How To Write a Concept Paper for Academic Research: An Ultimate Guide

A concept paper is one of the first steps in helping you fully realize your research project. Because of this, some schools opt to teach students how to write concept papers as early as high school. In college, professors sometimes require their students to submit concept papers before suggesting their research projects to serve as the foundations for their theses.
If you’re reading this right now, you’ve probably been assigned by your teacher or professor to write a concept paper. To help you get started, we’ve prepared a comprehensive guide on how to write a proper concept paper.
Related: How to Write Significance of the Study (with Examples)

Table of Contents
What is the concept paper, 1. academic research concept papers, 2. advertising concept papers, 3. research grant concept papers, concept paper vs. research proposal, tips for finding your research topic, 2. think of research questions that you want to answer in your project, 3. formulate your research hypothesis, 4. plan out how you will achieve, analyze, and present your data, 2. introduction, 3. purpose of the study, 4. preliminary literature review, 5. objectives of the study, 6. research questions and hypotheses, 7. proposed methodology, 8. proposed research timeline, 9. references, sample concept paper for research proposal (pdf), tips for writing your concept paper.
Generally, a concept paper is a summary of everything related to your proposed project or topic. A concept paper indicates what the project is all about, why it’s important, and how and when you plan to conduct your project.
Different Types of the Concept Paper and Their Uses

This type of concept paper is the most common type and the one most people are familiar with. Concept papers for academic research are used by students to provide an outline for their prospective research topics.
These concept papers are used to help students flesh out all the information and ideas related to their topic so that they may arrive at a more specific research hypothesis.
Since this is the most common type of concept paper, it will be the main focus of this article.
Advertising concept papers are usually written by the creative and concept teams in advertising and marketing agencies.
Through a concept paper, the foundation or theme for an advertising campaign or strategy is formed. The concept paper can also serve as a bulletin board for ideas that the creative and concept teams can add to or develop.
This type of concept paper usually discusses who the target audience of the campaign is, what approach of the campaign will be, how the campaign will be implemented, and the projected benefits and impact of the campaign to the company’s sales, consumer base, and other aspects of the company.
This type of concept paper is most common in the academe and business world. Alongside proving why your research project should be conducted, a research grant concept paper must also appeal to the company or funding agency on why they should be granted funds.
The paper should indicate a proposed timeline and budget for the entire project. It should also be able to persuade the company or funding agency on the benefits of your research project– whether it be an increase in sales or productivity or for the benefit of the general public.
It’s important to discuss the differences between the two because a lot of people often use these terms interchangeably.
A concept paper is one of the first steps in conducting a research project. It is during this process that ideas and relevant information to the research topic are gathered to produce the research hypothesis. Thus, a concept paper should always precede the research proposal.
A research proposal is a more in-depth outline of a more fleshed-out research project. This is the final step before a researcher can conduct their research project. Although both have similar elements and structures, a research proposal is more specific when it comes to how the entire research project will be conducted.
Getting Started on Your Concept Paper
1. find a research topic you are interested in.
When choosing a research topic, make sure that it is something you are passionate about or want to learn more about. If you are writing one for school, make sure it is still relevant to the subject of your class. Choosing a topic you aren’t invested in may cause you to lose interest in your project later on, which may lower the quality of the research you’ll produce.
A research project may last for months and even years, so it’s important that you will never lose interest in your topic.
- Look for inspiration everywhere. Take a walk outside, read books, or go on your computer. Look around you and try to brainstorm ideas about everything you see. Try to remember any questions you might have asked yourself before like why something is the way it is or why can’t this be done instead of that .
- Think big. If you’re having trouble thinking up a specific topic to base your research project on, choosing a broad topic and then working your way down should help.
- Is it achievable? A lot of students make the mistake of choosing a topic that is hard to achieve in terms of materials, data, and/or funding available. Before you decide on a research topic, make sure you consider these aspects. Doing so will save you time, money, and effort later on.
- Be as specific as can be. Another common mistake that students make is that they sometimes choose a research topic that is too broad. This results in extra effort and wasted time while conducting their research project. For example: Instead of “The Effects of Bananas on Hungry Monkeys” , you could specify it to “The Effects of Cavendish Bananas on Potassium-deficiency in Hungry Philippine Long-tailed Macaques in Palawan, Philippines”.
Now that you have a general idea of the topic of your research project, you now need to formulate research questions based on your project. These questions will serve as the basis for what your project aims to answer. Like your research topic, make sure these are specific and answerable.
Following the earlier example, possible research questions could be:
- Do Cavendish bananas produce more visible effects on K-deficiency than other bananas?
- How susceptible are Philippine long-tailed macaques to K-deficiency?
- What are the effects of K-deficiency in Philippine long-tailed macaques?
After formulating the research questions, you should also provide your hypothesis for each question. A research hypothesis is a tentative answer to the research problem. You must provide educated answers to the questions based on your existing knowledge of the topic before you conduct your research project.
After conducting research and collecting all of the data into the final research paper, you will then have to approve or disprove these hypotheses based on the outcome of the project.
Prepare a plan on how to acquire the data you will need for your research project. Take note of the different types of analysis you will need to perform on your data to get the desired results. Determine the nature of the relationship between different variables in your research.
Also, make sure that you are able to present your data in a clear and readable manner for those who will read your concept paper. You can achieve this by using tables, charts, graphs, and other visual aids.
Related: How to Make Conceptual Framework (with Examples and Templates)
Generalized Structure of a Concept Paper
Since concept papers are just summaries of your research project, they are usually short and no longer than 5 pages. However, for big research projects, concept papers can reach up to more than 20 pages.
Your teacher or professor may give you a certain format for your concept papers. Generally, most concept papers are double-spaced and are less than 500 words in length.
Even though there are different types of concept papers, we’ve provided you with a generalized structure that contains elements that can be found in any type of concept paper.

The title for your paper must be able to effectively summarize what your research is all about. Use simple words so that people who read the title of your research will know what it’s all about even without reading the entire paper.
The introduction should give the reader a brief background of the research topic and state the main objective that your project aims to achieve. This section should also include a short overview of the benefits of the research project to persuade the reader to acknowledge the need for the project.
The Purpose of the Study should be written in a way that convinces the reader of the need to address the existing problem or gap in knowledge that the research project aims to resolve. In this section, you have to go into more detail about the benefits and value of your project for the target audience/s.
This section features related studies and papers that will support your research topic. Use this section to analyze the results and methodologies of previous studies and address any gaps in knowledge or questions that your research project aims to answer. You may also use the data to assert the importance of conducting your research.
When choosing which papers and studies you should include in the Preliminary Literature Review, make sure to choose relevant and reliable sources. Reliable sources include academic journals, credible news outlets, government websites, and others. Also, take note of the authors for the papers as you will need to cite them in the References section.
Simply state the main objectives that your research is trying to achieve. The objectives should be able to indicate the direction of the study for both the reader and the researcher. As with other elements in the paper, the objectives should be specific and clearly defined.
Gather the research questions and equivalent research hypotheses you formulated in the earlier step and list them down in this section.
In this section, you should be able to guide the reader through the process of how you will conduct the research project. Make sure to state the purpose for each step of the process, as well as the type of data to be collected and the target population.
Depending on the nature of your research project, the length of the entire process can vary significantly. What’s important is that you are able to provide a reasonable and achievable timeline for your project.
Make sure the time you will allot for each component of your research won’t be too excessive or too insufficient so that the quality of your research won’t suffer.
Ensure that you will give credit to all the authors of the sources you used in your paper. Depending on your area of study or the instructions of your professor, you may need to use a certain style of citation.
There are three main citation styles: the American Psychological Association (APA), Modern Language Association (MLA), and the Chicago style.
The APA style is mostly used for papers related to education, psychology, and the sciences. The APA citation style usually follows this format:

