
Research Topics & Ideas: Environment
100+ Environmental Science Research Topics & Ideas

Finding and choosing a strong research topic is the critical first step when it comes to crafting a high-quality dissertation, thesis or research project. Here, we’ll explore a variety research ideas and topic thought-starters related to various environmental science disciplines, including ecology, oceanography, hydrology, geology, soil science, environmental chemistry, environmental economics, and environmental ethics.
NB – This is just the start…
The topic ideation and evaluation process has multiple steps . In this post, we’ll kickstart the process by sharing some research topic ideas within the environmental sciences. This is the starting point though. To develop a well-defined research topic, you’ll need to identify a clear and convincing research gap , along with a well-justified plan of action to fill that gap.
If you’re new to the oftentimes perplexing world of research, or if this is your first time undertaking a formal academic research project, be sure to check out our free dissertation mini-course. Also be sure to also sign up for our free webinar that explores how to develop a high-quality research topic from scratch.
Overview: Environmental Topics
- Ecology /ecological science
- Atmospheric science
- Oceanography
- Soil science
- Environmental chemistry
- Environmental economics
- Environmental ethics
- Examples of dissertations and theses
Topics & Ideas: Ecological Science
- The impact of land-use change on species diversity and ecosystem functioning in agricultural landscapes
- The role of disturbances such as fire and drought in shaping arid ecosystems
- The impact of climate change on the distribution of migratory marine species
- Investigating the role of mutualistic plant-insect relationships in maintaining ecosystem stability
- The effects of invasive plant species on ecosystem structure and function
- The impact of habitat fragmentation caused by road construction on species diversity and population dynamics in the tropics
- The role of ecosystem services in urban areas and their economic value to a developing nation
- The effectiveness of different grassland restoration techniques in degraded ecosystems
- The impact of land-use change through agriculture and urbanisation on soil microbial communities in a temperate environment
- The role of microbial diversity in ecosystem health and nutrient cycling in an African savannah
Topics & Ideas: Atmospheric Science
- The impact of climate change on atmospheric circulation patterns above tropical rainforests
- The role of atmospheric aerosols in cloud formation and precipitation above cities with high pollution levels
- The impact of agricultural land-use change on global atmospheric composition
- Investigating the role of atmospheric convection in severe weather events in the tropics
- The impact of urbanisation on regional and global atmospheric ozone levels
- The impact of sea surface temperature on atmospheric circulation and tropical cyclones
- The impact of solar flares on the Earth’s atmospheric composition
- The impact of climate change on atmospheric turbulence and air transportation safety
- The impact of stratospheric ozone depletion on atmospheric circulation and climate change
- The role of atmospheric rivers in global water supply and sea-ice formation

Topics & Ideas: Oceanography
- The impact of ocean acidification on kelp forests and biogeochemical cycles
- The role of ocean currents in distributing heat and regulating desert rain
- The impact of carbon monoxide pollution on ocean chemistry and biogeochemical cycles
- Investigating the role of ocean mixing in regulating coastal climates
- The impact of sea level rise on the resource availability of low-income coastal communities
- The impact of ocean warming on the distribution and migration patterns of marine mammals
- The impact of ocean deoxygenation on biogeochemical cycles in the arctic
- The role of ocean-atmosphere interactions in regulating rainfall in arid regions
- The impact of ocean eddies on global ocean circulation and plankton distribution
- The role of ocean-ice interactions in regulating the Earth’s climate and sea level

Tops & Ideas: Hydrology
- The impact of agricultural land-use change on water resources and hydrologic cycles in temperate regions
- The impact of agricultural groundwater availability on irrigation practices in the global south
- The impact of rising sea-surface temperatures on global precipitation patterns and water availability
- Investigating the role of wetlands in regulating water resources for riparian forests
- The impact of tropical ranches on river and stream ecosystems and water quality
- The impact of urbanisation on regional and local hydrologic cycles and water resources for agriculture
- The role of snow cover and mountain hydrology in regulating regional agricultural water resources
- The impact of drought on food security in arid and semi-arid regions
- The role of groundwater recharge in sustaining water resources in arid and semi-arid environments
- The impact of sea level rise on coastal hydrology and the quality of water resources

Topics & Ideas: Geology
- The impact of tectonic activity on the East African rift valley
- The role of mineral deposits in shaping ancient human societies
- The impact of sea-level rise on coastal geomorphology and shoreline evolution
- Investigating the role of erosion in shaping the landscape and impacting desertification
- The impact of mining on soil stability and landslide potential
- The impact of volcanic activity on incoming solar radiation and climate
- The role of geothermal energy in decarbonising the energy mix of megacities
- The impact of Earth’s magnetic field on geological processes and solar wind
- The impact of plate tectonics on the evolution of mammals
- The role of the distribution of mineral resources in shaping human societies and economies, with emphasis on sustainability
Topics & Ideas: Soil Science
- The impact of dam building on soil quality and fertility
- The role of soil organic matter in regulating nutrient cycles in agricultural land
- The impact of climate change on soil erosion and soil organic carbon storage in peatlands
- Investigating the role of above-below-ground interactions in nutrient cycling and soil health
- The impact of deforestation on soil degradation and soil fertility
- The role of soil texture and structure in regulating water and nutrient availability in boreal forests
- The impact of sustainable land management practices on soil health and soil organic matter
- The impact of wetland modification on soil structure and function
- The role of soil-atmosphere exchange and carbon sequestration in regulating regional and global climate
- The impact of salinization on soil health and crop productivity in coastal communities
Topics & Ideas: Environmental Chemistry
- The impact of cobalt mining on water quality and the fate of contaminants in the environment
- The role of atmospheric chemistry in shaping air quality and climate change
- The impact of soil chemistry on nutrient availability and plant growth in wheat monoculture
- Investigating the fate and transport of heavy metal contaminants in the environment
- The impact of climate change on biochemical cycling in tropical rainforests
- The impact of various types of land-use change on biochemical cycling
- The role of soil microbes in mediating contaminant degradation in the environment
- The impact of chemical and oil spills on freshwater and soil chemistry
- The role of atmospheric nitrogen deposition in shaping water and soil chemistry
- The impact of over-irrigation on the cycling and fate of persistent organic pollutants in the environment
Topics & Ideas: Environmental Economics
- The impact of climate change on the economies of developing nations
- The role of market-based mechanisms in promoting sustainable use of forest resources
- The impact of environmental regulations on economic growth and competitiveness
- Investigating the economic benefits and costs of ecosystem services for African countries
- The impact of renewable energy policies on regional and global energy markets
- The role of water markets in promoting sustainable water use in southern Africa
- The impact of land-use change in rural areas on regional and global economies
- The impact of environmental disasters on local and national economies
- The role of green technologies and innovation in shaping the zero-carbon transition and the knock-on effects for local economies
- The impact of environmental and natural resource policies on income distribution and poverty of rural communities
Topics & Ideas: Environmental Ethics
- The ethical foundations of environmentalism and the environmental movement regarding renewable energy
- The role of values and ethics in shaping environmental policy and decision-making in the mining industry
- The impact of cultural and religious beliefs on environmental attitudes and behaviours in first world countries
- Investigating the ethics of biodiversity conservation and the protection of endangered species in palm oil plantations
- The ethical implications of sea-level rise for future generations and vulnerable coastal populations
- The role of ethical considerations in shaping sustainable use of natural forest resources
- The impact of environmental justice on marginalized communities and environmental policies in Asia
- The ethical implications of environmental risks and decision-making under uncertainty
- The role of ethics in shaping the transition to a low-carbon, sustainable future for the construction industry
- The impact of environmental values on consumer behaviour and the marketplace: a case study of the ‘bring your own shopping bag’ policy
Examples: Real Dissertation & Thesis Topics
While the ideas we’ve presented above are a decent starting point for finding a research topic, they are fairly generic and non-specific. So, it helps to look at actual dissertations and theses to see how this all comes together.
Below, we’ve included a selection of research projects from various environmental science-related degree programs to help refine your thinking. These are actual dissertations and theses, written as part of Master’s and PhD-level programs, so they can provide some useful insight as to what a research topic looks like in practice.
- The physiology of microorganisms in enhanced biological phosphorous removal (Saunders, 2014)
- The influence of the coastal front on heavy rainfall events along the east coast (Henson, 2019)
- Forage production and diversification for climate-smart tropical and temperate silvopastures (Dibala, 2019)
- Advancing spectral induced polarization for near surface geophysical characterization (Wang, 2021)
- Assessment of Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter and Thamnocephalus platyurus as Tools to Monitor Cyanobacterial Bloom Development and Toxicity (Hipsher, 2019)
- Evaluating the Removal of Microcystin Variants with Powdered Activated Carbon (Juang, 2020)
- The effect of hydrological restoration on nutrient concentrations, macroinvertebrate communities, and amphibian populations in Lake Erie coastal wetlands (Berg, 2019)
- Utilizing hydrologic soil grouping to estimate corn nitrogen rate recommendations (Bean, 2019)
- Fungal Function in House Dust and Dust from the International Space Station (Bope, 2021)
- Assessing Vulnerability and the Potential for Ecosystem-based Adaptation (EbA) in Sudan’s Blue Nile Basin (Mohamed, 2022)
- A Microbial Water Quality Analysis of the Recreational Zones in the Los Angeles River of Elysian Valley, CA (Nguyen, 2019)
- Dry Season Water Quality Study on Three Recreational Sites in the San Gabriel Mountains (Vallejo, 2019)
- Wastewater Treatment Plan for Unix Packaging Adjustment of the Potential Hydrogen (PH) Evaluation of Enzymatic Activity After the Addition of Cycle Disgestase Enzyme (Miessi, 2020)
- Laying the Genetic Foundation for the Conservation of Longhorn Fairy Shrimp (Kyle, 2021).
Looking at these titles, you can probably pick up that the research topics here are quite specific and narrowly-focused , compared to the generic ones presented earlier. To create a top-notch research topic, you will need to be precise and target a specific context with specific variables of interest . In other words, you’ll need to identify a clear, well-justified research gap.
Need more help?
If you’re still feeling a bit unsure about how to find a research topic for your environmental science dissertation or research project, be sure to check out our private coaching services below, as well as our Research Topic Kickstarter .
Need a helping hand?
You Might Also Like:

research topics on climate change and environment
I wish to learn things in a more advanced but simple way and with the hopes that I am in the right place.
Thank so much for the research topics. It really helped
the guides were really helpful
Research topics on environmental geology
Thanks for the research topics….I need a research topic on Geography
I want the research on environmental planning and management
I want a topic on environmental sustainability
It good coaching
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Privacy Policy

Home » 500+ Environmental Research Topics
500+ Environmental Research Topics

Environmental research is a crucial area of study in today’s world, as we face an increasing number of complex and pressing environmental challenges. From climate change to pollution, biodiversity loss to natural resource depletion, there is an urgent need for scientific inquiry and investigation to inform policy, decision-making, and action. Environmental research encompasses a broad range of disciplines, including ecology, biology , geology, chemistry , and physics , among others, and explores a diverse array of topics , from ocean acidification to sustainable agriculture. Through rigorous scientific inquiry and a commitment to generating evidence-based solutions, environmental research plays a vital role in promoting the health and well-being of our planet and its inhabitants. In this article, we will cover some trending Environmental Research Topics.
Environmental Research Topics
Environmental Research Topics are as follows:
- Climate change and its impacts on ecosystems and society
- The effectiveness of carbon capture and storage technology
- The role of biodiversity in maintaining healthy ecosystems
- The impact of human activity on soil quality
- The impact of plastic pollution on marine life
- The effectiveness of renewable energy sources
- The impact of deforestation on local communities and wildlife
- The relationship between air pollution and human health
- The impact of agricultural practices on soil erosion
- The effectiveness of conservation measures for endangered species
- The impact of overfishing on marine ecosystems
- The role of wetlands in mitigating climate change
- The impact of oil spills on marine ecosystems
- The impact of urbanization on local ecosystems
- The impact of climate change on global food security
- The effectiveness of water conservation measures
- The impact of pesticide use on pollinators
- The impact of acid rain on aquatic ecosystems
- The impact of sea level rise on coastal communities
- The effectiveness of carbon taxes in reducing greenhouse gas emissions
- The impact of habitat destruction on migratory species
- The impact of invasive species on native ecosystems
- The role of national parks in biodiversity conservation
- The impact of climate change on coral reefs
- The effectiveness of green roofs in reducing urban heat island effect
- The impact of noise pollution on wildlife behavior
- The impact of air pollution on crop yields
- The effectiveness of composting in reducing organic waste
- The impact of climate change on the Arctic ecosystem
- The impact of land use change on soil carbon sequestration
- The role of mangroves in coastal protection and carbon sequestration
- The impact of microplastics on marine ecosystems
- The impact of ocean acidification on marine organisms
- The effectiveness of carbon offsets in reducing greenhouse gas emissions
- The impact of deforestation on climate regulation
- The impact of groundwater depletion on agriculture
- The impact of climate change on migratory bird populations
- The effectiveness of wind turbines in reducing greenhouse gas emissions
- The impact of urbanization on bird diversity
- The impact of climate change on ocean currents
- The impact of drought on plant and animal populations
- The effectiveness of agroforestry in improving soil quality
- The impact of climate change on water availability
- The impact of wildfires on carbon storage in forests
- The impact of climate change on freshwater ecosystems
- The effectiveness of green energy subsidies
- The impact of nitrogen pollution on aquatic ecosystems
- The impact of climate change on forest ecosystems
- The effectiveness of community-based conservation initiatives
- The impact of climate change on the water cycle
- The impact of mining activities on local ecosystems
- The impact of wind energy on bird and bat populations
- The effectiveness of bioremediation in cleaning up contaminated soil and water
- The impact of deforestation on local climate patterns
- The impact of climate change on insect populations
- The impact of agricultural runoff on freshwater ecosystems
- The effectiveness of smart irrigation systems in reducing water use
- The impact of ocean currents on marine biodiversity
- The impact of climate change on wetland ecosystems
- The effectiveness of green buildings in reducing energy use
- The impact of climate change on glacier retreat and sea level rise
- The impact of light pollution on nocturnal wildlife behavior
- The impact of climate change on desert ecosystems
- The effectiveness of electric vehicles in reducing greenhouse gas emissions
- The impact of ocean pollution on human health
- The impact of land use change on water quality
- The impact of urbanization on bird populations
- The impact of oil spills on marine ecosystems and wildlife
- The effectiveness of green energy storage technologies in promoting renewable energy use
- The impact of climate change on freshwater availability and water management
- The impact of industrial pollution on air quality and human health
- The effectiveness of urban green spaces in promoting human health and well-being
- The impact of climate change on snow cover and winter tourism
- The impact of agricultural land use on biodiversity and ecosystem services
- The effectiveness of green incentives in promoting sustainable consumer behavior
- The impact of ocean acidification on shellfish and mollusk populations
- The impact of climate change on river flow and flooding
- The effectiveness of green supply chain management in promoting sustainable production
- The impact of noise pollution on avian communication and behavior
- The impact of climate change on arctic ecosystems and wildlife
- The effectiveness of green marketing in promoting sustainable tourism
- The impact of microplastics on marine food webs and human health
- The impact of climate change on invasive species distributions
- The effectiveness of green infrastructure in promoting sustainable urban development
- The impact of plastic pollution on human health and food safety
- The impact of climate change on soil microbial communities and nutrient cycling
- The effectiveness of green technologies in promoting sustainable industrial production
- The impact of climate change on permafrost thaw and methane emissions
- The impact of deforestation on water quality and quantity
- The effectiveness of green certification schemes in promoting sustainable production and consumption
- The impact of noise pollution on terrestrial ecosystems and wildlife
- The impact of climate change on bird migration patterns
- The effectiveness of green waste management in promoting sustainable resource use
- The impact of climate change on insect populations and ecosystem services
- The impact of plastic pollution on human society and culture
- The effectiveness of green finance in promoting sustainable development goals
- The impact of climate change on marine biodiversity hotspots
- The impact of climate change on natural disasters and disaster risk reduction
- The effectiveness of green urban planning in promoting sustainable cities and communities
- The impact of deforestation on soil carbon storage and climate change
- The impact of noise pollution on human communication and behavior
- The effectiveness of green energy policy in promoting renewable energy use
- The impact of climate change on Arctic sea ice and wildlife
- The impact of agricultural practices on soil quality and ecosystem health
- The effectiveness of green taxation in promoting sustainable behavior
- The impact of plastic pollution on freshwater ecosystems and wildlife
- The impact of climate change on plant-pollinator interactions and crop production
- The effectiveness of green innovation in promoting sustainable technological advancements
- The impact of climate change on ocean currents and marine heatwaves
- The impact of deforestation on indigenous communities and cultural practices
- The effectiveness of green governance in promoting sustainable development and environmental justice
- The effectiveness of wetland restoration in reducing flood risk
- The impact of climate change on the spread of vector-borne diseases
- The effectiveness of green marketing in promoting sustainable consumption
- The impact of plastic pollution on marine ecosystems
- The impact of renewable energy development on wildlife habitats
- The effectiveness of environmental education programs in promoting pro-environmental behavior
- The impact of deforestation on global climate change
- The impact of microplastics on freshwater ecosystems
- The effectiveness of eco-labeling in promoting sustainable seafood consumption
- The impact of climate change on coral reef ecosystems
- The impact of air pollution on human health and mortality rates
- The effectiveness of eco-tourism in promoting conservation and community development
- The impact of climate change on agricultural production and food security
- The impact of wind turbine noise on wildlife behavior and populations
- The impact of light pollution on nocturnal ecosystems and species
- The effectiveness of green energy subsidies in promoting renewable energy use
- The impact of invasive species on native ecosystems and biodiversity
- The impact of climate change on ocean acidification and marine ecosystems
- The effectiveness of green public procurement in promoting sustainable production
- The impact of deforestation on soil erosion and nutrient depletion
- The impact of noise pollution on human health and well-being
- The effectiveness of green building standards in promoting sustainable construction
- The impact of climate change on forest fires and wildfire risk
- The impact of e-waste on human health and environmental pollution
- The impact of climate change on polar ice caps and sea levels
- The impact of pharmaceutical pollution on freshwater ecosystems and wildlife
- The effectiveness of green transportation policies in reducing carbon emissions
- The impact of climate change on glacier retreat and water availability
- The impact of pesticide use on pollinator populations and ecosystems
- The effectiveness of circular economy models in reducing waste and promoting sustainability
- The impact of climate change on coastal ecosystems and biodiversity
- The impact of plastic waste on terrestrial ecosystems and wildlife
- The effectiveness of green chemistry in promoting sustainable manufacturing
- The impact of climate change on ocean currents and weather patterns
- The impact of agricultural runoff on freshwater ecosystems and water quality
- The effectiveness of green bonds in financing sustainable infrastructure projects
- The impact of climate change on soil moisture and desertification
- The impact of noise pollution on marine ecosystems and species
- The effectiveness of community-based conservation in promoting biodiversity and ecosystem health
- The impact of climate change on permafrost ecosystems and carbon storage
- The impact of urbanization on water pollution and quality
- The effectiveness of green jobs in promoting sustainable employment
- The impact of climate change on wetland ecosystems and biodiversity
- The impact of plastic pollution on terrestrial ecosystems and wildlife
- The effectiveness of sustainable fashion in promoting sustainable consumption
- The impact of climate change on phenology and seasonal cycles of plants and animals
- The impact of ocean pollution on human health and seafood safety
- The effectiveness of green procurement policies in promoting sustainable supply chains
- The impact of climate change on marine food webs and ecosystems
- The impact of agricultural practices on greenhouse gas emissions and climate change
- The effectiveness of green financing in promoting sustainable investment
- The effectiveness of rainwater harvesting systems in reducing water use
- The impact of climate change on permafrost ecosystems
- The impact of coastal erosion on shoreline ecosystems
- The effectiveness of green infrastructure in reducing urban heat island effect
- The impact of microorganisms on soil fertility and carbon sequestration
- The impact of climate change on snowpack and water availability
- The impact of oil and gas drilling on local ecosystems
- The effectiveness of carbon labeling in promoting sustainable consumer choices
- The impact of marine noise pollution on marine mammals
- The impact of climate change on alpine ecosystems
- The effectiveness of green supply chain management in reducing environmental impact
- The impact of climate change on river ecosystems
- The impact of urban sprawl on wildlife habitat fragmentation
- The effectiveness of carbon trading in reducing greenhouse gas emissions
- The impact of ocean warming on marine ecosystems
- The impact of agricultural practices on water quality and quantity
- The effectiveness of green roofs in improving urban air quality
- The impact of climate change on tropical rainforests
- The impact of water pollution on human health and livelihoods
- The effectiveness of green bonds in financing sustainable projects
- The impact of climate change on polar bear populations
- The impact of human activity on soil biodiversity
- The effectiveness of waste-to-energy systems in reducing waste and emissions
- The impact of climate change on Arctic sea ice and marine ecosystems
- The impact of sea level rise on low-lying coastal cities and communities
- The effectiveness of sustainable tourism in promoting conservation and community development
- The impact of deforestation on indigenous peoples and their livelihoods
- The impact of climate change on sea turtle populations
- The effectiveness of carbon-neutral and carbon-negative technologies
- The impact of urbanization on water resources and quality
- The impact of climate change on cold-water fish populations
- The effectiveness of green entrepreneurship in promoting sustainable innovation
- The impact of wildfires on air quality and public health
- The impact of climate change on human migration patterns and social systems
- The impact of noise pollution on bird communication and behavior in urban environments
- The impact of climate change on estuarine ecosystems and biodiversity
- The impact of deforestation on water availability and river basin management
- The impact of climate change on plant phenology and distribution
- The effectiveness of green marketing in promoting sustainable consumer behavior
- The impact of plastic pollution on freshwater ecosystems and biodiversity
- The impact of climate change on marine plastic debris accumulation and distribution
- The effectiveness of green innovation in promoting sustainable technology development
- The impact of climate change on crop yields and food security
- The impact of noise pollution on human health and well-being in urban environments
- The impact of climate change on Arctic marine ecosystems and biodiversity
- The effectiveness of green transportation infrastructure in promoting sustainable mobility
- The impact of deforestation on non-timber forest products and forest-dependent livelihoods
- The impact of climate change on wetland carbon sequestration and storage
- The impact of plastic pollution on sea turtle populations and nesting behavior
- The impact of climate change on marine biodiversity and ecosystem functioning in the Southern Ocean
- The effectiveness of green certification in promoting sustainable agriculture
- The impact of climate change on oceanographic processes and upwelling systems
- The impact of noise pollution on terrestrial wildlife communication and behavior
- The impact of climate change on coastal erosion and shoreline management
- The effectiveness of green finance in promoting sustainable investment
- The impact of deforestation on indigenous communities and traditional knowledge systems
- The impact of climate change on tropical cyclones and extreme weather events
- The effectiveness of green buildings in promoting energy efficiency and carbon reduction
- The impact of plastic pollution on marine food webs and trophic interactions
- The impact of climate change on algal blooms and harmful algal blooms in marine ecosystems
- The effectiveness of green business partnerships in promoting sustainable development goals
- The impact of climate change on ocean deoxygenation and its effects on marine life
- The impact of noise pollution on human sleep and rest patterns in urban environments
- The impact of climate change on freshwater availability and management
- The effectiveness of green entrepreneurship in promoting social and environmental justice
- The impact of deforestation on wildlife habitat and biodiversity conservation
- The impact of climate change on the migration patterns and behaviors of birds and mammals
- The effectiveness of green urban planning in promoting sustainable and livable cities
- The impact of plastic pollution on microplastics and nanoplastics in marine ecosystems
- The impact of climate change on marine ecosystem services and their value to society
- The effectiveness of green certification in promoting sustainable forestry
- The impact of climate change on ocean currents and their effects on marine biodiversity
- The impact of noise pollution on urban ecosystems and their ecological functions
- The impact of climate change on freshwater biodiversity and ecosystem functioning
- The effectiveness of green policy implementation in promoting sustainable development
- The impact of deforestation on soil carbon storage and greenhouse gas emissions
- The impact of climate change on marine mammals and their ecosystem roles
- The effectiveness of green product labeling in promoting sustainable consumer behavior
- The impact of plastic pollution on coral reefs and their resilience to climate change
- The impact of climate change on waterborne diseases and public health
- The effectiveness of green energy policies in promoting renewable energy adoption
- The impact of deforestation on carbon storage and sequestration in peatlands
- The impact of climate change on ocean acidification and its effects on marine life
- The effectiveness of green supply chain management in promoting circular economy principles
- The impact of noise pollution on urban birds and their vocal communication
- The impact of climate change on ecosystem services provided by mangrove forests
- The effectiveness of green marketing in promoting sustainable fashion and textiles
- The impact of plastic pollution on deep-sea ecosystems and biodiversity
- The impact of climate change on marine biodiversity hotspots and conservation priorities
- The effectiveness of green investment in promoting sustainable infrastructure development
- The impact of deforestation on ecosystem services provided by agroforestry systems
- The impact of climate change on snow and ice cover and their effects on freshwater ecosystems
- The effectiveness of green tourism in promoting sustainable tourism practices
- The impact of noise pollution on human cognitive performance and productivity
- The impact of climate change on forest fires and their effects on ecosystem services
- The effectiveness of green labeling in promoting sustainable seafood consumption
- The impact of climate change on insect populations and their ecosystem roles
- The impact of plastic pollution on seabird populations and their reproductive success
- The effectiveness of green procurement in promoting sustainable public sector spending
- The impact of deforestation on soil erosion and land degradation
- The impact of climate change on riverine ecosystems and their ecosystem services
- The effectiveness of green certification in promoting sustainable fisheries
- The impact of noise pollution on marine mammals and their acoustic communication
- The impact of climate change on terrestrial carbon sinks and sources
- The effectiveness of green technology transfer in promoting sustainable development
- The impact of deforestation on non-timber forest products and their sustainable use
- The impact of climate change on marine invasive species and their ecological impacts
- The effectiveness of green procurement in promoting sustainable private sector spending
- The impact of plastic pollution on zooplankton populations and their ecosystem roles
- The impact of climate change on wetland ecosystems and their services
- The effectiveness of green education in promoting sustainable behavior change
- The impact of deforestation on watershed management and water quality
- The impact of climate change on soil nutrient cycling and ecosystem functioning
- The effectiveness of green technology innovation in promoting sustainable development
- The impact of noise pollution on human health in outdoor recreational settings
- The impact of climate change on oceanic nutrient cycling and primary productivity
- The effectiveness of green urban design in promoting sustainable and resilient cities
- The impact of plastic pollution on marine microbial communities and their functions
- The impact of climate change on coral reef bleaching and recovery
- The impact of deforestation on ecosystem services provided by community-managed forests
- The impact of climate change on freshwater fish populations and their ecosystem roles
- The effectiveness of green certification in promoting sustainable tourism
- The impact of noise pollution on human stress and cardiovascular health
- The impact of climate change on glacier retreat and their effects on freshwater ecosystems
- The effectiveness of green technology diffusion in promoting sustainable development
- The impact of plastic pollution on sea grass beds and their ecosystem services
- The impact of climate change on forest phenology and productivity.
- The effectiveness of green transportation policies in promoting sustainable mobility
- The impact of deforestation on indigenous peoples’ livelihoods and traditional knowledge
- The impact of climate change on Arctic ecosystems and their biodiversity
- The effectiveness of green building standards in promoting sustainable architecture
- The impact of noise pollution on nocturnal animals and their behavior
- The impact of climate change on migratory bird populations and their breeding success
- The effectiveness of green taxation in promoting sustainable consumption and production
- The impact of deforestation on wildlife corridors and ecosystem connectivity
- The impact of climate change on urban heat islands and their effects on public health
- The effectiveness of green labeling in promoting sustainable forestry practices
- The impact of plastic pollution on sea turtle populations and their nesting success
- The impact of climate change on invasive plant species and their ecological impacts
- The effectiveness of green business practices in promoting sustainable entrepreneurship
- The impact of noise pollution on urban wildlife and their acoustic communication
- The impact of climate change on alpine ecosystems and their services
- The effectiveness of green procurement in promoting sustainable agriculture and food systems
- The impact of deforestation on soil carbon stocks and their effects on climate change
- The impact of climate change on wetland methane emissions and their contribution to greenhouse gas concentrations
- The effectiveness of green certification in promoting sustainable forestry and timber production
- The impact of plastic pollution on marine mammal populations and their health
- The impact of climate change on marine fisheries and their sustainable management
- The effectiveness of green investment in promoting sustainable entrepreneurship and innovation
- The impact of noise pollution on bat populations and their behavior
- The impact of climate change on permafrost thaw and its effects on Arctic ecosystems
- The impact of deforestation on ecosystem services provided by sacred groves
- The impact of climate change on tropical cyclones and their impacts on coastal ecosystems
- The effectiveness of green technology transfer in promoting sustainable agriculture and food systems
- The impact of plastic pollution on benthic macroinvertebrate populations and their ecosystem roles
- The impact of climate change on freshwater invertebrate populations and their ecosystem roles
- The effectiveness of green tourism in promoting sustainable wildlife tourism practices
- The impact of noise pollution on amphibian populations and their communication
- The impact of climate change on mountain ecosystems and their biodiversity
- The effectiveness of green certification in promoting sustainable agriculture and food systems
- The impact of deforestation on indigenous peoples’ food security and nutrition
- The impact of climate change on plant-pollinator interactions and their ecosystem roles
- The impact of plastic pollution on freshwater ecosystems and their services
- The impact of climate change on oceanic currents and their effects on marine ecosystems
- The effectiveness of green investment in promoting sustainable transportation infrastructure
- The impact of noise pollution on human sleep quality and mental health
- The impact of climate change on marine viruses and their effects on marine life
- The effectiveness of green labeling in promoting sustainable packaging and waste reduction
- The impact of deforestation on ecosystem services provided by riparian forests
- The impact of climate change on insect-pollinated crops and their yields
- The effectiveness of green procurement in promoting sustainable waste management
- The impact of plastic pollution on estuarine ecosystems and their services
- The impact of climate change on groundwater recharge and aquifer depletion
- The effectiveness of green education in promoting sustainable tourism practices
- The impact of climate change on coral reefs and their biodiversity
- The effectiveness of green labeling in promoting sustainable clothing and textile production
- The impact of deforestation on riverine fish populations and their fishery-dependent communities
- The impact of climate change on mountain water resources and their availability
- The effectiveness of green certification in promoting sustainable tourism accommodations
- The impact of plastic pollution on deep-sea ecosystems and their biodiversity
- The impact of climate change on sea-level rise and its effects on coastal ecosystems and communities
- The effectiveness of green energy policies in promoting renewable energy production
- The impact of noise pollution on human cardiovascular health
- The impact of climate change on biogeochemical cycles in marine ecosystems
- The effectiveness of green labeling in promoting sustainable personal care and cosmetic products
- The impact of deforestation on carbon sequestration and its effects on climate change
- The impact of climate change on wildfire frequency and severity
- The effectiveness of green procurement in promoting sustainable energy-efficient technologies
- The impact of plastic pollution on beach ecosystems and their tourism potential
- The impact of climate change on marine mammals and their habitat range shifts
- The effectiveness of green urban design in promoting sustainable and livable neighborhoods
- The impact of noise pollution on urban human and wildlife communities
- The impact of climate change on soil microorganisms and their roles in nutrient cycling
- The effectiveness of green labeling in promoting sustainable electronics and e-waste management
- The impact of deforestation on watershed services and their effects on downstream ecosystems and communities
- The impact of climate change on human migration patterns and their impacts on urbanization
- The effectiveness of green investment in promoting sustainable water management and infrastructure
- The impact of plastic pollution on seabird populations and their nesting success
- The impact of climate change on ocean acidification and its effects on marine ecosystems
- The effectiveness of green certification in promoting sustainable fisheries and aquaculture
- The impact of noise pollution on terrestrial carnivore populations and their communication
- The impact of climate change on snow and ice dynamics in polar regions
- The effectiveness of green tourism in promoting sustainable cultural heritage preservation
- The impact of deforestation on riverine water quality and their effects on aquatic life
- The impact of climate change on forest fires and their ecological effects
- The effectiveness of green labeling in promoting sustainable home appliances and energy use
- The impact of plastic pollution on marine invertebrate populations and their ecosystem roles
- The impact of climate change on soil erosion and its effects on agricultural productivity
- The effectiveness of green procurement in promoting sustainable construction materials and waste reduction
- The impact of noise pollution on marine mammal populations and their behavior
- The impact of climate change on ocean circulation and its effects on marine life
- The effectiveness of green investment in promoting sustainable forest management
- The impact of deforestation on medicinal plant populations and their traditional uses
- The impact of climate change on wetland ecosystems and their carbon storage capacity
- The effectiveness of green urban planning in promoting sustainable and resilient cities
- The impact of plastic pollution on seabed ecosystems and their biodiversity
- The effectiveness of green certification in promoting sustainable palm oil production
- The impact of noise pollution on bird populations and their communication
- The impact of climate change on freshwater quality and its effects on aquatic life
- The effectiveness of green labeling in promoting sustainable food packaging and waste reduction
- The impact of deforestation on streamflow and its effects on downstream
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

