A systemic review on tuberculosis
Affiliations.
- 1 Department of Microbiology, Sri Devaraj Urs Medical College, Sri Devaraj Urs Academy of Higher Education and Research, Kolar, India.
- 2 Department of Microbiology, S Nijalingappa Medical College, Bagalkot, India.
- 3 SDM Narayanaya Heart Centre, Sri Dharmasthala Manjunatheshwara Medical College, Sri Dharmasthala Manjunatheshwara University, Dharwad, India. Electronic address: [email protected].
- PMID: 32825856
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijtb.2020.02.005
Tuberculosis (TB), which is caused by bacteria of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex, is one of the oldest diseases known to affect humans and a major cause of death worldwide. Tuberculosis continues to be a huge peril disease against the human population and according to WHO, tuberculosis is a major killer of the human population after HIV/AIDS. Tuberculosis is highly prevalent among the low socioeconomic section of the population and marginalized sections of the community. In India, National strategic plan (2017-2025) has a national goal of elimination of tuberculosis by 2025. It requires increased awareness and understanding of Tuberculosis. In this review article history, taxonomy, epidemiology, histology, immunology, pathogenesis and clinical features of both pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB) and extra-pulmonary tuberculosis (EPTB) has been discussed. A great length of detailed information regarding diagnostic modalities has been explained along with diagnostic algorithm for PTB and EPTB. Treatment regimen for sensitive, drug resistant and extensive drug resistant tuberculosis has been summarized along with newer drugs recommended for multi drug resistant tuberculosis. This review article has been written after extensive literature study in view of better understanding and to increase awareness regarding tuberculosis, as a sincere effort that will help eliminate tuberculosis off the face of the earth in near future.
Keywords: Immunology; Tuberculosis diagnosis; Tuberculosis pathogenesis; Tuberculosis treatment.
Copyright © 2020 Tuberculosis Association of India. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.

Publication types
- Historical Article
- Systematic Review
- Culture Techniques
- Extensively Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis
- History, 15th Century
- History, 16th Century
- History, 17th Century
- History, 18th Century
- History, 19th Century
- History, 20th Century
- History, Ancient
- Interferon-gamma Release Tests
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Nucleic Acid Amplification Techniques
- Polymerase Chain Reaction
- Tuberculin Test
- Tuberculosis* / diagnosis
- Tuberculosis* / epidemiology
- Tuberculosis* / history
- Tuberculosis* / immunology
- Tuberculosis, Multidrug-Resistant
- Tuberculosis, Pulmonary* / diagnosis
- Tuberculosis, Pulmonary* / epidemiology
- Tuberculosis, Pulmonary* / history
- Tuberculosis, Pulmonary* / immunology
- Open access
- Published: 10 September 2022
Living with tuberculosis: a qualitative study of patients’ experiences with disease and treatment
- Juliet Addo 1 ,
- Dave Pearce 2 ,
- Marilyn Metcalf 3 ,
- Courtney Lundquist 1 ,
- Gillian Thomas 4 ,
- David Barros-Aguirre 5 ,
- Gavin C. K. W. Koh 6 &
- Mike Strange 1
BMC Public Health volume 22 , Article number: 1717 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
10k Accesses
5 Citations
2 Altmetric
Metrics details
Although tuberculosis (TB) is a curable disease, treatment is complex and prolonged, requiring considerable commitment from patients. This study aimed to understand the common perspectives of TB patients across Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa throughout their disease journey, including the emotional, psychological, and practical challenges that patients and their families face.
This qualitative market research study was conducted between July 2020 and February 2021. Eight TB patients from each country ( n = 40) completed health questionnaires, video/telephone interviews, and diaries regarding their experiences of TB. Additionally, 52 household members were interviewed. Patients at different stages of their TB treatment journey, from a range of socioeconomic groups, with or without TB risk factors were sought. Anonymized data underwent triangulation and thematic analysis by iterative coding of statements.
The sample included 23 men and 17 women aged 13–60 years old, with risk factors for TB reported by 23/40 patients. Although patients were from different countries and cultural backgrounds, experiencing diverse health system contexts, five themes emerged as common across the sample. 1) Economic hardship from loss of income and medical/travel expenses. 2) Widespread stigma, delaying presentation and deeply affecting patients’ emotional wellbeing. 3) TB and HIV co-infection was particularly challenging, but increased TB awareness and accelerated diagnosis. 4) Disruption to family life strained relationships and increased patients’ feelings of isolation and loneliness. 5) The COVID-19 pandemic made it easier for TB patients to keep their condition private, but disrupted access to services.
Conclusions
Despite disparate cultural, socio-economic, and systemic contexts across countries, TB patients experience common challenges. A robust examination of the needs of individual patients and their families is required to improve the patient experience, encourage adherence, and promote cure, given the limitations of current treatment.
Peer Review reports
Tuberculosis (TB) is a communicable infectious disease affecting around one quarter of the world’s population [ 1 ]. The ‘BRICS’ countries of Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa account for 47% of the total number of TB cases annually [ 1 , 2 , 3 ].
Caused by the bacillus Mycobacterium tuberculosis , around 5–10% of those infected will develop active disease. In 2019, 10 million new active cases and 1.4 million deaths were reported [ 1 ]. In 2020, the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic severely impacted the reporting of new cases and impeded diagnosis and treatment [ 3 ]. Treatment for multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) also declined by 15% (from 177,100 in 2019 to 150,359 in 2020), with only about a third of patients who needed this treatment obtaining access [ 3 ].
Ambitious targets to end the TB epidemic by 2035 were established in 2015 by the WHO’s End TB Strategy [ 4 ], aligned with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals [ 5 ]. In 2018, a United Nations General Assembly High-Level Meeting on Tuberculosis resulted in a Political Declaration on Tuberculosis, committing to end TB globally by 2030 [ 6 ]. Achieving these goals requires more equitable deployment of existing measures, and the development of new tools for TB prevention, diagnosis and treatment [ 7 ]. Progress towards ending TB also demands that interventions are aligned to patients’ experiences and address the challenges that they face [ 8 , 9 ].
TB typically involves the lungs (pulmonary TB) and is acquired via inhalation of droplet nuclei in the air following exposure usually over several hours. Close contact and the infectiousness of the source patient are key risk factors for the infection of tuberculin-negative persons [ 10 ]. Current treatment of drug-susceptible TB requires combination therapy consisting of an intensive phase of 2 months of isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol, followed by a continuation phase of 4 months of isoniazid and rifampin [ 11 ]. Directly observed therapy (DOT) is recommended to ensure adherence to the complex regimen and to deter the emergence and spread of MDR-TB. Treatment is successful in around 85% of patients following 6 months’ therapy [ 1 ]. Also, individuals can become non-infectious within two weeks of treatment initiation, restraining disease transmission [ 1 ]. Thus, prompt initiation of therapy is important for both the patient and their close contacts. However, the management of TB is complicated by the increasing prevalence of MDR-TB, which requires prolonged and complex therapy, and is more likely to be associated with poor outcomes [ 12 ]. Even after successful treatment, patients may have ongoing lung disease and a decreased life expectancy [ 13 , 14 , 15 ].
The drugs used to treat tuberculosis are well understood clinically, and susceptibility testing will indicate which treatment regimen is appropriate [ 11 , 12 ]. However, treatment effectiveness depends on patient adherence to a demanding and lengthy treatment regimen with associated side effects. In this context, a patient-focused approach which considers the individual’s specific circumstances is needed to ensure sufficient adherence and good outcomes from therapy. Interest in this field has been building steadily and is most suited to a qualitative investigational approach which allows deep exploration of motivations, reactions, goals, aspirations, and circumstances. However, studies more often consider the challenges faced by healthcare workers caring for TB patients [ 16 ], or the implementation of new management tools [ 17 , 18 ].
Previous studies have examined how patients manage their illness and the impact that TB has on their daily lives, their families, and the wider community [ 19 , 20 ], as well as the stigma associated with poverty and HIV and the effects of discrimination [ 21 ]. However, defining studies on the experiences of TB patients and their families are not available for all the BRICS countries, and comparison between studies with different methodologies and objectives is problematic. It is, therefore, unclear to what extent the experiences of TB patients are shared across countries.
We report the findings of a qualitative evaluation of TB patients’ experiences across the five BRICS countries. The study aimed to identify commonalities across the different country contexts, by examining the perspectives of TB patients throughout their full disease journey, including the emotional, psychosocial and practical challenges that patients and their families face. A greater understanding of these factors could inform care more focused on patients’ needs, with the aim of improving outcomes and directing the development of new tools to end TB.
Study design
This qualitative market research study was designed collaboratively by GSK and Adelphi Research and conducted between July 2020 and February 2021 across the five BRICS countries (Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa). The study was non-interventional and without clinical endpoints. The aim was to achieve a better understanding of the TB market across the BRICS countries by identifying common challenges faced by TB patients and their families in their daily lives throughout their treatment journey.
The study conformed to ethical principles laid down in the Declaration of Helsinki, all national data protection laws and industry guidelines. Participants’ data was protected by compliance with General Data Protection Regulation [ 22 ]. All participating patients and household members provided written voluntary informed consent, and parents provided written consent for children under the age of consent. Consent was also provided for anonymized publication of the findings. For consent forms see supplementary materials, Additional file 1.
To investigate the experiences, meanings, and perspectives of TB patients, qualitative methodology was employed to identify themes within and across countries from in-depth interviews and self-recorded videos, supported by a self-completed health questionnaire.
Participants with experiences relevant to the study objectives were actively recruited from BRICS countries because they account for more TB cases than any other country in their respective WHO regions, and because of the different additional challenges confronting these countries such as the burden of TB-HIV co-infection in South Africa, the diversity of private sector care in India, and the burden of MDR-TB in India, China and Russia [ 1 , 2 , 23 ]. Remote data collection both preserved the privacy of participants and ensured the safety of moderators given the infectious nature of TB and the timing of the study during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Recruitment
Participants were recruited through independent healthcare fieldwork agencies in the different countries via referral from healthcare professionals and social or community workers, as well as using market research databases, posters and adverts in TB clinics, patient groups, and word of mouth referrals. Participants had the opportunity to discuss the study with recruiters before completing a screening guide to confirm patient eligibility (Additional file 2). Recruited participants received an honorarium at fair market value for their participation.
Recruitment continued until TB patients from 40 households, that is 8 per country, plus 1–5 members of their households had been sampled. The minimum target sample size was 80 participants. Previous studies have indicated that for this type of qualitative research as few as 6 interviews per setting are required to identify major themes [ 24 , 25 ], with saturation occurring within 12 interviews [ 26 ].
Participants
Eligible participants had a confirmed diagnosis of TB and were receiving treatment or had completed treatment within the previous 12 months. Close family and other household members were included where appropriate for support and additional information, except for China where the social stigma prevented discussion with individuals other than the patient. Participants were recruited from a range of socio-economic backgrounds, assessed based on income, education levels, and living standard. At least three participants from each country were to be female. The study sought to include a range of specific patient types, for example, persons living with HIV (PLWH), those with diabetes, smokers, those with a history of excessive alcohol consumption, and those with MDR-TB/relapsed TB. At least two patients per country were to be living in households which included a child diagnosed with TB or receiving preventive treatment. No participant was excluded because of lack of access to technology as the necessary equipment was loaned to participants where needed.
Data collection
The interview moderators, fluent in the local languages, were taken through a training process in each setting, detailing study objectives, inclusion criteria, and study methodology, followed by subsequent monitoring of the process and active feedback to ensure quality control. Data quality was assured by consistent and thorough briefing of the field workers, including regular follow up to ensure study procedures were followed. The discussion guide and videoing instructions were carefully designed to contain clear respondent instructions at each question.
Patients first completed a 5-min health questionnaire based on their physical health over the previous four weeks. Interviews with TB patients and household members were conducted remotely by a trained moderator in the form of either a 60-min video-streamed interview or a 60-min telephone interview. The questionnaire and interview guides are provided in the supplementary materials (Additional file 3). Participants also completed a 45-min follow up video task to create four short videos on a mobile phone in their own time to capture their personal experience, such as their living environment, changes in their living arrangements as a result of TB, the biggest challenges since the diagnosis, perception of the changes in their life from others around them, and their hopes and expectations for the future.
The interviews were transcribed verbatim from the original languages, that is: Brazil, Portuguese; Russia, Russian; India, Hindi and English; China, Mandarin; South Africa, English, Sesotho, isiZulu, Tswana, or Afrikaans with switching between languages as necessary. Following translation into English, the information was analysed manually using a thematic and comparative analysis approach to identify key themes both within countries and across all participants’ responses [ 27 , 28 ]. Analysts had no access to patient medical records and all patient identifying information was anonymized.
Interviews were coded thematically by three analysts, aiming to reach consensus through regular team meetings where the emerging findings were discussed. Additionally, non-verbal communication (including visual evidence of living conditions) present in the videos from the streamed interviews and the video tasks were shared with the full team at regular intervals and discussed/analysed using the thematic framework developed from the transcripts. Triangulation across the different data sources was done using cross-checking to assess convergence, complementarity and divergence at the individual participant level, between patients and their families, and at the country level between informants from the same country. The analysis was therefore grouped initially by country and then analysed for cross-cutting themes across all respondents. Quality control was achieved by continuous review by two senior analysts, one of whom was not involved in the initial analysis, plus a final check through all the analyses.
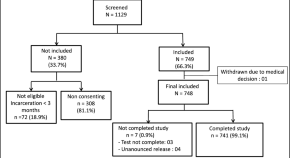
The sample consisted of 40 TB patients (8 from each country) plus 52 household members. Each patient was assigned an identifier to illustrate their country and number. Of the TB patients, 23 were men and 17 women, ranging between 13 and 60 years old. Fourteen were receiving first-line treatment, 10 second-line treatment, 2 patients had received multiple treatment lines, 11 had completed treatment, and 3 patients (all from Russia) were on a treatment break (Table 1 , Fig. 1 ). Risk factors for TB were reported in 23/40 patients, with some patients having multiple risk factors (Table 1 , Fig. 1 ). Most patients were of medium socio-economic status for their country (26/40), and no patients with high socio-economic status were recruited (Table 1 ). Except for India and South Africa, it was not possible to recruit at least two households with a child diagnosed with TB or receiving preventive treatment (Table 1 ).
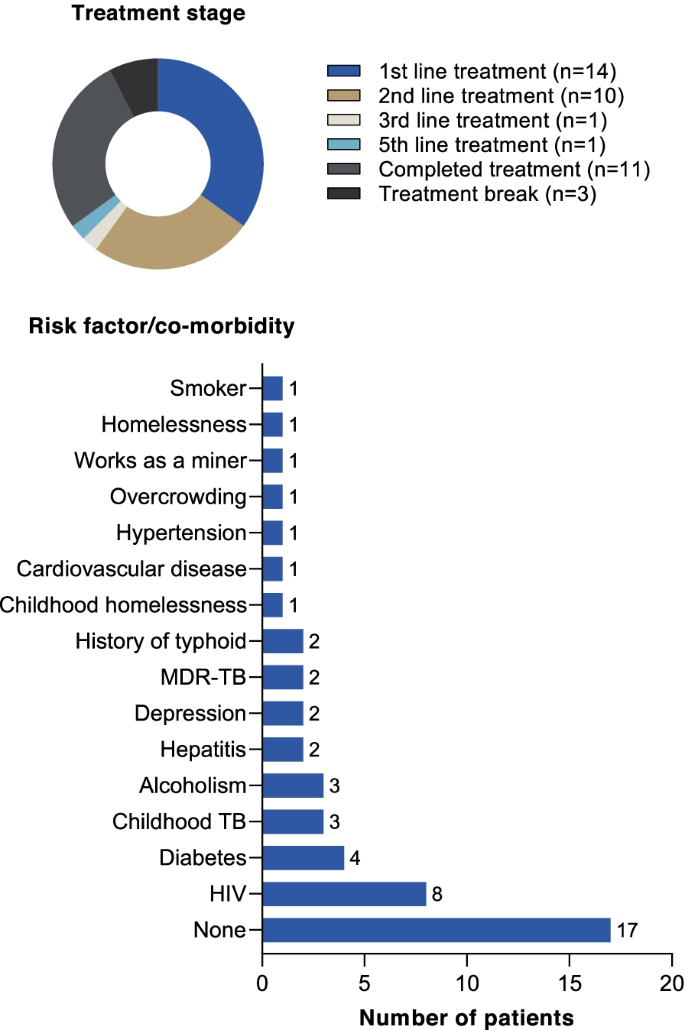
Summary of patient characteristics. Note that patients may have had more than one risk factor/co-morbidity
Patient health status
The self-reported health questionnaire indicated that most respondents (25/40) found that the physical impact of TB limited their activity. A higher proportion of patients who were currently receiving treatment (69.6% [16/23]) reported a physical impact of TB compared with those that had completed treatment (57.1% [8/14]) or who were on a treatment break (33.3% [1/3]). Most patients whose physical activity was impacted by TB reported that this affected them all or most of the time (88.0% [22/25]) (Fig. 2 A). Most patients (38/40) reported that their daily living was impacted in at least two ways (Fig. 2 B). Seven patients, five of whom were receiving treatment and two who had completed first-line treatment, stated that they were impacted by all six areas assessed (Fig. 2 B). Looking at specific impacts, the most reported were that TB stopped patients doing things that they liked to do (35/40), and economic hardship (28/40) (Fig. 2 C). Overall, it was clear that TB had significantly impaired the health status of patients and had a negative impact on daily living.
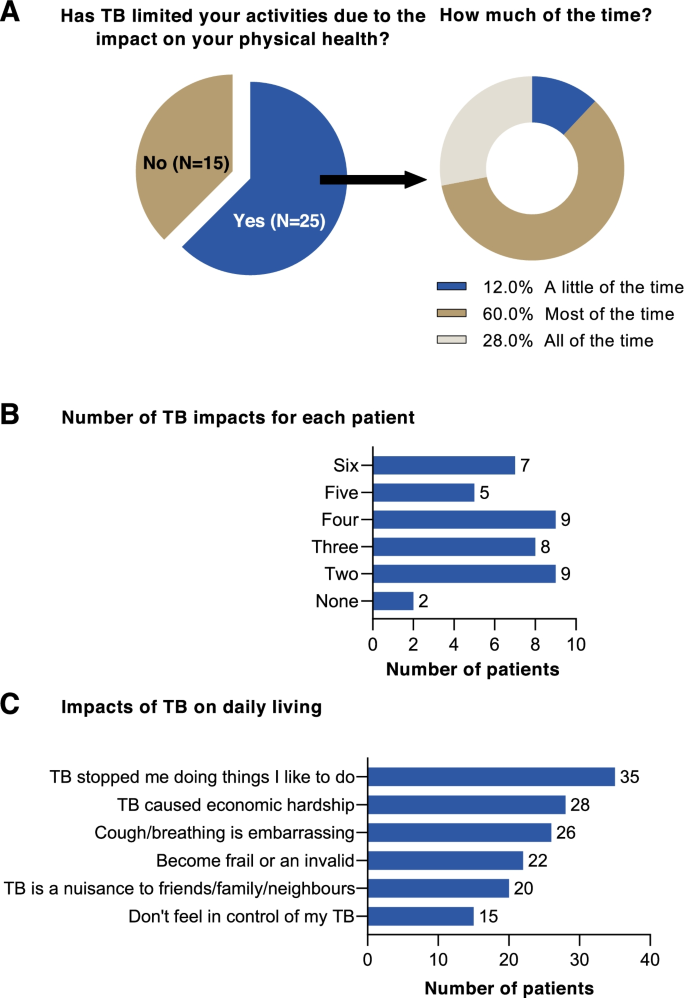
Results of a self-reported health questionnaire. A The effect of TB on limiting daily activity due to patients’ physical health; B ) the impact of TB on daily living; and C ) the number of impacts on daily living experienced by patients
Patient journey
Pre-diagnosis.