The MLA citation style is the format used by papers and manuscripts in disciplines related to the arts and humanities. The MLA citation style follows this format:

The Chicago citation style is usually used for papers related to business, history, and the fine arts. It follows this citation format:

This is a concept paper sample provided by Dr. Bernard Lango from the Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology (modified for use in this article). Simply click the link above the download the PDF file.
- Use simple, concise language. Minimize the use of flowery language and always try to use simple and easy-to-understand language. Too many technical or difficult words in your paper may alienate your readers and make your paper hard to read.
- Choose your sources wisely. When scouring the Internet for sources to use, you should always be wary and double-check the authenticity of your source. Doing this will increase the authenticity of your research project’s claims and ensure better data gathered during the process.
- Follow the specified format, if any. Make sure to follow any specified format when writing your concept paper. This is very important, especially if you’re writing your concept paper for class. Failure to follow the format will usually result in point deductions and delays because of multiple revisions needed.
- Proofread often. Make it a point to reread different sections of your concept paper after you write them. Another way you can do this is by taking a break for a few days and then coming back to proofread your writing. You may notice certain areas you’d like to revise or mistakes you’d like to fix. Make proofreading a habit to increase the quality of your paper.
Written by Ruth Raganit
in Career and Education , Juander How
Last Updated May 30, 2022 04:34 PM
Ruth Raganit
Ruth Raganit obtained her Bachelor of Science degree in Geology from the University of the Philippines – Diliman. Her love affair with Earth sciences began when she saw a pretty rock and wondered how it came to be. She also likes playing video games, doing digital art, and reading manga.
Browse all articles written by Ruth Raganit
Copyright Notice
All materials contained on this site are protected by the Republic of the Philippines copyright law and may not be reproduced, distributed, transmitted, displayed, published, or broadcast without the prior written permission of filipiknow.net or in the case of third party materials, the owner of that content. You may not alter or remove any trademark, copyright, or other notice from copies of the content. Be warned that we have already reported and helped terminate several websites and YouTube channels for blatantly stealing our content. If you wish to use filipiknow.net content for commercial purposes, such as for content syndication, etc., please contact us at legal(at)filipiknow(dot)net
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on October 12, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on November 21, 2023.

A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organized and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research proposals.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: “A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management”
- Example research proposal #2: “Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use”
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesize prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasize again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement .
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is relevant and worthy of being conducted.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, November 21). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved March 24, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-proposal/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

Community Blog
Keep up-to-date on postgraduate related issues with our quick reads written by students, postdocs, professors and industry leaders.
What is a Concept Paper and How do You Write One?
- By DiscoverPhDs
- August 26, 2020

What is a Concept Paper?
A concept paper is a short document written by a researcher before starting their research project, with the purpose of explaining what the study is about, why it is important and the methods that will be used.
The concept paper will include your proposed research title, a brief introduction to the subject, the aim of the study, the research questions you intend to answer, the type of data you will collect and how you will collect it. A concept paper can also be referred to as a research proposal.
What is the Purpose of a Concept Paper?
The primary aim of a research concept paper is to convince the reader that the proposed research project is worth doing. This means that the reader should first agree that the research study is novel and interesting. They should be convinced that there is a need for this research and that the research aims and questions are appropriate.
Finally, they should be satisfied that the methods for data collection proposed are feasible, are likely to work and can be performed within the specific time period allocated for this project.
The three main scenarios in which you may need to write a concept paper are if you are:
- A final year undergraduate or master’s student preparing to start a research project with a supervisor.
- A student submitting a research proposal to pursue a PhD project under the supervision of a professor.
- A principal investigator submitting a proposal to a funding body to secure financial support for a research project.
How Long is a Concept Paper?
The concept paper format is usually between 2 and 3 pages in length for students writing proposals for undergraduate, master’s or PhD projects. Concept papers written as part of funding applications may be over 20 pages in length.
How do you Write a Concept Paper?
There are 6 important aspects to consider when writing a concept paper or research proposal:
- 1. The wording of the title page, which is best presented as a question for this type of document. At this study concept stage, you can write the title a bit catchier, for example “Are 3D Printed Engine Parts Safe for Use in Aircraft?”.
- A brief introduction and review of relevant existing literature published within the subject area and identification of where the gaps in knowledge are. This last bit is particularly important as it guides you in defining the statement of the problem. The concept paper should provide a succinct summary of ‘the problem’, which is usually related to what is unknown or poorly understood about your research topic . By the end of the concept paper, the reader should be clear on how your research idea will provide a ‘solution’ to this problem.
- The overarching research aim of your proposed study and the objectives and/or questions you will address to achieve this aim. Align all of these with the problem statement; i.e. write each research question as a clear response to addressing the limitations and gaps identified from previous literature. Also give a clear description of your primary hypothesis.
- The specific data outputs that you plan to capture. For example, will this be qualitative or quantitative data? Do you plan to capture data at specific time points or at other defined intervals? Do you need to repeat data capture to asses any repeatability and reproducibility questions?
- The research methodology you will use to capture this data, including any specific measurement or analysis equipment and software you will use, and a consideration of statistical tests to help interpret the data. If your research requires the use of questionnaires, how will these be prepared and validated? In what sort of time frame would you plan to collect this data?
- Finally, include a statement of the significance of the study , explaining why your research is important and impactful. This can be in the form of a concluding paragraph that reiterate the statement of the problem, clarifies how your research will address this and explains who will benefit from your research and how.
You may need to include a short summary of the timeline for completing the research project. Defining milestones of the time points at which you intend to complete certain tasks can help to show that you’ve considered the practicalities of running this study. It also shows that what you have proposed is feasible in order to achieve your research goal.
If you’re pitching your proposed project to a funder, they may allocate a proportion of the money based on the satisfactory outcome of each milestone. These stakeholders may also be motivated by knowing that you intend to convert your dissertation into an article for journal publication; this level of dissemination is of high importance to them.
Additionally, you may be asked to provide a brief summary of the projected costs of running the study. For a PhD project this could be the bench fees associated with consumables and the cost of any travel if required.
Make sure to include references and cite all other literature and previous research that you discuss in your concept paper.
This guide gave you an overview of the key elements you need to know about when writing concept papers. The purpose of these are first to convey to the reader what your project’s purpose is and why your research topic is important; this is based on the development of a problem statement using evidence from your literature review.
Explain how it may positively impact your research field and if your proposed research design is appropriate and your planned research method achievable.

You’ll come across many academics with PhD, some using the title of Doctor and others using Professor. This blog post helps you understand the differences.

A well written figure legend will explain exactly what a figure means without having to refer to the main text. Our guide explains how to write one.