200+ Funny Research Topics

500+ Sports Research Topics

300+ American History Research Paper Topics

500+ Cyber Security Research Topics

500+ Economics Research Topics

500+ Physics Research Topics
- Research Paper Guides
- Research Paper Topics
Environmental Research Topics: 235 Ideas for Students
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Main Academic Essays
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Essay Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker

You may also like

Are you looking for environmental research paper topics? With ongoing debates about global warming, air pollution, and other issues, there is no shortage of exciting topics to craft a research paper around. Whether you’re studying ecology, geology, or marine biology, developing the perfect environmental research topic to get your science research assignment off the ground can be challenging. Stop worrying – we got you covered. Continue reading to learn about 235 different ideas on environmental research topics. In this article, we will discuss environmental topics and show you how to choose an interesting research topic for your subject. We will also provide a list of various environmental topics from our research paper services . In addition, we will present you with environmental science research topics, discuss other ideas about the environment for research papers, and offer our final thoughts on these topics for research papers.
Get in touch with our academic writing service and receive expert help. Let us know your topic, pay for research paper and get an excellent result in no time.
Joe Eckel is an expert on Dissertations writing. He makes sure that each student gets precious insights on composing A-grade academic writing.
Environmental topics provide an analysis of environmental issues and their effect on people, culture, nature, or a particular place, often interdisciplinary, drawing from sciences, politics, economics, sociology, and public policy. Topics about environmental science may include environmental justice, engineering and communication, regulation, economics, and health. Environment research topics may focus on environmental sustainability, impact assessment, management systems, and resources. In addition, these areas for research papers offer a few opportunities to explore our relationship with the environment and consider how human activities influence it through climate change, pollution, or other factors such as natural resource usage as well as biodiversity loss.
When choosing an environmental research topic, it is essential to consider what makes good environmental topics. Below is an expert list outlining what your topic should be like:
When choosing research topics for environmental science, it is essential to research the available information and determine its relevance. It all depends on whether the research topic is feasible and has the potential for exploration. Environmental issue topics should be well-defined and interesting to the researcher. The reason is that the researcher should be able to provide solutions or make suggestions on improvement strategies. You can follow the below steps when choosing environmental science topics for research:
Step 1: Identify topics that are relevant to your research context. Step 2: Develop a list of research areas by extracting critical concepts from the available literature.
Step 3: Select interesting and feasible topics by considering the methods available for analysis.
Step 4: Analyze these topics to identify the gaps in current research and formulate questions for further investigation. Step 5: Review the available literature to gain insights about the chosen topic and develop a research proposal.
Step 6: Consult experts in this field to get feedback and refine the proposed research.
Don’t have time for writing your environmental research paper? Count on StudyCrumb. Send us a ‘ write a research paper for me ’ message and get professional assistance in a timely manner.
Environmental topics for a research paper can be overwhelming to navigate due to the vast number of issues you can discuss in your article. To help narrow down your research paper search, below is a list of environmental research topics that include climate change, renewable energy, ecology, pollution, sustainability, endangered species, ecosystems, nature, and water management. You can choose one of them as a guide to writing an excellent essay
Climate change is one of the most pressing issues that humanity is currently facing due to increased temperature levels. Climate change is amongst the most debated environmental research topics among researchers, policymakers, and governments. Here are critical areas related to climate change that you can use for your environmental science research paper topics:
Renewable energy is essential due to its potential to reduce ecological damage from burning fossil fuels and provides valuable topics in environmental science. You can use renewable energy technologies as a cleaner alternative for generating electricity and heating. In addition, renewable energy is crucial for cooling homes and factories in the world. The following are environmental science topics for research paper on renewable energy:
Ecology studies how living organisms interact with each other and their environment. Also, it is an important area of research for understanding how the environment affects the function of various species and ecosystems. It also gives a background for one of the best environment research paper topics. Below are topics for environmental research paper on ecology:
Pollution is an issue at the forefront of scientific research. As one of the environmental science paper topics, it offers insights into how pollution destroys the environment and its negative impact on human and animal health. Stated below are hot environmental science research topics on pollution which you can use for your article:
One of the many topics for environmental research papers is sustainability. Sustainability is an important topic to explore, as it involves finding a way for humans to reduce their ecological footprint and ensure that the environment can recover from our activities. Stated below are environmental topics for research paper on sustainability which you can explore:
Endangered species are one of the environmental topics of great importance to research and find solutions for their conservation. Poaching, habitat destruction, and climate change negatively impact endangered species. Also, human activities have put other species at risk of extinction by competing for resources as well as introducing invasive species. Below is a list of cool environment topics to write about endangered species:
Ecosystems are fascinating to explore in environmental paper topics because they contain a variety of living organisms and are a complex web of interactions between species, the environment, and humans. The subject provides environmental issues topics for research paper essential in exploring the dynamics of ecosystems and their importance. Below is a list of topics for environmental science research paper:
Nature is a broad topic that includes ecological conservation, protection, and sustainability issues. Environmental research topics about nature allow us to explore areas that focus on preserving and conserving the environment. Research papers about nature can provide insight into utilizing nature as a resource, both from a practical and ecological aspect. Below is a list of environment topics that you can explore in your essays:
Water management is an issue that has a significant impact on the environment. Exploring a topic related to water management can provide experts, among others, with insights into environmental science issues and their implications. When it's time to write your project related to water management, you can explore the following topics for environmental issues:
Environmental science studies ecological processes and their interactions with living organisms. Exploring environmental science related topics can provide valuable insights into environmental science issues, their ecological implications, and conservation efforts. In addition, these topics can also be explored in different areas, providing a comprehensive understanding of how different factors impact the environment. This section delves into various environmental science topics for projects related to law, justice, policy, economics, biology, chemistry, and health science.
Environmental law governs environmental processes and their interactions with living organisms. Delving into environmental law can uncover invaluable information on environment paper topics, ranging from legal matters and their consequences to preservation initiatives. Students can use the following environmental issue topics for research papers for their essays:
Environmental justice seeks to ensure equitable treatment and meaningful involvement of all people in ecological protection, regardless of their race, sex, or economic status. Environment topics related to justice can provide valuable insights into ecological issues and their impacts. Listed below are justice-related Environmental topics to research:
Environmental policy is a set of laws, rules, and regulations created to protect the environment as well as its resources. Studying environment-related policies provides an area for students to explore a range of subjects related to the environment, ranging from local to global. Below are potential environmental sciences research topics for your reference.
Environmental economics seeks to understand environmental issues from an economic perspective. Examining environmental studies topics can offer insights into ecological conservation and sustainability while connecting protection efforts with economic interests and helping inform policies. The following are creative topics about environmental science related to economics:
>> Learn more: Economics Research Topics
Environmental biology is a field of science that focuses on understanding the interactions between living organisms and their environment. It covers environmental biology topics such as biodiversity, conservation, pollution, management, health, and sustainability. The following are environment research paper topics related to biology:
Keep in mind that we have a whole blog on biological topics if you need more ideas in this field.
Environmental chemistry research is a complex interdisciplinary field aiming to understand the behavior of a chemical process within an environment. It involves researching the impact of pollutants in the air, soil, water, and other ecological media. Possible research topics about the environment related to this field include:
Need more ideas? There is one more blog with chemistry research topics on our platform.
Environmental health is a diverse field focusing on the natural environment as well as its effects on human health. It is an interdisciplinary field that offers environment topics for research, such as environmental epidemiology, toxicology, and ecology, in addition to risk assessment. Provided below is a list of topics for an environmental science project that is suitable for your research paper:
Ecological crisis is a key issue that has continuously affected planet earth. People are becoming more aware of environmental problems as well as their impact on health, well-being, and quality of life. As such, ecological fields for research are becoming ever more critical. This section will explore interesting environmental topics related to current ecological issues, controversial, interesting topics, easy research questions for projects, as well as unique research areas which students might study. These environmental issue project ideas below will help you develop interesting fields for research papers.
Current ecological issues are a hot topic that has become increasingly important. They provide outstanding environmental issues to write about due to their impact on the environment and human health. The following are environmental issue topics for paper writing that are currently in discussion:
Environmental controversies constitute a significant challenge facing society today. From climate change to air and water pollution, the effects of human activity on our natural environment are increasingly becoming a focus of public debate and research. Research papers on environmental controversial topics can help inform the public as well as policymakers about the potential impacts of human activities on the environment. The following are examples of environmental controversy topics for research paper:
In the context of environmental subjects, research topics explore the effects of human activities on the environment as well as the potential solutions to the identified problems. In addition to providing insight into ecological protection and conservation, research areas in this category cover social issues related to environmentalism and ecological justice. Below are interesting environmental science topics to consider when looking for a research topic in the future:
When it comes to environmental science topics for project work, there are plenty of easy options. Research projects in this category can explore ecological issues as well as their consequences or potential solutions to these problems. The following is a list of the top fifteen most accessible environment project topics for your research project.
As environmental issues become increasingly complex, research fields for students become more varied. Unique environmental research topics for college students can range from local ecological concerns to global ones. The following are fifteen unique environmental science research topics for high school students and college students:
This article has provided 235 environmental science research topics for research papers as well as project work that high school and college students can use. Topics range from local issues, such as assessing air pollution levels in an urban area, to global concerns, like examining the ecological effects of plastic pollution. Whether its health risks are associated with air pollution in an environment or the impacts of industrialization, research can help shape your understanding of how to protect as well as preserve our planet. It is up to the students to identify good environmental research topics that are interesting and relevant to them and to delve deeper to understand the earth better.
- It should be interesting and relevant to your study field.
- It's essential to consider the topic's potential implications on environment-related policies. Think about the possible positive or negative effects this topic could have when implemented in terms of protecting our environment.
- A good topic should be specific enough to provide a focus for your research paper and allow you to explore a particular issue in depth.
- The research topic should be feasible and manageable to ensure that you can find the necessary information and resources.
- Environmental sciences research topics should be current and relevant to ecological developments.
- Causes and effects of climate change.
- Climate change adaptation strategies.
- Climate change impact on rural communities.
- Role of renewable energy sources in mitigating climate change.
- Carbon dioxide emission policies.
- Global warming and its impact on ocean acidification.
- Social effects of climate change.
- Permafrost melting and its implications.
- Role of international organizations in climate change.
- Climate change and forest fire: examining the role of climate change on wildfire season, frequency, and burned area.
- Renewable energy types, sources, and their impact on the environment.
- Economic benefits of renewable energy.
- Research on new technologies in renewable energy.
- Role of renewable energy in protecting businesses from legal actions.
- Hydropower and its role in renewable energy.
- Chemical batteries for renewable energy storage.
- Green microgrids in optimizing renewable energy usage.
- Ocean energy and its effects on the environment.
- Geothermal drilling and its consequences.
- Biomass resources and their use in renewable energy.
- Biodiversity conservation strategies.
- Impact of pollution on ecosystems.
- Ecological research on saving endangered species from extinction.
- Role of environment in migrations patterns of animals.
- Habitat fragmentation effects on the environment.
- Ecological implications of climate change.
- Ecology and pest control strategies.
- Ecological effects of deforestation.
- Ecology and conservation of marine life.
- Ecological consequences of urbanization.
- Air pollution: causes & effects.
- Water pollution and its consequences for people and other living organisms.
- Issue of urban & industrial pollution.
- Noise pollution and environment-related health risks.
- Marine plastic pollution in oceans.
- Radiological waste disposal policies.
- Nuclear energy, radiation & health impacts.
- Sustainable waste management solutions.
- Impact of pollution on biodiversity.
- Soil pollution and its effects on agriculture.
- Strategies for sustainable development.
- Renewable energy sources and their effects.
- Environmental sustainability and its economic benefits.
- Sustainable energy sources and their effects.
- Implications of sustainable agriculture on the environment.
- Ecological impacts of sustainable forestry.
- Social implications of renewable energy use.
- Strategies for mitigating ecological impact from unsustainable development.
- Psychological effects of ecological awareness on sustainable practices.
- Influence of ecological sustainability on economic growth.
- Endangered species conservation.
- Causes & effects of habitat fragmentation.
- Wildlife conservation strategies.
- Climate change impacts on endangered species.
- Illegal wildlife trade and trafficking.
- Marine protected areas for conserving marine life.
- Ecological restoration and reintroduction programs.
- Endangered species in developing nations.
- Human rights & animal welfare laws .
- Captive breeding for conservation purposes.
- Ecosystem services & their value.
- Climate change impacts on ecosystems.
- Hydrological cycle & effects on ecosystems.
- Ecological restoration & biodiversity conservation.
- Invasive species & their impact on native species.
- Biodiversity hotspots: areas of high endemism.
- Soil degradation & its impact on ecosystems.
- Sustainable forestry practices.
- Ecological restoration of wetlands.
- Nature conservation & preservation strategies.
- Climate change effects on natural environments.
- Natural resource management strategies.
- Policies for natural resources management.
- Impact of human development on wildlands.
- Sustainable use of natural resources.
- Role of ethics in nature conservation.
- De-extinction: pros & cons of bringing back extinct species.
- Protected areas & conservation of rare species.
- Water pollution & its control.
- Groundwater management strategies.
- Climate change impact on water resources.
- Integrated water resources management.
- Wetland conservation & restoration projects.
- Industrial effluents role in water pollution.
- Desalination technologies for freshwater production.
- Urbanization impact on groundwater resources.
- Inland & coastal water management strategies.
- Wastewater treatment & reuse technologies.
- Climate change liability & lawsuits.
- Strategies for conservation and protection under environmental law.
- Consequences of non-compliance with regulations on the environment.
- Impact of trade agreements on environment protection.
- Regulatory strategies for hazardous waste disposal.
- Strategies for enforcement and compliance with environment-related laws.
- International environment treaties and their implications.
- Effects of climate change legislation on the environment.
- Corporate environmental policies and regulations and their effects.
- Role of law in mitigating environment-related issues.
- Implications of unequal access to resources.
- Disproportionate impacts of climate change on vulnerable populations.
- Consequences of marginalization of marginalized communities from environmental processes.
- Links between poverty and environment degradation.
- Effects of non-participation in environment-related decision-making.
- Policies to ensure access to clean air and water.
- Impact of social inequality on environment protection.
- Intersection between gender, race, and environment justice.
- Ecological consequences of corporate negligence of marginalized communities.
- Disproportionate implications of climate change on vulnerable populations.
- Environmental policy initiatives' implications on global climate change.
- Effectiveness of carbon taxes for air pollution control.
- Land use and development impact on the environment.
- Water quality in the united states, focusing on natural resource governance.
- Educational initiative's impact on public opinion and policy outcomes.
- Social aspects of policy making and implementation on the environment.
- Promoting sustainability from a global perspective.
- Potential for justice initiatives in promoting equitable and effective management.
- Rise of green economy its impact.
- Environment policies and their potential for success.
- Economic impacts of regulating the environment.
- Strategies for environmentally sustainable economic growth.
- Consequences of non-compliance with environment-related regulations.
- Environment conservation and protection using economic incentives.
- Taxes and subsidies and their implications on the environment.
- Economic implications of climate change legislation.
- The private sector role in environment conservation and protection.
- Green finance role in mitigating ecological issues.
- Economics of pollution control and management.
- Conservation and protection of the environment in the face of economic interests.
- Biodiversity conservation in managing the environment.
- Role of biotechnology in reducing air pollution.
- Environment degradation and its consequences on wildlife.
- Role of microorganisms in maintaining soil fertility.
- Ecological consequences of over-exploitation of natural resources.
- Habitat fragmentation and its role in species conservation.
- Education's role in environment conservation.
- Environment degradation and its effects on food security.
- Invasive species and their impacts on ecosystem.
- Effect of agricultural chemicals on water systems.
- Air pollution control strategies and their effectiveness.
- Climate change impacts on aquatic ecosystems.
- Sources and implications of persistent organic pollutants.
- Air quality monitoring for urban areas.
- Water quality monitoring in coastal areas.
- Characterization and fate of toxic compounds in soil and groundwater.
- Impact of hazardous chemical waste on the environment.
- Monitoring and remediation of contaminated sites.
- The roles of environmental chemistry in climate change research.
- Air pollution effects on human health.
- Climate change effects on health.
- Water pollution and public health.
- Noise pollution effects on well-being.
- Mental health effects of environment-related toxins.
- Human health effects of natural disasters.
- Urbanization's effect on human health.
- Sustainable development and public health.
- Role of social media in promoting environmental health and awareness.
- Biodiversity preservation and its impact on human health.
- Global warming and how to prevent its impact.
- Sustainable energy and its role in protecting the environment.
- Water conservation practices.
- Renewable energy role in global ecological protection.
- Carbon footprint and climate change.
- Ozone layer depletion and its effects on human health.
- Plastic pollution and its impact.
- Land degradation and soil erosion.
- Energy industry activities effects on ecological health.
- Air pollution and its impact on human health.
- Deforestation and its consequences.
- Effect of agricultural practices on ecological health.
- Overuse and exploitation of natural resources.
- Industrial waste impact on health.
- Green technology role in ecological protection.
- Climate change: is human activity a primary cause of global warming.
- Deforestation: are current logging practices sustainable in the long term.
- Air pollution: what are the health impacts of air pollution.
- Water pollution: how is water pollution impacting biodiversity and ecosystems.
- Geothermal energy: what potential impacts does geothermal energy extraction have on the environment.
- Renewable energy: are wind and solar energy carbon-neutral.
- Arctic drilling: is drilling for oil in the arctic ocean a viable option given current climate conditions.
- Nuclear power: what health risks are associated with nuclear power plants.
- Biodiversity loss: what steps can you take to protect biodiversity from human activities.
- Endangered species: how protecting endangered species can impact conservation efforts and how they live.
- GMO foods: are genetically modified organisms safe for human consumption? how does GMO food affect humans.
- Pesticides: how does pesticide use affect our health and the environment.
- Ocean acidification: how is ocean acidification impacting marine ecosystems.
- Waste management: what are the most effective ways to manage waste and reduce pollution.
- Resource exploitation: how does the exploitation of natural resources impact local communities.
- Effects of environment-related toxins on human health.
- Climate change effects on coastal habitats.
- Agricultural activities impacts on the environment.
- Groundwater contamination and its effects on water quality.
- Pollution from factories and its impact on the environment.
- Waste management strategies and their impacts.
- Consequences of water contamination on local wildlife.
- Impacts of mining.
- Deforestation effects on ecosystems and species diversity.
- Industrial fishing practices effects.
- Sustainable forestry practices and their impact on ecosystems.
- Nuclear energy production and its consequences.
- Reducing emissions from vehicles and their effects on air quality.
- Landfills implications on the environment.
- Implications of plastic pollution.
- Air pollution levels impact on urban areas.
- Agricultural practices effects on the environment.
- Developing strategies for sustainable development.
- Causes of water contamination.
- Factors contributing to global warming.
- Natural disasters effects on the environment.
- Land use changes effects on the environment.
- Energy consumption impacts on the environment.
- Climate change effects on the environment.
- Industrialization and its consequences.
- Impact of plastic pollution.
- Health risks associated with air pollution.
- Deforestation impacts on the environment.
- Soil erosion and its effects on the environment.
- Causes and consequences of species extinction.
- Climate change impact on water quality.
- Acid rain and its effects.
- Urbanization's effect on biodiversity.
- Effects of offshore drilling.
- Ocean acidification and its impact.
- Impact of privatization on natural resources.
- Effectiveness of renewable energy sources.
- Relationship between energy consumption and the environment.
- Potential impacts regarding genetic engineering on biodiversity.
- Toxic waste disposal and its impacts.
- Environment-related policies impact on water quality.
- Deforestation and its effects on soil quality.
- Causes and consequences of ozone layer depletion.
- Relationship between pollution and public health issues.
What Are Environmental Topics?
What makes a good environmental research topic , how to choose environmental science topics, list of environment research paper topics, environmental research topics on climate change, environmental science research topics on renewable energy, environment research topics on ecology, research topics in environmental science about pollution, environmental topics for research papers on sustainability, environmental topics to write about endangered species, environmental research paper topics on ecosystems, environmental topics about nature, environmental issues topics on water management, environmental science topics in different areas, environmental law research topics, environmental justice research topics, environmental policy research paper topics, environmental economics research topics, environmental biology research topics, environmental chemistry research topics, environmental health science research topics, other ideas & topics about environment for research papers, current issues in environmental science, controversial environmental topics for research paper, interesting environmental research topics, easy environmental research questions for projects, unique environmental research topics for students, final thoughts on environmental topics for research papers.

