. Take the case of the collaboration between Starbucks and Spotify, for instance. This innovative alliance allowed Starbucks employees to influence the music played in stores via Spotify playlists, enhancing the in-store experience for customers. Simultaneously, Spotify users could access these playlists, driving user engagement on their platform. This symbiotic relationship amplified brand exposure for both parties, demonstrating the power of strategic partnerships.
- Experiment with new business models : Don’t be afraid to challenge conventional wisdom and explore alternative ways of delivering value to your customers. Innovative business models can often lead to significant growth opportunities. For instance, the subscription-based model adopted by companies like Dollar Shave Club and Spotify disrupted traditional sales models in their respective industries.
- Embrace a problem-solving mindset : Encourage your team to approach business challenges with a problem-solving mindset , focusing on finding creative solutions that deliver value to customers. This mindset can help drive innovation and uncover new business development opportunities. Tesla’s mission to combat climate change led to the development of its innovative electric vehicles and solar energy products.
- Role of Business Development in Sales
Integrating business development and sales strategies drive growth and revenue generation. Business development activities, such as lead generation , market research, and partnership development, support sales efforts. By identifying and nurturing leads, conducting market research to understand customer needs, and fostering strategic partnerships, business development teams can help sales teams close deals more effectively.
Conversely, insights from sales interactions can inform business development efforts and help refine marketing and sales strategies, contributing to the organization’s longevity.
In addition, when a company continually learns from its sales interactions and applies those insights to improve its offerings, messaging, and customer engagement tactics, it is better positioned to adapt to changing market conditions and customer preferences.
This adaptability ultimately leads to stronger customer relationships, increased customer loyalty, and sustained business growth, all contributing to the organization’s longevity.

Examples of successful sales development plans often include a strong focus on collaboration between business development and sales teams and the use of data-driven insights to optimize lead generation and conversion efforts. For instance, a software company wants to expand its market share in a new industry vertical.
To achieve this, the business development team conducts thorough market research to identify key players, customer pain points, and potential partnerships within the new industry. This information is then shared with the sales team, who uses the insights to tailor their pitches and address clients’ specific needs in the new market.
Simultaneously, the sales team shares feedback from client interactions, allowing the business development team to fine-tune their research and partnership strategies. This continuous learning and adaptation process leads to higher conversion rates and increased revenue and strengthens the company’s ability to thrive in the long term.
- Case Studies
Examining case studies of successful companies can provide valuable insights into how business development and sales strategies can be effectively integrated to drive growth and achieve long-term success.
- Amazon: Embracing Customer Obsession
Amazon’s relentless focus on customer satisfaction has driven its innovative business development and sales strategies. By leveraging data analytics and customer feedback, Amazon continually refines its offerings and sales approach to cater to customers’ evolving preferences. This customer-centric mindset has led to innovations such as Prime membership, one-click ordering, and Alexa voice assistant, which have enhanced the customer experience and fueled Amazon’s growth.
- Salesforce: Revolutionizing CRM through Collaboration
Salesforce, a pioneer in cloud-based customer relationship management (CRM) solutions, has successfully integrated business development and sales by fostering a collaborative culture . They encourage cross-functional teams to work together to identify new markets and develop innovative solutions. This collaborative approach has enabled Salesforce to remain at the forefront of the CRM market, continuously delivering cutting-edge products and services that meet customer needs.
- Slack: Transforming Workplace Communication
Slack, a widespread team collaboration platform, demonstrates the power of effectively integrating business development and sales strategies. By conducting extensive market research and user feedback, Slack identified a gap in the market for a user-friendly, intuitive communication tool. This insight led to the development of a platform that streamlined workplace communication, transforming how teams collaborate . Slack’s sales team leverages this value proposition to drive adoption, resulting in rapid growth and widespread industry acclaim.
Creating the right business development plan can significantly benefit any organization seeking growth and success. To maximize your chances of success, focus on understanding your organization’s unique needs, setting clear goals, conducting market research, and developing effective marketing and sales strategies. In addition, emphasize innovation, collaboration, and continuous improvement to stay ahead in the competitive business landscape.
