- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
- Finding Research Materials

*Education: Finding Research Materials
- Google Scholar tips and instructions
- Newspaper Articles
- Identify Empirical Articles
- Video Tutorials
- EDUC 508 Library Session
- Statistics and Data
- Tests & Measurements
- Citation Managers
- APA Style This link opens in a new window
- Scan & Deliver and Interlibrary Loan
- Educational Leadership
- Global Executive Ed.D.
- Marriage & Family Therapy
- Organizational Change & Leadership
- Literacy Education
- Accreditation
- Journal Ranking Metrics
- Publishing Your Research
- Education and STEM Databases
3 things to remember!
When using article databases, remember there are always three stages in your workflow:
1) Discovery: Do (and redo!) your searching, using varying terms and combining using the Boolean operators "and, or, not" to get good results. Your first search is not your best search, but rather an opportunity to learn how to immediately do a better search.

3) Organize it: Keep the "meta-information" about all the resources you found for your records and to make your bibliographies. You will find yourself returning to resources so having a system in place will save you time and aggravation later. USC Libraries has a subscription to the citation manager, RefWorks , that will help you organize the information you're collecting. For more information on other citation managers, check out this page .
Content in this guide has been adapted with permission from Scott Collard's NYU Libraries Education guide .
Article databases
The article databases listed below allow you to search for articles through multiple journals simultaneously. Click on the name of the database below to start searching. If you're off-campus, you'll be asked to log-in using your USC ID and password. For a list of all USC Libraries subscription databases, go to A-Z Database List .
- ERIC (ProQuest) This link opens in a new window Key database for education research and education literature. Database includes journal articles, conference proceedings, government documents and dissertations on topics about and related to education. Maintained by the Dept of Education.
- PsycINFO This link opens in a new window Abstracting and indexing database with more than 3 million records devoted to peer-reviewed literature of journal articles, chapters, books, dissertations and reports in psychology, the behavioral sciences, and mental health.
- PAIS Index This link opens in a new window Good resource for policy issues related to education. International in scope, with coverage of journal resources as well as "gray literature" like government information.
- Scopus This link opens in a new window Large abstract and citation database of peer-reviewed literature in science, technology, medicine, social sciences, and arts and humanities. Includes bibliometrics tools to track, analyze and visualize research.
- Web of Science This link opens in a new window Multidisciplinary database that provides citations covering high-impact journals in the sciences, social sciences, and arts and humanities, as well as international conference proceedings.
Finding books
If the library does not have the book you need, you can request it through interlibrary loan or recommend we add it to the library's collection .
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Google Scholar tips and instructions >>
- Last Updated: Mar 12, 2024 4:56 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/education
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Working with sources
How to Find Sources | Scholarly Articles, Books, Etc.
Published on June 13, 2022 by Eoghan Ryan . Revised on May 31, 2023.
It’s important to know how to find relevant sources when writing a research paper , literature review , or systematic review .
The types of sources you need will depend on the stage you are at in the research process , but all sources that you use should be credible , up to date, and relevant to your research topic.
There are three main places to look for sources to use in your research:
Research databases
- Your institution’s library
- Other online resources
Table of contents
Library resources, other online sources, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about finding sources.
You can search for scholarly sources online using databases and search engines like Google Scholar . These provide a range of search functions that can help you to find the most relevant sources.
If you are searching for a specific article or book, include the title or the author’s name. Alternatively, if you’re just looking for sources related to your research problem , you can search using keywords. In this case, it’s important to have a clear understanding of the scope of your project and of the most relevant keywords.
Databases can be general (interdisciplinary) or subject-specific.
- You can use subject-specific databases to ensure that the results are relevant to your field.
- When using a general database or search engine, you can still filter results by selecting specific subjects or disciplines.
Example: JSTOR discipline search filter

Check the table below to find a database that’s relevant to your research.
Google Scholar
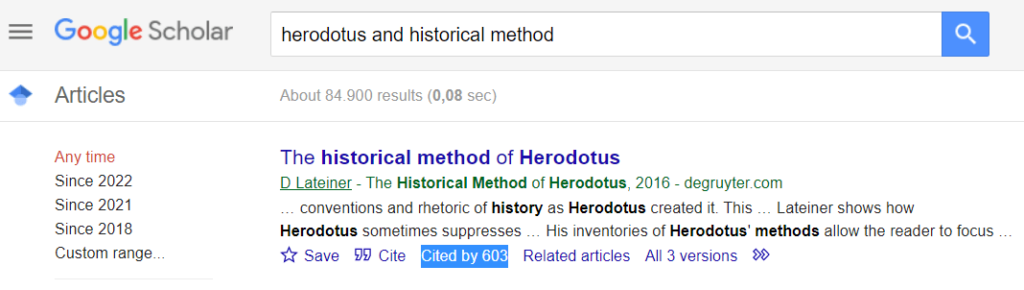
To get started, you might also try Google Scholar , an academic search engine that can help you find relevant books and articles. Its “Cited by” function lets you see the number of times a source has been cited. This can tell you something about a source’s credibility and importance to the field.
Example: Google Scholar “Cited by” function
Boolean operators
Boolean operators can also help to narrow or expand your search.
Boolean operators are words and symbols like AND , OR , and NOT that you can use to include or exclude keywords to refine your results. For example, a search for “Nietzsche NOT nihilism” will provide results that include the word “Nietzsche” but exclude results that contain the word “nihilism.”
Many databases and search engines have an advanced search function that allows you to refine results in a similar way without typing the Boolean operators manually.
Example: Project Muse advanced search

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
You can find helpful print sources in your institution’s library. These include:
- Journal articles
- Encyclopedias
- Newspapers and magazines
Make sure that the sources you consult are appropriate to your research.
You can find these sources using your institution’s library database. This will allow you to explore the library’s catalog and to search relevant keywords. You can refine your results using Boolean operators .
Once you have found a relevant print source in the library:
- Consider what books are beside it. This can be a great way to find related sources, especially when you’ve found a secondary or tertiary source instead of a primary source .
- Consult the index and bibliography to find the bibliographic information of other relevant sources.
You can consult popular online sources to learn more about your topic. These include:
- Crowdsourced encyclopedias like Wikipedia
You can find these sources using search engines. To refine your search, use Boolean operators in combination with relevant keywords.
However, exercise caution when using online sources. Consider what kinds of sources are appropriate for your research and make sure the sites are credible .
Look for sites with trusted domain extensions:
- URLs that end with .edu are educational resources.
- URLs that end with .gov are government-related resources.
- DOIs often indicate that an article is published in a peer-reviewed , scientific article.
Other sites can still be used, but you should evaluate them carefully and consider alternatives.
If you want to know more about ChatGPT, AI tools , citation , and plagiarism , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- ChatGPT vs human editor
- ChatGPT citations
- Is ChatGPT trustworthy?
- Using ChatGPT for your studies
- What is ChatGPT?
- Chicago style
- Paraphrasing
Plagiarism
- Types of plagiarism
- Self-plagiarism
- Avoiding plagiarism
- Academic integrity
- Consequences of plagiarism
- Common knowledge
You can find sources online using databases and search engines like Google Scholar . Use Boolean operators or advanced search functions to narrow or expand your search.
For print sources, you can use your institution’s library database. This will allow you to explore the library’s catalog and to search relevant keywords.
It is important to find credible sources and use those that you can be sure are sufficiently scholarly .
- Consult your institute’s library to find out what books, journals, research databases, and other types of sources they provide access to.
- Look for books published by respected academic publishing houses and university presses, as these are typically considered trustworthy sources.
- Look for journals that use a peer review process. This means that experts in the field assess the quality and credibility of an article before it is published.
When searching for sources in databases, think of specific keywords that are relevant to your topic , and consider variations on them or synonyms that might be relevant.
Once you have a clear idea of your research parameters and key terms, choose a database that is relevant to your research (e.g., Medline, JSTOR, Project MUSE).
Find out if the database has a “subject search” option. This can help to refine your search. Use Boolean operators to combine your keywords, exclude specific search terms, and search exact phrases to find the most relevant sources.
There are many types of sources commonly used in research. These include:
You’ll likely use a variety of these sources throughout the research process , and the kinds of sources you use will depend on your research topic and goals.
Scholarly sources are written by experts in their field and are typically subjected to peer review . They are intended for a scholarly audience, include a full bibliography, and use scholarly or technical language. For these reasons, they are typically considered credible sources .
Popular sources like magazines and news articles are typically written by journalists. These types of sources usually don’t include a bibliography and are written for a popular, rather than academic, audience. They are not always reliable and may be written from a biased or uninformed perspective, but they can still be cited in some contexts.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Ryan, E. (2023, May 31). How to Find Sources | Scholarly Articles, Books, Etc.. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/working-with-sources/finding-sources/
Is this article helpful?

Eoghan Ryan
Other students also liked, types of sources explained | examples & tips, primary vs. secondary sources | difference & examples, boolean operators | quick guide, examples & tips, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Search Site
Search catalog, finding research materials: the basics: article searching.
- Book Searching
- Article Searching
- More Guides
Finding Articles
The library subscribes to more than 200 specialized databases that are used to find articles and other sources for academic research. The following are basic steps for finding newspaper, magazine, scholarly journal, and other types of articles in these databases. For more in-depth assistance with this process, please Ask a Librarian .
- Choose a database. See our Subject Guides to find databases most suitable for research in your subject area(s). If you aren't sure where to begin, you might start with a general academic database such as EBSCO Academic Search Premier .
- Search for relevant articles. When you search a database, it is generally most effective to search using only the key concepts related to your topic, rather than entire sentences or lengthy phrases. For example, "psychology and domestic violence and family" is probably a better search than "psychological impact of domestic violence on families."
- Refine your search. As you search, keep your eyes open for other terms that might be useful for additional searches. Scan article abstracts (summaries) and subject classification terms that appear to help focus your search. Experiment with similar and related words in different combinations to see if you can obtain better results.

Journal Finder
Journal Finder can be used to determine whether the library subscribes to an electronic or print version of a particular journal, magazine, newspaper, or other periodical publication. Simply type in the name of the publication you are looking for to search for its availability at UofL. Journal Finder is especially useful for checking on the availability of a known article citation and/or looking for the full text of an article when the FindIt at UofL button does not appear in a database.
For assistance with finding articles or any other aspect of the research process, please Ask a Librarian .
- " Ask a Librarian
- Subject Guides
- " Journal Finder
- EBSCO Academic Search Complete
- << Previous: Book Searching
- Next: More Guides >>
- Last Updated: Aug 31, 2023 10:43 AM
- Librarian Login