The most common initial symptoms reported by patients were a long-lasting cough increasing in severity over time, fever, weight loss, and tiredness. Some patients experienced more severe symptoms such as haemoptysis, and pleural effusion. However, symptoms were often non-specific, and unless they were aware of a source of infection or had known risk factors (e.g. HIV), most patients did not consider TB as a potential cause. Notably, patients in South Africa were more likely to suspect TB because of a higher awareness in the community and the link with HIV. In India, recent typhoid infection was suspected as the cause of symptoms in some cases.
Patients tended to hope that the symptoms would resolve on their own using over-the-counter products and traditional medicine. Patients with addiction to alcohol did not always perceive the severity of their symptoms and were less willing to engage with healthcare providers. However, avoidance of healthcare providers was common across all settings, because of concerns for the associated costs.
“The symptoms were there for the last 2 ½ months but I did not know. He was coughing a lot, so I asked him to go to the doctor. He did not listen to me. He feared talking to the doctor.” Relative of TB patient, India (IN19). “One day, I started to have fever in the afternoon. After work, I went to receive infusion in a small local clinic. I remember my body temperature was 39.5 to 39.6 degrees Celsius. The doctor said my condition was very serious, so he prescribed 5 bottles of infusion to me, and I received all of them. But my fever persisted after such a lengthy infusion.” China (CN09).
The pathway for TB cases depended on symptom severity at presentation but navigating the healthcare system was tortuous for some patients. Patients first sought help using a familiar and accessible route (Fig. 3 ).
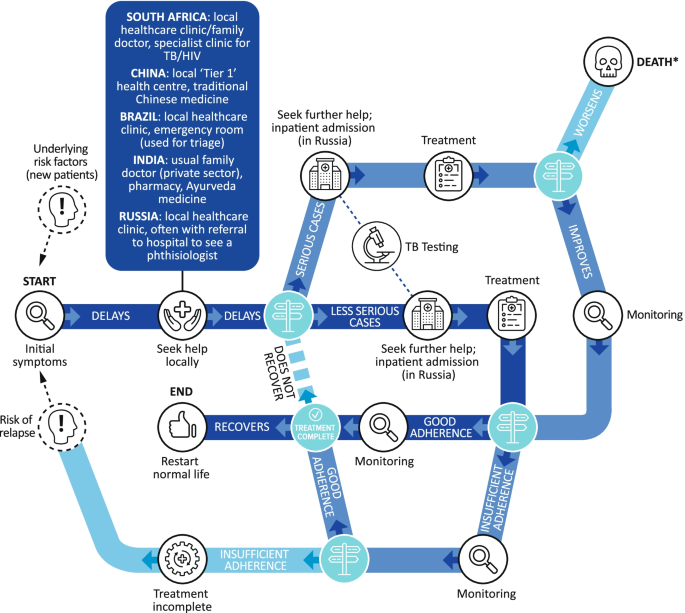
The TB patient pathway. *There were no deaths during the study
Across all countries, the TB diagnosis came as a shock to most patients – their initial thought was ‘Will I die?’. PLWH were less surprised as they were aware of the association with TB. Some patients in South Africa believed they had been vaccinated against TB as children and were therefore protected. Many patients questioned how they had caught TB and worried about the negative misconceptions associated with the disease, particularly in Russia and Brazil. Patients feared that they would be ostracized and shunned by their families and communities. Young people with TB feared for their future, for example their careers, education, and prospects of marriage. Further concerns expressed by patients included the potential disruption to their life, job security and providing for their dependents, especially in India. Overall, there was uncertainty among patients as to whether they could cope; some expressed the fear of unintentional disclosure of their TB diagnosis to others. Notably, across all countries, families were often fearful of the potential costs, with a lack of clarity regarding which elements of treatment would be covered by insurance (where available) or were refundable from the public health system.
“[I thought] it is some kind of prison disease, which occurs more and more often in people who have served a sentence somewhere. That is, more disadvantaged groups of the population. I always thought about it in this way until I met it myself.” Russia (RU10).
Following diagnosis, healthcare providers were quick to reassure patients that TB is treatable but that it will take time and that they must try not to infect others. In South Africa some patients reported being warned of drug resistance. However, beyond this, TB-focused education was limited, and patients often conducted their own research via the Internet and word of mouth, though patient-friendly resources were described as inadequate in some settings.
“[The nurse] said if you don’t take your meds, they send you to [a TB hospital] and then you will receive extreme treatment. They inject you with needles and stuff. That is if you don’t use this meds at home, they will send you there and stay for six months.” South Africa (SA05).
Treatment side effects, pill burden, lifestyle restrictions and the long-term commitment required were very challenging for patients (Fig. 4 ). Patients generally did not know the names of their medications, but described having to take many pills of different types several times a day. Patients reported intolerable side effects, including nausea and vomiting, and patients with MDR-TB faced painful daily injections. In Russia, and to a lesser extent in China, patients were admitted to hospital to increase adherence. In Russia, patients recounted being admitted to sanatoriums for the treatment of TB.
“I take many anti-TB pills every day, covering 4–5 classes, about 20 tablets in total. Sometimes, it’s difficult for me to take medication, as I was quite reluctant to take it initially, but I had no choice, but to take it as a treatment.” China (CN11).
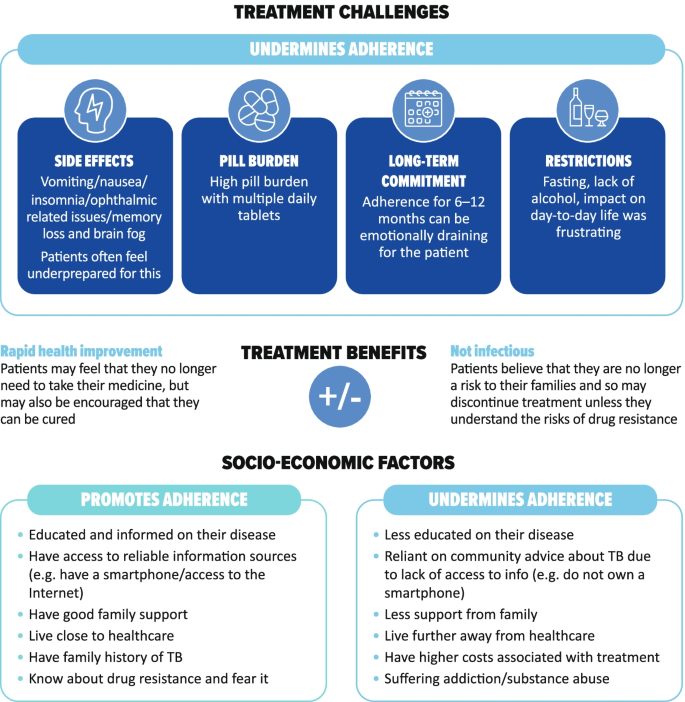
Factors identified by patients as affecting adherence to TB therapy
Monitoring and adherence
Across countries and socioeconomic bands, patients perceived minimal therapy monitoring by healthcare providers, with little evidence of DOT. It is possible that this was because of interruption to normal healthcare services because of the COVID-19 pandemic (see below). Most patients visited healthcare settings frequently to pick up their medications. Less frequently, their weight was measured during clinic visits, sputum tests were conducted, and some patients were informed when they were no longer infectious and could return to work/education. Family played a key role in monitoring during treatment, encouraging patients to continue with their treatment, sharing regular reminders, and helping to pick up medication from health centres. Motivation to comply was prompted by the desire to get back to normal family life and work, the fear of death, potential drug resistance, and hospitalization. Although patients would briefly lapse without serious consequences, they were usually encouraged to continue treatment by family and healthcare providers.
“Sometimes [redacted] forgets to take the medication, and I argue with him because if one of us forgets the treatment and the other one doesn’t then it won’t work, if we don’t take it together, it won’t work.” Brazil (BR04).
Once treatment was initiated, health improvements were quickly apparent to most patients, with resolution of fever and abatement in cough. Although this increased patients’ optimism and secured a return to some of their previous activities, it could also lead patients to believe that they had recovered, undermining adherence to therapy. Adherence was also jeopardized where there were high barriers to accessing treatment, a poor understanding of drug resistance, and when patients were alcohol dependent (Fig. 4 ). Patients who did adhere to treatment were often well supported by family and well informed of the consequences of non-adherence. Conversely, those who did not adhere to treatment were often unaware of the consequences.
“By December I was already feeling like I’m already cured, I nearly decided not to continue with the treatment.” South Africa (SA01). “Actually, they didn’t tell me about the details then. It was very important to emphasize it to me, but the physician didn’t do it. If he did, it would draw my attention and it won’t lead to drug resistance, as I often missed the dose I was supposed to take.” China (CN06). “I live in a little town which is quite far from the city. I can either go by bus which takes at least an hour and a half, or I can get to the nearest bullet train, but there aren’t many trains available and they are expensive.” China (CN08).
Completion of treatment
Eleven patients had completed treatment, 4 from South Africa, 4 from India, 2 from Brazil, and 1 from China. All had recovered, 10 following first-line treatment and 1 following second-line treatment (India). Some respondents said that their time in isolation was a time of reflection where their lives had been ‘put on pause’ making them ‘appreciate the little things in life’ they had really missed. A few patients said that their experience with TB has driven them to want to increase awareness, and remove stigma around the disease e.g., patients in Brazil and China set up informal support networks with fellow patients, particularly where patients met during hospital stays. Most patients expressed relief that they were cured, and that treatment was over, and were generally hopeful for their future.
"My TB is cured, and I want to start again with my studies. I was preparing for a railway job but I had to give that up because of TB. Now I will start my studies again and apply for a government job." India (IN04). "Thanks to this [TB] I got rid of bad habits, I do not drink alcohol now and smoke less… And I found a job, and I earn some money at the moment, during the first period my brother supported me fully, thanks to him, and my mother helped what she could.” Russia (RU05). "After these three months since I have recovered, this is what it has brought me, the willingness to fight, to battle, also to take even more care of my health, not just mine but also of people around me, and take this story, my testament, my lived experience with TB… So it’s a goal in my life, to spread information among all those who are close to me." Relative of TB patient (BR01).
Access to services
Before TB was diagnosed, in some cases patients consulted healthcare providers in the private sector, for example, the local family doctor, traditional medicine providers, or pharmacies. Following diagnosis, more affluent patients claimed on insurance or paid for private sector treatment due to poor perceptions of the public sector, and some sought support in the private sector for a ‘second opinion’ or for problems which they felt were not being addressed in the public sector. However, the majority of patients (36/40) obtained their TB care through the public sector; three patients used the private sector with one accessing both public and private sector healthcare. Treatment was provided for free through the national programs, with relatively good access in most settings, though travel distance and wait times were a barrier to access. There were reports of drug stock outs and out of pocket expenses for additional diagnostic tests or prescriptions, including having to pay for MDR-TB treatment in some settings (China). A minority of patients reported being turned away from the public sector for not having the correct paperwork or not being able to book an appointment. The public sector had a poor reputation for long queues and poor service and most patients aspired to be able to afford private treatment where services were described as being better.
“In public [sector healthcare] those nurses don’t care, I remember when I accompanied him, I was told I was not allowed to get inside, so he went in on his own. You go in pick up whatever you need and get out because those people don’t have time for anything.” Relative of TB patient, South Africa (SA01). “In the Government hospital, the doctors do not listen to us. They come when they wish and give medicines. As it is, the doctors do not listen to poor people. I had to buy some medicines from outside.” Relative of TB patient, India (IN17). “Obtaining the medication – because the drugs can only be obtained in the hospital, you can’t buy them in retail pharmacies. If I run out of my medication, I wouldn’t be able to buy it from the retail pharmacy, I would have to go the hospital, which is inconvenient.” China (CN08).
The use of sanatoriums in Russia was unique. Following diagnosis, patients were sent to a dedicated facility or a TB unit within a hospital where they remained for at least 3–4 months, though confinement could last for up to a year. They were only allowed to leave with permission, for example, at weekends or holidays. Although patients generally accepted that it was for the ‘greater good’ it was frightening at first because some other patients on the ward had very severe disease. However, some patients expressed surprise that other patients were ‘normal’, because they believed the disease to be often associated with homelessness and prisons.
“They told me I had a resistant form of TB and that the treatment is very, very long lasting. At first, they said I would have to be hospitalized three to four months and that then I would be able to go home but when I got to the hospital, the ‘girls’ told me that three to four months is optimistic… In short, eight months. Eight in the hospital and a year after the hospital. That was a shock.” Russia (RU12). “In my room there were all young women and all were so great. All of them were socially adapted: an accountant, a paediatrician student. So, let’s say it was good company.” Russia (RU01).
Thematic analysis
Five major themes were identified as common across all the countries studied (Fig. 5 ).
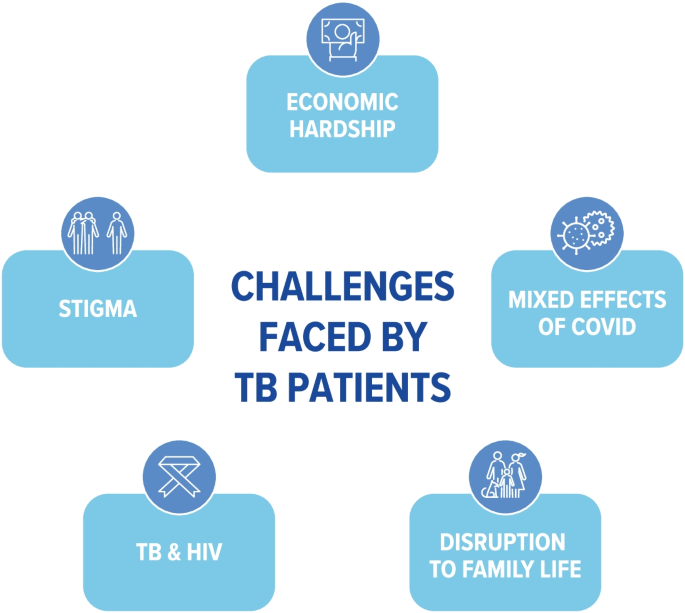
Thematic areas identified as common across five countries describing the challenges faced by TB patients
Economic hardship
Loss of earnings has the greatest economic impact for TB patients. Most patients stopped work because they felt too unwell to continue or were embarrassed by the symptoms, such as the persistent cough and severe weight loss. Some patients also felt the need to stay away from work to limit transmission to others or were ‘asked to leave’ by their employers as they were not covered by contracts. Many had no entitlement to sick pay. In some cases, patients were concerned that their financial situation could get worse as their diagnosis may mean prospective employers may be reluctant to take them on.
“The main problem is money. There is no problem greater than financial problems.” India (IN01). “I had to keep away from work because there was a lot of dust involved.” Brazil (BR15). “I cannot officially get a job, and I cannot unofficially either. But, what? Am I going to work as a loader? I cannot. This has seriously affected my finances… And who would hire if information comes out that there was TB? You will not get a job. I received a disability [payment].” Russia (RU05).
Even in regions where TB treatment was publicly funded, associated costs such as tests, hospitalization, prescriptions, travel, special food/supplements to manage weight loss, and medications to manage adverse effects were often borne by patients. The financial impact of TB meant that most patients had to rely on family or sometimes charities for support or take out loans. Time off for appointments still impacted earnings even after patients had returned to work.
“I also buy medications at my own expense [for gastric side effects] i.e. for TB, everything is free of charge due to the medical insurance policy, everything is fine, but if there is something secondary or something else not related to the diagnosis, then that is at your own expense.” Russia (RU07). “We are not educated people. I just wanted my child to recover. We are poor people; we could not work during lockdown. We had to borrow money from many people and requested help from doctors too. I thought my child would recover, but he did not. We were very stressed out.” Relative of TB patient, India (IN21). “To avoid delaying treatment, the doctor told me to take these four drugs upon diagnosis, and urged me to buy them elsewhere, as they were unavailable in the hospital. My wife found they were unavailable in many pharmacies either. Finally, she found them in several pharmacies, from where we bought them in early stage.” China (CN09).
Stigma associated with TB
Across all countries stigma was associated with TB, though it manifested in different ways. In China, TB was often kept a secret, even from family, whereas in South Africa, there was greater openness. In Brazil, though patients were open with family, there was reluctance to acknowledge their diagnosis with their community as TB is associated with wider social issues such as poverty, incarceration and ‘immoral lifestyles’. In India, TB patients felt discriminated against for other reasons, such as poverty, as well as TB. Stigma in Russia was related to the personal circumstances of the patient.
Young patients faced bullying at school/college and being dropped by friendship groups. Adults were ostracized by friends and relatives afraid of contracting TB, and relationships with friends and family suffered, leading to loneliness and depression. Respondents described instances when they were not invited to family events even after they had completed treatment and were cured. In some cases, TB appeared to ‘run in families’ meaning the stigma was intergenerational. Importantly, a family with TB was often considered a ‘low status’ family and this was compounded by the financial difficulties that accompany TB.
“A lot of my friends kept away from me because of this, because that’s what people know, that it’s contagious, but they don’t understand that the person on the other side is suffering as well, and we don’t only suffer a little bit, at least myself, it’s a very painful process, very painful, very complicated.” Relative of TB patient, Brazil (BR01). “The community was no longer as close to us because we are staying with a person that has TB – people at the queue at shops would turn around and come back when we have left.” Relative of TB patient, South Africa (SA14). “When a person has TB he becomes very annoyed as he has to go through a lot of things, plus there also comes a phase were people start avoiding you, they feel that if we come in contact with this person even we might acquire it.” India (IN01). “A person who has TB is not somebody who is well-regarded.” Brazil (BR04).
HIV co-infection played a major role in the TB experience, particularly in South Africa. Awareness of TB was higher among PLWH given their greater risk and regular contact with healthcare services. Also, the path to diagnosis was shorter given their engagement with HIV services with rapid referral reflecting the associated co-infection risks. In many cases, the HIV and TB clinics were co-located improving patient access. However, PLWH were highly aware of the stigma that TB carries with fear around the community reaction during the early stages of their journey.
"Now I’m scared I’m HIV positive, I have TB and now there’s Corona [COVID-19], what’s going to happen when I have all three of them?" South Africa (SA18). “So people were really scared, I think they are now more afraid of TB than HIV. I told my neighbour that I was diagnosed with TB and luckily she doesn’t talk much but still I was aware of their behaviour when they came by to do my laundry they would wait outside to hand it over to them and when they are done they would leave it by the door." South Africa (SA10).
Disruption to family life
A diagnosis of TB affects everyone in the household and the wider family. Cleaning and disinfecting routines have to be established and maintained, and there was a general awareness that separate cutlery must be used, living spaces needed good ventilation, and clothes and bedding should be washed more frequently. Sleeping arrangements to isolate TB patients were particularly problematic in India and South Africa where large families live together, and parental co-sleeping with children was no longer possible where this was practiced. In some cases, children were looked after in the homes of extended family members, away from parents with TB. Married patients feared abandonment or divorce and respondents felt ‘lucky’ that their partners had stayed with them despite their TB status. The reduced family contact, demands of treatment and financial hardship often strained family relationships.
“Life at home isn’t the same because I had to begin separating my cutlery and a glass – my clothes had to be washed separately, we have to clean down the house and open the windows to let the air circulate.” Brazil (BR15). “I’m worried I may infect my parents. So I’ve had to reduce my interactions with them, the time spent with them, the number of occasions I’m with them. And as they get older, they become confused and they don’t understand why I stay away.” China (CN08). “Our house always used to be full at weekends, friends would come around to watch films, sometimes we would make lunch, get pizza and sit and watch films, and then suddenly the house was empty.” Relative of TB patient, Brazil (BR01).
