Case Study Analysis: Examples + How-to Guide & Writing Tips
A case study analysis is a typical assignment in business management courses. The task aims to show high school and college students how to analyze a current situation, determine what problems exist, and develop the best possible strategy to achieve the desired outcome.
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!
Many students feel anxious about writing case analyses because being told to analyze a case study and provide a solution can seem like a big task. That is especially so when working with real-life scenarios. However, you can rest assured writing a case analysis paper is easier than you think. Just keep reading this article and you will find case study examples for students and the advice provided by Custom-writing experts!
- 👣 Main Steps
- 🕵 Preparing the Case

🔬 Analyzing the Case
- 📑 Format & Structure
- 🙅 Things to Avoid
- 🏁 Conclusion
🔗 References
👣 writing a case study analysis: main steps.
Business management is built on case analysis. Every single economic result shows that the methods and instruments employed were either well-timed and expedient, in the event of success, or not, in case of failure. These two options indicate whether the strategy is efficient (and should be followed) or requires corrections (or complete change). Such an approach to the case study will make your writing piece more proficient and valuable for the reader. The following steps will direct your plan for writing a case study analysis.
Step 1: Preliminary work
- Make notes and highlight the numbers and ideas that could be quoted.
- Single out as many problems as you can, and briefly mark their underlying issues. Then make a note of those responsible. In the report, you will use two to five of the problems, so you will have a selection to choose from.
- Outline a possible solution to each of the problems you found. Course readings and outside research shall be used here. Highlight your best and worst solution for further reference.
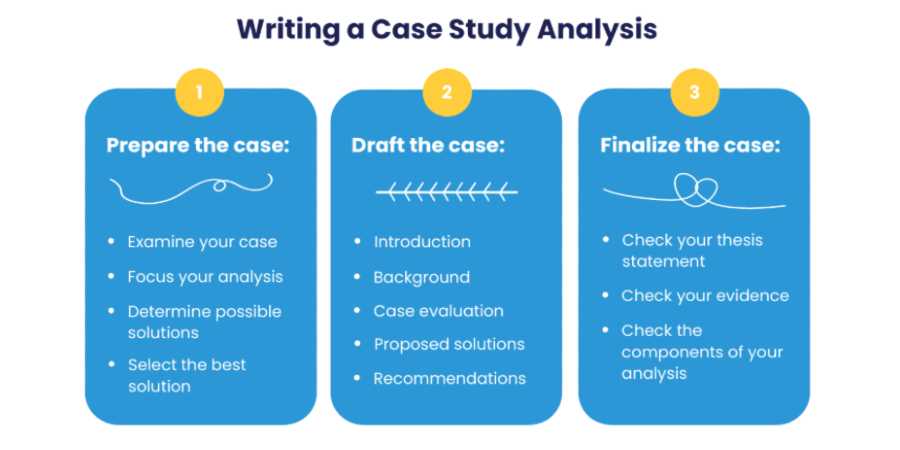
Step 2: Drafting the Case
- Provide a general description of the situation and its history.
- Name all the problems you are going to discuss.
- Specify the theory used for the analysis.
- Present the assumptions that emerged during the analysis, if any.
- Describe the detected problems in more detail.
- Indicate their link to, and effect on, the general situation.
- Explain why the problems emerged and persist.
- List realistic and feasible solutions to the problems you outlined, in the order of importance.
- Specify your predicted results of such changes.
- Support your choice with reliable evidence (i.e., textbook readings, the experience of famous companies, and other external research).
- Define the strategies required to fulfill your proposed solution.
- Indicate the responsible people and the realistic terms for its implementation.
- Recommend the issues for further analysis and supervision.
Step 3: Finalizing the Case
Like any other piece of writing, a case analysis requires post-editing. Carefully read it through, looking for inconsistencies and gaps in meaning. Your purpose is to make it look complete, precise, and convincing.
🕵 Preparing a Case for Analysis
Your professor might give you various case study examples from which to choose, or they may just assign you a particular case study. To conduct a thorough data analysis, you must first read the case study. This might appear to be obvious. However, you’d be surprised at how many students don’t take adequate time to complete this part.
Read the case study very thoroughly, preferably several times. Highlight, underline, flag key information, and make notes to refer to later when you are writing your analysis report.
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour
If you don’t have a complete knowledge of the case study your professor has assigned, you won’t conduct a proper analysis of it. Even if you make use of a business case study template or refer to a sample analysis, it won’t help if you aren’t intimately familiar with your case study.
You will also have to conduct research. When it comes to research, you will need to do the following:
- Gather hard, quantitative data (e.g. 67% of the staff participated in the meeting).
- Design research tools , such as questionnaires and surveys (this will aid in gathering data).
- Determine and suggest the best specific, workable solutions.
It would be best if you also learned how to analyze a case study. Once you have read through the case study, you need to determine the focus of your analysis. You can do this by doing the following:
Compare your chosen solutions to the solutions offered by the experts who analyzed the case study you were given or to online assignments for students who were dealing with a similar task. The experts’ solutions will probably be more advanced than yours simply because these people are more experienced. However, don’t let this discourage you; the whole point of doing this analysis is to learn. Use the opportunity to learn from others’ valuable experience, and your results will be better next time.
If you are still in doubt, the University of South Carolina offers a great guide on forming a case study analysis.
Receive a plagiarism-free paper tailored to your instructions. Cut 15% off your first order!
📑 Case Analysis Format & Structure
When you are learning how to write a case study analysis, it is important to get the format of your analysis right. Understanding the case study format is vital for both the professor and the student. The person planning and handing out such an assignment should ensure that the student doesn’t have to use any external sources .
In turn, students have to remember that a well-written case analysis provides all the data, making it unnecessary for the reader to go elsewhere for information.
Regardless of whether you use a case study template, you will need to follow a clear and concise format when writing your analysis report. There are some possible case study frameworks available. Still, a case study should contain eight sections laid out in the following format:
- Describe the purpose of the current case study;
- Provide a summary of the company;
- Briefly introduce the problems and issues found in the case study
- Discuss the theory you will be using in the analysis;
- Present the key points of the study and present any assumptions made during the analysis.
- Present each problem you have singled out;
- Justify your inclusion of each problem by providing supporting evidence from the case study and by discussing relevant theory and what you have learned from your course content;
- Divide the section (and following sections) into subsections, one for each of your selected problems.
- Present a summary of each problem you have identified;
- Present plausible solutions for each of the problems, keeping in mind that each problem will likely have more than one possible solution;
- Provide the pros and cons of each solution in a way that is practical.
- Conclusion . This is a summary of your findings and discussion.
- Decide which solution best fits each of the issues you identified;
- Explain why you chose this solution and how it will effectively solve the problem;
- Be persuasive when you write this section so that you can drive your point home;
- Be sure to bring together theory and what you have learned throughout your course to support your recommendations.
- Provide an explanation of what must be done, who should take action, and when the solution should be carried out;
- Where relevant, you should provide an estimate of the cost in implementing the solution, including both the financial investment and the cost in terms of time.
- References. While you generally do not need to refer to many external sources when writing a case study analysis, you might use a few. When you do, you will need to properly reference these sources, which is most often done in one of the main citation styles, including APA, MLA, or Harvard. There is plenty of help when citing references, and you can follow these APA guidelines , these MLA guidelines , or these Harvard guidelines .
- Appendices. This is the section you include after your case study analysis if you used any original data in the report. These data, presented as charts, graphs, and tables, are included here because to present them in the main body of the analysis would be disruptive to the reader. The University of Southern California provides a great description of appendices and when to make use of them.
When you’ve finished your first draft, be sure to proofread it. Look not only for potential grammar and spelling errors but also for discrepancies or holes in your argument.
You should also know what you need to avoid when writing your analysis.
Get an originally-written paper according to your instructions!
🙅 Things to Avoid in Case Analysis
Whenever you deal with a case study, remember that there are some pitfalls to avoid! Beware of the following mistakes:
- Excessive use of colloquial language . Even though it is a study of an actual case, it should sound formal.
- Lack of statistical data . Give all the important data, both in percentages and in numbers.
- Excessive details. State only the most significant facts, rather than drowning the reader in every fact you find.
- Inconsistency in the methods you have used . In a case study, theory plays a relatively small part, so you must develop a specific case study research methodology.
- Trivial means of research . It is critical that you design your own case study research method in whatever form best suits your analysis, such as questionnaires and surveys.
It is useful to see a few examples of case analysis papers. After all, a sample case study report can provide you with some context so you can see how to approach each aspect of your paper.
👀 Case Study Examples for Students
It might be easier to understand how a case study analysis works if you have an example to look at. Fortunately, examples of case studies are easy to come by. Take a look at this video for a sample case study analysis for the Coca-Cola Company.
If you want another example, then take a look at the one below!
Business Case Analysis: Example
CRM’s primary focus is customers and customer perception of the brand or the company. The focus may shift depending on customers’ needs. The main points that Center Parcs should consider are an increase in customer satisfaction and its market share. Both of these points will enhance customer perception of the product as a product of value. Increased customer satisfaction will indicate that the company provides quality services, and increased market share can reduce the number of switching (or leaving) customers, thus fostering customer loyalty.
Case Study Topics
- Equifax case study: the importance of cybersecurity measures .
- Study a case illustrating ethical issues of medical research.
- Examine the case describing the complications connected with nursing and residential care.
- Analyze the competitive strategy of Delta Airlines .
- Present a case study of an ethical dilemma showing the conflict between the spirit and the letter of the law.
- Explore the aspects of Starbucks’ marketing strategyin a case study.
- Research a case of community-based clinic organization and development.
- Customer service of United Airlines: a case study .
- Analyze a specific schizophrenia case and provide your recommendations.
- Provide a case study of a patient with hyperglycemia.
- Examine the growth strategy of United Healthcare.
- Present a case study demonstrating ethical issues in business.
- Study a case of the 5% shareholding rule application and its impact on the company.
- Case study of post-traumatic stress disorder .
- Analyze a case examining the issues of cross-cultural management .
- Write a case study exploring the ethical issues the finance manager of a long-term care facility can face and the possible reaction to them.
- Write a case study analyzing the aspects of a new president of a firm election.
- Discuss the specifics of supply chain management in the case of Tehindo company.
- Study a case of a life crisis in a family and the ways to cope with it.
- Case study of Tea Leaves and More: supply chain issues .
- Explore the case of ketogenic diet implementation among sportspeople.
- Analyze the case of Webster Jewelry shop and suggest some changes.
- Examine the unique aspects of Tea and More brand management .
- Adidas case study: an ethical dilemma .
- Research the challenges of Brazos Valley Food Bank and suggest possible solutions.
- Describe the case of dark web monitoring for business.
- Study a case of permissive parenting style .
- Case study of Starbucks employees.
- Analyze a case of workplace discrimination and suggest a strategy to avoid it.
- Examine a case of the consumer decision-making process and define the factors that influence it.
- Present a case study of Netflix illustrating the crucial role of management innovation for company development.
- Discuss a case describing a workplace ethical issue and propose ways to resolve it.
- Case study of the 2008 financial crisis: Graham’s value investing principles in the modern economic climate.
- Write a case study analyzing the harmful consequences of communication issues in a virtual team.
- Analyze a case that highlights the importance of a proper functional currency choice.
- Examine the case of Hitachi Power Systems management.
- Present a case study of medication research in a healthcare facility.
- Study the case of Fiji Water and the challenges the brand faces.
- Research a social problem case and suggest a solution.
- Analyze a case that reveals the connection between alcohol use and borderline personality disorder.
- Transglobal Airline case study: break-even analysis.
- Examine the case of Chiquita Brands International from the moral and business ethics points of view.
- Present a case study of applying for Social Security benefits.
- Study the case of a mass hacker attack on Microsoft clients and suggest possible ways to prevent future attacks.
- Case study of leadership effectiveness .
- Analyze a case presenting a clinical moral dilemma and propose ways to resolve it.
- Describe the case of Cowbell Brewing Company and discuss the strategy that made them successful.
- Write a case study of WeWork company and analyze the strengths and weaknesses of its strategy.
- Case study of medical ethical decision-making.
- Study the case of The Georges hotel and suggest ways to overcome its managerial issues.
🏁 Concluding Remarks
Writing a case study analysis can seem incredibly overwhelming, especially if you have never done it before. Just remember, you can do it provided you follow a plan, keep to the format described here, and study at least one case analysis example.
If you still need help analyzing a case study, your professor is always available to answer your questions and point you in the right direction. You can also get help with any aspect of the project from a custom writing company. Just tackle the research and hand over the writing, write a rough draft and have it checked by a professional, or completely hand the project off to an expert writer.
Regardless of the path you choose, you will turn in something of which you can be proud!
✏️ Case Study Analysis FAQ
Students (especially those who study business) often need to write a case study analysis. It is a kind of report that describes a business case. It includes multiple aspects, for example, the problems that exist, possible solutions, forecasts, etc.
There should be 3 main points covered in a case study analysis:
- The challenge(s) description,
- Possible solutions,
- Outcomes (real and/or foreseen).
Firstly, study some examples available online and in the library. Case study analysis should be a well-structured paper with all the integral components in place. Thus, you might want to use a template and/or an outline to start correctly.
A case study analysis is a popular task for business students. They typically hand it in the format of a paper with several integral components:
- Description of the problem
- Possible ways out
- Results and/or forecasts
Students sometimes tell about the outcome of their research within an oral presentation.
- Case Study: Academia
- Windows of vulnerability: a case study analysis (IEEE)
- A (Very) Brief Refresher on the Case Study Method: SAGE
- The case study approach: Medical Research Methodology
- Strengths and Limitations of Case Studies: Stanford University
- A Sample APA Paper: Radford University
- How to Write a Case Study APA Style: Seattle PI
- The Case Analysis: GVSU
- How to Outline: Purdue OWL
- Incorporating Interview Data: UW-Madison Writing Center
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

If you are a student, you might need to learn how to write a literature review at some point. But don’t think it’s the same as the book review or other types of academic writing you had to do in high school! A literature review is a close examination of...

So, have you been recently assigned a research project? Or, even worse, is it already due soon? The following research paper hacks will help you do it in record time. In the article, you’ll see ten things you can do to conduct a study and compose a piece like a...

Eating a delicacy, watching a good movie, and proving a point to an audience are the three things that make life seem better. Today, you’ll deal with the last one. You’re about to become a professional at public speaking and attention grabbing. Here, you can learn how to write a...
![sample analysis of case study Library Research Paper: Example & Writing Guide [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/library-with-books-284x122.jpeg)
What is a library research paper? It’s nothing more than an academic writing project that summarizes the information on a specific topic taken from primary and secondary sources. There are numerous library research examples you can find online. But to complete this assignment, you should simply follow these essential steps:...
![sample analysis of case study Research Analysis Paper: How to Analyze a Research Article [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/opened-book-library-table-284x153.jpg)
Do you need to write a research analysis paper but have no idea how to do that? Then you’re in the right place. While completing this type of assignment, your key aim is to critically analyze a research article. An article from a serious scientific journal would be a good...
![sample analysis of case study American Antiquity Style Guide: Citation Rules & Examples [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/education-concept-books-laptop-library-284x153.jpg)
American Antiquity is a professional quarterly journal, which contains various papers on the American archeology. It is incredibly popular among archeologists and the students majoring in history. The organization adopted the rules of The Society for American Archaeology (SAA) citation style. As a result: The journal includes numerous references that...

The most tedious and time-consuming part of any school or college written assignment is the bibliography. Sometimes, it can even be challenging! For example, if you’re confused by the variety of citation styles. This is probably when the most students wonder “Is there someone who could complete my assignment?” That...

An appendix is the part of the paper that contains supplementary material. The information from an appendix in paper writing is not essential. If the readers ignore this part, they still have to get the paper’s idea. Appendices help the readers to understand the research better. They might be useful...

Writing an abstract is one of the skills you need to master to succeed in your studies. An abstract is a summary of an academic text. It contains information about the aims and the outcomes of the research. The primary purpose of an abstract is to help readers understand what...

So you have to write a literature review. You find your favorite novel and then start analyzing it. This is how it’s usually done, right? It’s not. You have to learn the elements of literature review and how to deal with them.
![sample analysis of case study How to Write a Research Paper Step by Step [2024 Upd.]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/research-charts-284x153.jpg)
Only two words, but you already feel a chill down your spine. A research paper is no joke. It’s a super detailed piece of academic writing where you analyze a chosen issue in-depth. The main aim of such torture is to show how knowledgeable you are and that your opinion...

A research proposal is a text that suggests a topic or research problem, justifies the need to study it, and describes the ways and methods of conducting the study. Scholars usually write proposals to get funding for their research. In their turn, students might have to do that to get...
Quite an impressive piece The steps and procedures outlined here are well detailed and the examples facilitates understanding.
it was very helpful. I have an assessment to write where in I need to mention different effective components that are needed to compile a high quality case study assessment.
It is very important and helpful.
Thanks a lot. A knowledge shared with a structured template. Stay the course
Thanks for this valuable knowledge.I loved this. keep sharing. to know more about click Air India Case Study – Why Air India failed ?
This is going to be a great help in my monthly analysis requirements for my subject. Thank you so much.
Thank you very much for this insightful guidelines… It has really been a great tool for writing my project. Thanks once again.
This article was very helpful, even though I’ll have a clearer mind only after I do the case study myself but I felt very much motivated after reading this, as now I can at least have a plan of what to do compared to the clueless me I was before I read it. I hope if I have any questions or doubts about doing a case study I can clear it out here.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on 5 May 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 30 January 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organisation, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating, and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyse the case.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
Unlike quantitative or experimental research, a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
If you find yourself aiming to simultaneously investigate and solve an issue, consider conducting action research . As its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time, and is highly iterative and flexible.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience, or phenomenon.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data .
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis, with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results , and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyse its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, January 30). Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved 6 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/case-studies/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, correlational research | guide, design & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, descriptive research design | definition, methods & examples.
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
A case study research paper examines a person, place, event, condition, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis in order to extrapolate key themes and results that help predict future trends, illuminate previously hidden issues that can be applied to practice, and/or provide a means for understanding an important research problem with greater clarity. A case study research paper usually examines a single subject of analysis, but case study papers can also be designed as a comparative investigation that shows relationships between two or more subjects. The methods used to study a case can rest within a quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method investigative paradigm.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010 ; “What is a Case Study?” In Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London: SAGE, 2010.
How to Approach Writing a Case Study Research Paper
General information about how to choose a topic to investigate can be found under the " Choosing a Research Problem " tab in the Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper writing guide. Review this page because it may help you identify a subject of analysis that can be investigated using a case study design.
However, identifying a case to investigate involves more than choosing the research problem . A case study encompasses a problem contextualized around the application of in-depth analysis, interpretation, and discussion, often resulting in specific recommendations for action or for improving existing conditions. As Seawright and Gerring note, practical considerations such as time and access to information can influence case selection, but these issues should not be the sole factors used in describing the methodological justification for identifying a particular case to study. Given this, selecting a case includes considering the following:
- The case represents an unusual or atypical example of a research problem that requires more in-depth analysis? Cases often represent a topic that rests on the fringes of prior investigations because the case may provide new ways of understanding the research problem. For example, if the research problem is to identify strategies to improve policies that support girl's access to secondary education in predominantly Muslim nations, you could consider using Azerbaijan as a case study rather than selecting a more obvious nation in the Middle East. Doing so may reveal important new insights into recommending how governments in other predominantly Muslim nations can formulate policies that support improved access to education for girls.
- The case provides important insight or illuminate a previously hidden problem? In-depth analysis of a case can be based on the hypothesis that the case study will reveal trends or issues that have not been exposed in prior research or will reveal new and important implications for practice. For example, anecdotal evidence may suggest drug use among homeless veterans is related to their patterns of travel throughout the day. Assuming prior studies have not looked at individual travel choices as a way to study access to illicit drug use, a case study that observes a homeless veteran could reveal how issues of personal mobility choices facilitate regular access to illicit drugs. Note that it is important to conduct a thorough literature review to ensure that your assumption about the need to reveal new insights or previously hidden problems is valid and evidence-based.
- The case challenges and offers a counter-point to prevailing assumptions? Over time, research on any given topic can fall into a trap of developing assumptions based on outdated studies that are still applied to new or changing conditions or the idea that something should simply be accepted as "common sense," even though the issue has not been thoroughly tested in current practice. A case study analysis may offer an opportunity to gather evidence that challenges prevailing assumptions about a research problem and provide a new set of recommendations applied to practice that have not been tested previously. For example, perhaps there has been a long practice among scholars to apply a particular theory in explaining the relationship between two subjects of analysis. Your case could challenge this assumption by applying an innovative theoretical framework [perhaps borrowed from another discipline] to explore whether this approach offers new ways of understanding the research problem. Taking a contrarian stance is one of the most important ways that new knowledge and understanding develops from existing literature.
- The case provides an opportunity to pursue action leading to the resolution of a problem? Another way to think about choosing a case to study is to consider how the results from investigating a particular case may result in findings that reveal ways in which to resolve an existing or emerging problem. For example, studying the case of an unforeseen incident, such as a fatal accident at a railroad crossing, can reveal hidden issues that could be applied to preventative measures that contribute to reducing the chance of accidents in the future. In this example, a case study investigating the accident could lead to a better understanding of where to strategically locate additional signals at other railroad crossings so as to better warn drivers of an approaching train, particularly when visibility is hindered by heavy rain, fog, or at night.
- The case offers a new direction in future research? A case study can be used as a tool for an exploratory investigation that highlights the need for further research about the problem. A case can be used when there are few studies that help predict an outcome or that establish a clear understanding about how best to proceed in addressing a problem. For example, after conducting a thorough literature review [very important!], you discover that little research exists showing the ways in which women contribute to promoting water conservation in rural communities of east central Africa. A case study of how women contribute to saving water in a rural village of Uganda can lay the foundation for understanding the need for more thorough research that documents how women in their roles as cooks and family caregivers think about water as a valuable resource within their community. This example of a case study could also point to the need for scholars to build new theoretical frameworks around the topic [e.g., applying feminist theories of work and family to the issue of water conservation].
Eisenhardt, Kathleen M. “Building Theories from Case Study Research.” Academy of Management Review 14 (October 1989): 532-550; Emmel, Nick. Sampling and Choosing Cases in Qualitative Research: A Realist Approach . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2013; Gerring, John. “What Is a Case Study and What Is It Good for?” American Political Science Review 98 (May 2004): 341-354; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Seawright, Jason and John Gerring. "Case Selection Techniques in Case Study Research." Political Research Quarterly 61 (June 2008): 294-308.
Structure and Writing Style
The purpose of a paper in the social sciences designed around a case study is to thoroughly investigate a subject of analysis in order to reveal a new understanding about the research problem and, in so doing, contributing new knowledge to what is already known from previous studies. In applied social sciences disciplines [e.g., education, social work, public administration, etc.], case studies may also be used to reveal best practices, highlight key programs, or investigate interesting aspects of professional work.
In general, the structure of a case study research paper is not all that different from a standard college-level research paper. However, there are subtle differences you should be aware of. Here are the key elements to organizing and writing a case study research paper.
I. Introduction
As with any research paper, your introduction should serve as a roadmap for your readers to ascertain the scope and purpose of your study . The introduction to a case study research paper, however, should not only describe the research problem and its significance, but you should also succinctly describe why the case is being used and how it relates to addressing the problem. The two elements should be linked. With this in mind, a good introduction answers these four questions:
- What is being studied? Describe the research problem and describe the subject of analysis [the case] you have chosen to address the problem. Explain how they are linked and what elements of the case will help to expand knowledge and understanding about the problem.
- Why is this topic important to investigate? Describe the significance of the research problem and state why a case study design and the subject of analysis that the paper is designed around is appropriate in addressing the problem.
- What did we know about this topic before I did this study? Provide background that helps lead the reader into the more in-depth literature review to follow. If applicable, summarize prior case study research applied to the research problem and why it fails to adequately address the problem. Describe why your case will be useful. If no prior case studies have been used to address the research problem, explain why you have selected this subject of analysis.
- How will this study advance new knowledge or new ways of understanding? Explain why your case study will be suitable in helping to expand knowledge and understanding about the research problem.
Each of these questions should be addressed in no more than a few paragraphs. Exceptions to this can be when you are addressing a complex research problem or subject of analysis that requires more in-depth background information.
II. Literature Review
The literature review for a case study research paper is generally structured the same as it is for any college-level research paper. The difference, however, is that the literature review is focused on providing background information and enabling historical interpretation of the subject of analysis in relation to the research problem the case is intended to address . This includes synthesizing studies that help to:
- Place relevant works in the context of their contribution to understanding the case study being investigated . This would involve summarizing studies that have used a similar subject of analysis to investigate the research problem. If there is literature using the same or a very similar case to study, you need to explain why duplicating past research is important [e.g., conditions have changed; prior studies were conducted long ago, etc.].
- Describe the relationship each work has to the others under consideration that informs the reader why this case is applicable . Your literature review should include a description of any works that support using the case to investigate the research problem and the underlying research questions.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research using the case study . If applicable, review any research that has examined the research problem using a different research design. Explain how your use of a case study design may reveal new knowledge or a new perspective or that can redirect research in an important new direction.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies . This refers to synthesizing any literature that points to unresolved issues of concern about the research problem and describing how the subject of analysis that forms the case study can help resolve these existing contradictions.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research . Your review should examine any literature that lays a foundation for understanding why your case study design and the subject of analysis around which you have designed your study may reveal a new way of approaching the research problem or offer a perspective that points to the need for additional research.
- Expose any gaps that exist in the literature that the case study could help to fill . Summarize any literature that not only shows how your subject of analysis contributes to understanding the research problem, but how your case contributes to a new way of understanding the problem that prior research has failed to do.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important!] . Collectively, your literature review should always place your case study within the larger domain of prior research about the problem. The overarching purpose of reviewing pertinent literature in a case study paper is to demonstrate that you have thoroughly identified and synthesized prior studies in relation to explaining the relevance of the case in addressing the research problem.
III. Method
In this section, you explain why you selected a particular case [i.e., subject of analysis] and the strategy you used to identify and ultimately decide that your case was appropriate in addressing the research problem. The way you describe the methods used varies depending on the type of subject of analysis that constitutes your case study.
If your subject of analysis is an incident or event . In the social and behavioral sciences, the event or incident that represents the case to be studied is usually bounded by time and place, with a clear beginning and end and with an identifiable location or position relative to its surroundings. The subject of analysis can be a rare or critical event or it can focus on a typical or regular event. The purpose of studying a rare event is to illuminate new ways of thinking about the broader research problem or to test a hypothesis. Critical incident case studies must describe the method by which you identified the event and explain the process by which you determined the validity of this case to inform broader perspectives about the research problem or to reveal new findings. However, the event does not have to be a rare or uniquely significant to support new thinking about the research problem or to challenge an existing hypothesis. For example, Walo, Bull, and Breen conducted a case study to identify and evaluate the direct and indirect economic benefits and costs of a local sports event in the City of Lismore, New South Wales, Australia. The purpose of their study was to provide new insights from measuring the impact of a typical local sports event that prior studies could not measure well because they focused on large "mega-events." Whether the event is rare or not, the methods section should include an explanation of the following characteristics of the event: a) when did it take place; b) what were the underlying circumstances leading to the event; and, c) what were the consequences of the event in relation to the research problem.
If your subject of analysis is a person. Explain why you selected this particular individual to be studied and describe what experiences they have had that provide an opportunity to advance new understandings about the research problem. Mention any background about this person which might help the reader understand the significance of their experiences that make them worthy of study. This includes describing the relationships this person has had with other people, institutions, and/or events that support using them as the subject for a case study research paper. It is particularly important to differentiate the person as the subject of analysis from others and to succinctly explain how the person relates to examining the research problem [e.g., why is one politician in a particular local election used to show an increase in voter turnout from any other candidate running in the election]. Note that these issues apply to a specific group of people used as a case study unit of analysis [e.g., a classroom of students].
If your subject of analysis is a place. In general, a case study that investigates a place suggests a subject of analysis that is unique or special in some way and that this uniqueness can be used to build new understanding or knowledge about the research problem. A case study of a place must not only describe its various attributes relevant to the research problem [e.g., physical, social, historical, cultural, economic, political], but you must state the method by which you determined that this place will illuminate new understandings about the research problem. It is also important to articulate why a particular place as the case for study is being used if similar places also exist [i.e., if you are studying patterns of homeless encampments of veterans in open spaces, explain why you are studying Echo Park in Los Angeles rather than Griffith Park?]. If applicable, describe what type of human activity involving this place makes it a good choice to study [e.g., prior research suggests Echo Park has more homeless veterans].
If your subject of analysis is a phenomenon. A phenomenon refers to a fact, occurrence, or circumstance that can be studied or observed but with the cause or explanation to be in question. In this sense, a phenomenon that forms your subject of analysis can encompass anything that can be observed or presumed to exist but is not fully understood. In the social and behavioral sciences, the case usually focuses on human interaction within a complex physical, social, economic, cultural, or political system. For example, the phenomenon could be the observation that many vehicles used by ISIS fighters are small trucks with English language advertisements on them. The research problem could be that ISIS fighters are difficult to combat because they are highly mobile. The research questions could be how and by what means are these vehicles used by ISIS being supplied to the militants and how might supply lines to these vehicles be cut off? How might knowing the suppliers of these trucks reveal larger networks of collaborators and financial support? A case study of a phenomenon most often encompasses an in-depth analysis of a cause and effect that is grounded in an interactive relationship between people and their environment in some way.
NOTE: The choice of the case or set of cases to study cannot appear random. Evidence that supports the method by which you identified and chose your subject of analysis should clearly support investigation of the research problem and linked to key findings from your literature review. Be sure to cite any studies that helped you determine that the case you chose was appropriate for examining the problem.
IV. Discussion
The main elements of your discussion section are generally the same as any research paper, but centered around interpreting and drawing conclusions about the key findings from your analysis of the case study. Note that a general social sciences research paper may contain a separate section to report findings. However, in a paper designed around a case study, it is common to combine a description of the results with the discussion about their implications. The objectives of your discussion section should include the following:
Reiterate the Research Problem/State the Major Findings Briefly reiterate the research problem you are investigating and explain why the subject of analysis around which you designed the case study were used. You should then describe the findings revealed from your study of the case using direct, declarative, and succinct proclamation of the study results. Highlight any findings that were unexpected or especially profound.
Explain the Meaning of the Findings and Why They are Important Systematically explain the meaning of your case study findings and why you believe they are important. Begin this part of the section by repeating what you consider to be your most important or surprising finding first, then systematically review each finding. Be sure to thoroughly extrapolate what your analysis of the case can tell the reader about situations or conditions beyond the actual case that was studied while, at the same time, being careful not to misconstrue or conflate a finding that undermines the external validity of your conclusions.
Relate the Findings to Similar Studies No study in the social sciences is so novel or possesses such a restricted focus that it has absolutely no relation to previously published research. The discussion section should relate your case study results to those found in other studies, particularly if questions raised from prior studies served as the motivation for choosing your subject of analysis. This is important because comparing and contrasting the findings of other studies helps support the overall importance of your results and it highlights how and in what ways your case study design and the subject of analysis differs from prior research about the topic.
Consider Alternative Explanations of the Findings Remember that the purpose of social science research is to discover and not to prove. When writing the discussion section, you should carefully consider all possible explanations revealed by the case study results, rather than just those that fit your hypothesis or prior assumptions and biases. Be alert to what the in-depth analysis of the case may reveal about the research problem, including offering a contrarian perspective to what scholars have stated in prior research if that is how the findings can be interpreted from your case.
Acknowledge the Study's Limitations You can state the study's limitations in the conclusion section of your paper but describing the limitations of your subject of analysis in the discussion section provides an opportunity to identify the limitations and explain why they are not significant. This part of the discussion section should also note any unanswered questions or issues your case study could not address. More detailed information about how to document any limitations to your research can be found here .
Suggest Areas for Further Research Although your case study may offer important insights about the research problem, there are likely additional questions related to the problem that remain unanswered or findings that unexpectedly revealed themselves as a result of your in-depth analysis of the case. Be sure that the recommendations for further research are linked to the research problem and that you explain why your recommendations are valid in other contexts and based on the original assumptions of your study.
V. Conclusion
As with any research paper, you should summarize your conclusion in clear, simple language; emphasize how the findings from your case study differs from or supports prior research and why. Do not simply reiterate the discussion section. Provide a synthesis of key findings presented in the paper to show how these converge to address the research problem. If you haven't already done so in the discussion section, be sure to document the limitations of your case study and any need for further research.
The function of your paper's conclusion is to: 1) reiterate the main argument supported by the findings from your case study; 2) state clearly the context, background, and necessity of pursuing the research problem using a case study design in relation to an issue, controversy, or a gap found from reviewing the literature; and, 3) provide a place to persuasively and succinctly restate the significance of your research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with in-depth information about the topic.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is appropriate:
- If the argument or purpose of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize these points for your reader.
- If prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the conclusion of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration of the case study's findings that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from your case study findings.
Note that, depending on the discipline you are writing in or the preferences of your professor, the concluding paragraph may contain your final reflections on the evidence presented as it applies to practice or on the essay's central research problem. However, the nature of being introspective about the subject of analysis you have investigated will depend on whether you are explicitly asked to express your observations in this way.
Problems to Avoid
Overgeneralization One of the goals of a case study is to lay a foundation for understanding broader trends and issues applied to similar circumstances. However, be careful when drawing conclusions from your case study. They must be evidence-based and grounded in the results of the study; otherwise, it is merely speculation. Looking at a prior example, it would be incorrect to state that a factor in improving girls access to education in Azerbaijan and the policy implications this may have for improving access in other Muslim nations is due to girls access to social media if there is no documentary evidence from your case study to indicate this. There may be anecdotal evidence that retention rates were better for girls who were engaged with social media, but this observation would only point to the need for further research and would not be a definitive finding if this was not a part of your original research agenda.
Failure to Document Limitations No case is going to reveal all that needs to be understood about a research problem. Therefore, just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study , you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis. For example, the case of studying how women conceptualize the need for water conservation in a village in Uganda could have limited application in other cultural contexts or in areas where fresh water from rivers or lakes is plentiful and, therefore, conservation is understood more in terms of managing access rather than preserving access to a scarce resource.
Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings. If you do not, your reader may question the validity of your analysis, particularly if you failed to document an obvious outcome from your case study research. For example, in the case of studying the accident at the railroad crossing to evaluate where and what types of warning signals should be located, you failed to take into consideration speed limit signage as well as warning signals. When designing your case study, be sure you have thoroughly addressed all aspects of the problem and do not leave gaps in your analysis that leave the reader questioning the results.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Gerring, John. Case Study Research: Principles and Practices . New York: Cambridge University Press, 2007; Merriam, Sharan B. Qualitative Research and Case Study Applications in Education . Rev. ed. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 1998; Miller, Lisa L. “The Use of Case Studies in Law and Social Science Research.” Annual Review of Law and Social Science 14 (2018): TBD; Mills, Albert J., Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Putney, LeAnn Grogan. "Case Study." In Encyclopedia of Research Design , Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010), pp. 116-120; Simons, Helen. Case Study Research in Practice . London: SAGE Publications, 2009; Kratochwill, Thomas R. and Joel R. Levin, editors. Single-Case Research Design and Analysis: New Development for Psychology and Education . Hilldsale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1992; Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London : SAGE, 2010; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods . 6th edition. Los Angeles, CA, SAGE Publications, 2014; Walo, Maree, Adrian Bull, and Helen Breen. “Achieving Economic Benefits at Local Events: A Case Study of a Local Sports Event.” Festival Management and Event Tourism 4 (1996): 95-106.
Writing Tip
At Least Five Misconceptions about Case Study Research
Social science case studies are often perceived as limited in their ability to create new knowledge because they are not randomly selected and findings cannot be generalized to larger populations. Flyvbjerg examines five misunderstandings about case study research and systematically "corrects" each one. To quote, these are:
Misunderstanding 1 : General, theoretical [context-independent] knowledge is more valuable than concrete, practical [context-dependent] knowledge. Misunderstanding 2 : One cannot generalize on the basis of an individual case; therefore, the case study cannot contribute to scientific development. Misunderstanding 3 : The case study is most useful for generating hypotheses; that is, in the first stage of a total research process, whereas other methods are more suitable for hypotheses testing and theory building. Misunderstanding 4 : The case study contains a bias toward verification, that is, a tendency to confirm the researcher’s preconceived notions. Misunderstanding 5 : It is often difficult to summarize and develop general propositions and theories on the basis of specific case studies [p. 221].
While writing your paper, think introspectively about how you addressed these misconceptions because to do so can help you strengthen the validity and reliability of your research by clarifying issues of case selection, the testing and challenging of existing assumptions, the interpretation of key findings, and the summation of case outcomes. Think of a case study research paper as a complete, in-depth narrative about the specific properties and key characteristics of your subject of analysis applied to the research problem.
Flyvbjerg, Bent. “Five Misunderstandings About Case-Study Research.” Qualitative Inquiry 12 (April 2006): 219-245.
- << Previous: Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Next: Writing a Field Report >>
- Last Updated: May 7, 2024 9:45 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments
How to write a case study — examples, templates, and tools

