

How to Write a History Essay in IB
For a history essay, researching what we were studying was the most engaging method for understanding the material. I did well in history because I genuinely enjoyed the subject. Pay attention in class, look up videos on your own time, and explore different perspectives – hopefully you’ll enjoy the subject enough to have fun working on it too. This extra research while also be the foundation of your essay.
A strong thesis will provide an effective introduction to your history essay, so it is important to understand what you want to say with your essay and to spend some time refining the statement. I would suggest focusing on three major points in your thesis that you intend on developing in your essay.
As for the conclusion, this is where I would reframe your thesis as well as some of the main arguments and counterarguments you brought up in the body of the essay.
Now onto some broader essay tips. Don’t merely list the facts of an event, say why they matter and what they add to your argument. Adding counter arguments and debunking them is also key to building a strong argument. In addition, making essay outlines is probably my second best tip. They helped me structure my thoughts in order to deliver well-constructed arguments. Discussing the events in class and with friends also helped with recalling the information.
My best tip is to use historiography. Knowing the views and stances of different historians not only helped my understanding but is one of the criteria for a highly marked essay. Also, I find that knowing historiography helps greatly with structuring the essay, because you are able to interpret, interconnect and articulate events and evidence.
History is a fun course, and although it does consist of a lot of writing, with the right approach and attitude, I’m sure you can excel!
You may also like…
- Joanne’s thoughts on how to approach a History EE
- Tyus’s tips on how to get an A on your History EE
- Find IB information about History here
Share this:
Leave a reply cancel reply, discover more from iblieve.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

IB History: Writing Effective Paper 3 Essays

In the International Baccalaureate (IB) History course, Paper 3 assesses the "Aspects of the History of the Americas" for HL students. Writing effective essays for Paper 3 requires a combination of historical knowledge, critical analysis, and strong essay-writing skills. Here's a guide on how to write compelling Paper 3 essays:
1. Understanding the Assessment Criteria:
1. command terms:.
- Analyze, evaluate, and compare historical events.
- Clearly understand the meaning of each command term and tailor your response accordingly.
2. Historical Concepts:
- Demonstrate an understanding of key historical concepts such as causation, consequence, continuity, and change.
3. Synthesis:
- Integrate information from different sources and demonstrate the ability to synthesize knowledge.
2. Essay Structure:
1. introduction:.
- Provide a clear thesis statement that outlines the main argument of your essay.
- Offer a brief overview of the historical context.
2. Body Paragraphs:
- Start each paragraph with a topic sentence that relates to your thesis.
- Provide evidence, examples, and historical facts to support your arguments.
- Analyze and interpret the significance of the evidence.
3. Counterarguments:
- Address potential counterarguments to your thesis.
- Either refute counterarguments or incorporate them into your analysis to show a nuanced understanding.
4. Use of Historical Perspectives:
- Integrate different historical perspectives into your analysis.
- Discuss how the perspectives of different groups or individuals shape historical events.
5. Conclusion:
- Summarize your main arguments and restate your thesis.
- Provide a brief reflection on the broader historical significance of your analysis.
3. Historical Context and Background:
1. demonstrate contextual knowledge:.
- Begin your essay by providing the necessary historical context.
- Show an understanding of the broader historical forces at play during the period in question.
2. Chronological Organization:
- Organize your essay chronologically if it makes sense for the topic.
- Chronological organization helps demonstrate an understanding of the temporal development of events.
4. Analysis and Evaluation:
1. cause-and-effect relationships:.
- Analyze the cause-and-effect relationships between historical events.
- Examine the short-term and long-term consequences of key actions.
2. Historical Significance:
- Evaluate the historical significance of events, individuals, or developments.
- Discuss the impact of the chosen topic on the broader course of history.
3. Causal Links and Comparisons:
- Establish clear causal links between events.
- Make effective comparisons to highlight similarities and differences.
5. Use of Evidence:
1. primary and secondary sources:.
- Integrate evidence from both primary and secondary sources.
- Critically evaluate the reliability and bias of your sources.
2. Quantitative Data:
- Incorporate relevant quantitative data when applicable.
- Use statistics and figures to strengthen your arguments.
6. Writing Style:
1. clarity and cohesion:.
- Write in a clear and concise manner.
- Ensure that your essay flows logically from one point to the next.
2. Avoid Repetition:
- Avoid unnecessary repetition of ideas.
- Use varied sentence structures to maintain reader engagement.
3. Historical Terminology:
- Demonstrate a command of historical terminology.
- Use specific terms and concepts relevant to the time period.
7. Revision and Proofreading:
1. review your essay:.
- Take time to review and revise your essay.
- Check for coherence, consistency, and clarity.
2. Seek Feedback:
- Share your essay with peers or teachers for feedback.
- Consider their suggestions for improvement.
By following these guidelines, you can craft well-structured, insightful, and historically grounded essays for the IB History Paper 3. Remember to practice regularly and engage with a variety of historical sources to enhance your analytical and writing skills.
You Might Also Like

Planning for Successful College Applications
Know the right way for successful college application and how to get prepared for college admission to gain admission in your dream college - Read our blog

Apply for Federal Grants for College Education
Federal Grants are the popular sources of funding for higher education. If you are unaware of federal grants for college and how it works, then read our blog.

Know Why Demonstrated Interest is Crucial
If you want to gain admission in your dream college, you have to show your demonstrated interest to join the institution and why it is crucial

Free Resources

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, the complete ib extended essay guide: examples, topics, and ideas.
International Baccalaureate (IB)

IB students around the globe fear writing the Extended Essay, but it doesn't have to be a source of stress! In this article, I'll get you excited about writing your Extended Essay and provide you with the resources you need to get an A on it.
If you're reading this article, I'm going to assume you're an IB student getting ready to write your Extended Essay. If you're looking at this as a potential future IB student, I recommend reading our introductory IB articles first, including our guide to what the IB program is and our full coverage of the IB curriculum .
IB Extended Essay: Why Should You Trust My Advice?
I myself am a recipient of an IB Diploma, and I happened to receive an A on my IB Extended Essay. Don't believe me? The proof is in the IBO pudding:
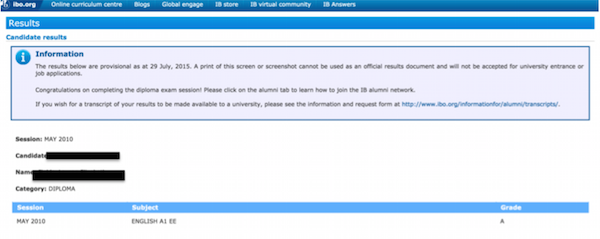
If you're confused by what this report means, EE is short for Extended Essay , and English A1 is the subject that my Extended Essay topic coordinated with. In layman's terms, my IB Diploma was graded in May 2010, I wrote my Extended Essay in the English A1 category, and I received an A grade on it.
What Is the Extended Essay in the IB Diploma Programme?
The IB Extended Essay, or EE , is a mini-thesis you write under the supervision of an IB advisor (an IB teacher at your school), which counts toward your IB Diploma (learn more about the major IB Diploma requirements in our guide) . I will explain exactly how the EE affects your Diploma later in this article.
For the Extended Essay, you will choose a research question as a topic, conduct the research independently, then write an essay on your findings . The essay itself is a long one—although there's a cap of 4,000 words, most successful essays get very close to this limit.
Keep in mind that the IB requires this essay to be a "formal piece of academic writing," meaning you'll have to do outside research and cite additional sources.
The IB Extended Essay must include the following:
- A title page
- Contents page
- Introduction
- Body of the essay
- References and bibliography
Additionally, your research topic must fall into one of the six approved DP categories , or IB subject groups, which are as follows:
- Group 1: Studies in Language and Literature
- Group 2: Language Acquisition
- Group 3: Individuals and Societies
- Group 4: Sciences
- Group 5: Mathematics
- Group 6: The Arts
Once you figure out your category and have identified a potential research topic, it's time to pick your advisor, who is normally an IB teacher at your school (though you can also find one online ). This person will help direct your research, and they'll conduct the reflection sessions you'll have to do as part of your Extended Essay.
As of 2018, the IB requires a "reflection process" as part of your EE supervision process. To fulfill this requirement, you have to meet at least three times with your supervisor in what the IB calls "reflection sessions." These meetings are not only mandatory but are also part of the formal assessment of the EE and your research methods.
According to the IB, the purpose of these meetings is to "provide an opportunity for students to reflect on their engagement with the research process." Basically, these meetings give your supervisor the opportunity to offer feedback, push you to think differently, and encourage you to evaluate your research process.
The final reflection session is called the viva voce, and it's a short 10- to 15-minute interview between you and your advisor. This happens at the very end of the EE process, and it's designed to help your advisor write their report, which factors into your EE grade.
Here are the topics covered in your viva voce :
- A check on plagiarism and malpractice
- Your reflection on your project's successes and difficulties
- Your reflection on what you've learned during the EE process
Your completed Extended Essay, along with your supervisor's report, will then be sent to the IB to be graded. We'll cover the assessment criteria in just a moment.

We'll help you learn how to have those "lightbulb" moments...even on test day!
What Should You Write About in Your IB Extended Essay?
You can technically write about anything, so long as it falls within one of the approved categories listed above.
It's best to choose a topic that matches one of the IB courses , (such as Theatre, Film, Spanish, French, Math, Biology, etc.), which shouldn't be difficult because there are so many class subjects.
Here is a range of sample topics with the attached extended essay:
- Biology: The Effect of Age and Gender on the Photoreceptor Cells in the Human Retina
- Chemistry: How Does Reflux Time Affect the Yield and Purity of Ethyl Aminobenzoate (Benzocaine), and How Effective is Recrystallisation as a Purification Technique for This Compound?
- English: An Exploration of Jane Austen's Use of the Outdoors in Emma
- Geography: The Effect of Location on the Educational Attainment of Indigenous Secondary Students in Queensland, Australia
- Math: Alhazen's Billiard Problem
- Visual Arts: Can Luc Tuymans Be Classified as a Political Painter?
You can see from how varied the topics are that you have a lot of freedom when it comes to picking a topic . So how do you pick when the options are limitless?