2019 Best Papers published in the Environmental Science journals of the Royal Society of Chemistry

In 2019, the Royal Society of Chemistry published 180, 196 and 293 papers in Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts , Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology , and Environmental Science: Nano , respectively. These papers covered a wide range of topics in environmental science, from biogeochemical cycling to water reuse to nanomaterial toxicity. And, yes, we also published papers on the topic of the environmental fate, behavior, and inactivation of viruses. 1–10 We are extremely grateful that so many authors have chosen our journals as outlets for publishing their research and are equally delighted at the high quality of the papers that we have had the privilege to publish.
Our Associate Editors, Editorial Boards, and Advisory Boards were enlisted to nominate and select the best papers from 2019. From this list, the three Editors-in-Chief selected an overall best paper from the entire Environmental Science portfolio. It is our pleasure to present the winners of the Best Papers in 2019 to you, our readers.
Overall Best Paper
In this paper, Johansson et al. examine sea spray aerosol as a potential transport vehicle for perfluoroalkyl carboxylic and sulfonic acids. The surfactant properties of these compounds are well known and, in fact, key to many of the technical applications for which they are used. The fact that these compounds are enriched at the air–water interface makes enrichment in sea spray aerosols seem reasonable. Johansson et al. systematically tested various perfluoroalkyl acids enrichment in aerosols under conditions relevant to sea spray formation, finding that longer chain lengths lead to higher aerosol enrichment factors. They augmented their experimental work with a global model, which further bolstered the conclusion that global transport of perfluoroalkyl acids by sea spray aerosol is and will continue to be an important process in determining the global distribution of these compounds.
Journal Best Papers
Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts
First Runner-up Best Paper: Yamakawa, Takami, Takeda, Kato, Kajii, Emerging investigator series: investigation of mercury emission sources using Hg isotopic compositions of atmospheric mercury at the Cape Hedo Atmosphere and Aerosol Monitoring Station (CHAAMS), Japan , Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts , 2019, 21 , 809–818, DOI: 10.1039/C8EM00590G .
Second Runner-up Best Paper: Avery, Waring, DeCarlo, Seasonal variation in aerosol composition and concentration upon transport from the outdoor to indoor environment , Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts , 2019, 21 , 528–547, DOI: 10.1039/C8EM00471D .
Best Review Article: Cousins, Ng, Wang, Scheringer, Why is high persistence alone a major cause of concern? Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts , 2019, 21 , 781–792, DOI: 10.1039/C8EM00515J .
Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology
First Runner-up Best Paper: Yang, Lin, Tse, Dong, Yu, Hoffmann, Membrane-separated electrochemical latrine wastewater treatment , Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol. , 2019, 5 , 51–59, DOI: 10.1039/C8EW00698A .
Second Runner-up Best Paper: Genter, Marks, Clair-Caliot, Mugume, Johnston, Bain, Julian, Evaluation of the novel substrate RUG™ for the detection of Escherichia coli in water from temperate (Zurich, Switzerland) and tropical (Bushenyi, Uganda) field sites , Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol. , 2019, 5 , 1082–1091, DOI: 10.1039/C9EW00138G .
Best Review Article: Okoffo, O’Brien, O’Brien, Tscharke, Thomas, Wastewater treatment plants as a source of plastics in the environment: a review of occurrence, methods for identification, quantification and fate , Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol. , 2019, 5 , 1908–1931, DOI: 10.1039/C9EW00428A .
Environmental Science: Nano
First Runner-up Best Paper: Janković, Plata, Engineered nanomaterials in the context of global element cycles , Environ. Sci.: Nano , 2019, 6 , 2697–2711, DOI: 10.1039/C9EN00322C .
Second Runner-up Best Paper: González-Pleiter, Tamayo-Belda, Pulido-Reyes, Amariei, Leganés, Rosal, Fernández-Piñas, Secondary nanoplastics released from a biodegradable microplastic severely impact freshwater environments , Environ. Sci.: Nano , 2019, 6 , 1382–1392, DOI: 10.1039/C8EN01427B .
Best Review Article: Lv, Christie, Zhang, Uptake, translocation, and transformation of metal-based nanoparticles in plants: recent advances and methodological challenges , Environ. Sci.: Nano , 2019, 6 , 41–59, DOI: 10.1039/C8EN00645H .
Congratulations to the authors of these papers and a hearty thanks to all of our authors. As one can clearly see from the papers listed above, environmental science is a global effort and we are thrilled to have contributions from around the world. In these challenging times, we are proud to publish research that is not only great science, but also relevant to the health of the environment and the public. Finally, we also wish to extend our thanks to our community of editors, reviewers, and readers. We look forward to another outstanding year of Environmental Science , reading the work generated not just from our offices at home, but also from back in our laboratories and the field.
Kris McNeill, Editor-in-Chief
Paige Novak, Editor-in-Chief
Peter Vikesland, Editor-in-Chief
- A. B Boehm, Risk-based water quality thresholds for coliphages in surface waters: effect of temperature and contamination aging, Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts , 2019, 21 , 2031–2041, 10.1039/C9EM00376B .
- L. Cai, C. Liu, G. Fan, C Liu and X. Sun, Preventing viral disease by ZnONPs through directly deactivating TMV and activating plant immunity in Nicotiana benthamiana , Environ. Sci.: Nano , 2019, 6 , 3653–3669, 10.1039/C9EN00850K .
- L. W. Gassie, J. D. Englehardt, N. E. Brinkman, J. Garland and M. K. Perera, Ozone-UV net-zero water wash station for remote emergency response healthcare units: design, operation, and results, Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol. , 2019, 5 , 1971–1984, 10.1039/C9EW00126C .
- L. M. Hornstra, T. Rodrigues da Silva, B. Blankert, L. Heijnen, E. Beerendonk, E. R. Cornelissen and G. Medema, Monitoring the integrity of reverse osmosis membranes using novel indigenous freshwater viruses and bacteriophages, Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol. , 2019, 5 , 1535–1544, 10.1039/C9EW00318E .
- A. H. Hassaballah, J. Nyitrai, C. H. Hart, N. Dai and L. M. Sassoubre, A pilot-scale study of peracetic acid and ultraviolet light for wastewater disinfection, Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol. , 2019, 5 , 1453–1463, 10.1039/C9EW00341J .
- W. Khan, J.-Y. Nam, H. Woo, H. Ryu, S. Kim, S. K. Maeng and H.-C. Kim, A proof of concept study for wastewater reuse using bioelectrochemical processes combined with complementary post-treatment technologies, Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol. , 2019, 5 , 1489–1498, 10.1039/C9EW00358D .
- J. Heffron, B. McDermid and B. K. Mayer, Bacteriophage inactivation as a function of ferrous iron oxidation, Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol. , 2019, 5 , 1309–1317, 10.1039/C9EW00190E .
- S. Torii, T. Hashimoto, A. T. Do, H. Furumai and H. Katayama, Impact of repeated pressurization on virus removal by reverse osmosis membranes for household water treatment, Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol. , 2019, 5 , 910–919, 10.1039/C8EW00944A .
- J. Miao, H.-J. Jiang, Z.-W. Yang, D.-y. Shi, D. Yang, Z.-Q. Shen, J. Yin, Z.-G. Qiu, H.-R. Wang, J.-W. Li and M. Jin, Assessment of an electropositive granule media filter for concentrating viruses from large volumes of coastal water, Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol. , 2019, 5 , 325–333, 10.1039/C8EW00699G .
- K. L. Nelson, A. B. Boehm, R. J. Davies-Colley, M. C. Dodd, T. Kohn, K. G. Linden, Y. Liu, P. A. Maraccini, K. McNeill, W. A. Mitch, T. H. Nguyen, K. M. Parker, R. A. Rodriguez, L. M. Sassoubre, A. I. Silverman, K. R. Wigginton and R. G. Zepp, Sunlight mediated inactivation of health relevant microorganisms in water: a review of mechanisms and modeling approaches, Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts , 2018, 20 , 1089–1122, 10.1039/C8EM00047F .
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Perspective
- Open access
- Published: 04 October 2019
Engaging with research impact assessment for an environmental science case study
- Kirstie A. Fryirs ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0541-3384 1 ,
- Gary J. Brierley ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1310-1105 2 &
- Thom Dixon ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4746-2301 3
Nature Communications volume 10 , Article number: 4542 ( 2019 ) Cite this article
15k Accesses
18 Citations
39 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Environmental impact
- Research management
An Author Correction to this article was published on 08 November 2019
This article has been updated
Impact assessment is embedded in many national and international research rating systems. Most applications use the Research Impact Pathway to track inputs, activities, outputs and outcomes of an invention or initiative to assess impact beyond scholarly contributions to an academic research field (i.e., benefits to environment, society, economy and culture). Existing approaches emphasise easy to attribute ‘hard’ impacts, and fail to include a range of ‘soft’ impacts that are less easy to attribute, yet are often a dominant part of the impact mix. Here, we develop an inclusive 3-part impact mapping approach. We demonstrate its application using an environmental initiative.
Similar content being viewed by others

Frequent disturbances enhanced the resilience of past human populations

Interviews in the social sciences

A unifying modelling of multiple land degradation pathways in Europe
Introduction.
Universities around the World are increasingly required to demonstrate and measure the impact of their research beyond academia. The Times Higher Education (THE) World University Rankings now includes a measure of knowledge transfer and impact as an indicator of an institution’s quality and the THE World University Rankings released their inaugural University impact rankings in 2019. With the global rise of impact assessment, most nations adopt a variant of the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) definition of impact 1 ; “the contribution that research makes to the economy, society, environment or culture, beyond the contribution to academic research.” Yet research impact mapping provides benefits beyond just meeting the requirements for assessment 1 . It provides an opportunity for academics to reflect on and consider the impact their research can, and should, have on the environment, our social networks and wellbeing, our economic prosperity and our cultural identities. If considered at the development stage of research practices, the design and implementation of impact mapping procedures and frameworks can provide an opportunity to better plan for impact and create an environment where impact is more likely to be achieved.
Almost all impact assessments use variants of the Research Impact Pathway (Fig. 1 ) as the conceptual framework and model with which to document, measure and assess environmental, social, economic and cultural impacts of research 1 . This Pathway starts with inputs, followed by activities. Outputs and outcomes are produced and these lead to impact. Writing for Nature Outlook: Assessing Science , Morgan 2 reported on how Australia’s Commonwealth Scientific and Research Organisation (CSIRO) mapped impact using this approach. However, the literature contains very few worked examples to guide academics and co-ordinators in the process of research impact mapping. This is particularly evident for environmental initiatives and innovations 3 , 4 .
Here we provide a new, 3-part impact mapping approach that can accommodate non-linearity in the impact pathway and can more broadly include and assess both ‘hard’ impacts, those that can be directly attributed to an initiative or invention, and ‘soft’ impacts, those that can be indirectly attributed to an initiative or invention. We then present a worked example for an environmental innovation called the River Styles Framework, developed at Macquarie University, Sydney, Australia. The River Styles Framework is an approach to analysis, interpretation and application of geomorphic insights into river landscapes as a tool to support management applications 5 , 6 . We document and map how this Framework has shaped, and continues to shape, river management practice in various parts of the world. Through mapping impact we demonstrate how the River Styles Framework has contributed to environmental, social and economic benefits at local, national and international scales. Cvitanovic and Hobday (2018) 3 in Nature Communications might consider this case study a ‘bright spot’ that sits at the environmental science-policy-practice interface and is representative of examples that are seldom documented.
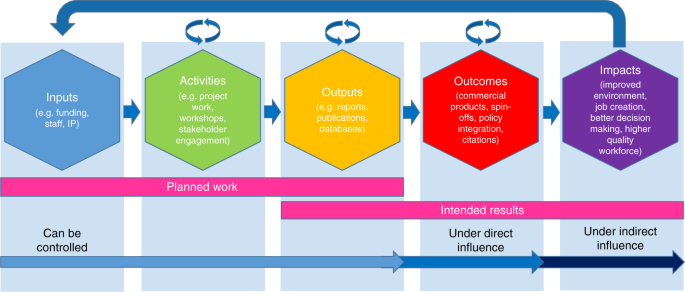
The Research Impact Pathway (modified from ref. 2 )
This case study is presented from the perspective of the researchers who developed the River Styles Framework, and the University Impact co-ordinator who has worked with the researchers to document and measure the impact as part of ex post assessment 1 , 7 . We highlight challenges in planning for impact, as the research impact pathway evolves and entails significant lag times 8 . We discuss challenges that remain in the mapping process, particularly when trying to measure and attribute ‘soft’ impacts such as a change in practice or philosophy, an improvement in environmental condition, or a reduction in community conflict to a particular initiative or innovation 9 . We then provide a personal perspective of the challenges faced and lessons learnt in applying and mapping research impact so that others, particularly in the environmental sciences and related interdisciplinary fields, can undertake similar exercises for their own research impact assessments.
Brief background on research impact assessment and reporting
Historical reviews of research policy record long-term shifts towards incorporation of concerns for research impact within national funding agencies. In the 1970s the focus was on ‘research utilisation’ 10 , more recently it has been on ‘knowledge mobilisation’ 11 . The focus is always on seeking to understand the actual manner and pathways through which research becomes incorporated into policy, and through which research has an economic, social, cultural and environmental impact. Often these are far from linear circumstances, entailing multiple pathways.
Since the 1980s, higher education systems around the world have been transitioning to performance-based research funding systems (PRFS). The initial application of the PRFS in university contexts occurred as part of the first Research Assessment Exercise (RAE) in the United Kingdom in 1986 12 . PRFS systems have been designed to reward and perpetuate the highest quality research, presenting notionally rational criteria with which to support more intellectually competitive institutions 13 . The United Kingdom’s (UK) RAE was replicated in Australia as the Research Quality Framework (RQF), and more recently as the Excellence in Research for Australia (ERA) assessment. In 2010, 15 countries engaged in some form of PRFS 14 . These frameworks focus almost solely on academic research performance and productivity, rather than the contribution and impact that research makes to the economy, society, environment or culture.
In the last decade, research policy frameworks have increasingly focused on facilitating national prosperity through the transfer, translation and commercialisation of knowledge 15 , 16 , combined with the integration of research findings into government policy-making 17 . In 2009, the Higher Education Funding Council for England conducted a year-long review and consultation process regarding the structure of the Research Excellence Framework (REF) 18 . Following this review, in 2010 the Higher Education Funding Council for England (HEFCE) commissioned a series of impact pilot studies designed to produce narrative-style case studies by 29 higher education institutions. The pilot studies featured five units of assessment: clinical medicine, physics, earth systems and environmental sciences, social work and social policy, and English language and literature 12 . These pilot studies became the basis of the REF conducted in the UK in 2014 9 , 19 with research impact reporting comprising a 20% component of the overall assessment.
In Canada, in 2009 and from 2014 the Canadian Academy of Health Sciences and Manitoba Research, respectively, developed an impact framework and narrative outputs to evaluate the returns on investment in health research 20 , 21 . Similarly the UK National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) regularly produces impact synthesis case studies 22 . In Ireland, in 2012, the Science Foundation Ireland placed research impact assessment at the core of its scientific and engineering research vision, called Agenda 2020 23 . In the United States, in 2016, the National Science Foundation, National Institute of Health, US Department of Agriculture, and US Environmental Protection Authority developed a repository of data and tools for assessing the impact of federal research and development investments 24 . In 2016–2017, the European Union (EU) established a high-level group to advise on how to maximise the impact of the EU’s investment in research and innovation, focussing on the future of funding allocation and the implementation of the remaining years of Horizon 2020 25 . In New Zealand, in 2017, the Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment released a discussion paper proposing the introduction of an impact ‘pillar’ into the science investment system 26 . In 2020, Hong Kong will include impact assessment in their Research Assessment Exercise (RAE) for the first time 27 . Other countries including Denmark, Finland and Israel have scoped the use of research impact assessments of their major research programs as part of the Small Advanced Economies Initiative 28 .
In 2017, the Australian Research Council (ARC) conducted an Engagement and Impact Assessment Pilot (EIAP) 7 . While engagement is not analogous to impact, it is an evidential mechanism that elucidates the potential beneficiaries, stakeholders, and partners of academic research 12 , 16 . In addition to piloting narrative-style impact case study reporting, the EIAP characterised and mapped patterns of academic engagement with end users that create and enable research impact. The 2017 EIAP assessed a selection of disciplines for engagement, and a selection of disciplines for impact. Environmental science was a discipline selected for the impact pilot. These pilots became the basis for the Australian Engagement and Impact (EI) assessment in 2018 7 that ran in parallel with the ERA, and from which the case study in this paper is drawn.
Research impact assessment does not just include ex post reporting that can feed into a national PRFS. A large component of academic impact assessment involves ex ante impact reporting in research funding applications. In both the UK and Australia, the perceived merit of a research funding application has been linked in part to its planning and potential for external research impact. In the UK this is labelled a ‘Pathways to Impact’ statement (used by the Research Council UK), in Australia this is an Impact statement (used by the ARC), with a national interest statement also implemented in 2018. These statements explicitly draw from the ‘pathway to impact’ model which simplifies a direct and linear relationship between research excellence, research engagement, and research impact 29 . These ex ante impact statements can be difficult for academics, especially early career researchers, if they do not understand the process, nature and timing of impact. This issue exists in ex post impact reporting and assessment as well, with many researchers finding it difficult to supply evidence that directly or indirectly links their research to impacts that may have taken decades to manifest 1 , 7 , 8 . Also, the simplified linearity of the Research Impact Pathway model makes it difficult to adequately represent the transformation of research into impact.
For research impact statements and assessments to be successful, researchers need to understand the patterns and pathways by which impact occurs prior to articulating how their own research project might achieve impact ex ante, or has had impact ex post. The quality of research impact assessment will improve if researchers and funding agencies understand the types and qualities of impact that can reasonably be expected to arise from a research project or initiative.
Given the plethora of interest in, and a growing global movement towards, both ex ante and ex post research impact assessment and reporting, it is surprising that very few published examples demonstrate how to map research impact. Even in the business, economics and corporate sectors where impact assessment and reporting is common practice 30 , 31 , 32 , very few published examples exist. This hinders prospects for researchers and co-ordinators to develop a more critical understanding of impact, inhibiting more nuanced understandings of the pathways to impact model. Mapping impact networks and recording a cartography of impact for research projects and initiatives provides an appropriate basis to conduct such tasks. This paper provides a new method by which this can be achieved.
The research impact pathway and impact mapping
Many impact assessment frameworks around the world have common characteristics, often structured around the Research Impact Pathway model (Fig. 1 ). This model can be identified in a series of 2009 and 2016 Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) reports that investigated the mechanisms of impact reporting 1 , 33 . The Research Impact Pathway is presented as a sequence of steps by which impact is realised. This pathway can be visualised for an innovation or initiative using an impact mapping approach. It starts with inputs that can include funding, staff, background intellectual property and support structures (e.g., administration, facilities). This is followed by activities or the ‘doing’ elements. This includes the work of discovery (i.e., research) and the translation—i.e., courses, workshops, conferences, and processes of community and stakeholder engagement.
Outputs are the results of inputs and activities. They includes publications, reports, databases, new intellectual property, patents and inventions, policy briefings, media, and new courses or teaching materials. Inputs, activities and outputs can be planned and somewhat controlled by the researcher, their collaborators and their organisations (universities). Outcomes then occur under direct influence of the researcher(s) with intended results. This may include commercial products and licences, job creation, new contracts, grants or programs, citations of work, new companies or spin-offs and new joint ventures and collaborations.
Impacts (sometimes called benefits) tend to occur via uptake and use of an innovation or initiative by independent parties under indirect (or no) influence from the original researcher(s). Impacts can be ‘hard’ or ‘soft’ and have intended and unintended consequences. They span four main areas outside of academia, including environmental, social, economic and cultural spaces. Impacts can include improvements in environmental health, quality of life, changes in industry or agency philosophy and practice, implementation or improvement in policy, improvements in monitoring and reporting, cost-savings to the economy or industry, generation of a higher quality workforce, job creation, improvements in community knowledge, better inter-personal relationships and collaborations, beneficial transfer and use of knowledge, technologies, methods or resources, and risk-reduction in decision making.
The challenge: applying the research impact pathway to map impact for a case study
The River Styles Framework 5 , 34 aligns with UN Sustainable Development Goals of Life on Land and Clean Water and Sanitation that have a 2020 target to “ensure the conservation, restoration and sustainable use of terrestrial and inland freshwater ecosystems and their services” and a 2030 target to urgently “implement integrated water resources management at all levels” 35 .
The River Styles Framework is a catchment-scale approach to analysis and interpretation of river geomorphology 36 . It is an open-ended, generic approach for use in any landscape or environmental setting. The Framework has four stages (see refs. 5 , 37 , 38 , 39 ); (1) Analysis of river types, behaviour and controls, (2) Assessment of river condition, (3) Forecasting of river recovery potential, and (4) Vision setting and prioritisation for decision making.
River Styles Framework development, uptake, extension and training courses have contributed to a global change in river management philosophy and practice, resulting in improved on-ground river condition, use of geomorphology in river management, and end-user professional development. Using the River Styles Framework has changed the way river management decisions are made and the level of intervention and resources required to reach environmental health targets. This has been achieved through the generation of catchment-scale and regional-level templates derived from use of the Framework 6 . These templates are integrated with other biophysical science tools and datasets to enhance planning, monitoring and forecasting of freshwater resources 6 . The Framework is based on foundation research on the form and function of streams and their interaction with the landscape through which they flow (fluvial geomorphology) 5 , 40 .
The Framework has a pioneering structure and coherence due to its open-ended and generic approach to river analysis and interpretation. Going well beyond off-the-shelf imported manuals for river management, the Framework has been adopted because of its innovative approach to geomorphic analysis of rivers. The Framework is tailored for the landscape and institutional context of any given place to produce scaffolded, coherent and consistent datasets for catchment-specific decision making. Through on-ground communication of place-based results, the application of the Framework spans local, state, national and international networks and initiatives. The quality of the underlying science has been key to generating the confidence required in industry and government to adopt geomorphology as a core scientific tool to support river management in a range of geographical, societal and scientific contexts 6 .
The impact of this case study spans conceptual use, instrumental use and capacity building 4 defined as ways of thinking and alerting policy makers and practitioners to an issue. Impact also includes direct use of research in policy and planning decisions, and education, training and development of end-users, respectively 4 , 41 , 42 . The River Styles Framework has led to establishment of new decision-making processes while also changing philosophy and practice so on-ground impacts can be realised.
Impact does not just occur at one point in time. Rather, it comes and goes or builds and is sustained. How this is represented and measured, particularly for an environmental case study, and especially for an initiative built around a Framework where a traditional ‘product’, ‘widget’, or ‘invention’ is not produced is challenging 4 . More traditional metrics-based indicators such as the number of lives saved or the amount of money generated cannot be deployed for these types of case studies 4 , 9 . It is particularly challenging to unravel the commercial value and benefits of adopting and using an initiative (or Framework) that is part of a much bigger, international paradigm shift in river management philosophy and practice.
Similarly, how do you measure environmental, social, economic or cultural impacts of an initiative where the benefits can take many years (and in the case of rivers, decades) to emerge, and how do you then link and attribute those impacts directly with the design, development, use and extension of that initiative in many different places at many different times? For the River Styles Framework, on-ground impacts in terms of improved river condition and recovery are occurring 43 , but other environmental, social and economic benefits may be years or decades away. Impactful initiatives in themselves often reshape the contextual setting that then frames the next phase of science and management practices which leads to further implications for policy and institutional settings, and for societal (socio-cultural) and environmental benefits. This is currently the case in assessing the impact of the River Styles Framework.
The method: a new, 3-part impact mapping approach
Using the River Styles framework as an environmental case study, Fig. 2 presents a 3-part impact mapping approach that contains (1) a context strip, (2) an impact map, and (3) soft impact intensity strips to capture the scope of the impact and the conditions under which it has been realised. This approach provides a template that can be used or replicated by others in their own impact mapping exercises 44 .
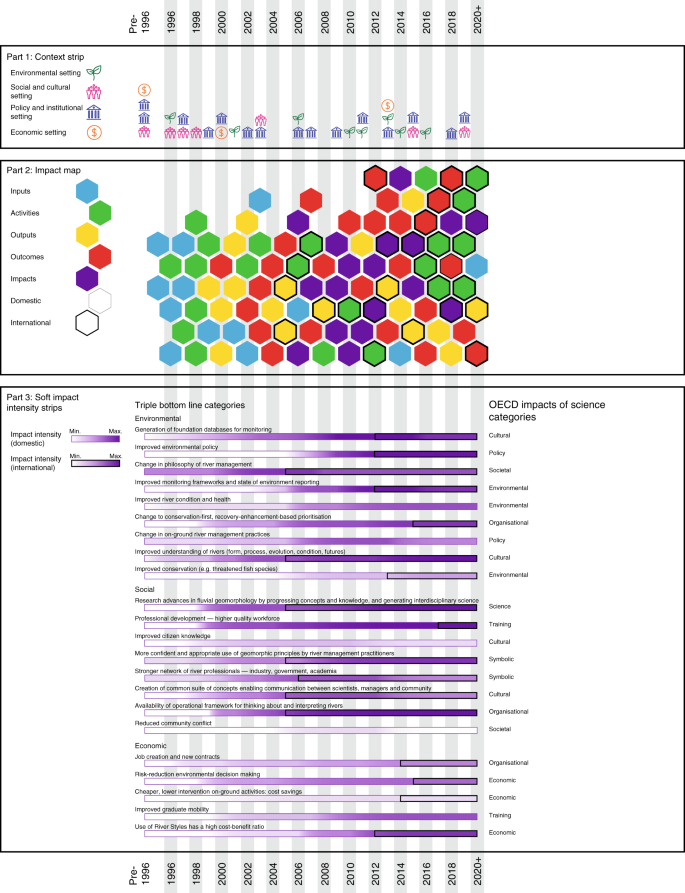
The research impact map for the River Styles Framework case study. This map contains 3 parts, a context strip, impact map and soft impact intensity strips
The cartographic approach to mapping impact shown in Fig. 2 provides a mechanism to display a large amount of complex information and interactions in a style that conveys and communicates an immediate snapshot of the research impact pathway, its components and associated impacts. The map can be analysed to identify patterns and interactions between components as part of ex post assessment, and as a basis for ex ante impact forecasting.
The 3-part impact map output is produced in an interactive online environment, acknowledging that impact maps are live, open-ended documents that evolve as new impacts emerge and inputs, activities, outputs and outcomes continue. The map changes when activities, outputs or outcomes that the developers had forgotten, or considered to be peripheral, later re-appear as having been influential to a stakeholder, community or network not originally considered as an end-user. Such activities, outputs and outcomes can be inserted into a live map to broaden its base and understand the impact. Also, by clicking on each icon on the map, pop-up bubbles contain details that are specific to each component of the case study. This functionality can also be used to journal or archive important information and evidence in the ‘back-end’ of the map. Such evidence is often required, or called upon, in research impact assessments. Figure 2 only provides a static reproduction of the map output for the River Styles Framework. The fully worked, interactive, River Styles Framework impact map can be viewed at https://indd.adobe.com/view/c9e2a270–4396–4fe3-afcb-be6dd9da7a36 .
Context is a key driver of research impact 1 , 45 . Context can provide goals for research agendas and impact that feeds into ex ante assessments, or provide a lens through which to analyse the conditions within which certain impacts emerged and occurred as part of ex post assessment. Part 1 of our mapping approach produces a context strip that situates the case study (Fig. 2 ). This strip is used to document settings occurring outside of academia before, during and throughout the case study. Context can be local, national or global and examples can be gathered from a range of sources such as reports, the media and personal experience. For the River Styles case study only key context moments are shown. Context for this case study is the constantly changing communities of practice in global river restoration that are driven by (or inhibited by) the environmental setting (coded with a leaf symbol), policy and institutional settings (coded with a building symbol), social and cultural settings (coded with a crowd symbol), and economic settings (coded with a dollar symbol). For most case studies, these extrinsic setting categories will be similar, but others can be added to this part of the map if needed.
Part 2 of our mapping approach produces an impact map using the Research Impact Pathway (Fig. 1 ). This impact map (Fig. 2 ) documents the time-series of inputs (coded with a blue hexagon), activities (coded with a green hexagon), outputs (coded with a yellow hexagon), outcomes (coded with a red hexagon) and impacts (coded with a purple hexagon) that occurred for the case study. Heavier bordered hexagons and intensity strips represent international aspects and uptake. To start, only the primary inputs, activities, outputs and outcomes are mapped. A hexagon appears when there is evidence that an input, activity, output or outcome has occurred. Evidence includes event advertisements, reports, publications, website mentions, funding applications, awards, personnel appointments and communications products.
However, in conducting this standard mapping exercise it soon became evident that it is difficult to map and attribute impacts, particularly for an initiative that has a wide range of both direct and indirect impacts. To address this, our approach distinguishes between ‘hard’ impacts and ‘soft’ impacts. Hard impacts can be directly attributed to an initiative or invention, whereas soft impacts can be indirectly attributed to an initiative or invention. The inclusion of soft impacts is critical as they are often an important and sometimes dominant part of the impact mix. Both quantitative and qualitative measures and evidence can be used to attribute hard or soft impacts. There is not a direct one-to-one relationship between quantitative measurement of hard impacts and qualitative appraisal of soft impacts.
Hard impacts are represented as purple hexagons in the body of the impact map. For the River Styles Framework we have only placed a purple hexagon on the impact map where the impact can be ‘named’ and for which there is ‘hard’ evidence (in the form of a report, policy, strategic plan or citation) that directly mentions and therefore attributes the impact to River Styles. Most of these are multi-year impacts and the position of the hexagons on the map is noted at the first mention.
For many case studies, particularly those that impact on the environment, society and culture, attributing impact directly to an initiative or invention is not necessarily easy or straighforward. To address this our approach contains a third element, soft impact intensity strips (Fig. 2 ) to recognise, document, capture and map the extent and influence of impact created by an initiative or invention. This is represented as a heat intensity chart (coded as a purple bar of varying intenstiy) and organised under the environmental, social and economic categories that are often used to measure Triple-Bottom-Line (TBL) benefits in sustainability and research and development (R&D) reporting (e.g., refs. 7 , 46 ). Within these broad categories, soft impacts are categorised according to the dimensions of impacts of science used by the OECD 1 . These include environmental, societal, cultural, economic, policy, organisational, scientific, symbolic and training impacts. Each impact strip for soft impacts uses different levels of purple shading (to match the purple hexagon colour in the impact map) to visualise the timing and intensity of soft impacts. For the River Styles Framework, the intensity of the purple colour is used to show those impacts that have been most impactful (darker purple), the timing of initiation, growth or step-change in intensity of each impact, the rise and wane of some impacts and the longevity of others. A heavy black border is used to note the timing of internationalisation of some impacts. This heat intensity chart was constructed by quantitatively representing qualitative sentiment in testimonials, interviews, course evaluations and feedback, surveys and questionnaires, acknowledgements and recognitions, documentation of collaborations and networks, use of River Styles concepts, and reports on the development of spin-off frameworks. Quantitative representations of qualitative sentiment was achieved through using the methods of time-series keyword searches and expert judgement. These are just two methods by which the level of heat intensity can be measured and assigned 9 .
The outcome: impact of the River Styles Framework case study
Figure 2 , and its interactive online version, present the impact map for the River Styles Framework initiative and Table 1 documents the detail of the River Styles impact story from pre-1996 to post-2020. The distribution of colour-coded hexagons and the intensity of purple on the soft impact intensity strips on Fig. 2 demonstrates the development and maturation of the initiative and the emergence of the impact.
In the first phase (pre-1996–2002), blue inputs, green activities and yellow output hexagons dominate. The next phase (2002–2005) was an intensive phase of output production (yellow hexagons). It is during this phase that red outcome hexagons appear and intensify. From 2006, purple impact hexagons appear for the first time, representing hard impact outside of academia. Soft impacts also start to emerge more intensely (Fig. 2 ). 2008–2015 represents a phase of domestic consolidation of yellow outputs, red outcomes and purple impacts, and the start of international uptake. Some of this impact is under direct influence and some is independent of the developers of the River Styles Framework (Fig. 1 ). The number of purple impact hexagons is more intense during the 2008–2015 period and soft impacts intensify further. 2016–2018 (and beyond) represents a phase of extension into international markets, collaborations and impact (heavier bordered hexagons and intensity strips; Fig. 2 ). The domestic impacts that emerged most intensively post-2006 continue in the background. Green activity hexagons re-appear during this period, much like the 1996–2002 phase, but in an international context. Foundational science (green activity hexagons) re-emerge, particularly internationally with new collaborations. At the same time, yellow outputs and red outcomes continue.
For the River Styles case study the challenge still remains one of how to adequately attribute, measure and provide evidence for soft impacts 4 that include:
a change in river management philosophy and practice
an improvement in river health and conservation of threatened species
the provision of an operational Framework that provides a common and consistent approach to analysis
the value of knowledge generation and databases for monitoring river health and informing river management decision-making for years to come
the integration into, and improvement in, river management policy
a change in prioritisation that reduces risk in decision-making and cost savings on-the-ground
professional development to produce a better trained, higher quality workforce and increased graduate employability
the creation of stronger networks of river professionals and a common suite of concepts that enable communication
more confident and appropriate use of geomorphic principles by river management practitioners
an improvement in citizen knowledge and reduced community conflict in river management practice
Lessons learnt by applying research impact mapping to a real case study
When applying the Research Impact Pathway and undertaking impact mapping for a case study it becomes obvious that generating and realising impact is not a linear process and it is never complete, and in many aspects it cannot be planned 8 , 9 , 29 . Rather, the pathway has many highways, secondary roads, intersections, some dead ends or cul-de-sacs and many unexpected detours of interest along the way.
Cycles of input, activity, outputs, outcomes and impact occur throughout the process. There are phases where greater emphasis is placed on inputs and activities, or phases of productivity that produce outputs and outcomes, and there are phases where the innovation or initiative gains momentum and produces a flurry of benefits and impacts. However, throughout the journey, inputs, activities, outputs and outcomes are always occurring, and the impact pathway never ends. Some impacts come and go while others are sustained.
The saying “being in the right place at the right time with the right people” has some truth. Impact can be probabilistically generated ex ante by the researcher(s) regularly placing themselves and their outputs in key locations or ‘rooms’ and in ‘moments’ where the chance of non-academic translation is high 47 . Context is also critical 45 . Economic, political, institutional, social and environmental conditions need to come together if an innovation or initiative is to ‘get off the ground’, gain traction and lead to impact (e.g., Fig. 2 ). Ongoing and sustained support is vital. An innovation funded 10 years ago may not receive funding today, or an innovation funded today may not lead to impact unless the right sets of circumstances and support are in place. This is, in part, a serendipitous process that involves the calculated creation of circumstances aligned to evoke the ‘black swan’ event of impact 48 . The ‘black swan’ effect, coined by Nassem Nicholas Taleb, is a metaphor for an unanticipated event that becomes reinterpreted through the benefit of hindsight, or alternatively, an event that exists ‘outside the model’. For example, black swans were presumed not to exist by Europeans until they were encountered in Australia and scientifically described in 1790. Such ‘black swan’ events are a useful device in ex post assessment for characterising those pivotal moments when a research program translates into research impact. While the exact nature of such events cannot be anticipated, by understanding the ways in which ‘black swan’ events take place in the context of research impact, researchers can manufacture scenarios that optimise their probability of provoking a ‘black swan’ event and therefore translating their research project into research impact, albeit in an unexpected way. One ‘black swan’ event for the River Styles Framework occurred between 1996–2002 (Table 1 ). Initial motivations for developing the Framework reflected inappropriate use of geomorphic principles derived elsewhere to address management concerns for distinctive river landscapes and ecosystems in Australia. Although initial applications and testing of the Framework were local (regional-scale), advice by senior-level personnel in the original funding agency, Land and Water Australia (blue input hexagon in 1997; Fig. 2 ), suggested we make principles generic such that the Framework can be used in any landscape setting. The impact of this ‘moment’ was only apparent much later on, when the Framework was adopted to inform place-based, catchment-specific river management applications in various parts of the world.
What is often not recognised is the time lag in the research impact process 9 . Depending on the innovation or initiative, this is, at best, a decadal process. Of critical importance is setting the foundations for impact. The ‘gem of an idea’ needs to be translated into a sound program of research, testing (proof of concept), peer-review and demonstration. These foundations must generate a level of confidence in the innovation or initiative before uptake. A level of branding may be required to make the innovation or initiative stand out from the crowd. Drivers are required to incentivise academics, both internal and external to their University setting, encouraging them to go outside their comfort zone to apply and translate their research in ‘real-world’ settings. Maintaining passion, patience and persistence throughout the journey are some of the most hidden and unrecognised parts of this process.
Some impacts are not foreseeable and surprises are inevitable. Activities, outputs and outcomes that may initially have seemed like a dead end, often re-appear in a different context or in a different network. Other outputs or outcomes take off very quickly and are implemented with immediate impact. Catalytic moments are sometimes required for uptake and impact to be realised 8 . These surprises are particularly obvious when an innovation or initiative enters the independent uptake stage, called impact under indirect influence on Fig. 1 . In this phase the originating researchers, developers or inventors are often absent or peripheral to the impact process. Other people or organisations have the confidence to use the innovation or initiative (as intended, or in some cases not as intended), and find new ways of taking the impact further. The innovation or initiative generates a life of its own in a snowball effect. Independent uptake is not easily measured, but it is a critical indicator of impact. Unless the foundations are solid and sound, prospects for sustained impact are diminished.
The maturity and type of impact also vary in different places at different times. This is particularly the case for innovations and initiatives where local and domestic uptake is strong, but international impact lags. Some places may be well advanced on the uptake part of the impact journey, firmly embedding the benefits while developing new extensions, add-ons and spin-offs with inputs and activities. Elsewhere, the uptake will only have just begun, such that outputs and outcomes are the primary focus for now, with the aim of generating impact soon. In some instances, authorities and practitioners are either unaware or are yet to be convinced that the innovation or initiative is relevant and useful for their circumstances. In these places the focus is on the inputs and activity phases necessary to generating outputs and outcomes relevant to their situation and context. Managing this variability while maintaining momentum is critical to creating impact.
Future directions for the practice of impact mapping and assessment
The process of engaging with impact and undertaking impact mapping for an environmental case study has been a reflective, positive but challenging experience. Our example is typical of many of the issues that must be addressed when undertaking research impact mapping and assessments where both ‘hard’ and ‘soft’ impacts are generated. Our 3-part impact mapping approach helps deal with these challenges and provides a mechanism to visualise and enhance communication of research impact to a broad range of scientists and policy practitioners from many fields, including industry and government agencies, as well as citizens who are interested in learning about the tangible and intangible benefits that arise from investing in research.
Such impact mapping work cannot be undertaken quickly 44 , 45 . Lateral thinking is required about what research impact really means, moving beyond the perception in academia that outputs and outcomes equals impact 4 , 9 , 12 . This is not the case. The research impact journey does not end at outcomes. The real measure of research impact is when an initiative gains a ‘life of its own’ and is independently picked-up and used for environmental, social or economic benefit in the ‘real-world’. This is when an initiative exits from the original researcher(s) owning the entirety of the impact, to one where the researcher(s) have an ongoing contribution to vastly scaled-up sets of collective impacts that are no longer controlled by any one actor, community or network. Penfield et al. 9 relates this to ‘knowledge creep’ where new data, information or frameworks become accepted and get absorbed over time.
Careful consideration of how an initiative is developed, emerges, is used, and the resulting benefits is needed to map impact. This process, in its own regard, provides solid foundations for future planning and consideration of possible (or maybe unforeseen) opportunities to develop the impact further as part of ex ante impact forecasting 1 , 44 . It’s value also lies in communicating and teaching others, using worked case studies, about what impact can mean, to demonstrate how it can evolve and mature, and outline the possible pathways of impact as part of ex post impact assessment 1 , 44 .
With greater emphasis being placed on impact in research policy and reporting in many parts of the world, it is timely to consider the level of ongoing support required to genuinely capture and assess impact over yearly and decadal timeframes 20 . Creation of environments and cultures in which impact can be incubated, nourished and supported aids effective planning, knowledge translation and engagement. Ongoing research is required to consider, more broadly and laterally, what is measured, what indicators are used, and the evidence required to assign attribution. This remains a challenge not just for the case study documented here, but for the process of impact assessment more generally 1 , 9 . Continuous monitoring of impacts (both intended and unintended) is needed. To do this requires support and systems to gather, archive and track data, whether quantitative or qualitative, and adequately build evidence portfolios 20 . A keen eye is needed to identify, document and archive evidence that may seem insignificant at the time, but can lead to a step-change in impact, or a re-appearance elsewhere on the pathway.
Impact reporting extends beyond traditional outreach and service roles in academia 16 , 19 . Despite the increasing recognition of the importance of impact and its permeation into academic lives, it is yet to be formally built into many academic and professional roles 9 . To date, the rewards are implicit rather than explicit 44 . Support is required if impact planning and reporting for assessment is to become a new practice for academics.
Managing the research impact process is vital, but it is also important to be open to new ideas and avenues for creating impact at different stages of the process. It is important to listen and to be attuned to developments outside of academia, and learn to live with the creative spark of uncertainty as we expect the unexpected!
Change history
08 november 2019.
An amendment to this paper has been published and can be accessed via a link at the top of the paper.
Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD). Enhancing Research performance through Evaluation, Impact Assessment and Priority Setting (Directorate for Science, Technology and Innovation, Paris, 2009). This is a ‘go-to’ guide for impact assessment in Research and Development, used in OECD countries .
Morgan, B. Income for outcome. Australia and New Zealand are experimenting with ways of assessing the impact of publicly funded research. Nat. Outlook 511 , S72–S75 (2014). This Nature Outlook article reports on how Australia’s Commonwealth Scientific and Research Organisation (CSIRO) mapped their research programs against impact classes using the Research Impact Pathway .
CAS Google Scholar
Cvitanovic, C. & Hobday, A. J. Building optimism at the environmental science-policy-practice interface through the study of bright spots. Nat. Commun. 9 , 3466 (2018). This Nature Communications paper presents a commentary on the key principles that underpin what are termed ‘bright spots’, case studies where science and research has successfully influenced and impacted on policy and practice, as a means to inspire optimism in humanity’s capacity to address environmental challenges .
Article ADS Google Scholar
Rau, H., Goggins, G. & Fahy, F. From invisibility to impact: recognising the scientific and societal relevance of interdisciplinary sustainability research. Res. Policy 47 , 266–276 (2018). This paper uses interdisciplinary sustainability research as a centrepiece for arguing the need for alternative approaches for conceptualising and measuring impact that recognise and capture the diverse forms of engagement between scientists and non-scientists, and diverse uses and uptake of knowledge at the science-policy-practice interface .
Article Google Scholar
Brierley, G. J. & Fryirs, K. A. Geomorphology and River Management: Applications of the River Styles Framework . 398 (Blackwell Publications, Oxford, 2005). This book contains the full River Styles Framework set within the context of the science of fluvial geomorphology .
Brierley, G. J. et al. Geomorphology in action: linking policy with on-the-ground actions through applications of the River Styles framework. Appl. Geogr. 31 , 1132–1143 (2011).
Australian Research Council (ARC). EI 2018 Framework (Commonwealth of Australia, Canberra, 2017). This document and associated website contains the procedures for assessing research impact as part of the Australian Research Council Engagement and Impact process, and the national report, outcomes and impact cases studies assessed in the 2018 round .
Matt, M., Gaunand, A., Joly, P.-B. & Colinet, L. Opening the black box of impact–Ideal type impact pathways in a pubic agricultural research organisation. Res. Policy 46 , 207–218 (2017). This article presents a metrics-based approach to impact assessment, called the Actor Network Theory approach, to systematically code variables used to measure ex-post research impact in the agricultural sector .
Penfield, T., Baker, M. J., Scoble, R. & Wykes, M. C. Assessment, evaluations, and definitions of research impact: a review. Res. Eval. 23 , 21–32 (2014). This article reviews the concepts behind research impact assessment and takes a focussed look at how impact assessment was implemented for the UK’s Research Excellence Framework (REF) .
Weiss, C. H. The many meanings of research utilization. Public Adm. Rev. 39 , 426–431 (1979).
Cooper, A. & Levin, B. Some Canadian contributions to understanding knowledge mobilisation. Evid. Policy 6 , 351–369 (2010).
Watermeyer, R. Issues in the articulation of ‘impact’: the responses of UK academics to ‘impact’ as a new measure of research assessment. Stud. High. Educ. 39 , 359–377 (2014).
Hicks, D. Overview of Models of Performance-based Research Funding Systems. In: Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), Performance-based Funding for Public Research in Tertiary Education Institutions: Workshop Proceedings . 23–52 (OECD Publishing, Paris, 2010). https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264094611-en (Accessed 27 Aug 2019).
Hicks, D. Performance-based university research funding systems. Res. Policy 41 , 251–26 (2012).
Etzkowitz, H. Networks of innovation: science, technology and development in the triple helix era. Int. J. Technol. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 1 , 7–20 (2002).
Perkmann, M. et al. Academic engagement and commercialisation: a review of the literature on university-industry relations. Res. Policy 42 , 423–442 (2013).
Leydesdorff, L. & Etzkowitz, H. Emergence of a Triple Helix of university—industry—government relations. Sci. Public Policy 23 , 279–286 (1996).
Google Scholar
Higher Education Funding Council for England (HEFCE). Research Excellence Framework . Second consultation on the assessment and funding of research. London. https://www.hefce.ac.uk (Accessed 12 Aug 2019).
Smith, S., Ward, V. & House, A. ‘Impact’ in the proposals for the UK’s Research Excellence Framework: Shifting the boundaries of academic autonomy. Res. Policy 40 , 1369–1379 (2011).
Canadian Academy of Health Sciences (CAHS). Making an Impact. A Preferred Framework and Indicators to Measure Returns on Investment in Health Research (Canadian Academy of Health Sciences, Ottawa, 2009). This report presents the approach to research impact assessment adopted by the health science industry in Canada using the Research Impact Pathway .
Research Manitoba. Impact Framework . Research Manitoba, Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada. (2012–2019). https://researchmanitoba.ca/impacts/impact-framework/ (Accessed 3 June 2019).
United Kingdom National Institute for Health Research (UKNIHR). Research and Impact . (NIHR, London, 2019).
Science Foundation Ireland (SFI). Agenda 2020: Excellence and Impact . (SFI, Dublin, 2012).
StarMetrics. Science and Technology for America’s Reinvestment Measuring the Effects of Research on Innovation , Competitiveness and Science . Process Guide (Office of Science and Technology Policy, Washington DC, 2016).
European Commission (EU). Guidelines on Impact Assessment . (EU, Brussels, 2015).
Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment (MBIE). The impact of science: Discussion paper . (MBIE, Wellington, 2018).
University Grants Committee. Panel-specific Guidelines on Assessment Criteria and Working Methods for RAE 2020. University Grants Committee, (Government of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, Hong Kong, 2018).
Harland, K. & O’Connor, H. Broadening the Scope of Impact: Defining, assessing and measuring impact of major public research programmes, with lessons from 6 small advanced economies . Public issue version: 2, Small Advanced Economies Initiative, (Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade, Dublin, 2015).
Chubb, J. & Watermeyer, R. Artifice or integrity in the marketization of research impact? Investigating the moral economy of (pathways to) impact statements within research funding proposals in the UK and Australia. Stud. High. Educ. 42 , 2360–2372 (2017).
Oliver Schwarz, J. Ex ante strategy evaluation: the case for business wargaming. Bus. Strategy Ser. 12 , 122–135 (2011).
Neugebauer, S., Forin, S. & Finkbeiner, M. From life cycle costing to economic life cycle assessment-introducing an economic impact pathway. Sustainability 8 , 428 (2016).
Legner, C., Urbach, N. & Nolte, C. Mobile business application for service and maintenance processes: Using ex post evaluation by end-users as input for iterative design. Inf. Manag. 53 , 817–831 (2016).
Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD). Fact sheets: Approaches to Impact Assessment; Research and Innovation Process Issues; Causality Problems; What is Impact Assessment?; What is Impact Assessment? Mechanisms . (Directorate for Science, Technology and Innovation, Paris, 2016).
River Styles. https://riverstyles.com (Accessed 2 May 2019).
United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org (Accessed 2 May 2019).
Kasprak, A. et al. The Blurred Line between form and process: a comparison of stream channel classification frameworks. PLoS ONE 11 , e0150293 (2016).
Fryirs, K. Developing and using geomorphic condition assessments for river rehabilitation planning, implementation and monitoring. WIREs Water 2 , 649–667 (2015).
Fryirs, K. & Brierley, G. J. Assessing the geomorphic recovery potential of rivers: forecasting future trajectories of adjustment for use in river management. WIREs Water 3 , 727–748 (2016).
Fryirs, K. A. & Brierley, G. J. What’s in a name? A naming convention for geomorphic river types using the River Styles Framework. PLoS ONE 13 , e0201909 (2018).
Fryirs, K. A. & Brierley, G. J. Geomorphic Analysis of River Systems: An Approach to Reading the Landscape . 345 (John Wiley and Sons: Chichester, 2013).
Meagher, L., Lyall, C. & Nutley, S. Flows of knowledge, expertise and influence: a method for assessing policy and practice impacts from social science research. Res. Eval. 17 , 163–173 (2008).
Meagher, L. & Lyall, C. The invisible made visible. Using impact evaluations to illuminate and inform the role of knowledge intermediaries. Evid. Policy 9 , 409–418 (2013).
Fryirs, K. A. et al. Tracking geomorphic river recovery in process-based river management. Land Degrad. Dev. 29 , 3221–3244 (2018).
Kuruvilla, S., Mays, N., Pleasant, A. & Walt, G. Describing the impact of health research: a Research Impact Framework. BMC Health Serv. Res. 6 , 134 (2006).
Barjolle, D., Midmore, P. & Schmid, O. Tracing the pathways from research to innovation: evidence from case studies. EuroChoices 17 , 11–18 (2018).
Department of Environment and Heritage (DEH). Triple bottom line reporting in Australia. A guide to reporting against environmental indicators . (Commonwealth of Australia, Canberra, 2003).
Le Heron, E., Le Heron, R. & Lewis, N. Performing Research Capability Building in New Zealand’s Social Sciences: Capacity–Capability Insights from Exploring the Work of BRCSS’s ‘sustainability’ Theme, 2004–2009. Environ. Plan. A 43 , 1400–1420 (2011).
Taleb, N. N. The Black Swan: The Impact of the Highly Improbable . 2nd edn. (Penguin, London, 2010).
Fryirs, K. A. & Brierley, G. J. Practical Applications of the River Styles Framework as a Tool for Catchment-wide River Management : A Case Study from Bega Catchment. (Macquarie University Press, Sydney, 2005).
Brierley, G. J. & Fryirs, K. A. (eds) River Futures: An Integrative Scientific Approach to River Repair . (Island Press, Washington, DC, 2008).
Fryirs, K., Wheaton, J., Bizzi, S., Williams, R. & Brierley, G. To plug-in or not to plug-in? Geomorphic analysis of rivers using the River Styles Framework in an era of big data acquisition and automation. WiresWater . https://doi.org/10.1002/wat2.1372 (2019).
Rinaldi, M. et al. New tools for the hydromorphological assessment and monitoring of European streams. J. Environ. Manag. 202 , 363–378 (2017).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Rinaldi, M., Surian, N., Comiti, F. & Bussettini, M. A method for the assessment and analysis of the hydromorphological condition of Italian streams: The Morphological Quality Index (MQI). Geomorphology 180–181 , 96–108 (2013).
Rinaldi, M., Surian, N., Comiti, F. & Bussettini, M. A methodological framework for hydromorphological assessment, analysis and monitoring (IDRAIM) aimed at promoting integrated river management. Geomorphology 251 , 122–136 (2015).
Gurnell, A. M. et al. A multi-scale hierarchical framework for developing understanding of river behaviour to support river management. Aquat. Sci. 78 , 1–16 (2016).
Belletti, B., Rinaldi, M., Buijse, A. D., Gurnell, A. M. & Mosselman, E. A review of assessment methods for river hydromorphology. Environ. Earth Sci. 73 , 2079–2100 (2015).
Belletti, B. et al. Characterising physical habitats and fluvial hydromorphology: a new system for the survey and classification of river geomorphic units. Geomorphology 283 , 143–157 (2017).
O’Brien, G. et al. Mapping valley bottom confinement at the network scale. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 44 , 1828–1845 (2019).
Sinha, R., Mohanta, H. A., Jain, V. & Tandon, S. K. Geomorphic diversity as a river management tool and its application to the Ganga River, India. River Res. Appl. 33 , 1156–1176 (2017).
O’Brien, G. O. & Wheaton, J. M. River Styles Report for the Middle Fork John Day Watershed, Oregon . Ecogeomorphology and Topographic Analysis Lab, Prepared for Eco Logical Research, and Bonneville Power Administration, Logan. 215 (Utah State University, Utah, 2014).
Marçal, M., Brierley, G. J. & Lima, R. Using geomorphic understanding of catchment-scale process relationships to support the management of river futures: Macaé Basin, Brazil. Appl. Geogr. 84 , 23–41 (2017).
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank Simon Mould for building the online interactive version of the impact map for River Styles and Dr Faith Welch, Research Impact Manager at the University of Auckland for comments on the paper. The case study documented in this paper builds on over 20 years of foundation research in fluvial geomorphology and strong and lasting collaboration between researchers, scientists and managers at various universities and government agencies in many parts of the world.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Environmental Sciences, Macquarie University, Sydney, NSW, 2109, Australia
Kirstie A. Fryirs
School of Environment, University of Auckland, Auckland, 1010, New Zealand
Gary J. Brierley
Research Services, Macquarie University, Sydney, NSW, 2109, Australia
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
K.F. conceived, developed and wrote this paper. G.B., T.D. contributed to, and edited, the paper. K.F., T.D. conceived, developed and produced the impact mapping toolbox.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Kirstie A. Fryirs .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
K.F. and G.B. are co-developers of the River Styles Framework. River Styles foundation research has been supported through competitive grant schemes and university grants. Consultancy-based River Styles short courses taught by K.F. and G.B. are administered by Macquarie University. River Styles contract research is administered by Macquarie University and University of Auckland. River Styles as a trade mark expires in May 2020. T.D. declares no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Peer review information Nature Communications thanks Barbara Belletti and Gary Goggins for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Fryirs, K.A., Brierley, G.J. & Dixon, T. Engaging with research impact assessment for an environmental science case study. Nat Commun 10 , 4542 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12020-z
Download citation
Received : 17 June 2019
Accepted : 15 August 2019
Published : 04 October 2019
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12020-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Applying a framework to assess the impact of cardiovascular outcomes improvement research.
- Mitchell N. Sarkies
- Suzanne Robinson
Health Research Policy and Systems (2021)
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing: Anthropocene newsletter — what matters in anthropocene research, free to your inbox weekly.
Accessibility Links
- Skip to content
- Skip to search IOPscience
- Skip to Journals list
- Accessibility help
- Accessibility Help
Click here to close this panel.