Mixed effects of COVID-19
Some TB patients observed that the COVID-19 pandemic normalized the idea of infection prevention, with mask wearing becoming common. Also, TB patients were able to hide their diagnosis more easily with social distancing measures. There was also less fear that they could infect the wider community. However, access to healthcare and medication was compromised with restrictions to movement and hospitals not accepting admissions for other conditions. Patients were fearful of ‘catching’ COVID-19 given their impaired respiratory health and existing co-morbidities, such as HIV and diabetes. Some respondents who were coming to the end of their isolation and anticipating greater freedoms and a return to a more normal life then faced COVID-19 restrictions.
“During the pandemic I was unable to go to the hospital for my regular follow-ups and prescription renewal, and so because of that my condition worsened, and I eventually ended up infecting my family.” CN08.
Assuming that efficacious treatment is provided, TB is curable. However, outcomes are often sub-optimal. This study aimed to explore common themes in the experiences of TB patients and their families in the five BRICS countries from diagnosis to completion of treatment. Using consistent methodology, economic hardship, stigma, TB-HIV co-infection, disruption to family life, and the mixed effects of COVID-19 were identified as themes encompassing the challenges facing TB patients across the five BRICS countries (Fig. 5 ). These factors, therefore, appear to be independent of the country setting. Further research should investigate the degree to which these factors and are potentially mutable by targeting systemic changes in healthcare and social provision and providing attention to patients’ individual needs.
Economic hardship was reported across all countries. TB is associated with economic vulnerability but can also drive families into poverty through loss of income, the costs of transportation and food supplements, and associated medical expenses [ 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 ]. Programs providing social protection to TB patients have been linked to improved outcomes and the increased uptake of preventive therapy but must be easily accessible [ 29 , 37 , 38 ]. Improvement of TB services can also reduce the number of families facing financial hardship [ 39 ]. Even though most healthcare systems in our study provided TB drugs free of charge, to be effective, treatment should encompass the wider economic impacts that patients experience. Despite various approaches, patients from all of the countries surveyed found themselves struggling financially and a more holistic approach to patient support is needed.
Stigma attached to TB is culturally distinct, but stems from a lack of awareness of TB and the persistence of stereotypes [ 40 , 41 ]. For example, in Russia, an association with prisons and poverty has persisted, despite TB affecting all sectors of society [ 42 ]. Stigma was most acutely felt in China, and a recent study described psychological distress in nearly two-thirds of TB patients, associated with a high experienced stigma [ 43 ]. In our study, some patients did not even disclose their diagnosis to close family. In newly diagnosed Chinese TB patients, non-disclosure of their TB status magnified patient-perceived stigma and was associated with depression – a risk factor for non-adherence [ 44 , 45 ]. Social support and doctor–patient communication appeared key factors for reducing TB-related stigma in China [ 46 ]. Also, educational approaches to raise awareness of TB diagnosis and treatment among the public are needed, particularly focused on those with low educational levels and more rural communities [ 40 , 47 , 48 ].
The association between TB and HIV is well documented. However, the impact on patients is less well understood. In this study, PLWH were more aware of TB and were more likely to seek care early and be diagnosed quickly. This is in contrast to a study in Thailand where PLWH had low TB awareness and attributed their early symptoms to AIDS, resulting in delayed TB diagnosis [ 49 ]. This emphasizes the importance of raising TB awareness in PLWH. In South Africa, TB and HIV services are often co-located and integrated [ 50 ]. However, a detailed analysis in South Africa of the challenges faced by PLWH who had MDR-TB highlighted similar issues to those described here for all TB patients, such as fear, stigma, dissociation from family and social networks, poor provider support, drug adverse events, and financial insecurity [ 51 ]. Also, patients tended to prioritize adherence to anti-retroviral therapy versus TB therapy because it was less challenging in terms of pill burden and adverse effects [ 52 ]. Until less demanding treatment regimens are available, targeted support to address the challenges of adherence in patients co-infected with TB-HIV is necessary.
The respondents in this study described a severely disrupted home life following a TB diagnosis. Patients were isolated and often infirm, and the economic and care responsibilities for family members were considerable. Families also suffered socially, being isolated or shunned by friends and the wider family. In many cases, it was family members who ensured adherence to medication, and social and family support for patients has been previously shown as a key factor in therapy adherence [ 41 , 53 , 54 ]. Despite this, the impact of the TB diagnosis on the family and how family members can best be supported has been rarely investigated [ 47 ], and we identify this as an important area for further research.
The COVID-19 epidemic has disrupted healthcare access globally [ 55 ]. In our study, TB patients reported drug shortages and restrictions to services during the period. TB patients also expressed concern regarding the consequences of contracting COVID-19. Similarly, a recent study in Brazil reported that TB patients were fearful of attending medical appointments [ 56 ]. TB patients do appear to be at greater risk of death or poor outcome with COVID-19 [ 57 ], and should therefore socially isolate or ‘shield’ [ 58 ]. TB patients did feel less stigmatized as social distancing and infection control measures were deployed for COVID-19. However, the interruption of treatment, with the risk of therapy failure, selection of MDR-TB, and increased transmissibility is a major threat to TB patients and their close contacts [ 59 ].
This study has several limitations. Although participants were identified through a variety of channels and a range of socioeconomic groups were sampled, this was not a randomized sample and we acknowledge that both marginalized and privileged groups may not engage in this kind of research. Also, there were no data on whether susceptibility testing was conducted following the TB diagnosis, so the appropriateness of therapy could not be assessed. Neither did we examine the differences between patients’ experiences of drug-susceptible versus MDR-TB; patients were not consistently aware of the difference and most patients were receiving or had recently completed first-line therapy. The patient pathway was not integrated into the thematic analysis but analysed separately in terms of the systemic challenges that patients face. This was because the complexity of the pathway did not map onto the themes in a meaningful way. For example, patients experienced economic hardship, stigma, and disruption to family life at most stages in the patient pathway, whereas TB-HIV co-infection had an important effect on the speed of diagnosis. Thus, patient pathway was examined systematically and separately to the thematic analysis which focused on the emotional, socio-economic and practical impacts of TB on patients’ daily lives. The analysis methods sought to remain impartial with repeated reviews by multiple analysts to reach consensus. However, the analysts were all based in the UK and we recognize that the cultural subtleties of some of the patients’ experiences may not have been fully appreciated.
In our study, TB patients’ perceptions and needs were expressed in their own words, from within their home environment, in confidence, to interviewers who were not involved in their healthcare. Most had struggled to adjust to their diagnosis, had poor access to information, lacked support from healthcare workers, were under significant financial pressure, and were highly conscious of stigma and the burden TB placed on their families.
Our findings highlight that much work still needs to be done before the goal of ending TB can be achieved. Structural changes require simplification of the TB patient pathway, reliable access to services, and the alleviation of financial pressures. Health education for patients, their families, healthcare providers and the public to increase awareness of TB symptoms and diagnosis, to encourage adherence, and to reduce stigma around the disease is needed. Importantly, TB patients do better with strong family and social networks to sustain them, and a greater understanding of how these can be better supported at the level of the individual patient throughout the TB treatment journey requires further investigation.
Despite the different cultural, political, and healthcare settings across the BRICS countries, TB patients faced very similar challenges. This commonality would not necessarily have been expected. It suggests that these factors are not only a product of the healthcare provision in the countries or the social, economic, and cultural pressures that patients face, but reflect an overarching insufficiency in the treatment of TB. The efficient delivery of comprehensive individualized care and support would certainly mitigate the negative impacts of TB on patients. However, these issues will likely not be fully resolved until treatment options are available that rapidly cure TB and prevent onward transmission.
Availability of data and materials
All relevant data are included in this publication. Recorded interviews will not be made available in order to maintain patient confidentiality. However, anonymised transcripts are available on reasonable request to the authors for ten years following study completion. For data requests please contact the corresponding author at [email protected].
Abbreviations
Coronavirus disease of 2019 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2)
Human immunodeficiency virus
Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis
People living with HIV
- Tuberculosis
World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis report 2021. 2021. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240037021 . Accessed 1 Nov 2021.
Creswell J, Sahu S, Sachdeva KS, Ditiu L, Barreira D, Mariandyshev A, Mingting C, Pillay Y. Tuberculosis in BRICS: challenges and opportunities for leadership within the post-2015 agenda. Bull World Health Organ. 2014;92(6):459–60.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis report 2020. 2020. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240013131 . Accessed 1 Nov 2021.
World Health Organization. The End TB Strategy: Global strategy and targets for tuberculosis prevention, care and control after 2015. 2014. https://www.who.int/tb/strategy/End_TB_Strategy.pdf . Accessed 4 July 2021.
Floyd K, Glaziou P, Houben R, Sumner T, White RG, Raviglione M. Global tuberculosis targets and milestones set for 2016–2035: definition and rationale. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2018;22(7):723–30.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
United Nations General Assembly. A/RES/73/3. Political declaration of the high-level meeting of the General Assembly on the fight against tuberculosis. 2018. https://www.un.org/en/ga/search/view_doc.asp?symbol=A/RES/73/3 . Accessed 4 July 2021.
World Health Organization. WHO consolidated guidelines on tuberculosis. Module 1: prevention – tuberculosis preventive treatment. 2020. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/who-consolidated-guidelines-on-tuberculosis-module-1-prevention-tuberculosis-preventive-treatment . Accessed 4 July 2020.
Shete PB, Reid M, Goosby E. Message to world leaders: we cannot end tuberculosis without addressing the social and economic burden of the disease. Lancet Glob Health. 2018;6(12):e1272–3.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Hoos A, Anderson J, Boutin M, Dewulf L, Geissler J, Johnston G, Joos A, Metcalf M, Regnante J, Sargeant I, et al. Partnering with patients in the development and lifecycle of medicines: A call for action. Ther Innov Regul Sci. 2015;49(6):929–39.
Reichler MR, Khan A, Yuan Y, Chen B, McAuley J, Mangura B, Sterling TR. Tuberculosis epidemiologic studies consortium task order team: Duration of exposure among close contacts of patients with infectious tuberculosis and risk of latent tuberculosis infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71(7):1627–34.
World Health Organization. Guidelines for treatment of drug-susceptible tuberculosis and patient care. 2017. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/255052/9789241550000-eng.pdf . Accessed 4 July 2021.
World Health Organization. WHO consolidated guidelines on tuberculosis. Module 4: treatment - drug-resistant tuberculosis treatment. 2020. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240007048 . Accessed 4 July 2021.
Hoger S, Lykens K, Beavers SF, Katz D, Miller TL. Longevity loss among cured tuberculosis patients and the potential value of prevention. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2014;18(11):1347–52.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Allwood BW, Byrne A, Meghji J, Rachow A, van der Zalm MM, Schoch OD. Post-tuberculosis lung disease: Clinical review of an under-recognised global challenge. Respiration. 2021;100(8):751–63.
Mkoko P, Naidoo S, Mbanga LC, Nomvete F, Muloiwa R, Dlamini S. Chronic lung disease and a history of tuberculosis (post-tuberculosis lung disease): Clinical features and in-hospital outcomes in a resource-limited setting with a high HIV burden. S Afr Med J. 2019;109(3):169–73.
Matakanye H, Ramathuba DU, Tugli AK. Caring for tuberculosis patients: Understanding the plight of nurses at a regional hospital in Limpopo Province, South Africa. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16(24):4977.
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
Thomas BE, Kumar JV, Periyasamy M, Khandewale AS, Hephzibah Mercy J, Raj EM, Kokila S, Walgude AS, Gaurkhede GR, Kumbhar JD, et al. Acceptability of the medication event reminder monitor for promoting adherence to multidrug-resistant tuberculosis therapy in two Indian cities: Qualitative study of patients and health care providers. J Med Internet Res. 2021;23(6): e23294.
Milligan H, Iribarren SJ, Chirico C, Telles H, Schnall R. Insights from participant engagement with the tuberculosis treatment support tools intervention: Thematic analysis of interactive messages to guide refinement to better meet end user needs. Int J Med Inform. 2021;149: 104421.
Dias AA, de Oliveira DM, Turato ER, de Figueiredo RM. Life experiences of patients who have completed tuberculosis treatment: a qualitative investigation in southeast Brazil. BMC Public Health. 2013;13:595.
Bhattacharya Chakravarty A, Rangan S, Dholakia Y, Rai S, Kamble S, Raste T, Shah S, Shah S, Mistry N. Such a long journey: What health seeking pathways of patients with drug resistant tuberculosis in Mumbai tell us. PLoS ONE. 2019;14(1): e0209924.
Courtwright A, Turner AN. Tuberculosis and stigmatization: pathways and interventions. Public Health Rep. 2010;125(Suppl 4):34–42.
The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union: Regulation (EU) 2016/679 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 27 April 2016 on the protection of natural persons with regard to the processing of personal data and on the free movement of such data, and repealing Directive 95/46/EC (General Data Protection Regulation). Official Journal of the European Union. 2016;L119:1-88.
An Q, Song W, Liu J, Tao N, Liu Y, Zhang Q, Xu T, Li S, Liu S, Li Y, et al. Primary drug-resistance pattern and trend in elderly tuberculosis patients in Shandong, China, from 2004 to 2019. Infect Drug Resist. 2020;13:4133–45.
Isman E, Ekeus C, Berggren V. Perceptions and experiences of female genital mutilation after immigration to Sweden: an explorative study. Sex Reprod Healthc. 2013;4(3):93–8.
Isman E, Mahmoud Warsame A, Johansson A, Fried S, Berggren V. Midwives’ experiences in providing care and counselling to women with female genital mutilation (FGM) related problems. Obstet Gynecol Int. 2013;2013:785148.
Guest G, Bunce A, Johnson L. How many interviews are enough?: An experiment with data saturation and variability. Field Methods. 2006;18:59–82.
Article Google Scholar
Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual Res Psychol. 2006;3:77–101.
Green J, Thorogood N. Qualitative methods for health research. 2nd ed. London: Sage; 2009.
Google Scholar
Aragao FBA, Arcencio RA, Fuentealba-Torres M, Carneiro TSG, Souza LLL, Alves YM, Fiorati RC. Impact of social protection programs on adults diagnosed with tuberculosis: systematic review. Rev Bras Enferm. 2021;74(3): e20190906.
Sinha P, Carwile M, Bhargava A, Cintron C, Acuna-Villaorduna C, Lakshminarayan S, Liu AF, Kulatilaka N, Locks L, Hochberg NS. How much do Indians pay for tuberculosis treatment? A cost analysis. Public Health Action. 2020;10(3):110–7.
Xu CH, Jeyashree K, Shewade HD, Xia YY, Wang LX, Liu Y, Zhang H, Wang L. Inequity in catastrophic costs among tuberculosis-affected households in China. Infect Dis Poverty. 2019;8(1):46.
Stracker N, Hanrahan C, Mmolawa L, Nonyane B, Tampi R, Tucker A, West N, Lebina L, Martinson N, Dowdy D. Risk factors for catastrophic costs associated with tuberculosis in rural South Africa. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2019;23(6):756–63.
Yang T, Chen T, Che Y, Chen Q, Bo D. Factors associated with catastrophic total costs due to tuberculosis under a designated hospital service model: a cross-sectional study in China. BMC Public Health. 2020;20(1):1009.
Lu L, Jiang Q, Hong J, Jin X, Gao Q, Bang H, DeRiemer K, Yang C. Catastrophic costs of tuberculosis care in a population with internal migrants in China. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020;20(1):832.
Moreira A, Kritski AL, Carvalho ACC. Social determinants of health and catastrophic costs associated with the diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis. J Bras Pneumol. 2020;46(5):e20200015.
Hutchison C, Khan MS, Yoong J, Lin X, Coker RJ. Financial barriers and coping strategies: a qualitative study of accessing multidrug-resistant tuberculosis and tuberculosis care in Yunnan, China. BMC Public Health. 2017;17(1):221.
Patel BH, Jeyashree K, Chinnakali P, Vijayageetha M, Mehta KG, Modi B, Chavda PD, Dave PV, Zala CC, Shewade HD, et al. Cash transfer scheme for people with tuberculosis treated by the National TB Programme in Western India: a mixed methods study. BMJ Open. 2019;9(12):e033158.
Rudgard WE, Evans CA, Sweeney S, Wingfield T, Lonnroth K, Barreira D, Boccia D. Comparison of two cash transfer strategies to prevent catastrophic costs for poor tuberculosis-affected households in low- and middle-income countries: An economic modelling study. PLoS Med. 2017;14(11):e1002418.
Verguet S, Riumallo-Herl C, Gomez GB, Menzies NA, Houben R, Sumner T, Lalli M, White RG, Salomon JA, Cohen T, et al. Catastrophic costs potentially averted by tuberculosis control in India and South Africa: a modelling study. Lancet Glob Health. 2017;5(11):e1123–32.
Lu SH, Tian BC, Kang XP, Zhang W, Meng XP, Zhang JB, Lo SK. Public awareness of tuberculosis in China: a national survey of 69 253 subjects. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2009;13(12):1493–9.
PubMed Google Scholar
Deshmukh RD, Dhande DJ, Sachdeva KS, Sreenivas AN, Kumar AMV, Parmar M. Social support a key factor for adherence to multidrug-resistant tuberculosis treatment. Indian J Tuberc. 2018;65(1):41–7.
Zvonareva O, van Bergen W, Kabanets N, Alliluyev A, Filinyuk O. Experiencing syndemic: Disentangling the biosocial complexity of tuberculosis through qualitative research. J Biosoc Sci. 2019;51(3):403–17.
Chen X, Wu R, Xu J, Wang J, Gao M, Chen Y, Pan Y, Ji H, Duan Y, Sun M, et al. Prevalence and associated factors of psychological distress in tuberculosis patients in Northeast China: a cross-sectional study. BMC Infect Dis. 2021;21(1):563.
Lee LY, Tung HH, Chen SC, Fu CH. Perceived stigma and depression in initially diagnosed pulmonary tuberculosis patients. J Clin Nurs. 2017;26(23–24):4813–21.
Qiu L, Tong Y, Lu Z, Gong Y, Yin X. Depressive symptoms mediate the associations of stigma with medication adherence and quality of life in tuberculosis patients in China. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2019;100(1):31–6.
Chen X, Du L, Wu R, Xu J, Ji H, Zhang Y, Zhu X, Zhou L. Tuberculosis-related stigma and its determinants in Dalian, Northeast China: a cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health. 2021;21(1):6.
Sathar F, Velen K, Peterson M, Charalambous S, Chetty-Makkan CM. “Knock”: a qualitative study exploring the experience of household contacts on home visits and their attitude towards people living with TB in South Africa. BMC Public Health. 2020;20(1):1047.
Rajalakshmi M, Kalaiselvan G, Sudhakar R, Dhikale PT. An exploratory mixed method study on the follow up status and quality of life among recurrent tuberculosis patients in South India. Indian J Tuberc. 2020;67(4):515–22.
Ngamvithayapong J, Winkvist A, Diwan V. High AIDS awareness may cause tuberculosis patient delay: results from an HIV epidemic area. Thailand AIDS. 2000;14(10):1413–9.
Lince-Deroche N, Leuner R, Kgowedi S, Moolla A, Madlala S, Manganye P, Xhosa B, Govathson C, White Ndwanya T, Long L. Voices from the front lines: A qualitative study of integration of HIV, tuberculosis, and primary healthcare services in Johannesburg, South Africa. PLoS ONE. 2020;15(10):e0230849.