How to Write a Stellar IB Extended Essay: 6 Essential Tips
Below are six key tips to keep in mind as you work on your Extended Essay for the IB DP. Follow these and you're sure to get an A!
#1: Write About Something You Enjoy
You can't expect to write a compelling essay if you're not a fan of the topic on which you're writing. For example, I just love British theatre and ended up writing my Extended Essay on a revolution in post-WWII British theatre. (Yes, I'm definitely a #TheatreNerd.)
I really encourage anyone who pursues an IB Diploma to take the Extended Essay seriously. I was fortunate enough to receive a full-tuition merit scholarship to USC's School of Dramatic Arts program. In my interview for the scholarship, I spoke passionately about my Extended Essay; thus, I genuinely think my Extended Essay helped me get my scholarship.
But how do you find a topic you're passionate about? Start by thinking about which classes you enjoy the most and why . Do you like math classes because you like to solve problems? Or do you enjoy English because you like to analyze literary texts?
Keep in mind that there's no right or wrong answer when it comes to choosing your Extended Essay topic. You're not more likely to get high marks because you're writing about science, just like you're not doomed to failure because you've chosen to tackle the social sciences. The quality of what you produce—not the field you choose to research within—will determine your grade.
Once you've figured out your category, you should brainstorm more specific topics by putting pen to paper . What was your favorite chapter you learned in that class? Was it astrophysics or mechanics? What did you like about that specific chapter? Is there something you want to learn more about? I recommend spending a few hours on this type of brainstorming.
One last note: if you're truly stumped on what to research, pick a topic that will help you in your future major or career . That way you can use your Extended Essay as a talking point in your college essays (and it will prepare you for your studies to come too!).
#2: Select a Topic That Is Neither Too Broad nor Too Narrow
There's a fine line between broad and narrow. You need to write about something specific, but not so specific that you can't write 4,000 words on it.
You can't write about WWII because that would be a book's worth of material. You also don't want to write about what type of soup prisoners of war received behind enemy lines, because you probably won’t be able to come up with 4,000 words of material about it. However, you could possibly write about how the conditions in German POW camps—and the rations provided—were directly affected by the Nazis' successes and failures on the front, including the use of captured factories and prison labor in Eastern Europe to increase production. WWII military history might be a little overdone, but you get my point.
If you're really stuck trying to pinpoint a not-too-broad-or-too-narrow topic, I suggest trying to brainstorm a topic that uses a comparison. Once you begin looking through the list of sample essays below, you'll notice that many use comparisons to formulate their main arguments.
I also used a comparison in my EE, contrasting Harold Pinter's Party Time with John Osborne's Look Back in Anger in order to show a transition in British theatre. Topics with comparisons of two to three plays, books, and so on tend to be the sweet spot. You can analyze each item and then compare them with one another after doing some in-depth analysis of each individually. The ways these items compare and contrast will end up forming the thesis of your essay!
When choosing a comparative topic, the key is that the comparison should be significant. I compared two plays to illustrate the transition in British theatre, but you could compare the ways different regional dialects affect people's job prospects or how different temperatures may or may not affect the mating patterns of lightning bugs. The point here is that comparisons not only help you limit your topic, but they also help you build your argument.
Comparisons are not the only way to get a grade-A EE, though. If after brainstorming, you pick a non-comparison-based topic and are still unsure whether your topic is too broad or narrow, spend about 30 minutes doing some basic research and see how much material is out there.
If there are more than 1,000 books, articles, or documentaries out there on that exact topic, it may be too broad. But if there are only two books that have any connection to your topic, it may be too narrow. If you're still unsure, ask your advisor—it's what they're there for! Speaking of advisors...

Don't get stuck with a narrow topic!
#3: Choose an Advisor Who Is Familiar With Your Topic
If you're not certain of who you would like to be your advisor, create a list of your top three choices. Next, write down the pros and cons of each possibility (I know this sounds tedious, but it really helps!).
For example, Mr. Green is my favorite teacher and we get along really well, but he teaches English. For my EE, I want to conduct an experiment that compares the efficiency of American electric cars with foreign electric cars.
I had Ms. White a year ago. She teaches physics and enjoyed having me in her class. Unlike Mr. Green, Ms. White could help me design my experiment.
Based on my topic and what I need from my advisor, Ms. White would be a better fit for me than would Mr. Green (even though I like him a lot).
The moral of my story is this: do not just ask your favorite teacher to be your advisor . They might be a hindrance to you if they teach another subject. For example, I would not recommend asking your biology teacher to guide you in writing an English literature-based EE.
There can, of course, be exceptions to this rule. If you have a teacher who's passionate and knowledgeable about your topic (as my English teacher was about my theatre topic), you could ask that instructor. Consider all your options before you do this. There was no theatre teacher at my high school, so I couldn't find a theatre-specific advisor, but I chose the next best thing.
Before you approach a teacher to serve as your advisor, check with your high school to see what requirements they have for this process. Some IB high schools require your IB Extended Essay advisor to sign an Agreement Form , for instance.
Make sure that you ask your IB coordinator whether there is any required paperwork to fill out. If your school needs a specific form signed, bring it with you when you ask your teacher to be your EE advisor.
#4: Pick an Advisor Who Will Push You to Be Your Best
Some teachers might just take on students because they have to and aren't very passionate about reading drafts, only giving you minimal feedback. Choose a teacher who will take the time to read several drafts of your essay and give you extensive notes. I would not have gotten my A without being pushed to make my Extended Essay draft better.
Ask a teacher that you have experience with through class or an extracurricular activity. Do not ask a teacher that you have absolutely no connection to. If a teacher already knows you, that means they already know your strengths and weaknesses, so they know what to look for, where you need to improve, and how to encourage your best work.
Also, don't forget that your supervisor's assessment is part of your overall EE score . If you're meeting with someone who pushes you to do better—and you actually take their advice—they'll have more impressive things to say about you than a supervisor who doesn't know you well and isn't heavily involved in your research process.
Be aware that the IB only allows advisors to make suggestions and give constructive criticism. Your teacher cannot actually help you write your EE. The IB recommends that the supervisor spends approximately two to three hours in total with the candidate discussing the EE.
#5: Make Sure Your Essay Has a Clear Structure and Flow
The IB likes structure. Your EE needs a clear introduction (which should be one to two double-spaced pages), research question/focus (i.e., what you're investigating), a body, and a conclusion (about one double-spaced page). An essay with unclear organization will be graded poorly.
The body of your EE should make up the bulk of the essay. It should be about eight to 18 pages long (again, depending on your topic). Your body can be split into multiple parts. For example, if you were doing a comparison, you might have one third of your body as Novel A Analysis, another third as Novel B Analysis, and the final third as your comparison of Novels A and B.
If you're conducting an experiment or analyzing data, such as in this EE , your EE body should have a clear structure that aligns with the scientific method ; you should state the research question, discuss your method, present the data, analyze the data, explain any uncertainties, and draw a conclusion and/or evaluate the success of the experiment.
#6: Start Writing Sooner Rather Than Later!
You will not be able to crank out a 4,000-word essay in just a week and get an A on it. You'll be reading many, many articles (and, depending on your topic, possibly books and plays as well!). As such, it's imperative that you start your research as soon as possible.
Each school has a slightly different deadline for the Extended Essay. Some schools want them as soon as November of your senior year; others will take them as late as February. Your school will tell you what your deadline is. If they haven't mentioned it by February of your junior year, ask your IB coordinator about it.
Some high schools will provide you with a timeline of when you need to come up with a topic, when you need to meet with your advisor, and when certain drafts are due. Not all schools do this. Ask your IB coordinator if you are unsure whether you are on a specific timeline.
Below is my recommended EE timeline. While it's earlier than most schools, it'll save you a ton of heartache (trust me, I remember how hard this process was!):
- January/February of Junior Year: Come up with your final research topic (or at least your top three options).
- February of Junior Year: Approach a teacher about being your EE advisor. If they decline, keep asking others until you find one. See my notes above on how to pick an EE advisor.
- April/May of Junior Year: Submit an outline of your EE and a bibliography of potential research sources (I recommend at least seven to 10) to your EE advisor. Meet with your EE advisor to discuss your outline.
- Summer Between Junior and Senior Year: Complete your first full draft over the summer between your junior and senior year. I know, I know—no one wants to work during the summer, but trust me—this will save you so much stress come fall when you are busy with college applications and other internal assessments for your IB classes. You will want to have this first full draft done because you will want to complete a couple of draft cycles as you likely won't be able to get everything you want to say into 4,000 articulate words on the first attempt. Try to get this first draft into the best possible shape so you don't have to work on too many revisions during the school year on top of your homework, college applications, and extracurriculars.
- August/September of Senior Year: Turn in your first draft of your EE to your advisor and receive feedback. Work on incorporating their feedback into your essay. If they have a lot of suggestions for improvement, ask if they will read one more draft before the final draft.
- September/October of Senior Year: Submit the second draft of your EE to your advisor (if necessary) and look at their feedback. Work on creating the best possible final draft.
- November-February of Senior Year: Schedule your viva voce. Submit two copies of your final draft to your school to be sent off to the IB. You likely will not get your grade until after you graduate.
Remember that in the middle of these milestones, you'll need to schedule two other reflection sessions with your advisor . (Your teachers will actually take notes on these sessions on a form like this one , which then gets submitted to the IB.)
I recommend doing them when you get feedback on your drafts, but these meetings will ultimately be up to your supervisor. Just don't forget to do them!

