Albert Einstein
One of the most influential scientists of the 20 th century, Albert Einstein was a physicist who developed the theory of relativity.

We may earn commission from links on this page, but we only recommend products we back.

Quick Facts
Early life, family, and education, einstein’s iq, patent clerk, inventions and discoveries, nobel prize in physics, wives and children, travel diaries, becoming a u.s. citizen, einstein and the atomic bomb, time travel and quantum theory, personal life, death and final words, einstein’s brain, einstein in books and movies: "oppenheimer" and more, who was albert einstein.
Albert Einstein was a German mathematician and physicist who developed the special and general theories of relativity. In 1921, he won the Nobel Prize in Physics for his explanation of the photoelectric effect. In the following decade, he immigrated to the United States after being targeted by the German Nazi Party. His work also had a major impact on the development of atomic energy. In his later years, Einstein focused on unified field theory. He died in April 1955 at age 76. With his passion for inquiry, Einstein is generally considered the most influential physicist of the 20 th century.
FULL NAME: Albert Einstein BORN: March 14, 1879 DIED: April 18, 1955 BIRTHPLACE: Ulm, Württemberg, Germany SPOUSES: Mileva Einstein-Maric (1903-1919) and Elsa Einstein (1919-1936) CHILDREN: Lieserl, Hans, and Eduard ASTROLOGICAL SIGN: Pisces
Albert Einstein was born on March 14, 1879, in Ulm, Württemberg, Germany. He grew up in a secular Jewish family. His father, Hermann Einstein, was a salesman and engineer who, with his brother, founded Elektrotechnische Fabrik J. Einstein & Cie, a Munich-based company that mass-produced electrical equipment. Einstein’s mother, the former Pauline Koch, ran the family household. Einstein had one sister, Maja, born two years after him.
Einstein attended elementary school at the Luitpold Gymnasium in Munich. However, he felt alienated there and struggled with the institution’s rigid pedagogical style. He also had what were considered speech challenges. However, he developed a passion for classical music and playing the violin, which would stay with him into his later years. Most significantly, Einstein’s youth was marked by deep inquisitiveness and inquiry.
Toward the end of the 1880s, Max Talmud, a Polish medical student who sometimes dined with the Einstein family, became an informal tutor to young Einstein. Talmud had introduced his pupil to a children’s science text that inspired Einstein to dream about the nature of light. Thus, during his teens, Einstein penned what would be seen as his first major paper, “The Investigation of the State of Aether in Magnetic Fields.”
Hermann relocated the family to Milan, Italy, in the mid-1890s after his business lost out on a major contract. Einstein was left at a relative’s boarding house in Munich to complete his schooling at the Luitpold.
Faced with military duty when he turned of age, Einstein allegedly withdrew from classes, using a doctor’s note to excuse himself and claim nervous exhaustion. With their son rejoining them in Italy, his parents understood Einstein’s perspective but were concerned about his future prospects as a school dropout and draft dodger.
Einstein was eventually able to gain admission into the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich, specifically due to his superb mathematics and physics scores on the entrance exam. He was still required to complete his pre-university education first and thus attended a high school in Aarau, Switzerland, helmed by Jost Winteler. Einstein lived with the schoolmaster’s family and fell in love with Winteler’s daughter Marie. Einstein later renounced his German citizenship and became a Swiss citizen at the dawn of the new century.
Einstein’s intelligence quotient was estimated to be around 160, but there are no indications he was ever actually tested.
Psychologist David Wechsler didn’t release the first edition of the WAIS cognitive test, which evolved into the WAIS-IV test commonly used today, until 1955—shortly before Einstein’s death. The maximum score of the current version is 160, with an IQ of 135 or higher ranking in the 99 th percentile.
Magazine columnist Marilyn vos Savant has the highest-ever recorded IQ at 228 and was featured in the Guinness Book of World Records in the late 1980s. However, Guinness discontinued the category because of debates about testing accuracy. According to Parade , individuals believed to have higher IQs than Einstein include Leonardo Da Vinci , Marie Curie , Nikola Tesla , and Nicolaus Copernicus .
After graduating from university, Einstein faced major challenges in terms of finding academic positions, having alienated some professors over not attending class more regularly in lieu of studying independently.
Einstein eventually found steady work in 1902 after receiving a referral for a clerk position in a Swiss patent office. While working at the patent office, Einstein had the time to further explore ideas that had taken hold during his university studies and thus cemented his theorems on what would be known as the principle of relativity.
In 1905—seen by many as a “miracle year” for the theorist—Einstein had four papers published in the Annalen der Physik , one of the best-known physics journals of the era. Two focused on the photoelectric effect and Brownian motion. The two others, which outlined E=MC 2 and the special theory of relativity, were defining for Einstein’s career and the course of the study of physics.
As a physicist, Einstein had many discoveries, but he is perhaps best known for his theory of relativity and the equation E=MC 2 , which foreshadowed the development of atomic power and the atomic bomb.
Theory of Relativity
Einstein first proposed a special theory of relativity in 1905 in his paper “On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies,” which took physics in an electrifying new direction. The theory explains that space and time are actually connected, and Einstein called this joint structure space-time.
By November 1915, Einstein completed the general theory of relativity, which accounted for gravity’s relationship to space-time. Einstein considered this theory the culmination of his life research. He was convinced of the merits of general relativity because it allowed for a more accurate prediction of planetary orbits around the sun, which fell short in Isaac Newton ’s theory. It also offered a more expansive, nuanced explanation of how gravitational forces worked.
Einstein’s assertions were affirmed via observations and measurements by British astronomers Sir Frank Dyson and Sir Arthur Eddington during the 1919 solar eclipse, and thus a global science icon was born. Today, the theories of relativity underpin the accuracy of GPS technology, among other phenomena.
Even so, Einstein did make one mistake when developing his general theory, which naturally predicted the universe is either expanding or contracting. Einstein didn’t believe this prediction initially, instead holding onto the belief that the universe was a fixed, static entity. To account for, this he factored in a “cosmological constant” to his equation. His later theories directly contracted this idea and asserted that the universe could be in a state of flux. Then, astronomer Edwin Hubble deduced that we indeed inhabit an expanding universe. Hubble and Einstein met at the Mount Wilson Observatory near Los Angeles in 1931.
Decades after Einstein’s death, in 2018, a team of scientists confirmed one aspect of Einstein’s general theory of relativity: that the light from a star passing close to a black hole would be stretched to longer wavelengths by the overwhelming gravitational field. Tracking star S2, their measurements indicated that the star’s orbital velocity increased to over 25 million kph as it neared the supermassive black hole at the center of the galaxy, its appearance shifting from blue to red as its wavelengths stretched to escape the pull of gravity.
Einstein’s E=MC²
Einstein’s 1905 paper on the matter-energy relationship proposed the equation E=MC²: the energy of a body (E) is equal to the mass (M) of that body times the speed of light squared (C²). This equation suggested that tiny particles of matter could be converted into huge amounts of energy, a discovery that heralded atomic power.
Famed quantum theorist Max Planck backed up the assertions of Einstein, who thus became a star of the lecture circuit and academia, taking on various positions before becoming director of the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Physics (today is known as the Max Planck Institute for Physics) from 1917 to 1933.
In 1921, Einstein won the Nobel Prize in Physics for his explanation of the photoelectric effect, since his ideas on relativity were still considered questionable. He wasn’t actually given the award until the following year due to a bureaucratic ruling, and during his acceptance speech, he still opted to speak about relativity.
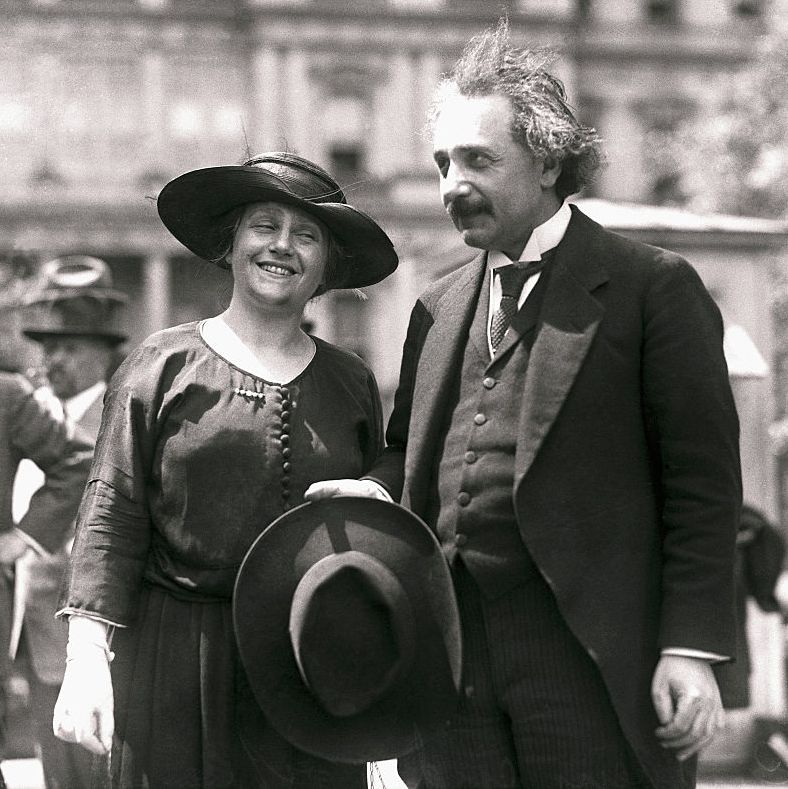