It’s a marketer’s job to communicate the effectiveness of a product or service to potential and current customers to convince them to buy and keep business moving. One of the best methods for doing this is to share success stories that are relatable to prospects and customers based on their pain points, experiences, and overall needs.
That’s where case studies come in. Case studies are an essential part of a content marketing plan. These in-depth stories of customer experiences are some of the most effective at demonstrating the value of a product or service. Yet many marketers don’t use them, whether because of their regimented formats or the process of customer involvement and approval.
A case study is a powerful tool for showcasing your hard work and the success your customer achieved. But writing a great case study can be difficult if you’ve never done it before or if it’s been a while. This guide will show you how to write an effective case study and provide real-world examples and templates that will keep readers engaged and support your business.
In this article, you’ll learn:
What is a case study?
How to write a case study, case study templates, case study examples, case study tools.
A case study is the detailed story of a customer’s experience with a product or service that demonstrates their success and often includes measurable outcomes. Case studies are used in a range of fields and for various reasons, from business to academic research. They’re especially impactful in marketing as brands work to convince and convert consumers with relatable, real-world stories of actual customer experiences.
The best case studies tell the story of a customer’s success, including the steps they took, the results they achieved, and the support they received from a brand along the way. To write a great case study, you need to:
- Celebrate the customer and make them — not a product or service — the star of the story.
- Craft the story with specific audiences or target segments in mind so that the story of one customer will be viewed as relatable and actionable for another customer.
- Write copy that is easy to read and engaging so that readers will gain the insights and messages intended.
- Follow a standardized format that includes all of the essentials a potential customer would find interesting and useful.
- Support all of the claims for success made in the story with data in the forms of hard numbers and customer statements.
Case studies are a type of review but more in depth, aiming to show — rather than just tell — the positive experiences that customers have with a brand. Notably, 89% of consumers read reviews before deciding to buy, and 79% view case study content as part of their purchasing process. When it comes to B2B sales, 52% of buyers rank case studies as an important part of their evaluation process.
Telling a brand story through the experience of a tried-and-true customer matters. The story is relatable to potential new customers as they imagine themselves in the shoes of the company or individual featured in the case study. Showcasing previous customers can help new ones see themselves engaging with your brand in the ways that are most meaningful to them.
Besides sharing the perspective of another customer, case studies stand out from other content marketing forms because they are based on evidence. Whether pulling from client testimonials or data-driven results, case studies tend to have more impact on new business because the story contains information that is both objective (data) and subjective (customer experience) — and the brand doesn’t sound too self-promotional.

Case studies are unique in that there’s a fairly standardized format for telling a customer’s story. But that doesn’t mean there isn’t room for creativity. It’s all about making sure that teams are clear on the goals for the case study — along with strategies for supporting content and channels — and understanding how the story fits within the framework of the company’s overall marketing goals.
Here are the basic steps to writing a good case study.
1. Identify your goal
Start by defining exactly who your case study will be designed to help. Case studies are about specific instances where a company works with a customer to achieve a goal. Identify which customers are likely to have these goals, as well as other needs the story should cover to appeal to them.
The answer is often found in one of the buyer personas that have been constructed as part of your larger marketing strategy. This can include anything from new leads generated by the marketing team to long-term customers that are being pressed for cross-sell opportunities. In all of these cases, demonstrating value through a relatable customer success story can be part of the solution to conversion.
2. Choose your client or subject
Who you highlight matters. Case studies tie brands together that might otherwise not cross paths. A writer will want to ensure that the highlighted customer aligns with their own company’s brand identity and offerings. Look for a customer with positive name recognition who has had great success with a product or service and is willing to be an advocate.
The client should also match up with the identified target audience. Whichever company or individual is selected should be a reflection of other potential customers who can see themselves in similar circumstances, having the same problems and possible solutions.
Some of the most compelling case studies feature customers who:
- Switch from one product or service to another while naming competitors that missed the mark.
- Experience measurable results that are relatable to others in a specific industry.
- Represent well-known brands and recognizable names that are likely to compel action.
- Advocate for a product or service as a champion and are well-versed in its advantages.
Whoever or whatever customer is selected, marketers must ensure they have the permission of the company involved before getting started. Some brands have strict review and approval procedures for any official marketing or promotional materials that include their name. Acquiring those approvals in advance will prevent any miscommunication or wasted effort if there is an issue with their legal or compliance teams.
3. Conduct research and compile data
Substantiating the claims made in a case study — either by the marketing team or customers themselves — adds validity to the story. To do this, include data and feedback from the client that defines what success looks like. This can be anything from demonstrating return on investment (ROI) to a specific metric the customer was striving to improve. Case studies should prove how an outcome was achieved and show tangible results that indicate to the customer that your solution is the right one.
This step could also include customer interviews. Make sure that the people being interviewed are key stakeholders in the purchase decision or deployment and use of the product or service that is being highlighted. Content writers should work off a set list of questions prepared in advance. It can be helpful to share these with the interviewees beforehand so they have time to consider and craft their responses. One of the best interview tactics to keep in mind is to ask questions where yes and no are not natural answers. This way, your subject will provide more open-ended responses that produce more meaningful content.
4. Choose the right format
There are a number of different ways to format a case study. Depending on what you hope to achieve, one style will be better than another. However, there are some common elements to include, such as:
- An engaging headline
- A subject and customer introduction
- The unique challenge or challenges the customer faced
- The solution the customer used to solve the problem
- The results achieved
- Data and statistics to back up claims of success
- A strong call to action (CTA) to engage with the vendor
It’s also important to note that while case studies are traditionally written as stories, they don’t have to be in a written format. Some companies choose to get more creative with their case studies and produce multimedia content, depending on their audience and objectives. Case study formats can include traditional print stories, interactive web or social content, data-heavy infographics, professionally shot videos, podcasts, and more.
5. Write your case study
We’ll go into more detail later about how exactly to write a case study, including templates and examples. Generally speaking, though, there are a few things to keep in mind when writing your case study.
- Be clear and concise. Readers want to get to the point of the story quickly and easily, and they’ll be looking to see themselves reflected in the story right from the start.
- Provide a big picture. Always make sure to explain who the client is, their goals, and how they achieved success in a short introduction to engage the reader.
- Construct a clear narrative. Stick to the story from the perspective of the customer and what they needed to solve instead of just listing product features or benefits.
- Leverage graphics. Incorporating infographics, charts, and sidebars can be a more engaging and eye-catching way to share key statistics and data in readable ways.
- Offer the right amount of detail. Most case studies are one or two pages with clear sections that a reader can skim to find the information most important to them.
- Include data to support claims. Show real results — both facts and figures and customer quotes — to demonstrate credibility and prove the solution works.
6. Promote your story
Marketers have a number of options for distribution of a freshly minted case study. Many brands choose to publish case studies on their website and post them on social media. This can help support SEO and organic content strategies while also boosting company credibility and trust as visitors see that other businesses have used the product or service.
Marketers are always looking for quality content they can use for lead generation. Consider offering a case study as gated content behind a form on a landing page or as an offer in an email message. One great way to do this is to summarize the content and tease the full story available for download after the user takes an action.
Sales teams can also leverage case studies, so be sure they are aware that the assets exist once they’re published. Especially when it comes to larger B2B sales, companies often ask for examples of similar customer challenges that have been solved.
Now that you’ve learned a bit about case studies and what they should include, you may be wondering how to start creating great customer story content. Here are a couple of templates you can use to structure your case study.
Template 1 — Challenge-solution-result format
- Start with an engaging title. This should be fewer than 70 characters long for SEO best practices. One of the best ways to approach the title is to include the customer’s name and a hint at the challenge they overcame in the end.
- Create an introduction. Lead with an explanation as to who the customer is, the need they had, and the opportunity they found with a specific product or solution. Writers can also suggest the success the customer experienced with the solution they chose.
- Present the challenge. This should be several paragraphs long and explain the problem the customer faced and the issues they were trying to solve. Details should tie into the company’s products and services naturally. This section needs to be the most relatable to the reader so they can picture themselves in a similar situation.
- Share the solution. Explain which product or service offered was the ideal fit for the customer and why. Feel free to delve into their experience setting up, purchasing, and onboarding the solution.
- Explain the results. Demonstrate the impact of the solution they chose by backing up their positive experience with data. Fill in with customer quotes and tangible, measurable results that show the effect of their choice.
- Ask for action. Include a CTA at the end of the case study that invites readers to reach out for more information, try a demo, or learn more — to nurture them further in the marketing pipeline. What you ask of the reader should tie directly into the goals that were established for the case study in the first place.
Template 2 — Data-driven format
- Start with an engaging title. Be sure to include a statistic or data point in the first 70 characters. Again, it’s best to include the customer’s name as part of the title.
- Create an overview. Share the customer’s background and a short version of the challenge they faced. Present the reason a particular product or service was chosen, and feel free to include quotes from the customer about their selection process.
- Present data point 1. Isolate the first metric that the customer used to define success and explain how the product or solution helped to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Present data point 2. Isolate the second metric that the customer used to define success and explain what the product or solution did to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Present data point 3. Isolate the final metric that the customer used to define success and explain what the product or solution did to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Summarize the results. Reiterate the fact that the customer was able to achieve success thanks to a specific product or service. Include quotes and statements that reflect customer satisfaction and suggest they plan to continue using the solution.
- Ask for action. Include a CTA at the end of the case study that asks readers to reach out for more information, try a demo, or learn more — to further nurture them in the marketing pipeline. Again, remember that this is where marketers can look to convert their content into action with the customer.
While templates are helpful, seeing a case study in action can also be a great way to learn. Here are some examples of how Adobe customers have experienced success.
Juniper Networks
One example is the Adobe and Juniper Networks case study , which puts the reader in the customer’s shoes. The beginning of the story quickly orients the reader so that they know exactly who the article is about and what they were trying to achieve. Solutions are outlined in a way that shows Adobe Experience Manager is the best choice and a natural fit for the customer. Along the way, quotes from the client are incorporated to help add validity to the statements. The results in the case study are conveyed with clear evidence of scale and volume using tangible data.

The story of Lenovo’s journey with Adobe is one that spans years of planning, implementation, and rollout. The Lenovo case study does a great job of consolidating all of this into a relatable journey that other enterprise organizations can see themselves taking, despite the project size. This case study also features descriptive headers and compelling visual elements that engage the reader and strengthen the content.
Tata Consulting
When it comes to using data to show customer results, this case study does an excellent job of conveying details and numbers in an easy-to-digest manner. Bullet points at the start break up the content while also helping the reader understand exactly what the case study will be about. Tata Consulting used Adobe to deliver elevated, engaging content experiences for a large telecommunications client of its own — an objective that’s relatable for a lot of companies.
Case studies are a vital tool for any marketing team as they enable you to demonstrate the value of your company’s products and services to others. They help marketers do their job and add credibility to a brand trying to promote its solutions by using the experiences and stories of real customers.
When you’re ready to get started with a case study:
- Think about a few goals you’d like to accomplish with your content.
- Make a list of successful clients that would be strong candidates for a case study.
- Reach out to the client to get their approval and conduct an interview.
- Gather the data to present an engaging and effective customer story.
Adobe can help
There are several Adobe products that can help you craft compelling case studies. Adobe Experience Platform helps you collect data and deliver great customer experiences across every channel. Once you’ve created your case studies, Experience Platform will help you deliver the right information to the right customer at the right time for maximum impact.
To learn more, watch the Adobe Experience Platform story .
Keep in mind that the best case studies are backed by data. That’s where Adobe Real-Time Customer Data Platform and Adobe Analytics come into play. With Real-Time CDP, you can gather the data you need to build a great case study and target specific customers to deliver the content to the right audience at the perfect moment.
Watch the Real-Time CDP overview video to learn more.
Finally, Adobe Analytics turns real-time data into real-time insights. It helps your business collect and synthesize data from multiple platforms to make more informed decisions and create the best case study possible.
Request a demo to learn more about Adobe Analytics.
https://business.adobe.com/blog/perspectives/b2b-ecommerce-10-case-studies-inspire-you
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/business-case
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/what-is-real-time-analytics


The Ultimate Guide to Qualitative Research - Part 1: The Basics

- Introduction and overview
- What is qualitative research?
- What is qualitative data?
- Examples of qualitative data
- Qualitative vs. quantitative research
- Mixed methods
- Qualitative research preparation
- Theoretical perspective
- Theoretical framework
- Literature reviews
Research question
- Conceptual framework
- Conceptual vs. theoretical framework
Data collection
- Qualitative research methods
- Focus groups
- Observational research
What is a case study?
Applications for case study research, what is a good case study, process of case study design, benefits and limitations of case studies.
- Ethnographical research
- Ethical considerations
- Confidentiality and privacy
- Power dynamics
- Reflexivity
Case studies
Case studies are essential to qualitative research , offering a lens through which researchers can investigate complex phenomena within their real-life contexts. This chapter explores the concept, purpose, applications, examples, and types of case studies and provides guidance on how to conduct case study research effectively.

Whereas quantitative methods look at phenomena at scale, case study research looks at a concept or phenomenon in considerable detail. While analyzing a single case can help understand one perspective regarding the object of research inquiry, analyzing multiple cases can help obtain a more holistic sense of the topic or issue. Let's provide a basic definition of a case study, then explore its characteristics and role in the qualitative research process.
Definition of a case study
A case study in qualitative research is a strategy of inquiry that involves an in-depth investigation of a phenomenon within its real-world context. It provides researchers with the opportunity to acquire an in-depth understanding of intricate details that might not be as apparent or accessible through other methods of research. The specific case or cases being studied can be a single person, group, or organization – demarcating what constitutes a relevant case worth studying depends on the researcher and their research question .
Among qualitative research methods , a case study relies on multiple sources of evidence, such as documents, artifacts, interviews , or observations , to present a complete and nuanced understanding of the phenomenon under investigation. The objective is to illuminate the readers' understanding of the phenomenon beyond its abstract statistical or theoretical explanations.
Characteristics of case studies
Case studies typically possess a number of distinct characteristics that set them apart from other research methods. These characteristics include a focus on holistic description and explanation, flexibility in the design and data collection methods, reliance on multiple sources of evidence, and emphasis on the context in which the phenomenon occurs.
Furthermore, case studies can often involve a longitudinal examination of the case, meaning they study the case over a period of time. These characteristics allow case studies to yield comprehensive, in-depth, and richly contextualized insights about the phenomenon of interest.
The role of case studies in research
Case studies hold a unique position in the broader landscape of research methods aimed at theory development. They are instrumental when the primary research interest is to gain an intensive, detailed understanding of a phenomenon in its real-life context.
In addition, case studies can serve different purposes within research - they can be used for exploratory, descriptive, or explanatory purposes, depending on the research question and objectives. This flexibility and depth make case studies a valuable tool in the toolkit of qualitative researchers.
Remember, a well-conducted case study can offer a rich, insightful contribution to both academic and practical knowledge through theory development or theory verification, thus enhancing our understanding of complex phenomena in their real-world contexts.
What is the purpose of a case study?
Case study research aims for a more comprehensive understanding of phenomena, requiring various research methods to gather information for qualitative analysis . Ultimately, a case study can allow the researcher to gain insight into a particular object of inquiry and develop a theoretical framework relevant to the research inquiry.
Why use case studies in qualitative research?
Using case studies as a research strategy depends mainly on the nature of the research question and the researcher's access to the data.
Conducting case study research provides a level of detail and contextual richness that other research methods might not offer. They are beneficial when there's a need to understand complex social phenomena within their natural contexts.
The explanatory, exploratory, and descriptive roles of case studies
Case studies can take on various roles depending on the research objectives. They can be exploratory when the research aims to discover new phenomena or define new research questions; they are descriptive when the objective is to depict a phenomenon within its context in a detailed manner; and they can be explanatory if the goal is to understand specific relationships within the studied context. Thus, the versatility of case studies allows researchers to approach their topic from different angles, offering multiple ways to uncover and interpret the data .
The impact of case studies on knowledge development
Case studies play a significant role in knowledge development across various disciplines. Analysis of cases provides an avenue for researchers to explore phenomena within their context based on the collected data.

This can result in the production of rich, practical insights that can be instrumental in both theory-building and practice. Case studies allow researchers to delve into the intricacies and complexities of real-life situations, uncovering insights that might otherwise remain hidden.
Types of case studies
In qualitative research , a case study is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Depending on the nature of the research question and the specific objectives of the study, researchers might choose to use different types of case studies. These types differ in their focus, methodology, and the level of detail they provide about the phenomenon under investigation.
Understanding these types is crucial for selecting the most appropriate approach for your research project and effectively achieving your research goals. Let's briefly look at the main types of case studies.
Exploratory case studies
Exploratory case studies are typically conducted to develop a theory or framework around an understudied phenomenon. They can also serve as a precursor to a larger-scale research project. Exploratory case studies are useful when a researcher wants to identify the key issues or questions which can spur more extensive study or be used to develop propositions for further research. These case studies are characterized by flexibility, allowing researchers to explore various aspects of a phenomenon as they emerge, which can also form the foundation for subsequent studies.
Descriptive case studies
Descriptive case studies aim to provide a complete and accurate representation of a phenomenon or event within its context. These case studies are often based on an established theoretical framework, which guides how data is collected and analyzed. The researcher is concerned with describing the phenomenon in detail, as it occurs naturally, without trying to influence or manipulate it.
Explanatory case studies
Explanatory case studies are focused on explanation - they seek to clarify how or why certain phenomena occur. Often used in complex, real-life situations, they can be particularly valuable in clarifying causal relationships among concepts and understanding the interplay between different factors within a specific context.