As a society-owned publisher with a legacy of serving scientific communities, we are committed to offering a home to all scientifically valid and rigorously reviewed research. In doing so, we aim to accelerate the dissemination of scientific knowledge and the advancement of scholarly communications to benefit all.
Environmental Research Communications supports this mission and actively demonstrates our core values of inclusive publishing and trusted science . To find out more about these values and how they can help you publish your next paper with us, visit our journal scope .
Purpose-led Publishing is a coalition of three not-for-profit publishers in the field of physical sciences: AIP Publishing, the American Physical Society and IOP Publishing.
Together, as publishers that will always put purpose above profit, we have defined a set of industry standards that underpin high-quality, ethical scholarly communications.
We are proudly declaring that science is our only shareholder.
Bibliometric analysis and systematic review of environmental, social, and governance disclosure papers: current topics and recommendations for future research
Nejla Ould Daoud Ellili 1
Published 2 September 2022 • © 2022 The Author(s). Published by IOP Publishing Ltd Environmental Research Communications , Volume 4 , Number 9 Citation Nejla Ould Daoud Ellili 2022 Environ. Res. Commun. 4 092001 DOI 10.1088/2515-7620/ac8b67
Article metrics
6114 Total downloads
Share this article
Author e-mails.
Author affiliations
1 College of Business Administration, Abu Dhabi University, United Arab Emirates
Nejla Ould Daoud Ellili https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1032-3965
- Received 12 May 2022
- Revised 4 August 2022
- Accepted 19 August 2022
- Published 2 September 2022
Peer review information
Method : Double-anonymous Revisions: 2 Screened for originality? No
Buy this article in print
This study analyzes the literature on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) disclosure by applying a bibliometric analysis of documents published in the Scopus database. The bibliometric analysis allows researchers to highlight the theoretical foundations of a specific research field, identify the main findings of previous studies, and determine future research ideas. This analysis was based on bibliometric authors' citation analysis, bibliometric papers' co-citation analysis, bibliometric references' co-citation analysis, bibliometric journals' co-citation analysis, co-occurrence keywords cartography analysis, trend and evolution analyses of ESG disclosure publications over the years, and qualitative content analysis. This study reviews 161 documents on ESG disclosure published in the Scopus database. Bibliometric analysis was conducted using VOSviewer, evolution analysis was performed using CiteSpace, and content analysis was performed using Wordstat. The study identified four major clusters: corporate social responsibility, corporate strategy, financial performance, and environmental economics. It also highlights the increasing number of citations and documents related to ESG disclosures. In addition, the journal 'Business Strategy and the Environment' significantly contributes to the ESG disclosure research field in terms of number of papers and citations. Additionally, this study highlights various future research opportunities in this field. The findings of this study have practical implications for ESG disclosure, such as the impact of integrating ESG into a company's business strategy on corporate and financial policies. This study is the only one to review key topics on ESG disclosure that can be largely used for ESG practices. This study provides an overview of how the literature on ESG disclosure has developed, as well as a summary of the most influential authors along with countries, organizations, and journal sources. This offers the opportunity for future research to focus on this topic.
Export citation and abstract BibTeX RIS
Original content from this work may be used under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 licence . Any further distribution of this work must maintain attribution to the author(s) and the title of the work, journal citation and DOI.
1. Introduction
This study focuses on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) disclosure, an area of great interest because of cumulative environmental and natural resource constraints. In the last decade, increasing environmental awareness of international legal bodies has prompted many countries to raise questions about sustainable development, and sustainability disclosure has attracted the interest of researchers and policymakers to examine the concept of a green economy [ 1 – 4 ].
At the international level, many organizations have developed various frameworks and procedures to help companies meet their disclosure obligations related to ESG issues. These organizations include the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), International Integrated Reporting Council (IIRC), Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP), and the United Nations Global Compact (UNGC). The developed frameworks provide companies with clear guidance on how to report their non-financial issues and help them identify and address their corporate social responsibility and environmental responsibilities.
In the last decade, ESG disclosure has become an integral part of investors' financial decisions, because of its ability to provide strong evidence of companies' commitment to environmental and social disclosure [ 5 – 9 ]. This concept has also attracted the attention of rating agencies such as Standard and Poor's, Moody's, and Fitch, which incorporate companies' ESG assessments to help them improve their scores and ratings.
Various studies have analyzed various aspects of ESG disclosure. A group of studies examined the extent of ESG disclosure and revealed that, although the level of ESG disclosure is still low, it has increased significantly over the years [ 10 – 12 ]. Other studies investigated the determinants of the extent of ESG disclosure [ 13 – 16 ]. Most studies focus on the impact of ESG disclosure on financial performance [ 17 – 21 ].
In recent years, bibliometric analysis has seen a significant growth in interest due to the increase of the number of software programs and multidisciplinary methods. This analytical method can help researchers identify trends in different research fields as well as journal performance. Through a bibliometric analysis, this study identified the most frequent ESG topics covered in the literature, identified various gaps in the literature, and identified paths for future research.
This study has six research questions. (1) What has been the trend in ESG disclosure publications over the years? (2) What authors, organizations, and countries have contributed the most to the research on ESG disclosure? (3) What are the most cited papers on ESG disclosure? (4) What are the most cited references in papers on ESG disclosure? (5) What are the most cited reference journals of papers on ESG disclosures? (6) What are the most frequent keywords and topics of ESG disclosure documents and their evolution over time? Questions two–five were answered by conducting bibliometric analyses, whereas question six was answered by employing two cartography analyses using VOSviewer and CiteSpace.
To the best of our knowledge, there is no single study on the bibliometric analysis of ESG disclosure papers published in the Scopus database. Therefore, this study sheds light on this topic. This study contributes to the literature by evaluating the most relevant topics in ESG disclosure research. The results identified four major clusters: corporate social responsibility, corporate strategy, financial performance, and environmental economics. In addition, the results reveal that the Journal of Business Strategy and the Environment makes an important contribution to the ESG disclosure research field in terms of papers and citations. Furthermore, this study identifies the authors, countries, organizations, and references that have been the most influential in publishing ESG disclosure studies in Scopus.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presents the methodology and data. Section 3 interprets the bibliometric results, section 4 presents the current topics and future research recommendations, and section 5 presents the conclusions.
2. Methodology and data
2.1. methodology.
This study applied trend, bibliometric, and content analyses using both quantitative and qualitative approaches [ 22 ]. Thus, the following analyses were conducted: (1) trend analysis, (2) bibliometric authors' citation analysis, (3) bibliometric papers' co-citation analysis, (4) bibliometric references' co-citation analysis, (5) bibliometric journals' co-citation analysis, (6) keywords and evolution analyses, and (7) qualitative content analysis. Bibliometric and evolution analyses were conducted using VOSviewer and Cite Space, respectively, whereas content analysis was performed using Wordstat.
The Scopus database was selected because it is the world's most comprehensive overview of research outputs and is considered to be the largest repository of academic research documents that are of acceptable quality [ 23 ]. In this study, we use the keyword 'ESG disclosure' or 'Environmental, Social and Governance disclosure' in the article title, abstract, or keywords. This yielded a total of 234 documents. The data were screened in multiple stages, as shown in figure 1 .
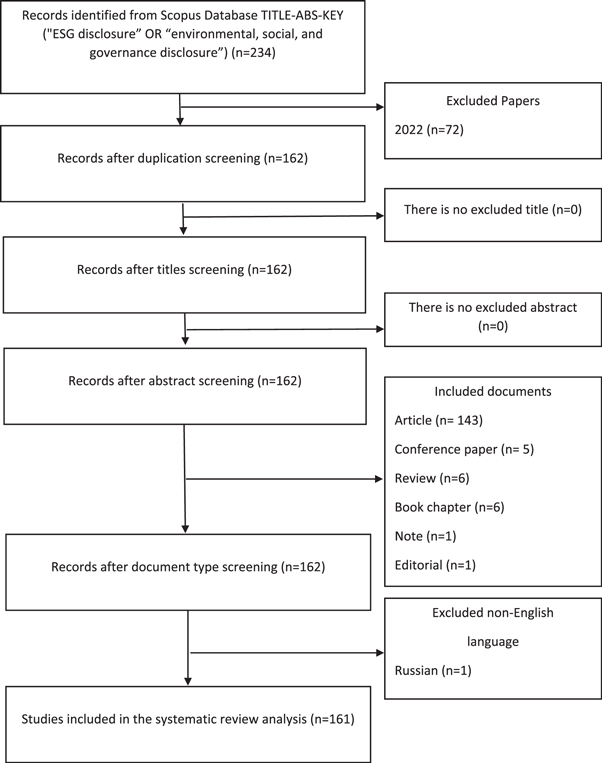
Figure 1. PRISMA diagram showing the number of documents at each stage of the screening process.
Download figure:
After the data were screened, they were exported to CSV Excel and uploaded to VOSviewer for bibliometric analysis. In addition, CVS Excel was converted to the Web of Sciences format and uploaded to CiteSapce. The data extraction and conversion steps are illustrated in figure 2 .
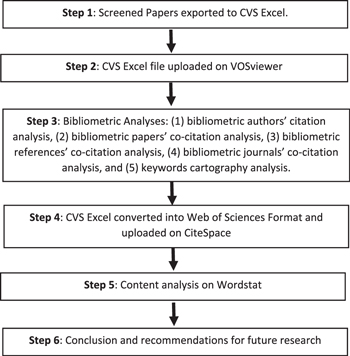
Figure 2. Data extraction steps.
3. Results of trend, bibliometric, evolution, and content analyses
This section summarizes the 161 documents on ESG disclosure included in this study by applying different trend, bibliometric, evolution, and content analyses.
3.1. Trend in publications on ESG disclosure
Figure 3 shows the number of articles published in the ESG disclosure research field. The first study on ESG disclosures was published in 2010. The development of this field was very slow during 2010–2017 with a maximum of 8 papers published per year. The number of ESG disclosures published documents increased in 2018, reaching 17 papers, and then continuing to increase until 2020 to reach the highest number of 48. In the following year, the number of papers witnessed a decrease, reaching a number of papers of 39. The increasing number of articles suggests that academic researchers are becoming more interested in ESG disclosure and are publishing their documents in the Scopus database. In this trend analysis, the increasing number of publications in the field of ESG disclosure is attributed not only to the growing recognition of the importance of this field but also to the increasing integration of ESG disclosure into business strategies and corporate reporting practices.
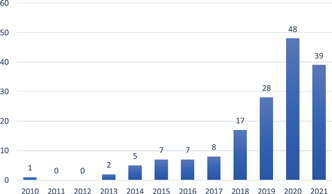
Figure 3. The trend in ESG disclosure publications.
3.2. The most influential authors, organizations, and countries
The top five cited authors, along with their respective organizations and countries, are presented in table 1 . It shows that the UK has two authors from the top five list (Buallay A. and Yu E), and Greece has two most-cited authors (Giannarakis and Konteos). The remaining country in table 1 is Australia, which is emerging in research on ESG disclosure.
Table 1. Most cited authors, organizations and countries.
3.3. The most cited papers
This section presents an analysis of the top ten cited documents on ESG disclosure published in the Scopus database from 2010 to 2021. Table 2 shows that the topics of the most cited papers were mainly related to the impact of ESG disclosure on financial performance [ 18 , 35 – 38 ]. Other studies have considered ESG disclosure as a practice of integrated reporting [ 1 , 39 , 40 ].
Table 2. Top 10 cited documents on ESG disclosure topic.
3.4. Most cited reference papers
This section presents the most cited references included in published documents on ESG disclosure. Table 3 lists the ten most cited reference papers. These studies focus on the following topics: (1) the relationship between corporate social responsibility disclosure and financial aspects [ 43 – 48 ], (2) the determinants and motives of corporate social responsibility disclosure [ 49 , 50 ], (3) the impact of corporate governance on corporate social responsibility disclosure [ 51 ], and (4) agency theory explaining engagement with stakeholders [ 52 ].
Table 3. Most cited reference papers in documents on ESG disclosure.
3.5. Most cited references journals
This section presents the top ten cited reference sources by employing a bibliographic coupling analysis. Table 4 lists the top journals that published papers on ESG disclosures. Nine of the ten journals were ranked as Q1, with high SNIP factors. Emerald has the highest number of papers on ESG disclosure, followed by Wiley. Business Strategy and Environment was the top journal with the highest number of papers (15) and citations (743).
Table 4. Most cited reference journals.
3.6. The most frequent keywords
Co-occurrence analysis of all keywords was applied to conceptualize the development and growth of ESG studies. To arrive at a meaningful analysis [ 22 ], a minimum threshold of two for the occurrence of a particular keyword was required and filtered. This resulted in 138 keywords for 568. The results are reported in figure 4 and show that the most frequently used words are corporate social responsibility, corporate governance, sustainable development, financial performance, and environmental economics. The frequent occurrence of these keywords among studies reflects more analyses applied to the impact of corporate governance mechanisms (including the ownership structure and board of directors) on ESG disclosure, as well as the impact of ESG disclosure on financial performance. The most commonly used theories are the agency, legitimacy, information asymmetry, and stakeholder theories.