Daftary A, Mondal S, Zelnick J, Friedland G, Seepamore B, Boodhram R, Amico KR, Padayatchi N, O’Donnell MR. Dynamic needs and challenges of people with drug-resistant tuberculosis and HIV in South Africa: a qualitative study. Lancet Glob Health. 2021;9(4):e479–88.
Daftary A, Padayatchi N, O’Donnell M. Preferential adherence to antiretroviral therapy over tuberculosis treatment: a qualitative study of drug-resistant TB/HIV co-infected patients in South Africa. Glob Public Health. 2014;9(9):1107–16.
Daniels J, Medina-Marino A, Glockner K, Grew E, Ngcelwane N, Kipp A. Masculinity, resources, and retention in care: South African men’s behaviors and experiences while engaged in TB care and treatment. Soc Sci Med. 2021;270: 113639.
da Silva RD, de Luna FDT, de Araujo AJ, Camelo ELS, Bertolozzi MR, Hino P, Lacerda SNB, Fook SML, de Figueiredo T. Patients’ perception regarding the influence of individual and social vulnerabilities on the adherence to tuberculosis treatment: a qualitative study. BMC Public Health. 2017;17(1):725.
Migliori GB, Thong PM, Akkerman O, Alffenaar JW, Alvarez-Navascues F, Assao-Neino MM, Bernard PV, Biala JS, Blanc FX, Bogorodskaya EM, et al. Worldwide effects of coronavirus disease pandemic on tuberculosis services, January-April 2020. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020;26(11):2709–12.
Santos FLD, Souza LLL, Bruce ATI, Crispim JA, Arroyo LH, Ramos ACV, Berra TZ, Alves YM, Scholze AR, Costa F, et al. Patients’ perceptions regarding multidrug-resistant tuberculosis and barriers to seeking care in a priority city in Brazil during COVID-19 pandemic: A qualitative study. PLoS ONE. 2021;16(4):e0249822.
Sy KTL, Haw NJL, Uy J. Previous and active tuberculosis increases risk of death and prolongs recovery in patients with COVID-19. Infect Dis (Lond). 2020;52(12):902–7.
Maciel ELN, Goncalves Junior E, Dalcolmo MMP. Tuberculosis and coronavirus: what do we know? Epidemiol Serv Saude. 2020;29(2):e2020128.
Singh A, Prasad R, Gupta A, Das K, Gupta N. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 and pulmonary tuberculosis: convergence can be fatal. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 2020;90(3):441–50.
European Pharmaceutical Market Research Association. Code of Conduct 2020. 2020. https://www.ephmra.org/media/4857/ephmra-2020-code-of-conduct-final.pdf . Accessed 8 Feb 2022.
International Chamber of Commerce, European Society for Opinion and Marketing Research. ICC/ESOMAR International Code on Market, Opinion and Social Research and Data Analytics. 2016. https://esomar.org/code-and-guidelines/icc-esomar-code . Accessed 8 February 2022.
British Healthcare Business Intelligence Association. Legal and Ethical Guidelines for Healthcare Market Research: Your essential guide. 2021. https://www.bhbia.org.uk/guidelines-and-legislation/legal-and-ethical-guidelines . Accessed 8 Feb 2022.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Naomi Richardson of Magenta Communications Ltd. in collaboration with Juliet Addo developed the first draft of this article from a research report, provided editorial and graphic services and was funded by GSK. Elizabeth Kehler, Francesca Trewartha and Thea Westwater Smith of Adelphi were co-authors of the original report and co-analysts. Carly Davies, Vera Gielen and Myriam Drysdale from GSK reviewed and provided comments on the screening and interview guides.
This study was funded by GSK Plc.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Global Health Catalyst, Global Health R&D, GSK, 980 Great West Road, Brentford, Middlesex, TW8 9GS, United Kingdom
Juliet Addo, Courtney Lundquist & Mike Strange
Product Development and Supply, GSK, Stevenage, United Kingdom
Dave Pearce
Global Medical, GSK, Research Triangle Park, USA
Marilyn Metcalf
Adelphi Research, Bollington, United Kingdom
Gillian Thomas
Global Health Pharma Research Unit, Tres Cantos, Spain
David Barros-Aguirre
Global Health Clinical, Stockley Park West, United Kingdom
Gavin C. K. W. Koh
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
J.A. made substantial contributions to the conception and design of the work, interpretation of the data and drafting of the manuscript. C.L., M.M., M.S., D.B-A., G.C.K.W.K. and D.P. made substantial contributions to the conception and design of the work and interpretation of the data and critically revised the manuscript for intellectual content. G.T. made significant contributions to the design of the work, the acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation of data for the work and critically revised the manuscript for intellectual content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Juliet Addo .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The research was conducted in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration, and all national data protection laws. In compliance with European Union and UK legislation, General Data Protection Regulation guidelines were followed to ensure full patient data confidentiality [ 22 ]. Informed consent was obtained electronically from all individual participants included in the study or their parents/guardians if under the age of consent. Consent was also provided for anonymized consolidated publication of the findings. Participants’ rights and privacy were protected at all times throughout the study. Participants were granted the right to withdraw from the study at any time during the study conduct and to withhold information as they saw fit. All information/data that could identify respondents to third parties was kept strictly confidential; all respondents remained anonymous by using nicknames for the study.
The study complied with international guidance on the conduct of market research, including the European Pharmaceutical Market Research Association (EphMRA) [ 60 ], the European Society for Opinion and Marketing Research (ESOMAR) [ 61 ], and the British Healthcare Business Intelligence Association (BHBIA) [ 62 ], and all other relevant national codes of conduct. Formal ethics approval was waived on the basis that only anonymised data were collected for market research purposes, without treatment intervention, the assessment of clinical endpoints, or the testing of any clinical hypothesis. Specifically, EphMRA defines market research as:
the systematic gathering and interpretation of information about individuals, organisations and marketplaces;
using the information gathering and analytical methods and techniques of the applied social, behavioural and data sciences;
its purpose is to gain insight or support decision making;
the identity of Market Research subjects will not be revealed to the user of the information without explicit consent, Market Research has no interest in the individual identity of Market Research subjects;
no direct action e.g. a sales approach will be taken in relation to individuals or organisations as a result of the Market Research (except following up adverse events when permitted), Market Research is not a commercial communication or a selling opportunity.
Market Research is defined by the objective(s) and the approach, not by the title of the work or those involved in it. Consequently, the EphMRA Code of Conduct includes areas such as digital listening (the use of social media content for Market Research), the use of observational/ethnographic approaches and work carried out online via mobile devices. Section 1.3 of the EphMRA code states that ‘Market Research (as defined above) relating to market or consumer behaviour of the sort that pharmaceutical companies routinely commission, whether involving healthcare professionals, patients, carers or members of the public does not require Clinical Research Ethics Committee or Independent Review Board approval (Institutional Review Board in the USA).’ [ 60 ]. Investigational tools and procedures were reviewed and approved by the GSK Medical Governance Boards in each participating country prior to recruitment to ensure that these were fully compliant with the above conditions and any additional national codes and legislation.
Consent for publication
Consent for publication is not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The following authors are employees of GSK (J.A., D.P., M.M., C.L., M.S., and D.B-A.) and hold stocks in GSK. G.C.K.W.K. is a former employee of GSK and holds stocks in the company. The opinions expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of their employers or organizations. G.T. is an employee of Adelphi Research which received funding from GSK Plc for the conduct of this study.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1..
Consent forms.
Additional file 2.
Screening questions.
Additional file 3.
Health questionnaire and interview guide.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Addo, J., Pearce, D., Metcalf, M. et al. Living with tuberculosis: a qualitative study of patients’ experiences with disease and treatment. BMC Public Health 22 , 1717 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-14115-7
Download citation
Received : 19 December 2021
Accepted : 30 August 2022
Published : 10 September 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-14115-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Treatment failure
BMC Public Health
ISSN: 1471-2458
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
Tuberculosis articles from across Nature Portfolio
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by strains of bacteria known as mycobacteria. The disease most commonly affects the lungs and can be fatal if not treated. However, most infected individuals show no disease symptoms. One third of the worlds population is thought to have been infected with TB.
Latest Research and Reviews
Analysis of the potential regulatory mechanisms of female and latent genital tuberculosis affecting ovarian reserve function using untargeted metabolomics
- Zhimin Wang
- Xueyan Zhang
- Xiujuan Chen
Age and sex influence antibody profiles associated with tuberculosis progression
Analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis -specific antibody responses in previously exposed South African cohorts reveals that profile features associated with progression to active tuberculosis are affected by age and sex.
- Leela R. L. Davies
- Chuangqi Wang
- Sarah M. Fortune
Bacterial diversity dominates variable macrophage responses of tuberculosis patients in Tanzania
- Hellen Hiza
- Michaela Zwyer
- Damien Portevin
Prevalence of pulmonary tuberculosis and HIV infections and risk factors associated to tuberculosis in detained persons in Antananarivo, Madagascar
- Fanjasoa Rakotomanana
- Anou Dreyfus
- Rindra V. Randremanana
The recent rapid expansion of multidrug resistant Ural lineage Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Moldova
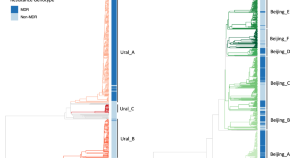
Chitwood et al. report on the rapid expansion of a Ural-lineage multidrug resistant strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Moldova. This strain has an estimated reproduction number more than two times greater than otherwise similar drug susceptible strains.
- Melanie H. Chitwood
- Caroline Colijn
- Benjamin Sobkowiak
Genomic insights into anthropozoonotic tuberculosis in captive sun bears ( Helarctos malayanus ) and an Asiatic black bear ( Ursus thibetanus ) in Cambodia
- Kirsty Officer
- Timothy M. Walker
- Bethany Jackson
News and Comment
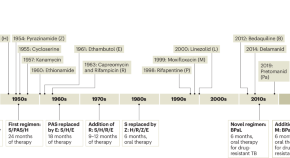
Restocking the tuberculosis drug arsenal
After many lean years, important progress has been made in updating the anti-tuberculosis drug armamentarium; a new drug that targets bacterial protein synthesis is one of several that could help transform the treatment of this neglected and deadly disease.
- Eric L. Nuermberger
- Richard E. Chaisson
Digital intervention improves tuberculosis treatment outcomes
An intervention that incorporates electronic pill boxes and remote adherence monitoring improved treatment success in patients with tuberculosis in Tibet — making this a promising strategy for low-resource settings.
- Karen O’Leary

A spotlight on the tuberculosis epidemic in South Africa
Tuberculosis is the leading cause of death from a single infectious agent, with over 25% of these occurring in the African region. Multi-drug resistant strains which do not respond to first-line antibiotics continue to emerge, putting at risk numerous public health strategies which aim to reduce incidence and mortality. Here, we speak with Professor Valerie Mizrahi, world-leading researcher and former director of the Institute of Infectious Disease and Molecular Medicine at the University of Cape Town, regarding the tuberculosis burden in South Africa. We discuss the challenges faced by researchers, the lessons that need to be learnt and current innovations to better understand the overall response required to accelerate progress.
Presumed ocular tuberculosis – need for caution before considering anti-tubercular therapy
- Rohan Chawla
- Urvashi B. Singh
- Pradeep Venkatesh
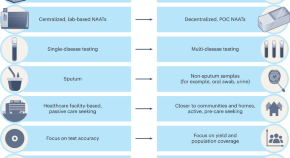
Transforming tuberculosis diagnosis
Diagnosis is the weakest aspect of tuberculosis (TB) care and control. We describe seven critical transitions that can close the massive TB diagnostic gap and enable TB programmes worldwide to recover from the pandemic setbacks.
- Madhukar Pai
- Puneet K. Dewan
- Soumya Swaminathan
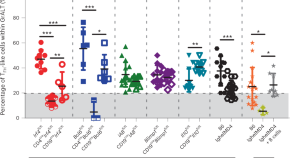

B cells and T follicular helper-like cells within lung granulomas are required for TB control
We show a crucial protective function for T follicular helper (T FH )-like cells localized within granuloma-associated lymphoid tissue for Mycobacterium tuberculosis control in mouse models of tuberculosis. Antigen-specific B cells contribute to this strategic localization and the maturation of cytokine-producing T FH -like cells.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
- Open access
- Published: 27 April 2024
Exploring health care providers’ engagement in prevention and management of multidrug resistant Tuberculosis and its factors in Hadiya Zone health care facilities: qualitative study
- Bereket Aberham Lajore 1 na1 nAff5 ,
- Yitagesu Habtu Aweke 2 na1 nAff6 ,
- Samuel Yohannes Ayanto 3 na1 nAff7 &
- Menen Ayele 4 nAff5
BMC Health Services Research volume 24 , Article number: 542 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
88 Accesses
Metrics details
Engagement of healthcare providers is one of the World Health Organization strategies devised for prevention and provision of patient centered care for multidrug resistant tuberculosis. The need for current research question rose because of the gaps in evidence on health professional’s engagement and its factors in multidrug resistant tuberculosis service delivery as per the protocol in the prevention and management of multidrug resistant tuberculosis.
The purpose of this study was to explore the level of health care providers’ engagement in multidrug resistant tuberculosis prevention and management and influencing factors in Hadiya Zone health facilities, Southern Ethiopia.
Descriptive phenomenological qualitative study design was employed between 02 May and 09 May, 2019. We conducted a key informant interview and focus group discussions using purposely selected healthcare experts working as directly observed treatment short course providers in multidrug resistant tuberculosis treatment initiation centers, program managers, and focal persons. Verbatim transcripts were translated to English and exported to open code 4.02 for line-by-line coding and categorization of meanings into same emergent themes. Thematic analysis was conducted based on predefined themes for multidrug resistant tuberculosis prevention and management and core findings under each theme were supported by domain summaries in our final interpretation of the results. To maintain the rigors, Lincoln and Guba’s parallel quality criteria of trustworthiness was used particularly, credibility, dependability, transferability, confirmability and reflexivity.
Total of 26 service providers, program managers, and focal persons were participated through four focus group discussion and five key informant interviews. The study explored factors for engagement of health care providers in the prevention and management of multidrug resistant tuberculosis in five emergent themes such as patients’ causes, perceived susceptibility, seeking support, professional incompetence and poor linkage of the health care facilities. Our findings also suggest that service providers require additional training, particularly in programmatic management of drug-resistant tuberculosis.
The study explored five emergent themes: patient’s underlying causes, seeking support, perceived susceptibility, professionals’ incompetence and health facilities poor linkage. Community awareness creation to avoid fear of discrimination through provision of support for those with multidrug resistant tuberculosis is expected from health care providers using social behavioral change communication strategies. Furthermore, program managers need to follow the recommendations of World Health Organization for engaging healthcare professionals in the prevention and management of multidrug resistant tuberculosis and cascade trainings in clinical programmatic management of the disease for healthcare professionals.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the infectious agent that causes multi-drug resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB), is resistant to at least rifampicin and isoniazid. Direct infection can cause the disease to spread, or it can develop secondary to improper management of tuberculosis among drug susceptible tuberculosis cases and associated poor adherence [ 1 ].
Multidrug-resistant strains of mycobacterium tuberculosis have recently emerged, which makes achieving “End TB Strategy” more difficult [ 2 ]. Multi drug resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) has been found to increasingly pose a serious threat to global and Ethiopian public health sector. Despite the fact that a number of risk factors for MDR-TB have been identified through various research designs, the epidemiology of this disease is complex, contextual, and multifaceted [ 1 ]. Quantitative studies demonstrate that prior treatment history [ 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 ], interrupted drug supply [ 8 ], inappropriate treatments and poor patient compliance [ 3 , 7 , 9 ], poor quality directly observed treatment short course (DOTS), poor treatment adherence [ 10 ], age [ 5 ], and malnutrition [ 11 ] were factors associated with multi drug resistant TB.
Globally, an estimated 20% of previously treated cases and 3.3% of new cases are thought to have MDR-TB; these levels have essentially not changed in recent years. Globally, 160,684 cases of multidrug-resistant TB and rifampicin-resistant TB (MDR/RR-TB) were notified in 2017, and 139,114 cases were enrolled into treatment in 2017 [ 12 ]. A systematic review in Ethiopia reported 2% prevalence of MDR-TB [ 3 ] that is higher than what is observed in Sub-Saharan Africa, 1.5% [ 13 ]. The prevalence of MDR-TB, according to the national drug-resistant tuberculosis (DR-TB) sentinel report, was 2.3% among newly diagnosed cases of TB and 17.8% among cases of TB who had already received treatment,. This suggests a rising trend in the prevalence of TB drug resistance compared to the results of the initial drug-resistant TB survey carried out in Ethiopia from 2003 to 2005 [ 14 ].
Ethiopia has placed strategies into place that emphasize political commitment, case finding, appropriate treatment, a continuous supply of second-line anti-TB medications of high quality, and a recording system. Due to other competing health priorities, the nation is having difficulty accelerating the scale-up of the detection, enrollment and treatment of drug-resistant TB patients [ 15 , 16 ]. To address these issues, the nation switched from a hospital-based to a clinic-based ambulatory model of care, which has allowed MDR-TB services to quickly decentralize and become more accessible. Accordingly, the nation has set up health facilities to act as either treatment initiating centers (TIC) or treatment follow-up centers (TFC) or both for improved referral and communication methods [ 15 ].
One of the key components of the “End TB strategy” is engagement of health care professionals in the prevention and management of multidrug resistant tuberculosis [ 17 ]. Inadequate engagement of healthcare providers is one aspect of the healthcare system that negatively influences MDR-TB prevention and control efforts [ 17 ]. This may be manifested in a number of ways, including inadequate understanding of drug-resistant tuberculosis, improper case identification, failure to initiate treatment again, placement of the wrong regimens, improper management of side effects and poor infection prevention [ 1 ]. These contributing factors are currently being observed in Ethiopia [ 18 ], Nigeria [ 7 , 19 , 20 ] and other countries [ 21 , 22 ]. According to a study conducted in Ethiopia, MDR-TB was linked to drug side effects from first-line treatments, being not directly observed, stopping treatment for at least a day, and retreating with a category II regimen [ 17 ].
This may be the result of a synergy between previously investigated and other contextual factors that have not yet been fully explored, such as professional engagement, beliefs, and poor preventive practices. The engagement of health professionals in MDR-TB prevention and control is assessed using a number of composite indicators. Health professionals may interact primarily inside the healthcare facilities. Typically, they play a significant role in connecting healthcare services with neighborhood-based activities [ 17 ]. One of the main research areas that have not sufficiently addressed is evidence indicating the status of healthcare professionals’ engagement and contextual factors in MDR-TB prevention and management.
It is increasingly urgent to identify additional and existing factors operating in a particular context that contribute to the development of the disease in light of the epidemic of drug resistance, including multi-drug resistance (MDR-TB) and extensively drug resistant TB (XDR-TB) in both new and previously treated cases of the disease [ 23 ]. In order to develop and implement control measures, it is therefore essential to operationally identify a number of contextual factors operating at the individual, community, and health system level.
Therefore, the overall purpose of this study was to explore the level of engagement of health care providers and contextual factors hindering/enabling the prevention and provision of patient-centered care for MDR-TB in health facilities, DOTS services centers and MDR-TB treatment initiation center [TIC], in Hadiya Zone, Southern Ethiopia.
Qualitative approach and research paradigm
Descriptive phenomenological qualitative study design was employed to explore factors influencing engagement of health professionals in MDR-TB prevention and management and thematic technique was employed for the analysis of the data.