Einstein married Mileva Maric on January 6, 1903. While attending school in Zurich, Einstein met Maric, a Serbian physics student. Einstein continued to grow closer to Maric, but his parents were strongly against the relationship due to her ethnic background.
Nonetheless, Einstein continued to see her, with the two developing a correspondence via letters in which he expressed many of his scientific ideas. Einstein’s father passed away in 1902, and the couple married shortly thereafter.
Einstein and Mavic had three children. Their daughter, Lieserl, was born in 1902 before their wedding and might have been later raised by Maric’s relatives or given up for adoption. Her ultimate fate and whereabouts remain a mystery. The couple also had two sons: Hans Albert Einstein, who became a well-known hydraulic engineer, and Eduard “Tete” Einstein, who was diagnosed with schizophrenia as a young man.
The Einsteins’ marriage would not be a happy one, with the two divorcing in 1919 and Maric having an emotional breakdown in connection to the split. Einstein, as part of a settlement, agreed to give Maric any funds he might receive from possibly winning the Nobel Prize in the future.
During his marriage to Maric, Einstein had also begun an affair some time earlier with a cousin, Elsa Löwenthal . The couple wed in 1919, the same year of Einstein’s divorce. He would continue to see other women throughout his second marriage, which ended with Löwenthal’s death in 1936.
In his 40s, Einstein traveled extensively and journaled about his experiences. Some of his unfiltered private thoughts are shared two volumes of The Travel Diaries of Albert Einstein .
The first volume , published in 2018, focuses on his five-and-a-half month trip to the Far East, Palestine, and Spain. The scientist started a sea journey to Japan in Marseille, France, in autumn of 1922, accompanied by his second wife, Elsa. They journeyed through the Suez Canal, then to Sri Lanka, Singapore, Hong Kong, Shanghai, and Japan. The couple returned to Germany via Palestine and Spain in March 1923.
The second volume , released in 2023, covers three months that he spent lecturing and traveling in Argentina, Uruguay, and Brazil in 1925.
The Travel Diaries contain unflattering analyses of the people he came across, including the Chinese, Sri Lankans, and Argentinians, a surprise coming from a man known for vehemently denouncing racism in his later years. In an entry for November 1922, Einstein refers to residents of Hong Kong as “industrious, filthy, lethargic people.”
In 1933, Einstein took on a position at the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey, where he would spend the rest of his life.
At the time the Nazis, led by Adolf Hitler , were gaining prominence with violent propaganda and vitriol in an impoverished post-World War I Germany. The Nazi Party influenced other scientists to label Einstein’s work “Jewish physics.” Jewish citizens were barred from university work and other official jobs, and Einstein himself was targeted to be killed. Meanwhile, other European scientists also left regions threatened by Germany and immigrated to the United States, with concern over Nazi strategies to create an atomic weapon.
Not long after moving and beginning his career at IAS, Einstein expressed an appreciation for American meritocracy and the opportunities people had for free thought, a stark contrast to his own experiences coming of age. In 1935, Einstein was granted permanent residency in his adopted country and became an American citizen five years later.
In America, Einstein mostly devoted himself to working on a unified field theory, an all-embracing paradigm meant to unify the varied laws of physics. However, during World War II, he worked on Navy-based weapons systems and made big monetary donations to the military by auctioning off manuscripts worth millions.
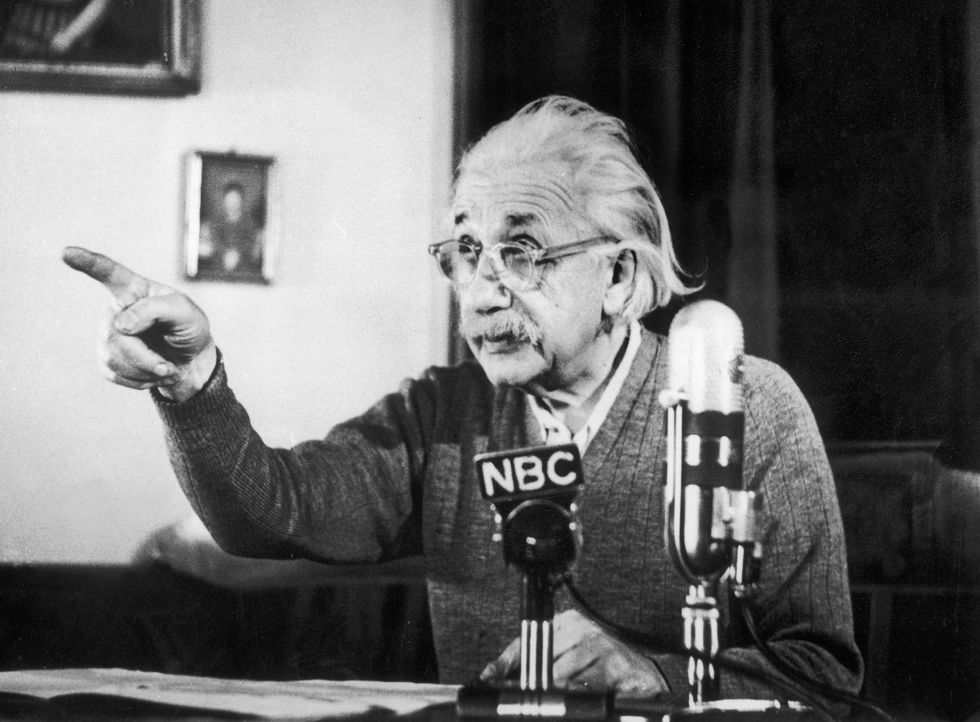

In 1939, Einstein and fellow physicist Leo Szilard wrote to President Franklin D. Roosevelt to alert him of the possibility of a Nazi bomb and to galvanize the United States to create its own nuclear weapons.
The United States would eventually initiate the Manhattan Project , though Einstein wouldn’t take a direct part in its implementation due to his pacifist and socialist affiliations. Einstein was also the recipient of much scrutiny and major distrust from FBI director J. Edgar Hoover . In July 1940, the U.S. Army Intelligence office denied Einstein a security clearance to participate in the project, meaning J. Robert Oppenheimer and the scientists working in Los Alamos were forbidden from consulting with him.
Einstein had no knowledge of the U.S. plan to use atomic bombs in Japan in 1945. When he heard of the first bombing at Hiroshima, he reportedly said, “Ach! The world is not ready for it.”
Einstein became a major player in efforts to curtail usage of the A-bomb. The following year, he and Szilard founded the Emergency Committee of Atomic Scientists, and in 1947, via an essay for The Atlantic Monthly , Einstein espoused working with the United Nations to maintain nuclear weapons as a deterrent to conflict.
After World War II, Einstein continued to work on his unified field theory and key aspects of his general theory of relativity, including time travel, wormholes, black holes, and the origins of the universe.
However, he felt isolated in his endeavors since the majority of his colleagues had begun focusing their attention on quantum theory. In the last decade of his life, Einstein, who had always seen himself as a loner, withdrew even further from any sort of spotlight, preferring to stay close to Princeton and immerse himself in processing ideas with colleagues.
In the late 1940s, Einstein became a member of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP), seeing the parallels between the treatment of Jews in Germany and Black people in the United States. He corresponded with scholar and activist W.E.B. Du Bois as well as performer Paul Robeson and campaigned for civil rights, calling racism a “disease” in a 1946 Lincoln University speech.
Einstein was very particular about his sleep schedule, claiming he needed 10 hours of sleep per day to function well. His theory of relativity allegedly came to him in a dream about cows being electrocuted. He was also known to take regular naps. He is said to have held objects like a spoon or pencil in his hand while falling asleep. That way, he could wake up before hitting the second stage of sleep—a hypnagogic process believed to boost creativity and capture sleep-inspired ideas.
Although sleep was important to Einstein, socks were not. He was famous for refusing to wear them. According to a letter he wrote to future wife Elsa, he stopped wearing them because he was annoyed by his big toe pushing through the material and creating a hole.
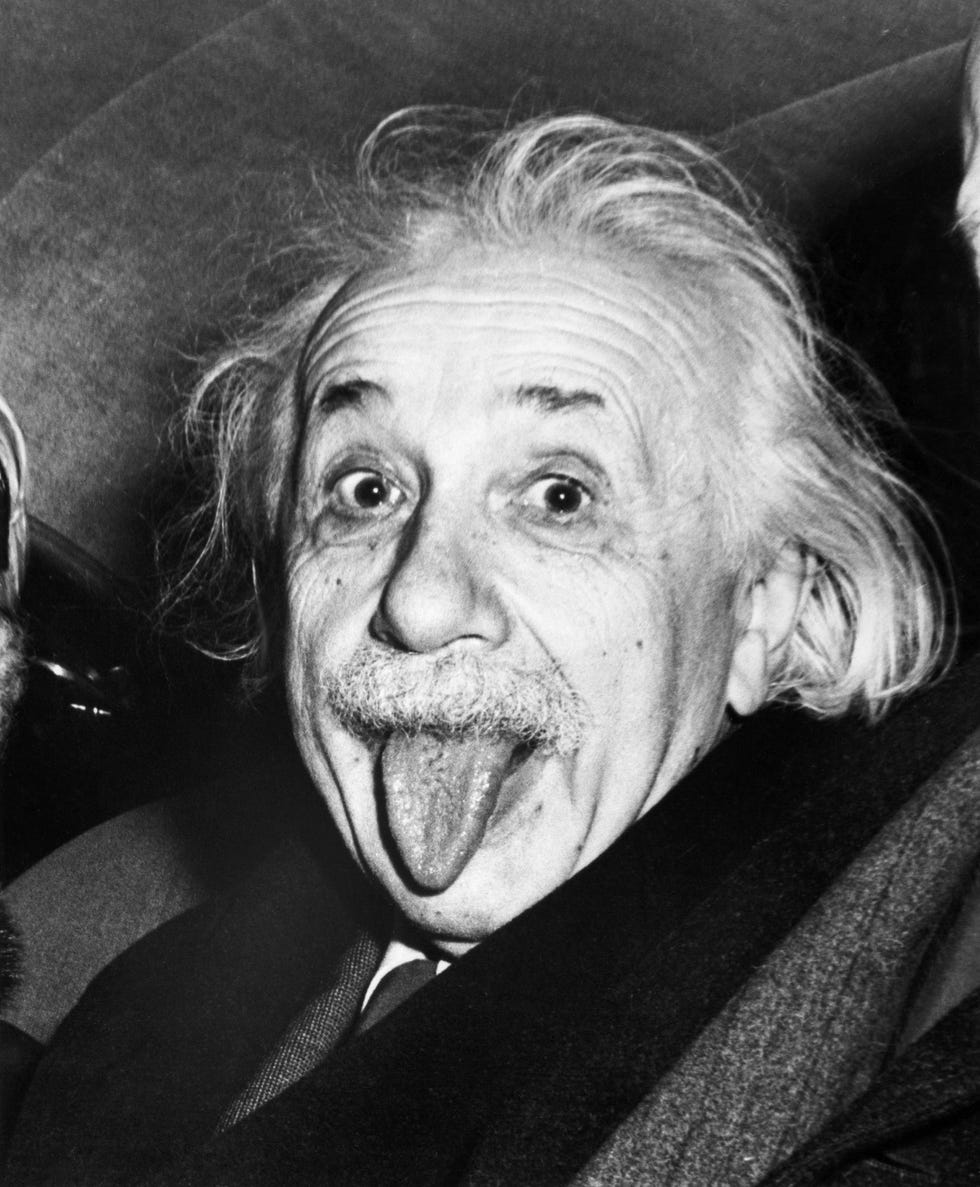

