Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Working with sources
- What Is Critical Thinking? | Definition & Examples

What Is Critical Thinking? | Definition & Examples
Published on May 30, 2022 by Eoghan Ryan . Revised on May 31, 2023.
Critical thinking is the ability to effectively analyze information and form a judgment .
To think critically, you must be aware of your own biases and assumptions when encountering information, and apply consistent standards when evaluating sources .
Critical thinking skills help you to:
- Identify credible sources
- Evaluate and respond to arguments
- Assess alternative viewpoints
- Test hypotheses against relevant criteria
Table of contents
Why is critical thinking important, critical thinking examples, how to think critically, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about critical thinking.
Critical thinking is important for making judgments about sources of information and forming your own arguments. It emphasizes a rational, objective, and self-aware approach that can help you to identify credible sources and strengthen your conclusions.
Critical thinking is important in all disciplines and throughout all stages of the research process . The types of evidence used in the sciences and in the humanities may differ, but critical thinking skills are relevant to both.
In academic writing , critical thinking can help you to determine whether a source:
- Is free from research bias
- Provides evidence to support its research findings
- Considers alternative viewpoints
Outside of academia, critical thinking goes hand in hand with information literacy to help you form opinions rationally and engage independently and critically with popular media.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Critical thinking can help you to identify reliable sources of information that you can cite in your research paper . It can also guide your own research methods and inform your own arguments.
Outside of academia, critical thinking can help you to be aware of both your own and others’ biases and assumptions.
Academic examples
However, when you compare the findings of the study with other current research, you determine that the results seem improbable. You analyze the paper again, consulting the sources it cites.
You notice that the research was funded by the pharmaceutical company that created the treatment. Because of this, you view its results skeptically and determine that more independent research is necessary to confirm or refute them. Example: Poor critical thinking in an academic context You’re researching a paper on the impact wireless technology has had on developing countries that previously did not have large-scale communications infrastructure. You read an article that seems to confirm your hypothesis: the impact is mainly positive. Rather than evaluating the research methodology, you accept the findings uncritically.
Nonacademic examples
However, you decide to compare this review article with consumer reviews on a different site. You find that these reviews are not as positive. Some customers have had problems installing the alarm, and some have noted that it activates for no apparent reason.
You revisit the original review article. You notice that the words “sponsored content” appear in small print under the article title. Based on this, you conclude that the review is advertising and is therefore not an unbiased source. Example: Poor critical thinking in a nonacademic context You support a candidate in an upcoming election. You visit an online news site affiliated with their political party and read an article that criticizes their opponent. The article claims that the opponent is inexperienced in politics. You accept this without evidence, because it fits your preconceptions about the opponent.
There is no single way to think critically. How you engage with information will depend on the type of source you’re using and the information you need.
However, you can engage with sources in a systematic and critical way by asking certain questions when you encounter information. Like the CRAAP test , these questions focus on the currency , relevance , authority , accuracy , and purpose of a source of information.
When encountering information, ask:
- Who is the author? Are they an expert in their field?
- What do they say? Is their argument clear? Can you summarize it?
- When did they say this? Is the source current?
- Where is the information published? Is it an academic article? Is it peer-reviewed ?
- Why did the author publish it? What is their motivation?
- How do they make their argument? Is it backed up by evidence? Does it rely on opinion, speculation, or appeals to emotion ? Do they address alternative arguments?
Critical thinking also involves being aware of your own biases, not only those of others. When you make an argument or draw your own conclusions, you can ask similar questions about your own writing:
- Am I only considering evidence that supports my preconceptions?
- Is my argument expressed clearly and backed up with credible sources?
- Would I be convinced by this argument coming from someone else?
If you want to know more about ChatGPT, AI tools , citation , and plagiarism , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- ChatGPT vs human editor
- ChatGPT citations
- Is ChatGPT trustworthy?
- Using ChatGPT for your studies
- What is ChatGPT?
- Chicago style
- Paraphrasing
Plagiarism
- Types of plagiarism
- Self-plagiarism
- Avoiding plagiarism
- Academic integrity
- Consequences of plagiarism
- Common knowledge
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
Critical thinking skills include the ability to:
You can assess information and arguments critically by asking certain questions about the source. You can use the CRAAP test , focusing on the currency , relevance , authority , accuracy , and purpose of a source of information.
Ask questions such as:
- Who is the author? Are they an expert?
- How do they make their argument? Is it backed up by evidence?
A credible source should pass the CRAAP test and follow these guidelines:
- The information should be up to date and current.
- The author and publication should be a trusted authority on the subject you are researching.
- The sources the author cited should be easy to find, clear, and unbiased.
- For a web source, the URL and layout should signify that it is trustworthy.
Information literacy refers to a broad range of skills, including the ability to find, evaluate, and use sources of information effectively.
Being information literate means that you:
- Know how to find credible sources
- Use relevant sources to inform your research
- Understand what constitutes plagiarism
- Know how to cite your sources correctly
Confirmation bias is the tendency to search, interpret, and recall information in a way that aligns with our pre-existing values, opinions, or beliefs. It refers to the ability to recollect information best when it amplifies what we already believe. Relatedly, we tend to forget information that contradicts our opinions.
Although selective recall is a component of confirmation bias, it should not be confused with recall bias.
On the other hand, recall bias refers to the differences in the ability between study participants to recall past events when self-reporting is used. This difference in accuracy or completeness of recollection is not related to beliefs or opinions. Rather, recall bias relates to other factors, such as the length of the recall period, age, and the characteristics of the disease under investigation.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Ryan, E. (2023, May 31). What Is Critical Thinking? | Definition & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved March 18, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/working-with-sources/critical-thinking/
Is this article helpful?

Eoghan Ryan
Other students also liked, student guide: information literacy | meaning & examples, what are credible sources & how to spot them | examples, applying the craap test & evaluating sources.
- International Center for the Assessment of Higher Order Thinking
- Our Team of Presenters
- Fellows of the Foundation
- Dr. Richard Paul
- Dr. Linda Elder
- Dr. Gerald Nosich
- Permission to Use Our Work
- Create a CriticalThinking.Org Account
- Contributions to the Foundation for Critical Thinking
- Contact Us - Office Information
- Testimonials
- Center for Critical Thinking
- The National Council for Excellence in Critical Thinking
- Main Library of Critical Thinking Resources
- Defining Critical Thinking
- About Critical Thinking
- A Brief History of the Idea of Critical Thinking
- Critical Thinking: Basic Questions & Answers
- Our Conception of Critical Thinking
- Sumner’s Definition of Critical Thinking
- Research in Critical Thinking
- Critical Societies: Thoughts from the Past
- Fundamentals of Critical Thinking
- Content Is Thinking, Thinking is Content
- Critical Thinking in Every Domain of Knowledge and Belief
- Using Intellectual Standards to Assess Student Reasoning
- Open-minded inquiry
- Valuable Intellectual Traits
- Universal Intellectual Standards
- Thinking With Concepts
- The Analysis & Assessment of Thinking
- Glossary of Critical Thinking Terms
- Distinguishing Between Inert Information, Activated Ignorance, Activated Knowledge
- Critical Thinking: Identifying the Targets
- Distinguishing Between Inferences and Assumptions
- Critical Thinking Development: A Stage Theory
- Becoming a Critic Of Your Thinking
- Bertrand Russell on Critical Thinking
- Richard Paul Anthology Classic
- Documenting the Problem
- Intellectual Foundations: The Key Missing Piece in School Restructuring
- Pseudo Critical Thinking in the Educational Establishment
- Research Findings and Policy Recommendations
- Why Students and Teachers Don’t Reason Well
- Critical Thinking in the Engineering Enterprise: Novices typically don't even know what questions to ask
- Critical Thinking Movement: 3 Waves
- Higher Education Instruction
- An Overview of How to Design Instruction Using Critical Thinking Concepts
- Recommendations for Departmental Self-Evaluation
- College-Wide Grading Standards
- Sample Course: American History: 1600 to 1800
- CT Class Syllabus
- Syllabus - Psychology I
- A Sample Assignment Format
- Grade Profiles
- Critical Thinking Class: Student Understandings
- Structures for Student Self-Assessment
- Critical Thinking Class: Grading Policies
- Socratic Teaching
- John Stuart Mill: On Instruction, Intellectual Development, and Disciplined Learning
- Critical Thinking and Nursing
- K-12 Instruction Strategies & Samples
- Tactical and Structural Recommendations
- Teaching Tactics that Encourage Active Learning
- The Art of Redesigning Instruction
- Making Critical Thinking Intuitive
- Remodelled Lessons: K-3
- Remodelled Lessons: 4-6
- Remodelled Lessons: 6-9
- Remodelled Lessons: High School
- Introduction to Remodelling: Components of Remodels and Their Functions
- Strategy List: 35 Dimensions of Critical Thought
- For Students
- Critical Thinking in Everyday Life: 9 Strategies
- Developing as Rational Persons: Viewing Our Development in Stages
- How to Study and Learn (Part One)
- How to Study and Learn (Part Two)
- How to Study and Learn (Part Three)
- How to Study and Learn (Part Four)
- The Art of Close Reading (Part One)
- The Art of Close Reading (Part Two)
- The Art of Close Reading (Part Three)
- Looking To The Future With a Critical Eye: A Message for High School Graduates
- For Young Students (Elementary/K-6)
- Issues in Critical Thinking
- Critical Thinking and the Social Studies Teacher
- Ethical Reasoning Essential to Education
- Ethics Without Indoctrination
- Engineering Reasoning
- Accelerating Change
- Applied Disciplines: A Critical Thinking Model for Engineering
- Global Change: Why C.T. is Essential To the Community College Mission
- Natural Egocentric Dispositions
- Diversity: Making Sense of It Through Critical Thinking
- Critical Thinking, Moral Integrity and Citizenship
- Critical Thinking and Emotional Intelligence
- The Questioning Mind
- Newton, Darwin, & Einstein
- The Role of Socratic Questioning in Thinking, Teaching, & Learning
- Complex Interdisciplinary Questions Exemplified: Ecological Sustainability
- The Critical Mind is A Questioning Mind
- Three Categories of Questions: Crucial Distinctions
- A History of Freedom of Thought
- Reading Backwards: Classic Books Online
- Professional Development
- The Center for Critical Thinking Community Online
- Customized Webinars and Online Courses for Faculty
- Certification in the Paul-Elder Approach to Critical Thinking
- Consulting for Leaders and Key Personnel at Your Organization
- K-12 Instruction
- Higher Education
- Business & Professional Groups
- Build a Local Critical Thinking Town Hall
- Critical Thinking Training for Law Enforcement
- Online Courses for Instructors
- Critical Thinking Therapy
- Bring Critical Thinking Into Your Website's Discussion
- The State of Critical Thinking Today
- Professional Development Model for K-12
- Professional Development Model - College and University
- Workshop Descriptions
- Mentor Program
- Inservice Information Request Form
- Institutions Using Our Approach to Critical Thinking
- Conferences & Events
- Upcoming Events in Critical Thinking
- 44th Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking
- Focal Session Descriptions
- Daily Schedule
- Call for Proposals
- Presuppositions of the 44th Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking
- Recommended Reading
- Conference Archives
- 43rd Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking
- Guest Presentation Program
- Register as an Ambassador
- Testimonials from Past Attendees
- Thank You to Our Donors
- Presuppositions of the Conference
- 42nd Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking
- Overview of Sessions (Flyer)
- Presuppositions of the Annual International Conference
- Testimonials from Past Conferences
- 41st Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking
- Recommended Publications
- Dedication to Our Donors
- 40th Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking
- Session Descriptions
- Testimonials from Prior Conferences
- International Critical Thinking Manifesto
- Scholarships Available
- 39th Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking
- Travel and Lodging Info
- FAQ & General Announcements
- Focal and Plenary Session Descriptions
- Program and Proceedings of the 39th Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking
- The Venue: KU Leuven
- Call for Critical Thinking Ambassadors
- Conference Background Information
- 38th Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking
- Call for Ambassadors for Critical Thinking
- Conference Focal Session Descriptions
- Conference Concurrent Session Descriptions
- Conference Roundtable Discussions
- Conference Announcements and FAQ
- Conference Program and Proceedings
- Conference Daily Schedule
- Conference Hotel Information
- Conference Academic Credit
- Conference Presuppositions
- What Participants Have Said About the Conference
- 37th Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking
- Registration & Fees
- FAQ and Announcements
- Conference Presenters
- 37th Conference Flyer
- Program and Proceedings of the 37th Conference
- 36th International Conference
- Conference Sessions
- Conference Flyer
- Program and Proceedings
- Academic Credit
- 35th International Conference
- Conference Session Descriptions
- Available Online Sessions
- Bertrand Russell Distinguished Scholar - Daniel Ellsberg
- 35th International Conference Program
- Concurrent Sessions
- Posthumous Bertrand Russell Scholar
- Hotel Information
- Conference FAQs
- Visiting UC Berkeley
- 34th INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE
- Bertrand Russell Distinguished Scholar - Ralph Nader
- Conference Concurrent Presenters
- Conference Program
- Conference Theme
- Roundtable Discussions
- Flyer for Bulletin Boards
- 33rd INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE
- 33rd International Conference Program
- 33rd International Conference Sessions
- 33rd International Conference Presenters
- The Bertrand Russell Distinguished Scholars Critical Thinking Conversations
- 33rd International Conference - Fees & Registration
- 33rd International Conference Concurrent Presenters
- 33rd International Conference - Hotel Information
- 33rd International Conference Flyer
- 32nd INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE
- 32nd Annual Conference Sessions
- 32nd Annual Conference Presenter Information
- 32nd Conference Program
- The Bertrand Russell Distinguished Scholars Critical Thinking Lecture Series
- 32nd Annual Conference Concurrent Presenters
- 32nd Annual Conference Academic Credit
- 31st INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE
- 31st Conference Sessions
- Comments about previous conferences
- Conference Hotel (2011)
- 31st Concurrent Presenters
- Registration Fees
- 31st International Conference
- 30th INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON CRITICAL THINKING
- 30th International Conference Theme
- 30th Conference Sessions
- PreConference Sessions
- 30th Concurrent Presenters
- 30th Conference Presuppositions
- Hilton Garden Inn
- 29th International Conference
- 29th Conference Theme
- 29th Conference Sessions
- 29th Preconference Sessions
- 29th Conference Concurrent Sessions
- 2008 International Conference on Critical Thinking
- 2008 Preconference Sessions (28th Intl. Conference)
- 2007 Conference on Critical Thinking (Main Page)
- 2007 Conference Theme and sessions
- 2007 Pre-Conference Workshops
- 2006 Annual International Conference (archived)
- 2006 International Conference Theme
- 2005 International Conference (archived)
- Prior Conference Programs (Pre 2000)
- Workshop Archives
- Spring 2022 Online Workshops
- 2021 Online Workshops for Winter & Spring
- 2019 Seminar for Military and Intelligence Trainers and Instructors
- Transportation, Lodging, and Recreation
- Seminar Flyer
- 2013 Spring Workshops
- Our Presenters
- 2013 Spring Workshops - Hotel Information
- 2013 Spring Workshops Flyer
- 2013 Spring Workshops - Schedule
- Spring Workshop 2012
- 2012 Spring Workshop Strands
- 2012 Spring Workshop Flier
- 2011 Spring Workshop
- Spring 2010 Workshop Strands
- 2009 Spring Workshops on Critical Thinking
- 2008 SPRING Workshops and Seminars on Critical Thinking
- 2008 Ethical Reasoning Workshop
- 2008 - On Richard Paul's Teaching Design
- 2008 Engineering Reasoning Workshop
- 2008 Academia sobre Formulando Preguntas Esenciales
- Fellows Academy Archives
- 2017 Fall International Fellows Academy
- 4th International Fellows Academy - 2016
- 3rd International Fellows Academy
- 2nd International Fellows Academy
- 1st International Fellows Academy
- Academy Archives
- October 2019 Critical Thinking Academy for Educators and Administrators
- Transportation, Lodging, and Leisure
- Advanced Seminar: Oxford Tutorial
- Recreational Group Activities
- Limited Scholarships Available
- September 2019 Critical Thinking Educators and Administrators Academy
- 2019 Critical Thinking Training for Trainers and Advanced Academy
- Academy Flyer
- Seattle, WA 2017 Spring Academy
- San Diego, CA 2017 Spring Academy
- 2016 Spring Academy -- Washington D.C.
- 2016 Spring Academy -- Houston, TX
- The 2nd International Academy on Critical Thinking (Oxford 2008)
- 2007 National Academy on Critical Thinking Testing and Assessment
- 2006 Cambridge Academy (archived)
- 2006 Cambridge Academy Theme
- 2006 Cambridge Academy Sessions
- Accommodations at St. John's College
- Assessment & Testing
- A Model for the National Assessment of Higher Order Thinking
- International Critical Thinking Essay Test
- Online Critical Thinking Basic Concepts Test
- Online Critical Thinking Basic Concepts Sample Test
- Consequential Validity: Using Assessment to Drive Instruction
- News & Announcements
- Newest Pages Added to CriticalThinking.Org
- Online Learning
- Critical Thinking Online Courses
- Critical Thinking Blog
- 2019 Blog Entries
- 2020 Blog Entries
- 2021 Blog Entries
- 2022 Blog Entries
- 2023 Blog Entries
- Online Courses for Your Students
- Webinar Q&A Sessions
- 2023 Webinar Archives
- 2022 Webinar Archives
- 2021 Webinar Archive
- 2020 Webinar Archive
- Guided Study Groups
- Critical Thinking Channel on YouTube
- CT800: Spring 2024
Translate this page from English...
*Machine translated pages not guaranteed for accuracy. Click Here for our professional translations.