Figure 4. Keywords analysis.
As shown in figure 4 , there are four major clusters: corporate social responsibility (red), corporate strategy (blue), financial performance (green), and environmental economics (yellow).
In the large corporate social responsibility cluster, there are four groups of studies:
- 1- In the first group, studies consider corporate social responsibility disclosure as a measure of corporate sustainability initiatives and practices [ 13 , 53 , 54 ].
- 2- In the second group, studies have elaborated on different ESG disclosure theories such as agency theory [ 55 – 57 ] and information asymmetry theory [ 58 , 59 ].
- 3- The third group of studies investigates the relationship between corporate governance, CSR disclosure [ 1 , 14 – 60 ], and ESG disclosure [ 41 , 61 ].
- 4- In the fourth group, studies explored the role of ESG disclosure in sustainable development [ 1 , 2 , 62 , 63 ] and transparency [ 32 , 64 – 66 ].
Studies in the corporate strategy cluster have considered ESG disclosure as a strategic approach integrated into a business strategy to improve corporate engagement with stakeholders [ 21 , 67 ] and corporate commitments toward the environment [ 2 , 63 ].
In the financial performance cluster, studies have mainly focused on analyzing the impact of ESG disclosure on corporate performance [ 17 – 21 ]. Some studies have focused only on developed countries [ 68 , 69 ] or emerging markets [ 5 , 42 , 60 ], whereas others have compared developed and developing countries [ 26 , 70 ].
There are two groups of studies on environmental economics clusters. The first group explained the necessity of disclosing an ESG report using legitimacy theory [ 1 , 71 – 74 ] and stakeholder theory [ 61 , 75 , 76 ]. The second group elaborated on the company's efforts to reduce carbon emissions and climate change [ 67 , 77 ].
In addition to VOSviewer, CiteSpace was used to analyze the most used keywords in the different stages and development patterns in the papers published by ESG disclosure. The most-cited keywords were calculated and arranged in CiteSpace by time and frequency to form the time view shown in figure 5 . The figure shows the most frequently used keywords during 2010–2021. The two keywords of 'corporate social responsibility' and 'corporate governance' were frequently included in papers till 2013, suggesting that early interest in ESG disclosure was closely related to corporate social responsibility and corporate governance. For instance, Giannarkis [ 13 ] explored the extent of corporate social responsibility information disclosed by US companies, and the ESG scores were considered determinants of the extent of this disclosure. Murphy and McGrath [ 78 ] explained the different motivations of ESG reports by considering, among others, the reduction of litigation in corporate governance. In the following three years, new keywords emerged, which can be divided into five main groups: (1) corporate governance mechanisms: institutional investors [ 79 ] and board gender diversity [ 41 , 80 ], 2- corporate environmental commitments: global reporting initiative [ 81 ], integrated reporting [ 40 , 82 , 83 ], and environmental economics [ 14 , 30 ], (3) theoretical framework: legitimacy theory [ 72 – 74 , 84 , 85 ], and stakeholder theory [ 61 , 76 , 80 ], (4) impacts of ESG disclosure: sustainable development [ 1 , 2 ], and performance [ 18 , 25 ], and (5) empirical approach: content analysis [ 86 , 87 ], bank [ 25 , 81 ], and developing countries [ 5 , 88 , 89 ]. In 2021, researchers were interested in examining the integration of ESG investment in business strategy [ 90 , 91 ] as well as the impact of ESG disclosure on the cost of debt [ 92 – 96 ]. The evolution of the topics reflects the fact that researchers have started to legitimize ESG disclosure through theories, understand its determinants, explore its extent, and then examine its potential associations with corporate governance, financial performance, and sustainable development in different institutional contexts. Most of these studies applied content analysis.

Figure 5. Evolution in ESG disclosure research documents over the years.
3.7. Content analysis of the previous research topics
In addition to bibliometric analysis, qualitative content analysis of titles and abstracts of ESG disclosure papers published in Scopus was conducted using Wordstat. The major themes were corporate governance mechanisms, methodology approach, performance, sample, corporate social responsibility, financial leverage, integrated reporting, sustainable development, green innovations, stakeholder engagement, and theory. Table 5 presents the results.
Table 5. Content analysis of the previous research topics on ESG disclosure.
Table 5 reveals a high similarity with the bibliometric keywords' clusters and the sub-cluster analysis included in section 3.6 . It indicates that the most frequent research themes in ESG disclosure are related to the association of ESG disclosure with corporate governance as well as with the corporate performance. The two additional themes are methodological approach and sample. Table 5 indicates that the panel data are the most common and the methodological approach applied in determining the extent of ESG disclosure relies on a proxy measured by the content analysis [ 72 , 86 , 87 ] or Bloomberg score [ 32 , 64 , 95 , 97 ]. With regard to the sample, the industry varies from one study to another. For instance, studies have focused on oil and gas companies [ 98 – 100 ], while others have analyzed the supply chain industry [ 64 , 101 ].
4. Current topics and recommendations for future research
In addition to the analysis of titles and abstracts of previous ESG disclosure papers, another content analysis was conducted on the current topics of the most recent papers published until July 25th, 2022. The results are presented in table 6 .
Table 6. Content analysis of the current research topics on ESG disclosure.
Table 6 reveals that most of the research topics are similar to previous ones, including stakeholder engagement, performance, corporate governance mechanisms, corporate social responsibility, sustainable development, and environmental economics. However, in the methodology approach, there is a higher focus on regressions than on the content analysis considered in previous studies. In addition, the airline industry has recently been included in a sample of recent studies [ 102 , 103 ]. The new topics that have emerged in recent studies are investment efficiency and ESG ratings.
Recent studies agree that ESG disclosure increases corporate transparency and hence improves capital investment efficiency by mitigating under- and over-investment problems [ 8 , 104 ]. In addition, there is greater interest in examining the impact of ESG disclosure on ESG ratings [ 105 – 108 ].
- 1- Future research on ESG disclosure may include the following topics: the COVID-19 pandemic, which has caused a global crisis, and it would be interesting to consider it as a recent topic to examine its impact on the extent of ESG disclosure and analyze the commitment of the companies towards not only their stakeholders but also the whole community.
- 2- Earnings management: Earnings management practices relate to information manipulation. It would be interesting to analyze the impact of ESG disclosure on these practices to assess corporate transparency.
- 3- Diverse samples: Most studies on ESG disclosure consider listed companies in different financial markets. It would be interesting to include other types of organizations (such as family businesses, small and medium enterprises) as well as other types of industries (such as education, tourism, and real estate).
- 4- External corporate governance mechanisms: In the analysis of the association between ESG disclosure and corporate governance, there was only consideration of internal mechanisms (such as ownership structure and board of directors), while further studies should include external mechanisms (such as market competition) because of their potential impact on ESG disclosure.
- 5- Moderating role: The previous studies have investigated the direct relationships between ESG disclosure and other corporate and financial aspects, while it would be interesting to analyze the moderating role that could be played by ESG disclosure in other relationships, such as: the relationship between corporate governance and financial performance.
5. Conclusion
This study analyzes published ESG disclosure papers in Scopus to determine their contributions to the ESG literature, identify the key concepts and ideas related to this field, and propose recommendations for future research.
By applying several bibliometric, trend, and content analyses, the most productive authors, along with organizations and countries, have been identified. In addition, the results identify five major clusters: sustainability, ESG disclosure, corporate social responsibility, environmental, and environmental disclosure. Moreover, the results reveal that the Journal of Business Strategy and the Environment has experienced increasingly important growth in the ESG disclosure research papers and citations, reflecting its significant contribution to the ESG research field.
This study has theoretical and practical implications. First, it aims to provide a comprehensive overview of ESG literature by identifying the most significant studies and topics related to this field. Second, it helps researchers gain an idea about the most recent ESG topics as well as the most cited papers and relevant references. Third, the findings of this study can be used by ESG disclosure researchers to identify areas of future research that they should focus on. For instance, they can analyze various issues related to the COVID-19 pandemic to manage ESG disclosure efficiently. In addition, it has been observed that there is a gap in the literature regarding the associations between ESG disclosure and earnings management practices which is considered an unexplored research field. In addition, most studies have relied on legitimacy and stakeholder theories. Because the dynamics of the business environment can change over time, it is important for researchers to constantly evolve their theories to improve their findings. Moreover, the main thrust of ESG disclosure theories has been adopted as a uniform approach, but it can also be applied in different ways depending on the characteristics of corporate governance and institutional frameworks.
This study also highlights the importance of optimizing ESG disclosure to address critical corporate decisions, such as strategic investment decisions and earnings management. This field has been acknowledged as leading research exploring the various characteristics of strategic ESG integration into a company's business. Much research should be conducted in this field, as most studies have focused on the impact of ESG disclosure on financial performance, as well as the impact of corporate governance (including the attributes of the board of directors) on the extent of ESG disclosure.
The importance of ESG practices is acknowledged by society and investors who are not only interested in financial performance, but also in corporate environmental and social performance. Companies should not only focus on achieving financial success but should also contribute to achieving development goals at all levels of a company's strategic and financial decisions. This will be of great interest to future research. The internal ESG policies of companies should not only be designed to maximize financial performance, but also to promote sustainable development goals in preventing climate change, pollution, and social and gender inequality.
Future studies should examine other databases to analyze trends in the ESG disclosure field. This study focuses only on documents published in the Scopus database. Despite these limitations, this study provides a useful overview of the previous and current literature on ESG disclosure.
Data availability statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available upon reasonable request from the author.
Funding statement
This study was not supported by any funding source.

Conflict of interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Literature Review.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Wiley Open Access Collection

What really matters for successful research environments? A realist synthesis
Rola ajjawi.
1 Centre for Research in Assessment and Digital Learning (CRADLE), Deakin University, Geelong, Victoria, Australia
Paul E S Crampton
2 Research Department of Medical Education, University College London, London, UK
3 Monash Centre for Scholarship in Health Education (MCSHE), Faculty of Medicine, Nursing and Health Sciences, Monash University, Clayton, Victoria, Australia
Charlotte E Rees
Associated data.
Table S2. MeSH terms and a selection of key terms utilised in the database searches.
Table S3. Inclusion and exclusion criteria with respect to topic, recentness and type of article.
Table S4. Refined inclusion and exclusion criteria to include contextual parameters.
Table S5. Studies by type: qualitative, quantitative and mixed‐methods.
Research environments, or cultures, are thought to be the most influential predictors of research productivity. Although several narrative and systematic reviews have begun to identify the characteristics of research‐favourable environments, these reviews have ignored the contextual complexities and multiplicity of environmental characteristics.
The current synthesis adopts a realist approach to explore what interventions work for whom and under what circumstances.
We conducted a realist synthesis of the international literature in medical education, education and medicine from 1992 to 2016, following five stages: (i) clarifying the scope; (ii) searching for evidence; (iii) assessing quality; (iv) extracting data, and (v) synthesising data.
We identified numerous interventions relating to research strategy, people, income, infrastructure and facilities (IIF), and collaboration. These interventions resulted in positive or negative outcomes depending on the context and mechanisms fired. We identified diverse contexts at the individual and institutional levels, but found that disciplinary contexts were less influential. There were a multiplicity of positive and negative mechanisms, along with three cross‐cutting mechanisms that regularly intersected: time; identity, and relationships. Outcomes varied widely and included both positive and negative outcomes across subjective (e.g. researcher identity) and objective (e.g. research quantity and quality) domains.
Conclusions
The interplay among mechanisms and contexts is central to understanding the outcomes of specific interventions, bringing novel insights to the literature. Researchers, research leaders and research organisations should prioritise the protection of time for research, enculturate researcher identities, and develop collaborative relationships to better foster successful research environments. Future research should further explore the interplay among time, identity and relationships.
Short abstract
This realist review shows when and why interventions related to research strategy; people; income, infrastructure and facilities; and collaboration result in positive or negative research environments. Findings indicate that protected time, researcher identities and collaborative relationships are important for fostering successful research environments.
Introduction
Research environments matter. Environmental considerations such as robust cultures of research quality and support for researchers are thought to be the most influential predictors of research productivity. 1 , 2 Over 25 years ago, Bland and Ruffin 1 identified 12 characteristics of research‐favourable environments in the international academic medicine literature spanning the period from the mid‐1960s to 1990 (Box 1 ). Although these characteristics are aspirational in flavour, how they interplay to influence research productivity within increasingly complex institutional structures is not yet known. Indeed, although existing reviews have begun to help us better understand what makes for successful research environments, this research has typically ignored the contextual complexities and multiplicity of environmental characteristics 1 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 and has focused on narrow markers of productivity such as the quantity of research outputs (e.g. ref. 7 ) The current realist synthesis, therefore, aims to address this gap in the research literature by reviewing more recent literature ( 1992–2016 ) and exploring the features of successful research environments in terms of which interventions work, for whom, how and in what circumstances.
Characteristics of successful research environments 1
- Clear organisational research goals
- Research productivity as a priority and at least equal priority to other activities
- A robust research culture with shared research values
- A positive group climate
- Participative governance structures
- Non‐hierarchical and decentralised structures
- Good communication and professionally meaningful relationships between team members
- Decent resources such as people, funding, research facilities and time
- Larger group size, moderately established teams and diversity
- Rewards for research success
- Recruitment and selection of talented researchers
- Research‐oriented leaders with research expertise and skill
The contextual background for understanding successful research environments
Against a backdrop of the mass production of education, reduced government funding for research and ‘new managerialist’ cultures in higher education, 8 , 9 increased scrutiny of the quantity and quality of research, the research environments in which research is produced and the impacts of research has become inevitable. 10 Indeed, in higher education institutions (HEIs) globally, research productivity is being measured as part of individual researcher and research group key performance indicators. 7 In many countries, such as Australia, Hong Kong, New Zealand and the UK, 11 HEI research is measured on a national scale through government‐led research assessments. Such research measurement has contributed to the allocation of funding to universities and differentiation of universities in the competitive marketplace, with some solidifying their institutional identities as ‘research‐intensive’ and others emphasising their relative ‘newcomer‐to‐research’ status (e.g. previously ‘teaching‐intensive’ universities). 9 , 12 , 13 Such institutional differentiation also parallels that of individual academics within universities, who are increasingly encouraged to take either ‘research‐active’ or ‘education‐focused’ career pathways. 8 , 9 It is these broader national and institutional constraints that inevitably impact on research environments at the level of units, centres, departments and schools within universities (the level of ‘research environment’ that we focus on in this paper). Table S1 provides definitions of key terms.
Key features of research environments identified in previous reviews
Evans defines a research environment as including: ‘shared values, assumptions, beliefs, rituals and other forms of behaviour whose central focus is the acceptance and recognition of research practice and output as valued, worthwhile and pre‐eminent activity.’ 14 Previous reviews have tended to focus on interventions aimed at individual researchers, such as research capacity building, 4 , 5 , 7 and with individual‐level outcomes, such as increased numbers of grants or publications. 4 , 5 , 7 These reviews have typically concluded that research capacity‐building interventions lead to positive research outcomes. 4 , 5 , 7 Furthermore, the reviews have identified both individual and institutional enablers to research. Individual enablers included researchers’ intrinsic motivation to conduct research. 6 , 7 Institutional enablers included peer support, encouragement and review, 7 mentoring and collaboration, 4 , 5 research leadership, 5 , 6 institutional structures, processes and systems supporting research, such as clear strategy, 5 , 6 protected time and financial support. 5 Although these reviews have begun to shed light on the features of successful research environments, they have significant limitations: (i) they either include studies of low to moderate quality 4 , 5 or fail to check the quality of studies included, 7 and (ii) they do not explore what works for whom and under what circumstances, but instead focus on what works and ignore the influence of the context in which interventions are implemented and ‘how’ outcomes come about. Indeed, Mazmanian et al. 4 concluded in their review: ‘…little is known about what works best and in what situations.’
Conceptual framework: a realist approach
Given the gaps in the research literature and the importance of promoting successful research environments for individuals’ careers, institutional prestige and the knowledge base of the community, we thought a realist synthesis would be most likely to elucidate how multiple complex interventions can influence success. Realism assumes the existence of an external reality (a real world), but one that is filtered (i.e. perceived, interpreted and responded to) through human senses, volitions, language and culture. 15 A realist approach enables the development and testing of theory for why interventions may or may not work, for whom and under what circumstances. 16 It does this through recognising that interventions do not directly cause outcomes; instead, participants’ reactions and responses to the opportunities provided by the intervention trigger outcomes. This approach can allow researchers to identify causal links in complex situations, such as those between interventions and the contexts in which they work, how they work (mechanisms) and their outcomes. 17 Although the context–mechanism–outcome (CMO) approach is not necessarily linear, it can help to provide explanations that privilege contextual variability. 18
Aligned with the goals of realist research, this synthesis aims to address the following research question: What are the features of successful research environments, for whom, how and in what circumstances?
We followed five stages of realist synthesis: (i) clarifying scope; (ii) searching for evidence; (iii) assessing quality; (iv) extracting data, and (v) synthesising data. 19 Our methods also follow the RAMESES ( r ealist a nd m eta‐narrative e vidence s ynthesis: e volving s tandards) reporting guidelines. 20
Clarifying the scope
We first clarified the scope of our realist synthesis by identifying relevant interventions based on the Research Excellence Framework (REF) 2014 environment assessment criteria. The REF is a national exercise assessing the quality of research produced by UK HEIs, its impact beyond academia, and the environment that supports research. The assessment criteria indicated in the REF2014 environment template included the unit's research strategy , its people (including staffing strategy, staff development and research students), its income, infrastructure and facilities (IIF), as well as features of collaboration . 21 These guided our search terms (see stage 2 below). We chose to use these quality markers as they informed the UK national assessment exercise, upon which other national exercises are often based. In addition, these criteria were explicit, considered and implementable, and were developed through consensus. Like other realist syntheses, 18 , 22 , 23 ours considered a multiplicity of different interventions rather than just one and some of the papers we reviewed combined multiple interventions.
Based on previous reviews, 1 , 4 , 5 , 7 our initial programme theory speculated that interventions aligned to having an explicit research strategy, staff development opportunities, funding and establishing research networks would be effective for creating successful research environments (Fig. (Fig.1 1 gives further details of our initial programme theory).

Initial programme theory
Searching for empirical evidence
We devised search terms as a team and refined these iteratively with the help of a health librarian experienced in searching. We split the research question into three key concepts: (i) research environment; (ii) discipline, and (iii) research indicator (i.e. positive or negative). We then used variations of these terms to search the most relevant databases including MEDLINE, ProQuest, Scopus, CINAHL (Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature) and Web of Science. Table S2 illustrates the MeSH terms and provides a selection of key terms utilised in the database searches.
We were interested in comparing research cultures across the disciplines of medical education, education and medicine for two key reasons. Firstly, the discipline of medical education consists of a rich tapestry of epistemological approaches including biomedical sciences, social sciences and education, and medicine. 24 , 25 Secondly, there have been disciplinary arguments in the literature about whether medical education should be constructed as medicine or social science. 24 , 26
We agreed various inclusion and exclusion criteria with respect to topic, recentness and type of article (Table S3 ), as well as refined criteria to include contextual parameters (Table S4 ). We chose 1992 as the start date for our search period as 1992 saw the first published literature review about productive research environments in the academic medicine literature. 1
Study selection
The first top‐level search elicited 8527 journal articles across all databases. Once duplicate results had been removed, and ‘topic’ and ‘recentness’ study parameters reinforced, 420 articles remained. The searching and selection process is summarised in a PRISMA ( p referred r eporting i tems for s ystematic reviews and m eta‐ a nalyses) diagram (Fig. (Fig.2). 2 ). Three research assistants and one of the authors (PESC) initially assessed relevance by reviewing abstracts using preliminary inclusion criteria. If any ambiguities were found by any of the reviewers, abstracts were checked by one of the other two researchers (RA and CER). Where divergent views existed, researchers discussed the reasons why and agreed on whether to include or exclude. A 10% sample of these 420 abstracts were double‐checked by an additional two researchers, including a number of articles previously excluded, for quality control purposes.