One of the most recognizable photos of the 20 th century shows Einstein sticking out his tongue while leaving his 72 nd birthday party on March 14, 1951.
According to Discovery.com , Einstein was leaving his party at Princeton when a swarm of reporters and photographers approached and asked him to smile. Tired from doing so all night, he refused and rebelliously stuck his tongue out at the crowd for a moment before turning away. UPI photographer Arthur Sasse captured the shot.
Einstein was amused by the picture and ordered several prints to give to his friends. He also signed a copy of the photo that sold for $125,000 at a 2017 auction.
Einstein died on April 18, 1955, at age 76 at the University Medical Center at Princeton. The previous day, while working on a speech to honor Israel’s seventh anniversary, Einstein suffered an abdominal aortic aneurysm.
He was taken to the hospital for treatment but refused surgery, believing that he had lived his life and was content to accept his fate. “I want to go when I want,” he stated at the time. “It is tasteless to prolong life artificially. I have done my share, it is time to go. I will do it elegantly.”
According to the BBC, Einstein muttered a few words in German at the moment of his death. However, the nurse on duty didn’t speak German so their translation was lost forever.
In a 2014 interview , Life magazine photographer Ralph Morse said the hospital was swarmed by journalists, photographers, and onlookers once word of Einstein’s death spread. Morse decided to travel to Einstein’s office at the Institute for Advanced Studies, offering the superintendent alcohol to gain access. He was able to photograph the office just as Einstein left it.
After an autopsy, Einstein’s corpse was moved to a Princeton funeral home later that afternoon and then taken to Trenton, New Jersey, for a cremation ceremony. Morse said he was the only photographer present for the cremation, but Life managing editor Ed Thompson decided not to publish an exclusive story at the request of Einstein’s son Hans.
During Einstein’s autopsy, pathologist Thomas Stoltz Harvey had removed his brain, reportedly without his family’s consent, for preservation and future study by doctors of neuroscience.
However, during his life, Einstein participated in brain studies, and at least one biography claimed he hoped researchers would study his brain after he died. Einstein’s brain is now located at the Princeton University Medical Center. In keeping with his wishes, the rest of his body was cremated and the ashes scattered in a secret location.
In 1999, Canadian scientists who were studying Einstein’s brain found that his inferior parietal lobe, the area that processes spatial relationships, 3D-visualization, and mathematical thought, was 15 percent wider than in people who possess normal intelligence. According to The New York Times , the researchers believe it might help explain why Einstein was so intelligent.
In 2011, the Mütter Museum in Philadelphia received thin slices of Einstein’s brain from Dr. Lucy Rorke-Adams, a neuropathologist at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, and put them on display. Rorke-Adams said she received the brain slides from Harvey.
Since Einstein’s death, a veritable mountain of books have been written on the iconic thinker’s life, including Einstein: His Life and Universe by Walter Isaacson and Einstein: A Biography by Jürgen Neffe, both from 2007. Einstein’s own words are presented in the collection The World As I See It .
Einstein has also been portrayed on screen. Michael Emil played a character called “The Professor,” clearly based on Einstein, in the 1985 film Insignificance —in which alternate versions of Einstein, Marilyn Monroe , Joe DiMaggio , and Joseph McCarthy cross paths in a New York City hotel.
Walter Matthau portrayed Einstein in the fictional 1994 comedy I.Q. , in which he plays matchmaker for his niece played by Meg Ryan . Einstein was also a character in the obscure comedy films I Killed Einstein, Gentlemen (1970) and Young Einstein (1988).
A much more historically accurate depiction of Einstein came in 2017, when he was the subject of the first season of Genius , a 10-part scripted miniseries by National Geographic. Johnny Flynn played a younger version of the scientist, while Geoffrey Rush portrayed Einstein in his later years after he had fled Germany. Ron Howard was the director.
Tom Conti plays Einstein in the 2023 biopic Oppenheimer , directed by Christopher Nolan and starring Cillian Murphy as scientist J. Robert Oppenheimer during his involvement with the Manhattan Project.
- The world is a dangerous place to live; not because of the people who are evil, but because of the people who don’t do anything about it.
- A question that sometimes drives me hazy: Am I or are the others crazy?
- A person who never made a mistake never tried anything new.
- Logic will get you from A to B. Imagination will take you everywhere.
- I want to go when I want. It is tasteless to prolong life artificially. I have done my share, it is time to go. I will do it elegantly.
- If you can’t explain it simply, you don’t understand it well enough.
- Nature shows us only the tail of the lion. But there is no doubt in my mind that the lion belongs with it even if he cannot reveal himself to the eye all at once because of his huge dimension. We see him only the way a louse sitting upon him would.
- [T]he distinction between past, present, and future is only an illusion, however persistent.
- Living in this “great age,” it is hard to understand that we belong to this mad, degenerate species, which imputes free will to itself. If only there were somewhere an island for the benevolent and the prudent! Then also I would want to be an ardent patriot.
- I, at any rate, am convinced that He [God] is not playing at dice.
- How strange is the lot of us mortals! Each of us is here for a brief sojourn; for what purpose he knows not, though he sometimes thinks he senses it.
- I regard class differences as contrary to justice and, in the last resort, based on force.
- I have never looked upon ease and happiness as ends in themselves—this critical basis I call the ideal of a pigsty. The ideals that have lighted my way, and time after time have given me new courage to face life cheerfully, have been Kindness, Beauty, and Truth.
- My political ideal is democracy. Let every man be respected as an individual and no man idolized. It is an irony of fate that I myself have been the recipient of excessive admiration and reverence from my fellow-beings, through no fault and no merit of my own.
- The most beautiful experience we can have is the mysterious. It is the fundamental emotion that stands at the cradle of true art and true science. Whoever does not know it and can no longer wonder, no longer marvel, is as good as dead, and his eyes are dimmed.
- An autocratic system of coercion, in my opinion, soon degenerates. For force always attracts men of low morality, and I believe it to be an invariable rule that tyrants of genius are succeeded by scoundrels.
- My passionate interest in social justice and social responsibility has always stood in curious contrast to a marked lack of desire for direct association with men and women. I am a horse for single harness, not cut out for tandem or team work. I have never belonged wholeheartedly to country or state, to my circle of friends, or even to my own family.
- Everybody is a genius.
Fact Check: We strive for accuracy and fairness. If you see something that doesn’t look right, contact us !
The Biography.com staff is a team of people-obsessed and news-hungry editors with decades of collective experience. We have worked as daily newspaper reporters, major national magazine editors, and as editors-in-chief of regional media publications. Among our ranks are book authors and award-winning journalists. Our staff also works with freelance writers, researchers, and other contributors to produce the smart, compelling profiles and articles you see on our site. To meet the team, visit our About Us page: https://www.biography.com/about/a43602329/about-us
Tyler Piccotti first joined the Biography.com staff as an Associate News Editor in February 2023, and before that worked almost eight years as a newspaper reporter and copy editor. He is a graduate of Syracuse University. When he's not writing and researching his next story, you can find him at the nearest amusement park, catching the latest movie, or cheering on his favorite sports teams.
Nobel Prize Winners
The Solar Eclipse That Made Albert Einstein a Star

14 Hispanic Women Who Have Made History

Marie Curie

Martin Luther King Jr.

Henry Kissinger

Malala Yousafzai

Jimmy Carter

10 Famous Poets Whose Enduring Works We Still Read

22 Famous Scientists You Should Know

Wole Soyinka

Jean-Paul Sartre
- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
Albert Einstein
By: History.com Editors
Updated: May 16, 2019 | Original: October 27, 2009

The German-born physicist Albert Einstein developed the first of his groundbreaking theories while working as a clerk in the Swiss patent office in Bern. After making his name with four scientific articles published in 1905, he went on to win worldwide fame for his general theory of relativity and a Nobel Prize in 1921 for his explanation of the phenomenon known as the photoelectric effect. An outspoken pacifist who was publicly identified with the Zionist movement, Einstein emigrated from Germany to the United States when the Nazis took power before World War II. He lived and worked in Princeton, New Jersey, for the remainder of his life.
Einstein’s Early Life (1879-1904)
Born on March 14, 1879, in the southern German city of Ulm, Albert Einstein grew up in a middle-class Jewish family in Munich. As a child, Einstein became fascinated by music (he played the violin), mathematics and science. He dropped out of school in 1894 and moved to Switzerland, where he resumed his schooling and later gained admission to the Swiss Federal Polytechnic Institute in Zurich. In 1896, he renounced his German citizenship, and remained officially stateless before becoming a Swiss citizen in 1901.
Did you know? Almost immediately after Albert Einstein learned of the atomic bomb's use in Japan, he became an advocate for nuclear disarmament. He formed the Emergency Committee of Atomic Scientists and backed Manhattan Project scientist J. Robert Oppenheimer in his opposition to the hydrogen bomb.
While at Zurich Polytechnic, Einstein fell in love with his fellow student Mileva Maric, but his parents opposed the match and he lacked the money to marry. The couple had an illegitimate daughter, Lieserl, born in early 1902, of whom little is known. After finding a position as a clerk at the Swiss patent office in Bern, Einstein married Maric in 1903; they would have two more children, Hans Albert (born 1904) and Eduard (born 1910).
Einstein’s Miracle Year (1905)
While working at the patent office, Einstein did some of the most creative work of his life, producing no fewer than four groundbreaking articles in 1905 alone. In the first paper, he applied the quantum theory (developed by German physicist Max Planck) to light in order to explain the phenomenon known as the photoelectric effect, by which a material will emit electrically charged particles when hit by light. The second article contained Einstein’s experimental proof of the existence of atoms, which he got by analyzing the phenomenon of Brownian motion, in which tiny particles were suspended in water.
In the third and most famous article, titled “On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies,” Einstein confronted the apparent contradiction between two principal theories of physics: Isaac Newton’s concepts of absolute space and time and James Clerk Maxwell’s idea that the speed of light was a constant. To do this, Einstein introduced his special theory of relativity, which held that the laws of physics are the same even for objects moving in different inertial frames (i.e. at constant speeds relative to each other), and that the speed of light is a constant in all inertial frames. A fourth paper concerned the fundamental relationship between mass and energy, concepts viewed previously as completely separate. Einstein’s famous equation E = mc2 (where “c” was the constant speed of light) expressed this relationship.
From Zurich to Berlin (1906-1932)
Einstein continued working at the patent office until 1909, when he finally found a full-time academic post at the University of Zurich. In 1913, he arrived at the University of Berlin, where he was made director of the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Physics. The move coincided with the beginning of Einstein’s romantic relationship with a cousin of his, Elsa Lowenthal, whom he would eventually marry after divorcing Mileva. In 1915, Einstein published the general theory of relativity, which he considered his masterwork. This theory found that gravity, as well as motion, can affect time and space. According to Einstein’s equivalence principle–which held that gravity’s pull in one direction is equivalent to an acceleration of speed in the opposite direction–if light is bent by acceleration, it must also be bent by gravity. In 1919, two expeditions sent to perform experiments during a solar eclipse found that light rays from distant stars were deflected or bent by the gravity of the sun in just the way Einstein had predicted.
The general theory of relativity was the first major theory of gravity since Newton’s, more than 250 years before, and the results made a tremendous splash worldwide, with the London Times proclaiming a “Revolution in Science” and a “New Theory of the Universe.” Einstein began touring the world, speaking in front of crowds of thousands in the United States, Britain, France and Japan. In 1921, he won the Nobel Prize for his work on the photoelectric effect, as his work on relativity remained controversial at the time. Einstein soon began building on his theories to form a new science of cosmology, which held that the universe was dynamic instead of static, and was capable of expanding and contracting.
Einstein Moves to the United States (1933-39)
A longtime pacifist and a Jew, Einstein became the target of hostility in Weimar Germany, where many citizens were suffering plummeting economic fortunes in the aftermath of defeat in the Great War. In December 1932, a month before Adolf Hitler became chancellor of Germany, Einstein made the decision to emigrate to the United States, where he took a position at the newly founded Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey . He would never again enter the country of his birth.
By the time Einstein’s wife Elsa died in 1936, he had been involved for more than a decade with his efforts to find a unified field theory, which would incorporate all the laws of the universe, and those of physics, into a single framework. In the process, Einstein became increasingly isolated from many of his colleagues, who were focused mainly on the quantum theory and its implications, rather than on relativity.
Einstein’s Later Life (1939-1955)
In the late 1930s, Einstein’s theories, including his equation E=mc2, helped form the basis of the development of the atomic bomb. In 1939, at the urging of the Hungarian physicist Leo Szilard, Einstein wrote to President Franklin D. Roosevelt advising him to approve funding for the development of uranium before Germany could gain the upper hand. Einstein, who became a U.S. citizen in 1940 but retained his Swiss citizenship, was never asked to participate in the resulting Manhattan Project , as the U.S. government suspected his socialist and pacifist views. In 1952, Einstein declined an offer extended by David Ben-Gurion, Israel’s premier, to become president of Israel .
Throughout the last years of his life, Einstein continued his quest for a unified field theory. Though he published an article on the theory in Scientific American in 1950, it remained unfinished when he died, of an aortic aneurysm, five years later. In the decades following his death, Einstein’s reputation and stature in the world of physics only grew, as physicists began to unravel the mystery of the so-called “strong force” (the missing piece of his unified field theory) and space satellites further verified the principles of his cosmology.

HISTORY Vault: Secrets of Einstein's Brain
Originally stolen by the doctor trusted to perform his autopsy, scientists over the decades have examined the brain of Albert Einstein to try and determine what made this seemingly normal man tick.

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
Biography Online

Albert Einstein Biography

Einstein is also well known as an original free-thinker, speaking on a range of humanitarian and global issues. After contributing to the theoretical development of nuclear physics and encouraging F.D. Roosevelt to start the Manhattan Project, he later spoke out against the use of nuclear weapons.
Born in Germany to Jewish parents, Einstein settled in Switzerland and then, after Hitler’s rise to power, the United States. Einstein was a truly global man and one of the undisputed genius’ of the Twentieth Century.
Early life Albert Einstein
Einstein was born 14 March 1879, in Ulm the German Empire. His parents were working-class (salesman/engineer) and non-observant Jews. Aged 15, the family moved to Milan, Italy, where his father hoped Albert would become a mechanical engineer. However, despite Einstein’s intellect and thirst for knowledge, his early academic reports suggested anything but a glittering career in academia. His teachers found him dim and slow to learn. Part of the problem was that Albert expressed no interest in learning languages and the learning by rote that was popular at the time.
“School failed me, and I failed the school. It bored me. The teachers behaved like Feldwebel (sergeants). I wanted to learn what I wanted to know, but they wanted me to learn for the exam.” Einstein and the Poet (1983)
At the age of 12, Einstein picked up a book on geometry and read it cover to cover. – He would later refer to it as his ‘holy booklet’. He became fascinated by maths and taught himself – becoming acquainted with the great scientific discoveries of the age.
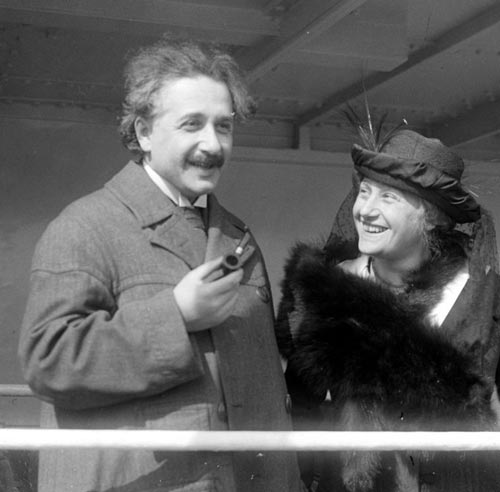

Albert Einstein with wife Elsa
Despite Albert’s independent learning, he languished at school. Eventually, he was asked to leave by the authorities because his indifference was setting a bad example to other students.
He applied for admission to the Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich. His first attempt was a failure because he failed exams in botany, zoology and languages. However, he passed the next year and in 1900 became a Swiss citizen.
At college, he met a fellow student Mileva Maric, and after a long friendship, they married in 1903; they had two sons before divorcing several years later.
In 1896 Einstein renounced his German citizenship to avoid military conscription. For five years he was stateless, before successfully applying for Swiss citizenship in 1901. After graduating from Zurich college, he attempted to gain a teaching post but none was forthcoming; instead, he gained a job in the Swiss Patent Office.
While working at the Patent Office, Einstein continued his own scientific discoveries and began radical experiments to consider the nature of light and space.