Intrinsic, instrumental, and collective case studies
These three categories of case studies focus on the nature and purpose of the study. An intrinsic case study is conducted when a researcher has an inherent interest in the case itself. Instrumental case studies are employed when the case is used to provide insight into a particular issue or phenomenon. A collective case study, on the other hand, involves studying multiple cases simultaneously to investigate some general phenomena.
Each type of case study serves a different purpose and has its own strengths and challenges. The selection of the type should be guided by the research question and objectives, as well as the context and constraints of the research.
The flexibility, depth, and contextual richness offered by case studies make this approach an excellent research method for various fields of study. They enable researchers to investigate real-world phenomena within their specific contexts, capturing nuances that other research methods might miss. Across numerous fields, case studies provide valuable insights into complex issues.
Critical information systems research
Case studies provide a detailed understanding of the role and impact of information systems in different contexts. They offer a platform to explore how information systems are designed, implemented, and used and how they interact with various social, economic, and political factors. Case studies in this field often focus on examining the intricate relationship between technology, organizational processes, and user behavior, helping to uncover insights that can inform better system design and implementation.
Health research
Health research is another field where case studies are highly valuable. They offer a way to explore patient experiences, healthcare delivery processes, and the impact of various interventions in a real-world context.

Case studies can provide a deep understanding of a patient's journey, giving insights into the intricacies of disease progression, treatment effects, and the psychosocial aspects of health and illness.
Asthma research studies
Specifically within medical research, studies on asthma often employ case studies to explore the individual and environmental factors that influence asthma development, management, and outcomes. A case study can provide rich, detailed data about individual patients' experiences, from the triggers and symptoms they experience to the effectiveness of various management strategies. This can be crucial for developing patient-centered asthma care approaches.
Other fields
Apart from the fields mentioned, case studies are also extensively used in business and management research, education research, and political sciences, among many others. They provide an opportunity to delve into the intricacies of real-world situations, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of various phenomena.
Case studies, with their depth and contextual focus, offer unique insights across these varied fields. They allow researchers to illuminate the complexities of real-life situations, contributing to both theory and practice.
Whatever field you're in, ATLAS.ti puts your data to work for you
Download a free trial of ATLAS.ti to turn your data into insights.
Understanding the key elements of case study design is crucial for conducting rigorous and impactful case study research. A well-structured design guides the researcher through the process, ensuring that the study is methodologically sound and its findings are reliable and valid. The main elements of case study design include the research question , propositions, units of analysis, and the logic linking the data to the propositions.
The research question is the foundation of any research study. A good research question guides the direction of the study and informs the selection of the case, the methods of collecting data, and the analysis techniques. A well-formulated research question in case study research is typically clear, focused, and complex enough to merit further detailed examination of the relevant case(s).
Propositions
Propositions, though not necessary in every case study, provide a direction by stating what we might expect to find in the data collected. They guide how data is collected and analyzed by helping researchers focus on specific aspects of the case. They are particularly important in explanatory case studies, which seek to understand the relationships among concepts within the studied phenomenon.
Units of analysis
The unit of analysis refers to the case, or the main entity or entities that are being analyzed in the study. In case study research, the unit of analysis can be an individual, a group, an organization, a decision, an event, or even a time period. It's crucial to clearly define the unit of analysis, as it shapes the qualitative data analysis process by allowing the researcher to analyze a particular case and synthesize analysis across multiple case studies to draw conclusions.
Argumentation
This refers to the inferential model that allows researchers to draw conclusions from the data. The researcher needs to ensure that there is a clear link between the data, the propositions (if any), and the conclusions drawn. This argumentation is what enables the researcher to make valid and credible inferences about the phenomenon under study.
Understanding and carefully considering these elements in the design phase of a case study can significantly enhance the quality of the research. It can help ensure that the study is methodologically sound and its findings contribute meaningful insights about the case.
Ready to jumpstart your research with ATLAS.ti?
Conceptualize your research project with our intuitive data analysis interface. Download a free trial today.
Conducting a case study involves several steps, from defining the research question and selecting the case to collecting and analyzing data . This section outlines these key stages, providing a practical guide on how to conduct case study research.
Defining the research question
The first step in case study research is defining a clear, focused research question. This question should guide the entire research process, from case selection to analysis. It's crucial to ensure that the research question is suitable for a case study approach. Typically, such questions are exploratory or descriptive in nature and focus on understanding a phenomenon within its real-life context.
Selecting and defining the case
The selection of the case should be based on the research question and the objectives of the study. It involves choosing a unique example or a set of examples that provide rich, in-depth data about the phenomenon under investigation. After selecting the case, it's crucial to define it clearly, setting the boundaries of the case, including the time period and the specific context.
Previous research can help guide the case study design. When considering a case study, an example of a case could be taken from previous case study research and used to define cases in a new research inquiry. Considering recently published examples can help understand how to select and define cases effectively.
Developing a detailed case study protocol
A case study protocol outlines the procedures and general rules to be followed during the case study. This includes the data collection methods to be used, the sources of data, and the procedures for analysis. Having a detailed case study protocol ensures consistency and reliability in the study.
The protocol should also consider how to work with the people involved in the research context to grant the research team access to collecting data. As mentioned in previous sections of this guide, establishing rapport is an essential component of qualitative research as it shapes the overall potential for collecting and analyzing data.
Collecting data
Gathering data in case study research often involves multiple sources of evidence, including documents, archival records, interviews, observations, and physical artifacts. This allows for a comprehensive understanding of the case. The process for gathering data should be systematic and carefully documented to ensure the reliability and validity of the study.
Analyzing and interpreting data
The next step is analyzing the data. This involves organizing the data , categorizing it into themes or patterns , and interpreting these patterns to answer the research question. The analysis might also involve comparing the findings with prior research or theoretical propositions.
Writing the case study report
The final step is writing the case study report . This should provide a detailed description of the case, the data, the analysis process, and the findings. The report should be clear, organized, and carefully written to ensure that the reader can understand the case and the conclusions drawn from it.
Each of these steps is crucial in ensuring that the case study research is rigorous, reliable, and provides valuable insights about the case.
The type, depth, and quality of data in your study can significantly influence the validity and utility of the study. In case study research, data is usually collected from multiple sources to provide a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case. This section will outline the various methods of collecting data used in case study research and discuss considerations for ensuring the quality of the data.
Interviews are a common method of gathering data in case study research. They can provide rich, in-depth data about the perspectives, experiences, and interpretations of the individuals involved in the case. Interviews can be structured , semi-structured , or unstructured , depending on the research question and the degree of flexibility needed.
Observations
Observations involve the researcher observing the case in its natural setting, providing first-hand information about the case and its context. Observations can provide data that might not be revealed in interviews or documents, such as non-verbal cues or contextual information.
Documents and artifacts
Documents and archival records provide a valuable source of data in case study research. They can include reports, letters, memos, meeting minutes, email correspondence, and various public and private documents related to the case.

These records can provide historical context, corroborate evidence from other sources, and offer insights into the case that might not be apparent from interviews or observations.
Physical artifacts refer to any physical evidence related to the case, such as tools, products, or physical environments. These artifacts can provide tangible insights into the case, complementing the data gathered from other sources.
Ensuring the quality of data collection
Determining the quality of data in case study research requires careful planning and execution. It's crucial to ensure that the data is reliable, accurate, and relevant to the research question. This involves selecting appropriate methods of collecting data, properly training interviewers or observers, and systematically recording and storing the data. It also includes considering ethical issues related to collecting and handling data, such as obtaining informed consent and ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of the participants.
Data analysis
Analyzing case study research involves making sense of the rich, detailed data to answer the research question. This process can be challenging due to the volume and complexity of case study data. However, a systematic and rigorous approach to analysis can ensure that the findings are credible and meaningful. This section outlines the main steps and considerations in analyzing data in case study research.
Organizing the data
The first step in the analysis is organizing the data. This involves sorting the data into manageable sections, often according to the data source or the theme. This step can also involve transcribing interviews, digitizing physical artifacts, or organizing observational data.
Categorizing and coding the data
Once the data is organized, the next step is to categorize or code the data. This involves identifying common themes, patterns, or concepts in the data and assigning codes to relevant data segments. Coding can be done manually or with the help of software tools, and in either case, qualitative analysis software can greatly facilitate the entire coding process. Coding helps to reduce the data to a set of themes or categories that can be more easily analyzed.
Identifying patterns and themes
After coding the data, the researcher looks for patterns or themes in the coded data. This involves comparing and contrasting the codes and looking for relationships or patterns among them. The identified patterns and themes should help answer the research question.
Interpreting the data
Once patterns and themes have been identified, the next step is to interpret these findings. This involves explaining what the patterns or themes mean in the context of the research question and the case. This interpretation should be grounded in the data, but it can also involve drawing on theoretical concepts or prior research.
Verification of the data
The last step in the analysis is verification. This involves checking the accuracy and consistency of the analysis process and confirming that the findings are supported by the data. This can involve re-checking the original data, checking the consistency of codes, or seeking feedback from research participants or peers.
Like any research method , case study research has its strengths and limitations. Researchers must be aware of these, as they can influence the design, conduct, and interpretation of the study.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of case study research can also guide researchers in deciding whether this approach is suitable for their research question . This section outlines some of the key strengths and limitations of case study research.
Benefits include the following:
- Rich, detailed data: One of the main strengths of case study research is that it can generate rich, detailed data about the case. This can provide a deep understanding of the case and its context, which can be valuable in exploring complex phenomena.
- Flexibility: Case study research is flexible in terms of design , data collection , and analysis . A sufficient degree of flexibility allows the researcher to adapt the study according to the case and the emerging findings.
- Real-world context: Case study research involves studying the case in its real-world context, which can provide valuable insights into the interplay between the case and its context.
- Multiple sources of evidence: Case study research often involves collecting data from multiple sources , which can enhance the robustness and validity of the findings.
On the other hand, researchers should consider the following limitations:
- Generalizability: A common criticism of case study research is that its findings might not be generalizable to other cases due to the specificity and uniqueness of each case.
- Time and resource intensive: Case study research can be time and resource intensive due to the depth of the investigation and the amount of collected data.
- Complexity of analysis: The rich, detailed data generated in case study research can make analyzing the data challenging.
- Subjectivity: Given the nature of case study research, there may be a higher degree of subjectivity in interpreting the data , so researchers need to reflect on this and transparently convey to audiences how the research was conducted.
Being aware of these strengths and limitations can help researchers design and conduct case study research effectively and interpret and report the findings appropriately.

Ready to analyze your data with ATLAS.ti?
See how our intuitive software can draw key insights from your data with a free trial today.
Business growth
Marketing tips
16 case study examples (+ 3 templates to make your own)
I like to think of case studies as a business's version of a resume. It highlights what the business can do, lends credibility to its offer, and contains only the positive bullet points that paint it in the best light possible.
Imagine if the guy running your favorite taco truck followed you home so that he could "really dig into how that burrito changed your life." I see the value in the practice. People naturally prefer a tried-and-true burrito just as they prefer tried-and-true products or services.
To help you showcase your success and flesh out your burrito questionnaire, I've put together some case study examples and key takeaways.
What is a case study?
A case study is an in-depth analysis of how your business, product, or service has helped past clients. It can be a document, a webpage, or a slide deck that showcases measurable, real-life results.
For example, if you're a SaaS company, you can analyze your customers' results after a few months of using your product to measure its effectiveness. You can then turn this analysis into a case study that further proves to potential customers what your product can do and how it can help them overcome their challenges.
It changes the narrative from "I promise that we can do X and Y for you" to "Here's what we've done for businesses like yours, and we can do it for you, too."
16 case study examples
While most case studies follow the same structure, quite a few try to break the mold and create something unique. Some businesses lean heavily on design and presentation, while others pursue a detailed, stat-oriented approach. Some businesses try to mix both.
There's no set formula to follow, but I've found that the best case studies utilize impactful design to engage readers and leverage statistics and case details to drive the point home. A case study typically highlights the companies, the challenges, the solution, and the results. The examples below will help inspire you to do it, too.
1. .css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class]{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;cursor:pointer;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class]{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} Volcanica Coffee and AdRoll

People love a good farm-to-table coffee story, and boy am I one of them. But I've shared this case study with you for more reasons than my love of coffee. I enjoyed this study because it was written as though it was a letter.
In this case study, the founder of Volcanica Coffee talks about the journey from founding the company to personally struggling with learning and applying digital marketing to finding and enlisting AdRoll's services.
It felt more authentic, less about AdRoll showcasing their worth and more like a testimonial from a grateful and appreciative client. After the story, the case study wraps up with successes, milestones, and achievements. Note that quite a few percentages are prominently displayed at the top, providing supporting evidence that backs up an inspiring story.
Takeaway: Highlight your goals and measurable results to draw the reader in and provide concise, easily digestible information.
2. Taylor Guitars and Airtable

This Airtable case study on Taylor Guitars comes as close as one can to an optimal structure. It features a video that represents the artistic nature of the client, highlighting key achievements and dissecting each element of Airtable's influence.
It also supplements each section with a testimonial or quote from the client, using their insights as a catalyst for the case study's narrative. For example, the case study quotes the social media manager and project manager's insights regarding team-wide communication and access before explaining in greater detail.
Takeaway: Highlight pain points your business solves for its client, and explore that influence in greater detail.
3. EndeavourX and Figma

My favorite part of Figma's case study is highlighting why EndeavourX chose its solution. You'll notice an entire section on what Figma does for teams and then specifically for EndeavourX.
It also places a heavy emphasis on numbers and stats. The study, as brief as it is, still manages to pack in a lot of compelling statistics about what's possible with Figma.
Takeaway: Showcase the "how" and "why" of your product's differentiators and how they benefit your customers.
4. ActiveCampaign and Zapier

Zapier's case study leans heavily on design, using graphics to present statistics and goals in a manner that not only remains consistent with the branding but also actively pushes it forward, drawing users' eyes to the information most important to them.
The graphics, emphasis on branding elements, and cause/effect style tell the story without requiring long, drawn-out copy that risks boring readers. Instead, the cause and effect are concisely portrayed alongside the client company's information for a brief and easily scannable case study.
Takeaway: Lean on design to call attention to the most important elements of your case study, and make sure it stays consistent with your branding.
5. Ironclad and OpenAI
In true OpenAI fashion, this case study is a block of text. There's a distinct lack of imagery, but the study features a narrated video walking readers through the product.
The lack of imagery and color may not be the most inviting, but utilizing video format is commendable. It helps thoroughly communicate how OpenAI supported Ironclad in a way that allows the user to sit back, relax, listen, and be impressed.
Takeaway: Get creative with the media you implement in your case study. Videos can be a very powerful addition when a case study requires more detailed storytelling.
6. Shopify and GitHub

GitHub's case study on Shopify is a light read. It addresses client pain points and discusses the different aspects its product considers and improves for clients. It touches on workflow issues, internal systems, automation, and security. It does a great job of representing what one company can do with GitHub.
To drive the point home, the case study features colorful quote callouts from the Shopify team, sharing their insights and perspectives on the partnership, the key issues, and how they were addressed.
Takeaway: Leverage quotes to boost the authoritativeness and trustworthiness of your case study.
7 . Audible and Contentful

Contentful's case study on Audible features almost every element a case study should. It includes not one but two videos and clearly outlines the challenge, solution, and outcome before diving deeper into what Contentful did for Audible. The language is simple, and the writing is heavy with quotes and personal insights.
This case study is a uniquely original experience. The fact that the companies in question are perhaps two of the most creative brands out there may be the reason. I expected nothing short of a detailed analysis, a compelling story, and video content.
Takeaway: Inject some brand voice into the case study, and create assets that tell the story for you.
8 . Zoom and Asana
Asana's case study on Zoom is longer than the average piece and features detailed data on Zoom's growth since 2020. Instead of relying on imagery and graphics, it features several quotes and testimonials.
It's designed to be direct, informative, and promotional. At some point, the case study reads more like a feature list. There were a few sections that felt a tad too promotional for my liking, but to each their own burrito.
Takeaway: Maintain a balance between promotional and informative. You want to showcase the high-level goals your product helped achieve without losing the reader.
9 . Hickies and Mailchimp

I've always been a fan of Mailchimp's comic-like branding, and this case study does an excellent job of sticking to their tradition of making information easy to understand, casual, and inviting.
It features a short video that briefly covers Hickies as a company and Mailchimp's efforts to serve its needs for customer relationships and education processes. Overall, this case study is a concise overview of the partnership that manages to convey success data and tell a story at the same time. What sets it apart is that it does so in a uniquely colorful and brand-consistent manner.
Takeaway: Be concise to provide as much value in as little text as possible.
10. NVIDIA and Workday
The gaming industry is notoriously difficult to recruit for, as it requires a very specific set of skills and experience. This case study focuses on how Workday was able to help fill that recruitment gap for NVIDIA, one of the biggest names in the gaming world.
Though it doesn't feature videos or graphics, this case study stood out to me in how it structures information like "key products used" to give readers insight into which tools helped achieve these results.
Takeaway: If your company offers multiple products or services, outline exactly which ones were involved in your case study, so readers can assess each tool.
11. KFC and Contentful
I'm personally not a big KFC fan, but that's only because I refuse to eat out of a bucket. My aversion to the bucket format aside, Contentful follows its consistent case study format in this one, outlining challenges, solutions, and outcomes before diving into the nitty-gritty details of the project.
Say what you will about KFC, but their primary product (chicken) does present a unique opportunity for wordplay like "Continuing to march to the beat of a digital-first drum(stick)" or "Delivering deep-fried goodness to every channel."
Takeaway: Inject humor into your case study if there's room for it and if it fits your brand.
12. Intuit and Twilio

Twilio does an excellent job of delivering achievements at the very beginning of the case study and going into detail in this two-minute read. While there aren't many graphics, the way quotes from the Intuit team are implemented adds a certain flair to the study and breaks up the sections nicely.
It's simple, concise, and manages to fit a lot of information in easily digestible sections.
Takeaway: Make sure each section is long enough to inform but brief enough to avoid boring readers. Break down information for each section, and don't go into so much detail that you lose the reader halfway through.
13. Spotify and Salesforce

Salesforce created a video that accurately summarizes the key points of the case study. Beyond that, the page itself is very light on content, and sections are as short as one paragraph.
I especially like how information is broken down into "What you need to know," "Why it matters," and "What the difference looks like." I'm not ashamed of being spoon-fed information. When it's structured so well and so simply, it makes for an entertaining read.
Takeaway: Invest in videos that capture and promote your partnership with your case study subject. Video content plays a promotional role that extends beyond the case study in social media and marketing initiatives .
14. Benchling and Airtable

Benchling is an impressive entity in its own right. Biotech R&D and health care nuances go right over my head. But the research and digging I've been doing in the name of these burritos (case studies) revealed that these products are immensely complex.
And that's precisely why this case study deserves a read—it succeeds at explaining a complex project that readers outside the industry wouldn't know much about.
Takeaway: Simplify complex information, and walk readers through the company's operations and how your business helped streamline them.
15. Chipotle and Hubble

The concision of this case study is refreshing. It features two sections—the challenge and the solution—all in 316 words. This goes to show that your case study doesn't necessarily need to be a four-figure investment with video shoots and studio time.
Sometimes, the message is simple and short enough to convey in a handful of paragraphs.
Takeaway: Consider what you should include instead of what you can include. Assess the time, resources, and effort you're able and willing to invest in a case study, and choose which elements you want to include from there.
16. Hudl and Zapier
I may be biased, but I'm a big fan of seeing metrics and achievements represented in branded graphics. It can be a jarring experience to navigate a website, then visit a case study page and feel as though you've gone to a completely different website.
The Zapier format provides nuggets of high-level insights, milestones, and achievements, as well as the challenge, solution, and results. My favorite part of this case study is how it's supplemented with a blog post detailing how Hudl uses Zapier automation to build a seamless user experience.
The case study is essentially the summary, and the blog article is the detailed analysis that provides context beyond X achievement or Y goal.
Takeaway: Keep your case study concise and informative. Create other resources to provide context under your blog, media or press, and product pages.
3 case study templates
Now that you've had your fill of case studies (if that's possible), I've got just what you need: an infinite number of case studies, which you can create yourself with these case study templates.
Case study template 1

If you've got a quick hit of stats you want to show off, try this template. The opening section gives space for a short summary and three visually appealing stats you can highlight, followed by a headline and body where you can break the case study down more thoroughly. This one's pretty simple, with only sections for solutions and results, but you can easily continue the formatting to add more sections as needed.
Case study template 2

For a case study template with a little more detail, use this one. Opening with a striking cover page for a quick overview, this one goes on to include context, stakeholders, challenges, multiple quote callouts, and quick-hit stats.
Case study template 3

Whether you want a little structural variation or just like a nice dark green, this template has similar components to the last template but is designed to help tell a story. Move from the client overview through a description of your company before getting to the details of how you fixed said company's problems.
Tips for writing a case study
Examples are all well and good, but you don't learn how to make a burrito just by watching tutorials on YouTube without knowing what any of the ingredients are. You could , but it probably wouldn't be all that good.
Writing a good case study comes down to a mix of creativity, branding, and the capacity to invest in the project. With those details in mind, here are some case study tips to follow:
Have an objective: Define your objective by identifying the challenge, solution, and results. Assess your work with the client and focus on the most prominent wins. You're speaking to multiple businesses and industries through the case study, so make sure you know what you want to say to them.
Focus on persuasive data: Growth percentages and measurable results are your best friends. Extract your most compelling data and highlight it in your case study.
Use eye-grabbing graphics: Branded design goes a long way in accurately representing your brand and retaining readers as they review the study. Leverage unique and eye-catching graphics to keep readers engaged.
Simplify data presentation: Some industries are more complex than others, and sometimes, data can be difficult to understand at a glance. Make sure you present your data in the simplest way possible. Make it concise, informative, and easy to understand.
Use automation to drive results for your case study
A case study example is a source of inspiration you can leverage to determine how to best position your brand's work. Find your unique angle, and refine it over time to help your business stand out. Ask anyone: the best burrito in town doesn't just appear at the number one spot. They find their angle (usually the house sauce) and leverage it to stand out.
In fact, with the right technology, it can be refined to work better . Explore how Zapier's automation features can help drive results for your case study by making your case study a part of a developed workflow that creates a user journey through your website, your case studies, and into the pipeline.
Case study FAQ
Got your case study template? Great—it's time to gather the team for an awkward semi-vague data collection task. While you do that, here are some case study quick answers for you to skim through while you contemplate what to call your team meeting.
What is an example of a case study?
An example of a case study is when a software company analyzes its results from a client project and creates a webpage, presentation, or document that focuses on high-level results, challenges, and solutions in an attempt to showcase effectiveness and promote the software.
How do you write a case study?
To write a good case study, you should have an objective, identify persuasive and compelling data, leverage graphics, and simplify data. Case studies typically include an analysis of the challenge, solution, and results of the partnership.
What is the format of a case study?
While case studies don't have a set format, they're often portrayed as reports or essays that inform readers about the partnership and its results.
Related reading:
How Hudl uses automation to create a seamless user experience
How to make your case studies high-stakes—and why it matters
How experts write case studies that convert, not bore
Get productivity tips delivered straight to your inbox
We’ll email you 1-3 times per week—and never share your information.

Hachem Ramki
Hachem is a writer and digital marketer from Montreal. After graduating with a degree in English, Hachem spent seven years traveling around the world before moving to Canada. When he's not writing, he enjoys Basketball, Dungeons and Dragons, and playing music for friends and family.
- Content marketing
Related articles

14 types of email marketing to experiment with
14 types of email marketing to experiment...
8 business anniversary marketing ideas and examples worth celebrating
8 business anniversary marketing ideas and...
A guide to verticalization: What it is, when to try it, and how to get started
A guide to verticalization: What it is, when...

12 Facebook ad copy examples to learn from
Improve your productivity automatically. Use Zapier to get your apps working together.

The Ultimate Guide on Writing an A+ Case Study Analysis + 15 Examples

Struggle with writing a case study analysis? You are in the right place! Below, we will show you nuts and bolts of this type of paper, how to write it, and share 15 distinct essay examples. Plus, you will find the case study checklist to keep your writing on track.
What is a Case Study Analysis?
Case study analysis topics.
- Important Aspects
You might ask, what is a case study analysis ? With this type of work, you take an actual situation from a specific discipline, such as business or education. The goal is to find a solution, analyze the outcomes of the situation, or evaluate it.

Case study analysis does not target one specific theory or piece of knowledge. It requires a universal application of several theories and methods for research and review. Hence, it can be helpful for many disciplines at once. If you need to look at some examples, head over to our essay database .
There are several steps you need to take for a successful analysis depending on the type of your case study. Here are the most critical universal points:
- Analyze the problem from different perspectives. Use the theories and methods you have learned about in the classroom.
- Devise a series of solutions or outcomes. You need to analyze their advantages and weaknesses.
- Provide the best solution according to your analysis. You must present solid arguments for why you have suggested it.
- Demonstrate well-grounded research in your case study analysis You should not make claims without proof.
- Provide credible references for any theory that you mention in your analysis. You do not want your work to be discarded because of plagiarism.
If you want to start the business in the future, case study analysis is essential for your education. It can give you a taste of what your career is might include.
Are you panicking because you have never written anything like this before? Don’t worry! After going through the guidelines in this article, you will get a better sense of what is required from you. It will not seem as scary anymore. 😊
- Business ethics: the case study
- Comparing Johnson and Johnson and Pfizer vaccines
- Theories of criminal law
- Recklessness as a symptom of antisocial personality disorder
- Differences between nursing care & residential care
- Strengths and weaknesses of Microsoft Corporation
- Farming the Cerrado : advantages and disadvantages of soybean farming in Brazil
- McKinsey opioid scandal: the case study
- General Electric vs. General Motors
- How much longer will Lake Mead last?
- Organizational issues of the City Centre Hospital
- How to use fact patterns to your advantage
- Prevention and control of sexually transmitted infections
- The role of gender in the workplace
- Blue ocean market: Uber case study
- Five stages of a child’s development
- The importance of health history in treating severe pain
- How does Equifax protect personal data?
- Adidas and healthy lifestyle promotion
- Long-term value for the organization as a result of high-quality customer service
- The missions of community-based clinics
- Operations management: Apple case study
- Emergency management of Fournier’s gangrene
- The outcome of the Hamdi v. Rumsfeld case
- What are the seven principles of ethics in research?
- Tea Leaves and More : issues and solutions
- The effect of transformational leadership on employee productivity
- Inventory management as a solution for understocking and overstocking
- Strength and conditioning training: the case study
- History of Nike corporation
- Positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia
- Anxiety-related habits during post-traumatic stress disorder
- The issue of Starbucks employees wearing union pins
- How does Delta Airlines increase its competitive advantage?
- Why was Anne Hutchinson a threat to authorities?
15 Case Study Analysis Examples
We have prepared 15 examples of case study analysis, so you can get an idea of how they should look. The disciplines are broad and there is something here for everyone. Check out the table below!
Let’s concentrate on the format for case study analysis!
Case Study Analysis: Format
In this section, we will get you acquainted with different types of case studies. We will focus on the difference between multiple and single case study analysis. Additionally, we will show you how to organize all of your ideas into an outline. Hence, your work will be understandable and complete.
- Types of Case Studies
There are several distinct types of case studies , each with its nuances. The choice will depend on the needs of your investigation. We will focus on Illustrative, Exploratory, Cumulative, and Critical Instance studies. Let’s explore each of them one by one.
- Illustrative Case Studies Illustrative case studies are the most common type. They are very descriptive, and the main goal is to help you understand the situation. You are typically given one or two instances of an event. Illustrative case studies answer two questions: What is happening? Why is it happening? The case study is explained in great detail, including location, key players, roles, influence, and involvement. The focus of illustrative case studies is to maintain the reader’s interest. Hence, the language should be understandable, but it should not be oversimplified. It is not preferred to quote more than two instances as the case study might become too complicated.
- Exploratory Case Studies Exploratory case studies are mainly used in Social Sciences. They tend to focus on real-life contexts for situations. They are implemented before a large-scale investigation to help develop the case for more advanced research processes. Exploratory case studies aim to research a specific topic in detail to help you reach a complete understanding of it. You need to identify questions that can later be answered as part of a more extensive examination. Your initial research might reveal very persuasive details. However, it is crucial to remember that concluding before the large-scale investigation is counterproductive.
- Cumulative Case Studies The idea of a cumulative case study is to gather information and details from many data sources to claim a general phenomenon. Cumulative case studies eliminate the need for additional and expensive new studies, which are simply repetitions of the old ones. If you properly analyze all of the case study data that exists, you will realize that everything you are looking for is already there. However, it is essential to look at the existing research from a new perspective to ensure it fits the current challenges and needs.
- Critical Instance Case Studies Critical instance case studies are similar to cumulative but work oppositely. Instead of defining a general phenomenon based on little research, it tries to understand a specific case based on generalized findings. Critical instance case studies help answer cause and effect questions. The adequate specification of your evaluation question is the most crucial part of your analysis.
- Single vs. Multiple Case Study
Your case study can either include a single case or multiple cases . In this section, we will discuss the benefits of both:
- Single Case Study Single case studies are less expensive and do not take as much time. When examining one case, it is easier to put all of your energy into it and get a deeper understanding of the subject. Since the study is more careful, you can look at one thing from many different perspectives. Usually, in a single case study, the case is more critical and unique , and it is possible to focus on a more longitudinal research.
- Multiple Case Study When studying several cases, you can understand the critical similarities and differences among them. If you base your research on many cases, it will be more robust and reliable. Such analysis allows you to form broader research questions. Hence, you can end up with a more convincing theory.
Now, let’s talk about the backbone of every study: the outline!