Researchers’ characteristics and reflexivity
Three Principal investigators conducted this study. Two of them had Masters of public health in Epidemiology and Reproductive health and PhD candidates and the third one had Bachelor’s degree in public health with clinical experience in the area of Tuberculosis prevention and management and MPH in Biostatistics. The principal investigators have research experience with published articles in different reputable journals. There were no prior contacts between researchers and participants before the study whereas researchers have built positive rapport with study participants during data collection to foster open communication and trust and had no any assumptions and presuppositions about the research topic and result.
Context/ study setting and period
The study was conducted between 2 and 9 May, 2019 in Hadiya Zone with more than 1.7 million people residing in the Zone. There are 300 health posts, 63 health centers, 3 functional primary hospitals and 1 comprehensive specialized hospital in the Zone. Also, there are more than 350 private clinics and 1 private hospital in the Zone. All of the public health facilities and some private health facilities provide directly observed short course treatment (DOTS) service for tuberculosis patients. There are more than eight treatment initiation centers (TICs) for MDR-TB patients in Hadiya Zone. MDR-TB (Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis) treatment initiation centers are specialized facilities that provide comprehensive care, diagnosis and treatment initiation, psychosocial support, and follow up services to individuals with MDR-TB. The linkage between MDR-TB treatment initiation centers and other healthcare facilities lies in the coordination of care, referral pathways, and collaboration to ensure comprehensive and integrated care for individuals with MDR-TB. Overall, healthcare providers play a crucial role in the management of MDR-TB by providing specialized care, ensuring treatment adherence, monitoring progress and outcomes, and supporting individuals in achieving successful treatment outcomes and improved health.
Units of study and sampling strategy
Our study participants were health care professionals working in MDR-TB TICs in both private and public health facilities, and providing DOTS services, MDR-TB program leaders in treatment initiation centers, as well as TB focal persons, disease prevention and health promotion focal person, and project partners from district health offices. The study involved four focus group discussion (FGDs) and five key informants’ interview (KII) with a total of 26 participants to gather the necessary information. Expert purposive sampling technique was employed and sample size was determined based on the saturation of idea required during data collection process.
Data collection methods and instruments
Focus group discussion and face to face key informants’ interviews were employed to collect the data. We conducted a total of four FGD and five key informants’ interviews with participants chosen from DOTS providing health facilities and MDR-TB program leaders in treatment initiation centers, as well as TB focal persons and project partners from district health offices and disease prevention and health promotion focal person. One of the FGDs was conducted among health professionals from the public MDR-TB treatment initiation centers. Three FGDs were conducted among disease prevention and health promotion focal persons, TB focal persons and DOTS providers in public health facilities (health centers).
An observation checklist was developed to assess the general infection prevention and control measures used by specific healthcare facilities in the study area. We used unstructured FGD guide, key informant interview guide, observation checklist and audio recorders to collect primary data and it was collected using local language called Amharic. Prior to data collection, three people who are not among principal investigators with at least a master’s degree in public health and prior experience with qualitative research were trained by principal investigators. Three of them acts as a tape recorder, a moderator, and as a note taker alternatively. The length of FGD ranged from 58 to 82 min and that of key informants’ interview lasted from 38 to 56 min.
Data processing and data analysis
Memos were written immediately after interviews followed by initial analysis. Transcription of audio records was performed by principal investigators. The audio recordings and notes were refined, cleaned and matched at the end of each data collection day to check for inconsistencies, correct errors, and modify the procedures in response to evolving study findings for subsequent data collection. Transcribed interviews, memos, and notes from investigator’s observation were translated to English and imported to Open Code 4.02 [ 2 ] for line by line coding of data, and categorizing important codes (sub theming). The pre-defined themes for MDR-TB prevention and control engagement were used to thematize the line-by-line codes, categories, and meanings using thematic analysis. Finally, the phenomenon being studied was explained by emerging categories and themes. Explanations in themes were substantiated by participants’ direct quotations when necessary.
Trustworthiness
Phone calls and face to face briefing were requested from study participants when some expressions in the audio seems confusing while transcripts were performed. To ensure the credibility of the study, prolonged engagement was conducted, including peer debriefing with colleagues of similar status during data analysis and inviting available study participants to review findings to ensure as it is in line with their view or not. Memos of interviews and observation were crosschecked while investigator was transcribing to ensure credibility of data as well as to triangulate investigator’s categorizing and theming procedures. For transferability, clear outlines of research design and processes were provided, along with a detailed study context for reader judgment. Dependability was ensured through careful recording and transcription of verbal and non-verbal data, and to minimize personal bias, scientific procedures were followed in all research stages. Conformability was maintained by conducting data transcription, translation, and interpretation using scientific methods. Researchers did all the best to show a range of realities, fairly and faithfully. Finally, an expert was invited to put sample of codes and categories to emerged corresponding categories and themes respectively.
Demographic characteristics of study participants
Four focus group discussions and five key informants’ interviews were conducted successfully. There were 26 participants in four focus group discussions, and key informants’ interview. Ages of participants ranges from 20 to 50 years with an average age of 33.4 ± 6.24 SD years. Participants have five to ten years of professional experience with DOTS services (Table 1 ).
Emergent themes and subthemes
The study explored how health care providers’ engagement in MDR-TB prevention and management was influenced. The investigation uncovered five major themes. These themes were the patient’s underlying causes, seeking support, perceived susceptibility, healthcare providers’ incompetence, and poor linkage between health facilities. Weak community TB prevention, health system support, and support from colleagues were identified subthemes in the search for help by health professionals whereas socioeconomic constraints, lack of awareness, and fear of discrimination were subthemes under patients underlying factors (Fig. 1 ).
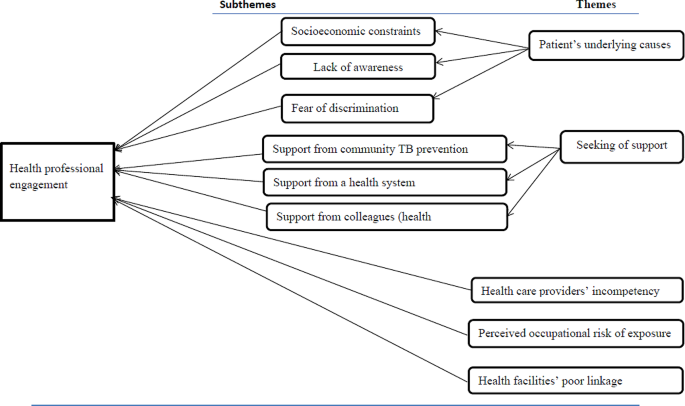
Themes and subthemes emerged from the analysis of health professionals’ engagement in MDR-TB prevention and management study in Hadiya zone’s health facilities, 2019
The patient’s underlying causes
This revealed why TB/MDR-TB treatment providers believe health professionals are unable to provide standard MDR-TB services. The subthemes include TB/MDR-TB awareness, fear of discrimination, and patients’ socioeconomic constraints.
Socioeconomic constraints
According to our research, the majority of healthcare professionals who provided directly observed short-course treatment services mentioned socioeconomic constraints as barriers to engage per standard and provide MDR-TB prevention and management service. More than half of the participants stated that patients’ primary reasons include lack of money for house rental close to the treatment centers, inability to afford food and other expenses, and financial constraints to cover transportation costs.
In addition to this, patients might have additional responsibilities to provide food and cover other costs for their families’ need. The majority of health care professionals thought that these restrictions led to their poor engagement in MDR-TB prevention and management. One of the focus groups’ discussants provided description of the scenario in the following way:
“…. I have many conversations with my TB/MDR-TB patients. They fail to complete DOTS or treatment intensive care primarily as a result of the requirement of prolonged family separation. They might provide most of the family needs, including food and other expenses” (FGD-P01).
Lack of awareness about MDR-TB
This subtheme explains how MDR-TB patients’ knowledge of the illness can make it more difficult for health professionals to provide DOTS or TICs services. The majority of DOTS providers stated that few TB or MDR-TB patients were aware of how MDR-TB spreads, how it is treated, and how much medication is required. Additionally, despite the fact that they had been educated for the disease, majority of patients did not want to stop contact with their families or caregivers. A health care provider stated,
“…. I provided health education for MDR-TB patients on how the disease is transmitted and how they should care for their family members. They don’t care; however, give a damn about their families .” (FGD-P05).
Some healthcare professionals reported that some patients thought that MDR-TB could not be cured by modern medication. One medical professional described the circumstance as follows:
“…. I noticed an MDR-TB patient who was unwilling to be screened. He concluded that modern medication is not effective and he went to spiritual and traditional healers” (FGD-P02).
As a result, almost all participants agreed on the extent to which patient knowledge of TB and MDR-TB can influence a provider’s engagement to MDR-TB services. The majority suggested that in order to improve treatment outcomes and preventive measures, the media, community leaders, health development armies, one-to-five networks, non-governmental organizations, treatment supporters, and other bodies with access to information need to put a lot of efforts.
Fear of discrimination
According to our research, about a quarter of healthcare professionals recognized that patients’ fear of discrimination prevents them from offering MDR-TB patients the DOTS services they need, including counseling index cases and tracing contact histories.
HEWs, HDAs, and 1-to-5 network members allegedly failed to monitor and counsel the index cases after their immediate return to their homes, according to the opinions from eight out of twenty-six healthcare professionals. The patients began to engage in routine social and political activities with neighbors while hiding their disease status. A healthcare professional described this situation as follows:
“…. I understood from my MDR-TB patient’s words that he kept to himself and avoided social interaction. He made this decision as a result of stigmatization by locals, including health extension workers. As a result, the patient can’t attend social gatherings. …. In addition, medical professionals exclude MDR-TB patients due to fear of exposures. As a result, patients are unwilling to undergo early screening” (FGD-P04).
Professionals’ perceived risk of occupational exposure
This theme highlights the anxiety that healthcare workers experience because of MDR-TB exposure when providing patient care. Our research shows that the majority of health professionals viewed participation as “taking coupons of death.” They believed that regardless of how and where they engaged in most healthcare facilities, the risk of exposure would remain the same. According to our discussion and interview, lack of health facility’s readiness takes paramount shares for the providers’ risk of exposures and their susceptibility.
According to the opinion from the majority of FGD discussants and in-depth interviewees, participants’ self-judgment score and our observation, the majority of healthcare facilities that offer DOTS for DS-TB and MDR-TB did not create or uphold standards in infection prevention in the way that could promote better engagement. These include poor maintenance of care facilities, lack of personal protective equipment, unsuitable facility design for service provision, lack of patient knowledge regarding the method of MDR-TB transmission, and lack of dedication on the part of health care staff.
As one of our key informant interviewees [District Disease Prevention Head], described health professionals’ low engagement has been due to fear of perceived susceptibility. He shared with us what he learned from a community forum he moderated.
Community forum participant stated that “… There was a moment a health professional run-away from the TB unit when MDR-TB patient arrived. At least they must provide the necessary service, even though they are not willing to demonstrate respectful, compassionate, or caring attitude to MDR-TB patients” (KII-P01). Besides , one of the FGD discussants described the circumstance as follows:
“…. Emm…. Because most health facilities or MDR-TB TIC are not standardized, I am concerned about the risk of transmission. They are crammed together and poor ventilation is evident as well as their configuration is improper. Other medical services are causing the TICs to become overcrowded. Most patients and some medical professionals are unconcerned with disease prevention ” (FGD-P19).
Participants’ general fear of susceptibility may be a normal psychological reaction and may serve as a motivation for taking preventative actions. However, almost all participants were concerned that the main reasons for their fear were brought up by the improper application of programmatic management and MDR-TB treatment standards and infection prevention protocols in healthcare facilities.
Health care providers’ incompetence
This theme illustrates how professionalism and dedication impact participation in MDR-TB prevention and management. The use of DS-TB prevention and management by health professionals was also taken into account because it is a major factor in the development of MDR-TB. This theme includes the participants’ perspectives towards other healthcare workers involved in and connected to MDR-TB.
Nearly all of the participants were aware of the causes and danger signs of MDR-TB. The majority of the defined participants fit to the current guidelines. However, participants in focus groups and key informant interviews have brought up shortcomings in MDR-TB service delivery practice and attitude. We looked at gaps among healthcare professionals’ knowledge, how they use the national recommendations for programmatic management and prevention of MDR-TB, prevent infections, take part in community MDR-TB screenings, and collaborate with other healthcare professionals for better engagement.
More than half of the participants voiced concerns about their attitudes and skill sets when using MDR-TB prevention and management guideline. When asked about his prior experiences, one of the focus group participants said:
“…. Ok, let me tell you my experience, I was new before I attended a training on MDR-TB. I was unfamiliar with the MDR-TB definition given in the recommendations. When I was hired, the health center’s director assigned me in the TB unit. I faced difficulties until I received training” (FGD-P24). Furthermore , one of the key informant interview participants shared a story: “…. In my experience, the majority of newly graduated health professionals lack the required skill. I propose that pre-service education curricula to include TB/MDR-TB prevention and management guideline trainings” (KII-P01).
The majority of participants mentioned the skill gap that was seen among health extension workers and laboratory technicians in the majority of healthcare facilities. Some of the participants in the in-depth interviews and FGD described the gaps as follows:
“…. According to repeated quality assurance feedbacks, there are many discordant cases in our [ District TB Focal Person ] case. Laboratory technicians who received a discrepant result (KII-P01) are not given training which is augmented by shared story from FGD discussants, “According to the quality assurance system, laboratory technicians lack skill and inconsistent results are typical necessitating training for newly joining laboratory technicians” (FGD-P20).
Through our discussions, we explored the level of DOTS providers’ adherence to the current TB/MDR-TB guideline. As a result, the majority of participants pointed out ineffective anti-TB management and follow-up care. One of the participants remembered her practical experience as follows:
“…. In my experience, the majority of health professionals fail to inform patients about the drug’s side effects, follow-up procedures, and other techniques for managing the burden of treatment. Only the anti-TB drug is provided, and the patient is left alone. The national treatment recommendation is not properly implemented by them” (FGD-P04).
Many barriers have been cited as reasons that might have hindered competencies for better engagement of health professionals. Training shortage is one of the major reasons mentioned by many of the study participants. One of discussants from private health facility described the problem as
“…. We are incompetent, in my opinion. Considering that we don’t attend update trainings. Many patients who were diagnosed negative at private medical facilities turned out to be positive, and vice versa which would be risky for drug resistance” (FGD-P14) which was supported by idea from a participant in our in-depth interview: “…. We [Program managers] are running short of training for our health care providers at different health centers and revealed that four out of every five healthcare professionals who work in various health centers are unaware of the TB/MDR-TB new guideline” (KII-P02).
Seeking support
This theme focuses on the significance and effects of workplace support in the engagement of MDR-TB prevention and control. This also explains the enabling and impeding elements in the engagement condition of health professionals. Three elements make up the theme: coworkers (other health professionals) in the workplace, support from community TB prevention actors, and a healthcare system.
Support from community TB prevention actors
This subtheme includes the assistance provided to study participants by important parties such as community leaders, the health development army, and other stakeholders who were involved in a community-based TB case notification, treatment adherence, and improved patient outcomes.
Many of the study participants reported that health extension workers have been poorly participating in MDR-TB and TB-related community-based activities like contact tracing, defaulter tracing, community forums, health promotion, and treatment support. One study participant described their gap as follows:
“…. I understood that people in the community were unaware of MDR-TB. The majority of health extension workers do not prioritize raising community awareness of MDR-TB” (FGD-P13). This was supported by idea from a district disease prevention head and stated as: “…. There is no active system for contacts tracing. Health educators send us information if they find suspected cases. However, some patients might not show up as expected. We have data on three family members who tested positive for MDR-TB” (KII-P3).
Support from a health system
The prime focus of this subtheme is on the enabling elements that DOTS providers require assistance from the current healthcare system for better engagement. All study participants expressed at least two needs to be met from the health system in order for them to effectively participate in MDR-TB prevention, treatment, and management. All study participants agreed that issues with the health system had a negative impact on their engagement in the prevention, treatment, diagnosis, and management of MDR-TB in almost all healthcare facilities. Poor conditions in infrastructure, resources (supplies, equipment, guidelines, and other logistics), capacity building (training), supportive supervision, establishment of public-private partnerships, and assignment of motivated and trained health professionals are some of the barriers that needs to be worked out in order to make them engage better. One of the participants pronounces supplies and logistics problems as:
“…. The health center I worked in is listed as a DOTS provider. However, it lacks constant electricity, a working microscope, lab supplies, medications, etc, and we refer suspected cases to nearby health centers or district hospitals for AFB-examination and, “Sometimes we use a single kit for many patients and wait for the medication supply for three or more weeks and patients stops a course of therapy that might induce drug resistance” (FGD-PI04) which was augmented by statement from FGD participant who works at a treatment initiation center: “…. We faced critical shortage of supplies and hospital administrators don’t care about funding essential supplies for patient care. For instance, this hospital (the hospital in which this FGD was conducted) can easily handle N-95 masks. Why then they (hospital administrators working in some TIC) can’t do it?” (FGD-P18).”
Regarding in-service training on MDR-TB, almost all participants pointed out shortage of on-job training mechanisms. One of our FGD participants said:
“…. I missed the new training on MDRTB programmatic management guidelines. I’ve heard that new updates are available. I still work using the old standard” (FGD-PI05). A health professional working in private clinic heightens the severity of training shortage as: “…. We have not participated in TB/MDR-TB guidelines training. You know, most of for-profit healthcare facilities do not provide any training for their staff. I’m not sure if I’m following the (TB/MDR-TB) guideline” (FGD-P14). One of our key informant interview participants; MDR-TB center focal person suggested the need for training as: “…. I’ve received training on the MDR-TB services and public-private partnership strategy. It was crucial in my opinion for better engagement. It is provided for our staff [MDRTB center focal person]. However, this has not yet been expanded to other health facilities” (KII-P04).
Concerning infrastructures, transportation problem was one of the frequently mentioned obstacles by many participants that hinder engagement in MDR-TB/TB service. This factor had a negative impact to both sides (health professionals and patients). One of discussants said:
“…. I face obstacles such as transport cost to perform effective TB/MDR-TB outreach activities like health education, tracing family contacts and defaulters and community mobilization. Rural kebeles are far apart from each other. How can I support 6 rural Kebeles?” (FGD-P01). One of the participants; MDR-TB treatment centers supervisor/program partner seconded the above idea as: “…. I suggest government must establish a system to support health professionals working in remote health care facilities in addition to MDR-TB centers. I guess there are more than 30 government health centers and additional private clinics. We can’t reach them all due to transportation challenges” (KII-P05). One of the participants , a district disease prevention head added: “…. Our laboratory technicians take sample from MDR-TB suspects to the post office and then, the post office sends to MDR-TB site. Sometimes, feedback may not reach timely. There is no any system to cover transportation cost. That would make case detection challenging” (FGD-P02).
Support from colleagues
Study participants stated the importance of having coworker with whom they could interconnect. However, eight participants reported that they were discriminated by their workmates for various reasons, such as their perceived fear of exposure to infection and their perception as if health professionals working in TB/MDR-TB unit get more training opportunities and other incentives. One of the focus group discussants said:
“…. My colleagues [health professional working out of MDR-TB TICs] stigmatize us only due to our work assignment in MDR-TB clinic. I remember that one of my friends who borrowed my headscarf preferred to throw it through a window than handing-over it back safely. Look, how much other health professionals are scared of working in MDR-TB unit. This makes me very upset. I am asking myself that why have I received such training on MDR-TB?” (FGD-P04).
Some of the participants also perceived that, health professionals working in MDR-TB/TB unit are the only responsible experts regarding MDR-TB care and treatment. Because, other health professionals consider training as if it is an incentive to work in such units. One of the FGD discussants described:
“… Health professionals who work in other service units are not volunteer to provide DOTS if TB focal person/previously trained staffs are not available. Patients wait for longer time” (FGD-P11).
