- Search Search Please fill out this field.

What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans for May 2024 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How To Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Plan Smarter, Grow Faster:
25% Off Annual Plans! Save Now

0 results have been found for “”
Return to blog home
What Is a Business Plan? Definition and Planning Essentials Explained
Posted february 21, 2022 by kody wirth.

What is a business plan? It’s the roadmap for your business. The outline of your goals, objectives, and the steps you’ll take to get there. It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance.
A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and pursue growth. In short, a business plan is a lot of different things. It’s more than just a stack of paper and can be one of your most effective tools as a business owner.
Let’s explore the basics of business planning, the structure of a traditional plan, your planning options, and how you can use your plan to succeed.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a document that explains how your business operates. It summarizes your business structure, objectives, milestones, and financial performance. Again, it’s a guide that helps you, and anyone else, better understand how your business will succeed.
Why do you need a business plan?
The primary purpose of a business plan is to help you understand the direction of your business and the steps it will take to get there. Having a solid business plan can help you grow up to 30% faster and according to our own 2021 Small Business research working on a business plan increases confidence regarding business health—even in the midst of a crisis.
These benefits are directly connected to how writing a business plan makes you more informed and better prepares you for entrepreneurship. It helps you reduce risk and avoid pursuing potentially poor ideas. You’ll also be able to more easily uncover your business’s potential. By regularly returning to your plan you can understand what parts of your strategy are working and those that are not.
That just scratches the surface for why having a plan is valuable. Check out our full write-up for fifteen more reasons why you need a business plan .
What can you do with your plan?
So what can you do with a business plan once you’ve created it? It can be all too easy to write a plan and just let it be. Here are just a few ways you can leverage your plan to benefit your business.
Test an idea
Writing a plan isn’t just for those that are ready to start a business. It’s just as valuable for those that have an idea and want to determine if it’s actually possible or not. By writing a plan to explore the validity of an idea, you are working through the process of understanding what it would take to be successful.
The market and competitive research alone can tell you a lot about your idea. Is the marketplace too crowded? Is the solution you have in mind not really needed? Add in the exploration of milestones, potential expenses, and the sales needed to attain profitability and you can paint a pretty clear picture of the potential of your business.
Document your strategy and goals
For those starting or managing a business understanding where you’re going and how you’re going to get there are vital. Writing your plan helps you do that. It ensures that you are considering all aspects of your business, know what milestones you need to hit, and can effectively make adjustments if that doesn’t happen.
With a plan in place, you’ll have an idea of where you want your business to go as well as how you’ve performed in the past. This alone better prepares you to take on challenges, review what you’ve done before, and make the right adjustments.
Pursue funding
Even if you do not intend to pursue funding right away, having a business plan will prepare you for it. It will ensure that you have all of the information necessary to submit a loan application and pitch to investors. So, rather than scrambling to gather documentation and write a cohesive plan once it’s relevant, you can instead keep your plan up-to-date and attempt to attain funding. Just add a use of funds report to your financial plan and you’ll be ready to go.
The benefits of having a plan don’t stop there. You can then use your business plan to help you manage the funding you receive. You’ll not only be able to easily track and forecast how you’ll use your funds but easily report on how it’s been used.
Better manage your business
A solid business plan isn’t meant to be something you do once and forget about. Instead, it should be a useful tool that you can regularly use to analyze performance, make strategic decisions, and anticipate future scenarios. It’s a document that you should regularly update and adjust as you go to better fit the actual state of your business.
Doing so makes it easier to understand what’s working and what’s not. It helps you understand if you’re truly reaching your goals or if you need to make further adjustments. Having your plan in place makes that process quicker, more informative, and leaves you with far more time to actually spend running your business.
What should your business plan include?
The content and structure of your business plan should include anything that will help you use it effectively. That being said, there are some key elements that you should cover and that investors will expect to see.
Executive summary
The executive summary is a simple overview of your business and your overall plan. It should serve as a standalone document that provides enough detail for anyone—including yourself, team members, or investors—to fully understand your business strategy. Make sure to cover the problem you’re solving, a description of your product or service, your target market, organizational structure, a financial summary, and any necessary funding requirements.
This will be the first part of your plan but it’s easiest to write it after you’ve created your full plan.
Products & Services
When describing your products or services, you need to start by outlining the problem you’re solving and why what you offer is valuable. This is where you’ll also address current competition in the market and any competitive advantages your products or services bring to the table. Lastly, be sure to outline the steps or milestones that you’ll need to hit to successfully launch your business. If you’ve already hit some initial milestones, like taking pre-orders or early funding, be sure to include it here to further prove the validity of your business.
Market analysis
A market analysis is a qualitative and quantitative assessment of the current market you’re entering or competing in. It helps you understand the overall state and potential of the industry, who your ideal customers are, the positioning of your competition, and how you intend to position your own business. This helps you better explore the long-term trends of the market, what challenges to expect, and how you will need to initially introduce and even price your products or services.
Check out our full guide for how to conduct a market analysis in just four easy steps .
Marketing & sales
Here you detail how you intend to reach your target market. This includes your sales activities, general pricing plan, and the beginnings of your marketing strategy. If you have any branding elements, sample marketing campaigns, or messaging available—this is the place to add it.
Additionally, it may be wise to include a SWOT analysis that demonstrates your business or specific product/service position. This will showcase how you intend to leverage sales and marketing channels to deal with competitive threats and take advantage of any opportunities.
Check out our full write-up to learn how to create a cohesive marketing strategy for your business.
Organization & management
This section addresses the legal structure of your business, your current team, and any gaps that need to be filled. Depending on your business type and longevity, you’ll also need to include your location, ownership information, and business history. Basically, add any information that helps explain your organizational structure and how you operate. This section is particularly important for pitching to investors but should be included even if attempted funding is not in your immediate future.
Financial projections
Possibly the most important piece of your plan, your financials section is vital for showcasing the viability of your business. It also helps you establish a baseline to measure against and makes it easier to make ongoing strategic decisions as your business grows. This may seem complex on the surface, but it can be far easier than you think.
Focus on building solid forecasts, keep your categories simple, and lean on assumptions. You can always return to this section to add more details and refine your financial statements as you operate.
Here are the statements you should include in your financial plan:
- Sales and revenue projections
- Profit and loss statement
- Cash flow statement
- Balance sheet
The appendix is where you add additional detail, documentation, or extended notes that support the other sections of your plan. Don’t worry about adding this section at first and only add documentation that you think will be beneficial for anyone reading your plan.
Types of business plans explained
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. So, to get the most out of your plan, it’s best to find a format that suits your needs. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan
The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used for external purposes. Typically this is the type of plan you’ll need when applying for funding or pitching to investors. It can also be used when training or hiring employees, working with vendors, or any other situation where the full details of your business must be understood by another individual.
This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix. We recommend only starting with this business plan format if you plan to immediately pursue funding and already have a solid handle on your business information.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
The structure ditches a linear structure in favor of a cell-based template. It encourages you to build connections between every element of your business. It’s faster to write out and update, and much easier for you, your team, and anyone else to visualize your business operations. This is really best for those exploring their business idea for the first time, but keep in mind that it can be difficult to actually validate your idea this way as well as adapt it into a full plan.
One-page business plan
The true middle ground between the business model canvas and a traditional business plan is the one-page business plan. This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. It basically serves as a beefed-up pitch document and can be finished as quickly as the business model canvas.
By starting with a one-page plan, you give yourself a minimal document to build from. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences making it much easier to elaborate or expand sections into a longer-form business plan. This plan type is useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Now, the option that we here at LivePlan recommend is the Lean Plan . This is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance.
It holds all of the benefits of the single-page plan, including the potential to complete it in as little as 27-minutes . However, it’s even easier to convert into a full plan thanks to how heavily it’s tied to your financials. The overall goal of Lean Planning isn’t to just produce documents that you use once and shelve. Instead, the Lean Planning process helps you build a healthier company that thrives in times of growth and stable through times of crisis.
It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
Try the LivePlan Method for Lean Business Planning
Now that you know the basics of business planning, it’s time to get started. Again we recommend leveraging a Lean Plan for a faster, easier, and far more useful planning process.
To get familiar with the Lean Plan format, you can download our free Lean Plan template . However, if you want to elevate your ability to create and use your lean plan even further, you may want to explore LivePlan.
It features step-by-step guidance that ensures you cover everything necessary while reducing the time spent on formatting and presenting. You’ll also gain access to financial forecasting tools that propel you through the process. Finally, it will transform your plan into a management tool that will help you easily compare your forecasts to your actual results.
Check out how LivePlan streamlines Lean Planning by downloading our Kickstart Your Business ebook .
Like this post? Share with a friend!
Posted in Business Plan Writing
Join over 1 million entrepreneurs who found success with liveplan, like this content sign up to receive more.
Subscribe for tips and guidance to help you grow a better, smarter business.
You're all set!
Exciting business insights and growth strategies will be coming your way each month.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
What is a Business Plan? Definition, Tips, and Templates
Published: June 07, 2023
In an era where more than 20% of small enterprises fail in their first year, having a clear, defined, and well-thought-out business plan is a crucial first step for setting up a business for long-term success.

Business plans are a required tool for all entrepreneurs, business owners, business acquirers, and even business school students. But … what exactly is a business plan?

In this post, we'll explain what a business plan is, the reasons why you'd need one, identify different types of business plans, and what you should include in yours.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a documented strategy for a business that highlights its goals and its plans for achieving them. It outlines a company's go-to-market plan, financial projections, market research, business purpose, and mission statement. Key staff who are responsible for achieving the goals may also be included in the business plan along with a timeline.
The business plan is an undeniably critical component to getting any company off the ground. It's key to securing financing, documenting your business model, outlining your financial projections, and turning that nugget of a business idea into a reality.
What is a business plan used for?
The purpose of a business plan is three-fold: It summarizes the organization’s strategy in order to execute it long term, secures financing from investors, and helps forecast future business demands.
Business Plan Template [ Download Now ]

Working on your business plan? Try using our Business Plan Template . Pre-filled with the sections a great business plan needs, the template will give aspiring entrepreneurs a feel for what a business plan is, what should be in it, and how it can be used to establish and grow a business from the ground up.
Purposes of a Business Plan
Chances are, someone drafting a business plan will be doing so for one or more of the following reasons:
1. Securing financing from investors.
Since its contents revolve around how businesses succeed, break even, and turn a profit, a business plan is used as a tool for sourcing capital. This document is an entrepreneur's way of showing potential investors or lenders how their capital will be put to work and how it will help the business thrive.
All banks, investors, and venture capital firms will want to see a business plan before handing over their money, and investors typically expect a 10% ROI or more from the capital they invest in a business.
Therefore, these investors need to know if — and when — they'll be making their money back (and then some). Additionally, they'll want to read about the process and strategy for how the business will reach those financial goals, which is where the context provided by sales, marketing, and operations plans come into play.
2. Documenting a company's strategy and goals.
A business plan should leave no stone unturned.
Business plans can span dozens or even hundreds of pages, affording their drafters the opportunity to explain what a business' goals are and how the business will achieve them.
To show potential investors that they've addressed every question and thought through every possible scenario, entrepreneurs should thoroughly explain their marketing, sales, and operations strategies — from acquiring a physical location for the business to explaining a tactical approach for marketing penetration.
These explanations should ultimately lead to a business' break-even point supported by a sales forecast and financial projections, with the business plan writer being able to speak to the why behind anything outlined in the plan.
.webp)
Free Business Plan Template
The essential document for starting a business -- custom built for your needs.
- Outline your idea.
- Pitch to investors.
- Secure funding.
- Get to work!
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Free Business Plan [Template]
Fill out the form to access your free business plan., 3. legitimizing a business idea..
Everyone's got a great idea for a company — until they put pen to paper and realize that it's not exactly feasible.
A business plan is an aspiring entrepreneur's way to prove that a business idea is actually worth pursuing.
As entrepreneurs document their go-to-market process, capital needs, and expected return on investment, entrepreneurs likely come across a few hiccups that will make them second guess their strategies and metrics — and that's exactly what the business plan is for.
It ensures an entrepreneur's ducks are in a row before bringing their business idea to the world and reassures the readers that whoever wrote the plan is serious about the idea, having put hours into thinking of the business idea, fleshing out growth tactics, and calculating financial projections.
4. Getting an A in your business class.
Speaking from personal experience, there's a chance you're here to get business plan ideas for your Business 101 class project.
If that's the case, might we suggest checking out this post on How to Write a Business Plan — providing a section-by-section guide on creating your plan?
What does a business plan need to include?
- Business Plan Subtitle
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- The Business Opportunity
- Competitive Analysis
- Target Market
- Marketing Plan
- Financial Summary
- Funding Requirements
1. Business Plan Subtitle
Every great business plan starts with a captivating title and subtitle. You’ll want to make it clear that the document is, in fact, a business plan, but the subtitle can help tell the story of your business in just a short sentence.
2. Executive Summary
Although this is the last part of the business plan that you’ll write, it’s the first section (and maybe the only section) that stakeholders will read. The executive summary of a business plan sets the stage for the rest of the document. It includes your company’s mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals.
3. Company Description
This brief part of your business plan will detail your business name, years in operation, key offerings, and positioning statement. You might even add core values or a short history of the company. The company description’s role in a business plan is to introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way.
4. The Business Opportunity
The business opportunity should convince investors that your organization meets the needs of the market in a way that no other company can. This section explains the specific problem your business solves within the marketplace and how it solves them. It will include your value proposition as well as some high-level information about your target market.

5. Competitive Analysis
Just about every industry has more than one player in the market. Even if your business owns the majority of the market share in your industry or your business concept is the first of its kind, you still have competition. In the competitive analysis section, you’ll take an objective look at the industry landscape to determine where your business fits. A SWOT analysis is an organized way to format this section.
6. Target Market
Who are the core customers of your business and why? The target market portion of your business plan outlines this in detail. The target market should explain the demographics, psychographics, behavioristics, and geographics of the ideal customer.
7. Marketing Plan
Marketing is expansive, and it’ll be tempting to cover every type of marketing possible, but a brief overview of how you’ll market your unique value proposition to your target audience, followed by a tactical plan will suffice.
Think broadly and narrow down from there: Will you focus on a slow-and-steady play where you make an upfront investment in organic customer acquisition? Or will you generate lots of quick customers using a pay-to-play advertising strategy? This kind of information should guide the marketing plan section of your business plan.
8. Financial Summary
Money doesn’t grow on trees and even the most digital, sustainable businesses have expenses. Outlining a financial summary of where your business is currently and where you’d like it to be in the future will substantiate this section. Consider including any monetary information that will give potential investors a glimpse into the financial health of your business. Assets, liabilities, expenses, debt, investments, revenue, and more are all useful adds here.
So, you’ve outlined some great goals, the business opportunity is valid, and the industry is ready for what you have to offer. Who’s responsible for turning all this high-level talk into results? The "team" section of your business plan answers that question by providing an overview of the roles responsible for each goal. Don’t worry if you don’t have every team member on board yet, knowing what roles to hire for is helpful as you seek funding from investors.
10. Funding Requirements
Remember that one of the goals of a business plan is to secure funding from investors, so you’ll need to include funding requirements you’d like them to fulfill. The amount your business needs, for what reasons, and for how long will meet the requirement for this section.
Types of Business Plans
- Startup Business Plan
- Feasibility Business Plan
- Internal Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Business Acquisition Plan
- Business Repositioning Plan
- Expansion or Growth Business Plan
There’s no one size fits all business plan as there are several types of businesses in the market today. From startups with just one founder to historic household names that need to stay competitive, every type of business needs a business plan that’s tailored to its needs. Below are a few of the most common types of business plans.
For even more examples, check out these sample business plans to help you write your own .
1. Startup Business Plan

