
MLA 9th Edition Formatting
A Simple, Step-by-Step Guide + Free Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewer: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | July 2023
Formatting your paper in MLA style can feel like a pretty daunting task . In this post, we’ll show you exactly how to set up your paper for MLA (9th edition), as quickly and easily as possible. We’ll also share our popular free MLA template , to help you fast-track your writing.
Overview: MLA 9th Edition Formatting
- Structure and layout
- General page setup
- The opening section
- The main body
- Works cited (reference list)
- Free MLA 9 template
MLA Structure and Layout
Let’s start by looking at the overall structure of a typical student paper formatted for MLA 9th edition, before diving into the details of each section. For the most part, MLA papers follow a standardised structure, consisting of the following parts:
The opening section : While MLA doesn’t require a dedicated title page (unlike APA ), it does require an opening section that details some important information about yourself, your university and the paper itself.
The main body : The main body begins directly after the opening section on the first page. This is the “heart” of your paper and there are a very specific requirements regarding how you present and format this content.
The appendix (or appendices): While using an appendix in a student paper is relatively uncommon, you’ll place this section directly after the main body section, if required by your university.
The “Works Cited” list : This section is equivalent to what we’d usually call a references page and it’s where you’ll detail all the reference information corresponding to the in-text citations in the main body of your paper.
These four sections form the standard structure and order of a student paper using MLA 9th edition. As we mentioned, not all sections are always required , so be sure to double check what your university expects from you before submitting. Also, it’s always a good idea to ask your university if they have any style requirements in addition to the standard MLA specification.
Now that we’ve got a big-picture view of the typical paper structure, let’s look at the specific formatting requirements for each of these sections.
Generic Page Setup
Before you jump into writing up your paper, you’ll first need to set up your document to align with MLA’s generic page requirements. Alternatively, you can download our MLA paper template (which comes fully preformatted).
MLA 9th edition requires a 1-inch margin on all sides , for all pages. That said, if you’re writing a dissertation, thesis or any document that will ultimately be printed and bound, your university will likely require a larger left margin to accommodate for physical binding.
Fonts & sizing
MLA does not require that you use any specific font, but we do recommend sticking to the tried and tested , well-accepted fonts. For example, you might consider using one of the following:
- Sans serif fonts : Calibri (11), Arial (11), or Lucida Sans Unicode (10)
- Serif fonts : Times New Roman (12), Georgia (11), or Computer Modern (10)
Whichever font you opt for, be sure to use it consistently throughout your paper . Don’t chop and change, or use different fonts for different parts of the document (e.g., different fonts for the body text and the headings). Also, keep in mind that while MLA does not have a specific font requirement, your university may have its own preference or requirement. So, be sure to check with them beforehand regarding any additional specifications they may have.
In general, all text throughout your document needs to be left-aligned and should not be justified (i.e., leave an uneven right edge). You might consider using a different alignment for section headings, but in general, it’s best to keep things simple .
Line spacing
MLA 9th edition requires double line spacing throughout the document . There should also be no extra space before and after paragraphs . This applies to all sections of the paper, including the “Works Cited” page (more on this later).
Page header
Last but not least, you’ll need to set up a running header for your document. This should contain your last name, followed by the page number. Both of these should be positioned in the top right corner of all pages (even the first page). On a related note, there’s no need for you to include any footer content unless your university specifically requests it.
Now that we’ve looked at the generic formatting considerations, let’s dive into the specific requirements for each section of your paper.
The Opening Section
While MLA-formatted papers typically don’t require a title page, there are very specific requirements regarding the opening section of the first page .
Here’s how you can set your first page up for MLA 9th edition.
- On the first line, write your full name (flush left)
- On a new line, write your professor or instructor’s full name
- On a new line, write the course code and course name
- On a new line, write the full date spelt out (e.g., 15 June 2023)
- On a new line, write the full title of your paper , centre-aligned and using title case (consider using a title case converter if you’re not familiar with this)
- On a new line, begin your body content
All of the above should be in plain, unformatted font – in other words, you don’t need to apply any boldfacing, underlining , etc. That said, you should use italics whenever you’re writing out the titles of other works (for example, titles of books or articles).
To make it all a little more tangible, below is an example of a first page formatted according to the MLA specifications that we just covered.

The Main Body
While the formatting requirements for the body section are relatively light for MLA (at least when compared to APA ), there are still quite a few important things to pay attention to. Here’s what you need to know to get started.
Each of your paragraphs needs to start on a new line , and the first sentence of each paragraph requires a half-inch indent (while the rest of the paragraph is flush left aligned). Note that each paragraph simply starts on a new line and doesn’t require an additional blank line.
MLA 9th edition is fairly flexible in terms of heading formatting. There is no specified formatting, so you can decide what works best for you. However, there are still a few basic rules you need to follow:
- All your headings should be written in title case – never use all caps
- There should be no period following a heading
- Each heading level needs to be uniquely formatted and easily distinguishable from other levels (for example, a distinct difference in terms of boldfacing, underlining or italicisation)
- You can have as many heading levels as you need, but each level must have at least two instances
Abbreviations
When using abbreviations, you’ll need to make sure that you’re using the MLA version of the abbreviation . Below we’ve listed a few common ones you should be aware of:
- Appendix: app.
- Circa: c. or ca.
- Chapter: ch.
- Column: col.
- Definition: def.
- Department: dept.
- Example: e.g.
- Edition: ed.
- Figure: fig.
- Foreword: fwd.
- That is: i.e.
- Journal: jour.
- Library: lib.
- Manuscript(s): MS
- Number: no.
- Quoted in: qtd. in
- Revised: rev.
- Section: sec. or sect.
- Series: ser.
- Translation: trans.
- Version: vers.
- Variant: var.
- Volume: vol.
If you’re interested, you can find a more comprehensive list here . Alternatively, if you have access to the MLA 9th edition handbook, you can find the full list in the first appendix.