The early bird DOES get the worm!
How Is the IB Extended Essay Graded?
Extended Essays are graded by examiners appointed by the IB on a scale of 0 to 34 . You'll be graded on five criteria, each with its own set of points. You can learn more about how EE scoring works by reading the IB guide to extended essays .
- Criterion A: Focus and Method (6 points maximum)
- Criterion B: Knowledge and Understanding (6 points maximum)
- Criterion C: Critical Thinking (12 points maximum)
- Criterion D: Presentation (4 points maximum)
- Criterion E: Engagement (6 points maximum)
How well you do on each of these criteria will determine the final letter grade you get for your EE. You must earn at least a D to be eligible to receive your IB Diploma.
Although each criterion has a point value, the IB explicitly states that graders are not converting point totals into grades; instead, they're using qualitative grade descriptors to determine the final grade of your Extended Essay . Grade descriptors are on pages 102-103 of this document .
Here's a rough estimate of how these different point values translate to letter grades based on previous scoring methods for the EE. This is just an estimate —you should read and understand the grade descriptors so you know exactly what the scorers are looking for.
Here is the breakdown of EE scores (from the May 2021 bulletin):
How Does the Extended Essay Grade Affect Your IB Diploma?
The Extended Essay grade is combined with your TOK (Theory of Knowledge) grade to determine how many points you get toward your IB Diploma.
To learn about Theory of Knowledge or how many points you need to receive an IB Diploma, read our complete guide to the IB program and our guide to the IB Diploma requirements .
This diagram shows how the two scores are combined to determine how many points you receive for your IB diploma (3 being the most, 0 being the least). In order to get your IB Diploma, you have to earn 24 points across both categories (the TOK and EE). The highest score anyone can earn is 45 points.
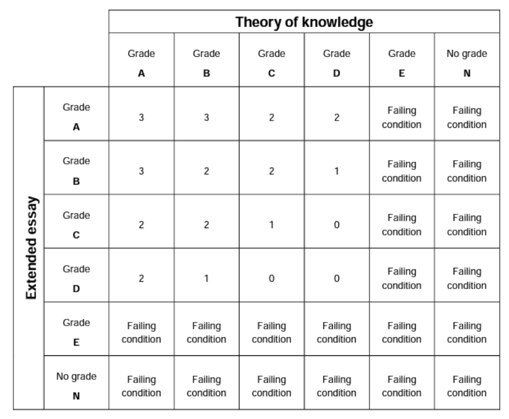
Let's say you get an A on your EE and a B on TOK. You will get 3 points toward your Diploma. As of 2014, a student who scores an E on either the extended essay or TOK essay will not be eligible to receive an IB Diploma .
Prior to the class of 2010, a Diploma candidate could receive a failing grade in either the Extended Essay or Theory of Knowledge and still be awarded a Diploma, but this is no longer true.
Figuring out how you're assessed can be a little tricky. Luckily, the IB breaks everything down here in this document . (The assessment information begins on page 219.)
40+ Sample Extended Essays for the IB Diploma Programme
In case you want a little more guidance on how to get an A on your EE, here are over 40 excellent (grade A) sample extended essays for your reading pleasure. Essays are grouped by IB subject.
- Business Management 1
- Chemistry 1
- Chemistry 2
- Chemistry 3
- Chemistry 4
- Chemistry 5
- Chemistry 6
- Chemistry 7
- Computer Science 1
- Economics 1
- Design Technology 1
- Design Technology 2
- Environmental Systems and Societies 1
- Geography 1
- Geography 2
- Geography 3
- Geography 4
- Geography 5
- Geography 6
- Literature and Performance 1
- Mathematics 1
- Mathematics 2
- Mathematics 3
- Mathematics 4
- Mathematics 5
- Philosophy 1
- Philosophy 2
- Philosophy 3
- Philosophy 4
- Philosophy 5
- Psychology 1
- Psychology 2
- Psychology 3
- Psychology 4
- Psychology 5
- Social and Cultural Anthropology 1
- Social and Cultural Anthropology 2
- Social and Cultural Anthropology 3
- Sports, Exercise and Health Science 1
- Sports, Exercise and Health Science 2
- Visual Arts 1
- Visual Arts 2
- Visual Arts 3
- Visual Arts 4
- Visual Arts 5
- World Religion 1
- World Religion 2
- World Religion 3

What's Next?
Trying to figure out what extracurriculars you should do? Learn more about participating in the Science Olympiad , starting a club , doing volunteer work , and joining Student Government .
Studying for the SAT? Check out our expert study guide to the SAT . Taking the SAT in a month or so? Learn how to cram effectively for this important test .
Not sure where you want to go to college? Read our guide to finding your target school . Also, determine your target SAT score or target ACT score .
Want to improve your SAT score by 160 points or your ACT score by 4 points? We've written a guide for each test about the top 5 strategies you must be using to have a shot at improving your score. Download it for free now:

As an SAT/ACT tutor, Dora has guided many students to test prep success. She loves watching students succeed and is committed to helping you get there. Dora received a full-tuition merit based scholarship to University of Southern California. She graduated magna cum laude and scored in the 99th percentile on the ACT. She is also passionate about acting, writing, and photography.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
Extended essay
The extended essay is an independent, self-directed piece of research, finishing with a 4,000-word paper.
One component of the International Baccalaureate® (IB) Diploma Programme (DP) core, the extended essay is mandatory for all students.
Read about the extended essay in greater detail.
You can also read about how the IB sets deadlines for the extended essay , find examples of extended essay titles from previous DP students and learn about the world studies extended essay .
Learn more about the extended essay in a DP workshop for teachers .
DP subject briefs
Find out about what each subject offers within the Diploma Programme (DP).
Our DP subject briefs—for both standard and higher level—contain information about core requirements, aims and assessment.
- Explore the DP subject briefs

We use cookies on this site. By continuing to use this website, you consent to our use of these cookies. Read more about cookies
Tips for success: How to write Section 2 of your IB History IA

March 27th, 2020 Last updated: April 11th, 2023
Having chosen the topic of your History IA, designed your question and researched your IA, the next step will be to write Section 2. This should be done before attempting Section 1 and, in this blog, Anna outlines what is expected.
Section 2: The Investigation (worth 15 marks out of 25)
What is expected in the investigation.
- It must answer your question.
- It must be structured.
- It must contain critical analysis that is focused clearly on the question being investigated.
- It must also include a conclusion that the student draws from their analysis.
- It must effectively use a range of sources to support the arguments.
- It must show a range of perspectives and these should be evaluated.
It is recommended you write 1300 word.
In other words, it is like an essay but you can use subheadings if you so wish.
Need help with your History IB? Meet our IB Tutors here
For a good History IA structure you simply need the following:
- Introduction
- Main body with paragraphs (with or without subheadings)
What should be included in my introduction?
- One paragraph only – approximately 200 words
- A brief context to introduce the question.
- Set the scene / generate reader interest by establishing why this question was important at the time, and remains relevant today.
- Highlight the scope of your question – what will it focus on and what dates you will be covering.
- Method – Outline how the essay will be approached, and the main conclusions that will be reached.
- State the different historical perspectives that exist in relation to the question.
- Do NOT carry out any analysis here.
Example Introduction
To what extent did World War II lead to women in the United States becoming permanent participants of the labor force?
Few historians would disagree that World War II brought about a dramatic increase in female participation in the American labor force during the early 1940s. Between 1940 and 1944, women’s participation in the workforce rose by 23.5% (Clark, Summers 8), a change affecting women of all ages (See Table 1 of the Appendix). As a whole, women workers grew by 5 million in the 1941-1944 period (Anderson 239), with one-sixth of the working women being employed by a war related industry (Goldin 753). The war was therefore responsible for the unquestionable incorporation of women into the American labor force. However, historians disagree on the extent to which these changes had long-term effects. While some refer to this war as a “watershed” event leading to the permanent incorporation of women into the labor force, others refute this statement by arguing that the war’s influence on women’s employment “appears to have been more modest” (Goldin 741).
What should be included in my main body?
For structure, there should be a number of paragraphs. These could be thematically or chronologically approached. Each focus section could have a subheading, if suitable.
- Approximately 3 to 4 main paragraphs
- Each paragraph should have a specific focus, point of view or theme.
- Within each paragraph, start with a clear topic sentence which is clearly focused on the question.
- Carefully select and properly reference evidence.
- Use quotes as necessary, try NOT to use quotes longer than 10 words, or paraphrase, but ensure you footnote or reference all evidence.
- Stress the value of the evidence you use, but also acknowledge its limitations, with reference to Origin, Purpose and Content as appropriate.
- Try to show more than one perspective.
An example paragraph
However, the late postwar period gave way to a reversal of this initially unfavorable effect, for women’s employment soared in the 1947-1950 years. In this period the percentage of working women between 25-64 years of age increased from by 2% (Clark, Summers 1982), and that of working married women rose from 20% to 23.8% (Goldin 742). Additionally, the number of employed female operatives in metals and machinery manufacturing increased 4 History teacher support material 7 Example 2 (Name) (Candidate Number) from 175,246 to 331,140 between 1940 and 1950. (Blackwelder 145). Also, twice as many women were employed in California in 1949 as had been employed in 1940 (Chafe 161). These examples of growth have led some to point out that the war did, indeed, have, a “long-term rather than temporary impact on women’s place in the labor force” (Blackwelder 147). The 5.25 million female increase in the labor force between 1940 and 1949 (Chafe 161) further strengthens the point that the war was, despite the initial postwar setback, a “milestone for women in America.” (Chafe 172). Conversely, it seems relevant that only 22% of the eventual 1950 women workers joined during the war years (Goldin 744) and that more than half of the women employed in 1950 had been employed before the United State’s entry in the war (Goldin 744). “Rosies” of 1944 were only 20 % of the eventual 1951 employment among married women (Goldin 750). These figures indicate that a majority of the jobs offered during the war period disappeared at its conclusion, and, consequently, that the women that participated in the labor force during the war years only constituted a small percentage of the late postwar employment. This suggests that the changes brought about by the war were more moderate than suggested by enthusiastic modern historians such as Blackwelder, who, perhaps in an effort to analyze an extensive time period, might have failed to examine short-term trends, consequently venturing to claim that “World War II had clearly accelerated the feminization of the U.S. labor force and increased employment among married women.” (Blackwelder 146).
- The first sentence clearly relates to the question.
- Evidence is well-selected – good use of statistics to support the argument.
- Perspectives have been included and evaluated.
- Critical thinking is present.
- Each piece of evidence has been cited appropriately.
What should be included in my conclusion?
- One paragraph only – approximately 150 words.
- Provides a direct answer to the question by synthesising (combining) the main points of the essay.
- DO NOT argue against your thesis in your introduction.
An example conclusion
To what extent did World War II lead to women in the United States becoming per manent participants of the labor force?
It, therefore, seems that World War II was indeed, responsible for an incorporation of females in the American labor force during the war years, an increase that is likely to have lead to a change in the perspective of male employers and public officials towards women employees, and might have played important role in the rise in women’s employment during the late postwar period. However, evidence regarding the percentage of “Rosies” that were to form part of the postwar labor force suggests that the conflict did not secure a permanent incorporation of war female workers into the American labor force. World War II can therefore be seen as responsible for a number of significant ideological changes regarding women’s employment but its direct influence in terms of persistence of women’s participation in the labor force appears to have been modest.
- Relates clearly to the question.
- It is consistent with the thesis stated in the introduction.
- It is consistent the evidence and arguments provided in the main body.
- No new evidence is provided.
The IA used is an exemplar from the IBO – to read the full IA please click here.
If you liked this article, subscribe to our newsletter
By subscribing to our newsletter you agree to receive email from us and agree to our Terms and Conditions*
Join the discussion! Cancel reply
How to get full marks on source questions in history a level: 3. using knowledge to assess the accuracy of a source.