As one of the most common types of business plans, a startup business plan is for new business ideas. This plan lays the foundation for the eventual success of a business.
The biggest challenge with the startup business plan is that it’s written completely from scratch. Startup business plans often reference existing industry data. They also explain unique business strategies and go-to-market plans.
Because startup business plans expand on an original idea, the contents will vary by the top priority goals.
For example, say a startup is looking for funding. If capital is a priority, this business plan might focus more on financial projections than marketing or company culture.
2. Feasibility Business Plan
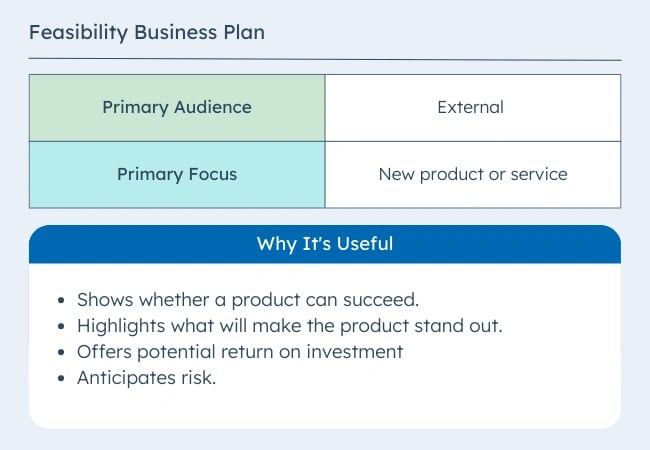
This type of business plan focuses on a single essential aspect of the business — the product or service. It may be part of a startup business plan or a standalone plan for an existing organization. This comprehensive plan may include:
- A detailed product description
- Market analysis
- Technology needs
- Production needs
- Financial sources
- Production operations
According to CBInsights research, 35% of startups fail because of a lack of market need. Another 10% fail because of mistimed products.
Some businesses will complete a feasibility study to explore ideas and narrow product plans to the best choice. They conduct these studies before completing the feasibility business plan. Then the feasibility plan centers on that one product or service.
3. Internal Business Plan

Internal business plans help leaders communicate company goals, strategy, and performance. This helps the business align and work toward objectives more effectively.
Besides the typical elements in a startup business plan, an internal business plan may also include:
- Department-specific budgets
- Target demographic analysis
- Market size and share of voice analysis
- Action plans
- Sustainability plans
Most external-facing business plans focus on raising capital and support for a business. But an internal business plan helps keep the business mission consistent in the face of change.
4. Strategic Business Plan

Strategic business plans focus on long-term objectives for your business. They usually cover the first three to five years of operations. This is different from the typical startup business plan which focuses on the first one to three years. The audience for this plan is also primarily internal stakeholders.
These types of business plans may include:
- Relevant data and analysis
- Assessments of company resources
- Vision and mission statements
It's important to remember that, while many businesses create a strategic plan before launching, some business owners just jump in. So, this business plan can add value by outlining how your business plans to reach specific goals. This type of planning can also help a business anticipate future challenges.
5. Business Acquisition Plan

Investors use business plans to acquire existing businesses, too — not just new businesses.
A business acquisition plan may include costs, schedules, or management requirements. This data will come from an acquisition strategy.
A business plan for an existing company will explain:
- How an acquisition will change its operating model
- What will stay the same under new ownership
- Why things will change or stay the same
- Acquisition planning documentation
- Timelines for acquisition
Additionally, the business plan should speak to the current state of the business and why it's up for sale.
For example, if someone is purchasing a failing business, the business plan should explain why the business is being purchased. It should also include:
- What the new owner will do to turn the business around
- Historic business metrics
- Sales projections after the acquisition
- Justification for those projections
6. Business Repositioning Plan
.webp?width=650&height=450&name=businessplan_6%20(1).webp)
When a business wants to avoid acquisition, reposition its brand, or try something new, CEOs or owners will develop a business repositioning plan.
This plan will:
- Acknowledge the current state of the company.
- State a vision for the future of the company.
- Explain why the business needs to reposition itself.
- Outline a process for how the company will adjust.
Companies planning for a business reposition often do so — proactively or retroactively — due to a shift in market trends and customer needs.
For example, shoe brand AllBirds plans to refocus its brand on core customers and shift its go-to-market strategy. These decisions are a reaction to lackluster sales following product changes and other missteps.
7. Expansion or Growth Business Plan
When your business is ready to expand, a growth business plan creates a useful structure for reaching specific targets.
For example, a successful business expanding into another location can use a growth business plan. This is because it may also mean the business needs to focus on a new target market or generate more capital.
This type of plan usually covers the next year or two of growth. It often references current sales, revenue, and successes. It may also include:
- SWOT analysis
- Growth opportunity studies
- Financial goals and plans
- Marketing plans
- Capability planning
These types of business plans will vary by business, but they can help businesses quickly rally around new priorities to drive growth.
Getting Started With Your Business Plan
At the end of the day, a business plan is simply an explanation of a business idea and why it will be successful. The more detail and thought you put into it, the more successful your plan — and the business it outlines — will be.
When writing your business plan, you’ll benefit from extensive research, feedback from your team or board of directors, and a solid template to organize your thoughts. If you need one of these, download HubSpot's Free Business Plan Template below to get started.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in August 2020 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

24 of My Favorite Sample Business Plans & Examples For Your Inspiration
![le business plan definition How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/executive-summary-example_5.webp)
How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]

Maximizing Your Social Media Strategy: The Top Aggregator Tools to Use

The Content Aggregator Guide for 2023
![le business plan definition 7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/gantt-chart-example.jpg)
7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]
![le business plan definition The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/flowchart%20templates.jpg)
The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]

16 Best Screen Recorders to Use for Collaboration

The 25 Best Google Chrome Extensions for SEO

Professional Invoice Design: 28 Samples & Templates to Inspire You
Customers’ Top HubSpot Integrations to Streamline Your Business in 2022
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
What is a Business Plan? Definition and Resources

9 min. read
Updated May 10, 2024
If you’ve ever jotted down a business idea on a napkin with a few tasks you need to accomplish, you’ve written a business plan — or at least the very basic components of one.
The origin of formal business plans is murky. But they certainly go back centuries. And when you consider that 20% of new businesses fail in year 1 , and half fail within 5 years, the importance of thorough planning and research should be clear.
But just what is a business plan? And what’s required to move from a series of ideas to a formal plan? Here we’ll answer that question and explain why you need one to be a successful business owner.
- What is a business plan?

A business plan lays out a strategic roadmap for any new or growing business.
Any entrepreneur with a great idea for a business needs to conduct market research , analyze their competitors , validate their idea by talking to potential customers, and define their unique value proposition .
The business plan captures that opportunity you see for your company: it describes your product or service and business model , and the target market you’ll serve.
It also includes details on how you’ll execute your plan: how you’ll price and market your solution and your financial projections .
Reasons for writing a business plan
If you’re asking yourself, ‘Do I really need to write a business plan?’ consider this fact:
Companies that commit to planning grow 30% faster than those that don’t.
Creating a business plan is crucial for businesses of any size or stage. It helps you develop a working business and avoid consequences that could stop you before you ever start.
If you plan to raise funds for your business through a traditional bank loan or SBA loan , none of them will want to move forward without seeing your business plan. Venture capital firms may or may not ask for one, but you’ll still need to do thorough planning to create a pitch that makes them want to invest.
But it’s more than just a means of getting your business funded . The plan is also your roadmap to identify and address potential risks.
It’s not a one-time document. Your business plan is a living guide to ensure your business stays on course.
Related: 14 of the top reasons why you need a business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
What research shows about business plans
Numerous studies have established that planning improves business performance:
- 71% of fast-growing companies have business plans that include budgets, sales goals, and marketing and sales strategies.
- Companies that clearly define their value proposition are more successful than those that can’t.
- Companies or startups with a business plan are more likely to get funding than those without one.
- Starting the business planning process before investing in marketing reduces the likelihood of business failure.
The planning process significantly impacts business growth for existing companies and startups alike.
Read More: Research-backed reasons why writing a business plan matters
When should you write a business plan?
No two business plans are alike.
Yet there are similar questions for anyone considering writing a plan to answer. One basic but important question is when to start writing it.
A Harvard Business Review study found that the ideal time to write a business plan is between 6 and 12 months after deciding to start a business.
But the reality can be more nuanced – it depends on the stage a business is in, or the type of business plan being written.
Ideal times to write a business plan include:
- When you have an idea for a business
- When you’re starting a business
- When you’re preparing to buy (or sell)
- When you’re trying to get funding
- When business conditions change
- When you’re growing or scaling your business
Read More: The best times to write or update your business plan
How often should you update your business plan?
As is often the case, how often a business plan should be updated depends on your circumstances.
A business plan isn’t a homework assignment to complete and forget about. At the same time, no one wants to get so bogged down in the details that they lose sight of day-to-day goals.
But it should cover new opportunities and threats that a business owner surfaces, and incorporate feedback they get from customers. So it can’t be a static document.
Related Reading: 5 fundamental principles of business planning
For an entrepreneur at the ideation stage, writing and checking back on their business plan will help them determine if they can turn that idea into a profitable business .
And for owners of up-and-running businesses, updating the plan (or rewriting it) will help them respond to market shifts they wouldn’t be prepared for otherwise.
It also lets them compare their forecasts and budgets to actual financial results. This invaluable process surfaces where a business might be out-performing expectations and where weak performance may require a prompt strategy change.
The planning process is what uncovers those insights.
Related Reading: 10 prompts to help you write a business plan with AI
- How long should your business plan be?
Thinking about a business plan strictly in terms of page length can risk overlooking more important factors, like the level of detail or clarity in the plan.
Not all of the plan consists of writing – there are also financial tables, graphs, and product illustrations to include.
But there are a few general rules to consider about a plan’s length:
- Your business plan shouldn’t take more than 15 minutes to skim.
- Business plans for internal use (not for a bank loan or outside investment) can be as short as 5 to 10 pages.
A good practice is to write your business plan to match the expectations of your audience.
If you’re walking into a bank looking for a loan, your plan should match the formal, professional style that a loan officer would expect . But if you’re writing it for stakeholders on your own team—shorter and less formal (even just a few pages) could be the better way to go.
The length of your plan may also depend on the stage your business is in.
For instance, a startup plan won’t have nearly as much financial information to include as a plan written for an established company will.
Read More: How long should your business plan be?
What information is included in a business plan?
The contents of a plan business plan will vary depending on the industry the business is in.
After all, someone opening a new restaurant will have different customers, inventory needs, and marketing tactics to consider than someone bringing a new medical device to the market.
But there are some common elements that most business plans include:
- Executive summary: An overview of the business operation, strategy, and goals. The executive summary should be written last, despite being the first thing anyone will read.
- Products and services: A description of the solution that a business is bringing to the market, emphasizing how it solves the problem customers are facing.
- Market analysis: An examination of the demographic and psychographic attributes of likely customers, resulting in the profile of an ideal customer for the business.
- Competitive analysis: Documenting the competitors a business will face in the market, and their strengths and weaknesses relative to those competitors.
- Marketing and sales plan: Summarizing a business’s tactics to position their product or service favorably in the market, attract customers, and generate revenue.
- Operational plan: Detailing the requirements to run the business day-to-day, including staffing, equipment, inventory, and facility needs.
- Organization and management structure: A listing of the departments and position breakdown of the business, as well as descriptions of the backgrounds and qualifications of the leadership team.
- Key milestones: Laying out the key dates that a business is projected to reach certain milestones , such as revenue, break-even, or customer acquisition goals.
- Financial plan: Balance sheets, cash flow forecast , and sales and expense forecasts with forward-looking financial projections, listing assumptions and potential risks that could affect the accuracy of the plan.
- Appendix: All of the supporting information that doesn’t fit into specific sections of the business plan, such as data and charts.
Read More: Use this business plan outline to organize your plan
- Different types of business plans
A business plan isn’t a one-size-fits-all document. There are numerous ways to create an effective business plan that fits entrepreneurs’ or established business owners’ needs.
Here are a few of the most common types of business plans for small businesses:
- One-page plan : Outlining all of the most important information about a business into an adaptable one-page plan.
- Growth plan : An ongoing business management plan that ensures business tactics and strategies are aligned as a business scales up.
- Internal plan : A shorter version of a full business plan to be shared with internal stakeholders – ideal for established companies considering strategic shifts.
Business plan vs. operational plan vs. strategic plan
- What questions are you trying to answer?
- Are you trying to lay out a plan for the actual running of your business?
- Is your focus on how you will meet short or long-term goals?
Since your objective will ultimately inform your plan, you need to know what you’re trying to accomplish before you start writing.
While a business plan provides the foundation for a business, other types of plans support this guiding document.
An operational plan sets short-term goals for the business by laying out where it plans to focus energy and investments and when it plans to hit key milestones.
Then there is the strategic plan , which examines longer-range opportunities for the business, and how to meet those larger goals over time.
Read More: How to use a business plan for strategic development and operations
- Business plan vs. business model
If a business plan describes the tactics an entrepreneur will use to succeed in the market, then the business model represents how they will make money.
The difference may seem subtle, but it’s important.
Think of a business plan as the roadmap for how to exploit market opportunities and reach a state of sustainable growth. By contrast, the business model lays out how a business will operate and what it will look like once it has reached that growth phase.
Learn More: The differences between a business model and business plan
- Moving from idea to business plan
Now that you understand what a business plan is, the next step is to start writing your business plan .
The best way to start is by reviewing examples and downloading a business plan template. These resources will provide you with guidance and inspiration to help you write a plan.
We recommend starting with a simple one-page plan ; it streamlines the planning process and helps you organize your ideas. However, if one page doesn’t fit your needs, there are plenty of other great templates available that will put you well on your way to writing a useful business plan.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.

Table of Contents
- Reasons to write a business plan
- Business planning research
- When to write a business plan
- When to update a business plan
- Information to include
- Business vs. operational vs. strategic plans
Related Articles