Choosing & Using Sources: A Guide to Academic Research
(48 reviews)
Cheryl Lowry, Ohio State University
Copyright Year: 2016
Publisher: Ohio State University Libraries
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Elbert Davis, Assistant Professor, Marshall University on 10/24/21
The author does an incredible job in explaining the research process, from choosing a research question to how to search for sources (and citing those sources), and more. There are relevant self-check quizzes throughout the book to check for... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
The author does an incredible job in explaining the research process, from choosing a research question to how to search for sources (and citing those sources), and more. There are relevant self-check quizzes throughout the book to check for understanding, along with other supplemental resources. As the book was published through The Ohio State University, some of the sources are only available to OSU students, but the author makes it clear when this is the case.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
The author did an excellent job with the accuracy of the book, Two specific examples that stood out: taking care to mention that Wikipedia is a great as a starting point, but not as an endpoint for research. Lowry also clearly explained that educational use did not automatically mean fair use, which seems to be an issue with students and faculty alike.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
The book should remain relevant in years to come, as academic research seems to follow the same basic pattern. The only issue would be if The Ohio State University changes the links used in the book, although I expect these to be easy to update. The book would still be able to be used without the supplemental links though.
Clarity rating: 5
The book seems to be targeting an introductory audience. Lowry does a great job of breaking down the jargon of academic research into plain English for the beginning researcher.
Consistency rating: 5
I thought the author used approprate terminology for a student learning about academic research.
Modularity rating: 5
The book is designed into specific chapters for the different aspects of choosing a source. While there are specific sections devoted to The Ohio State University library, I would not expect to have any trouble assigning the other chapters in my courses.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
The author started at the beginning, with how to design a research question before going into choosing a source, which gave good background knowledge.
Interface rating: 5
The contents of the book were clean and crisp. No distortions were noted. Navigation from the table of contents was easy.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
No grammatical errors were noted.
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
Nothing offensive was in the book.
I have a difficult time in getting beginning graduate student to understand the different types of sources and fair use. I think using most chapters of this book would help a great deal in that comprehension.
Reviewed by Kelly LeFave, Instructor, Portland Community College on 6/15/21
This student friendly overview of academic research, including a strong focus on information literacy, covers many of the salient points that college level writing and writing for research classes curricula contain, making it a strong choice as a... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
This student friendly overview of academic research, including a strong focus on information literacy, covers many of the salient points that college level writing and writing for research classes curricula contain, making it a strong choice as a comprehensive and useful overview. Chapters include enough depth of coverage to make the leap from information to practice for students; self-directed activities are provided to check knowledge, work through concept applications, and offer more specifics. The book provides an easy-to-navigate Table of Contents, but an Index and Glossary do not seem to be available.
Content Accuracy rating: 4
Some errors appear that a thorough proofread would catch. Some resources may need to be updated since information practices and modes change so quickly; some references and links direct students to OSU information that would not apply to all readers.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 4
The book’s topic – academic research – necessarily demands constant updating given our fast-changing digital landscape and the shifting paradigms we are witnessing for locating and evaluating information in our times. Resources can become obsolete fairly quickly in this environment. The book’s content is largely up-to-date, though a thorough review of linked resources, perhaps annually, would be beneficial. For instance, a video on RSS mentioned a Google feature that looks to be no longer available, though finding alternatives proves simple when searched online. The book’s organization makes updating or replacing linked resources easy, so keeping the content relevant would be straightforward with regular review.
Content is presented in a style engaging for students, using the “you” pronoun address to walk readers through a thinking process that applies and links ideas to practice; this effective approach is used for many of the book’s concepts. The writing strikes a good stylistic balance between engaging the student reader and informing/challenging that same reader by modeling research brainstorming or methods. The style seems appropriate for college level readers and college level curricula. The topic of academic research does include some technical terms at times, but the book’s approach is to define and explain such terms a part of its content.
Stylistically and organizationally, the content is consistent and easy-to-follow. A user begins to anticipate knowledge check activities or “try it out” activities at particular points in each section. The knowledge check quizzes, which are simplified multiple choice questions, seem at odds with the highly contextualized concept explanations in much of the book’s prose; perhaps a different approach to knowledge check quizzing, which as an element can be helpful, would work better.
Modularity rating: 4
Headings and subheadings follow a logical organization and are easy to navigate in the book. Some sections do refer to—and link to—other book sections, but most would work as stand-alone modules. An instructor or course designer could pick and choose sections and adapt them for their own purposes. As a whole, the book remains self-referential to the context of a specific university, which limits the easy adaptation of the book, and perhaps even sections, for faculty and course designers at other educational institutions.
The book’s organization is easy to navigate and coheres with the overall focus on presenting academic research and information literacy in a way that invites students toward a practical and fuller understanding. Topic order makes sense and is organized via headings and subheadings well.
Overall, no significant navigation issues or interface distractions.
A few errors that look like typos remain in the book. Otherwise, grammatical errors are not an issue for readability.
Cultural Relevance rating: 4
A more nuanced and inclusive awareness of cultural relevance and diversity is worth considering for the book. The choice of some example topics, such as school shootings, might be distracting or traumatic for some student populations, while adding more examples that showcase interests or topics related to non-dominant cultural ideas would widen the sense of inclusivity throughout the book. Choices might be contingent on the demographics of the Ohio State University population, but more awareness of this aspect of the book might also make it more appealing as a resource for others to adapt
Reviewed by Nell McCabe, Associate Professor, Berkshire Community College on 6/15/21
This text is very-student friendly and covers all aspects of writing a student research paper, including steps that students frequently overlook such as the value of preliminary research and the different ways to incorporate different kinds of... read more
This text is very-student friendly and covers all aspects of writing a student research paper, including steps that students frequently overlook such as the value of preliminary research and the different ways to incorporate different kinds of information in a paper.
This text provides a well-balanced, research-driven approach to guiding students through the process of writing an academic research paper. Spelling mistakes, flaw grammar and usage, and factual errors are few and far between (as in I didn't find any during the course of this review).
Kinds of sources and the means of evaluating them are broad enough to be long-lasting, but the examples and other supporting details are timely and relevant.
This text uses student-friendly language and avoids jargon and other symptoms of academia run amok, while still maintaining high standards and expectations for students. Connections between the different stages of conducting research and developing an argument are well laid out and clear.
Terms associated with locating, evaluating, and incorporating a range of different kinds of sources are clear and consistent throughout the text.
The chapters do stand alone and I could image someone using bits and pieces or leaving out bits and pieces, but since the text is primarily focused on supporting the needs of a college research throughout the research process, it is hard to image much need for separating it into discrete modules. You could certainly rearrange the order of the chapters too if that worked better for your approach to teaching student research.
The flow of one chapter into the next is well-integrated and smooth. The order of the chapters
I had no issues with the interface; everything worked as expected.
Cultural Relevance rating: 3
The book does not go out of its way to make obviously inclusive examples. Increasing the cultural perspectives represented in the examples would enhance the overall value of this text.
Reviewed by Darci Adolf, Director of Library & Media Services, Oregon Coast Community College on 6/11/21
I found "Choosing and Using Sources" to be quite comprehensive and included the major areas that I cover in my LIB 101 Research skills class. In my class I like to cover each area of Eisenberg's Big6 Research model: Task definition, information... read more
I found "Choosing and Using Sources" to be quite comprehensive and included the major areas that I cover in my LIB 101 Research skills class. In my class I like to cover each area of Eisenberg's Big6 Research model: Task definition, information seeking strategies, location and access, use of information, synthesis, and evaluation. I was pleased to find the subject of synthesis covered under the writing chapter-- many research textbooks leave this out. I did not find anything that talked about Evaluation of the process and product. Also, I would've liked to have seen social justice and equity issues in information publishing and access addressed as a chapter or portion of a chapter. The textbook has a great Table of Contents, but no index.
This textbook seems to contain accurate and error-free content. I spot-checked most of the chapters and didn't find anything I didn't believe to be true, and links weren't broken. Because this book is mostly factual in nature, there aren't areas where an author's opinion was used over facts, and opinions seem to be be appropriate and unbiased. For example, the author remarks on the use of blogs in research: "Blogs – Frequently updated websites that do not necessarily require extensive technical skills and can be published by virtually anyone for no cost to themselves other than the time they devote to content creation." This is a wide-held belief among librarians.
The content appeared to be up-to-date throughout the book. The area that might change the quickest is the types of sources, Chapter 2 in the book. They did a good job including an overview of all of the major source types and should stay relevant for a good period of time. Because they've listed these source types in a single chapter, updates to the text should be fairly straight forward and easy to do without disturbing much of the rest of the book.
Clarity rating: 4
The text was clear to me, a seasoned librarian. But I think there were terms used throughout the textbook that might not be familiar to a student first starting out in library research. So I would add some clarification around some of the language if I were using this textbook for a lower-level class. For example: There are several types of specialized databases listed including: Bibliographic, Full-text, Multimedia, etc. Many first year students wouldn't know those terms, or others such as "circulation, World-cat, discharge, InterLibrary Loan" and so forth.
The text was consistent throughout in terms of terminology and the overall frame. As I mentioned previously, some of the terms might need to be defined for the first-year student, either in-text or in a separate glossary. The framework is well-done, with clear chapters and sections--it was definitely written by those who teach research at the college level.
The textbook has 13 chapters that are again sub-divided into six or more sub-topics. This makes it very easy for an instructor to pick and choose which topics to cover. The thirteen broader subjects makes it easy to use the entire textbook for a term-- or just choose the pieces you want to use. For example, I would use the "Ethical Use and Citing Sources" chapter if I were doing a one-shot in a classroom, but might choose to use most of the chapters for an online class.
The structure was easy to follow. If I were setting it up myself, I'd probably combine the chapters on Ethical Use of Sources (Ethical Use and Citing Sources, Why Cite Sources, and Challenges in Citing Sources) with the chapter on "How to Cite Sources," but it's easier to have them separate and combine them for a class than to have a big block of text that would make it difficult to work through.
The textbook online version was done in Wordpress, and was easy to view and navigate. There were several other choices for students, including a PDF that could be viewed off line. There were charts, graphs, and links throughout that added to the content, but not so much as to be distracting. Any visuals were simple and enough white space was left as to not overwhelm, with colors that were contrasting visually.
I spot-checked throughout the text in each chapter and did not find any grammatical errors.
The textbook seemed to be inclusive of all races, ethnicities, and backgrounds.
Ohio State University has included a lot of links to their own pages, handouts, and resources that would need to be changed or omitted by a new user. For example, they have a handout from the OSU Writing Center, and they link to the OSU World Cat platform. These would need to be changed by the adopter.
Reviewed by Kaia Henrickson, Assistant Professor of Library & Information Science, Information Literacy Librarian, University of Alaska, Southeast on 11/4/20, updated 12/16/20
This text does a good job highlighting the steps in the research process, from formulating a strong research question, to finding and evaluating sources, to incorporating ideas from research into writing, and finally, to citing and using sources... read more
This text does a good job highlighting the steps in the research process, from formulating a strong research question, to finding and evaluating sources, to incorporating ideas from research into writing, and finally, to citing and using sources properly. Each chapter can stand on its own as useful content for a research-based course, or the entire text could be used to walk students through the entire research and writing process. Based on tutorials created for Ohio State University Libraries, some sections, like Chapter 5 on search tools as well as some of the activities, are fairly specific to OSU. Still, much of the text and many of the activities are applicable to all student researchers. This would be a great base text for someone who wanted to remix and add in information from their own university library and student service supports to replace the OSU-focused sections.
The material is accurate overall.
Text content, as well as videos and activities, are fairly current. Sections are small, so making updates should be fairly easy.
While the text is generally clear, there are sections that are a bit cumbersome or wordy. The Evaluating Sources section, especially, seems overly complicated.
References and links to other helpful sections within the text are appropriate and useful. Key concepts and ideas are repeated and built upon as the text progresses.
Each chapter is divided into manageable sections, and there are few sections which require a lot of scrolling. Those that are longer are broken up by subheadings. Embedded video content, visuals, and boxes are used to break up the text for easier reading and more visual appeal.
The text clearly progresses through the steps in the research and writing process from start to finish, but it can also be accessed by section if a particular subtopic is all that is needed. Each chapter stands on its own, as well as being integrated into the whole.
Interface rating: 3
The web version of the text has no paragraph indents or lines of space between paragraphs, which makes it a bit difficult to read, especially when there are longer blocks of text. There are many videos included that only have automatically-created closed captions (and a few with no closed captions available at all). A few of the graphics are blurry, but most visual and audiovisual content is clear and easy to read. With some of the linked activities, it is unclear what to do when you have selected an incorrect answer, and there is not much feedback for students who answer questions incorrectly.
Grammatical Errors rating: 4
There are a few typos and other minor issues here and there in the text. Some of the linked activities have more significant errors.
The text is not culturally insensitive, but it also doesn't present much in the way of diversity in examples or ideas. In addition, there is a noticeable amount content that is focused on Ohio State University resources and students, and this may not be relevant for readers from other universities.
Reviewed by Marybeth Beller, Associate Professor, Marshall University on 3/13/20
The book provides a thorough review of the research process; that said, a professor will have to add discipline-specific information and requirements, such as expected citation practices and research methods. read more
The book provides a thorough review of the research process; that said, a professor will have to add discipline-specific information and requirements, such as expected citation practices and research methods.
I found no errors in the text.
I will use this book for my undergraduate research course as it gives a very good introduction to research, from narrowing the topic to turning questions into hypotheses.
The book is very clear and provides graphs, links and videos for the reader to have additional information as needed.
Each chapter is organized similarly to the others and is written in the same easy-to-follow, technical-free language. It removes any inhibitions a reader might have.
Each chapter section has its own heading and link. The entire book could be assigned or sections of the book could be just as easily assigned. A drop-down table of contents menu allows the reader to move freely between topics.
This guide is beautifully organized for the beginning researcher but can easily be followed through the table of contents for students needed refreshers on particular elements of research.
I found no interface issues at all in navigating the book.
There were no grammatical errors in the text.
I believe the book would be welcomed by a diverse group of people. There is no insensitive language or use of poor examples in the book.
I really enjoyed the organization of the book and that the author takes the time to include links to additional information as well as videos for students who want to spend more time with a particular concept.
Reviewed by Racheal Rothrock, Assistant Professor, Miami University on 2/28/20
The text is comprehensive in its covering of topics related to choosing and using sources, though it does not go into great depth for each topic. Rather this text provides a broad overview around the topic of sources. This text seems to be written... read more
The text is comprehensive in its covering of topics related to choosing and using sources, though it does not go into great depth for each topic. Rather this text provides a broad overview around the topic of sources. This text seems to be written for an upper-level, undergraduate student audience. No glossary is provided.
This information is presented in an unbiased way that informs on the topic rather than presenting a strong bias or slant toward a particular type of source (though, there is cultural bias—see review comments in “cultural” section). The text does provide details on what approaches might be more helpful in certain situations. This provides a balance of usefulness for students trying to determine which sources to use, while also not assigning value to some sources over others or create a hierarchy.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 3
The text demonstrates a current understanding around the topic of sources, taking into account the shift away from paper and toward digital sources. While overall this text should be useful for several years, there are some areas that may require updating (e.g. links, OSU policies or statements, specifics about various citation styles, software options available, copyright laws, etc.). Throughout the text, the authors do depend on examples that are specific to OSU (e.g. a section on “WorldCat@OSU”), and this might provide less useful for non-OSU students.
The text is written with simple language and explanations are given for more technical terminology (e.g. peer-reviewed, quantitative, qualitative, etc.).
Little specialized terminology is used throughout the text, however, the language and terminology used is consistent throughout. The format, structure, and approach the authors use, is also consistent throughout the text and forms a cohesive narrative.
The text is broken up by main topics and then within each topic, subtopics are provided to support the main topic. The length of each subtopic is fairly brief and examples are provided throughout with graphical separation for clarity. While the topics and subtopics support each other, each subtopic could be assigned individually and would maintain usefulness.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 4
Overall, the organization is logical and clear. There are a few topics that might be shifted in their order, but this is not a critical need. For instance, moving the information about copyright closer to the section on ethical use of sources might make sense, but does not overly disrupt the general flow of the text.
There are no significant issues. A fixed bar at the bottom of the screen allows for navigation to pages directly preceding and proceeding the current page and a clickable contents button at the top right side of the page allows further navigation between sections. Overall, visuals do not appear to be distorted, however, many of the visuals are quite large, taking up the majority of the screen, and could be reduced in size without losing effectiveness. Additionally, on pages 9 and 11, a graphic is presented that contains text that is too small to read. While it is not necessary to read the text in the visual in order to understand the lesson of the section, because it is provided, it would be reasonable to make this large enough to be legible.
The text seems to be free of any major grammatical errors.
This text is written from an academic, western cultural perspective that is relevant to the particular topic and audience (i.e. “A guide to academic research”), but does not take into other ontological or epistemological scholarly perspectives (e.g. testimonios or oral histories as significant sources). The visuals and examples do privilege the U.S. and mainstream cultures, such as through a photo of a White woman using her Mac computer in a library, a photo of a football team, an illustration with the U.S. flag in it, an example question of “How has NASA helped America,” an example opinion of “George Clooney is the sexiest actor alive,” etc. The text is not overtly insensitive or offensive, but it also does not appear to take up or address non-dominant perspectives and cultures in any substantive way.
Reviewed by Audrey Besch, Temporary Faculty , East Tennessee State University on 10/31/19
This text is very comprehensive! From choosing sources to the final research project, this book does a wonderful job of providing all the steps. read more
This text is very comprehensive! From choosing sources to the final research project, this book does a wonderful job of providing all the steps.
Information is accurate for the purposes of writing research and using sources.
Up-to-date and relevant, this text does a good job of outlining various types of sources that can be used and the appropriate ways in which to use them.
Very easy to read content that would be great for students, especially those who are just starting the academic writing process for research.
The text remained consistent in it's use of terminology and framework.
Text has an appropriate use of subheadings and includes activity sections that focus on concepts. Material was broken into easy to grasp ways that didn't seem too lengthy.
Content is well organized and in a logical format for the content provided.
Book did not have any navigation issues and all images were appropriately used for content.
To the extent of my knowledge, there were no grammatical errors in this text.
There were no culturally insensitive issues or offensive language in this text that I could find.
Reviewed by Kris Frykman, Community Faculty, Minnesota State University System on 10/18/19
Comprehensive overview, with examples, to punctuate learning. read more
Comprehensive overview, with examples, to punctuate learning.
Clear, accurate process in showcasing academic research.
Appropriate book for researchers of all levels.
Chapter follow-up questions and videos are included to further enhance clarity.
Terminology and examples are included to further make the content accessible for the reader.
The book is divided in sections so that students can study and apply one concept at a time.
Content is clearly organized.
Charts, diagrams, examples, and videos are highlighted to exemplify key contents.
No discernable grammatical errors.
Appropriately culturally sensitive.
Reviewed by TyRee Jenks, Research Librarian & Library Instruction Coordinator, Montana State University - Billings on 7/31/19
The text is very comprehensive and covers all the necessary aspects of information literacy and student research. There is no index or glossary included, but terms are well explained within the text. The extensive coverage of topics, like types... read more
The text is very comprehensive and covers all the necessary aspects of information literacy and student research. There is no index or glossary included, but terms are well explained within the text. The extensive coverage of topics, like types of sources and copyright, was thorough while not being so in-depth as to bore students. The activities, quizzes, and short videos reinforce the concepts covered in the chapters and add interest, however some quizzes would benefit from additional explanation as to why answers are right or wrong.
The content of the text seems to be accurate. Very minor spelling errors and a copy/paste duplicate. No apparent bias.
Content is up to date and relevant for students while being broad enough to be useful for a longer period of time. Updating information would be easy. The text contains a lot of hyperlinks that an instructor would need to stay on top of to keep the links current. In some cases the links were to very reliable sources that will remain stable for a long time (i.e. Purdue OWL) while others are more transient (i.e. YouTube videos).
In general the text is clear, including good explanations of terms and concepts. It contains very little jargon and the prose is accessible. In “The Details Are Tricky” section, the finer points of primary, secondary, or tertiary information could be confusing to students who are trying to comprehend the basics. The author’s inclusion of informative tables with sample responses as well as the blank template for students to use was helpful.
There is consistent use of terminology and layout throughout the text.
The book has good modularity, excellent graphics, and the text and/or activities can easily be used at the point of need in an information literacy class or one that is discipline specific. Chapters can be used individually or rearranged as needed.
Overall the organizational flow worked well, however the chapters on copyright and fair use might make more sense when grouped with the chapters on the ethical use of sources and how to cite sources.
The EPUB and web versions of the text are easy to navigate with a clickable table of contents and left/right arrow navigation at the bottom of each page. Other than some images that could be resized, the formatting lent itself to consistency throughout the text giving students a uniform experience. In some cases the URL links were just written text instead of hyperlinked which was a little inconsistent. Pleasant graphics added value, explained concepts, balanced out the text, and added visual interest. The inclusion of links that lead out to further explanations of concepts (i.e. the peer review process or how to read a scholarly article) are a nice addition.
There are no major grammatical errors that would be distracting to the reader.
The text is applicable to students in all disciplines, and there are no concerns about cultural relevance or insensitivity. The text is heavily OSU centric (i.e. referencing the OSU code of conduct and requiring students to log in to OSU resources for some activities and examples) and requires effort on the part of instructors at other institutions to make the necessary changes making the content applicable at their institution.
With modifications this text could be incorporated into a three credit information literacy course for undergraduates or into other disciplines. The fair use and copyright sections could be useful to instructors as well as students. Could easily integrate with the ACRL Framework. There is some great general information on writing and making an argument that are applicable across disciplines.
Reviewed by Eric Bradley, Research and Instruction Librarian, Goshen College on 5/31/19
The focus of the book is on published sources for college level research and writing. In this area it is comprehensive. It does not address other areas of academic research. read more
The focus of the book is on published sources for college level research and writing. In this area it is comprehensive. It does not address other areas of academic research.
The content is accurate, error-free, and politically neutral. The last piece makes this a excellent source in the current United States political climate.
Content reflects the current realities of the information landscape. Several of the chapters use up-to-date wording that may need to be updated more frequently, but the excellent modularity of the text allows for accommodation.
The book is straight forward and uses contemporary language of the information and academic landscapes.
The text follows a consistent framework throughout the book.
The text is divided in a way to teach across a course. While the text builds upon itself, many of the chapters stand alone well. I have skipped several chapters of the text and it has not caused any disruption with students.
Excellent organization. The text guides the reader step by step through the research process.
Interface rating: 4
The overall interface is strong. The images and charts are excellent, although the use of branded logos in some of the images may become dated.
No grammatical errors noted.
The text is focused on academic research practices for a North American context. While not culturally insensitive or offensive in any way, it does not take into consideration research practices of other cultures.
I use this text as a replacement of Booth et al.’s Craft of Research. Beside the benefits of being a open textbook, this text provides a more relevant guide to finding sources in the current academic environment.
Reviewed by Kathleen Murphy, Coordinator and Assistant Professor of Music Thearpy, Loyola University-New Orleans on 4/30/19
This book includes all relevant information to help students choose appropriate sources for an academic research paper. It clearly defines different types of sources that can be used, and the difference between primary and secondary sources. It... read more
This book includes all relevant information to help students choose appropriate sources for an academic research paper. It clearly defines different types of sources that can be used, and the difference between primary and secondary sources. It gives an overview of how to search various databases, and defines and describes boolean operators. The chapter on ethical uses of sources clearly defines plagiarism and how and when to cite so as to avoid plagiarizing. The chapter on copyright is an excellent addition; that information is not common in many texts related to academic writing. Each chapter contains extra activities students can work on independently to help with understanding and application of the material covered.
Overall, I found the book to be accurate. I did find one error in Chapter 7. In the section titled "Challenges in Citing Sources" the entry labeled "Running out of Time" was repeated. In regards to bias--I did not find the content to be biased; however, the majority of links where students could go to get extra information were connected to Ohio State University. The one notable exception were the links to the Perdue Online Writing Lab.
The content is up-to-date and relevant. Choosing and using sources for an academic paper has not changed much. What has changed is how to access and find the sources to choose and use. This book does a nice job of explaining how to find sources--databases, google scholar, and search engines. My only concern is the frequent suggestion to search Wikipedia. As an academic, I find this a little troubling. To the author's credit, they did not that one should not cite Wikipedia or use information from Wikipedia in an academic paper. I am not able to comment on ease of updating information, as that is a technical issue.
The book is written in clear, accessible language, with limited "jargon." At times I found the writing to be too simple, written more for high school students than college students. Definitions are provided for all relevant terms.
The book is internally consistent. It moves through the process of choosing and using sources in a linear fashion. However, to their credit, the authors note that writing an academic research paper is not always a linear process.
Each chapter is broken up into smaller units that cover a topic relevant to the chapter theme. Sections of this book could be assigned as individual assignments based on areas of difficultly students seem to be having. Alternatively, a professor could develop a class session or two around each of the chapters. These book seems to be very versatile; there are links to previous chapters that readers can click on to refresh their memories.
The topics in the text are presented in a logical and clear way. The book moves through each topic associated with choosing and using sources in sequence that most researchers would follow. The table of contents, with main headings and subtopics provide a step-by-step guide to help undergraduate students through the research process.
There are many links in throughout the book that students can click on to get more information or to practice skills. Navigation back to the main text is a little trickier. Sometimes, clicking on the back arrow will get the reader back to the page s/he was studying before clicking on the hyperlink. More often, however, the back arrow will take the reader back to the Table of Contents, or front cover of the book. Not all the links worked when I went through the book
I did not fine any grammatical or mechanical errors. I think the book is well-written and appropriate for high school students. I think the language may be too simplistic for most college students.
I did not come across anything that was culturally insensitive or offensive in any way.
I think this book is an excellent resource for high school students, and maybe college freshman who need help in choosing and using sources for an academic paper. The book is logical, gives an overview of the process and provides excellent examples and extra activities to enhance learning. I think it also could be used as a self-study guide.
Reviewed by Miguel Valderrama, Adjunct Assistant Professor, New York City College of Technology on 4/7/19
This book is a great resource of all steps needed to be taken in an academic research process. The book's index clearly displays a suggested methodology to follow and makes it easier to comeback for the review of previous chapters. In general the... read more
This book is a great resource of all steps needed to be taken in an academic research process. The book's index clearly displays a suggested methodology to follow and makes it easier to comeback for the review of previous chapters. In general the book is easy to read and every time a new world or a particular terminology related to the topic comes up, it is clearly defined and put into context.
This book collects a series of methodologies that have been proven to be efficient when they are put into use during the process of academic research. These techniques are not only presented and described to the readers, they are also actively used in the various examples, pretty much in every chapter in the book. These techniques may not be the only way a person can start and develop a research process but they are certainly a clear and convenient way to do so for beginners. There may be complex terminology entered to the discussion which may slow down the reading process. However, this is effectively addressed by separated easy to access links; This provide more in detail definitions and exercises from a particular section.
This book is a guide that presents many particularities of research methods and techniques that have been used for long time. These methodologies have been proven to be very effective in academic research. This book not only collects many of these techniques but carefully relate them to new searching tools that are part of the communication era we live in nowadays. This was not the case just couple of decades ago. I anticipate long life to the methodologies presented in this text with years or decades before they could become obsolete. Within this context, the searching tools may keep changing but the methodologies that are used here could keep working efficiently; at least as a way to approach to a research process for an undergrad student.
The author uses a clear and easy way to understand the language and terminology that makes part of a research process. Without getting too deep into technical terminology the book marks clearly words that deserve more understanding and usually provides separate links which connects the reader with a deeper explanation. The text doesn't have very large paragraphs all around which to me allows readers to keep a good and dynamic paste. Links to previous discussed topics presents a quick way to review previous content without loosing the paste.
Consistency rating: 4
Through out the entire text it is consistent that at the beginning of every chapter there's a statement related to what the previous set of contents was, also in several parts of the book this first paragraph makes a point about how this relates to what it is about to be presented in that chapter. This is why several words allusive to the subject of research are reuse constantly in different chapters. This makes lots of sense to me as a way to keep the reader's familiarity with these terms which will also ended up increasing retentivity levels in the subject. Since the book is clearly broken down into steps they all seemed to be well placed in order to present a cohesive structure that guides the process of research.
Academic research it is a process that should be flexible by nature in many ways. Even though some parts of the process could be done simultaneously to others, this will definitely not apply to all of them. This book brings up an interesting way to order this process which even though may look rigid at times it tries to make sure that some parts are developed before others in the research. It is presented that way so that there's enough understanding of the bases before there can be any progression or even conclusions. This is mostly reflected in the techniques that are presented, where some of then have as their main job to detonate creative thinking. For example: the importance of the set of questions that are asked at the beginning is that the answers will be used mostly to clarify the end goals of a research.
This text is organized following a clear and efficient way to develop an academic research process. It is well distributed in chapters that are all connected to each other in one or other way. The book is efficient at establishing this connections, specially at the beginning and end of every chapter where there's mentioning of the previous and following topic's main ideas. This helps readers to keep track with the overall content.
This book presents an excellent graphic approach to expose its content. The electronic version has the really nice feature of having the index accessible at any point of the reading process. This text is full of links that are either deeper explanations of a particular topic or a set of exercises that are directly related to what the reader is learning. If the idea was to present the information in a format that doesn't look congested to the eyes and that it is not distracting the reader from the important ideas, the editors made an excellent job. This book can't be easier to read, follow through and understand.
Besides a couple of punctuation spaces here and then I was not able to perceive any major grammatical errors. The book is well written all around. Punctuation is pretty much excellent and its composition keeps the reader in track with the content effectible.
Particularly the topics used as examples were very diverse in therms of gender allusion, cultural backgrounds and specialized fields. Research is a process that apply to all disciplines and the professionals working in them. This makes the research process a particularly broad one. The book makes efforts to present this idea by using numerous examples that connect with different segments of the population at numerous levels.
This books is an excellent tool available to anyone who wishes to start a serious research process in almost any particular professional area or field, even amateur researchers can benefit from its content. The book was written to merge the topic content with a series of exercises, tests and examples using a cohesive testing dynamic that helps to increase retention. This dynamic becomes the most efficient way to understand what it takes to start a professional research. The steps to follow the process are laid out clearly in this guide and the important things that need to be taking in account during the research process are highlighted and deconstructed to obtain a deeper overall understanding by the reader or researcher. The fact that the reader is being quizzed constantly during the entire book generates a stronger connection with the important subjects and a good way to evaluate the reader's understanding in real time as well. Highly recommended to undergrad and graduate students and perhaps even amateur researchers becoming familiar with the process of research as well.
Reviewed by Cindy Gruwell, Professor/Research Librarian, Minnesota State on 1/11/19
Choosing and Using Sources does a very good job of covering the topic of Academic Research. Each chapter focuses on an aspect of the research process and thoroughly covers the content with easy to read text and examples/activities for student... read more
Choosing and Using Sources does a very good job of covering the topic of Academic Research. Each chapter focuses on an aspect of the research process and thoroughly covers the content with easy to read text and examples/activities for student practice. Most importantly first-year students through seniors should find the content informative and presented in a collegial format.
All of the content is accurate and explained in a manner that is easy to grasp. There are some minor typos in some of the activities, but they do not confuse the reader. The text is bias-free and includes interesting examples that students can relate to.
The overall content is highly relevant and will age very well. Updates would definite be easy to handle and manipulate. By breaking down each chapter into a variety of content areas, readers will be able to focus and review areas of concern.
Having read several print and online texts of a similar nature, it was a pleasure to come across a text that is clean, consistent, and concise. Each topic has an appropriate amount of information to get the point across as well as tips that lead the reader to additional information. The presentation is consistent throughout without any bloating often found in print texts.
The authors of the text did an excellent job of producing an online text that is consistent and easy to use. No tricks that make it difficult to navigate or confusing to read.
One aspect of the text that I especially like is the modularity that allows for the use of a particular chapter or page(s). Too often texts have chapters that make readers feel like there is no end in sight. The concise nature of this work blends extremely well with the modularity of the complete text.
What makes this text easy to adapt is the layout from beginning to end. Each chapter and section scaffolds upon the other which will allow students to build their skills in a natural manner. Knowledge attained will easily transfer from one topic to another as they move through the book.
While I believe that the text is excellent and I have adopted it for my class, I do find myself frustrated by not being able to move from one section to another within a chapter without having to go back to the contents list. This surprised me because most books and tutorials have forward and backward links, especially within chapters.
There are a few grammatical (spelling) errors in several of the exercises, however, they do not interfere or confuse the reader.
This is definitely a professional work that has no cultural issues and is an excellent example of a non-biased text.
While looking for an OER text I was delighted to come across this book. The content and flow fit in with my class content extremely well and is an excellent resources for courses in the liberal arts, general research, and library-centric classes.
Reviewed by Kathy Moss, Clinical Professor, University of Missouri on 11/27/18
The hyperlinks and examples include a wide range of topics that include cooking, surgery, architecture and sports. read more
The hyperlinks and examples include a wide range of topics that include cooking, surgery, architecture and sports.
Credit is given to an editor, production and design specialists, as well as several content contributors. No additional information is provided to support inference regarding author credibility.
The open textbook Choosing & Using Sources: A Guide to Academic Research presented material that is relevant to my current issues course, including Background reading, Developing a complex research question, Classifying sources, and Evaluating sources.
The topics are presented clearly, using an engaging conversational style and frequent tips and activities. A reader who has no background in information science may be hampered by some terms used in the book (e.g., blog, podcast, Wikipedia, browser, database, Gawker, Reddit). The book does give intentional attention to the technology-naïve audience with some skills (Control-F) and topics (brief description of LexisNexis Academic, Lantern Online).
Terms and organizational framework are consistent throughout the text.
I plan to assign particular chapters of this text that are most relevant to my course's goals. The consistency of the text's terminology and organization should permit this reading plan with minimal distraction to the reader.
The information is clearly organized with a contents listing, chapter numbers and section headers. This organization facilitates easy access for learners with a specific interest in a single topic.
The author’s frequent use of hyperlinks invites students to explore topics more in-depth.
I note a few minor typographical errors that did not adversely affect my ability to comprehend the text.
The book includes examples of non-Western sources such as the allAfrica news database. Some of the links and examples are only available to individuals who have accounts with The Ohio State University. Though the book includes examples in audio and video formats, it could be improved by giving specific attention to topics related to accessibility.
The book provides the opportunity for readers to apply the topics by analyzing its frequent examples.
Reviewed by Lori Meier, Associate Professor, East Tennessee State University on 11/8/18
This text is exceedingly comprehensive. It addresses all elements of academic research (i.e. choosing questions, exploring and selecting sources, searching strategies, citation issues, copyright) as well as providing abundant links for student... read more
This text is exceedingly comprehensive. It addresses all elements of academic research (i.e. choosing questions, exploring and selecting sources, searching strategies, citation issues, copyright) as well as providing abundant links for student use. It is lacking an index or glossary - although many concepts are defined in the various chapters.
This book is accurate and comprehensive. I would not hesitate to use this resource with undergraduate or graduate students as a beginning primer for research.
The book is relevant and timely in regards to the various resources and tech tools it mentions (Google Scholar, EndNote, Ref Works). Given the subject matter I suspect that this book will have longevity to users.
The text is clear and provides definitions for jargon/technical terminology that is used. It is very comprehensive which might be a bit intimidating for the first time reader, but all elements needed for cogent research are included and therefore necessary. I appreciate the use of student scenarios as a way to step-by-step show the thinking process of choosing research questions.
Very consistent and thorough.
This text would be ideal for use as single chapters in courses where the content is needed. While the content is crafted with Ohio State University students in mind it is still very relevant for use by students and scholars. I am already thinking how I might use this next semester with an undergraduate honor's thesis student - both as modules to be read but also as a reference source.
The book is organized in a logical manner but spends only a brief amount of time about qualitative and quantitative research as peer-reviewed sources and only gives basic definitions for those two terms. I would perhaps suggest an additional section on qual/quant/mixed methods research methodology and perhaps a quick overview of research methods or samples via discipline. Additionally, a mention of the common IRB process for Human Subject Research might be helpful to those students using academic sources that discuss that process. It is a very clear text and this could be added with just a few pages of information that might be beneficial to students.
Navigation links worked well for me. The book is easy to read and the display features are not troublesome to me.
Grammatically sound.
Appropriate and is accessible to a wide audience.
Reviewed by Kathy Lamb, ELL Specialist/ English Instructor, Miami University on 8/2/18
The text covers most areas of academic research, and has a table of contents but no glossary, which is much needed. Topics are clear and concise, transitioning smoothly from general to more specific, such as “What is a Research Question?” to... read more
The text covers most areas of academic research, and has a table of contents but no glossary, which is much needed. Topics are clear and concise, transitioning smoothly from general to more specific, such as “What is a Research Question?” to “Narrowing Topics” and finding “Related Terms”. Perfect for college freshmen.
The content is accurate, error-free and unbiased.
The source is up-to-date and it would be relatively easy to update information.
The text is easily understand and flows in a clear manner. Ideas and topics progress easily and examples are used to offer context.
Ideas build one upon another and academic vocabulary is repeated throughout.
Some parts of the book seem a little “text heavy”, but overall it is well organized with efficient flow. The embedded links in the text connect earlier concepts
One problematic is that there lacks a glossary. The table of contents is very long, but broken down so that one is able to easily reference topics. Chapters are concise enough to be read in a timely manner and effectively used.
For some of the online activities it was confusing to discern which answers were correct or incorrect. And, after clicking on and completing an activity one must go back to the former page in order to navigate further. On the other hand, being able to access other information about the chapter topics via link is a handy tool.
There are no grammatical errors.
This book is culturally relevant and not offensive or insensitive in any way.
Reviewed by Sara Abrahamson, Faculty, Minneosta West Community and Technical College on 8/2/18
This text is very comprehensive. The complete research process is broken down from start to finish. read more
This text is very comprehensive. The complete research process is broken down from start to finish.
Very accurate information.
The content is very relative to today's researchers and does a fine job of detailing types of sources.
Very easy to read with content that is easily understood by even a first-time researcher.
The content was very consistent and easy to follow because if it.
LOVED the easy of reading because of the small, digestible informational pieces!
The flow of the text was perfect, following the research process from beginning to end.
I enjoyed the hyperlinked Activities, however, they did not all work for me.
No grammatical errors found.
Very culturally unbiased.
Excellent text that I wished I had years ago!
Reviewed by Justin Megahan, Librarian / Associate Professor, Fontbonne University on 6/19/18
The text does a good job covering academic research. There is a table of contents, but I feel like a glossary and index would be helpful for this book. read more
The text does a good job covering academic research. There is a table of contents, but I feel like a glossary and index would be helpful for this book.
The content is accurate. I did not notice any errors.
The content is up-to-date. There are many databases and websites referred to in the text so it is important to check those relevant links on occasion. It would be straightforward to update the text as needed.
The text clearly steps the reader through the research process. The process is discussed in detail over the 13 chapters.
The text is consistent.
The book is modular. Chapters can be rearranged without confusion. The Copyright Chapter is a good example of a component that can be used separately as a supplemental reading in another course.
The book is organized logically. The addition of a glossary and index could help navigation.
The book has images, charts, and videos that are useful. There are quick activity questions that tests the students’ knowledge on the current topic. These activities do link out to OSU’s site so it is important to make sure those links continue to stay active.
The text contains no grammatical errors.
This book does not have cultural concerns.
Many links direct the reader to OSU resources that have restricted access. The discussion of OSU resources and tools needs to be modified to fit the reader’s institutional resources. “ACTIVITY: Quantitative vs. Qualitative” has a link that is no longer working.
Reviewed by Jane Theissen, Reference Librarian/Professor, Fontbonne University on 5/21/18
The research process is explained in detail, from how to develop a research question to where and how to research through the application of copyright, fair use and citation styles. read more
The research process is explained in detail, from how to develop a research question to where and how to research through the application of copyright, fair use and citation styles.
The content is accurate and unbiased. Most of the links, which are plentiful and well placed, are either broken or link to resources at OSU's library, which I could not access. Use of this book would require time to correct this.
The content is stable. Other than updating the links, little would need to be done to use this text.
Very clearly written; jargon is appropriately explained. Self-checks allow students to make sure they understand the material.
Each section logically builds on the previous, and tone is consistent throughout.
The text has a great deal of modularity. Each section is listed in the Table of Contents and covers a few pages or less. There is no index. It is easy to find and move to sections quickly. the structure allows one to pull sections out for other courses (which I have done).
The research process is explained step-by-step with appropriate detail and excellent graphics.
Images, charts, and diagrams serve to explain and support the text. Many seem rather large and I found them a bit distracting. Additionally, there are page breaks in strange places, leaving large blocks of white space on pages while the narrative continued on the next page. This was very confusing. It would also be helpful if the links would open in a new window.
It seemed inclusive where applicable.
This text impressed me as appropriate for high school students or college freshmen.
Reviewed by Laura Heinz, Librarian, Texas Tech University on 3/27/18
This book provides beginning student researchers with a clear and complete path to the research process for class assignments and undergraduate research projects. read more
This book provides beginning student researchers with a clear and complete path to the research process for class assignments and undergraduate research projects.
The content is presented is accurate and in an unbiased manner for students to easily grasp the process and concepts.
This book was written in 2016 and may need some minor updates. The material is presented in a logical manner that leads students through the process as they begin their research. Each chapter can be used independently as the instructor fits the chapters into course content.
This book is easily understood by an undergraduate and doesn't require extra readings or content to be understood. It is concise and clear which will be appreciated by the student as they conduct research.
This book is consistent in it's framework which leads the student to each step logically avoiding confusion or frustration.
The chapters can easily be used independently and refer students to other chapters with supporting information.
The book is written to lead students in a logical manner through the research process. The length of the chapters allows a student to easily read the chapter for that step in their research, apply it and refer to it easily.
The book downloads easily onto a laptop or e-reader. The graphics display nicely on either size screen and enhance the text.
No grammatical errors were noticed.
This book is not culturally insensitive or offensive in any way. Examples used are appropriate.
This book introduces beginning student researchers to the academic research process in a thoughtful and deliberate manner. The books lack of jargon and abbreviations will help international students learn how to better navigate an academic library for research. Instructors in all disciplines should consider this book as an additional textbook for their classes requiring research for assignments, class projects and/or papers.
Reviewed by Hilary Johnson, Learning & Teaching Librarian, The Open University on 3/27/18
The text does not include an index or glossary. However, it covers a complex (and dry) subject in an economical and stimulating fashion. Each reader would learn about the subject from the basic text but the authors have enriched the text by... read more
The text does not include an index or glossary. However, it covers a complex (and dry) subject in an economical and stimulating fashion. Each reader would learn about the subject from the basic text but the authors have enriched the text by embedding audio-visual resources, download-and-keep checklists and formative activities of excellent quality.Chapter 9 'Making an Argument' is particularly strong and complements Chapter 1's analysis of research questions well. It is an excellent resource for undergraduates, post-graduates and beyond, and could also be useful for professionals researching topics to support evidence-based practice protocols.
More tips about applying facets to search results on services like Summon, EDS or Primo would be a useful addiition. I was surprised the authors did not employ language to frame the skill development in the language of 'employability' and life-skills, which might hook readers who are not planning to engage in academic research in the long-term.
The accuracy of the book was excellent, My score would have been 5, except the advice about copyright legislation and fair use is only applicable to students of Ohio State or elsewhere in the USA; so an institution in the Britain, Ireland or Europe would not be able to use or recommend chapters 11 or 12. However, these chapters are well-judged for the intended audience; succinct and comprehensible, where so many guides are too woolly or arcane to be useful to a general readership.
Chapter 1 had a dead link to an audio-visual resource. The explanation of how to use Wikipedia for academic study was nuanced, classic and practical. The explanation of how to use truncation and wildcards were similarly time- (and platform-) proof. There is much current interest in 'fake news' and the manipulation of Facebook and Google algorithms. So it could be timely to add a section on the known issues and some practical strategies to compensate for them.
The authors use excellent, clear English that should be comprehensible to anyone with academic english reading proficiency. My only qualms related to an ambiguous use of the term "poster" (this word has a particular meaning in an academic setting which was not explained) and more extensively around the slightly simplistic and dated language used for the university library catalogue and abstract & indexing databases. One of the activity sheets is structured like a decision-tree and starts with the question "are you working from a database"; with modern resource discovery platforms and other aggregating tools, students may not be able to tell whether they are looking at results from a single database, all the databases from one supplier or multiple databases from a variety of suppliers.
The stylesheet and planning of content is elegant and the quality is consistent throughout the text.
Each chapter is split into useful subsections, with clear formatting to demarcate between topics, tips and activities. The authors have also helpfully embedded hyperlinks to relevant chapters or sections earlier or later in the book.The length of individual subsections is consistent to make reading online easy (balancing scrolling and page turning). However, the length of embedded audio-visual materials varies so a student planning their time might be surprised in places.
The text has a sensible progression of topics, with hyperlinks back and forwards to connect relevant topics. And the final chapter, 'Roles of Research Sources', pulls together the lessons learnt with a useful acronym (BEAM), giving the book a strong ending.
I accessed the text on a variety of browsers, screen sizes and operating systems without any problems with the interface.
I only spotted two minor errors - site instead of cite and White's definition (page 186) without an apostrophe.
Not all the video materials embedded are captioned making them inaccessible to some categories of disabled users.
Reviewed by Lydia Bales, Academic Skills Tutor & Librarian, Staffordshire University on 2/1/18
Considering the book is not overly large, the guide manages to be very through and comprehensive guide to locating sources and using them correctly. It even goes further in giving some great information on making an argument and writing out the... read more
Considering the book is not overly large, the guide manages to be very through and comprehensive guide to locating sources and using them correctly. It even goes further in giving some great information on making an argument and writing out the research. The chapters are in easily digestible chunks covering the process of searching and evaluating resources in a useful and cross-discipline manner. It covers the source search process of research in an easily digestible manner.
The topics are accurate and have been written in a way that they will not date too much. The links and examples of the services provided may need updating to keep them accurate but the nature of the online format makes this easily possible. The Copyright chapter is obviously only applicable to those studying in the US. Having a version of this chapter available discussing copyright law in the UK could be useful any access the course for a different location.
The topics, examples and videos used are relevant and useful and should not date too much. The links and examples of the services provided may need updating to keep them accurate but the nature of the online format makes this easily possible. Some of the examples and links are specific to Ohio State and America and this can limit the relevance for students who do not have the ability to access Ohio State resources or are not based in America. Also the copyright section specfically is obviously only US copyright law limiting it's usefulness for students based in other locations.
The writing style is straightforward and easy to follow. It is sometimes slightly repetitive but overall the information is clearly presented and the vocabulary used is not too advanced. The style is informal and it makes a weighty topic much easier to process. I think it would be useful to have a glossary in the resource for students who maybe have not come across some of the topic specific words before and need them defining.
I was impressed with the consistency considering the work is made up of different author’s contributions. I could not identify different voices within the text, which helped improve the flow of the work. The arrangement of the contents tab is very useful to help navigate to specific sections of chapters as well as the overall chapter.
The layout of the book makes this modular. You can choose which sections to look at in any order and they read clearly and separately well. The other sections are signposted throughout the text and you can link back through to these using the hyperlinks provided. I think the order could be slightly improved by moving the citing and copyright information after the information on argument and writing but because you can choose how to read the book then it is not really an issue. I think it is important to note that if you cannot play the video content or the links in the book are Ohio State Specific the book does lose some of its positive features.
Overall, the structure is straightforward and logical. It flows in a manner that is easy to read and to process. Using the navigation you can work your way through the book in any order you feel is appropriate. As I stated I feel the referencing and copyright information could be in a different place but because you can choose to read this in a different order, it does not really matter.
Having read the online version on both a PC and a tablet I found the interface both easy to use and accessible. The page and chapter length worked well on both platforms and it was easy to access the links and activities contained within the resource. I could not access the videos on the PC due to not having Adobe Flash and it would be useful to have known I would require this to access the resource in its entirety. The video content is a refreshing change to just text and the images used are overall relevant. The videos do not all include a text version and this would be useful for accessibility. A few of them do have this option. Some of the images in the text viewed blurry on my PC and tablet. I am not sure if this was an issue with my own software or an error in the book.
I did not notice any errors during this read through. In some places, the text was a bit repetitive but this not disrupt the flow too drastically.
The examples used are not offensive and are diverse in their range. They have not given examples that define the guide for specific subset of students, which makes it more applicable.
Just for accessibility purposes, I think all the videos need a text version not just some. In addition, the RefWorks program has now been updated and it is called New Refworks with a changed logo and this could be updated in the book along with the guide to setting up Refworks if your institution subscribes. I feel that there are many links that you could not access unless you were an Ohio State user and this could disrupt the flow of the book for some users.
Reviewed by Lori Jacobson, Associate Director, Curriculum Development, William & Mary Writing Resources Center on 2/1/18
The book provides a comprehensive introduction to the use of sources in academic writing. read more
The book provides a comprehensive introduction to the use of sources in academic writing.
The book is a polished, professional and appropriate tool to help students improve their information literacy.
The content is relevant for undergraduate students and their instructors. It focuses primarily on fundamental approaches to finding, evaluating, and deploying sources in order to enter the scholarly conversation. While the authors occasionally mention a specific tool, or insert links to outside sources, these are placed within "Tip" boxes that can easily be updated.
Because this book was created for students at Ohio State University, it is sometimes quite specific about tools or processes that are unique to OSU. Instructors using this book at other institutions may sometimes need to suggest their own's institution's available tools to keep the text relevant for their students.
The book is well-crafted for an undergraduate audience, taking an easy-going, friendly tone and clearly defining key terms and concepts. It is also accessibly structured, making it fairly easy for users to jump between topics, rather than requiring a linear read. Links between related sections are provided wherever it is appropriate.
The book uses a consistent design scheme and structure. Features that appear in each chapter include graphics, tip boxes, examples, activities, and summaries.
Each unit of the text stands on its own and could be easily assigned as an individual reading. Rather than being self-referential, the text will suggest that more information on a related topic can be found in one of the other modules.
The text is organized to flow in roughly the same sequence as a typical research project. Students who are reading the text while working on a project should find individual sections logically presented and relevant. This is clearly not a text designed as background reading; rather it functions best as "just in time" information for students working through the research process.
I found the text quite easy to use in it its online form. It is visually appealing, easy to navigate, and thoughtfully arranged.
I noticed a couple of typos, but no significant grammatical errors.
The examples provided are of broad interest, and most readers will have some familiarity with them. There were no insensitive or offensive comments or examples.
Choosing & Using Sources: A Guide to Academic Research is a practical tool for novice researchers. It asks students to begin the process with a research question, and then provides a step-by-step approach to creating the question. All the other chapters flow from this effective beginning, and should increase students' information literacy by helping them understand types of sources available to researchers, the relationship between sources and information needs, how sources should be evaluated, and how they can be deployed effectively and ethically. Additional chapters on argumentation and copyright round out the book's overall usefulness to students engaged in a research project. This book could be easily paired with a staged research project, and would provide students with the "just-in-time" information they need to successfully complete the assignment.
Reviewed by Kristin Green, Reference and Instruction Librarian, Penn State Worthington Scranton on 2/1/18
The aspects of academic research that are prudent to cover within the first year of any undergraduate student's general education are all covered within this textbook. From an introduction to the ethics of source use to crafting basic Boolean... read more
The aspects of academic research that are prudent to cover within the first year of any undergraduate student's general education are all covered within this textbook. From an introduction to the ethics of source use to crafting basic Boolean search strings, all facets of entering scholarly discourse are addressed in brief chapters that feel modern and accessible. While instructors may wish to supplement or replace some of the exercise sets in the text with their own assessments, the content of the text provides ample coverage if selected to serve as a primary textbook for a foundational information literacy course.
The book is accurate in addressing the current state of the information landscape as encountered in the realm of academic research, as well as the legalities of copyright and fair use.
All content within this book is current and the content within chapters sections are written in a style that today's undergraduate students will be able to learn easily from. Many of the concepts, processes, and principles that are covered in the text have an inherent longevity that will prolong the relevance of this text past its initial publication date. However some chapter sections, tutorials, and videos are institution-specific reducing the overall relevancy of using the entire text at other locations.
The text is written in a clear and concise style that current students will find very accessible. The authors consciously defined any technical terminology or jargon as it was introduced throughout the chapters. Furthermore, the technical concepts that were more complex to define are often accompanied by visuals to help convey what is being defined.
The terminology and format of the book, along with the linked exercise sets and visualizations, provide a solid consistency that will helps students focus on learning the content rather than being bogged down with understanding the textbook format.
Instructors could easily parse different chapters of this book to use for modular instruction, especially in "one-shot" or other limited instructional scenarios. Some of the chapters are a bit self-referential which may generate a minor degree of confusion if used out of the holistic context.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 3
While there is a logical flow to most of the chapters, some seem a little out of place such as the "Making an Argument" chapter. I would have preferred a division of chapters into sections, where the writing-related chapters were separated from the source-related chapters. I also think the chapters that covered Copyright, Fair Use, ethical source use, and citations would have a stronger flow if organized together in their own section.
The ability to navigate through the book from the table of contents page is a great feature for students, especially when the instructor is choosing to assign only particular chapters or work through some of the chapters in a different sequence. The linked exercise sets are also easy to navigate through, allowing students to focusing on applying learned concepts rather than learning new interfaces. However, throughout my review some of the linked external content would not open for me and links to external materials always have the possibility of changing which may result in future inaccessibility
No grammatical errors were detected when reviewing this book.
This book is not offensive nor culturally insensitive in any manner.
For any instructor looking for an open textbook to orient undergraduate students to the basics of the academic research and writing processes while simultaneously providing context of contemporary issues surrounding these scholarly activities, this is a comprehensive and accessible choice!
Reviewed by Anne Behler, Information Literacy Librarian & Instruction Coordinator, The Pennsylvania State University on 2/1/18
This text offers a comprehensive breakdown of the academic research process, with special effort made to demystify jargon that may present itself in either the classroom or library environment. Beginning with establishing a research question and... read more
This text offers a comprehensive breakdown of the academic research process, with special effort made to demystify jargon that may present itself in either the classroom or library environment. Beginning with establishing a research question and carrying through to integrating and citing sources, the text includes practical tools for students to use in their own research, as well as links to supplemental information. If anything, the text errs on the side of providing too much information, such that a novice researcher may feel overloaded.
The text offers an accurate articulation of the research process, and avoids bias by covering a wide variety of potential information sources, including the use of web search engines other than Google.
Because the information landscape is constantly shifting, the text will require fairly frequent review. This is particularly important when it comes to how web sources are addressed. For example, the book does not address fake news and/or dealing with problematic web resources, and it glosses over use of social media as an information source. However, the concepts related to the research process itself change very little, and the information presented about them has staying power.
The text is written in accessible language, and works to address uses of jargon that are typical within the academic environment by providing explanations for what professors typically want when they request a particular item in the research process. This is an effective way to establish relevance with students, as well as clarify academic expectations.
The language within the text is consistent and accessible, with helpful insertions of definitions and/or links to explanatory supplementary information online.
The text's sections are clearly and logically labeled, and could very easily be plugged into a course in part or whole.
The order of topics in the text follow the research assignment process, from point of assignment decoding through to writing and source citation. Given the audience for the text and its intended purpose, this makes great sense.
The text contains links to many outside web sources that may provide helpful supplemental information for the reader; however many of these links were found to be dead. Comprehensive review of all links is highly recommended. In addition, I recommend continuing review of available videos related to the topics, as many selected are either rudimentary or contain dated material.
The writing and grammatical quality of this text are of the highest quality.
The text is culturally relevant and inclusive in its examples.
As stated, this book holds great utility and relevance, but requires updating for links to external web resources. It will also need to be adapted to keep up with the changing landscape of information sources themselves.
Reviewed by Craig Larson, Librarian, North Hennepin Community College on 2/1/18
The book is very comprehensive, sometimes almost too much so (sections on copyright seem to be more detailed than the average college student would need or perhaps be interested in; the section on the lifecycle of information, while interesting,... read more
The book is very comprehensive, sometimes almost too much so (sections on copyright seem to be more detailed than the average college student would need or perhaps be interested in; the section on the lifecycle of information, while interesting, also is a bit questionable as to its overall relevance). Instructors who choose this book for a one- or two-credit information literacy course will have much more material at their hands than they can reasonably cover in a semester. This book would make a good companion volume to just about any course involving research.
The content is accurate and unbiased. As an example, I was interested to find that the author actually recommends that students use Wikipedia, at least in the very early stages of research, to get an overall picture of their topic. So many college instructors, regardless of the subject, seem to have a strong aversion to Wikipedia. Here, the author actually goes into some detail on how using the references in an entry can lead the researcher to additional sources he/she might not find through other means. Some of the activities are a bit misleading or written in such a way that there could be more than one right answer, which isn't necessarily an error, but could be tightened up a bit.
The content is largely relevant and up-to-date, though I was a bit surprised to not find a section addressing "fake news," which has become such a watchword over the past year. I was also a bit surprised that, although the author has a section talking about which "neighborhood" certain types of information "hangs out," there wasn't a discussion of different domain names, such as ".edu," ".org," and ".com" and what they indicate to readers. Also hampering the book's relevance somewhat is an overabundance of examples and activities that require an Ohio State student ID to log-in. Many of these would have to be re-worked or re-written for the book to be useful at other schools.
In large part, the book is clearly written and new ideas are clearly explained. The writer does a pretty good job of avoiding jargon and technical terminology or where it can't be avoided, of providing examples and clear definitions of terms. Some of the activities aren't so clearly written that there is one obviously correct answer. Also, some of the scoring of activities isn't clear enough to indicate to the user what was wrong and why it was wrong or even the correct answer that should have been chosen. Not every concept is adequately explained or thoroughly developed (for instance, the crucial process of moving from an initial reading to a research question could use further clarification and development). Another area that could use further discussion and development would be how to use databases.
The book is largely consistent, though there are occasions where the consistency falls through. For example, most of the accompanying activities will open in a new window, but not all. There were several occasions where this reader closed out an activity window and closed out the entire book as well. This is an area that someone really should take a look at, as it can be confusing and irritating for the user. Also, the fact that many of the book's activities require an Ohio State student ID effectively locks out users from other institutions.
The book is largely modular, with sections that can easily be broken apart and assigned at different points in the course. There is a very useful table of contents, broken down by subject into smaller pieces that can easily be accessed. As mentioned previously, the book is very comprehensive, almost too much so at times, so having this table of contents is very helpful.
The book is fairly-well organized, though there are things placed in odd locations that could be touched on earlier or later, as the case may be. For instance, there is a good discussion fairly late in the book about deciding whether to quote, paraphrase, or summarize, which would have been much more useful if it was placed in the section of the book that directly addresses each of those activities. Instead, it is placed in a section on academic integrity (which, again, is very Ohio State-specific, too much so, really). I also question the relevance of a chapter on creating an academic argument, which if it is to be included at all, would seem to make much more sense earlier in the book, when students are learning the basics of research and how to apply it to their writing.
The book is largely free of significant issues, although as mentioned previously, many of the activities require an Ohio State student ID to log-in and use, which makes them useless to students from other institutions. Also, the activities are sometimes difficult to follow--one doesn't know why one answered incorrectly or what the correct answer even is in some instances. And the fact that some activities open a new browser window and some don't can also be confusing. There are a few activities that lead to broken links.
There are the occasional run-on sentences and spelling mistakes in the text. It's almost impossible not to have some issues in this area. However, the infrequent errors don't detract from the book or its overall usefulness, though it might be a good idea for someone to go through the text and try to clear some of these up.
The book does a good job of avoiding being culturally insensitive or offensive. Activities and examples are written in such a way as to be inclusive. Many of the examples link directly to sites that deal with minority themes and issue.
I think, on the whole, this is a very useful book and one that could be put to immediate use in many instances. However, the number of activities and examples that require an Ohio State student ID to access make this less relevant than it could be if the author had striven for more universal examples.
Reviewed by Mairéad Hogan, Lecturer, National University of Ireland, Galway on 2/1/18
This book covers the subject matter in a comprehensive and detailed way. The way in which the material is presented is very suitable for students who have not previously been involved in academic research as it starts at the very beginning and... read more
This book covers the subject matter in a comprehensive and detailed way. The way in which the material is presented is very suitable for students who have not previously been involved in academic research as it starts at the very beginning and assumes no prior knowledge. It has additional features that help to reinforce the material, such as activities and MCQs. These help to reinforce the learning and test the reader’s understanding. Additionally, the examples used are very useful and helpful in gaining understanding of the subject matter.
It goes into the material in depth and not only tells students how to progress their research but also explains clearly why they should be doing it this way. For example, it explains to students how to differentiate between good and bad sources. However, I have one small concern with this aspect. They do not tell students how to differentiate between different standards of peer-reviewed journals. They do mention looking at citation count but state that is not a useful measure for very recent articles. Some discussion on determining the quality of the journal itself would be helpful. For example, looking at citation counts for the journal, rather than the article would be one example, as would looking at rankings.
Overall, I would see this as an excellent reference book to last students through their academic careers.
The material itself is accurate. However, many of the links to additional material either do not work or are inaccessible to those without OSU credentials.
The material is mainly presented in a way that will last. However, many of the links no longer work so these should be checked and alternatives put in on a regular basis. Additionally, there are links to videos that may not be there in the future, although all I clicked on were available. However, the text description of the videos did not work. Many of the activities (MCQ’s etc) have a dated feel about them in terms of layout and interaction. The design of them could do with some updating.
The writing itself is very clear and easy to understand. Diagrams are used to good effect to clarify concepts (e.g. use of Venn diagrams to explain Boolean concepts). However, some of the terminology is not as clearly defined as it could be. While terms are generally explained clearly in the text, it would be nice to have a glossary of terms. Additionally, the MCQs are not always clear as if the reader gets an answer wrong it is not always apparent which is the correct one.
The book is consistent in writing style and interface.
The book is structured in a modular format whereby the reader can dip in and out of different sections, as they need to. Equally, for a student starting out, it is structured in a way that is likely to follow the steps in the same order as the student, making it a good companion to their research projects.
The book was organised in a very natural and sensible way and flowed smoothly from one topic to another. Links were provided to related sections of the book where relevant so that if the reader forgot what was meant by a particular topic, they could easily hop back and forth. The book started at the very beginning with good coverage of developing a research question and then progressed through tools and sources to help with this. The additional activities were all web based, which works fine if you have easy access. However, I was using a kindle with poor broadband so struggled to access it at times. It also felt a bit disruptive leaving the book to do the activities. It’s also not always clear whether links lead to another part of the book or to an external site. The tips are a useful addition. The stand out when flicking through the book and help to reinforce the important points. It is also useful the ways steps are clearly broken down into sub-steps.
I downloaded it to Kindle, and found a number of issues. It struggled to deal with larger fonts, resulting in some text not being visible.. There were also references to “the bottom of the page” but the bottom of the page varies depending on font size. Not all of the activities worked. Some of the activities required OSU credentials to access them, which was frustrating.
There were some minor grammatical and typographical errors but nothing major.
The book is very US centric in its use of examples. For example, there is an American football example and news sources referred to are US based generally. Additionally, copyright discussion is US centric.
Overall, I found this to be an excellent book that will help students in their research projects. I think it is a book that they will use for a number of years as it is has sufficient depth to help at different levels. The one main change I would make would be to broaden OSU references and activities so they are referring to databases in general, for example, rather than simply talking about the OSU one. Much of the material is relevant regardless of institution but a reader unfamiliar with databases would not be aware of this and might skip over some very useful information.
Reviewed by Anthony Patterson, Assistant Professor, North Carolina Central University on 2/1/18
Choosing and Using Sources is an extremely thorough text taking readers through the research process from formulating research questions to fair use and copy right issues. I particularly liked the online examples and resources including quizzes... read more
Choosing and Using Sources is an extremely thorough text taking readers through the research process from formulating research questions to fair use and copy right issues. I particularly liked the online examples and resources including quizzes and videos. The table of contents is thorough but there is not a glossary. While this is a strong text some discussion of theory and how theoretical frameworks are used in academic writing.
While the text could have addressed additional areas, the authors were accurate and detailed. Chapter 8 - How to Cite Sources is well done and accurately takes novel researchers through when they should and should not provide citations.
The authors present how to develop, approach, and conduct sound research in a well thought out format. This text is up-to-date addressing issues like Wikipedia and Google Scholar. While issues around these information sources will change, the way this text is set up, it can easily be updated in the future.
The book is well written, clear, and easy to follow. Jargon such as primary, secondary, and tertiary sources were explained clearly with appropriate examples. This text will be accessible for my students and most others pursuing advanced degrees.
The authors are consistent throughout the text when discussing topics like presenting arguments and the relationship this has with concepts like research questions and the sources researcher select. While consistency is expected is difficult to do especially when writing as a team. More impressively is the consistency of supplemental materials throughout the text.
The book has long chapters and occasionally I had some difficulty knowing where one section ended and another began but overall it is readily divisible. Another important aspect of the text are the supplemental materials like online quizzes and videos which are also clearly align with the sections in the text.
I was skeptical at first when I began reading but the overall organization of this text is good. Even though the text is about writing and sources, a section of theory and incorporating theoretical frameworks would have strengthen the book. However the topics selected flowed well and led potential researchers through a logical process.
A few problems linking to sum supplemental materials but overall I was impressed by the quality of the graphics as well as the links to quizzes and videos that were provided.
I did not come across any grammatical or typographical issues.
I did not see any cultural insensitive examples or information provided. However I also did not see a lot of racial or ethnic diversity in examples throughout this text. Overall, I feel the authors approached the subject matter appropriately.
Reviewed by Rachelle Savitz, Assistant Professor, Clemson University on 2/1/18
The text is quite comprehensive regarding finding, using, and understanding sources. It provides the process of sourcing from start to finish with examples and activities provided throughout to support the reader. Various ways to find sources... read more
The text is quite comprehensive regarding finding, using, and understanding sources. It provides the process of sourcing from start to finish with examples and activities provided throughout to support the reader. Various ways to find sources are described. There is a focus throughout on software and databases for the students at the authors institution and that can be confusing to readers from other institutions. The information provided regarding citing, ethics and copyright, and fair use was informative and would be beneficial to the reader. There were sections throughout that could have been more in depth and more specific. For instance, when going over the various ways to cite sources, additional examples could be provided and the version/edition should be listed. For instance, was the APA citation in APA 6th edition format? Also, make sure to address citing from secondary sources as students do this often and tend to cite what they read even if they read it from another text. The TOC was helpful and allowed ease of understanding what was to be covered in each section. One main complain that I have was regarding the additional information provided to help the reader in writing a paper. This information would be helpful for basic college writing but not for academic writing, thesis or dissertation writing. The sections required for some of these papers are not discussed and the text eludes that the sections provided regarding writing an argumentative piece would be appropriate for all. Also, synthesizing information could be explained a bit more and with more depth. Synthesizing includes more than critiquing and summarizing. All in all, the sourcing information is spectacular and the additional information could be expanded upon.
Accuracy of sourcing was spot on. Some of the additional categories discussed, as mentioned in the first section of this review, could be expanded upon to fully explain that category, if it is to be included in the book. The examples and activities provided were quite good and would be very beneficial for students to apply what they are learning in real-life contexts. Links were provided for extending information. I did not attempt to open every link but making sure they are up-to-date will be important as time goes forward. I also feel that the section on popular texts can be misleading. Stating that the Washington Post is "popular" eludes that it is not reliable or valid. This is not necessarily true as many experts in various fields write sections in "popular" newspapers.
As previously stated, a lot of links go to OSU resources. This could be problematic for any reader that is not at OSU. More information should be provided to support any student in the world as that part would be confusing to many students.
The text is easy to read and follow. All new information is explained and then examples and activities are provided. This is student friendly and allows any reader to quickly follow along and understand what is being stated, especially regarding the sourcing elements. As stated above, there are some sections that could/should be expanded upon for clarity and this might be best for beginning university students but the text was easy to understand in regards to sourcing, citing, and fair use. More information on how to use the sources and sections of papers would be beneficial to all students.
Each chapter seemed to follow a similar structure that followed the TOC.
Modularity rating: 3
Reading the book online provides ability to chunk the text based on assignments and can be read chapter by chapter, entirety or starting at different places. Due to the extensive amount of outside links and examples, this would be quite different if read in paper format. This book truly has to be read online to ensure benefit from all of the additional activities, links, examples, sources, etc. In addition, the many links specific to OSU would not be helpful for other students.
The organization is consistent from chapter to chapter. Information is explained and then examples and activities are provided to further knowledge. This works well for readers that needs examples.
Using a laptop provided no issues. However, when using a smartphone, the pages changed in size and various display features did not load properly or at all.
Very few grammatical errors were noticed.
No cultural issues noticed other than the many OSU references and sources. This could be offensive to other institutions as they will not be able to access many of the links.
Reviewed by Scott Rice, Associate Professor, Appalachian State University on 2/1/18
The book is very comprehensive which sometimes detracted from its usefulness. There were a few units that may be superfluous, but I did appreciate that the author seemed to err on the side of inclusivity, leaving it to other adoptees how much... read more
The book is very comprehensive which sometimes detracted from its usefulness. There were a few units that may be superfluous, but I did appreciate that the author seemed to err on the side of inclusivity, leaving it to other adoptees how much content they might use and repurpose.
The book is error-free and appears to be free of bias.
The book is pitched to an Ohio State University audience, so some of the resources pointed to would not be the same as a potential adopter's institution might select. In addition, the book needs some updating regarding the impact of social media on the information cycle. Social media formats are mentioned, but a fuller treatment of how they fit into the information climate would be a good addition.
The text was clear and easy to read, and provided numerous examples for its points. It also did not rely on jargon in its explanations, which makes it much more accessible.
The text was consistent in its use of terms. I found its tone consistent, as well as the level of explanation for the wide variety of concepts explored.
The organization of the text into units makes it very easy to break the content apart into smaller units and use it for a variety of purposes. I could see using the content for different parts of several courses, as well as incorporating it into e-learning content.
The topics are presented in a logical fashion, following the path that a typical research assignment might take. This will also make it easier to fit within the flow of a course that uses the textbook to teach about the process of academic research.
The interface of the text itself works appropriately, but some of the ancillary quizzes and extra material did not work so well. Many of the graphics did not work as well within the pdf format as they do in the web format.
The textbook was free of grammatical errors and was easy to read.
The text did not appear to be culturally insensitive.
I am exploring the creation of a for-credit information literacy class at my institution and this book is a possible candidate for adoption for the course.
Reviewed by Bryan Gattozzi, Lecturer, General Studies Writing, Bowling Green State University on 2/1/18
I was impressed how the text began helping students understand the benefits of leading a research project by writing research question(s), following with assessment of research methods, and thinking about research writing as an avenue to test a... read more
I was impressed how the text began helping students understand the benefits of leading a research project by writing research question(s), following with assessment of research methods, and thinking about research writing as an avenue to test a hypothesis instead of one simply confirming a previous, and perhaps uninformed, belief.
The book didn't seem to dismiss any possible research method. Instead it provided suggestions of how and when any individual research method may be relevant.
The book was published last academic year and the content included is still relevant, mostly because best-practices in research (and research writing) haven't changed much.
The volume of research methods students can use given the internet's power is ever increasing, yet the book does well to isolate a handful of long standing tenets that academic writers have used for decades while allowing for discussion of web-based writing and multi-modal presentation methods instructors may increasingly require students to use.
Each section is concise, clear, and easy to follow . . . for me.
I assume students will be capable of reading the text, performing quizzes provided, and plotting out a research path to complete their assignment(s).
Then again, as an academic I obsess over these issues. I can see a student yawning while reading this text.
The content isn't especially fun to read yet the information provided in relevant and time-saving if students are willing to relax, read actively, and apply the material to the assignment their instructor has given.
I don't imagine many students would seek the book out and read about research methods, yet an instructor can pair excerpts from the book with specific assignments along a student's research path to help the student retain and apply the helpful suggestions in the book.
The text does well to allow students to name the process they're going through when composing a research question then deciding on what research path fits their question. Students are guided to consider what blend of qualitative / quantitative, primary / secondary / tertiary, or public / professional / scholarly research will fit their research and writing goals.
The book refers back to the same terms throughout and provides students with active learning worksheets to plot a research AND writing plan to complete their work, one they could conceivably follow throughout their academic and professional career.
Each subheading contains, on average, not more than a page of content allowing instructors the ability to easily limit reading assignments from the book to concise, focused sections.
The book is very process-based, and follows the workflow necessary to write a successful academic researched assignment.
The limit of this strategy might be students being overwhelmed with so much discussion of process they'd be paralyzed to inaction.
An instructor, then, would have to be direct in assigning reading materials relevant to a student's immediate research goal.
I like how the text follows the path a student would follow: from narrowing a research question, selecting and reviewing research materials, then choosing how to implement them ethically in writing.
It also details how to process research considerations students may not consider including how to archive research results, to respect copyright law when publishing blog posts or submitting student work to an online repository.
The text contains many online activities, sample research artifacts, and instructional handouts. Some require on Ohio State student authentication. The text is still useful without access to these materials, though an instructor would have to alert students to this issue.
Text was proofread well.
Didn't see any culturally insensitive content.
Reviewed by Jonathan Grunert, Assistant Professor of Library Services: Information Literacy Coordinator, Colorado State University - Pueblo on 2/1/18
This textbook covers the concepts found in the ACRL frameworks in a way that is meaningful and accessible to academic researchers at all levels. It adequately provides a discussion of the complete research process, with clear signposts as to which... read more
This textbook covers the concepts found in the ACRL frameworks in a way that is meaningful and accessible to academic researchers at all levels. It adequately provides a discussion of the complete research process, with clear signposts as to which steps writers might need to revisit to improve their work.
The content appears to be accurate to 2016, with some acknowledgement that finding sources is an activity that has seen many changes in the past few decades, and will likely seem more, and rapidly.
Information discovery and retrieval is a rapidly changing process in a changing field. But much of the content in this textbook—as far as general advice and instruction for finding resources and the ways to use them—remains relevant. As information processes change and as information uses change, I have no doubt that librarians will be at the forefront of maintaining the relevance of a textbook like this one through various edition changes.
This textbook is clear, and accessible to researchers at all levels. Jargon, where present, is well-explained, and the contexts for the various components of the textbook are provided.
The text and frameworks in this book are consistent with ACRL frameworks as well as with the ways librarians tend to talk about finding and using sources. Furthermore, the book consistently uses the same terminologies to clearly explain sometimes difficult practices.
I would be very comfortable using any chapter of this book to teach a component of the academic research process. The chapters are discrete, with well-defined boundaries. The modularity of this textbook helps reinforce the overarching idea in this book: the iterative research process. Students might read the chapters in virtually any order, and come away with a valuable understanding of the research process.
This textbook presents the research process in the way that many students and faculty think about the process—from the perspective of the end goal, and through the organizational structure of an academic paper. But, it also indicates throughout the process places when the researcher needs to revisit an earlier step, to modify the project, or to make the end product more meaningful.
No issues in the interface; nothing distracting from the content.
Some minor punctuation errors, but no grammatical errors that distract from the content.
This textbook comes from an American perspective for ways of searching for, retrieving, and using information, as well as the traditionally American ways of constructing arguments. Though there is not discussion of other cultural ways of arguing academically, this textbook does not dismiss or otherwise denigrate other cultures; nor is it insensitive in any way.
Many examples are university-specific to the libraries at Ohio State University, as should be expected from a textbook such as this. As such, this book will be most helpful to students using the book at OSU. However, instructors using this book need to be aware of this focus, and must prepare to supplement with materials accessible by researchers outside OSU.
Reviewed by Susan Nunamaker, Lecturer, Clemson University on 2/1/18
This textbook is comprehensive. It goes in-depth covering the topics of research questions (specifically how to narrow down topics), types of sources, sources and information needs, precision searching, search tools, evaluating sources, ethical... read more
This textbook is comprehensive. It goes in-depth covering the topics of research questions (specifically how to narrow down topics), types of sources, sources and information needs, precision searching, search tools, evaluating sources, ethical use of sources, how to cite sources, making an argument, writing tips, copyright basics, fair use, and roles of resource sources. The textbook hits all of the topics that I plan to cover in my upcoming classroom-based research course with the exception of techniques for completing and writing a literature review. The textbook touches on the topic through a section on "background reading", but does not go in-depth. Otherwise, the textbook covers every aspect of academic research.
I found no errors or bias issues in my initial first read of the textbook.
The information and techniques provided within this textbook are up-to-date and relevant for academic research. I reviewed several textbooks before choosing this one for my upcoming masters-level classroom-based research course. I chose this book because of its relevance in regard to the practical skills needed in order to complete research assignments within the course, as well as, writing a capstone research paper.
This textbook is clear and exceptionally readable. It is organized by research skills in an order that makes sense to the reader. For example, the book begins with a chapter on choosing one's research question. Verbiage is clear and concise for all levels of academia to be able to effectively utilize this text.
This textbook is consistent in terms of terminology and framework. Each chapter of the textbook builds on the last. The reader is not necessarily expected to have prior knowledge of research before reading chapter one, but should easily be able to have a good frame of reference for academic research by the end of the textbook due to its high-quality framework for scaffolding knowledge with each chapter.
This textbook does a great job of sectioning academic research into small bites for the reader. It was easy for me to create modules from the textbook's chapters, spreading the information within the text over an 8-week course. The modularity of this textbook was a selling point for utilizing the textbook with students.
This is a well-organized textbook. Each chapter builds on prior chapters. Chapters are organized in a logical manner. The first chapter begins with the purpose of research questions and builds content to assist the reader in narrowing down options for research questions. The textbook progresses to assist the reader in building skills as an academic researcher throughout the textbook.
No interface issues were discovered during my initial exposure to the online format. I printed the PDF (because I still love paper) and all display features printed properly. The online navigation is easy to use and pleasing to the eye, as well.
No grammar issues were detected during my initial review of the textbook.
This text is not culturally insensitive or offensive in my opinion.
This is an excellent textbook if you are looking to utilize it to introduce students to the academic research and writing process. Its layout and design and conducive to module-based instruction, and the content is well thought out and beneficial.
Reviewed by Diane Kauppi, Library Faculty, Technical Services & Systems, Ruth A Myers Library at Fond du Lac Tribal & Community College on 2/1/18
The text did a great job of covering the subject and the table of contents were laid out well. The content was well thought out. read more
The text did a great job of covering the subject and the table of contents were laid out well. The content was well thought out.
I found the accuracy to be good. The content is a good representation of what a student needs to know in order better understanding library research.
The content itself is good & should stand the test of time for the near future. The only exception is that even though it's only one year from the publishing date (2016) many of the links are broken. And I would have preferred a OER text that was geared more generally for application to any institution vs. the inclusion of OSU specific references, links, resources.
For a text written to a 4-year university/college audience the text was good. For a 2-year community college audience some of the terminology would need to be defined.
I found the consistency to be good. It followed through each section with including tips, activities, etc.
I think the modularity was good. And the text could easily be broken down into smaller sections to be used as units by themselves or refresher units. The only issue would be where there are links within a module that link to other modules. Add to this that these links didn't work-- I rec'd errors each time I tried a module link.
The overall organization and flow as great. As stated on p 6 ("... as though you are conducting a research project while reading them [the sections]...") this made my logical side happy.
I like the links to activities for students to practice the skills being taught. The problem though was that many of the links no longer work. Additionally, many of the links are to areas not available to users who are not affiliated with OSU. And as mentioned in another review section, module links to other modules didn't work either.
I found the grammar to be quite good with only a few exceptions or where it was clunky at times.
I thought the text was neutral in this area. Nothing that blatantly jumped out at me.
I appreciated the link to application of research to other areas of our lives outside of academic research. I try to get this point across to students, especially when they are hesitant and resistant to library research. I found the "tips" & "summaries" to be a nice added 'pop' & easy for referring back to later. I liked the bold letters/words for emphasis. And the suggestion to "brush up" on p 31 was a nice touch vs outwardly assuming they don't know. The downloadable templates are a great resource for students. Overall, I found the text to be a good resource.
Reviewed by Kristine Roshau, Instructional Technology Specialist and PT Faculty Librarian, Central Oregon Community College on 8/15/17
This text is extensive! Like the title suggests, it truly is a full guide to academic research, from developing a topic, finding sources, and using them appropriately. It also follows the logical order of the search process, from identifying an... read more
This text is extensive! Like the title suggests, it truly is a full guide to academic research, from developing a topic, finding sources, and using them appropriately. It also follows the logical order of the search process, from identifying an information need, evaluating source quality (and purpose), and how to perform complex searches. It also highlights several common areas where academic research can be performed, from the college library catalog to specialized databases and how to find academic sources on the free web.
The book also covers what to do once sources have been found, including the importance of properly citing sources, ethical use of source material, and how to cite unusual or non-standard source material. It then moves into addressing the writing process: developing an argument and idea, writing tips, and a large section on copyright, fair use, creative commons, and public domain.
The table of contents is very granular, which is helpful. The sections vary in length, but given the overall size of the book (190 pages) having a very specific TOC is useful when returning to the text as a reference source.
I did not find any objectionable or questionable content. The authors have done a good job of selecting examples for each section (often with associated online activities or examples linked out to the web) that are varied and unbiased, but also represent realistic examples of what students might be encountering during their research process. I was really pleased when looking through the section on citing sources - styles can change, but the book is written in such a way as to be comprehensive about the purpose of citing sources, and links out to many helpful web sources, citation tools, etc so the information will remain accurate in the textbook even if the style guides themselves are updated in the future.
The section on copyright is similarly done.
See previous note - it is clear the authors have taken care to include examples that will remain relevant, not evaporate into popular culture, and provide flexibility where the content may be updated or changes (such as copyright law and citation style guides). They do provide a LOT of external links and activities, not all produced by Ohio State. So it's possible that some of their links may break in the future. It does appear that they have made an effort to either link to open sources they control, or which are unlike to change significantly (ie: government websites).
If I were using this text, I would probably modify some of the resource sections (eg: databases) to reflect those that the students at my institution have access to, though the writers do make a point of identifying OSU access-only resources where applicable. I would also update the copyright/plagiarism section to include our college's student handbook blurbs, etc.
The tone is extremely approachable in all of the areas I checked. This is extremely important in academic research where there are a lot of areas of possible legal entanglement, and the authors have done a credible job of breaking down complex concepts into approachable prose and examples.
The textbook is consistent in both writing and structure; however, I do with the table of contents was split into sections in the same way the content is. Page numbers are given though, so that's not really a big deal. There were one or two places where I saw formatting errors, but nothing overly distracting - it did not adversely effect the content.
It is visually appealing and for the most part, easy to navigate. No huge blocks of text, and it also intersperses activities, tips, and examples. The text is also organized in such a way that it can be used as a reference, without needing to be read from start to finish in order to make sense, which is helpful for the researcher who may need to pop in for just pieces of the work.
However, there is a strong presence of external sources (often OSU library webpages) and activities that are linked out of the text. The writing itself is certainly standalone, but the book would lose a lot of its character if it were printed and not viewed digitally. I would have liked a References or bibliographic section that listed some of these resources, but there wasn't one, meaning the user would not be able to search for the resource if the linked text didn't work.
I can see the potential for too many asides for activities to be distracting, but they are generally held to the end of their relevant sections, so it wasn't too overwhelming. The organization follows a logical research process, walking the reader through from beginning to end.
As mentioned before, there are a few places where it looks like images have distorted the intended formatting, pushing items to empty pages, etc. But these instances are rare. A few of the images could be higher resolution, but they were certainly legible (and I was viewing this text at 125% zoom on a larger screen, so my experience is probably not representative of every reader).
It is long though, and I would have loved to be able to jump to sections through anchor bookmarks in the content page - that would be a nice touch.
I also found a few broken links, which is not totally surprising, given the volume of them in this book.
None noticed in this review.
No objectionable content found - the authors have chosen inclusive examples wherever possible, while remaining realistic about subjects students might be researching.
Not all of the links to activities are self-describing (there are no plain URLs, but many of the activity links contain the same 'Open Activity in Web Browser' text, which would be confusing if a user was navigating with a screen reader.
Reviewed by Deborah Finkelstein, Adjunct Professor, George Mason University on 6/20/17
The book is very comprehensive. The authors consistently explain concepts well and provide easy-to-understand examples that are approachable for the undergraduate audience. For example, the authors don’t just say, “narrow down your source,” they... read more
The book is very comprehensive. The authors consistently explain concepts well and provide easy-to-understand examples that are approachable for the undergraduate audience. For example, the authors don’t just say, “narrow down your source,” they go through steps to narrow it down, walking students through the process. (p 9) Very thorough. They also spend a page and a half giving examples of “Regular Question” vs. “Research Question.” (p 13-14) This ensures that students will understand the difference. They also do well with explaining fact vs. option, objective vs. subjective, primary vs. secondary vs. tertiary sources, popular vs. professional vs. scholarly magazines, when to quote vs. paraphrase vs. summarize, and other concepts that are critical to performing research.
The book does not have an index. The table of contents is quite thorough and very useful in understanding the breakdown of the book or locating certain topics.
The book is error-free.
There are many digital examples in the text. As long as authors make updates as technology inevitably changes in the future, the book should remain relevant.
The book has a conversational tone that is connective, trustworthy, and approachable for the undergraduate audience. This makes it easy to read and easy to understand.
The book is very consistent with tone, and terminology.
In the introduction, the book encourages students to “jump around a bit in this guide to meet your needs.” (p 5). The book stays true to this idea. Students could read the book straight through, but it is well-designed for “jumping around.” The sections stand alone, and instructors could easily assign sections in the book out of order. This book could be used as the only textbook in a classroom, or an instructor could use these modules to supplement an existing textbook. Topics are easily found in the book thanks to an excellent table of contents, a clear organizational structure, and a great use of headers.
The book is well-organized and follows a logical structure. Individual topics are also well-organized. The authors break processes into step-by-step, making is easy for students to learn.
Great use of visual aids. For example, there is a chart on how to narrow down research topic (p 9), and a chart on the roles of resources in research (p 179). These items are great for visual learners, and they make the text come alive while emphasizing important concepts.
The book shares links to outside sources. This provides students that would like more information that is beyond the book with resources. It additionally provides students links to activities, such as one that asks them if a source is primary, secondary, or tertiary (p 34). On occasion, it links to outside companies, such as citation management software, news outlets, and social media, making the book a resource. In this way, the book utilizes the medium of a digital book.
The book is free of grammatical errors.
The book is culturally sensitive. The book is designed for Ohio University students. Examples given occasionally apply to Ohio, such as when the authors are providing examples of newspapers, they list two out of six that are from Ohio, including the campus newspaper (p 43) There is also a link to the OSU Libraries’ newspaper database (p 44), and when talking about citation management software, they mention the three that are available at OSU. It’s not a large enough issue that one should not use the book; it’s still easy to understand, but it is a limitation and worth mentioning to students.
I teach a 300-level English class on performing research and writing research papers. I plan to utilize this book next semester due to the excellent organization of modules, the approachable tone, and the great explanations and examples.
Reviewed by Constance Chemay, Head of Public Services, Library Services; Asst. Professor, User Instruction, River Parishes Community College, Gonzales, LA on 6/20/17
The book does an excellent job covering the subject, and even goes beyond what its title suggests, with chapters on writing and formulating an argument. The chapters on copyright and fair use are exceptional. However, it lacks both a glossary and... read more
The book does an excellent job covering the subject, and even goes beyond what its title suggests, with chapters on writing and formulating an argument. The chapters on copyright and fair use are exceptional. However, it lacks both a glossary and an index. Some terms are defined in their appropriate chapters, but not all. Some students, particularly first-year or those who may be enrolled in developmental courses, would benefit greatly from a glossary. The activities, while appropriate for their contexts, are mixed in their effectiveness; some provide good feedback with clarification, but most offer little more than a smiley face for a correct answer or an “x” for a wrong answer with no other feedback.
For the most part, this book is accurate and unbiased, but one area where I noticed discrepancies is the chapter on citing sources. MLA released its 8th edition in April 2016, yet the examples provided are 7th edition. I also noticed errors in the example for APA; only the first word, proper nouns, and those following major punctuation marks are to be capitalized in article titles following APA formating guidelines. Regarding bias, the book is unbiased; however, I disagree with the discussion of news sources regarding mainstream versus non-mainstream (or mainline as used in the text); main-stream media includes "traditional" sources, e.g., television, newspapers, and radio, as opposed to online sources, especially social media. The authors’ inclusion of Fox News, a right-leaning national television news network, a contemporary of CBS, NBC, and ABC, as non-mainline rather than mainline shows bias, in my opinion. It’s difficult to find news from any news source, mainstream or not, right, left or center, that doesn’t have some bias or opinions in its reporting.
This textbook itself is written so that it will be relevant for a long time. However, there are some exceptions. The discussion of citation styles uses examples for MLA that reflect the 7th edition rather than the 8th, which was released in April 2016. The book covers this discrepancy somewhat with its tip regarding choosing a citation style, with its remarks that styles do change and its recommendation to check with one’s instructors. Another issue is the potential for link rot regarding external websites; in fact there are a few dead links in the text and activities already. A couple of online resources mentioned and linked to, IPL2 and the Statistical Abstracts of the US, have been retired for at least a couple of years, which makes me wonder about when the book was actually last reviewed edited.
The book is well-written, easy to read, conversational. Most technical language is defined and used appropriately.
This book is consistent in terms of its terminology and framework.
This book is extremely modular in its organization at the chapter level and within the chapters. It can be easily reordered to meet specific course or instructor needs. It does refer to other sections of the text, but these references are appropriate, emphasizing more in-depth information elsewhere in the book. Sections that are unique to OSU can be replaced/revised to make the text relevant to other institutions as needed.
It is well organized and reflects the processes and stages of research. While the research process is not linear, the topics are presented in a logical manner that guides students through the process. I did note that a couple of sections in chapter 7, on ethical use of sources don’t really seem to fit there, however. The paragraphs on page 118 discussing a lack of understanding of the materials and lack of time might fit better in other chapters.
While the online version works well, the PDF format has issues. Some of the in-text navigation links work (the TOC links) while others found throughout the text don’t, often giving an “error: unknown export format” message. There are also a few dead links in both the online and PDF formats, as well as in some of the online activities. Some links direct users to OSU Libraries’ resources, either their catalog or their licensed databases, but not all such links are clearly identified as such.
Grammatical Errors rating: 3
For the most part, this text is well-written, grammatically; however, it does have a few grammatical/typographical errors, possibly more than one might expect from a text of this length, and assuming that the author is most likely a committee rather than an individual, more eyes reviewing the text should catch such errors. There are also instances of tense inconsistencies, shifting from present to past in the same sentence. Two paragraphs on page 47, under “Finding Data in Articles . . .,” repeat the same four sentences verbatim in different order. This occurs again on page 88. While these are not grammatical errors, they are certainly editorial errors. Most of the online activities have typos, as well, more so than the textbook.
This textbook is not culturally insensitive or offensive.
I do like this book. I think it puts the topic in terms that students can readily use and understand. I'd even recommend the chapters on copyright and fair use to faculty! I do think that it could benefit from the inclusion of a glossary and an index, as well as regular and frequent review, especially in regards to the linked resources. The PDF version definitely needs revisions since it seems that most of the in-text referral links throughout the text don’t work. Since it is tailored to OSU’s library resources, any instruction librarian using the book can substitute content relevant to his/her institution; non-library faculty using the text can consult their own librarians for help with this.
Reviewed by Dawn Kennedy, Ed.S, Health Education, Anoka-Ramsey Community College on 4/11/17
Choosing & Using Sources: A Guide to Academic Research serves as an excellent guide for teaching the research process. It takes the learner through the process of academic research and writing in an easy to understand manner. As an educator... read more
Choosing & Using Sources: A Guide to Academic Research serves as an excellent guide for teaching the research process. It takes the learner through the process of academic research and writing in an easy to understand manner. As an educator in a community college setting, I am working with students who are new to the research process. This text will be useful when working with students to start developing the appropriate process of research writing. The text has neither a back-of-the-book index nor a glossary. It is beneficial that key terms are defined throughout the chapters.
The information presented in the text is accurate at this point in time and unbiased. One concern is that some of The information presented in the text is accurate at this point in time and unbiased. One concern is that some of the links do not work.
Content is up-to-date at this point in time. Most examples and exercises are arranged separately from the main text and can be updated as needed. Some of the content links to the Ohio State University Libraries databases which may not be assessable to students outside that institution.
This text is clearly written, well-illustrated, and user-friendly for the undergraduate audience. It avoids technical jargon and provides definitions where appropriate.
Choosing & Using Sources: A Guide to Academic Research is consistent in terms of terminology and framework.
Regarding the book’s modularity, users of this text can be selective in chapter choice. In this sense the text is useful to instructors and students who wish to focus on a single component and /or use the text as a reference. For a better understanding of the research process in its entirety, reading the text in the order written may prove to be more beneficial.
The text's organization mirrors the research process in a logical, clear manner. Chapters 1-8 lead the reader through the basics of research literacy and research skills; chapters nine and ten explain the process for making an argument and writing tips; Subsequent chapters zero in on copyright and Fair Use information. Key concepts and points are supported with highlights, examples and colorful illustrations.
The text displays generous use of visuals which are clear and free of distortion. The activities provided support the concepts and skills being addressed and are easy to navigate. One concern is the activities which are linked to Ohio State University may not provide access to all, resulting in limited access of information and frustration for the reader.
• The text is not culturally insensitive or offensive in any way.
This is a text does an excellent job of explaining the research process in a logical manner. The text uses examples, illustrations, and skill practice to support the learning process. I recommend this text for use in it's entirely for teaching and learning the research process and as a resource for the rest of us.
Reviewed by Scott Miller, Reference and Instruction Librarian, Rogue Community College on 4/11/17
The book is very comprehensive and even goes beyond what might be expected in this kind of textbook. Along with choosing and using sources, the authors include a section on making an argument. Topics are dealt with appropriately and the text... read more
The book is very comprehensive and even goes beyond what might be expected in this kind of textbook. Along with choosing and using sources, the authors include a section on making an argument. Topics are dealt with appropriately and the text employs tests and activities along the way. I found some of the activities were not particularly well designed and sometimes answers to questions were based on assumptions by the authors as to context that in real life may or may not be appropriate. For instance, they claim that the periodical/journal title "Coral Reefs" is a scholarly journal, but judging by the title alone in a real life exercise there is no way to know whether it is scholarly or popular in nature.
There could have been more discussion about context and how it defines whether a sources is primary, secondary or tertiary. '
What the this textbook does not have is any kind of index or glossary, which I found disappointing.
I did not find any instances of inaccuracies in the text. I did find, however, some assumptions in the text that were not always warranted. I took issue with the assumption that mainline news sources are objective (p. 42). It is very clear that news articles are often biased. I think telling students that mainline news sources are objective effectively disarms instead of promotes critical thinking by students doing research.
On page 126 there is a discussion about using quotations where the authors say that all quotes are to be put within quotation marks. This is not true of block quotes in MLA or APA style and they omit any mention of it.
This textbook should retain its relevancy for several years, but it will lose its effectiveness very soon, since many of the dozens and dozens of links in the text will surely break before long. In the short term the links are a great feature, but they do severely limit the longevity of the book. I also found them annoyingly pervasive.
It should also be noted that the MLA citation example on page 122 uses the outdated MLA 7th edition guidelines.
Overall, I thought the book was very clearly written and easy to follow. The one section I struggled reading was the section on sources and information need. It seemed to want much more editing and was often wordy and almost obscure.
I did not notice any lack of consistency in terminology or framework.
This is one the book's strengths. It was clearly organized into topics and subtopics which sometimes could be addressed in an order chosen by an instructor. There were, however, occasional self-references to earlier sections or previously used external sources.
Moving from the simpler aspects of choosing and evaluating sources to the more complex uses of them and how arguments are constructed made good sense.
Interface rating: 2
I found the interface to have significant problems. At least a dozen links would not work from the PDF text when opened in Firefox. I often got the message, "error: unknown export format." The links seemed to work when viewing the text online, however.
The textbook's usefulness outside of Ohio State is severely limited by the frequent use of sources only available through OSU student logins. The textbook was written for OSU students, but it really fails as a textbook for any other institution unless it is significantly modified.
I found a few missing punctuation marks, and only two missing or wrong words in sentences. For a textbook this long, that's very good.
The textbook used interesting and non-offensive examples.
While it's a good textbook for choosing and using information sources it suffers from being too specifically written for OSU students, as well as including an overabundance of links that will reduce its longevity. Not including any kind of index or glossary is also a drawback.
Reviewed by Vanessa Ruccolo, Advanced Instructor of English, Virginia Tech on 2/8/17
Ch. 1 has a great overview of regular versus research questions and the difference between qualitative and quantitative research. Ch. 2 covers primary, secondary, and tertiary sources as well as popular, professional, and scholarly. Ch. 3... read more
Ch. 1 has a great overview of regular versus research questions and the difference between qualitative and quantitative research. Ch. 2 covers primary, secondary, and tertiary sources as well as popular, professional, and scholarly. Ch. 3 includes a source plan (i.e. what do you need the sources for and what is your plan). Ch. 4 gives tips and hints for searching on a library database. Ch. 5 gives different search options, like the library or Google Scholar. Ch. 6 is all about evaluating the sources you find, including clues about sussing out bias and thoroughness, as well as discussing currency of topic. Ch. 7 discusses why you should cite sources. Ch. 8 discusses ways to cite sources. Ch. 9 is looking at argument as dialog and what is necessary in that exchange and a recommended order of components. Ch. 10 covers quoting, paraphrasing,and summarizing and signal phrases. Ch. 11, 12 are copyright and fair use. Ch. 13 covers the roles or research.
I will use Ch. 1 and 2 in my classes, as I think the breakdown of research is useful and clear. Ch. 3 also has useful imbedded tools that will help students plan; Ch. 4 and 5 might be used as references post-library visit. I will also use Ch. 6 and Ch. 10.
I think the information provided for distinguishing scholarly, popular, and professional is helpful and I hope the resources help students understand good, reliable sources a bit better. The same is true for searching for sources, and I think the sections on search engines and evaluation of sources are going to be quite useful.
While the information on copyright, fair use, and why and ways to cite sources is fine, I won't be using these for my English classes as I find them not as helpful or relevant.
I think the book is quite accurate in terms of information provided. They use sources that both I and my students use, so clearly the book is addressing real needs in the classroom. It also makes suggestions that reinforce the concepts our librarians share with the students and instructors, so I find this to be extremely helpful.
The book suggests Purdue OWL, a source I also use; however, I realized this year that OWL was behind in updating some of the MLA citation changes. So that's something maybe for the book authors to note or address when recommending websites.
With that said, I think the book covers key specifics like university library websites, Google Scholar, and search engines, in broad enough terms to keep it relevant. Also, the graphics are simple and not dated, and there is one drawing of the "outernet" that shows what social media, Youtube, etc. would look like in the "real, outer" world. This drawing is the only thing I saw that might be dated soon, but its point is still solid.
Very easy to read, clear terminology and explanation of terms, and lists are also provided to help break up each page's prose, which means the information is presented in a visually clear form as well.
I think the consistency of terminology as well as the scaffolding makes sense on the whole. I didn't seem places where the language changed or seemed to have several writers or definitions.
Perhaps one of the best parts of this book is how each chapter is contained, succinct, includes an activity, but still builds on and with the other chapters. Each chapter is stand-alone and clear and easy to read online, or if you chose to print it. The creators clearly had the online reader in mind, however, and the chapter lengths and fonts are comfortable.
Overall, I like the organization, specifically for chapters 10-6. I would change the order of the final chapters so that Ch. 9 and 10 come before Ch. 7, 8, 11, 12. I would also move Ch. 13 "The Roles of Research" to earlier in the book, perhaps around Ch. 3 or Ch. 6. If I use these materials, I will reorder some of the chapters for my class so that the scaffolding and explanations work a bit more side by side.
Again, comfortable, easy-to-read pages, simple graphics and the charts used are helpful and appropriate. I especially appreciated that the authors didn't use images that showed people or figures that could both date the book and also make students feel talked down to - I hate images like this and refuse to use textbooks that incorporate them, so kudos!
Additional resources are easy to access.
I wish the email option (for sending yourself a page) pulled up a screen in which I could type the email I wanted it sent to. Instead, it pulls up Messenger, which I don't use.
The Table of Contents didn't let me jump to the chapter when I pulled down the menu. Was that just my computer/browser?
Now, I didn't read through as though I was grading (it is winter break, after all!) but nothing jumped off the page. If something had, if there had been a mistake, I would still use the text; if there had been several, I would have considered abandoning it for class. However, the information is still so good I i might have told my students to find the grammar mistakes as part of an assignment just so that I could use the research parts still; however, I didn't not see any.
No, nothing. Perhaps if the authors include more examples for citations they could pull from culturally different sources then, but the material here was so broad in terms of textual sources it was in no way exclusive.
I will be using parts of this book in my English classes. Well done to the authors - a helpful, free supplement.
Reviewed by Dale Jenkins, Advanced Instructor, Virginia Polytechnic Institute & State University (Virginia Tech) on 2/8/17
Having taught freshmen how to write college research papers for the past 18 years, I gave the text high marks on addressing all of the key elements college students need to engage in academic research. read more
Having taught freshmen how to write college research papers for the past 18 years, I gave the text high marks on addressing all of the key elements college students need to engage in academic research.
The text implements content from a host of sources which is extremely useful, but the grammar needs a few tweaks.
This represents a strong aspect of the text. The writers did a good job of winnowing out unnecessary components of the research process, although my freshmen would not delve into the Fair Use and Copyright chapters.
The book gets outstanding marks on clarity. Students will find this to be a definite strength of the text.
The authors did a good job with consistency. I kept my students in mind as I evaluated this aspect of the text.
Students would find this book extremely accessible in terms of modularity. I don't see them being overwhelmed by the text or high-brow jargon.
I noted a logical progression to all thirteen of the chapters. Students in upper-level classes would find the chapters on Fair Use and Copyright more significant in their academic studies.
The hyperlinks and the interactive elements of the book will be extremely appealing to students as well as being substantive.
The book still needs some work in this regard. Pronouns don't always agree with the antecedents, and I noted several shifts in voice in the text.
The text doesn't have any instances of cultural insensitivity, and I pay close attention to this aspect of textbooks when I peruse them for potential use in my courses.
The hyperlinks, using different types of media, and the chapters on "Why Precision Searching?" and the discussion of plagiarism proved to be well-crafted and accessible for students. I also commend the authors for the lack of jargon that would leave students in its wake.
Reviewed by Jarrod Dunham, Instructor - English Composition, Portland Community College on 2/8/17
A very comprehensive guide to the writing of the research paper. I've taught research writing for several years, and this book covers all the material I'd typically cover in a class. Previously I've not used a textbook in that class, but I'm... read more
A very comprehensive guide to the writing of the research paper. I've taught research writing for several years, and this book covers all the material I'd typically cover in a class. Previously I've not used a textbook in that class, but I'm teaching an online section this term and find that the book offers a very effective substitute for the lectured and activities I'd otherwise be presenting in class.
This text is accurate and up-to-date with the most recent developments and issues in the field.
This text is very much up-to-date. It shows an awareness of changing conventions in academic writing, and emphasizes the latest technological tools for researching and managing citations. It frequently links to outside resources, which could be problematic in the event those resources were removed or relocated, but in practice I never encountered such an issue.
Clarity is one of the book's strengths. It is written in clear, simple, and concise prose, resisting the kind of "academese" that is frequently employed in textbooks and gives students a false impression of what academic writing should look like. I found all of the content very easy to understand, and, although it's intended for slightly more advanced classes, accessible for Freshman writing students.
The text is highly consistent, both in terms of the terminology it employs, its organizational structure, and its systematic incorporation of tips, learning activities, and quizzes.
The book is divided into 13 chapters, each of which addresses particular aspects of research writing and can be employed on its own, or in conjunction with other related chapters. I found that assigning chapters in order was generally perfectly appropriate, although there was no issue with assigning the odd chapter out of order - links to previous or later content are provided where appropriate, so students can easily navigate to other relevant sections of the text.
This text is very nicely organized. It moves from the beginning stages of the pre-writing process - choosing a topic and identifying appropriate guiding questions - through the research to the writing of the paper itself. I found that the organizational structure of the text very closely mirrored the structure I use myself in teaching research writing. As such, adopting this text for the course (and adapting the course to the text) was a delightfully straightforward exercise.
The interface of the text is excellent. It is very easy to navigate, very attractive, and all tools work as intended. Some features are only available to those with Ohio State University log-ins, which yields a handful of frustrating moments, but in general I didn't find this to be a significant issue.
The text is error free and written in a simple, accessible, and engaging style. It's not merely an easy read, but one that effectively models clear and concise academic prose for writing students.
To the extent such issues come into play, the text is inclusive and culturally sensitive. The content of the text is mostly neutral on such issues - they simply tend not to come into play - but I was pleased to find a comprehensive chapter on the ethical use of sources, which introduces an ethical dimension to the research and writing process that many students may not anticipate or otherwise be prepared to navigate.
Overall I was quite pleased with this text. In my online section of Research Paper Writing, I have assigned nine of the thirteen chapters, and am very pleased with the breadth of content covered thereby. With one exception, I've been able to assign those chapters in the order they appear in the book, which simplified the planning process for myself, and offers a structure to the course that will be more readily apparent to my students as well. Late chapters on Copyrights Basics and Fair Use struck me as unnecessary and a little off topic, but it is of course easy to simply not assign those chapters, and since this is not a print book they have no bearing on materials costs.
For an online class like the one I am currently teaching, this is an excellent primary text. Even in a face-to-face class it could prove to be a very useful supplemental text. Normally I resist the use of supplemental texts in face-to-face classes, but since this one is free it is ideal for that purpose: instructors and students can simply rely on it to whatever extent feels useful.
Reviewed by Jennifer Lantrip, Reference Librarian, Umpqua Community College on 2/8/17
This book is an excellent source for guiding undergraduate students through the research process, from understanding the purposes for doing research and writing a research question, to composing a thesis and contributing to a scholarly... read more
This book is an excellent source for guiding undergraduate students through the research process, from understanding the purposes for doing research and writing a research question, to composing a thesis and contributing to a scholarly conversation. Students learn where and how to find relevant sources and how to evaluate and use them ethically. The main text is supplemented with links to useful resources, videos, worksheets, examples, and exercises. These are all high quality sources, making this a comprehensive resource for teaching information literacy and the research process. While no index or glossary is provided, terms are well defined within the text. Links are provided to other sections within the text where terms are further discussed.
The content is error-free, unbiased, and accurate. Ideas and concepts are in accordance with the Association of College and Research Libraries’ “Framework for Information Literacy for Higher Education,” with the exception of several small sections that could easily be clarified or adapted.
The opening section of Chapter 3 states that researchers should find sources in order to meet their information needs. However, it states that one information need is “to convince your audience that your answer is correct or, at least, the most reasonable answer.” This should be clarified for students so that they understand that they should start their research with an open mind as opposed to looking for sources which support their predetermined thesis.
The section “The Sources to Meet Needs” in Chapter 3 states that convincing one’s audience is an information need and that students should find sources based upon what their audience would be convinced by. Researchers should not choose their sources based upon what would convince their audience, but rather upon what sources best answer their research question. The most relevant and highest quality sources should not be omitted from the research process because the researcher does not think that his/her audience would be convinced by them. It is part of the researcher’s job to educate and convince his/her audience why the chosen sources and the research are relevant and of high quality.
Chapter 13 mentions briefly, “Putting your sources to work for you in these roles can help you write in a more powerful, persuasive way—to, in fact, win your argument.” It is very important for researchers to make convincing arguments through using quality sources, doing quality research, and presenting the information in an understandable way. Students should understand that the goal of scholarly conversation is not to “win” arguments, but rather to contribute to the world’s shared knowledge. While one argument may hold for a time, it will most likely be refined in some way by future researchers.
The main content of each chapter is current and does not contain terms that will soon be outdated. Specific examples and exercises are arranged separately from the main chapter text and can be updated independently. Some of the content discusses and links to Ohio State University Libraries databases which are unavailable to students at other institutions. While some of this knowledge is transferable, the specific information about these databases is unique to OSU Libraries. It would be useful if this information could be generalized in the main flow of the text so that it would be applicable for students at other institutions.
This text is very readable and easy to understand. Concepts are explained clearly. Exercises and examples are provided to help students grasp each new concept. It is written in a casual tone that appears to make an effort to put its readers at ease while giving solid information about how to complete research and writing assignments successfully.
The terminology used in this book and its framework are consistent. Each chapter, chapter sections, examples, and exercises are organized in a consistent manner throughout the book, making it easy to follow. Students can refer to specific sections of the book or read it straight through. Because links are provided to sections of the book where important terms are defined or discussed further, students can easily jump to relevant sections of the book.
The book is divided into chapters and subsections which lead the reader seamlessly and logically through the research process. The book could easily be assigned to be read linearly, but it would also work well for instructors to assign specific chapters as applicable to the course content.
This book takes students through the research process in logical steps, from choosing and refining research questions, to producing and sharing what they have learned. For students who are unfamiliar with the research process, it would be most useful to read the book linearly as each chapter prepares students for future chapters.
This text is easy to navigate in both the PDF and online versions. Images are clear. There are currently no broken links. The contents in the PDF version could be made clearer by making a greater distinction between the main chapter and chapter section titles.
The text has negligible grammatical errors.
This text is not culturally insensitive or offensive.
I highly recommend this book for teaching information literacy and the research process to undergraduates.
Reviewed by Patricia Akhimie, Asst. Prof of English, Rutgers University-Newark on 2/8/17
This textbook does not include an index or glossary but is full-text searchable, returning a an easy to read and access menu of clickable search results to take readers directly to the desired information. In addition, an expandable Table of... read more
This textbook does not include an index or glossary but is full-text searchable, returning a an easy to read and access menu of clickable search results to take readers directly to the desired information. In addition, an expandable Table of Contents for the book is available as a tab so that readers can view an overview of topics and jump to other sections at any time. This textbook offers a review of research methods that is certainly comprehensive. Instructors will likely find that individual sections, rather than the whole work, are most useful in planning lessons and constructing student assignments in research based and writing intensive courses at the undergraduate level.
This textbook is accurate in its representation of research methods and of the reasoning behind these approaches. In addition, details about citation styles, and search tools, seem error-free. Treatments of the more complex aspects of research, such as constructing an argument, are unbiased and thorough.
The textbook should be useful to students and instructors for some time. It should be noted, however, that research software and citation styles are updated, though infrequently. Thus, the video walkthroughs of particular databases, for example, may be obsolete or misleading after some time.
This textbook is remarkably lucid and approachable for undergraduate readers. Discussions of complex ideas are illustrated with useful graphics that readers and instructors will find particularly helpful. The video walkthroughs are perhaps the most attractive illustrations for instructors. These guides will be appealing and easy to use for students intimidated by large databases and their idiosyncrasies.
The textbook is immanently usable. It is consistent in its tone as well as in its use of terms.
It is clear that this textbook has been designed with modularity in mind. Individual sections will be more useful than others, depending on the type and level of the class. In addition, sections can easily be assigned at different points over the course of a semester. For example, sections might be assigned at intervals that reflect the stages of the development of undergraduate student’s independent research paper. The section on formulating research questions might appear early in the semester, the section on citation styles toward the end.
The organization of the book reflects the stages of research. This means that navigating the textbook will be intuitive.
Navigating this textbook will be intuitive, the Table of Contents tab makes moving between sections very easy.
Readers will find the textbook free of simple typos and errors.
Readers will find the textbook inclusive. Some readers may find that the attempt made in the textbook to speak to research in the humanities, social sciences and sciences has meant that discussions can be vague at times but this is to be expected in a textbook on this topic aimed at a broad range of readers and researchers.
Reviewed by Heather Jerónimo, Assistant Professor, University of Northern Iowa on 2/8/17
This text is a comprehensive review of the various types of sources one might need to complete a research project or paper. The book begins with a clear explanation of how to formulate a research question, while the majority of the chapters focus... read more
This text is a comprehensive review of the various types of sources one might need to complete a research project or paper. The book begins with a clear explanation of how to formulate a research question, while the majority of the chapters focus on finding and evaluating sources. The topics in this text are well-chosen and reflect several aspects of academic writing in which beginning researchers might struggle, such as how to do a precision search, understanding biased versus unbiased sources, and how to decide between quoting or paraphrasing. This book is written at a level that undergraduates should easily be able to comprehend, while the content of the chapters gets increasingly detailed and complex throughout the book. There is no index or glossary at the back of the book, but there is a very complete table of contents at the beginning of the text. Readers might find it useful if the chapter titles in the table of contents were in bold, as the detailed breakdown of sections—while helpful—can be overwhelming when one is looking for the main categories of the book.
The text provides helpful and unbiased examples for how to do research in many different areas. The practice activities relate quite well to the content of the chapters, although some links do not work. One of the strengths of the text is its applicability in a general sense to many different types of research.
In most chapters the information is kept very general, allowing the text to enjoy relative longevity, as the process of how to conduct academic research, cite quotes, etc., likely will not change drastically in the near future. For example, in the section on databases, different types of databases are explained, but the author does not reference many specific databases to which students may or may not have access. With an understanding of the concept, students then are equipped to find the databases that pertain to their field and that are offered by their institutions. There are several references to Ohio State throughout the text that will not be helpful to all readers, but they do not impede the reader’s comprehension of the text.
It is a very readable text, written at a level that makes it easily accessible to undergraduate students. The author has avoided jargon that would be confusing to the readers.
Even though the book gives examples of various types of research and sources, it maintains a high level of consistency throughout.
The chapters are clearly divided in a way that allows the reader the option to skip between chapters or to read the chapters in succession. This text could be put to a variety of uses within the classroom. As an instructor, one could use it as a primary text for a Research Methods or Composition class. One could also suggest that students read only certain sections in a class that was not primarily focused on the writing of research papers but that had a research component. This text is a valuable how-to manual that students can reference throughout their academic journey.
The text has a logical organization and flow. The book transitions from more basic information at the beginning to more specialized knowledge in later chapters, allowing students to gradually become more immersed in the topic. The structure permits students to read the text from cover to cover, or to read only the information and chapters about which they are curious. The activities serve as good checkpoints to assess students’ knowledge and break up longer readings.
The interface of the text is easy to manage and does not distract from the content. The placement and accessibility of the activities provide quick and easy checks to assess whether students have understood the concepts of the chapters. The images support the text and are linked closely to the message.
There are few grammatical errors in this text.
The text is not culturally insensitive or offensive. Like many textbooks, it could be more intentional in its inclusion of a variety of races, ethnicities, and backgrounds, perhaps in the examples or practice activities.
Reviewed by Dr. William Vann, Information Studies Faculty, Minneapolis Community and Technical College on 12/5/16
While there is neither a back-of-the-book index nor a compiled glossary in this outstanding textbook (key terms are defined, however, throughout the chapters), one cannot deny its comprehensiveness. In fact, this text covers so much ground it is... read more
While there is neither a back-of-the-book index nor a compiled glossary in this outstanding textbook (key terms are defined, however, throughout the chapters), one cannot deny its comprehensiveness. In fact, this text covers so much ground it is unlikely to be used in its entirety for any single college course. Information literacy and research skills courses will find the first eight chapters to be a robust introduction to their subject matter, replete with interactive activities and auto-graded assessments. Composition courses engaged in research-based writing will likely work through the first eight chapters selectively, but then dwell on chapters nine and ten on argument formation and writing. Such courses may also benefit from the excellent chapter thirteen on Joseph Bizup's BEAM method of deploying research sources in scholarly communication. Chapters eleven and twelve on copyright and fair use, respectively, are likely to be used only by advanced undergraduates, faculty, and professional librarians, but they do serve as a handy reference nonetheless.
All of the chapters of this textbook contain authoritative and accurate information, in line with national information literacy standards and sound pedagogical methods for composition and critical thinking. The only section of the text I took issue with was the "Fact or Opinion" part of the second chapter, where the authors try to distinguish between fact, opinion, subjective information, and objective information. The authors' attempt results in claims like "the death penalty is wrong" being rendered as opinions, while claims like "women should stock up on calcium to ensure strong bones" are judged to be subjective information. Facts and objective information are superior, on this way of thinking, because they are the result of research studies, particularly empirical, quantitative ones.
I suspect that this way of drawing the distinction would do little to challenge the naive relativism most undergraduates bring to the classroom. (How many of us, when analyzing a text with beginning undergraduates, have had to entertain the question "Isn't that just the author's opinion though?") A better approach would be to talk about claims that are empirically justified (facts), claims that are justified, but not empirically (value judgments - "x is wrong", prescriptive claims - "women should do x"), and claims that are not adequately justified by any means (opinions). In this way, answering a research question like "Is the death penalty unjust?" is not merely an exercise in subjective opinion-making, but rather an exploration of reasoned argumentation, only some of which may be empirical or based on research studies.
The text is current and will likely be so for some time. Examples, activities, and tips are marked off from the main chapter prose, so will be easy to refresh when necessary.
There is no lack of technical terms in the world of information studies, but this textbook does a fine job of providing definitions where appropriate in each chapter. Concepts and methods are explained in context, and illustrative, easy-to-follow examples adorn each chapter.
The only area of the text that falls a little short on clarity is the interactive activities. These are usually multiple choice or matching questions, but some of the word choice in questions left this reader confused, and in some cases the instructions could have been more explicit.
Being authored by committee, we might expect this textbook to suffer in the consistency category. Yet it does not, thanks again to the fine editing job by Cheryl Lowry. Perhaps the book's provenance as a series of online tutorials put together by librarians and faculty at OSU is partly responsible for this.
As the authors suggest on the first page, the research process isn't always linear. So reading a text modeled on the research process oughtn't to be a straightforward chapter-by-chapter march either. Consequently, faculty and students can comfortably read this text selectively and skip chapters as needed. For the most holistic understanding of the research process, however, it would be sensible to work through at least chapters one through eight in their entirety.
I appreciate how the text's organization mirrors the research process itself. The first chapter takes on research questions, exactly where student researchers need to begin their projects. Subsequent chapters explore types of information sources, how to find and evaluate them, and finally how to deploy them in a well-argued scholarly product. The writing in each chapter is clear and crisp, with important concepts amplified by colorful visualizations.
As mentioned above, the chapters on copyright and fair use which occur near the end of the book feel like a logical interruption to the book's flow, and they might well fit more comfortably as appendices for occasional reference by advanced undergraduates, faculty, and librarians.
The "look and feel" of this textbook is clean and very intuitive to navigate through. The design strikes a pleasing balance between prose, graphics, and special formatting features like the explanatory, grey-background "TIPS" found in each chapter. Subheadings, bulleted and ordered lists, and judicious font choices make the text easy to read in all its online file formats.
One weakness of the interface is that several of the linked activities point to OSU Libraries' resources, thus requiring OSU authentication to be accessed. While it is understandable that the authors wanted to include their libraries' proprietary information sources in the activities - these are the sources their students and faculty will be using in actual practice, after all - this obviously makes this text less of an "open" textbook. Those outside of the OSU community who would like to adopt this textbook will therefore have to come up with their own replacement activities in such cases, or do without.
A few of the links in the text did lead me to a curious OSU server error message: "Error: Unknown export format", but I expect these links will be repaired as they are reported to the authors.
This textbook has clearly been edited with careful eyes by Cheryl Lowry, as grammatical errors are few to none. The grammatical hygiene of the text can probably also be attributed to its collective authorship - over a dozen librarians and faculty of the Ohio State University Libraries developed the content, which was born out of a series of online tutorials.
This textbook is culturally relevant in its use of examples and depictions of college students.
This text is a substantial contribution to the open textbook movement, and its quality easily meets or exceeds anything comparable in the commercial publishing arena. Highly recommended.
Reviewed by Kelly McKenna, Assistant Professor, Colorado State University on 12/5/16
The book provides a thorough introduction and how to regarding sources in academic writing. With the exception of the first chapter on writing research questions, the rest of the book is focused on sources, which is relevant for any type of... read more
The book provides a thorough introduction and how to regarding sources in academic writing. With the exception of the first chapter on writing research questions, the rest of the book is focused on sources, which is relevant for any type of academic writing not just research papers. The information is relevant across disciplines and readable to a wide audience. It is clearly written for and geared towards undergraduate students, particularly from Ohio State University. The index is detailed making it easy to locate specific information and includes hyperlinks for clear navigation. A slightly altered index format would make the chapter topics more readily available and accessed. All subjects and chapters are aligned rather than clearly indicating each of the chapters found within the text.
Content throughout the book is accurate and clearly written. There does not appear to bias in reading the material. The book includes numerous resources linked throughout the text, however some are no longer active resulting in error messages.
Due to the significant number of links throughout the book, it is likely updates will be necessary on a consistent basis. These links are extremely beneficial, so ensuring they are accurate and up to date is essential to the content of this book. Much of the book reads as a "how to" regarding sources, so although practices for scholarly writing will likely not become obsolete the sources and technology used to locate the sources will evolve.
The informal tone of the text is engaging and applicable for the intended audience. The writers are aware of their audience, avoiding technical jargon. Also, throughout the book they provide numerous examples, resources, activities, and tips to provide insight and relevancy to students.
The structure of the book is clear and well organized with each chapter providing scaffolding for the next. Although the text is internally consistent regarding terminology there are formatting differences between and within some chapters. Blue boxes throughout the text contain tips, examples, answers, etc. Organization, readability, and consistency could be improved if these were constant throughout the text similar to the presentation of activities in the text.
Sections of the book could be easily assigned and read in isolation. Subsections of material are clearly marked and chapters are presented in organized fashion with clear delineation between segments. The inclusion of numerous activities, examples, resources, and tips improve modularity.
The book is created as a tool for students completing academic writing and follows this course. Topics contained in the book are presented in a clear and logical structure. As mentioned above, with exception of the first chapter, the material is relevant to all undergraduate academic writing, not just research.
The layout and display work well as a PDF or electronic book. Numerous visuals are included throughout and are free of distortion or other distracting or confusing issues. As mentioned above, the index could be improved by clearly articulating the subheadings as within a chapter.
The book contains minimal to no grammatical errors.
The book is not culturally insensitive or offensive in any way.
Some sections of the book are specific to Ohio State University potentially limiting its relevancy and audience in specific chapters or sections.
Table of Contents
- 1. Research Questions
- 2. Types of Sources
- 3. Sources and Information Needs
- 4. Precision Searching
- 5. Search Tools
- 6. Evaluating Sources
- 7. Ethical Use of Sources
- 8. How to Cite Sources
- 9. Making an Argument
- 10. Writing Tips
- 11. Copyright Basics
- 12. Fair Use
- 13. Roles of Research Sources
Ancillary Material
About the book.
Choosing & Using Sources presents a process for academic research and writing, from formulating your research question to selecting good information and using it effectively in your research assignments. Additional chapters cover understanding types of sources, searching for information, and avoiding plagiarism. Each chapter includes self-quizzes and activities to reinforce core concepts and help you apply them. There are also appendices for quick reference on search tools, copyright basics, and fair use.
What experts are saying about Choosing & Using Sources: A Guide to Academic Research :
“…a really fantastic contribution that offers a much needed broadened perspective on the process of research, and is packed to the brim with all kinds of resources and advice on how to effectively use them. The chapter on plagiarism is really excellent, and the chapter on searching for sources is utterly brilliant.”
– Chris Manion, PhD Coordinator of Writing Across the Curriculum at Ohio State University
“… an excellent resource for students, with engaging content, graphics, and examples—very compelling. The coverage of copyright is outstanding.”
– J. Craig Gibson Co-chair of ACRL's Task Force on Information Literacy Competency Standards for Higher Education
About the Contributors
Cheryl Lowry , training and education specialist, Ohio State University Libraries.
Contribute to this Page
- UConn Library
- Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide
- Strategies to Find Sources
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide — Strategies to Find Sources
- Getting Started
- Introduction
- How to Pick a Topic
- Evaluating Sources & Lit. Reviews
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
The Research Process
![finding research materials Interative Litearture Review Research Process image (Planning, Searching, Organizing, Analyzing and Writing [repeat at necessary]](https://libapps.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/64450/images/ResearchProcess.jpg)
Planning : Before searching for articles or books, brainstorm to develop keywords that better describe your research question.
Searching : While searching, take note of what other keywords are used to describe your topic, and use them to conduct additional searches
♠ Most articles include a keyword section
♠ Key concepts may change names throughout time so make sure to check for variations
Organizing : Start organizing your results by categories/key concepts or any organizing principle that make sense for you . This will help you later when you are ready to analyze your findings
Analyzing : While reading, start making notes of key concepts and commonalities and disagreement among the research articles you find.
♠ Create a spreadsheet to record what articles you are finding useful and why.
♠ Create fields to write summaries of articles or quotes for future citing and paraphrasing .
Writing : Synthesize your findings. Use your own voice to explain to your readers what you learned about the literature on your topic. What are its weaknesses and strengths? What is missing or ignored?
Repeat : At any given time of the process, you can go back to a previous step as necessary.
Advanced Searching
All databases have Help pages that explain the best way to search their product. When doing literature reviews, you will want to take advantage of these features since they can facilitate not only finding the articles that you really need but also controlling the number of results and how relevant they are for your search. The most common features available in the advanced search option of databases and library online catalogs are:
- Boolean Searching (AND, OR, NOT): Allows you to connect search terms in a way that can either limit or expand your search results
- Proximity Searching (N/# or W/#): Allows you to search for two or more words that occur within a specified number of words (or fewer) of each other in the database
- Limiters/Filters : These are options that let you control what type of document you want to search: article type, date, language, publication, etc.
- Question mark (?) or a pound sign (#) for wildcard: Used for retrieving alternate spellings of a word: colo?r will retrieve both the American spelling "color" as well as the British spelling "colour."
- Asterisk (*) for truncation: Used for retrieving multiple forms of a word: comput* retrieves computer, computers, computing, etc.
Want to keep track of updates to your searches? Create an account in the database to receive an alert when a new article is published that meets your search parameters!
- EBSCOhost Advanced Search Tutorial Tips for searching a platform that hosts many library databases
- Library's General Search Tips Check the Search tips to better used our library catalog and articles search system
- ProQuest Database Search Tips Tips for searching another platform that hosts library databases
There is no magic number regarding how many sources you are going to need for your literature review; it all depends on the topic and what type of the literature review you are doing:
► Are you working on an emerging topic? You are not likely to find many sources, which is good because you are trying to prove that this is a topic that needs more research. But, it is not enough to say that you found few or no articles on your topic in your field. You need to look broadly to other disciplines (also known as triangulation ) to see if your research topic has been studied from other perspectives as a way to validate the uniqueness of your research question.
► Are you working on something that has been studied extensively? Then you are going to find many sources and you will want to limit how far back you want to look. Use limiters to eliminate research that may be dated and opt to search for resources published within the last 5-10 years.
- << Previous: How to Pick a Topic
- Next: Evaluating Sources & Lit. Reviews >>
- Last Updated: Sep 21, 2022 2:16 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/literaturereview
13.1 The Research Process: Where to Look for Existing Sources
Learning outcomes.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Locate and evaluate primary and secondary research materials, including journal articles and essays, books, scholarly and professionally established and maintained databases or archives, and informal electronic networks and Internet sources.
- Apply methods and technologies commonly used for research in various fields.
Once you have chosen your argumentative research topic, developed a workable research question, and devised a plan for your research as described in Argumentative Research: Enhancing the Art of Rhetoric with Evidence , you are ready to begin the task usually associated with the term research —namely, the collection of sources. One key point to remember at this stage is intentionality; that is, begin with a research plan rather than a collection of everything you find related to your topic. Without a plan, you easily may end up overwhelmed by too many unusable sources. A carefully considered research plan will save you time and energy and help make your search for sources more productive. Access to information is generally not a problem; the problem is knowing where to find the information you need and how to distinguish among types and qualities of sources. In short, finding sources is all about sorting, selecting, and evaluating.
Your specific methods for collecting sources will depend on the details of your research project. However, a good strategy to begin with is to think in terms of needs: What do you need, as the researcher and writer? What do your readers need? This kind of needs assessment is similar to the considerations you make about the rhetorical situation when writing an analysis or argument.
Review Table 13.1 as you conduct a source “needs assessment.”
Generating Key Words
Before you begin locating sources, consider the research terms you will use to find these sources. Most research is categorized according to key terms that are important for understanding the topic and/or methodologies. When beginning the research process, you may find that the ideas or words associated with your topic are not yielding results when you search library or Internet databases (organized collections of information).
If you are running into challenges locating information related to your topic, you may not have chosen the specific key terms needed. Because libraries and online databases generate search results based on algorithms that target keywords, the best way to find the appropriate terminology associated with your topic is to practice generating key terms. You may need a range of keywords, some for library searches and others for online searches. When considering the difference between keyword searches in academic libraries versus online sources, note that most academic libraries use Library of Congress Subject Headings (LCSH) for subject searches of their online catalogs. Many databases use subject searches based on algorithms that may be unique to that database. Don’t become discouraged if you find that the terms for searching in your academic library may be somewhat different from the terms for searching online. As you begin to find sources related to your subject, take notes on the variety of terms that describe your research area. These notes will come in handy as both keyword and subject searches throughout your research process.
The following steps and examples will help you get started:
- Begin by limiting your topic to one or two sentences or questions. ( What effects do a region’s water and temperatures have on fall foliage? )
- Highlight specific words that are key to understanding or finding answers to your question. ( What effects do the amount of water a region gets and temperatures for that region have on colors of fall foliage? )
- Consider words assumed but not mentioned in your question. For instance, the example question implies a search around trees and rainfall; however, trees and rainfall are not mentioned. Add these words to the words highlighted in your question.
- Consider synonyms for the words you highlighted. A search for synonyms for fall yields harvest , autumn , and autumnal equinox . A search for synonyms for leaves yields foliage , fronds , and stalks . Be sure you understand the meaning of each synonym so that you can choose those that best capture the concepts you seek to research.
- Try different combinations of the key terms and synonyms to help you find as many sources as you can.
You can find more information about key terms and searches by consulting Writing Process: Informing and Analyzing .
Locating Sources
Once you have identified sources to fit both your and your readers’ needs, you can begin to locate these sources. Throughout the research process, look for sources that will provide enough information for you to form your own opinions or answer your research question(s). Use source materials as support for your own words and ideas. The following are possible locations for source materials:
While much of your writing and research work happens online, libraries remain indispensable to research. Your university’s physical and/or online library is a valuable resource, providing access to databases, books and periodicals (both print and electronic), and other media that might not otherwise be accessible. In many cases, experienced people are available with discipline-specific research advice. To take full advantage of library resources, keep the following suggestions in mind:
- Visit early and often. As soon as you receive a research assignment, visit the library (physically, virtually, or both) to discover resources available for your project. Even if your initial research indicates a wealth of material, you may be unable to find everything during your first search. You may find that a book has been checked out or that your library doesn’t subscribe to a certain periodical. Furthermore, going to the library can be extremely helpful because you likely will see a range of additional sources simply by looking around the areas in which you locate initial sources.
- Check general sources first. Look at dictionaries, encyclopedias, atlases, and yearbooks for background information about your topic. An hour spent with these sources will give you a quick overview of the scope of your topic and lead you to more specific information.
- Talk to librarians. At first, you might show a librarian your assignment and explain your topic and research plans. Later, you might ask for help in finding a particular source or finding out whether the library has additional sources you have not checked yet. Librarians are professional information experts; don’t hesitate to use their expertise.
General Reference Works
General reference works provide background information and basic facts about a topic. To locate these sources, you will need a variety of tools, including the online catalog and databases, as well as periodical indexes. To use these resources effectively, follow this four-step process:
- Consult general reference works to gain background information and basic facts.
- Consult specialized reference works to find relevant articles on all topics.
- Consult the library’s online catalog to identify library books on your topic.
- Consult other sources as needed.
The summaries, overviews, and definitions in general reference works can help you decide whether to pursue a topic further and where to turn next for information. Because the information in these sources is necessarily general, they will not be sufficient alone as the basis for most research projects and are not strong sources to cite in research papers.
Following are some of the most useful general reference works to provide context and background information for research projects:
- Almanacs and yearbooks provide up-to-date information, including statistics on politics, agriculture, economics, and population. See especially the Facts on File World News Digest (1940–present), an index to current events reprinted in newspapers worldwide, and the World Almanac and Book of Facts (1868–present), which reviews important events of the past year as well as data on a wide variety of topics, including sports, government, science, business, and education. In addition to current publications, almanacs from recent years or from many years ago provide information about the times in which they were written.
- Atlases such as the Hammond World Atlas , the National Geographic Atlas of the World , and the Times Atlas of the World can help you identify places anywhere in the world and provide information on population, climate, and industry.
- Biographical dictionaries contain information about people who have made some mark on history in many different fields. Consult the following: Contemporary Authors (I962–present), containing short biographies of authors who have published during the year; Current Biography (1940–present), containing articles and photographs of people in the news; and Who’s Who in America (1899–present), the standard biographical reference for living Americans.
- Dictionaries contain definitions and histories of words, along with their syllabication, and correct spelling and usage.
- Encyclopedias provide basic information, explanations, and definitions of virtually every topic, concept, country, institution, historical person or movement, and cultural artifact imaginable. One-volume works such as the Random House Encyclopedia and the Columbia Encyclopedia give brief overviews. Larger works, such as the New Encyclopædia Britannica (32 volumes, also online), contain more detailed information.
Databases, usually accessed directly through your library website, are indispensable tools for finding both journal and general-audience articles. Some databases contain general-interest information, indexing articles from newspapers, magazines, and sometimes scholarly journals as well. While these databases can be useful when you begin your research, once you have focused your research topic, you likely will need to use subject databases, which index articles primarily from specialized scholarly and technical journals.
The difference between scholarly journal and other articles is important. Although at times these lines are blurred, think of articles found in popular journals or magazines as published widely and usually addressing a general audience. Such materials are useful for obtaining introductory or background information on a topic as well as a sense of the range of factors to consider. Indeed, these sources may help you narrow your topic by giving you a basic understanding of the range and scope of the “conversation” you are entering in your research process. Scholarly journal articles , on the other hand, typically are written and published by academic researchers. These publications often have more specialized information and vocabulary and are most useful after you have narrowed your topic and developed specific research questions. Within the range of scholarly articles are those that are peer reviewed or found in peer-reviewed journals. These journal articles are generally more specific and contain more reliable information because they are written by experts and reviewed by other experts in the field before the article is published. See Compiling Sources for an Annotated Bibliography for more information about peer-reviewed publications.
A good starting point for research is a general-interest database , which covers a wide range of topics from many sources. Several major general-interest databases are listed below; however, many others may be available at your library. A librarian likely can help you find those that may be specific to your university.
- Academic OneFile from Gale . Based on the access capabilities of your institution, you may be able to use this database, which indexes citations, abstracts, and some full texts in such subjects as the physical sciences, technology, medicine, social sciences, the arts, theology, literature, and more. By using this database, you may be able to retrieve the full text of articles provided in PDF and HTML formats and audio versions of texts in MP3 format.
- Academic Search Complete from EBSCOhost. Your library also may provide you with access to this database, which indexes citations, abstracts, and full text from journal articles, books, reports, and conference proceedings in all disciplines. An advantage of this database is that you can retrieve full-text articles provided in PDF and HTML forms. Academic Search Complete also provides searchable cited references for nearly 1,000 journals.
- CQ Researcher . This general database is unique because it publishes well-researched, single-themed 12,000-word reports by respected journalists who have established ethos because of their history of in-depth, unbiased coverage of health, social trends, criminal justice, international affairs, education, the environment, technology, and the economy. These reports can be beneficial at any research stage because they provide an overview, background, chronology, assessment of the current situation, tables and maps, pro/con statements from opposing positions, and bibliographies. Files from before 1996 are in HTML format; newer ones, beginning January 1996, are PDFs.
- Factiva . Many students find Factiva a useful general tool because it provides full-text news articles and business/industry information from newswires, newspapers, business and industry magazines, television and radio transcripts, financial reports, and news service photos. Within the Factiva database, most content is HTML, though other formats are available for export. The database contains news sources from 1979 to the present and financial data from the 1960s to the present.
- Google . One of the most frequently used databases for any research is Google. Students often use Google to begin their searches because they can find material from many different sources, both formal and informal, including blogs, journals, websites, and popular magazines. For academic research, you may find it useful to begin with a general Google search and then move to Google Scholar . Google Scholar provides a simple way to do a broad search for scholarly literature across a variety of disciplines and sources—articles, theses, books, et cetera. Within the Google database, you will also find more information or effective uses of Google for your research purposes. See Compiling Sources for an Annotated Bibliography for more information about Google Scholar.
- Opposing Viewpoints in Context from Gale . As you familiarize yourself with your topic, you may find this database helpful for understanding the parameters of the discussion on your topic. Opposing Viewpoints offers over 20,000 pro/con viewpoint essays on controversial issues and current events, plus thousands of topic overviews, primary source documents, social activist biographies, court case overviews, related full-text periodical articles, statistical tables, and multimedia content.
- Gale in Context . This database provides curated topic pages that combine academic journal articles, primary sources, reference works, essays, news sources, multimedia, and biographies about people, events, places, and time periods.
- Web of Science from Clarivate Analytics . The three Web of Science databases index citations from journal articles and conference proceedings in the sciences, social sciences, arts, and humanities. You can access cited reference searches, analyze trends and patterns, and create visual representations of citation relationships. Its contents date from 1900 to the present.
Government Documents
The U.S. government publishes numerous reports, pamphlets, catalogs, and newsletters on most issues of national concern. To access documents from published in 1976 and onward, consult the Catalog of U.S. Government Publications . To find documents published prior to 1976, consult the Monthly Catalog of United States . Both resources should be available electronically and contain listings for materials in formats such as nonprint media, records, CDs, audiocassettes, videotapes, slides, photographs, and other media. Many of these publications may be located through your university’s library catalog as well. Consult a librarian to find out what government documents are available to you and in what forms.
Archives/Special Collections
Many libraries have donated records, papers, or writings that make up archives or special collections containing manuscripts, rare books, architectural drawings, historical photographs and maps, and so on. These, as well as items of local interest such as community and family histories, artifacts, and other memorabilia, are usually found in a special room or section of the library. By consulting these collections or archives, you also may find local or regional atlases, maps, and geographic information systems (GIS). Maps and atlases depict more than roads and boundaries. They include information on population density, language patterns, soil types, and much more. And, as discussed later in this chapter, these materials can figure into research projects as primary data.
University libraries’ special collections often house items donated by alumni, families, and other community groups. For example, one state university library’s special collections, housing a collection of Black Panther and American Communist Party newspapers and pamphlets, celebrated Black History Month with an exhibit featuring the Black Panther Party and the Black Power movement. Included in the exhibit were Black Panther newspapers and pamphlets published in the 1960s and 1970s, as well as earlier civil rights literature from the American Communist Party. This exhibit not only helped students become aware of information about the time and movement but also demonstrated the range and depth of the university’s archive collection.
Interlibrary Loans
Even though libraries house many materials, you may need a source unavailable at your library. If so, you usually can get the source through a networked system called interlibrary loans. Your library will borrow the source for you and provide some guidance as to the form of the materials and how long you will have access to them.
Whichever search tool you use, nothing is magic about information gathered. You will need to use critical skills to evaluate materials gathered from sources, and you will still need to ask these basic questions: Is the author identified? ls that person a professional in the field or an interested amateur? What are their biases likely to be? Does the document represent an individual’s opinion or peer-reviewed research?
Evaluating Sources
One key to judging the validity of sources is analysis. You already may be familiar with analysis, which involves looking at texts, media, or other artifacts to examine their individual parts and make interpretive claims about them. In the research process, analysis involves collecting data, deciding how you want to use that data (what are you looking for?), and applying those criteria to your data. For example, if you were looking at how the presence of social media has changed in television programs in the last five to seven years, you would determine what shows you want to view and what patterns you want to study.
As you analyze sources, you evaluate them in terms of your research needs. On the basis of your needs assessment, you will determine whether a source is acceptable or unacceptable, good or bad, trustworthy or biased. Although firm categories can be useful, you may find a more nuanced evaluation helpful as well. When you look for sources and evaluate them, begin with general questions such as these:
- How do I want to use this source?
- Am I able to use it in that way?
- Might this source be more valuable if used in another way?
When you ask whether a source is acceptable, the answer usually depends on what you want to do with it. Even biased, false, or misleading material can be useful, depending on how a researcher puts it to use. For instance, you may be writing about a particular historical event and come across a magazine article featuring a biased account of that event. If your purpose is to write a brief but accurate description of the event, then this account is of little use. But what if your purpose is to write a critical analysis of the ways in which misleading media coverage of an event has influenced public perception of it? Suddenly, the biased account becomes useful as a specific example of the media coverage you wish to analyze.
A source’s value, therefore, is a function of your purpose for it. Labeling a source as good or bad, truthful or misleading, doesn’t really evaluate its use to you as a researcher and writer; truthful sources can be used poorly, and misleading sources can be used effectively. What matters is whether the source fits your purpose.
Finally, when evaluating a source, consider time ( when was it judged true? ) and perspective ( who said it was true, and for what reason? ).
Locate the Date
Most documents, especially those created since the advent of copyright laws at the end of the 19th century, include their date of publication. Pay attention to the date a source was created, and reflect on what might have happened since then. Information may be outdated and useless. On the other hand, it may still be highly useful—and continuing usefulness is the reason many old texts remain in circulation. Once you locate the source’s date, you can decide whether it will be relevant for your purpose. If you are studying change over time, for example, old statistical information would be useful baseline data to demonstrate what has changed. But if you are studying current culture, dated information may be misleading. In other words, when evaluating whether a dated source serves your purpose, know what that purpose is.
Identify Perspective
To identify and evaluate perspective, ask what viewpoint, or perspective, it represents. Who created the source, and for what purpose? This question can be difficult to answer immediately because an author’s viewpoint is not always identified or summarized in the source itself—and when it is, the information provided, being a creation of the author, cannot always be believed. To trust a source, you need to analyze its assumptions, evidence, biases, and reasoning, which together constitute the author’s perspective. ln essence, you need to ask these questions: What is this writer’s purpose? Is it scholarly analysis, political advocacy, entertainment, or something else? Consider the following:
- Will a quick perusal of the introduction or first chapter reveal the writer’s assumptions about the subject or audience?
- Can you tell which statements are facts, which are inferences drawn from facts, and which are strictly opinions?
- Does a first reading of the evidence persuade you? Is the logic of the position apparent and/or credible?
- Does the writer omit relevant points?
- Do the answers to these questions make you more or less willing to accept the author’s conclusions?
Although trying to answer these questions about every source may seem daunting or even futile at first, have patience and give the research process the time it needs. At the beginning of a research project, when you are still trying to gain context and overview and have looked at only one source, you likely will have difficulty recognizing an author’s purpose and viewpoint. However, as you read further and begin to compare and contrast one source with another, differences will emerge, especially if you read extensively and take notes. The more differences you note, the more critically aware you become and the more you understand how and where a source might help you.
Review Critically
To review a source with a critical eye, ask both first and second questions of the text. The answers to first questions are generally factual, the result of probing the text (identifying the title, table of contents, chapter headings, index, and so on). The answers to second questions are more inferential, the result of analyzing assertions, evidence, and language in the text (identifying the perspective of the author and their sources).
Review Internally
Does information in one source support or contradict information in other sources? Do a subject search of the author across platforms to find out how other experts view the author and how your source fits in with the author’s other works.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Authors: Michelle Bachelor Robinson, Maria Jerskey, featuring Toby Fulwiler
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Writing Guide with Handbook
- Publication date: Dec 21, 2021
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/13-1-the-research-process-where-to-look-for-existing-sources
© Dec 19, 2023 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