Einstein in 1921
He published his first scientific paper in 1900, and by 1905 had completed his PhD entitled “ A New Determination of Molecular Dimensions . In addition to working on his PhD, Einstein also worked feverishly on other papers. In 1905, he published four pivotal scientific works, which would revolutionise modern physics. 1905 would later be referred to as his ‘ annus mirabilis .’
Einstein’s work started to gain recognition, and he was given a post at the University of Zurich (1909) and, in 1911, was offered the post of full-professor at the Charles-Ferdinand University in Prague (which was then part of Austria-Hungary Empire). He took Austrian-Hungary citizenship to accept the job. In 1914, he returned to Germany and was appointed a director of the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Physics. (1914–1932)
Albert Einstein’s Scientific Contributions
Quantum Theory
Einstein suggested that light doesn’t just travel as waves but as electric currents. This photoelectric effect could force metals to release a tiny stream of particles known as ‘quanta’. From this Quantum Theory, other inventors were able to develop devices such as television and movies. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1921.
Special Theory of Relativity
This theory was written in a simple style with no footnotes or academic references. The core of his theory of relativity is that:
“Movement can only be detected and measured as relative movement; the change of position of one body in respect to another.”
Thus there is no fixed absolute standard of comparison for judging the motion of the earth or plants. It was revolutionary because previously people had thought time and distance are absolutes. But, Einstein proved this not to be true.
He also said that if electrons travelled at close to the speed of light, their weight would increase.
This lead to Einstein’s famous equation:
Where E = energy m = mass and c = speed of light.
General Theory of Relativity 1916
Working from a basis of special relativity. Einstein sought to express all physical laws using equations based on mathematical equations.
He devoted the last period of his life trying to formulate a final unified field theory which included a rational explanation for electromagnetism. However, he was to be frustrated in searching for this final breakthrough theory.
Solar eclipse of 1919
In 1911, Einstein predicted the sun’s gravity would bend the light of another star. He based this on his new general theory of relativity. On 29 May 1919, during a solar eclipse, British astronomer and physicist Sir Arthur Eddington was able to confirm Einstein’s prediction. The news was published in newspapers around the world, and it made Einstein internationally known as a leading physicist. It was also symbolic of international co-operation between British and German scientists after the horrors of the First World War.
In the 1920s, Einstein travelled around the world – including the UK, US, Japan, Palestine and other countries. Einstein gave lectures to packed audiences and became an internationally recognised figure for his work on physics, but also his wider observations on world affairs.
Bohr-Einstein debates
During the 1920s, other scientists started developing the work of Einstein and coming to different conclusions on Quantum Physics. In 1925 and 1926, Einstein took part in debates with Max Born about the nature of relativity and quantum physics. Although the two disagreed on physics, they shared a mutual admiration.
As a German Jew, Einstein was threatened by the rise of the Nazi party. In 1933, when the Nazi’s seized power, they confiscated Einstein’s property, and later started burning his books. Einstein, then in England, took an offer to go to Princeton University in the US. He later wrote that he never had strong opinions about race and nationality but saw himself as a citizen of the world.
“I do not believe in race as such. Race is a fraud. All modern people are the conglomeration of so many ethnic mixtures that no pure race remains.”
Once in the US, Einstein dedicated himself to a strict discipline of academic study. He would spend no time on maintaining his dress and image. He considered these things ‘inessential’ and meant less time for his research. Einstein was notoriously absent-minded. In his youth, he once left his suitcase at a friends house. His friend’s parents told Einstein’s parents: “ That young man will never amount to anything, because he can’t remember anything.”
Although a bit of a loner, and happy in his own company, he had a good sense of humour. On January 3, 1943, Einstein received a letter from a girl who was having difficulties with mathematics in her studies. Einstein consoled her when he wrote in reply to her letter
“Do not worry about your difficulties in mathematics. I can assure you that mine are still greater.”
Einstein professed belief in a God “Who reveals himself in the harmony of all being”. But, he followed no established religion. His view of God sought to establish a harmony between science and religion.
“Science without religion is lame, religion without science is blind.”
– Einstein, Science and Religion (1941)
Politics of Einstein
Einstein described himself as a Zionist Socialist. He did support the state of Israel but became concerned about the narrow nationalism of the new state. In 1952, he was offered the position as President of Israel, but he declined saying he had:
“neither the natural ability nor the experience to deal with human beings.” … “I am deeply moved by the offer from our State of Israel, and at once saddened and ashamed that I cannot accept it.”

Einstein receiving US citizenship.
Albert Einstein was involved in many civil rights movements such as the American campaign to end lynching. He joined the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) and considered racism, America’s worst disease. But he also spoke highly of the meritocracy in American society and the value of being able to speak freely.
On the outbreak of war in 1939, Einstein wrote to President Roosevelt about the prospect of Germany developing an atomic bomb. He warned Roosevelt that the Germans were working on a bomb with a devastating potential. Roosevelt headed his advice and started the Manhattan project to develop the US atom bomb. But, after the war ended, Einstein reverted to his pacifist views. Einstein said after the war.
“Had I known that the Germans would not succeed in producing an atomic bomb, I would not have lifted a finger.” (Newsweek, 10 March 1947)
In the post-war McCarthyite era, Einstein was scrutinised closely for potential Communist links. He wrote an article in favour of socialism, “Why Socialism” (1949) He criticised Capitalism and suggested a democratic socialist alternative. He was also a strong critic of the arms race. Einstein remarked:
“I do not know how the third World War will be fought, but I can tell you what they will use in the Fourth—rocks!”

Rabindranath Tagore and Einstein
Einstein was feted as a scientist, but he was a polymath with interests in many fields. In particular, he loved music. He wrote that if he had not been a scientist, he would have been a musician. Einstein played the violin to a high standard.
“I often think in music. I live my daydreams in music. I see my life in terms of music… I get most joy in life out of music.”
Einstein died in 1955, at his request his brain and vital organs were removed for scientific study.
Citation: Pettinger, Tejvan . “ Biography of Albert Einstein ”, Oxford, www.biographyonline.net 23 Feb. 2008. Updated 2nd March 2017.
Albert Einstein – His Life and Universe

Albert Einstein – His Life at Amazon
Related pages

53 Interesting and unusual facts about Albert Einstein.

19 Comments
Albert E is awesome! Thanks for this website!!
- January 11, 2019 3:00 PM
Albert Einstein is the best scientist ever! He shall live forever!
- January 10, 2019 4:11 PM
very inspiring
- December 23, 2018 8:06 PM
Wow it is good
- December 08, 2018 10:14 AM
Thank u Albert for discovering all this and all the wonderful things u did!!!!
- November 15, 2018 7:03 PM
- By Madalyn Silva
Thank you so much, This biography really motivates me a lot. and I Have started to copy of Sir Albert Einstein’s habit.
- November 02, 2018 3:37 PM
- By Ankit Gupta
Sooo inspiring thanks Albert E. You helped me in my report in school I love you Albert E. 🙂 <3
- October 17, 2018 4:39 PM
- By brooklynn
By this inspired has been I !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
- October 12, 2018 4:25 PM
- By Richard Clarlk
Albert Einstein: Biography, facts and impact on science
A brief biography of Albert Einstein (March 14, 1879 - April 18, 1955), the scientist whose theories changed the way we think about the universe.

- Einstein's birthday and education
Einstein's wives and children
How einstein changed physics.
- Later years and death
Gravitational waves and relativity
Additional resources.
Albert Einstein was a German-American physicist and probably the most well-known scientist of the 20th century. He is famous for his theory of relativity , a pillar of modern physics that describes the dynamics of light and extremely massive entities, as well as his work in quantum mechanics , which focuses on the subatomic realm.
Albert Einstein's birthday and education
Einstein was born in Ulm, in the German state of Württemberg, on March 14, 1879, according to a biography from the Nobel Prize organization . His family moved to Munich six weeks later, and in 1885, when he was 6 years old, he began attending Petersschule, a Catholic elementary school.
Contrary to popular belief, Einstein was a good student. "Yesterday Albert received his grades, he was again number one, and his report card was brilliant," his mother once wrote to her sister, according to a German website dedicated to Einstein's legacy. But when he later switched to the Luitpold grammar school, young Einstein chafed under the school's authoritarian attitude, and his teacher once said of him, "never will he get anywhere."
In 1896, at age 17, Einstein entered the Swiss Federal Polytechnic School in Zurich to be trained as a teacher in physics and mathematics. A few years later, he gained his diploma and acquired Swiss citizenship but was unable to find a teaching post. So he accepted a position as a technical assistant in the Swiss patent office.
Related: 10 discoveries that prove Einstein was right about the universe — and 1 that proves him wrong
Einstein married Mileva Maric, his longtime love and former student, in 1903. A year prior, they had a child out of wedlock, who was discovered by scholars only in the 1980s, when private letters revealed her existence. The daughter, called Lieserl in the letters, may have been mentally challenged and either died young or was adopted when she was a year old. Einstein had two other children with Maric, Hans Albert and Eduard, born in 1904 and 1910, respectively.
Einstein divorced Maric in 1919 and soon married his cousin Elsa Löwenthal, with whom he had been in a relationship since 1912.
Einstein obtained his doctorate in physics in 1905 — a year that's often known as his annus mirabilis ("year of miracles" in Latin), according to the Library of Congress . That year, he published four groundbreaking papers of significant importance in physics.
The first incorporated the idea that light could come in discrete particles called photons. This theory describes the photoelectric effect , the concept that underpins modern solar power. The second explained Brownian motion, or the random motion of particles or molecules. Einstein looked at the case of a dust mote moving randomly on the surface of water and suggested that water is made up of tiny, vibrating molecules that kick the dust back and forth.
The final two papers outlined his theory of special relativity, which showed how observers moving at different speeds would agree about the speed of light, which was a constant. These papers also introduced the equation E = mc^2, showing the equivalence between mass and energy. That finding is perhaps the most widely known aspect of Einstein's work. (In this infamous equation, E stands for energy, m represents mass and c is the constant speed of light).
In 1915, Einstein published four papers outlining his theory of general relativity, which updated Isaac Newton's laws of gravity by explaining that the force of gravity arose because massive objects warp the fabric of space-time. The theory was validated in 1919, when British astronomer Arthur Eddington observed stars at the edge of the sun during a solar eclipse and was able to show that their light was bent by the sun's gravitational well, causing shifts in their perceived positions.
Related: 8 Ways you can see Einstein's theory of relativity in real life
In 1921, he won the Nobel Prize in physics for his work on the photoelectric effect, though the committee members also mentioned his "services to Theoretical Physics" when presenting their award. The decision to give Einstein the award was controversial because the brilliant physicist was a Jew and a pacifist. Anti-Semitism was on the rise and relativity was not yet seen as a proven theory, according to an article from The Guardian .
Einstein was a professor at the University of Berlin for a time but fled Germany with Löwenthal in 1933, during the rise of Adolf Hitler. He renounced his German citizenship and moved to the United States to become a professor of theoretical physics at Princeton, becoming a U.S. citizen in 1940.
During this era, other researchers were creating a revolution by reformulating the rules of the smallest known entities in existence. The laws of quantum mechanics had been worked out by a group led by the Danish physicist Niels Bohr , and Einstein was intimately involved with their efforts.
Bohr and Einstein famously clashed over quantum mechanics. Bohr and his cohorts proposed that quantum particles behaved according to probabilistic laws, which Einstein found unacceptable, quipping that " God does not play dice with the universe ." Bohr's views eventually came to dominate much of contemporary thinking about quantum mechanics.