In-text citations
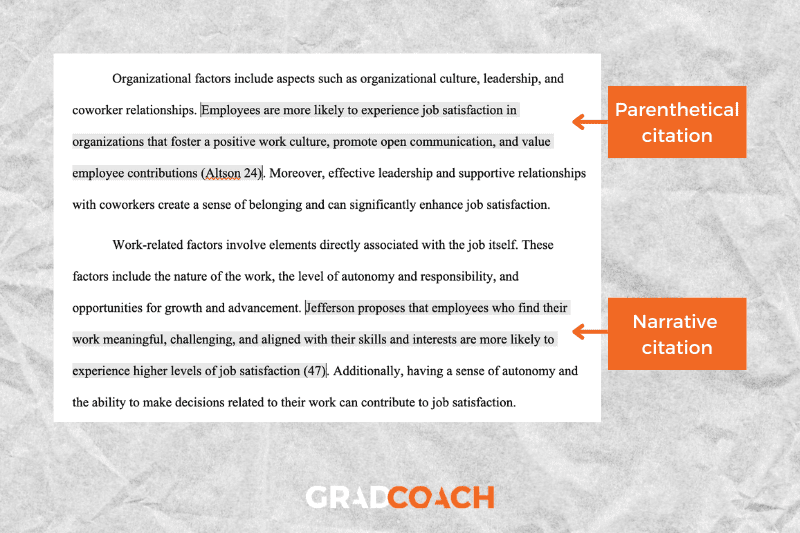
MLA 9 has a very specific set of requirements regarding how to cite your sources within the body of your paper. Here are some of the most important things to help you get started with MLA citations.
Author-page number system: in-text citations consist of (at a minimum) the lead author’s last name, followed by the page number of the paragraph you are citing. There is no comma between the two components (only a space).
Types of citations: MLA allows two types of in-text citations: parenthetical and narrative . Parenthetical citations feature the author and page number in parentheses (brackets) at the end of the respective sentence. Here’s an example:
MLA 9th edition is easy to grasp if you visit the Grad Coach blog (Jansen 13).
Narrative citations, on the other hand, weave the author’s name into the flow of the sentence and then present the publication date in parentheses at the end of the sentence. Here’s an example:
Jansen states that MLA 9th edition is easy for students to grasp if they visit the Grad Coach blog (13).
In general, it’s a good idea to utilise a mix of both in your writing. Narrative citations are particularly useful when you want to highlight or contrast authors or their viewpoints, while parenthetical citations are useful when you want to strengthen your own academic voice. In other words, both formats have their respective strengths and weaknesses, so try to use citation format strategically in your writing.
Quotations: when quoting text verbatim from a source, there is no need to do anything differently in terms of the citation itself, but do remember to wrap the verbatim text in quotation marks. Here’s an example:
Jansen proposes that MLA 9th edition is “easy to grasp if you visit the Grad Coach blog” (13).
Multiple authors: when citing resources that were authored by three or more people, you only need to list the lead author, followed by “et al.”. Here’s an example:
MLA 9th edition is easy to grasp if you visit the Grad Coach blog (Jansen et al. 13).
Below are a few more examples from our free MLA template .
Please keep in mind that this is not an exhaustive list of all the MLA 9th edition citation-related requirements – just a shortlist of the most commonly relevant ones. If you’d like to learn more, consult the MLA handbook .
The Works Cited (Reference List)
The final section that you’ll need to pay close attention to is the “Works Cited” page, which should contain a list of reference information for all the sources cited in the body of the paper. Again, MLA has a quite a meaty set of specifications regarding the content and formatting of this list, but we’ll cover the basics here to get your started on the right foot.
Basic setup
Your reference list needs to start on a new page and should be titled “Works Cited”. The title should be unformatted and centred . The reference list should then start on the next line. As with the rest of your document, you should use double line spacing throughout.
When it comes to the reference list itself, you’ll need to keep the following in mind:
- All the sources that you cited in the body of your document should feature in the reference list. Make sure that every citation is accounted for .
- The references should be ordered alphabetically , according to the lead author’s last name .
- The exact information required within each entry depends on the type of content being referenced (e.g., a journal article, web page, etc.)
- Components that may need to feature (other than the author) include the title of the source, the title of the container, other contributors, the article version or number, the publisher, the publication date, and the location.
- All references should be left-aligned and should use a hanging indent – i.e., the second line of any given reference (if it has one) should be indented a half inch.
We have to stress that these are just the basics. MLA 9th edition requires that your references be structured and formatted in a very specific way , depending on the type of resource. If you plan to draft your reference list manually, it’s important to consult your university’s style guide or the MLA manual itself. This leads us to our next point…
In general, it’s a bad idea to write your reference list manually . Given the incredibly high level of intricacy involved, it’s highly likely that you’ll make mistakes if you try to craft this section yourself. A better solution is to use (free) reference management software such as Mendeley or Zotero . Either of these will take care of the formatting and content for you, and they’ll do a much more accurate job of it too.
If you’re not familiar with any sort of reference management software, be sure to check out our easy-to-follow Mendeley explainer video below.
Wrapping Up
In this post, we’ve provided a primer covering how to format your paper according to MLA 9th edition. To recap, we’ve looked at the following:
- The structure and layout
- The general page setup
- The “Works Cited” page (reference list)
Remember to always check your university’s style guide to familiarise yourself with any additional requirements they may. Also, if your university has specified anything that contrasts what we’ve discussed here, please do follow their guidance .
If you need any help formatting your paper for MLA 9, take a look at our “done for you” language editing and proofreading service . Simply send us your document and we’ll take care of all the MLA formatting intracies on your behalf.
You Might Also Like:

Very well recounted!
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Explore our new content updates to the MLA Handbook Plus platform!
What’s New on MLA Handbook Plus ?
What is mla handbook plus .
MLA Handbook Plus is a new, subscription-based digital product providing online access to the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook. To learn more about MLA Handbook… Read More
What’s New in the Ninth Edition of the MLA Handbook (Spring 2021)
Published in April 2021, the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook works as both a textbook and a reference guide. You can order a copy… Read More
MLA Guide to Digital Literacy , 2nd Edition: An Interview with the Author
by Ellen C. Carillo
Ellen C. Carillo talks to the MLA about the MLA Guide to Digital Literacy , second edition. Read More
How do I alphabetize a works-cited-list entry that begins with a hashtag or another symbol?
The MLA recommends that writers should “ignore symbols when alphabetizing” (“How”). This includes hashtags. Thus, if an entry begins with a hashtag or another symbol,… Read More
Teaching Resources
A Century of Queer Korean Fiction : An Interview with Samuel Perry
Toward Educational Justice: An Interview with the Editors of Teaching Literature and Writing in Prisons
Henrique Maximiano Coelho Neto’s Sphinx: A Neo-Gothic Novel from Brazil : An Interview with M. Elizabeth Ginway
A Reflection on Disability Studies: Enabling the Humanities on Its Twentieth Anniversary
Teaching Claire de Duras’s Ourika
Teaching Nineteenth-Century Activist Rhetorics Today: An Interview
How and Why to Teach Late-Twentieth-Century Mexicana and Chicana Writers: An Interview
Advice from the Editors
Similar but Different: Using Compare with and Compare to
Forego versus Forgo
Was and Were with the Subjunctive
Their , There , and They’re : Learn the Difference
Attributive Nouns; or, Why There Is Sometimes No Apostrophe in Terms Such As Teachers Union
Terms for Key Concepts
Laying versus Lying
Getting to the Bottom of Principle and Principal
Ask the MLA
How do i cite a work accessed through wayback machine .
Wayback Machine is an archive of websites that lives on the Internet Archive ’s site, so you would treat the Internet Archive as the container of… Read More
How do I style the title of a fairy tale?
Fairy tales are typically enclosed in quotation marks, in the style of other short-form works. Some people may not know that Disney’s 1989 film The … Read More
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
What Is the MLA Format for an Essay?

4-minute read
- 12th October 2023
When writing academic essays, adhering to the proper formatting guidelines is crucial. One of the most widely used styles for academic writing is the Modern Language Association (MLA) format. However, MLA is more than just providing in-text citations and a Works Cited page . If you’re curious, read on.
Today’s post will explore:
● What MLA format is.
● Why it is important.
● How to correctly format essays in MLA style .
What Is MLA Format?
MLA format is a set of guidelines established by the Modern Language Association for writing and documenting research papers, essays, and scholarly articles. These guidelines provide a standardized way to structure and format academic writing, making it easier for readers to understand and engage with the content.
Why Is MLA Format Important?
MLA format serves several important purposes in academic writing:
1. Clarity and Readability
Thanks to its standardized layout and citation style, MLA ensures your essay is easy to read and comprehend.
2. Academic Integrity
Properly citing sources demonstrates academic integrity by giving credit to the original authors and avoiding plagiarism .
3. Consistency
MLA provides a consistent and uniform structure for essays, making it easier for readers and instructors to navigate your work.
4. Publication Standards
Many academic journals and publishers require submissions to follow MLA guidelines, making it crucial for researchers and authors.
How to Format Your Essay in MLA Style
Now, let’s go through step-by-step instructions to help you correctly format your essay.
1. Margins and Page Layout
● Go to the Page Layout settings in your word processor and set one-inch margins on all sides of the paper.
● Set the text to be left-aligned.
● Choose a legible 12-point font (e.g., Times New Roman or Arial).
2. Create a Title Page
● Include your name, instructor’s name, course title, and the date in the upper left-hand corner.
● Center the title of your essay, using standard capitalization (no bold, italics, or underlining).
3. Insert Header and Page Numbers
● Create a header in the upper right-hand corner with your last name and page number (e.g., Jones 1).
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
4. Use Proper Line Spacing
● Use double-spacing throughout the entire essay, including the Works Cited page.
5. In-Text Citations
● Cite sources within your essay using parenthetical citations (author’s last name and page number).
Example: We have no time to appreciate the finer things in life (Toldo 201)
● Include a Works Cited page with full bibliographic details for all cited sources.
● Ensure that in-text citations correspond to entries in the Works Cited page.
6. Works Cited Page
● You must start the list with the title Works Cited.
● List all sources used in alphabetical order by the author’s last name.
● Follow a specific format for different types of sources (books, journal articles, websites, etc.).
MLA format is essential to academic writing, ensuring clarity, consistency, and proper citation of sources. As MLA is a widely used style, you’ll have a few essays during your undergraduate years that will require you to adhere to its standards. You can confidently format your essays in MLA style, impressing your professors and maintaining academic integrity by following our guidelines in this post.
We strongly recommend proofreading your essay once it’s finished. Proofreading can be challenging, so we recommend asking our proofreading experts to review your writing . They’ll ensure perfect grammar, spelling, and punctuation. Additionally, they can check that your essay adheres to MLA standards. Consider submitting a 500-word document for free!
Happy learning and happy writing!
1. Is MLA the same as APA or Chicago Turabian?
No! MLA formatting is different from other referencing styles such as APA and Chicago Turabian. If you’re used to using APA or Chicago, you’ll have to familiarize yourself with MLA.
2. Will failing to adhere to MLA affect my essay’s grade?
If your essay is required to be in MLA format, it must adhere to the standards. You can expect the professor to deduct marks for failing to adhere to MLA.
3. Can I write References or Reference List instead of Works Cited?
The title for the list of references must be Works Cited. Again, you could lose marks for deviating from the required title.
4. How will I know if my essay needs to be in MLA?
The essay rubric will usually state the required referencing style. Otherwise, we recommend checking with your professor.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...

Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
9-minute read
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...
2-minute read
How to Cite the CDC in APA
If you’re writing about health issues, you might need to reference the Centers for Disease...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Home / MLA Sample Paper
MLA Sample Paper
Mla sample paper #1.
If you’ve been wondering how to produce a research paper that is strong in both formatting and writing, you’ve come to the right place.
Check out our first sample paper below. It is a helpful and clearly labeled visual aid to refer to. Note that while these sample papers do not include MLA abstracts , you should check with your instructor to see if an abstract should be included.
Visual Sample Paper
The example research paper below is one that was written in college for a course on the Inklings. The Inklings were a group of writers in England before WWII, including C.S. Lewis and J.R.R. Tolkien.
The abbreviated MLA paper below (linked here without annotations) is about J.R.R. Tolkien’s Lord of the Rings and how the author used myth, story, and song to link all of his works together. Tolkien is famous for creating a fantasy universe called Middle-earth, which readers can’t truly understand until they read all of the books about Middle-earth ( The Silmarillian, The Hobbit, and The Lord of the Rings ).
Since we’re here to learn how to format an essay, we’ve pointed out some important things about the paper to help you write a correctly formatted essay.
For starters, the essay is in MLA format. That means it follows the style manual of the Modern Language Association, which tells you how to format the paper itself and every source you cite. You’ll also see notes like how long a paragraph should be, how to use commas properly, and how to correctly punctuate a title. Some of these guidelines are different from those in APA format , so be sure to confirm you are using the correct style in your paper.
Pay special attention to the MLA format works cited. We only used one type of source (books), but both citations are correct according to the 9th edition of MLA, published in 2021. When you’re writing your own paper, you need to make sure you always use the most recent edition of the style manual. You’ll also want to check with your instructor to see if you need to include an MLA annotated bibliography with your paper, which contains additional information summarizing and evaluating each source after the regular citation.
Whether you need MLA, APA citations , or Chicago style notes, look up the latest edition before turning in a paper.