Case Study Outline
Before writing any paper, you should first prepare an outline. It not only makes your job easier but also enhances the organization of your paper. You should put all of your ideas down and try to understand which order and format will best suit your analysis.
We have tried to simplify the process by preparing a sample outline for your case study analysis. It will help you understand what your paper should include.
- Introduction Firstly, you should introduce your reader to the case, assuming they have no prior knowledge. Describe all the challenges and mention the most important details.
- Answers to the Questions There will probably be some questions about your case. It would be best if you answered all of them in an organized manner. Make sure not to make it too obvious. Answer them in such a way that it seems like a part of your analysis.
- Challenges Though you talk about the challenges in your introduction a little bit, it is essential to go into more detail within the main paragraphs to make sure your readers understand them. It will improve the comprehension of solutions later.
- Solutions Introduce each solution you have devised. Evaluate those based on different theories and mechanisms. All of your propositions need to be solid and well-designed. Your case study evaluation should be informative and engaging.
- Final Statement In this part of your paper, you should state which solution best fits the case according to your broader analysis. You should compare it with the others and explain why you have chosen it.
- Conclusion The conclusion is the last thing you need to write. There is nothing specific that should be included. Make sure that your paper comes to a logical end.
- References Of course, you need to reference all of the theories and practices mentioned in your paper for your analysis to be solid and well-grounded. The style of your references will depend on the format assigned by your instructor.
This is how a typical case study analysis should look like. We mentioned this format for you to imagine the standard thought process that goes into making outlines. First, organize your research and divide it into parts to achieve an exciting and compelling paper. The type of case study analysis with which you are dealing also matters.
Now, here’s how you start writing!
How to Write Case Study Analysis: Important Aspects
In this section, you will find everything you need to kickstart writing your paper. Firstly, we will go through the things you need to have ready before you start. Then, we will show you how to do adequate research. Finally, we will give you a case study checklist to make it easier to complete the tasks throughout your analysis.
Before You Start
It is vital to choose an appropriate case study topic first. It should be exciting and relevant to your area of study. Once you select your topic, you need to choose an applicable case study . There are several criteria that you need to keep in mind in your search of a case study:
- The case study should complement your topic of research For example, if the topic you have chosen is related to marketing, it would be weird if your case study was about banking. However, a case study about how a famous company handles its marketing would be very acceptable.
- The case study should apply to the phenomena that you have chosen to research Make sure that the way the company handles its marketing can be generalized to benefit other companies. It needs to be universally reusable.
- The case study cannot be outdated You need to know that you can apply the outcome of your research to the modern world. Everything needs to be analyzed from the perspective of today.
- Decide whether you need a single or multiple case study You can go through the comparison above once again. Try to understand which one suits your topic best.
Do you already have the topic? Let’s get your researching skills up to date!

Case Study Research
When doing case study research, simply googling something rains down tons of sources full of information. However, most of those sources cannot be trusted, especially when writing an academic paper. The references are the most crucial part of such papers. If they are poor, then your essay has no reliable basis. Hence, you need to look for official sources, such as university websites or scholarly articles. Remember that Wikipedia is not a valid source !
Throughout the process, have your research question in mind. It is easy to get carried away and read every exciting article on the topic. Nonetheless, it would be best to have a specific goal to ensure your research is practical and not wasting your time.
Finally, keep your research up to date! Remember that you are looking for information that applies to the current world and its challenges. You need to look for modern solutions to the given problem.
We are almost there! Let’s make sure you can tick off every item in this checklist !
Checklist for Case Study Analysis
Go through this checklist. It will help you keep your case study research and writing on track.
- Choose the topic.
- Decide whether you are going to do single or multiple case study.
- Identify the type of your case study.
- They are relevant to the topic.
- Their outcome can be generalized to fit other cases within the same area of research.
- They are not outdated.
- Define a clear case study research question.
- Make sure that the sources of your research are credible and up to date.
- Identify the theories and methodologies you are going to use to analyze the case.
- Use more than one point of view to examine the case, and look at it from different perspectives.
- Have a clear outline of what you are going to include in your paper.
- Write and proofread your paper.
Have you completed every item on this list? Congratulations! You are done with your case study analysis!
❓ What is the difference between case study and case analysis?
Case study and case analysis both provide you with a topic and require extensive research. However, a case study must be taken from real life. For example, a student might analyze Coca-Cola’s financial results and come up with brilliant results that can significantly impact the company. If you send this kind of case study analysis to the company, you might even get a reward. Case analysis focuses more on problems and solutions, whereas case studies can include general research and evaluation.
❓ What are the stages of a case study?
There are four main stages of a case study:
- analyzing the case,
- identifying its challenges,
- devising a set of possible solutions or outcomes,
- evaluating those outcomes.
To ensure the success of your analysis, you should go over all of these stages with equal diligence.
❓ What is the purpose of a case study?
The purpose of a case study analysis is to describe a case in detail and identify the main issues with it. Afterwards, these issues need to be analyzed based on appropriate theories from the discipline that you have learned about in class. Finally, you need to recommend a list of actions that should be performed for that case.
❓ What are the qualities of a good case study?
Here are some qualities of a good case study:
- It is written in a formal, academic language with good grammar and coherent structure.
- All of the claims made in the case study have a reasonable basis and can be proven.
- The case study does not overload the readers with unnecessary information. It is clear and to the point.
- The information is passed to the reader in an organized manner. It has flow, and it is easy to keep up with the extensive academic research.
- What is a Case Study Analysis
- Illustrative Case Studies
- Exploratory Case Study Example
- Definition of Cumulative Case Studies
- Definition of Critical Instance Case Studies
- A Comparative Study of Single and Multiple Case Studies
- How to Choose an Applicable Study
- Case Study Checklist
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter X
- Share to LinkedIn
You might also like
Being productive at home: 25 tips for students & remote workers, the future is here: assistive technology for learning disabilities, dual degree vs. double major: what’s the difference & are they worth it.
Sales CRM Terms
What is Case Study Analysis? (Explained With Examples)
Oct 11, 2023

Case Study Analysis is a widely used research method that examines in-depth information about a particular individual, group, organization, or event. It is a comprehensive investigative approach that aims to understand the intricacies and complexities of the subject under study. Through the analysis of real-life scenarios and inquiry into various data sources, Case Study Analysis provides valuable insights and knowledge that can be used to inform decision-making and problem-solving strategies.
1°) What is Case Study Analysis?
Case Study Analysis is a research methodology that involves the systematic investigation of a specific case or cases to gain a deep understanding of the subject matter. This analysis encompasses collecting and analyzing various types of data, including qualitative and quantitative information. By examining multiple aspects of the case, such as its context, background, influences, and outcomes, researchers can draw meaningful conclusions and provide valuable insights for various fields of study.
When conducting a Case Study Analysis, researchers typically begin by selecting a case or multiple cases that are relevant to their research question or area of interest. This can involve choosing a specific organization, individual, event, or phenomenon to study. Once the case is selected, researchers gather relevant data through various methods, such as interviews, observations, document analysis, and artifact examination.
The data collected during a Case Study Analysis is then carefully analyzed and interpreted. Researchers use different analytical frameworks and techniques to make sense of the information and identify patterns, themes, and relationships within the data. This process involves coding and categorizing the data, conducting comparative analysis, and drawing conclusions based on the findings.
One of the key strengths of Case Study Analysis is its ability to provide a rich and detailed understanding of a specific case. This method allows researchers to delve deep into the complexities and nuances of the subject matter, uncovering insights that may not be captured through other research methods. By examining the case in its natural context, researchers can gain a holistic perspective and explore the various factors and variables that contribute to the case.
1.1 - Definition of Case Study Analysis
Case Study Analysis can be defined as an in-depth examination and exploration of a particular case or cases to unravel relevant details and complexities associated with the subject being studied. It involves a comprehensive and detailed analysis of various factors and variables that contribute to the case, aiming to answer research questions and uncover insights that can be applied in real-world scenarios.
When conducting a Case Study Analysis, researchers employ a range of research methods and techniques to collect and analyze data. These methods can include interviews, surveys, observations, document analysis, and experiments, among others. By using multiple sources of data, researchers can triangulate their findings and ensure the validity and reliability of their analysis.
Furthermore, Case Study Analysis often involves the use of theoretical frameworks and models to guide the research process. These frameworks provide a structured approach to analyzing the case and help researchers make sense of the data collected. By applying relevant theories and concepts, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the underlying factors and dynamics at play in the case.
1.2 - Advantages of Case Study Analysis
Case Study Analysis offers numerous advantages that make it a popular research method across different disciplines. One significant advantage is its ability to provide rich and detailed information about a specific case, allowing researchers to gain a holistic understanding of the subject matter. Additionally, Case Study Analysis enables researchers to explore complex issues and phenomena in their natural context, capturing the intricacies and nuances that may not be captured through other research methods.
Moreover, Case Study Analysis allows researchers to investigate rare or unique cases that may not be easily replicated or studied through experimental methods. This method is particularly useful when studying phenomena that are complex, multifaceted, or involve multiple variables. By examining real-world cases, researchers can gain insights that can be applied to similar situations or inform future research and practice.
Furthermore, this research method allows for the analysis of multiple sources of data, such as interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, which can contribute to a comprehensive and well-rounded examination of the case. Case Study Analysis also facilitates the exploration and identification of patterns, trends, and relationships within the data, generating valuable insights and knowledge for future reference and application.
1.3 - Disadvantages of Case Study Analysis
While Case Study Analysis offers various advantages, it also comes with certain limitations and challenges. One major limitation is the potential for researcher bias, as the interpretation of data and findings can be influenced by preconceived notions and personal perspectives. Researchers must be aware of their own biases and take steps to minimize their impact on the analysis.
Additionally, Case Study Analysis may suffer from limited generalizability, as it focuses on specific cases and contexts, which might not be applicable or representative of broader populations or situations. The findings of a case study may not be easily generalized to other settings or individuals, and caution should be exercised when applying the results to different contexts.
Moreover, Case Study Analysis can require significant time and resources due to its in-depth nature and the need for meticulous data collection and analysis. This can pose challenges for researchers working with limited budgets or tight deadlines. However, the thoroughness and depth of the analysis often outweigh the resource constraints, as the insights gained from a well-conducted case study can be highly valuable.
Finally, ethical considerations also play a crucial role in Case Study Analysis, as researchers must ensure the protection of participant confidentiality and privacy. Researchers must obtain informed consent from participants and take measures to safeguard their identities and personal information. Ethical guidelines and protocols should be followed to ensure the rights and well-being of the individuals involved in the case study.
2°) Examples of Case Study Analysis
Real-world examples of Case Study Analysis demonstrate the method's practical application and showcase its usefulness across various fields. The following examples provide insights into different scenarios where Case Study Analysis has been employed successfully.
2.1 - Example in a Startup Context
In a startup context, a Case Study Analysis might explore the factors that contributed to the success of a particular startup company. It would involve examining the organization's background, strategies, market conditions, and key decision-making processes. This analysis could reveal valuable lessons and insights for aspiring entrepreneurs and those interested in understanding the intricacies of startup success.
2.2 - Example in a Consulting Context
In the consulting industry, Case Study Analysis is often utilized to understand and develop solutions for complex business problems. For instance, a consulting firm might conduct a Case Study Analysis on a company facing challenges in its supply chain management. This analysis would involve identifying the underlying issues, evaluating different options, and proposing recommendations based on the findings. This approach enables consultants to apply their expertise and provide practical solutions to their clients.
2.3 - Example in a Digital Marketing Agency Context
Within a digital marketing agency, Case Study Analysis can be used to examine successful marketing campaigns. By analyzing various factors such as target audience, message effectiveness, channel selection, and campaign metrics, this analysis can provide valuable insights into the strategies and tactics that contribute to successful marketing initiatives. Digital marketers can then apply these insights to optimize future campaigns and drive better results for their clients.
2.4 - Example with Analogies
Case Study Analysis can also be utilized with analogies to investigate specific scenarios and draw parallels to similar situations. For instance, a Case Study Analysis could explore the response of different countries to natural disasters and draw analogies to inform disaster management strategies in other regions. These analogies can help policymakers and researchers develop more effective approaches to mitigate the impact of disasters and protect vulnerable populations.
In conclusion, Case Study Analysis is a powerful research method that provides a comprehensive understanding of a particular individual, group, organization, or event. By analyzing real-life cases and exploring various data sources, researchers can unravel complexities, generate valuable insights, and inform decision-making processes. With its advantages and limitations, Case Study Analysis offers a unique approach to gaining in-depth knowledge and practical application across numerous fields.
About the author

Arnaud Belinga

Close deals x2 faster with
Breakcold sales crm.
SEE PRICING
*No credit card required
Related Articles

What is the 80-20 rule? (Explained With Examples)

What is the ABCD Sales Method? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Accelerated Sales Cycle? (Explained With Examples)

What is Account-Based Marketing (ABM)? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Account Manager? (Explained With Examples)

What is Account Mapping? (Explained With Examples)

What is Account-Based Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Ad Targeting? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Addressable Market? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Adoption Curve? (Explained With Examples)

What is an AE (Account Executive)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Affiliate Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is AI in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is an AI-Powered CRM? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Alternative Close? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Annual Contract Value? (ACV - Explained With Examples)

What are Appointments Set? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Assumptive Close? (Explained With Examples)

What is Automated Outreach? (Explained With Examples)

What is Average Revenue Per Account (ARPA)? (Explained With Examples)

What is B2B (Business-to-Business)? (Explained With Examples)

What is B2G (Business-to-Government)? (Explained With Examples)

What is B2P (Business-to-Partner)? (Explained With Examples)

What is BANT (Budget, Authority, Need, Timing)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Behavioral Economics in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Benchmark Data? (Explained With Examples)

What is Benefit Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What are Benefit Statements? (Explained With Examples)

What is Beyond the Obvious? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Bootstrapped Startup? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Bottom of the Funnel (BOFU)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Bounce Rate? (Explained With Examples)

What is Brand Awareness? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Break-Even Point? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Breakup Email? (Explained With Examples)

What is Business Development? (Explained With Examples)

What are Business Insights? (Explained With Examples)

What is Business Process Automation? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Buyer Persona? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Buyer's Journey? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Buying Cycle? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Buying Signal? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Buying Team? (Explained With Examples)

What is a C-Level Executive? (Explained With Examples)

What is Call Logging? (Explained With Examples)

What is Call Recording? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Call-to-Action (CTA)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Challenger Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Chasing Lost Deals? (Explained With Examples)

What is Churn Prevention? (Explained With Examples)

What is Churn Rate? (Explained With Examples)

What is Click-Through Rate (CTR)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Client Acquisition? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Closing Ratio? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Ben Franklin Close? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cognitive Bias in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cognitive Dissonance in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cold Calling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cold Outreach? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Competitive Advantage? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Competitive Analysis? (Explained With Examples)

What is Competitive Positioning? (Explained With Examples)

What is Conceptual Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Consultative Closing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Consultative Negotiation? (Explained With Examples)

What is Consultative Prospecting? (Explained With Examples)

What is Consultative Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Content Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Content Syndication? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Conversion Funnel? (Explained With Examples)

What is Conversion Optimization? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Conversion Path? (Explained With Examples)

What is Conversion Rate? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cost-Per-Click (CPC)? (Explained With Examples)

What is a CRM (Customer Relationship Management)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cross-Cultural Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Cross-Sell Ratio? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cross-Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer-Centric Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer-Centric Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer Journey Mapping? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Customer Journey? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer Profiling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer Retention? (Explained With Examples)

What is Dark Social? (Explained With Examples)

What is Data Enrichment? (Explained With Examples)

What is Data Segmentation? (Explained With Examples)

What is Database Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What are Decision Criteria? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Decision Maker? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Decision-Making Unit (DMU)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Demand Generation? (Explained With Examples)

What is Digital Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Direct Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Discovery Call? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Discovery Meeting? (Explained With Examples)

What are Discovery Questions? (Explained With Examples)

What is Door-to-Door Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Drip Campaign? (Explained With Examples)

What is Dunning? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Early Adopter? (Explained With Examples)

What is Elevator Pitch? (Explained With Examples)

What is Email Hygiene? (Explained With Examples)


What is Email Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Emotional Intelligence Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Engagement Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Engagement Rate? (Explained With Examples)

What is Engagement Strategy? (Explained With Examples)

What is Feature-Benefit Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Field Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Follow-Up? (Explained With Examples)

What is Forecast Accuracy? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Funnel? (Explained With Examples)

What is Gamification in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Gatekeeper Strategy? (Explained With Examples)

What is Gatekeeper? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Go-to Market Strategy? (Explained With Examples)

What is Growth Hacking? (Explained With Examples)

What is Growth Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Guerrilla Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is High-Ticket Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Holistic Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Ideal Customer Profile (ICP)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Inbound Lead Generation? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Inbound Lead? (Explained With Examples)

What is Inbound Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Inbound Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Influencer Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Inside Sales Representative? (Explained With Examples)

What is Inside Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Insight Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Key Account? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Key Performance Indicator (KPI)? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Landing Page? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lead Database? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Lead Enrichment? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lead Generation? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lead Nurturing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lead Qualification? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lead Scoring? (Explained With Examples)

What are LinkedIn InMails? (Explained With Examples)

What is LinkedIn Sales Navigator? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lost Opportunity? (Explained With Examples)

What is Market Positioning? (Explained With Examples)

What is Market Research? (Explained With Examples)

What is Market Segmentation? (Explained With Examples)

What is MEDDIC? (Explained With Examples)

What is Middle Of The Funnel (MOFU)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Motivational Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is a MQL (Marketing Qualified Lead)? (Explained With Examples)

What is MRR Growth? (Explained With Examples)

What is MRR (Monthly Recurring Revenue)? (Explained With Examples)

What is N.E.A.T. Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Neil Rackham's Sales Tactics? (Explained With Examples)

What is Networking? (Explained With Examples)

What is NLP Sales Techniques? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Net Promotion Score? (NPS - Explained With Examples)

What is Objection Handling Framework? (Explained With Examples)

What is On-Hold Messaging? (Explained With Examples)

What is Onboarding in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Online Advertising? (Explained With Examples)

What is Outbound Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Pain Points Analysis? (Explained With Examples)

What is Permission Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Personality-Based Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Persuasion Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Pipeline Management? (Explained With Examples)

What is Pipeline Velocity? (Explained With Examples)

What is Predictive Lead Scoring? (Explained With Examples)

What is Price Negotiation? (Explained With Examples)

What is Price Objection? (Explained With Examples)

What is Price Sensitivity? (Explained With Examples)

What is Problem-Solution Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Product Knowledge? (Explained With Examples)

What is Product-Led-Growth? (Explained With Examples)

What is Prospecting? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Qualified Lead? (Explained With Examples)

What is Question-Based Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Referral Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Relationship Building? (Explained With Examples)

What is Revenue Forecast? (Explained With Examples)

What is a ROI? (Explained With Examples)

What is Sales Automation? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Bonus Plan? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Champion? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Collateral? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Commission Structure Plan? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales CRM? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Cycle? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Demo? (Explained With Examples)

What is Sales Enablement? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Flywheel? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Funnel? (Explained With Examples)

What are Sales KPIs? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Meetup? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Pipeline? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Pitch? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Playbook? (Explained With Examples)
Try breakcold now, are you ready to accelerate your sales pipeline.
Join over +1000 agencies, startups & consultants closing deals with Breakcold Sales CRM
Get Started for free
Sales CRM Features
Sales CRM Software
Sales Pipeline
Sales Lead Tracking
CRM with social media integrations
Social Selling Software
Contact Management
CRM Unified Email LinkedIn Inbox
Breakcold works for many industries
CRM for Agencies
CRM for Startups
CRM for Consultants
CRM for Small Business
CRM for LinkedIn
CRM for Coaches
Sales CRM & Sales Pipeline Tutorials
The 8 Sales Pipeline Stages
The Best CRMs for Agencies
The Best CRMs for Consultants
The Best LinkedIn CRMs
How to close deals in 2024, not in 2010
CRM automation: from 0 to PRO in 5 minutes
LinkedIn Inbox Management
LinkedIn Account-Based Marketing (2024 Tutorial with video)
Tools & more
Sales Pipeline Templates
Alternatives
Integrations
CRM integration with LinkedIn
© 2024 Breakcold
Privacy Policy
Terms of Service
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
What Is a Case Study?
Weighing the pros and cons of this method of research
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Cara Lustik is a fact-checker and copywriter.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Cara-Lustik-1000-77abe13cf6c14a34a58c2a0ffb7297da.jpg)
Verywell / Colleen Tighe
- Pros and Cons
What Types of Case Studies Are Out There?
Where do you find data for a case study, how do i write a psychology case study.
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
The point of a case study is to learn as much as possible about an individual or group so that the information can be generalized to many others. Unfortunately, case studies tend to be highly subjective, and it is sometimes difficult to generalize results to a larger population.
While case studies focus on a single individual or group, they follow a format similar to other types of psychology writing. If you are writing a case study, we got you—here are some rules of APA format to reference.
At a Glance
A case study, or an in-depth study of a person, group, or event, can be a useful research tool when used wisely. In many cases, case studies are best used in situations where it would be difficult or impossible for you to conduct an experiment. They are helpful for looking at unique situations and allow researchers to gather a lot of˜ information about a specific individual or group of people. However, it's important to be cautious of any bias we draw from them as they are highly subjective.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Case Studies?
A case study can have its strengths and weaknesses. Researchers must consider these pros and cons before deciding if this type of study is appropriate for their needs.
One of the greatest advantages of a case study is that it allows researchers to investigate things that are often difficult or impossible to replicate in a lab. Some other benefits of a case study:
- Allows researchers to capture information on the 'how,' 'what,' and 'why,' of something that's implemented
- Gives researchers the chance to collect information on why one strategy might be chosen over another
- Permits researchers to develop hypotheses that can be explored in experimental research
On the other hand, a case study can have some drawbacks:
- It cannot necessarily be generalized to the larger population
- Cannot demonstrate cause and effect
- It may not be scientifically rigorous
- It can lead to bias
Researchers may choose to perform a case study if they want to explore a unique or recently discovered phenomenon. Through their insights, researchers develop additional ideas and study questions that might be explored in future studies.
It's important to remember that the insights from case studies cannot be used to determine cause-and-effect relationships between variables. However, case studies may be used to develop hypotheses that can then be addressed in experimental research.
Case Study Examples
There have been a number of notable case studies in the history of psychology. Much of Freud's work and theories were developed through individual case studies. Some great examples of case studies in psychology include:
- Anna O : Anna O. was a pseudonym of a woman named Bertha Pappenheim, a patient of a physician named Josef Breuer. While she was never a patient of Freud's, Freud and Breuer discussed her case extensively. The woman was experiencing symptoms of a condition that was then known as hysteria and found that talking about her problems helped relieve her symptoms. Her case played an important part in the development of talk therapy as an approach to mental health treatment.
- Phineas Gage : Phineas Gage was a railroad employee who experienced a terrible accident in which an explosion sent a metal rod through his skull, damaging important portions of his brain. Gage recovered from his accident but was left with serious changes in both personality and behavior.
- Genie : Genie was a young girl subjected to horrific abuse and isolation. The case study of Genie allowed researchers to study whether language learning was possible, even after missing critical periods for language development. Her case also served as an example of how scientific research may interfere with treatment and lead to further abuse of vulnerable individuals.
Such cases demonstrate how case research can be used to study things that researchers could not replicate in experimental settings. In Genie's case, her horrific abuse denied her the opportunity to learn a language at critical points in her development.
This is clearly not something researchers could ethically replicate, but conducting a case study on Genie allowed researchers to study phenomena that are otherwise impossible to reproduce.
There are a few different types of case studies that psychologists and other researchers might use:
- Collective case studies : These involve studying a group of individuals. Researchers might study a group of people in a certain setting or look at an entire community. For example, psychologists might explore how access to resources in a community has affected the collective mental well-being of those who live there.
- Descriptive case studies : These involve starting with a descriptive theory. The subjects are then observed, and the information gathered is compared to the pre-existing theory.
- Explanatory case studies : These are often used to do causal investigations. In other words, researchers are interested in looking at factors that may have caused certain things to occur.
- Exploratory case studies : These are sometimes used as a prelude to further, more in-depth research. This allows researchers to gather more information before developing their research questions and hypotheses .
- Instrumental case studies : These occur when the individual or group allows researchers to understand more than what is initially obvious to observers.
- Intrinsic case studies : This type of case study is when the researcher has a personal interest in the case. Jean Piaget's observations of his own children are good examples of how an intrinsic case study can contribute to the development of a psychological theory.
The three main case study types often used are intrinsic, instrumental, and collective. Intrinsic case studies are useful for learning about unique cases. Instrumental case studies help look at an individual to learn more about a broader issue. A collective case study can be useful for looking at several cases simultaneously.
The type of case study that psychology researchers use depends on the unique characteristics of the situation and the case itself.
There are a number of different sources and methods that researchers can use to gather information about an individual or group. Six major sources that have been identified by researchers are:
- Archival records : Census records, survey records, and name lists are examples of archival records.
- Direct observation : This strategy involves observing the subject, often in a natural setting . While an individual observer is sometimes used, it is more common to utilize a group of observers.
- Documents : Letters, newspaper articles, administrative records, etc., are the types of documents often used as sources.
- Interviews : Interviews are one of the most important methods for gathering information in case studies. An interview can involve structured survey questions or more open-ended questions.
- Participant observation : When the researcher serves as a participant in events and observes the actions and outcomes, it is called participant observation.
- Physical artifacts : Tools, objects, instruments, and other artifacts are often observed during a direct observation of the subject.
If you have been directed to write a case study for a psychology course, be sure to check with your instructor for any specific guidelines you need to follow. If you are writing your case study for a professional publication, check with the publisher for their specific guidelines for submitting a case study.
Here is a general outline of what should be included in a case study.
Section 1: A Case History
This section will have the following structure and content:
Background information : The first section of your paper will present your client's background. Include factors such as age, gender, work, health status, family mental health history, family and social relationships, drug and alcohol history, life difficulties, goals, and coping skills and weaknesses.
Description of the presenting problem : In the next section of your case study, you will describe the problem or symptoms that the client presented with.
Describe any physical, emotional, or sensory symptoms reported by the client. Thoughts, feelings, and perceptions related to the symptoms should also be noted. Any screening or diagnostic assessments that are used should also be described in detail and all scores reported.
Your diagnosis : Provide your diagnosis and give the appropriate Diagnostic and Statistical Manual code. Explain how you reached your diagnosis, how the client's symptoms fit the diagnostic criteria for the disorder(s), or any possible difficulties in reaching a diagnosis.
Section 2: Treatment Plan
This portion of the paper will address the chosen treatment for the condition. This might also include the theoretical basis for the chosen treatment or any other evidence that might exist to support why this approach was chosen.
- Cognitive behavioral approach : Explain how a cognitive behavioral therapist would approach treatment. Offer background information on cognitive behavioral therapy and describe the treatment sessions, client response, and outcome of this type of treatment. Make note of any difficulties or successes encountered by your client during treatment.
- Humanistic approach : Describe a humanistic approach that could be used to treat your client, such as client-centered therapy . Provide information on the type of treatment you chose, the client's reaction to the treatment, and the end result of this approach. Explain why the treatment was successful or unsuccessful.
- Psychoanalytic approach : Describe how a psychoanalytic therapist would view the client's problem. Provide some background on the psychoanalytic approach and cite relevant references. Explain how psychoanalytic therapy would be used to treat the client, how the client would respond to therapy, and the effectiveness of this treatment approach.
- Pharmacological approach : If treatment primarily involves the use of medications, explain which medications were used and why. Provide background on the effectiveness of these medications and how monotherapy may compare with an approach that combines medications with therapy or other treatments.
This section of a case study should also include information about the treatment goals, process, and outcomes.
When you are writing a case study, you should also include a section where you discuss the case study itself, including the strengths and limitiations of the study. You should note how the findings of your case study might support previous research.
In your discussion section, you should also describe some of the implications of your case study. What ideas or findings might require further exploration? How might researchers go about exploring some of these questions in additional studies?
Need More Tips?
Here are a few additional pointers to keep in mind when formatting your case study:
- Never refer to the subject of your case study as "the client." Instead, use their name or a pseudonym.
- Read examples of case studies to gain an idea about the style and format.
- Remember to use APA format when citing references .
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011;11:100.
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011 Jun 27;11:100. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Gagnon, Yves-Chantal. The Case Study as Research Method: A Practical Handbook . Canada, Chicago Review Press Incorporated DBA Independent Pub Group, 2010.
Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods . United States, SAGE Publications, 2017.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
- Privacy Policy