Critical Thinking: Where to Begin

- For College and University Faculty
- For College and University Students
- For High School Teachers
- For Jr. High School Teachers
- For Elementary Teachers (Grades 4-6)
- For Elementary Teachers (Kindergarten - 3rd Grade)
- For Science and Engineering Instruction
- For Business and Professional Development
- For Nursing and Health Care
- For Home Schooling and Home Study
If you are new to critical thinking or wish to deepen your conception of it, we recommend you review the content below and bookmark this page for future reference.
Our Conception of Critical Thinking...

"Critical thinking is the intellectually disciplined process of actively and skillfully conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and/or evaluating information gathered from, or generated by, observation, experience, reflection, reasoning, or communication, as a guide to belief and action. In its exemplary form, it is based on universal intellectual values that transcend subject matter divisions: clarity, accuracy, precision, consistency, relevance, sound evidence, good reasons, depth, breadth, and fairness..."
"Critical thinking is self-guided, self-disciplined thinking which attempts to reason at the highest level of quality in a fairminded way. People who think critically attempt, with consistent and conscious effort, to live rationally, reasonably, and empathically. They are keenly aware of the inherently flawed nature of human thinking when left unchecked. They strive to diminish the power of their egocentric and sociocentric tendencies. They use the intellectual tools that critical thinking offers – concepts and principles that enable them to analyze, assess, and improve thinking. They work diligently to develop the intellectual virtues of intellectual integrity, intellectual humility, intellectual civility, intellectual empathy, intellectual sense of justice and confidence in reason. They realize that no matter how skilled they are as thinkers, they can always improve their reasoning abilities and they will at times fall prey to mistakes in reasoning, human irrationality, prejudices, biases, distortions, uncritically accepted social rules and taboos, self-interest, and vested interest.
They strive to improve the world in whatever ways they can and contribute to a more rational, civilized society. At the same time, they recognize the complexities often inherent in doing so. They strive never to think simplistically about complicated issues and always to consider the rights and needs of relevant others. They recognize the complexities in developing as thinkers, and commit themselves to life-long practice toward self-improvement. They embody the Socratic principle: The unexamined life is not worth living , because they realize that many unexamined lives together result in an uncritical, unjust, dangerous world."
Why Critical Thinking?

The Problem:
Everyone thinks; it is our nature to do so. But much of our thinking, left to itself, is biased, distorted, partial, uninformed, or down-right prejudiced. Yet the quality of our lives and that of what we produce, make, or build depends precisely on the quality of our thought. Shoddy thinking is costly, both in money and in quality of life. Excellence in thought, however, must be systematically cultivated.
A Brief Definition:
Critical thinking is the art of analyzing and evaluating thinking with a view to improving it. The Result:
A well-cultivated critical thinker:
- raises vital questions and problems, formulating them clearly and precisely;
- gathers and assesses relevant information, using abstract ideas to interpret it effectively;
- comes to well-reasoned conclusions and solutions, testing them against relevant criteria and standards;
- thinks openmindedly within alternative systems of thought, recognizing and assessing, as need be, their assumptions, implications, and practical consequences; and
- communicates effectively with others in figuring out solutions to complex problems.
Critical thinking is, in short, self-directed, self-disciplined, self-monitored, and self-corrective thinking. It requires rigorous standards of excellence and mindful command of their use. It entails effective communication and problem-solving abilities, and a commitment to overcoming our native egocentrism and sociocentrism. Read more about our concept of critical thinking .
The Essential Dimensions of Critical Thinking
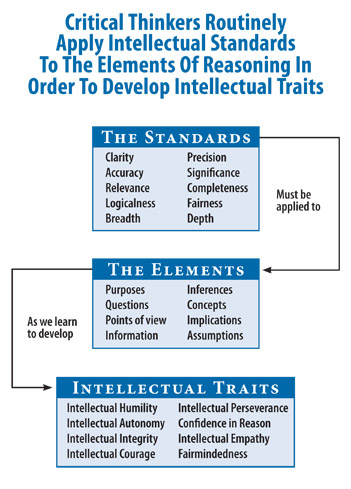
Our conception of critical thinking is based on the substantive approach developed by Dr. Richard Paul and his colleagues at the Center and Foundation for Critical Thinking over multiple decades. It is relevant to every subject, discipline, and profession, and to reasoning through the problems of everyday life. It entails five essential dimensions of critical thinking:
At the left is an overview of the first three dimensions. In sum, the elements or structures of thought enable us to "take our thinking apart" and analyze it. The intellectual standards are used to assess and evaluate the elements. The intellectual traits are dispositions of mind embodied by the fairminded critical thinker. To cultivate the mind, we need command of these essential dimensions, and we need to consistently apply them as we think through the many problems and issues in our lives.
The Elements of Reasoning and Intellectual Standards
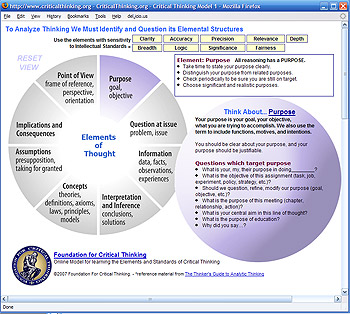
To learn more about the elements of thought and how to apply the intellectual standards, check out our interactive model. Simply click on the link below, scroll to the bottom of the page, and explore the model with your mouse.
Why the Analysis of Thinking Is Important If you want to think well, you must understand at least the rudiments of thought, the most basic structures out of which all thinking is made. You must learn how to take thinking apart. Analyzing the Logic of a Subject When we understand the elements of reasoning, we realize that all subjects, all disciplines, have a fundamental logic defined by the structures of thought embedded within them. Therefore, to lay bare a subject’s most fundamental logic, we should begin with these questions:

Going Deeper...