MLA Sample Paper #2
See below for an example paper or click below to download it as a Word Document.
The MLA header should be one inch from the top and left margins. The heading and the entire paper should be double spaced.
Eli YaffarabeProfessor Rapheor
28 August 2018
Privatization of Prisons in Texas
The privatization of governmental services has increased dramatically in the past decade as local, state, and federal agencies have searched for ways to cut costs while still meeting their mandated responsibility to provide various public services. This privatizing trend has particularly affected the criminal justice system. Since the early 1990s, privatized correctional facilities have increased significantly, nationally and statewide. This policy has far-ranging consequences not only within the criminal justice system, but as an instructive example for government officials when considering the costs and benefits of privatization as a public policy option. By 2001, thirty states, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico had privately-operated correctional facilities (Austin and Coventry 4). This movement has incited considerable debate and controversy, mainly because prison privatization calls for giving the private sector direct control over the lives of a captive human population.
Surprisingly, there has been little objective and concrete analysis of the privatization of prisons in the United States. This is probably for two reasons: first, ideological arguments on the matter have pushed out substantive research, and second, because this trend has only recently accelerated in the U.S. and mainly on a state level. However, case studies and statistics at the state level are more accessible. With capacity for over 30,000 prisoners in 43 facilities, the state of Texas has privatized more of its prison system than any state in the nation (McDonald and Patten Jr. iv).
Yaffarabe 2
Public policy concerning the criminal justice system has become more daunting and important in the last decade. The problems in the system are twofold: an overcrowding prison population, mainly due to “three strikes” legislation and reducing early parole; and the costs of operating prisons with this growing population (Austin and Coventry). According to the most recent U.S. Department of Justice survey, slightly over 2.2 million people were incarcerated in correctional facilities in this country in 2003. In comparison, in 1993, 1.37 million people were imprisoned in this country (Beck and Harrison 1).
At the same time, the growth of privately operated correctional facilities has increased significantly in this country. Private prisons now hold 95,522 inmates in this country, which is 6.5 percent of total prisoners (Beck and Harrison 5). In Texas, 16,570 inmates (10 percent of its prison population) are held in private facilities, about 10,000 more than the next highest state. Furthermore, six states had at least 25 percent of their prison population housed in private prisons, led by New Mexico (44%), Alaska (31%), and Montana (29%). These current statistics show that while state governments have been forced to manage and operate overcrowded and over-capacity prisons at considerable costs, many have turned to the private sector to operate prisons (McDonald and Patten Jr.). According to the General Accounting Office, prison operating costs have grown steadily since 1980, increasing almost 550 percent since 1980 based on inflation-adjusted dollars (Austin and Coventry 1).
Prison privatization started in the early 1980s, ostensibly to ease the burden on taxpayers by offering financial relief to private companies to run state prisons. Thomas Beasley founded Corrections Corporation of America in 1983, “the nation’s leader in the construction and management of private prisons” (Darling). That year, Corrections Corporation of America set up the first privately-operated prison in Tennessee. Since then, the number of private
Yaffarabe 3
correctional facility firms has grown to 14 (Austin and Coventry 3). The privatization of prisons occurs in two ways. First, state government can contract out (or outsource) specific services in a correctional facility to a private company after a bidding process. Second, and more radically, private companies build their own privately-managed prisons and contract with state governments to house their inmates. This latter approach, giving private correctional facility firms wide latitude over inmates, is taken in the Texas criminal justice system. In fact, many of these privately operated facilities “have no relationship at all with the state governments in these states, other than an obligation to pay corporate income taxes” (McDonald and Patten Jr. v).
(Due to its length, the remainder of this sample paper is omitted).
Yaffarabe 4
Works Cited Page
Austin, James, and Garry Coventry. Emerging Issues on Privatized Prisons . Bureau of Justice Assistance, Feb. 2001, www.ncjrs.gov/pdffiles1/bja/181249.pdf.
Beck, Allen J., and Paige Harrison. Prisoners in 2003 . Bureau of Justice Statistics, Nov. 2004, www.bjs.gov/content/pub/pdf/p03.pdf.
McDonald, Douglas, and Carl Patten Jr. Governments’ Management of Private Prisons . Abt Associates, 15 Sept. 2003, www.ncjrs.gov/pdffiles1/nij/grants/203968.pdf.
Darling, Michael. “Pitt News: University of Pittsburgh Shouldn’t Lend Its Name to Prison Privatization.” CorpWatch , 15 Nov. 2004, corpwatch.org/article/pitt-news-univeristy-pittsburgh-shouldnt-lend-its-name-prison-privatization.
MLA Formatting Guide
MLA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Sample Paper
- Works Cited
- MLA 8 Updates
- MLA 9 Updates
- View MLA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all MLA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
An in-text citation is a short citation that is placed next to the text being cited. The basic element needed for an in-text citation is the author’s name . The publication year is not required in in-text citations. Sometimes, page numbers or line numbers are also included, especially when text is quoted from the source being cited. In-text citations are mentioned in the text in two ways: as a citation in prose or a parenthetical citation.
Citation in prose
Citations in prose are incorporated into the text and act as a part of the sentence. Usually, citations in prose use the author’s full name when cited the first time in the text. Thereafter, only the surname is used. Avoid including the middle initial even if it is present in the works-cited-list entry. An example of the first citation in prose for a source with one author is given below:
Doug Barry explains the status of the UK.
Parenthetical
Parenthetical citations add only the author’s surname at the end of the sentence in parentheses. An example of a parenthetical citation is given below:
The status of the UK is explained (Barry).
Examples of in-text citations
Here are a few examples of in-text citations for works with various numbers and types of authors:
Use both the first name and surname of the author if you are mentioning the author for the first time in the prose. In subsequent occurrences, use only the author’s surname. Always use only the author’s surname in parenthetical citations.
Citation in prose:
First mention: Stephen George asserts …. (17).
Subsequent occurrences: George argues …. (17).
Parenthetical:
…. (George 17).
Two authors
Use the first name and surname of both authors if you are mentioning the work for the first time in the prose. In subsequent occurrences, use only the surnames of the two authors. Always use only the authors’ surnames in parenthetical citations. Use “and” to separate the two authors in parenthetical citations.
First mention: Kane Williams and Clark Ronald ….
Subsequent occurrences: Williams and Ronald ….
…. (Williams and Ronald).
Three or more authors
For citations in prose, use the first name and surname of the first author followed by “and others” or “and colleagues.” For parenthetical citations, use only the surname of the first author followed by “et al.”
Krishnan Sethu and colleagues…. or Krishnan Sethu and others ….
…. (Sethu et al.).
Corporate author
For citations in prose, treat the corporate author like you would treat the author’s name. For parenthetical citations, shorten the organization name to the shortest noun phrase. For example, shorten the Modern Language Association of America to Modern Language Association.
The Language Literary Association of Canada….
…. (Language Literary Association).
If there is no author for the source, use the source’s title in place of the author’s name for both citations in prose and parenthetical citations.
When you add such in-text citations, italicize the text of the title. If the source title is longer than a noun phrase, use a shortened version of the title. For example, shorten the title Fantastic Beasts and Where to Find Them to Fantastic Beasts .
Endgame explains …. (121).
…. ( Endgame 121).
In MLA style, two types of citations are used to cite a source: a short citation used within the text (called the in-text citation) and a full citation (called the works cited list entry) within the works cited list, which appears at the end of a paper.
The works cited list entry provides the complete details of a source. An in-text citation is a short citation that is placed next to the text being cited. The in-text citation lets the reader know that the information is derived from the cited source, and helps the reader find the full citation within the works cited list.
In order to properly cite a source in MLA style, you must have both citation types in your paper. Every in-text citation has a works cited list entry. Every works cited list entry has at least one (maybe more) corresponding in-text citation.
In-text citations
The basic element needed for an in-text citation is the author’s surname . The publication year is not required in in-text citations. Sometimes, page numbers or line numbers are also included, especially when text is quoted from the source being cited.
First mention: Sian Anderson studies ….
Subsequent occurrences: Anderson analyzes ….
….(Anderson)
or if quoting directly:
…(Anderson 9)
First mention: Paul Fin and Anna Gabriel ….
Subsequent occurrences: Fin and Gabriel ….
….(Fin and Gabriel)
…(Fin and Gabriel 27)
Paul Hill and colleagues…. or Paul Hill and others ….
….(Hill et al.)
…(Hill et al. 138)
Examples of works cited list entries
Below are a few examples of different types of works cited list entries. The examples given are for one author.
Steinman, Louise. The Knowing Body: Elements of Contemporary Performance and Dance . Shambhala Publications, 1986.
Journal article
Barad, K. “Nature’s Queer Performativity.” Qui Parle , vol. 19, no. 2, 2011, pp. 121–58.
Webpage of a website
Midgelow, Vida L. “Experiences and Perceptions of the Artistic Doctorate: A Survey Report.” Artistic Doctorates in Europe, 5 Feb. 2018, www.artisticdoctorates.com/2017/12/28/experiences-and-perceptions-of-the-artistic-doctorate-survey-report/ .
YouTube video
“Behind the Scenes Chili’s Baby Back Ribs Spot.” YouTube , uploaded by Alvin Chea, 11 Sept. 2017, www.youtube.com/watch?v=gTDLh7gNRYA .
MLA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started