Home » Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Table of Contents

A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation.
It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied. Case studies typically involve multiple sources of data, including interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, which are analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, and grounded theory. The findings of a case study are often used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Types of Case Study
Types and Methods of Case Study are as follows:
Single-Case Study
A single-case study is an in-depth analysis of a single case. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand a specific phenomenon in detail.
For Example , A researcher might conduct a single-case study on a particular individual to understand their experiences with a particular health condition or a specific organization to explore their management practices. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a single-case study are often used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Multiple-Case Study
A multiple-case study involves the analysis of several cases that are similar in nature. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to identify similarities and differences between the cases.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a multiple-case study on several companies to explore the factors that contribute to their success or failure. The researcher collects data from each case, compares and contrasts the findings, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as comparative analysis or pattern-matching. The findings of a multiple-case study can be used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Exploratory Case Study
An exploratory case study is used to explore a new or understudied phenomenon. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to generate hypotheses or theories about the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an exploratory case study on a new technology to understand its potential impact on society. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as grounded theory or content analysis. The findings of an exploratory case study can be used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Descriptive Case Study
A descriptive case study is used to describe a particular phenomenon in detail. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to provide a comprehensive account of the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a descriptive case study on a particular community to understand its social and economic characteristics. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a descriptive case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Instrumental Case Study
An instrumental case study is used to understand a particular phenomenon that is instrumental in achieving a particular goal. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand the role of the phenomenon in achieving the goal.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an instrumental case study on a particular policy to understand its impact on achieving a particular goal, such as reducing poverty. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of an instrumental case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Case Study Data Collection Methods
Here are some common data collection methods for case studies:
Interviews involve asking questions to individuals who have knowledge or experience relevant to the case study. Interviews can be structured (where the same questions are asked to all participants) or unstructured (where the interviewer follows up on the responses with further questions). Interviews can be conducted in person, over the phone, or through video conferencing.
Observations
Observations involve watching and recording the behavior and activities of individuals or groups relevant to the case study. Observations can be participant (where the researcher actively participates in the activities) or non-participant (where the researcher observes from a distance). Observations can be recorded using notes, audio or video recordings, or photographs.
Documents can be used as a source of information for case studies. Documents can include reports, memos, emails, letters, and other written materials related to the case study. Documents can be collected from the case study participants or from public sources.
Surveys involve asking a set of questions to a sample of individuals relevant to the case study. Surveys can be administered in person, over the phone, through mail or email, or online. Surveys can be used to gather information on attitudes, opinions, or behaviors related to the case study.
Artifacts are physical objects relevant to the case study. Artifacts can include tools, equipment, products, or other objects that provide insights into the case study phenomenon.
How to conduct Case Study Research
Conducting a case study research involves several steps that need to be followed to ensure the quality and rigor of the study. Here are the steps to conduct case study research:
- Define the research questions: The first step in conducting a case study research is to define the research questions. The research questions should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the case study phenomenon under investigation.
- Select the case: The next step is to select the case or cases to be studied. The case should be relevant to the research questions and should provide rich and diverse data that can be used to answer the research questions.
- Collect data: Data can be collected using various methods, such as interviews, observations, documents, surveys, and artifacts. The data collection method should be selected based on the research questions and the nature of the case study phenomenon.
- Analyze the data: The data collected from the case study should be analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, or grounded theory. The analysis should be guided by the research questions and should aim to provide insights and conclusions relevant to the research questions.
- Draw conclusions: The conclusions drawn from the case study should be based on the data analysis and should be relevant to the research questions. The conclusions should be supported by evidence and should be clearly stated.
- Validate the findings: The findings of the case study should be validated by reviewing the data and the analysis with participants or other experts in the field. This helps to ensure the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Write the report: The final step is to write the report of the case study research. The report should provide a clear description of the case study phenomenon, the research questions, the data collection methods, the data analysis, the findings, and the conclusions. The report should be written in a clear and concise manner and should follow the guidelines for academic writing.
Examples of Case Study
Here are some examples of case study research:
- The Hawthorne Studies : Conducted between 1924 and 1932, the Hawthorne Studies were a series of case studies conducted by Elton Mayo and his colleagues to examine the impact of work environment on employee productivity. The studies were conducted at the Hawthorne Works plant of the Western Electric Company in Chicago and included interviews, observations, and experiments.
- The Stanford Prison Experiment: Conducted in 1971, the Stanford Prison Experiment was a case study conducted by Philip Zimbardo to examine the psychological effects of power and authority. The study involved simulating a prison environment and assigning participants to the role of guards or prisoners. The study was controversial due to the ethical issues it raised.
- The Challenger Disaster: The Challenger Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Space Shuttle Challenger explosion in 1986. The study included interviews, observations, and analysis of data to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
- The Enron Scandal: The Enron Scandal was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Enron Corporation’s bankruptcy in 2001. The study included interviews, analysis of financial data, and review of documents to identify the accounting practices, corporate culture, and ethical issues that led to the company’s downfall.
- The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster : The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the nuclear accident that occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan in 2011. The study included interviews, analysis of data, and review of documents to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
Application of Case Study
Case studies have a wide range of applications across various fields and industries. Here are some examples:
Business and Management
Case studies are widely used in business and management to examine real-life situations and develop problem-solving skills. Case studies can help students and professionals to develop a deep understanding of business concepts, theories, and best practices.
Case studies are used in healthcare to examine patient care, treatment options, and outcomes. Case studies can help healthcare professionals to develop critical thinking skills, diagnose complex medical conditions, and develop effective treatment plans.
Case studies are used in education to examine teaching and learning practices. Case studies can help educators to develop effective teaching strategies, evaluate student progress, and identify areas for improvement.
Social Sciences
Case studies are widely used in social sciences to examine human behavior, social phenomena, and cultural practices. Case studies can help researchers to develop theories, test hypotheses, and gain insights into complex social issues.
Law and Ethics
Case studies are used in law and ethics to examine legal and ethical dilemmas. Case studies can help lawyers, policymakers, and ethical professionals to develop critical thinking skills, analyze complex cases, and make informed decisions.
Purpose of Case Study
The purpose of a case study is to provide a detailed analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. A case study is a qualitative research method that involves the in-depth exploration and analysis of a particular case, which can be an individual, group, organization, event, or community.
The primary purpose of a case study is to generate a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case, including its history, context, and dynamics. Case studies can help researchers to identify and examine the underlying factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and detailed understanding of the case, which can inform future research, practice, or policy.
Case studies can also serve other purposes, including:
- Illustrating a theory or concept: Case studies can be used to illustrate and explain theoretical concepts and frameworks, providing concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Developing hypotheses: Case studies can help to generate hypotheses about the causal relationships between different factors and outcomes, which can be tested through further research.
- Providing insight into complex issues: Case studies can provide insights into complex and multifaceted issues, which may be difficult to understand through other research methods.
- Informing practice or policy: Case studies can be used to inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
Advantages of Case Study Research
There are several advantages of case study research, including:
- In-depth exploration: Case study research allows for a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. This can provide a comprehensive understanding of the case and its dynamics, which may not be possible through other research methods.
- Rich data: Case study research can generate rich and detailed data, including qualitative data such as interviews, observations, and documents. This can provide a nuanced understanding of the case and its complexity.
- Holistic perspective: Case study research allows for a holistic perspective of the case, taking into account the various factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the case.
- Theory development: Case study research can help to develop and refine theories and concepts by providing empirical evidence and concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Practical application: Case study research can inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
- Contextualization: Case study research takes into account the specific context in which the case is situated, which can help to understand how the case is influenced by the social, cultural, and historical factors of its environment.
Limitations of Case Study Research
There are several limitations of case study research, including:
- Limited generalizability : Case studies are typically focused on a single case or a small number of cases, which limits the generalizability of the findings. The unique characteristics of the case may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, which may limit the external validity of the research.
- Biased sampling: Case studies may rely on purposive or convenience sampling, which can introduce bias into the sample selection process. This may limit the representativeness of the sample and the generalizability of the findings.
- Subjectivity: Case studies rely on the interpretation of the researcher, which can introduce subjectivity into the analysis. The researcher’s own biases, assumptions, and perspectives may influence the findings, which may limit the objectivity of the research.
- Limited control: Case studies are typically conducted in naturalistic settings, which limits the control that the researcher has over the environment and the variables being studied. This may limit the ability to establish causal relationships between variables.
- Time-consuming: Case studies can be time-consuming to conduct, as they typically involve a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific case. This may limit the feasibility of conducting multiple case studies or conducting case studies in a timely manner.
- Resource-intensive: Case studies may require significant resources, including time, funding, and expertise. This may limit the ability of researchers to conduct case studies in resource-constrained settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide

Survey Research – Types, Methods, Examples
Do Your Students Know How to Analyze a Case—Really?
Explore more.
- Case Teaching
- Student Engagement
J ust as actors, athletes, and musicians spend thousands of hours practicing their craft, business students benefit from practicing their critical-thinking and decision-making skills. Students, however, often have limited exposure to real-world problem-solving scenarios; they need more opportunities to practice tackling tough business problems and deciding on—and executing—the best solutions.
To ensure students have ample opportunity to develop these critical-thinking and decision-making skills, we believe business faculty should shift from teaching mostly principles and ideas to mostly applications and practices. And in doing so, they should emphasize the case method, which simulates real-world management challenges and opportunities for students.
To help educators facilitate this shift and help students get the most out of case-based learning, we have developed a framework for analyzing cases. We call it PACADI (Problem, Alternatives, Criteria, Analysis, Decision, Implementation); it can improve learning outcomes by helping students better solve and analyze business problems, make decisions, and develop and implement strategy. Here, we’ll explain why we developed this framework, how it works, and what makes it an effective learning tool.
The Case for Cases: Helping Students Think Critically
Business students must develop critical-thinking and analytical skills, which are essential to their ability to make good decisions in functional areas such as marketing, finance, operations, and information technology, as well as to understand the relationships among these functions. For example, the decisions a marketing manager must make include strategic planning (segments, products, and channels); execution (digital messaging, media, branding, budgets, and pricing); and operations (integrated communications and technologies), as well as how to implement decisions across functional areas.
Faculty can use many types of cases to help students develop these skills. These include the prototypical “paper cases”; live cases , which feature guest lecturers such as entrepreneurs or corporate leaders and on-site visits; and multimedia cases , which immerse students into real situations. Most cases feature an explicit or implicit decision that a protagonist—whether it is an individual, a group, or an organization—must make.
For students new to learning by the case method—and even for those with case experience—some common issues can emerge; these issues can sometimes be a barrier for educators looking to ensure the best possible outcomes in their case classrooms. Unsure of how to dig into case analysis on their own, students may turn to the internet or rely on former students for “answers” to assigned cases. Or, when assigned to provide answers to assignment questions in teams, students might take a divide-and-conquer approach but not take the time to regroup and provide answers that are consistent with one other.
To help address these issues, which we commonly experienced in our classes, we wanted to provide our students with a more structured approach for how they analyze cases—and to really think about making decisions from the protagonists’ point of view. We developed the PACADI framework to address this need.
PACADI: A Six-Step Decision-Making Approach
The PACADI framework is a six-step decision-making approach that can be used in lieu of traditional end-of-case questions. It offers a structured, integrated, and iterative process that requires students to analyze case information, apply business concepts to derive valuable insights, and develop recommendations based on these insights.
Prior to beginning a PACADI assessment, which we’ll outline here, students should first prepare a two-paragraph summary—a situation analysis—that highlights the key case facts. Then, we task students with providing a five-page PACADI case analysis (excluding appendices) based on the following six steps.
Step 1: Problem definition. What is the major challenge, problem, opportunity, or decision that has to be made? If there is more than one problem, choose the most important one. Often when solving the key problem, other issues will surface and be addressed. The problem statement may be framed as a question; for example, How can brand X improve market share among millennials in Canada? Usually the problem statement has to be re-written several times during the analysis of a case as students peel back the layers of symptoms or causation.
Step 2: Alternatives. Identify in detail the strategic alternatives to address the problem; three to five options generally work best. Alternatives should be mutually exclusive, realistic, creative, and feasible given the constraints of the situation. Doing nothing or delaying the decision to a later date are not considered acceptable alternatives.
Step 3: Criteria. What are the key decision criteria that will guide decision-making? In a marketing course, for example, these may include relevant marketing criteria such as segmentation, positioning, advertising and sales, distribution, and pricing. Financial criteria useful in evaluating the alternatives should be included—for example, income statement variables, customer lifetime value, payback, etc. Students must discuss their rationale for selecting the decision criteria and the weights and importance for each factor.
Step 4: Analysis. Provide an in-depth analysis of each alternative based on the criteria chosen in step three. Decision tables using criteria as columns and alternatives as rows can be helpful. The pros and cons of the various choices as well as the short- and long-term implications of each may be evaluated. Best, worst, and most likely scenarios can also be insightful.
Step 5: Decision. Students propose their solution to the problem. This decision is justified based on an in-depth analysis. Explain why the recommendation made is the best fit for the criteria.
Step 6: Implementation plan. Sound business decisions may fail due to poor execution. To enhance the likeliness of a successful project outcome, students describe the key steps (activities) to implement the recommendation, timetable, projected costs, expected competitive reaction, success metrics, and risks in the plan.
“Students note that using the PACADI framework yields ‘aha moments’—they learned something surprising in the case that led them to think differently about the problem and their proposed solution.”
PACADI’s Benefits: Meaningfully and Thoughtfully Applying Business Concepts
The PACADI framework covers all of the major elements of business decision-making, including implementation, which is often overlooked. By stepping through the whole framework, students apply relevant business concepts and solve management problems via a systematic, comprehensive approach; they’re far less likely to surface piecemeal responses.
As students explore each part of the framework, they may realize that they need to make changes to a previous step. For instance, when working on implementation, students may realize that the alternative they selected cannot be executed or will not be profitable, and thus need to rethink their decision. Or, they may discover that the criteria need to be revised since the list of decision factors they identified is incomplete (for example, the factors may explain key marketing concerns but fail to address relevant financial considerations) or is unrealistic (for example, they suggest a 25 percent increase in revenues without proposing an increased promotional budget).
In addition, the PACADI framework can be used alongside quantitative assignments, in-class exercises, and business and management simulations. The structured, multi-step decision framework encourages careful and sequential analysis to solve business problems. Incorporating PACADI as an overarching decision-making method across different projects will ultimately help students achieve desired learning outcomes. As a practical “beyond-the-classroom” tool, the PACADI framework is not a contrived course assignment; it reflects the decision-making approach that managers, executives, and entrepreneurs exercise daily. Case analysis introduces students to the real-world process of making business decisions quickly and correctly, often with limited information. This framework supplies an organized and disciplined process that students can readily defend in writing and in class discussions.
PACADI in Action: An Example
Here’s an example of how students used the PACADI framework for a recent case analysis on CVS, a large North American drugstore chain.
The CVS Prescription for Customer Value*
PACADI Stage
Summary Response
How should CVS Health evolve from the “drugstore of your neighborhood” to the “drugstore of your future”?
Alternatives
A1. Kaizen (continuous improvement)
A2. Product development
A3. Market development
A4. Personalization (micro-targeting)
Criteria (include weights)
C1. Customer value: service, quality, image, and price (40%)
C2. Customer obsession (20%)
C3. Growth through related businesses (20%)
C4. Customer retention and customer lifetime value (20%)
Each alternative was analyzed by each criterion using a Customer Value Assessment Tool
Alternative 4 (A4): Personalization was selected. This is operationalized via: segmentation—move toward segment-of-1 marketing; geodemographics and lifestyle emphasis; predictive data analysis; relationship marketing; people, principles, and supply chain management; and exceptional customer service.
Implementation
Partner with leading medical school
Curbside pick-up
Pet pharmacy
E-newsletter for customers and employees
Employee incentive program
CVS beauty days
Expand to Latin America and Caribbean
Healthier/happier corner
Holiday toy drives/community outreach
*Source: A. Weinstein, Y. Rodriguez, K. Sims, R. Vergara, “The CVS Prescription for Superior Customer Value—A Case Study,” Back to the Future: Revisiting the Foundations of Marketing from Society for Marketing Advances, West Palm Beach, FL (November 2, 2018).
Results of Using the PACADI Framework
When faculty members at our respective institutions at Nova Southeastern University (NSU) and the University of North Carolina Wilmington have used the PACADI framework, our classes have been more structured and engaging. Students vigorously debate each element of their decision and note that this framework yields an “aha moment”—they learned something surprising in the case that led them to think differently about the problem and their proposed solution.
These lively discussions enhance individual and collective learning. As one external metric of this improvement, we have observed a 2.5 percent increase in student case grade performance at NSU since this framework was introduced.
Tips to Get Started
The PACADI approach works well in in-person, online, and hybrid courses. This is particularly important as more universities have moved to remote learning options. Because students have varied educational and cultural backgrounds, work experience, and familiarity with case analysis, we recommend that faculty members have students work on their first case using this new framework in small teams (two or three students). Additional analyses should then be solo efforts.
To use PACADI effectively in your classroom, we suggest the following:
Advise your students that your course will stress critical thinking and decision-making skills, not just course concepts and theory.
Use a varied mix of case studies. As marketing professors, we often address consumer and business markets; goods, services, and digital commerce; domestic and global business; and small and large companies in a single MBA course.
As a starting point, provide a short explanation (about 20 to 30 minutes) of the PACADI framework with a focus on the conceptual elements. You can deliver this face to face or through videoconferencing.
Give students an opportunity to practice the case analysis methodology via an ungraded sample case study. Designate groups of five to seven students to discuss the case and the six steps in breakout sessions (in class or via Zoom).
Ensure case analyses are weighted heavily as a grading component. We suggest 30–50 percent of the overall course grade.
Once cases are graded, debrief with the class on what they did right and areas needing improvement (30- to 40-minute in-person or Zoom session).
Encourage faculty teams that teach common courses to build appropriate instructional materials, grading rubrics, videos, sample cases, and teaching notes.
When selecting case studies, we have found that the best ones for PACADI analyses are about 15 pages long and revolve around a focal management decision. This length provides adequate depth yet is not protracted. Some of our tested and favorite marketing cases include Brand W , Hubspot , Kraft Foods Canada , TRSB(A) , and Whiskey & Cheddar .

Art Weinstein , Ph.D., is a professor of marketing at Nova Southeastern University, Fort Lauderdale, Florida. He has published more than 80 scholarly articles and papers and eight books on customer-focused marketing strategy. His latest book is Superior Customer Value—Finding and Keeping Customers in the Now Economy . Dr. Weinstein has consulted for many leading technology and service companies.

Herbert V. Brotspies , D.B.A., is an adjunct professor of marketing at Nova Southeastern University. He has over 30 years’ experience as a vice president in marketing, strategic planning, and acquisitions for Fortune 50 consumer products companies working in the United States and internationally. His research interests include return on marketing investment, consumer behavior, business-to-business strategy, and strategic planning.

John T. Gironda , Ph.D., is an assistant professor of marketing at the University of North Carolina Wilmington. His research has been published in Industrial Marketing Management, Psychology & Marketing , and Journal of Marketing Management . He has also presented at major marketing conferences including the American Marketing Association, Academy of Marketing Science, and Society for Marketing Advances.
Related Articles

We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
35+ SAMPLE Case Study Analysis in PDF | MS Word
Case study analysis | ms word, 35+ sample case study analysis, what is a case study analysis, examples of case study analyses, types of case studies, how to write a case study analysis, what are some examples of case study analysis, what are the different types of case studies, why is case study analysis essential in social research, how to write an effective case study report, how long should a case study analysis be.

Generic Case Study Analysis

Sample Case Study Analysis Template

Case Study Value Chain Analysis

Basic Case Study Analysis Template
Case Study Skills Analysis Template

Case Study Research Analysis Template

Simple Case Study Analysis Template

Case Study Quantitative Analysis Template

Case Study Data Analysis Template

Estimation Techniques Case Study Analysis

Multiple-Case Study Analysis

Case Study Strategies Analysis
Case Study in Algorithm Analysis

Investment Analysis Case Study

Case Study and Production Analysis

Case Study Research Analysis Example

Project Case Study Analysis Template

Case Study Family Impact Analysis

Case Study on Curves Analysis

Case Study Experiential Analysis Template
Case Study Taxation Analysis

Case Study Medication Analysis

Meta Case Study Analysis

Case Study Health Care Analysis

Case Study Institute Analysis

Bank Case Study Analysis Template

Case Study Smartphone Analysis Template

Crime Analysis Case Study

Case Study Exercise Analysis

Multiple Case Study Analysis Template

Marketing Case Study Analysis

Battery Abuse Case Study Analysis
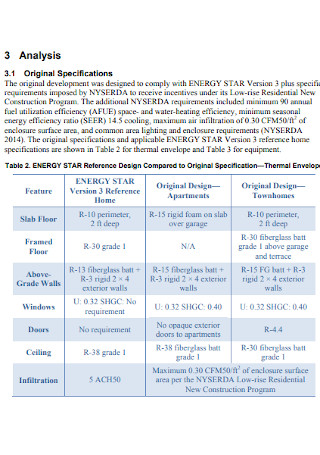
Multifamily Case Study Analysis

Company Case Study Analysis Template

Teaching Case Study Analysis Template

Evaluative Case Study Analysis
1. architecture case study analysis , 2. business marketing case study analysis , 3. user research case study analysis, 4. psychology case study analysis, step 1: create an introduction, step 2: present the case study, step 3: provide the solution and implementation, step 4: discuss the end results, step 5: proofread and revise the analysis, step 6: finalize the case study analysis, share this post on your network, file formats, word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates, you may also like these articles, 25+ sample business impact analysis templates in pdf | ms word.
As the COVID-19 continues and has already affected many lives of people worldwide, there is also big economic damage that negatively affected the global economy. According to Statista's estimate,…
53+ SAMPLE Analysis Report Templates in PDF | MS Word | Google Docs | Apple Pages
Are you familiar with those complex statistical graphs, detailed organizational charts, or tables presented in business? Such visual representations are useful to give information, define relationships, and show patterns of…
browse by categories
- Questionnaire
- Description
- Reconciliation
- Certificate
- Spreadsheet
Information
- privacy policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Schedule an Appointment

- Undergraduate Students in AS&E and SMFA
- Graduate Students in AS&E and SMFA
- Faculty & Staff
- Parents and Families
- What is a Career Community?
- Reflect, Discover & Explore Multiple Interests
- Arts, Communications & Media
- Education, Nonprofit & Social Impact
- Engineering, Technology & Physical Sciences
- Finance, Consulting, Entrepreneurship & Business
- Government, International Affairs & Law
- Healthcare, Life Sciences & the Environment
- Exploring Your Interests, Careers & Majors
- Writing Resumes & Cover Letters
- Finding an Internship
- Finding Jobs & Fellowships
- Preparing for Interviews
- Applying to Graduate & Professional School
- First Generation
- International Students
- Black, Indigenous & People of Color
- Students with Disabilities
- Students with Undocumented Status
- Women & Gender
- For Employers
- Contact & Location
- Career Fellows
- Career Services by School
Case Interview: Complete Prep Guide
- Share This: Share Case Interview: Complete Prep Guide on Facebook Share Case Interview: Complete Prep Guide on LinkedIn Share Case Interview: Complete Prep Guide on X
Welcome to our preparation tips for case interviews! Whether you are just curious about case interviews or are planning to apply for consulting internships or full-time jobs, these tips and resources will help you feel more prepared and confident.