- Herron School of Art
- Ruth Lilly Law
- Ruth Lilly Medical
- School of Dentistry
Introduction to Library Research - Overview of the Research Process
- 1: Your Question
- 2: Background Information
- Types of Sources
Find Library Resources
Search strategies for databases, what do library databases contain.
- Scholarly v. Popular Sources
- Primary v. Secondary Sources
- 5: Organize, Write, & Cite

Detailed description of, "Types of Sources"
1. Finding a variety of sources (books, articles, news, etc.) on your topic
- OneSearch, available from the library home page , allows you to search almost all our databases and IUCAT. So you can find books, articles, news, dissertations, etc.
- Start here if you're not sure what kinds-of resources might be available on your topic.
- If you only want to find books, skip to #2. If you only want articles, skip to #3.
2. Finding Books, Journals (not individual articles), CDs, DVDs, and other items
- You'll find most books by searching IUCAT , the online catalog for all the Indiana University libraries. For help searching IUCAT, Ask A Librarian .
- Once you perform your search, you'll see a list of records (not ranked by relevance) of the books, journals, and other items containing the keywords you searched.
- Publication information
- Subject headings (Tip: Click on a subject heading to find similar items.)
- Call Number (You’ll need this information to find the book on the library shelves.)
- Library (If the item is not in Indianapolis, you can request items from other IU libraries with the red “ Request This ” button in the record. Note, this can take 4-7 days.)
- 3rd floor shelves if the call number starts with the letters A-N.
- 4th floor shelves if the call number starts with the letters P-Z.
- Tip: Browse the shelves around a call number for more items on the same topic.
- Use your Crimson Card to check out books at the Circulation Desk on the 2nd floor.
- Get items from libraries outside the IU system with Interlibrary Loan . (This usually takes at least 7-10 days.)
- Then e-books are for you. Most of our e-books can be found by title in IUCAT , but you can also go directly to our e-book databases and search by title or you can see a list of e-book platforms .
3. Finding Articles (scholarly, magazine, newspaper, etc)
- Search databases using the tips in the “Search Strategies for Databases” box, below.
- Understand the scope of the database. Some cover multiple subjects and others cover a specific discipline. If you aren’t finding what you need, you might need to try another database.
- If you have trouble accessing our resources, go to Can't Connect? .
- You can also Ask a Librarian .
- Once you perform a search, you'll see a list of results (articles that match your keywords). Most databases try to be like Google, which means your results will rank by relevance.
- If you need recent articles, peer-reviewed (scholarly) articles, or if you only want to see articles which can be viewed online, you can limit your search. Use the database's search options.
- If the full text of the article is available through the database, you'll see links to view the article in HTML and/or PDF format.
- If the full text of the article is not available through the database, you'll see the red “Find It” button. Click the link to be taken to full-text options. If IUPUI doesn’t have access to the full-text, you can get articles from other libraries with Interlibrary Loan . (This may take anywhere from 24 hours to 10 days.)
Before you start entering any search terms, spend a few minutes trying to think of as many relevant terms and combinations of terms as you can . This will help you to avoid getting stuck in a rut with the first terms that come to mind.
If you need help in coming up with terms, you may want to try the "Thesaurus" or "Subject Headings" features in the database you've chosen.
Check out the "Help" or "Search Tips" to learn some of the search features specific to that database. Most databases provide similar features, but the methods may vary. Some common tricks:
- truncation = To use truncation, enter the root of a search term and replace the ending with an * (asterisk). For example, type comput* to find the words computes, computer, computing or computational .
- searching a phrase = Typically, when a phrase is enclosed by double quotations marks, the exact phrase is searched. For example, "employee retention" searches for the two words as a phrase.
- AND combines search terms so that each search result contains all of the terms. For example, travel AND Europe finds articles that contain both travel and Europe .
- OR combines search terms so that each search result contains at least one of the terms. For example, college OR university finds results that contain either college or university .
- NOT excludes terms so that each search result does not contain any of the terms that follow it. For example, television NOT cable finds results that contain television but not cable .
- Putting it all together : You can combine these Boolean terms with truncation and phrase searching to create powerful search statements. For example, if you are interested in what motivates students in higher education, you might try a search that looks like: (college* OR universit* OR "higher education") AND (student* OR undergraduate* OR "graduate student*") AND motivat*
Try the databases' Advanced Search feature, which usually gives you the ability to search multiple fields (author, title, keyword, subject, etc) with one search and may offer additional ways to expand or limit your search.
If your first search strategy does not work, try another approach . Remember that you can also get help from the library. Check out the links below.
- Ask A Librarian
- Subject Librarians

Detailed description of, "What do library databases contain?"
- << Previous: 2: Background Information
- Next: 4: Read & Evaluate >>
- Last Updated: Jul 18, 2023 8:11 AM
- URL: https://iupui.libguides.com/howtoresearch
Getting Started with Library Research
Research needs and requirements vary with each assignment, project, or paper. Although there is no single “right” way to conduct research, certain methods and skills can make your research efforts more efficient and effective.
If you have questions or can’t find what you need, ask a librarian .
Developing a Research Topic
All research starts with a question.
- Discuss your ideas with a librarian or with your professor.
- Formulate a research question and identify keywords.
- Search subject-focused encyclopedias, books, and journals to see what kind of information already exists on your topic. If you are having trouble finding information, you may need to change your search terms or ask for help.
Additional resources:
- Library Research at Cornell
- Research Guides
Using the Library to Find Research Materials
The Library is the top resource when it comes to locating and accessing research materials.
- Use the library catalog to find materials such as books, music, videos, journals, and audio recordings in our collections.
- Search databases to find articles, book chapters, and other sources within a specific subject area or discipline.
- For materials the Library does not own, use BorrowDirect or Interlibrary Loan for quick and easy access.
- Each library unit has unique collections and subject knowledge. See individual library websites for additional resources in specific subject areas.
- Check out our library research guides for lists of resources curated by library staff. Browse by subject or find guides specific to course offerings.
Evaluating Sources
When using a book, article, report, or website for your research, it is important to gauge how reliable the source is. Visit these research guides for more information:
- How to distinguish scholarly vs non-scholarly sources
- Tips for critically analyzing information sources
- Identify misinformation, disinformation, and propaganda
Citing Sources
When writing a research paper, it is important to cite the sources you used in a way that would enable a reader to easily find them.
- Citation Management
- How to Prepare an Annotated Bibliography
- Code of Academic Integrity
University Library
Find Research Materials - Ask Us
Search strategies and tools.
- Library Catalog Learn how to use the library catalog to identify specific research materials or search by topic.
- Cited Reference Searching Find articles that have cited a key resource and will likely be relevant to your research.
- Citation Management Software Overview tools for making your research process more efficient by tracking articles of interest and related citation information.
Find Materials by Type
- Find Background Information A list of sources to consult for facts and other background information, such as encyclopedias, news articles, dictionaries, and bibliographies.
- Find Articles and Journals Find specific articles and journals with titles and other citation information, or learn how to search for articles on particular topics.
- Find and Use E-Books Find specific e-books and e-audiobooks, and learn about how to use our e-book platforms and e-book readers.
- Find Media Find film and video, video games, and more.
- Find and Use Images Use the Library’s databases and websites to find and use images in your research projects.
- Find Visual Resource Collections Find free and licensed image and video collections related to spectific subject areas.
- Find Music Materials A guide on finding music materials at the library and beyond.
- Find Dissertations How to find dissertations conferred in Illinois and across the world.
- Find Conference Proceedings How to find conference proceedings with the library catalog and other search tools.
- Find Data Information on finding numeric and spatial data in our collections and elsewhere.
- Find Primary Source Materials How to locate digital and print primary source materials beyond University of Illinois libraries.
- Find Government Information The home page for Government Information Services provides information on collections, research tools, online government resources, public services, and more.
- Find Digital Collections An overview by format and subject area of the highlights of the U of I’s digitized collections and how to find them online.
Borrowing and Using
- Borrowing Privileges Basic information on borrowing privileges divided by type of affiliation.
- Access Databases from On and Off Campus Information on how to access the library’s wide verse of electronic resources, including ejournals, ebooks, databases, and more.
- Distance Learners and Instructors A guide on resources for distance learners and instructors in online or off-campus courses through Center for Innovation in Teaching & Learning at the U of I.
- Reciprocal Borrowing Privileges for visiting scholars at U of I, and for Illinois patrons visiting other libraries.
- Sending Materials through Campus Mail Step-by-step instructions on how to request materials to be delivered through campus mail.
Evaluate Sources
- Evaluate Information Resources Learn factors to consider when evaluating information resources including books, articles, and websites.
Ask a Librarian
- Email via Web Form
- Text: (217) 686-4361
- Phone: (217) 333-2291
Get help with
- Developing Your Research
- Finding Research Materials
- Writing Your Research
- Sharing Your Research
Reference management. Clean and simple.
The top list of academic search engines
1. Google Scholar
4. science.gov, 5. semantic scholar, 6. baidu scholar, get the most out of academic search engines, frequently asked questions about academic search engines, related articles.
Academic search engines have become the number one resource to turn to in order to find research papers and other scholarly sources. While classic academic databases like Web of Science and Scopus are locked behind paywalls, Google Scholar and others can be accessed free of charge. In order to help you get your research done fast, we have compiled the top list of free academic search engines.
Google Scholar is the clear number one when it comes to academic search engines. It's the power of Google searches applied to research papers and patents. It not only lets you find research papers for all academic disciplines for free but also often provides links to full-text PDF files.
- Coverage: approx. 200 million articles
- Abstracts: only a snippet of the abstract is available
- Related articles: ✔
- References: ✔
- Cited by: ✔
- Links to full text: ✔
- Export formats: APA, MLA, Chicago, Harvard, Vancouver, RIS, BibTeX
BASE is hosted at Bielefeld University in Germany. That is also where its name stems from (Bielefeld Academic Search Engine).
- Coverage: approx. 136 million articles (contains duplicates)
- Abstracts: ✔
- Related articles: ✘
- References: ✘
- Cited by: ✘
- Export formats: RIS, BibTeX

CORE is an academic search engine dedicated to open-access research papers. For each search result, a link to the full-text PDF or full-text web page is provided.
- Coverage: approx. 136 million articles
- Links to full text: ✔ (all articles in CORE are open access)
- Export formats: BibTeX
Science.gov is a fantastic resource as it bundles and offers free access to search results from more than 15 U.S. federal agencies. There is no need anymore to query all those resources separately!
- Coverage: approx. 200 million articles and reports
- Links to full text: ✔ (available for some databases)
- Export formats: APA, MLA, RIS, BibTeX (available for some databases)
Semantic Scholar is the new kid on the block. Its mission is to provide more relevant and impactful search results using AI-powered algorithms that find hidden connections and links between research topics.
- Coverage: approx. 40 million articles
- Export formats: APA, MLA, Chicago, BibTeX

Although Baidu Scholar's interface is in Chinese, its index contains research papers in English as well as Chinese.
- Coverage: no detailed statistics available, approx. 100 million articles
- Abstracts: only snippets of the abstract are available
- Export formats: APA, MLA, RIS, BibTeX

RefSeek searches more than one billion documents from academic and organizational websites. Its clean interface makes it especially easy to use for students and new researchers.
- Coverage: no detailed statistics available, approx. 1 billion documents
- Abstracts: only snippets of the article are available
- Export formats: not available
Consider using a reference manager like Paperpile to save, organize, and cite your references. Paperpile integrates with Google Scholar and many popular databases, so you can save references and PDFs directly to your library using the Paperpile buttons:
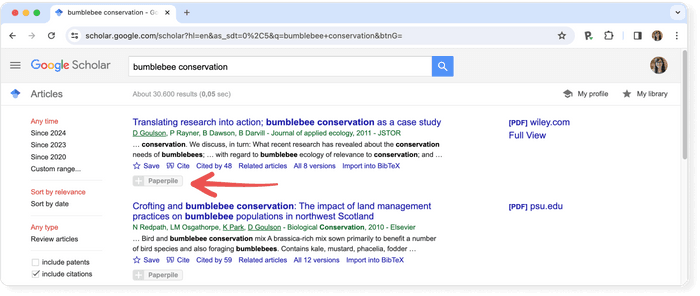
Google Scholar is an academic search engine, and it is the clear number one when it comes to academic search engines. It's the power of Google searches applied to research papers and patents. It not only let's you find research papers for all academic disciplines for free, but also often provides links to full text PDF file.
Semantic Scholar is a free, AI-powered research tool for scientific literature developed at the Allen Institute for AI. Sematic Scholar was publicly released in 2015 and uses advances in natural language processing to provide summaries for scholarly papers.
BASE , as its name suggest is an academic search engine. It is hosted at Bielefeld University in Germany and that's where it name stems from (Bielefeld Academic Search Engine).
CORE is an academic search engine dedicated to open access research papers. For each search result a link to the full text PDF or full text web page is provided.
Science.gov is a fantastic resource as it bundles and offers free access to search results from more than 15 U.S. federal agencies. There is no need any more to query all those resources separately!
Eight Ways (and More) To Find and Access Research Papers
This blog is part of our Research Smarter series. You’ll discover the various search engines, databases and data repositories to help you along the way. Click on any of the following links for in an in-depth look at how to find relevant research papers, journals , and authors for your next project using the Web of Science™. You can also check out our ultimate guides here , which include tips to speed up the writing process.
If you’re in the early stages of your research career, you’re likely struggling to learn all you can about your chosen field and evaluate your options. You also need an easy and convenient way to find the right research papers upon which to build your own work and keep you on the proper path toward your goals.
Fortunately, most institutions have access to thousands of journals, so your first step should be to be to check with library staff and find out what is available via your institutional subscriptions.
For those who may be unfamiliar with other means of access, this blog post – the first in a series devoted to helping you “research smarter” – will provide a sampling of established data sources for scientific research. These include search engines, databases, and data repositories.
Search Engines and Databases
You may have already discovered that the process of searching for research papers offers many choices and scenarios. Some search engines, for example, can be accessed free of charge. Others require a subscription. The latter group generally includes services that index the contents of thousands of published journals, allowing for detailed searches on data fields such as author name, institution, title or keyword, and even funding sources. Because many journals operate on a subscription model too, the process of obtaining full-text versions of papers can be complicated.
On the other hand, a growing number of publishers follow the practice of Open Access (OA) , making their journal content freely available. Similarly, some authors publish their results in the form of preprints, posting them to preprint servers for immediate and free access. These repositories, like indexing services, differ in that some concentrate in a given discipline or broad subject area, while others cover the full range of research.
Search Engines
Following is a brief selection of reputable search engines by which to locate articles relevant to your research.
Google Scholar is a free search engine that provides access to research in multiple disciplines. The sources include academic publishers, universities, online repositories, books, and even judicial opinions from court cases. Based on its indexing, Google Scholar provides citation counts to allow authors and others to track the impact of their work.
The Directory of Open Access Journals ( DOAJ ) allows users to search and retrieve the article contents of nearly 10,000 OA journals in science, technology, medicine, social sciences, and humanities. All journals must adhere to quality-control standards, including peer review.
PubMed , maintained by the US National Library of Medicine, is a free search engine covering the biomedical and life sciences. Its coverage derives primarily from the MEDLINE database, covering materials as far back as 1951.
JSTOR affords access to more than 12 million journal articles in upwards of 75 disciplines, providing full-text searches of more than 2,000 journals, and access to more than 5,000 OA books.
Selected Databases
The following selection samples a range of resources, including databases which, as discussed above, index the contents of journals either in a given specialty area or the full spectrum of research. Others listed below offer consolidated coverage of multiple databases. Your institution is likely subscribed to a range of research databases, speak to your librarian to see which databases you have access to, and how to go about your search.
Web of Science includes The Web of Science Core Collection, which covers more than 20,000 carefully selected journals, along with books, conference proceedings, and other sources. The indexing also captures citation data, permitting users to follow the thread of an idea or development over time, as well as to track a wide range of research-performance metrics. The Web of Science also features EndNote™ Click , a free browser plugin that offers one-click access to the best available legal and legitimate full-text versions of papers. See here for our ultimate guide to finding relevant research papers on the Web of Science .
Science.gov covers the vast territory of United States federal science, including more than 60 databases and 2,200-plus websites. The many allied agencies whose research is reflected include NASA, the US Department of Agriculture, and the US Environmental Protection Agency.
CiteSeerx is devoted primarily to information and computer science. The database includes a feature called Autonomous Citation Indexing, designed to extract citations and create a citation index for literature searching and evaluation.
Preprint and Data Repositories
An early form of OA literature involved authors, as noted above, making electronic, preprint versions of their papers freely available. This practice has expanded widely today. You can find archives devoted to a single main specialty area, as well as general repositories connected with universities and other institutions.
The specialty archive is perhaps best exemplified by arXiv (conveniently pronounced “archive,” and one of the earliest examples of a preprint repository). Begun in 1991 as a physics repository, ArXiv has expanded to embrace mathematics, astronomy, statistics, economics, and other disciplines. The success of ArXiv spurred the development of, for example, bioArXiv devoted to an array of topics within biology, and for chemistry, ChemRxiv .
Meanwhile, thousands of institutional repositories hold a variety of useful materials. In addition to research papers, these archives store raw datasets, graphics, notes, and other by-products of investigation. Currently, the Registry of Open Access Repositories lists more than 4,700 entries.
Reach Out Yourself?
If the resources above don’t happen to result in a free and full-text copy of the research you seek, you can also try reaching out to the authors yourself.
To find who authored a paper, you can search indexing platforms like the Web of Science , or research profiling systems like Publons™ , or ResearchGate , then look to reach out to the authors directly.
So, although the sheer volume of research can pose a challenge to identifying and securing needed papers, plenty of options are available.
Related posts
Unlocking u.k. research excellence: key insights from the research professional news live summit.

For better insights, assess research performance at the department level

Getting the Full Picture: Institutional unification in the Web of Science

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Finding Materials in the Library
Learning objectives.
By the end of this chapter, you will be able to:
- Search for physical materials using your online library catalog
- Describe how libraries organize physical materials on the shelves
Introduction to College Research Copyright © by Walter D. Butler; Aloha Sargent; and Kelsey Smith is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Med Libr Assoc
- v.106(4); 2018 Oct
A systematic approach to searching: an efficient and complete method to develop literature searches
Associated data.
Creating search strategies for systematic reviews, finding the best balance between sensitivity and specificity, and translating search strategies between databases is challenging. Several methods describe standards for systematic search strategies, but a consistent approach for creating an exhaustive search strategy has not yet been fully described in enough detail to be fully replicable. The authors have established a method that describes step by step the process of developing a systematic search strategy as needed in the systematic review. This method describes how single-line search strategies can be prepared in a text document by typing search syntax (such as field codes, parentheses, and Boolean operators) before copying and pasting search terms (keywords and free-text synonyms) that are found in the thesaurus. To help ensure term completeness, we developed a novel optimization technique that is mainly based on comparing the results retrieved by thesaurus terms with those retrieved by the free-text search words to identify potentially relevant candidate search terms. Macros in Microsoft Word have been developed to convert syntaxes between databases and interfaces almost automatically. This method helps information specialists in developing librarian-mediated searches for systematic reviews as well as medical and health care practitioners who are searching for evidence to answer clinical questions. The described method can be used to create complex and comprehensive search strategies for different databases and interfaces, such as those that are needed when searching for relevant references for systematic reviews, and will assist both information specialists and practitioners when they are searching the biomedical literature.
INTRODUCTION
Librarians and information specialists are often involved in the process of preparing and completing systematic reviews (SRs), where one of their main tasks is to identify relevant references to include in the review [ 1 ]. Although several recommendations for the process of searching have been published [ 2 – 6 ], none describe the development of a systematic search strategy from start to finish.
Traditional methods of SR search strategy development and execution are highly time consuming, reportedly requiring up to 100 hours or more [ 7 , 8 ]. The authors wanted to develop systematic and exhaustive search strategies more efficiently, while preserving the high sensitivity that SR search strategies necessitate. In this article, we describe the method developed at Erasmus University Medical Center (MC) and demonstrate its use through an example search. The efficiency of the search method and outcome of 73 searches that have resulted in published reviews are described in a separate article [ 9 ].
As we aimed to describe the creation of systematic searches in full detail, the method starts at a basic level with the analysis of the research question and the creation of search terms. Readers who are new to SR searching are advised to follow all steps described. More experienced searchers can consider the basic steps to be existing knowledge that will already be part of their normal workflow, although step 4 probably differs from general practice. Experienced searchers will gain the most from reading about the novelties in the method as described in steps 10–13 and comparing the examples given in the supplementary appendix to their own practice.
CREATING A SYSTEMATIC SEARCH STRATEGY
Our methodology for planning and creating a multi-database search strategy consists of the following steps:
- Determine a clear and focused question
- Describe the articles that can answer the question
- Decide which key concepts address the different elements of the question
- Decide which elements should be used for the best results
- Choose an appropriate database and interface to start with
- Document the search process in a text document
- Identify appropriate index terms in the thesaurus of the first database
- Identify synonyms in the thesaurus
- Add variations in search terms
- Use database-appropriate syntax, with parentheses, Boolean operators, and field codes
- Optimize the search
- Evaluate the initial results
- Check for errors
- Translate to other databases
- Test and reiterate
Each step in the process is reflected by an example search described in the supplementary appendix .
1. Determine a clear and focused question
A systematic search can best be applied to a well-defined and precise research or clinical question. Questions that are too broad or too vague cannot be answered easily in a systematic way and will generally result in an overwhelming number of search results. On the other hand, a question that is too specific will result into too few or even zero search results. Various papers describe this process in more detail [ 10 – 12 ].
2. Describe the articles that can answer the question
Although not all clinical or research questions can be answered in the literature, the next step is to presume that the answer can indeed be found in published studies. A good starting point for a search is hypothesizing what the research that can answer the question would look like. These hypothetical (when possible, combined with known) articles can be used as guidance for constructing the search strategy.
3. Decide which key concepts address the different elements of the question
Key concepts are the topics or components that the desired articles should address, such as diseases or conditions, actions, substances, settings, domains (e.g., therapy, diagnosis, etiology), or study types. Key concepts from the research question can be grouped to create elements in the search strategy.
Elements in a search strategy do not necessarily follow the patient, intervention, comparison, outcome (PICO) structure or any other related structure. Using the PICO or another similar framework as guidance can be helpful to consider, especially in the inclusion and exclusion review stage of the SR, but this is not necessary for good search strategy development [ 13 – 15 ]. Sometimes concepts from different parts of the PICO structure can be grouped together into one search element, such as when the desired outcome is frequently described in a certain study type.
4. Decide which elements should be used for the best results
Not all elements of a research question should necessarily be used in the search strategy. Some elements are less important than others or may unnecessarily complicate or restrict a search strategy. Adding an element to a search strategy increases the chance of missing relevant references. Therefore, the number of elements in a search strategy should remain as low as possible to optimize recall.
Using the schema in Figure 1 , elements can be ordered by their specificity and importance to determine the best search approach. Whether an element is more specific or more general can be measured objectively by the number of hits retrieved in a database when searching for a key term representing that element. Depending on the research question, certain elements are more important than others. If articles (hypothetically or known) exist that can answer the question but lack a certain element in their titles, abstracts, or keywords, that element is unimportant to the question. An element can also be unimportant because of expected bias or an overlap with another element.

Schema for determining the optimal order of elements
Bias in elements
The choice of elements in a search strategy can introduce bias through use of overly specific terminology or terms often associated with positive outcomes. For the question “does prolonged breastfeeding improve intelligence outcomes in children?,” searching specifically for the element of duration will introduce bias, as articles that find a positive effect of prolonged breastfeeding will be much more likely to mention time factors in their titles or abstracts.
Overlapping elements
Elements in a question sometimes overlap in their meaning. Sometimes certain therapies are interventions for one specific disease. The Lichtenstein technique, for example, is a repair method for inguinal hernias. There is no need to include an element of “inguinal hernias” to a search for the effectiveness of the Lichtenstein therapy. Likewise, sometimes certain diseases are only found in certain populations. Adding such an overlapping element could lead to missing relevant references.
The elements to use in a search strategy can be found in the plot of elements in Figure 1 , by following the top row from left to right. For this method, we recommend starting with the most important and specific elements. Then, continue with more general and important elements until the number of results is acceptable for screening. Determining how many results are acceptable for screening is often a matter of negotiation with the SR team.
5. Choose an appropriate database and interface to start with
Important factors for choosing databases to use are the coverage and the presence of a thesaurus. For medically oriented searches, the coverage and recall of Embase, which includes the MEDLINE database, are superior to those of MEDLINE [ 16 ]. Each of these two databases has its own thesaurus with its own unique definitions and structure. Because of the complexity of the Embase thesaurus, Emtree, which contains much more specific thesaurus terms than the MEDLINE Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) thesaurus, translation from Emtree to MeSH is easier than the other way around. Therefore, we recommend starting in Embase.
MEDLINE and Embase are available through many different vendors and interfaces. The choice of an interface and primary database is often determined by the searcher’s accessibility. For our method, an interface that allows searching with proximity operators is desirable, and full functionality of the thesaurus, including explosion of narrower terms, is crucial. We recommend developing a personal workflow that always starts with one specific database and interface.
6. Document the search process in a text document
We advise designing and creating the complete search strategies in a log document, instead of directly in the database itself, to register the steps taken and to make searches accountable and reproducible. The developed search strategies can be copied and pasted into the desired databases from the log document. This way, the searcher is in control of the whole process. Any change to the search strategy should be done in the log document, assuring that the search strategy in the log is always the most recent.
7. Identify appropriate index terms in the thesaurus of the first database
Searches should start by identifying appropriate thesaurus terms for the desired elements. The thesaurus of the database is searched for matching index terms for each key concept. We advise restricting the initial terms to the most important and most relevant terms. Later in the process, more general terms can be added in the optimization process, in which the effect on the number of hits, and thus the desirability of adding these terms, can be evaluated more easily.
Several factors can complicate the identification of thesaurus terms. Sometimes, one thesaurus term is found that exactly describes a specific element. In contrast, especially in more general elements, multiple thesaurus terms can be found to describe one element. If no relevant thesaurus terms have been found for an element, free-text terms can be used, and possible thesaurus terms found in the resulting references can be added later (step 11).
Sometimes, no distinct thesaurus term is available for a specific key concept that describes the concept in enough detail. In Emtree, one thesaurus term often combines two or more elements. The easiest solution for combining these terms for a sensitive search is to use such a thesaurus term in all elements where it is relevant. Examples are given in the supplementary appendix .
8. Identify synonyms in the thesaurus
Most thesauri offer a list of synonyms on their term details page (named Synonyms in Emtree and Entry Terms in MeSH). To create a sensitive search strategy for SRs, these terms need to be searched as free-text keywords in the title and abstract fields, in addition to searching their associated thesaurus terms.
The Emtree thesaurus contains more synonyms (300,000) than MeSH does (220,000) [ 17 ]. The difference in number of terms is even higher considering that many synonyms in MeSH are permuted terms (i.e., inversions of phrases using commas).
Thesaurus terms are ordered in a tree structure. When searching for a more general thesaurus term, the more specific (narrower) terms in the branches below that term will also be searched (this is frequently referred to as “exploding” a thesaurus term). However, to perform a sensitive search, all relevant variations of the narrower terms must be searched as free-text keywords in the title or abstract, in addition to relying on the exploded thesaurus term. Thus, all articles that describe a certain narrower topic in their titles and abstracts will already be retrieved before MeSH terms are added.
9. Add variations in search terms (e.g., truncation, spelling differences, abbreviations, opposites)
Truncation allows a searcher to search for words beginning with the same word stem. A search for therap* will, thus, retrieve therapy, therapies, therapeutic, and all other words starting with “therap.” Do not truncate a word stem that is too short. Also, limitations of interfaces should be taken into account, especially in PubMed, where the number of search term variations that can be found by truncation is limited to 600.
Databases contain references to articles using both standard British and American English spellings. Both need to be searched as free-text terms in the title and abstract. Alternatively, many interfaces offer a certain code to replace zero or one characters, allowing a search for “pediatric” or “paediatric” as “p?ediatric.” Table 1 provides a detailed description of the syntax for different interfaces.
Field codes in five most used interfaces for biomedical literature searching
Searching for abbreviations can identify extra, relevant references and retrieve more irrelevant ones. The search can be more focused by combining the abbreviation with an important word that is relevant to its meaning or by using the Boolean “NOT” to exclude frequently observed, clearly irrelevant results. We advise that searchers do not exclude all possible irrelevant meanings, as it is very time consuming to identify all the variations, it will result in unnecessarily complicated search strategies, and it may lead to erroneously narrowing the search and, thereby, reduce recall.
Searching partial abbreviations can be useful for retrieving relevant references. For example, it is very likely that an article would mention osteoarthritis (OA) early in the abstract, replacing all further occurrences of osteoarthritis with OA . Therefore, it may not contain the phrase “hip osteoarthritis” but only “hip oa.”
It is also important to search for the opposites of search terms to avoid bias. When searching for “disease recurrence,” articles about “disease free” may be relevant as well. When the desired outcome is survival , articles about mortality may be relevant.
10. Use database-appropriate syntax, with parentheses, Boolean operators, and field codes
Different interfaces require different syntaxes, the special set of rules and symbols unique to each database that define how a correctly constructed search operates. Common syntax components include the use of parentheses and Boolean operators such as “AND,” “OR,” and “NOT,” which are available in all major interfaces. An overview of different syntaxes for four major interfaces for bibliographic medical databases (PubMed, Ovid, EBSCOhost, Embase.com, and ProQuest) is shown in Table 1 .
Creating the appropriate syntax for each database, in combination with the selected terms as described in steps 7–9, can be challenging. Following the method outlined below simplifies the process:
- Create single-line queries in a text document (not combining multiple record sets), which allows immediate checking of the relevance of retrieved references and efficient optimization.
- Type the syntax (Boolean operators, parentheses, and field codes) before adding terms, which reduces the chance that errors are made in the syntax, especially in the number of parentheses.
- Use predefined proximity structures including parentheses, such as (() ADJ3 ()) in Ovid, that can be reused in the query when necessary.
- Use thesaurus terms separately from free-text terms of each element. Start an element with all thesaurus terms (using “OR”) and follow with the free-text terms. This allows the unique optimization methods as described in step 11.
- When adding terms to an existing search strategy, pay close attention to the position of the cursor. Make sure to place it appropriately either in the thesaurus terms section, in the title/abstract section, or as an addition (broadening) to an existing proximity search.
The supplementary appendix explains the method of building a query in more detail, step by step for different interfaces: PubMed, Ovid, EBSCOhost, Embase.com, and ProQuest. This method results in a basic search strategy designed to retrieve some relevant references upon which a more thorough search strategy can be built with optimization such as described in step 11.
11. Optimize the search
The most important question when performing a systematic search is whether all (or most) potentially relevant articles have been retrieved by the search strategy. This is also the most difficult question to answer, since it is unknown which and how many articles are relevant. It is, therefore, wise first to broaden the initial search strategy, making the search more sensitive, and then check if new relevant articles are found by comparing the set results (i.e., search for Strategy #2 NOT Strategy #1 to see the unique results).
A search strategy should be tested for completeness. Therefore, it is necessary to identify extra, possibly relevant search terms and add them to the test search in an OR relationship with the already used search terms. A good place to start, and a well-known strategy, is scanning the top retrieved articles when sorted by relevance, looking for additional relevant synonyms that could be added to the search strategy.
We have developed a unique optimization method that has not been described before in the literature. This method often adds valuable extra terms to our search strategy and, therefore, extra, relevant references to our search results. Extra synonyms can be found in articles that have been assigned a certain set of thesaurus terms but that lack synonyms in the title and/or abstract that are already present in the current search strategy. Searching for thesaurus terms NOT free-text terms will help identify missed free-text terms in the title or abstract. Searching for free-text terms NOT thesaurus terms will help identify missed thesaurus terms. If this is done repeatedly for each element, leaving the rest of the query unchanged, this method will help add numerous relevant terms to the query. These steps are explained in detail for five different search platforms in the supplementary appendix .
12. Evaluate the initial results
The results should now contain relevant references. If the interface allows relevance ranking, use that in the evaluation. If you know some relevant references that should be included in the research, search for those references specifically; for example, combine a specific (first) author name with a page number and the publication year. Check whether those references are retrieved by the search. If the known relevant references are not retrieved by the search, adapt the search so that they are. If it is unclear which element should be adapted to retrieve a certain article, combine that article with each element separately.
Different outcomes are desired for different types of research questions. For instance, in the case of clinical question answering, the researcher will not be satisfied with many references that contain a lot of irrelevant references. A clinical search should be rather specific and is allowed to miss a relevant reference. In the case of an SR, the researchers do not want to miss any relevant reference and are willing to handle many irrelevant references to do so. The search for references to include in an SR should be very sensitive: no included reference should be missed. A search that is too specific or too sensitive for the intended goal can be adapted to become more sensitive or specific. Steps to increase sensitivity or specificity of a search strategy can be found in the supplementary appendix .
13. Check for errors
Errors might not be easily detected. Sometimes clues can be found in the number of results, either when the number of results is much higher or lower than expected or when many retrieved references are not relevant. However, the number expected is often unknown, and very sensitive search strategies will always retrieve many irrelevant articles. Each query should, therefore, be checked for errors.
One of the most frequently occurring errors is missing the Boolean operator “OR.” When no “OR” is added between two search terms, many interfaces automatically add an “AND,” which unintentionally reduces the number of results and likely misses relevant references. One good strategy to identify missing “OR”s is to go to the web page containing the full search strategy, as translated by the database, and using Ctrl-F search for “AND.” Check whether the occurrences of the “AND” operator are deliberate.
Ideally, search strategies should be checked by other information specialists [ 18 ]. The Peer Review of Electronic Search Strategies (PRESS) checklist offers good guidance for this process [ 4 ]. Apart from the syntax (especially Boolean operators and field codes) of the search strategy, it is wise to have the search terms checked by the clinician or researcher familiar with the topic. At Erasmus MC, researchers and clinicians are involved during the complete process of structuring and optimizing the search strategy. Each word is added after the combined decision of the searcher and the researcher, with the possibility of directly comparing results with and without the new term.
14. Translate to other databases
To retrieve as many relevant references as possible, one has to search multiple databases. Translation of complex and exhaustive queries between different databases can be very time consuming and cumbersome. The single-line search strategy approach detailed above allows quick translations using the find and replace method in Microsoft Word (<Ctrl-H>).
At Erasmus MC, macros based on the find-and-replace method in Microsoft Word have been developed for easy and fast translation between the most used databases for biomedical and health sciences questions. The schema that is followed for the translation between databases is shown in Figure 2 . Most databases simply follow the structure set by the Embase.com search strategy. The translation from Emtree terms to MeSH terms for MEDLINE in Ovid often identifies new terms that need to be added to the Embase.com search strategy before the translation to other databases.

Schematic representation of translation between databases used at Erasmus University Medical Center
Dotted lines represent databases that are used in less than 80% of the searches.
Using five different macros, a thoroughly optimized query in Embase.com can be relatively quickly translated into eight major databases. Basic search strategies will be created to use in many, mostly smaller, databases, because such niche databases often do not have extensive thesauri or advanced syntax options. Also, there is not much need to use extensive syntax because the number of hits and, therefore, the amount of noise in these databases is generally low. In MEDLINE (Ovid), PsycINFO (Ovid), and CINAHL (EBSCOhost), the thesaurus terms must be adapted manually, as each database has its own custom thesaurus. These macros and instructions for their installation, use, and adaptation are available at bit.ly/databasemacros.
15. Test and reiterate
Ideally, exhaustive search strategies should retrieve all references that are covered in a specific database. For SR search strategies, checking searches for their recall is advised. This can be done after included references have been determined by the authors of the systematic review. If additional papers have been identified through other non-database methods (i.e., checking references in included studies), results that were not identified by the database searches should be examined. If these results were available in the databases but not located by the search strategy, the search strategy should be adapted to try to retrieve these results, as they may contain terms that were omitted in the original search strategies. This may enable the identification of additional relevant results.
A methodology for creating exhaustive search strategies has been created that describes all steps of the search process, starting with a question and resulting in thorough search strategies in multiple databases. Many of the steps described are not new, but together, they form a strong method creating high-quality, robust searches in a relatively short time frame.
Our methodology is intended to create thoroughness for literature searches. The optimization method, as described in step 11, will identify missed synonyms or thesaurus terms, unlike any other method that largely depends on predetermined keywords and synonyms. Using this method results in a much quicker search process, compared to traditional methods, especially because of the easier translation between databases and interfaces (step 13). The method is not a guarantee for speed, since speed depends on many factors, including experience. However, by following the steps and using the tools as described above, searchers can gain confidence first and increase speed through practice.
What is new?
This method encourages searchers to start their search development process using empty syntax first and later adding the thesaurus terms and free-text synonyms. We feel this helps the searcher to focus on the search terms, instead of on the structure of the search query. The optimization method in which new terms are found in the already retrieved articles is used in some other institutes as well but has to our knowledge not been described in the literature. The macros to translate search strategies between interfaces are unique in this method.
What is different compared to common practice?
Traditionally, librarians and information specialists have focused on creating complex, multi-line (also called line-by-line) search strategies, consisting of multiple record sets, and this method is frequently advised in the literature and handbooks [ 2 , 19 – 21 ]. Our method, instead, uses single-line searches, which is critical to its success. Single-line search strategies can be easily adapted by adding or dropping a term without having to recode numbers of record sets, which would be necessary in multi-line searches. They can easily be saved in a text document and repeated by copying and pasting for search updates. Single-line search strategies also allow easy translation to other syntaxes using find-and-replace technology to update field codes and other syntax elements or using macros (step 13).
When constructing a search strategy, the searcher might experience that certain parentheses in the syntax are unnecessary, such as parentheses around all search terms in the title/abstract portion, if there is only one such term, there are double parentheses in the proximity statement, or one of the word groups exists for only one word. One might be tempted to omit those parentheses for ease of reading and management. However, during the optimization process, the searcher is likely to find extra synonyms that might consist of one word. To add those terms to the first query (with reduced parentheses) requires adding extra parentheses (meticulously placing and counting them), whereas, in the latter search, it only requires proper placement of those terms.
Many search methods highly depend on the PICO framework. Research states that often PICO or PICOS is not suitable for every question [ 22 , 23 ]. There are other acronyms than PICO—such as sample, phenomenon of interest, design, evaluation, research type (SPIDER) [ 24 ]—but each is just a variant. In our method, the most important and specific elements of a question are being analyzed for building the best search strategy.
Though it is generally recommended that searchers search both MEDLINE and Embase, most use MEDLINE as the starting point. It is considered the gold standard for biomedical searching, partially due to historical reasons, since it was the first of its kind, and more so now that it is freely available via the PubMed interface. Our method can be used with any database as a starting point, but we use Embase instead of MEDLINE or another database for a number of reasons. First, Embase provides both unique content and the complete content of MEDLINE. Therefore, searching Embase will be, by definition, more complete than searching MEDLINE only. Second, the number of terms in Emtree (the Embase thesaurus) is three times as high as that of MeSH (the MEDLINE thesaurus). It is easier to find MeSH terms after all relevant Emtree terms have been identified than to start with MeSH and translate to Emtree.
At Erasmus MC, the researchers sit next to the information specialist during most of the search strategy design process. This way, the researchers can deliver immediate feedback on the relevance of proposed search terms and retrieved references. The search team then combines knowledge about databases with knowledge about the research topic, which is an important condition to create the highest quality searches.

Limitations of the method
One disadvantage of single-line searches compared to multi-line search strategies is that errors are harder to recognize. However, with the methods for optimization as described (step 11), errors are recognized easily because missed synonyms and spelling errors will be identified during the process. Also problematic is that more parentheses are needed, making it more difficult for the searcher and others to assess the logic of the search strategy. However, as parentheses and field codes are typed before the search terms are added (step 10), errors in parentheses can be prevented.
Our methodology works best if used in an interface that allows proximity searching. It is recommended that searchers with access to an interface with proximity searching capabilities select one of those as the initial database to develop and optimize the search strategy. Because the PubMed interface does not allow proximity searches, phrases or Boolean “AND” combinations are required. Phrase searching complicates the process and is more specific, with the higher risk of missing relevant articles, and using Boolean “AND” combinations increases sensitivity but at an often high loss of specificity. Due to some searchers’ lack of access to expensive databases or interfaces, the freely available PubMed interface may be necessary to use, though it should never be the sole database used for an SR [ 2 , 16 , 25 ]. A limitation of our method is that it works best with subscription-based and licensed resources.
Another limitation is the customization of the macros to a specific institution’s resources. The macros for the translation between different database interfaces only work between the interfaces as described. To mitigate this, we recommend using the find-and-replace functionality of text editors like Microsoft Word to ease the translation of syntaxes between other databases. Depending on one’s institutional resources, custom macros can be developed using similar methods.
Results of the method
Whether this method results in exhaustive searches where no important article is missed is difficult to determine, because the number of relevant articles is unknown for any topic. A comparison of several parameters of 73 published reviews that were based on a search developed with this method to 258 reviews that acknowledged information specialists from other Dutch academic hospitals shows that the performance of the searches following our method is comparable to those performed in other institutes but that the time needed to develop the search strategies was much shorter than the time reported for the other reviews [ 9 ].
CONCLUSIONS
With the described method, searchers can gain confidence in their search strategies by finding many relevant words and creating exhaustive search strategies quickly. The approach can be used when performing SR searches or for other purposes such as answering clinical questions, with different expectations of the search’s precision and recall. This method, with practice, provides a stepwise approach that facilitates the search strategy development process from question clarification to final iteration and beyond.
SUPPLEMENTAL FILE
Acknowledgments.
We highly appreciate the work that was done by our former colleague Louis Volkers, who in his twenty years as an information specialist in Erasmus MC laid the basis for our method. We thank Professor Oscar Franco for reviewing earlier drafts of this article.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

9.6: Finding and Evaluating Research Sources
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 58153
Introduction
In order to create rhetorically effective and engaging pieces, research writers must be able to find appropriate and diverse sources and to evaluate those sources for usefulness and credibility. This chapter discusses how to locate such sources and how to evaluate them. On the one hand, this is a chapter about the nuts and bolts of research. If you have written research papers before, searching for sources and citing them in your paper may, at times, have appeared to you as purely mechanical processes, chores necessary to produce a paper. On the other hand, when writers work with research sources, first finding and then evaluating them, they do rhetorical work. Finding good sources and using them effectively helps you to create a message and a persona that your readers are more likely to accept, believe, and be interested in than if unsuitable and unreliable sources are used. This chapter covers the various kinds of research sources available to writers. It discusses how to find, evaluate, and use primary and secondary sources, printed and online ones.
Types of Research Sources
It is a well-known cliché: we live in an information age. Information has become a tangible commodity capable of creating and destroying wealth, influencing public opinion and government policies, and effecting social change. As writers and citizens, we have unprecedented access to different kinds of information from different sources. Writers who hope to influence their audiences need to know what research sources are available, where to find them, and how to use them.
Primary and Secondary Sources
Definition of primary sources.
Let us begin with the definition of primary and secondary sources. A primary research sources is one that allows you to learn about your subject “firsthand.” Primary sources provide direct evidence about the topic under investigation. They offer us “direct access” to the events or phenomena we are studying. For example, if you are researching the history of World War II and decide to study soldiers’ letters home or maps of battlefields, you are working with primary sources. Similarly, if you are studying the history of your hometown in a local archive that contains documents pertaining to that history, you are engaging in primary research. Among other primary sources and methods are interviews, surveys, polls, observations, and other similar “firsthand” investigative techniques. The fact that primary sources allow us “direct access” to the topic does not mean that they offer an objective and unbiased view of it. It is therefore important to consider primary sources critically and, if possible, gather multiple perspectives on the same event, time period, or questions from multiple primary sources.
Definition of Secondary Sources
Secondary sources describe, discuss, and analyze research obtained from primary sources or from other secondary sources. Using the previous example about World War II, if you read other historians’ accounts of it, government documents, maps, and other written documents, you are engaging in secondary research. Some types of secondary sources with which you are likely to work include books, academic journals, popular magazines and newspapers, websites, and other electronic sources. The same source can be both primary and secondary, depending on the nature and purpose of the project. For example, if you study a culture or group of people by examining texts they produce, you are engaging in primary research. On the other hand, if that same group published a text analyzing some external event, person, or issue and if your focus is not on the text’s authors but on their analysis, you would be doing secondary research. Secondary sources often contain descriptions and analyses of primary sources. Therefore, accounts, descriptions, and interpretations of research subjects found in secondary sources are at least one step further removed from what can be found in primary sources about the same subject. And while primary sources do not give us a completely objective view of reality, secondary sources inevitably add an extra layer of opinion and interpretation to the views and ideas found in primary sources. All texts are rhetorical creations, and writers make choices about what to include and what to omit. As researchers, we need to understand that and not rely on either primary or secondary sources blindly.
Writing Activity: Examining the Same Topic through Primary and Secondary Sources
Primary and secondary sources can offer writers different views of the same topic. This activity invites you to explore the different perspectives that you may get after investigating the same subject through primary and secondary sources. It should help us see how our views of different topics depend on the kinds of sources we use. Find several primary sources on a topic that interests you. Include archival documents, first- hand accounts, lab experiment results, interviews, surveys, and so on. Depending on how much time you have for this project, you may or may not be able to consult all of the above source types. In either case, try to consult sources of three or four different kinds. Next, write a summary of what you learned about your subject as a result of your primary-source investigation. Mention facts, dates, important people, opinions, theories, and anything that seems important or interesting. Now, conduct a brief secondary-source search on the same subject. Use books, journals, popular magazines and newspapers, Internet sites, and so on. Write a summary of your findings. Finally, compare the two summaries. What differences do you see? What new ideas, perspectives, ideas, or opinions did your secondary-source search yield? As a result of these two searches, have you obtained different accounts of the same research subject? Pay special attention to the differences in descriptions, accounts, or interpretations of the same subject. Notice what secondary sources add to the treatment of the subject and what they take away, compared to the primary sources.
Print and Electronic Sources
Researcher have at their disposal both printed and electronic sources. Before the advent of the Internet, most research papers were written with the use of printed sources only. Until fairly recently, one of the main stated goals of research writing instruction was to give students practice in the use of the library. Libraries are venerable institutions, and therefore printed sources have traditionally been seen (with good reason, usually,) as more solid and reliable than those found on the Internet. With the growing popularity of the Internet and other computerized means of storing and communicating information, traditional libraries faced serious competition for clients. It has become impractical if not impossible for researchers to ignore the massive amount of information available to them on the Internet or from other online sources. As a result, it is not uncommon for many writers beginning a research project to begin searching online rather than at a library or a local archive. For example, several times in the process of writing this essay, when I found myself in need of information fast, I opened my Web browser and researched online. With the popularity of the Internet ever increasing, it has become common practice for many student writers to limit themselves to online research and to ignore the library. While there are some cases when a modified version of such an approach to searching may be justifiable (more about that later), it is clear that by using only online research sources, a writer severely limits his or her options. This section covers three areas. First, we will discuss the various types of printed and online sources as well the main similarities and differences between them. Next, I’d like to offer some suggestions on using your library effectively and creatively. Finally, we will examine the topic of conducting online searches, including methods of evaluating information found on the Internet.
Know Your Library
It is likely that your college or university library consists of two parts. One is the brick and mortar building, often at a central location on campus, where you can go to look for books, magazines, newspapers, and other publications. The other part is online. Most good libraries keep a collection of online research databases that are supported, at least in part, by your tuition and fees, and to which only people who are affiliated with the college or the university that subscribes to these databases have access. Let us begin with the brick and mortar library. If you have not yet been to your campus library, visit it soon. Larger colleges and universities usually have several libraries that may specialize in different academic disciplines. As you enter the library, you are likely to find a circulation desk (place where you can check out materials) and a reference desk. Behind the reference desk you will find reference librarians. Instead of wandering around the library alone, hoping to hit the research sources that you need for your project, it is a good idea to talk to a reference librarian at the beginning of every research project, especially if you are at a loss for a topic or research materials. Your brick and mortar campus library is likely to house the following types of materials:
- Books (these include encyclopedias, dictionaries, indexes, and so on)
- Academic Journals
- Popular magazines
- Government documents
- A music and film collection (on CDs, VHS tapes, and DVDs)
- A CD-Rom collection
- A microfilm and microfiche collection
- Special collections, such as ancient manuscripts or documents related to local history and culture.
According to librarian Linda M. Miller, researchers need to “gather relevant information about a topic or research question thoroughly and efficiently. To be thorough, it helps to be familiar with the kinds of resources that the library holds, and the services it provides to enable access to the holdings of other libraries” (2001, 61). Miller’s idea is a simple one, yet it is amazing how many inexperienced writers prefer to use the first book or journal they come across in the library as the basis for their writing and do not take the time to learn what the library has to offer. Here are some practical steps that will help you learn about your library:
Take a tour of the library with your class or other groups if such tours are available. While such group tours are generally less effective than conducting your own searches of a topic that interests you, they will give you a good introduction to the library and, perhaps, give you a chance to talk to a librarian.
Check your library’s website to see if online “virtual” tours are available. At James Madison University where I work, the librarians have developed a series of interactive online activities and quizzes which anyone wishing to learn about the JMU libraries can take in their spare time.
Talk to reference librarians! They are truly your best source of information. They will not get mad at you if you ask them too many questions. Not only are they paid to answer your questions, but most librarians love what they do and are eager to share their expertise with others.
Go from floor to floor and browse the shelves. Learn where different kinds of materials are located and what they look like.
Pay attention to the particulars of your campus library’s architecture. I am an experienced library user, but it look me some time, after I arrived at my university for the first time, to figure out that our library building has an annex that can only be accessed by taking a different elevator from the one leading to the main floors.
Use the library not only as a source of knowledge but as a source of entertainment and diversion. I like going to the library to browse through new fiction acquisitions. Many campus libraries also have excellent film and music collections.
The items on the list above will help you to acquire a general understanding of your campus library. However, the only way to gain an in-depth and meaningful knowledge of your library is to use it for specific research and writing projects. No matter how attentive you are during a library tour or while going from floor to floor and learning about all the different resources your library has to offer, it is during searchers that you conduct for your research projects that you will become most interested and involved in what you are doing. Here, therefore, is an activity that combines the immediate goal of finding research sources for a research project with the more long-term goal of knowing what your campus library has to offer.
Activity: Conducting a Library Search for a Writing Project
If you have a research and writing topic in mind for your next project, head for your brick-and-mortar campus library. As soon as you enter the building, go straight to the reference desk and talk to a reference librarian. Be aware that some of the people behind the reference desk may be student assistants working there. As a former librarian assistant myself and as a current library user, I know that most student assistants know their job rather well, but sometimes they need help from the professionals. So, don’t be surprised if the first person you approach refers you to someone else. Describe your research interests to the librarian. Be proactive. The worst disservice you can do yourself at this point is to look, sound, and act disinterested. Remember that the librarian can be most helpful if you are passionate about the subject of your research and if—this is very important—the paper you are writing is not due the next day. So, before you go to the library, try to narrow your topic or formulate some specific research questions. For example, instead of saying that you are interested in dolphins, you might explain that you are looking for information about people who train dolphins to be rescue animals. If the librarian senses that you have a rather vague idea about what to research and write about, he or she may point you to general reference sources such as indexes, encyclopedias, and research guides. While those may prove to be excellent thought-triggering publications, use them judiciously and don’t choose the first research topic you find just because your library has a lot of resources on it. After all, your research and writing will be successful only when you are deeply interested in and committed to your investigation. If you have a more definite idea about what you would like to research and write about, the reference librarian will likely point you to the library’s online catalog. I have often seen librarians working alongside students to help them identify or refine a writing topic. Find several different types of materials pertaining to your topic. Include books and academic articles. Don’t forget popular magazines and newspapers—the popular press covers just about any subject, event, or phenomena, and such articles may bring a unique perspective not found in academic sources. Also, don’t neglect to look in the government documents section to see if there has been any legislation or government regulation relevant to your research subject. Remember that at this stage your goal is to learn as much as you can about your topic by casting your research net as far and wide as you can. So, do not limit yourself to the first few sources you will find. Keep looking, and remember that your goal is to find the best information available. You will probably have to look in a variety of sources. If you are pressed for time you may not be able to study the books dedicated to your topic in detail. In this case, you may decide to focus your research entirely on shorter texts, such as journal and magazine articles, websites, government documents, and so on. However it is always a good idea to at least browse through the books on your topic to see whether they contain any information or leads worth investigating further.
Cyber Library
Besides the brick and mortar buildings, nearly all college and university libraries have a Web space that is a gateway to more documents, resources, and information than any library building can house. From your library’s website, you can not only search the library’s holdings but also access millions of articles, electronic books, and other resources available on the Internet. It is a good idea to conduct a search from your campus library page rather than from your favorite search engine. There are three reasons for that. First, most of the materials you will find through your library site are accessible to paying subscribers only and cannot be found via any search engine. Second, online library searches return organized and categorized results, complete with the date of publication and source—something that cannot be said about popular search engines. Finally, by searching online library databases you can be reasonably sure that the information you retrieve is reliable.
So, what might you expect to find on your library’s website? The site of the library at James Madison University where I work offers several links. In addition to the link to the library catalog, there is a Quick Reference link, a link called Research Databases, a Periodical Locator, Research Guides, and Internet Search. There are also links to special collections and to the featured or new electronic databases to which the library has recently subscribed. While your school library may use other names for these links, the kinds of resources they offer will be similar to what JMU’s library has to offer. Most of these links are self-explanatory. Obviously, the link to the library catalog allows you to search your brick and mortar library’s collection. A periodical locator search will tell you what academic journals, popular magazines, and newspapers are available at your library. The Internet search option will allow you to search the World Wide Web, except that your library’s Internet searching function will probably allow you to conduct meta-searches—i.e., searches using many search engines simultaneously. Where a link like Research Databases or Research Guides will take you is a little less obvious. Therefore I will cover these two types of library resources in some detail. Let us start with the research databases. An average-size college or university subscribes to hundreds, if not thousands, of online databases on just about every subject. These databases contain, at a minimum, information about titles, authors, and sources of relevant newspaper and journal articles, government documents, online archive materials, and other research sources. Most databases provide readers with abstracts (short summaries) of those materials, and a growing number of online databases offer full texts of articles. From the research-database home page, it is possible to search for a specific database or by subject. Research-guide websites are similar to the database home pages, except that, in addition to database links, they often offer direct connections to academic journals and other relevant online resources on the research subject. Searching online is a skill that can only be learned through frequent practice and critical reflection. Therefore, in order to become a proficient user of your library’s electronic resources, you will need to visit the library’s website often and conduct many searches. Although most library websites are organized according to similar principles and offer similar types of resources, it will be up to you as a researcher and learner to find out what your school library has to offer and to learn to use those resources. I hope that the following activities will help you in that process.
Activity: Exploring your Cyber Library
Go to your school library’s website and explore the kinds of resources it has to offer.
Conduct searches on a subject you are currently investigating or interested in investigating in the future, using the a periodical locator resource (if your library has one). Then, conduct similar searches of electronic databases and research guides.
Summarize, whether in an oral presentation or in writing, your search process and the kinds of sources you have found. Pay attention to particular successes and failures that occurred as you searched.
Print Sources or Electronic?
In the early years of the Internet, there was widespread mistrust of the World Wide Web and the information it had to offer. While some of this mistrust is still present (and justifiable), the undeniable fact is that the authority of the Internet as a legitimate and reliable source of information has increased considerably in recent years. For example, academic journals in almost every discipline complement their printed volumes with Web versions, and some are now only available online. These online journals employ the same rigorous submission review processes as their printed counterparts. Complete texts of academic and other books are sometimes available on the Internet. Respected specialized databases and government document collections are published entirely and exclusively online. Print and electronic sources are not created equal, and although online and other electronic texts are gaining ground as legitimate research resources, there is still a widespread and often justified opinion among academics and other writers that printed materials make better research sources. Some materials available in some libraries simply cannot be found online and vice versa. For example, if you are a Shakespeare scholar wishing to examine manuscripts from the Elizabethan times, you will not find them online. To get to them, you will have to visit the Folger Shakespeare Library in Washington, DC, or a similar repository of Elizabethan manuscripts. On the other hand, if you are researching the Creative Commons movement, which is a community dedicated to reforming copyright laws in this country, then your best bet is to begin your search on the Internet at http://www.creativecommons.org/ . Surely, after reading the website, you will need to augment your research by reading other related materials, both online and in print, but in this case, starting online rather than in the library is a reasonable idea. As a researching writer, you should realize that printed and electronic sources are not inherently bad or good. Either type can be reliable or unreliable; either can be appropriate or inappropriate for a specific research project. It is up to researchers and writers to learn how to select both print and electronic sources judiciously and how to evaluate them for their reliability and appropriateness for particular purposes.
Determining the Suitability and Reliability of Research Sources
Much of the discussion about the relative value of printed and electronic—especially Internet—sources revolves around the issue of reliability. When it comes to libraries, the issue is more or less clear. Libraries keep books, journals, ands other publications that usually undergo a rigorous pre- and post-publication review process. It is reasonable to assume that your campus library contains very few or no materials that are blatantly unreliable or false, unless those materials are kept there precisely to demonstrate their unreliability and falsehood. As a faculty member, I am sometimes asked by my university librarians to recommend titles in my academic field that our university library should own. Of course my opinion (or that of another faculty member) does not completely safeguard against the library acquiring materials that contain errors and or misleading information; we use our experience and knowledge in the field to recommend certain titles and omit certain others. Faculty recommendations are the last stage of long process before a publication gets to a campus library. Before that, every book, journal article, or other material undergoes a stringent review from the publisher’s editors and other readers. And while researchers still need to use sound judgment in deciding which library sources to use in their project, the issue is usually one of relevance and suitability for a specific research project and specific research questions rather than one of whether the information presented in the source is truthful or not. The same is true of some electronic sources. Databases and other research sources published on CD-ROMs, as well as various online research websites that accompany many contemporary writing textbooks, for example, are subject to the same strict review process as their printed counterparts. Information contained in specialized academic and professional databases is also screened for reliability and accuracy. If, as we have established, most of the materials you are likely to encounter in your campus library are generally trustworthy, then your task as a researcher is to determine the relevance of the information contained in books, journals, and other materials for your particular research project. It is a simple question, really: will my research sources help me answer the research questions that I am posing in my project? Will they help me learn as much as I can about my topic and create a rhetorically effective and interesting text for my readers? Consider the following example. Recently, the topic of the connection between certain antidepressant drugs and suicidal tendencies among teenagers who take those drugs has received a lot of media coverage. Suppose you are interested in researching this topic further. Suppose, too, that you want not only to give statistical information about the problem in your paper but also to study firsthand accounts of the people who have been negatively affected by the antidepressants. When you come to your campus library, you have no trouble locating the latest reports and studies that give you a general overview of your topic, including rates of suicidal behavior in teenagers who took the drugs, tabulated data on the exact relationships between the dosage of the drugs and the changes in the patients’ moods, and so on. All this may be useful information, and there is a good chance that, as a writer, you will still find a way to use it in your paper. You could, for example, provide the summary of the statistics in order to introduce the topic to your readers. However, this information does not fulfill your research purpose completely. You want to understand what it is like to be a teenager whose body and mind have been affected by the antidepressants, yet the printed materials you have found so far offer no such insight. They fulfill your goal only partially. To find such firsthand accounts, then, you will either have to keep looking in the library or conduct interviews with people who have been affected by these drugs.
Suitability of Sources
Determine how suitable a particular source is for your current research project. To do this, consider the following factors:
- Scope: What topics and subtopics does the source cover? Is it a general overview of your subject or it is a specialized resource?
- Audience: Who is the intended audience for the text? If the text itself is too basic or too specialized, it may not match the expectations and needs of your own target audience.
- Timeliness: When was the source published? Does it represent the latest information, theories, and views? Bear in mind, though, that if you are conducting a historical investigation, you will probably need to consult older materials, too.
What are credentials of the author(s)? This may be particularly important when you use Internet sources, since there are so few barriers to publishing online. One needn’t have an academic degree or credentials to make one’s writing publicly available. As part of your evaluation of the source’s authority, you should also pay attention to the kinds of external sources that were used during its creation. Look through the bibliography or list of works cited attached to the text. Not only will it help you determine how reliable and suitable the source is, but it may also provide you with further leads for your own research. Try asking the above questions of any source you are using for a research project you are currently conducting.
Reliability of Internet Sources
Charles Lowe, the author of the essay “The Internet Can Be a Wonderful Place, but . . .” offers the following opinion of the importance of the Internet as a research source for contemporary researchers:
To a generation raised in the electronic media culture, the Internet is an environment where you feel more comfortable, more at home than the antiquated libraries and research arenas of the pre-electronic, print culture. To you, instructors just don’t get it when they advise against using the Internet for research or require the bulk of the sources for a research paper to come from the library (129-130).
Indeed, the Internet has become the main source of information not only for college students, but also for many people outside academia. And while I do not advise you to stay away from the Internet when researching and I generally do not require my own students to use only printed sources, I do know that working with Internet sources places additional demands on the researcher and the writer. Because much of the Internet is a democratic, open space, and because anyone with a computer can post materials online, evaluating online sources is not always easy. A surprisingly large number of people believe much of the information on the Internet, even if this information is blatantly misleading or its authors have a self-serving agenda. I think many students uncritically accept information they find on the Internet because some of the sites on which this information appears look and sound very authoritative. Used to believing the published word, inexperienced writers often fall for such information as legitimate research data. So, what are some of strategies you can use to determine that reliability? The key to successful evaluation of Internet research sources, as any other research sources, is application of your critical reading and thinking skills. In order to determine the reliability of any source, including online sources, it is advisable to conduct a basic rhetorical analysis of that source. When deciding whether to use a particular website as a research source, every writer should ask and answer the following questions:
- Who is the author (or, authors) of the website and the materials presented on it? What is known about the site’s author(s) and its publishers and their agendas and goals?
- What is the purpose of the website?
- Who is the target audience of the website
- How do the writing style and the design of the website contribute to (or detract from) its meaning?
Website Authors and Publishers
As with a printed source, first we need to consider the author and the publisher of a website. Lowe suggests that we start by looking at the tag in the website’s URL. Whether it is a “.com,” an “.org,” a “.net, “or an “.edu” site can offer useful clues about the types and credibility of materials located on the site. In addition to the three most common URL tags listed above, websites of military organizations use the extension “.mil” while websites hosted in other countries have other tags that are usually abbreviations of those countries’ names. Sites of government agencies end in “.gov.” For example, most sites hosted in Great Britain have the tag “.uk,” which stands for “United Kingdom.” Websites based in Italy usually have the tag “.it,” and so on. Typically, a “.com” site is set up to sell or promote a product or service. Therefore, if you are researching Nike shoes, you will probably not want to rely on http://www.nike.com/ if you want to get a more objective review of the product. While Nike’s website may provide some useful information about the products it sells, the site’s main purpose is to sell Nike’s goods, playing up the advantages of their products. Keep in mind that not all “.com” websites try to sell something. Sometimes academics and other professionals obtain “.com” addresses because they are easy to obtain. For example, the professional website of Charles Lowe (cited above) is located at http://www.cyberdash.com/ . Political candidates running for office often also choose “.com” addresses for their campaign websites. In every case, you need to apply your critical reading skills and your judgment when evaluating a website. The “.org” sites usually belong to organizations, including political groups. These sites can present some specific challenges to researchers trying to evaluate their credibility and usefulness. To understand these challenges, let us consider the “.org” sites of two political research organizations, also known as “think tanks.” One is the conservative Heritage Foundation ( http://www.heritage.org ), and the other is the traditionally liberal Center for National Policy ( http://www.cnponline.org ). Both sites have “About” pages intended to explain to their readers the goals and purposes of the organizations they represent. The Heritage Foundation’s site contains the following information:
. . . The Heritage Foundation is a research and educational institute—a think tank—whose mission is to formulate and promote conservative public policies based on the principles of free enterprise, limited government, individual freedom, traditional American values, and a strong national defense. ( http://www.heritage.org/about )
This statement can tell a researcher a lot about the research articles and other materials contained in the site. It tells us that the authors of the site are not neutral, nor do they pretend to be. Instead, they are advancing a particular political agenda, so, when used as research sources, the writings on the site should not be seen as unbiased “truths” but as arguments. The same is true of the Center for National Policy’s website, although its authors use a different rhetorical strategy to explain their political commitments. They write:
The Center for National Policy (CNP) is a nonprofit, nonpartisan public policy organization located in Washington, DC. Founded in 1981, the center’s mission is to engage national leaders with new policy options and innovative programs designed to advance progressive ideas in the interest of all Americans ( http://www.cnponline.org/people_and_programs.html )
It takes further study of the center’s website, as well as sure knowledge of the American political scene, to realize that the organization leans toward the left of the political spectrum. The websites of both organizations contain an impressive amount of research, commentary, and other materials designed to advance the groups’ causes. When evaluating “.org” sites, it is important to realize that they belong to organizations, and each organization has a purpose or a cause. Therefore, each organizational website will try to advance that cause and fulfill that purpose by publishing appropriate materials. Even if the research and arguments presented on those sites are solid (and they often are), there is no such thing as an unbiased and disinterested source. This is especially true of political and social organizations whose sole purpose is to promote agendas. The Internet addresses ending in “.edu” are rather self-evident—they belong to universities and other educational institutions. On these sites we can expect academic articles and other writings, as well as papers and other works created by students. These websites are also useful resources if you are looking for information on a specific college or university. Be aware, though, that typically any college faculty member or student can obtain Web space from their institution and publish materials of their own choosing there. Thus some of the texts that appear on “.edu” sites may be personal rather than academic. In recent years, some political research organizations have begun to use Web addresses with the “.edu” tag. One of these organizations is The Brookings Institution, whose address is http://www.brookings.edu . Government websites that end in “.gov” can be useful sources of information on the latest legislation and other regulatory documents. The website with a “.net” extension can belong to commercial organizations or online forums.
Website Content
Now that we have established principles for evaluating the authors and publishers of Web materials, let us look at the content of the writing. As I have stated above, like all writing, Web writing is argumentative; therefore it is important to recognize that authors of Web texts work to promote their agendas or highlight the events, organizations, and opinions that they consider right, important, and worthy of public attention. Different writers work from different assumptions and try to reach different audiences. Websites of political organizations are prime examples of that.
Activity: Evaluating Website Content
Go to one of the following websites: The Heritage Foundation ( http://www.heritage.org ), The Center for National Policy ( http://www.cnponline.org ), The Brookings Institution ( http://www.brookings.edu ), or The American Enterprise Institute ( http://www.aei.org ). Or choose another website suggested by your instructor. Browse through the site’s content and consider the following questions:
- What is the purpose of the site?
- What is its intended audience? How do we know?
- What are the main subjects discussed on the sites?
- What assumptions and biases do the authors of the publications on the site seem to have? How do we know?
- What research methods and sources do the authors of these materials use? How does research help the writers of the site state their case?
Apply the same analysis to any online sources you are using for one of your research projects.
Website Design and Style
The style and layout of any text is a part of that text’s message, and online research sources are no exception. Well-designed and written websites add to the ethos (credibility) of their authors while badly designed and poorly written ones detract from it. Sometimes, however, a website with a good-looking design can turn out to be an unreliable or unsuitable research source.
In Place of a Conclusion: Do Not Accept A Source Just Because It Sounds or Looks Authoritative
Good writers try to create authoritative texts. Having authority in their writing helps them advance their arguments and influence their audiences. To establish such authority, writers use a variety of methods. As has been discussed throughout this essay, it is important for any researcher to recognize authoritative and credible research sources. On the other hand, it is also important not to accept authoritative sources without questioning them. After all, the purpose of every researched piece of writing is to create new views and new theories on the subject, not to repeat the old ones, however good and well presented those old theories may be. Therefore, when working with reliable and suitable research sources, consider them solid foundations that will help you to achieve a new understanding of your subject, which will be your own. Applying the critical source-evaluation techniques discussed in this essay will help you to accomplish this goal.
- Finding and Evaluating Research Sources. Authored by : Pavel Zemliansky. Located at : http://www.saylor.org/site/wp-content/uploads/2011/01/ENGL002-Chapter-4-Research-Writing.pdf . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Learning how to find, evaluate, and use resources to explore a topic in depth
Series Editor : Michael Theall, Youngstown State University Authors : Gail MacKay, Indiana University Kokomo; Barbara Millis, University of Nevada-Reno; Rebecca Brent, Education Designs, Inc.
At institutions of higher education across the U.S., information literacy (IL) is being integrated into general education curricula as a specific learning objective. The Association of College and Research Libraries (ACRL) (1) defines information literate students as those who “recognize when information is needed and have the ability to locate, evaluate, and use effectively the needed information.” As the world moves toward a knowledge-based economy, information literacy becomes a crucial component of preparing students for the lifelong learning that current and future job markets demand.
IDEA Research Report #1 (2) states that, “…It is important to recognize that much of the subject matter content which students learn today will be outdated in 5-10 years after they graduate.” Thus, an emphasis on lifelong learning seems imperative. Canja (3), for example, suggests that “… Lifelong learning has become an economic necessity for national and global productivity. With the decline in birth rates in major developed countries, persons—still active, still healthy—must continue in the workforce, trained and retrained” (p. 27). Ironically, IDEA Research Report #1 also finds that the objectives identified as emphasizing lifelong learning (Learning to find and use resources, and Gave tests/projects that covered most important points) were identified as “Important” or “Essential” in only about 30% of the classes using IDEA. The ACRL (1) notes, “Information literacy forms the basis for lifelong learning. It is common to all disciplines, to all learning environments, and to all levels of education. It enables learners to master content and extend their investigations, become more self-directed, and assume greater control over their own learning.” However, information literacy does not concern itself only with technical resources. Successful students and workers must also be able to affiliate with others and to seek and find expertise among the human resources that are available (4).
Seeking out information resources and then using them to address a question or a problem are engaging activities, and there are several attached benefits. First is recognition of the value of the resources. Next is application of the new information and the construction of new knowledge. Intrinsic motivation results from the realization that learning is taking place and ultimately, these practical and motivational effects promote continued use of the resources, lifelong learning, and facilitates deep learning.
For example, here are key components that characterize a deep, rather than a surface approach to learning. Rhem (5) summarizes them as follows:
Motivational context: We learn best what we feel a need to know. Intrinsic motivation remains inextricably bound to some level of choice and control. Courses that remove these take away the sense of ownership and kill one of the strongest elements in lasting learning.
Learner activity: Deep learning and “doing” travel together. Doing in itself isn’t enough. Faculty must connect activity to the abstract conceptions that make sense of it, but passive mental postures lead to superficial learning.
Interaction with others: As Noel Entwistle put it in a recent email message, “The teacher is not the only source of instruction or inspiration.”
A well-structured knowledge base: This does not just mean presenting new material in an organized way. It also means engaging and reshaping, when necessary, the concepts students bring with them. Deep approaches and learning for understanding are integrative processes. The more fully new concepts can be connected with students’ prior experience and existing knowledge, the more it is they will be impatient with inert facts and eager to achieve their own synthesis (p. 4).
If instructors are to motivate students to acquire the skills of information literacy that will help them to remain lifelong learners, then they need to design research projects and assignments that get students into the knowledge base and engage them in critical thinking activities through active learning and interaction with one another. Through such sequenced assignments, students can learn how to answer relevant questions and to solve challenging problems.
Keep in mind that an important component of finding and using resources to explore topics is evaluating the quality of those resources. In an information-rich world, students must be able to determine if a resource is reliable and valid enough to use in their work. These information literacy skills (and even quantitative literacy skills–see the Teaching Note, “Learning appropriate methods for collecting, analyzing, and interpreting numerical information”) must be taught. See the Teaching Note, “Encouraged students to use multiple resources (e.g. Internet, library holdings, outside experts) to improve understanding,” for more ideas.
Teaching This Objective
The most relevant IDEA instructional method is “encouraged students to use multiple resources to improve understanding.” This Learning Note complements Baron’s with some general guidelines that focus on developing good research projects or assignments to assist with “learning how to find and use resources for answering questions or solving problems” and attempts to help instructors provide students with effective and feasible assignments. With today’s information overload, students need guidance in locating and using appropriate resources for answering questions and solving problems. Students must hone these skills throughout their lives. Academic librarians can serve as an instructor’s best ally.
Other IDEA instructional methods that are important to Objective #9 include items #2 Finding ways to help students answer their own questions, #8 Stimulating intellectual effort, #15 Inspiring students to set and achieve goals, #18 Asking students to help each other understand ideas or concepts, and #19 Assigning work that requires original or creative thinking. These relationships are logical because the nature of investigative activity requires intellectual effort, focused exploration, and creativity, and the connections between problem solving and gathering information and evidence have been well-documented (6). These methods support many of the specific hints described below.
Motivation as a starting point. Locating information for its own sake provides practice, but it fails to engage motivated students in productive work linked to an understood outcome. Feldman suggests that student achievement remains strongly correlated to the perceived outcomes of instruction (7). The relevance of assigned work is also critical to student’s active engagement (8) and a major predictor of student ratings of their teachers (9). Thus, skill development becomes much more productive when there is a clearly understood link between the assigned work and specific learning goals or tangible products. The real-world analog is obvious: people do not search for information unless they have a reason to do so. Because in many teaching-learning situations, teachers expect students to explore issues and topics that may not intrinsically interest them, demonstrating relevance and utility become critical first steps in getting students engaged (See “Related course material to real-life situations” and “Introduced stimulating ideas about the subject”). Allowing students some choice of topic or project can motivate them to take a deeper approach to learning (10).
Sequence the research project or assignment. If instructors want students to learn to find and use resources to tackle stimulating questions and challenging problems through research, they need to design sequenced activities that motivate students and get them into the knowledge base. This can often be accomplished through the individual work that students do either as discrete homework assignments or as smaller parts of an extended research project. What becomes of these assignments or project components is critical for deep learning. Instructors should design in-class exercises where learners are actively engaged with the material they prepared individually and with each other (11).
A. Planning
- Arrange for library instruction. Even students who have achieved some level of proficiency with library research will benefit from the reinforcement and enhancement of their skills. Require attendance. Attend yourself, asking questions as a learner.
- Bring the class to the library or ask a librarian to come to your classroom when they are ready to begin their project, not in advance. Students learn best when there is an immediate and applicable need.
- Send a copy of the assignment to the instruction librarian at your campus. Ask for input before finalizing the assignment. Librarians, for example, are highly skeptical of the academic value of commonly assigned “Library Scavenger Hunts.”
- Include homegrown resource guides, sometimes called “pathfinders,” in your initial quest for student library sources. Often campus instruction and reference librarians develop these guides for various fields or disciplines. If your field is not included, ask the library to develop a resource guide for your area. These subject guides provide students with suggestions for “where to start” their research. Included in the guides are both print and electronic sources such as subject encyclopedias; specialized periodical indexes such as Applied Science and Technology Index ; PsycINFO ; or Sociological Abstracts ; also included are reference works or standards in the field such as The Physician’s Desk Reference (PDR) ; CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics ; or the Statistical Abstract of the United States .
- Consider alternatives to the conventional research paper. Excellent assignment ideas reside on the Web, often at other campus library sites (12, 13, 14, 15, 16).
B. Designing
- Provide your expectations for the assignment in writing to your students. Let them know what the assignment involves and what you expect them to learn from the experience. “I don’t know what s/he wants” is a student lament transcending the ages. Make their day; tell them. To help students fully understand these expectations in practice, consider providing strong and weak samples of typical segments of the project or assignment to discuss and critique in class.
- Specify how the assignment fits with the goals or objectives of the course to show relevance. Be as explicit as possible. Share this information, also, with instruction librarians to help them determine appropriate sources.
- Provide students with the grading criteria in writing for the project or assignment.
- Offer a variety of flexible topics, encouraging students to choose ones that interest them.
- Review the student-selected topics to see that they are appropriate and achievable. Avoid very current or local topics if students need scholarly sources as scholarly peer reviewed journals take time to reach publication.
- Place materials on “Reserve,” if necessary, to avoid having 30 students compete for six books.
- Discuss the role of attribution and documentation in a community of scholars. Include a policy on plagiarism in the syllabus. Emphasize the ethical use of information and of the avoidance of plagiarism. Aside from ethics, there are also copyright laws, both national and international, to consider. Specifically discuss appropriate and inappropriate use of online material, a gray area for many students.
- Announce which style manual you expect students to use. Be very specific about documentation for online sources. Many style manuals are difficult to interpret.
Provide opportunities to engage in deep learning. As noted in the background section, the key components characterizing deep learning are motivation context, learner activity, interaction with others, and a well-structured knowledge base (5). As an example, faculty members can ask students, as part of a larger research project, to prepare paired annotations based on the double entry journal recommended by writing across the curriculum and classroom assessment experts (17). The teacher or the students identify a pool of articles on the question or problem at hand. Each student, working individually out-of-class, prepares a reflective commentary on one of the articles or chapters. They do so using a double column format (a Microsoft Word table works beautifully) where they cite the key points of the research article on the left-hand side and reactions, questions, commentary, and connections with other readings on the right, aligning the key point with the reflective commentary. The entries in these columns will not be the same length. When students come to class, the teacher randomly pairs them with another student who has read and analyzed the same research article. The two partners now read one another’s reflective commentaries, comparing both the key points they have identified and their specific responses to them. They discuss their reasons for the choices they made. Then working together, they prepare a composite annotation summarizing the article (See IDEA Paper No. 38).
This activity should be repeated several times during the semester, pairing different students. It enables students to reflect on their own thinking skills (metacognition) and to compare their thinking with those of other students. The more paired annotations they complete, the more skilled students become at identifying key points in an article and “using resources for answering questions or solving problems.” This structure thus enables teachers to sequence learning in meaningful ways. It builds critical thinking and writing skills by having students analyze and then compare their responses to the same piece of writing. It has the additional virtue of being relevant to virtually any discipline. Over the course of the semester, students build a repertoire of annotated research articles they can bring to bear on the given question or problem.
A note about technology. A thorough discussion of the ways in which new technologies can support and supplement students’ efforts to find and use resources is beyond the scope of this Note. However, we should mention at minimum, that the bounty that awaits students who explore web-based resources comes with a price: the equally large amount of inaccurate, incomplete, and sometimes distorted information that can be found in any web search. The critical issue for teachers is to construct assignments that require specific information known to exist and is accessible with minimum interference from useless, irrelevant, or biased data . Your resource librarian can be a tremendous asset in saving you hours of work (e.g., training students on effective and efficient search strategies and helping everyone to avoid wasting time and effort on valueless information). All disciplines and courses deal with electronic information and we cannot ignore its potential value. What is important to remember in constructing assignments is that the work must have a meaningful relationship to a clearly stated outcome. There has to be a tangible “payoff” in terms of students being able to connect the work to an understood and desired result.
Assessing This Objective
- Develop a rubric (or a form) to assess the announced grading criteria. For example, assign a certain number of points for each component of a project or assignment (see 2 below). What percentage of the total will the final paper and bibliography be? Note what happens if any of the required items are a day late; two days late; etc. What percentage will mechanics—spelling, punctuation, grammar—contribute to the final grade?
- Sequence parts of the project or assignment by establishing intermittent deadlines along the way. This practice not only helps prevent procrastination, but also helps to deter plagiarism. For example, have due dates for the overall topic and the thesis statement, due dates for a preliminary bibliography of “X” number of sources, an outline, a first draft, oral presentation, written or in-class peer reviews, etc.
- Require critical thinking. If students are using Web sites, for example, ask for the background or credentials of the author; ask for the date of last revision if currency is important; ask if students found any bias on the site; and ask why they selected this site from among all the others.
- Make use of peer reviewing throughout the research project or assignment to provide an additional source of feedback and add to the active learning and student interactions essential for deep learning. Have students exchange drafts and apply the rubric or checklist that will be used to assess the assignment. The opportunity for critical review of another draft and seeing comments from a peer will help them more fully understand the expectations, leading to better final products.
- Review respected resources such as the Tutorial for Developing and Evaluating Library Assignments at the University of Maryland University College, Adelphi, MD (18) and the Scoring Criteria for Development/Resource-Based Learning Project at Delta College, University Center, MI (19).
- Association of College and Research Libraries (ACRL). (2006). Information literacy competency standards for higher education. American Library Association. Retrieved September 27, 2006 from http://www.ala.org/ala/acrl/acrlstandards/standardsguidelines.htm
- Hoyt, D. P., & Perera, S. (2000). Teaching approach, instructional objectives, and learning: IDEA research report #1 . Manhattan, KS: IDEA Center, Kansas State University.
- Canja, E. T. (2002). Lifelong learning: Challenges and opportunities. CAEL Forum and News , 26-29.
- Klemp, G. O. (1977). Three factors of success. In D. W. Vermilye (Eds.) Relating work and education: Current issues in higher education 1977 . San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
- Rhem, J. (1995). Close-up: Going deep. The National Teaching and Learning Forum, 5 (1), 4.
- See the Problem Based Learning website at: http://www.samford.edu/pbl/ for many resources and references. Retrieved September 27, 2006.
- Feldman, K. A. (1989). The association between student ratings of specific instructional dimensions and student achievement: Refining and extending the synthesis of data from multisection validity studies. Research in Higher Education, 30 , 583-645.
- Theall, M. (1999). What have we learned? A synthesis and some guidelines for effective motivation in higher education. In M. Theall (Eds.) “Motivation from within: Encouraging faculty and students to excel.” New Directions for Teaching and Learning, 78 . San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
- Franklin, J. L., & Theall, M. (1995). The relationship of disciplinary differences and the value of class preparation time to student ratings of instruction. In N. Hativa & M. Marincovich (Eds.) “Disciplinary differences in teaching and learning: Implications for practice.” New Directions for Teaching and Learning, 64 . San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
- Felder, R.M., & Brent, R. (2005). Understanding student differences. Journal of Engineering Education, 94 (1), 57-72. Retrieved September 27, 2006 from http://www.ncsu.edu/effective_teaching/Papers/Understanding_Differences.pdf
- Millis, B. J. (2006). Helping faculty learn to teach better and “smarter” through sequenced activities. In S. Chadwick-Blossy & D.R. Robertson (Eds.). To Improve the Academy , Vol 24. (pp. 216-230). Bolton, MA: POD Network and Anker Publications.
- Designing assignments , University of Washington Libraries.
- Effective assignments using library and Internet resources . (2004). Teaching Library, University of California, Berkeley. Retrieved September 27, 2006 from http://www.lib.berkeley.edu/TeachingLib/assignments.html
- Fister, B., & Fuhr, S. (2001). Suggestions for assignments. Enhancing developmental research skills in the undergraduate curriculum . Folke Bernadotte Memorial Library, Gustavus Adolphus College. Retrieved September 27, 2006 from http://www.gustavus.edu/oncampus/academics/library/IMLS/assignmentsuggestions.html
- Recommendations for creating effective library assignments. (2005). Mitchell Memorial Library, Library Instructional Services, Mississippi State University. Retrieved September 27, 2006 from http://library.msstate.edu/content/templates/?a=323&z=74
- Creative assignments using information competency and writing. (2006). Ohio University, Athens OH. Retrieved September 27, 2006 from http://www.library.ohiou.edu/inst/creative.html
- Millis, B., & Cottell, P. (1998). Cooperative learning for higher education faculty. Greenwood Press: American Council on Education, Oryx Press.
- Kelley, K., & McDonald, R. (2005). Section 4: Designing assignments that contain writing and research. In Information literacy and writing assessment project: Tutorial for developing and evaluating assignments . Information and Library Services, University of Maryland University College.
- Examples of good assessments . (2006). Delta College Library, Delta College. Retrieved September 27, 2006 from http://www.delta.edu/library/assessments.html
- IDEA Paper No. 38: Enhancing Learning – and More! – Through Cooperative Learning , Millis
- IDEA Paper No. 41: Student Goal Orientation, Motivation, and Learning , Svinicki
- from http://ejournals.library.gatech.edu/ijsotel/index.php/ijsotel/article/view/19/18
- Gaining A Basic Understanding of the Subject
- Developing knowledge and understanding of diverse perspectives, global awareness, or other cultures
- Learning to apply course material
- Developing specific skills, competencies, and points of view needed by professionals in the field most closely related to this course
- Acquiring skills in working with others as a member of a team
- Developing creative capacities
- Gaining a broader understanding and appreciation of intellectual/cultural activity
- Developing skill in expressing myself orally or in writing
- Developing ethical reasoning and/or ethical decision making
- Learning to analyze and critically evaluate ideas, arguments, and points of view
- Learning to apply knowledge and skills to benefit others or serve the public good
- Learning appropriate methods for collecting, analyzing, and interpreting numerical information
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Finding Aids

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This resource discusses conducting research in a variety of archives. It also discusses a number of considerations and best practices for conducting archival research.
This resources was developed in consultation with Purdue University Virginia Kelly Karnes Archives and Special Collections staff.
If you want to find research materials in archives, you will need to read a Finding Aid. This document describes the materials in an archival collection and gives you a summary of the materials housed in that collection. Reading a Finding Aid before viewing a collection can help save time and ensure that you find materials relevant to your research. In many ways, a Finding Aid is like a library catalog entry because it provides you with information about the contents of a book and what materials are in an archival collection. When you search an archival website, your search results will likely direct you to a Finding Aid of a collection.
You may wonder: “If I find a collection that I’m interested in, why can’t I just check it out to determine if it is what I need for my research?” The answer to this question reveals how archives are different from libraries. First, archival materials never leave the archives, so all collections must be viewed in the archives. Second, some archival collections are quite large. It would take a long time to study an entire collection to determine if it is relevant to your research. To save you time and make your research experience easier, a Finding Aid contains three unique elements that will help you determine if a particular collection is worth studying: the Scope and Content Note, Biographical/Administrative History Note, and Contents Listing.
Scope and Content Note
A Scope and Content Note is a brief summary of the contents of a collection. In addition to a summary, a Scope and Content Note also contains highlights and limitations of a collection so that researchers can know whether the collection will be useful for their research. Sometimes a Scope and Content Note is called a “Scope Note.”
A Scope and Content Note often begins by briefly explaining where the collection came from (e.g. a family or corporation), what years the collection covers (e.g. 1882-1967), and the general kinds of materials it contains—such as letters, reports, or photographs. If a collection is large, you may encounter a list of series in the Scope and Content Note or in another part of the Finding Aid. A series is a group of archival materials within a collection that are alike in some way. Sometimes materials in a series are of the same format, such as a series of photographs. Other times, materials in a series share the same function, such as a series of business meeting minutes. You can use series to guide your research. If you are searching for a particular topic within a collection, you may search for a series that relates to your topic and exclude series that are not related. Below you will find an example of a Scope and Content Note from a collection in Purdue’s Karnes Archives and Special Collections.
Biographical/Administrative History Note
A Biographical/Administrative History Note explains the history of the creator of the collection. If the creator of the collection is a person, then the Note will provide a biography. If the creator of the collection is an institution or business, then the Note will provide an administrative history. Sometimes this section is called a “Background.”
A Biographical/Administrative History Note provides information that establishes an historical context for the collection. In other words, this Note tells researchers the history of the people and organizations involved in creating the materials in the collection. The Note might include information on significant dates, major events, and important people related to the collection. You can use the Biographical/Administrative History Note to determine basic facts about the people and organizations in the collection. For example, if you are looking for information on people who attended a particular university, you might search a Biographical Note to determine if a particular person attended the university you are researching. Below you will find an example of a Biographical/Administrative History Note from a collection in Purdue’s Karnes Archives and Special Collections.
Contents Listing
A Contents Listing is a list of the materials in a collection that also includes information about the physical location of the materials. For example, many collections are housed in boxes. A Contents Listing will give you a list of boxes and the materials housed in each box. Sometimes a Contents Listing is referred to as “Container Contents” or an “Inventory.”
You can use a Contents Listing to determine which boxes hold materials that would be relevant to your research. Inventories vary in length and detail. Some inventories list every single item in a collection. If the collection is large, the Contents Listing will be quite long, and it may take you some time to find the materials that you are looking for. In this case, it may be useful to first examine the Scope Note and find the series that is most relevant to your research topic. This may help narrow your search by restricting it to only the boxes in that series. Other inventories do not list every single item. Instead, they may give a summary of materials housed in a folder or a box. For example, a Contents Listing may state that a folder contains reports from a certain date range. If you are looking for reports from these years, this folder may be worth examining in detail.
Research Methodologies
- Quantitative Research Methodologies
- Qualitative Research Methodologies
- Systematic Reviews
- Finding Articles by Methodology
- Design Your Research Project
Library Help
Searching with keywords.
One option for finding articles that used a specific research methodology is to run a database search using your methodology as a keyword. You can often search just by a type of methodology if you're looking for any examples using the method, or you can combine your topic with a type of methodology.
For best results, make sure that filters for peer-reviewed/scholarly journals are checked.
- cancer AND treatment AND "systematic review"
- "consumer behavior" AND "grounded theory"
- "alternative fuels" AND experiment
Because methodologies are not always readily apparent in the title or abstract, you may need to skim through the methodology section of an article to make sure it's relevant.
Searching With Filters
Some databases include filters among their advanced search options that you can use to search for studies that use specific research methodologies. This method isn't foolproof. Not all methodologies will be available in these filters and articles that don't have their methodologies listed in the database record may be overlooked.
Using the Methodology Filter
- Use the library's list of databases to find a subject-appropriate database. Not all databases have a methodology filter, but there are several databases in health sciences, behavioral sciences, and the physical sciences that do, such as APA PsycInfo.
- A-Z Database List Full list of databases available through the Fulton Library, with recommendations for researching specific subjects.
- If necessary, navigate to the database's advanced search page and look for the methodology filter. This example comes from APA PsycINFO:

- Choose the methodology you need and run your search. You don't always need to have a topic in the main search box to run this type of search, if you are simply looking for examples.
Using the Subject Filter
Another option — which is available in databases that don't have a specific filter for methodologies — is to use the subject filter that appears on the results page of many of the library's databases. These filters take the most frequently occurring assigned keywords and subjects to help you weed out irrelevant results. Because these assigned terms can also include methodology information, you can use these filters to locate articles that use specific methodologies.
To get started:
- Begin a search on your topic.
- Click All Filters below the search box.
- Open Subjects . You will need to expand the list of subjects to find all relevant methodologies.
- Select the relevant methodologies.
- Click Apply Filters
- The options on the subject filter will change as your search changes. Check back periodically to see if there are additional useful items that you can filter for.

Full List, With Methodologies Highlighted

- Call : 801.863.8840
- Text : 801.290.8123
- In-Person Help
- Email a Librarian
- Make an Appointment
- << Previous: Systematic Reviews
- Next: Design Your Research Project >>
- Last Updated: Apr 5, 2024 11:11 AM
- URL: https://uvu.libguides.com/methods
Ask Yale Library
My Library Accounts
Find, Request, and Use
Help and Research Support
Visit and Study
Explore Collections
Research organization and citation tools for ANTH303: Home
- Note Taking & Citation Management
- Evaluate Sources
- Find Journal Articles
- Find Newspapers
- Find Special Collections
- Remote Access
- Video Tutorials
About This Guide
Yale Library is a big place : with over a dozen libraries, over 15 million books, and an innumerable number of special collections, journal and newspaper articles, media, data sets... the list goes on and on. No matter your familiarity with research in general , there's more to learn to ensure you're finding the best possible sources for your research.
This guide includes general advice for discovering books, e-books, journals and newspapers, databases, and primary sources, as well as information to support research organization along the way.
Find a Librarian
Everyone needs help from time to time! Find your Subject Specialist Librarian , or request a research consultation and we'll match you with a librarian in your field of study.
Library Workshops
Finding research material at yale.
While you are affiliated with Yale, use the Yale Library website as your starting point for research . By accessing material through the website - books, articles, and even databases - you will connect to the material that we have already purchased for you to use! Here are some resources to get you started:
- Quicksearch A single-search option to discover books & e-books, scholarly articles, special collections, and more. A great place to access print and online library resources to avoid paywalls!
- Articles+ Discover thousands of journal articles, newspaper & magazine articles, ebooks, and more. A single-search through *most* of the library's database subscriptions.
- Find Databases Locate a subject-specific database by name (e.g.: JSTOR) or keyword (e.g.: "Art history")
- Video Tutorials 2-3 minute video tutorials on research techniques for Yale Library's collections and services, including finding books/e-books, articles, digital collections, data sets, and more.
- Ask Yale Library For help with library and research related questions, chat, email, text, or call us - or browse our extensive list of FAQs
- Next: Note Taking & Citation Management >>
- Last Updated: Apr 5, 2024 9:24 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/ANTH303-2024
Site Navigation
P.O. BOX 208240 New Haven, CT 06250-8240 (203) 432-1775
Yale's Libraries
Bass Library
Beinecke Rare Book and Manuscript Library
Classics Library
Cushing/Whitney Medical Library
Divinity Library
East Asia Library
Gilmore Music Library
Haas Family Arts Library
Lewis Walpole Library
Lillian Goldman Law Library
Marx Science and Social Science Library
Sterling Memorial Library
Yale Center for British Art
SUBSCRIBE TO OUR NEWSLETTER
@YALELIBRARY

Yale Library Instagram
Accessibility Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Giving Privacy and Data Use Contact Our Web Team
© 2022 Yale University Library • All Rights Reserved
Libraries | Research Guides
Poli_sci_395: human rights and the environment (suiseeya).
- Get Started
- Evaluate Information
- Find Scholarly Articles
Finding books, book chapters (and online articles or other items) at Northwestern
Requesting materials beyond northwestern.
- Find Data and Statistics
- Find News Sources
- Government and IGO Resources
- Think Tanks, NGOs, Advocacy Groups
- Support and Resources about Research Methods
- Cite Sources
Use NUsearch , Northwestern University Library's search tool, to find books, book chapters, articles, documents, video, sound recordings, and other items across many subjects on both the Evanston and Chicago campus libraries of Northwestern University
HINT: use the NUsearch Advanced Search page to build keyword searches more easily
For example, the search below, making use of the Boolean operators AND and OR, find sources that are about Cambodia and carbon emissions as well as sources about Southeast Asia and carbon emissions .

- WorldCat This link opens in a new window The world's most comprehensive catalog of library holdings, particularly (though not exclusively) from North American libraries, containing over 2,000,000,000 records from over 10,000 libraries.
- Interlibrary Loan If you need a book, article or other item not owned or not available at NU, you can place an ILL request
- << Previous: Find Scholarly Articles
- Next: Find Data and Statistics >>
- Last Updated: Apr 5, 2024 2:40 PM
- URL: https://libguides.northwestern.edu/humanrightsandtheenvironment
Recent Headlines
- SUNY ESF Launches New Safety App
SUNY ESF Leads Groundbreaking Research in Groundwater’s Role in Ecosystem Sustainability
- Life on the ESF Campus: A Glimpse Inside Centennial Hall
- ESF’s Dr. Yaqi You Receives Prestigious NSF CAREER Award
Submit a News Story

Dr. Melissa Rohde
Syracuse, N.Y. – April 2, 2024 – Until now, groundwater – a critical water resource around the globe, especially in dry regions – has been largely unstudied in its importance and role in sustaining ecosystems. A new groundbreaking research effort led by the SUNY College of Environmental Science and Forestry (ESF) in partnership with University of California Santa Barbara (UCSB), Cardiff University, and Desert Research Institute (DRI) examines the relationship between groundwater and ecosystems across California. Their innovative findings are featured in Nature Water .
Led by Dr. Melissa Rohde, who completed the study as part of her doctoral research in Dr. John Stella’s Riparian Echohydrology Lab at ESF, the team used satellite imagery and groundwater monitoring data to identify thresholds of groundwater depth and seasonal change that can support sensitive ecosystems throughout California under the state’s Sustainable Groundwater Management Act framework.
“A vast majority of our planet’s freshwater is groundwater, but we don’t acknowledge or manage it sustainably, resulting in serious consequences for humans and natural ecosystems,” said Dr. Rohde, now Principal at Rohde Environmental Consulting, LLC. “Groundwater is critical for many ecosystems, but their water requirements are rarely accounted for by water agencies and conservationists. To reconcile that, our study provides a simple and practical approach to detect ecological thresholds and targets that can be used by practitioners to allocate and manage water resources.”
Utilizing 38 years of Landsat satellite images (1985-2022) and statewide groundwater well data, the study examined impacts on key plant communities. A major challenge was to develop standardized metrics that can be applied across diverse ecosystems with site-specific water conditions. The team applied a common data transformation method in a new way to identify thresholds of vegetation greenness and groundwater depth over time that can determine groundwater needs for ecosystems, helping to inform decisions about water use and planning.
“Groundwater-dependent ecosystems such as wetlands, floodplains, and riparian zones have a very outsized importance on biodiversity. Upwards of 80 to 90 percent of species in a general region may be dependent on these ecosystems in some form or another,” said Dr. Stella, study co-author and Vice President for Research at ESF. “We applied a simple statistical approach to very large data sets to identify warning signs and conservation targets for a great diversity of ecosystem types.”
The vast geographic scope and long timeline covered by the study, allowed the team to evaluate how large-scale systems respond to major climate shocks such as the historical California drought that occurred from 2012—2016, as well as where individual groundwater-dependent ecosystems can serve as resilient drought refugia.
“This type of study, covering the entire state of California over close to 40 years, has really only become possible in the past few years and shows the promise for similar studies over a much larger geographic area using the approach pioneered by Dr. Rohde,” remarked co-author, Dr. Dar Roberts from UCSB.
It was discovered that during drought events, groundwater-dependent vegetation that maintains a connection to groundwater can serve as critical drought refugia for associated species, such as riparian birds or fish. However, when groundwater levels deepen beyond plants’ rooting zones during drought, these safe havens can be lost.
"A key takeaway from this study is that we can use what we know about how deep the roots of different types of plants tend to be to approximate what groundwater levels are needed to maintain ecosystem health,” said co-author Dr. Christine Albano from DRI. “We found that vegetation was healthier where groundwater levels were within about 1 meter of maximum root depth, as compared to where groundwater was deeper."
The research team is hopeful that their approach and findings can help inform water management decisions in California and beyond.
"This study arms groundwater managers with an intuitive, site-specific measure that can provide a data-driven foundation to guide water allocation and ecosystem restoration efforts," said co-author and professor Kelly Caylor from UCSB.
“Globally, there are increasing efforts to manage groundwater resources for multiple purposes, not only to support drinking water needs or high-value agriculture. Our work provides a sound basis on which to develop clear guidelines for how to manage groundwater to support a wide range of needs within drainage basins in California and beyond,” said co-author Prof. Michael Singer from Cardiff University.
About SUNY ESF
The SUNY College of Environmental Science and Forestry (ESF) is dedicated to the study of the environment, developing renewable technologies, and building a sustainable and resilient future through design, policy, and management of the environment and natural resources. Members of the College community share a passion for protecting the health of the planet and a deep commitment to the rigorous application of science to improve the way humans interact with the world. The College offers academic programs ranging from the associate of applied science to the Doctor of Philosophy. ESF students live, study and do research on the main campus in Syracuse, N.Y., and on 25,000 acres of field stations in a variety of ecosystems across the state.
Finds at Schöningen show wood was crucial raw material 300,000 years ago
Research team discovers sophisticated processing of archaeological wood.
During archaeological excavations in the Schöningen open-cast coal mine in 1994, the discovery of the oldest, remarkably well-preserved hunting weapons known to humanity caused an international sensation. Spears and a double-pointed throwing stick were found lying between animal bones about ten meters below the surface in deposits at a former lakeshore. In the years that followed, extensive excavations have gradually yielded numerous wooden objects from a layer dating from the end of a warm interglacial period 300,000 years ago. The findings suggested a hunting ground on the lakeshore. An interdisciplinary research team from the Universities of Göttingen and Reading (UK), and the Lower Saxony State Office for Cultural Heritage (NLD) has now examined all the wood objects for the first time. State-of-the-art imaging techniques such as 3D microscopy and micro-CT scanners have produced surprising results. The research was published in PNAS.
This is the first time that researchers have been able to demonstrate new ways of handling and working the wood, such as the "splitting technique." Small pieces of split wood were sharpened, for example to use them in processing hunted animals. First author Dr Dirk Leder from NLD says: "There is evidence of much more extensive and varied processing of spruce and pine wood than previously thought. Selected logs were shaped into spears and throwing sticks and brought to the site, while broken tools were repaired and recycled on site." At least 20 spears and throwing sticks had been left behind on the former lakeshore. This doubles the number of known wooden weapons at the site. Dr Tim Koddenberg from the University of Göttingen explains: "The extraordinary state of preservation of the Schöningen wood has enabled us, for the first time, to document and identify the woodworking techniques in detail thanks to state-of-the-art microscopy methods."
The wide range of woodworking techniques used, as well as the various weapons and tools of early humans, show the outstanding importance of wood as a raw material, which is almost never preserved from this period. The Schöningen finds bear witness to extensive experience in woodworking, technical know-how and sophisticated work processes. Project leader Professor Thomas Terberger, who works at the NLD and the University of Göttingen, states: "Wood was a crucial raw material for human evolution, but it is only in Schöningen that it has survived from the Palaeolithic period in such quality." Schöningen is therefore part of the internationally outstanding cultural heritage of early humans. Only recently, the site was included in the nomination list for UNESCO World Heritage Site at the request of the state of Lower Saxony.
The study was funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) and the Ministry of Science and Culture of Lower Saxony.
- Earth Science
- Ancient Civilizations
- Origin of Life
- Lost Treasures
- Radiocarbon dating
- Homo antecessor
- Homo (genus)
- Neandertal interaction with Cro-Magnons
- Homo heidelbergensis
Story Source:
Materials provided by University of Göttingen . Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Related Multimedia :
- Spears and throwing sticks
Journal Reference :
- Dirk Leder, Jens Lehmann, Annemieke Milks, Tim Koddenberg, Michael Sietz, Matthias Vogel, Utz Böhner, Thomas Terberger. The wooden artifacts from Schöningen’s Spear Horizon and their place in human evolution . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences , 2024; 121 (15) DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2320484121
Cite This Page :
Explore More
- Drug Development Made Easier
- RNA That Doesn't Age
- 'Rainbow' Detected On an Exoplanet
- Spears and Throwing Sticks 300,000 Years Old
- High Carbon Impact of Tourism at Yellowstone
- Extreme Starburst Galaxy
- Asthma: Disease May Be Stoppable
- Stellar Collisions and Zombie-Like Survivors
- Tiny Robot Swarms Inspired by Herd Mentality
- How the Brain Regulates Emotions
Trending Topics
Strange & offbeat.
share this!
April 4, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
written by researcher(s)
More than 80% of the EU's farming subsidies support emissions-intensive animal products
by Anniek Kortleve, Helen Harwatt, José Manuel Mogollón and Paul Behrens, The Conversation
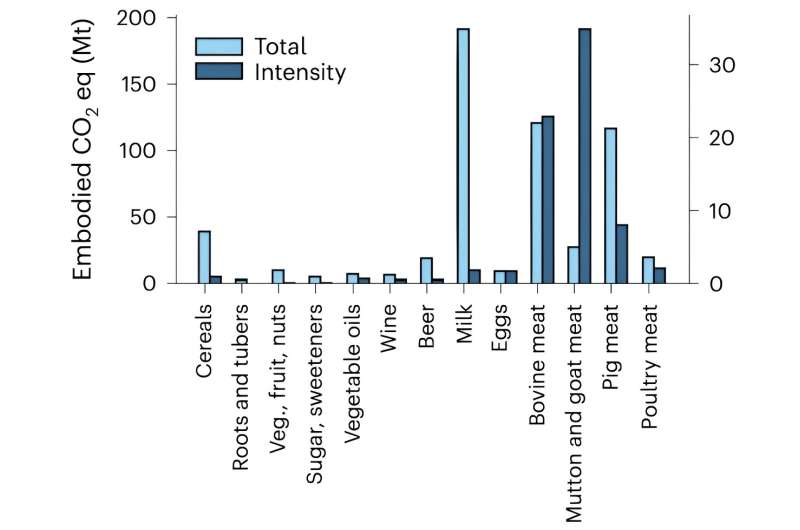
The vast majority of the EU's agricultural subsidies are supporting meat and dairy farming rather than sustainable plant alternatives. That's the key finding of our new research, published in Nature Food , in which for the first time we were able to fully account for crops and other plants grown to feed animals.
The subsidies operate through the EU's common agricultural policy (known as the CAP). This plays a critical role in shaping farming across Europe, but has been the subject of intense criticism for years.
Critics say it supports big landowners over smaller farmers, that its environmental payments represent only a small portion of the budget, and that it is vulnerable to corruption .
While some EU policymakers want to make the CAP more sustainable by including more environmental provisions, they face opposition from lobby groups and protests by farmers. But our work shows these environmental improvements are sorely needed as more than 80% of CAP funds support animal-based products.
These products overwhelmingly drive the EU's food-related greenhouse gas emissions, biodiversity loss, water consumption , air pollution, water pollution and more.
Meat is cheaper than it would be in a fairer market
The CAP is the largest single EU expenditure, accounting for roughly 38% of total spending. We found that of the €57 billion (£49 billion) annual CAP budget, €46 billion (£39 billion) was directed towards animal-based products, mostly foods like beef, pork, chicken, dairy and eggs.
These estimates are from 2013—the most recent year for the food supply model we used—but the proportion of the subsidy has changed very little since then. Our estimates are higher than was previously thought because we now have a more complete picture of the subsidies that animal feed also receives.
For example, a French farmer growing wheat for pig or chicken feed will receive a subsidy for that wheat on top of the subsidy received by a livestock farmer in Denmark who imports that feed. On this basis, we show that CAP support roughly doubles for animal-based foods. For example, beef CAP subsidies increase from €0.71/kg to €1.42/kg once feed is included.
This does not directly translate into the price on the shelves, as there are many other distortions in the current food system. But it gives a sense of the relative difference between animal and plant products.
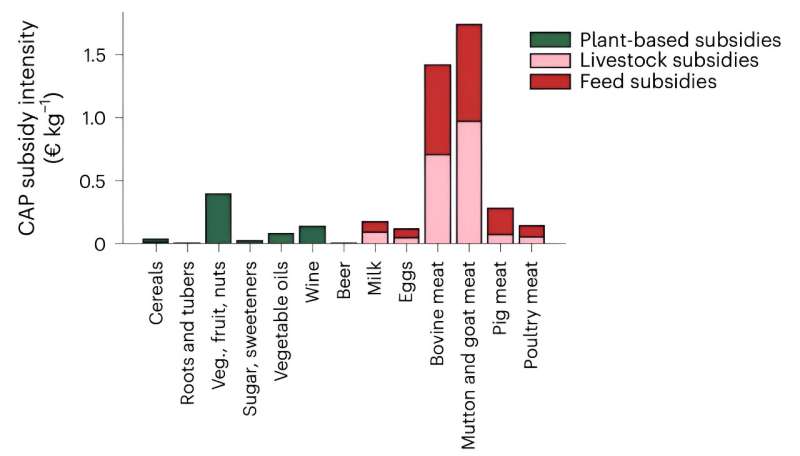
The result is an uneven playing field in which animal products are cheaper than they would be otherwise, thanks to the additional subsidies. It makes fruits, vegetables and nuts appear relatively more expensive than meat or dairy, which flies in the face of efforts to reduce the environmental damage of the EU's food system and to encourage healthier eating.
The global food system on its own is enough to blow past the climate targets of 1.5°C and even 2°C of warming . We'll need drastic action to transition fast enough to not only reduce this environmental impact , but to be resilient to more extreme weather driven by climate change.
Scientific consensus now shows that a shift to mainly plant-based diets is the biggest single opportunity to reduce these food-related environmental impacts, especially in high-income nations .
Such shifts may even release land to help meet climate targets and improve food security . Yet CAP subsidies are perpetuating the existing system, not helping in transitioning the system.
Subsidized food is being exported away
The use of public funds in the CAP aims to ensure healthy, safe and secure food production for the EU. But these subsidies are also influencing production and consumption in other countries that import food from the EU.
We find that 12% of the CAP budget ends up subsiding the price of exports to non-EU countries. Perhaps surprisingly, much of these exports head towards higher-income nations. In fact, in 2013, the US effectively imported more CAP money via food imports from the EU than all the CAP money that went to Denmark.
It's the same for China, importing more than the money going to the Netherlands. This ultimately makes the convergence on healthy and sustainable diets at the global level more difficult.
More broadly, farmers are under huge pressure from issues such as climate-driven extreme weather and increasing production costs due to inflation. But we know that without significant green reforms—including the reform of the CAP—the increasing costs of environmental damage will make things even worse in future.
To build a food system that is more sustainable, more resilient and better for public health, farming subsidies will have to be reformed. The recent watering down of green EU policy is a step backwards, and can only be an act of self-harm over the longer term.
Journal information: Nature Food
Provided by The Conversation
Explore further
Feedback to editors
Scientists investigate information propagation in interacting bosonic systems
4 hours ago

DESI first-year data delivers unprecedented measurements of expanding universe
21 hours ago

Saturday Citations: AI and the prisoner's dilemma; stellar cannibalism; evidence that EVs reduce atmospheric CO₂
Apr 6, 2024

Huge star explosion to appear in sky in once-in-a-lifetime event
Innovative sensing platform unlocks ultrahigh sensitivity in conventional sensors
Nonvolatile quantum memory: Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits

Can language models read the genome? This one decoded mRNA to make better vaccines
A simple, inexpensive way to make carbon atoms bind together

Dinosaur study challenges Bergmann's rule

Study: Focusing immediately on the benefits of waiting might help people improve their self-control
Apr 5, 2024
Relevant PhysicsForums posts
What do large moles on the body indicate.
Mar 30, 2024
Avian flu - A new study led by a team from the University of Maryland
Mar 27, 2024
Are all biological catabolic reactions exergonic?
Mar 20, 2024
A First of Its Kind: A Calcium-based signal in the Human Brain
Mar 18, 2024
Biological culture and cultural biology
Mar 17, 2024
Potentially fatal dog parasite found in the Colorado River
Mar 15, 2024
More from Biology and Medical
Related Stories

82% of EU farm subsidies bolster high emissions foods: Study
Apr 1, 2024

Q&A: Veganuary—the environmental benefits of a low and no meat diet
Jan 19, 2024

Meat alternatives could feed humans more sustainably
Dec 11, 2023

Study shows how the meat and dairy sector resists competition from alternative animal products
Aug 18, 2023

Post-Brexit trade deals may cause 1,500 additional diet-related deaths every year—new study
Jun 29, 2021

Change food choices to increase chances of tackling global warming, say researchers
Jun 15, 2023
Recommended for you

Study reports that people and environment both benefit from diversified farming, while bottom lines also thrive
Apr 4, 2024
Criollo cattle: Could an old breed be the beef industry's answer to climate change?
Apr 3, 2024

How AI and deeper roots can help soil store more carbon
Apr 2, 2024

Researchers discover corn reduces arsenic toxicity in soil

Golfers' risk from pesticides used on turf grass is likely low, studies find

Scientist taps into lobsters' unusual habits to conquer the more than 120-year quest to farm them
Mar 29, 2024
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Finding Research Materials - *Education - Research Guides at University of Southern California. When using article databases, remember there are always three stages in your workflow: 1) Discovery: Do (and redo!) your searching, using varying terms and combining using the to get good results. Your first search is not your best search, but rather ...
Still, Google Books is a great first step to find sources that you can later look for at your campus library. 6. Science.gov. If you're looking for scientific research, Science.gov is a great option. The site provides full-text documents, scientific data, and other resources from federally funded research.
Research databases. You can search for scholarly sources online using databases and search engines like Google Scholar. These provide a range of search functions that can help you to find the most relevant sources. If you are searching for a specific article or book, include the title or the author's name. Alternatively, if you're just ...
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions.
The library subscribes to more than 200 specialized databases that are used to find articles and other sources for academic research. The following are basic steps for finding newspaper, magazine, scholarly journal, and other types of articles in these databases. For more in-depth assistance with this process, please Ask a Librarian.
Choosing & Using Sources presents a process for academic research and writing, from formulating your research question to selecting good information and using it effectively in your research assignments. Additional chapters cover understanding types of sources, searching for information, and avoiding plagiarism. Each chapter includes self-quizzes and activities to reinforce core concepts ...
Analyzing: While reading, start making notes of key concepts and commonalities and disagreement among the research articles you find. ♠ Create a spreadsheet to record what articles you are finding useful and why. ♠ Create fields to write summaries of articles or quotes for future citing and paraphrasing. Writing: Synthesize your findings ...
Students often use Google to begin their searches because they can find material from many different sources, both formal and informal, including blogs, journals, websites, and popular magazines. For academic research, you may find it useful to begin with a general Google search and then move to Google Scholar. Google Scholar provides a simple ...
truncation = To use truncation, enter the root of a search term and replace the ending with an * (asterisk).For example, type comput* to find the words computes, computer, computing or computational.; searching a phrase = Typically, when a phrase is enclosed by double quotations marks, the exact phrase is searched.For example, "employee retention" searches for the two words as a phrase.
The Library is the top resource when it comes to locating and accessing research materials. Use the library catalog to find materials such as books, music, videos, journals, and audio recordings in our collections.; Search databases to find articles, book chapters, and other sources within a specific subject area or discipline.; For materials the Library does not own, use BorrowDirect or ...
Find and Use Images Use the Library's databases and websites to find and use images in your research projects. Find Visual Resource Collections Find free and licensed image and video collections related to spectific subject areas. Find Music Materials A guide on finding music materials at the library and beyond.
Get 30 days free. 1. Google Scholar. Google Scholar is the clear number one when it comes to academic search engines. It's the power of Google searches applied to research papers and patents. It not only lets you find research papers for all academic disciplines for free but also often provides links to full-text PDF files.
The Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ) allows users to search and retrieve the article contents of nearly 10,000 OA journals in science, technology, medicine, social sciences, and humanities. All journals must adhere to quality-control standards, including peer review. PubMed, maintained by the US National Library of Medicine, is a free ...
The good news is that in this lesson, we will cover some basic tips for locating research materials in order to produce a professional and credible paper. First of all, before you begin writing a ...
Learning Objectives. By the end of this chapter, you will be able to: Search for physical materials using your online library catalog. Describe how libraries organize physical materials on the shelves. Previous: Conclusion.
1. Determine a clear and focused question. A systematic search can best be applied to a well-defined and precise research or clinical question. Questions that are too broad or too vague cannot be answered easily in a systematic way and will generally result in an overwhelming number of search results.
Finding good sources and using them effectively helps you to create a message and a persona that your readers are more likely to accept, believe, and be interested in than if unsuitable and unreliable sources are used. This chapter covers the various kinds of research sources available to writers.
Ironically, IDEA Research Report #1 also finds that the objectives identified as emphasizing lifelong learning (Learning to find and use resources, and Gave tests/projects that covered most important points) were identified as "Important" or "Essential" in only about 30% of the classes using IDEA. The ACRL (1) notes, "Information ...
Reading a Finding Aid before viewing a collection can help save time and ensure that you find materials relevant to your research. In many ways, a Finding Aid is like a library catalog entry because it provides you with information about the contents of a book and what materials are in an archival collection. When you search an archival website ...
One option for finding articles that used a specific research methodology is to run a database search using your methodology as a keyword. You can often search just by a type of methodology if you're looking for any examples using the method, or you can combine your topic with a type of methodology. For best results, make sure that filters for ...
Finding Research Material at Yale. While you are affiliated with Yale, use the Yale Library website as your starting point for research. By accessing material through the website - books, articles, and even databases - you will connect to the material that we have already purchased for you to use! Here are some resources to get you started:
Use NUsearch, Northwestern University Library's search tool, to find books, book chapters, articles, documents, video, sound recordings, and other items across many subjects on both the Evanston and Chicago campus libraries of Northwestern University. HINT: use the NUsearch Advanced Search page to build keyword searches more easily. For example, the search below, making use of the Boolean ...
A good source for finding statistics Which research materials are found in library databases Skills Practiced. This quiz and worksheet allow students to test the following skills:
However, research on MXenes for supercapacitor applications has been primarily focused on Ti3C2, even though there are more than 20 other members of this large family of materials already available.
Vol 383, Issue 6690. pp. 1418 - 1420. DOI: 10.1126/science.adl0677. People living in urban and industrialized societies, which are expanding globally, spend more than 90% of their time in the indoor environment, breathing indoor air (IA). Despite decades of research and advocacy, most countries do not have legislated indoor air quality (IAQ ...
Groundwater - a critical water resource around the globe, especially in dry regions - has been largely unstudied in its importance and role in sustaining ecosystems. A new groundbreaking research effort led by the SUNY College of Environmental Science and Forestry examines the relationship between groundwater and ecosystems across California. Their innovative findings are featured in ...
Finds at Schöningen show wood was crucial raw material 300,000 years ago. ScienceDaily . Retrieved April 6, 2024 from www.sciencedaily.com / releases / 2024 / 04 / 240404190733.htm
Meat is cheaper than it would be in a fairer market. The CAP is the largest single EU expenditure, accounting for roughly 38% of total spending. We found that of the €57 billion (£49 billion ...