In the third post in this series, we will look at how to show A Level examiners that you can assess the accuracy of sources. People in the past did not always give an impression consistent with the facts available to us. Good historians will compare the information presented by any source to what they already know of the period.
Author Owl Tutors Read 6 minutes
Tips for Success: Approaching your IB History Extended Essay Topic

In this blog, Anna outlines the initial steps to choosing an IB History Extended Essay topic and question as well as how to approach the planning process.
Author Anna Read 4 minutes
How to get full marks on source questions in History A Level: 2. Using the content of the source (A grade)

This is the second post in a series that shows you how to approach source questions in History A Level, and hopefully also how exciting analysing primary source material can be. In this blog, Andrew sets out how to raise the quality of your answer to A* level by showing understanding of the source in context, and focusing on the question.
Author Owl Tutors Read 5 minutes
How to get full marks on source questions in History A Level: 1. Using the content of the source (C grade)

Source questions are often the aspect of A-Level History that students find most difficult, but can also be one of the most exciting aspects of the course. Every source provides a window into the ideas, emotions, and thought processes of past human beings. Andrew covers the basics of writing about the information drawn from the source.

Tips for success: How to write Section 3 of your IB History IA

Having successfully written Sections 1 and 2 of your History IA, it is now time to reflect and write Section 3. In this blog, Anna will walk you through the necessary steps to help you gain full marks for this section.
Author Owl Tutors Read 3 minutes
Tips for success: How to research your IB History IA

Once you have chosen the topic and question of your History IA, it's time to get researching! In this blog, Anna sets out some top tips on how best to research and record notes. Research in itself is a vitally important skill assessed throughout the IB Diploma - getting this right can mean the difference between a History IA's success and failure.
Author Anna Read 3 minutes
7 Tips for Choosing a Successful IB History IA Topic and Question

Choosing the right History topic and question for YOU can make the difference between success and failure. Below are 7 steps to help you choose an appropriate topic and question.
You might be interested in
How to get a 9 in gcse history.
Author: Chloe
Tips for success: How to write Section 1 of your IB History IA
How to get full marks on source questions in history a-level: 4. using the provenance of the source to assess reliability.
+44 020 3457 8474 [email protected]
Owl Tutors Limited Company Number: 07679444 VAT Number 182078794 Unit 2A, The Plough Brewery 516 Wandsworth Road London SW8 3JX United Kingdom
2024 Copyright Owl Tutors | Terms & Conditions | UK | Privacy Policy

- History Extended Essay: Definition, Outline, Assessment Criteria
Welcome to the guide on History Extended Essays!
This guide is designed to provide you with an understanding of what a History Extended Essay is, outline the components that need to be included in your paper and provide tips on how to write a successful essay.
This guide will cover:
Definition of a History Extended Essay
Outline of a history extended essay, assessment criteria for history extended essays.
- Brainstorming Process
Writing Strategies
- Citing Sources
Advice on Referencing
Evidence analysis and synthesis, proofreading and finalizing.
By the end of this guide, you should be able to confidently write and submit a History Extended Essay that meets the criteria and will get you the grades you want.
You will learn how to develop great research questions, structure your essay, analyze evidence, and use the right referencing system. We’ll also provide guidance on how to proofread your work and finish it to a high standard.
We hope this guide helps you on your journey to success!

🎓✍️ Struggling with your IB Extended Essay? ✍️🎓 Let our team of expert IB Writers be your guiding light! With an extensive track record of excellence in IB education, we are well-versed in the requirements and expectations of the IB Extended Essay. 🌟 Our accomplished writers are all experienced professionals who will provide you with a personalized and original masterpiece.We do not use AI! We take pride in delivering unique, high-quality extended essays that will impress your professor. Unlock your academic potential with our IB Extended Essay Writing Service today! 💡📚🔝
A History Extended Essay is an essay form that requires a student to provide an in-depth analysis of a chosen topic or event. It typically requires research, evidence collection, and thoughtful reflection on the part of the student. The essay should be structured logically, with a clear beginning, middle, and end. The goal is to demonstrate a thorough understanding of the chosen topic or event and to provide original insights and argumentation.
The essay should contain a thesis statement that sets out the main argument, and the body should then provide evidence and discussion to support the thesis. The essay should have a conclusion that summarises the findings, arguments, and evidence presented. Additionally, it should contain appropriate citations to sources throughout and a bibliography section at the end.
History Extended Essay essays can be written from many different perspectives, including geographical, chronological, political, social, and economic. Good research questions should be open-ended and enable exploration and discovery of multiple viewpoints.
Constructing an effective outline for your History Extended Essay is essential to ensure that you create a clear and cohesive essay. The following advice will help you to create an outline that will enable you to craft a well-structured and successful essay.
Your essay should include three main sections: the introduction, main body, and conclusion. Each section has a particular purpose and contributes to the overall structure and argument of the essay.
Introduction
The introduction of your essay should serve two key purposes. First, you should provide a brief overview of the topic of your extended essay and its context. Second, you should introduce your research question and make it clear to the reader why this is an interesting area of study that is worthy of further investigation.
The main body of your essay should be dedicated to outlining and elaborating upon the evidence that you have gathered in support of your research question. This should include both primary sources such as documents, photographs, and artifacts, and secondary sources such as scholarly works and historical analyses. By carefully examining, analyzing, and interpreting this evidence, you can develop your own arguments and insights in order to answer your research question.
The conclusion of your essay should bring your main argument to a close and suggest future avenues for study. You should also link back to the introduction, summarizing the main points of the essay. This is an important part of the essay because it shows readers what the main point of the essay was and how it reaches a conclusion.
By using these tips, you can ensure that your History Extended Essay has a clear and concise structure that allows you to clearly express your argument. With careful planning and preparation, you can be certain that your essay will be well-written and successful. Good luck!
Understanding the criteria by which your History Extended Essay will be judged is essential to achieving the highest mark. The assessment criteria splits into 5 categories: knowledge and understanding; problem-solving ability; critical thinking; research skills; and writing and presentation. In this section, we will explain each of these criteria in detail.
Knowledge and Understanding
In assessing knowledge and understanding, markers will look to see how well you have absorbed information and facts related to your research question and topic. They will want to know to what extent you have engaged with content which goes beyond the scope of the research question. Further, they will be interested in how you have used that knowledge in constructing a compelling argument in your essay.
Problem-Solving Ability
This criterion focuses on two things: how well you have identified and defined the key problem in your essay and how effectively you have created a solution. Markers will be looking to assess your ability to think pragmatically and solve problems logically. You should pay particular attention to the evidence you present and the structure of your essay when trying to demonstrate your problem-solving skills.
Critical Thinking
To score highly for critical thinking, markers will want to see that you have considered both sides of the argument. Demonstrating critical engagement with the sources you use and providing evidence in support of your own views will be important here. Your essay should also show independent and creative thought, as well as an awareness of wider contexts, such as international or political implications.
Research Skills
To excel at this criterion, you must demonstrate a comprehensive knowledge of different source materials and an understanding of how to best utilize them. You should strive to come to conclusions independently and provide clear evidence in support of those conclusions. In addition, you must ensure that this evidence has been transcribed accurately.
Writing and Presentation
Finally, your essay should be presented impeccably and be free of spelling, grammar and punctuation errors. The essay should have been carefully proofread before handing it in. The content should be clearly structured and organized and the language should be concise and even-toned. Depending on the task, diagrams and illustrations might be necessary, as well as references and bibliography.
Brainstorming Process: How To Develop Brilliant Ideas
Brainstorming is an essential part of writing a successful History Extended Essay. It involves researching, identifying, and analyzing the facts, evidence, and arguments as well as coming up with interesting ideas and research questions.
The first step to brainstorming is to start by asking yourself questions, such as: What would be an interesting topic? What key arguments can I make? What evidence do I need to support those claims? Such questions will help guide your research.
Next, you should research your topic. Start by searching online, reading books, and watching videos or documentaries related to the subject. This will provide you with the necessary information to develop your research question or topic.
Once you have gathered sufficient information, it’s time to analyze it. Ask yourself questions such as: What are the main points? What evidence does each point have? What opposing views exist? By identifying and questioning the different arguments, you will be able to develop more robust and thorough ideas.
Finally, once you have carefully examined the available materials, you should create a list of potential research questions or topics. You should also think of ways to defend or challenge any of the points you have identified. Doing so will help you develop brilliant research questions, evidence and arguments for your essay.
Writing is an essential skill and being able to write effectively with structure, clarity and focus is an invaluable part of success in essay writing. Being able to convey arguments, ideas and facts in a succinct and clear manner is essential for an extended essay . Here are some tips to help you write clearly and effectively.
A well-structured essay is the key to an effective paper. You should start by creating an outline that shows what you plan to cover in each section. Your introduction should be succinct and give a brief overview of the main points of your argument. The body section should include evidence and analysis, using examples when necessary. Finally, your conclusion should draw everything together, summarize the points you have made and provide your reader with any conclusions you have reached.
It’s important to ensure the sentences you use are concise and easy to understand. Make sure to use straightforward language, avoid overly complicated phrasing and make sure each sentence expresses one clear idea. It’s also imperative to break long sentences up into shorter ones and use active voice as much as possible.
In order to write clearly, you must maintain a clear focus throughout your essay. Stick to the point and avoid drifting off topic. Make sure each paragraph has a purpose and don’t engage in digressions or include irrelevant information. You should also ensure that each paragraph connects logically to the one before it and the one after.
Using these strategies when writing your history extended essay can help make sure that your essay is clear, organized and informative. Being aware of these tips and taking the time to incorporate them into your writing process can help you create a successful essay.
Citing Sources – Accuracy and Integrity
When writing a History Extended Essay it is essential that you cite the sources you use in the correct way. Doing so not only strengthens your essay, but also prevents any accusations of plagiarism. Citing your sources accurately shows your reader that you understand the ideas you are writing about and that you have conducted your research responsibly.
By citing your sources you will allow other scholars to identify and verify the information you have gathered for your essay. Every time you refer to a source that is not your own words or ideas, you should acknowledge it by providing a proper citation. Citations are also important when quoting someone else’s ideas, using statistics or any other type of evidence or data.
Failure to accurately cite your sources can lead to accusations of plagiarism, which can have serious consequences. The most common form of plagiarism occurs when you fail to cite a source or incorrectly cite a source.
There are several different citation styles that you need to be aware of before beginning your essay. You should make sure to review each one and decide which will be best for your essay. This guide provides an overview of the different citation methods along with advice on how to use them effectively.
In short, citing your sources accurately and with integrity will ensure that your work is taken seriously and will help to prevent any accusations of plagiarism. It is essential that you familiarize yourself with the different citation styles, and practice citing your sources correctly throughout the writing process.
It is important to reference the sources you use when completing a History Extended Essay. This will demonstrate that you have done your research and allow your essay to be accepted as an academic piece of work. There are several different referencing systems available and it is important to understand how each one works and how to use them effectively.
One common system is the Harvard referencing system. This system requires you to cite the source in the body of the text, followed by a full reference in the bibliography. The ‘in text’ citation should include the author’s name, the year of publication and the page number (if applicable). The full reference should include all the relevant details such as the author’s name, year of publication, specific book title and publisher.
Another popular referencing system is the American Psychological Association (APA) system. This system also requires an ‘in text’ citation and a full reference. The ‘in text’ citation should include the author’s name and year of publication, as well as the page number. The full reference should include all the relevant details, including the author’s name, year of publication, specific book title, place of publication and publisher, as well as any other relevant information.
It is important to make sure that all of the references included in your extended essay are accurate and up-to-date. To make sure this is the case, you should use reliable sources and check the most recent editions of any books you consult. It is also important to check that you have correctly cited the sources in your extended essay, as failure to do so can lead to accusations of plagiarism.
By understanding and correctly using different referencing systems, you can ensure that your extended essay is properly researched and cited. This will help to demonstrate your academic integrity and ensure that your essay is accepted as the pieces of work that it is.
When it comes to writing a History Extended Essay, it’s important to understand the different methods of examining, interpreting, and making use of evidence. Evidence analysis and synthesis can help you to more effectively support your argument when writing an essay.
To begin any analysis and synthesis of evidence, you’ll need to identify the source of the evidence. Ask yourself “Where does this evidence come from?” Is it primary or secondary? What is the author’s perspective? Then, take into account the reliability and accuracy of the source. Also consider the relevancy to your particular topic or argument.
Once you have identified the source, you can start examining and interpreting the evidence. Begin by asking yourself what is being said, and what is the overall opinion of the author? How do they back up their opinion or point of view? Is there bias or any other potential conflict of interest present in the source?
Next, you’ll want to synthesize the evidence. Compile all sources that are related to your argument and look for similarities and differences. You can also compare and contrast different interpretations of the same evidence. This will help you to develop your own opinion on the topic and will enable you to better articulate your argument.
Finally, once you’ve analyzed and synthesized the evidence, make sure that you are able to explain how the evidence ties into your argument. Make sure to cite your sources properly so that your readers can verify where you got your information. Additionally, think about the implications of the evidence and how it might be applicable to other topics or arguments.
Evidence analysis and synthesis is an important part of writing a successful History Extended Essay. By understanding and utilizing these techniques, you will be able to better support your arguments and draw stronger conclusions from your evidence.
Writing A Strong Conclusion
Now that you have completed your history extended essay, it is time to write a strong conclusion to wrap up all of the points discussed. A conclusion should summarize all points made in the essay without introducing new ideas or evidence. Making sure to review and edit following the completion of your first draft is also an important part of the essay-writing process.
When summarizing the points of your essay, it is helpful to revisit the thesis statement and main argument of your paper. Make sure to include the key points and conclusions that you’ve reached in your research. Additionally, be sure to demonstrate how the argument you set out to make in the introduction ties together in the end.
Editing and revising are important steps in creating a great essay. Read over each sentence, making sure that your arguments make sense and flow logically. Check for any grammar and spelling mistakes, and pay special attention to the structure of your sentences. If you feel stuck or confused during this process, looking at model essays can be helpful.
Finally, make sure to follow the citation rules. Be sure your sources are correctly cited and the references are accurate. Citing your sources correctly shows that you have done your research and supports your argument.
Conclusion writing can be tricky, but with the right approach and some practice, you can create a strong conclusion for your History Extended Essay. By following these steps, you can ensure that your essay reaches its full potential and makes a lasting impression on its readers.
Appendix: Examples of Extended Essay Outlines and Evaluation Criteria
Included in the appendix section is an optional resource of sample examples that can help guide you in writing your extended essay. It will include a list of extended essay outlines, evaluation criteria and a recommended reading list. This resource can be beneficial to student’s when brainstorming topics, developing research questions or revising your paper before submission.
Extended Essay Outlines
An extended essay outline will help students define the structure of their paper and organize their argument. The outline will provide a framework for the student to follow and ensure that the points discussed clearly explain the topic question. The outline should also include evidence, analysis and synthesis.
- The introduction should explain the context of the essay and the research question.
- The main body of the essay should include the literature review, analysis of evidence and conclusion.
- The end of the essay should wrap up the argument and discuss the implications of the research.
Evaluation Criteria
When it comes to evaluating an extended essay, there are certain criteria that students should be aware of. The essay should be evaluated based on the research question, the quality of evidence presented, the relevance of the sources used and the way in which the student has synthesized and analyzed the evidence.
- The essay should answer the research question clearly and accurately.
- The source of evidence used must be reliable and up-to-date.
- The evidence should be used to support the argument and conclusions of the essay.
- The structure and language of the essay should be clear and concise.
- Analysis and synthesis of the evidence should be detailed and accurate.
Recommended Reading List and Other Resources
It is important to keep up to date with the latest publications and resources available in order to write an effective extended essay. Here is an example of possible resources that can be included in your reading list: academic journals, books, reports, websites, and interviews.
To ensure accuracy, accuracy and integrity of sources, it is important to cite each resource clearly in your paper. Recommended citation style vary depending on the course being studied, so it is best to check with your professor which citation style to use.
In conclusion, a comprehensive appendix section can be a great asset for writing a successful history extended essay. It can provide additional knowledge and resources for students to refer to in the organization of their paper and to evaluate the success of their writing.
Proofreading and finalizing your History Extended Essay before submission is a crucial step that can mean the difference between success and failure. It is important to take the time to proofread your essay to ensure it is of the highest possible quality.
Before you begin proofreading, read through the essay and assess it for any possible errors. Take the time to review for mistakes in terms of accuracy, spelling, grammar, and style, as well as any incomplete information or incorrect facts.
Once you have identified potential errors and mistakes, begin making corrections where necessary. Pay attention to errors in punctuation and formatting, as well as facts that may need to be revised. Also, check for consistency in style, structure, and formatting throughout the document.
It is also important to check that all sources are cited correctly, and that any quotations used are accurate and referenced properly. Then, review the essay one last time to make sure that all corrections have been made.
Finally, be sure to check the essay against the criteria outlined by the assignment and make any necessary adjustments. Once you have proofread the essay and made all necessary corrections, you should feel confident that your History Extended Essay is complete and ready for submission.
- Last Edit 11 May 2023