Microsoft 365 Life Hacks > Writing > Writing an Essay in MLA Format
Writing an Essay in MLA Format
Knowing how to write a Modern Language Association—or MLA—essay is an essential part of making it through school these days. Be warned, however, that daunting little tasks await around every corner—whether it’s knowing where to set your margins, how to edit a header, the right way to format a heading, and beyond!

While we can’t write your paper for you, this guide can certainly help you understand the proper MLA format for your essay. Keep reading to learn about writing an MLA-format paper with some tips for making sure it’s done right the first time.

Get the most out of your documents with Word
Elevate your writing and collaborate with others - anywhere, anytime
What is an MLA-format essay? It’s not uncommon for associations and organizations to follow a standard format and writing style. The Associated Press (AP) and University of Chicago styles are most common in professional settings. News outlets typically prefer the AP style, while businesses and creative agencies will choose the Chicago style. Academia, on the other hand, traditionally follows APA and MLA styles. APA (not the same as AP style) comes from the American Psychological Association and is used in scholarly articles. An MLA-format essay fits the established style for citing references and formatting essays established by the Modern Language Association.
Required elements of an MLA-format paper. MLA is the preferred style when writing an essay in high school and most college settings. As with other writing styles, there are specific characteristics and items an MLA-format paper needs to include to fit the bill of the style. Every MLA-format essay must include the following:
- One-inch margins
- Double-spaced text
- Easy-to-read font (typically Times New Roman) in size 12
- New paragraphs indented 0.5 inches
- Italicized media titles (books, magazines, etc.), no underlining
- Page numbers in the header 0.5 inches from the top of the page
- Oxford comma
- Center-justified title
- Headings and subheadings
- Clearly labeled and titled tables and figures
- Parenthetical citations
In addition to the listed elements above, every MLA essay must include a Works Cited. MLA format doesn’t require a title page, but it also doesn’t deem them unnecessary, so it’s up to your professor whether you’ll need one or not. One way to take the edge off the process of writing this type of essay is to use a free template or a handy built-in tool that helps you build bibliographies and more.

Tips for meeting MLA formatting guidelines. It’s said that the devil is in the details, and it’s never truer than when it comes to MLA-format essays. The following tips are areas to pay attention to when writing your essay:
- Set your margins. Your software might be set to one-inch margins, double-spaced text, and 0.5-inch indentations by default—but you can save yourself the trouble (and a headache) later in the writing process by adjusting them before you get started. Of course, one of the best parts about using a computer to write your essay is that you can always make adjustments later.
- Straighten out your headings . One area students might miss with MLA formatting is with the title, headings, and subheadings. It’s normal to want to use bold or italicized typeface on your titles and headings to make them stand out from the rest of the text. MLA style specifically calls for them to match the rest of the text without any alterations aside from title case. A centered or left-justified heading will stand out enough from the rest of your text that it needn’t any additional adjustments.
- Understand subheadings. While primary headings aren’t to receive any special formatting, subheadings will be changed to set them apart from their headings. For example, if your heading is about mammals, you might have subheadings about land and water mammals. You can further organize your water mammals subheading into types of whales and dolphins. Using subheadings helps to organize your writing and makes it easier to consume as a reader.
- Know how to cite your work. The information you’re presenting in your essay didn’t mysteriously appear from out of the ether. You need to give credit where it’s due when writing an MLA-format paper, so you’re giving credit to the original author of your sources. You can also improve your writing credibility and avoid plagiarism. Plagiarism is one of the biggest academic offenses a student can commit and could lead to expulsion in some cases. Properly citing your work with parenthetical citations and quoting authors when necessary will help to keep you covered.
When it comes down to it, practice makes perfect. The more essays you write, the better you’ll become at writing and meeting the expectations of MLA style. Before you know it, MLA format will be second nature, and everything will fall into place.
Still having a hard time visualizing what an MLA essay looks like? Check out a sample paper so you can see first-hand how they’re formatted!
Get started with Microsoft 365
It’s the Office you know, plus the tools to help you work better together, so you can get more done—anytime, anywhere.
Topics in this article
More articles like this one.