Health facilities’ poor linkage
This theme demonstrates how various healthcare facilities, including private and public healthcare facilities such as, health posts, health care centers and hospitals, and healthcare professionals working at various levels of the healthcare system in relation to TB/MDR-TB service, are inter-linked or communicating with one another.
Many study participants noted a lack of coordination between higher referral hospitals, TB clinics, health posts, and health centers. Additionally, the majority of the assigned healthcare professionals had trouble communicating with patients and their coworkers. A focus group discussant also supported this idea as
“…. There is a lack of communication between us [DOTS providers at treatment initiation centers] and health posts, health centers, and private clinics. We are expected to support about 30 public health facilities. It’s of too much number, you know. They are out of our reach. We only took action when a problem arose” (FGD-P16).
Significant number of participants had raised the problem of poor communication between health facilities and treatment initiation centers. One of the interviewees [program manager] said:
“…. I see that one of our challenges is the weak referral connections between treatment initiation centers and health centers. As a result, improper sample transfer to Gene- Xpert sites and irregular postal delivery are frequent” . “Our; DOTS staff at the MDR-TB center, DOTS staff at the health center, and health extension workers are not well connected to one another. Many patients I encountered came to this center [MDR-TB center] after bypassing both health post and health center. Poor linkage and communication, in my opinion, could be one of the causes. The same holds true for medical facilities that are both public and private ” (KII-P02).
Engagement of individual healthcare providers is one of the peculiar interventions to achieve the goal of universal access to drug resistance tuberculosis care and services [ 17 ]. Healthcare providers engagement in detecting cases, treating and caring for multidrug resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) may be influenced by various intrinsic (individual provider factors) and extrinsic (peer, health system, political and other factors) [ 15 ]. Our study explored engagement of individual DOTS providers and factors that influence their engagement in MDR-TB prevention and management service. This is addressed through five emergent themes and subthemes as clearly specified in our results section.
The findings showed patients’ socioeconomic constraints were important challenges that influence health professionals’ engagement, and provision of MDR-TB prevention and management services. Although approaches differ, studies in Ethiopia [ 24 ], South Africa [ 25 ] and India [ 26 , 27 ] documented that such factors influence health providers’ engagement in the prevention and management of multi drug resistant tuberculosis. Again, the alleviation of these factors demands the effort from patients, stakeholders working on TB, others sectors, and the healthcare system so that healthcare providers can deliver the service more effectively in their day-to-day activities and will be more receptive to the other key factors.
We explored participants’ experiences on how patients’ awareness about drug sensitive or multi drug resistant tuberculosis influenced their engagement. Accordingly, participants encountered numerous gaps that restricted their interactions with TB/MDR-TB patients. In fact, our study design and purposes vary, studies [ 28 , 29 , 30 ] indicated that patients awareness influenced providers decision in relation to MDR-TB services and patients’ awareness status is among factors influencing healthcare providers’ decision making about the care the MDR-TB patient receives. As to our knowledge, patients’ perceived fear of discrimination was not documented whether it had direct negative impact on reducing providers’ engagement. Therefore, patients’ awareness creation is an important responsibility that needs to be addressed by the community health development army, health extension workers, all other healthcare providers and stakeholder for better MDR-TB services and patient outcomes.
Our study indicates that healthcare providers perceived that they would be exposed to MDR-TB while they are engaged. Some of the participants were more concerned about the disadvantages of engagement in providing care to MDR-TB patients which were predominantly psychological and physical pressure. In this context, the participants emphasized that engagement in MDR-TB patient care is “always being at risk” and expressed a negative attitude. This finding is similar to what has been demonstrated in a cross-sectional study conducted in South Africa in which majority of healthcare providers believed their engagement in MDR-TB services would risk their health [ 21 ].
However, majority of the healthcare providers demonstrated perceived fear of exposures mainly due to poor infection prevention practices and substandard organization of work environment in most TB/MDR-TB units. This is essentially reasonable fear, and needs urgent intervention to protect healthcare providers from worsening/reducing their effective engagement in MDR-TB patient care. On the other side of the coin, perceived risk of occupational exposure to infection could be source for taking care of oneself to combat the spread of the infection.
In our study, healthcare provider’s capability (competence) also had an impact on their ability to engage in prevention and management of MDR-TB. Here, participants had frequently raised their and other healthcare providers’ experience regarding skill gaps, negative attitude towards the service unit they were working in, ineffective use of MDR-TB guideline, poor infection prevention practices and commitment. In addition, many health professionals report serious problems regarding case identification and screening, drug administration, and side effect management. These findings were supported by other studies in Ethiopia [ 7 ] and in Nigeria [ 19 , 20 ]. This implies an urgent need for training of health care worker on how to engage in prevention and management of multidrug resistant TB.
Moreover, our findings provide insights into the role of community TB prevention actors, currently functioning health system, and colleagues and other stakeholders’ regarding healthcare providers’ engagement. Participants emphasized that support from community TB prevention actors is a key motivation to effectively engage on management and prevention roles towards MDR-TB. Evidence shows that community TB prevention is one of the prominent interventions that study participants would expect in DOTS provision as community is the closest source of information regarding the patients [ 31 , 32 ].
Similarly, all participants had pointed out the importance of support from a health system directly or indirectly influence their engagement in the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and management of MDR-TB. Researches indicated that health system supports are enabling factors for healthcare providers in decision making regarding TB/MDR-TB prevention and treatment [ 33 ]. This problem is documented by the study done in Ethiopia [ 22 ]. In addition, support from colleagues and other stakeholders was also a felt need to engage in MDR-TB which was supported by the World Health Organization guideline which put engagement in preventing MDR-TB and providing patients centered care needs collaborative endeavor among healthcare providers, patients, and other stakeholders [ 17 ].
Participants showed that there were poor linkage among/within DOTS providers working in health post (extension workers), health centers, hospitals and MDRTB treatment initiation centers. Our finding is consistent with a research in South Africa which shows poor health care attitude is linked to poor treatment adherence [ 34 ]. Our study implies the need for further familiarization especially on clinical programmatic management of drug resistant tuberculosis. Moreover, program managers need to follow health professionals’ engagement approaches recommended by the World Health Organization: End TB strategy [ 17 ].
Limitations of the study
There are some limitations that must be explicitly acknowledged. First, participants from private health facilities were very few, which might have restricted the acquisition and incorporation of perspectives from health care providers from private health care facilities. Second, healthcare providers’ engagement was not measured from patient side given that factors for engagement may differ from what has been said by the healthcare provides. Third, power relationships especially among focus group discussant in MDR-TB treatment initiation centers might have influenced open disclosures of some sensitive issues.
The study showed how healthcare provider’s engagement in MDR-TB management and prevention was influenced. Accordingly, patient’s underlying causes, seeking support, perceived occupational exposure, healthcare provider’s incompetence and health facilities poor linkage were identified from the analysis. Weak community TB prevention efforts, poor health system support and support from colleagues, health care providers’ incompetence and health facilities poor linkage were among identified factors influencing engagement in MDR – TB prevention and management. Therefore, measures need to be in place that avert the observed obstacles to health professionals’ engagement including further quantitative studies to determine the effects of the identified reasons and potential factors in their engagement status.
Furthermore, our findings pointed out the need for additional training of service providers, particularly in clinical programmatic management of drug-resistant tuberculosis. Besides, program managers must adhere to the World Health Organization’s recommendations for health professional engagement. Higher officials in the health sector needs to strengthen the linkage between health facilities and service providers at different levels. Community awareness creation to avoid fear of discrimination including provision of support for those with MDR-TB is expected from health experts through implementation of social behavioral change communication activities.
Abbreviations
Directly observed treatment short-course
Drug susceptible tuberculosis
Millennium development goals
Multidrug resistant tuberculosis
Sustainable development goals
Tuberculosis
Treatment initiation center
World Health Organization
Extensively drug resistant TB
WHO. Companion handbook to the WHO guidelines for the programmatic management of drug-resistant tuberculosis. WHO; Geneva, Switherland. 2014.
WHO. Implementing the end TB Strategy: The Essentials. WHO, Geneva. Switherland; 2015.
Eshetie S, Gizaw M, Dagnew M, Kumera G, Woldie H, Fikadu A. et.al. Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in Ethiopian settings and its association with previous history of anti-tuberculosis treatment: a systematic review and meta-analysis Ethiopia: efforts to expand diagnostic services, treatment and care. BMC Antimicrobial Resist Infect Control. 2014;3:31.
Biadglegne F, Sack U, Rodloff AC. Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in Ethiopia: efforts to expand diagnostic services, treatment and care. BMC Antimicro Resist Infect Control. 2014;3:31.
Lema NA, Majigo M, Mbelele PM, Abade AMIM. Risk factors associated with multidrug resistant tuberculosis among patients referred to Kibong’oto Infectious Disease Hospital in northern Tanzania. Tanzania J Health Res. 2016;18:4.
Mekonnen F, Tessema B, Moges F, Gelaw A, Eshetie S. G. K. Multidrug resistant tuberculosis: prevalence and risk factors in districts of metema and west armachiho, Northwest Ethiopia. BMC Infect Dis. 2015;15:461.
Selamawit H, Girmay M, Belaineh G, Muluken M, Alemayehu M, et al. PS. Determinants of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in patients who underwent first-line treatment in Addis Ababa: a case control study. BMC Public Health 2013. 2013;13:782.
Google Scholar
Safwat TM, Elmasry AA, Mohamed A. Prevalence of multi-drug resistant tuberculosis in abbassia Chest hospital from july 2006 to december 2009. Egyptian J Bronchol. 2011;5(2):124–30.
World Health Organization. WHO Global tuberculosis report 2015. Geneva: WHO. 2015.
Rifat M, Hall J, Oldmeadow C, Husain A, Hinderaker SG. AH. M. Factors related to previous tuberculosis treatment of patients with multidrug resistant tuberculosis in Bangladesh. BMJ Open. 2015;5.
Gupta KB, Gupta R, Atreja A, Verma MSV. Tuberculosis and nutrition. Lung India: Offic Organ of Indian Chest Soc. 2009;26(1):9–16. https://doi.org/10.4103/0970-2113.45198 . 2009.
World Health Organization. WHO Global tuberculosis report 2018. Geneva: WHO. 2018.
Deus L, Willy S, Kenneth M, George WK, Frank JCMJ. et al. Variation and risk factors of drug resistant tuberculosis in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 2015;15.
Federal Ministry of Health. Guidelines for Clinical and Programmatic Management of TB, TB/HIV and Leprosy in Ethiopia. Fifth Edition. Addis Ababa. March, 2013.
FDRE/MOH. Guidelines on programmatic management of drug resistant tuberculosis in Ethiopia. 2ND ED.2014 ADDIS ABABA. 2014.
CSIS. Center for Strategic and International Studies. As Ethiopia moves toward tuberculosis elimination, success requires higher investment: A report of CSIS global health policy center. CSIS, Washinton DC, America. 2016.
World Health organization. Framework for the engagement of all health care providers in the management of drug resistant tuberculosis. Geneva; Switherland. WHO 2015.
Vries G, Tsolova S, Anderson LF, Gebhard AC, Helda E, Hollo V. Health system factors influencing management of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in four European Union countries - learning from country experiences. BMC Public Health. 2017;17:334.
Isara AR, Akpodiete A. Concerns about the knowledge and attitude of multidrug resistant tuberculosis among health care workers and patients in Delta State, Nigeria. Nigerian J Clin Pract. 2015;18:5.
Luka MI, Idris SH, Patrick N, Ndadilnasiya EW, Moses OA, Phillip P., et al. Health care workers’ knowledge and attitude towards TB patients under Direct Observation of Treatment in Plateau state Nigeria, 2011. Pan Afr Med J. 2014;18 (Supp1):8.
Malangu N, Adebanjo OD. Knowledge and practices about multidrug-resistant tuberculosis amongst healthcare workers in Maseru. Afr J Prm Health Care Fam Med. 2015;7:1.
Molla Y, Jerene D, Jema I, Nigussie G, Kebede T, Kassie Y. et.al. The experience of scaling up a decentralized, ambulatory model of care for management of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in two regions of Ethiopia. J Clinic Tubercul Other Mycobacter Dis. 2017;7:28–33.
Merza MA, Farnia P, Tabarsi P, Khazampour M, Masjedi MR. AA. V. Anti-tuberculosis drug resistance and associated risk factors in a tertiary level TB centre in Iran: a retrospective analysis. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2011;5(7):511–19.
Gebremariam MK, Bjune GA. FJ. Barriers and facilitators of adherence to TB treatment in patients on concomitant TB and HIV treatment: a qualitative study. BMC Public Health. 2010;10:651.
Suri AGK. S. C. Voices from the Field: Perspectives from Community Health Workers on Health Care Delivery in Rural KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. J Infect Dis. 2007;196:S505–11.
Deshmukh RD, Dhande DJ, Sachdeva KS, Sreenivas AN, Kumar AMV. M. P. Social support a key factor for adherence to multidrug-resistant tuberculosis treatment. Indian J Tubercul. 2017.
Samuel B, Volkmann T, Cornelius S, Mukhopadhay S, Mitra K, Kumar AM., et al. Relationship between Nutritional Support and Tuberculosis Treatment Outcomes in West Bengal, India. J Tuberc Res. 2016;4(4):213–19.
NC. E. The making of a public health problem: multi-drug resistant tuberculosis in India. Health Policy Plan 2013;28:375–85.
Gler MT, Podewils LJ, Munez N, Galipot M, Quelapio MID, Tupasi TE. Impact of patient and program factors on default during treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2012;16(7):955–60. https://doi.org/10.5588/ijtld.11.0502 .
Article CAS Google Scholar
Horter S, Stringer B, Greig J, Amangeldiev A, Tillashaikhov MN, Parpieva N., et al. Where there is hope: a qualitative study examining patients’ adherence to multidrug resistant tuberculosis treatment in Karakalpakstan, Uzbekistan. BMC Infect Dis. 2016;16:362.
Naidoo P, Niekerk MV, Toit ED, Beyers N, Leon N. Pathways to multidrug-resistant tuberculosis diagnosis and treatment initiation: a qualitative comparison of patients’ experiences in the era of rapid molecular diagnostic tests. BMC Health Serv Res. 2015;15:488.
WHO. ENGAGE-TB. Training of community health workers and community volunteers. Integrating community-based tuberculosis activities into the work of nongovernmental and other civil society organizations. 2015.
Gerard de Vries S, Tsolova FL, Anderson AC, Gebhard E, Heldal et al. Health system factors influencing management of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in four European Union countries - learning from country experiences BMC Public Health. 2017;17:334. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-017-4216-9 .
Finlay A, Lancaster JHT, Weyer K, Miranda A. M. W. Patient- and Provider level risk factors associated with default from tuberculosis treatment, South Africa: a case control study. BMC Publich Health. 2012;12:56.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge Hosanna College of Health Sciences Research and community service directorate for providing us the opportunity and necessary fund to conduct this research. Our appreciation also goes to heads of various health centers, hospitals, district health and Hadiya Zone Health office for unreserved cooperation throughout data collection.
The authors declare that this study received funding from Hosanna College of Health Sciences. The funder was not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article or the decision to submit it for publication.
Author information
Bereket Aberham Lajore & Menen Ayele
Present address: Hossana College of Health Sciences, Hosanna, SNNPR, Ethiopia
Yitagesu Habtu Aweke
Present address: College of Health Sciences, School of Public Health, Addis Ababa University, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Samuel Yohannes Ayanto
Present address: College of Health Sciences, Institute of Public Health, Department of -Population and Family Health, Jimma University, Jimma, Ethiopia
Bereket Aberham Lajore, Yitagesu Habtu Aweke and Samuel Yohannes Ayanto contributed equally to this work.
Authors and Affiliations
Department of Family Health, Hossana College of health sciences, Hossana, Ethiopia
Bereket Aberham Lajore
Department of Health informatics, Hossana College of Health Sciences, Hossana, Ethiopia
Department of Midwifery, Hossana College of Health Sciences, Hossana, Ethiopia
Department of Clinical Nursing, Hossana College of Health Sciences, Hossana, Ethiopia
Menen Ayele
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Bereket Aberham Lajore, Yitagesu Habtu Aweke, and Samuel Yohannes Ayanto conceived the idea and wrote the proposal, participated in data management, analyzed the data and drafted the paper and revised the analysis and subsequent draft of the paper. Menen Ayele revised and approved the proposal, revised the analysis and subsequent draft of the paper. Yitagesu Habtu and Bereket Aberham Lajore wrote the main manuscript text and prepared all tables. All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Bereket Aberham Lajore .
Ethics declarations
All methods and report contents were performed in accordance with the standards for reporting qualitative research.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethical approval was obtained from Institutional review board [IRB] of Hossana College of health sciences after reviewing the protocol for ethical issues and provided a formal letter of permission to concerned bodies in the health system. Accordingly, permission to conduct this study was granted by respective health facilities in Hadiya zone. Confidentiality of the information was assured and participants’ autonomy not to participate or to opt-out at any stage of the interview were addressed. Finally, informed consent was obtained from the study participants after detailed information.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Lajore, B.A., Aweke, Y.H., Ayanto, S.Y. et al. Exploring health care providers’ engagement in prevention and management of multidrug resistant Tuberculosis and its factors in Hadiya Zone health care facilities: qualitative study. BMC Health Serv Res 24 , 542 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-10911-6
Download citation
Received : 27 February 2023
Accepted : 27 March 2024
Published : 27 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-10911-6
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Healthcare providers
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]

- Report Highlights
- EU-Summaries

- About the publications
Drug-resistant Tuberculosis
- Level 1: Summary
- Level 2: Details
7. Conclusions
- 7.1 Magnitude and trends of drug-resistant tuberculosis
- 7.2 Extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis (XDR-TB)
- 7.3 Drug-resistant tuberculosis and HIV
- 7.4 Survey coverage and methods
- 7.5 Tuberculosis control and drug-resistant tuberculosis
In 2006, approximately half a million new cases of multidrug resistant tuberculosis ( MDR-TB ) emerged in the world. China and India are estimated to carry 50% of the global burden of cases, and the Russian Federation is estimated to carry a further 7%.
Globally, MDR-TB makes up 4.6% of all cases of tuberculosis but, in some parts of the former Soviet Union, this proportion exceeds 35%. The patients in these countries have forms of tuberculosis that are resistant to a wide range of drugs, with the highest rates of extensively drug resistant tuberculosis ( XDR-TB ) in the world.
China has the second highest proportion of MDR-TB among TB cases but, in absolute terms, it has the highest number of MDR-TB cases in the world. The high proportion of drug-resistant TB among new cases in China suggests a concerning level of transmission of drug-resistant forms of TB.
In most countries where cases of TB are relatively few, the absolute numbers of cases of drug-resistant tuberculosis as well as the proportions of resistance are stable. Trend results are good in Hong Kong where MDR-TB is falling faster than tuberculosis. In Peru and in South Korea, tuberculosis is declining but MDR-TB is increasing. In Peru this could be due to a weakening in the control of the disease but in South Korea it may be due to changes in the surveillance method and not reflect a true worsening of the situation.
In the Baltic countries, tuberculosis is declining and levels of MDR-TB are relatively stable. However, in parts of the Russian Federation drug-resistance is rising rapidly, both in absolute numbers and in terms of proportion among new TB cases. Tuberculosis control is improving but there is a large pool of long-term cases that continues to fuel the epidemic . Current efforts to control the disease will have to be accelerated to have any impact in what appears to be a growing epidemic of drug-resistant tuberculosis.
Extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis ( XDR-TB ) can only be treated with a handful of drugs and these are more expensive and have worse side-effects than those used to treat multidrug-resistant tuberculosis ( MDR-TB ).
Extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis is widespread and 45 countries have reported at least one case. There is a significant problem within countries of the former Soviet Union, where cases of XDR-TB are high both in absolute and in relative terms. Levels of resistance to second-line drugs are also high in Japan and South Korea, and moderate in South Africa.
Elsewhere, in Africa, levels of extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis seem to be low. XDR-TB is likely to emerge as a result of inappropriate use of second-line anti-tuberculosis drugs , but these drugs are not yet widely used in the region
In order to understand the extent and the pattern of extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis throughout the world, all countries need to increase their efforts to measure resistance to second-line anti-tuberculosis drugs .
There is a significant association between HIV and multidrug-resistant tuberculosis ( MDR-TB ). A major reason for this association might be environmental: people become infected with both HIV and MDR-TB in places where patients are in close contact with each other such as health care facilities and prisons. Improving infection control in these settings may be critical to reducing the number of people infected with both HIV and multidrug-resistant tuberculosis .
People who have both infections at the same time are likely to die from TB unless they are diagnosed and treated quickly. This is a great concern for countries without sufficient testing facilities.
It is extremely important to develop methods that can detect drug-resistant tuberculosis quickly, particularly for HIV infected patients.
Monitoring of drug resistance should be part of routine surveillance, but this requires culture and drug susceptibility testing to be the standard of diagnosis. Since many countries do not yet have these facilities, surveys are important to determine the extent of the drug resistance problem. Survey coverage and reliability of data are increasing, but major gaps remain. For instance, it is very difficult to determine trends in most high burden countries.
The largest obstacle is the lack of laboratory capacity. Testing for resistance to second-line drugs is not available in most countries and it has been difficult to introduce HIV testing as part of the general care for tuberculosis . Supranational reference laboratories will continue to provide testing for resistance while countries develop their own national facilities.
New methods to detect and monitor drug-resistant tuberculosis are being developed. Special studies are necessary to answer questions such as the risk factors for acquiring drug-resistant tuberculosis, or how the disease is transmitted in different populations .
The main priority for all countries is to prevent the development of drug resistant tuberculosis but all cases that emerge have to be treated properly.
Some countries need to develop ways of detecting and treating drug-resistant cases quickly. This is particularly important in countries with high proportions of anti- tuberculosis drug resistance , countries with high absolute numbers of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis ( MDR-TB ), and countries with a TB population heavily co- infected with HIV .
New drugs to treat multidrug-resistant tuberculosis are urgently needed.
To control MDR-TB there needs to be a coordinated effort from all countries. The three priority areas include improvements in infection control measures to prevent transmission, expansion of testing services to detect cases quickly, and community involvement to ensure patients get tested and take all their drugs regularly. Most importantly, all patients must be registered in a suitable treatment programme.
- 1. What is tuberculosis and why is it a concern?
- 2. What is the Global Project on Anti-tuberculosis Drug Resistance Surveillance?
- 3. What are current trends in drug-resistant tuberculosis?
- 4. Why do HIV and tuberculosis form a lethal combination?
- 5. What is the status of drug-resistant tuberculosis in the different WHO regions?
- 6. Why is it difficult to gather information on drug-resistant tuberculosis?
- Accidental poisoning
- Acrylamide in food
- Acupuncture
- Agriculture
- Aids Epidemic
- Air Pollution Europe
- Air quality in Europe
- Allergenic fragrances
- Aluminium exposure
- Animal testing
- Antibiotic resistance
- Antibiotics Research
- Antimicrobial resistance
- Aquatic environment
- Arctic Climate Change
- Artificial Light
- Artificial Light and Health
- Aspartame Reevaluation
- Aspirin & Cancer
- Benzodiazepines
- Biodiversity
- Biological Diversity
- Biosecurity
- Bisphenol A
- CO 2 Capture & Storage
- Cancer rates and mortality, types and causes
- Chemical Mixtures
- Children & Screens
- Chlorine Sodium Hypochlorite
- Chlorpyrifos pesticide
- Chronic Diseases on Labour Practices
- Circular Economy
- Climate Change
- Climate Change Mitigation
- Climate impact of shale gas
- Climate impacts adaptation
- Dental Amalgams
- Dental Fillings
- Desertification
- Diet & Nutrition
- Ecosystem Change
- Effects of cannabis
- Electromagnetic Fields
- Electronic Cigarettes
- Endocrine Disruptors
- Endocrine disrupting properties of pesticides
- Endocrine disruptors risks
- Energy Saving Lamps
- Energy Technologies
- Epidemic diseases
- Estrogen-progestogen cancer risk
- Europe Green Deal
- Evaluation of endocrine disruptors
- Exposure to chemical mixtures
- Fisheries and aquaculture
- Fluorinated gases
- Food & Agriculture
- Food Wastage
- Forests & Energy
- Forests & agriculture land use
- Fukushima Consequences
- Fukushima accident
- Genetically Modified Crops
- Geothermal Energy
- Global Biodiversity Outlook 4
- Global Public Health Threats
- Global Warming
- Gluten intolerance
- Glyphosate and cancer
- Hazardous chemicals
- Health Effects of Electromagnetic Fields
- Health Environment Management
- Illicit drugs in Europe
- Impacts of a 4°C global warming
- India Millennium Development Goals
- Indonesian forests
- Indoor Air Quality
- Land Degradation and Desertification
- Lyme Disease
- Marine Litter
- Marine litter
- Mercury from dental amalgam
- Mercury in CFL
- Metal-on-Metal hip implants
- Methylene glycol
- Mineral extraction risks
- Multiple vaccinations
- Nano-silica
- Nanomaterials
- Nanotechnologies
- Neonicotinoids
- Nitrogen Dioxide
- Non-human primates
- Organic Food
- Ozone layer depletion
- Parabens used in cosmetics
- Particulate Matter
- Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA)
- Personal Music Players & Hearing
- Pesticides occupational risks
- Pharmaceuticals environment
- Phosphate resources
- Phthalates Comparison
- Phthalates in school supplies
- Poly brominated flame retardant decaBDE
- Power lines
- Psychoactive Drugs
- Radiological nuclear emergency
- Respiratory Diseases
- Safety of Cosmetics
- Safety of sunscreens
- Sand Extraction
- Security Scanners
- Silver Nanoparticles
- Single-use plastics
- Soils degradation
- Solar Energy
- State of the European Environment
- Static Fields
- Substitution of harmful chemicals
- Sulfaxoflor Pesticide
- Sunbeds & UV radiation
- Sustainable oceans
- Synthetic Biology
- Thorium nuclear fuel
- Tidal Energy
- Titanium dioxide nanoparticles
- Tooth Whiteners
- Transgenic salmon
- Tuberculosis
- Wastewater management
- Water Disinfectants
- Water Resources
- Water Resources Assessments
- Water resources
- Wind Resources
- X-Ray Full-Body Scanners

Get involved!
This summary is free and ad-free, as is all of our content. You can help us remain free and independant as well as to develop new ways to communicate science by becoming a Patron!
- Terms & Conditions

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.

StatPearls [Internet].
Tuberculosis.
Rotimi Adigun ; Rahulkumar Singh .
Affiliations
Last Update: July 11, 2023 .
- Continuing Education Activity
Tuberculosis (TB) is a human disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It mainly affects the lungs, making pulmonary disease the most common presentation. Other commonly affected organ systems include the respiratory system, the gastrointestinal (GI) system, the lymphoreticular system, the skin, the central nervous system, the musculoskeletal system, the reproductive system, and the liver. In the past few decades, there has been a concerted global effort to eradicate tuberculosis. Despite the gains in tuberculosis control and the decline in both new cases and mortality, it still accounts for a huge burden of morbidity and mortality worldwide. This activity reviews the evaluation and management of tuberculosis and highlights the role of interprofessional team members in collaborating to provide well-coordinated care and enhance outcomes for affected patients.
- Identify the epidemiology of tuberculosis.
- Review the presentation of a patient with tuberculosis.
- Outline the treatment and management options available for tuberculosis.
- Employ interprofessional team strategies for improving care and outcomes in patients with tuberculosis.
- Introduction
Tuberculosis (TB) is an ancient human disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis which mainly affects the lungs, making pulmonary disease the most common presentation (K Zaman, 2010) [1] . However, TB is a multi-systemic disease with a protean presentation. The organ system most commonly affected includes the respiratory system, the gastrointestinal (GI) system, the lymphoreticular system, the skin, the central nervous system, the musculoskeletal system, the reproductive system, and the liver [2] [3] .
Evidence of TB has been reported in human remains dated thousands of years (Hershkovitz et al., 2017, K Zaman, 2010). For a human pathogen with no known environmental reservoir, Mycobacterium tuberculosis has honed the art of survival and has persisted in human communities from antiquity through modern times.
In the past few decades, there has been a concerted global effort to eradicate TB. These efforts had yielded some positive dividends, especially since 2000 when the World Health Organization (WHO, 2017) estimated that the global incidence rate for tuberculosis has fallen by 1.5% every year. Furthermore, mortality arising from tuberculosis has significantly and steadily declined. The World Health Organization (WHO, 2016) reports a 22% drop in global TB mortality from 2000 through 2015.
Despite the gains in tuberculosis control and the decline in both new cases and mortality, TB still accounts for a huge burden of morbidity and mortality worldwide. The bulk of the global burden of new infection and tuberculosis death is borne by developing countries, with 6 countries, India, Indonesia, China, Nigeria, Pakistan, and South Africa, accounting for 60% of TB death in 2015 (WHO, 2017). [4]
Tuberculosis remains a significant cause of both illness and death in developed countries, especially among individuals with a suppressed immune system [5] [6] . People with HIV are particularly vulnerable to death due to tuberculosis. Tuberculosis accounted for 35% of global mortality in individuals with HIV/AIDS in 2015. (W.H.O, 2017). Children are also vulnerable, and tuberculosis was responsible for one million illnesses in children in 2015, according to the WHO.
M. tuberculosis causes tuberculosis. M. tuberculosis is an alcohol and acid-fast bacillus. It is part of a group of organisms classified as the M. tuberculosis complex. Other members of this group are Mycobacterium africanum, Mycobacterium bovis, and Mycobacterium microti [1] . Most other mycobacteria organisms are classified as non-tuberculous or atypical mycobacterial organisms.
M. tuberculosis is a non-spore-forming, non-motile, obligate-aerobic, facultative, catalase-negative, intracellular bacteria. The organism is neither gram-positive nor gram-negative because of a very poor reaction with the Gram stain. Weakly positive cells can sometimes be demonstrated on Gram stain, a phenomenon known as "ghost cells."
The organism has several unique features compared to other bacteria, such as the presence of several lipids in the cell wall, including mycolic acid, cord factor, and Wax-D. The high lipid content of the cell wall is thought to contribute to the following properties of M. tuberculosis infection:
- Resistance to several antibiotics
- Difficulty staining with Gram stain and several other stains
- Ability to survive under extreme conditions such as extreme acidity or alkalinity, low oxygen situation, and intracellular survival(within the macrophage)
The Ziehl-Neelsen stain is one of the most commonly used stains to diagnose T.B. The sample is initially stained with carbol fuchsin (pink color stain), decolorized with acid-alcohol, and then counter-stained with another stain (usually, blue-colored methylene blue). A positive sample would retain the pink color of the original carbol fuchsin, hence the designation, alcohol, and acid-fast bacillus (AAFB).
- Epidemiology
Geographic Distribution
Tuberculosis is present globally [1] . However, developing countries account for a disproportionate share of tuberculosis disease burden. In addition to the six countries listed above, several countries in Asia, Africa, Eastern Europe, and Latin and Central America continue to have an unacceptably high burden of tuberculosis.
In more advanced countries, high-burden tuberculosis is seen among recent arrivals from tuberculosis-endemic zones, healthcare workers, and HIV-positive individuals. The use of immunosuppressive agents such as long-term corticosteroid therapy has also been associated with an increased risk.
More recently, the use of a monoclonal antibody targeting the inflammatory cytokine, tumor necrotic factor alpha (TNF-alpha), has been associated with an increased risk. Antagonists of this cytokine include several monoclonal antibodies (biologics) used for the treatment of inflammatory disorders. Drugs in this category include infliximab, adalimumab, etanercept, and golimumab. Patients using any of these medications should be monitored for tuberculosis before and during the period of drug treatment.
Other Major Risk Factors
- Socioeconomic factors: Poverty, malnutrition, wars
- Immunosuppression: HIV/AIDS, chronic immunosuppressive therapy (steroids, monoclonal antibodies against tumor necrotic factor), a poorly developed immune system (children, primary immunodeficiency disorders)
- Occupational: Mining, construction workers, pneumoconiosis (silicosis)
Multi-Drug Resistant Tuberculosis (MDR-TB) and Extremely Multi-Drug Resistant Tuberculosis (XDR-TB)
- This refers to tuberculosis with strains of Mycobacterium which have developed resistance to the classic anti-tuberculosis medications. TB is especially a problem among patients with HIV/AIDS. Resistance to multiple anti-tuberculosis medications, including at least the two standard anti-tuberculous medications, Rifampicin or Isoniazid, is required to make a diagnosis of MDR-TB.
- Seventy-five percent of MDR-TB is considered primary MDR-TB, caused by infection with MDR-TB pathogens. The remaining 25% are acquired and occur when a patient develops resistance to treatment for tuberculosis. Inappropriate treatment for tuberculosis because of several factors such as antibiotic abuse; inadequate dosage; incomplete treatment, is the number one cause of acquired MDR-TB.
- This is a more severe type of MDR-TB. Diagnosis requires resistance to at least four anti-tuberculous medications, including resistance to Rifampicin, Isoniazid, and resistance to any two of the newer anti-tuberculous medications. The newer medications implicated in XDR-TB are the fluoroquinolones (Levofloxacin and moxifloxacin) and the injectable second-line aminoglycosides, Kanamycin, Capreomycin, and amikacin.
- The mechanism of developing XDR-TB is similar to the mechanism for developing MDR-TB.
- XDR -TB is an uncommon occurrence.
- Pathophysiology
Although usually a lung infection, tuberculosis is a multi-system disease with protean manifestation. The principal mode of spread is through the inhalation of infected aerosolized droplets.
The body's ability to effectively limit or eliminate the infective inoculum is determined by the immune status of the individual, genetic factors, and whether it is a primary or secondary exposure to the organism. Additionally, M. tuberculosis possesses several virulence factors that make it difficult for alveolar macrophages to eliminate the organism from an infected individual. The virulence factors include the high mycolic acid content of the bacteria's outer capsule, which makes phagocytosis to be more difficult for alveolar macrophages. Furthermore, some of the other constituents of the cell wall, such as the cord factor, may directly damage alveolar macrophages. Several studies have shown that mycobacteria tuberculosis prevents the formation of an effective phagolysosome, hence, preventing or limiting the elimination of the organisms.
The first contact of the Mycobacterium organism with a host leads to manifestations known as primary tuberculosis. This primary TB is usually localized to the middle portion of the lungs, and this is known as the Ghon focus of primary TB. In most infected individuals, the Ghon focus enters a state of latency. This state is known as latent tuberculosis.
Latent tuberculosis is capable of being reactivated after immunosuppression in the host. A small proportion of people would develop an active disease following first exposure. Such cases are referred to as primary progressive tuberculosis. Primary progressive tuberculosis is seen in children, malnourished people, people with immunosuppression, and individuals on long-term steroid use.
Most people who develop tuberculosis do so after a long period of latency (usually several years after the initial primary infection). This is known as secondary tuberculosis. Secondary tuberculosis usually occurs because of the reactivation of latent tuberculosis infection. The lesions of secondary tuberculosis are in the lung apices. A smaller proportion of people who develop secondary tuberculosis do so after getting infected a second time (re-infection).
The lesions of secondary tuberculosis are similar for both reactivation and reinfection in terms of location (at the lung apices), and the presence of cavitation enables a distinction from primary progressive tuberculosis which tends to be in the middle lung zones and lacks marked tissue damage or cavitation.
Type-IV Hypersensitivity and Caseating Granuloma
Tuberculosis is a classic example of a cell-mediated delayed type IV hypersensitivity reaction.
Delayed Hypersensitivity Reaction: By stimulating the immune cells (the helper T-Lymphocyte, CD4+ cells), Mycobacterium tuberculosis induces the recruitment and activation of tissue macrophages. This process is enhanced and sustained by the production of cytokines, especially interferon-gamma.
Two main changes involving macrophages occur during this process, namely, the formation of multinucleated giant cells and the formation of epithelioid cells. Giant cells are aggregates of macrophages that are fused together and function to optimize phagocytosis. The aggregation of giant cells surrounding the Mycobacterium particle and the surrounding lymphocytes and other cells is known as a granuloma.
Epithelioid cells are macrophages that have undergone a change in shape and have developed the ability for cytokine synthesis. Epithelioid cells are modified macrophages and have a flattened (spindle-like shape) as opposed to the globular shape characteristic of normal macrophages. Epithelioid cells often coalesce together to form giant cells in a tuberculoid granuloma.
In addition to interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma), the following cytokines play important roles in the formation of a tuberculosis granuloma, Interleukin-4 (IL-4), Interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrotic factor-alpha (TNF-alpha).
The appearance of the granuloma in tuberculosis has been described as caseous or cheese-like on gross examination. This is principally explained by the rich mycolic acid content of the mycobacterium cell wall. Because of this unique quality, the term caseous or caseating necrosis has been used to describe granulomatous necrosis caused by mycobacteria tuberculosis.
Histologically, caseous necrosis would present as a central area of uniform eosinophilia on routine hematoxylin and eosin stain.
- Histopathology
The granuloma is the diagnostic histopathological hallmark of tuberculosis.
The defining features of the granuloma of tuberculosis are:
- Caseation or caseous necrosis is demonstrable as a region of central eosinophilia.
- Multinucleated giant cells
- History and Physical
A chronic cough, hemoptysis, weight loss, low-grade fever, and night sweats are some of the most common physical findings in pulmonary tuberculosis.
Secondary tuberculosis differs in clinical presentation from primary progressive disease. In secondary disease, the tissue reaction and hypersensitivity are more severe, and patients usually form cavities in the upper portion of the lungs.
Pulmonary or systemic dissemination of the tubercles may be seen in active disease, and this may manifest as miliary tuberculosis characterized by millet-shaped lesions on chest x-ray. Disseminated tuberculosis may also be seen in the spine, the central nervous system, or the bowel.
Screening Tests
Tuberculin skin testing: Mantoux test (skin testing with PP D)
The Mantoux reaction following the injection of a dose of PPD (purified protein derivative) is the traditional screening test for exposure to Tuberculosis. The result is interpreted taking into consideration the patient's overall risk of exposure. Patients are classified into 3 groups based on the risk of exposure with three corresponding cut-off points. The 3 major groups used are discussed below.
Low Risk
- Individuals with minimal probability of exposure are considered to have a positive Mantoux test only if there is very significant induration following intradermal injection of PPD. The cut-off point for this group of people (with minimal risk of exposure) is taken to be 15 mm.
Intermediate Risk
- Individuals with intermediate probability are considered positive if the induration is greater than 10 mm.
- Individuals with a high risk of a probability of exposure are considered positive if the induration is greater than 5 mm.
Examples of Patients in the Different Risk Categories
- Low Risk/Low Probability: Patients with no known risk of exposure to TB. Example: No history of travel, military service, HIV-negative, no contact with a chronic cough patient, no occupational exposure, no history of steroids. Not a resident of a TB-endemic region.