Nick Radlinsky
Nick Radlinsky is a devoted educator, marketing specialist, and management expert with more than 15 years of experience in the education sector. After obtaining his business degree in 2016, Nick embarked on a quest to achieve his PhD, driven by his commitment to enhancing education for students worldwide. His vast experience, starting in 2008, has established him as a reputable authority in the field.
Nick's article, featured in Routledge's " Entrepreneurship in Central and Eastern Europe: Development through Internationalization ," highlights his sharp insights and unwavering dedication to advancing the educational landscape. Inspired by his personal motto, "Make education better," Nick's mission is to streamline students' lives and foster efficient learning. His inventive ideas and leadership have contributed to the transformation of numerous educational experiences, distinguishing him as a true innovator in his field.
📚🔍 Explore a Wide Range of IB Extended Essay Topics! 🔍📚
- IB History Extended Essay Topics
- How Long is Extended Essay? Minimum and Maximum Word Count
- Psychology Extended Essay Topics
- Computer Science Extended Essay Topics
- IB EE vs IA. What are the Main Differences?
- Literature Extended Essay Topics
- Law Extended Essay Topics and Tips
- How to Write a Winning IB Business Management Extended Essay
- How Long Does It Take to Write an IB Extended Essay?
- How to Pick an Interesting Topic for Your Extended Essay
- How to choose a research question for your IB extended essay

IB Internal Assessment Rubric and Grading Criteria
The IB IA rubric is carefully structured to assess students’ understanding, skills and application of subject matter in a nuanced and comprehensive manner. Each subject rubric, whether for sciences such as Biology and Chemistry, humanities such as History and Psychology, or Mathematics, emphasizes a unique set of criteria tailored to assess specific competencies and skills.

Visual Arts IA Topics: The Best Topic Ideas
In the vast world of art, the possibilities for your IA topic are nearly limitless. Yet, this abundance of choice can sometimes feel overwhelming. Whether you’re drawn to traditional painting techniques, the avant-garde movements of the 20th century, or the intersection of digital media and art, your chosen topic should ignite a spark of curiosity and passion within you.

Theatre IA Topics: SL and HL Topic Ideas
Choosing the right topic for IA in the IB Theatre course is a crucial step that significantly influences your research process and overall learning experience. Whether in the Standard Level or Higher Level track, selecting your topic requires careful thought and consideration, aiming to balance personal interest with academic rigor. This guide offers a rich array of topic ideas and research questions to spark your creativity and intellectual curiosity in the vast world of theatre.

Music IA Topics for SL and HL Students
When selecting a topic for your IB Music Internal Assessment, both SL and HL students face a unique set of challenges and opportunities. As a seasoned IB educator with years of experience guiding students through this process, I’ve come to recognize the importance of choosing a topic that aligns with the IB criteria and resonates with your musical interests and strengths.

Film IA Topics: SL and HL Topic Ideas
Choosing a topic for your IB Film Internal Assessment (IA) can be exciting and daunting. Whether you’re enrolled in the Standard Level (SL) or Higher Level (HL), the key is to select an option that not only intrigues you but also meets the criteria of the IB Film course. In this article, we dig into a variety of creative and thought-provoking ideas for both SL and HL Film IA topics.

IB Dance IA Topics: SL and HL Ideas
When it comes to the IB Dance Internal Assessment (IA), students face the exciting challenge of exploring a topic that resonates with their interests and meets the academic rigor of the IB curriculum. I’ve seen how choosing the right topic can set the stage for an enriching learning experience. In this article, I’m thrilled to share some engaging topic ideas for both SL and HL students aimed at sparking creativity and intellectual curiosity.
© 2023 I Bstudenthelp.com. This website is owned and operated by Udeepi OU Harju maakond, Tallinn, Lasnamäe linnaosa, Sepapaja tn 6, 15551. Disclaimer : Services we provide are only to assist the buyer like a guideline to complete any kind of writing assignment. Privacy Policy Terms and Conditions Cookie Policy Revision Policy Refund Policy

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
History Extended Essay: Definition, Outline, Assessment Criteria
by Antony W
September 3, 2022

History Extended Essay is an assignment that gives you the opportunity to conduct in-depth research in an area of your interest – and of local, regional, and global significance.
Your research should clearly demonstrate a structured essay that addresses your research question in-depth.
The research question should encourage investigation that leads to in-depth analysis and critical commentary.
Rather than focusing on the “how” or “what” type of questions, focus on the “how successful” or “how significant” questions because they get you involved in comprehensive analysis of the issue you want to investigate.
Writing an extended essay in history isn’t hard, but it can be challenging if you struggle with history topic selection , extensive research, and writing.
That’s why we’re here to help.
Don’t let your IB History Extended Essay give you sleepless nights or wait until the last minute. Hire our team of IB experts to help you write and score an A in the subject.
- Get 100% unique history EE written on any topic and completed on time.
- Take advantage of our 25% off discount on your first order if you’re new to Help for Assessment
However, if you have the time to write your History EE and you need a complete guide to help you through the process, keep reading.
What is IB History Extended Essay?

What is IB History Extended Essay?
An IB History Extended Essay is a 4,000-word long essay that offers a more in-depth exploration of a topic of your interest with an emphasis on primary sources.
The Extended Essay in History requires thorough, independent research of the topic.
As you work on the essay, you’ll develop and sharpen your research, analytical, and communication skills.
By the time you complete this assignment, you’ll not only have a clear idea of the kind of research professors will expect you to do in university but also develop the capacity to analyze, evaluate, and synthesize knowledge.
How to Write a History Extended Essay Based on the Assessment Criteria
The following assessment criteria will help you to write a comprehensive, A-level Extended Essay in History:
1. Focus and Method (6 Points)
Your research issue must be historical, confined to a specific period, country, people, or events that took place 10 or more years ago.
Make the research question specific and straightforward to allow in-depth analysis and wide enough for the word limit.
To get an A, ensure your topic is accurate, properly focused, and clearly stated. Your research methodology must be exhaustive, effective, and credible.
2. Knowledge and Understanding (5-6 Points)
Demonstrate that you understand the research question you selected in the wider historical context.
Also, you should show a proper use of relevant historical terms and concepts and, while you’re at it, stick to the ten-year rule.
To get a 6, show in your History Extended Essay an in-depth knowledge and understanding of the selected topic. Then, use the methods learned in the coursework and textbooks to explore the topic effectively.
3. Critical Thinking (12 Points)
To get 12 points for critical thinking, your History Extended Essay should demonstrate a crucial engagement with the past .
Don’t quote what you read from other sources.
Instead, go as far as to explore and analyze the sources to come up with a compelling argument supported by analysis of the research material followed by consistent conclusions.
Examiners are interested in your analytical skills, not your ability to describe historical events. Once you’ve identified your position relative to your sources, draw convincing arguments for or against it.
Follow that by giving an analysis of the evidence, making sure you explain how reliable and/or accurate you think the evidence is.
Overall, your essay must have:
- A reasoned argument developed from your research
- A critical evaluation of your research
- A structure and coherent argument where minor inconsistencies don’t hinder the main argument or invalidate the conclusion
- A conclusion consistent with the material analyzed
4. Presentation (4 Points)
Presentation evaluates how well you’ve structured your essay in relation to the acceptable academic standards.
- Include section structure with a logical arrangement and the required formatting.
- Use charts, graphs, tables, and related figures ONLY where you feel they illustrate points more clearly, and make sure you name and explain them well.
- Acknowledge figures, calculations, text, and any other element used directly from a source.
Because your intention is score good marks for presentation, your History Extended Essay should have a clear layout that supports and simplifies the reading and evaluation of the work.
5. Engagement (6 Points)
Engagement evaluates how well you interact with the research process.
To score a six, you need to demonstrate a high level of engagement with clear insights so that your supervisor can clearly see your thoughts and decision-making process.
To do this, give clear evidence for your conclusions without making assumptions.
The best way to explain personal engagement is y being critical with your own methods and conclusion, even to the extent where you show where you think you should have done better.
If you can describe the challenges you face and the solutions you adopted, you’ll score a six.
Your reflections also count as far as engagement is concerned.
If anything, you need to make sure they communicate a high degree of intellectual and personal engagement with the research question developed during the initial stages.
Lastly, ensure you us your own voice to show authenticity, a creative approach, and an intellectual initiative.
History Extended Essay Format/Outline
What remains now is to write your essay.
But first, since organization counts towards the total points for presentation, we need to outline the essay in an acceptable extended essay format.
Here’s one example.

You should note that the title page, table of contents, bibliography, appendix, and the various figures do not count towards the word count.
However, figures with a lot of words will be added. Also, anything past 4000 words will not be read or graded.
We already have a full article on how to choose a history EE essay which you can check out here on our blog's article section. You will also find lots of sample topics to help you get started.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.
IBDP History
Website by Jo Thomas & Keely Rogers
Updated 3 April 2024
InThinking Subject Sites
Subscription websites for IB teachers & their classes
Find out more
- www.thinkib.net
- IBDP Biology
- IBDP Business Management
- IBDP Chemistry
- IBDP Economics
- IBDP English A Literature
- IBDP English A: Language & Literature
- IBDP English B
- IBDP Environmental Systems & Societies
- IBDP French B
- IBDP Geography
- IBDP German A: Language & Literature
- IBDP Maths: Analysis & Approaches
- IBDP Maths: Applications & Interpretation
- IBDP Physics
- IBDP Psychology
- IBDP Spanish A
- IBDP Spanish Ab Initio
- IBDP Spanish B
- IBDP Visual Arts
- IBMYP English Language & Literature
- IBMYP Resources
- IBMYP Spanish Language Acquisition
- IBCareer-related Programme
- IBSchool Leadership
Disclaimer : InThinking subject sites are neither endorsed by nor connected with the International Baccalaureate Organisation.
InThinking Subject Sites for IB Teachers and their Classes
Supporting ib educators.
- Comprehensive help & advice on teaching the IB diploma.
- Written by experts with vast subject knowledge.
- Innovative ideas on ATL & pedagogy.
- Detailed guidance on all aspects of assessment.
Developing great materials
- More than 14 million words across 24 sites.
- Masses of ready-to-go resources for the classroom.
- Dynamic links to current affairs & real world issues.
- Updates every week 52 weeks a year.
Integrating student access
- Give your students direct access to relevant site pages.
- Single student login for all of your school’s subscriptions.
- Create reading, writing, discussion, and quiz tasks.
- Monitor student progress & collate in online gradebook.
Meeting schools' needs
- Global reach with more than 200,000 users worldwide.
- Use our materials to create compelling unit plans.
- Save time & effort which you can reinvest elsewhere.
- Consistently good feedback from subscribers.
For information about pricing, click here
Download brochure
See what users are saying about our Subject Sites:
Find out more about our Student Access feature:
- 5. Extended Essay: Graded student examples
- The IB Core
- Extended Essay

This section includes some samples of EEs that have received A grades. A ll of these EEs have been marked according to the new criteria.
EE Sample 1: Causes of the Philippine Revolution of 1896-1898 (New criteria A grade)
Ee sample 2: the french revolution and the role of women 1789 to 1815 (new criteria a grade), ee sample 3: the causes of the holodomor famine, 1932 - 33 (new criteria a grade), ee sample 4: us intervention in lebanon 1958 (new criteria a grade), ee sample 5. causes of the algerian war (new criteria a grade), ee sample 6: the reforms of lázaro cárdenas’ presidency (new criteria a grade).
NEW - ADDED MAY 2022

Introduction
Step 1: learn the syllabus, step 2: study the past paper questions, step 3: read, write, and think, step 4: get more examples & ideas, step 5: know your time during the exam, historiography, what to aim for, how to write faster by hand, how much to write.
All historical arguments contained or referred to in this article are solely for exam preparation and do not necessarily reflect the view of the author.
This article includes:
- Steps for IB DP History paper 2 revision;
- Some extra tips (they can’t really fit into the steps);
- Study resources;
- My brief essay outlines,
which worked together to help me reach a 7 on paper 2 in my M21 history SL final exam.
This article works best for:
- Final exam prep;
- Short-term revision;
- Developing exam skills, not necessarily historical skills;
- SL students who need to know just enough for paper 2, not any more content for paper 3.
This article uses topic 10 authoritarian states (20th century) as an example.
In my blog article “ Short-Term Revision ”, I mentioned some of my experience preparing for the DP History final exam. I’ll try not to repeat too much of that here.
TL;DR is at the end of this article.
Learn the syllabus by heart.
For example, this is the IB syllabus for topic 10 authoritarian states:

Completing this revision step means that you can recall exactly what’s in the table. By that, I mean every single word in the table . Do make sure you read the description paragraph above, too, but you don’t need to learn it by heart.
Once you do this, every time when you come across a fact, a historical event, or a historiography, you can immediately identify the sub-topic you can use it for in an essay. Then, you can easily think about your arguments and try to structure your essays every time you revise factual information.
Look at the past paper questions to see what have already been asked, and when. The IB questions don’t tend to repeat a lot, especially not in successive exam sessions. This means you can guess the questions that are likely to come up on your exam paper, althugh officially, the IB discourages doing this.
Here are all the past paper questions summarized in one document, both organized by year and by syllabus theme:

You can download the document as an annotated PDF here , or access it here as a google doc without annotations.
This document doesn’t include the M21 questions, because I made it for my own revision before M21. The M21 TZ2 questions for topic 10 roughly stated:
Evaluate the impact of foreign policy on the maintenance of power in two authoritarian states. “Full control was not always achieved in authoritarian states.” Discuss with reference to two authoritarian states.
According to this thread on Reddit , treatment of opposition instead of foreign policy came up for TZ1.
What I found was that:
- Almost every sub-topic appeared fewer than twice in past papers.
- There’s usually a gap of around 2 exam sessions (e.g from M18 to N19) between the questions under the same sub-topic.
- The past paper questions (not counting the specimen papers here) never repeat exactly . They can be similar, but always with a slightly different emphasis.
- Usually, only 2 of the sub-topics (emergence, maintenance, and policy) appear in one exam session , except for once in N19 where question 2 was on both maintenance and policy.
- The appearance of sub-topics is quite balanced.
- It’s very rare that a question asks for only one authoritarian state— only happened twice . (Highlighted in yellow.)
- A few questions have appeared only once or never.
So I made guesses based on the findings and other information, and altered my revision plans:
I chose to ignore emergence and turned to focus on the other two sub-topics. My thinking process is outlined in a section of my blog article “Short-Term Revision”.
The things in pink are what I thought, when I was revising, that would be likely to come up. They were either questions that had never come up before under the current syllabus, or those that had only come up once. Most of them also fitted in the “2 exam session gap” time frame. Those were my priorities.
Apart from these, I was convinced that preparing for compare and contrast, or at least formulating arguments for two states , would be necessary.
Take concise, structured notes for every topic that you revise, especially those that are likely to come up based on what have been asked before. But only take notes if you know you can use them to support your arguments, or you’ll just waste time.
You can follow a textbook to save your time researching, which I found to be extremely helpful. I have talked about some history textbooks in this blog post: My Experience & Tips for IB Textbooks: History SL .
As you take notes, also write down thoughtful arguments . If you’re like me who wants to be safe, you can do that for every single possible essay question. Knowing the syllabus by heart helps a lot here, because that helps you formulate your own IB style questions quickly.
Try to come up with counter-arguments and then counter those counter-arguments to strengthen your original arguments. Add the “debates” into your essay, even if those are just your thoughts going back and forth.
I find it helpful to write out complete sentences when I work on my arguments. That helps me to clear up my own ideas and saves me time structuring my sentences during a tight essay exam. Then, I recommend that you condense the arguments so that you can remember them. I also prefer typing over writing on paper because I can write much faster by typing, and I can organize digital files better than physical ones.
As an example, I wrote a 3-line outline for every essay question I could think of. Each line (out of the 3 lines) summarizes a paragraph in my essay. Of course, this is after thinking about or writing out more detailed notes for my arguments and supporting evidence. This is a preview:

You can download the complete PDF document here . Unfortunately, I don’t have any detailed notes because I lost a lot of data on my laptop during a system update.
There’re a lot of my own short-hand notations in the document. So if you do use this to revise and find something confusing, don’t hesitate to ask me in the comments or via email (see the end of my “About” page). I’ll try my best to recall what I meant.
To emphasis, I repeat: all historical arguments contained or referred to in this article are solely for exam preparation and do not necessarily reflect my view.
This step can be done together with step 3. Sometimes you might run out of ideas or get confused about what kind of arguments the IB likes. Reading more essays can help. Especially, the good ones can give you some inspiration, as well as some excellent arguments to agree with or argue against in your own essay.
Some places to get example essays:
- Textbook appendices
- P2 Example 18 , scored 13/15
- P2 Example 19 , scored 13/15
- Your school teacher
- Your own paper 2 practices over the 2 years
- Your classmates' essays
I recommend that you get a physical copy of each example essay along with examiner’s comments (if any), so that you can read and annotate it carefully.
If you can’t find existing essays, write them yourself ! Write full essays, paragraphs, introduction, even just a short thesis, and kindly ask your teacher for feedback. Try out new writing approaches because you might find better ways to write. You don’t have to time yourself while writing these. At this point, getting feedback is the most important because it helps you improve and further develop your skills and arguments!
To get ideas for essays, you can also look at the indicative content in IB markschemes . The indicative content tends to be more detailed for papers testing the old syllabus (before first assessment 2017) but the new markschemes can also give you some hint.
Get used to the exam environment by practicing timed paper 2 exams. But it’s fine if you do it at the very end of your revision, because knowing what to write can help you write faster than doing anything else, including doing timed paper 2 exams.
However, it’s still important to plan your time prior to the exam and closely follow the plan. In this way, during the exam, you can stay calm so you don’t rush or forget about your arguments.
As an example, this is my plan, with all time and durations in minutes:
At the very beginning of my exam, I quickly calculated the exact time when I would need to finish each task. For example, if the reading time started at 8:33, I would calculate that I would need to finish my mental outline at 8:38, my written outline at 8:43, my intro at 8:48, etc. I wrote down the minute digits on a scratch paper so that during the exam, I could quickly check if my progress matched my plan.
It is possible to get to 12/15 with only a name-dropping of a historian and his/her argument. True personal story. I did that on my final exam.
Take a look at the example paper 2 essays in the Teacher Support Material , too, especially examples 18 and 19. (I’ve mentioned them above.) No historiography, no quoting of historians, but, bang—they both got 13/15 for the topic 10 question.
As long as there are decent original arguments in an essay, the lack of historians' views is fine , unless you’re aiming for 14 or 15 marks. This really alleviated a lot of stress for me.
You don’t need to have a 7 in every single component to get an overall 7 .
This is how I did my calculation before I took my M21 exams.
I used the IB M19 boundaries for SL TZ2, which was the most recent May exam-route session with available grade boundaries:
Using the modified marks and weightings in M21, I calculated that the number of marks needed to get a 7 for paper 2 was 12/15.
So I calculated that if I got:
- Paper 1: 17/24,
- Paper 2: 12/15,
then my total scaled score (out of 100) would be $\frac{20}{25} \times 25 + \frac{17}{24} \times 30 + \frac{12}{15} \times 45 \approx 77.3 %$, which is higher than 74, the boundary for getting an overall 7.
This is true for N20 and M18, too, and should be true for most exam sessions.
Let’s continue to use M19 as our example. The boundary for an overall 7 is slightly lower, so one can afford to lose one or more points. The following combination of marks can all give an overall 7.
Try calculating the overall result for different combinations and choose to work towards the one that seems the most realistic for you. Once you know what marks you need in each component, you have a more specific and a more accomplishable goal.
Notice that because paper 2 is weighted the more heavily (45%), getting a reasonably high mark on paper 2 is more important than on paper 1 or IA .
You don’t have to write prettily, or even clearly—as long as it’s legible in the context. This is my hand-writing at full speed:

Both my teacher and the examiner grading my final exam papers managed to recognize my writing.
Pick a pen in which the ink can flow smoothly and which you don’t need to press hard on the paper to write with.
If your pen has a cap, leave it off the end of the pen. It takes you more effort to move the pen when the cap is attached to the end, especially when you write a lot. I learned this from this YouTube video .
4 sides (on A4 size paper) should be enough. I even wrote only 3 sides several times and that was fine. Quality over quantity.
When we had timed, in-class summative assessments, I almost never managed to finish my essays.
And, although I usually wrote only a few sides, although I couldn’t really finish the essays, I could still get 10-12 marks out of 15. So, absolutely no worries if you can’t finish your essays or you only write 3 sides.
Feel free to ask me any questions in the comments or via email (see the end of my “About” page). I might share a few of my own history essay practices in the future but that’s not guaranteed 😅
- Learn by heart exactly what’s covered in the paper 2 topic you’re studying.
- Look for patterns in the past paper questions and prioritize the ones that you think are likely to come up.
- As you take notes for the possible essay questions, develop strong arguments that can stand counter-arguments.
- Read exemplar/example essays and indicative content in IB markschemes. Write your own essays/paragraphs and ask your teacher for feedback if you can’t find others' essays.
- Plan how much time you’ll use for each paragraph beforehand, so you don’t panic during an exam.
- You don’t need historiography to get to 12/15 (or you only need to name-drop one or two historians if that counts).
- You don’t need all 7s in all component to get an overall 7. Calculate how many marks you need to get the overall grade that you want to narrow down your goal.
- To write faster, use a smooth, light-weight pen. It’s alright to have messy (but legible) hand-writing.
- It’s fine if you write 3-4 sides on A4 size paper or you can’t finish your essays.
Extended Essay Writers

How to Write a History Extended Essay for IB Success?

Luke MacQuoid
Having been through the IB program’s roller coaster, I’ve picked up a thing or two about writing the ideal History extended essay. Now, let me share my experience to guide you on this academic task.
IB History Extended Essay: Assessment Criteria & Word Count
First and foremost, let’s talk about the word count. The maximum limit for an IB extended essay is 4,000 words . However, this does not include the abstract, footnotes, bibliography, or appendices. Sticking to this limit is crucial; any essay exceeding this will be penalized in the assessment. It taught me an invaluable lesson in brevity and precision, ensuring every word served a purpose.
Regarding assessment criteria, the IB History extended essay is evaluated based on specific benchmarks. These include:
- Focus/Method (6 points) . It assesses the clarity of your research question, the scope of your study, and the method deployed for the research.
- Knowledge and Understanding (6 points) . Here, the emphasis is on your grasp of the chosen topic and its context.
- Critical Thinking (12 points) . It’s a very hefty one. It evaluates the analysis, discussion, and evaluation of the essay.
- Presentation (4 points) . While content is king, presentation is equally crucial. It assesses the structure, layout, and formal elements of the essay.
- Engagement (6 points) . It reflects your engagement with the topic and how well you’ve reflected on the research process.
The IB History extended essay is not just an academic task; it’s a rite of passage for every IB student. It teaches discipline, research acumen, analytical prowess, and, most importantly, the art of presenting complex ideas in an accessible manner.
Importance of Picking the Right Extended Essay History Topics
Selecting a topic isn’t just about ticking off a checklist. It’s about laying the groundwork for an essay you’ll be invested in for months. The right topic is akin to a guiding star, keeping your research and writing focused. It’s not an overstatement to say that half the battle is won when choosing a topic that aligns well with the IB criteria and your interests.
Tips for Choosing Engaging Extended Essay Topics in History
While there isn’t a one-size-fits-all approach, some general pointers have stood the test of time. Remember that the topic should have sufficient resources available for research, yet it shouldn’t be so broad that it becomes overwhelming.
From what I’ve seen and experienced, topics rooted in a specific event, person, or period often yield the most compelling essays. For instance, instead of attempting to cover the entirety of World War II, you might focus on a particular campaign or a leader’s strategic decisions.
Furthermore, topics that challenge popular narratives or introduce fresh perspectives can be enriching. Not only do they offer a chance to showcase your analytical skills, but they also highlight your ability to think critically.
Lastly, always be open to feedback. Discuss your potential topics with teachers, peers, or mentors. An outsider’s perspective often clarifies or introduces angles you hadn’t considered. And if you want to find some actual History extended essay topics , follow this link to another article in our blog.
Structuring Your IB History Extended Essay
Now, onto the nitty-gritty – the structure. An organized essay is like a well-oiled machine. Each section plays a pivotal role. Start with a compelling introduction, follow it up with solid arguments, and conclude in a manner that leaves an impression. Here’s a guide on how to structure your IB History extended essay to maximize clarity and coherence.
1. Introduction: Setting the Stage
Your introduction should be clear and captivating. Begin with a brief overview of the topic to give readers a context. Follow this with your research question, setting the tone for the investigation. It’s also a good place to briefly hint at the significance or relevance of your topic in a broader historical context. Remember, the introduction is your first impression; make it count!
2. Research Question or Hypothesis
Clearly state the question you intend to answer or the hypothesis you aim to test. It provides direction and purpose to your essay.
3. Background or Historical Context
Before getting into the core arguments, provide readers with a brief background of the period, event, or phenomenon you’re examining. This foundation ensures that readers, regardless of their prior knowledge, understand the backdrop against which your research unfolds.