A case interview is a role playing exercise in which an employer assesses how logically and persuasively you can present a case. Rather than seeing if you get the “correct” answer, the objective is to evaluate your thought process. ( Adapted with permission from Case In Point: Complete Case Interview Preparation by Marc Cosentino).
Case interviews are very commonly used in the interview process for consulting firms and companies in similar industries. In the case interview, you will typically be given a business problem and then asked to solve it in a structured way. Learning this structure takes preparation and practice. You can learn more and practice using the resources listed below.
Why are Case Interviews Used?
Case interviews allow employers to test and evaluate the following skills:
- Analytical skills and logical ability to solve problems
- Structure and thought process
- Ability to ask for relevant data/information
- Tolerance for ambiguity and data overload
- Poise and communication skills under pressure and in front of a client
How can I prepare for Case Interviews?
1.) Read Management Consulted’s “Case Interview: Complete Prep Guide (2024)”
Management Consulted is a FREE resource for Tufts students : case and consulting resources such as 500 sample cases, Case Interview Bootcamp, Market Sizing Drills, Math Drills, case videos, consulting firm directory, and more
2.) Review additional resources:
- Case in Point – This book, by Marc Cosentino, is a comprehensive guide that walks you through the case interview process from beginning to end. This guide has helped many students over the years and can serve as an excellent foundation for how to approach business problems
- Casequestions.com – The companion website to Marc Cosentino’s book listed above offers preparation for case interviews, along with links to top 50 consulting firms
- Management Consulting Case Interviews: Cracking The Case – tips for case interviews from the other side of the table, from Argopoint, a Boston management consulting firm specializing in legal department consulting for Fortune 500 companies
- Preplounge.com – Free case preparation access for to up to 6 practice interviews with peers, selected cases, and video case solutions
- RocketBlocks – Features consulting preparation such as drills and coaching
- Practice sample online cases on consulting firm websites such as McKinsey , BCG , Bain , Deloitte and more!
3.) Schedule a mock case interview appointment with Karen Dankers or Kathy Spillane , our advisors for the Finance, Consulting, Entrepreneurship, and Business Career Community.
4.) PRACTICE PRACTICE PRACTICE cases out loud on your own (yes, that can feel odd) or preferably, with another person. See #2 and #3 above for resources and ideas to find partners to practice live cases
5.) Enjoy and have fun solving business problems!
Top 10 Project Management Case Studies with Examples 2024
1. nasa's mars exploration rover: innovative project management in space exploration., 2. apple's iphone development: delivering revolutionary products with precision., 3. tesla's gigafactory construction: exemplary project execution in renewable energy., 4. netflix's content expansion: agile management in the entertainment industry., 5. amazon's prime air drone delivery: pioneering logistics project management., 6. google's waymo self-driving cars: cutting-edge technology meets project efficiency., 7. mcdonald's digital transformation: adaptive project management in fast food., 8. ikea's sustainable store design: eco-friendly project implementation in retail., 9. unicef's vaccine distribution: humanitarian project management at scale., 10. spacex's starlink satellite network: revolutionizing global connectivity with project prowess., discover more stories.
Effect of high-risk pregnancy on prenatal stress level: a prospective case-control study
- Open access
- Published: 11 May 2024
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Hülya Türkmen ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6187-9352 1 ,
- Bihter Akın ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3591-3630 2 &
- Yasemin Erkal Aksoy ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7453-1205 2
The study aimed to determine the effects of high-risk pregnancy on prenatal stress levels. The study was conducted with a case-control design in Turkey in September-December 2019. The sample included pregnant women diagnosed with high-risk pregnancy and were at their 36th or later gestational weeks as the case group ( n = 121) and healthy pregnant women as the control group ( n = 245). The Antenatal Perceived Stress Inventory (APSI) and the Revised Prenatal Distress Questionnaire (NUPDQ-17 Item Version) were used to assess the stress levels of the participants in the study. It was determined that high-risk pregnancy was associated with higher rates of prenatal stress (APSI: p < 0.001, effect size = 0.388; NUPDQ: p = 0.002, effect size = 0.272) compared to the control group. The results of the linear regression analysis showed that high-risk pregnancy affected APSI (R 2 = 0.043, p < 0.001) and NUPDQ (R 2 = 0.033, p = 0.009) scores, but education levels, number of pregnancies, and number of abortions did not affect APSI and NUPDQ scores. According to the results of this study, high-risk pregnant women are in a risk group for stress. It is of great importance for the course of a pregnancy that healthcare professionals assess the stress levels of pregnant women in the high-risk pregnancy category and provide psychological support to pregnant women who have high stress levels or are hospitalized.
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
A high-risk pregnancy is a significant health problem that threatens the health of the pregnant woman, the health of her fetus, and ultimately the health of her newborn, increases the risk of morbidity and mortality, and has physiological, psychological, social, and economic aspects (Cincioğlu et al., 2020 ; Gözüyeşil & Düzgün, 2021 ; Sinaci et al., 2020 ). Chronic diseases existing before pregnancy and problems that arise during pregnancy can make a pregnancy risky. Pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus, preeclampsia/eclampsia, potential threat of preterm labor, cervical insufficiency, premature rupture of membranes, vaginal bleeding, Rh incompatibility, intrauterine growth retardation, and infections are in the high-risk category (Gözüyeşil & Düzgün, 2021 ; Sinaci et al., 2020 ; ACOG, 2019 ; Soğukpınar et al., 2018 ; Üzar-Özçetin & Erkan, 2019 ; ACOG, 2018 ).
Approximately 10% of all pregnancies in the world are considered to be in the high-risk category (Cincioğlu et al., 2020 ; Gourounti et al., 2015a , b ; Göüyeşil & Düzgün, 2021 ; Sinaci et al., 2020 ; Soğukpınar et al., 2018 ; Üzar-Özçetin & Erkan, 2019 ). According to Turkey Demographic and Health Survey (TNSA) 2018 data, 35% of pregnancies in Turkey are in the high-risk category (Hacettepe University Institute of Population Studies, 2019 ).
Good mental health during pregnancy is important for the health of both the pregnant woman and her fetus (Gümüşdaş et al., 2014 ). In a high-risk pregnancy, the normal outcome of the pregnancy and the birth of a healthy baby are threatened. These pregnant women have a variety of health needs that must be met. If these needs are not met, the mother may experience extreme stress and anxiety (Ölçer & Oskay, 2015 ). In the case of intense stress caused by the risks of pregnancy, the elevation of catecholamines such as cortisol and epinephrine may increase the possibility of pregnancy complications (e.g., preeclampsia) and adversely affect pregnancy outcomes (e.g., intrauterine growth retardation) (Atasever & Çelik, 2018 ; Cetin et al., 2017 ; Deshpande, 2016 ; Gözüyeşil & Düzgün, 2021 ; Riggin, 2020 ; Traylor et al., 2020 ; Yüksel et al., 2013 ). Moreover, newborns exposed to extreme stress during the intrauterine period may have permanent health problems later in their lives (Graignic-Philippe et al., 2014 ; MacKinnon et al., 2018 ; Van De Loo et al., 2016 ).
It is seen that distress in pregnancy has a high prevalence ranging between 11.9% and 63.5% in studies conducted in Turkey (Yüksel et al., 2013 ; Çapık et al., 2015 ; Gözüyeşil & Düzgün, 2021 ). It is very important that health professionals identify pregnant women at risk of stress to ensure a healthy pregnancy process and protect the fetus and newborn from the harmful effects of stress. This way, more careful monitoring of pregnant women at risk of stress can be ensured, and the negative consequences of stress can be prevented with appropriate interventions (Williamson et al., 2023 ; Atasever & Çelik, 2018 ; Pinar et al., 2022 ). It is reported in the international literature that mental problems such as anxiety and stress are more common in high-risk pregnancies than in healthy pregnancies (Byatt et al., 2014 ; Abedian et al., 2015 ; Gourounti et al., 2015a , b ). In Turkey, there are few studies examining the prenatal stress levels of high-risk pregnant women. However, in these studies, the prenatal stress levels of women with healthy and high-risk pregnancies were not compared, and only the stress levels of high-risk pregnancies were determined (Gözüyeşil & Düzgün, 2021 ; Üzar-Özçetin & Erkan, 2019 ). Current evidence indicates that studies describing the concept of prenatal stress in high-risk pregnancies with different diagnoses are needed to learn more about the complex aspects of prenatal stress and identify the sociodemographic and obstetric factors that may lead to high-risk pregnancies for early diagnosis (Pinar et al., 2022 ; Hung et al., 2021 ; Gözüyeşil & Düzgün, 2021 ; Mete et al., 2020 ; Üzar-Özçetin & Erkan, 2019 ; Atasever & Çelik, 2018 ). For this reason, it is thought that this study will guide healthcare professionals who provide care for women with high-risk pregnancies about the services they will provide.
This study aims to prospectively determine the effects of high-risk pregnancies on prenatal stress levels compared to healthy pregnant women, using two different measurement instruments.
Materials and methods
Research questions.
Does high-risk pregnancy have an impact on prenatal stress?
What are the factors affecting the prenatal distress levels of women diagnosed with high-risk pregnancy?
Is there a difference in prenatal stress levels among different high-risk pregnancy diagnoses?
Design and settings
This case-control study was conducted to determine the difference between the stress levels of women with healthy and high-risk pregnancies. In other words, it was aimed to determine the suspected causal effect of high-risk pregnancy on prenatal stress levels. This case-control study was carried out between September and December 2019 at the Obstetrics and Gynecology Inpatient and Outpatient Clinics of Atatürk City Hospital in the Balıkesir province of Turkey. The case and control groups included women who were selected from the same hospital.
The hospital where the study was conducted hosted a total of 4,152 deliveries in 2018. Approximately 10% of all pregnancies are considered to be in the high-risk category (Sinaci et al., 2020 ). The sample size required to conduct the study was calculated as 134 high-risk pregnant women using the Epi Info StatCalc program based on an assumed population size of 4152, prevalence of 10%, margin of error of 5%, and in a 95% confidence interval. The study was completed with a total of 384 pregnant women, including 134 high-risk pregnant women and 250 healthy pregnant women, who accepted to participate in the study and filled out the consent form. However, the data of 13 pregnant women in the case group and 5 pregnant women in the control group were excluded from the study because they filled out the data collection forms incompletely. For the case group ( n = 121), the post hoc power analysis (G*Power 3.1) revealed a medium effect size and a power of 0.421.
The inclusion criteria of the study were being in a gestational week further than 36 weeks, not having a psychiatric diagnosis, and being 18 years old or order. Pregnant women who were hospitalized in the Obstetrics and Gynecology Inpatient Clinic, were diagnosed with high-risk pregnancy by a physician, and met the inclusion criteria were included in the high-risk pregnancy group. In the control group, pregnant women who were healthy, were at or above their 36th gestational week, and visited the Outpatient Clinics were included. Women who wanted to leave the study or responded incompletely to the data collection forms were excluded. After those who met the inclusion criteria were included, no pregnant women withdrew from the study by their own accord. However, 18 pregnant women were excluded from the study because they filled out the forms incompletely.
High-risk pregnancies were defined as the presence of one or more of the following: pre-existing chronic diseases, preeclampsia, gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), vaginal bleeding, placenta previa, threat of preterm labor, premature rupture of membranes, intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR), fetal anomaly/distress, multiple pregnancy, polyhydramnios/oligohydramnios, Rh incompatibility, and infectious diseases (Cincioğlu et al., 2020 ; Gözüyeşil & Düzgün, 2021 ; Sinaci et al., 2020 ; Üzar-Özçetin & Erkan, 2019 ).
Data collection
A Personal Information Form, the Antenatal Perceived Stress Inventory, and the Prenatal Distress Questionnaire were administered to the participants. The participants were informed about the study, the purpose of the study was explained to them, and their written consent was obtained. The data collection forms were administered to the participants by the first author. The data were collected based on the self-reports of the participants. The data collection period was between September and December 2019. The interviews lasted about 15 min for each participant.
Personal information form
The form which was prepared by the researchers in line with the literature consisted of a total of 20 questions on some characteristics of the participants, including their sociodemographic characteristics and obstetric history (Gözüyeşil & Düzgün, 2021 ; Mete et al., 2020 ; Üzar-Özçetin & Erkan, 2019 ; Atasever & Çelik, 2018 ).
Antenatal perceived stress inventory (APSI)
The Turkish validity and reliability study of the inventory developed by Razurel et al. ( 2014 ) to assess perceived stress in the prenatal period was performed by Atasever and Çelik ( 2018 ). The inventory is applied to pregnant women at the 36th -39th gestational weeks. It is a 5-point Likert-type scale (very much = 5 points, much = 4 points, quite = 3 points, a little = 2 points, none = 1 point) and consists of 12 items and 3 dimensions. Its dimensions are Medical and Obstetric Risks/Fetal Health, Psychosocial Changes during Pregnancy, and Prospect of Childbirth. The minimum and maximum scores that can be obtained from the inventory are 12 and 60. High scores indicate high levels of stress perceived by pregnant women. In the study conducted by Atasever and Çelik, Cronbach’s alpha internal consistency coefficient for APSI was found to be 0.70, while this coefficient was found as 0.81 in this study.
Revised prenatal distress questionnaire ((NUPDQ)-17 Item Version)
The questionnaire developed by Yali and Lobel ( 1999 ) to determine the levels of stress experienced by women regarding pregnancy-related issues was revised by Lobel ( 2008 ). The Turkish validity and reliability study of the questionnaire was performed by Yüksel et al. ( 2011 ). The questionnaire is in the form of a 3-point Likert-type scale (very much = 2 points, a little = 1 point, none = 0 point) and consists of 17 items. The questionnaire is unidimensional. The minimum and maximum scores that can be obtained from the questionnaire are 0 and 34. High scores indicate that pregnant women have high levels of prenatal distress. Cronbach’s alpha internal consistency coefficient for NUPDQ was found to be 0.85 in the study performed by Yüksel et al., while it was found as 0.82 in this study.
Statistical analysis
Frequency, percentage, mean, and standard deviation values were used in the data analyses. Whether the data had normal distribution was tested using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. The Chi-squared test and independent-samples t-test methods were used to identify the differences between groups in terms of the sociodemographic and obstetric information of the participants. The Mann-Whitney U Test was used to determine the differences between the case and control groups in terms of their total APSI, APSI subscale, and total NUPDQ scores. The Type I error level was accepted as p < 0.05. A Cohen’s d value of 0.20 is considered to indicate a small effect size, a value of 0.50 is considered to show a medium effect size, and a value of 0.80 or greater is interpreted as a large effect size (Özsoy & Özsoy, 2013 ). Since education, number of pregnancies, and number of miscarriages, which are thought to have an impact on stress levels, may be confounding factors, the linear regression analysis in this study was carried out to determine whether these factors or high-risk pregnancy affected the stress levels of the participants (Models 1 and 2). As a result of the Mann-Whitney U Test, a significant difference was found between high-risk pregnancies and healthy pregnancies in terms of “psychosocial changes during pregnancy” and “prospect of childbirth”. For this reason, APSI dimensions were collected in a single model, and a linear regression analysis was performed for the further analysis of the relationship between high-risk pregnancy and the APSI dimension scores of the participants (Model 3). The variable with the highest β coefficient was considered the relatively most significant independent variable. Multicollinearity was ignored in case of Tolerance > 0.20 and variance inflation factors (VIF) < 10. R 2 shows what percentage of the dependent variable is explained by the independent variables. According to Cohen, R 2 values of 0.0196, 0.1300, and 0.2600 are the lower thresholds for small, medium, and large effect sizes, respectively (Özsoy & Özsoy, 2013 ). One-Way MANOVA was also conducted to see whether there was a difference in stress levels during pregnancy between the case and control groups. The comparison of the stress levels of the participants in the case group based on their diagnoses was conducted with the Kruskal-Wallis test.
Ethical considerations
For the study to be carried out, approval was obtained from the Clinical Research Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Medicine of the University, and written permission was obtained from the institution where the study would be conducted (2019/123). The purpose of the study was explained to the pregnant women who agreed to participate, and they were informed that their identifying information would be kept confidential. The written consent of the participants was obtained with the Volunteer Information Form. The participants in both the case and control groups who were thought to need counseling were referred to a specialist for psychological support.
Table 1 shows the sociodemographic and obstetric characteristics of the participants. There was no significant difference between the women in the case and control groups in terms of age, whether they had an income-generating job, income status, place of residence, parity, number of living children, status of having a planned pregnancy, and smoking status ( p > 0.05). It was determined that the participants in the case group had significantly lower education levels than those in the control group ( p < 0.001). Moreover, the number of pregnancies ( p = 0.036) and the number of abortions ( p = 0.012) in the case group were found significantly higher than those in the control group. These results supported the hypothesis that some sociodemographic and obstetric characteristics of women are associated with high-risk pregnancies.
According to the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test results, the total APSI and NUPDQ scores of the participants were not normally distributed ( p < 0.001). Table 2 shows the stress levels of the participants compared based on their scale scores. The total APSI ( p < 0.001, Cohen’s d = 0.388) and total NUPDQ ( p = 0.002, Cohen’s d = 0.272) scores of the participants in the case group were significantly higher than those of the participants in the control group. The APSI Psychosocial Changes during Pregnancy ( p < 0.001, Cohen’s d = 0.473) and Prospect of Childbirth ( p < 0.001, Cohen’s d = 0.314) dimension scores of the participants in the case group were also significantly higher than those of the participants in the control group. These results supported the hypothesis that prenatal stress levels are higher in high-risk pregnancies than in healthy pregnancies.
Table 3 shows the stress levels of the participants with different diagnoses in the case group. In terms of risky pregnancies, the most frequently observed diagnoses were the threat of preterm labor in 37.2% of the participants in the case group, vaginal bleeding/placenta previa in 20.7%, and gestational diabetes mellitus in 10.7%. No statistically significant correlation was found between the diagnoses of the participants in the case group and their total APSI or NUPDQ scores ( p > 0.05). This result did not support the hypothesis that there is a difference in prenatal stress levels based on differences in high-risk pregnancy diagnoses.
In the linear regression analysis, Model 1 included APSI on education, gravidity, number of abortions, and high-risk pregnancy, and it was determined that there was a significant relationship between APSI and high-risk pregnancies, where the former explained 4.3% of the total variance in the latter (R 2 = 0.043) ( p < 0.001). Model 2 included NUPDQ on education, gravidity, number of abortions, and high-risk pregnancy, and it was determined that there was a significant relationship between NUPDQ and high-risk pregnancies, where the former explained 3.3% of the total variance in the latter (R 2 = 0.033) ( p = 0.009). Model 3 included APSI dimensions, and it was determined that there was a significant relationship between psychosocial changes during pregnancy and high-risk pregnancy, where the former explained 5.7% of the total variance in the latter ( R = 0.057) ( p < 0.001) (Table 4 ).
As a result of the MANOVA, it was determined that having a high-risk or a pregnancy was associated with significant differences in the combined set of dependent variables (APSI and NUPDQ total scores), F = 6.231, p = 0.002, Wilk’s Lambda = 0.967. There were significant differences between the case and control groups in terms of their APSI psychosocial changes during pregnancy and prospect of childbirth dimension scores, F = 7.258, p < 0.001, Pillai’s Trace = 0.057. (Table 5 ).
This study determined the stress levels of pregnant women with high-risk and healthy pregnancies. Stress experienced in high-risk pregnancies can have negative effects in terms of the pregnancy process and maternal and fetal health (Atasever & Çelik, 2018 ; Gözüyeşil & Düzgün, 2021 ; Riggin, 2020 ; Traylor et al., 2020 ; Yüksel et al., 2011 ). Therefore, it is thought that the results of this study will contribute to the literature.
It was determined in this study that the education levels of the high-risk pregnant women, who constituted the case group, were lower compared to the healthy pregnant women in the control group. Other studies in the literature have shown that risk factors in pregnancy are at higher rates in women with low educational levels (Annagür et al., 2014 ; Soğukpınar et al., 2018 ; Topalahmetoğlu et al., 2017 ; Türkmen, 2019 ). It is thought that as education levels increase, the knowledge levels of pregnant women about the management of risk factors in pregnancy increase, and these situations are intervened with in the early period. Moreover, high education levels can also prevent factors that may cause a high-risk pregnancy such as malnutrition, ill-advised exercise practices, and lack of antenatal care. For this reason, considering the results of our study, it is recommended that health professionals provide education to pregnant women with low education levels about prenatal care, proper nutrition, exercise, and antenatal follow-ups.
The numbers of pregnancies and abortions among the participants in the case group in this study were significantly higher compared to those in the control group. In the study by Orbay et al. ( 2017 ), the number of pregnancies among pregnant women with GDM was lower than the number of pregnancies among those without GDM. Cincioğlu et al. ( 2020 ) found the mean number of abortions among pregnant women with risky pregnancies to be 1.31 ± 0.71. As the number of pregnancies increases, the potential risks of pregnancy also increase. More frequent monitoring of pregnant women with a high number of abortions by health professionals and providing information about family planning methods to women with a high number of pregnancies will prevent high-risk pregnancies.
High-risk pregnancies consist of many obstetric pathologies including maternal chronic diseases. Every pathologic condition experienced during pregnancy can affect the women’s stress levels (Sinaci et al., 2020 ). In this study, two different scales were used to measure the stress levels of the participants, and the stress levels of the participants in the case group were found to be higher than the stress levels of those in the control group. Gözübebek and Düzgün (2021) stated that 63.5% of pregnant women diagnosed with risky pregnancies experienced distress. Üzar-Özçetin and Erkan ( 2019 ) reported high perceived stress levels in high-risk pregnant women. In their meta-analysis study, Amiri and Behnezhad ( 2019 ) revealed that diabetes during pregnancy was a risk factor for anxiety symptoms, and diabetes increased the risk of anxiety by up to 48%. Other studies in the literature have shown that high-risk pregnant women also have high anxiety levels (Byatt et al., 2014 ; Denis et al., 2012 ; Gourounti et al., 2015a , b ; McDonald et al., 2021 ; Orbay et al., 2017 ; Sinaci et al., 2020 ; Hung et al., 2021 ).
It was reported that low education levels, having a history of abortion, and a high number of pregnancies may cause prenatal stress (Atasever & Çelik, 2018 ). In this study, lower education levels and higher numbers of pregnancies and abortions were found in the case group than in the healthy control group. Since low education levels and high numbers of pregnancies and abortions were thought to be potential confounding factors in terms of prenatal stress, further analyses tests were performed, and it was determined that these factors did not affect stress levels to a significant extent. The research in this field may benefit from a more in-depth exploration of potential implications and confounding factors related to education.
In the studies performed by Üzar-Özçetin and Erkan ( 2019 ) and Yüksel et al. ( 2013 ), it was found that the stress levels of pregnant women who had experienced hospitalization due to any risk during pregnancy were high. It is considered that diagnosis methods, treatment methods, symptoms, complications, and their effects on the fetus for high-risk pregnancies cause great stress in pregnant women, and the fact that some pregnant women spend this process in the hospital increases their stress levels even further. For this reason, considering the results of our study, it is recommended that healthcare professionals inform the pregnant woman about her diagnosis and symptoms and explain each procedure to be performed, and that healthcare institutions provide more comfortable hospital rooms.
In this study, it was seen that the prenatal stress levels of the participants were high in terms of psychosocial changes during pregnancy. Intense stress can cause a sense of helplessness and hopelessness by depleting the energy of individuals, as well as negatively affecting their physical and mental health (Sharma & Rush, 2014 ). For this reason, healthcare professionals have an important role in the care of pregnant women with high-risk pregnancies. They should take an active role in the early diagnosis of at-risk pregnant women through qualified home visits and by initiating and continuing treatment. Advanced clinical guidelines and case management models should be developed for women having high-risk pregnancies.
In the study by Pinar et al. ( 2022 ), women with high-risk pregnancies were given training on stress management. After the training program, it was determined that 51.4% of the women in the intervention group and 75.7% in the control group experienced stress. Based on these results, it is recommended that healthcare professionals provide training, to ensure the active participation of the pregnant woman and her partner, on stress management to reduce the perceived stress, anxiety, and hopelessness levels of women in high-risk pregnancy cases. Additionally, these pregnant women should be provided with methods to cope with stress such as breathing exercises, relaxation exercises, appropriate physical exercises, visualization/yoga, massage therapy, music therapy, explanations about social support factors, and practices strengthening their spirituality (Ölçer & Oskay, 2015 ).
In this study, no significant difference was found in the prenatal stress levels of the participants in the case group based on their obstetric diagnoses of high-risk pregnancy. In the study by Byatt et al. ( 2014 ), no significant difference was identified between obstetric diagnoses in terms of anxiety levels in pregnant women. A high-risk pregnancy causes high stress levels in pregnant women due to similar diagnostic tests, treatment methods, hospitalization, complications, and fetal outcomes (Kent et al., 2015 ).
It is thought that high stress levels are not associated with obstetric diagnoses, and similar stress levels are experienced by all pregnant women aware of any risky situation during their pregnancies. Nevertheless, an increase in stress levels in risky pregnancies such as cases of preeclampsia may cause a further aggravation in the clinical status of women. Healthcare professionals should be aware of the higher stress levels of these pregnant women, they should help the pregnant woman express her feelings and thoughts by providing a reassuring communication environment, and plan appropriate consultancy, intervention, and care routines to help reduce their stress levels. These professionals can also coach high-risk pregnant women in terms of stress reduction and coping mechanisms. Pregnant women with high stress levels should be referred to a specialist for psychological support and therapy.
Strengths and limitations
The strength of this study was its prospective design with a control group. In this study, the use of two similar scales in terms of measuring the stress levels of pregnant women provided rigor and transparency compared to data obtained in previous studies. Since these scales were included in studies in Turkey only in the context of testing their validity and reliability in Turkish, it was decided to use them in the study as they measure stress levels in the prenatal period. A limitation of the study was that the pre-pregnancy stress levels of the participants, which would affect their present condition, were not measured in the study. Women with high stress levels before pregnancy have a higher risk of high-risk pregnancy. In other words, instead of high-risk pregnancy increasing stress levels, high stress levels may have affected the high-risk pregnancy statuses of the women. The results of the study also revealed a significant difference in education levels between the case and control groups. However, as a result of further analyses, it was determined that education did not affect prenatal stress levels.
In this study, it was determined that high-risk pregnancy affected prenatal stress. Moreover, it was found that the participants in the case group who had high-risk pregnancies had lower education levels and higher numbers of pregnancies and abortions compared to the participants in the control group with healthy pregnancies. This is why healthcare professionals are recommended to bear in mind that pregnant women with low education levels and a high number of pregnancies and abortions are at risk of high-risk pregnancies and monitor these pregnant women more frequently and carefully.
It is of great importance for the course of a pregnancy that healthcare professionals assess the stress levels of pregnant women in the high-risk pregnancy category, provide psychological support to pregnant women who have high stress levels or are hospitalized, offer them counseling and training opportunities (e.g., relaxation exercises, breathing exercises, practices strengthening their spirituality, music therapy), take appropriate precautions, and refer these pregnant women to specialists if needed. Moreover, since the stress levels of these pregnant women will increase even more during childbirth, alternative methods to reduce the fear of childbirth and childbirth pain should be explained.
It is recommended to organize educational programs such as trainings, seminars, and conferences on stress management during pregnancy for health professionals working in family health centers, community health centers, and gynecology departments.
Consequently, more studies with larger sample sizes are needed to compare diagnostic stress levels in high-risk pregnancies. In addition to prenatal stress and childbirth fear levels, future studies should also determine the stress levels of women before pregnancy for similar comparisons between high-risk and healthy pregnancies.
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abedian, Z., Soltani, N., Mokhber, N., & Esmaily, H. (2015). Depression and anxiety in pregnancy and postpartum in women with mild and severe preeclampsia. Iranian Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Research , 20 , 454–459.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
ACOG (2018). Practice Bulletin 190 Summary: Gestational diabetes Mellitus. Obstetrics and Gynecology, 31 (2), 406–408.
Google Scholar
ACOG. (2019). American College of Obstetricians and gynecologists’ Committee on Practice bulletins-obstetrics and the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine. ACOG Practice Bulletin 204: Fetal growth restriction. Obstetrics and Gynecology , 133 (2), 97–109.
Amiri, S., & Behnezhad, S. (2019). Diabetes and anxiety symptoms: A systematic review and meta-analysis. The International Journal of Psychiatry in Medicine . https://doi.org/10.1177/0091217419837407
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Annagür, B. B., Kerimoğlu, Ö. S., Gündüz, Ş., & Tazegül, A. (2014). Are there any differences in psychiatric symptoms and eating attitudes between pregnant women with hyperemesis gravidarum and healthy pregnant women? Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research , 40 (4), 1009–1014.
Atasever, İ., & Çelik, A. S. (2018). The validity and reliability of the Antenatal Perceived stress inventory Turkish version: A methodological study. Health Care Women International , 39 (10), 1140–1151. https://doi.org/10.1080/07399332.2018.1469635
Article Google Scholar
Byatt, N., Hicks-Courant, K., Davidson, A., Levesque, R., Mick, E., Allison, J., et al. (2014). Depression and anxiety among high-risk pregnancy obstetric inpatients. General Hospital Psychiatry , 36 , 644–649.
Çapık, A., Apay, E., S., & Sakar, T. (2015). Determination of the level of distress in pregnant women. Journal of Anatolia Nursing and Health Science , 18 , 196–203.
Cetin, O., Guzel Ozdemir, P., Kurdoglu, Z., & Sahin, H. G. (2017). Investigation of maternal psychopathological symptoms, dream anxiety and insomnia in preeclampsia. The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine , 30 (20), 2510–2515.
Cincioğlu, E., Durat, G., Öztürk, S., & Akbaş, H. (2020). Mental States and coping styles with stress of women in high-risk pregnancy. Health and Society , 20 (3), 148–157.
Denis, A., Michaux, P., & Callahan, S. (2012). Factors implicated in moderating the risk for depression and anxiety in high risk pregnancy. Journal of Reproductive and Infant Psychology , 30 (2), 124–134. https://doi.org/10.1080/02646838.2012.677020
Deshpande, J. (2016). The effect of selected aspect of Garbha Sanskar on stress, coping strategies and wellbeing of antenatal mothers. International Journal of - Science and Research , 5 (3), 588–591.
Gourounti, K., Karapanou, V., Karpathiotaki, N., & Vaslamatzis, G. (2015a). Anxiety and depression of high risk pregnant women hospitalized in two public hospital settings in Greece. International Archives of Internal Medicine , 8 (25), 1–6.
Gourounti, K., Karpathiotaki, N., & Vaslamatzis, G. (2015b). Psychosocial stress in high risk pregnancy. International Archives of Internal Medicine , 8 , 1–9.
Gözüyeşil, E., & Düzgün, A. A. (2021). Prenatal distress and the contributing factors in high-risk pregnant women. Journal of Education and Research in Nursing , 18 (2), 183–189.
Graignic-Philippe, R., Dayan, J., Chokron, S., Jacquet, A. Y., & Tordjman, S. (2014). Effects of prenatal stress on fetal and child development: A critical literature review. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews , 43 , 137–162.
Gümüşdaş, M., Apay, S. E., & Özorhan, E. Y. (2014). Comparison of Psycho-Social Health in pregnant women with and without risk. Journal of Health Science and Profession , 1 (2), 32–42.
Hacettepe University Institute of Population Studies 2018. (2019). Turkey demographic and health survey . Hacettepe University Institute of Population Studies, T.R. Presidency of Turkey Directorate of Strategy and Budget and TUBİTAK.
Hung, H. Y., Su, P. F., Wu, M. H., & Chang, Y. J. (2021). Status and related factors of depression, perceived stress, and distress of women at home rest with threatened preterm labor and women with healthy pregnancy in Taiwan. Journal of Affective Disorders , 280 (1), 156–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2020.10.062
Kent, R. A., Yazbek, M., Heyns, T., & Coetzee, I. (2015). The support needs of high-risk antenatal patients in prolonged hospitalization. Midwifery , 31 (1), 164–169.
Lobel, M. (2008). The Stony Brook pregnancy project: Revised prenatal distress questionnaire (NUPDQ): 17-Item version . NUPDQ2.DOC.
MacKinnon, N., Kingsbury, M., Mahedy, L., Evans, J., & Colman, I. (2018). The association between prenatal stress and externalizing symptoms in childhood: Evidence from the Avon Longitudinal Study of parents and children. Biological Psychiatry , 83 (2), 100–108.
McDonald, H. M., Sherman, K. A., & Kasparian, N. A. (2021). Factors associated with psychological distress among Australian women during pregnancy. Personality and Individual Differences , 172 , 1–9.
Mete, S., Fata, S., & Özberk, H. (2020). Comparison of stress levels in Risky and Non-risky pregnancies. Journal of Academic Research in Nursing , 6 (3), 554–560. https://doi.org/10.5222/jaren.2020.93898
Ölçer, Z., & Oskay, U. (2015). Stress in high-risk pregnancies and coping methods. Journal of Education and Research in Nursing , 12 (2), 85–92.
Orbay, E., Tüzün, S., Çınkıt, B., Ölmez, M. B., Tekin, S., Purut, E., et al. (2017). Antenatal anxiety in pregnant women with gestational diabetes Mellitus. Ankara Medical Journal , 2 , 111–118.
Özsoy, G., & Özsoy, S. (2013). Effect size reporting in educational research. Elementary Education Online , 12 (2), 334–346.
Pinar, S. E., Daglar, G., & Aksoy, O. D. (2022). The effect of stress management training on perceived stress, anxiety and hopelessness levels of women with high-risk pregnancy. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology , 42 (1), 17–22. https://doi.org/10.1080/01443615.2020.1867970
Razurel, C., Kaiser, B., Dupuis, M., Antonietti, J. P., Citherlet, C., Epiney, M., & Sellenet, C. (2014). Validation of the antenatal perceived stress inventory. Journal of Health Psychology , 19 (4), 471–481.
Riggin, L. (2020). The assocation between gestational diabetes and mental illness: A scoping review. Canadian Journal of Diabetes , 44 (6), 566–571.
Sharma, M., & Rush, S. E. (2014). Mindfulness-based stress reduction as a stress management intervention for healthy individuals: A systematic review. Journal of Evidence-Based Integrative Medicine , 19 , 271–286.
Sinaci, S., Tokalioglu, E. Ö., Ocal, D., Atalay, A., Yilmaz, G., Keskin, H. L., et al. (2020). Does having a high-risk pregnancy influence anxiety level during the COVID-19 pandemic? European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology , 255 , 190–196.
Soğukpınar, N., Akmeşe, Z. B., Hadimli, A., Balçik, M., & Akin, B. (2018). Risky pregnancy Profile in Maternity hospitals: Sample of Izmir Province. Journal of Academic Research in Nursing , 4 (1), 37–44. https://doi.org/10.5222/jaren.2018.037
Topalahmetoğlu, Y., Altay, M. M., Cırık, D. A., Tohma, Y. A., Çolak, E., Çoşkun, B., et al. (2017). Depression and anxiety disorder in hyperemesis gravidarum: A prospective case-control study. Turkish Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology , 14 , 214–219. https://doi.org/10.4274/tjod.78477
Traylor, C. S., Johnson, J. D., Kimmel, M. C., & Manuck, T. A. (2020). Effects of psychological stress on adverse pregnancy outcomes and nonpharmacologic approaches for reduction: An expert review. American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology MFM , 2 (4), 100229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajogmf.2020.100229
Türkmen, H. (2019). The effect of hyperemesis gravidarum on prenatal adaptation and quality of life: A prospective case–control study. Journal of Psychosomatic Obstetrics & Gynecology , 40 , 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/0167482x.2019.1678020
Üzar-Özçetin, Y. S., & Erkan, M. (2019). Resilience, perceived stress and psychosocial health of high-risk pregnant women. Cukurova Medical Journal , 44 (3), 1017–1026. https://doi.org/10.17826/cumj.502989
Van De Loo, K. F., Van Gelder, M. M., Roukema, J., Roeleveld, N., Merkus, P. J., & Verhaak, C. M. (2016). Prenatal maternal psychological stress and childhood asthma and wheezing: A meta-analysis. European Respiratory Journal , 47 (1), 133–146.
Williamson, S. P., Moffitt, R. L., Broadbent, J., Neumann, D. L., & Hamblin, P. S. (2023). Coping, wellbeing, and psychopathology during high-risk pregnancy: A systematic review. Midwifery , 116 , 1–11.
Yali, M. A., & Lobel, M. (1999). Coping and distress in pregnancy: An investigation of medically high risk women. Journal of Psychosomatic Obstetrics & Gynecology , 20 , 39–52.
Yüksel, F., Akın, S., & Durna, A. (2011). The Turkish adaptation of the revised prenatal distress questionnaire: A reliability/validity and factor analysis study. Journal of Education and Research in Nursing , 8 , 43–51.
Yüksel, F., Akin, S., & Durna, Z. (2013). Prenatal distress in Turkish pregnant women and factors associated with maternal prenatal distress. Journal of Clinical Nursing , 23 (1–2), 54–64.
PubMed Google Scholar
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors express thanks to the mothers for participation in the study.
Open access funding provided by the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Türkiye (TÜBİTAK). No funding was received to conduct the study.
Open access funding provided by the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Türkiye (TÜBİTAK).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Midwifery, Faculty of Health Sciences, Balıkesir University, Balıkesir, Turkey
Hülya Türkmen
Department of Midwifery, Faculty of Health Sciences, Selçuk University, Konya, Turkey
Bihter Akın & Yasemin Erkal Aksoy
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Study conception and design: Hülya TÜRKMEN. Data collection: Hülya TÜRKMEN. Data analysis and interpretation: Hülya TÜRKMEN. Drafting of the article: Hülya TÜRKMEN, Bihter AKIN, Yasemin ERKAL AKSOY. Critical revision of the article: Hülya TÜRKMEN, Bihter AKIN, Yasemin ERKAL AKSOY.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Hülya Türkmen .
Ethics declarations
For the study to be carried out, approval was obtained from the Clinical Research Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Medicine of the University, and written permission was obtained from the institution where the study would be conducted (2019/123).
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest is reported by the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Türkmen, H., Akın, B. & Erkal Aksoy, Y. Effect of high-risk pregnancy on prenatal stress level: a prospective case-control study. Curr Psychol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-024-05956-z
Download citation
Accepted : 28 March 2024
Published : 11 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-024-05956-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- High-risk pregnancy
- Prenatal stress
- Psychosocial changes during pregnancy
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 12 May 2024
Validation of the Polish version of the Johns Hopkins Learning Environment Scale–a confirmatory factor analysis
- Dorota Wójcik 1 ,
- Leszek Szalewski 2 ,
- Adam Bęben 3 ,
- Iwona Ordyniec-Kwaśnica 3 &
- Robert B. Shochet 4
Scientific Reports volume 14 , Article number: 10843 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
- Health care
- Medical research