The Critical Thinking Bookstore
Our online bookstore houses numerous books and teacher's manuals , Thinker's Guides , videos , and other educational materials .
Learn From Our Fellows and Scholars
Watch our Event Calendar , which provides an overview of all upcoming conferences and academies hosted by the Foundation for Critical Thinking. Clicking an entry on the Event Calendar will bring up that event's details, and the option to register. For those interested in online learning, the Foundation offers accredited online courses in critical thinking for both educators and the general public, as well as an online test for evaluating basic comprehension of critical thinking concepts . We are in the process of developing more online learning tools and tests to offer the community.
Utilizing this Website
This website contains large amounts research and an online library of articles , both of which are freely available to the public. We also invite you to become a member of the Critical Thinking Community , where you will gain access to more tools and materials. If you cannot locate a resource on a specific topic or concept, try searching for it using our Search Tool . The Search Tool is at the upper-right of every page on the website.

- LEARNING SKILLS
- Study Skills
- Critical Thinking
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Learning Skills:
- A - Z List of Learning Skills
- What is Learning?
- Learning Approaches
- Learning Styles
- 8 Types of Learning Styles
- Understanding Your Preferences to Aid Learning
- Lifelong Learning
- Decisions to Make Before Applying to University
- Top Tips for Surviving Student Life
- Living Online: Education and Learning
- 8 Ways to Embrace Technology-Based Learning Approaches
Critical Thinking Skills
- Critical Thinking and Fake News
- Understanding and Addressing Conspiracy Theories
- Critical Analysis
- Top Tips for Study
- Staying Motivated When Studying
- Student Budgeting and Economic Skills
- Getting Organised for Study
- Finding Time to Study
- Sources of Information
- Assessing Internet Information
- Using Apps to Support Study
- What is Theory?
- Styles of Writing
- Effective Reading
- Critical Reading
- Note-Taking from Reading
- Note-Taking for Verbal Exchanges
- Planning an Essay
- How to Write an Essay
- The Do’s and Don’ts of Essay Writing
- How to Write a Report
- Academic Referencing
- Assignment Finishing Touches
- Reflecting on Marked Work
- 6 Skills You Learn in School That You Use in Real Life
- Top 10 Tips on How to Study While Working
- Exam Skills
- Writing a Dissertation or Thesis
- Research Methods
- Teaching, Coaching, Mentoring and Counselling
- Employability Skills for Graduates
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
What is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking is the ability to think clearly and rationally, understanding the logical connection between ideas. Critical thinking has been the subject of much debate and thought since the time of early Greek philosophers such as Plato and Socrates and has continued to be a subject of discussion into the modern age, for example the ability to recognise fake news .
Critical thinking might be described as the ability to engage in reflective and independent thinking.
In essence, critical thinking requires you to use your ability to reason. It is about being an active learner rather than a passive recipient of information.
Critical thinkers rigorously question ideas and assumptions rather than accepting them at face value. They will always seek to determine whether the ideas, arguments and findings represent the entire picture and are open to finding that they do not.
Critical thinkers will identify, analyse and solve problems systematically rather than by intuition or instinct.
Someone with critical thinking skills can:
Understand the links between ideas.
Determine the importance and relevance of arguments and ideas.
Recognise, build and appraise arguments.
Identify inconsistencies and errors in reasoning.
Approach problems in a consistent and systematic way.
Reflect on the justification of their own assumptions, beliefs and values.
Critical thinking is thinking about things in certain ways so as to arrive at the best possible solution in the circumstances that the thinker is aware of. In more everyday language, it is a way of thinking about whatever is presently occupying your mind so that you come to the best possible conclusion.
Critical Thinking is:
A way of thinking about particular things at a particular time; it is not the accumulation of facts and knowledge or something that you can learn once and then use in that form forever, such as the nine times table you learn and use in school.
The Skills We Need for Critical Thinking
The skills that we need in order to be able to think critically are varied and include observation, analysis, interpretation, reflection, evaluation, inference, explanation, problem solving, and decision making.
Specifically we need to be able to:
Think about a topic or issue in an objective and critical way.
Identify the different arguments there are in relation to a particular issue.
Evaluate a point of view to determine how strong or valid it is.
Recognise any weaknesses or negative points that there are in the evidence or argument.
Notice what implications there might be behind a statement or argument.
Provide structured reasoning and support for an argument that we wish to make.
The Critical Thinking Process
You should be aware that none of us think critically all the time.
Sometimes we think in almost any way but critically, for example when our self-control is affected by anger, grief or joy or when we are feeling just plain ‘bloody minded’.
On the other hand, the good news is that, since our critical thinking ability varies according to our current mindset, most of the time we can learn to improve our critical thinking ability by developing certain routine activities and applying them to all problems that present themselves.
Once you understand the theory of critical thinking, improving your critical thinking skills takes persistence and practice.
Try this simple exercise to help you to start thinking critically.
Think of something that someone has recently told you. Then ask yourself the following questions:
Who said it?
Someone you know? Someone in a position of authority or power? Does it matter who told you this?
What did they say?
Did they give facts or opinions? Did they provide all the facts? Did they leave anything out?
Where did they say it?
Was it in public or in private? Did other people have a chance to respond an provide an alternative account?
When did they say it?
Was it before, during or after an important event? Is timing important?
Why did they say it?
Did they explain the reasoning behind their opinion? Were they trying to make someone look good or bad?
How did they say it?
Were they happy or sad, angry or indifferent? Did they write it or say it? Could you understand what was said?
What are you Aiming to Achieve?
One of the most important aspects of critical thinking is to decide what you are aiming to achieve and then make a decision based on a range of possibilities.
Once you have clarified that aim for yourself you should use it as the starting point in all future situations requiring thought and, possibly, further decision making. Where needed, make your workmates, family or those around you aware of your intention to pursue this goal. You must then discipline yourself to keep on track until changing circumstances mean you have to revisit the start of the decision making process.
However, there are things that get in the way of simple decision making. We all carry with us a range of likes and dislikes, learnt behaviours and personal preferences developed throughout our lives; they are the hallmarks of being human. A major contribution to ensuring we think critically is to be aware of these personal characteristics, preferences and biases and make allowance for them when considering possible next steps, whether they are at the pre-action consideration stage or as part of a rethink caused by unexpected or unforeseen impediments to continued progress.
The more clearly we are aware of ourselves, our strengths and weaknesses, the more likely our critical thinking will be productive.
The Benefit of Foresight
Perhaps the most important element of thinking critically is foresight.
Almost all decisions we make and implement don’t prove disastrous if we find reasons to abandon them. However, our decision making will be infinitely better and more likely to lead to success if, when we reach a tentative conclusion, we pause and consider the impact on the people and activities around us.
The elements needing consideration are generally numerous and varied. In many cases, consideration of one element from a different perspective will reveal potential dangers in pursuing our decision.
For instance, moving a business activity to a new location may improve potential output considerably but it may also lead to the loss of skilled workers if the distance moved is too great. Which of these is the more important consideration? Is there some way of lessening the conflict?
These are the sort of problems that may arise from incomplete critical thinking, a demonstration perhaps of the critical importance of good critical thinking.
Further Reading from Skills You Need

The Skills You Need Guide for Students

Develop the skills you need to make the most of your time as a student.
Our eBooks are ideal for students at all stages of education, school, college and university. They are full of easy-to-follow practical information that will help you to learn more effectively and get better grades.
In Summary:
Critical thinking is aimed at achieving the best possible outcomes in any situation. In order to achieve this it must involve gathering and evaluating information from as many different sources possible.
Critical thinking requires a clear, often uncomfortable, assessment of your personal strengths, weaknesses and preferences and their possible impact on decisions you may make.
Critical thinking requires the development and use of foresight as far as this is possible. As Doris Day sang, “the future’s not ours to see”.
Implementing the decisions made arising from critical thinking must take into account an assessment of possible outcomes and ways of avoiding potentially negative outcomes, or at least lessening their impact.
- Critical thinking involves reviewing the results of the application of decisions made and implementing change where possible.
It might be thought that we are overextending our demands on critical thinking in expecting that it can help to construct focused meaning rather than examining the information given and the knowledge we have acquired to see if we can, if necessary, construct a meaning that will be acceptable and useful.
After all, almost no information we have available to us, either externally or internally, carries any guarantee of its life or appropriateness. Neat step-by-step instructions may provide some sort of trellis on which our basic understanding of critical thinking can blossom but it doesn’t and cannot provide any assurance of certainty, utility or longevity.
Continue to: Critical Thinking and Fake News Critical Reading
See also: Analytical Skills Understanding and Addressing Conspiracy Theories Introduction to Neuro-Linguistic Programming (NLP)

- Get started with computers
- Learn Microsoft Office
- Apply for a job
- Improve my work skills
- Design nice-looking docs
- Getting Started
- Smartphones & Tablets
- Typing Tutorial
- Online Learning
- Basic Internet Skills
- Online Safety
- Social Media
- Zoom Basics
- Google Docs
- Google Sheets
- Career Planning
- Resume Writing
- Cover Letters
- Job Search and Networking
- Business Communication
- Entrepreneurship 101
- Careers without College
- Job Hunt for Today
- 3D Printing
- Freelancing 101
- Personal Finance
- Sharing Economy
- Decision-Making
- Graphic Design
- Photography
- Image Editing
- Learning WordPress
- Language Learning
- Critical Thinking
- For Educators
- Translations
- Staff Picks
- English expand_more expand_less
Critical Thinking and Decision-Making - What is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking and decision-making -, what is critical thinking, critical thinking and decision-making what is critical thinking.

Critical Thinking and Decision-Making: What is Critical Thinking?
Lesson 1: what is critical thinking, what is critical thinking.
Critical thinking is a term that gets thrown around a lot. You've probably heard it used often throughout the years whether it was in school, at work, or in everyday conversation. But when you stop to think about it, what exactly is critical thinking and how do you do it ?
Watch the video below to learn more about critical thinking.
Simply put, critical thinking is the act of deliberately analyzing information so that you can make better judgements and decisions . It involves using things like logic, reasoning, and creativity, to draw conclusions and generally understand things better.
This may sound like a pretty broad definition, and that's because critical thinking is a broad skill that can be applied to so many different situations. You can use it to prepare for a job interview, manage your time better, make decisions about purchasing things, and so much more.
The process
As humans, we are constantly thinking . It's something we can't turn off. But not all of it is critical thinking. No one thinks critically 100% of the time... that would be pretty exhausting! Instead, it's an intentional process , something that we consciously use when we're presented with difficult problems or important decisions.
Improving your critical thinking

In order to become a better critical thinker, it's important to ask questions when you're presented with a problem or decision, before jumping to any conclusions. You can start with simple ones like What do I currently know? and How do I know this? These can help to give you a better idea of what you're working with and, in some cases, simplify more complex issues.
Real-world applications

Let's take a look at how we can use critical thinking to evaluate online information . Say a friend of yours posts a news article on social media and you're drawn to its headline. If you were to use your everyday automatic thinking, you might accept it as fact and move on. But if you were thinking critically, you would first analyze the available information and ask some questions :
- What's the source of this article?
- Is the headline potentially misleading?
- What are my friend's general beliefs?
- Do their beliefs inform why they might have shared this?

After analyzing all of this information, you can draw a conclusion about whether or not you think the article is trustworthy.
Critical thinking has a wide range of real-world applications . It can help you to make better decisions, become more hireable, and generally better understand the world around you.

/en/problem-solving-and-decision-making/why-is-it-so-hard-to-make-decisions/content/
Critical Thinking Definition, Skills, and Examples
- Homework Help
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Graduate School
- Business School
- Distance Learning
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/ADHeadshot-Cropped-b80e40469d5b4852a68f94ad69d6e8bd.jpg)
- Indiana University, Bloomington
- State University of New York at Oneonta
Critical thinking refers to the ability to analyze information objectively and make a reasoned judgment. It involves the evaluation of sources, such as data, facts, observable phenomena, and research findings.
Good critical thinkers can draw reasonable conclusions from a set of information, and discriminate between useful and less useful details to solve problems or make decisions. Employers prioritize the ability to think critically—find out why, plus see how you can demonstrate that you have this ability throughout the job application process.
Why Do Employers Value Critical Thinking Skills?
Employers want job candidates who can evaluate a situation using logical thought and offer the best solution.
Someone with critical thinking skills can be trusted to make decisions independently, and will not need constant handholding.
Hiring a critical thinker means that micromanaging won't be required. Critical thinking abilities are among the most sought-after skills in almost every industry and workplace. You can demonstrate critical thinking by using related keywords in your resume and cover letter, and during your interview.
Examples of Critical Thinking
The circumstances that demand critical thinking vary from industry to industry. Some examples include:
- A triage nurse analyzes the cases at hand and decides the order by which the patients should be treated.
- A plumber evaluates the materials that would best suit a particular job.
- An attorney reviews evidence and devises a strategy to win a case or to decide whether to settle out of court.
- A manager analyzes customer feedback forms and uses this information to develop a customer service training session for employees.
Promote Your Skills in Your Job Search
If critical thinking is a key phrase in the job listings you are applying for, be sure to emphasize your critical thinking skills throughout your job search.
Add Keywords to Your Resume
You can use critical thinking keywords (analytical, problem solving, creativity, etc.) in your resume. When describing your work history , include top critical thinking skills that accurately describe you. You can also include them in your resume summary , if you have one.
For example, your summary might read, “Marketing Associate with five years of experience in project management. Skilled in conducting thorough market research and competitor analysis to assess market trends and client needs, and to develop appropriate acquisition tactics.”
Mention Skills in Your Cover Letter
Include these critical thinking skills in your cover letter. In the body of your letter, mention one or two of these skills, and give specific examples of times when you have demonstrated them at work. Think about times when you had to analyze or evaluate materials to solve a problem.
Show the Interviewer Your Skills
You can use these skill words in an interview. Discuss a time when you were faced with a particular problem or challenge at work and explain how you applied critical thinking to solve it.
Some interviewers will give you a hypothetical scenario or problem, and ask you to use critical thinking skills to solve it. In this case, explain your thought process thoroughly to the interviewer. He or she is typically more focused on how you arrive at your solution rather than the solution itself. The interviewer wants to see you analyze and evaluate (key parts of critical thinking) the given scenario or problem.
Of course, each job will require different skills and experiences, so make sure you read the job description carefully and focus on the skills listed by the employer.
Top Critical Thinking Skills
Keep these in-demand critical thinking skills in mind as you update your resume and write your cover letter. As you've seen, you can also emphasize them at other points throughout the application process, such as your interview.
Part of critical thinking is the ability to carefully examine something, whether it is a problem, a set of data, or a text. People with analytical skills can examine information, understand what it means, and properly explain to others the implications of that information.
- Asking Thoughtful Questions
- Data Analysis
- Interpretation
- Questioning Evidence
- Recognizing Patterns
Communication
Often, you will need to share your conclusions with your employers or with a group of colleagues. You need to be able to communicate with others to share your ideas effectively. You might also need to engage in critical thinking in a group. In this case, you will need to work with others and communicate effectively to figure out solutions to complex problems.
- Active Listening
- Collaboration
- Explanation
- Interpersonal
- Presentation
- Verbal Communication
- Written Communication
Critical thinking often involves creativity and innovation. You might need to spot patterns in the information you are looking at or come up with a solution that no one else has thought of before. All of this involves a creative eye that can take a different approach from all other approaches.
- Flexibility
- Conceptualization
- Imagination
- Drawing Connections
- Synthesizing
Open-Mindedness
To think critically, you need to be able to put aside any assumptions or judgments and merely analyze the information you receive. You need to be objective, evaluating ideas without bias.
- Objectivity
- Observation
Problem Solving
Problem-solving is another critical thinking skill that involves analyzing a problem, generating and implementing a solution, and assessing the success of the plan. Employers don’t simply want employees who can think about information critically. They also need to be able to come up with practical solutions.
- Attention to Detail
- Clarification
- Decision Making
- Groundedness
- Identifying Patterns
More Critical Thinking Skills
- Inductive Reasoning
- Deductive Reasoning
- Noticing Outliers
- Adaptability
- Emotional Intelligence
- Brainstorming
- Optimization
- Restructuring
- Integration
- Strategic Planning
- Project Management
- Ongoing Improvement
- Causal Relationships
- Case Analysis
- Diagnostics
- SWOT Analysis
- Business Intelligence
- Quantitative Data Management
- Qualitative Data Management
- Risk Management
- Scientific Method
- Consumer Behavior
Key Takeaways
- Demonstrate that you have critical thinking skills by adding relevant keywords to your resume.
- Mention pertinent critical thinking skills in your cover letter, too, and include an example of a time when you demonstrated them at work.
- Finally, highlight critical thinking skills during your interview. For instance, you might discuss a time when you were faced with a challenge at work and explain how you applied critical thinking skills to solve it.
University of Louisville. " What is Critical Thinking ."
American Management Association. " AMA Critical Skills Survey: Workers Need Higher Level Skills to Succeed in the 21st Century ."
- How To Become an Effective Problem Solver
- 2020-21 Common Application Essay Option 4—Solving a Problem
- College Interview Tips: "Tell Me About a Challenge You Overcame"
- Types of Medical School Interviews and What to Expect
- The Horse Problem: A Math Challenge
- What to Do When the Technology Fails in Class
- A Guide to Business Letters Types
- Landing Your First Teaching Job
- How to Facilitate Learning and Critical Thinking
- Best Majors for Pre-med Students
- Problem Solving in Mathematics
- Discover Ideas Through Brainstorming
- What You Need to Know About the Executive Assessment
- Finding a Job for ESL Learners: Interview Basics
- Finding a Job for ESL Learners
- Job Interview Questions and Answers
- The Open University
- Guest user / Sign out
- Study with The Open University
My OpenLearn Profile
Personalise your OpenLearn profile, save your favourite content and get recognition for your learning
Critical thinking – A skill and a process

Now, that oversimplified approach to learning certainly is the first step to studying as well. However, in order to be successful in our studies, we need to do more than just contain and repeat information. We need to be able to assess the value of the information, its correctness, and its contribution to any given debate. Ideally, we are able to put it into context with other aspects of our knowledge, too. This is what makes us students, this is what makes us critical thinkers.
Critical thinking is not just one skill, rather it is the result of a number of skills applied effectively. In order to be able to think critically, you’ll need to be able reason. You’ll need to be able to assess the source of the information you’re given and you’ll be able to reflect on its accuracy or validity, depending on your task.
By thinking critically, you are applying each of those skills in order to evaluate the information in front of you. This can be a theory, a new research result, or even a news item. Critical thinking allows you to apply an objective approach to your learning, rather than subjectively following either the proposed information you’re given, or your own opinion rather than clear and convincing arguments and facts.
Critical thinking is a process of continuing evaluation and reflection. It is most powerful, when leading to a change of view in ourselves or in others.
This is where critical thinking becomes relevant outside the world of studying. By being critical of what we read, hear and see, we are engaging with the society we live in actively. We are not perceiving anything as given, but are rather reflecting on the value and correctness of the way society works.
This helps us to be better employees, by reflecting on where processes and ways of working can be improved. It helps us to more engaged citizens, as we are reflecting on political campaigns and their truthfulness and value for us when we are asked to participate in an election. Critical thinking pushes ourselves and our environment to continuously adapt and improve.
When you think critically, you open up a whole new way of engaging with the world around you.
Find out more about 'Go the Distance'

Am I ready to be a distance learner?
Distance learning can open up opportunities for study. You might have not studied for a while, you might be returning to education, or you might not have had the chance to study at a higher level before. This free course, Am I ready to be a distance learner?, will help to boost your confidence. You'll explore useful skills so you can discover ...
Free course
Level: 1 Introductory

Taking your first steps into higher education
What is university study like? Is it for me? If you are asking yourself these questions, this free course is for you. Taking your first steps into higher education provides insights into how subjects are studied at university. This introduction to carefully selected materials helps you decide what you might want to study. You will be ...

Are you ready for postgraduate study?
This free course, Are you ready for postgraduate study, will help you to become familiar with the requirements and demands of postgraduate study and ensure you are ready to develop the skills and confidence to pursue your learning further.
Level: 3 Advanced
Become an OU student
Ratings & comments, share this free course, copyright information, publication details.
- Originally published: Wednesday, 15 November 2017
- Body text - Creative Commons BY-NC-SA 4.0 : The Open University
- Image 'angels with a book statue' - Copyright free
- Image 'Am I ready to be a distance learner?' - Copyright free
- Image 'Are you ready for postgraduate study?' - Copyright free
- Image 'Taking your first steps into higher education' - Copyright: Image courtesy of chanpipat at FreeDigitalPhotos.net
Rate and Review
Rate this article, review this article.
Log into OpenLearn to leave reviews and join in the conversation.
Article reviews
For further information, take a look at our frequently asked questions which may give you the support you need.

- Schools & departments

Critical thinking
Advice and resources to help you develop your critical voice.
Developing critical thinking skills is essential to your success at University and beyond. We all need to be critical thinkers to help us navigate our way through an information-rich world.
Whatever your discipline, you will engage with a wide variety of sources of information and evidence. You will develop the skills to make judgements about this evidence to form your own views and to present your views clearly.
One of the most common types of feedback received by students is that their work is ‘too descriptive’. This usually means that they have just stated what others have said and have not reflected critically on the material. They have not evaluated the evidence and constructed an argument.
What is critical thinking?
Critical thinking is the art of making clear, reasoned judgements based on interpreting, understanding, applying and synthesising evidence gathered from observation, reading and experimentation. Burns, T., & Sinfield, S. (2016) Essential Study Skills: The Complete Guide to Success at University (4th ed.) London: SAGE, p94.
Being critical does not just mean finding fault. It means assessing evidence from a variety of sources and making reasoned conclusions. As a result of your analysis you may decide that a particular piece of evidence is not robust, or that you disagree with the conclusion, but you should be able to state why you have come to this view and incorporate this into a bigger picture of the literature.
Being critical goes beyond describing what you have heard in lectures or what you have read. It involves synthesising, analysing and evaluating what you have learned to develop your own argument or position.
Critical thinking is important in all subjects and disciplines – in science and engineering, as well as the arts and humanities. The types of evidence used to develop arguments may be very different but the processes and techniques are similar. Critical thinking is required for both undergraduate and postgraduate levels of study.
What, where, when, who, why, how?
Purposeful reading can help with critical thinking because it encourages you to read actively rather than passively. When you read, ask yourself questions about what you are reading and make notes to record your views. Ask questions like:
- What is the main point of this paper/ article/ paragraph/ report/ blog?
- Who wrote it?
- Why was it written?
- When was it written?
- Has the context changed since it was written?
- Is the evidence presented robust?
- How did the authors come to their conclusions?
- Do you agree with the conclusions?
- What does this add to our knowledge?
- Why is it useful?
Our web page covering Reading at university includes a handout to help you develop your own critical reading form and a suggested reading notes record sheet. These resources will help you record your thoughts after you read, which will help you to construct your argument.
Reading at university
Developing an argument
Being a university student is about learning how to think, not what to think. Critical thinking shapes your own values and attitudes through a process of deliberating, debating and persuasion. Through developing your critical thinking you can move on from simply disagreeing to constructively assessing alternatives by building on doubts.
There are several key stages involved in developing your ideas and constructing an argument. You might like to use a form to help you think about the features of critical thinking and to break down the stages of developing your argument.
Features of critical thinking (pdf)
Features of critical thinking (Word rtf)
Our webpage on Academic writing includes a useful handout ‘Building an argument as you go’.
Academic writing
You should also consider the language you will use to introduce a range of viewpoints and to evaluate the various sources of evidence. This will help your reader to follow your argument. To get you started, the University of Manchester's Academic Phrasebank has a useful section on Being Critical.
Academic Phrasebank
Developing your critical thinking
Set yourself some tasks to help develop your critical thinking skills. Discuss material presented in lectures or from resource lists with your peers. Set up a critical reading group or use an online discussion forum. Think about a point you would like to make during discussions in tutorials and be prepared to back up your argument with evidence.
For more suggestions:
Developing your critical thinking - ideas (pdf)
Developing your critical thinking - ideas (Word rtf)
Published guides
For further advice and more detailed resources please see the Critical Thinking section of our list of published Study skills guides.
Study skills guides

- Programs & Services
- Delphi Center
Ideas to Action (i2a)
- What is Critical Thinking?

The ability to think critically calls for a higher-order thinking than simply the ability to recall information.
Definitions of critical thinking, its elements, and its associated activities fill the educational literature of the past forty years. Critical thinking has been described as an ability to question; to acknowledge and test previously held assumptions; to recognize ambiguity; to examine, interpret, evaluate, reason, and reflect; to make informed judgments and decisions; and to clarify, articulate, and justify positions (Hullfish & Smith, 1961; Ennis, 1962; Ruggiero, 1975; Scriven, 1976; Hallet, 1984; Kitchener, 1986; Pascarella & Terenzini, 1991; Mines et al., 1990; Halpern, 1996; Paul & Elder, 2001; Petress, 2004; Holyoak & Morrison, 2005; among others).
After a careful review of the mountainous body of literature defining critical thinking and its elements, UofL has chosen to adopt the language of Michael Scriven and Richard Paul (2003) as a comprehensive, concise operating definition:
Critical thinking is the intellectually disciplined process of actively and skillfully conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and/or evaluating information gathered from, or generated by, observation, experience, reflection, reasoning, or communication, as a guide to belief and action.
Paul and Scriven go on to suggest that critical thinking is based on: "universal intellectual values that transcend subject matter divisions: clarity, accuracy, precision, consistency, relevance, sound evidence, good reasons, depth, breadth, and fairness. It entails the examination of those structures or elements of thought implicit in all reasoning: purpose, problem, or question-at-issue, assumptions, concepts, empirical grounding; reasoning leading to conclusions, implication and consequences, objections from alternative viewpoints, and frame of reference. Critical thinking - in being responsive to variable subject matter, issues, and purposes - is incorporated in a family of interwoven modes of thinking, among them: scientific thinking, mathematical thinking, historical thinking, anthropological thinking, economic thinking, moral thinking, and philosophical thinking."
This conceptualization of critical thinking has been refined and developed further by Richard Paul and Linder Elder into the Paul-Elder framework of critical thinking. Currently, this approach is one of the most widely published and cited frameworks in the critical thinking literature. According to the Paul-Elder framework, critical thinking is the:
- Analysis of thinking by focusing on the parts or structures of thinking ("the Elements of Thought")
- Evaluation of thinking by focusing on the quality ("the Universal Intellectual Standards")
- Improvement of thinking by using what you have learned ("the Intellectual Traits")
Selection of a Critical Thinking Framework
The University of Louisville chose the Paul-Elder model of Critical Thinking as the approach to guide our efforts in developing and enhancing our critical thinking curriculum. The Paul-Elder framework was selected based on criteria adapted from the characteristics of a good model of critical thinking developed at Surry Community College. The Paul-Elder critical thinking framework is comprehensive, uses discipline-neutral terminology, is applicable to all disciplines, defines specific cognitive skills including metacognition, and offers high quality resources.
Why the selection of a single critical thinking framework?
The use of a single critical thinking framework is an important aspect of institution-wide critical thinking initiatives (Paul and Nosich, 1993; Paul, 2004). According to this view, critical thinking instruction should not be relegated to one or two disciplines or departments with discipline specific language and conceptualizations. Rather, critical thinking instruction should be explicitly infused in all courses so that critical thinking skills can be developed and reinforced in student learning across the curriculum. The use of a common approach with a common language allows for a central organizer and for the development of critical thinking skill sets in all courses.
- SACS & QEP
- Planning and Implementation
- Why Focus on Critical Thinking?
- Paul-Elder Critical Thinking Framework
- Culminating Undergraduate Experience
- Community Engagement
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What is i2a?
Copyright © 2012 - University of Louisville , Delphi Center
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} Join us: Learn how to build a trusted AI strategy to support your company's intelligent transformation, featuring Forrester .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Register now .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Collaboration |
- How to build your critical thinking ski ...
How to build your critical thinking skills in 7 steps (with examples)

Critical thinking is, well, critical. By building these skills, you improve your ability to analyze information and come to the best decision possible. In this article, we cover the basics of critical thinking, as well as the seven steps you can use to implement the full critical thinking process.
Critical thinking comes from asking the right questions to come to the best conclusion possible. Strong critical thinkers analyze information from a variety of viewpoints in order to identify the best course of action.
Don’t worry if you don’t think you have strong critical thinking abilities. In this article, we’ll help you build a foundation for critical thinking so you can absorb, analyze, and make informed decisions.
What is critical thinking?
Critical thinking is the ability to collect and analyze information to come to a conclusion. Being able to think critically is important in virtually every industry and applicable across a wide range of positions. That’s because critical thinking isn’t subject-specific—rather, it’s your ability to parse through information, data, statistics, and other details in order to identify a satisfactory solution.
Decision-making tools for agile businesses
In this ebook, learn how to equip employees to make better decisions—so your business can pivot, adapt, and tackle challenges more effectively than your competition.

Top 8 critical thinking skills
Like most soft skills, critical thinking isn’t something you can take a class to learn. Rather, this skill consists of a variety of interpersonal and analytical skills. Developing critical thinking is more about learning to embrace open-mindedness and bringing analytical thinking to your problem framing process.
In no particular order, the eight most important critical thinking skills are:
Analytical thinking: Part of critical thinking is evaluating data from multiple sources in order to come to the best conclusions. Analytical thinking allows people to reject bias and strive to gather and consume information to come to the best conclusion.
Open-mindedness: This critical thinking skill helps you analyze and process information to come to an unbiased conclusion. Part of the critical thinking process is letting your personal biases go and coming to a conclusion based on all of the information.
Problem solving : Because critical thinking emphasizes coming to the best conclusion based on all of the available information, it’s a key part of problem solving. When used correctly, critical thinking helps you solve any problem—from a workplace challenge to difficulties in everyday life.
Self-regulation: Self-regulation refers to the ability to regulate your thoughts and set aside any personal biases to come to the best conclusion. In order to be an effective critical thinker, you need to question the information you have and the decisions you favor—only then can you come to the best conclusion.
Observation: Observation skills help critical thinkers look for things beyond face value. To be a critical thinker you need to embrace multiple points of view, and you can use observation skills to identify potential problems.
Interpretation: Not all data is made equal—and critical thinkers know this. In addition to gathering information, it’s important to evaluate which information is important and relevant to your situation. That way, you can draw the best conclusions from the data you’ve collected.
Evaluation: When you attempt to answer a hard question, there is rarely an obvious answer. Even though critical thinking emphasizes putting your biases aside, you need to be able to confidently make a decision based on the data you have available.
Communication: Once a decision has been made, you also need to share this decision with other stakeholders. Effective workplace communication includes presenting evidence and supporting your conclusion—especially if there are a variety of different possible solutions.
7 steps to critical thinking
Critical thinking is a skill that you can build by following these seven steps. The seven steps to critical thinking help you ensure you’re approaching a problem from the right angle, considering every alternative, and coming to an unbiased conclusion.
First things first: When to use the 7 step critical thinking process
There’s a lot that goes into the full critical thinking process, and not every decision needs to be this thought out. Sometimes, it’s enough to put aside bias and approach a process logically. In other, more complex cases, the best way to identify the ideal outcome is to go through the entire critical thinking process.
The seven-step critical thinking process is useful for complex decisions in areas you are less familiar with. Alternatively, the seven critical thinking steps can help you look at a problem you’re familiar with from a different angle, without any bias.
If you need to make a less complex decision, consider another problem solving strategy instead. Decision matrices are a great way to identify the best option between different choices. Check out our article on 7 steps to creating a decision matrix .
1. Identify the problem
Before you put those critical thinking skills to work, you first need to identify the problem you’re solving. This step includes taking a look at the problem from a few different perspectives and asking questions like:
What’s happening?
Why is this happening?
What assumptions am I making?
At first glance, how do I think we can solve this problem?
A big part of developing your critical thinking skills is learning how to come to unbiased conclusions. In order to do that, you first need to acknowledge the biases that you currently have. Does someone on your team think they know the answer? Are you making assumptions that aren’t necessarily true? Identifying these details helps you later on in the process.
2. Research
At this point, you likely have a general idea of the problem—but in order to come up with the best solution, you need to dig deeper.
During the research process, collect information relating to the problem, including data, statistics, historical project information, team input, and more. Make sure you gather information from a variety of sources, especially if those sources go against your personal ideas about what the problem is or how to solve it.
Gathering varied information is essential for your ability to apply the critical thinking process. If you don’t get enough information, your ability to make a final decision will be skewed. Remember that critical thinking is about helping you identify the objective best conclusion. You aren’t going with your gut—you’re doing research to find the best option
3. Determine data relevance
Just as it’s important to gather a variety of information, it is also important to determine how relevant the different information sources are. After all, just because there is data doesn’t mean it’s relevant.
Once you’ve gathered all of the information, sift through the noise and identify what information is relevant and what information isn’t. Synthesizing all of this information and establishing significance helps you weigh different data sources and come to the best conclusion later on in the critical thinking process.
To determine data relevance, ask yourself:
How reliable is this information?
How significant is this information?
Is this information outdated? Is it specialized in a specific field?
4. Ask questions
One of the most useful parts of the critical thinking process is coming to a decision without bias. In order to do so, you need to take a step back from the process and challenge the assumptions you’re making.
We all have bias—and that isn’t necessarily a bad thing. Unconscious biases (also known as cognitive biases) often serve as mental shortcuts to simplify problem solving and aid decision making. But even when biases aren’t inherently bad, you must be aware of your biases in order to put them aside when necessary.
Before coming to a solution, ask yourself:
Am I making any assumptions about this information?
Are there additional variables I haven’t considered?
Have I evaluated the information from every perspective?
Are there any viewpoints I missed?
5. Identify the best solution
Finally, you’re ready to come to a conclusion. To identify the best solution, draw connections between causes and effects. Use the facts you’ve gathered to evaluate the most objective conclusion.
Keep in mind that there may be more than one solution. Often, the problems you’re facing are complex and intricate. The critical thinking process doesn’t necessarily lead to a cut-and-dry solution—instead, the process helps you understand the different variables at play so you can make an informed decision.
6. Present your solution
Communication is a key skill for critical thinkers. It isn’t enough to think for yourself—you also need to share your conclusion with other project stakeholders. If there are multiple solutions, present them all. There may be a case where you implement one solution, then test to see if it works before implementing another solution.
7. Analyze your decision
The seven-step critical thinking process yields a result—and you then need to put that solution into place. After you’ve implemented your decision, evaluate whether or not it was effective. Did it solve the initial problem? What lessons—whether positive or negative—can you learn from this experience to improve your critical thinking for next time?
Depending on how your team shares information, consider documenting lessons learned in a central source of truth. That way, team members that are making similar or related decisions in the future can understand why you made the decision you made and what the outcome was.
Example of critical thinking in the workplace
Imagine you work in user experience design (UX). Your team is focused on pricing and packaging and ensuring customers have a clear understanding of the different services your company offers. Here’s how to apply the critical thinking process in the workplace in seven steps:
Start by identifying the problem
Your current pricing page isn’t performing as well as you want. You’ve heard from customers that your services aren’t clear, and that the page doesn’t answer the questions they have. This page is really important for your company, since it’s where your customers sign up for your service. You and your team have a few theories about why your current page isn’t performing well, but you decide to apply the critical thinking process to ensure you come to the best decision for the page.
Gather information about how the problem started
Part of identifying the problem includes understanding how the problem started. The pricing and packaging page is important—so when your team initially designed the page, they certainly put a lot of thought into it. Before you begin researching how to improve the page, ask yourself:
Why did you design the pricing page the way you did?
Which stakeholders need to be involved in the decision making process?
Where are users getting stuck on the page?
Are any features currently working?
Then, you research
In addition to understanding the history of the pricing and packaging page, it’s important to understand what works well. Part of this research means taking a look at what your competitor’s pricing pages look like.
Ask yourself:
How have our competitors set up their pricing pages?
Are there any pricing page best practices?
How does color, positioning, and animation impact navigation?
Are there any standard page layouts customers expect to see?
Organize and analyze information
You’ve gathered all of the information you need—now you need to organize and analyze it. What trends, if any, are you noticing? Is there any particularly relevant or important information that you have to consider?
Ask open-ended questions to reduce bias
In the case of critical thinking, it’s important to address and set bias aside as much as possible. Ask yourself:
Is there anything I’m missing?
Have I connected with the right stakeholders?
Are there any other viewpoints I should consider?
Determine the best solution for your team
You now have all of the information you need to design the best pricing page. Depending on the complexity of the design, you may want to design a few options to present to a small group of customers or A/B test on the live website.
Present your solution to stakeholders
Critical thinking can help you in every element of your life, but in the workplace, you must also involve key project stakeholders . Stakeholders help you determine next steps, like whether you’ll A/B test the page first. Depending on the complexity of the issue, consider hosting a meeting or sharing a status report to get everyone on the same page.
Analyze the results
No process is complete without evaluating the results. Once the new page has been live for some time, evaluate whether it did better than the previous page. What worked? What didn’t? This also helps you make better critical decisions later on.
Critically successful
Critical thinking takes time to build, but with effort and patience you can apply an unbiased, analytical mind to any situation. Critical thinking makes up one of many soft skills that makes you an effective team member, manager, and worker. If you’re looking to hone your skills further, read our article on the 25 project management skills you need to succeed .
Related resources

How Asana uses Asana to streamline project intake processes

How Asana uses work management for smoother creative production

Don’t like giving feedback? These 20 tips are for you

Work schedule types: How to find the right approach for your team
Critical thinking definition

Critical thinking, as described by Oxford Languages, is the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgement.
Active and skillful approach, evaluation, assessment, synthesis, and/or evaluation of information obtained from, or made by, observation, knowledge, reflection, acumen or conversation, as a guide to belief and action, requires the critical thinking process, which is why it's often used in education and academics.
Some even may view it as a backbone of modern thought.
However, it's a skill, and skills must be trained and encouraged to be used at its full potential.
People turn up to various approaches in improving their critical thinking, like:
- Developing technical and problem-solving skills
- Engaging in more active listening
- Actively questioning their assumptions and beliefs
- Seeking out more diversity of thought
- Opening up their curiosity in an intellectual way etc.
Is critical thinking useful in writing?
Critical thinking can help in planning your paper and making it more concise, but it's not obvious at first. We carefully pinpointed some the questions you should ask yourself when boosting critical thinking in writing:
- What information should be included?
- Which information resources should the author look to?
- What degree of technical knowledge should the report assume its audience has?
- What is the most effective way to show information?
- How should the report be organized?
- How should it be designed?
- What tone and level of language difficulty should the document have?
Usage of critical thinking comes down not only to the outline of your paper, it also begs the question: How can we use critical thinking solving problems in our writing's topic?
Let's say, you have a Powerpoint on how critical thinking can reduce poverty in the United States. You'll primarily have to define critical thinking for the viewers, as well as use a lot of critical thinking questions and synonyms to get them to be familiar with your methods and start the thinking process behind it.
Are there any services that can help me use more critical thinking?
We understand that it's difficult to learn how to use critical thinking more effectively in just one article, but our service is here to help.
We are a team specializing in writing essays and other assignments for college students and all other types of customers who need a helping hand in its making. We cover a great range of topics, offer perfect quality work, always deliver on time and aim to leave our customers completely satisfied with what they ordered.
The ordering process is fully online, and it goes as follows:
- Select the topic and the deadline of your essay.
- Provide us with any details, requirements, statements that should be emphasized or particular parts of the essay writing process you struggle with.
- Leave the email address, where your completed order will be sent to.
- Select your prefered payment type, sit back and relax!
With lots of experience on the market, professionally degreed essay writers , online 24/7 customer support and incredibly low prices, you won't find a service offering a better deal than ours.
More From Forbes
The seven key steps of critical thinking.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Shutterstock
As leaders, it is our job to get the very best out of our workforce. We focus on how best to motivate, inspire and create an environment in which employees are satisfied, engaged and productive. This leads us to deliver an excellent customer/client experience.
But all in all, the effort we put into growing our workforce, we often forget the one person who is in constant need of development: ourselves. In particular, we neglect the soft skills that are vital to becoming the best professional possible — one of them being critical thinking.
When you're able to critically think, it opens the door for employee engagement, as you become the go-to person for assistance with issues, challenges and problems. In turn, you teach your workforce how to critically think and problem solve.
Let’s take a look at the key steps in developing critical thinking skills.
What Is Critical Thinking?
One of my favorite definitions of critical thinking comes from Edward Glaser. He said , “The ability to think critically, as conceived in this volume, involves three things:
1. An attitude of being disposed to consider in a thoughtful way the problems and subjects that come within the range of one’s experiences
2. Knowledge of the methods of logical inquiry and reasoning
3. Some skill in applying those methods."
In short, the ability to think critically is the art of analyzing and evaluating data for a practical approach to understanding the data, then determining what to believe and how to act.
The three characteristics of critical thinking include:
• Being quick and decisive: One of the most admirable leadership qualities the ability to be quick and decisive with decisions. There are times where an answer just needs to be given and given right now. But that doesn't mean you should make a decision just to make one. Sometimes, quick decisions can fall flat. I know some of mine have.
• Being resourceful and creative: Over the years, members of my workforce have come to me with challenges and have needed some creativity and resourcefulness. As they spell out the situation, you listen to the issue, analyze their dilemma and guide them the best way possible. Thinking outside the box and sharing how to get there is a hallmark of a great leader.
• Being systematic and organized: Martin Gabel is quoted as saying , “Don’t just do something, stand there.” Sometimes, taking a minute to be systematic and follow an organized approach makes all the difference. This is where critical thinking meets problem solving. Define the problem, come up with a list of solutions, then select the best answer, implement it, create an evaluation tool and fine-tune as needed.
Components Of Critical Thinking
Now that you know the what and why of becoming a critical thinker, let’s focus on the how best to develop this skill.
1. Identify the problem or situation, then define what influenced this to occur in the first place.
2. Investigate the opinions and arguments of the individuals involved in this process. Any time you have differences of opinions, it is vital that you research independently, so as not to be influenced by a specific bias.
3. Evaluate information factually. Recognizing predispositions of those involved is a challenging task at times. It is your responsibility to weigh the information from all sources and come to your own conclusions.
4. Establish significance. Figure out what information is most important for you to consider in the current situation. Sometimes, you just have to remove data points that have no relevance.
5. Be open-minded and consider all points of view. This is a good time to pull the team into finding the best solution. This point will allow you to develop the critical-thinking skills of those you lead.
6. Take time to reflect once you have gathered all the information. In order to be decisive and make decisions quickly, you need to take time to unwrap all the information and set a plan of attack. If you are taking time to think about the best solution, keep your workforce and leaders apprised of your process and timeline.
7. Communicate your findings and results. This is a crucial yet often overlooked component. Failing to do so can cause much confusion in the organization.
Developing your critical-thinking skills is fundamental to your leadership success. As you set off to develop these abilities, it will require a clear, sometimes difficult evaluation of your current level of critical thinking. From there you can determine the best way to polish and strengthen your current skill set and establish a plan for your future growth.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
- India Today
- Business Today
- Reader’s Digest
- Harper's Bazaar
- Brides Today
- Cosmopolitan
- Aaj Tak Campus
- India Today Hindi
IIT Delhi starts new MA course to foster critical thinking in society
Iit delhi has introduced a new two-year ma programme in culture, society, and thought, offering interdisciplinary insights into sociology, literature, and philosophy. the application process begins on march 20..
Listen to Story

Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Delhi has broken new ground in academia with the launch of a pioneering MA programme. The Department of Humanities and Social Sciences introduced the MA in Culture, Society, and Thought, a two-year full-time course delving into sociology, literature, and philosophy.
Prospective candidates with a bachelor's degree in any discipline are eligible for the programme, provided they maintain a minimum of 55% or equivalent CGPA in BA.
ADMISSION PROCESS
Applicants undergo shortlisting based on an entrance examination or GATE 2024 score, followed by an interview process for final selection.
The fee structure aligns with other postgraduate programmes at IIT Delhi.
The MA programme equips graduates for diverse career paths in research, academia, social work, media, and policymaking, fostering opportunities in government and non-governmental organizations.
Professor Farhana Ibrahim, Head of the Department of Humanities and Social Sciences, IIT Delhi, underscored the programme's interdisciplinary approach and its potential to redefine humanities and social science research.
- Pharmaceutical Engineering Magazine
- Online Exclusives
- Special Reports
- Facilities & Equipment
- Information Systems
- Product Development
- Production Systems
- Quality Systems
- Regulatory Compliance
- Research + Development
- Supply Chain Management
- White Papers
- iSpeak Blog
- Editorial Calendar
- Article of the Year
- Submit an Article
- Editorial Team
Computer Software Assurance and the Critical Thinking Approach