4. Body: The Heart of Your Essay
Each paragraph should present a distinct argument or point substantiated with evidence. Start each section with a clear topic sentence, followed by evidence and your analysis. Ensure that the evidence you present directly supports your arguments.
5. Conclusion: Tying It All Together
Reiterate the significance of your research question and concisely summarize your main arguments. Discuss the implications of your findings and hint at areas for future research. The conclusion should leave the reader with a sense of closure and completeness.
6. Bibliography or Works Cited
Always list all the sources you consulted. Adhere to a specific citation style (like MLA, APA, or Chicago) as guided by your instructor. This section is crucial for academic integrity and to acknowledge the works of scholars and researchers you’ve referenced.
7. Appendices
If you have additional data, charts, or images that supplement your essay but might disrupt its flow, include them in the appendices.
How to Write History Extended Essay: Research and Sources
At the heart of every compelling History extended essay lies a foundation of robust research. The right blend of primary and secondary sources can enrich your narrative, offering your arguments diverse perspectives and concrete evidence. However, not all sources are created equal. In my time grappling with historical essays, I learned that the credibility of your sources could make or break your work:
- Primary sources – like letters, diaries, treaties, artifacts, or contemporary records – offer firsthand accounts of the events. They’re the raw materials, providing a direct window into the past. While they are invaluable, it’s essential to approach them with a critical lens, considering the context in which they were produced and potential biases they might carry.
- Secondary sources , such as books, academic papers, and historians’ interpretations, provide a step back. They offer analyses, building upon primary sources and prior research. These are great for understanding the broader context and seeing where your research fits into the larger historical discourse.
However, a word of caution! In the digital age, while access to information has become more accessible, so has the proliferation of inaccurate or biased content. Constantly evaluate the reliability of your sources. Who’s the author? What’s their background? Is the publication reputable? Cross-referencing facts with multiple reliable sources is an excellent habit to cultivate.
Organizing Your Research Effectively
Research for an extended essay isn’t done in a day or two; it’s a prolonged process, and without a system, it’s easy to lose track or get overwhelmed. So, start with a research log. Whenever you find a potential source, jot down its details and key points or quotes you might want to reference. It saves time later and ensures you keep track of valuable information.

Need help with your IB extended essay?
From research and analysis to structuring and editing, our skilled mentors will be by your side, helping you craft an exceptional extended essay that not only meets the wordcount and stringent IB criteria but also reflects your passion for selected IB group .
Another helpful tactic is categorizing sources based on themes or arguments they’ll support in your essay. It can be done using physical index cards, digital tools like Evernote, or simple spreadsheets. Color coding can also be a visually effective method to differentiate between primary and secondary sources or historical themes.
Remember to refine and prune your sources constantly. Only some things you come across will make the final cut. As your essay evolves, specific sources might become redundant or less relevant. It’s okay to let them go.
Lastly, back up your research. There’s nothing worse than losing weeks of work to a technical glitch. Regularly save your work on cloud storage, external drives, or printed copies.
Writing IB History EE with Clarity and Precision
Historical writing is a dance between fact and narrative.
Here are some techniques that have stood me in good stead:
- Thesis Statement . Every History extended essay should have a clear thesis or central argument.
- Topic Sentences . Begin each paragraph with a clear topic sentence. It directs the paragraph and makes your essay more navigable for readers.
- Concrete Evidence . Always back up your claims with evidence from reliable sources. Quoting primary sources lends authenticity to your arguments.
- Different Sentence Structures . While clarity is critical, variety keeps the reader engaged. Mix short, impactful sentences with longer, more descriptive ones.
- Consistent Tense . In historical writing, it’s easy to jumble past and present tenses. Decide on a tense (usually past for historical events) and stick to it.
- Active Voice . While passive voice isn’t incorrect, active voice makes your writing more dynamic and direct.
- Transition Phrases . These are the bridges between your ideas, ensuring a smooth flow. Phrases like “furthermore,” “however,” or “in contrast” guide the reader through your arguments.
- Personal Insight . While working within the boundaries of historical facts, feel free to offer your interpretations or insights, especially if you can back them up with evidence.
And, of course, as I’ve come to value deeply over the years, proofread, proofread, and proofread some more. It isn’t just about catching typos but refining arguments, improving flow, and ensuring clarity.
History Extended Essay Examples: Learning from the Best
Examining stellar History extended essay examples is one of the best ways to understand what works. They offer a practical insight into structure, content, and presentation. Reading a well-crafted essay can sometimes spark ideas or approaches you hadn’t previously considered.
While samples are invaluable, remember to maintain your unique voice. The individual touch, rigorous research, and clarity will make your IB History EE stand out.
In wrapping up, always reflect upon your path in writing a History extended essay. From my experience, the process often offers as much learning as the content itself.
There’s a world of resources out there for the keen IB student. Be it books, online databases, or writing tools, always rely on reputable sources. Your essay reflects your hard work; ensure you give it the best. You can always contact us if you need help writing an extended essay .
Luke MacQuoid has extensive experience teaching English as a foreign language in Japan, having worked with students of all ages for over 12 years. Currently, he is teaching at the tertiary level. Luke holds a BA from the University of Sussex and an MA in TESOL from Lancaster University, both located in England. As well to his work as an IB Examiner and Master Tutor, Luke also enjoys sharing his experiences and insights with others through writing articles for various websites, including extendedessaywriters.com blog

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Now onto some broader essay tips. Don't merely list the facts of an event, say why they matter and what they add to your argument. Adding counter arguments and debunking them is also key to building a strong argument. In addition, making essay outlines is probably my second best tip. They helped me structure my thoughts in order to deliver ...
The key components of the IB History Paper 2 essay include: 1. Source Analysis: - You are required to analyze the provided sources critically. Consider the origin, purpose, context, and content of each source. Pay attention to biases, perspectives, and limitations of the sources. 2.
Here's a guide on how to write compelling Paper 3 essays: 1. Understanding the Assessment Criteria: 1. Command Terms: - Analyze, evaluate, and compare historical events. - Clearly understand the meaning of each command term and tailor your response accordingly. 2.
Conclusion. References and bibliography. Additionally, your research topic must fall into one of the six approved DP categories, or IB subject groups, which are as follows: Group 1: Studies in Language and Literature. Group 2: Language Acquisition. Group 3: Individuals and Societies. Group 4: Sciences.
Knowing how to answer your IB History essay prompt is essential to achieving your best. In this article, our IB HIstory expert and author, Joe Gauci, shares his top tips on how to write an effective compare and contrast essay for your IB History exams. You can also see his analysis of an example answer and learn how to improve your responses to ...
The extended essay is an independent, self-directed piece of research, finishing with a 4,000-word paper. One component of the International Baccalaureate® (IB) Diploma Programme (DP) core, the extended essay is mandatory for all students. Read about the extended essay in greater detail. You can also read about how the IB sets deadlines for ...
to teach the subject of their essays or suitably familiar enough with the subject area to provide adequate supervision and advisement over the course of the research and writing process. The essays are graded by examiners appointed by the Chief Examiner of each subject in the IB Office in Cardiff, Wales. Class of 2021 Extended Essay Due Dates
Tips for success: How to write Section 2 of your IB History IA. Having chosen the topic of your History IA, designed your question and researched your IA, the next step will be to write Section 2. This should be done before attempting Section 1 and, in this blog, Anna outlines what is expected.
4. Essay writing: Papers 2 and 3. 4. Essay writing: Papers 2 and 3. Papers Two and Three of your IB history examination are assessed through essay writing; thus a large part of your history course will be devoted to practising essay writing, both in non-timed and in timed conditions.
A History Extended Essay is an essay form that requires a student to provide an in-depth analysis of a chosen topic or event. It typically requires research, evidence collection, and thoughtful reflection on the part of the student. The essay should be structured logically, with a clear beginning, middle, and end.
The extended essay in history is a 4000-word essay written after thorough, independent research on a chosen topic. It is designed to prepare students for the undergraduate research they will be expected to do in university. Apart from this, it is also designed to develop and sharpen the student's research, analytical, and communication skills.
How do you incorporate different perspectives into your essays? Higher and Standard Level IB History candidates tackling Paper 2 and Higher Level candidates writing essays for Paper 3 need to be able to show an awareness and evaluation of 'different perspectives' in order to access the second highest mark band (10-12 out of 15) and provide an evaluation of different perspectives integrated ...
What IB History students need to know about their exam essays. Higher and Standard Level History candidates tackling Paper 2 and Higher Level candidates writing essays for Paper 3 need to be able to show an awareness and evaluation of 'different perspectives' in order to access the second highest mark band (10-12 out of 15) and provide an evaluation of different perspectives integrated into ...
The following assessment criteria will help you to write a comprehensive, A-level Extended Essay in History: 1. Focus and Method (6 Points) Your research issue must be historical, confined to a specific period, country, people, or events that took place 10 or more years ago.. Make the research question specific and straightforward to allow in-depth analysis and wide enough for the word limit.
This video focuses on how to write a top-notch thesis statement. Every Paper 2 and Paper 3 IB History essay needs one!
A walk through Paper 2 of the IB History Exam, including a discussion of the rubric and some tips for success.
Develop strong writing skills: IB History involves a great deal of writing, including essays and research papers. Students should work on developing strong writing skills, including the ability to construct clear and effective arguments. Understand the historical context: In order to fully understand the events and trends being studied in IB ...
CAS and History; Extended Essay; 1. Extended Essay: Choosing topics and questions; 2. Extended Essay: Research and referencing tips; 3. Extended Essay: Applying criteria A - D; 4. Extended Essay: Applying criterion E; 5. Extended Essay: Graded student examples; EE Sample 1: Causes of the Philippine Revolution of 1896-1898 (New criteria A grade)
The most important thing to remember when you write an IB History essay is to answer the question. This sounds simple, but the majority of people lose most of their marks by drifting off topic (if you don't address the question, it's impossible to score more than 40% on a history essay). The next thing to consider is the title.
Step 5: Know your time during the exam. Get used to the exam environment by practicing timed paper 2 exams. But it's fine if you do it at the very end of your revision, because knowing what to write can help you write faster than doing anything else, including doing timed paper 2 exams.
Writing IB History EE with Clarity and Precision. Historical writing is a dance between fact and narrative. Here are some techniques that have stood me in good stead: Thesis Statement. Every History extended essay should have a clear thesis or central argument. Topic Sentences. Begin each paragraph with a clear topic sentence.