The Johns Hopkins Learning Environment Scale (JHLES) was developed by Robert B. Shochet, Jorie M. Colbert and Scott M. Wright of the Johns hopkins university school of medicine and consists of 28 items used to evaluate perception of the academic environment. The objective was to translate and adapt the JHLES to Polish cultural conditions and to validate the Polish version of the tool. The JHLES questionnaire was completed by students of all years (first–fifth) of the faculties of dental medicine at the Medical University of Lublin and the Medical University of Gdańsk. The total surveyed population consisted of 597 students. The overall reliability of the tool was excellent. Confirmatory factor analysis was performed in order to confirm structural consistency with the original JHLES tool. Consequently, all indices had acceptable values (close to 1 or 0, depending on the case), and there was consistency in the results, which shows that the JHLES model is supported by the data. In the present study, the JHLES has been validated in a sample of dental students for the first time in Poland and Europe. Our study provided good evidence for the reliability and validity of the Polish version of the JHLES. In conclusion, the Polish-language version of the JHLES questionnaire is a reliable and valid instrument for analysing the learning environment for students, and its factor structure is supported by the data.
Introduction
Recently many authors have witnessed a trend toward increased attention being paid to the learning environment-related aspects 1 , 2 . As the needs of students evolve, universities have to meet the challenge and introduce changes that respond to these evolving demands. The learning environment encompasses a wide range of domains related to educational, physical, social, and psychological contexts that have a subsequent impact on the professional skills of the students 3 , 4 , 5 . Bonsaken and other authors reported that the perceived quality of the learning environment directly impacted students’ learning and exam results, their satisfaction with the course or study programme, their personal well-being and overall academic achievement 3 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 .
According to Bloom definition, the educational or learning environment concept can be defined: “the conditions, external stimuli, and forces which may be physical, social, as well as intellectual forces which challenge the individual and influence students’ learning outcomes” 10 , 10 .
Assessment of the learning environment is important for enabling improvement in the quality of the curriculum. The most often used and most available way of assessing the learning environment assessment is the evaluation of students’ perception of this environment 10 , 13 . So far, the Polish learning environment has not been assessed on a large scale and in order to carry out such assessment it is necessary to adapt the appropriate tools. The research will allow these tools to be used later to assess the learning environment of Polish medical schools.
According to the study by Rusticus et al., the learning environment can be divided into four spheres: psychological, social, cultural and physical 14 . Those engaged in the process of education (both the student and the educator) and also the setting have an impact on the whole learning environment 15 . Focusing only on one aspect, such as student’s perspective, may be insufficient for proper/comprehensive assessment of the learning environment 16 . Thus, it is important to conduct studies to determine the mutual influence of different aspects.
Acton and McNeil described the interrelationship between different dimensions of the learning environments such as space, pedagogy and learning 17 , 18 .
The psychological aspect of the learning environment refers to feelings as well as the preparation for learning and teaching on the part of students, academic staff and other people engaged in education (e.g. administration, technical support, etc.). Meanwhile, from the social perspective, the relationships among these stakeholders and the emotions associated with education and handling matters connected with the education process at university are relevant, as well as the motivation and expectations of both students and educators. Ideally, these expectations should be similar. An extremely important factor is cultural tolerance, especially in the case of learning environments made up of people from different cultural backgrounds. Misunderstandings due to such issues could have a very negative impact on the whole learning environment. Also, one cannot ignore the conditions of the premises where classes are held, which may also have a significant impact on the quality of education, and thus perception of learning environment. As pointed out by McNeil and Borg, it is not only about the halls and rooms where the classes take place, but also about the space available for students to meet, self-study and rest 17 .
Consequently, there is the need to develop a tool for the assessment of the quality of the learning environment within universities. In 1997, Roff et al. developed the Dundee Ready Educational Environment Measure (DREEM) questionnaire 19 , which remained the gold standard for assessment of the quality of the learning environment in medical universities for many years. Over time, more modern questionnaires emerged that raised important issues that do not have their counterparts in DREEM. For this reason, the Johns Hopkins Learning Environment Scale (JHLES) questionnaire has been used increasingly in recent years to assess the learning environments within medical universities worldwide. It is also a newer questionnaire that deals with current issues of safety and inclusion of medical students. In addition, the JHLES questionnaire is based on an earlier in-depth literature review and the criteria used to determine the strength of validity evidence in a systematic review of studies that assessed medical students’ and residents’ perceptions of the learning environment 4 , 20
The JHLES is a 28-item assessment tool designed for measuring students’ perceptions of the academic environment. It was designed by Robert B. Shochet, Jorie M. Colbert and Scott M. Wright of the John Hopkins University School of Medicine 11 The JHLES was developed using a consistent methodology starting in 2012 and a Likert scale is used to gradeits items. Assessing students’ perceptions of the institutional curriculum, environment, and possibilities, as well as their relationships with peers and university staff and their level of involvement in the academic community, is the goal of the JHLES. The JHLES has been modified, translated, and utilized in a few countries so far. In Brazil Damiano et al demonstrated reliability and validity for the JHLES. as feasible option for measuring learning environment in Brazilian medical students 21 . In China the JHLES was utilized to assess medical students’ perceptions of medical school learning environment; the main goal of Zhou et al study was to identify influencing factors for medical students’ perception levels 22 .In Malaysia Tackett et al validated the JHLES and measured the learning environment using two tools: JHLES and DREEM 23 , 24 . The JHLES has not been translated or validated for Polish conditions until now.
Materials and methods
The objective here was to translate and adapt the JHLES questionnaire to Polish cultural conditions and validate the Polish version of the tool.
This study was part of a project fully funded by the National Science Centre. The aim of the project was to validate DREEM and JHLES. The validation of the DREEM questionnaire has already been published 25 . The aim of the project was also to validate a more modern questionnaire that is becoming increasingly popular. In addition, there are Items in the JHLES that raise important issues (e.g. 24–26) that have no equivalent in the DREEM, both questionnaires complement each other well. The two validations are not presented in one paper, as most journals have a page or character limit for papers. The project manager decided that this route would be more accessible for future readers. Acquiring adequate research tools is crucial for analyzing the educational environment, our study will enable both methods (the JHLES and DREEM) to be employed to examine the educational environment of Polish medical schools in the future.
Evaluating the learning environment is beneficial because it can reveal how students perceive their surroundings and allow teachers to analyse, plan, and integrate effective teaching strategies to improve it.
To the best of the authors’ knowledge, neither the dental community nor the other medical students involved in this study participated in any other established process for evaluating the learning environment And it was decided that every dental student from the two colleges that were chosen would take part in this investigation.
The objective of the study consisted of the translation, cultural adaptation, and validation of the JHLES questionnaire. As no universal guidelines are available for cultural adaptation of surveys, the authors followed the methodology described in previous studies 26 .
The original JHLES questionnaire is presented in Table 1 .
The JHLES questionnaire was completed by students of all years (first–fifth year) of the faculties of dental medicine at the Medical University of Lublin and the Medical University of Gdansk. The total surveyed population consisted of 650 studentsand their characteristics are given in Table 2 . The study was carried out during April–June 2022 and was approved by the Bioethics Committees at the Medical University of Lublin and the Medical University of Gdańsk, as well as by the authorities of both universities. The deans of the various schools of dentistry gave permission for the study to be conducted and the collaborators involved with the schools received written instructions on how to implement the project. One of the authors also carried out the research in both universities.
The questionnaire was handed out to the students during their classes. Before starting the survey, each collaborator briefly clarified the aims of the study and the method by which the data will be processed, particularly emphasizing aspects of voluntary participation and anonymity. Sociodemographic data such as age, gender, academic year and origin were also collected 25 .
Participants and criteria for eligibility
All 418 undergraduate full-time students from the end of the first year through to the fifth year of the Medical University of Lublin and 348 from the Medical University of Gdansk present during the classes when the JHLES and DREEM were administered were invited to participate in this study. Inclusion criteria were to be a dentistry student and give consent for participation in the study. Exclusion criteria were previous participation in a pilot study; lack of consent to participate in the study; and failure to complete the questionnaire twice. Polish medical schools have a 5 years curriculum: the first 2 years are preclinical, followed by 2 years of clinical activity and the last year as mostly hospital activities. Students were informed that 35 days later they would have both the JHLES and DREEM retested. Both questtionnaires were validated simultaneously 25 .
Students who agreed to participate in the survey received no remuneration in any form. The first round of testing lasted approximately 30 min, and the second round about 20 min. To compare both the test and the retest data, students were asked to encode their surveys; surveys were pseudoanonymized, and the students were able to obtain a number from the random number generator. Surveys that had not been encoded or had no matching test/retest surveys were excluded from study 25 .
Sample size selection was based on the generally accepted rule of thumb that there must be at least 5–15 cases per estimated parameter in the confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) 25 .
Characteristics of the sample
The primary sample consisted of 650 undergraduate students (498 females, 152 males) recruited from various departments within the Lublin and Gdańsk universities. Of 650 observations in our sample, the 53 (8.2%) contained 1 to 6 missing values. Within each question, the proportion of missing data did not exceed 1.06% (see Fig. 1 in the Appendices section).
Translation and transcultural adaptation validity
Firstly, permission to translate and adapt the questionnaires was obtained from the authors. Secondly, the author and two other individuals with a fluent command of English while having Polish as their mother tongue translated the questionnaires into Polish. All three versions were compared and consolidated into a consensus version consistent with the original in terms of terminology, semantics, and concept. A separate consensus was reached for each questionnaire item. Minor changes were introduced to ensure the JHLES was adequate for Polish academic culture. Following the translation of both scales into Polish, they were sent to two native speakers of English who independently translated both questionnaires back into English. In this way, a total of four questionnaires were back-translated, two versions of DREEM and two versions of the JHLES. The two versions of back translations were sent to the original authors so that the final wording of the questionnaires could be determined. The final versions of the questionnaires were translated into Polish by the author and two professional translators and later submitted for consultation and a pilot study with a group of 10–15 members of the Polish Association of Dental Students. Following the consultation and pilot study, final amendments were made to the questionnaires by the Polish authors (Table 3 ).
The cultural adaptation involved adjusting the questionnaire to the Polish academic environment: for example, the term “School of Medicine” was replaced by “Medical University” because in Poland only medical universities exist; “faculty advisors” was replaced by “coordinators/tutors” because they fulfil a similar function in Poland; and due to the dissimilarity of the Polish language, questions were replaced by statements so that the questionnaire could be understandable and grammatically correct. Furthermore, female grammatical forms (Polish: feminatywy), female variants of performers of actions and personal characteristic names were added. Women are named in terms of their titles, fulfilled functions, held positions, practiced professions, nationality, background, faith, convictions, psychological and physical qualities, and performed activities. They represent a class of lexemes with permanent female grammatical gender that consists of syntactically independent nouns. They do not include adjectives or verbs, in the case of which gender is an inflectional category. By adding female grammatical forms, we wanted to address both female and male students 25 .
Questions 1, 2 and 5 were converted into statements in order to standardize the answers on the Likert scale. For each statement, students could answer: strongly agree, agree, disagree, strongly disagree, strongly disagree. If Items 1, 2 and 5 had remained questions, the answers for these three items would have had to be changed to Polish. All changes were approved by the author of the questionnaire and also checked by a professional language corrector.
Items 6 and 10 were also accepted by the author of the original questionnaire and there were no queries during the pilot study or the target study.
Statistical analysis
Basic descriptive statistics were tabulated with tests for significant differences applied as appropriate. Basic descriptive statistics were used for the study group characteristics and the JHLES results as well as for medical university, gender, and academic year.
Overall JHLES scores were computed by summing across survey items for each scale.
Spearman correlation coefficients were calculated to determine associations between each of the JHLES scales and their respective subcategories or domains.
The reliability of the JHLES questionnaire (both the global scale and the subscales) was evaluated for internal consistency using Cronbach’s α, the value of which is between 0 and 1. This coefficient reflects the homogeneity of the scale, which is the level to which it can be regarded as a measure of a single construct 27 . Following the methodology of Dimoliatis et al., we estimated ‘expected’ α values for the various subscales and compared them with the ‘observed’values 28 .
The significance level of the statistical tests in this analysis was set at α = 0.05 and the normality of the distributions of the variables was analysed using the Shapiro–Wilk test. Numerical variables with distributions that deviated from the normal distribution were reported as the median with quartiles ( Mdn ; Q1 , Q3 ) and normally distributed variables as the mean and standard deviation ( M ; SD ).
Confirmatory factor analysis
The confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) model was specified based on the theoretical framework proposed for measurement to assess students’ perceptions of the medical school learning environment. It was hypothesized that the 28-item JHLES would load onto seven latent factors: community of peers; faculty relationships; academic climate; meaningful engagement; mentoring; inclusion and safety; and physical space. Indicator variables were defined by Likert scale items with values from 1 to 5.
We conducted CFA to test our hypothesized measurement model. A diagonally weighted least squares (DWLS) estimator was performed, which is appropriate for our ordinal data and the optimization method used was NLMINB (non-linear minimization).
The model fit was assessed using several fit indices, including the comparative fit index (CFI), tucker-lewis index (TLI), and root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA), standardized root mean square residual (RSMR).
We also employed Little’s MCAR (missing completely at random) test to evaluate whether the occurrence of missing data in our dataset was completely random 29 .
Differences between groups
Welch’s t test was used for variables with normal distribution and two groups. The effect size was calculated using Hedges g -measure. And the effect obtained was interpreted based on Cohen’s convention 30 .
Welch’s ANOVA test was used for variables with a normal distribution and number of groups above and the effect size was calculated using the omega squared effect size measure. The obtained effect was interpreted based on Field’s convention 31 . Significance between pairs of groups was tested using the Games-Howell test. To account for multiple comparisons between pairs of groups, the significance level was adjusted using the Holm correction.
Correlation analysis
Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient (rho) was used to measure the strength and direction of association between two numerical variables when at least one variable was not normally distributed; statistical significance was calculated using the algorithm AS 89 32 .
Statistical environment
Analyses were conducted using the R Statistical language (version 4.1.1; R Core Team, 2021) 33 on Windows 10 Pro 64 bit (OS build 19045), using the packages lavaanPlot (version 0.6.2), report (version 0.5.7; Makowski D et al., 2023), ggstatsplot (version 0.9.3; Patil I, 2021) 34 , lavaan (version 0.6.12) 35 , gtsummary (version 1.6.2) 36 , naniar (version 1.0.0) 37 , ggplot2 (version 3.4.0) 38 , readxl (version 1.3.1) 39 , dplyr (version 1.1.2) 40 , effectsize (version 0.8.3) 41 and psych (version 2.1.6) 42 .
Ethical approval and consent to participate
He study was approved by the Bioethics Committees at the Medical University of Lublin (KE-0254/61/03/2022) and the Medical University of Gdańsk (KE-0254/61/03/2022) as well as by the authorities of both universities. All methods were carried out in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects.
Handling missing data
The output from Little’s MCAR test was χ 2 = 1279.222, p < 0.001 providing strong evidence against the null hypothesis (data are Missing Completely At Random). This suggested that the occurrence of missing data was systematic and might be related to either observed or unobserved data. The lack of randomness prevented imputation of data, therefore observations with missing values were removed from the dataset. The characteristics of the final sample are presented in Table 2 . The overall response rates were 325/418 (78%) and 272/348 (78%) respectively.
As shown by the correlation analysis (Table 4 ), positive corrected item-subscale and item-total correlations were identified for nearly all item pairs. Correlations between items within each subscale were stronger than those between items from different subscales. Strong positive correlations were identified within the individual subscales, with the exception of Subscale 7, where moderate correlations were identified for Item 27.
Reliability analysis
We estimated the ‘expected’ Cronbach’s α values in the different subscales and compared them with the ‘observed’ values 28 . The overall reliability of the tool was 0,896.
The study was carried out using a test–retest design and therefore intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) were also determined for the purpose of reliability assessment (Table 5 ).
The model fitted normally after 113 iterations. The number of parameters of final model was 77, with 597 observations.
First, we tested the baseline model, which assumes no relationships among the variables. The chi-square test of the baseline model was statistically significant: χ 2 (378) = 13,611.73, p < 0.001. This result indicated a poor fit of the data to a model assuming no relationships among variables. In other words, it suggested that there were indeed significant relationships among the variables in our dataset, as the likelihood of the observed data giving a model of independence was near zero, p < 0.001.
The chi-square test of user model fit was significant: χ 2 (329) = 526.77, p < 0.001. This was because the chi-square test is sensitive to sample size, and for a large sample, even minor discrepancies between the observed and model-implied covariance matrices can result in a significant chi-square value.
Other fit indices also supported the adequacy of the model: the CFI was 0.985, TLI was 0.983, RMSEA was 0.032, ( 90% confidence interval [ 90% CI ] = 0.027, 0.037) and SRMR = 0.052. Results are presented in Table 6 43 .
In summary, our model demonstrated good fit across the different fit indices, suggesting that the proposed factor structure adequately represents the relationships among the observed variables.
Parameter estimates
The standardized factor loadings were all significant, demonstrating that each item was significantly related to its respective factor. The loadings and covariance magnitudes, as well as the significance levels, can be found in the path diagram for the fitted CFA model in Fig. 1 .
Path diagram of the confirmatory factor analysis model.
JHLES overall score
The distribution of JHLES overall scores for the group of individuals without missing data ( N = 597) is shown in Fig. 2 (see Fig. 2 in the Appendices section). Visually, the distribution in the form of a histogram and density plot did not deviate from the normal distribution, as evidenced by the result of the Shapiro–Wilk test, W = 0.99, p = 0.067. The mean overall test score was 89.98 (13.75).
JHLES overall score versus year of study
The results of Welch’s ANOVA test showed a significantly higher total JHLES test score for the subjects of the first year of study, M = 97.21, SD = 13.78, compared to the other years of study, second year, M = 90.10 , SD = 13.33 , third year, M = 88.91, SD = 13.1, fourth year, M = 86.30, SD = 13.18, andfifth year, M = 87.76, SD = 12.91. The estimated effect was of moderate magnitude. No significant differences were found between the other groups. For a graphical visualization of the results, see Fig. 3 (see Fig. 3 in the Appendices section).
JHLES overall score versus gender
The results of Welch's t-test showed no significant differences between the total score of females, M = 89.81, SD = 13.67, and males, M = 90.61, SD = 14.06, p = 0.560. The effect obtained was of small size. For a graphical visualization of the results, see Fig. 4 (see Fig. 4 in the Appendices section).
JHLES overall score versus university
The results of Welch’s t -test showed that the total JHLES core in the Gdańsk University group, M = 87.9, SD = 13.69 was significantly lower than the total score in the Lublin group, M = 91.73, SD = 13.56, p < 0.001. The effect obtained was of small size (see Fig. 5 in the Appendices section).
JHLES overall score versus endorsement
The results of the Welch’s ANOVAtest showed a significantly higher total JHLES test score for the subjects with exceptional endorsement, M = 109.14, SD = 17.42, compared to the other endorsement levels, of good, M = 95.39, SD = 10.07, fair, M = 81.21, SD = 10.22, and poor, M = 68.07, SD = 11.50.
In addition, the score of the group with good endorsement was significantly higher compared to the groups with fair and poor endorsement. Conversely, the score of the fair group was significantly higher than that of the poor endorsement group. The estimated effect was of large magnitude.
For a graphical visualization of the results, see Fig. 6 (see Fig. 6 in the Appendices section).
JHLES overall score versus age
The results of the correlation analysis, rho = − 0.21, p = 0.001, showed a significant negative relationship between the JHLES total score and the age of the participants. The total score thus decreased significantly with increasing age.
Convergent validity
The convergent validity of the test can be measured by demonstrating a positive correlation between measures of related constructs. In other words, if two scales are related, a subject who scores high on one scale should also score high on the other. Pearson’s r (ranging between 1 and −1), is used to estimate correlation by revealing the strength and direction of the relationship between variables. Comparing the total results of JHLES and DREEM surveys, Pearson’s rho amounted to 0.797, (p < 0.001).
The aim of this study was to develop the Polish-adapted version of the JHLES questionnaire. This was the first validation of this tool in Polish conditions as well as the first validation to be performed on such a large group of subjects. Validation was performed using the less common test–retest method and the CFA. Validity analysis also included corrected correlations for the original JHLES structure (item–total and item–subscale), following the recommendations established by Stuive et al 44 . A minimum threshold value of 0.20 was set for the absolute value of the corrected correlations in order to consider it to support construct validity 45 .
The validated questionnaire appears to presentgood internal reliability, as evidenced by its internal consistency and the test–retest consistency indicative of the temporal stability of the results. The overall reliability of the tool was good, near to excellent 0,896 Medium or good consistency (ICC) was demonstrated for individual items, with items 3, 17, 25 and 28 showing good consistency as assessed according to the newest and most restrictive ICC interpretation criteria 46 .
CFA facilitated the development of a model presenting good fitting metrics. Individual items were positively correlated with one another, with the best correlations observed between items within the same subscales. Our study featured the JHLES being used in the largest study group to date (N = 597) and the correlation between the average scores of all items of the JHLES forboth periods was very high (Pearson’s r = 0.790; p < 0.001). Factor analysis is among the most useful methods for studying and validating the internal structure of instruments 47 , 48 and CFA specifically addresses the relationships between latent variables or factors and observed measures or indicators (e.g. test items). The chi-square testresults might indicate that the model does. Not fit well, but it is important to remember that this test is highly dependent on sample size. In this instance, the ‘relative chi-square’ (the chi-square statistic divided by its degrees of freedom) was 1.6. Thus, the relative chi-square was less than 5, and the outcome was deemed acceptable.
The fit indices also supported the adequacy of the model: the CFI was 0.985, TLI was 0.983, RMSEA was 0.032, (90% CI = 0.027, 0.037) and SRMR = 0.052, The requirements set by Hu and Bentler for an acceptable match (the CFI, TLI values above 0.95, RMSEA values below 0.06 and SRMR below 0.08) are thus met by our fit indices 43 . The results were consistent due to all indices being within acceptable ranges (close to 1 or 0 depending on the situation), which shows that the JHLES model is supported by the data 43 . The correlation coefficients between the JHLES and another tool based on a similar theoretical concept, namely the DREEM, was indicative of the relevance of the newly developed tool. Statistical analysis revealed a significant correlation. Coefficients between the total results of theJHLES and DREEM surveys (p < 0.001). The correlation was positive, i.e. higher total JHLES scores corresponding to higher total DREEM scores. Pearson’s rho amounted to 0.797 also indicating a very strong correlation 25 . This strong correlation coefficients between the DREEM and JHLES total scores suggesting that both questionnaires may measure the same overall concept—the learning environment.
Damiano et al also performed an adaptation of the JHLES and Medical School Learning Environment Scale (MSLES) questionnaires to obtain results with appropriate validity (in terms of content, internal structure, psychometric properties, and relation to other variables). The JHLES instrument has good reliability, with Cronbach α = 0.809. Stability was assessed using test–retest reliability via Pearson’s r and ICCs. The 45-day test–retest comparison resulted in Pearson’s r = 0.757 (p < 0.001) and a ’single measures ‘ ICC of 0.757 ( p < 0.001). The MSLES global score showed a significant ( p < 0.05) and positive correlation with the learning environment, both for school endorsement ( r = 0.321), and overall learning environment perception ( r = 0.505). Findings included good test–retest reliability and convergent validity, both of which were significantly correlated with each other, as well as with two questions on overall learning environment perception and school endorsement. The authors had validated the surveys using principal component analysis; the Brazilian version of the questionnaire contained significant differences as compared to the original, with only Factors 3 (Academic Climate), 5 (Physical Space), 6 (Inclusion and Safety), and 7 (Mentoring) maintaining the same structure as the original version. Despite the changes, all subdomains of the Brazilian JHLES and the original versions had similar Cronbach’s α coefficients for comparisons among both the original and the factor revised JHLES and its correlations with each JHLES subdomain 21 .
In a study by Tackett et al, the JHLES showed high internal reliability for the total JHLES score (α = 0.92) and the seven subdomains (α = 0.56–0.85). Each of its seven domains had values of Cronbach’s α within acceptable limits. Similar values were obtained in our study. According to Tackett et al., the corrected item-total correlations for the JHLES showed that all but two items had correlation coefficients above the acceptable level of 0.30 23 . In our study, individual items were positively correlated with one anotheraand the best correlations were observed between items within the same subscales.
Tackett et al. (2015) performed assessment of the DREEM and JHLES in Malaysian medical schools. Their result showed that the DREEM and JHLES scores were highly correlated with one another overall (r = 0.73), with stronger correlations at the Perdana University School of Medicine (r = 0.80) and Cyberjaya University College of Medical Sciences (r = 0.80) compared to Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine (r = 0.64). Our results showed a very strong correlation (r = 0.797). The very strong correlation between the DREEM and JHLES total scores suggests that both questionnaires may measure the same overall construct 24 . In our study, the values of Cronbach’s α for individual scales ranged between 0.554 and 0.901 (Table 7 ), which translated to good (Scales 1 and 2), acceptable (Scale 3 and 4), and excellent (Scale 5) reliability. The overall reliability of the tool was excellent. ICCs were also determined for reliability assessment. Medium or good consistency was demonstrated for individual items, with Items 17 and 28 showing good consistency as assessed according to the newest and most restrictive ICC interpretation criteria 46 . Our results showed that the correlation was positive, with higher total JHLES scores corresponding to higher total DREEM scores. Pearson’s r was 0.797, indicating a very strong correlation 25 .
Limitations
Our study was carried out in two of the ten medical universities in Poland, therefore careful consideration should be paid to the results obtained using the JHLES tool when attempting to generalize these results to other institutions. Furthermore, both the JHLES and DREEM questionnaires were completed on the same day, which might have resulted in the correlation between instruments being stronger than if they were completed at different times. The reason for the lower reliability of Subscale 7 is probably the lack of campus at the Medical University of Gdańsk. Polish students may not consider university buildings as a campus, as well as an important part of the learning environment.
Conclusions
Our study provided good evidence for the reliability and validity of the Polish version of the JHLES. In conclusion, the Polish-language version of the JHLES questionnaire is a reliable and valid instrument for analysing the learning environment for students, and its factor structure is supported by the data. The validated questionnaire is presented in Table 2 . The use of standardized tools for the assessment of learning environments will lead to a better understanding of the local functioning of such environments and facilitate comparison of these environments with those in other countries. Improved functioning of educational environments in Poland is also to be expected.
In future studies, it will be possible to assess the factors causing differences in perception of the learning environment. It will become possible to assess the relationship between the learning environment and the professional development and clinical competencies of students of medical universities in Poland.
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are available in Mendeley Data https://doi.org/10.17632/36zpwkbny3.1
Abbreviations
Comparative fit index
Dundee ready educational environment measure
Goodness of fit index
Intraclass correlation coefficients
Johns Hopkins Learning Environment Scale
Modification indices
Principal component analysis
Root mean square eror of approximation
Standardized root-mean-square residual
Sample size
First quartile
Third quartile
Standard deviation
P-value of statistical test
P-value with Holm adjustment for multiple comparisons
90% Confidence interval
Welch’s ANOVA test statistic
Student’s t -test statistic
Hedges g effect size
Omega-square effect size
Statistic of Shapiro–Wilk test
Chi-square test statistic
Degrees of freedom
The Spearman correlation coefficient
Sellberg, M., Palmgren, P. J. & Möller, R. A cross-sectional study of clinical learning environments across four undergraduate programs using the undergraduate clinical education environment measure. BMC Med. Educ. 21 , 258 (2021).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Isba, R., Rousseva, C., Woolf, K. & Byrne-Davis, L. Development of a brief learning environment measure for use in healthcare professions education: The healthcare education micro learning environment measure (HEMLEM). BMC Med. Educ. 20 , 1–9 (2020).
Article Google Scholar
Hutchinson, L. Education environment. Bmj 326 , 810–812 (2003).
Shochet, R. B., Colbert-Getz, J. M., Levine, R. B. & Wright, S. M. Gauging events that influence students’ perceptions of the medical school learning environment: Findings from one institution. Acad. Med. 88 , 246–252 (2013).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Genn, J. AMEE medical education guide no. 23 (part 1): Curriculum, environment, climate, quality and change in medical education—A unifying perspective. Med. Teach. 23 , 337–344 (2001).
Bonsaksen, T. et al. Associations between occupational therapy students’ academic performance and their study approaches and perceptions of the learning environment. BMC Med. Educ. 21 , 1–8 (2021).
Aluri, V. L. & Fraser, B. J. Students’ perceptions of mathematics classroom learning environments: Measurement and associations with achievement. Learn. Environ. Res. 22 , 409–426 (2019).
Bonem, E. M., Fedesco, H. N. & Zissimopoulos, A. N. What you do is less important than how you do it: The effects of learning environment on student outcomes. Learn. Environ. Res. 23 , 27–44 (2020).
Thygesen, H. et al. Associations between learning environment variables and satisfaction with the education program among occupational therapy students. Ir. J. Occup. Ther. 48 , 91–100 (2020).
Shrestha, E., Mehta, R. S., Mandal, G., Chaudhary, K. & Pradhan, N. Perception of the learning environment among the students in a nursing college in Eastern Nepal. BMC Med. Educ. 19 , 1–7 (2019).
Shochet, R. B., Colbert-Getz, J. M. & Wright, S. M. The Johns Hopkins Learning Environment Scale: Measuring medical students’ perceptions of the processes supporting professional formation. Acad. Med. 90 , 810–818 (2015).
Bloom, B. S. Stability and Change in Human Characteristics (Wiley, 1964).
Google Scholar
Farajpour, A., Esnaashari, F. F., Hejazi, M. & Meshkat, M. Survey of midwifery students’ perception of the educational environment based on DREEM model at Islamic Azad University of Mashhad in the academic year 2014. Res. Dev. Med. Educ. 4 , 41–45 (2014).
Rusticus, S. A., Pashootan, T. & Mah, A. What are the key elements of a positive learning environment? Perspectives from students and faculty. Learn. Environ. Res. 26 , 161–175 (2023).
Rusticus, S. A., Wilson, D., Casiro, O. & Lovato, C. Evaluating the quality of health professions learning environments: Development and validation of the health education learning environment survey (HELES). Eval. Health Prof. 43 , 162–168 (2020).
Schussler, E. E., Weatherton, M., Chen Musgrove, M. M., Brigati, J. R. & England, B. J. Student perceptions of instructor supportiveness: What characteristics make a difference?. CBE Life Sci. Educ. 20 , 29 (2021).
McNeil, J. & Borg, M. Learning spaces and pedagogy: Towards the development of a shared understanding. Innov. Educ. Teach. Int. 55 , 228–238 (2018).
Acton, R. Innovating lecturing: Spatial change and staff-student pedagogic relationships for learning. J. Learn. Spaces 7 , 1–15 (2018).
Roff, S. et al. Development and validation of the dundee ready education environment measure (DREEM). Med. Teach. 19 , 295–299 (1997).
Colbert-Getz, J. M., Kim, S., Goode, V. H., Shochet, R. B. & Wright, S. M. Assessing medical students’ and residents’ perceptions of the learning environment: Exploring validity evidence for the interpretation of scores from existing tools. Acad. Med. 89 , 1687–1693 (2014).
Damiano, R. F. et al. Measuring students’ perceptions of the medical school learning environment: Translation, transcultural adaptation, and validation of 2 instruments to the Brazilian portuguese language. J. Med. Educ. Curric. Dev. 7 , 238212052090218 (2020).
Zhou, Z. et al. Nomograms for predicting medical students’ perceptions of the learning environment: Multicenter evidence from medical schools in China. Front. Public Health 10 , 825279 (2022).
Tackett, S. et al. Profiling medical school learning environments in Malaysia: A validation study of the Johns Hopkins Learning Environment Scale. J. Educ. Eval. Health Prof. 12 , 39 (2015).
Tackett, S. et al. Learning environment assessments of a single curriculum being taught at two medical schools 10,000 miles apart. BMC Med. Educ. 15 , 105 (2015).
Wójcik, D., Szalewski, L., Bęben, A., Ordyniec-Kwaśnica, I. & Roff, S. Validation of the Polish version of the DREEM questionnaire—A confirmatory factor analysis. BMC Med. Educ. 23 , 1–13 (2023).
Tomás, I. et al. Psychometric validation of the Spanish version of the dundee ready education environment measure applied to dental students. Eur. J. Dent. Educ. 18 , 162–169 (2014).
Taber, K. S. The use of cronbach’s alpha when developing and reporting research instruments in science education. Res. Sci. Educ. 48 , 1273–1296 (2018).
Dimoliatis, I., Vasilaki, E., Anastassopoulos, P., Ioannidis, J. & Roff, S. Validation of the Greek Translation of the Dundee Ready Education Environment Measure (DREEM) 17
Little, R. J. A test of missing completely at random for multivariate data with missing values. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 83 , 1198–1202 (1988).
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences New York 54 (Academic, 1988).
Field, A. Discovering Statistics Using IBM SPSS Statistics (Sage, 2013).
Best, D. & Roberts, D. Algorithm AS 89: The upper tail probabilities of Spearman’s rho. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C Appl. Stat. 24 , 377–379 (1975).
Team RC. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Supplemental Information References S.1 371–378 (2021)
Lishinski, A. lavaanPlot: Path Diagrams for’Lavaan’Models via’DiagrammeR’. Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN) (2021)
Rosseel, Y. lavaan: An R package for structural equation modeling. J. Stat. Soft. 48 , 1–36 (2012).
Daniel, D. S., Whiting, K., Curry, M., Lavery, J. A. & Larmarange, J. Reproducible summary tables with the gtsummary package. R J. 13 , 570–580 (2021).
Tierney, N. & Cook, D. Expanding tidy data principles to facilitate missing data exploration, visualization and assessment of imputations. J. Stat. Softw. 105 , 1–31 (2023).
Wickham, H., Chang, W. & Wickham, M. H. Package ‘ggplot2’. Creat. Elegant Data Vis. Using Gramm. Gr. Vers. 2 , 1–189 (2016).
Wickham, H. & Bryan, J. readxl: Read Excel Files. R Package Version 1.3. 1 . (2019)
Wickham, H., François, R., Henry, L., Müller, K. dplyr: A Grammar of Data Manipulation. R Package Version 1.1.2. Computer software] https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=dplyr (2023).
Ben-Shachar, M., Lüdecke, D. & Makowski, D. effectsize: Estimation of effect size indices and standardized parameters. J. Open Sour. Softw. 5 , 2815 (2020).
Article ADS Google Scholar
Revelle, W. psych: Procedures for Psychological, Psychometric, and Personality Research. Northwestern University, Evanston, Illinois R Package Version 229 (2021)
Hu, L. & Bentler, P. M. Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Str. Equ. Model. A Multidiscip. J. 6 , 1–55 (1999).
Stuive, I., Kiers, H. A., Timmerman, M. E. & ten Berge, J. M. The empirical verification of an assignment of items to subtests: The oblique multiple group method versus the confirmatory common factor method. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 68 , 923–939 (2008).
Bowling, A. Research Methods in Health: Investigating Health and Health Services (McGraw-hill Education, 2014).
Bobak, C. A., Barr, P. J. & O’Malley, A. J. Estimation of an inter-rater intra-class correlation coefficient that overcomes common assumption violations in the assessment of health measurement scales. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 18 , 93 (2018).
Jöreskog, K. G. A general approach to confirmatory maximum likelihood factor analysis. ETS Res. Bull. Ser. 1967 , 183–202 (1967).
Tavakol, M. & Wetzel, A. Factor analysis: A means for theory and instrument development in support of construct validity. Int. J. Med. Educ. 11 , 245–247 (2020).
Download references
This research was funded in whole or in part by the National Science Centre, Poland 2021/05/X/HS6/01258. For the purpose of open access, the author has applied a CC-BY public copyright licence to any Author Accepted Manuscript (AAM) version arising from this submission.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Dental Prosthetics, Medical University of Lublin, Lublin, Poland
Dorota Wójcik
Digital Dentistry Lab, Department of Dental and Maxillofacial Radiodiagnostics, Medical University of Lublin, Lublin, Poland
Leszek Szalewski
Department of Dental Prosthetics, Medical University of Gdańsk, Gdańsk, Poland
Adam Bęben & Iwona Ordyniec-Kwaśnica
Department of Medicine, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York City, NY, USA
Robert B. Shochet
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
D.W. and L.S. Conceptualization, Resources, Writing-original draft, Visualization, Investigation, D.W, L.S, R.S. Methodology, Writing-review & editing D.W., L.S, A.B., I.O.K. Investigation D.W.: Formal analysis, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition, All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Dorota Wójcik .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary figures., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Wójcik, D., Szalewski, L., Bęben, A. et al. Validation of the Polish version of the Johns Hopkins Learning Environment Scale–a confirmatory factor analysis. Sci Rep 14 , 10843 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-61391-x
Download citation
Received : 07 January 2024
Accepted : 06 May 2024
Published : 12 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-61391-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Medical education
- JHLES questionnaire
- Dental students
- Learning environment
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.