Choosing a good PhD supervisor will be paramount to your success as a PhD student, but what qualities should you be looking for? Read our post to find out.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.

Browse PhDs Now

An In Press article is a paper that has been accepted for publication and is being prepared for print.

This article will answer common questions about the PhD synopsis, give guidance on how to write one, and provide my thoughts on samples.

Fabian’s in the final year of his PhD research at Maastricht University. His project is about how humans learn numbers and how hands might help that process; this is especially useful for children developing their maths skills.

Nina’s in the first year of her PhD in the Department of Psychology at the University of Bath. Her project is focused on furthering our understanding of fatigue within adolescent depression.
Join Thousands of Students
What (Exactly) Is A Research Proposal?
A simple explainer with examples + free template.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020 (Updated April 2023)
Whether you’re nearing the end of your degree and your dissertation is on the horizon, or you’re planning to apply for a PhD program, chances are you’ll need to craft a convincing research proposal . If you’re on this page, you’re probably unsure exactly what the research proposal is all about. Well, you’ve come to the right place.
Overview: Research Proposal Basics
- What a research proposal is
- What a research proposal needs to cover
- How to structure your research proposal
- Example /sample proposals
- Proposal writing FAQs
- Key takeaways & additional resources
What is a research proposal?
Simply put, a research proposal is a structured, formal document that explains what you plan to research (your research topic), why it’s worth researching (your justification), and how you plan to investigate it (your methodology).
The purpose of the research proposal (its job, so to speak) is to convince your research supervisor, committee or university that your research is suitable (for the requirements of the degree program) and manageable (given the time and resource constraints you will face).
The most important word here is “ convince ” – in other words, your research proposal needs to sell your research idea (to whoever is going to approve it). If it doesn’t convince them (of its suitability and manageability), you’ll need to revise and resubmit . This will cost you valuable time, which will either delay the start of your research or eat into its time allowance (which is bad news).

What goes into a research proposal?
A good dissertation or thesis proposal needs to cover the “ what “, “ why ” and” how ” of the proposed study. Let’s look at each of these attributes in a little more detail:
Your proposal needs to clearly articulate your research topic . This needs to be specific and unambiguous . Your research topic should make it clear exactly what you plan to research and in what context. Here’s an example of a well-articulated research topic:
An investigation into the factors which impact female Generation Y consumer’s likelihood to promote a specific makeup brand to their peers: a British context
As you can see, this topic is extremely clear. From this one line we can see exactly:
- What’s being investigated – factors that make people promote or advocate for a brand of a specific makeup brand
- Who it involves – female Gen-Y consumers
- In what context – the United Kingdom
So, make sure that your research proposal provides a detailed explanation of your research topic . If possible, also briefly outline your research aims and objectives , and perhaps even your research questions (although in some cases you’ll only develop these at a later stage). Needless to say, don’t start writing your proposal until you have a clear topic in mind , or you’ll end up waffling and your research proposal will suffer as a result of this.
Need a helping hand?
As we touched on earlier, it’s not good enough to simply propose a research topic – you need to justify why your topic is original . In other words, what makes it unique ? What gap in the current literature does it fill? If it’s simply a rehash of the existing research, it’s probably not going to get approval – it needs to be fresh.
But, originality alone is not enough. Once you’ve ticked that box, you also need to justify why your proposed topic is important . In other words, what value will it add to the world if you achieve your research aims?
As an example, let’s look at the sample research topic we mentioned earlier (factors impacting brand advocacy). In this case, if the research could uncover relevant factors, these findings would be very useful to marketers in the cosmetics industry, and would, therefore, have commercial value . That is a clear justification for the research.
So, when you’re crafting your research proposal, remember that it’s not enough for a topic to simply be unique. It needs to be useful and value-creating – and you need to convey that value in your proposal. If you’re struggling to find a research topic that makes the cut, watch our video covering how to find a research topic .

It’s all good and well to have a great topic that’s original and valuable, but you’re not going to convince anyone to approve it without discussing the practicalities – in other words:
- How will you actually undertake your research (i.e., your methodology)?
- Is your research methodology appropriate given your research aims?
- Is your approach manageable given your constraints (time, money, etc.)?
While it’s generally not expected that you’ll have a fully fleshed-out methodology at the proposal stage, you’ll likely still need to provide a high-level overview of your research methodology . Here are some important questions you’ll need to address in your research proposal:
- Will you take a qualitative , quantitative or mixed -method approach?
- What sampling strategy will you adopt?
- How will you collect your data (e.g., interviews, surveys, etc)?
- How will you analyse your data (e.g., descriptive and inferential statistics , content analysis, discourse analysis, etc, .)?
- What potential limitations will your methodology carry?
So, be sure to give some thought to the practicalities of your research and have at least a basic methodological plan before you start writing up your proposal. If this all sounds rather intimidating, the video below provides a good introduction to research methodology and the key choices you’ll need to make.
How To Structure A Research Proposal
Now that we’ve covered the key points that need to be addressed in a proposal, you may be wondering, “ But how is a research proposal structured? “.
While the exact structure and format required for a research proposal differs from university to university, there are four “essential ingredients” that commonly make up the structure of a research proposal:
- A rich introduction and background to the proposed research
- An initial literature review covering the existing research
- An overview of the proposed research methodology
- A discussion regarding the practicalities (project plans, timelines, etc.)
In the video below, we unpack each of these four sections, step by step.
Research Proposal Examples/Samples
In the video below, we provide a detailed walkthrough of two successful research proposals (Master’s and PhD-level), as well as our popular free proposal template.
Proposal Writing FAQs
How long should a research proposal be.
This varies tremendously, depending on the university, the field of study (e.g., social sciences vs natural sciences), and the level of the degree (e.g. undergraduate, Masters or PhD) – so it’s always best to check with your university what their specific requirements are before you start planning your proposal.
As a rough guide, a formal research proposal at Masters-level often ranges between 2000-3000 words, while a PhD-level proposal can be far more detailed, ranging from 5000-8000 words. In some cases, a rough outline of the topic is all that’s needed, while in other cases, universities expect a very detailed proposal that essentially forms the first three chapters of the dissertation or thesis.
The takeaway – be sure to check with your institution before you start writing.
How do I choose a topic for my research proposal?
Finding a good research topic is a process that involves multiple steps. We cover the topic ideation process in this video post.
How do I write a literature review for my proposal?
While you typically won’t need a comprehensive literature review at the proposal stage, you still need to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the key literature and are able to synthesise it. We explain the literature review process here.
How do I create a timeline and budget for my proposal?
We explain how to craft a project plan/timeline and budget in Research Proposal Bootcamp .
Which referencing format should I use in my research proposal?
The expectations and requirements regarding formatting and referencing vary from institution to institution. Therefore, you’ll need to check this information with your university.
What common proposal writing mistakes do I need to look out for?
We’ve create a video post about some of the most common mistakes students make when writing a proposal – you can access that here . If you’re short on time, here’s a quick summary:
- The research topic is too broad (or just poorly articulated).
- The research aims, objectives and questions don’t align.
- The research topic is not well justified.
- The study has a weak theoretical foundation.
- The research design is not well articulated well enough.
- Poor writing and sloppy presentation.
- Poor project planning and risk management.
- Not following the university’s specific criteria.
Key Takeaways & Additional Resources
As you write up your research proposal, remember the all-important core purpose: to convince . Your research proposal needs to sell your study in terms of suitability and viability. So, focus on crafting a convincing narrative to ensure a strong proposal.
At the same time, pay close attention to your university’s requirements. While we’ve covered the essentials here, every institution has its own set of expectations and it’s essential that you follow these to maximise your chances of approval.
By the way, we’ve got plenty more resources to help you fast-track your research proposal. Here are some of our most popular resources to get you started:
- Proposal Writing 101 : A Introductory Webinar
- Research Proposal Bootcamp : The Ultimate Online Course
- Template : A basic template to help you craft your proposal
If you’re looking for 1-on-1 support with your research proposal, be sure to check out our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the proposal development process (and the entire research journey), step by step.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling Udemy Course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:
51 Comments
I truly enjoyed this video, as it was eye-opening to what I have to do in the preparation of preparing a Research proposal.
I would be interested in getting some coaching.
I real appreciate on your elaboration on how to develop research proposal,the video explains each steps clearly.
Thank you for the video. It really assisted me and my niece. I am a PhD candidate and she is an undergraduate student. It is at times, very difficult to guide a family member but with this video, my job is done.
In view of the above, I welcome more coaching.
Wonderful guidelines, thanks
This is very helpful. Would love to continue even as I prepare for starting my masters next year.
Thanks for the work done, the text was helpful to me
Bundle of thanks to you for the research proposal guide it was really good and useful if it is possible please send me the sample of research proposal
You’re most welcome. We don’t have any research proposals that we can share (the students own the intellectual property), but you might find our research proposal template useful: https://gradcoach.com/research-proposal-template/
Cheruiyot Moses Kipyegon
Thanks alot. It was an eye opener that came timely enough before my imminent proposal defense. Thanks, again
thank you very much your lesson is very interested may God be with you
I am an undergraduate student (First Degree) preparing to write my project,this video and explanation had shed more light to me thanks for your efforts keep it up.
Very useful. I am grateful.
this is a very a good guidance on research proposal, for sure i have learnt something
Wonderful guidelines for writing a research proposal, I am a student of m.phil( education), this guideline is suitable for me. Thanks
You’re welcome 🙂
Thank you, this was so helpful.
A really great and insightful video. It opened my eyes as to how to write a research paper. I would like to receive more guidance for writing my research paper from your esteemed faculty.
Thank you, great insights
Thank you, great insights, thank you so much, feeling edified
Wow thank you, great insights, thanks a lot
Thank you. This is a great insight. I am a student preparing for a PhD program. I am requested to write my Research Proposal as part of what I am required to submit before my unconditional admission. I am grateful having listened to this video which will go a long way in helping me to actually choose a topic of interest and not just any topic as well as to narrow down the topic and be specific about it. I indeed need more of this especially as am trying to choose a topic suitable for a DBA am about embarking on. Thank you once more. The video is indeed helpful.
Have learnt a lot just at the right time. Thank you so much.
thank you very much ,because have learn a lot things concerning research proposal and be blessed u for your time that you providing to help us
Hi. For my MSc medical education research, please evaluate this topic for me: Training Needs Assessment of Faculty in Medical Training Institutions in Kericho and Bomet Counties
I have really learnt a lot based on research proposal and it’s formulation
Thank you. I learn much from the proposal since it is applied
Your effort is much appreciated – you have good articulation.
You have good articulation.
I do applaud your simplified method of explaining the subject matter, which indeed has broaden my understanding of the subject matter. Definitely this would enable me writing a sellable research proposal.
This really helping
Great! I liked your tutoring on how to find a research topic and how to write a research proposal. Precise and concise. Thank you very much. Will certainly share this with my students. Research made simple indeed.
Thank you very much. I an now assist my students effectively.
Thank you very much. I can now assist my students effectively.
I need any research proposal
Thank you for these videos. I will need chapter by chapter assistance in writing my MSc dissertation
Very helpfull
the videos are very good and straight forward
thanks so much for this wonderful presentations, i really enjoyed it to the fullest wish to learn more from you
Thank you very much. I learned a lot from your lecture.
I really enjoy the in-depth knowledge on research proposal you have given. me. You have indeed broaden my understanding and skills. Thank you
interesting session this has equipped me with knowledge as i head for exams in an hour’s time, am sure i get A++
This article was most informative and easy to understand. I now have a good idea of how to write my research proposal.
Thank you very much.
Wow, this literature is very resourceful and interesting to read. I enjoyed it and I intend reading it every now then.
Thank you for the clarity
Thank you. Very helpful.
Thank you very much for this essential piece. I need 1o1 coaching, unfortunately, your service is not available in my country. Anyways, a very important eye-opener. I really enjoyed it. A thumb up to Gradcoach
What is JAM? Please explain.
Thank you so much for these videos. They are extremely helpful! God bless!
very very wonderful…
thank you for the video but i need a written example
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
We use cookies on this site to enhance your experience
By clicking any link on this page you are giving your consent for us to set cookies.
A link to reset your password has been sent to your email.
Back to login
We need additional information from you. Please complete your profile first before placing your order.
Thank you. payment completed., you will receive an email from us to confirm your registration, please click the link in the email to activate your account., there was error during payment, orcid profile found in public registry, download history, understanding and developing a concept paper.
- Charlesworth Author Services
- 15 December, 2021
A concept paper, simply put, is a one- to two-page written document describing an idea for a project . At this stage, there is no need to flesh out details, but rather just introduce the overall rationale of the project, how it’ll be carried out and the expected outcomes. There is no hard rule as to how this should be structured, but below are some tips on what to include and why to include them.
Discuss the rationale
The need for the project is an important aspect to address, and is often something a funding body might look for when considering funding a project. A concept paper might be the first thing a funding round requests to get an idea of what the project is all about. So make sure that it includes:
- Importance of the work being proposed
- What the impact (not the same as ‘ impact factor ’ – see later below) will be
- How the outcomes of your project might meet or respond to the need
- Priorities of your intended audience
Outline your methodology and procedures
Your overall methodology , i.e. how you intend to approach your work, should be outlined here to give your reader an idea of how you propose to achieve your research objectives. Mentioning the proposed methodology in advance allows them to conduct an independent evaluation into whether it is a valid approach.
Further, you should highlight some exciting, specific procedures or methods that you might be especially well-placed to perform. For example, your institute may have a specific piece of equipment, or you may have access to very high quality expertise. This will inspire confidence in the review panel that you are well-positioned to take the project on.
Describe the potential impact
Impact is a term often thrown around in research circles, usually relating to the ‘impact factor’ of a journal. Impact in this instance does not refer to that. The impact that you should be describing here is the real-world impact of your work.
Will your idea or innovation change people’s lives? Will it save the taxpayer money? How will it do those things?
Make sure you describe impacts that go beyond discovering something new to shaking up your research community.
A concept paper is a loose framework by which you are able to quickly communicate an idea for a piece of work you might want to do in the future. At the very least, it can help you put ideas to paper and look at them as a whole, allowing you to critically assess what is needed to make it a reality. In the best case scenario, a concept paper might be used to advance your grant applications or attract investment for your idea. Whatever you are using it for, it is a valuable piece of writing that can help you formalise your idea and make it a reality.
Read next (second) in series: Writing a successful Research Proposal
Maximise your publication success with Charlesworth Author Services.
Charlesworth Author Services, a trusted brand supporting the world’s leading academic publishers, institutions and authors since 1928.
To know more about our services, visit: Our Services
Share with your colleagues
Related resources.

Writing a successful Research Proposal
Charlesworth Author Services 08/03/2022 00:00:00

Concept Paper vs. Research Proposal – and when to use each

Preparing and writing your PhD Research Proposal
Charlesworth Author Services 02/08/2021 00:00:00
Related webinars

Bitesize Webinar: Writing Competitive Grant Proposals: Module 1- Unpacking the Request for Proposals
Charlesworth Author Services 09/03/2021 00:00:00

Bitesize Webinar: Writing Competitive Grant Proposals: Module 2- Choosing the Right Funder

Bitesize Webinar: Writing Competitive Grant Proposals: Module 3- Structuring the Proposal

Bitesize Webinar: Writing Competitive Grant Proposals: Module 4- Developing a Grant Budget

How to write the Rationale for your research
Charlesworth Author Services 19/11/2021 00:00:00

A guide to finding the right Funding Agency for your project
Charlesworth Author Services 27/01/2021 00:00:00


Difference between Methodology and Method
Charlesworth Author Services 15/12/2021 00:00:00

How to Write a PhD Concept Paper

A concept paper – or concept note – is one of the initial requirements of a PhD programme. It is normally written during the PhD application process as well as early on in the programme once a student has been admitted.
A concept paper is basically a shorter version of a research proposal – in most cases between 2,000 and 2,500 words – that expresses the research ideas of the potential PhD student.
Besides being short, it should be concise yet have adequate details to convince the Department the student is applying to that he/she is worth being admitted to the programme.
Example of a title with a sub-title
References/bibliography, why do phd programmes require applicants to submit a concept paper.
A concept paper serves four main purposes:
- It gives the Department the student is applying to an idea of the student’s research interests.
- Based on point one, it informs the Department whether the student will be a good fit to the Department or not. To be a good fit, the research interests of the applicant should match those of the Department’s faculty.
- Based on the two points above, it enables the Department to offer support to the student throughout his/her PhD studies in the form of supervision and mentorship.
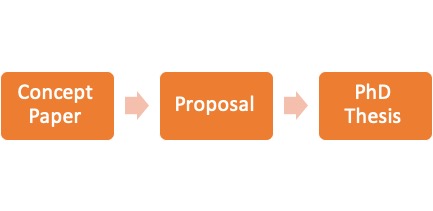
- Because the concept paper is written – and must be accepted – before the full proposal, it saves the student time and effort that would otherwise be spent on topics that may end up being rejected by the Department. A concept paper is therefore the first step to writing the PhD thesis/dissertation (see the figure below).
Format of a PhD Concept Paper
The format of a concept paper might vary from one university to another. A PhD student should therefore read the guidelines provided by his/her University of interest before writing a concept paper.
In general, the following is a common format of a concept paper:
Title of proposed study
The title of the proposed study is the first element of a concept paper.
The title should describe what the study is about by highlighting the variables of the study and the relationship between the variables if applicable.
The title should be short and specific: it is best to have a title that is not more than 15 words’ long.
Example of a title:
Use of Mobile Phone Applications for Weight Management in the United States
In order to add more specificity to the title, you can add a subtitle to the main title. The title and subtitle should be separated by a full colon.
Use of Mobile Phone Applications for Weight Management in the United States:
A Behavioural Economics’ Analysis
Background to the study
The background to the study contains the following elements:
- The history of the topic, both globally and in the proposed location of your study.
- What other researchers have found out from their own studies.
- What the gaps in the existing literature are, that is, what the other researchers have not addressed.
- What your study will contribute towards filling the identified gaps.
The implication of the above is that one must have conducted some literature review prior to writing the background to the study.
Statement of the problem
The statement of the problem is a clear description of the issue that the study will address, the relevance of the issue, the importance (benefits) of addressing the issue, and the method the researcher will use to address the issue.
Goal and objectives of the study
Once you have identified the problem of your study, the next step is to write the goal and objectives of the study. There is a difference between these two:
The goal of the study is a broad statement of what the researcher hopes to accomplish at the end of the study. The goal should also be related to the problem statement.
Any given project should have one goal because having many goals would lead to confusion. However, that one goal can have multiple elements in it, which would be accomplished through the project’s objectives.
The objectives of the study, on the other hand, are specific and detailed statements of how the researcher will go about accomplishing the stated goal.
The objectives should:
- Support the accomplishment of the goal.
- Follow a sequence, that is, like a step-by-step order. This will help you frame the activities needed to be undertaken in a logical manner so that the goal is achieved.
- Be stated using action verbs, for instance, “to identify”, “to create”, “to establish”, “to measure”, etc.
- Be about 3-4: having too few of objectives will limit the scope of your PhD dissertation, while having too many objectives may complicate the dissertation.
- Be SMART, that is, Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, and Time-bound.
The video below clearly explains how to set SMART goals and objectives:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MAhs-m6cNzY
Important tip 1: depending on your PhD programme, you may be required to have at least 3 journal papers to qualify for graduation. Each of your objectives can be converted into a separate journal paper on its own.
Research questions and hypotheses
Every PhD dissertation needs research questions. Research questions will help the student stay focused on his/her research.
The aim of the research is to provide answers to the research questions. The answers to the questions will form the thesis statement.
Examples of research questions:
In the title example given earlier about use of mobile phone applications for weight management in the United States, a student may be interested in the following questions:
- To what extent do adults in the United States use mobile phone applications to manage their weight?
- Is there any gender disparity in the use of mobile phone apps for weight management in the United States?
- How effective are mobile apps for weight management in the United States?
Good research questions are those that can be explored deeply and widely as well as defended using evidence. Questions with ‘yes” or “no” responses are not academic-worthy.
When developing research questions, you also need to think about the data that will be required to answer the questions. Do you have access to that data? If no, will your time and financial resources allow you to collect that data?
Important tip 2: Your PhD study is time-limited therefore data requirement issues need to be thought through at the initial stages of your concept paper writing so that you don’t waste too much time either collecting the data in the future or trying to access the data if it already exists elsewhere.
Preliminary literature review
At the concept paper stage, a preliminary literature review serves three main purposes:
- It shows whether you have knowledge of the current state of debate about your chosen topic.
- It shows whether you are familiar with the experts in your chosen topic.
- It also helps you identify the research gaps.
Proposed research design, methods and procedures
This sections provides a brief overview of the research methodology that you will adopt in your study. Some issues to consider include:
- Will your study use quantitative, qualitative or mixed-methods approach?
- Will you use secondary or primary data?
- What will be the sources of your data? Will you need any ethical clearance from your university before collecting data?
- Will the data sources be readily accessible?
- Will you use external assistance for data collection? Or will you do all the data collection yourself?
- How will the data be analysed? Which softwares will you use? Are you competent in those softwares?
While the above issues are important to think through, please note that the research design and methods will be informed by your research objectives and research questions. As an illustration:
A research question that aims to measure the effect of one (or more) variable(s) on another variable will definitely require quantitative research methods.
On the other hand, a research question that aims to explain the existence of a phenomenon will render itself to the use of qualitative research methods.
Contribution to knowledge
This is perhaps the most important aspect of a PhD dissertation. Your concept note needs to briefly highlight how your project will add value to knowledge.
Making significant contribution to knowledge at the PhD level does not mean a Nobel prize standard of knowledge (this you can do after your PhD when you’ll have all the time in the world to do so). You can achieve this in various ways:
- New applications of existing ideas.
- New interpretations of previous ideas.
- Investigating an existing issue in a new location.
- Development of a new theory.
- Coming up with a new technique, among others.
The last section of the concept paper is the reference list or bibliography. This is the section that lists the literatures that you have reviewed and cited in your paper.
There is a slight difference between a reference list and a bibliography:
A reference list includes all those studies that have been directly cited in the paper.
A bibliography, on the other hand, includes all those studies that have been directly cited in the paper as well as those that were reviewed and consulted but not cited in the paper.
When creating the reference list/bibliography, one should be mindful of the referencing style that is required by their PhD department (that is, whether APA, MLA, Chicago, Havard, etc).
Final Thoughts on Writing a PhD Concept Paper
The concept paper is the first step to writing the PhD dissertation. Once accepted, the student will proceed to writing the proposal, which will then be defended before proceeding with writing the full dissertation.
The concept paper is a mini-proposal and has most of the components expected in the proposal.
However, the concept paper should be short and precise while at the same time have adequate information to enable the PhD Committee of the PhD Programme the student is applying to judge if the student will be a good fit to the programme or not.
Related posts
How To Choose a Research Topic For Your PhD Thesis (7 Key Factors to Consider)
Comprehensive Guidelines for Writing a PhD Thesis Proposal (+ free checklist for PhD Students)
Grace Njeri-Otieno
Grace Njeri-Otieno is a Kenyan, a wife, a mom, and currently a PhD student, among many other balls she juggles. She holds a Bachelors' and Masters' degrees in Economics and has more than 7 years' experience with an INGO. She was inspired to start this site so as to share the lessons learned throughout her PhD journey with other PhD students. Her vision for this site is "to become a go-to resource center for PhD students in all their spheres of learning."
Recent Content
SPSS Tutorial #11: Correlation Analysis in SPSS
In this post, I discuss what correlation is, the two most common types of correlation statistics used (Pearson and Spearman), and how to conduct correlation analysis in SPSS. What is correlation...
SPSS Tutorial #10: How to Check for Normality of Data in SPSS
The normality assumption states that the data is normally distributed. This post touches on the importance of normality of data and illustrates how to check for normality of data in SPSS. Why...
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step [Template]
How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step [Template]
Table of Contents

How To Write a Research Proposal
Writing a Research proposal involves several steps to ensure a well-structured and comprehensive document. Here is an explanation of each step:
1. Title and Abstract
- Choose a concise and descriptive title that reflects the essence of your research.
- Write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. It should provide a brief overview of your proposal.
2. Introduction:
- Provide an introduction to your research topic, highlighting its significance and relevance.
- Clearly state the research problem or question you aim to address.
- Discuss the background and context of the study, including previous research in the field.
3. Research Objectives
- Outline the specific objectives or aims of your research. These objectives should be clear, achievable, and aligned with the research problem.
4. Literature Review:
- Conduct a comprehensive review of relevant literature and studies related to your research topic.
- Summarize key findings, identify gaps, and highlight how your research will contribute to the existing knowledge.
5. Methodology:
- Describe the research design and methodology you plan to employ to address your research objectives.
- Explain the data collection methods, instruments, and analysis techniques you will use.
- Justify why the chosen methods are appropriate and suitable for your research.
6. Timeline:
- Create a timeline or schedule that outlines the major milestones and activities of your research project.
- Break down the research process into smaller tasks and estimate the time required for each task.
7. Resources:
- Identify the resources needed for your research, such as access to specific databases, equipment, or funding.
- Explain how you will acquire or utilize these resources to carry out your research effectively.
8. Ethical Considerations:
- Discuss any ethical issues that may arise during your research and explain how you plan to address them.
- If your research involves human subjects, explain how you will ensure their informed consent and privacy.
9. Expected Outcomes and Significance:
- Clearly state the expected outcomes or results of your research.
- Highlight the potential impact and significance of your research in advancing knowledge or addressing practical issues.
10. References:
- Provide a list of all the references cited in your proposal, following a consistent citation style (e.g., APA, MLA).
11. Appendices:
- Include any additional supporting materials, such as survey questionnaires, interview guides, or data analysis plans.
Research Proposal Format
The format of a research proposal may vary depending on the specific requirements of the institution or funding agency. However, the following is a commonly used format for a research proposal:
1. Title Page:
- Include the title of your research proposal, your name, your affiliation or institution, and the date.
2. Abstract:
- Provide a brief summary of your research proposal, highlighting the research problem, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes.
3. Introduction:
- Introduce the research topic and provide background information.
- State the research problem or question you aim to address.
- Explain the significance and relevance of the research.
- Review relevant literature and studies related to your research topic.
- Summarize key findings and identify gaps in the existing knowledge.
- Explain how your research will contribute to filling those gaps.
5. Research Objectives:
- Clearly state the specific objectives or aims of your research.
- Ensure that the objectives are clear, focused, and aligned with the research problem.
6. Methodology:
- Describe the research design and methodology you plan to use.
- Explain the data collection methods, instruments, and analysis techniques.
- Justify why the chosen methods are appropriate for your research.
7. Timeline:
8. Resources:
- Explain how you will acquire or utilize these resources effectively.
9. Ethical Considerations:
- If applicable, explain how you will ensure informed consent and protect the privacy of research participants.
10. Expected Outcomes and Significance:
11. References:
12. Appendices:
Research Proposal Template
Here’s a template for a research proposal:
1. Introduction:
2. Literature Review:
3. Research Objectives:
4. Methodology:
5. Timeline:
6. Resources:
7. Ethical Considerations:
8. Expected Outcomes and Significance:
9. References:
10. Appendices:
Research Proposal Sample
Title: The Impact of Online Education on Student Learning Outcomes: A Comparative Study
1. Introduction
Online education has gained significant prominence in recent years, especially due to the COVID-19 pandemic. This research proposal aims to investigate the impact of online education on student learning outcomes by comparing them with traditional face-to-face instruction. The study will explore various aspects of online education, such as instructional methods, student engagement, and academic performance, to provide insights into the effectiveness of online learning.
2. Objectives
The main objectives of this research are as follows:
- To compare student learning outcomes between online and traditional face-to-face education.
- To examine the factors influencing student engagement in online learning environments.
- To assess the effectiveness of different instructional methods employed in online education.
- To identify challenges and opportunities associated with online education and suggest recommendations for improvement.
3. Methodology
3.1 Study Design
This research will utilize a mixed-methods approach to gather both quantitative and qualitative data. The study will include the following components:
3.2 Participants
The research will involve undergraduate students from two universities, one offering online education and the other providing face-to-face instruction. A total of 500 students (250 from each university) will be selected randomly to participate in the study.
3.3 Data Collection
The research will employ the following data collection methods:
- Quantitative: Pre- and post-assessments will be conducted to measure students’ learning outcomes. Data on student demographics and academic performance will also be collected from university records.
- Qualitative: Focus group discussions and individual interviews will be conducted with students to gather their perceptions and experiences regarding online education.
3.4 Data Analysis
Quantitative data will be analyzed using statistical software, employing descriptive statistics, t-tests, and regression analysis. Qualitative data will be transcribed, coded, and analyzed thematically to identify recurring patterns and themes.
4. Ethical Considerations
The study will adhere to ethical guidelines, ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of participants. Informed consent will be obtained, and participants will have the right to withdraw from the study at any time.
5. Significance and Expected Outcomes
This research will contribute to the existing literature by providing empirical evidence on the impact of online education on student learning outcomes. The findings will help educational institutions and policymakers make informed decisions about incorporating online learning methods and improving the quality of online education. Moreover, the study will identify potential challenges and opportunities related to online education and offer recommendations for enhancing student engagement and overall learning outcomes.
6. Timeline
The proposed research will be conducted over a period of 12 months, including data collection, analysis, and report writing.
The estimated budget for this research includes expenses related to data collection, software licenses, participant compensation, and research assistance. A detailed budget breakdown will be provided in the final research plan.
8. Conclusion
This research proposal aims to investigate the impact of online education on student learning outcomes through a comparative study with traditional face-to-face instruction. By exploring various dimensions of online education, this research will provide valuable insights into the effectiveness and challenges associated with online learning. The findings will contribute to the ongoing discourse on educational practices and help shape future strategies for maximizing student learning outcomes in online education settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Proposal – Types, Examples, and Writing Guide

Business Proposal – Templates, Examples and Guide

How to choose an Appropriate Method for Research?

Grant Proposal – Example, Template and Guide

Research Proposal – Types, Template and Example

How To Write A Business Proposal – Step-by-Step...
- How It Works
- Prices & Discounts
How to Write a Concept Paper for a PhD: A 10-Step Guide
Table of contents
You’re ready to enroll for your Ph.D. studies but feeling anxious. You don’t know whether your application will be accepted or what it would take to be accepted.
Aside from your academic qualifications, a concept paper is one of the most critical determinants. If you’re planning to pursue a Ph.D., you need to learn how to write an effective concept paper to convince your professors.
Writing a concept paper requires strong analytical skills, advanced research knowledge, and excellent writing skills.
This blog post will give you a step-by-step guide on how to write a concept paper for a Ph.D. to get you a step closer to becoming a doctor of philosophy.
What is a concept paper for Ph.D.?
A concept paper for a Ph.D. is a written statement outlining the objectives and concepts of a proposed research study. It acts as an introduction to your dissertation or full thesis.
It is also an important part of the application process for Ph.D. programs and helps the admissions committee evaluate a student's research potential.
It typically includes background information on the topic to be studied, an overview of existing research, and the proposed research design. It also highlights potential results from the proposed study and their practical applications.
Ultimately, concept papers for Ph.D. programs help determine whether a student is qualified to pursue doctoral-level work in their chosen field.
How long is a Ph.D. concept paper?
The length of your concept paper will depend on your field of study and the requirements set by your university. Generally speaking, most universities expect concept papers to be between 3-5 pages long. Some papers may be longer or shorter depending on how much detail your project entails.
Key takeaways
A concept paper for Ph.D. includes:
- Background information on the topic;
- Overview of existing research;
- Proposed research design;
- Potential results from the study;
- Practical applications of the study.
How to Write a Concept Paper for Ph.D.?
An effective concept paper will help you get approval from your professor or adviser to begin your doctoral work.
What are the characteristics of a good concept paper?
A good concept paper should present an idea or topic in a clear and concise manner. It should provide an overview of what the research project will cover and explain why it’s important.
Additionally, it should highlight any potential implications of the research study and how they can be addressed or minimized. The goal of the paper is to convince the reader that your proposed project is worth pursuing and that it contributes new knowledge to your field of study.
What are the 5 elements of a concept paper?
The five elements of a concept paper are:
- Background;
- Purpose statement;
- Problem statement;
- Research questions or hypotheses;
- Significance or implications for practice.
These elements work together to provide a comprehensive overview of your proposed research project and show why it’s worth pursuing.
Here are the steps to write an outstanding concept paper that stands no chance of being rejected.
1. Define the title and purpose of your study
The first step in writing a concept paper is defining the title and purpose of your study. What will your research be about? And what are you trying to accomplish through it?
The title and purpose of your study will set the foundation for your concept paper. This part should be concise and clear so that readers understand the basis and significance of your research. When formulating the title, ensure it accurately reflects the main focus of your entire research study.
2. Describe the background and scope of your study
The next step is to provide an overview of the background information of your study topic and explain how it relates to your proposed project.
When describing the background of your study, you need to provide some context about why this topic is important enough to warrant academic inquiry.
Highlight any existing studies or theories related to your topic so that readers understand why you have chosen it as part of your dissertation research.
3. Identify the problem statement
Next, identify a problem statement that outlines what issue or gap in the knowledge you are attempting to address through your research project. Every good concept paper should include a well thought problem statement.
Your problem statement should be precise and concise so readers can easily understand what they can expect from reading further.
Here, you should make it clear why there’s a need for further investigation in your chosen field and how your research will contribute new insights into existing knowledge.
4. List your goals and objectives
Now that you’ve established your problem statement, you need to outline the specific goals and objectives that will guide you through your research.
Here, you outline what steps you’ll take and what specifically you hope to achieve in every stage of the study. This could mean anything from creating new theories, testing existing theories or models, exploring the techniques used in other studies, etc.
Your goals and objectives will give the readers a heads-up about what outcomes they can expect from the project.
Ensure whatever goals and objectives you list are measurable and achievable within the scope of your research study.
5. Formulate research questions
Next, formulate detailed research questions (and accompanying hypotheses) based on the topic you plan to explore.
These questions should include the variables you plan to manipulate or measure during data collection. Ensure the questions are clear and written in simple language so readers can understand what you’ll address through the study.
Also, don’t forget to create hypotheses for every research question you write. These are specific claims that will act as the starting points for further inquiry and potential conclusions for the study.
6. Explain the theoretical framework of the study
Once you’ve formulated your research questions, the next step is to explain the theoretical framework or foundational concept of the study.
Identify and briefly explain the theories that inspired you and connect them back to your intended study.
This will set out the context of your project and show that you’ve read and understood existing knowledge on the subject. This theoretical knowledge will come in handy if your application is accepted.
7. Write the literature review
The next step is to write the literature review . Here, you identify information and existing knowledge from previous studies and other published articles.
Your literature review should also include summaries or reviews of key texts related to your topic. You can get information for this section from peer-reviewed articles and online journals like OpenDOAR and CORE.
Remember, all the facts, statistics, and other relevant information must be accompanied by appropriate citations and references.
8. Describe the proposed research methodology
After writing the literature review, go ahead and describe the research design and methodology you’ll be employing.
Some of the critical details to include in this section include:
- What data collection methods you’ll use? (e.g., surveys, interviews, or questionnaires).
- How many participants will form your sample size?
- What data analysis methods will you use? (e.g., qualitative versus quantitative).
Be sure to highlight any ethical considerations involved in your research methodology. For instance, explain the informed consent procedures you’ll use if your research involves human participation.
Also, explain how you’ll minimize the potential risks associated with participating in your research activities.
9. Explain the significance of the study (and its implications)
Now that you’ve explained the methodology, it’s time to let the readers understand why this study is important and why it makes a significant contribution to existing research.
Additionally, explain how this study will impact theory development and its significance for policymakers or practitioners in your field of study.
You should also discuss any potential implications of conducting this research (e.g., ethical considerations or political ramifications).
10. Include references/bibliography
Finally, include references or a bibliography at the end of your concept paper to build credibility for your research paper.
A bibliography enables you to give credit where it belongs by recognizing the owners of your reference materials.
Ensure you format references properly according to the style specified by the institution you’re applying to. This could be for example APA , MLA, or Harvard referencing style .
What is the difference between a concept paper and a research paper?
A concept paper outlines what you plan to do (in future tense), while a research paper explains what you did (in past tense) after completing your research project. In other words, a concept paper serves as an introduction to your research, while a research paper provides evidence-based results from experiments conducted during your study.
Final thoughts
The thought of writing a concept paper for your Ph.D. can be intimidating at first. However, once you know the right approach to take and invest enough time, the writing process becomes hassle-free.
Start by brainstorming your ideas, researching related topics, and creating an outline. Also, ensure you clearly define your concept and know the exact approach you’ll be taking. This way, you won’t find yourself stuck when your concept paper has been approved for further research.
After completing the paper, revise it to ensure everything is clear and accurate with no typos. In the end, you’ll have an excellent concept paper that will pave the way for you to pursue your doctoral studies.
If you need help writing a concept paper for your Ph.D., turn to Writers Per Hour for assistance. With expert Doctoral writers on the team, we can draft a compelling concept paper that is 100% original and written from scratch as per your requirements.
Share this article
Achieve Academic Success with Expert Assistance!
Crafted from Scratch for You.
Ensuring Your Work’s Originality.
Transform Your Draft into Excellence.
Perfecting Your Paper’s Grammar, Style, and Format (APA, MLA, etc.).
Calculate the cost of your paper
Get ideas for your essay

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A concept paper primarily focuses on introducing the basic idea, intended research question, and the framework that will guide the research. Purpose of a Concept Paper. A concept paper serves as an initial document, commonly required by private organizations before a formal proposal submission.
follow these steps: 1. Concept paper title. Every pa per must have a title and concept paper is not left out as one needs to have a title that. summarizes what the paper is about. The title should ...
Research grant concept papers. Concept Paper vs. Research Proposal. Getting Started on Your Concept Paper. 1. Find a research topic you are interested in. Tips for finding your research topic. 2. Think of research questions that you want to answer in your project. 3.
On the surface, concept papers sound like they do the same job as a research proposal - and essentially, they do. Both are designed to communicate the rationale, methodology and outcomes of a proposed piece of work. The difference between the two lies mostly in the level of detail and the potential audience, based on which your approach ...
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management".
1. To explore and expand an idea: Researchers can use concept papers to transform an incipient research idea into a focused, high-quality study proposal. The paper is also a means to obtain feedback that can be used to strengthen a detailed proposal at a later stage. 2. To draw the interest of funding agencies: Through an effective concept ...
to interest potential funders. to develop potential solutions or investigations into project ideas. to determine whether a project idea is fundable. to serve as the foundation of a full proposal. Funders that request concept papers often provide a template or format. If templates or formats are not provided, the following can serve as a useful ...
The concept paper will include your proposed research title, a brief introduction to the subject, the aim of the study, the research questions you intend to answer, the type of data you will collect and how you will collect it. A concept paper can also be referred to as a research proposal.
1. To explore and expand an idea: Researchers can use concept papers to transform an incipient research idea into a focused, high-quality study proposal. The paper is also a means to obtain ...
Funders often ask for brief 1- to 5-page concept papers (also called "white papers" in the government contracting sector) prior to submission of a full proposal. This helps them save time by eliminating ideas that are not likely to be funded. Applicants may use concept papers in any of the following ways: to interest potential funders;
The purpose of the research proposal (its job, so to speak) is to convince your research supervisor, committee or university that your research is suitable (for the requirements of the degree program) and manageable (given the time and resource constraints you will face). The most important word here is "convince" - in other words, your ...
A pre-proposal or white paper is. a concise, authoritative document that presents a summary of the proposed research, methodology, team, and an estimated budget. Unlike proposals, which include more extensive information, white papers offer a brief overview of. a research project in a way that explores why it would be important to a funder.
A concept paper might be the first thing a funding round requests to get an idea of what the project is all about. So make sure that it includes: Importance of the work being proposed. What the impact (not the same as ' impact factor ' - see later below) will be. How the outcomes of your project might meet or respond to the need.
of the proposal. However, they differ from both research proposal and original research paper in lacking a detailed plan and methodology for a specific study as in research proposal provides and exclusion of the findings and analysis of a completed research project as in an original research paper. A concept paper primarily focuses on
The concept paper, sometimes called a prospectus, preliminary proposal, or pre-proposal, is a useful tool for several purposes. It helps clarify and organize ideas in a written form and provides the basis for a funding search. From the concept paper, an individual is able to develop any number of grant applications for the same idea.
A concept paper is basically a shorter version of a research proposal - in most cases between 2,000 and 2,500 words - that expresses the research ideas of the potential PhD student. Besides being short, it should be concise yet have adequate details to convince the Department the student is applying to that he/she is worth being admitted to ...
Descriptions for each component of your idea - Because a concept paper is essentially a brief version of a full proposal, completing it will compel you to carefully and thoughtfully think through your entire research project. Targeting potential funders - After reviewing your concept paper, C3's Research
Here is an explanation of each step: 1. Title and Abstract. Choose a concise and descriptive title that reflects the essence of your research. Write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. It should provide a brief overview of your proposal. 2.
The technique of using the short title instead of "this study" or "this project" in the concept paper can help embed the content of your research proposal in the project officer's mind, a tremendous advantage given the hundreds of proposals they review. A concept paper is an overview of your proposed research.
A concept paper for a Ph.D. is a written statement outlining the objectives and concepts of a proposed research study. It acts as an introduction to your dissertation or full thesis. It is also an important part of the application process for Ph.D. programs and helps the admissions committee evaluate a student's research potential.
FORMAT OF A CONCEPT PAPER/ RESEARCH PROPOSAL Tentative Title Background/ Justification/ Introduction (100-500 words) General Objective and Specific Objectives (in point form) Literature Review (briefly indicating the significant ones) Methodology (materials and methods) o Study site/s o Design of experiment / Survey
This means you do not need to wait for a funding agency to put out a call for proposals that matches your research to share your project ideas. ... OSPR is happy to review and offer edits and revisions on concept papers and proposals. Unless the sponsor guidelines state otherwise, your concept paper should have 1" margins, use an 11- or 12 ...