13 Min. Read
How to Write an Online Fitness Business Plan

12 Min. Read
Free Amazon FBA Business Plan PDF [2024 Template + Sample Plan]

8 Min. Read
How to Format a Business Plan in 8 Simple Steps

6 Min. Read
How to Write Your Business Plan Cover Page + Template
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
What Is a Business Plan?
Business Plan Explained in Less Than 5 Minutes
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/KhadijaKhartit-4f144e2b63ee4dd4af60ac8a02233c50.jpg)
Definition and Examples of a Business Plan
How a business plan works, types of business plans, business plan vs. business model.
Geber86 / Getty Images
A business plan is a detailed written document that describes your business’s activities, goals, and strategy. A strong plan outlines everything from the products a company sells to the executive summary to the overall management. In essence, a business plan should guide a founder’s actions through each stage of growth
Think of your business plan as a road map. It documents the various stages of starting and running your business, including business activities and objectives. Business plans create the structure you need to make decisions by outlining the financial and operational goals you’re striving toward.
One of the most common reasons for crafting a business plan is to attract investors—and, in return, receive funding. As an early stage company, for example, you may leverage your business plan to convince investors or banks that your entity is credible and worthy of funding. The business plan should prove that their money will be returned .
A business plan can also be useful for when a well-developed company goes through a merger or acquisition . As outlined by the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA), a merger creates a new entity via the combination of two businesses. An acquisition, on the other hand, is when a company is purchased and absorbed into an existing business. In either case, a business plan helps establish relationships between business entities, making a merger or acquisition more likely.
- Alternate name : Strategic plan
A business plan is a formalized outline of the business operations, finances, and goals you aim to achieve to be a successful company. When designing a business plan, companies have leeway for how long, short, or detailed it can be. So long as it outlines the foundational aspects of the business, in most cases, it will be effective.
The most common type of business plan is a traditional business plan. This style tends to have the following common elements, generally in this order.
- Executive summary : Tells your reader why your company will be successful. Includes the company’s mission statement , product information, and basics regarding the business structure.
- Company description : Where you brag about your entity’s strengths. Answer the question, what problem is your team solving?
- Market analysis : A deep dive into your industry and the competition. Consider why competitors are successful. How can your offering do it better? If applicable, how can you enhance the experience for the consumer?
- Management plan : Outlines leadership structure of the company and may be best detailed as a chart. This way, readers can see exactly who is planning to run the company and how they will impact growth.
- Marketing and sales plan : Details how you’ll attract consumers with your product or service, and how you will retain those customers. All strategies outlined in this section, such as the use of digital marketing , will be referenced in your financial plan.
- Funding request : For those companies asking for funding, this is where you’ll detail the amount of funding you’ll need to achieve your goals. Clearly explain how much you need and what it will be used for.
- Financial plan : Convinces the reader that your company is financially stable and can turn a profit . You will need to include a balance sheet , an income statement, and the cash flow statement (or cash flow projection, in the case of a new venture).
- Appendix : Where any supporting documents, such as legal documents, licenses of employees, and pictures of the product will be included.
Your company’s business plan should fit your needs, which will often depend on what stage of growth you are in. If you are considering starting a new venture, for example, writing a detailed business plan can help prove if your concept is viable or not.
If your business is seeking financial capital, though, you will want your business plan to be investor-ready. This will require you to have a funding request section, which would be placed right above your financial plan.
You should avoid using lofty terms or technical jargon that those outside your team won’t understand. A business plan is meant to be shared with those inside and outside your organization. Simple and effective language is best.
Your business’s stage impacts the length and detail of a business plan. As discussed, a traditional plan follows a detailed structure, from the executive summary to the appendix. It is a lengthier document, often amounting to dozens of pages, and is often used when seeking funding to prove business viability. In most cases, crafting a traditional plan will take lots of due diligence work.
The other main type of business plan is a lean startup plan. A lean startup plan is much more high-level and shorter than the traditional version. Companies just starting development will often create a lean startup plan to help them navigate where they should start. These can be as short as one or two pages.
A lean plan will include the following elements.
- Key partnerships : Notes other services or businesses you will work with, such as manufacturers and suppliers.
- Key activities and resources : Outlines how your company will gain a competitive advantage and create value for your consumers. Resources you may leverage include capital, staff, or intellectual property.
- Value proposition : Clearly defines the unique value your company offers.
- Customer relationships : Details the customer experience from start to finish.
- Channels : How will you stay connected with your customers? Detail those methods here.
- Cost structure and revenue streams : Details the most significant costs you will face as well as how your business will actually make money.
Remember that business plans are meant to change as your company grows or pivots. You should actively review and edit your business plan to keep it up to date with business activities. For example, you may start with a lean plan and move to a traditional plan when you hit the fundraising stage.
A business plan may often be confused with a business model, and it is easy to understand why. Simply put, a business plan is the holistic overview of the business, while a business model is a skeleton for how money will be made.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines a business’s operations, finances, and goals. It guides the business’s day-to-day decisions.
- A business plan is necessary for your company’s success, as it creates a path to scalability.
- There are two main types of business plans: a traditional business plan and a lean startup plan.
- A traditional business plan will be essential when you begin to seek debt or equity capital for your company.
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Merge and Acquire Businesses .” Accessed June 8, 2021.
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ." Accessed June 8, 2021.
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
Business Plan
By Entrepreneur Staff
Business Plan Definition:
A written document describing the nature of the business, the sales and marketing strategy, and the financial background, and containing a projected profit and loss statement
A business plan is also a road map that provides directions so a business can plan its future and helps it avoid bumps in the road. The time you spend making your business plan thorough and accurate, and keeping it up-to-date, is an investment that pays big dividends in the long term.
Your business plan should conform to generally accepted guidelines regarding form and content. Each section should include specific elements and address relevant questions that the people who read your plan will most likely ask. Generally, a business plan has the following components:
Title Page and Contents A business plan should be presented in a binder with a cover listing the name of the business, the name(s) of the principal(s), address, phone number, e-mail and website addresses, and the date. You don't have to spend a lot of money on a fancy binder or cover. Your readers want a plan that looks professional, is easy to read and is well-put-together.
Include the same information on the title page. If you have a logo, you can use it, too. A table of contents follows the executive summary or statement of purpose, so that readers can quickly find the information or financial data they need.
Executive Summary The executive summary, or statement of purpose, succinctly encapsulates your reason for writing the business plan. It tells the reader what you want and why, right up front. Are you looking for a $10,000 loan to remodel and refurbish your factory? A loan of $25,000 to expand your product line or buy new equipment? How will you repay your loan, and over what term? Would you like to find a partner to whom you'd sell 25 percent of the business? What's in it for him or her? The questions that pertain to your situation should be addressed here clearly and succinctly.
The summary or statement should be no more than half a page in length and should touch on the following key elements:
- Business concept describes the business, its product, the market it serves and the business' competitive advantage.
- Financial features include financial highlights, such as sales and profits.
- Financial requirements state how much capital is needed for startup or expansion, how it will be used and what collateral is available.
- Current business position furnishes relevant information about the company, its legal form of operation, when it was founded, the principal owners and key personnel.
- Major achievements points out anything noteworthy, such as patents, prototypes, important contracts regarding product development, or results from test marketing that have been conducted.
Description of the Business The business description usually begins with a short explanation of the industry. When describing the industry, discuss what's going on now as well as the outlook for the future. Do the necessary research so you can provide information on all the various markets within the industry, including references to new products or developments that could benefit or hinder your business. Base your observations on reliable data and be sure to footnote and cite your sources of information when necessary. Remember that bankers and investors want to know hard facts--they won't risk money on assumptions or conjecture.
When describing your business, say which sector it falls into (wholesale, retail, food service, manufacturing, hospitality and so on), and whether the business is new or established. Then say whether the business is a sole proprietorship, partnership, C or Sub chapter S corporation. Next, list the business' principals and state what they bring to the business. Continue with information on who the business' customers are, how big the market is, and how the product or service is distributed and marketed.
Description of the Product or Service The business description can be a few paragraphs to a few pages in length, depending on the complexity of your plan. If your plan isn't too complicated, keep your business description short, describing the industry in one paragraph, the product in another, and the business and its success factors in two or three more paragraphs.
When you describe your product or service, make sure your reader has a clear idea of what you're talking about. Explain how people use your product or service and talk about what makes your product or service different from others available in the market. Be specific about what sets your business apart from those of your competitors.
Then explain how your business will gain a competitive edge and why your business will be profitable. Describe the factors you think will make it successful. If your business plan will be used as a financing proposal, explain why the additional equity or debt will make your business more profitable. Give hard facts, such as "new equipment will create an income stream of $10,000 per year" and briefly describe how.
Other information to address here is a description of the experience of the other key people in the business. Whoever reads your business plan will want to know what suppliers or experts you've spoken to about your business and their response to your idea. They may even ask you to clarify your choice of location or reasons for selling this particular product.
Market Analysis A thorough market analysis will help you define your prospects as well as help you establish pricing, distribution, and promotional strategies that will allow your company to be successful vis-à-vis your competition, both in the short and long term.
Begin your market analysis by defining the market in terms of size, demographics, structure, growth prospects, trends, and sales potential. Next, determine how often your product or service will be purchased by your target market. Then figure out the potential annual purchase. Then figure out what percentage of this annual sum you either have or can attain. Keep in mind that no one gets 100 percent market share, and that a something as small as 25 percent is considered a dominant share. Your market share will be a benchmark that tells you how well you're doing in light of your market-planning projections.
You'll also have to describe your positioning strategy. How you differentiate your product or service from that of your competitors and then determine which market niche to fill is called "positioning." Positioning helps establish your product or service's identity within the eyes of the purchaser. A positioning statement for a business plan doesn't have to be long or elaborate, but it does need to point out who your target market is, how you'll reach them, what they're really buying from you, who your competitors are, and what your USP (unique selling proposition) is.
How you price your product or service is perhaps your most important marketing decision. It's also one of the most difficult to make for most small business owners, because there are no instant formulas. Many methods of establishing prices are available to you, but these are among the most common.
- Cost-plus pricing is used mainly by manufacturers to assure that all costs, both fixed and variable, are covered and the desired profit percentage is attained.
- Demand pricing is used by companies that sell their products through a variety of sources at differing prices based on demand.
- Competitive pricing is used by companies that are entering a market where there's already an established price and it's difficult to differentiate one product from another.
- Markup pricing is used mainly by retailers and is calculated by adding your desired profit to the cost of the product.
You'll also have to determine distribution, which includes the entire process of moving the product from the factory to the end user. Make sure to analyze your competitors' distribution channels before deciding whether to use the same type of channel or an alternative that may provide you with a strategic advantage.
Finally, your promotion strategy should include all the ways you communicate with your markets to make them aware of your products or services. To be successful, your promotion strategy should address advertising, packaging, public relations, sales promotions and personal sales.
Competitive Analysis The purpose of the competitive analysis is to determine:
- the strengths and weaknesses of the competitors within your market.
- strategies that will provide you with a distinct advantage.
- barriers that can be developed to prevent competition from entering your market.
- any weaknesses that can be exploited in the product development cycle.
The first step in a competitor analysis is to identify both direct and indirect competition for your business, both now and in the future. Once you've grouped your competitors, start analyzing their marketing strategies and identifying their vulnerable areas by examining their strengths and weaknesses. This will help you determine your distinct competitive advantage.
Whoever reads your business plan should be very clear on who your target market is, what your market niche is, exactly how you'll stand apart from your competitors, and why you'll be successful doing so.
Operations and Management The operations and management component of your plan is designed to describe how the business functions on a continuing basis. The operations plan highlights the logistics of the organization, such as the responsibilities of the management team, the tasks assigned to each division within the company, and capital and expense requirements related to the operations of the business.
Financial Components of Your Business Plan After defining the product, market and operations, the next area to turn your attention to are the three financial statements that form the backbone of your business plan: the income statement, cash flow statement, and balance sheet.
The income statement is a simple and straightforward report on the business' cash-generating ability. It is a scorecard on the financial performance of your business that reflects when sales are made and when expenses are incurred. It draws information from the various financial models developed earlier such as revenue, expenses, capital (in the form of depreciation), and cost of goods. By combining these elements, the income statement illustrates just how much your company makes or loses during the year by subtracting cost of goods and expenses from revenue to arrive at a net result, which is either a profit or loss. In addition to the income statements, include a note analyzing the results. The analysis should be very short, emphasizing the key points of the income statement. Your CPA can help you craft this.
The cash flow statement is one of the most critical information tools for your business, since it shows how much cash you'll need to meet obligations, when you'll require it and where it will come from. The result is the profit or loss at the end of each month and year. The cash flow statement carries both profits and losses over to the next month to also show the cumulative amount. Running a loss on your cash flow statement is a major red flag that indicates not having enough cash to meet expenses-something that demands immediate attention and action.
The cash flow statement should be prepared on a monthly basis during the first year, on a quarterly basis for the second year, and annually for the third year. The following 17 items are listed in the order they need to appear on your cash flow statement. As with the income statement, you'll need to analyze the cash flow statement in a short summary in the business plan. Once again, the analysis doesn't have to be long and should cover highlights only. Ask your CPA for help.
The last financial statement you'll need is a balance sheet. Unlike the previous financial statements, the balance sheet is generated annually for the business plan and is, more or less, a summary of all the preceding financial information broken down into three areas: assets, liabilities and equity.
Balance sheets are used to calculate the net worth of a business or individual by measuring assets against liabilities. If your business plan is for an existing business, the balance sheet from your last reporting period should be included. If the business plan is for a new business, try to project what your assets and liabilities will be over the course of the business plan to determine what equity you may accumulate in the business. To obtain financing for a new business, you'll need to include a personal financial statement or balance sheet.
In the business plan, you'll need to create an analysis for the balance sheet just as you need to do for the income and cash flow statements. The analysis of the balance sheet should be kept short and cover key points.
Supporting Documents In this section, include any other documents that are of interest to your reader, such as your resume; contracts with suppliers, customers, or clients, letters of reference, letters of intent, copy of your lease and any other legal documents, tax returns for the previous three years, and anything else relevant to your business plan.
Some people think you don't need a business plan unless you're trying to borrow money. Of course, it's true that you do need a good plan if you intend to approach a lender--whether a banker, a venture capitalist or any number of other sources--for startup capital. But a business plan is more than a pitch for financing; it's a guide to help you define and meet your business goals.
Just as you wouldn't start off on a cross-country drive without a road map, you should not embark on your new business without a business plan to guide you. A business plan won't automatically make you a success, but it will help you avoid some common causes of business failure, such as under-capitalization or lack of an adequate market.
As you research and prepare your business plan, you'll find weak spots in your business idea that you'll be able to repair. You'll also discover areas with potential you may not have thought about before--and ways to profit from them. Only by putting together a business plan can you decide whether your great idea is really worth your time and investment.
More from Business Plans
Financial projections.
Estimates of the future financial performance of a business
Financial Statement
A written report of the financial condition of a firm. Financial statements include the balance sheet, income statement, statement of changes in net worth and statement of cash flow.
Executive Summary
A nontechnical summary statement at the beginning of a business plan that's designed to encapsulate your reason for writing the plan
Latest Articles
My startup couldn't raise vc funding, so we became profitable. here's how we did it — and how you can too..
Four months ago, my startup reached profitability for the first time. It came after more than a year of active work and planning, and here's what it took.
Warren Buffett Had to Work From His iPhone After Telephone Lines Went Down at Berkshire Hathaway: 'I'm Glad We Didn't Sell All of Our Apple'
Berkshire sold around $20 billion worth of Apple recently.

Clinton Sparks Podcast: From Hit Records to Humanitarian Powerhouse, Akon Shares His Entrepreneurial Journey
This podcast is a fun, entertaining and informative show that will teach you how to succeed and achieve your goals with practical advice and actionable steps given through compelling stories and conversations with Clinton and his guests.

- Customer Reviews
- Net 30 Account
- Wise Services
- Steps & Timeline
- Work at a Glance
- Market Research at a Glance
- Business Plan Writing Services
- Bank Business Plan
- Investor Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Cannabis Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Corporate Business Plan
- Merge and Acquisition Business Plan (M&A)
- Private Placement Memorandums (PPM)
- Sample Business Plans
- Professional Feasibility Study
- PowerPoint Presentations
- Pitch Deck Presentation Services
- Business Plan Printing
- Market Research
- L-1 Business Plan
- E-2 Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- EB-5 Regional Centers
- Immigration Attorneys
- Nonprofit Business Plan
- Exit Business Planning
- Business Planning
- Business Formation
- Business License
- Business Website
- Business Branding
- Business Bank Account
- Digital Marketing
- Business Funding Resources
- Small Business Loans
- Venture Capital
- Net 30 Apply

What is a business plan? Definition, Purpose, and Types
In the world of business, a well-thought-out plan is often the key to success. This plan, known as a business plan, is a comprehensive document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies , and financial projections. Whether you’re starting a new business or looking to expand an existing one, a business plan is an essential tool.
As a business plan writer and consultant , I’ve crafted over 15,000 plans for a diverse range of businesses. In this article, I’ll be sharing my wealth of experience about what a business plan is, its purpose, and the step-by-step process of creating one. By the end, you’ll have a thorough understanding of how to develop a robust business plan that can drive your business to success.
What is a business plan?
Purposes of a business plan, what are the essential components of a business plan, executive summary, business description or overview, product and price, competitive analysis, target market, marketing plan, financial plan, funding requirements, types of business plan, lean startup business plans, traditional business plans, how often should a business plan be reviewed and revised, what are the key elements of a lean startup business plan.
- What are some of the reasons why business plans don't succeed?
A business plan is a roadmap for your business. It outlines your goals, strategies, and how you plan to achieve them. It’s a living document that you can update as your business grows and changes.
Looking for someone to write a business plan?
Find professional business plan writers for your business success.
These are the following purpose of business plan:
- Attract investors and lenders: If you’re seeking funding for your business , a business plan is a must-have. Investors and lenders want to see that you have a clear plan for how you’ll use their money to grow your business and generate revenue.
- Get organized and stay on track: Writing a business plan forces you to think through all aspects of your business, from your target market to your marketing strategy. This can help you identify any potential challenges and opportunities early on, so you can develop a plan to address them.
- Make better decisions: A business plan can help you make better decisions about your business by providing you with a framework to evaluate different options. For example, if you’re considering launching a new product, your business plan can help you assess the potential market demand, costs, and profitability.