Einstein's later years and death
After he retired in 1945, Einstein spent most of his later years trying to unify gravity with electromagnetism in what's known as a unified field theory . Einstein died of a burst blood vessel near his heart on April 18, 1955, never unifying these forces.
Einstein's body was cremated and his ashes were spread in an undisclosed location, according to the American Museum of Natural History . But a doctor performed an unauthorized craniotomy before this and removed and saved Einstein's brain.
The brain has been the subject of many tests over the decades, which suggested that it had extra folding in the gray matter, the site of conscious thinking. In particular, there were more folds in the frontal lobes, which have been tied to abstract thought and planning. However, drawing any conclusions about intelligence based on a single specimen is problematic.
Related: Where is Einstein's brain?
In addition to his incredible legacy regarding relativity and quantum mechanics, Einstein conducted lesser-known research into a refrigeration method that required no motors, moving parts or coolant. He was also a tireless anti-war advocate, helping found the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists , an organization dedicated to warning the public about the dangers of nuclear weapons .
Einstein's theories concerning relativity have so far held up spectacularly as a predictive models. Astronomers have found that, as the legendary physicist anticipated, the light of distant objects is lensed by massive, closer entities, a phenomenon known as gravitational lensing, which has helped our understanding of the universe's evolution. The James Webb Space Telescope , launched in Dec. 2021, has utilized gravitational lensing on numerous occasions to detect light emitted near the dawn of time , dating to just a few hundred million years after the Big Bang.
In 2016, the Advanced Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory also announced the first-ever direct detection of gravitational waves , created when massive neutron stars and black holes merge and generate ripples in the fabric of space-time. Further research published in 2023 found that the entire universe may be rippling with a faint "gravitational wave background," emitted by ancient, colliding black holes.
Find answers to frequently asked questions about Albert Einstein on the Nobel Prize website. Flip through digitized versions of Einstein's published and unpublished manuscripts at Einstein Archives Online. Learn about The Einstein Memorial at the National Academy of Sciences building in Washington, D.C.
This article was last updated on March 11, 2024 by Live Science editor Brandon Specktor to include new information about how Einstein's theories have been validated by modern experiments.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.

Adam Mann is a freelance journalist with over a decade of experience, specializing in astronomy and physics stories. He has a bachelor's degree in astrophysics from UC Berkeley. His work has appeared in the New Yorker, New York Times, National Geographic, Wall Street Journal, Wired, Nature, Science, and many other places. He lives in Oakland, California, where he enjoys riding his bike.
Giant 'rogue waves' of invisible matter might be disrupting the orbits of stars, new study hints
Can mirrors facing each other create infinite reflections?
James Webb telescope detects 1-of-a-kind atmosphere around 'Hell Planet' in distant star system
Most Popular
- 2 Cave of Crystals: The deadly cavern in Mexico dubbed 'the Sistine Chapel of crystals'
- 3 'The most critically harmful fungi to humans': How the rise of C. auris was inevitable
- 4 2,500-year-old Illyrian helmet found in burial mound likely caused 'awe in the enemy'
- 5 32 of the most colorful birds on Earth
- 2 32 of the most colorful birds on Earth
- 3 Can mirrors facing each other create infinite reflections?
- 4 Roman-era skeletons buried in embrace, on top of a horse, weren't lovers, DNA analysis shows
- 5 Papua New Guineans, genetically isolated for 50,000 years, carry Denisovan genes that help their immune system, study suggests
Biography: Albert Einstein
- Famous Inventions
- Famous Inventors
- Patents & Trademarks
- Invention Timelines
- Computers & The Internet
- American History
- African American History
- African History
- Ancient History and Culture
- Asian History
- European History
- Latin American History
- Medieval & Renaissance History
- Military History
- The 20th Century
- Women's History
Legendary scientist Albert Einstein (1879 - 1955) first gained worldwide prominence in 1919 after British astronomers verified predictions of Einstein's general theory of relativity through measurements taken during a total eclipse. Einstein's theories expanded upon universal laws formulated by physicist Isaac Newton in the late seventeenth century.
Before E=MC2
Einstein was born in Germany in 1879. Growing up, he enjoyed classical music and played the violin. One story Einstein liked to tell about his childhood was when he came across a magnetic compass. The needle's invariable northward swing, guided by an invisible force, profoundly impressed him as a child. The compass convinced him that there had to be "something behind things, something deeply hidden."
Even as a small boy Einstein was self-sufficient and thoughtful. According to one account, he was a slow talker, often pausing to consider what he would say next. His sister would recount the concentration and perseverance with which he would build houses of cards.
Einstein's first job was that of patent clerk. In 1933, he joined the staff of the newly created Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey. He accepted this position for life, and lived there until his death. Einstein is probably familiar to most people for his mathematical equation about the nature of energy, E = MC2.
E = MC2, Light and Heat
The formula E=MC2 is probably the most famous calculation from Einstein's special theory of relativity . The formula basically states that energy (E) equals mass (m) times the speed of light (c) squared (2). In essence, it means mass is just one form of energy. Since the speed of light squared is an enormous number, a small amount of mass can be converted to a phenomenal amount of energy. Or if there's a lot of energy available, some energy can be converted to mass and a new particle can be created. Nuclear reactors, for instance, work because nuclear reactions convert small amounts of mass into large amounts of energy.
Einstein wrote a paper based on the new understanding of the structure of light. He argued that light can act as though it consists of discrete, independent particles of energy similar to particles of a gas. A few years before, Max Planck's work had contained the first suggestion of discrete particles in energy. Einstein went far beyond this though and his revolutionary proposal seemed to contradict the universally accepted theory that light consists of smoothly oscillating electromagnetic waves. Einstein showed that light quanta, as he called the particles of energy, could help to explain phenomena being studied by experimental physicists. For example, he explained how light ejects electrons from metals.
While there was a well-known kinetic energy theory that explained heat as an effect of the ceaseless motion of atoms, it was Einstein who proposed a way to put the theory to a new and crucial experimental test. If tiny but visible particles were suspended in a liquid, he argued, the irregular bombardment by the liquid's invisible atoms should cause the suspended particles to move in a random jittering pattern. This should be observable through a microscope. If the predicted motion is not seen, the whole kinetic theory would be in grave danger. But such a random dance of microscopic particles had long since been observed. With the motion demonstrated in detail, Einstein had reinforced the kinetic theory and created a powerful new tool for studying the movement of atoms.
- Biography of Albert Einstein, Theoretical Physicist
- The Life and Work of Albert Einstein
- Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases
- Einstein's Theory of Relativity
- What Is a Photon in Physics?
- Introduction to the Major Laws of Physics
- Fundamental Physical Constants
- A Brief History of Atomic Theory
- Quantum Physics Overview
- Top 10 Weird but Cool Physics Ideas
- 10 Things You Don't Know About Albert Einstein
- Wave Particle Duality and How It Works
- Topics Typically Covered in Grade 11 Chemistry
- The Physics of a Car Collision
- Photon Definition
- An Introduction to Black Holes
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Albert Einstein Essay

Read Albert Einstein Essay on Vedantu
Albert Einstein was a Theoretical Physicist of German origin. He is the one who developed a pillar of modern Physics, the Theory of Relativity. Be it his mass-energy equivalence formula or his law of photoelectric effect, the theories he postulated changed the history of science forever. His works are still studied in standard institutions of learning throughout the world.
About Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein was born on 14th March 1879 in Ulm in the Kingdom of Wurttemberg in the German empire. His father's name was Herman Einstein and his mother's name was Pauline Koch. His father worked as a salesman and as an engineer. In 1880, his father along with his family moved to Munich. His father and his uncle founded Elektrotechnische Fabrik J. Einstein & Cie. It is a company that manufactures electrical equipment based on direct current.
After birth, Albert Einstein's head was much larger than his body and he was born as a deformed abnormal child. Usually, children start speaking at the age of 2, but Albert Einstein started speaking after 4 years of age. When Einstein was 5 years old, his father gifted him with a magnetic compass on his birthday. The needle of the compass used to be in the North Direction, and seeing this, he became very fascinated and developed an interest to explore science well.
His Childhood
Albert Einstein was born on 14th March 1879, in Ulm, where his family ran a small shop. He had two siblings, an elder sister named Maja and a younger brother named Hans Albert. The Einsteins were non-observant Jews and moved to Munich when Albert was one year old. His parents wanted him to become a businessman, but he showed scientific inclinations from his childhood days. From 1890, the family resided in Milan where Einstein underwent Technical High School education. Since his father had relocated to Italy for work purposes, Albert Einstein decided not to move with his family to Berlin after matriculating from the Zurich Polytechnic in 1896.
He had problems with authority and left his academic institutions without a degree on several occasions. He started working as a patent clerk at the Swiss Patent Office in 1902, where he spent most of his time on theoretical physics. In 1905, he published four papers that revolutionized Physics. They were on (I) Brownian motion, (ii) photoelectric effect, (iii) special relativity and (iv) equivalence of mass and energy, which is famously known as the E=mc 2 equation. He worked on unified field Theory for more than ten years but was unable to complete it.
At the age of 5, he joined the Catholic Elementary School in Munich. After that, he enrolled in Luitpold Gymnasium, where he received his primary and secondary school education. When Albert Einstein was 15 years old, his father wanted him to do electrical engineering but Einstein used to fight with the authority of his school, about their way of teaching. He believed that due to so many strict rules and regulations in the school, the creative mind of children was lost and they only knew the strict rote learning. Einstein was thrown out of school too many times due to this behavior of his. He used to fight with his teachers, he also raised questions about their way of teaching.
At the age of 12, Einstein started learning Calculus on his own, and when he became 14 years old, he mastered Integral and Differential Calculus. Einstein got married in 1903 to Marci. In 1904 his son named Hans Albert Einstein was born, and in 1910 his second son Eduard was born.
Contribution Towards Science
Albert received a patent officer job at the Federal Office for Intellectual Property in Bern, Switzerland, at the age of 23, after completing college. While working there, he completed his Ph.D., after which he became a professor at the University of Zurich. During this period he gave the theory of mass-energy (E = mc 2 ). The atomic bombs dropped in Japan were built on this principle. However, throughout his life, Albert Einstein was against the atomic bomb dropped on Japan. He then gave a new theory of relativity, falsifying the old rules of relativity given by Isaac Newton, which proved that time and light are not constant. If traveling at the speed of light, i.e. 300000 km, it will be slow, and millions of years have passed on Earth. That is, he proved that time travel can be done. However, till date scientists have not been able to build a spaceship that can travel at the speed of light.
In 1977, NASA conducted an experiment to prove this theory in which they set the clock in a satellite and were left to orbit the Earth. After a few years, when the satellite's clock was checked, it was much slower than the Earth's clock. In this theory of quantum physics, Indian scientist Satyendra Nath Bose wrote a letter from India to Albert Einstein in which he said that Newton's relativity theory is wrong. Albert Einstein then agreed to the letter of Satyendra Nath Bose, and he published that paper and later gave a new theory of relativity. Albert Einstein made many other inventions with this theory.
He received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1981 for his photoelectric effect. In 1933, Hitler killed millions of people in Germany, and at the same time, Albert Einstein was changing the whole world with science. He went to America from Europe forever, taking the citizenship there because Hitler placed a reward of \[$\]5000 on Albert Einstein's head and burned all his research books.
Moving to the United States
During World War-I, he was invited to join the Bureau of Standards in Washington before accepting its offer officially. He moved to the United States of America with his family in April 1933 after Hitler's rise to power.
He advised breaking up Bell Labs and nationalizing the electricity supply industry, worked on defense projects during World War II, and became a citizen of the United States in 1940.
In 1951, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to Theoretical Physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect."
Albert Einstein died on 18th April 1955 at Princeton Hospital, New Jersey. He was 76 years old.
Death and Awards
On 17th April 1955, Einstein underwent internal bleeding in the Lower Abdominal, and he was taken to a hospital where the doctor asked him to undergo a surgery. Albert Einstein refused to undergo the surgery, and said that he would go when he wanted, and that it is tasteless to prolong life artificially. He told me that he would like to die like that. Later research was done on Albert Einstein's brain and it was found that the parts of Einstein's brain that were for mathematical calculus had developed 15% more as compared to the brains of normal people.
The whole world celebrates Albert Einstein's birthday on 14th March as World Genius Day. He had published more than 300 research papers on science in his life and had contributed to the advancement of science. This is the reason that Times magazine has awarded Albert Einstein the title of Person of the Century. Einstein received numerous awards and honors, and in 1922, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect".
Conclusion
Albert Einstein was one of the best scientists, mathematicians, and physicists of the 20th century. In the early twentieth century, Albert Einstein formulated theories that changed the thinking of physicists and non-specialists alike. He will always be remembered for his law of photoelectric effect and mass-energy equivalence formula. His body of work is studied in universities across the world to this day. He is a famous and known name in the world of Physics, he also achieved a lot, and was awarded the Nobel Prize for his commendable research and accomplishments.