- Intermediate Risk/Probability: Residents of TB-endemic countries (Latin America, Sub -Sahara Africa, Asia), workers or residents of shelters, Medical or microbiology department personnel.
- High Risk/Probability: HIV-positive patient, a patient with evidence of the previous TB such as the healed scar on an x-ray), contact with chronic cough patients.
Note that a Mantoux test indicates exposure or latent tuberculosis. However, this test lacks specificity, and patients would require subsequent visits for interpreting the results as well as chest x-ray for confirmation. Although relatively sensitive, the Mantoux reaction is not very specific and may give false-positive reactions in individuals who have been exposed to the BCG vaccine.
Interferon release assays (IGRA, Quantiferon Assays)
This is a tuberculosis screening test that is more specific and equally as sensitive as the Mantoux test. This test assays for the level of the inflammatory cytokine, especially interferon-gamma.
The advantages of antigen-specific stimulation of IFN-γ release, especially in those with prior vaccination with BCG vaccine, include the test requires a single blood draw, obviating the need for repeat visits to interpret results. Furthermore, additional investigations, such as HIV screening, could be performed (after patient consent) on the same blood draw.
Quantiferon's disadvantages include cost and the technical expertise required to perform the test.
Screening in Immunocompromised Patients
Immunocompromised patients may show lower levels of reaction to PPD or false-negative Mantoux because of cutaneous anergy.
A high level of suspicion should be entertained when reviewing negative screening tests for tuberculosis in HIV-positive individuals.
The Significance of Screening
A positive screening test indicates exposure to tuberculosis and a high chance of developing active tuberculosis in the future. Tuberculosis incidence in patients with positive Mantoux test averages between 2% to 10% without treatment.
Patients with a positive test should have a chest x-ray as a minimum diagnostic test. In some cases, these patients should have additional tests. Patients meeting the criteria for latent tuberculosis should receive prophylaxis with isoniazid.
Screening Questionnaires for Resource-Poo r Settings
Several screening questionnaires have been validated to enable healthcare workers working in remote and resource-poor environments to screen for tuberculosis.
These questionnaires make use of an algorithm that combines several clinical signs and symptoms of tuberculosis. Some of the commonly used symptoms are:
- Chronic cough
- Weight loss
- Fever and night sweats
- History of contact
- Blood in sputum
Several studies have confirmed the utility of using several criteria rather than a focus on only chronic cough or weight loss.
Confirmatory and Diagnostic Tests
- A chest x-ray is indicated to rule out or rule in the presence of active disease in all screening test-positive cases.
- Acid Fast Staining-Ziehl-Neelsen
- Nuclear Amplification and Gene-Based Tests: These represent a new generation of diagnostic tools for tuberculosis. These tests enable the identification of bacteria or bacteria particles by making use of DNA-based molecular techniques.
The new molecular-based techniques are faster and enable rapid diagnosis with high precision. Confirmation of TB could be made in hours rather than the days or weeks it takes to wait for a standard culture. This is very important, especially among immunocompromised hosts where there is a high rate of false-negative results. Some molecular-based tests also allow for the identification of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis.
- Treatment / Management
Latent Tuberculosis
2020 LTBI treatment guidelines include the NTCA- and CDC-recommended treatment regimens that comprise three preferred rifamycin-based regimens and two alternative monotherapy regimens with daily isoniazid. These are only recommended for persons infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis that is presumed to be susceptible to isoniazid or rifampin. A regimen of 3 months of once-weekly isoniazid plus rifapentine is a preferred regimen that is strongly recommended for children aged more than 2 years and adults. Another option is 4 months of daily rifampin for HIV-negative adults and children of all ages. Three months of daily isoniazid plus rifampin is a preferred treatment that is conditionally recommended for adults and children of all ages and for patients with HIV. Regimens of 6 or 9 months of daily isoniazid are alternative recommended regimens.
Treatment of Active Infection
Treatment of confirmed TB requires a combination of drugs. Combination therapy is always indicated, and monotherapy should never be used for tuberculosis. The most common regimen for TB includes the following anti-TB medications:
First-Line Medications, Group 1
- Isoniazid - Adults (maximum): 5 mg/kg (300 mg) daily; 15 mg/kg (900 mg) once, twice, or three times weekly.Children (maximum): 10-15 mg/kg (300 mg) daily; 20--30 mg/kg (900 mg) twice weekly (3).Preparations. Tablets (50 mg, 100 mg, 300 mg); syrup (50 mg/5 ml); aqueous solution (100 mg/ml) for IV or IM injection.
- Rifampicin - Adults (maximum): 10 mg/kg (600 mg) once daily, twice weekly, or three times weekly.Children (maximum): 10-20 mg/kg (600 mg) once daily or twice weekly.Preparations. Capsules (150 mg, 300 mg)
- Rifabutin- Adults (maximum): 5 mg/kg (300 mg) daily, twice, or three times weekly. When rifabutin is used with efavirenz the dose of rifabutin should be increased to 450--600 mg either daily or intermittently.Children (maximum): Appropriate dosing for children is unknown. Preparations: Capsules (150 mg) for oral administration.
- RIfapentine - Adults (maximum): 10 mg/kg (600 mg), once weekly (continuation phase of treatment)Children: The drug is not approved for use in children.Preparation. Tablet (150 mg, film-coated).
- Pyrazinamide - Adults: 20-25 mg/kg per day. Children (maximum): 15-30 mg/kg (2.0 g) daily; 50 mg/kg twice weekly (2.0 g).Preparations. Tablets (500 mg).
- Ethambutol - Adults: 15-20 mg/kg per day: Children (maximum): 15-20 mg/kg per day (2.5 g); 50 mg/kg twice weekly (2.5 g). The drug can be used safely in older children but should be used with caution in children in whom visual acuity cannot be monitored (generally less than 5 years of age) (66). In younger children, EMB can be used if there is a concern with resistance to INH or RIF.Preparations. Tablets (100 mg, 400 mg) for oral administration.
Isoniazid and Rifampicin follow a 4-drug regimen (usually including Isoniazid, Rifampicin, Ethambutol, and Pyrazinamide) for 2 months or six months. Vitamin B6 is always given with Isoniazid to prevent neural damage (neuropathies).
Several other antimicrobials are effective against tuberculosis, including the following categories:
Second-Line Anti-tuberculosis Drugs, Group 2
Injectable aminoglycosides and injectable polypeptides
Injectable aminoglycosides
- Streptomycin
Injectable polypeptides
- Capreomycin
- Viomycin
Second - Line Anti-Tuberculosis Drugs, Group 3, Oral and Injectable Fluoroquinolones
Fluoroquinolones
- Levofloxacin
- Moxifloxacin
- Gatifloxacin
Second-Line Anti-tuberculosis Drugs, Group 4
- Para-aminosalicylic acid
- Cycloserine
- Ethionamide
- Prothionamide
- Thioacetazone
Third- Line Anti-Tuberculosis Drugs, Group 5
These are medications with variable but unproven efficacy against TB. They are used for total drug-resistant TB as drugs of last resort.
- Clofazimine
- Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid
- Imipenem/cilastatin
- Clarithromycin
MDR-TB, XDR-TB
Multi-drug-resistant TB is becoming increasingly common.
The combination of first-line and second-line medications is used at high doses to treat this condition.
Bedaquiline
On December 28, 2012, the United States Food and Drug Administration Agency (FDA) approved Bedaquiline as a drug for treating MDR-TB. This is the first FDA approval for an anti-TB medication in 40 years. While showing remarkable promise in drug-resistant tuberculosis, cost remains a big obstacle to delivering this drug to the people most affected by MDR-TB.
Clinical and Laboratory Monitoring
Liver function tests are required for all patients taking isoniazid. Other monitoring in TB includes monitoring for retinopathies for patients on ethambutol.
Treatment of Patients with HIV
In patients with active TB and HIV with severe immunosuppression (CD4+ 60/microliter), the recommendations are to immediately start antituberculous therapy, followed by the initiation of anti-retroviral after 2 to 4 weeks. Delaying treatment with antiretroviral drugs prevents the development of immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS). This is a syndrome characterized by paradoxical worsening of symptoms of primary disease when treatment with antiretroviral agents is initiated. The presenting infection should be treated immediately, and retroviral should start no earlier than 2 weeks. The earlier the antiretroviral agents are initiated, the greater the likelihood of IRIS. Unnecessary delay of antiretroviral therapy leads to an increased risk of death from AIDS.
- Differential Diagnosis
Tuberculosis is a great mimic and should be considered in the differential diagnosis of several systemic disorders. The following is a non-exhaustive list of conditions to be strongly considered when evaluating the possibility of pulmonary tuberculosis.
- Non-tuberculous mycobacterium
- Fungal infection
- Histoplasmosis
- Sarcoidosis
- Toxicity and Adverse Effect Management
Side Effect associated with most commonly used anti-TB drugs [7]
1) Isoniazid- Asymptomatic elevation of aminotransferases (10-20%), clinical hepatitis (0.6%), peripheral neurotoxicity, hypersensitivity. [8]
2) Rifampin- Pruritis, nausea & vomiting, flulike symptoms, hepatotoxicity, orange discoloration of bodily fluid.
3) Rifabutin- Neutropenia, uveitis (0.01%), polyarthralgias, hepatotoxicity (1%))
4) Rifapentine- Similar to rifampin
5) Pyrazinamide- Hepatotoxicity (1%), nausea & vomiting, polyarthralgias (40%), acute gouty arthritis, rash, and photosensitive dermatitis
6) Ethambutol- Retrobulbar neuritis (18%)
One of the most important aspects of tuberculosis treatment is close follow-up and monitoring for these side effects. Most of these side effects can be managed by either close monitoring or adjusting the dose. In some cases, the medication needs to be discontinued, and second-line therapy should be considered if other alternatives are not available.
The majority of patients with a diagnosis of TB have a good outcome. This is mainly because of effective treatment. Without treatment mortality rate for tuberculosis is more than 50%.
The following group of patients is more susceptible to worse outcomes or death following TB infection:
- Extremes of age, elderly, infants, and young children
- Delay in receiving treatment
- Radiologic evidence of extensive spread.
- Severe respiratory compromise requiring mechanical ventilation
- Immunosuppression
- Multidrug resistance (MDR) tuberculosis
- Complications
Most patients have a relatively benign course. Complications are more frequently seen in patients with the risk factors mentioned above. Some of the complications associated with tuberculosis are:
- Extensive lung destruction
- Damage to cervical sympathetic ganglia leading to Horner's syndrome.
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome
- Milliary spread (disseminated tuberculosis), including TB meningitis.
- Pneumothorax
- Systemic amyloidosis
- Pearls and Other Issues
Tuberculosis is a preventable and treatable infectious disease. Having said that, it is still one of the major contributors to morbidity and mortality in developing countries where we are still struggling to provide adequate access to care. Other challenges include lack of awareness, delayed diagnosis, poor accessibility to medication and vaccination as well as medication adherence. DOTS (Direct Observed Therapy), proposed by WHO, has been very effective in recent years to improve adherence to treatment in tuberculosis patients. [9] [10] Also, vaccination drive in developing countries has played a bigger role in decreasing the prevalence of this infection. The preventive effect of BCG vaccination is controversial, but many studies have identified vaccination as a very important tool in the fight against tuberculosis, and we need to keep our focus on childhood vaccination, especially in developing countries. [11] WHO and other health organizations have to continue their investment in developing strategies and research until we eradicate this disease from the world map. New antituberculosis drugs need to be developed to shorten or otherwise simplify the treatment of tuberculosis caused by drug-susceptible organisms, to improve the treatment of drug-resistant tuberculosis, and to provide more efficient and effective treatment of latent tuberculosis infection.
- Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
A team approach involving nurses, clinicians, and technicians will lead to the best outcomes in treating patients with tuberculosis. [Level 5]
- Review Questions
- Access free multiple choice questions on this topic.
- Comment on this article.
Granuloma of Tuberculosis. Arrows pointed at multi-nucleated giant cells. Contributed By Dr. Rotimi Adigun (with permission from Kingston General Hospital)
Disclosure: Rotimi Adigun declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Rahulkumar Singh declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ), which permits others to distribute the work, provided that the article is not altered or used commercially. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal.
- Cite this Page Adigun R, Singh R. Tuberculosis. [Updated 2023 Jul 11]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
In this Page
Bulk download.
- Bulk download StatPearls data from FTP
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Similar articles in PubMed
- Review Tuberculosis. [Major Infectious Diseases. 2017] Review Tuberculosis. Bloom BR, Atun R, Cohen T, Dye C, Fraser H, Gomez GB, Knight G, Murray M, Nardell E, Rubin E, et al. Major Infectious Diseases. 2017 Nov 3
- Active Tuberculosis. [StatPearls. 2024] Active Tuberculosis. Jilani TN, Avula A, Zafar Gondal A, Siddiqui AH. StatPearls. 2024 Jan
- Review The global tuberculosis epidemic and progress in care, prevention, and research: an overview in year 3 of the End TB era. [Lancet Respir Med. 2018] Review The global tuberculosis epidemic and progress in care, prevention, and research: an overview in year 3 of the End TB era. Floyd K, Glaziou P, Zumla A, Raviglione M. Lancet Respir Med. 2018 Apr; 6(4):299-314.
- Fighting the tuberculosis epidemic in the Western Pacific region: current situation and challenges ahead. [Kekkaku. 2010] Fighting the tuberculosis epidemic in the Western Pacific region: current situation and challenges ahead. van Maaren PJ. Kekkaku. 2010 Jan; 85(1):9-16.
- Consensus statement. Global burden of tuberculosis: estimated incidence, prevalence, and mortality by country. WHO Global Surveillance and Monitoring Project. [JAMA. 1999] Consensus statement. Global burden of tuberculosis: estimated incidence, prevalence, and mortality by country. WHO Global Surveillance and Monitoring Project. Dye C, Scheele S, Dolin P, Pathania V, Raviglione MC. JAMA. 1999 Aug 18; 282(7):677-86.
Recent Activity
- Tuberculosis - StatPearls Tuberculosis - StatPearls
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Introduction. Tuberculosis (TB) represents a major global health threat that, despite being preventable and treatable, is the 13th leading cause of death worldwide and the second leading infectious killer after coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) [1, 2].In the past decades, the TB burden has been slowly decreasing; however, with the emergence of COVID-19 and the current political conflicts ...
Abstract. Tuberculosis (TB) remains one of the deadliest infectious diseases responsible for millions of deaths annually across the world. In this paper we present a general overview of TB ...
Abstract and Figures. Tuberculosis Is a major bluster to humanity resist to progress in health-care systems and the widespread weapon of TB control programs. The World Health Organization (WHO ...
Tuberculosis (TB) is an airborne disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) that usually affects the lungs leading to severe coughing, fever, and chest pains. Although current research in the past four years has provided valuable insight into TB transmission, diagnosis, and treatment, much remains to be discovered to effectively decrease the incidence of and eventually eradicate TB.
Tuberculosis (TB) is the second leading infectious killer after COVID-19, causing 10 million new cases and claiming the lives of more than 1.5 million people every year []; furthermore, a growing number of multidrug-resistant TB strains constitute a major health threat.During long co-evolution, Mycobacterium tuberculosis has developed a plethora of molecular mechanisms that successfully bypass ...
Abstract. Tuberculosis (TB), an old disease caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis is still responsible for more deaths worldwide each year than any other infectious disease, including ...
Conclusion. The repercussions of ... Fox, W., Ellard, G. A. & Mitchison, D. A. Studies on the treatment of tuberculosis undertaken by the British Medical Research Council tuberculosis units, 1946 ...
Tuberculosis (TB), a preventable and curable disease, is claimed as the second largest number of fatalities, and there are 9,025 cases reported in the United States in 2018. Many researchers have done a lot of research and achieved remarkable results, but TB is still a severe problem for human beings. The study is a further exploration of the prevention and control of tuberculosis.
The shift in our understanding will have implications for research efforts geared towards new drugs and vaccines (Fig. 1).Because infecting M. tuberculosis bacteria are thought to be in an altered ...
This qualitative market research study was conducted between July 2020 and February 2021. Eight TB patients from each country (n = 40) completed health questionnaires, video/telephone interviews, and diaries regarding their experiences of TB. Additionally, 52 household members were interviewed.
Tuberculosis is highly prevalent among the low socioeconomic section of the population and marginalized sections of the community. In India, National strategic plan (2017-2025) has a national goal of elimination of tuberculosis by 2025. It requires increased awareness and understanding of Tuberculosis. In this review article history, taxonomy ...
The 2019 Lancet Commission on Tuberculosis laid out an optimistic vision for how to build a tuberculosis-free world through smart investments based on sound science and shared responsibility.1 Since then, several major strides have been made towards ending tuberculosis, including substantive improvements in treatment outcomes for people with drug-resistant disease.2,3 Although COVID-19 has ...
Tuberculosis (TB) is a communicable infectious disease affecting around one quarter of the world's population [].The 'BRICS' countries of Brazil , Russia, India, China, and South Africa account for 47% of the total number of TB cases annually [1,2,3].Caused by the bacillus Mycobacterium tuberculosis, around 5-10% of those infected will develop active disease.
Tuberculosis Research and Treatment publishes original research articles and review articles related to all aspects of tuberculosis, from the immunological basis of disease to translational and clinical research. ... Conclusion. The antituberculosis drug nonadherence is high. Marital status, educational status, drug side effects, HIV screening ...
Tuberculosis, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis), remains a formidable global health challenge, affecting a substantial portion of the world's population. The current tuberculosis vaccine, bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG), offers limited protection against pulmonary tuberculosis in adults, underscoring the critical need for innovative vaccination strategies. Cytokines are ...
1. Introduction. Tuberculosis (TB) is still a major global health problem as the global incidence in 2018 was estimated to be 10.0 millions, and the mortality 1.2 millions .The World Health Organization (WHO) and the United Nations' Millennium Development Goals (MDG) together with the Stop TB Strategy have developed strategies for eliminating TB, which have led to a decline in absolute ...
Tuberculosis is the leading cause of death from a single infectious agent, with over 25% of these occurring in the African region. Multi-drug resistant strains which do not respond to first-line ...
Tuberculosis (TB) research and innovation is essential to achieve the global TB targets of the United Nations (UN) Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the World Health Organization (WHO) End TB Strategy. The SDG target is to "end the epidemic" by 2030; more specific targets for 2030 set in the End TB Strategy are a 90% reduction in TB ...
Worldwide, tuberculosis (TB) is the leading cause of death from a single infectious disease agent (1) and the leading cause of death among persons living with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV ...
Engagement of healthcare providers is one of the World Health Organization strategies devised for prevention and provision of patient centered care for multidrug resistant tuberculosis. The need for current research question rose because of the gaps in evidence on health professional's engagement and its factors in multidrug resistant tuberculosis service delivery as per the protocol in the ...
Conclusions. 7.1 Magnitude and trends of drug-resistant tuberculosis. 7.2 Extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis (XDR-TB) 7.3 Drug-resistant tuberculosis and HIV. 7.4 Survey coverage and methods. 7.5 Tuberculosis control and drug-resistant tuberculosis.
Virtue and Action: Selected Papers Rosalind Hursthouse, edited by Julia Annas and Jeremy Reid, Oxford University Press, 2023, pp. vii + 368, USD125.00 (hardback), ISBN 9780192895844.
Tuberculosis (TB) is an ancient human disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis which mainly affects the lungs, making pulmonary disease the most common presentation (K Zaman, 2010) [1]. However, TB is a multi-systemic disease with a protean presentation. The organ system most commonly affected includes the respiratory system, the gastrointestinal (GI) system, the lymphoreticular system ...