The executive summary is the most important part of your business plan, even though it’s the last one you’ll write. It’s the first section that potential investors or lenders will read, and it may be the only one they read. The executive summary sets the stage for the rest of the document by introducing your company’s mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals.
The business description section of your business plan should introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way. It should include your business name, years in operation, key offerings, positioning statement, and core values (if applicable). You may also want to include a short history of your company.
In this section, the company should describe its products or services , including pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other relevant information could include production and manufacturing processes, patents, and proprietary technology.
Every industry has competitors, even if your business is the first of its kind or has the majority of the market share. In the competitive analysis section of your business plan, you’ll objectively assess the industry landscape to understand your business’s competitive position. A SWOT analysis is a structured way to organize this section.
Your target market section explains the core customers of your business and why they are your ideal customers. It should include demographic, psychographic, behavioral, and geographic information about your target market.
Marketing plan describes how the company will attract and retain customers, including any planned advertising and marketing campaigns . It also describes how the company will distribute its products or services to consumers.
After outlining your goals, validating your business opportunity, and assessing the industry landscape, the team section of your business plan identifies who will be responsible for achieving your goals. Even if you don’t have your full team in place yet, investors will be impressed by your clear understanding of the roles that need to be filled.
In the financial plan section,established businesses should provide financial statements , balance sheets , and other financial data. New businesses should provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years, and may also request funding.
Since one goal of a business plan is to secure funding from investors , you should include the amount of funding you need, why you need it, and how long you need it for.
- Tip: Use bullet points and numbered lists to make your plan easy to read and scannable.
Access specialized business plan writing service now!
Business plans can come in many different formats, but they are often divided into two main types: traditional and lean startup. The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) says that the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
Lean startup business plans are short (as short as one page) and focus on the most important elements. They are easy to create, but companies may need to provide more information if requested by investors or lenders.
Traditional business plans are longer and more detailed than lean startup business plans, which makes them more time-consuming to create but more persuasive to potential investors. Lean startup business plans are shorter and less detailed, but companies should be prepared to provide more information if requested.
Need Guidance with Your Business Plan?
Access 14 free business plan samples!
A business plan should be reviewed and revised at least annually, or more often if the business is experiencing significant changes. This is because the business landscape is constantly changing, and your business plan needs to reflect those changes in order to remain relevant and effective.
Here are some specific situations in which you should review and revise your business plan:
- You have launched a new product or service line.
- You have entered a new market.
- You have experienced significant changes in your customer base or competitive landscape.
- You have made changes to your management team or organizational structure.
- You have raised new funding.
A lean startup business plan is a short and simple way for a company to explain its business, especially if it is new and does not have a lot of information yet. It can include sections on the company’s value proposition, major activities and advantages, resources, partnerships, customer segments, and revenue sources.
What are some of the reasons why business plans don't succeed?

- Unrealistic assumptions: Business plans are often based on assumptions about the market, the competition, and the company’s own capabilities. If these assumptions are unrealistic, the plan is doomed to fail.
- Lack of focus: A good business plan should be focused on a specific goal and how the company will achieve it. If the plan is too broad or tries to do too much, it is unlikely to be successful.
- Poor execution: Even the best business plan is useless if it is not executed properly. This means having the right team in place, the necessary resources, and the ability to adapt to changing circumstances.
- Unforeseen challenges: Every business faces challenges that could not be predicted or planned for. These challenges can be anything from a natural disaster to a new competitor to a change in government regulations.
What are the benefits of having a business plan?
- It helps you to clarify your business goals and strategies.
- It can help you to attract investors and lenders.
- It can serve as a roadmap for your business as it grows and changes.
- It can help you to make better business decisions.
How to write a business plan?
There are many different ways to write a business plan, but most follow the same basic structure. Here is a step-by-step guide:
- Executive summary.
- Company description.
- Management and organization description.
- Financial projections.
How to write a business plan step by step?
Start with an executive summary, then describe your business, analyze the market, outline your products or services, detail your marketing and sales strategies, introduce your team, and provide financial projections.
Why do I need a business plan for my startup?
A business plan helps define your startup’s direction, attract investors, secure funding, and make informed decisions crucial for success.
What are the key components of a business plan?
Key components include an executive summary, business description, market analysis, products or services, marketing and sales strategy, management and team, financial projections, and funding requirements.
Can a business plan help secure funding for my business?
Yes, a well-crafted business plan demonstrates your business’s viability, the use of investment, and potential returns, making it a valuable tool for attracting investors and lenders.
Quick Links

- Investor Business Plans
- M&A Business Plan
- Private Placement
- Feasibility Study
- Hire a Business Plan Writer
- Business Valuation Calculator
- Business Plan Examples
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Plan Template
- Business Plan Pricing Guide
- Business Plan Makeover
- SBA Loans, Bank Funding & Business Credit
- Finding & Qualifying for Business Grants
- Leadership for the New Manager
- Content Marketing for Beginners
- All About Crowdfunding
- EB-5 Regional Centers, A Step-By-Step Guide
- Logo Designer
- Landing Page
- PPC Advertising

- Business Entity
- Business Licensing
- Virtual Assistant
- Business Phone
- Business Address
- E-1 Visa Business Plan
- EB1-A Visa Business Plan
- EB1-C Visa Business Plan
- EB2-NIW Business Plan
- H1B Visa Business Plan
- O1 Visa Business Plan
- Business Brokers
- Merger & Acquisition Advisors
- Franchisors
Proud Sponsor of
- 1-800-496-1056

- (613) 800-0227

- +44 (1549) 409190

- +61 (2) 72510077


Try for free
Business Plan
Who should write a business plan, pros and cons of a business plan, the anatomy of a business plan, .css-uphcpb{position:absolute;left:0;top:-87px;} what is a business plan, definition of a business plan.
A business plan is a strategic document which details the strategic objectives for a growing business or startup, and how it plans to achieve them.
In a nutshell, a business plan is a written expression of a business idea and will describe your business model, your product or service, how it will be priced, who will be your target market, and which tactics you plan to use to reach commercial success.
Whilst every enterprise should have a plan of some sort, a business plan is of particular importance during the investment process. Banks, venture capitalists, and angel investors alike will need to see a detailed plan in order to make sound investment decisions — think of your plan as a way of convincing them your idea is worth their resources.
Roadmapping From A to Z

Business plans can also be useful as a guide to keeping a new business on track, especially in the first few months or years when the road ahead isn’t too clear.
Starting a business isn’t an exact science. Some companies organically develop out of trial and error, while others are plotted out from start to finish.
So if you’re asking whether your company needs a lengthy business plan, the answer would be ‘no’. That said, there are definitely a few situations in which writing a plan makes sense and can help increase the chances of a business becoming successful:
In situations when the market is new and untested — or simply volatile — it can be very helpful to have a business plan to refer back to when the road ahead isn’t clear.
For those who have an exciting business idea but haven’t necessarily distilled it down into black-and-white. Writing a business plan is a great way to look at a concept from all angles and spot any potential pitfalls.
How to write a business plan?
The most important step in writing a business plan is to identify its purpose.
Who are you trying to attract with it, and why?
Here are a few key pointers for writing a business plan:
Are you looking to secure a bank loan, get funding from private investors, or to lure skilled professionals to join you?
Include a brief history of your business, the concept, and the products or services. Keep it professional and transparent.
Don’t exaggerate your experience or skills, and definitely don’t leave out information investors need to know. They’ll find out at some point, and if they discover you lied, they could break off their involvement. Trust is crucial.
Explain what the product or service your business offers in simplistic terms.
Watch out for complex language and do whatever you can to prevent readers from becoming confused.
Focus on the benefits the business offers, how it solves the core audience’s problem(s), and what evidence you have to prove that there is a space in the market for your idea. It’s important to touch on the market your business will operate in, and who your main competitors are.
Another essential aspect of writing an effective business plan is to keep it short and sweet. Just focus on delivering the crucial information the reader has to know in order to make a decision. They can always ask you to elaborate on certain points later.
Still, deciding whether or not a business plan will benefit you at this stage of your venture?
Let’s look at a few reasons why you might (or might not) want to write a business plan.
A business plan will help you to secure funding even when you have no trading history. At the seed stage, funding is all-important — especially for tech and SaaS companies. It’s here that a business plan can become an absolute lifesaver.
Your business plan will maintain a strategic focus as time goes on. If you’ve ever heard of “mission creep”, you’ll know how important an agreed can be — and your business plan serves exactly that purpose.
Having a plan down in black and white will help you get other people on board . Again, with no trading history, it can be hard to convince new partners that you know what you’re doing. A business plan elegantly solves this problem.
Your business plan can cause you to stop looking outward. Sometimes, especially in business, you need to be reactive to market conditions. If you focus too much on your original business plan, you might make mistakes that can be costly or miss golden opportunities because they weren’t in the plan.
A lot of time can be wasted analyzing performance. It’s easy to become too focused on the goals and objectives in your business plan — especially when you’re not achieving them. By spending too much time analyzing past performance and looking back, you may miss out on other ways to push the business forward.
A business plan is out of date as soon as it’s written. We all know how quickly market conditions change. And, unfortunately, certain elements in your business plan may have lost relevance by the time you’re ready to launch. But there is another way — by transferring your strategic plan into an actionable roadmap , you can get the best of both worlds. The business plan contains important detail that is less likely to change, such as your mission statement and target audience, and the roadmap clarifies a flexible, adaptable, route forward.
So, you’ve decided to write a business plan — a great choice!
But now comes the tricky task of actually writing it.
This part can be a little frustrating because there is no one-size-fits-all template appropriate for all business plans. The best approach, in fact, is to look at common ingredients of a business plan and pick out the ones that make sense for your venture.
The key elements of a great business plan include:
An overview of the business concept . This is sometimes referred to as an executive summary and it’s essentially the elevator pitch for your business.
A detailed description of the product or service. It’s here that you’ll describe exactly what your core offering will be — what’s your USP , and what value do you deliver?
An explanation of the target audience. You need a good understanding of who you’ll be selling your product or service to, backed up by recent market research.
Your sales and marketing strategy. Now that you know who you’re targeting, how do you plan to reach them? Here you can list primary tactics for finding and maintaining an engaged client base.
Your core team . This section is all about people: do you have a team behind you already? If not, how will you build this team and what will the timeline be? Why are you the right group of people to bring this idea to the market? This section is incredibly important when seeking external investment — in most cases, passion can get you much further than professional experience.
Financial forecasts . Some investors will skim the executive summary and skip straight to the finances — so expect your forecasts to be scrutinized in a lot of detail. Writing a business plan for your eyes only? That’s fine, but you should still take time to map out your financial requirements: how much money do you need to start? How do you plan to keep money coming in? How long will it take to break even ? Remember, cash is king. So you need a cash flow forecast that is realistic, achievable and keeps your business afloat, especially in the tricky first few years.

General FAQ
Glossary categories.

Feedback Management

Prioritization

Product Management

Product Strategy

Roadmapping
Build great roadmaps
Book a demo
Experience the new way of doing product management

Que doit contenir un business plan ? Exemple de plan gratuit à télécharger
Vo us avez une super idée et voulez la concrétiser sur le terrain en créant votre propre société ? Ou tout simplement, vous êtes déjà chef d’entreprise et souhaitez développer ou modifier votre activité. Tout cela se prépare grâce à un bon business plan.
La création d’un business plan (ou plan d’affaires) est indispensable pour l’élaboration de votre feuille de route. En effet, avant de vous lancer et de vous engager dans des démarches souvent compliquées, il est indispensable de bien étudier votre projet entrepreneurial.
- Qu’est-ce qu’un business plan ?
, reprise ou développement d’activité porté par le chef d’entreprise.
Monter un business plan , c’est mettre son projet sur papier. Cette démarche, est souvent plus compliquée qu’il n’y paraît, mais elle permet de clarifier le projet et d’en mesurer la viabilité, tant du point de vue financier que marketing, industriel, commercial et humain. Car il est probable que le développement de votre concept vous amène à devoir vous entourer de ressources complémentaires.
C’est à l’aide de votre business plan dûment établi que vous parviendrez à convaincre vos futurs associés ou encore les banques qui vous aideront à financer votre projet. Il est donc primordial de travailler sur ce document pour en faire un atout !
- Que trouve-t-on dans un business plan ?
Le business plan présente le projet de création d’entreprise : objectifs, risques, contraintes, ainsi que les éléments à mettre en œuvre pour atteindre cet objectif. Il servira ensuite, une fois le projet entré dans une phase pratique, de vérifier qu’il reste bien en phase avec l’idée initiale tout en l’adaptant, à la marge, en fonction des besoins économiques.
Un business plan doit aborder des points essentiels et répondre aux questions suivantes (liste non exhaustive) :
- Quel problème vais-je résoudre ?
- À quel marché mon problème s’adresse-t-il ?
- Quelle est ma proposition de valeur ?
- Quelle sera ma stratégie commerciale ?
- Qu’est-ce qui différencie ma proposition de valeur de celle de mes concurrents ?
- Quelles preuves puis-je apporter montrant qu’il existe une attente du marché pour mon offre / ma proposition de valeur dans les conditions attendues ?
- Qu’est-ce qui protège mon offre contre la concurrence ?
- Comment vais-je mettre en œuvre mon projet ?
- De quoi ai-je besoin pour mettre en œuvre mon projet ?
- De quoi est-ce que je dispose pour mettre en œuvre mon projet ?
- Quelles solutions ai-je identifiées pour trouver les compétences et ressources manquantes pour mon projet ?
- Quelle rentabilité attendre de mon entreprise ?
- Comment financer mon projet ?
- Quel retour sur investissement pour les partenaires ?
A partir de 20€
A partir de 39,90 €
Voir le comparatif complet
- Faut-il faire son business plan seul ?
Le business plan doit impérativement être réalisé par le porteur de projet ou l’équipe fondatrice. Ce sont les seuls qui ont :
- la connaissance, la compréhension et la créativité nécessaires au projet pour le faire aboutir ;
- la légitimité pour s’engager sur la stratégie, le plan d’action et les choix fondamentaux qui seront présentés dans le business plan ;
- la connaissance des moyens et des efforts qu’ils sont prêts à mettre en place, mais aussi des limites et des contraintes dont il faut tenir compte pour mener à bien la création de l’entreprise.
Toutefois, faire un business plan n’est pas simple. Faire appel à de l’aide extérieure contribue souvent à la qualité du travail. L’aide peut venir d’un échange, plus ou moins long et régulier avec un partenaire ou une personne d’expérience. De nombreux créateurs font appel à un expert (expert-comptable, coach, conseil …) pour s’assurer de la qualité de leur modèle économique, de la faisabilité du projet ainsi que pour la partie chiffrée qui est souvent un peu plus technique.
Il peut aussi être utile de s’appuyer sur un modèle de business plan et/ou sur un business plan existant pour structurer votre démarche, et vous encourager à étudier chacun des aspects du projet tout en contribuant à la qualité de son contenu. Dans ce cas, l’idéal est de trouver un partenaire qui apporte un peu plus que de simples exemples qui peuvent être trouvés gratuitement sur le net. Ce dernier doit vous aider à structurer votre démarche, mais aussi à élaborer un contenu de qualité grâce à des éléments tels que le business modèle Canvas , l’analyse SWOT, les chiffres de votre secteur d’activité…
- Existe-t-il un modèle type de business plan ?
. Pour autant, il est difficile de proposer un business plan type pour deux raisons essentielles :
- Tout d’abord, chaque projet est différen t. Utiliser un modèle de business plan pour réaliser le vôtre risque de dénaturer le projet et le faire ressembler aux autres. Il est important de réaliser votre business plan, afin qu’ il vous ressemble et qu’il soit unique . Par exemple si vous comptez créer un club de padel, vous allez rédiger un business plan pour le padel .
- La démarche nécessaire pour monter son business plan est importante. Elle fait partie du processus de formation du dirigeant. C’est en réalisant votre business plan que vous apprendrez à vous projeter dans votre future entreprise.
Pour faire votre business plan, il faut aborder un certain nombre d’éléments dans un ordre qui permettra au lecteur de découvrir l’intérêt de votre projet :
La description du projet
Il faudra nécessairement commencer par parler du projet afin que le lecteur sache de quoi il s’agit. À la fin de cette partie, il doit savoir quel problème vous allez résoudre et avec quelle solution(s). L’idée est de faire une introduction synthétique qui explique la problématique et décrit la solution proposée.
L’identification du besoin : Quel problème vais-je résoudre ?
Créer une entreprise c’est apporter une solution aux besoins exprimés par un marché. Votre business plan doit commencer par présenter et définir le besoin. Celui-ci, appelé aussi « pain point » pour point de douleur peut s’exprimer sous la forme d’un problème, d’un manque, d’un besoin, d’une envie … Il peut être conscient ou inconscient. L’important c’est de l’identifier et de le présenter de manière à ce que le lecteur comprenne la nature du besoin que votre proposition de valeur va combler.
Le marché : À quel marché mon problème s’adresse-t-il ?
Sauf cas exceptionnel (Apple par exemple), le marché ne s’adapte pas, c’est donc à vous de déterminer, analyser, mesurer et segmenter votre marché . Vous devez avoir étudié votre marché afin de vous être assuré que votre projet répond à une demande qui est réelle, exprimée et suffisante. Il faut aussi vous assurer que le montant que les acheteurs accepteront de payer sera suffisant pour rentabiliser et pérenniser votre activité.
Le rôle de votre business plan est de présenter le marché, ses composantes, sa segmentation, ses contraintes… au lecteur. Après avoir abordé le marché en général, il faudra décrire votre marché cible, quelle est sa taille, ses acteurs, son mode de fonctionnement…etc. Ce marché cible peut être composé de plusieurs segments.
Il faudra ensuite établir votre stratégie commerciale à l’aide d’outils marketing comme le SWOT , l’analyse Pestel ou certains outils de web stratégie. Après avoir défini votre stratégie, il faudra expliquer pourquoi vous choisissez ce marché cible et en quoi votre solution est adaptée pour ce marché.
À la fin de cette partie le lecteur doit avoir identifié le problème, mesuré le potentiel du marché et avoir une idée de la stratégie de création à développer.
La proposition de valeur : Quelle est ma proposition de valeur ?
Il faut ensuite décrire votre projet qui repose sur une proposition de valeur. La proposition de valeur décrit la promesse et la valeur ajoutée que votre projet apporte aux utilisateurs et aux clients de votre future société.
C’est la raison pour laquelle vos futurs clients vont acheter votre offre commerciale. Votre proposition doit être claire, synthétique et apporter des réponses aux 3 questions suivantes :
- Quel problème je veux solutionner ?
- En quoi la solution est-elle efficace et unique ?
- Quels résultats concrets / mesurables peut-on obtenir grâce à mon offre commerciale ?
Une proposition de valeur a plusieurs caractéristiques :
- Elle présente les problèmes solutionnés : les clients cibles ont des problèmes et des besoins pour lesquels ils se fixent des objectifs. La proposition d’une possible solution entraîne une liste inconsciente d’objections. Votre proposition de valeur doit désamorcer ces objections.
- Elle doit aussi prévoir la manière dont vous allez parvenir à présenter votre offre aux futurs clients : le « go to market ».
- Elle répond au pourquoi et pas au comment. Les clients achètent un produit ou un service qui répond à un pourquoi, pas à un comment. Pour un client, le pourquoi d’une offre à plus de valeur que le comment, on achète une voiture pour se déplacer, le comment ne nous intéresse qu’accessoirement, et encore.
- Bien que ce soit difficile, elle doit être claire et simple. Il faudra donc faire une synthèse de votre projet en écartant, supprimant, enlevant, épurant encore et encore des éléments jusqu’à obtenir l’essence essentielle du projet.
C’est dans cette partie, qu’il vous faudra répondre aux questions :
- Qu’est-ce qui différencie ma proposition de valeur de celle de mes concurrents ?
- Quelles preuves puis-je apporter montrant qu’il existe une attente du marché pour mon offre / ma proposition de valeur dans les conditions attendues ?
- Qu’est-ce qui protège mon offre contre la concurrence ?
Après avoir expliqué ce que vous allez vendre et sur quel marché, il faut présenter l’équipe. En quoi vous (seul ou en équipe) êtes les personnes les plus qualifiées pour mettre en œuvre le projet ? En quoi êtes-vous légitimes pour porter ce projet (compétences, brevets, connaissances du marché, complémentarité entre associés …).
Le modèle économique
Comment allez-vous gagner de l’argent ? Comment comptez-vous monter votre business ? On ne crée pas une entreprise pour se faire plaisir, il faut expliquer aux futurs lecteurs la manière dont vous allez faire du business et leur montrer en quoi l’entreprise que vous allez créer sera rentable, pérenne et capable de se développer .
Le prévisionnel
Un prévisionnel se faisant à partir d’hypothèses, il est forcément faux, mais il apporte un certain nombre de réponses intéressantes.
Il comprendra nécessairement, un bilan prévisionnel, un compte de résultat prévisionnel, un plan de trésorerie prévisionnel et un plan d’investissement. L’idéal est de présenter une version réaliste accompagnée d’une version optimiste et une autre pessimiste.
Remarque :
Attention à ne pas présenter des chiffres délirants, peu d’entreprises peuvent réaliser des millions d’euros de CA en quelques années.
Vous pensez être rentable en 12 mois, atteindre votre seuil de rentabilité, votre point mort ou votre break Even en 18 mois … N’hésitez pas à ajouter entre 6 et 12 mois, vous serez sans doute plus proche de la réalité !
- Réaliser un business plan : Les 2 principales méthodes
On peut considérer deux méthodes pour réaliser un business plan : La première consiste à se baser sur un plan existant. Cette méthode convient particulièrement aux projets conventionnels qui ne nécessitent pas de personnaliser le business plan pour présenter le projet.
Lorsqu’un projet est innovant ou plus créatif, il peut être intéressant de se baser sur une liste de questions qui vous aideront à structurer votre rédaction.
Créer son business plan à partir d’un plan préétabli
La méthode à suivre pour créer un business plan à partir d’un plan préétabli.
Créer un business plan à partir d’un plan existant se fait en deux étapes préparatoire avant la rédaction :
- la première étape consiste à définir la structure du document en s’appuyant sur le plan existant qu’on personnalisera en fonction du projet à présenter. Cela permet de lister et ordonner l’ensemble des sujets à évoquer pour que le document soit le clair et pertinent possible.
- la seconde étape consiste à détailler le contenu de chaque partie en listant les points à évoquer et les références à faires aux autres parties. On pensera aussi à lister les chiffres et à adapter en cas d’évolution e certains éléments comme le prévisionnel. Tant que le document n’est pas figé, il peut être intéressant de noter sur un document à part ou de faire ressortir (en les mettant en couleur par exemple) les points susceptibles d’évoluer.
Une fois le document préparé, il vous suffit de vous lancer dans la rédaction du contenu du business plan. Pensez à conserver la trame de préparation, cela facilite le travail de reprise ou d’adaptation souvent nécessaire.
Exemple de plan de business plan
Voici un plan de business plan que vous pouvez utiliser comme base de travail. Il vous suffit de le copier ou de le télécharger gratuitement.
Plan de Business Plan gratuit LEBLOGDUDIRIGEANT
Voici les grandes lignes du plan que vous pouvez suivre pour structurer votre business plan :
- Introduire votre business plan,
- Présentation du projet et de son origine,
- Démontrer la faisabilité et l’intérêt du projet,
- Présenter les caractéristiques et votre offre de bien et/ou service,
- Présentation des éléments structurant la mise en œuvre du projet
- Le lancement de l’entreprise et de son activité.
Voici le détail du plan que vous pouvez suivre pour élaborer votre business plan
Introduction du business plan
- Le résumé du business plan ou executive summary
- L’identité de la société
La présentation du projet et de son origine
- L’identification du besoin : à quel besoin allez-vous répondre ?
- La présentation du projet de création
- Les étapes de mise en place du projet
Démontrer la faisabilité et l’intérêt du projet
- Les conclusions de l’étude de marché
- La mise en place d’un modèle économique rentable
Présenter les caractéristiques et votre offre de bien et/ou service
- Présenter l’offre commerciale de l’entreprise dans le business plan
- La validation de votre offre par les clients
- Qui porte le projet
- L’organisation de l’entreprise
- Présenter la stratégie générale
- Présenter la stratégie opérationnelle dans le business plan
- Le point de synthèse prélancement
Présentation des éléments structurant la mise en œuvre du projet,
- Choisir un local
Déterminer les objectifs de l’entreprise dans le business plan
Choisir sa forme juridique
Présenter votre prévisionnel financier dans votre business plan
- Le compte de résultat prévisionnel
- Le tableau de trésorerie
- Le plan de financement initial
- Le bilan prévisionnel
- Les ratios financiers
Présenter le besoin d’investissement dans votre business plan
- Vos besoins financiers
- Comment vous allez utiliser votre financement
Choisir sa domiciliation
Immatriculer son entreprise
Adapter et faire relire votre business plan
Cliquez ici pour télécharger la version PDF
Cliquez ici pour télécharger la version Word
Pour avoir plus d’informations sur la nature du contenu et avoir des conseils de rédaction concrets, n’hésitez pas à lire notre Guide complet pour rédiger son business plan étape par étape.
Créer son business plan à partir d’une liste de questions
Plutôt que de vous structurer la rédaction du document à partir d’un modèle de business plan qui est rarement adapté à votre projet, il est possible de construire votre propre structure ou modèle de business plan en suivant la liste de questions ci-dessous.
Les réponses que vous apporterez à ces questions vous aideront à aborder l’ensemble des aspects de votre projet. Attention, cette liste n’est pas exhaustive, pensez à la compléter et à insister sur les points qui vous semblent importants.
A. Définition du projet
La première étape pour faire un business plan, consiste à définir votre projet.
Cette étape indispensable doit répondre à la question : quoi vendre ? Quels sont les produits ou services que vous souhaitez vendre ?
Pour répondre à ces questions, vous pouvez structurer votre réflexion en vous posant les questions suivantes :
1 – Prestation ou produit,
i. Quels produits ou services allez-vous commercialiser ?
ii. Quelles fonctionnalités comportera votre produit
iii. À quels besoin ou problème client votre produit répond-il ?
2 – Aspect novateur : quelle sera ma proposition de valeur ?
i. En quoi votre projet est-il novateur ou original ?
ii. Qu’est ce que votre projet, produit et/ou service apporte de plus que vos concurrents ?
iii. Quelles sont les fonctionnalités essentielles de votre produit ?
iv. Comment votre projet se distinguera-t-il des autres ?
3 – Quel marché votre projet vise-t-il ?
i. Quel type de marché visez-vous (marché de niche, mass market, marché naissant, marché de proximité, marché technique, B to B, B to C, …) ?
ii. Le marché est-il uniforme ou multiple, national ou international, direct ou indirect ?
iii. Votre projet est-il « scalable », c’est à dire duplicable sur d’autres marchés ?
4 – Comment fonctionne le marché cible ?
i. Le marché est-il naissant ou ancien.
ii. Votre mode de distribution nécessite-t-il de transformer les marchés (rupture technologique …)
iii. Le marché fonctionne-t-il avec des intermédiaires, des proscripteurs, des prestataires incontournables ?
B. Choix stratégiques
La deuxième étape doit répondre aux questions, à qui vendre et/ou ?
Ce sont vos clients potentiels et votre marché cible (votre étude de marché). Pour rédiger cette partie, répondez aux questions suivantes :
1 – Les clients : qui sont mes clients potentiels ? Quelles sont ses caractéristiques ?
i. Clientèle existante
ii. Clientèle à développer, prospecter
iii. Identification des besoins
iv. Habitudes de consommation
v. Quelle est ma clientèle type (âge, CSP, …)
2 – Le marché : quels sont mes marchés cibles ? que mon projet vise-t-il ?
iii. Votre projet est-il « scalable », c’est-à-dire duplicable sur d’autres marchés ?
iv. Quels sont les différents segments du ou des marchés cibles ?
v. Typologie de segment
vi. Taille des segments
vii. Quels sont les segments les plus intéressants ? Pourquoi ?
3 – Les paramètres du marché : quels sont la configuration et le fonctionnement du marché que vous souhaitez conquérir ?
i. Les spécificités des marchés visés :
a. Taille, part de marché, volume, évolution passée et à venir, Taux de croissance
b. Existe-t-il des barrières à l’entrée du marché (Technologique, Investissement, Réglementation, Marque …)
c. Le marché est-il naissant ou ancien ?
d. Votre mode de distribution nécessite-t-il de transformer les marchés (rupture technologique, disruptive …),
e. Le marché fonctionne-t-il avec des intermédiaires, des prescripteurs, des prestataires incontournables ?
4 – La stratégie commerciale : comment est mon environnement concurrentiel ? Comment je me positionne face à mes concurrents ?
i. Nature de la concurrence ?
a. Les types de concurrents (directs, indirects, en devenir (innovation, lancement de projet …)
b. Quelles sont les stratégies de mes concurrents (positionnement, service ….)
ii. Comment vais-je me différencier ?
a. Mon niveau de service, mes fonctionnalités, mon niveau de qualité comparé à celui des concurrents
b. Quel sera mon positionnement ?
c. Quelle sera mon organisation (qui fait quoi avec quels outils quelles compétences …) ?
5 – Votre stratégie : quelle stratégie dois-je mettre en place ?
i. Les résultats de mon SWOT
a. Mes forces, mes faiblesses,
b. Les marchés opportuns (océan bleu ? Océan rouge), les marchés pièges (menaces)
c. Mes marchés prioritaires (les plus facile à intégrer, les plus rentables, …)
d. Ma stratégie de développement
ii. Ma stratégie marketing et de communication
a. Comment me faire connaître ? Avec quel budget ? Dans quels délais ?
b. Quels seront mes outils de communication ? Quel budget ?
c. Qui se chargera de la communication ?
iii. Quel est le taux de pénétration du marché attendu ? Comment sera-t-il mesuré ?
iv. Quelle sera ma rentabilité par marché, par segment, par produit ?
v. Mon plan de développement point par point, étape par étape
C. Choix opérationnels
Cette étape consiste à mettre en place un plan d’action opérationnel pour atteindre les objectifs de résultat.
Cette étape doit répondre aux questions suivantes : quels choix opérationnels vais-je privilégier ? Pourquoi est-ce que je privilégie ces choix, et quels résultats puis-je en attendre ?
1 – Plans opérationnels
i. Marketing
ii. Commercial
iii. Industriel et technique
iv. Logistique
v. Administratif
vi. Ressources humaines
2 – Mes besoins financiers & bilan prévisionnel
i. Quels investissements faut-il réaliser ?
a. Description des investissements (nature, date, montant, durée)
b Ce que les investissements vont apporter (apport technologique, différenciation, ROI (financier, performance, qualité …).
c. Risques liés aux investissements et/ou aux non-investissement
iv. Le plan de financement
a. Les besoins financiers nécessaires (nature, montant date, durée …)
b. Le tableau de financement
c. Calcul du besoin en fonds de roulement
v. Le prévisionnel financier
a. Le bilan prévisionnel
b. Le compte de résultat prévisionnel
c. Le plan de trésorerie prévisionnel
d. Budget prévisionnel
e. Le point mort et le seuil de rentabilité,
f. Le calcul de la capacité d’autofinancement
viii. La rentabilité du projet
a. Quel gain pour les clients, pour l’entreprise, pour les investisseurs (service, qualité, environnement …)
b. Le calcul de la rentabilité financière
3 – Réglementation en vigueur
4 – Étapes avec rétroplanning
D. Les Ressources du projet
1 – Équipe, compétences nécessaires
3 – Partenaires, investisseurs
4 – Acteurs clés
- La rédaction de votre business plan
Ceci n’est qu’un exemple de ce qu’on peut trouver dans un business plan, et il faudra bien évidemment adapter votre dossier à votre projet et au métier. Mais sachez que plus le business plan sera précis et détaillé, mieux il vous aidera à finaliser – ou non – le projet en cours.
Vous devez vous poser des questions à chaque étape, l’idéal pour ne rien oublier étant de se servir de la méthode QQOQCP qui est un excellent aide-mémoire : Quoi, Qui, Où, Quand, Comment, Pourquoi :
- Qui ? Qui est concerné : responsables, acteurs, clients, fournisseurs…
- Quoi ? Quel est votre produit ? Votre idée ?
- Où ? Où allez-vous installer votre entreprise ? Dans quel secteur d’activité ?
- Quand ? Quand démarrer concrètement le projet ? Rétroplanning avec date de démarrage, installation, lancement produit, publicité, démarchage… et vente.
- Comment ? Quels moyens mettre en œuvre ? Matériel, procédures, aspect légal, publicité, commercial ? Méthodes utilisées ?
- Pourquoi ? 5 bonnes raisons pour créer ce business ? Que va-t-il apporter ? Quelle est sa valeur ajoutée ?
- Vous pouvez rajouter une autre question, à notre sens primordiale : Combien ? Quels fonds faut-il libérer ? Combien pensez-vous investir, gagner ensuit e ?
- La finalité du business plan
Il faut aussi penser à adapter votre business plan en fonction de son destinataire.
Un banquier, un investisseur privé, un futur associé, un partenaire potentiel n’auront pas les mêmes attentes ni la même lecture. Si le business plan contribue à la maturité de votre projet, c’est aussi un élément commercial essentiel pour votre projet de création d’entreprise.
Il vous faudra du temps et beaucoup d’énergie pour monter ce business plan, mais nous ne pouvons que vous conseiller de vous y atteler en ne négligeant aucun détail, car il sera la base de présentation de votre future affaire tout autant qu’une aide inestimable pour aller de l’avant. De plus, si le projet est bancal et mérite d’être approfondi ou modifié, c’est grâce aux différentes études menées pour finaliser ce plan que vous vous en rendrez compte.
Le business plan est un indispensable pour toute création ou reprise d’entreprises, quel que soit son secteur d’activité, ou son statut juridique ( micro-entrepreneur, entreprise individuelle, SASU, EURL, etc.).
Pour aller plus loin
- Les étapes du business plan
- Exemple de business plan
- Business plan en ligne : tableau comparatif
J'accepte la politique de traitement des données
Articles pour aller plus loin
- A quoi sert le Business plan ?
- Business plan en ligne : Comparateur de prix
- Exemples de Business Plan
- Guide détaillé pour faire votre business plan
- Monter le Business Plan
- Vivre une aventure transformante Notre Méthode
- Prendre une nouvelle dimension Découvrir CPA France
- Près de chez vous Nos campus
J'accepte de recevoir les actualités du blog du dirigeant*
- 30 Août 2019
Le blog du dirigeant vous propose de revenir en détail sur cette possibilité. 1 – La restitution du CICE : une restitution en principe différée Pour rappel, le CICE donne lieu à un avantage fiscal égal à 6 % des rémunérations brutes versées soumises à cotisations sociales. Concernant ses modalités d’utilisation, le CICE a par […]
- 9 Août 2021
Pour que cette étape importante de votre création d’entreprise soit bénéfique, il faut donc intégrer un incubateur en sachant exactement à quelle offre de services s’attendre. Il faut aussi choisir un incubateur adapté à son modèle économique et son secteur d’activité. Voici notre avis sur l’incubateur en tant que service aux porteurs de projets, et […]
- 24 Avr 2024
Le Blog du Dirigeant vous présente Olino, ex Riskee et leurs services ! Pour qui ? Olino est une assurance uniquement réservée aux professionnels. Toutes les entreprises et secteurs d’activités peuvent s’assurer sur Olino, auto-entrepreneurs, TPE, PME, starts up, profession libérale, agent immobilier… Pour quels types de contrat ? Les contrats proposés par Olinoont vocation à couvrir […]
- 24 Jan 2024
Ouvrir un compte bancaire professionnel pour votre SASU est donc une étape obligatoire. Vous pouvez procéder à cette formalité lors de la création de votre société ou après son immatriculation au registre du commerce et des sociétés (RCS). L’ouverture d’un compte bancaire obéit à certaines règles que doit connaître un entrepreneur. Afin de vous aider […]
Enregistrer mon nom, mon e-mail et mon site dans le navigateur pour mon prochain commentaire.
Nous utilisons des cookies pour recueillir des données anonymes sur votre utilisation de notre site. Ces informations nous aident à améliorer votre expérience en ligne en comprenant mieux comment vous interagissez avec notre contenu et nos fonctionnalités.
Il est important de noter que ces cookies ne sont utilisés : ni pour créer des profils d'utilisateurs, ni réaliser un suivi individuel.
Cependant, le refus des cookies peut limiter certaines fonctionnalités et rendre votre expérience sur notre site moins enrichissante.
Javascript est desactivé dans votre navigateur.
République Française
Entreprendre .Service-Public.fr
Le site officiel d'information administrative pour les entreprises
- Accéder au site pour les particuliers
Sélectionnez une commune dans la liste des suggestions
Une erreur est survenue pendant la recherche, merci de réessayer.
Partager la page
Votre abonnement a bien été pris en compte
Vous serez alerté(e) par email dès que la page « Projet de création d'entreprise : comment faire un business plan » sera mise à jour significativement.
Vous pouvez à tout moment supprimer votre abonnement dans votre compte service-public.fr .
Votre abonnement n’a pas pu être pris en compte.
Vous devez vous connecter à votre espace personnel afin de vous abonner à la mise à jour de cette page.
Être alerté(e) en cas de changement
Ce sujet vous intéresse ? Connectez-vous à votre compte et recevez une alerte par email dès que l’information de la page « Projet de création d'entreprise : comment faire un business plan » est mise à jour.
Pour vous abonner aux mises à jour des pages service-public.fr, vous devez activer votre espace personnel .
Vous serez alerté(e) par courriel dès que la page « Projet de création d'entreprise : comment faire un business plan » sera mise à jour significativement.
ACTIVER MON ESPACE PERSONNEL
Projet de création d'entreprise : comment faire un business plan
Vérifié le 26 septembre 2023 - Direction de l'information légale et administrative (Premier ministre)
Personne qui investit de l'argent dans une entreprise innovante à fort potentiel. Elle est expérimentée et apporte des contacts, conseils. Elle espère faire une plus-value.
Autres cas ?
Reprise d’entreprise : bâtir un business plan
Vous avez un projet de création d'entreprise ? Le business plan (ou plan d'affaires) est un document écrit qui présente en détail votre projet de création entreprise. Le business plan sera l'outil pour convaincre les banques et les investisseurs . Nous vous expliquons comment faire un business plan étape par étape .
La démarche par étapes
1 Ce qu'il faut savoir avant de faire votre business plan
À quoi sert le business plan , un guide et un outil vendeur.
Le business plan doit être vendeur , rassurant , c'est-à-dire réaliste.
Vous devez le construire à partir du terrain , de vos recherches et de votre analyse .
Il doit prouver que votre projet de création d'entreprise est sérieux .
Le business plan doit être à la fois synthétique et très précis avec des prévisions chiffrées .
Un outil adapté à chaque investisseur
Votre business plan est l' outil pour convaincre les investisseurs et tous ceux qui soutiendront votre projet.
Il s'adresse donc aux investisseurs suivants :
- Collectivités locales
- Business angels : titleContent
- Futurs associés
- Tous ceux auprès de qui vous cherchez des fonds
À savoir
En fonction de l'investisseur à qui vous vous adressez, vous mettez certaines informations en avant.
Vous devez donc faire plusieurs versions de votre business plan selon chaque destinataire .
Les étapes du business plan
Le business plan est un document qui se construit en 5 étapes :
- Introduction ou pitch de présentation
- Présentation de votre produit (ou service)
- Présentation de votre business model (appelé aussi stratégie commerciale )
- Votre étude de marché (synthèse)
- Votre prévisionnel financier (synthèse)
2 Préparer un pitch de présentation
À quoi sert un pitch de présentation .
Le pitch de présentation du business plan est aussi appelé executive summary .
Il s'agit de la présentation de votre projet de création d'entreprise.
Il doit être condensé .
Son objectif est de convaincre un interlocuteur.
Vous devez convaincre dans un temps court .
L' objectif de cette synthèse est de prouver :
- Votre capacité à créer et diriger une entreprise
- Votre adéquation avec le projet
- Votre sérieuse préparation du projet
- Si vous êtes plusieurs associés, votre cohésion d'équipe
Il est conseillé de rédiger plusieurs versions de cette présentation selon chaque investisseur à convaincre.
- Pour convaincre un investisseur public, vous insisterez davantage sur le service que vous rendez à la société.
- Pour convaincre un business angel : titleContent , vous insisterez sur le caractère innovant de votre offre.
Ces informations doivent permettre de comprendre quelles sont vos idées , vos valeurs , ce qui vous motive , donc le sens de votre projet .
Si vous êtes plusieurs à porter le projet de création, on doit sentir la cohésion de l' équipe et la complémentarité des membres.
Cette présentation doit prouver votre capacité à créer et diriger une entreprise sur le court et le long terme .
Quel est le contenu du pitch ?
Cette présentation doit permettre de répondre aux questions suivantes :
- Qui êtes-vous et quels sont les membres de votre équipe (collaborateurs, associés) ?
- Quel est votre projet ? Il s'agit du nom de votre entreprise, sa forme juridique, sa domiciliation, la nature de l'activité, l'histoire du projet.
- Quelle est votre cible ? Il s'agit de montrer que vous avez identifié vos futurs clients.
- Quel est l' environnement ? Il s'agit de montrer que vous avez identifié la concurrence, les contraintes, les risques, les tendances de votre marché, etc.
- Quelles sont vos ambitions de développement ? Il s'agit de montrer que vous avez une vision du projet à court , moyen et long terme .
La présentation du business plan est en partie un résumé de l' étude de marché .
3 Expliquer quel est votre produit ou service
Vous décrivez ce que vous allez vendre .
Cette description doit être précise, concise, claire.
Il faut éviter d'employer des termes trop techniques.
Vous devez être compris par des personnes qui ne connaissent rien à votre domaine d'activité.
Vous pouvez faire des schémas, dessins, etc. pour accompagner cette description du produit.
4 Définir la stratégie marketing ou business model
Qu'est-ce que le business model d'une entreprise .
Vous devez présenter comment vous allez vendre votre produit ou votre service.
Le business model s'appelle de différentes façons : une stratégie marketing , une stratégie commerciale, un " mix-marketing " ou encore un modèle économique .
Le business model de votre entreprise doit répondre aux questions suivantes :
- De quelle façon allez-vous faire la promotion et la publicité de votre entreprise, de votre produit ou service ?
- Quels seront vos tarifs ?
- Quels seront vos fournisseurs ?
- Par qui sera fabriqué votre produit ou service ?
- Quels seront vos canaux de distribution , où sera vendu votre produit ou service (internet, réseaux professionnels, boutiques etc.) ?
- Quelle sera la relation avec vos clients, comment les fidéliser ?
- Où seront stockés vos produits ?
- Quelles seront les pistes de développement de votre activité (internet, national, international, etc.) ?
Avez-vous analysé les contraintes ?
Il s'agit de prévoir ce qui peut freiner votre activité .
Vous devez identifier ce qui peut faire grimper vos coûts : stockage, production, distribution, communication.
- Le cours fluctuant des matières premières influe-t-il sur votre production ?
- Les fournisseurs du secteur ont-ils un monopole ?
- La demande vis-à-vis de votre produit est-elle saisonnière ?
Vous devez prouver que vous avez réfléchi aux solutions suivantes :
- Comment dépasser les contraintes
- Comment faire face à des pertes de bénéfices, à une hausse de vos charges, à de nouveaux concurrents, etc.
5 Rédiger la synthèse de votre étude de marché
L'objectif de l'étude de marché et de sa synthèse est d'expliquer :
- Quels sont vos futurs clients ?
- Quelle plus-value votre produit apporte-t-il sur le marché ?
- Dans quel environnement s'insère votre future activité ?
Nous vous expliquons en détail comment faire une étude de marché dans notre fiche sur l'étude de marché .
6 Rédiger la synthèse du prévisionnel financier
L'objectif d'un prévisionnel financier est de montrer que votre entreprise sera rentable .
Il est aussi appelé plan de financements ou budget prévisionnel .
Le prévisionnel financier (ou budget prévisionnel) fait partie de votre étude de marché. Il s'agit de la dernière partie de votre étude de marché.
Vous devez construire ce budget sur les 3 années à venir .
Vous devez chiffrer :
- Vos charges, les dépenses nécessaires
- Vos recettes (chiffre d'affaires)
- Vos besoins de financements
- Les fluctuations de votre activité et celles du marché
Il se déroule en 4 parties :
- Compte de résultat
- Plan de financement
- Budget ou plan de trésorerie
Ces 4 parties correspondent à 4 tableaux chiffrés.
Nous vous expliquons en détail les 4 étapes d'un budget prévisionnel dans notre fiche sur l'étude de marché .
Services en ligne et formulaires
Trouver un accompagnement adapté à la création de votre entreprise
Service en ligne
Lister vos concurrents
Outil de recherche
Insee : portrait économique d'un territoire
Projet de création d’entreprise : comment faire une étude de marché
Recherche de financements pour créer ou reprendre une entreprise
Réseau entreprendre : des entrepreneurs vous aident à créer
Réseau entreprendre
Cette page vous a-t-elle été utile ?
- 1 Pas du tout Cette page ne pas m'a pas du tout été utile
- 2 Un peu Cette page m'a été un peu utile
- 3 Moyen Cette page m'a été moyennement utile
- 4 Beaucoup Cette page m'a été très utile
- 5 Parfait ! Cette page m'a été parfaitement utile
Pas du tout
L’équipe entreprendre.Service-Public.fr vous remercie
Je vais sur la page d’accueil
Vous avez noté 1 sur 5 : Pas du tout
Vous avez noté 2 sur 5 : Un peu
Vous avez noté 3 sur 5 : Moyen
Vous avez noté 4 sur 5 : Beaucoup
Vous avez noté 5 sur 5 : Parfait !
Je fais une remarque sur cette page
L’équipe entreprendre.Service-Public.fr vous remercie pour vos remarques utiles à l'amélioration du site.
Pour des raisons de sécurité, nous ne pouvons valider ce formulaire suite à une trop longue période d’inactivité. Merci de recharger la page si vous souhaitez le soumettre à nouveau.
Une erreur technique s'est produite. Merci de réessayer ultérieurement.
Vos remarques pour améliorer la page
La page est-elle facile à comprendre , l’information a-t-elle été utile .