COMMENTS
Identify the key problems and issues in the case study. Formulate and include a thesis statement, summarizing the outcome of your analysis in 1-2 sentences. Background. Set the scene: background information, relevant facts, and the most important issues. Demonstrate that you have researched the problems in this case study. Evaluation of the Case
Case study examples. Case studies are proven marketing strategies in a wide variety of B2B industries. Here are just a few examples of a case study: Amazon Web Services, Inc. provides companies with cloud computing platforms and APIs on a metered, pay-as-you-go basis.
Case study is unbounded and relies on gathering external information; case analysis is a self-contained subject of analysis. The scope of a case study chosen as a method of research is bounded. However, the researcher is free to gather whatever information and data is necessary to investigate its relevance to understanding the research problem.
Take a look at this video for a sample case study analysis for the Coca-Cola Company. If you want another example, then take a look at the one below! Business Case Analysis: Example. Example: CRM's primary focus is customers and customer perception of the brand or the company. The focus may shift depending on customers' needs.
1. Preparation. Just like with any study, it's important to first prepare to conduct the case analysis. To begin, review the details of the case you're analyzing to make sure you understand it thoroughly. Consider taking the time to write notes and questions you have, highlight some data points you want to remember and identify the main ...
The purpose of case study research is twofold: (1) to provide descriptive information and (2) to suggest theoretical relevance. Rich description enables an in-depth or sharpened understanding of the case. It is unique given one characteristic: case studies draw from more than one data source. Case studies are inherently multimodal or mixed ...
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data. Example: Mixed methods case study. For a case study of a wind farm development in a ...
A case study research paper examines a person, place, event, condition, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis in order to extrapolate key themes and results that help predict future trends, illuminate previously hidden issues that can be applied to practice, and/or provide a means for understanding an important research problem with greater clarity.
How to Analyze a Case Study Adapted from Ellet, W. (2007). The case study handbook. Boston, MA: Harvard Business School. A business case simulates a real situation and has three characteristics: 1. a significant issue, 2. enough information to reach a reasonable conclusion, 3. no stated conclusion. A case may include 1. irrelevant information 2.
Case study examples. While templates are helpful, seeing a case study in action can also be a great way to learn. Here are some examples of how Adobe customers have experienced success. Juniper Networks. One example is the Adobe and Juniper Networks case study, which puts the reader in the customer's shoes.
Case studies play a significant role in knowledge development across various disciplines. Analysis of cases provides an avenue for researchers to explore phenomena within their context based on the collected data. Analysis of qualitative data from case study research can contribute to knowledge development.
For example, the case study quotes the social media manager and project manager's insights regarding team-wide communication and access before explaining in greater detail. Takeaway: Highlight pain points your business solves for its client, and explore that influence in greater detail. 3. EndeavourX and Figma.
This is a financial case study with its nuances. It would be good to take into account if you are dealing with a case study in finance. 4. Knowledge Dissemination. This case study focuses on the Amish population and their usage of non-traditional medicine. This analysis discusses the case on several levels.
15 Real-Life Case Study Examples. Now that you understand what a case study is, let's look at real-life case study examples. In this section, we'll explore SaaS, marketing, sales, product and business case study examples with solutions. Take note of how these companies structured their case studies and included the key elements.
Case Study Analysis is a widely used research method that examines in-depth information about a particular individual, group, organization, or event. It is a comprehensive investigative approach that aims to understand the intricacies and complexities of the subject under study. Through the analysis of real-life scenarios and inquiry into ...
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
A single-case study is an in-depth analysis of a single case. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand a specific phenomenon in detail. ... Examples of Case Study. Here are some examples of case study research: The Hawthorne Studies: Conducted between 1924 and 1932, the Hawthorne Studies were a series of case ...
A case study is a detailed analysis of a specific topic in a real-world context. It can pertain to a person, place, event, group, or phenomenon, among others. The purpose is to derive generalizations about the topic, as well as other insights. Case studies find application in academic, business, political, or scientific research.
Give students an opportunity to practice the case analysis methodology via an ungraded sample case study. Designate groups of five to seven students to discuss the case and the six steps in breakout sessions (in class or via Zoom). Ensure case analyses are weighted heavily as a grading component. We suggest 30-50 percent of the overall course ...
Stories about business analysis practitioners for business analysis practitioners. Business analysis case study examples correspond to the various aspects of business like management, marketing, competition, or research and development.
A case study is one of the most commonly used methodologies of social research. This article attempts to look into the various dimensions of a case study research strategy, the different epistemological strands which determine the particular case study type and approach adopted in the field, discusses the factors which can enhance the effectiveness of a case study research, and the debate ...
Step 1: Create an Introduction. You need to have a clear and noteworthy idea of what is particularly interesting and unique about the case study you want to analyze. So, make a thought-provoking introduction to convey your main idea and purpose to the reader. Describe the case study in a historical or social context.
A case study is therefore both a process of inquiry about the case at hand and the product of that inquiry. (Bloomberg, 2018, p. 276) Case studies use more than one form of data either within a research paradigm (multimodal ), or more than one form of data from different paradigms (mixed methods).
Case interviews allow employers to test and evaluate the following skills: Analytical skills and logical ability to solve problems. Structure and thought process. Ability to ask for relevant data/information. Tolerance for ambiguity and data overload. Poise and communication skills under pressure and in front of a client.
Since 2004, the agency has developed more than 400 Impact Case Studies that illustrate AHRQ's contributions to healthcare improvement. Available online and searchable via an interactive map , the Impact Case Studies help to tell the story of how AHRQ-funded research findings, data and tools have made an impact on the lives of millions of ...
Top 10 Project Management Case Studies with Examples 2024. 1. NASA's Mars Exploration Rover: Innovative project management in space exploration. 2. Apple's iPhone Development: Delivering revolutionary products with precision. 3. Tesla's Gigafactory Construction: Exemplary project execution in renewable energy.
The study aimed to determine the effects of high-risk pregnancy on prenatal stress levels. The study was conducted with a case-control design in Turkey in September-December 2019. The sample included pregnant women diagnosed with high-risk pregnancy and were at their 36th or later gestational weeks as the case group (n = 121) and healthy pregnant women as the control group (n = 245). The ...
Sample size selection was based on the generally accepted rule of thumb that there must be at least 5-15 cases per estimated parameter in the confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) 25 ...
It . We validate LUPINE and its variant, LUPINE_single (for single time point analysis) in simulated data and three case studies, where we highlight LUPINE's ability to identify relevant taxa in each study context, across different experimental designs (mouse and human studies, with or without interventions, as short or long time courses).