As you develop your plan, create actionable steps and regularly monitor progress to ensure continuous growth and identify areas for improvement. By embracing a culture of innovation, teamwork, and continuous learning, your organization will be well-equipped to navigate business development challenges and achieve long-term growth and success.
Financial Advisor Daniel Brown is an experienced and knowledgeable financial advisor at spoolah.com. He has been in this industry since 2008 and has a strong understanding of economic trends, all types of financial planning, ways of creating plans for meeting short-term and long-term financial goals, etc.
Table of Contents
Business view all, exploring career options: is capital goods a good career path, is healthcare a good career path, from idea to life: how to start a contractor business, paying yourself as a business owner.
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- March Madness
- AP Top 25 Poll
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Tax changes small business owners should be aware of as the tax deadline looms
FILE - A cash register is seen on the front counter at the Alpha Shoe Repair Corp., Feb. 3, 2023, in New York. As Tax Day, April 15, approaches, there are plenty of things small business owners should keep in mind when filing taxes this year. (AP Photo/Mary Altaffer, File)

- Copy Link copied
As Tax Day approaches, there are plenty of things small business owners should keep in mind when filing taxes this year.
April 15 is still the annual tax deadline for many small businesses although, unlike individuals, small businesses can have varying deadlines depending on the type of company, the state the taxes are filed in, and other factors. Quarterly estimated tax payments are generally required throughout the year. And certain types of small businesses had to file by March 15.
Since business tax filing is complex, most experts recommend small business owners work with a professional tax adviser rather than trying to file on their own or even with tax-filing software.
“Taxes should not be scary, especially when you have a certified tax professional or someone who is your trusted adviser,” said Amber Kellogg, vice president of affiliate origination and management at business consultancy Occams Advisory. “I always say you don’t go to the dentist to get your oil changed, and you certainly shouldn’t do (taxes) yourself unless you’re an expert.”
But even if small business owners aren’t filing taxes themselves, it’s still important to stay informed about any tax changes during the year. Here are things small business owners should consider as the April 15 deadline looms.
Consider an extension
Because of some pending tax legislation in Congress this year, Mitch Gerstein, senior tax adviser at accounting firm Isdaner & Co., said it might be a good idea to file for an extension. When you file an extension you still pay estimated taxes, but final paperwork isn’t due until September.
This gives your tax provider adequate time to file a return. And it’s cheaper to file an extension than an amended return, which costs more in administrative fees.
One reason Gerstein recommends an extension this year: a bonus depreciation write-off used by many small businesses is set to decrease for 2023. The bonus depreciation allowance was designed to spur capital purchases and it let businesses write off 100% of certain new and used assets in 2022. But beginning in 2023, that will decrease to 80% for used assets, dropping another 20% each year thereafter. However, a tax bill pending in Congress could restore the write-off to 100%. It’s rare that there is such a significant tax bill pending in Congress when taxes are due, Gerstein said.
Optimize your retirement plan
The Secure Act 2.0 passed by Congress in late 2022 gives small businesses some tax advantages if they offer a retirement plan. There’s a tax credit for small businesses starting new employee plans. The credit is up to 100% of the startup costs for adopting and maintaining a new 401(k) plan, capped at $5,000. There’s also a tax credit based on employer contribution, up to $1,000 annually per employee, over the plan’s first five years.
Changes in research and development write-offs
Scott Orn, chief operating officer of Kruze Consulting, works with startups backed by venture capital. Orn said the number one concern his clients are calling about is “Section 174,” a part of the tax code that involves writing off research and development costs.
In the past, companies were able to deduct 100% of research and development expenses from their taxable income. That was helpful because often that deduction meant the company was operating at a loss and wouldn’t have to pay taxes.
But starting in 2022 due to new legislation, companies have had to “capitalize” the expense – or spread it out over several years. That means they must now write off the expenses over five years for U.S.-based R&D, or 15 years for foreign R&D expenses.
Large and small companies alike are affected by the change, but small businesses are hurt the most, Orn said.
“(Small businesses) are the ones who are swinging into profit where they thought they were like safely losing money and not ever going to pay taxes for a while,” Orn said. “And that’s why it’s such a big surprise for them. It’s hurting people, it’s like it’s a lot of money these companies don’t have.”
Avoid underpayment penalties
Yet another reason for small business owners to use a tax professional is the fact that underpaying will cost more this year. In the past, underpayment penalties hovered at around 3%, but this year they’re more than double at 8% . That’s because the penalties are based on the federal short term interest rate plus three points, said Danny Castro, Florida Market Tax Leader at BDO USA, part of BDO Global, a global accounting network.
“The cost of underpayment is as high as it’s been in a long time,” he said.
One credit to skip: the ERC
At one time, the pandemic-era Employee Retention Credit seemed like a boon for small businesses. Designed to help small businesses keep employees during pandemic-era shutdowns, the generous credit let businesses file amended tax returns to claim the credit.
But that led to a cottage industry of scammers trying to entice small businesses to help them file for the credit – for a fee – even if they didn’t qualify. The IRS has launched several initiatives to claw back some money improperly given to businesses. To date, the IRS said 500 taxpayers have given back $225 million via a voluntary disclosure program, which ended on March 22, that let small businesses who thought they received the credit in error give back the money and keep 20%. And 1,800 businesses have withdrawn unprocessed claims totaling $251 million.
Get organized, stay organized
The best thing small businesses can do to help their tax advisers file their taxes is stay organized. A shoe box full of receipts isn’t helpful when trying to file timely taxes. Owners should log receipts in an orderly database they can turn over to their adviser. And stay on top of quarterly estimated payments.
“(Small business owners) need to be able to keep accurate records throughout the year and not have to go back in April and go, gosh, what what was this receipt for,” said Occams Advisory’s Amber Kellogg, “Keeping those, accurate records is very, very important.”
This story has been corrected to show that BDO USA is part of BDO Global, not BBO Global.

This new 'blended-wing' plane looks like a military stealth bomber and just got the green light to fly after decades of development
- California aerospace startup JetZero got the green light to fly its new "Pathfinder" aircraft.
- The twinjet features a unique "blended-wing body" and is expected to carry up to 250 people.
- The wing poses complex challenges, but JetZero says it's a sound concept for reducing CO2 emissions.

Aerospace companies across the globe are breaking from the norm of producing traditional "tube and wing" aircraft and instead looking into futuristic technologies that will make flying more efficient and eco-friendly.
There are already concepts like zero-emission electric aircraft, supersonic jets , and even hypersonic ones. But the latest example of these new plane types is "Pathfinder" — a stealth bomber-looking jet designed by the California-based aerospace company JetZero .
The twinjet features a unique "blended-wing body," or BWB, a design where the wing and fuselage are combined into one.
After years of development, JetZero has built a 1:8 demonstrator , and the Federal Aviation Administration just gave the funky-shaped craft the green light to fly, CNN reported on Thursday.
JetZero confirmed the news to Business Insider, saying "flights will start in the coming months" to test the "stability and control characteristics of JetZero's blended wing body design, as well as the operation of its innovative landing gear system."
The FAA told BI on Thursday that it "does not comment on ongoing certification projects" and that "safety will dictate the timeline."
JetZero is building a single-deck, very widebody airliner
JetZero touts its future very widebody airliner as a "middle market" passenger airliner with space for up to 250 people, meaning its rows could stretch 15 or 20 seats across, JetZero cofounder and CEO Tom O'Leary told CNN.
The jet would be a replacement option for traditional twin-engine widebodies like the Boeing 767, for example, according to JetZero.
"The jetliner can fit seamlessly into today's infrastructure," the company told BI. "Passenger capacity of a small widebody but the weight, and engine requirement, of a single-aisle jet."
Pathfinder also has military applications, with the US Air Force awarding $235 million to JetZero in August to develop a commercial-scale demonstrator, which JetZero told BI it plans to build by 2027.
The company said it expects the certified airliner to enter the market as soon as 2030, which aviation analyst Bailey Miles at consulting firm AviationValues told CNN is "inconceivable" considering the complexities of the BWB design.
Related stories
Still, he said the concept "holds immense promise as a game changer in the aviation industry."
The blended-wing body significantly reduces fuel burn but will face design challenges
JetZero said it chose this specific BWB design due to its carbon-reducing benefits.
According to the US Air Force, the all-in-one wing reduces drag by 30% and increases lift — effectively reducing fuel burn and increasing global reach.
Moreover, JetZero said the engines will eventually be developed to run on hydrogen, which would be zero-emissions. In the interim, initial versions of Pathfinder would boast 50% less fuel burn using borrowed engines, like those from the Boeing 737, CNN reported.
University of Illinois aerospace professor Michael Bragg told Business Insider that the development of lighter yet still strong composite materials is key to reducing fuel burn on BWB aircraft designs such as Pathfinder.
He also said that engineers have distributed the load across the entire aircraft, which negates the "bending moment" between the tube and wings on a traditional airplane. The composite technology makes this new load bearing possible, Bragg told BI.
Despite Pathfinder's sound design on paper, Bragg said proving and certifying a brand-new aircraft concept is much more challenging than developing a traditionally shaped jetliner.
"The product is essentially a new airframe and flight controls married to existing systems already certified for commercial flight," JetZero told BI.
The classic tube-and-wing plane design dates back to the 1950s dawn of the jet age on aircraft like the Boeing 707 and Douglas DC-8 and has continued to today on modern widebodies like the Airbus A350 and the future Boeing 777X.
Such time-tested technology has a successful track record, so there has been little incentive to change the conventional aircraft design over the decades as using proven technology minimizes safety risks and is easier for production, Bragg said.
"A lot of that is because of manufacturing," he said. "It's easy to manufacture a tube, and, although not as easy, it's a well-known process of how to build the wings to attach."
Beyond the assembly line, Bragg told BI that JetZero must ensure passengers are comfortable inside Pathfinder's unique shape.
For example, he told BI the pressurization inside the plane — which is what helps humans breathe at high altitudes — is difficult to design in the very widebody structure. And most of those 200+ passengers would be in the middle section without a window, which Bragg told BI could put off travelers.
JetZero says on its website that its cabin is more efficient for boarding and deplaning, and will have space for every person's cabin luggage.
Pathfinder is 100 years in the making
JetZero's Pathfinder is poised to be a groundbreaking technology should it ever hit the market, but it's not a new idea.
Engineers were reported by CNN to have crafted a similar blended-wing shape some 100 years ago. Later, American aircraft industrialist and designer Jack Northrop built his famous "Flying Wing" aircraft in the 1940s, laying the framework for the eventual B-2 bomber .
Development picked up in 1988 when McDonnell Douglas responded to NASA's challenge to build more revolutionary aircraft designs, which was followed by MD's merger with Boeing in 1997 and the later building of the X-48B/C BWBs made jointly by NASA and Boeing.
Watch: Tesla-powered flying car doesn't require a license
- Main content

- River City Live
- Newsletters
BREAKING NEWS
LIVE: Gov. DeSantis, head of Florida DMV hold news conference in St. Petersburg
2 warnings and an advisory in effect for 7 regions in the area, developer says dia wants to end negotiations for laura street trio, letter from developer says it still hopes to come to agreement with city.
Ashley Harding , Reporter/Weekend Anchor
JACKSONVILLE, Fla. – The future of the Laura Street Trio project in downtown Jacksonville might be in jeopardy according to a new letter from the developer that was shared by The Jaxson Mag on social media.
The developer says his firm got a termination letter from the Downtown Investment Authority related to the historic buildings at Laura and Forsyth streets.
Recommended Videos
The developer’s letter said that on Wednesday, it got a notice that the DIA submitted paperwork to end negotiations between the city and the development team.
The buildings known as the “Laura Street Trio” have stood vacant for decades, but their history in downtown Jacksonville is undeniable.
In the letter, the developer wrote:
“The properties’ significant historic context and important location in the epicenter of our downtown make this project critical to the continued revitalization of our city.”
The developer has been trying for years to turn the historic buildings into a hotel, apartments and retail shops.
Check out our weekly newsletter compiled by Consumer Investigative Reporter Tiffany Salameh.
But it’s going to require city money, and coming to an agreement on a city investment in the project has been the issue.
If a deal isn’t reached, there’s a chance the buildings could come down.
In the letter, the developer hints that the project might not be happening – and doesn’t seem all that surprised.
“On April 9th, we received a notice that a DIA Resolution has been submitted to terminate the negotiations with the development team to move the project forward, seemingly reflective of most development projects proposed by private interests for Downtown Jacksonville.”
The latest attempt between the developer and the city to get the project off the ground involved the city using $22 million to back up a construction plan.
But the City Council said there were just too many unanswered questions.
Last June, the Downtown Investment Authority board voted to send a term sheet, including $36.5 million in incentives, to the City Council without a recommendation for or against it.
DIA staff reported at the time that the developer did not meet certain criteria for incentives.
For now, the project’s future is in wait-and-see mode. The developer also wrote his commitment to the project is still 100%.
He ended by saying:
“It is our hope that we and the City of Jacksonville can come to an agreement on terms to move this important project forward as soon as possible.”
Mayor Donna Deegan is holding a news conference Wednesday to talk about downtown projects.
News4JAX will work to get answers about the Laura Street Trio and where it stands, along with other projects.
Copyright 2024 by WJXT News4JAX - All rights reserved.
About the Author
Ashley harding.
Ashley Harding joined the Channel 4 news team in March 2013. She reports for and anchors The Morning Show.
Click here to take a moment and familiarize yourself with our Community Guidelines.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Onboarding New Employees — Without Overwhelming Them
- Julia Phelan

Give people the space and time they need to thrive in their new job.
A great onboarding experience can keep new hires engaged and committed, and increase their learning and preparedness for their new role. In trying to ensure new employees feel supported and properly prepared, some organizations flood new hires with far too much information. Even if managers have the best intentions, bombarding new hires with tasks — such as asking them to read every single page of the employee manual or requiring them to get set-up on Slack, email, Box, and all the other platforms all at once — will backfire. Three strategies can help organizations mitigate this overload and ensure employees have the space, time, and mental resources available to learn and thrive in their new job.
We know that effectively onboarding new employees has huge value. A good onboarding process — with clear information on job requirements, organizational norms, and performance expectations — not only enhances employee productivity but helps increase loyalty and engagement, and decrease s turnover .
- JP Julia Phelan , Ph.D. is a learning design consultant and expert in applying learning science principles to create effective learning experiences. She works with organizations to help build a strong workplace learning culture by improving training design, implementation, and outcomes. She is the co-founder of To Eleven , and a former UCLA education research scientist. Connect with her on LinkedIn .
Partner Center

COMMENTS
Now that you're in the growth stage of your business, set things in motion with a business development plan. A business development plan sets goals for growth and explains how you will achieve them. It can have a short-term or long-term focus. Review and revise your plan as often as you can. And keep building on it as your business evolves.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
As the road map for a business's development, the business plan. Defines the vision for the company. Establishes the company's strategy. Describes how the strategy will be implemented. Provides a framework for analysis of key issues. Provides a plan for the development of the business. Helps the entrepreneur develop and measure critical ...
A business plan is a document that communicates a company's goals and ambitions, along with the timeline, finances, and methods needed to achieve them. Additionally, it may include a mission statement and details about the specific products or services offered. A business plan can highlight varying time periods, depending on the stage of your company and its goals.
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include. 1. Create an executive summary. Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
Step #3: Conduct Your Market Analysis. Step #4: Research Your Competition. Step #5: Outline Your Products or Services. Step #6: Summarize Your Financial Plan. Step #7: Determine Your Marketing Strategy. Step #8: Showcase Your Organizational Chart. 14 Business Plan Templates to Help You Get Started.
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
Learn about the best business plan software. 1. Write an executive summary. This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your ...
A business development plan is a document put together by the business owner with the aim to grow and improve their business. The plan will set goals for growth and explain how you will achieve them. A business development strategy can have a short-term or long-term focus, or both. They should also be constantly reviewed and revised as things ...
A business development plan, or business plan, should describe the organization's objectives and how it intends to achieve them, including financial goals, expected costs, and targeted milestones ...
The traditional business plan is a long document that explores each component in depth. You can build a traditional business plan to secure funding from lenders or investors. The lean start-up business plan focuses on the key elements of a business's development and is shorter than the traditional format.
Let's go over the steps you should take to create a strategic plan. 1. Download our strategic plan template. First, download our free growth strategy template to create a rock-solid strategic plan. With this template, you can map a growth plan for increasing sales, revenue, and customer acquisition rates.
5. Structure, Suppliers and Operations. This section of your simple business plan template explores how to structure and operate your business. Details include the type of business organization ...
Developing a Business Plan. This chapter describes the purposes, principles, and the general concepts and tools for business planning, and the process for developing a business plan. Business plans are developed for both internal and external purposes. Internally, entrepreneurs develop business plans to help put the pieces of their business ...
Chapter 1 - Developing a Business Plan. Chapter 2 - Essential Initial Research. Chapter 3 - Business Models. Chapter 4 - Initial Business Plan Draft. Chapter 5 - Making the Business Plan Realistic. Chapter 6 - Making the Plan Appeal to Stakeholders and Desirable to the Entrepreneur. Chapter 7 - Finishing the Business Plan.
The business development plan is a key document that helps you map your ecosystem and strategize your business development efforts. It consists of a research part and an action part. In the first part, you analyze your market, competitors, and customers. In the second, you use your insights to build value propositions, content plans, and ...
1. Analyze The Competition. Every great business plan is based on research. Well, most great plans are based on research. Ice cream at midnight is rarely planned, but it's pretty great. The first thing I do when creating a business development strategy is to review the company and consider the target market.
Articulate how and why these opportunities will help grow the business. 4. List funding sources. Your plan should include not just the amount of funding you'll need, but how you plan to get it — loans, equity investors or crowdfunding, for example. Now is the time to come up with an in-depth funding strategy.
Developing a Business Plan. An important task in starting a new venture is to develop a business plan. As the phrase suggests, a business plan is a "road map" to guide the future of the business or venture. The elements of the business plan will impact the daily decisions of the business and provide direction for expansion, diversification, and ...
4. Financials. Include a cash flow forecast, usually broken down on a monthly basis and presented as a spreadsheet. Also add your financial statements (balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement and statement of retained earnings). And if you're a new business, list start-up costs.
What is a Business Development Plan? A business development plan is a strategic roadmap that helps a company grow and succeed. It outlines the steps and strategies needed to achieve specific business goals. These goals may include identifying new opportunities, expanding into new markets, forging partnerships, and improving overall performance.
Optimize your retirement plan. The Secure Act 2.0 passed by Congress in late 2022 gives small businesses some tax advantages if they offer a retirement plan. There's a tax credit for small businesses starting new employee plans. The credit is up to 100% of the startup costs for adopting and maintaining a new 401 (k) plan, capped at $5,000.
The TNAU has categorised FPOs under coconut, paddy, millets and maize, fruits and vegetables, oil seeds and other crops. Experts vet the existing plans and enable FPOs to take the implementation ...
After years of development, JetZero has built a 1:8 demonstrator, and the Federal Aviation Administration just gave the funky-shaped craft the green light to fly, CNN reported on Thursday ...
Still, the new concept includes many of the same elements as the Tempe plan. The 110 acres would include the team's practice facility and business headquarters, a 3,500-seat theater, and the usual recipe of residential (1,900 units), retail, office and experiential attractions.
A community plan in the works for the Yolo County community of Dunnigan would allow new housing and commercial development, including a 54-acre site between Interstate 5 and the Old Town area ...
The developer's letter said that on Wednesday, it got a notice that the DIA submitted paperwork to end negotiations between the city and the development team. The buildings known as the "Laura ...
A great onboarding experience can keep new hires engaged and committed, and increase their learning and preparedness for their new role. In trying to ensure new employees feel supported and ...
The new Concept Plan is fully compliant with Fingal County Council's adopted strategy for Dublin Airport, as outlined in the Fingal Development Plan 2023 to 2029 and the Dublin Airport Local Area ...