What is independent publishing?
Avoid the hassle of shopping your book around to publishing houses. Publish your book independently and understand the benefits it provides for your as an author.

What are literary tropes?
Engage your audience with literary tropes. Learn about different types of literary tropes, like metaphors and oxymorons, to elevate your writing.

What are genre tropes?
Your favorite genres are filled with unifying tropes that can define them or are meant to be subverted.

What is literary fiction?
Define literary fiction and learn what sets it apart from genre fiction.

Everything you need to achieve more in less time
Get powerful productivity and security apps with Microsoft 365

Explore Other Categories
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Format an Essay
Last Updated: April 11, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Carrie Adkins, PhD and by wikiHow staff writer, Aly Rusciano . Carrie Adkins is the cofounder of NursingClio, an open access, peer-reviewed, collaborative blog that connects historical scholarship to current issues in gender and medicine. She completed her PhD in American History at the University of Oregon in 2013. While completing her PhD, she earned numerous competitive research grants, teaching fellowships, and writing awards. There are 11 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 87,369 times.
You’re opening your laptop to write an essay, knowing exactly what you want to write, but then it hits you—you don’t know how to format it! Using the correct format when writing an essay can help your paper look polished and professional while earning you full credit. There are 3 common essay formats—MLA, APA, and Chicago Style—and we’ll teach you the basics of properly formatting each in this article. So, before you shut your laptop in frustration, take a deep breath and keep reading because soon you’ll be formatting like a pro.
Setting Up Your Document

- If you can’t find information on the style guide you should be following, talk to your instructor after class to discuss the assignment or send them a quick email with your questions.
- If your instructor lets you pick the format of your essay, opt for the style that matches your course or degree best: MLA is best for English and humanities; APA is typically for education, psychology, and sciences; Chicago Style is common for business, history, and fine arts.

- Most word processors default to 1 inch (2.5 cm) margins.

- Do not change the font size, style, or color throughout your essay.

- Change the spacing on Google Docs by clicking on Format , and then selecting “Line spacing.”
- Click on Layout in Microsoft Word, and then click the arrow at the bottom left of the “paragraph” section.

- Using the page number function will create consecutive numbering.
- When using Chicago Style, don’t include a page number on your title page. The first page after the title page should be numbered starting at 2. [4] X Research source
- In APA format, a running heading may be required in the left-hand header. This is a maximum of 50 characters that’s the full or abbreviated version of your essay’s title. [5] X Research source

- For APA formatting, place the title in bold at the center of the page 3 to 4 lines down from the top. Insert one double-spaced line under the title and type your name. Under your name, in separate centered lines, type out the name of your school, course, instructor, and assignment due date. [6] X Research source
- For Chicago Style, set your cursor ⅓ of the way down the page, then type your title. In the very center of your page, put your name. Move your cursor ⅔ down the page, then write your course number, followed by your instructor’s name and paper due date on separate, double-spaced lines. [7] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source

- Double-space the heading like the rest of your paper.
Writing the Essay Body

- Use standard capitalization rules for your title.
- Do not underline, italicize, or put quotation marks around your title, unless you include other titles of referred texts.

- A good hook might include a quote, statistic, or rhetorical question.
- For example, you might write, “Every day in the United States, accidents caused by distracted drivers kill 9 people and injure more than 1,000 others.”

- "Action must be taken to reduce accidents caused by distracted driving, including enacting laws against texting while driving, educating the public about the risks, and giving strong punishments to offenders."
- "Although passing and enforcing new laws can be challenging, the best way to reduce accidents caused by distracted driving is to enact a law against texting, educate the public about the new law, and levy strong penalties."

- Use transitions between paragraphs so your paper flows well. For example, say, “In addition to,” “Similarly,” or “On the other hand.” [12] X Research source

- A statement of impact might be, "Every day that distracted driving goes unaddressed, another 9 families must plan a funeral."
- A call to action might read, “Fewer distracted driving accidents are possible, but only if every driver keeps their focus on the road.”
Using References

- In MLA format, citations should include the author’s last name and the page number where you found the information. If the author's name appears in the sentence, use just the page number. [14] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- For APA format, include the author’s last name and the publication year. If the author’s name appears in the sentence, use just the year. [15] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- If you don’t use parenthetical or internal citations, your instructor may accuse you of plagiarizing.

- At the bottom of the page, include the source’s information from your bibliography page next to the footnote number. [16] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- Each footnote should be numbered consecutively.

- If you’re using MLA format, this page will be titled “Works Cited.”
- In APA and Chicago Style, title the page “References.”

- If you have more than one work from the same author, list alphabetically following the title name for MLA and by earliest to latest publication year for APA and Chicago Style.
- Double-space the references page like the rest of your paper.
- Use a hanging indent of 0.5 inches (1.3 cm) if your citations are longer than one line. Press Tab to indent any lines after the first. [17] X Research source
- Citations should include (when applicable) the author(s)’s name(s), title of the work, publication date and/or year, and page numbers.
- Sites like Grammarly , EasyBib , and MyBib can help generate citations if you get stuck.
Formatting Resources

Expert Q&A
You might also like.