FAQs on Albert Einstein Essay
1. Why did Albert Einstein Have No Social Life?
Albert Einstein was a very intelligent person. He had no time for a social life because he was always busy with his research and work. Albert Einstein had more than 40 publications to his credit. His life and work were on research and inventions. His life revolved around his work and family. The work-life of Albert Einstein is an inspiration to all the people who are working day and night to achieve something great in their lives. One of the best scientists, mathematicians and physicists of the 20th century was none other than Albert Einstein. His achievement includes the most discussed formula in his name- the mass-energy equivalence equation. He was known for the impact he made on the world of physics and also for the awards and honors he received in his lifetime.
2. What Was the Theory of Relativity by Albert Einstein?
The theory of relativity is the scientific theory developed by Albert Einstein between 1905 and 1915. It is a theory of gravity and space-time. The theory revolutionized physics by proposing that the laws of physics are the same for all inertial frames of reference. That is, the laws of physics are the same whether an observer is stationary or in motion. The theory also proposed that the speed of light is a constant for all observers, regardless of their relative motion. This was a radical departure from classical mechanics and Newton's view of the universe. His theory is the basis for many features of our modern life and is used in daily applications. You can learn more about the theory of relativity in any good physics textbook.
3. What Did Albert Einstein Do for Science?
Albert Einstein was a German theoretical physicist who developed the theory of general relativity, effecting a revolution in physics. He is best known in popular culture for his mass-energy equivalence formula E = mc 2 (which has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation"). He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect". This makes Einstein the only physicist to win twice. He is also known for his other great works, such as the world's smallest unit of time and explaining the Brownian motion of particles. His life's work has had a great impact on the modern world and the way we see things.
4. What Awards Did Albert Einstein Receive in His Lifetime?
Albert Einstein was one of the most genius scientists of all time. He is known for his great works in Physics. He also received a lot of awards in his lifetime. Albert Einstein won the Nobel Prize in 1921 for physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect". He is the only physicist to have been awarded a Nobel Prize twice. In 1921, he received the Nobel Prize in physics. In his acceptance lecture, titled "The Field Theory of Matter", he provided what is now viewed as a foundation for relativistic quantum field theory. Einstein was voted number 3 in BBC's poll of the 100 Greatest Britons.
5. Why Was Einstein Thought of as a Genius?
Albert Einstein was a brilliant and intelligent man. He changed the world because of his scientific ideas and theories. He is known for the mass-energy equivalence formula (E=mc 2 ); he came up with it in 1905; before coming to this theory, he did not have any notable publications. However, by the end of this year, he had already submitted two articles to Annalen der Physik. One of these was on the photoelectric effect, while the other was on "A new determination of molecular dimensions". Albert Einstein is considered a genius because he looked at things in an entirely different way than anyone else did before him. He also had wonderful ideas about space and time that changed the way we think about those things.
6. What Were the Names of Albert Einstein’s Father and Mother?
Albert Einstein was born on 14th March 1879 in Ulm in the Kingdom of Wurttemberg in the German empire. His father’s name was Herman Einstein and His Mother’s name was Pauline Koch.
7. How Albert Einstein Was Different from Normal Kids?
After birth, Albert Einstein's head was much larger than his body and he was born as a deformed abnormal child. Usually, children start speaking at the age of 2, but in the case of Albert Einstein, he started speaking after 4 years of age. At the age of 12, Einstein learning Calculus and when he became 14 years old he had mastered Integral and Differential Calculus which is obviously not normal for any other kid.
Essay on Albert Einstein
500 words essay on albert einstein.
Albert Einstein was a physicist who is responsible for developing the famous general theory of relativity. Furthermore, he is one of the most influential and celebrated scientists of the 20th century. Let’s take a look at the life and achievements of this genius with the essay on Albert Einstein.

Essay On Albert Einstein
Early Life of Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein was born in Germany into a Jewish family on 14th March 1879. Furthermore, Einstein had to deal with speech difficulties early on but was a brilliant student at his elementary school. His father, Hermann Einstein founded an electrical equipment manufacturing company with the help of his brother.
At the age of five, Albert’s father showed him a pocket compass . Moreover, this made him realize that the needle was moving due to something in empty space. According to Einstein, this experience left a deep and lasting impression on him.
In 1889, a ten-year-old Albert became introduced to popular science and philosophy texts. This happened due to a family friend named Max Talmud.
Albert Einstein spent time on books like Kant’s ‘Critique of Pure Reason’ and ‘Euclid’s Elements’. From the latter book, Albert developed an understanding of deductive reasoning. Furthermore, by the age of 12, he was able to learn Euclidian geometry from a school booklet.
Einstein’s father’s intention was to see his son pursue electrical engineering. However, a clash took place between Albert and the authorities. This was because Albert had resentment for rote learning as, according to him, it was against creative thought.
Achievements of Albert Einstein
In 1894, Einstein’s father’s business failed and his family went to Italy. At this time, Einstein was only fifteen. During this time, he wrote ‘The Investigation of the State of Aether in Magnetic Fields’, which was his first scientific work.
In 1901, there was the publishing of a paper by Einstein on the capillary forces of a straw in the prestigious ‘Annalen der Physik’. Furthermore, his graduation took place from ETH with a diploma in teaching.
In the year 1905, while working in the patent office, there took place the publishing of four papers by Einstein in the prestigious journal ‘Annalen der Physik’. Experts recognize all four papers as tremendous achievements of Albert Einstein. Therefore, people call the year 1905 as Einstein’s wonderful year’.
The four papers were special relativity, photoelectric effect, Brownian motion , and equivalence of matter and energy. He also made the discovery of the famous equation, E = mc².
The theory of relativity was completed by Einstein in 1915. The confirmation of his theory was by British astronomer, Sir Arthur Eddington, during the solar eclipse of 1919.
There was the continuation of research works by Einstein and finally, in 1921, his efforts bore fruits. Most noteworthy, the Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Albert Einstein for his services to Theoretical Physics.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas

Conclusion of the Essay on Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein’s contribution to the field of physics is priceless. Furthermore, his ideas and theories are still authoritative for many physicists. Einstein’s lasting legacy in physics will continue to be an inspiration for young science enthusiasts.
FAQs For Essay on Albert Einstein
Question 1: What is the legacy of Albert Einstein?
Answer 1: Albert Einstein is one of the world’s greatest physicists and a Nobel Laureate. Furthermore, his greatest achievement is the theory of relativity which made a significant change in our understanding of the universe like. However, this wasn’t his only legacy as Einstein was also a refugee and a humanitarian.
Question 2: What is the equation E = MC 2 ?
Answer 2: Einstein’s E = MC 2 is the world’s most famous equation. Furthermore, this equation means that energy is equal to mass times the speed of light squared. Moreover, on the most basic level, this equation tells us that energy and mass happen to be interchangeable and that they are different forms of the same thing.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Albert Einstein: His Life and Impact on Science Essay (Biography)
Introduction, biography of albert einstein, contributions of albert einstein, relevance of albert einstein, my impression of albert einstein, works cited.
No study of physics is complete without a reference to Albert Einstein and his general theory of relativity that revolutionized the notions of space and time and the fresh understanding of gravity. It is this new understanding of space, time, and gravity that has enabled human development in several spheres of activity including our understanding of our universe and the interaction of the bodies present. (1).
Albert Einstein was born in 1897 into a middle-class family of German Jews. He did not talk until he was three years of age, which caused his parents to believe that this genius would be deficient in mental abilities. By the time he was fifteen Einstein was bored with the education provided through learning things by heart and under the strict supervision of the tutors. So he gave up his high school studies. He wandered around before finally entering the Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich, even though he had not passed his high school. At the institute, he enjoyed the practical and skipped the theoretical classes. Yet, he graduated exceptionally well. Finding a job was hard and he landed up as a patent examiner in 1900, which was also the year he got married.
Over the next five years, he also devoted his energies to the creation of his theories of relativity in four fundamental papers, which he published in 1905. In 1909 Einstein took up his first full-time job in his favorite subject of physics as an assistant professor in physics at the University of Zurich. The next few years saw Einstein continuing as an academician, with the only change being the change in 1914, when he shifted from teaching to research. In 1915 Einstein published his revolutionary general theory of relativity.
The aftermath of the First World War saw turmoil in Germany and Einstein dabbled in politics from 1918. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in physics in 1921. By 1933 the Nazis had gained power in Germany. Disillusioned by this Einstein moved to the United States of America and joined the U.S.A and joined the Institute for Advanced Studies at Princeton. The possibility of the development of the atom bomb led to Einstein voicing his opposition to it to the President of the U.S.A in 1939. He also became an American citizen in the same year. In 1952 he was offered the post of President by Israel, which he turned down. He died in 1955. (1).
Einstein’s contributions to the study of physics are many. His special theory of relativity helps in the reconciliation of the two branches of physics in mechanics and electromagnetism. In his general theory of relativity, the principle of relativity is extended into non-uniform motion, which leads to a new understanding of gravitation and removes the anomalies that physics faced with the Newtonian theories on gravity. His theories have also made contributions to the understanding of relativistic cosmology, capillary action, and critical opulence. His works have helped in resolving the traditional problems that existed between statistical mechanics and its application to quantum theory and provided an explanation for the Brownian movement of molecules. He has also contributed in the areas of atomic transition probabilities and the quantum theory of mono-atomic gas. His works also contributed to laying the foundation for the photon theory, the conception of the unified field theory, and the geometrization of physics. (2).
In his early life Einstein gave up the traditional model of education in trying to stuff down what was already known and the lack of encouragement provided for innovative thinking. His refusal to go down this well-trodden path allowed him to think outside of the traditional knowledge. (2). This was to prove useful when he turned his attention to molecular reality and the molecular basis of statistical physics in which the then existent theoretical physics frameworks and the results of observations and experiments differed. The result was the contributions that he made that had a profound impact on all the human development that is seen around us in the various fields of physics, mathematics, and astronomy. The example that Einstein has set has led to encouragement for innovative thinking in the field of education and the many things like space travel that we today take for granted. (3).
This study of the biography of Albert Einstein has provided me with several insights and enlightened me. The first is that there is more to learn and experience than what is already known. The second is that innovative thinking and extending this thinking into the deeper planes will assist me in applying the current body of knowledge to develop a better understanding of physics. My final insight is that many of the fruits of physics that we enjoy in our everyday lives are the results of scientists thinking outside the box to provide greater insights into the mysteries of the world that we live in.
- “ Albert Einstein in Brief ”. The Center for History of Physics. 2009. Web.
- Biographiq. Albert Einstein: The Man Behind the Theories (Biography) Filiquarian Publishing, LLC, 2008.
- Pais, Abraham & Penrose, Roger. Subtle Is the Lord: The Science and the Life of Albert Einstein Oxford University Press: Oxford, 2005.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2022, June 1). Albert Einstein: His Life and Impact on Science. https://ivypanda.com/essays/a-brief-biography-of-albert-einstein/
"Albert Einstein: His Life and Impact on Science." IvyPanda , 1 June 2022, ivypanda.com/essays/a-brief-biography-of-albert-einstein/.
IvyPanda . (2022) 'Albert Einstein: His Life and Impact on Science'. 1 June.
IvyPanda . 2022. "Albert Einstein: His Life and Impact on Science." June 1, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/a-brief-biography-of-albert-einstein/.
1. IvyPanda . "Albert Einstein: His Life and Impact on Science." June 1, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/a-brief-biography-of-albert-einstein/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Albert Einstein: His Life and Impact on Science." June 1, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/a-brief-biography-of-albert-einstein/.
- Albert Einstein as an Influential Scientist
- Albert Einstein, His Life and Career
- Zurich Insurance Company's Risk Management Principles
- A High-Resolution Thin-Film Probe: Development and Application
- Quantum Mechanics: Determinants
- CP & CV Measurement for an Ideal Gas: Laboratory Experiment
- Biological Effects of Laser
- Anomalous Expansion of Water: A Home Experiment
- CBSE Class 10th
- CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore
Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Main Question Paper
- JEE Main Cutoff
- JEE Main Advanced Admit Card
- AP EAPCET Hall Ticket
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- KCET Result
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2023
- CAT 2023 College Predictor
- CMAT 2024 Admit Card
- TS ICET 2024 Hall Ticket
- CMAT Result 2024
- MAH MBA CET Cutoff 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- NEET Rank Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Admit Card 2024
- NEET PG Application Form 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top NLUs Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Predictors & Articles
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- NID DAT Syllabus 2025
- NID DAT 2025
- Design Colleges in India
- Top NIFT Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Interior Design Colleges in India
- Top Graphic Designing Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Interior Design Colleges in Bangalore
- NIFT Result 2024
- NIFT Fees Structure
- NIFT Syllabus 2025
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission 2024
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- LPU NEST 2024
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET Exam City Intimation Slip 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET Mock Test 2024
- CUET Admit card 2024
- CUET PG Syllabus 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Syllabus 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- CUET UG Admit Card 2024 (Out) Live
- CUET 2024 Admit Card
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Essay on Albert Einstein
Science reached a high peak with the great scientist Albert Einstein. He is known as one of the greatest thinkers and scientists of the twentieth century. He is the one who advanced the pillar of Modern Physics. Albert Einstein is best known for introducing the theory of relativity in Physics, which helped us to understand time, universe, gravity, and space. Here are a few sample essays on Albert Einstein.
100 Words Essay on Albert Einstein
200 words essay on albert einstein, 500 words essay on albert einstein.

Published in 1905, Einstein's first article established him as one of the world’s premier scientists. Einstein admired the environment much more compared to other children and wished to spend more time with nature as the sounds and sights fascinated him. While employed in the patent office, Einstein did not miss the opportunity to solve the beam light problem, which he had been fascinated with since he was 16. Albert Einstein spent his entire life working for harmony and abominated war. Albert was in support of the American Civil Right Movement, and he was totally against violence. For his law of photoelectric effect, Einstein received a Nobel Prize in Physics in 1921.
Born on March 14, 1879, Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist. Albert studied in a Catholic Elementary School in Munich. He was then transferred to the Luitpold Gymnasium (today known as Albert Einstein Gymnasium) at 8, where he received primary and secondary education. Albert Einstein was not much of a fan of education, yet he enjoyed learning and reading independently. Einstein had these two ‘wonders’ in his early years, which affected him greatly. At age five, an encounter with a compass mystified him that the invisible forces could divert the needle. Secondly, at age 12, he found a book of geometry, which he devoured, and gave it the name “sacred little geometry book”.
Contribution To Physics
He significantly contributed to Physics in 1905 when he developed the Theory of Special Relativity. From a young age, Einstein excelled in Physics and Maths and even discovered his original Pythagorean theorem at age 12. His father wanted him to go with Electrical Engineering, but Einstein did not agree with him and resented the school’s regiment and the teaching method. Einstein was much ahead of his peers in Maths and Physics and excelled in them. His passion for algebra and geometry convinced everyone that nature could be understood as a mathematical structure. He was also awarded a Federal Teaching Diploma.
Einstein was one of the founding members of the German Democratic Party in 1918. He was critical of capitalism and was a socialist. Impressed by Mahatma Gandhi, Einstein described him as a role model for future generations and exchanged written letters with him. Einstein was totally in support of non-violence. He was also a Nobel Prize winner.
Childhood Issues | Einstein was unable to speak in his childhood because his skull was larger than the rest of his body. Slowly and gradually, his head began to improve and take shape. Still, everyone believed him to be sick until that time.
Religious Beliefs | Albert Einstein did not believe in any personal God for all the fates, destiny and actions. He also clarified that he was not an atheist and instead called himself a deeply religious non-believer. He observed and admitted that without ethical culture, there is no stand for salvation for humanity.
Stint With Music | Einstein’s mother played the piano quite well and wanted her son to learn the same, so he could develop a love for music. At age 5, Einstein began to play the piano, though he did not enjoy it much. He discovered the violin sonatas of Mozart at age 13, and at that time, he started to enjoy music. Einstein played Chamber music for his friends and family.
Contribution To Physics | He received the Nobel Prize in Physics for his discovery of the Photoelectric Effect. He also launched the new science of Cosmology. A Nobel Prize was awarded in 1993 to the discoverers of gravitational waves predicted by Einstein.
Death | Einstein died in the University Medical Centre of Princeton and Plainsboro, after his death, during an autopsy, the pathologist removed Einstein’s brain without the permission of his family and preserved it to know the real cause of Einstein’s intelligence. Einstein’s legacy was passed on to other scientists.
An Incident From Einstein’s Life
In 1919, at the University of Berlin, while working as a theoretical physics professor, Einstein theorised that an impending solar eclipse would provide a rare opportunity to observe gravity’s effect on light. The reports proved his observation to be correct. This observation of Einstein sent a shock wave through the scientific community and the world. Einstein spent the next few years travelling, speaking engagements, and receiving awards. He also founded the Hebrew University in Jerusalem in 1921 and won the Nobel Prize in the same year.
What Do We Learn From Einstein?
Albert Einstein had the ability to think outside of the square and apply great imagination and creativity to science. This ability of his influenced many people to think outside their comfort zone, explore chances and the world around them. Einstein gave way to many younger generations to think and rethink what they want to do and focus on it, to give their hundred percent in achieving their desired goals. Einstein also taught us not to blindly believe in whatever is being told but to question everything and look for reasons. Albert Einstein taught us to live in the moment and to keep going in the right direction, and success will automatically follow. One should make mistakes but also learn from them, as one who does not commit mistakes practically does not do anything.
Applications for Admissions are open.

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)
Register FREE for ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)

JEE Main Important Physics formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Physics formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

PW JEE Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for JEE coaching

PW NEET Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for NEET coaching

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Certifications
We Appeared in
Albert Einstein’s Biography
How it works
Albert Einstein was a great physicist and mathematician and was known for his theories on relativity, and of matter and heat. Einstein was born on March 14th, 1879 in Württemberg, Germany. As a child, Einstein was mesmerized in music (he played the violin), mathematics and science. Einstein became religious at age 12, even composing several songs in praise of God and also singing religious songs on the way to school. After he read science books that opposed his religious beliefs. This challenge to established authority left a deep and lasting impression.
A turning point occurred when Einstein was 16. Talmud had earlier introduced him to a children’s science series by Aaron Bernstein, the author imagined riding alongside electricity that was traveling inside a telegraph wire.
Einstein asked himself the question that would dominate his thinking for the next 10 years: What would a light beam look like if you could run alongside it? In 1894, he dropped out of school and moved to Switzerland, where he resumes his schooling and later gained admission to the Swiss Federal Polytechnic Institute in Zurich. Albert was Alone and repelled by the looming prospect of military duty when he turned 16. Einstein ran away six months later and was on the doorstep of his surprised parents. His parents realized the big problems that he faced as a school dropout with no employable skills. Einstein fell in love with his fellow student Mileva Maric, but his parents opposed the match and he lacked the money to marry. Einstein’s relationship with Maric was serious, but his parents opposed the relationship.
His mother especially objected to her Serbian background. Einstein disobeyed his parents, but in January 1902 Albert and Maric had a child. The child’s name was Lieserl, whose fate is unknown. The year 1902 was maybe the lowest point in his life. He could not marry Maric and support a family without a job. His father’s business went bankrupt. Desperate and unemployed, Einstein took lowly jobs tutoring children but was fired from those jobs. Later that year, Einstein’s father became seriously ill. However, just before he died, he gave his blessing for his son to marry Maric.
For years, Einstein would experience sadness remembering that his father had died thinking of him as a failure. When a steady income was given to him for the first time, Einstein felt confident enough to marry Maric. He did on January 6, 1903. Their children, Hans Albert and Eduard, were born in Bern in 1904 and 1910. In hindsight, Einstein’s job at the patent office was a blessing. At first Einstein’s 1905 papers were ignored by the physics community. This changed after he received the attention from one physicist, the most influential physicist of his generation, Max Planck, the founder of the quantum theory.
Even as his fame grew, Einstein’s marriage was falling apart. He was constantly on the road, speaking at international conferences, and lost in contemplation of relativity. The couple frequently argued about their children and their finances. Convinced that his marriage was doomed, Einstein began an affair with a cousin, Elsa Löwenthal, whom he later married. When he finally divorced Mileva in 1919, he agreed to give her the money he might receive if he ever won a Nobel Prize. In 1921 Einstein began the first of several world tours, visiting the United States, England, Japan, and France. Everywhere he went, the crowds numbered in the thousands. En route from Japan, he had received the Nobel Prize for Physics, but for the photoelectric effect rather than for his relativity theories.
In November 1915 Einstein finally completed the general theory of relativity, which was his masterpiece. In the summer of 1915, Einstein had given six two-hour lectures at the University of Göttingen that thoroughly explained an incomplete version of general relativity. Einstein’s work was interrupted by World War 1, he would write, “At such a time as this, one realizes what a sorry species of animal one belongs to.” After the war, two expeditions were sent to test Einstein’s prediction of the deflected starlight near the Sun. One set sailed off the coast of West Africa and the other sailed off the coast of Northern Brazil. On November 6 the results were announced in London at a joint meeting of the Royal Society and the Royal Astronomical Society.
In 1921, he won the Nobel Prize for his work on the photoelectric effect, as his work on relativity remained controversial at the time. Einstein became the target of hostility in Weimar Germany, where many citizens were suffering plummeting economic fortunes in the aftermath of defeat in the Great War. In December 1932, Einstein decided to move to the United States, where he took a position at the newly founded Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey. He never went back to his hometown in Germany. By the time Einstein’s wife Elsa died in 1936, he had been involved for more than a decade with his efforts to find a unified field theory.
Einstein became increasingly isolated from many of his colleagues. They were focused mainly on the quantum theory and its implications, rather than on relativity. In the late 1930s, Einstein’s theories, including his equation E=mc2, which helped form the basis of the development of the atomic bomb. Einstein became a U.S. citizen in 1940. But, his Swiss citizenship was never asked to participate in the resulting Manhattan Project. The U.S. government suspected his socialist and pacifist views. Einstein declined an offer by David Ben-Gurion, Israel’s premier, to become president of Israel.
Einstein died on 18th April 1955 due to internal bleeding. He refused surgery saying: “I want to go when I want. It is tasteless to prolong life artificially. I have done my share, it is time to go. I will do it elegantly.” He died and given us numerous important theories and concepts to the world that are being used to this date. The strong force, a major piece of any unified field theory, was still a total mystery in Einstein’s lifetime. Nevertheless, Einstein’s work continues to win Nobel Prizes for succeeding physicists. New generations of space satellites have continued to verify the cosmology of Einstein. Also, many leading physicists are trying to finish Einstein’s ultimate dream of a “theory of everything.”
Cite this page
Albert Einstein's biography. (2019, Apr 03). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/albert-einsteins-biography/
"Albert Einstein's biography." PapersOwl.com , 3 Apr 2019, https://papersowl.com/examples/albert-einsteins-biography/
PapersOwl.com. (2019). Albert Einstein's biography . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/albert-einsteins-biography/ [Accessed: 15 May. 2024]
"Albert Einstein's biography." PapersOwl.com, Apr 03, 2019. Accessed May 15, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/albert-einsteins-biography/
"Albert Einstein's biography," PapersOwl.com , 03-Apr-2019. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/albert-einsteins-biography/. [Accessed: 15-May-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2019). Albert Einstein's biography . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/albert-einsteins-biography/ [Accessed: 15-May-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers

Two Books on Einstein and the World He Made
A lbert Einstein is one of the most written-about figures of the 20th century, and for good reason. His theories upended the system that physicists had used to describe the world since Newton. Along the way, he became a figure of public fascination—a true celebrity. Now two books further scrutinize different aspects of the man.
Samuel Graydon’s “Einstein in Time and Space” is not an exhaustive biography. Instead it presents 99 vignettes, most of them one to three pages long, that highlight key qualities of this complex person: the curious child, the rebellious student, the serial adulterer, the wily prankster, the loyal friend, the civil-rights defender, the intellect unsurpassed in his time. Mr. Graydon, the science editor at the Times Literary Supplement, has chosen his number of chapters in a playful homage to the atomic number of the element einsteinium.
Even if readers are familiar with these stories, Mr. Graydon’s approach often delivers a fresh take on episodes not strongly emphasized in other biographies. Here is Einstein the engineer patenting a unique refrigerator design and a hearing aid. There he is building a miniature cable car out of matchboxes for his young son Hans. “That was one of the nicest toys I had,” Hans later recalled.
As a correspondent, Einstein could be quite impish: “So, what are you up to, you frozen whale, you smoked, dried, canned piece of soul, or whatever else I would like to hurl at your head?” he once wrote to a friend. While starting his career in Bern, Switzerland, the young physicist formed a little club called the Olympia Academy with two friends to discuss science and philosophy. “Einstein, despite being the youngest,” writes Mr. Graydon, “was elected president, earning him the title ‘Albert Ritter von Steissbein’ (roughly, ‘Sir Albert, Knight of Backside’). A certificate was made up, featuring a drawing of a bust of Einstein beneath a string of sausages.”
Mr. Graydon’s stated goal is to point out “the inconsistencies inherent in a life, the inexplicable, incompatible, insane motivations that punctuate days and years.” The author notes how Einstein, a devoted pacifist, maintained a close friendship with the German chemist Fritz Haber, who pioneered the use of both chlorine and mustard gas during World War I. He observes that the deep thinker didn’t pass up the chance to party with the movie stars Charlie Chaplin, Mary Pickford and Douglas Fairbanks when out in California.
The book also includes moments of quiet dignity, such as the story of the black contralto Marian Anderson, who had been invited in 1937 to give a concert at Princeton University but was denied a room at the local hotel due to her race. Einstein simply prepared a room for her at his home, an invitation that was extended from that day forward whenever she visited the town.
Mr. Graydon has woven from these separate strands a compelling and beautifully written narrative, though I have one caveat. In his acknowledgments, the author admits that he “lightly fictionalized” a few chapters about representative days at Einstein’s office. Given the wealth of material on hand, a summary of Einstein’s life hardly needs any false embellishments.
While “Einstein in Time and Space” primarily concentrates on Einstein’s personal experiences, Hanoch Gutfreund and Jürgen Renn’s “The Einsteinian Revolution” delves deeply into his science. Mr. Gutfreund, the academic director of the Albert Einstein Archives at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, and Mr. Renn, the director of the Max Planck Institute for the History of Science in Berlin, have written extensively on Einstein and with this book take on a particular challenge: “to dispel the popular myth that Albert Einstein, the unconventional scientific genius, instigated an overwhelming scientific revolution through pure thought alone.” They succeed in that goal, along the way providing an excellent overview of Einstein’s major discoveries, from his early work on quantum theory to general relativity, the new law of gravity that overturned Newton. It is a welcome addition to any collection of books on modern physics.
A true understanding of Einstein’s accomplishments, they write, demands a revision of the legendary concept of the “paradigm shift.” The notion was introduced in 1962 by the historian of science Thomas Kuhn, who argued that a scientific revolution suddenly replaces a previous system of knowledge with a new one unconnected to the past. But Messrs. Gutfreund and Renn prefer to view Einstein’s work as an evolutionary process, where the new system is built upon the scientific scaffolding already in place.
In the late 19th century, that scaffolding was constructed around three dominant areas of physics: mechanics, thermodynamics and electromagnetism. Troubling puzzles were beginning to arise at the intersections between these fields, and many scientists attempted to find solutions within their own isolated specialties. But Einstein—with his deep reading of the scientific literature and the philosophy of science, his constant dialogues with scientific friends, and his careful attention to new experimental discoveries—stood above those boundaries, enabling him to perceive an entirely new vista.
The authors provide a detailed examination of Einstein’s annus mirabilis in 1905, when he recognized that light can act like a particle as well as a wave; proved that atoms exist; linked matter with energy in that celebrated equation E=mc2; and, with the special theory of relativity, swept away the idea that we live in a fixed space governed by a universal clock.
Before these discoveries, the authors note, the Dutch physicist Hendrik Lorentz had developed a mathematical scheme to explain the behavior of charged particles moving through the ether—the medium that supposedly permeates physical space to allow light to travel. Lorentz’s equations foresaw many of the phenomena later explained by special relativity. But his physical interpretation, complicated and full of assumptions, was still rooted in classical physics. Einstein jettisoned this kludge by doing away with the ether, recognizing that space and time are not absolute and declaring that the speed of light is a constant whether a body is stationary or in motion.
Einstein didn’t arrive at this solution in a single eureka moment. It was the result of deep reflection over the years, influenced by such philosophers as David Hume, who questioned the causal relations between events; Ernst Mach, who objected to Newton’s idea of absolute space; and Henri Poincaré, who early on noted the possible relativity of time. Einstein stood upon the shoulders of giants to gain his new perspective.
While “The Einsteinian Revolution” is written for a general audience, a background in physics helps make certain sections more accessible. Yet the authors’ overall thesis is clear and convincing. “The substance of Einstein’s work was not new,” they stress, “but rather was the result of an accumulation of knowledge over centuries; it was his conceptual organization that was new.” Their book, along with Mr. Graydon’s “Einstein in Time and Space,” enhances our understanding of both a great scientist and an exemplary humanist.
Ms. Bartusiak is a professor emeritus at MIT and the author of “Einstein’s Unfinished Symphony.”


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Albert Einstein (born March 14, 1879, Ulm, Württemberg, Germany—died April 18, 1955, Princeton, New Jersey, U.S.) was a German-born physicist who developed the special and general theories of relativity and won the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1921 for his explanation of the photoelectric effect.
Physicist Albert Einstein developed the theory of relativity and won the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics. Read about his inventions, IQ, wives, death, and more.
Einstein's Early Life (1879-1904) Born on March 14, 1879, in the southern German city of Ulm, Albert Einstein grew up in a middle-class Jewish family in Munich.
Signature. Albert Einstein ( / ˈaɪnstaɪn / EYEN-styne; [4] German: [ˈalbɛɐt ˈʔaɪnʃtaɪn] ⓘ; 14 March 1879 - 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist who is widely held to be one of the greatest and most influential scientists of all time. Best known for developing the theory of relativity, Einstein also made ...
Albert Einstein was born in Württemberg, Germany, on March 14, 1879 (Meltzer 2). Less than two months after his birth his family relocated to Munich where he started his education. As years passed by, Einstein and his family again relocated, this time to Switzerland, where the young Albert gained a diploma in physics and mathematics (Lakin 20).
Hoffmann, Albert Einstein: Creator and Rebel (New York: Viking, 1972), p. 18. t A. Einstein, Essays in Science (New York: Philosophical Library, 1934), p. 114. ALBERT EINSTEIN 99 bulldog tenacity of purpose, and an openness to try any route ... told in more than one biography, but nowhere better than in Einstein's own sketch of his life, so ...
Albert Einstein Biography. Born in Germany in 1879, Albert Einstein is one of the most celebrated scientists of the Twentieth Century. His theories on relativity laid the framework for a new branch of physics, and Einstein's E = mc 2 on mass-energy equivalence is one of the most famous formulas in the world. In 1921, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for his contributions to ...
A brief biography of Albert Einstein (March 14, 1879 - April 18, 1955), the scientist whose theories changed the way we think about the universe. Albert Einstein was a German-American physicist ...
Before E=MC2. Einstein was born in Germany in 1879. Growing up, he enjoyed classical music and played the violin. One story Einstein liked to tell about his childhood was when he came across a magnetic compass. The needle's invariable northward swing, guided by an invisible force, profoundly impressed him as a child.
Albert Einstein is one of the most influential figures in history of humanity. His works not only in physics but also in philosophy have been of great influence and have also stirred controversy to the world today as when they were written. Arguments have been put forward that he has been of greater influence than fellow historical figures as ...
Conclusion. Albert Einstein was one of the best scientists, mathematicians, and physicists of the 20th century. In the early twentieth century, Albert Einstein formulated theories that changed the thinking of physicists and non-specialists alike. He will always be remembered for his law of photoelectric effect and mass-energy equivalence formula.
Albert Einstein 1879-1955. German-born American physicist and philosopher. Einstein is generally acknowledged as the preeminent scientist of the twentieth century who challenged and disproved ...
A visiting medical student named "Max Talmud introduced him to Euclid's book entitled Elements ." 7 Later on Einstein referred to this masterpiece as "the holy little geometry book." 8. Although he had a brilliant mind, he had trouble finishing his studies. He finally graduated in 1900 and earned a degree in physics.
Albert Einstein was one of the greatest geniuses in the history of science. His theories, or ideas, led to new ways of thinking about the universe .
500 Words Essay On Albert Einstein. Albert Einstein was a physicist who is responsible for developing the famous general theory of relativity. Furthermore, he is one of the most influential and celebrated scientists of the 20th century. Let's take a look at the life and achievements of this genius with the essay on Albert Einstein.
Essays in Science. Albert Einstein. Open Road Media, Sep 27, 2011 - Science - 130 pages. The Authorized Albert Einstein Archives Edition: An homage to the men and women of science, and an exposition of Einstein's place in scientific history. In this fascinating collection of articles and speeches, Albert Einstein reflects not only on the ...
Biography of Albert Einstein. Albert Einstein was born in 1897 into a middle-class family of German Jews. He did not talk until he was three years of age, which caused his parents to believe that this genius would be deficient in mental abilities. By the time he was fifteen Einstein was bored with the education provided through learning things ...
500 Words Essay on Albert Einstein. Einstein was one of the founding members of the German Democratic Party in 1918. He was critical of capitalism and was a socialist. Impressed by Mahatma Gandhi, Einstein described him as a role model for future generations and exchanged written letters with him. Einstein was totally in support of non-violence ...
Essay Example: Albert Einstein was a great physicist and mathematician and was known for his theories on relativity, and of matter and heat. Einstein was born on March 14th, 1879 in Württemberg, Germany. As a child, Einstein was mesmerized in music (he played the violin), mathematics and science
Samuel Graydon's "Einstein in Time and Space" is not an exhaustive biography. Instead it presents 99 vignettes, most of them one to three pages long, that highlight key qualities of this ...