Comment rédiger un business plan en 2022 : le guide complet
Vous souhaitez lancer votre business ou vous tentez de décrocher un prêt pour votre entreprise ? Dans les deux cas, vous allez devoir rédiger un business plan. Si l’opération semble rébarbative, sachez que faire un business plan est un excellent moyen d’analyser votre idée de projet et de repérer d’éventuels problèmes que vous n’auriez pas vu. C’est l’opportunité d’étudier en profondeur tous les aspects de votre idée d’entreprise.
Cet article vous apprendra comment faire un business plan efficace pour votre projet d’entreprise. Nous aborderons les sujets suivants :
- Qu’est-ce qu’un business plan ?
Comment faire un business plan ?
- Comment construire un business plan et les éléments qui doivent y figurer
- Business plan : exemple pour vous inspirer et modèle de business plan gratuit
- Des suggestions de logiciel business plan gratuit
Tout savoir sur comment faire un business plan, c’est parti !
Commencez à vendre maintenant avec Shopify

Business plan : définition
Qu’est-ce qu’un business plan ? Il s’agit d’un document formel qui présente vos objectifs de développement et la stratégie pour les atteindre. Les études montrent que les entrepreneurs qui se lancent avec un business plan fondent des entreprises ayant plus de succès. C’est la clé d’une croissance équilibrée, vous guidant à travers les étapes de votre développement, limitant les risques et vous aidant à sécuriser des apports financiers (entre autres avantages). On parle parfois de plan d’affaire en français.
Faire un business plan : objectifs
La plupart des banques et institutions financières exigent que vous leur transmettiez un business plan détaillé pour obtenir des fonds . Puisque les business en dropshipping demandent peu de budget pour démarrer, vous n’avez peut-être pas besoin d’apport financier et ne voyez pas l’intérêt de faire un business plan.
Cependant, vous pourriez en avoir besoin pour enlever une limite un peu trop stricte sur votre carte de crédit alors que votre entreprise grandit, ou même pour ouvrir un compte bancaire. Cela varie d’une banque à l’autre.
→ Click Here to Launch Your Online Business with Shopify
Si vous développez votre entreprise, faire un business plan vous servira pour augmenter votre capital, créer une stratégie de croissance, trouver de nouvelles opportunités et limiter les risques. Il a été démontré que faire un business plan donne deux fois plus de chances d’obtenir des fonds et même de réussir.
Si vous démarrez une entreprise, utilisez votre business plan pour identifier les forces et les faiblesses de votre projet, communiquer votre vision aux autres et établir des prévisions justes.
Le business plan concerne tous les types d’entreprises. Il est ainsi possible de faire un business plan auto-entrepreneur.

Comment faire un business plan : les grandes étapes
Un business plan passe par 5 grandes étapes : établir des objectifs, rechercher des données, comprendre sa cible, choisir un format et rédiger.
Faire un business plan étape 1 : établir des objectifs
Il y a deux questions clés à se poser ici :
- Qu’espérez-vous accomplir avec votre business ?
- Qu’espérez-vous accomplir avec votre business plan ?
Aborder votre business plan dans cette perspective vous aidera à vous concentrer sur l’objectif final à travers le processus de rédaction. Cela guidera votre manière d’orienter votre business plan. C’est aussi un moyen d’établir des critères d’évaluation de votre succès.
Faire un business plan étape 2 : la recherche de données
Avant de rédiger votre business plan, rassemblez les informations et données dont vous aurez besoin. Cela comprend des informations sur votre marché et votre industrie – et notamment les chiffres clés et les grandes tendances
Ce sera beaucoup plus facile de démarrer avec toutes les informations à disposition, plutôt que de faire les recherches au fur et à mesure de votre progression.
Par exemple, si vous voulez lancer un business e-commerce, étudiez les chiffres e-commerce France . Votre business plan doit démontrer votre parfaite connaissance du marché.
Faire un business plan étape 3 : comprendre votre audience
Parce que les business plans peuvent servir différents objectifs, vous ne le présenterez pas forcément à la même audience. Il est important de s’adapter aux personnes qui vont le lire, de penser à ce que vous souhaitez obtenir d’elles et aux doutes que ces personnes pourraient avoir.
Ainsi, vous pouvez adapter votre business plan en fonction de ces différents objectifs. Votre audience détermine donc le type ou le format de business plan à utiliser. Ce qui nous amène au point suivant…
Faire un business plan étape 4 : choisir un format
Il existe actuellement deux types de business plans :
- Le business plan traditionnel s’adresse aux entrepreneurs qui veulent créer un business plan détaillé pour eux-mêmes ou pour trouver des financements.
- Le business plan simplifié, concerne les entrepreneurs qui veulent pitcher leurs projets et tient en une seule page. Il est très utilisé par les start-ups.
Si le business plan ne concerne que vous-même et vos collaborateurs, faites un business plan simplifié ou une version personnalisée de la version traditionnelle, avec seulement les sections dont vous avez besoin.
Si vous en avez besoin pour trouver des fonds ou pour d’autres objectifs, choisissez la version traditionnelle et complétez soigneusement toutes les parties en prêtant une attention particulière aux projections financières.
Faire un business plan étape 5 : rédiger !
Une fois vos objectifs bien définis, le marché analysé et votre cible identifiée, vous pouvez commencer à rédiger !
Alors, comment rédiger un business plan ? Un business plan contient généralement les information suivantes, dans un ordre qui peut varier :
Résumé du projet
Description de l’entreprise.
- Produit et service
Étude de marché
Analyse swot.
- Marketing et sales
Management et organisation
- Apport financier
- Projection financière
Pour vous aider à faire votre business plan, nous allons détailler chacun de ces éléments, avant de nous pencher sur les ressources pour trouver un exemple de business plan et un modèle business plan, notamment un modèle de business plan gratuit PowerPoint.
Avant cela, une remarque : tandis que vous rédigez votre business plan, prenez le temps non seulement d’analyser votre idée de business, mais également vous-même. Posez-vous les questions suivantes pour vous aider à faire le point sur votre entreprise au fur et à mesure :
- Pourquoi je veux lancer ou développer une/mon entreprise ?
- Est-ce que mes objectifs (personnels et professionnels) et valeurs correspondent à mon idée de business ?
- De quels revenus ai-je besoin de gagner pour moi-même ?
- Quelles éducation, expérience et compétences dois-je apporter à mon business ?

Faire un business plan : les différentes parties
Voici comment rédiger chaque partie de votre business plan, avec les informations à inclure.
Le résumé du projet est la première partie de votre business plan, c’est là que vous devez accrocher le lecteur. Chaque business plan débute de cette façon, même les plus basiques. Résumez tout votre business plan en une page, en soulignant les détails qui éveilleront la curiosité de vos investisseurs et soutiens potentiels.
Expliquez l’objectif de votre business, votre marché cible, ce qui vous différencie de la concurrence, dites-en un peu à votre sujet et sur les personnes au cœur de votre entreprise et présentez des projections réalistes sur le succès potentiel de votre entreprise.
Bien que cette partie soit la première de votre business plan, rédigez-la après avoir écrit tout le reste. Ce sera beaucoup plus facile parce que vous n’aurez plus qu’à ressortir les sections les mieux écrites pour les agencer dans votre première partie.
Cette partie devrait comprendre des détails basiques tels que :
- Statut juridique (micro-entreprise, société ou autreetc…)
- Numéro SIRET
- Date de création
- Responsable légal
- Nombre de salariés
Le concept de votre entreprise, votre philosophie et vos valeurs, votre vision, vos objectifs à court et long terme et les étapes de développement, ainsi qu’une rapide présentation de votre industrie, du marché, des perspectives et de vos concurrents devraient aussi être inclus dans la description de votre entreprise.
Produits et services
La section produits et services détaille ce que vous prévoyez de vendre aux consommateurs. Dans le cas d’un business plan dédié au dropshipping, cette section devrait expliquer quels produits tendance vous comptez vendre, le problème que ce produit résout pour vos clients, comment vous déterminez vos prix par rapport à vos concurrents, la marge commerciale attendue, les informations liées à la production et à la livraison.
Rappelez-vous d’inclure la proposition commerciale unique pour chaque produit ou catégorie de produits, comme les accords exclusifs avec des fournisseurs, la capacité d’obtenir des produits rares ou très demandés grâce à vos relations un service client personnalisé ou d’autres avantages.
Pour les business en dropshipping vendant des centaines voire des milliers de produits, détaillez les catégories principales de produits et le nombre d’articles que vous prévoyez de proposer dans chaque catégorie. De cette façon, il sera plus facile de visualiser l’ensemble de votre offre et de déterminer si vous avez besoin de plus de produits dans telle ou telle catégorie.
La section étude de marché de votre business plan vous permet de partager les recherches effectuées pour en apprendre plus sur votre clientèle, les acheteurs potentiels ou vos produits.
Votre audience voudra savoir si vous avez de solides connaissances sur votre industrie, le paysage concurrentiel et ceux qui devraient devenir vos clients.
Il est important de démontrer que le marché est assez dynamique pour accueillir vos produits, pour être compétitif et/ou faire un bon retour sur investissement .
Pour compléter la section étude de marché de votre business plan, vérifiez les ressources suivantes de votre industrie, de votre secteur et des recherches économiques locales :
L’ union des Français de l’étranger propose des ressources pour les gens qui souhaitent lancer une entreprise dans un pays étranger.
Les ambassades françaises de la plupart des pays disposent d’une section entreprise avec des informations pour les personnes souhaitant vendre à l’étranger. Cette section comportera un guide basique de démarrage, des liens vers des rapports ou des données économiques, des évènements professionnels et d’autres liens utiles pour une région en particulier.
Statista propose aussi des statistiques gratuites et payantes, ainsi que des études de plus de 18 000 ressources, incluant des rapports d’industrie, des rapports nationaux, des études de marché, des rapports prévisionnels et d’autres études de consommateurs.
Utilisez ces sites et d’autres pour en apprendre plus sur les projections de développement de votre industrie et de son potentiel. Vous pourrez aussi utiliser les réseaux sociaux tels que Facebook audience insights pour estimer la taille de votre marché cible sur le plus grand réseau social.
Un autre moyen de faire des recherches sur votre marché et vos produits consiste à utiliser Google Trends . Cet outil gratuit vous permet de voir à quelle fréquence sur une période donnée, les gens recherchent les produits que votre entreprise propose. Assurez-vous d’expliquer clairement comment votre business prévoit de capitaliser sur ces tendances.
Certains business plans comprennent également une analyse SWOT. Il s’agit d’une page qui résume les forces, les faiblesses, les opportunités et les menaces. Les forces et les faiblesses seront internes, tandis que les opportunités et les menaces seront externes.
En fonction de ce que révèle cette section, vous déciderez si oui ou non, vous souhaitez intégrer cette analyse dans votre business plan.
Marketing et ventes
Connaître son marché cible, c’est déjà la moitié du travail fait. Dans la section marketing et ventes, expliquez comment vous comptez atteindre votre cible et lui vendre vos produits. Présentez les stratégies marketing et communication que vous comptez utiliser pour faire connaître votre produit auprès de clients potentiels, le marketing de référencement, le marketing de réseaux sociaux , le marketing de contenu , l’ email marketing et les canaux publicitaires.
Si vous ne savez pas vraiment comment promouvoir vos produits, analysez vos concurrents pour trouver un peu d’inspiration. Étudiez les stratégies marketing de vos concurrents vous aidera à concevoir les vôtres pour développer une base clients et ainsi pousser votre business au niveau supérieur.
Faites une recherche Google avec les noms de vos concurrents pour trouver leurs sites Internet, leurs comptes sociaux et le contenu qu’ils ont créé pour promouvoir leurs produits. Regardez comment ils utilisent chaque canal pour attirer de nouveaux clients vers leur boutique en ligne.
Insérez dans votre business plan une description de la façon dont vous comptez convertir ces cibles en clients réels, grâce à vos messages marketing et de communication. Pour les boutiques en dropshipping, les conversions se passeront typiquement sur votre site Internet lorsque les visiteurs achètent vos produits.

Dans la partie management et organisation de votre business plan, décrivez la structure de votre entreprise. La plupart du temps, les entreprises sont déclarées sous forme demicro -entreprise (un fondateur), une société (deux ou plusieurs fondateurs) ou des coopératives.
Rédigez une présentation courte de chacun des membres clés de votre entreprise. Si vous êtes auto-entrepreneur, ajoutez les éléments de votre parcours professionnel qui vous aideront à gérer votre entreprise. Si vous avez un ou plusieurs partenaires et salariés, faites de même pour eux.
Pensez à cet exercice comme un excellent moyen d’évaluer les forces de chaque personne dirigeant votre entreprise. Lors de cette auto-évaluation, vous serez capable d’identifier les aspects de votre business qui seront faciles à gérer pour vous et ceux que vous feriez mieux de déléguer à des freelances , des partenaires, des employés ou des services sous-traitants. C’est aussi un bon moyen d’optimiser les forces de l’entreprise pour maximiser sa croissance.
Apports financiers
Dans le cas d’une start-up en dropshipping, il y a peu de chance que vous ayez besoin de trouver des fonds puisque l’attrait de ce modèle économique est justement le peu de fonds requis pour se lancer. Cela dit, si vous cherchez un prêt, c’est dans cette section que vous indiqueriez le montant souhaité, comment vous prévoyez de l’investir et comment vous voyez votre retour sur investissement.
Un autre moyen d’exploiter cette section consiste à analyser l’investissement que vous avez ou comptez obtenir lors du lancement ou du développement de votre entreprise. Cela devrait inclure tous les éléments : des ordinateurs pour gérer le site Internet aux frais mensuels pour d’autres services marketing ou commerciaux.
Projections financières
Dans les projections financières, partagez les prévisions de revenus et charges pour les cinq premières années de votre entreprise. L’idée ici est de montrer que le revenu escompté permettra d’atteindre rapidement un retour sur investissement, qu’il s’agisse de vos finances personnelles ou d’un apport au capital.

Si vous êtes à la recherche de fonds, vous aurez besoin de rentrer dans les détails concernant vos revenus, le budget prévisionnel, l’état des flux de trésorerie et les budgets d’investissement. Si vous n’avez pas besoin de fonds, vous ne perdrez pas votre temps à créer ce type de projections financières, qui vous permettront de faire des prévisions réalistes pour le futur de votre entreprise.
Annexe
L’annexe de votre business plan doit comprendre tout document supplémentaire que vous jugerez nécessaire, en fonction de votre business plan. Cela peut inclure, mais n’est pas limité à :
- Historique de crédits
- Brochures de produits
- Références
- Documents légaux
- Contacts fournisseurs
Si vous soumettez votre business plan dans le but d’obtenir des financements, contactez le prêteur pour connaître la documentation requise pour votre demande.

Business plan : exemple et modèle de business plan gratuit
Pour faire un business plan, le plus simple est souvent de se baser sur un exemple de business plan création d’entreprise ou un modèle de business plan gratuit. Alors, où trouver un business plan en ligne ? Quel site propose un business plan exemple concret ?
Voici quelques ressources très utiles pour faire un business plan, pour ne pas partir de zéro :
- La Chambre de Commerce et d’Industrie de Paris (CCI) a développé une plateforme gratuite qui permet de construire son business plan en ligne. Sur CCI Business Builder , vous pourrez construire un business plan pas à pas, à partir d’un modèle de business plan.
- Le site creerentreprise.fr offre un modèle de business plan gratuit Powerpoint pour start-up. Vous pourrez compléter le document directement.
- BPI France a créé un modèle de business plan gratuit / modèle de présentation de projet pour aider les entrepreneurs qui se lancent. Le template se présente sous forme d’un guide PDF à télécharger.
- Le magazine L’Express propose plus de 150 modèles de business plan à télécharger. Vous êtes sûr de trouver un exemple de business plan gratuit pour vos besoins !
- Shopify met aussi à disposition un modèle de business plan gratuit, en anglais. Ce business plan à télécharger se présente sous la forme d’un document Word, avec les grandes parties du business plan.
Logiciel business plan gratuit

Autre approche pour faire un business plan : utiliser un logiciel business plan gratuit. Si la plupart des logiciels de création de business plan sont payants, nous avons trouvé pour vous 2 solutions gratuites :
- Montpellier Business Plan est un logiciel de business plan gratuit à télécharger. Il permet de construire un business plan pas à pas et de construire un prévisionnel en testant plusieurs scénarios.
- Bpi France propose une application gratuite pour faire son business plan en ligne, dans le cadre de son offre Pass Entrepreneur. Vous devrez créer un compte pour pouvoir y accéder.
Ces 2 options de logiciel business plan gratuit devraient répondre à vos besoins.
Comme vous pouvez le voir, rédiger un business plan pour votre entreprise de dropshipping est un très bon moyen de valider votre idée d’entreprise, de percevoir les forces et les faiblesses de votre projet et de mettre toutes les chances de votre côté pour réussir votre aventure en tant qu’entrepreneur. Si vous ne l’avez pas déjà fait, prenez le temps de créer un business plan pour lancer ou développer votre business dropshipping en 2022 !
Découvrez d'autres conseils utiles sur comment faire un business plan dans cet article de Shopify.
- Rédiger un résumé de son projet
- Inclure une description de l’entreprise
- Présenter ses produits et services
- Faire une étude de marché
- Réaliser une analyse SWOT
- Détailler sa stratégie marketing et ventes
- Présenter le management et l’organisation
- Indiquer ses apports financiers
- Réaliser une projection financière
- Préparer les annexes
Vous souhaitez en savoir plus ?
- Nom d’entreprise : Générateur de nom d’entreprise
- Que vendre sur Internet ? Comment trouver des produits dropshipping
- Les 20 avantages et inconvénients de l’e-commerce à connaître
- La signification des couleurs en communication et marketing

Comment Vendre des Tableaux en Ligne : Stratégies et Plateformes (2024)
Découvrez les meilleures plateformes pour vendre vos tableaux ou vos oeuvres en ligne et vous faire connaître en tant q…

Comment vendre sur Facebook : Stratégies et astuces (2024)
Découvrez comment optimiser vos ventes sur Facebook avec des stratégies et astuces clés pour 2024.

Hashtags Instagram : 300+ Meilleurs hashtags Instagram pour plus de J'aime
Découvrez la puissance des hashtags Instagram pour augmenter la visibilité et l'engagement. Apprenez comment ils foncti…
Nous utilisons des cookies pour vous proposer la meilleure expérience possible sur notre site. Merci d’accepter ceci pour que nous puissions continuer à personnaliser notre contenu pour vous. Pour plus d’informations, lire notre Politique de confidentialité.
- Skip to menu
- Aller au contenu
Je recherche
Définition du business plan : Qu’est-ce c’est ?
Qu’est-ce qu’un business plan ? Telle est la question que se posent bon nombre d’entrepreneurs… Un business plan est un document écrit permettant de formaliser un projet de création d’entreprise, de reprise d’entreprise ou de développement d’activité. Compta-Facile vous présente sa fiche complète consacrée à la définition du business plan .
Qu’est-ce qu’un business plan ?
Par définition , un business plan , également appelé plan d’affaires (ou, par abus de langage, « prévisionnel financier « ) est un dossier qui est constitué à l’occasion :
- D’une création d’entreprise,
- D’une reprise d’entreprise
Ou d’une modification d’activité (adjonction ou suppression).

Pour plus d’informations : quand faut-il établir un business plan ?
Le business plan est un document écrit qui fera l’objet d’entretien avec différents interlocuteurs et qui doit nécessairement répondre aux questions suivantes :
- Qui est le porteur de projet ? Quel est son parcours ?
- Que compte-t-il vendre ? A qui va-t-il le vendre ?
- Qui sont ses concurrents ? De quels avantages dispose-t-il par rapport à ceux-ci ?
- Comment souhaite-t-il déployer son projet ? Selon quel calendrier ?
- Quels sont les besoins financiers générés par son projet ?
- Comment pense-t-il les faire financier ?
- Quel retour sur investissement anticipe-t-il ?
Il présente l’ensemble des actions qui seront conduites par l’entreprise, les moyens qu’elle va déployer pour y parvenir et la période qu’elle se fixe pour atteindre ses objectifs.
Quelle est l’utilité d’un business plan ?
Un business plan a une visée argumentaire et a vocation à convaincre le destinataire pour lequel il a été rédigé. C’est d’ailleurs sa fin en soi. Il doit permettre à l’entreprise :
- D’obtenir un financement bancaire,
- De bénéficier de participations de la part d’investisseurs externes,
- De négocier des tarifs préférentiels et des délais de paiement auprès d’un futur fournisseur.
Pour plus d’informations : à quoi sert un business plan ?
Que contient un business plan ?
Sur le plan du contenu , un business plan doit présenter deux volets :
- Une partie rédactionnelle
Le porteur de projet y évoque son idée, l’ analyse qu’il a faite de ses concurrents , le positionnement stratégique qu’il souhaite adopter, l’intensité de la concurrence présente sur son marché, les moyens dont il dispose pour parvenir à satisfaire sa demande et le cadre juridique de l’opération.
- Une partie financière
Elle contient un ensemble de tableaux financiers tels que le compte de résultat prévisionnel ,le bilan prévisionnel , le plan de financement prévisionnel ou encore le budget de trésorerie . Ils s’articulent plus ou moins entre eux et mettent en évidence différentes notions clefs comme le besoin en fonds de roulement ( BFR ), la capacité d’autofinancement ( CAF ), différents ratios financiers, etc.
Pour plus d’informations : quel est le contenu d’un business plan ? [the_ad_placement id= »corps-article-expert-comptable-business-plan »]
Quels sont les destinataires d’un business plan ?
Multiples sont les destinataires d’un business plan.
En premier lieu, il s’agit du porteur de projet lui-même. Le business plan va lui permettre de structure ses idées, d’affiner son projet, de mettre en évidence ses forces et ses faiblesse et de s’assurer de sa viabilité.
Ensuite, il s’adresse aux apporteurs de fonds , c’est-à-dire les banques (pour les prêts) et les investisseurs (pour les participations au capital et les autres formes de participation). Il doit prouver la pérennité du projet et mettre en lumière le retour sur investissement attendu.
Enfin, il a vocation à convaincre les futurs partenaires de l’entreprise de commercer avec celle-ci. Il permet de négocier des délais de paiement ou des prix en fonction des volumes de commandes. Il doit prouver la solidité financière du projet ainsi que son ampleur.
Pour plus d’informations : quels sont les destinataires d’un business plan ?
Comment faire un business plan ?
Un business plan comporte généralement une vingtaine de pages mais la structure de ce document dépend de son destinataire . En effet, un business plan ne sera pas rédigé de la même façon s’il à vocation à convaincre un banquier ou un investisseur. Cela étant dit, chaque partie doit tout de même contenir un minimum d’informations.
Il doit être clair et aéré, compréhensible sur le plan rédactionnelle et cohérent sur le plan financier.
Pour plus d’informations : comment faire un business plan ?
Partager l'article :
Donnez-lui une note !
Merci pour votre vote.
Thibaut CLERMONT , mémorialiste en expertise-comptable et fondateur de Compta-Facile, site d'information sur la comptabilité .
A lire aussi...

Orientation assumée du projet de la loi de finances 2024, le crédit d’impôt au titre des investissements dans l’industrie verte soutient les entreprises engagées dans l’énergie décarbonée. Le dispositif pourrait, d’après Bercy, s’élever […]

A l'heure du numérique, de nombreux experts-comptables proposent des solutions en ligne. Que valent-elles ? Sont-elles avantageuses ? Quels sont leurs inconvénients ? Compta-Facile fait le point en répondant à la question fondamentale […]

Un expert-comptable peut vérifier la comptabilité d'une entreprise, quel que soit son statut juridique. La mission qu'il va exercer dépend des besoins de l'entreprise ainsi que de ses souhaits. Est-ce obligatoire ? En quoi consiste la mission comptable que vous pourriez lui confier ?

En contrepartie de l'exercice de sa mission, un expert-comptable perçoit une rémunération appelée "honoraires". Cette rémunération doit respecter certaines règles. Tout ce qu'il faut savoir sur les honoraires d'un expert-comptable.
Abonnez-vous à la newsletter !

1 commentaire
Meriem Charrad
Bonjour, tout simplement merci.
Répondre Annuler la réponse
Votre adresse e-mail ne sera pas publiée. Les champs obligatoires sont indiqués avec *
Commentaire *
Enregistrer mon nom, mon e-mail et mon site dans le navigateur pour mon prochain commentaire.
J’ai lu et j’accepte la politique de confidentialité *
Qu'est-ce qu'un business plan? Notre explication
Qu'est ce qu'un business plan?
Un business plan ou plan d'affaires est un document ayant pour objectif de convaincre un décideur d'investir dans un projet entrepreneurial. Le business plan doit répondre aux questions suivantes :
- Qui sommes-nous (structure juridique, actionnariat, emplacement, etc.)?
- Que vendons-nous (produit, service)?
- A qui (clients)?
- Comment (réseau de distribution, plan commercial)?
- Qui sont nos concurrents?
- Quel est le calendrier (étapes clés)?
- Comment le produit est il fabriqué (processus de fabrication, fournisseurs, technologie, etc.)?
- Quels sont les besoins financiers (montant, type de financement)?
- Quel est le retour sur investissement (prévision de trésorerie)?
Quelle est la structure type d'un business plan?
Un business plan suit généralement l'ordre suivant :
- Société (qui sommes nous ?)
- Produits et Services (que vendons nous?)
- Etude de marché (à qui?)
- Stratégie (comment?, qui sont nos concurrents?, quel est le calendrier?)
- Opérations (comment le produit est il fabriqué?)
- Plan Financier (quels sont les besoins financiers?, quel est le retour sur investissement?)
Bien qu'il existe une structure de business plan type, il est important de noter que le plan doit être adapté à la fois au lecteur et au projet.
Business plan sur mesure
Le business plan a une visée argumentaire : il doit démontrer que le projet est attractif. La structure du business plan doit donc être adaptée en fonction du projet afin de le mettre en valeur.
Le lecteur du business plan décidera de poursuivre le projet (ou de l'abandonner) suivant la balance entre les risques et les opportunités de gains qui lui sont associés. La perception des risques dépendra de l'identité du lecteur : les banques, les managers, et les actionnaires ont tous une façon d'appréhender les risques qui leur est propre.
Il est donc important de bien comprendre la grille d'analyse qu'utilisera le destinataire du plan pour prendre sa décision d'investissement avant d'écrire le plan afin de pouvoir adapter celui-ci en conséquence. Vous trouverez plus d'informations sur la façon dont les investisseurs analysent les business plans dans notre article .
1 business plan = 2 documents
Il y a presque deux documents différents dans un business plan. Le résumé ("executive summary" en anglais) et le reste.
Le résumé est la section la plus importante du business plan, elle a pour objectif de donner envie à l'investisseur dans savoir plus sur le projet en répondant de façon succincte à toutes les questions énoncées ci-dessus.
Après avoir lu le résumé, et s'il est intéressé par le projet, l'investisseur explorera certaines des autres sections du business plan dans le but d'obtenir plus de détail sur les points qui lui paraissent importants.
Pour plus de détails sur comment écrire un business plan nous vous invitons à lire notre guide du business plan .

Fondateur & CEO at The Business Plan Shop Ltd
Guillaume Le Brouster est un entrepreneur et un financier chevronné.
Guillaume est entrepreneur depuis plus de dix ans et possède une expérience directe en création, gestion et développement d'une entreprise prospère.
Avant d'être dirigeant d'entreprise, Guillaume a travaillé en banque d'affaires et en capital-investissement, où il a passé la plupart de son temps à créer des prévisions financières complexes, à rédiger des plans d'affaires et à analyser des états financiers pour prendre des décisions en matière de financement et d'investissement.
Guillaume est titulaire d'un Master en Finance de l'ESCP Business School et d'une Maîtrise des Sciences en Gestion de l'Université de Paris Dauphine.
Vous voulez écrire facilement votre business plan ?
Essayez gratuitement notre logiciel de business plan .
Vérifiez que votre projet peut-être rentable et obtenez un business plan professionnel pour votre recherche de financement
Ne partez pas d'une page blanche !
La version complète de The Business Plan Shop donne accès à plus de 50 modèles de business plan.

Besoin d'un business plan professionnel ? Découvrez notre solution
Créez facilement votre business plan !

Réaliser un business plan convaincant est facile avec The Business Plan Shop
Pas prêt à essayer notre outil en ligne ? Obtenez plus d'informations

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
It's the roadmap for your business. The outline of your goals, objectives, and the steps you'll take to get there. It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance. A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and ...
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines ...
If capital is a priority, this business plan might focus more on financial projections than marketing or company culture. 2. Feasibility Business Plan. This type of business plan focuses on a single essential aspect of the business — the product or service. It may be part of a startup business plan or a standalone plan for an existing ...
A Harvard Business Review study found that the ideal time to write a business plan is between 6 and 12 months after deciding to start a business. But the reality can be more nuanced - it depends on the stage a business is in, or the type of business plan being written. Ideal times to write a business plan include: When you have an idea for a ...
v. t. e. A business plan is a formal written document containing the goals of a business, the methods for attaining those goals, and the time-frame for the achievement of the goals. It also describes the nature of the business, background information on the organization, the organization's financial projections, and the strategies it intends to ...
Definition. A business plan is a detailed written document that describes your business's activities, goals, and strategy. A strong plan outlines everything from the products a company sells to the executive summary to the overall management. In essence, a business plan should guide a founder's actions through each stage of growth.
1. Executive summary. This short section introduces the business plan as a whole to the people who will be reading it, including investors, lenders, or other members of your team. Start with a sentence or two about your business, development goals, and why it will succeed. If you are seeking funding, summarise the basics of the financial plan. 2.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Business Plan Definition: A written document describing the nature of the business, the sales and marketing strategy, and the financial background, and containing a projected profit and loss statement
To get a better sense of what a 21st century business plan is, it's best to look at what it's not. Or, more specifically, what it's not anymore. When most people think about a business plan, the first thing that usually comes to mind is an incredibly dense, 50-plus-page manifesto that's as hard to write as it is to read.
Business Plan Definition. A business plan is a written document that outlines a company's goals, strategies, financial projections, and operational details, serving as a roadmap for its future growth and success. So you have a great business idea that you've decided to make a reality, and now you're planning on filling out all of the ...
A business plan is an important document for entrepreneurs of all stripes - whether you're just starting out or have been in business for a longer period of time. Your business plan tells ...
This plan, known as a business plan, is a comprehensive document that outlines a company's goals, strategies, and financial projections. Whether you're starting a new business or looking to expand an existing one, a business plan is an essential tool. As a business plan writer and consultant, I've crafted over 15,000 plans for a diverse ...
A business plan is a strategic document which details the strategic objectives for a growing business or startup, and how it plans to achieve them. In a nutshell, a business plan is a written expression of a business idea and will describe your business model, your product or service, how it will be priced, who will be your target market, and ...
Un business plan est un document synthétique qui permet à un entrepreneur de présenter de manière simple et efficace les tenants et aboutissants de son projet. Il doit présenter de façon argumentée le besoin de financement et le potentiel de rentabilité du projet ainsi que la vision du futur dirigeant concernant son entreprise.
business plan: A business plan is a document demonstrating the feasibility of a prospective new business and providing a roadmap for its first several years of operation.
Le business plan est un document écrit, servant à éclairer les parties prenantes sur la viabilité du projet de création. , reprise ou développement d'activité porté par le chef d'entreprise. Monter un business plan, c'est mettre son projet sur papier. Cette démarche, est souvent plus compliquée qu'il n'y paraît, mais elle ...
Vous avez un projet de création d'entreprise ? Le business plan (ou plan d'affaires) est un document écrit qui présente en détail votre projet de création entreprise. Le business plan sera l'outil pour convaincre les banques et les investisseurs. Nous vous expliquons comment faire un business plan étape par étape.
Faire un business plan étape 2 : la recherche de données. Avant de rédiger votre business plan, rassemblez les informations et données dont vous aurez besoin. Cela comprend des informations sur votre marché et votre industrie - et notamment les chiffres clés et les grandes tendances.
Que contient un business plan ? Sur le plan du contenu, un business plan doit présenter deux volets :. Une partie rédactionnelle; Le porteur de projet y évoque son idée, l'analyse qu'il a faite de ses concurrents, le positionnement stratégique qu'il souhaite adopter, l'intensité de la concurrence présente sur son marché, les moyens dont il dispose pour parvenir à satisfaire sa ...
Le business plan a une visée argumentaire : il doit démontrer que le projet est attractif. La structure du business plan doit donc être adaptée en fonction du projet afin de le mettre en valeur. Le lecteur du business plan décidera de poursuivre le projet (ou de l'abandonner) suivant la balance entre les risques et les opportunités de ...
Le business plan est un document str... Coralie, de L-Expert-comptable.com, vous explique à quoi sert un business plan et tout ce qu'il faut savoir à son sujet.