PRISMA flow diagram of the selection process
Assessment of quality
We assessed the journal articles for relevance and rigour. 20 We defined an article's relevance according to ‘whether it can contribute to theory building and/or testing’. 20 Following the relevance check and ‘type’ exclusions to original research papers, 100 articles remained, which were then assessed for rigour. Although we chose to narrow down to original research, we kept relevant articles such as systematic reviews and opinion pieces to inform the introduction and discussion sections of this paper.
We defined rigour as determining ‘whether the method used to generate the particular piece of data is credible and trustworthy’. 20 We used two pre‐validated tools to assess study quality: the Medical Education Research Study Quality Instrument (MERSQI) to assess the quality of quantitative research, 27 , 28 and the Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP) qualitative checklist for qualitative and mixed‐method studies. 29 Both tools are used to consider the rigour of study design, sampling, type of data, data analysis and outcomes/findings, and have been employed in previous reviews. 23 , 30
Following the quality assessment, 47 articles remained and were then subjected to data extraction and synthesis. Five papers were excluded as they did not contribute to our theory building or lacked CMO configurations (CMOCs). We kept notes of the reasons for excluding studies and resolved doubts through discussion (Fig. (Fig.2 2 ).
Data extraction
Two data‐rich articles containing multiple CMOCs were inductively and deductively (based on the initial programme theory) coded by all of us to ensure consistency. We then discussed any similarities and differences in our coding. As is inherent in the challenges of realist approaches, we found differences in our identifications of CMOCs, which often related to how one particular component (e.g. time) could be an outcome at one moment and a mechanism the next. This alerted us to overlapping constructs, which we then explored as we coded remaining papers. To collect data across all remaining papers, we extracted information relating to: study design, methods and sample size; study setting; intervention focus; contexts of the intervention; mechanisms generated in the results, and outcomes. The key CMOCs in all 42 articles were identified primarily from the results sections of the papers. The process of data extraction and analysis was iterative with repeated discussion among the researchers of the demi‐regularities (i.e. patterns of CMOCs) in relation to the initial programme theory and negotiations of any differences of opinion.
Data synthesis
Finally, we interrogated our data extraction to look for patterns across our data/papers. We used an interpretative approach to consider how our data compared with our initial programme theory in order to develop our modified programme theory.
Characteristics of the studies
The 42 papers represented the following disciplines: medical education ( n = 4, 10%); 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 education ( n = 18, 43%), 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 and medicine ( n = 20, 48%). 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 , 64 , 65 , 66 , 67 , 68 , 69 , 70 , 71 , 72 There were 26 (62%) qualitative studies, 11 (26%) quantitative studies and five (12%) mixed‐methods studies (Table S5 ). The studies were from countries across the globe, including Australia ( n = 10, 24%), the USA ( n = 7, 17%), the UK ( n = 6, 14%), Canada ( n = 4, 10%), South Africa ( n = 4, 10%), Denmark ( n = 2, 5%), Turkey ( n = 2, 5%) and others ( n = 7, 17%) (e.g. Belgium, China, Germany, New Zealand and the Philippines). The research designs varied but common approaches included qualitative interviews, surveys, documentary/bibliographic analysis, case studies and mixed‐methods studies. Study participants included academics, teachers, health care professionals, senior directors, PhD students, early‐career researchers (ECRs) and senior researchers. Table S6 lists the individual contexts, interventions, mechanisms and outcomes identified from individual papers.
Extending our initial programme theory
A key finding from our realist synthesis was that the same interventions fired either positive or negative mechanisms leading to positive or negative outcomes, respectively, depending on context. Surprisingly, the CMOCs were mostly consistent across the three disciplines (i.e. medical education, education and medicine) with local contexts seemingly interplaying more strongly with outcomes. Therefore, we present these disciplinary contexts here as merged, but we highlight any differences by disciplinary context where relevant.
Having a research strategy promoted a successful research environment when it enabled appropriate resources (including time) and valuing of research; however, it had negative consequences when it too narrowly focused on outputs, incentives and rewards. In terms of people , individual researchers needed to be internally motivated and to have a sense of belonging, and protected time and access to capacity‐building activities in order to produce research. Lack of knowledge, researcher identity, networks and time, plus limited leadership support, acted as mechanisms leading to negative research outcomes. The presence of IIF was overwhelmingly indicated as necessary for successful research environments and their absence was typically detrimental. Interestingly, a few papers reported that external funding could have negative consequences because short‐term contracts, reduced job security and the use of temporary junior staff can lead to weak research environments. 40 , 67 , 71 Finally, collaboration was crucial for successful research mediated through trusting respectful relationships, supportive leadership and belongingness. Poor communication and competitive cultures, however, worked to undermine collaboration, leading to isolation and low self‐esteem, plus decreased research engagement and productivity. Table Table1 1 highlights illustrative CMOCs for each intervention extending our initial programme theory.
Positive and negative context–mechanism–outcome configurations (CMOCs) for each intervention
CMOCs indicated in bold highlight the three cross‐cutting themes of time, identity and relationships.
ECRs = early‐career researchers.
Key cross‐cutting mechanisms: time, identity and relationships
As Table Table1 1 shows, the same intervention can lead to positive or negative outcomes depending on the particular contexts and mechanisms triggered. This highlights greater complexity than is evident at first glance. Cross‐cutting these four interventions were three mechanisms that were regularly identified as critical to the success (or not) of a research environment: time; researcher identities, and relationships. We now present key findings for each of these cross‐cutting mechanisms and discuss how their inter‐relations lead to our modified programme theory (Fig. (Fig.3). 3 ). Note that although we have tried to separate these three mechanisms for ease of reading, they were often messily entangled. Table Table2 2 presents quotes illustrating the way in which each mechanism mediates outcomes within particular circumstances.

Modified programme theory. ECR = early‐career researcher
Time, identity and relationships as cross‐cutting mechanisms mediating successful research environments
Time was identified as an important mechanism for mobilising research outcomes across our three disciplines. Time was conceptualised severally including as: protected time; workload pressures influencing time available; efficient use of time; flexible use of time; making time, and time in career. The two most commonly considered aspects were protected time and workload implications. Protected time was largely talked about in the negative across a variety of contexts and disciplines, with lack of protected time leading to lack of researcher engagement or inactivity and reduced research productivity. 32 , 35 , 37 , 41 , 44 , 47 , 49 , 61 , 62 , 63 , 67 Also across a variety of contexts and disciplines, and acting as a positive mechanism, available protected time was found to lead to increased research productivity and active research engagement. 31 , 36 , 40 , 48 , 49 , 63 , 65 With regard to workload, limitations on the time available for research imposed by excessive other workloads led to reduced research activity, lower research productivity, poor‐quality research and reduced opportunity to attend research training. 40 , 41 , 47 , 49 , 60 , 67 Juggling of multiple responsibilities, such as clinical, teaching, administrative and leadership roles, also inhibited research productivity by diminishing the time available for research. 35 , 40 , 49 The alignment of research with other non‐research work was described as driving efficiencies in the use of time leading to greater research productivity (Table (Table2, 2 , quote 1).
Identity was also an important mechanism for mobilising research outcomes across our three disciplines. Interpretations included personal identities (e.g. gender), professional identity (e.g. as a primary practitioner or a primary researcher), and social identity (e.g. sense of belongingness). Researcher identity was often referred to in relation to first‐career practitioners (and therefore second‐career researchers). Sharp et al. 48 defined these as participants recruited into higher education not directly from doctoral study but on the basis of their extensive ‘first‐order’ knowledge and pedagogical expertise. These were also practitioners conducting research in schools or hospitals. Identities were also referenced in relation to early, mid‐career or senior researchers. Academic staff working in academic institutions needed to develop a sense of researcher identity, belongingness, self‐efficacy for research and autonomy to increase their satisfaction, competence and research activity. 39 , 40 , 44 , 46 , 51 , 67 For first‐career practitioners (i.e. teachers, doctors), the research needed to be highly relevant and aligned to their primary identity work in order to motivate them. 53 , 59 , 62 , 65 This alignment was described as having a strong research–teaching nexus. 40 , 48 Linked to this concept was the need for first‐career practitioners to see the impact of research in relation to their primary work (e.g. patient‐ or student‐oriented) to facilitate motivation and to develop a researcher identity (Table (Table2, 2 , quote 2). 36 , 37 , 41 , 49 , 53 , 54 , 67 Where research was seen as irrelevant to primary identity work (e.g. English language teaching, general practice), there was research disengagement. 37 , 48 , 52 , 59 , 67
Relationships
For all researchers and across our three disciplines, relationships were important in the mediating of successful research environments. 31 , 34 , 38 , 39 , 41 , 44 , 57 , 60 , 66 , 67 Positive research relationships were characterised by mutual trust and respect, 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 54 , 66 , 72 whereas others described them as friendships that take time to develop. 51 Mutually supportive relationships seemed to be particularly relevant to ECRs in terms of developing confidence, self‐esteem and research capacity and making identity transitions. 35 , 43 , 48 , 58 , 67 Relationships in the form of networks were considered to improve the quality of research through multicentre research and improved collaboration. 33 , 60 Supportive leadership as a particular form of relationship was an important mechanism in promoting a successful research environment. Supportive leaders needed to monitor workloads, set the vision, raise awareness of the value of research, and provide positive role‐modelling, thereby leading to increased productivity, promoting researcher identities and creating thriving research environments (Table (Table2, 2 , quote 3). 31 , 34 , 37 , 38 , 40 , 41 , 43 , 44 , 46 , 48 , 49 , 53 , 55 , 62 Research leadership, however, could be influenced negatively by the context of compliance and counting in current university cultures damaging relationships, creating a loss of motivation, and raising feelings of devalue. Indeed, the failure of leaders to recognise researcher identities led to negative research productivity. 36 , 37 , 38 , 43 , 46 , 48 , 49
Intersections between time, identity and relationships within successful research environments
Time and identity.
Time and identity intersected in interesting ways. Firstly, time was a necessary enabler for the development of a researcher identity. 37 , 38 , 41 , 48 , 49 , 54 , 59 , 61 , 63 , 65 , 67 , 69 Secondly, those who identified as researchers (thus holding primary researcher identities) used their time efficiently to favour research activity outcomes despite a lack of protected time. 35 , 43 Conversely, for other professors who lacked personal determination and resilience for research, having protected time did not lead to better research activity. 43 This highlights the fact that time alone is insufficient to support a successful research environment, and that it is how time is utilised and prioritised by researchers that really matters (Table (Table2, 2 , quote 4).
Identity and relationships
Interventions aimed at developing researcher identity consistently focused on relationship building across the three disciplines. The interventions that supported identity transitions into research included formal research training, 44 , 48 , 52 , 68 mentoring, 41 , 48 , 57 , 65 , 72 writing groups, 72 and collaboration with peers and other researchers, 39 , 41 , 43 operating through multiple mechanisms including relationships. The mechanisms included self‐esteem/confidence, increased networks, external recognition as a researcher, belongingness, and self‐efficacy. 35 , 41 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 52 , 57 Furthermore, our data suggest that leadership can be an enabler to the development of a researcher identity. In particular, leadership enabled research autonomy, recognition and empowerment, and fostered supportive mentoring environments, leading to researcher identity development and research productivity (Table (Table2, 2 , quote 5). 34 , 38 , 46 , 48
Time and relationships
Relationships were developed and sustained over time (Table (Table2, 2 , quote 6). Across the three disciplines, the role of leaders (managers, directors, deans) was to acknowledge and raise awareness of research, and then to prioritise time for research against competing demands, leading to effective research networks, cohesion and collaboration. 31 , 34 , 38 , 43 , 46 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 53 , 55 , 70 Second‐career PhD students who did not invest time in establishing relationships with researchers in their new disciplines (as they already had strong supportive networks in their original disciplines) found that they had limited research networks following graduation. 48
Summary of key findings
Our initial programme theory was based on previous literature reviews 1 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 and on the REF2014 criteria. 10 , 21 However, we were able to develop a modified programme theory on the basis of our realist synthesis, which highlights novel findings in terms of what really matters for successful research environments. Firstly, we found that key interventions led to both positive (subjective and objective) and negative (subjective and objective) outcomes in various contexts. Interestingly, we did not identify any outcomes relating to research impact despite impact nowadays being considered a prominent marker of research success, alongside quantitative metrics such as number of publications, grant income and h‐indices. 21 Secondly, we found that disciplinary contexts appeared to be less influential than individual, local and institutional contexts. Finally, our modified programme theory demonstrates a complex interplay among three cross‐cutting mechanisms (time, researcher identity and relationships) as mechanisms underpinning both successful and unsuccessful research environments.
Key findings and comparisons with the existing literature
Our research supports the findings of earlier reviews 1 , 5 , 6 , 7 regarding the importance of having a clear research strategy, an organisation that values research, research‐oriented leadership, access to resources (such as people, funding, research facilities and time), and meaningful relationships. However, our research extends these findings considerably by flagging up the indication that a clear linear relationship, whereby the presence of these interventions will necessarily result in a successful research environment, does not exist. For example, instituting a research strategy can have negative effects if the indicators are seen as overly narrow in focus or output‐oriented. 38 , 40 , 46 , 47 , 64 Similarly, project money can lead to the employment of more part‐time staff on fixed‐term contracts, which results in instability, turnover and lack of research team expertise. 40 , 67 , 71
Our findings indicate that the interplays among time, identity and relationships are important considerations when implementing interventions promoting research environments. Although time was identified as an important mechanism affecting research outcomes within the majority of papers, researcher identity positively affected research outcomes even in time‐poor situations. Indeed, we found that identity acted as a mechanism for research productivity that could overcome limited time through individuals efficiently finding time to prioritise research through their motivation and resilience. 35 , 43 Time was therefore more than just time spent doing research, but also included investment in developing a researcher identity and relationships with other researchers over time. 37 , 38 , 41 , 48 , 49 , 54 , 59 , 61 , 63 , 67 , 69 Relationship‐building interventions were also found to be effective in supporting difficult identity transitions into research faced by ECRs and those with first‐career practitioner backgrounds. Supportive leadership, as a particular form of relationship, could be seen as an enabler to the provision of protected time and a reasonable workload, allowing time for research and for researcher identity formation. 34 , 38 , 46 , 48 Indeed, our realist synthesis findings highlight the central importance of researcher identity and thus offer a novel explanation for why research environments may not flourish even in the presence of a research strategy, resources (e.g. time) and valuing of research.
Researcher identity is complex and intersects with other identities such as those of practitioner, teacher, leader and so on. Brew et al. 39 , 73 , 74 explored researcher identification and productivity by asking researchers if they considered themselves to be ‘research‐active’ and part of a research team. Those who identified as researchers prioritised their work differently: those who were highly productive prioritised research, whereas those in the low‐productivity group prioritised teaching. 73 Interestingly, highly productive researchers tended to view research as a social phenomenon with publications, presentations and grants being ‘traded’ in academic networks. Brew et al. 39 explain that: ‘…the trading view relates to a self‐generating researcher identity. Researcher identity develops in the act of publication, networks, collaborations and peer review. These activities support a person's identification as a researcher. They also, in turn, influence performance measures and metrics.’ Although the relationships among identity, identification and productivity are clearly complex, we explored a broader range of metrics in our realist synthesis than just productivity.
Methodological strengths and limitations
This is the first study to explore this important topic using realist synthesis to better understand the influence of context and how particular interventions lead to outcomes. We followed RAMESES 20 guidelines and adopted a rigorous team‐based approach to each analytic stage, conducting regular quality checks. The search was not exhaustive as we could have ‘exploded’ the interventions and performed a comprehensive review of each in its own right (e.g. mentoring). However, for pragmatic reasons and to answer our broad research questions, we chose not to do this, as suggested by Wong et al. 20 Although all members of the team had been involved in realist syntheses previously, the process remained messy as we dealt with complex phenomena. The messiness often lies in untangling CMOCs and identifying recurrent patterns in the large amounts of literature reviewed.
Implications for education and research
Our findings suggest that interventions related to research strategy, people, IIF and collaboration are supported under the ‘right’ conditions. We need to focus on time, identity and relationships (including leadership) in order to better mobilise the interventions to promote successful research environments.
Individuals need to reflect on how and why they identify as researchers, including their conceptions of research and their working towards the development of a researcher identity such that research is internally motivated rather than just externally driven. Those who are second‐career researchers or those with significant teaching or practitioner roles could seek to align research with their practice while they establish wider research networks.
We recommend that research leaders support individuals to develop their researcher identity, be seen to value research, recognise that research takes time, and provide access to opportunities promoting research capacity building, strong relationships and collaboration. Leaders, for example, may introduce interventions that promote researcher identities and build research relationships (e.g. collaborations, networking, mentoring, research groups etc.), paying attention to the ways in which competitive or collaborative cultures are fostered. Browne et al. 75 recently recommended discussions around four categories for promoting identity transition: reflection on self (values, experiences and expectations); consideration of the situation (circumstances, concerns); support (what is available and what is needed), and strategies (personal strategies to cope with change and thrive). With the professionalisation of medical education, 76 research units are increasingly likely to contain a mixture of first‐ and second‐career researchers, and our review suggests that discussions about conceptions of research and researcher identity would be valuable.
Finally, organisations need to value research and provide access to resources and research capacity‐building activities. Within the managerialist cultures of HEIs, compliance and counting have already become dominant discourses in terms of promotion and success. Policymakers should therefore consider ways in which HEIs recognise, incentivise and reward research in all its forms (including subjective and objective measures of quantity, quality and impact) to determine the full effects of their policies on research environments.
Future research would benefit from further exploration of the interplay among time, identities and relationships (including leadership) in different contexts using realist evaluation. 77 Specifically, as part of realist approaches, longitudinal audio‐diaries 78 could be employed to explore researcher identity transitions over time, particularly for first‐career practitioners transitioning into second‐career researchers.
Contributors
RA and CER were responsible for the conception of the synthesis. All authors contributed to the protocol development. RA and PESC carried out the database searches. All authors sifted for relevance and rigour, analysed the papers and contributed to the writing of the article. All authors approved the final manuscript for publication.
Conflicts of interest
Ethical approval.
not required.
Supporting information
Table S1. Definitions of key terms.
Table S6. Contexts, interventions, mechanisms and outcomes identified in individual studies.
Acknowledgements
we thank Andy Jackson, Learning and Teaching Librarian, University of Dundee, Dundee, UK, for his advice and help in developing our literature searches. We also thank Laura McDonald, Paul McLean and Eilidh Dear, who were medical students at the University of Dundee, for their help with database searches and with sifting papers for relevance and rigour. We would also like to thank Chau Khuong, Australian Regenerative Medicine Institute, Monash University, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, for her work in designing Figs Figs1 1 and and3 3 .
Advertisement
Low-carbon economy and policy implications: a systematic review and bibliometric analysis
- Research Article
- Published: 29 April 2022
- Volume 29 , pages 65432–65451, ( 2022 )
Cite this article

- Jingtian Wang 1 ,
- Yi Zhou 2 &
- Fang Lee Cooke 2
1643 Accesses
8 Citations
15 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
In the face of the rapid increase of carbon emissions, climate warming, and an epidemic situation, low-carbon economy is attracting growing attention. Using bibliometric analysis and machine learning methods, the paper conducts a systematic review in the low-carbon economy. Using the Web of Science Core Collection database, 1433 articles from 1990 to 2021 were selected for review. We find that the trajectories of the low-carbon economy research can be divided into four phases: exploration, fermentation, rising, and flourishing. The low-carbon economy research can be categorized into five clusters: low-carbon energy policy, carbon footprint and carbon trading, energy–economy–environment system, energy efficiency and its decomposition, and carbon emission drivers. The findings of this review study shed light on the role and effects of low-carbon economic policies on energy futures.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
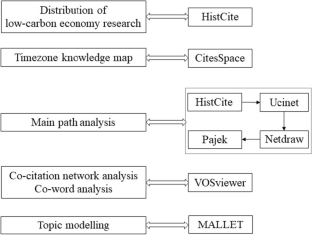
Similar content being viewed by others
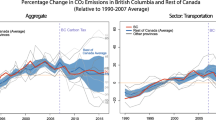
Does a Carbon Tax Reduce CO2 Emissions? Evidence from British Columbia

Carbon Footprint: Concept, Methodology and Calculation
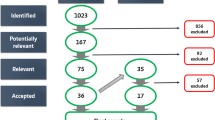
Distributional Impacts of Carbon Pricing: A Meta-Analysis
Data availability.
The datasets used during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Akef I, Arango JSM, Xu X (2016) Mallet vs GenSim: topic modeling for 20 news groups report. Univ Ark Little Rock Law J 2(19179):39205 (10.13140/RG)
Google Scholar
Ang BW, Zhang FQ, Choi KH (1998) Factorizing changes in energy and environmental indicators through decomposition. Energy 23(6):489–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-5442(98)00016-4
Article Google Scholar
Ang BW (2000) Decomposition analysis for policymaking in energy: which is the preferred method? Energy Policy 32(9):1131–1139. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-4215(03)00076-4
Ang BW, Zhang FQ (2004) A survey of index decomposition analysis in energy and environmental studies. Energy 25(12):1149–1176. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-5442(00)00039-6
Ang BW (2005) The LMDI approach to decomposition analysis: a practical guide. Energy Policy 33(7):867–871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2003.10.010
Ang JB (2007) CO2 emissions, energy consumption, and output in France. Energy Policy 35(10):4772–4778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2007.03.032
Babiker MH, Reilly JM, Mayer M, Eckaus RS, Sue Wing I, Hyman RC (2001) The MIT emissions prediction and policy analysis (EPPA) model: revisions, sensitivities, and comparisons of results.
Babiker MH, Metcalf GE, Reilly J (2003) Tax distortions and global climate policy. J Environ Econ Manag 46(2):269–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0095-0696(02)00039-6
Benavides C, Gonzales L, Diaz M, Fuentes R, Garcia G et al (2015) The Impact of a Carbon Tax on the Chilean Electricity Generation Sector. Energies 8(4):2674–2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8042674
Bhattacharya M, Paramati SR, Ozturk I, Bhattacharya S (2016) The effect of renewable energy consumption on economic growth: evidence from top 38 countries. Appl Energ 162:733–741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.10.104
Braulio-Gonzalo M, Bovea MD (2020) Relationship between green public procurement criteria and sustainability assessment tools applied to office buildings. Environ Impact Asses 81:106310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2019.106310
Brookes G, McEnery T (2019) The utility of topic modelling for discourse studies: a critical evaluation. Discourse Stud 21(1):3–21. https://doi.org/10.1177/1461445618814032
Campiglio E (2016) Beyond carbon pricing: the role of banking and monetary policy in financing the transition to a low-carbon economy. Ecol Econ 121:220–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2015.03.020
Cao K, Xu X, Wu Q, Zhang Q (2017) Optimal production and carbon emission reduction level under cap-and-trade and low carbon subsidy policies. J Clean Prod 167:505–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.07.251
Capros P, Tasios N, De Vita A, Mantzos L, Paroussos L (2012a) Model-based analysis of decarbonising the EU economy in the time horizon to 2050. Energy Strateg Rev 1(2):76–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esr.2012.06.003
Capros P, Tasios N, De Vita A, Mantzos L, Paroussos L (2012b) Transformations of the energy system in the context of the decarbonisation of the EU economy in the time horizon to 2050. Energy Strateg Rev 1(2):85–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esr.2012.06.001
Capros P, Paroussos L, Fragkos P, Tsani S, Boitier B et al (2014) European decarbonisation pathways under alternative technological and policy choices: A multi-model analysis. Energy Strateg Rev 2(3–4):231–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esr.2013.12.007
Carron-Arthur B, Reynolds J, Bennett K, Bennett A, Griffiths KM (2016) What’s all the talk about? Topic modelling in a mental health Internet support group. BMC Psychiatry 16(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-016-1073-5
Charnes A, Cooper WW, Rhodes E (1978) Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. Eur J Oper Res 2:429–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-2217(78)90138-8
Chen C, Chen C (2003) Mapping scientific frontiers. Springer-Verlag, London, England
Chen ZM, Liu Y, Qin P, Zhang B, Lester L et al (2015) Environmental externality of coal use in China: welfare effect and tax regulation. Appl Energ 156:16–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.06.066
Chen K, Zhang Y, Fu X (2019) International research collaboration: an emerging domain of innovation studies? Res Policy 48(1):149–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2018.08.005
Choi Y, Zhang N, Zhou P (2012) Efficiency and abatement costs of energy-related CO2 emissions in China: a slacks-based efficiency measure. Appl Energ 98:198–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2012.03.024
Cojoianu TF, Clark GL, Hoepner AG, Veneri P, Wójcik D (2020) Entrepreneurs for a low carbon world: how environmental knowledge and policy shape the creation and financing of green start-ups. Res Policy 49(6):103988. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2020.103988
Cui LB, Fan Y, Zhu L, Bi QH (2014) How will the emissions trading scheme save cost for achieving China’s 2020 carbon intensity reduction target? Appl Energy 136, 1043–1052. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.05.021
Dai S, Duan X, Zhang W (2020) Knowledge map of environmental crisis management based on keywords network and co-word analysis, 2005–2018. J Clean Prod 262:121168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121168
Dantu R, Dissanayake I, Nerur S (2021) Exploratory analysis of internet of things (IoT) in healthcare: a topic modelling & co-citation approaches. Inform Syst Manage 38(1):62–78. https://doi.org/10.1080/10580530.2020.1746982
Dietz T, Rosa EA (1994) Rethinking the environmental impacts of population, affluence, and technology. Hum Ecol Rev 1(2):277–300
Dutta A (2018) Modeling and forecasting the volatility of carbon emission market: The role of outliers, time-varying jumps and oil price risk. J Clean Prod 172:2773–2781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.11.135
Du L, Li X, Zhao H, Ma W, Jiang P (2018) System dynamic modeling of urban carbon emissions based on the regional National Economy and Social Development Plan: A case study of Shanghai city. J Clean Prod 172:1501–1513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.128
Department of Trade and Industry, U. K (2003) Our energy future — creating a low carbon economy. The Stationery Office. https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/our-energy-future-creating-a-low-carbon-economy
Ehrilich PR, Holdren JP (1971) Impact of population growth. Science 171(3977):1212–1217
Fan D, Lo CK, Ching V, Kan CW (2014) Occupational health and safety issues in operations management: a systematic and citation network analysis review. Int J Prod Econ 158:334–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2014.07.025
Fang K, Dong L, Ren J, Zhang Q, Han L, Fu H (2017) Carbon footprints of urban transition: Tracking circular economy promotions in Guiyang, China. Ecol Model 365:30–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2017.09.024
Foxon TJ (2011) A coevolutionary framework for analysing a transition to a sustainable low carbon economy. Ecol Econ 70(12):2258–2267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2011.07.014
Gabrielatos C, Baker P (2008) Fleeing, sneaking, flooding: a corpus analysis of discursive constructions of refugees and asylum seekers in the UK press, 1996–2005. J Engl Linguist 36:5–38. https://doi.org/10.1177/0075424207311247
Geels FW (2002) Technological transitions as evolutionary reconfiguration processes: a multi-level perspective and a case-study. Res Policy 31(8–9):1257–1274. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-7333(02)00062-8
Grossman GM, Krueger AB (1995) Economic Growth and the Environment. Q J Econ 110(2):353–377. https://doi.org/10.2307/2118443
Gomi K, Shimada K, Matsuoka Y (2010) A low-carbon scenario creation method for a local-scale economy and its application in Kyoto city. Energy Policy 38(9):4783–4796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2009.07.026
Goulder LH (1995) Environmental taxation and the double dividend: a reader’s guide. Int Tax Public Finan 2:157–183. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00877495
Goulder LH, Schneider SH (1999) Induced technological change and the attractiveness of CO2 abatement policies. Resour Energy Econ 21(3–4):211–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0928-7655(99)00004-4
Hache E, Palle A (2019) Renewable energy source integration into power networks, research trends and policy implications: a bibliometric and research actors survey analysis. Energy Policy 124:23–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2018.09.036
Halicioglu F (2009) An econometric study of CO2 emissions, energy consumption, income and foreign trade in Turkey. Energy Policy 37:1156–1164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2008.11.012
Hu JL, Wang SC (2006) Total-Factor Energy Efficiency of Regions in China. Energy Policy 34:3206–3217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2005.06.015
Hu Z, Yuan J, Hu Z (2011) Study on China’s low carbon development in an Economy–Energy–Electricity–Environment framework. Energy Policy 39(5):2596–2605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2011.02.028
Ji CJ, Li XY, Hu YJ, Wang XY, Tang BJ (2019) Research on carbon price in emissions trading scheme: a bibliometric analysis. Nat Hazards 99(3):1381–1396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-018-3433-6
Jiang B, Sun ZQ, Liu MQ (2010) China’s energy development strategy under the low-carbon economy. Energy 35(11):4257–4264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2009.12.040
Jiang K, Ashworth P (2021) The development of carbon capture utilization and storage (CCUS) research in China: a bibliometric perspective. Renew Sust Energ Rev 138:110521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2020.110521
Article CAS Google Scholar
Kawase R, Matsuoka Y, Fujino J (2006) Decomposition analysis of CO2 emission in long-term climate stabilization scenarios. Energy Policy 34(15):2113–2122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2005.02.005
Kaya Y (1989) Impact of carbon dioxide emission on gnp growth: interpretation of proposed scenarios; presentation to the energy and industry subgroup; Response Strategies Working Group. IPCC: Paris, France, pp 1–25
Kern F, Rogge KS, Howlett M (2019) Policy mixes for sustainability transitions: new approaches and insights through bridging innovation and policy studies. Res Policy 48(10):103832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2019.103832
Leontief W (1970) Environmental repercussions and the economic structure: an input-output approach. Rev Econ Stat 52(3):262–271. https://doi.org/10.2307/1926294
Li B, Hu K, Lysenko V, Khan KY, Wang Y, Jiang Y, Guo Y (2022) A scientometric analysis of agricultural pollution by using bibliometric software VoSViewer and Histcite™. Environ Sci Pollut R 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18491-w
Li H, Bao Q, Ren X, Xie Y, Ren J, Yang Y (2017) Reducing rebound effect through fossil subsidies reform: a comprehensive evaluation in China. J Clean Prod 141:305–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.09.108
Li W, Zhang YW, Lu C (2018) The impact on electric power industry under the implementation of national carbon trading market in China: a dynamic CGE analysis. J Clean Prod 200:511–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.07.325
Lin B, Xu M (2019) Good subsidies or bad subsidies? Evidence from low-carbon transition in China’s metallurgical industry. Energy Econ 83:52–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2019.06.015
Liu X, Ishikawa M, Wang C, Dong Y, Liu W (2010) Analyses of CO2 emissions embodied in Japan-China trade. Energy Policy 38(3):1510–1518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2009.11.034
Lyu XH, Shi A, Wang X (2020) Research on the impact of carbon emission trading system on low-carbon technology innovation. Carbon Manag 11(2):183–193. https://doi.org/10.1080/17583004.2020.1721977
Mathews JA (2008) How carbon credits could drive the emergence of renewable energies. Energy Policy 36(10):3633–3639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2008.05.033
Mallapaty S (2020) How China could be carbon neutral by mid-century. Nature 586(7830):482–483. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-02927-9
McFarland JR, Reilly JM, Herzog HJ (2004) Representing energy technologies in top-down economic models using bottom-up information. Energy Econ 26(4):685–707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2004.04.026
Meng L, Guo JE, Chai J, Zhang Z (2011) China’s regional CO2 emissions: characteristics, inter-regional transfer and emission reduction policies. Energy Policy 39(10):6136–6144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2011.07.013
Meng S, Siriwardana M, McNeill J (2013) The environmental and economic impact of the carbon tax in Australia. Environ Resour Econ 54:313–332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10640-012-9600-4
Meng XC, Seong YH, Lee MK (2021) Research characteristics and development trend ofgGlobal low-carbon power—based on bibliometric analysis of 1983–2021. Energies 14(16):4983. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14164983
Miles MB, Huberman AM (1994) Qualitative data analysis. Sage, Thousand Oaks, CA
Niknejad N, Nazari B, Foroutani S, Hussin ARBC (2022) A bibliometric analysis of green technologies applied to water and wastewater treatment. Environ Sci Pollut R 1-15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18705-1
Nong D, Meng S, Siriwardana M (2017) An assessment of a proposed ETS in Australia by using the MONASH-Green model. Energy Policy 108:281–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2017.06.004
Nwaobi GC (2004) Emission policies and the Nigerian economy: simulations from a dynamic applied general equilibrium model. Energ Econ 26(5):921–936. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2004.04.003
OECD (2002) Indicators to measure decoupling of environmental pressure from economic growth. OECD, Paris
Omoregbe O, Mustapha AN, Steinberger-Wilckens R, El-Kharouf A, Onyeaka H (2020) Carbon capture technologies for climate change mitigation: a bibliometric analysis of the scientific discourse during 1998–2018. Energy Rep 6:1200–1212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2020.05.003
Paltsev SV (2001) The Kyoto Protocol: Regional and sectoral contributions to the carbon leakage. Energ J 22(4):53–79. https://doi.org/10.5547/ISSN0195-6574-EJ-Vol22-No4-3
Peng Y, Bai X (2018) Experimenting towards a low-carbon city: Policy evolution and nested structure of innovation. J Clean Prod 174:201–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.116
Pritchard A (1969) Statistical Bibliography or Bibliometrics. J Doc 25(4):348–349
Reuveny R (2007) Climate change-induced migration and violent conflict. Polit Geogr 26:656–673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polgeo.2007.05.001
Roughgarden T, Schneider SH (1999) Climate change policy: quantifying uncertainties for damages and optimal carbon taxes. Energy Policy 27(7):415–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-4215(99)00030-0
Sandoval R, Karplus VJ, Paltsev S, Reilly JM (2009) Modelling prospects for hydrogen-powered transportation until 2100. J Transp Econ Policy 43(3):291–316
Schandl H, Hatfield-Dodds S, Wiedmann T, Geschke A, Cai Y et al (2016) Decoupling global environmental pressure and economic growth: scenarios for energy use, materials use and carbon emissions. J Clean Prod 132:45–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.06.100
Schneider M, Holzer A, Hoffmann VH (2008) Understanding the CDM’s contribution to technology transfer. Energy Policy 36(8):2930–2938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2008.04.009
Schroeder PM, Chapman RB (2014) Renewable energy leapfrogging in China’s urban development? Current status and outlook. Sustain Cities Soc 11:31–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2013.11.007
Shang T, Yang L, Liu P, Shang K, Zhang Y (2020) Financing mode of energy performance contracting projects with carbon emissions reduction potential and carbon emissions ratings. Energy Policy 144:111632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2020.111632
Shimada K, Tanaka Y, Gomi K, Matsuoka Y (2007) Developing a long-term local society design methodology towards a low-carbon economy: an application to Shiga Prefecture in Japan. Energy Policy 35(9):4688–4703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2007.03.025
Simoes S, Nijs W, Ruiz P, Sgobbi A, Thiel C (2017) Comparing policy routes for low-carbon power technology deployment in EU-an energy system analysis. Energy Policy 101:353–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2016.10.006
Small H (1973) Co-citation in the scientific literature: A new measure of the relationship between two documents. J Am Soc Inf Sci Tec 24(4):265–269. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.4630240406
Su M, Liang C, Chen B, Chen S, Yang Z (2012) Low-carbon development patterns: observations of typical Chinese cities. Energies 5(2):291–304. https://doi.org/10.3390/en5020291
Tang KY, Chang CY, Hwang GJ (2021) Trends in artificial intelligence-supported e-learning: a systematic review and co-citation network analysis (1998-2019). Interact Learn Envir 1-19. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2021.1875001
Tapio P (2005) Towards a theory of decoupling: degree of decoupling in the EU and the case of road traffic in Finland between 1970 and 2001. Transp Policy 12(2):137–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranpol.2005.01.001
Timilsina GR (2009) Carbon tax under the clean development mechanism: a unique approach for reducing greenhouse gas emissions in developing countries. Clim Policy 9(2):139–154. https://doi.org/10.3763/cpol.2008.0546
Unruh GC (2000) Understanding carbon lock-in. Energy Policy 28(12):817–830. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-4215(00)00070-7
Unruh GC (2002) Escaping carbon lock-in. Energy Policy 30(4):317–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-4215(01)00098-2
Uyterlinde MA, Junginger M, de Vries HJ, Faaij AP, Turkenburg WC (2007) Implications of technological learning on the prospects for renewable energy technologies in Europe. Energy Policy 35(8):4072–4087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2007.02.004
Verbruggen A (2008) Renewable and nuclear power: A common future? Energy Policy 36(11):4036–4047. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2008.06.024
Verbruggen A, Lauber V (2009) Basic concepts for designing renewable electricity support aiming at a full-scale transition by 2050. Energy Policy 37(12):5732–5743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2009.08.044
Viola L, Verheul J (2020) Mining ethnicity: discourse-driven topic modelling of immigrant discourses in the USA, 1898–1920. Digit Scholarsh Hum 35(4):921–943. https://doi.org/10.1093/llc/fqz068
Wang P, Wu W, Zhu B, Wei Y (2013a) Examining the impact factors of energy-related CO2 emissions using the STIRPAT model in Guangdong Province, China. Appl Energ 106:65–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.01.036
Wang S, Fang C, Ma H, Wang Y, Qin J (2014) Spatial differences and multi-mechanism of carbon footprint based on GWR model in provincial China. J Geogr Sci 24(4):612–630. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-014-1109-z
Wang T, Watson J (2010) Scenario analysis of China’s emissions pathways in the 21st century for low carbon transition. Energy Policy 38(7):3537–3546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2010.02.031
Wang X, Zhu Y, Sun H, Jia F (2018) Production decisions of new and remanufactured products: implications for low carbon emission economy. J Clean Prod 171:1225–1243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.053
Wang Y, Zhao H, Li L, Liu Z, Liang S (2013b) Carbon dioxide emission drivers for a typical metropolis using input–output structural decomposition analysis. Energy Policy 58:312–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2013.03.022
Wang L, Zhao L, Mao G, Zuo J, Du H (2017) Way to accomplish low carbon development transformation: a bibliometric analysis during 1995–2014. Renew Sust Energ Rev 68:57–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.08.021
Weber G, Cabras I (2017) The transition of Germany’s energy production, green economy, low-carbon economy, socio-environmental conflicts, and equitable society. J Clean Prod 167:1222–1231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.07.223
Wing IS (2006) The synthesis of bottom-up and top-down approaches to climate policy modeling: electric power technologies and the cost of limiting US CO2 emissions. Energy Policy 34(18):3847–3869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2005.08.027
Wissema W, Dellink R (2007) AGE analysis of the impact of a carbon energy tax on the Irish economy. Ecol Econ 61(4):671–683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2006.07.034
Xu M, Lin B, Wang S (2021) Towards energy conservation by improving energy efficiency? Evidence from China’s Metallurgical Industry Energy 216:119255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.119255
Yan Z, Du K, Yang Z, Deng M (2017) Convergence or divergence? Understanding the global development trend of low-carbon technologies. Energy Policy 109:499–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2017.07.024
Yin H, Zhao J, Xi X, Zhang Y (2019) Evolution of regional low-carbon innovation systems with sustainable development: an empirical study with big-data. J Clean Prod 209:1545–1563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.11.001
Ying D, Chowdhury GG, Foo S (2001) Bibliometric cartography of information retrieval research by using co-word analysis. Inform Process Manag 37(6):817–842. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0306-4573(00)00051-0
York R, Rosa EA, Dietz T (2003) STIRPAT, IPAT and ImPACT: analytic tools for unpacking the driving forces of environmental impacts. Ecol Econ 46(3):351–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-8009(03)00188-5
Yu H, Wei YM, Tang BJ, Mi Z, Pan SY (2016) Assessment on the research trend of low-carbon energy technology investment: a bibliometric analysis. Appl Energ 184:960–970. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.07.129
Zeng DZ, Cheng L, Shi L, Luetkenhorst W (2021) China’s green transformation through eco-industrial parks. World Dev 140:105249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2020.105249
Zhang J, Zeng W, Wang J, Yang F, Jiang H (2017) Regional low-carbon economy efficiency in China: analysis based on the Super-SBM model with CO2 emissions. J Clean Prod 163:202–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.06.111
Zhang N, Wang B, Liu Z (2016a) Carbon emissions dynamics, efficiency gains, and technological innovation in China’s industrial sectors. Energy 99:10–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2016.01.012
Zhang Y, Da Y (2015) The decomposition of energy-related carbon emission and its decoupling with economic growth in China. Renew Sust Energ Rev 41:1255–1266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.09.021
Zhang Z (2010) China in the transition to a low-carbon economy. Energy Policy 38(11):6638–6653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2010.06.034
Zhang K, Wang Q, Liang QM, Chen H (2016b) A bibliometric analysis of research on carbon tax from 1989 to 2014. Renew Sust Energ Rev 58:297–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.12.089
Zhen W, Qin Q, Kuang Y, Huang N (2017) Investigating low-carbon crop production in Guangdong Province, China (1993–2013): A decoupling and decomposition analysis. J Clean Prod 146:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.05.022
Zhou P, Ang BW, Han JY (2010) Total factor carbon emission performance: a Malmquist index analysis. Energ Econ 32:194–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2009.10.003
Zhou X, Zhang J, Li J (2013) Industrial structural transformation and carbon dioxide emissions in China. Energy Policy 57:43–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2012.07.01
Zhou X, Tao X, Rahman MM, Zhang J (2017) Coupling topic modelling in opinion mining for social media analysis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Web Intelligence 533–540. https://doi.org/10.1145/3106426.3106459
Download references
This article is an outcome of a project funded by the Woodside Monash Energy Partnership- WMEP-IT-2A-001.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Applied Economics, Renmin University, Beijing, China
Jingtian Wang
Department of Management, Monash University, Monash, Australia
Yi Zhou & Fang Lee Cooke
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
The inception of the paper stemmed from a project: ‘Low Carbon Economy: A Multi-Level and Multi-Disciplinary Analysis of the Role of Stakeholders’ funded by the Woodside Monash Energy Partnership and led by Fang Lee Cooke. All authors contributed to the conception and design of the paper. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Jingtian Wang under the guidance of Yi Zhou and Fang Lee Cooke. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Jingtian Wang. Yi Zhou and Fang Lee Cooke provided advice on the draft and revised sections of the manuscript. All authors participated in revisions of the manuscript and read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jingtian Wang .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Roula Inglesi-Lotz
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Explanation of the criteria and rationale.
Criterion 1: We follow previous literature reviews (e.g., Fan et al, 2014 and Li et al. 2022 ) to only include publications in ‘articles’ type in our analysis because they are peer-reviewed research papers. They had rigorous review processes to make sure the research findings are robust. We only include publications in English as integrating multiple languages is a big challenge for doing the bibliometric analysis (Li et al. 2022 and Niknejad et al. 2022 ). First, the software that we use to do the bibliometric analysis can only process one language at a time. Second, transferring the research papers from other languages to English may cause interpretation and copyrights problems. Third, the citation information may not be used as they are in different languages. Although we only include publications in English, we do not exclude scholars in a specific area as the Web of Science Core Collection platform collects the relevant research of scholars all over the world.
Criterion 2: According to our research theme, we identify the research categories that are highly related to low-carbon economies such as economics, international relations, public environmental occupational health, business, public administration, ethics, urban studies, law, development studies, social sciences inte-discipline, political science, and social issues.
Criterion 3: We carefully reviewed each literature and captured the antecedents, strategies, aspects, and outcomes of each literature to ensure that the research topics have implications for low-carbon economy and its transformation. Discrepancies were resolved through back-and-forth discussions until we reached an agreement on which studies should be included.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Wang, J., Zhou, Y. & Cooke, F.L. Low-carbon economy and policy implications: a systematic review and bibliometric analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29 , 65432–65451 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20381-0
Download citation
Received : 25 November 2021
Accepted : 18 April 2022
Published : 29 April 2022
Issue Date : September 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20381-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Bibliometrics
- Energy policy
- Low-carbon economy
- Machine learning
- Systematic review
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Environmental Changes Are Fueling Human, Animal and Plant Diseases, Study Finds
Biodiversity loss, global warming, pollution and the spread of invasive species are making infectious diseases more dangerous to organisms around the world.

By Emily Anthes
Several large-scale, human-driven changes to the planet — including climate change, the loss of biodiversity and the spread of invasive species — are making infectious diseases more dangerous to people, animals and plants, according to a new study.
Scientists have documented these effects before in more targeted studies that have focused on specific diseases and ecosystems. For instance, they have found that a warming climate may be helping malaria expand in Africa and that a decline in wildlife diversity may be boosting Lyme disease cases in North America.
But the new research, a meta-analysis of nearly 1,000 previous studies, suggests that these patterns are relatively consistent around the globe and across the tree of life.
“It’s a big step forward in the science,” said Colin Carlson, a biologist at Georgetown University, who was not an author of the new analysis. “This paper is one of the strongest pieces of evidence that I think has been published that shows how important it is health systems start getting ready to exist in a world with climate change, with biodiversity loss.”
In what is likely to come as a more surprising finding, the researchers also found that urbanization decreased the risk of infectious disease.
The new analysis, which was published in Nature on Wednesday, focused on five “global change drivers” that are altering ecosystems across the planet: biodiversity change, climate change, chemical pollution, the introduction of nonnative species and habitat loss or change.
The researchers compiled data from scientific papers that examined how at least one of these factors affected various infectious-disease outcomes, such as severity or prevalence. The final data set included nearly 3,000 observations on disease risks for humans, animals and plants on every continent except for Antarctica.
The researchers found that, across the board, four of the five trends they studied — biodiversity change, the introduction of new species, climate change and chemical pollution — tended to increase disease risk.
“It means that we’re likely picking up general biological patterns,” said Jason Rohr, an infectious disease ecologist at the University of Notre Dame and senior author of the study. “It suggests that there are similar sorts of mechanisms and processes that are likely occurring in plants, animals and humans.”
The loss of biodiversity played an especially large role in driving up disease risk, the researchers found. Many scientists have posited that biodiversity can protect against disease through a phenomenon known as the dilution effect.
The theory holds that parasites and pathogens, which rely on having abundant hosts in order to survive, will evolve to favor species that are common, rather than those that are rare, Dr. Rohr said. And as biodiversity declines, rare species tend to disappear first. “That means that the species that remain are the competent ones, the ones that are really good at transmitting disease,” he said.
Lyme disease is one oft-cited example. White-footed mice, which are the primary reservoir for the disease, have become more dominant on the landscape, as other rarer mammals have disappeared, Dr. Rohr said. That shift may partly explain why Lyme disease rates have risen in the United States. (The extent to which the dilution effect contributes to Lyme disease risk has been the subject of debate, and other factors, including climate change, are likely to be at play as well.)
Other environmental changes could amplify disease risks in a wide variety of ways. For instance, introduced species can bring new pathogens with them, and chemical pollution can stress organisms’ immune systems. Climate change can alter animal movements and habitats, bringing new species into contact and allowing them to swap pathogens .
Notably, the fifth global environmental change that the researchers studied — habitat loss or change — appeared to reduce disease risk. At first glance, the findings might appear to be at odds with previous studies, which have shown that deforestation can increase the risk of diseases ranging from malaria to Ebola. But the overall trend toward reduced risk was driven by one specific type of habitat change: increasing urbanization.
The reason may be that urban areas often have better sanitation and public health infrastructure than rural ones — or simply because there are fewer plants and animals to serve as disease hosts in urban areas. The lack of plant and animal life is “not a good thing,” Dr. Carlson said. “And it also doesn’t mean that the animals that are in the cities are healthier.”
And the new study does not negate the idea that forest loss can fuel disease; instead, deforestation increases risk in some circumstances and reduces it in others, Dr. Rohr said.
Indeed, although this kind of meta-analysis is valuable for revealing broad patterns, it can obscure some of the nuances and exceptions that are important for managing specific diseases and ecosystems, Dr. Carlson noted.
Moreover, most of the studies included in the analysis examined just a single global change drive. But, in the real world, organisms are contending with many of these stressors simultaneously. “The next step is to better understand the connections among them,” Dr. Rohr said.
Emily Anthes is a science reporter, writing primarily about animal health and science. She also covered the coronavirus pandemic. More about Emily Anthes
Explore the Animal Kingdom
A selection of quirky, intriguing and surprising discoveries about animal life..
Scientists say they have found an “alphabet” in the songs of sperm whales , raising the possibility that the animals are communicating in a complex language.
Indigenous rangers in Australia’s Western Desert got a rare close-up with the northern marsupial mole , which is tiny, light-colored and blind, and almost never comes to the surface.
For the first time, scientists observed a primate in the wild treating a wound with a plant that has medicinal properties.
A new study resets the timing for the emergence of bioluminescence back to millions of years earlier than previously thought.
Scientists are making computer models to better understand how cicadas emerge collectively after more than a decade underground .
Innovative Statistics Project Ideas for Insightful Analysis
Table of contents
- 1.1 AP Statistics Topics for Project
- 1.2 Statistics Project Topics for High School Students
- 1.3 Statistical Survey Topics
- 1.4 Statistical Experiment Ideas
- 1.5 Easy Stats Project Ideas
- 1.6 Business Ideas for Statistics Project
- 1.7 Socio-Economic Easy Statistics Project Ideas
- 1.8 Experiment Ideas for Statistics and Analysis
- 2 Conclusion: Navigating the World of Data Through Statistics
Diving into the world of data, statistics presents a unique blend of challenges and opportunities to uncover patterns, test hypotheses, and make informed decisions. It is a fascinating field that offers many opportunities for exploration and discovery. This article is designed to inspire students, educators, and statistics enthusiasts with various project ideas. We will cover:
- Challenging concepts suitable for advanced placement courses.
- Accessible ideas that are engaging and educational for younger students.
- Ideas for conducting surveys and analyzing the results.
- Topics that explore the application of statistics in business and socio-economic areas.
Each category of topics for the statistics project provides unique insights into the world of statistics, offering opportunities for learning and application. Let’s dive into these ideas and explore the exciting world of statistical analysis.
Top Statistics Project Ideas for High School
Statistics is not only about numbers and data; it’s a unique lens for interpreting the world. Ideal for students, educators, or anyone with a curiosity about statistical analysis, these project ideas offer an interactive, hands-on approach to learning. These projects range from fundamental concepts suitable for beginners to more intricate studies for advanced learners. They are designed to ignite interest in statistics by demonstrating its real-world applications, making it accessible and enjoyable for people of all skill levels.
Need help with statistics project? Get your paper written by a professional writer Get Help Reviews.io 4.9/5
AP Statistics Topics for Project
- Analyzing Variance in Climate Data Over Decades.
- The Correlation Between Economic Indicators and Standard of Living.
- Statistical Analysis of Voter Behavior Patterns.
- Probability Models in Sports: Predicting Outcomes.
- The Effectiveness of Different Teaching Methods: A Statistical Study.
- Analysis of Demographic Data in Public Health.
- Time Series Analysis of Stock Market Trends.
- Investigating the Impact of Social Media on Academic Performance.
- Survival Analysis in Clinical Trial Data.
- Regression Analysis on Housing Prices and Market Factors.
Statistics Project Topics for High School Students
- The Mathematics of Personal Finance: Budgeting and Spending Habits.
- Analysis of Class Performance: Test Scores and Study Habits.
- A Statistical Comparison of Local Public Transportation Options.
- Survey on Dietary Habits and Physical Health Among Teenagers.
- Analyzing the Popularity of Various Music Genres in School.
- The Impact of Sleep on Academic Performance: A Statistical Approach.
- Statistical Study on the Use of Technology in Education.
- Comparing Athletic Performance Across Different Sports.
- Trends in Social Media Usage Among High School Students.
- The Effect of Part-Time Jobs on Student Academic Achievement.
Statistical Survey Topics
- Public Opinion on Environmental Conservation Efforts.
- Consumer Preferences in the Fast Food Industry.
- Attitudes Towards Online Learning vs. Traditional Classroom Learning.
- Survey on Workplace Satisfaction and Productivity.
- Public Health: Attitudes Towards Vaccination.
- Trends in Mobile Phone Usage and Preferences.
- Community Response to Local Government Policies.
- Consumer Behavior in Online vs. Offline Shopping.
- Perceptions of Public Safety and Law Enforcement.
- Social Media Influence on Political Opinions.
Statistical Experiment Ideas
- The Effect of Light on Plant Growth.
- Memory Retention: Visual vs. Auditory Information.
- Caffeine Consumption and Cognitive Performance.
- The Impact of Exercise on Stress Levels.
- Testing the Efficacy of Natural vs. Chemical Fertilizers.
- The Influence of Color on Mood and Perception.
- Sleep Patterns: Analyzing Factors Affecting Sleep Quality.
- The Effectiveness of Different Types of Water Filters.
- Analyzing the Impact of Room Temperature on Concentration.
- Testing the Strength of Different Brands of Batteries.
Easy Stats Project Ideas
- Average Daily Screen Time Among Students.
- Analyzing the Most Common Birth Months.
- Favorite School Subjects Among Peers.
- Average Time Spent on Homework Weekly.
- Frequency of Public Transport Usage.
- Comparison of Pet Ownership in the Community.
- Favorite Types of Movies or TV Shows.
- Daily Water Consumption Habits.
- Common Breakfast Choices and Their Nutritional Value.
- Steps Count: A Week-Long Study.
Business Ideas for Statistics Project
- Analyzing Customer Satisfaction in Retail Stores.
- Market Analysis of a New Product Launch.
- Employee Performance Metrics and Organizational Success.
- Sales Data Analysis for E-commerce Websites.
- Impact of Advertising on Consumer Buying Behavior.
- Analysis of Supply Chain Efficiency.
- Customer Loyalty and Retention Strategies.
- Trend Analysis in Social Media Marketing.
- Financial Risk Assessment in Investment Decisions.
- Market Segmentation and Targeting Strategies.
Socio-Economic Easy Statistics Project Ideas
- Income Inequality and Its Impact on Education.
- The Correlation Between Unemployment Rates and Crime Levels.
- Analyzing the Effects of Minimum Wage Changes.
- The Relationship Between Public Health Expenditure and Population Health.
- Demographic Analysis of Housing Affordability.
- The Impact of Immigration on Local Economies.
- Analysis of Gender Pay Gap in Different Industries.
- Statistical Study of Homelessness Causes and Solutions.
- Education Levels and Their Impact on Job Opportunities.
- Analyzing Trends in Government Social Spending.
Experiment Ideas for Statistics and Analysis
- Multivariate Analysis of Global Climate Change Data.
- Time-Series Analysis in Predicting Economic Recessions.
- Logistic Regression in Medical Outcome Prediction.
- Machine Learning Applications in Statistical Modeling.
- Network Analysis in Social Media Data.
- Bayesian Analysis of Scientific Research Data.
- The Use of Factor Analysis in Psychology Studies.
- Spatial Data Analysis in Geographic Information Systems (GIS).
- Predictive Analysis in Customer Relationship Management (CRM).
- Cluster Analysis in Market Research.
Conclusion: Navigating the World of Data Through Statistics
In this exploration of good statistics project ideas, we’ve ventured through various topics, from the straightforward to the complex, from personal finance to global climate change. These ideas are gateways to understanding the world of data and statistics, and platforms for cultivating critical thinking and analytical skills. Whether you’re a high school student, a college student, or a professional, engaging in these projects can deepen your appreciation of how statistics shapes our understanding of the world around us. These projects encourage exploration, inquiry, and a deeper engagement with the world of numbers, trends, and patterns – the essence of statistics.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
Environmental Justice Research Paper Topics

This guide provides a comprehensive list of environmental justice research paper topics , meticulously organized into ten categories, each featuring ten unique and engaging subjects. It also offers expert advice on how to select a topic and how to structure and write an environmental justice research paper. Furthermore, it introduces iResearchNet’s professional writing services, which can assist students in creating custom research papers on any topic.
100 Environmental Justice Research Paper Topics
Environmental justice is a significant and dynamic field of study. It intersects with various disciplines, including law, policy, public health, urban planning, and climate science. The following comprehensive list of environmental justice research paper topics is divided into ten categories, each with ten topics. These topics are designed to inspire students to explore the diverse aspects of environmental justice and contribute to this important discourse.
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
Environmental Justice and Policy
- The role of policy in promoting environmental justice
- The impact of the Clean Air Act on marginalized communities
- Environmental justice in urban planning policies
- The role of the EPA in ensuring environmental justice
- Policy analysis of the National Environmental Policy Act
- The influence of local government on environmental justice outcomes
- The role of international policy in promoting environmental justice
- Environmental justice implications of waste management policies
- The impact of zoning laws on environmental justice
- Policy solutions for addressing environmental racism
Case Studies in Environmental Justice
- Flint water crisis: A case study in environmental injustice
- The impact of Hurricane Katrina on low-income communities
- Case study of indigenous rights and environmental justice
- Environmental justice issues in the Dakota Access Pipeline project
- Case study: Environmental justice in the aftermath of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill
- The impact of industrial pollution: A case study of Cancer Alley, Louisiana
- Case study: The fight for environmental justice in the Amazon Rainforest
- The impact of mining activities on local communities: A case study
- Case study: Environmental justice and the Navajo Nation
- The Love Canal disaster: A case study in environmental injustice
Environmental Justice and Health
- The impact of environmental injustice on public health
- Correlation between air pollution and health disparities
- The impact of water pollution on marginalized communities
- Environmental racism and its impact on health outcomes
- The relationship between food deserts and environmental justice
- The health impacts of hazardous waste disposal in marginalized communities
- The correlation between environmental justice and mental health
- The impact of noise pollution on health in urban areas
- Health outcomes related to poor housing and environmental justice
- The role of occupational health in environmental justice
Environmental Justice and Climate Change
- The impact of climate change on marginalized communities
- Climate justice: Ensuring fair adaptation strategies
- The role of climate change in exacerbating environmental injustices
- The impact of sea-level rise on low-income coastal communities
- Climate change, environmental justice, and the Paris Agreement
- The role of climate justice in international climate negotiations
- The impact of extreme weather events on marginalized communities
- Climate refugees: An emerging environmental justice issue
- The intersection of climate justice and renewable energy policies
- The role of climate change in urban heat islands and environmental justice
Environmental Justice and Activism
- The role of activism in promoting environmental justice
- The environmental justice movement in the 1980s
- The impact of social media on environmental justice activism
- The role of youth activism in the environmental justice movement
- The influence of the Black Lives Matter movement on environmental justice
- The role of indigenous activism in promoting environmental justice
- Activism strategies for addressing environmental racism
- The impact of community organizing on local environmental justice outcomes
- The role of art and culture in environmental justice activism
- Activism and the fight for clean water in Flint, Michigan
Environmental Justice and Education
- The role of education in promoting environmental justice
- Environmental justice in the school curriculum
- The impact of environmental education on community awareness and action
- The role of higher education institutions in promoting environmental justice
- Environmental justice and science education
- The role of environmental education in empowering marginalized communities
- Environmental justice education programs
- The impact of environmental education on policy and legislation
- Environmental justice in environmental studies programs
- The role of experiential learning in environmental justice education
Environmental Justice and Indigenous Rights
- The impact of environmental injustice on indigenous communities
- Indigenous rights and environmental justice in the Amazon
- The role of indigenous knowledge in environmental justice
- The impact of land rights on environmental justice in indigenous communities
- The Dakota Access Pipeline and indigenous rights
- Indigenous rights and the fight against deforestation
- The impact of mining on indigenous communities and lands
- Indigenous rights in international environmental law
- The role of indigenous communities in biodiversity conservation and environmental justice
Environmental Justice and Urban Planning
- The role of urban planning in promoting or hindering environmental justice
- The impact of gentrification on environmental justice
- Urban green spaces and environmental justice
- The role of transportation planning in environmental justice
- Environmental justice in urban redevelopment projects
- The impact of housing policy on environmental justice
- Urban agriculture and environmental justice
- The role of community participation in urban planning for environmental justice
- Urban heat islands and environmental justice
- The impact of urban sprawl on environmental justice
Environmental Justice and Corporate Responsibility
- The role of corporations in promoting or hindering environmental justice
- Corporate pollution and environmental justice
- The impact of corporate social responsibility initiatives on environmental justice
- The role of the fossil fuel industry in environmental justice
- The impact of corporate lobbying on environmental justice policies
- Environmental justice and the tech industry
- The role of greenwashing in environmental justice
- Corporate accountability and environmental justice
- The impact of supply chains on environmental justice
- Environmental justice in the garment industry
Environmental Justice and International Perspectives
- Comparative analysis of environmental justice in different countries
- The role of international law in promoting environmental justice
- Environmental justice in the Global South
- The impact of globalization on environmental justice
- Environmental justice and the European Union
- The role of international organizations in promoting environmental justice
- Environmental justice in developing vs. developed countries
- The impact of international trade on environmental justice
- Environmental justice and the United Nations
- The role of international climate agreements in promoting environmental justice
In conclusion, these environmental justice research paper topics provide a broad overview of the various aspects of environmental justice. They highlight the intersectionality of environmental justice, touching on policy, health, climate change, activism, education, indigenous rights, urban planning, corporate responsibility, and international perspectives. Each topic offers a unique opportunity to delve into the complexities of environmental justice and contribute to this important field of study. Remember, the goal is not just to understand the issues but also to explore potential solutions and strategies for achieving environmental justice.
Environmental Justice Research Guide
In today’s world, environmental justice has become a crucial topic of concern for environmental scientists, policymakers, and communities around the globe. The concept of environmental justice centers on the fair distribution of environmental benefits and burdens, ensuring that all individuals, regardless of their race, socioeconomic status, or geographical location, have equal access to a clean and healthy environment. As students studying environmental science, it is vital to delve into the realm of environmental justice and explore its multifaceted dimensions. One powerful way to do so is through research papers that shed light on various aspects of environmental justice and propose solutions to the challenges faced.
This page aims to provide a comprehensive resource for students in the field of environmental science who are interested in writing research papers on environmental justice. Whether you are exploring this topic for the first time or seeking to deepen your understanding of specific issues, this page will guide you through the process of choosing compelling environmental justice research paper topics, offering expert advice on effective research methodologies, and providing insights on how to structure and write an impactful environmental justice research paper.
The field of environmental justice encompasses a broad range of topics, including but not limited to pollution disparities, environmental racism, indigenous rights, climate justice, and sustainable development. By delving into these areas, you can contribute to the growing body of knowledge surrounding environmental justice and play a role in advocating for a more equitable and sustainable world.
As environmental science students, you possess a unique opportunity to make a difference through your research. By studying environmental justice and shedding light on its complexities, you can contribute to the development of evidence-based policies, raise awareness among communities, and drive positive change. This page will serve as your guide, equipping you with the necessary tools, knowledge, and inspiration to embark on a meaningful research journey focused on environmental justice.
Throughout this page, you will find valuable resources, expert advice, and practical tips to assist you in selecting an impactful research paper topic, conducting rigorous research, and effectively communicating your findings. Additionally, we will introduce you to the writing services offered by iResearchNet, which provide expert assistance and support in crafting custom environmental justice research papers tailored to your unique requirements.
Choosing an Environmental Justice Research Topic
Choosing the right environmental justice research paper topic is a critical step in your journey to explore and address the complexities of environmental justice issues. To help you in this process, we have compiled expert advice and practical tips to guide your selection. By following these recommendations, you can ensure that your research paper tackles a relevant and impactful aspect of environmental justice. Consider the following tips:
- Identify your area of interest : Start by reflecting on your personal interests within the field of environmental justice. Consider environmental justice research paper topics that resonate with you, whether they relate to climate change, pollution, indigenous rights, urban planning, or other related areas. Engaging with a topic you are passionate about will enhance your motivation and dedication to the research process.
- Stay informed : Keep yourself updated on current environmental justice issues through reputable sources such as academic journals, policy reports, and news articles. This will help you identify emerging environmental justice research paper topics and gaps in the existing literature, allowing you to contribute new insights and perspectives.
- Narrow down your focus : Environmental justice is a broad field, so it is important to narrow down your focus to a specific aspect or dimension. This could be based on geographic location, affected communities, policy frameworks, or specific environmental challenges. A focused research question will enable you to delve deeper into the topic and provide a more comprehensive analysis.
- Conduct preliminary research : Before finalizing your research topic, conduct preliminary research to gain a better understanding of the existing literature and identify any gaps or areas that require further investigation. This will inform your research question and help you refine your topic.
- Engage with diverse perspectives : Environmental justice encompasses various social, economic, and political dimensions. Consider incorporating diverse perspectives into your research by examining different stakeholder viewpoints, marginalized communities, or international perspectives. This will provide a more comprehensive understanding of environmental justice issues.
- Consider interdisciplinary approaches : Environmental justice is inherently interdisciplinary, as it intersects with fields such as sociology, political science, economics, and law. Explore opportunities to integrate insights from different disciplines into your research to offer a holistic perspective on the topic.
- Collaborate with experts : Engage with professors, mentors, or professionals who specialize in environmental justice. Seek their guidance in refining your research topic, accessing relevant resources, and connecting with experts in the field. Collaborative discussions can provide valuable insights and help shape your research direction.
- Assess feasibility : Evaluate the feasibility of your research topic in terms of data availability, research methods, and time constraints. Ensure that you have access to relevant data sources, methodologies to analyze the data, and sufficient time to conduct your research effectively.
- Consider real-world implications : Environmental justice research should have practical implications and contribute to positive change. Assess how your research can inform policy development, influence community actions, or contribute to environmental justice movements. Aim for research that goes beyond academic exploration and has tangible impacts.
- Seek feedback : Share your research topic and ideas with peers, professors, or experts in the field. Seek their feedback and suggestions to refine your topic and ensure its relevance and significance. Incorporating multiple perspectives will strengthen the quality and impact of your research.
By considering these expert tips, you will be equipped with the necessary guidance to select a compelling and meaningful environmental justice research paper topic. Remember, the topic you choose will shape the direction and impact of your research, so invest time and thought into this crucial step. Embrace the opportunity to contribute to the ongoing dialogue on environmental justice and strive to make a positive difference in the lives of affected communities.
How to Write an Environmental Justice Research Paper
Writing an environmental justice research paper requires careful planning, organization, and a deep understanding of the subject matter. To help you navigate this process and produce a high-quality research paper, we have compiled a list of ten practical tips. By following these guidelines, you can effectively convey your ideas, analyze complex issues, and contribute to the field of environmental justice. Consider the following tips:
- Define your research question : Start by clearly defining your research question or objective. This will provide a focused direction for your paper and guide your research efforts. Ensure that your research question is specific, concise, and relevant to the field of environmental justice.
- Conduct a literature review : Before diving into your research, conduct a comprehensive literature review to familiarize yourself with the existing knowledge and research gaps in the area of environmental justice. This will help you situate your work within the broader context and identify key themes, theories, and methodologies that have been employed in previous studies.
- Gather and analyze data : Environmental justice research often involves collecting and analyzing various types of data, including quantitative data, qualitative data, and case studies. Depending on your research question, determine the most appropriate data collection methods and analytical tools to support your analysis.
- Consider ethical considerations : Environmental justice research often involves working with marginalized communities or studying sensitive environmental justice research paper topics. Take into account ethical considerations, such as informed consent, privacy, and confidentiality, when conducting research. Ensure that your research adheres to ethical guidelines and safeguards the rights and well-being of the participants.
- Adopt an interdisciplinary approach : Environmental justice issues are complex and multifaceted, requiring an interdisciplinary approach. Draw insights from various disciplines such as environmental science, sociology, law, policy studies, and economics. Integrate different perspectives to gain a holistic understanding of the issues at hand.
- Use appropriate research methodologies : Select research methodologies that align with your research question and objectives. This could include qualitative methods such as interviews, focus groups, or case studies, or quantitative methods such as surveys or statistical analysis. Justify your choice of methodology and ensure its appropriateness for your research.
- Structure your paper effectively : Organize your research paper into logical sections, including an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, analysis, and conclusion. Ensure a clear and coherent flow of ideas throughout the paper, with each section contributing to the overall argument or research objective.
- Provide critical analysis : In an environmental justice research paper, it is essential to provide critical analysis of the data and literature. Evaluate the strengths and limitations of existing studies, identify gaps in knowledge, and propose new insights or alternative approaches to addressing environmental justice issues.
- Support your arguments with evidence : Use empirical evidence, data, and scholarly sources to support your arguments and claims. Cite relevant research studies, reports, and legal documents to strengthen the credibility of your analysis. Ensure proper citation and referencing using the appropriate style guide (e.g., APA, MLA).
- Consider policy implications: Environmental justice research often has policy implications. Discuss the potential policy recommendations or interventions that arise from your findings. Consider how your research can inform decision-making processes, advocate for social justice, or contribute to the development of more equitable environmental policies.
By following these tips, you can navigate the process of writing an environmental justice research paper with confidence. Remember to maintain a clear focus, critically analyze the literature and data, and contribute new insights to the field. With careful planning and rigorous research, your paper can make a valuable contribution to the understanding and advancement of environmental justice.
Custom Research Paper Writing Services
When it comes to writing an environmental justice research paper, we understand that students may face various challenges. The intricacies of the subject, the extensive research required, and the pressure to deliver a high-quality paper can be overwhelming. That’s why iResearchNet is here to support you. Our writing services provide a convenient and reliable solution for students seeking assistance with their environmental justice research papers. By ordering a custom paper from us, you can benefit from the expertise of our degree-holding writers and ensure a well-crafted and comprehensive research paper. Here are thirteen features of our writing services that make us the ideal choice for your environmental justice research paper:
- Expert degree-holding writers : We have a team of highly qualified writers who specialize in environmental science and related fields. They possess advanced degrees and have extensive experience in conducting research and writing academic papers.
- Custom written works : Every research paper we deliver is 100% original and tailored to your specific requirements. Our writers follow your instructions and conduct in-depth research to produce a unique and customized paper.
- In-depth research : Our writers are skilled in conducting thorough research on environmental justice topics. They have access to a wide range of scholarly resources and databases, ensuring that your paper is well-researched and based on credible sources.
- Custom formatting : We adhere to different formatting styles, including APA, MLA, Chicago/Turabian, and Harvard. Our writers are familiar with these formatting guidelines and ensure that your paper meets the specified style requirements.
- Top quality : We strive for excellence in every aspect of our writing services. Our writers are committed to delivering high-quality papers that meet academic standards and demonstrate critical thinking, analytical skills, and a deep understanding of environmental justice issues.
- Customized solutions : We understand that each research paper is unique, and we tailor our services to your specific needs. Whether you require assistance with topic selection, data analysis, or literature review, we can provide customized solutions to meet your requirements.
- Flexible pricing : We offer competitive and flexible pricing options to accommodate different budgets. We understand that students often have financial constraints, and we strive to provide affordable services without compromising on quality.
- Short deadlines : We are equipped to handle tight deadlines, with the ability to deliver research papers in as little as three hours. Our writers are skilled in working efficiently without compromising on the quality and depth of research.
- Timely delivery : We understand the importance of timely submission, and we prioritize delivering your paper on time. You can rely on us to meet your deadlines and ensure that you have sufficient time to review the paper before submission.
- 24/7 support : Our customer support team is available round the clock to assist you with any queries or concerns. Whether you have questions about the ordering process or need updates on your paper, our dedicated support team is ready to help.
- Absolute privacy : We prioritize the privacy and confidentiality of our clients. Rest assured that your personal information and the details of your order will be treated with the utmost confidentiality.
- Easy order tracking : Our user-friendly platform allows you to easily track the progress of your order. You can communicate directly with your assigned writer, provide additional instructions, and stay updated on the status of your paper.
- Money-back guarantee : We are confident in the quality of our services. In the rare event that you are not satisfied with the delivered paper, we offer a money-back guarantee, ensuring your satisfaction and peace of mind.
With our comprehensive writing services, you can trust iResearchNet to deliver a custom environmental justice research paper that meets your academic requirements and exceeds your expectations. Place your order today and let our expert writers provide you with the assistance you need to excel in your studies.
Take the Next Step Towards Academic Success
Are you ready to take your environmental justice research paper to the next level? Don’t let the challenges of the writing process hold you back. Place your trust in iResearchNet’s writing services and let us help you achieve your academic goals. With our expert writers, customized solutions, and commitment to top quality, we are the ideal choice for students seeking assistance with their environmental justice research papers.
Once you’ve placed your order, we will assign a dedicated writer who specializes in environmental science and environmental justice. You will have the opportunity to communicate directly with your writer, discussing your ideas, providing additional materials, and ensuring that your paper reflects your unique perspective.
Don’t let the complexities of writing an environmental justice research paper deter you from achieving success. Place your order today and let our writing services support you in your academic journey. With iResearchNet, you can trust that your research paper will be in the hands of professionals who are dedicated to your success.
Unlock your potential and elevate your research papers with iResearchNet’s custom writing services. Order now and experience the difference we can make in your academic pursuits.
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

Much more than a world first image of radioactive cesium atoms
Thirteen years after the nuclear disaster at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP), a breakthrough in analysis has permitted a world first: direct imaging of radioactive cesium (Cs) atoms in environmental samples.
The groundbreaking analysis, completed by a team of researchers in Japan, Finland, America, and France, analyzing materials emitted from the damaged FDNPP reactors, reveals important insights into the lingering environmental and radioactive waste management challenges faced in Japan. The study, titled ""Invisible" radioactive cesium atoms revealed: Pollucite inclusion in cesium-rich microparticles (CsMPs) from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant" has just been published in the Journal of Hazardous Materials.
The Fukushima Daiichi Meltdowns: A Continuing Engineering and Environmental Puzzle
In 2011, after the Great Tōhoku Earthquake and Tsunami, 3 nuclear reactors at the FDNPP underwent meltdowns due to a loss of back-up power and cooling. Since then, extensive research efforts have focused on understanding the properties of fuel debris (the mixture of melted nuclear fuels and structural materials), found within the damaged reactors. That debris must be carefully removed and disposed of.
However, many uncertainties remain concerning the physical and chemical state of the fuel debris and this greatly complicates retrieval efforts.
Attempts to Understand the Chemistry of Radioactive Cesium Results in a World First
A significant amount of radioactive Cs was released from the damaged Fukushima Daiichi reactors in particulate form. The particles, termed Cs-rich microparticles (CsMPs), are poorly soluble, small (< 5 µm) and have a glass-like composition.
Prof. Satoshi Utsunomiya from Kyushu University, Japan, led the current study. He explained that the CsMPs "formed in the bottom of the damaged reactors during the meltdowns, when molten nuclear fuel impacted concrete."
After formation, many CsMPs were lost from the reactor containment into the surrounding environment.
Detailed characterization of CsMPs has revealed important clues about the mechanisms and extent of the meltdowns. However, despite abundant Cs in the microparticles, direct atomic scale imaging of radioactive Cs in the particles has proven impossible.
Prof. Gareth Law , a study collaborator from the University of Helsinki, explained that "this means we lack full information on the chemical form of Cs in the particles and fuel debris."
Utsunomiya continued, "whilst Cs in the particles is present at reasonably high concentrations, it is often still too low for successful atomic scale imaging using advanced electron microscopy techniques. When Cs is found at a high enough concentration, we have found that the electron beam damages the sample, rendering resulting data useless." However, in the team's previous work using a state-of-the-art high-resolution high-angle annular dark-field scanning transmission electron microscope (HR-HAADF-STEM), they found inclusions of a mineral called pollucite (a zeolite) within CsMPs. Law explained that "in past analysis we showed that the iron-rich pollucite inclusions in the CsMPs contained >20 wt.% Cs. In nature, pollucite is generally aluminum-rich.
The pollucite in the CsMPs was clearly different to that in nature indicating it formed in the reactors." Utsunomiya continued, "because we knew that most of the Cs in CsMPs is fission derived, we thought that analysis of the pollucite could yield the first ever direct images of radioactive Cs atoms."
Zeolites can become amorphous when subjected to electron beam irradiation, but that damage is related to the composition of the zeolite, and the team found that some pollucite inclusions were stable in the electron beam.
Learning this and informed by modelling, the team set about pain-staking analysis that saw Utsunomiya, graduate student Kanako Miyazaki, and the team finally image radioactive Cs atoms.
Utsunomiya explained:
"It was incredibly exciting to see the beautiful pattern of Cs atoms in the pollucite structure, where about half of the atoms in the image correspond to radioactive Cs."
He continued: "this is first time humans have directly imaged radioactive Cs atoms in an environmental sample. Finding concentrations of radioactive Cs high enough in environmental samples that would permit direct imaging is unusual and presents safety issues. Whilst it was exciting to make a scientific world first image, at the same time it's sad that this was only possible due to a nuclear accident."
More than an Imaging Breakthrough
Utsunomiya emphasized that the study's findings are broader than mere imaging of radioactive Cs atoms: "Our work sheds light on pollucite formation and the likely heterogeneity of Cs distribution within the FDNPP reactors and the environment."
Law further underscored relevance: "we unequivocally demonstrate a new Cs occurrence associated with the materials emitted from the FDNPP reactors. Finding Cs containing pollucite in CsMPs likely means it also remains in the damaged reactors; as such, its properties can now be considered in reactor decommissioning and waste management strategies."
Collaborator Emeritus Prof. Bernd Grambow from Subatech, IMT Atlantique Nantes University, added that: "we should now also begin to consider the environmental behavior or Cs-pollucite and its possible impacts. It likely behaves differently to other forms of Cs fallout documented thus far. Also,the effect on human health might have to be considered. The chemical reactivity of pollucite in the environment and in body fluids is certainly different than that of other forms of deposited radioactive Cs." Finally reflecting on the study's significance, Prof. R od Ewing from Stanford University underscored the pressing need for continued research to inform debris removal strategies and environmental remediation: "yet again, we see that the pain-staking analytical efforts of international scientists really can unlock the mysteries of nuclear accidents, aiding long-term recovery efforts."
The study, titled "Invisible radioactive cesium atoms revealed: Pollucite inclusion in cesium-rich microparticles (CsMPs) from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant," is published in the Journal of Hazardous Materials. The work was supported by bilateral funding from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science and the Research Council of Finland.
- Weapons Technology
- Nuclear Energy
- Materials Science
- Renewable Energy
- Energy and the Environment
- Environmental Science
- Hazardous Waste
- Nuclear power plant
- Chernobyl disaster
- Effects of nuclear explosions
- Radioactive waste
- Nuclear fission
- Nuclear reaction
Story Source:
Materials provided by University of Helsinki . Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Journal Reference :
- Kanako Miyazaki, Masato Takehara, Kenta Minomo, Kenji Horie, Mami Takehara, Shinya Yamasaki, Takumi Saito, Toshihiko Ohnuki, Masahide Takano, Hiroyuki Shiotsu, Hajime Iwata, Gianni F. Vettese, Mirkka P. Sarparanta, Gareth T.W. Law, Bernd Grambow, Rodney C. Ewing, Satoshi Utsunomiya. “Invisible” radioactive cesium atoms revealed: Pollucite inclusion in cesium-rich microparticles (CsMPs) from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant . Journal of Hazardous Materials , 2024; 470: 134104 DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.134104
Cite This Page :
Explore More
- High-Efficiency Photonic Integrated Circuit
- Life Expectancy May Increase by 5 Years by 2050
- Toward a Successful Vaccine for HIV
- Highly Efficient Thermoelectric Materials
- Toward Human Brain Gene Therapy
- Whale Families Learn Each Other's Vocal Style
- AI Can Answer Complex Physics Questions
- Otters Use Tools to Survive a Changing World
- Monogamy in Mice: Newly Evolved Type of Cell
- Sustainable Electronics, Doped With Air
Trending Topics
Strange & offbeat.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Topics & Ideas: Environmental Chemistry. The impact of cobalt mining on water quality and the fate of contaminants in the environment. The role of atmospheric chemistry in shaping air quality and climate change. The impact of soil chemistry on nutrient availability and plant growth in wheat monoculture.
Environmental Research Topics. Environmental Research Topics are as follows: Climate change and its impacts on ecosystems and society. The effectiveness of carbon capture and storage technology. The role of biodiversity in maintaining healthy ecosystems. The impact of human activity on soil quality. The impact of plastic pollution on marine life.
Toxic waste disposal and its impacts. Environment-related policies impact on water quality. Deforestation and its effects on soil quality. Causes and consequences of ozone layer depletion. Relationship between pollution and public health issues. A list of 200 top environmental science topics for research papers. Global warming.
2) Renewable Energy. Renewable energy is another fairly mainstream topic in which there is much to learn and research. Although scientists have identified many forms of sustainable energy, such as wind, solar, and hydroelectric power, questions remain about how to best implement these energy sources.
In 2019, the Royal Society of Chemistry published 180, 196 and 293 papers in Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts, Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology, and Environmental Science: Nano, respectively. These papers covered a wide range of topics in environmental science, from biogeochemical cycling to water reuse to ...
Whether you're majoring in environmental science or hoping to write a compelling research paper, here are some of the most interesting environmental science topics you can pursue right now. 1. Climate Change. One thing is certain: We'll always have an environment. The question is whether or not it'll be an environment we can actually live in.
This comprehensive list of environmental issues research paper topics provides a wide range of areas to choose from for your research. The topics cover major environmental issues, from climate change and air pollution to biodiversity loss and overpopulation. Each of these topics can be explored from various angles, providing a rich source of ...
This comprehensive guide on environmental research paper topics is designed to assist students and researchers in the field of environmental science. It provides a broad range of potential research topics, expert advice on selecting a topic and writing a research paper, and information about the custom writing services offered by iResearchNet.
Economic and ecological systems are closely interlinked at a global and a regional level, offering a broad variety of important research topics in environmental and resource economics. The successful identification of key challenges for current and future research supports development of novel theories, empirical applications, and appropriate policy designs. It allows establishing a future ...
Impact assessment is embedded in many national and international research rating systems. Most applications use the Research Impact Pathway to track inputs, activities, outputs and outcomes of an ...
The advent of new data acquisition and handling techniques has opened the door to alternative and more comprehensive approaches to environmental monitoring that will improve our capacity to understand and manage environmental systems. Researchers have recently begun using machine learning (ML) techniques to analyze complex environmental systems and their associated data. Herein, we provide an ...
This paper reviews the interdisciplinary collaboration between Environmental Sciences and Statistics. The usage of statistical methods as a problem-solving tool for handling environmental problems is the key element of this approach. This paper enhances a clear pavement for environmental scientists as well as quantitative researchers for their further collaborative learning with an analytical ...
•From the analysis of tens of thousands of papers the main research areas were found. •The main topics in the field are: catalysis and advanced materials, pollution and toxicity removal, biomass and bioenergy, water and wastewater treatment, and sustainability and management.
Despite a surge in research on mitigating environmental degradation and creating environmental awareness in recent past, researcher and other policmakers are still of the view that environmental destruction is on the rise, thereby calling into question the viability of these works to address the problem. This study, therefore, seeks to conduct a trend analysis to examine the knowledge gaps in ...
This paper is not a systematic literature review of a topic in environmental health (e.g., the review of air pollution effects on gynecological outcomes ) nor a review of a group of methods to address a specific research question (e.g., a review on methods to assess exposures to environmental mixtures in health studies [4•]).
This Special Issue of the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health (IJERPH) incorporates 19 articles that broaden EJ research by considering emerging topics such as energy, food, drinking water, flooding, sustainability, and gender dynamics, including issues in Canada, the UK, and Eastern Europe.
Increasing demands on ecosystems, decreasing biodiversity, and climate change are among the most pressing environmental issues of our time. As changing weather conditions are leading to increased vector-borne diseases and heat- and flood-related deaths, it is entering collective consciousness: environmental issues are human health issues. In public health, the field addressing these issues is ...
These environmental economics research paper topics cover a wide range of issues in the field of environmental economics, from policy and law to energy and agriculture. They provide a starting point for your research and can be tailored to fit your specific interests and the requirements of your assignment. Remember, choosing the right topic is ...
The bibliometric analysis allows researchers to highlight the theoretical foundations of a specific research field, identify the main findings of previous studies, and determine future research ideas. This analysis was based on bibliometric authors' citation analysis, bibliometric papers' co-citation analysis, bibliometric references' co ...
We use topic modeling to study research articles in environmental and resource economics journals in the period 2000-2019. Topic modeling based on machine learning allows us to identify and track latent topics in the literature over time and across journals, and further to study the role of different journals in different topics and the changing emphasis on topics in different journals. The ...
Introduction. Research environments matter. Environmental considerations such as robust cultures of research quality and support for researchers are thought to be the most influential predictors of research productivity.1, 2 Over 25 years ago, Bland and Ruffin1 identified 12 characteristics of research‐favourable environments in the international academic medicine literature spanning the ...
Increased interest in sustainability and related issues has led to the development of disclosed corporate information on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues. Additionally, questions have arisen about whether these disclosures affect the firm's value. Therefore, we conducted a bibliometric analysis coupled with a systematic literature review (SLR) of the current literature in ...
This page presents an extensive resource on environmental history research paper topics, catering to students navigating the fascinating and ever-evolving field of environmental history.Environmental history encompasses the study of human interaction with the environment over time, and it has emerged as an essential discipline, mirroring our growing understanding of our relationship with the ...
2.1. Research Framework. We used the deep-learning language model BERTopic to classify peatland-related studies and analyze their trends. After searching "peatland" on the academic publication data platform ScienceDirect, we collected the titles and abstracts of peatland-related papers published between 1953 and 2022.
In the face of the rapid increase of carbon emissions, climate warming, and an epidemic situation, low-carbon economy is attracting growing attention. Using bibliometric analysis and machine learning methods, the paper conducts a systematic review in the low-carbon economy. Using the Web of Science Core Collection database, 1433 articles from 1990 to 2021 were selected for review. We find that ...
By Emily Anthes. May 8, 2024. Several large-scale, human-driven changes to the planet — including climate change, the loss of biodiversity and the spread of invasive species — are making ...
1.2 Statistics Project Topics for High School Students. 1.3 Statistical Survey Topics. 1.4 Statistical Experiment Ideas. 1.5 Easy Stats Project Ideas. 1.6 Business Ideas for Statistics Project. 1.7 Socio-Economic Easy Statistics Project Ideas. 1.8 Experiment Ideas for Statistics and Analysis. 2 Conclusion: Navigating the World of Data Through ...
100 Environmental Justice Research Paper Topics. Environmental justice is a significant and dynamic field of study. It intersects with various disciplines, including law, policy, public health, urban planning, and climate science. The following comprehensive list of environmental justice research paper topics is divided into ten categories ...
Finally reflecting on the study's significance, Prof. Rod Ewing from Stanford University underscored the pressing need for continued research to inform debris removal strategies and environmental ...