In 2022, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued their draft guidance “Computer Software Assurance for Production and Quality System Software” 1 to enhance the computer validation process required by predicate rules, either in the pharmaceutical or medical device space. The critical thinking approach was introduced by ISPE GAMP® Guides and emphasizes a focus on clear thinking through a plan, then creating documentation from a process perspective. These methods combined create the optimal replacement for computer system validation (CSV).
- 1 US Food and Drug Administration. “Computer Software Assurance for Production and Quality System Software. Draft Guidance for Industry and Food and Drug Administration Staff.” September 2022. https://www.fda.gov/media/161521/download
New FDA draft guidance marked a transition to computer software assurance (CSA) in 2022 1 . Historically, CSV practices unfortunately focused on generating great amounts of paper-based testing records, and it was believed that the larger the stack of documentation, the better the quality and effort when validating a computerized system and eventually presenting it to the FDA.
The reality is that a mountain of paperwork did not equate to proper CSV, which resulted in a failure to fully ensure the product quality, data integrity, or patient safety. Critical thinking is a term that was introduced by GAMP guidance (initially in ISPE GAMP® Good Practice Guide: Enabling Innovation 2 and then more recently in ISPE GAMP® 5: A Risk-Based Approach to Compliant GxP Computerized Systems (Second Edition) 3 ), and it focuses on those critical considerations missed by CSV.
When applied, this critical thinking approach potentially results in the conclusion that a tremendous amount of documentation cannot possibly represent quality, especially when inspectors continue to identify a multitude of issues during inspections. These issues stem from items including, but not limited to, segregation of duties, data integrity potential violations, and whether the system works as intended after testing.
The FDA draft guidance states 1 : “Computer software assurance is a risk-based approach for establishing and maintaining confidence that software is fit for its intended use. This approach considers the risk of compromised safety and/or quality of the device (should the software fail to perform as intended) to determine the level of assurance effort and activities appropriate to establish confidence in the software. Because the computer software assurance effort is risk-based, it follows a least-burdensome approach, where the burden of validation is no more than necessary to address the risk. Such an approach supports the efficient use of resources, in turn promoting product quality.”
UTILIZATION OF THE CRITICAL THINKING APPROACH
The critical thinking approach can be used in potentially limiting testing evidence for low-risk functionalities through the following use of innovative testing approaches: unscripted and scripted testing.
Unscripted Testing
This is dynamic testing in which the tester’s actions are not prescribed by written instructions in a test case. This can include:
- Ad hoc testing: A concept derived from unscripted practice that focuses primarily on performing testing that does not rely on large amounts of documentation (e.g., test procedures) to execute
- Error-guessing: A test design technique in which test cases are derived on the basis of the tester’s knowledge of past failures or general knowledge of failure modes
- Exploratory testing: Experience-based testing in which the tester spontaneously designs and executes tests based on the tester’s existing relevant knowledge, prior exploration of the test item (including results from previous tests), and heuristic logical rules regarding common software behaviors and types of failure
Scripted Testing
This is dynamic testing in which the tester’s actions are prescribed by written instructions in a test case. It includes:
- Robust scripted testing: Scripted testing efforts in which the risk of the computer system or automation includes evidence of repeatability, traceability to requirements, and auditability
- Limited scripted testing: A hybrid approach of scripted and unscripted testing that is appropriately scaled according to the risk of the computer system or automation. These test methods require that the tester, through training and/or experience, has the knowledge to devise appropriate tests
WHY SOFTWARE ASSURANCE IS CRITICAL
Software assurance saves time and money. Software quality assurance ensures that developers find bugs and errors at the early stages of software development when less amount of time and money is required to fix them. The CSA approach provides flexibility and agility in helping ensure that the software is maintained in a validated state.
In determining the risk-based approach for software systems, the main intent is to use a risk-based methodology to ensure targeted and focused validation. This confirms that the computerized system is functioning for its prescribed, intended use, focusing (i.e., limiting a larger amount of documented evidence) on those functionalities that may directly impact patient safety and product quality.
For example, a software feature, function, or operation might pose a high process risk when its failure to perform as intended may result in a quality problem that foreseeably could compromise patient safety. In addition, software features and functions may maintain process parameters—such as temperature, pressure, or humidity—that affect the physical properties of product or manufacturing processes which are identified as essential to product safety and quality.
THE CSA RISK FRAMEWORK
The CSA risk framework is a risk-based approach intended to help manufacturers establish and maintain the reliability and safety of computer software throughout the life cycle, reducing the testing effort. Several steps must be taken to ensure the successful implementation of the CSA approach.
Identifying the Intended Use
Manufacturers must first determine whether the software is intended for use as part of production or the quality system. In general, software is either used directly as part of production or the quality system, or it supports production or the quality system.
Software that is used directly as part of production or the quality system includes software intended for automating production processes, inspection, testing, or the collection and processing of production data. It also includes software intended for automating quality system processes, collection, and the processing of quality system data, or maintaining a quality record established under the quality system regulation.
Manufacturers must validate software with these intended uses to ensure that it is reliable and functions as intended according to the associated risk. This is critical for both the pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical industries, as well as medical device manufacturers.
Determining the Risk-Based Approach
The CSA risk framework provides guidance on identifying and mitigating the risks associated with software validation and includes examples of applying the framework to various CSA situations. Once it has been determined that a software feature, function, or operation is intended for use as part of production or the quality system, a risk-based approach should be used to determine the appropriate assurance activities.
This approach involves identifying historical software failures, determining whether such a failure poses a high process risk, and systematically selecting and performing assurance activities commensurate with the medical device or process risk. The risk-based analysis for production or quality system software should consider which failures are historically known (as opposed to likely) and the risks resulting from each such failure.
Process risks refer to the potential to compromise production or the quality system, whereas direct system risks refer to the potential for a device to harm the patient or user. In CSA, the risk determination is therefore a key element to be carefully designed and executed to focus validation testing on the functionalities oriented to manage high-risk processes.
The CSA risk framework is a risk-based approach intended to help manufacturers establish and maintain the reliability and safety of computer software throughout the life cycle, reducing the testing e ort. Several steps must be taken to ensure the successful implementation of the CSA approach.
Determining the Appropriate Assurance Activities
Different types of assurance activities should be considered, corresponding with the system risk or process risk. For software features, functions, or operations that pose a high process risk, assurance activities should be considered higher corresponding with the system risk. Conversely, for software features, functions, or operations that do not pose a high process risk, appropriate assurance activities should be considered lower corresponding to the risk identified.
- 1 a b US Food and Drug Administration. “Computer Software Assurance for Production and Quality System Software. Draft Guidance for Industry and Food and Drug Administration Staff.” September 2022. https://www.fda.gov/media/161521/download
- 2 International Society for Pharmaceutical Engineering. ISPE GAMP® Good Practice Guide: Enabling Innovation. North Bethesda, MD: International Society for Pharmaceutical Engineering, 2021.
- 3 International Society for Pharmaceutical Engineering. ISPE GAMP® 5 Guide: A Risk-Based Approach to Compliant GxP Computerized Systems (Second Edition). North Bethesda, MD: International Society for Pharmaceutical Engineering, 2022.

CSA AND REQUIRED RECORDS
CSA enforces the need for regulated companies to establish the appropriate record. When establishing the record, the manufacturer should capture sufficient objective evidence to demonstrate that the software feature, function, or operation was assessed and performs as intended. In general, the record should include:
- The intended use of the software feature, function, or operation
- The determination of risk of the software feature, function, or operation
- Documentation of the assurance activities conducted
- The date of testing activities and the name of the person conducting them
- Establishing review and approval, when appropriate
The documentation of assurance activities should not include more evidence than necessary. However, it should retain sufficient details to serve as a baseline for improvements or as a reference point if issues occur. To reduce the need for manual or paper-based documentation, the FDA recommends that manufacturers “leverage automated traceability, testing, and the electronic capture of work performed to document the results. As a least burdensome method, FDA recommends the use of electronic records, such as system logs, audit trails, and other data generated by the software . . . in establishing the record associated with assurance activities” 1 .
THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN CSV AND CSA
CSA is a new way of looking at the traditional CSV approach through consideration of risk whereby the focus is on what matters—patient safety, product quality, and data integrity. A comparison of the two approaches for assurance activities and records is shown in Table 1.
The focus of CSV is a decision to carry out excessive and unnecessary tasks/testing, which creates excessive documentation, and too much time is spent on testing on all system functionalities. In comparison, when using CSA, the primary focus allows manufacturers to leverage principles such as risk-based testing, unscripted testing, continuous performance monitoring, and data monitoring, as well as validation activities performed by other entities (e.g., developers, suppliers). The CSA approach provides flexibility and agility in helping assure that the software maintains a validated state. This allows for assurance that the data provided is accurate, compliant, and more efficient.
In Figure 1, the left triangle represents the CSV approach, and the right triangle shows the differences that occur with CSA. As shown, in CSV, the decision to carry out excessive and unnecessary tasks/testing with documentation is the primary function, whereas critical thinking comes last. Issues and potential enhancements are identified in the last stages of the processes, resulting in a need for reworking and a waste of resources.

Current thinking with respect to GAMP® 5 Second Edition promotes a risk-based approach to ensure fitness of the system for its intended use 3 . In many instances of validation strategy, people do not apply critical thinking to ensure that the approach they are taking is customized and proportionate to the needs of the specific system they are validating: for example, when implementing the 21 CFR Part 11 requirement of segregation of duties (SOD), where roles and privileges are properly defined, configured, and followed 4 5 .
Using critical thinking (instead of having general training on the system regarding SOD), a customized/tailored approach to system training around the routine tasks of the different system user types should be followed. This will ensure that each user type is given training centered on their specific tasks and responsibilities so that SOD is clearly defined and followed.
Critical thinking is the most advantageous process for companies and manufacturers. It ensures that issues and enhancements are determined in the first stages, thereby focusing proper efforts toward assurance needs. Thus, it results in better-defined testing activities to ultimately ensure proper intended use and working functionality of the computerized system.
TRANSITIONING FROM CSV TO CSA
Organizations that want to pivot from a CSV to a CSA approach need to properly invest in activities and apply critical thinking to how software assurance will be performed and to how time and efforts will be allocated to achieve these tasks. For example, if a firm is implementing a new laboratory or manufacturing software/computerized system, the firm should apply critical thinking to assess the system and functional requirements risks as well as the intended use of the system, instead of spending significant time on excessive testing or documentation. This is because risk determination is the CSA core process.
The computerized system should be explored for what its intended use will be, what the key functions are, and what risks lie with its functionalities. Its potential impact on product quality and patient safety, historical issues, data integrity, and potential violations should also be assessed. This is necessary to properly outline the strategy of assurance and testing activities before the true efforts on documentation begin.
In addition, after the initial critical thinking phase of the process, teams should decide the key software assurance activities that must be performed to determine what needs to be tested and how testing should be documented. This will determine the amount of testing and evidence required to prove that the test function is working as intended.
The culmination of the activities previously mentioned should then be combined with a proper vendor risk management inspection program—especially for information technology service providers and technology vendors—that should include equipment and software-computerized systems.
Vendor risk management, audits, and inspection programs currently represent significant industry gaps. Performing these activ ities and having vendors’ quality systems assessed, when in good standing and documented, can potentially be further leveraged. This is especially true with commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) and software as a service (SaaS) platforms when leveraging these vendor audits/inspections to minimize out-of-the-box functionality testing or excessive service testing/verification.
The activities previously mentioned are a recommended way of pivoting from CSV to CSA in practice—and from a CSA perspective. It is equally important to shift and develop an organization’s mindset and culture to change from CSV to a CSA approach with critical thinking.
Having a proper quality system with a good foundation that establishes a vendor risk management or vendor audit program is a necessity.
The risk-based analysis for production or quality system software considers factors that may impact or prevent the software from performing as intended, such as proper system configuration and management, security of the system, data storage, data transfer, or operation error. Thus, a risk-based analysis for production or quality system software should consider which failures are reasonably foreseeable (as opposed to likely) and the risks resulting from each such failure.
Pivoting from CSV to CSA and using critical thinking can help the industry become more compliant and drive processes to be more agile while also ensuring better data integrity, product quality, and patient safety. It will also concurrently ensure that a stronger focus on validation of computerized systems will come with a more focused risk-based approach. Industry examples of CSA implementation while demonstrating new strategies with effective critical thinking can help ensure that the new paradigm will result in also using a risk-based approach to work smarter and not harder.
KEY STRATEGIES FOR CSA IMPLEMENTATION
Key strategies for effective implementation of better computerized systems with more efficient and agile processes and less work can produce more targeted efficiency with improved outcomes for product quality, patient safety, and data integrity.
As an example, COTS spreadsheet software may be composed of various functions with different intended uses. Based on FDA guidance on CSA, when using the basic input functions of the COTS spreadsheet software for the intended use of documenting the time and temperature readings for a curing process, a manufacturer may not need to perform additional assurance activities beyond those conducted by the COTS software developer and initial installation and configuration 1 .
The intended use of the software—documenting readings—only supports maintaining the quality system record and poses a low process risk. As such, initial activities such as the vendor assessment and software installation and configuration may be sufficient to establish that the software is fit for its intended use and is maintained in a validated state.
However, if a manufacturer uses built-in functions of the COTS spreadsheet to create custom formulas that are directly used in production or the quality system, then additional risks may be present. For example, if a custom formula automatically calculates time and temperature statistics to monitor the performance and suitability of the curing process, then additional validation by the manufacturer might be necessary. Therefore, having a proper quality system with a good foundation that establishes a vendor risk management or vendor audit program is a necessity.
Using the SaaS Model
The increased utilization of SaaS solutions with cloud computing combined with proper and actual vendor audits (i.e., focused to verify the current practices of the vendor and not limited to high-level verifications) and a third-party vendor risk management program produces benefits. It allows for leveraging within the CSA approach (with SaaS solutions that have a good audit history) and for a reduction of the overall scope of SaaS solution and COTS functionality validation testing.
Manufacturers are responsible for determining the appropriate assurance activities to ensure the software features, functions, or operations are in a validated state. Some possible assurance activities and considerations (such as leveraging vendor risk management programs or third-party vendor audits, e.g., in SaaS or cloud computing vendors) reduce the amount of testing while leveraging any of the aforementioned activities. This is potentially combined with historical vendor testing data, COTS functionality, and overall historical data/experience with the software or vendor.
Benefits of the SaaS model
The SaaS model of selling software has become increasingly popular over the years due to its many advantages. The SaaS model allows customers to pay for only the services they use, eliminating upfront costs associated with purchasing and maintaining physical infrastructure or exhaustively upgrading on-premise versions.
Advantages of cloud technologies
The benefits of cloud computing for pharmaceutical companies are numerous, and include faster time to market, scalability, flexibility, cost savings, better collaboration, advanced security, and data loss prevention. In addition, new instances can be implemented, or old instances can be retired in seconds, allowing developers to accelerate development with quicker deployments.
Cloud computing enables the pharmaceutical community to innovate rapidly, manage changes effortlessly, and deliver new medicines to the market faster. Cloud-based infrastructure offers secure storage for sizable and sensitive information. It also supports data security, integrity, and compliance with regulatory entities.
Key Metrics for Success
An important step to determine successful implementation and delivery of a CSA approach is to ensure proper formulation and monitoring of key metrics or key performance indicators (KPIs). Examples include:
- Return on investment: Cost savings for overall reduction in the duration needed to ensure the software is working as intended
- Writing: Significant reduction in the writing of test scripts and protocols
- Execution: Significant reduction in the execution and testing of test scripts and protocols
- Review of key deliverables: Significant reduction in the review of key deliverables
- Approval of key deliverables: Significant reduction in the approval of key deliverables
The overall benefits include a shorter duration for testing with quicker approval times and less production issues. This also potentially produces fewer issues during an audit or inspection where the system can be shown to be tested properly to ensure it is functioning correctly. Thus, it also potentially reduces risk in data integrity, product quality, and patient safety.
GAMP® 5 Second Edition provides further detailed guidance on how to apply CSA and critical thinking. The opportunities and concepts discussed in the FDA draft guidance on scope of testing and the use of the most appropriate types of testing can readily be adopted and implemented within the system life cycle approach described in GAMP® 5 Second Edition .
Critical thinking emphasizes a focus on, first, clearly thinking through a plan and then creating documentation from a process perspective. Although this critical thinking theory started with medical devices, it can apply to any pharmaceutical or biotechnology product. Instead of companies generating mountains of paperwork that “say” the product is safe, CSA can reduce the amount of testing and documentation. It offers greater efficiency, creates fewer steps, and ensures safer products, and, therefore, better patient outcomes.
Digital systems are increasingly being proliferated by industry, and manufacturers must eventually become up to date with technology. Electronic data can be more readily accessible, retrieved, analyzed, and presented with more efficiency, especially during an audit or inspection. This is another benefit of a CSA approach.
CSA, with GAMP in mind, starts with critical thinking instead of first developing the documentation; this can work for paper documents as well as computer system digital formats. The focus is on quality aspects—assurance means more focus on patient safety and data integrity, which is where the most risk lies. Documentation should then be created accordingly. Rather than focusing on paper-based exercises, which can create problems, the focus should be on thought. This means thinking through a plan, testing to minimize risks (ensuring the software and its functions are working as intended), focusing on quality, and then creating documentation from a process perspective.
However, pharmaceutical companies should be careful to consider that FDA guidance is still a draft when deciding how to apply it: It may change before the issue is in its final version. Furthermore, at this stage, it is unclear how many other different national authorities around the world will accept the CSA draft guidance. Pharmaceutical facilities that must concurrently comply with US FDA and other national authorities will need to balance to what extent they apply the CSA draft guidance. This will ensure that they do not inadvertently fail to adhere to the mix of different regulatory expectations that are applicable to their facilities.
The current draft of the FDA guidance applies to the medical device and biologics space, although the governing principles are expected to be agreed on and recommended by regulatory agencies also in the pharmaceutical space. Meanwhile, a number of regulated companies of all the previously mentioned regulated spaces have initiated the process of switching from a CSV repetitive strategy (where persons are used just to re-execute the validation approach established in the past) to a critical thinking approach. This transition should be carefully planned and deployed because it requires a substantial change in the mindset of all actors involved in the assurance activities related to a computer system.
- 4 US Food and Drug Administration. “CFR - Code of Federal Regulations Title 21, Annex 11.” March 1997. www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/CFRSearch.cfm?CFRPart=11
- 5 US Food and Drug Administration. “Part 11, Electronic Records; Electronic Signatures - Scope and Application, Guidance for Industry.” September 2003. www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/part-11-electronic-records-electronic-signatures-scope-and-application
Not a Member Yet?
To continue reading this article and to take advantage of full access to Pharmaceutical Engineering magazine articles, technical reports, white papers and exclusive content on the latest pharmaceutical engineering news, join ISPE today. In addition to exclusive access to all of the content in Pharmaceutical Engineering magazine, you will get online access to 24 ISPE Good Practice Guides, exclusive networking events, regulatory resources, Communities of Practice, and more.
Learn more about the valuable benefits you'll receive with an ISPE membership.
Join Today Member Login
Related Articles

Pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities produce a variety of products, including highly potent products that require safety measures to prevent adverse health effects on patients and operators. To ensure safety, these facilities use containment equipment to minimize the risk of contamination. This article presents criteria for selecting containment equipment, considering both...

The world is beginning to grasp the huge challenge of achieving net-zero carbon emissions, or carbon neutrality, by 2050. Many countries have committed to achieving this ambitious goal. As a major global industry, the pharmaceutical sector has a significant role to play. For thermal energy–intensive industries, such as pharmaceutical manufacturing, the long-term future options to maintain...

As the pharma industry moves to an ambitious Validation 4.0 paradigm, computerized systems play a pivotal role in enabling the rapid transition. Innovation and agility in computerized system validation (CSV) received a strong push in the second half of 2022 with the publication of the FDA draft guidance on “Computer Software Assurance for Production and Quality System Software”

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Critical thinking is important in all disciplines and throughout all stages of the research process. The types of evidence used in the sciences and in the humanities may differ, but critical thinking skills are relevant to both. In academic writing, critical thinking can help you to determine whether a source: Is free from research bias ...
Critical Thinking as Defined by the National Council for Excellence in Critical Thinking, 1987 . ... Critical thinking is the intellectually disciplined process of actively and skillfully conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and/or evaluating information gathered from, or generated by, observation, experience, reflection ...
Critical Thinking. Critical thinking is a widely accepted educational goal. Its definition is contested, but the competing definitions can be understood as differing conceptions of the same basic concept: careful thinking directed to a goal. Conceptions differ with respect to the scope of such thinking, the type of goal, the criteria and norms ...
"Critical thinking is the intellectually disciplined process of actively and skillfully conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and/or evaluating information gathered from, or generated by, observation, experience, reflection, reasoning, or communication, as a guide to belief and action.
Critical thinking is the analysis of available facts, evidence, observations, ... Within the framework of scientific skepticism, the process of critical thinking involves the careful acquisition and interpretation of information and use of it to reach a well-justified conclusion. The concepts and principles of critical thinking can be applied ...
Critical thinking skills differ from individual to individual and are utilized in various ways. Examples of common critical thinking skills include: ... Critical thinking, in part, is the cognitive process of reading the situation: the words coming out of their mouth, their body language, their reactions to your own words. Then, you might ...
Critical Thinking is the process of using and assessing reasons to evaluate statements, assumptions, and arguments in ordinary situations. The goal of this process is to help us have good beliefs, where "good" means that our beliefs meet certain goals of thought, such as truth, usefulness, or rationality. Critical thinking is widely ...
The Skills We Need for Critical Thinking. The skills that we need in order to be able to think critically are varied and include observation, analysis, interpretation, reflection, evaluation, inference, explanation, problem solving, and decision making. Think about a topic or issue in an objective and critical way.
Critical thinking, in educational theory, mode of cognition using deliberative reasoning and impartial scrutiny of information to arrive at a possible solution to a problem. ... In addition, some theorists have insisted that critical thinking be regarded and valued as a process and not as a goal-oriented skill set to be used to solve problems.
Critical thinking is the process of independently analyzing, synthesizing, and evaluating information as a guide to behavior and beliefs. The American Philosophical Association has defined critical thinking as "the process of purposeful, self-regulatory judgment. The process gives reasoned consideration to evidence, contexts, conceptualizations ...
Critical thinking is a kind of thinking in which you question, analyse, interpret , evaluate and make a judgement about what you read, hear, say, or write. The term critical comes from the Greek word kritikos meaning "able to judge or discern". Good critical thinking is about making reliable judgements based on reliable information.
Definition. Simply put, critical thinking is the act of deliberately analyzing information so that you can make better judgements and decisions. It involves using things like logic, reasoning, and creativity, to draw conclusions and generally understand things better. This may sound like a pretty broad definition, and that's because critical ...
Critical thinking refers to the ability to analyze information objectively and make a reasoned judgment. It involves the evaluation of sources, such as data, facts, observable phenomena, and research findings. Good critical thinkers can draw reasonable conclusions from a set of information, and discriminate between useful and less useful ...
Critical thinking allows you to apply an objective approach to your learning, rather than subjectively following either the proposed information you're given, or your own opinion rather than clear and convincing arguments and facts. Critical thinking is a process of continuing evaluation and reflection. It is most powerful, when leading to a ...
Key Takeaways. Researchers propose six levels of critical thinkers: Unreflective thinkers, Challenged thinkers, Beginning thinkers, Practicing thinkers, Advanced thinkers, and Master thinkers. The ...
"Writing is thinking on paper." (Zinsser, 1976, p. vii) Google the term "critical thinking." How many hits are there? On the day this tutorial was completed, Google found about 65,100,000 results in 0.56 seconds. That's an impressive number, and it grows more impressively large every day. That's because the nation's educators, business leaders, and political…
Critical thinking is the art of making clear, reasoned judgements based on interpreting, understanding, applying and synthesising evidence gathered from observation, reading and experimentation. ... Critical thinking shapes your own values and attitudes through a process of deliberating, debating and persuasion.
Critical thinking is the intellectually disciplined process of actively and skillfully conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and/or evaluating information gathered from, or generated by, observation, experience, reflection, reasoning, or communication, as a guide to belief and action. Paul and Scriven go on to suggest that ...
The critical thinking process doesn't necessarily lead to a cut-and-dry solution—instead, the process helps you understand the different variables at play so you can make an informed decision. 6. Present your solution. Communication is a key skill for critical thinkers.
A Systematic Process for Critical Thinking "The essence of the independent mind lies not in what it thinks, but in how it thinks." ― Christopher Hitchens, Letters to a Young Contrarian . Critical thinking can sometimes be a convoluted and mysterious process; this resource provides a systematic, critical
In fact, I maintain that critical thinking is best construed as a dynamic process between arousing and resolving states of doubt. Once the expansive skills of critical thinking such as perspective-taking have generated a state of doubt, then the more narrowing critical thinking skills such as reflection and reasoning can work toward resolving ...
Critical thinking, as described by Oxford Languages, is the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgement. Active and skillful approach, evaluation, assessment, synthesis, and/or evaluation of information obtained from, or made by, observation, knowledge, reflection, acumen or conversation, as a guide to belief and action, requires the critical thinking process ...
5. Be open-minded and consider all points of view. This is a good time to pull the team into finding the best solution. This point will allow you to develop the critical-thinking skills of those ...
IIT Delhi has introduced a new two-year MA programme in Culture, Society, and Thought, offering interdisciplinary insights into sociology, literature, and philosophy. The application process begins on March 20. Listen to Story Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Delhi has broken new ground in ...
In 2022, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued their draft guidance "Computer Software Assurance for Production and Quality System Software"1 to enhance the computer validation process required by predicate rules, either in the pharmaceutical or medical device space. The critical thinking approach was introduced by ISPE GAMP® Guides and emphasizes a focus on clear thinking ...
Critical Thinking. Critical thinking is a widely accepted educational goal. Its definition is contested, but the competing definitions can be understood as differing conceptions of the same basic concept: careful thinking directed to a goal. Conceptions differ with respect to the scope of such thinking, the type of goal, the criteria and norms ...
For more than 20 years, the VA has offered a year-long clinical residency for BSN students between their junior and senior years. VA-STEP is designed to increase participants' clinical skills, clinical judgment, and critical thinking while caring for our nation's Veterans. This program provides opportunities including didactic or classroom experiences and clinical practice with a qualified ...