- ↑ https://www.une.edu.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0010/392149/WE_Formatting-your-essay.pdf
- ↑ https://content.nroc.org/DevelopmentalEnglish/unit10/Foundations/formatting-a-college-essay-mla-style.html
- ↑ https://camosun.libguides.com/Chicago-17thEd/titlePage
- ↑ https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/paper-format/page-header
- ↑ https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/paper-format/title-page
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/chicago_manual_17th_edition/cmos_formatting_and_style_guide/general_format.html
- ↑ https://www.uvu.edu/writingcenter/docs/basicessayformat.pdf
- ↑ https://www.deanza.edu/faculty/cruzmayra/basicessayformat.pdf
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_in_text_citations_the_basics.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/in_text_citations_the_basics.html
- ↑ https://library.menloschool.org/chicago
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Maansi Richard
May 8, 2019
Did this article help you?

Jan 7, 2020

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Cite your MLA source. Start by applying these MLA format guidelines to your document: Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman. Set 1 inch page margins. Use double line spacing. Include a ½" indent for new paragraphs. Include a four-line MLA heading on the first page. Center the paper's title.
In the case of a group project, list all names of the contributors, giving each name its own line in the header, followed by the remaining MLA header requirements as described below. Format the remainder of the page as requested by the instructor. In the upper left-hand corner of the first page, list your name, your instructor's name, the ...
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
MLA Formatting and Style Guide Overview of how to create MLA in-text citations and reference lists In-Text Citations ... General guidelines for referring to the works of others in your essay Works Cited Page. Resources on writing an MLA style works cited page, including citation formats. Basic Format ...
Here's how you can set your first page up for MLA 9th edition. On the first line, write your full name (flush left) On a new line, write your professor or instructor's full name. On a new line, write the course code and course name. On a new line, write the full date spelt out (e.g., 15 June 2023)
MLA research paper format requires that the entire research paper or MLA format essay includes double-spaced lines. Double-spaced lines should be found in between the written body of the work, in the heading, and also on the MLA reference page. ... It's appropriate to add lists into an MLA format essay as long as the proper rules are followed.
Get started with MLA style. Learn how to document sources, set up your paper, and improve your teaching and writing. Document Sources Works Cited Quick Guide Learn how to use the MLA format template. Digital Citation Tool Build citations with our interactive template. In-Text Citations Get help with in-text citations. Endnotes and Footnotes Read our …
Congratulations to the students whose essays were selected for the 2023 edition of Writing with MLA Style! Essays were selected as examples of excellent student writing that use MLA style for citing sources. Essays have been lightly edited. If your institution subscribes to MLA Handbook Plus, you can access annotated versions of the essays selected …
MLA Style Center, the only authorized Web site on MLA style, provides free resources on research, writing, and documentation. ... About MLA Handbook Plus; Formatting Your Research Project; Interactive Practice Template; ... Sample Essays: Writing with MLA Style; Using MLA Format; Works Cited: A Quick Guide; Teaching Resources. A Century of ...
1. Clarity and Readability. Thanks to its standardized layout and citation style, MLA ensures your essay is easy to read and comprehend. 2. Academic Integrity. Properly citing sources demonstrates academic integrity by giving credit to the original authors and avoiding plagiarism. 3. Consistency.
MLA Sample Paper #1. If you've been wondering how to produce a research paper that is strong in both formatting and writing, you've come to the right place. Check out our first sample paper below. It is a helpful and clearly labeled visual aid to refer to. Note that while these sample papers do not include MLA abstracts, you should check ...
MLA is the preferred style when writing an essay in high school and most college settings. As with other writing styles, there are specific characteristics and items an MLA-format paper needs to include to fit the bill of the style. Every MLA-format essay must include the following: One-inch margins. Double-spaced text.
To create an MLA format title page, list the following on separate lines, left-aligned at the top of the page: Then leave a few blank lines and list the title of the paper, centered and in title case, halfway down the page. All text should be double-spaced and in the same font as the rest of the paper. Note: If you're using a title page ...
MLA Handbook, or Purdue OWL. This how-to guide focuses on formatting only. There are several elements of an MLA-style document that are required for proper formatting. Essays written in MLA do not typically require a cover page, but some instructors may want one. Follow instructors' directions regarding this requirement. The basic
Like the rest of an MLA format paper, the Works Cited should be left-aligned and double-spaced with 1-inch margins. You can use our free MLA Citation Generator to create and manage your Works Cited list. Choose your source type and enter the URL, DOI or title to get started. Generate accurate MLA citations with Scribbr
If your instructor lets you pick the format of your essay, opt for the style that matches your course or degree best: MLA is best for English and humanities; APA is typically for education, psychology, and sciences; Chicago Style is common for business, history, and fine arts. 2. Set your margins to 1 inch (2.5 cm) for all style guides.
MLA General Format MLA Formatting and Style Guide; MLA In-Text Citations: The Basics; MLA Formatting Lists MLA Formatting Quotations; MLA Endnotes and Footnotes; MLA Works Cited Page: Basic Format; MLA Works Cited Page: Books; MLA Works Cited Page: Periodicals; MLA Works Cited: Electronic Sources (Web Publications) MLA Works Cited: Other Common ...
In-text citations: Author-page style. MLA format follows the author-page method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the page number (s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken must appear in the text, and a complete reference should appear on your Works Cited page. The author's name may appear either in the ...
Start the quotation on a new line, with the entire quote indented 1/2 inch from the left margin while maintaining double-spacing. Your parenthetical citation should come after the closing punctuation mark. When quoting verse, maintain original line breaks. (You should maintain double-spacing throughout your essay.)
Begin your Works Cited page on a separate page at the end of your research paper. It should have the same one-inch margins and last name, page number header as the rest of your paper. Label the page Works Cited (do not italicize the words Works Cited or put them in quotation marks) and center the words Works Cited at the top of the page.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue.