Reference management. Clean and simple.

How to write an excellent thesis conclusion [with examples]

Restate the thesis
Review or reiterate key points of your work, explain why your work is relevant, a take-away for the reader, more resources on writing thesis conclusions, frequently asked questions about writing an excellent thesis conclusion, related articles.
At this point in your writing, you have most likely finished your introduction and the body of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper . While this is a reason to celebrate, you should not underestimate the importance of your conclusion. The conclusion is the last thing that your reader will see, so it should be memorable.
A good conclusion will review the key points of the thesis and explain to the reader why the information is relevant, applicable, or related to the world as a whole. Make sure to dedicate enough of your writing time to the conclusion and do not put it off until the very last minute.
This article provides an effective technique for writing a conclusion adapted from Erika Eby’s The College Student's Guide to Writing a Good Research Paper: 101 Easy Tips & Tricks to Make Your Work Stand Out .
While the thesis introduction starts out with broad statements about the topic, and then narrows it down to the thesis statement , a thesis conclusion does the same in the opposite order.
- Restate the thesis.
- Review or reiterate key points of your work.
- Explain why your work is relevant.
- Include a core take-away message for the reader.
Tip: Don’t just copy and paste your thesis into your conclusion. Restate it in different words.
The best way to start a conclusion is simply by restating the thesis statement. That does not mean just copying and pasting it from the introduction, but putting it into different words.
You will need to change the structure and wording of it to avoid sounding repetitive. Also, be firm in your conclusion just as you were in the introduction. Try to avoid sounding apologetic by using phrases like "This paper has tried to show..."
The conclusion should address all the same parts as the thesis while making it clear that the reader has reached the end. You are telling the reader that your research is finished and what your findings are.
I have argued throughout this work that the point of critical mass for biopolitical immunity occurred during the Romantic period because of that era's unique combination of post-revolutionary politics and innovations in smallpox prevention. In particular, I demonstrated that the French Revolution and the discovery of vaccination in the 1790s triggered a reconsideration of the relationship between bodies and the state.
Tip: Try to reiterate points from your introduction in your thesis conclusion.
The next step is to review the main points of the thesis as a whole. Look back at the body of of your project and make a note of the key ideas. You can reword these ideas the same way you reworded your thesis statement and then incorporate that into the conclusion.
You can also repeat striking quotations or statistics, but do not use more than two. As the conclusion represents your own closing thoughts on the topic , it should mainly consist of your own words.
In addition, conclusions can contain recommendations to the reader or relevant questions that further the thesis. You should ask yourself:
- What you would ideally like to see your readers do in reaction to your paper?
- Do you want them to take a certain action or investigate further?
- Is there a bigger issue that your paper wants to draw attention to?
Also, try to reference your introduction in your conclusion. You have already taken a first step by restating your thesis. Now, check whether there are other key words, phrases or ideas that are mentioned in your introduction that fit into your conclusion. Connecting the introduction to the conclusion in this way will help readers feel satisfied.
I explored how Mary Wollstonecraft, in both her fiction and political writings, envisions an ideal medico-political state, and how other writers like William Wordsworth and Mary Shelley increasingly imagined the body politic literally, as an incorporated political collective made up of bodies whose immunity to political and medical ills was essential to a healthy state.
Tip: Make sure to explain why your thesis is relevant to your field of research.
Although you can encourage readers to question their opinions and reflect on your topic, do not leave loose ends. You should provide a sense of resolution and make sure your conclusion wraps up your argument. Make sure you explain why your thesis is relevant to your field of research and how your research intervenes within, or substantially revises, existing scholarly debates.
This project challenged conventional ideas about the relationship among Romanticism, medicine, and politics by reading the unfolding of Romantic literature and biopolitical immunity as mutual, co-productive processes. In doing so, this thesis revises the ways in which biopolitics has been theorized by insisting on the inherent connections between Romantic literature and the forms of biopower that characterize early modernity.
Tip: If you began your thesis with an anecdote or historical example, you may want to return to that in your conclusion.
End your conclusion with something memorable, such as:
- a call to action
- a recommendation
- a gesture towards future research
- a brief explanation of how the problem or idea you covered remains relevant
Ultimately, you want readers to feel more informed, or ready to act, as they read your conclusion.
Yet, the Romantic period is only the beginning of modern thought on immunity and biopolitics. Victorian writers, doctors, and politicians upheld the Romantic idea that a "healthy state" was a literal condition that could be achieved by combining politics and medicine, but augmented that idea through legislation and widespread public health measures. While many nineteenth-century efforts to improve citizens' health were successful, the fight against disease ultimately changed course in the twentieth century as global immunological threats such as SARS occupied public consciousness. Indeed, as subsequent public health events make apparent, biopolitical immunity persists as a viable concept for thinking about the relationship between medicine and politics in modernity.
Need more advice? Read our 5 additional tips on how to write a good thesis conclusion.
The conclusion is the last thing that your reader will see, so it should be memorable. To write a great thesis conclusion you should:
The basic content of a conclusion is to review the main points from the paper. This part represents your own closing thoughts on the topic. It should mainly consist of the outcome of the research in your own words.
The length of the conclusion will depend on the length of the whole thesis. Usually, a conclusion should be around 5-7% of the overall word count.
End your conclusion with something memorable, such as a question, warning, or call to action. Depending on the topic, you can also end with a recommendation.
In Open Access: Theses and Dissertations you can find thousands of completed works. Take a look at any of the theses or dissertations for real-life examples of conclusions that were already approved.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Degrees
- Doctoral Studies
- Theses and Dissertations
How to Restate a Thesis
Last Updated: February 27, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was reviewed by Gerald Posner . Gerald Posner is an Author & Journalist based in Miami, Florida. With over 35 years of experience, he specializes in investigative journalism, nonfiction books, and editorials. He holds a law degree from UC College of the Law, San Francisco, and a BA in Political Science from the University of California-Berkeley. He’s the author of thirteen books, including several New York Times bestsellers, the winner of the Florida Book Award for General Nonfiction, and has been a finalist for the Pulitzer Prize in History. He was also shortlisted for the Best Business Book of 2020 by the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 384,005 times.
A thesis statement serves as your paper’s (or speech’s) guiding idea, alerting readers to the main points of your paper and the direction it will take. A thesis restatement, which comes in the paper’s conclusion, is the thesis’s kindred spirit, though not its identical twin. It differs from the thesis in both word choice and sentence structure. Restating your thesis at the end of the paper allows you to remind your readers of what you have proven in your body paragraphs and helps to bring your paper to a successful close.
Working out the Restatement Basics

- Sketching out a rough conclusion (the main points you want to get across) will give you an idea of the best place for the restated thesis before you actually try your hand at writing the restatement.
- Depending on the nature of your paper or of your conclusion, you may want to open your conclusion with a question or some other kind of rhetorical device, rather than a restatement of the thesis. While writing often follows prescribed formulas (such as the 5-paragraph essay), there is no one-size-fits-all approach for writing a concluding paragraph, and you may need to try out several positions for your thesis restatement to find out what works best.

- You can use the restated thesis to provide a greater level of sophistication or emotional impact to the original argument. For example, if your initial argument was that buying pets as holiday gifts is dangerous, you might restate your thesis this way: "Remember: buying that puppy as a Christmas present might seem like a good idea at the time, but it could end in the tragedy of another homeless dog by Easter."
- You can also restate your thesis to incorporate the relationship you've built with your reader. For example, if your essay was about developing business partnerships, you could begin your restatement by saying something like, "As a businessperson...." Not only will this make your restatement different from the original, but it will also help draw connections with important elements from the essay/speech.

- For example, if you have written an essay about alcohol use on college campuses, you could revisit the "So what?" question in your conclusion by providing a statement about what that means for students and for college officials. It could look something like this: "Because alcohol abuse depends on more than just the legal drinking age, it is crucial that students be educated about how alcohol abuse occurs, and also that college officials broaden their perspective to include a greater variety of aspects."

- You may be able to use something like “In conclusion” at the end of a speech, however. Signaling or signposting words—like “in conclusion” or “next”—are very important in speeches because listeners only have one chance to follow along with what you’re saying, and these words help them to keep their place.

- Avoid saying things like, “It seems like” or “It is possible that” in the restatement. One exception would be if this conditional language is part of your original thesis statement and your paper is devoted to discussing a topic that is only a possibility, not something you are stating is definitely the case. Otherwise, maintain a level of confidence.
- While maintaining confidence is crucial to the success of your paper, it’s important to acknowledge when opposition exists and not to use absolute statements which may alienate readers. Confidence in your position and in the fact that you’ve proven your point is one thing; blind certainty in your opinion is another!
Making the Restatement Distinct from the Thesis

- You can use your word processor’s thesaurus function for this, an online thesaurus, or a good old-fashioned paper thesaurus. If you use a thesaurus, however, check your chosen word in the dictionary to ensure that you know its precise meaning. Thesauruses group words very loosely by general meaning, and there is often a significant difference in connotation between them.
- It’s not necessary to change every single word, such as prepositions (“in,” “on,” “above,” “over”) and articles (“a,” “an,” and “the”). Spend your time focusing on words/phrases that receive the most emphasis, like those that are central to the points you’re making.

- Try varying your sentences by starting with different parts of speech. For example, if you began the original thesis with a prepositional phrase, start the restatement with the subject of the sentence. For instance, if the thesis starts out “Around the turn of the nineteenth century in England, women frequently…”, you might start your restatement out with something like “Women in early nineteenth-century….”
- Another way to vary the structure is to present your points in a different order. Many thesis statements include three ideas, presented in the order in which they will be discussed in the body paragraphs. When restating, you can list the points in an alternate order.

Community Q&A
- When restating your thesis, if you find that the statement doesn’t fit your paper anymore, you’ll want to go back to the body of your paper and try to find where things went off track. You may find that you need to revise the original thesis to reflect what you actually wrote in the paper, or that parts of the body of the paper need to be revised to better suit the thesis. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
- While restating your thesis is essential to the conclusion of your paper or speech, it’s not enough. You will need to emphasize main points and, depending on the assignment/goal of the paper, you may also need to call your audience to action, discuss the implications of what you have talked about in the paper, or make predictions for the future. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
- Think of the restatement as a new, more powerful version of your thesis—you’ve written the paper and learned a lot over that process, and now you have all of this knowledge to draw on. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://wts.indiana.edu/writing-guides/writing-conclusions.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/cliches/
- ↑ https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/conclusion
- ↑ https://lsa.umich.edu/sweetland/undergraduates/writing-guides/how-do-i-write-an-intro--conclusion----body-paragraph.html
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Bob Lanchester
May 26, 2017
Did this article help you?
Madison Luoma
Mar 14, 2019
Petch Phanpha
Oct 2, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve
notifications_active To return to the old version of the website Click here
Master the Art: How to Restate a Thesis
Mastering the art of restating a thesis: your guide to academic precision, hook: unveiling the power of thesis restatement.
In academic writing, mastering how to restate a thesis effectively is paramount for leaving a lasting impact on your readers. Similar to a conductor orchestrating a symphony, skillful restatement harmonizes your ideas, ensuring clarity and resonance. Crafting an effective restatement of the thesis is akin to distilling the essence of your argument into a potent elixir—one that leaves a lasting impression on your readers. While the task may seem daunting, employing the right techniques can transform this endeavor nce of restating your thesis and explore strategies for achieving this in the thesis conclusion of your paper.
By condensing these sections, you can maintain the article’s clarity and coherence while making it more concise and reader-friendly.
The Significance of Thesis Restatement in Academic Writing
In the intricate tapestry of academic discourse, the thesis statement stands as a beacon of clarity, guiding readers through the labyrinth of your arguments. However, its significance extends beyond mere introduction; it serves as the linchpin of your entire paper, encapsulating the essence of your research or analysis. Yet, as the final crescendo approaches, the thesis deserves a moment of resplendent reaffirmation—a chance to resonate in the minds of your audience.
Overview of What the Article Will Cover
Throughout this guide, we’ll unravel the mysteries of thesis restatement, exploring its significance and providing strategies for crafting impactful restatements. From dissecting the anatomy of a thesis statement to showcasing examples and offering practical exercises, we’ll equip you with the tools necessary for academic precision. Additionally, we’ll demonstrate restate thesis example instances to illustrate effective application.
Understanding and Crafting a Strong Thesis Statement
In academic writing, a strong thesis statement serves as the cornerstone of your argument, guiding your readers through the complexities of your paper. Let’s outline the key characteristics that make a thesis statement effective:
- Specificity: A strong thesis statement is clear and precise, providing a focused direction for your paper. For example: Thesis: “The rise of social media has transformed communication, but it has also raised concerns about privacy and authenticity.”
- Debatable: An effective thesis statement presents an argument or perspective that invites discussion and analysis rather than stating an indisputable fact. For instance: Thesis: “The portrayal of female characters in classic literature reflects societal attitudes towards gender roles and expectations.”
- Evidence-Based: A robust thesis statement is supported by evidence or reasoning, demonstrating your engagement with the topic and your ability to construct a compelling argument. Consider: Thesis: “Drawing on cognitive psychology theories, this study investigates the impact of mindfulness meditation on reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression among college students.”
Restating your thesis effectively in the conclusion of your paper is crucial for reinforcing your main argument and leaving a lasting impression on your audience. But how do you restate a thesis in a way that is both impactful and memorable? Let’s explore some strategies and techniques to achieve this.
The Purpose of Restating a Thesis
In academic writing, the restatement of the thesis serves several crucial purposes. Firstly, it acts as a guiding light, illuminating the main argument and reminding readers of the paper’s central proposition. By encapsulating the main argument in a succinct and memorable manner, the restatement ensures that readers depart with a crystal-clear understanding of the writer’s intentions. Additionally, as the final act of the paper unfolds, the restatement serves as a poignant reminder of the intellectual journey that has transpired. It echoes like a refrain, drawing attention to the central theme or argument that has permeated every paragraph and citation, reinforcing its enduring relevance in the broader scholarly discourse. Lastly, the restatement strengthens the overall coherence and cohesion of the paper, binding together the various strands of thought and ensuring structural integrity.
Techniques for Effective Restatement
Crafting an effective restatement of the thesis is akin to distilling the essence of your argument into a potent elixir—one that leaves a lasting impression on your readers. While the task may seem daunting, employing the right techniques can transform this endeavor into a seamless and impactful conclusion to your academic paper. Let’s explore some key techniques for how to restate your thesis in a compelling manner:
- Summarizing Without Repetition
Avoid the temptation to simply repeat the original thesis verbatim. Instead, strive to encapsulate the main argument in a fresh and succinct manner. Consider paraphrasing the thesis statement while retaining its core essence. Focus on conveying the central idea without regurgitating the exact wording, allowing for a sense of closure while avoiding redundancy.
Example: Original Thesis: “The proliferation of social media has revolutionized communication, but it has also raised concerns about privacy and authenticity.” Restatement: “In summary, while social media has transformed how we communicate, it has also sparked debates surrounding privacy and authenticity.”
- Emphasizing Key Points
Highlighting the key points of your argument in the restatement can reinforce their significance and leave a lasting impression on your readers. Identify the main themes or findings of your paper and ensure that they are prominently featured in the restatement. This serves to underscore the importance of your argument and provides a concise recapitulation of your paper’s main contributions.
Example: Original Thesis: “The implementation of sustainable farming practices is essential for mitigating the environmental impact of agriculture and ensuring food security.” Restatement: “In conclusion, the adoption of sustainable farming methods is crucial not only for environmental preservation but also for safeguarding our global food supply.”
- Incorporating New Insights or Perspectives
While the restatement should echo the main argument of your paper, it also offers an opportunity to introduce fresh insights or perspectives that have emerged throughout your discussion. Consider how your analysis has evolved and whether there are any additional points you wish to emphasize in the conclusion. By integrating new insights into the restatement, you demonstrate the depth of your engagement with the topic and leave readers with food for thought.
Example: Original Thesis: “The portrayal of female characters in classic literature reflects societal attitudes towards gender roles and expectations.” Restatement: “In retrospect, the depiction of female characters in classic literature not only mirrors historical gender norms but also invites critical reflection on the evolution of societal perceptions of femininity and empowerment.”
Incorporating these techniques into your restatement can elevate it from a mere summary to a compelling synthesis of your paper’s main arguments. By summarizing without repetition, emphasizing key points, and incorporating new insights, you can craft a restatement that resonates with your readers and leaves a lasting impression long after they’ve finished reading.
Strategies for Crafting Impactful Restatements
Crafting an impactful restatement of the thesis requires strategic approaches tailored to the nuances of each situation. Here are concise strategies to consider:
- Analyzing the Context and Audience: Consider the broader context in which your paper exists and the expectations of your audience. Tailor your restatement to resonate with the interests and concerns of your readers, ensuring relevance and engagement within the larger scholarly discourse.
- Tailoring the Restatement to Suit Different Types of Papers: Recognize that different types of academic papers may require different approaches. While a concise summary may suffice for shorter papers, a more comprehensive restatement may be necessary for longer works. Consider the scope and complexity of your paper when determining the appropriate level of detail and nuance.
- Using Language that Reflects Confidence and Authority: Adopt a tone of confidence and conviction in your restatement. Avoid hedging or equivocation, and make declarative statements that leave no doubt about the significance of your argument and the validity of your conclusions.
By implementing these strategies, you can craft restatements that resonate with your audience, reinforce the strength of your argument, and leave a lasting impression.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid in Restating a Thesis
Crafting an effective restatement of the thesis requires finesse and attention to detail. Here are the key pitfalls to avoid and straightforward guidance on how to steer clear of them:
- Merely Repeating the Thesis Without Adding Value: Avoid simply regurgitating the original thesis statement without offering any additional insight or analysis. Expand upon the original thesis by summarizing the main argument in a fresh and engaging way. Reflect on the key points of your paper and consider their broader implications or significance to add depth and nuance to your restatement.
- Introducing New Information in the Restatement: Resist the temptation to introduce new information or ideas in the restatement of the thesis. The conclusion of your paper is not the place to unveil novel findings or introduce fresh arguments. Stick to summarizing and reinforcing the main argument, avoiding tangential topics or straying from the scope of your paper.
- Underestimating the Importance of Clarity and Coherence: Prioritize clarity and coherence in your restatement. Ensure that your restatement ties together the various threads of your argument in a cohesive and compelling manner, providing readers with a sense of closure and resolution. Avoid ambiguity or vagueness, and use language that is clear, concise, and to the point.
By avoiding these common pitfalls, you can craft restatements that enhance the clarity and impact of your paper, leaving a lasting impression on your readers.
Examples of Effective Restatements
Examining successful restatements from academic papers offers valuable insights into the strategies and techniques employed to reinforce the thesis and leave a lasting impression on the reader. Let’s deconstruct a few restate thesis example, and highlight the key elements that contribute to their effectiveness:
Example 1: Original Thesis: “The rise of social media has revolutionized communication, but it has also raised concerns about privacy and authenticity.” Restatement: “In conclusion, the transformative impact of social media on communication cannot be overstated. However, as we navigate this digital landscape, it is imperative to address the pressing issues of privacy and authenticity.” Key Elements: Synthesis of Main Points: The restatement succinctly summarizes the main argument while emphasizing the transformative nature of social media on communication. Relevance to Conclusion: It sets the stage for the conclusion by highlighting the importance of addressing privacy and authenticity in the digital age. Clarity and Conciseness: The language is clear and concise, ensuring that the restatement effectively reinforces the thesis without unnecessary repetition. Example 2: Original Thesis: “Effective leadership is essential for driving organizational success and fostering a positive work culture.” Restatement: “In summary, the role of effective leadership in shaping organizational success and cultivating a supportive work environment cannot be overstated. As we strive to navigate the complexities of the modern workplace, it is crucial to prioritize the development of strong leadership skills.” Key Elements: Emphasis on Importance: The restatement underscores the significance of effective leadership in achieving organizational goals and fostering a positive work culture. Forward-Looking Perspective: It looks to the future, urging readers to prioritize the development of leadership skills in the face of evolving workplace challenges. Elegance in Expression: The language is elegant and persuasive, enhancing the impact of the restatement and leaving a memorable impression on the reader. Example 3: Original Thesis: “The findings of this study highlight the importance of early childhood education in promoting cognitive development and academic success.” Restatement: “In conclusion, the findings of this study underscore the critical role of early childhood education in shaping cognitive development and laying the foundation for academic achievement. As we consider the implications of these findings, it is evident that investing in quality early childhood education programs is essential for the future success of our society.” Key Elements: Summarization of Findings: The restatement summarizes the key findings of the study, reinforcing the importance of early childhood education. Call to Action: It goes beyond summary to advocate for action, emphasizing the need to invest in quality early childhood education programs. Clarity and Conviction: The language is clear and persuasive, conveying a sense of urgency and conviction that resonates with the reader.
In conclusion, these examples illustrate how effective restatements reinforce the thesis, set the stage for the conclusion, and leave a lasting impression on the reader. By synthesizing main points, emphasizing importance, and using clear and persuasive language, these restatements effectively encapsulate the essence of the paper and underscore its significance in the broader context of academic discourse.
Refining Your Restatement Skills
Improving your ability to craft effective restatements requires a proactive approach and dedication to practice. Here are actionable steps and tips to refine your restatement skills:
- Seeking Feedback from Peers or Instructors: Share your restatements with peers, instructors, or mentors and solicit their input. Ask for specific feedback on clarity, coherence, and effectiveness in reinforcing the thesis. Constructive criticism can provide valuable insights and help identify areas for improvement.
- Utilizing Online Resources and Writing Centers: Take advantage of the wealth of online resources and writing centers available to support your academic writing endeavors. Many universities offer writing assistance services, including workshops, tutorials, and one-on-one consultations with writing tutors. These resources can provide guidance on structuring restatements, refining language, and enhancing overall writing proficiency.
- The Importance of Continuous Practice and Refinement: Set aside dedicated time for writing exercises focused specifically on crafting restatements. Experiment with different techniques, styles, and approaches to see what works best for you. Keep a journal or log of your restatements and reflect on your progress over time. Consistent practice will help sharpen your skills and deepen your understanding of effective restatement strategies.
By incorporating these steps and tips into your writing process, you can refine your restatement skills and enhance the clarity, coherence, and impact of your academic writing.
Mastering the art of thesis restatement is transformative, elevating academic writing to new heights of clarity and impact. As we conclude our exploration, let’s recap the significance of this vital aspect of academic discourse and its profound implications for your writing prowess.
Recap of Significance:
Restating the thesis serves as a beacon of clarity, guiding readers through the labyrinth of your arguments and reinforcing the central proposition of your paper. It provides a moment of reflection amidst the intellectual journey, offering a succinct summary of key points while underscoring their enduring relevance in the broader scholarly discourse.
Encouragement for Implementation:
To my fellow scholars, I encourage you to implement the techniques and strategies discussed with confidence and enthusiasm. By mastering thesis restatement, you’ll refine your ability to distill complex ideas into clear and persuasive arguments, leaving a lasting impression on your readers.
Emphasizing Transformative Impact:
As you incorporate these strategies into your writing process, you’ll experience a transformative impact on your academic writing prowess. Your restatements will become more concise, compelling, and impactful, resonating with clarity, coherence, and conviction.
In conclusion, the art of thesis restatement is not merely a technical skill but a powerful tool that can elevate your academic writing to new heights. Embrace it with confidence, implement the techniques learned, and watch as your papers resonate with clarity, coherence, and conviction.
- Skip to Content
- Skip to Main Navigation
- Skip to Search

Indiana University Bloomington Indiana University Bloomington IU Bloomington

- Mission, Vision, and Inclusive Language Statement
- Locations & Hours
- Undergraduate Employment
- Graduate Employment
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Newsletter Archive
- Support WTS
- Schedule an Appointment
- Online Tutoring
- Before your Appointment
- WTS Policies
- Group Tutoring
- Students Referred by Instructors
- Paid External Editing Services
- Writing Guides
- Scholarly Write-in
- Dissertation Writing Groups
- Journal Article Writing Groups
- Early Career Graduate Student Writing Workshop
- Workshops for Graduate Students
- Teaching Resources
- Syllabus Information
- Course-specific Tutoring
- Nominate a Peer Tutor
- Tutoring Feedback
- Schedule Appointment
- Campus Writing Program
Writing Tutorial Services
Writing conclusions.
Though expectations vary from one discipline to the next, the conclusion of your paper is generally a place to explore the implications of your topic or argument. In other words, the end of your paper is a place to look outward or ahead in order to explain why you made the points you did.
Writing the Conclusion
In the past, you may have been told that your conclusion should summarize what you have already said by restating your thesis and main points. It is often helpful to restate your argument in the conclusion, particularly in a longer paper, but most professors and instructors want students to go beyond simply repeating what they have already said. Restating your thesis is just a short first part of your conclusion. Make sure that you are not simply repeating yourself; your restated thesis should use new and interesting language.
After you have restated your thesis, you should not just summarize the key points of your argument. Your conclusion should offer the reader something new to think about—or, at the very least, it should offer the reader a new way of thinking about what you have said in your paper.
You can employ one of several strategies for taking your conclusion that important step further:
- Answer the question, "So what?"
- Connect to a larger theme from the course
- Complicate your claim with an outside source
- Pose a new research question as a result of your paper's findings
- Address the limitations of your argument
The strategy you employ in writing a conclusion for your paper may depend upon a number of factors:
- The conventions of the discipline in which you are writing
- The tone of your paper (whether your paper is analytical, argumentative, explanatory, etc.)
- Whether your paper is meant to be formal or informal
Choose a strategy that best maintains the flow and tone of your paper while allowing you to adequately tie together all aspects of your paper.
The Final "So what?" Strategy
Part of generating a thesis statement sometimes requires answering the "so what?" question—that is, explaining the significance of your basic assertion. When you use the "so what?" strategy to write your conclusion, you are considering what some of the implications of your argument might be beyond the points already made in your paper. This strategy allows you to leave readers with an understanding of why your argument is important in a broader context or how it can apply to a larger concept.
For example, consider a paper about alcohol abuse in universities. If the paper argues that alcohol abuse among students depends more on psychological factors than simply the availability of alcohol on campus, a "so what?" conclusion might tie together threads from the body of the paper to suggest that universities are not approaching alcohol education from the most effective perspective when they focus exclusively on limiting students' access to alcohol.
To use this strategy, ask yourself, "How does my argument affect how I approach the text or issue?"
The "Connecting to a Course Theme" Strategy
When you use the "connecting to a course theme" strategy to write your conclusion, you are establishing a connection between your paper's thesis and a larger theme or idea from the course for which you are writing your paper.
For example, consider a paper about mothers and daughters in Eudora Welty's Delta Wedding for a class called "The Inescapable South." This paper argues that a strong dependence on the mother is analogous to a strong dependence on the South. A "connecting to a course theme" conclusion for this paper might propose that Welty's daughter characters demonstrate what type of people can and cannot escape the South.
To use this strategy, ask yourself, "What is an overall theme of this course? How does my paper's thesis connect?"
The "Complicating Your Claim" Strategy
When you use the "complicating your claim" strategy to write your conclusion, you are using one or more additional resources to develop a more nuanced final thesis. Such additional resources could include a new outside source or textual evidence that seemingly contradicts your argument.
For example, consider a paper about Ireland's neutrality during World War II. This paper argues that Ireland refused to enter the war because it wanted to assert its sovereignty, not because it had no opinion about the conflict. A "complicating your claim" conclusion for this paper might provide historical evidence that Ireland did aid the Allies, suggesting that the Irish were more influenced by international diplomacy than their formal neutrality might suggest.
To use this strategy, ask yourself, "Is there any evidence against my thesis?" or "What does an outside source have to say about my thesis?"
The "Posing a New Question" Strategy
When you use the "posing a new question" strategy to write your conclusion, you are inviting the reader to consider a new idea or question that has appeared as a result of your argument.
For example, consider a paper about three versions of the folktale "Rapunzel." This paper argues that German, Italian, and Filipino versions of "Rapunzel" all vary in terms of characterization, plot development, and moral, and as a result have different themes. A "posing a new question" conclusion for this paper might ask the historical and cultural reasons for how three separate cultures developed such similar stories with such different themes.
To use this strategy, ask yourself, "What new question has developed out of my argument?"
The "Addressing Limitations" Strategy
When you use the "addressing limitations" strategy to write your conclusion, you are discussing the possible weaknesses of your argument and, thus, the fallibility of your overall conclusion. This strategy is often useful in concluding papers on scientific studies and experiments.
For example, consider a paper about an apparent correlation between religious belief and support for terrorism. An "addressing limitations" conclusion for this paper might suggest that the apparent correlation relies on the paper's definition of "terrorism" and, since the definition is not objective, the apparent correlation might have been wrongly identified.
To use this strategy, ask yourself, "In what aspects is my argument lacking? Are there circumstances in which my conclusions might be wrong?"
Polishing Your Conclusion—and Your Paper
After you've completed your conclusion, look over what you have written and consider making some small changes to promote clarity and originality:
- Unless your discipline requires them, remove obvious transitions like "in conclusion," "in summary," and "in result" from your conclusion; they get in the way of the actual substance of your conclusion.
- Consider taking a strong phrase from your conclusion and using it as the title or subtitle of your paper.
Also, be sure to proofread your conclusion carefully for errors and typos. You should double-check your entire paper for accuracy and correct spelling as well.
Produced by Writing Tutorial Services, Indiana University, Bloomington, IN
Writing Tutorial Services social media channels
- How It Works
- PhD thesis writing
- Master thesis writing
- Bachelor thesis writing
- Dissertation writing service
- Dissertation abstract writing
- Thesis proposal writing
- Thesis editing service
- Thesis proofreading service
- Thesis formatting service
- Coursework writing service
- Research paper writing service
- Architecture thesis writing
- Computer science thesis writing
- Engineering thesis writing
- History thesis writing
- MBA thesis writing
- Nursing dissertation writing
- Psychology dissertation writing
- Sociology thesis writing
- Statistics dissertation writing
- Buy dissertation online
- Write my dissertation
- Cheap thesis
- Cheap dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Pay for thesis
- Pay for dissertation
- Senior thesis
- Write my thesis
How to Restate A Thesis: Your Detailed Guide

A thesis acts as your research paper’s main pillar, guiding the readers to the key points on the paper and the direction that you took. A thesis statement comes at the introduction, but you will need to restate it in the conclusion. Notably, a lot of students find this challenging and keep asking, “How do you rephrase a thesis statement?” and “Are you supposed to reword your thesis in the conclusion paragraph?”
To help you restate thesis of your paper appropriately, we have highlighted the key steps that you should follow. Make sure to also check the examples and practice the different ways to restate a thesis until you can hack it like a pro.
What Does Restate Thesis Mean?
Before we can look at the steps involved in restating a thesis, it is important to start by asking the questions, “What does restating means?” and “How long does a thesis restate have to be?”
Restating means that you are highlighting something that you had already brought out, in this case, the “thesis of your paper.” Therefore, you are simply reminding the readers about the points that you were trying to put across in the entire paper, but without sounding repetitive. When it comes to length, there is no specific rule on it, but you should try to make it approximately the same length as the original thesis.
When you restate thesis and conclude the paper well, your work will look complete, professional and earn you a better grade.
Restate Thesis Statement: Decide Where to Position It
In most cases, college students restate the thesis at the start of their conclusion. You might also want to place it on a different section of the conclusion, other than the beginning of the conclusion. When teaching students how to restate a thesis in a conclusion, we recommend them to use the method that will make their work look unique.
For example, instead of restating the thesis as the first sentence, consider starting the conclusion with a rhetoric question followed by your restated thesis statement. Here is an example below. “Will we ever appreciate the importance of saving our rainforests? Rainforests act as the largest carbon sinks on the globe, as well as home to thousands of species, and everyone can play a role in their protection.”
Note that since there is no specific formula on how to restate a thesis statement , it is advisable to start by crafting a draft conclusion and then decide where to position it. Actually, you might consider several positions until you get the perfect spot.
How to Rephrase a Thesis: Make It to have a Deeper Impact
By the time a reader gets to the conclusion of your work, it implies that he/she has already read the entire paper and has a clear idea about your stand on the topic. Therefore, you should take advantage of this and rephrase the thesis statement to deliver a deeper level of emotional effect.
One way of driving this deeper emotional impact is addressing the reader directly, and here is an example. If you were working on a paper with a topic, such as cybersecurity for startups, a good way to start restating the thesis might be:
- “As a startup enterprise owner …”
- “To strengthen your information security as a small business owner …”
Ways to Restate a Thesis: Answer the Question, “So What?”
The stated thesis at the start of your introduction might not provide the answer to the question, “so what?” However, the restated thesis , in your conclusion, should comprehensively answer the question. The answer seeks to inform the reader about the significance of the arguments in the paper to avoid leaving him/her hanging.
For example, if your paper was talking about teenage alcohol and substance abuse, make sure to answer the question “So what?” by showing what it does to teenagers. This can be something such as this; “ Additional awareness of the dangers of substance abuse, such as alcohol, should be emphasized because teenagers are more prone and likely to give in because of peer pressure rather than the implications of substance abuse.”
Avoid Making Apologies when Rewording a Thesis
When working on the conclusion of your paper, it is prudent to be confident that you provided ample proof in the body. Therefore, as you restate the thesis, you should not make apologetic statements because they undermine your argument. Such statements, which you should avoid, include:
“It appears that …. “ “It is possible that …” “It is my opinion that …”
The only time when using such statements when restating your thesis might be okay is when the topic of discussion was simply a possibility.
Restate Thesis Statement by Varying the Tense
When writing an paper, the thesis statement at the introduction might have been done in the future tense, informing the reader what to anticipate in the rest of the paper.
For example, a paper looking at coal production might have a thesis such as this, “ I will examine the effects of using coal in Azerbaijan ….” When restating the thesis, you can change the tense, and put it in the past, so that it looks something like this, “ I evaluated the how harmful the use of coal is to the environment in Azerbaijan …”
Seek Writing Help to Restate Thesis of Your Paper
When you work on any piece of assignment, how you wrap it up, especially in the conclusion, is very important to avoid leaving your reader in suspense. In this post, we have demonstrated how to restate a thesis statement, but you should consider reading a carefully done restate thesis and practice more to hone your skills. However, if you are still finding the task a challenge, even after reading a restate thesis example, consider seeking writing help from an expert.
We have a pool of qualified writers who are ready to help you with your academic assignments, and all you have to do is ask us for help to “restate my thesis.” They know how to start a paper, write the body professionally, and restate the thesis like pros. Furthermore, our services are cheap, and you can count on our writers for quality work and top grades.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Comment * Error message
Name * Error message
Email * Error message
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
As Putin continues killing civilians, bombing kindergartens, and threatening WWIII, Ukraine fights for the world's peaceful future.
Ukraine Live Updates
- Generating Ideas
- Drafting and Revision
- Sources and Evidence
- Style and Grammar
- Specific to Creative Arts
- Specific to Humanities
- Specific to Sciences
- Specific to Social Sciences
- CVs, Résumés and Cover Letters
- Graduate School Applications
- Other Resources
- Hiatt Career Center
- University Writing Center
- Classroom Materials
- Course and Assignment Design
- UWP Instructor Resources
- Writing Intensive Requirement
- Criteria and Learning Goals
- Course Application for Instructors
- What to Know about UWS
- Teaching Resources for WI
- FAQ for Instructors
- FAQ for Students
- Journals on Writing Research and Pedagogy
- University Writing Program
- Degree Programs
- Majors and Minors
- Graduate Programs
- The Brandeis Core
- School of Arts and Sciences
- Brandeis Online
- Brandeis International Business School
- Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
- Heller School for Social Policy and Management
- Rabb School of Continuing Studies
- Precollege Programs
- Faculty and Researcher Directory
- Brandeis Library
- Academic Calendar
- Undergraduate Admissions
- Summer School
- Financial Aid
- Research that Matters
- Resources for Researchers
- Brandeis Researchers in the News
- Provost Research Grants
- Recent Awards
- Faculty Research
- Student Research
- Centers and Institutes
- Office of the Vice Provost for Research
- Office of the Provost
- Housing/Community Living
- Campus Calendar
- Student Engagement
- Clubs and Organizations
- Community Service
- Dean of Students Office
- Orientation
- Spiritual Life
- Graduate Student Affairs
- Directory of Campus Contacts
- Division of Creative Arts
- Brandeis Arts Engagement
- Rose Art Museum
- Bernstein Festival of the Creative Arts
- Theater Arts Productions
- Brandeis Concert Series
- Public Sculpture at Brandeis
- Women's Studies Research Center
- Creative Arts Award
- Our Jewish Roots
- The Framework for the Future
- Mission and Diversity Statements
- Distinguished Faculty
- Nobel Prize 2017
- Notable Alumni
- Administration
- Working at Brandeis
- Commencement
- Offices Directory
- Faculty & Staff
- Alumni & Friends
- Parents & Families
- 75th Anniversary
- New Students
- Shuttle Schedules
- Support at Brandeis
Writing Resources
Constructing effective conclusions.
This handout is available for download in DOCX format and PDF format .
Though the final paragraph in an essay is commonly referred to as the conclusion, it is not traditionally the place in which the author draws new conclusions that were not mentioned previously in the essay. Rather, the goal of an essay's conclusion is to bring the paper full circle by revisiting the large-scale ideas stated in the introduction, but with the refined perspective created by the preceding arguments in the body of the paper. Conclusions often return to the thesis—which the preceding essay has attempted to make compelling—in an attempt to briefly assess its significance in some larger context.
Conceptual Components
Revisiting the thesis.
Just as the preceding body paragraphs attempted to draw more general conclusions from specific pieces of evidence, the concluding paragraph of an essay reestablishes the essay's overall argument using the more specific claims argued in the body. Though the thesis is generally reintroduced the first sentence in the conclusion, the remainder of the paragraph should be used to ensure that this return to the thesis moves beyond simply reproducing the introduction.
Recontextualization
Just as your introduction acts as a bridge that transports your readers from their own lives into the textual space of your analysis, your conclusion provides a bridge to help your readers make the transition back to their daily lives. This is done most effectively by emphasizing a context for your ideas that makes them relevant or meaningful for your reader. In some cases, this context may be different from the one established in your conclusion, and it may push slightly beyond the boundaries of the writing prompt.
Structural Components
Evolved thesis.
Many strong conclusions restate the thesis—in different language from the introduction—in the opening sentence. This allows the concluding paragraph to establish something more than the introduction in which the thesis is usually stated near the end. Restating the paper's overall argument at the beginning of the conclusion allows for a brief exploration of your essay's context or broader implications in the final paragraph.
Motive (with a twist)
In guiding your readers out of the textual space of your paper, it is important to remind them why your arguments are significant. You don't want your readers to finish your paper thinking “so what?” To prevent this, use your conclusion to reestablish the relevance of your thesis.
Limitations
Acknowledging the limitations of your argument, while optional, can be an effective way of clarifying the scope of your thesis, particularly in an essay whose claims are rather ambitious. Acknowledging that there are questions that need further research or that your argument is unlikely to convince those who approach the topic with a different set of assumptions is also a useful strategy for bolstering your credibility.
Because an essay is but a small part of a larger discourse on its topic, it is important to describe how your conclusion may serve as a steppingstone for further research. Implicitly you are saying, "Now that I have proven the thesis of my essay, what new questions can we ask about this topic?" In a way, looking ahead to a new question does the work of the three previous components: proposing new areas of inquiry reinforces that you have proven your thesis ; showing that, with further research, your claims could have broader implications remotivates your argument; acknowledging that other questions still remain acknowledges the limitations of your central claim.
Final Thought
Since it is the last thing they will read, you want your final sentence to stick in your readers' minds. Whether you choose to end with emphasis, wit, or wonder, your final sentence should be in some way memorable without departing significantly from the overall tone of your essay.
Credit: University Writing Program, Brandeis University, 2020.
- Resources for Students
- Writing Intensive Instructor Resources
- Research and Pedagogy
- Buy Custom Assignment
- Custom College Papers
- Buy Dissertation
- Buy Research Papers
- Buy Custom Term Papers
- Cheap Custom Term Papers
- Custom Courseworks
- Custom Thesis Papers
- Custom Expository Essays
- Custom Plagiarism Check
- Cheap Custom Essay
- Custom Argumentative Essays
- Custom Case Study
- Custom Annotated Bibliography
- Custom Book Report
- How It Works
- +1 (888) 398 0091
- Essay Samples
- Essay Topics
- Research Topics
- Writing Tips
How to Restate Your Thesis: 5 Strategies
November 22, 2023
Examining the Purpose of Restating Your Thesis
Restating your thesis in the conclusion of your essay serves a vital purpose in reinforcing the main argument and leaving a lasting impact on your readers. This section will explore the significance of restating your thesis and why it is not merely a repetitive exercise.
- Reinforcement: Restating your thesis reaffirms the central idea of your essay. By reasserting your main argument, you emphasize its importance and remind readers of the key point you want them to remember.
- Summarization: Restating your thesis allows you to summarize the main points and evidence presented in your essay. It provides a succinct overview that helps consolidate the information and reinforce your main argument.
- Closure: Restating your thesis brings a sense of closure to your essay. It signals to the reader that you have reached the end of your discussion and allows for a satisfying and cohesive conclusion.
- Lasting Impact: By restating your thesis effectively, you can leave a lasting impression on your readers. It helps solidify your argument in their minds and prompts them to reflect upon the ideas presented long after reading your essay.
In the following sections, we will explore various strategies and examples to help you master the art of restating your thesis in a compelling and impactful way.
5 Strategies for Effective Restatement of Your Thesis
Restating your thesis effectively requires more than simply repeating your thesis statement. Instead, it involves summarizing your main points and findings while communicating the overall significance of the argument.
Summarize Your Main Points
Summarizing your main points is a crucial step in restating your thesis effectively. It allows you to remind your readers of the key arguments, evidence, and examples presented in your essay. Here are some strategies to help you summarize your main points:
- Identify the main points: Review your essay and identify the main arguments or supporting points that you have made. These are the key ideas that contribute to your overall thesis.
- Condense the information: Take each main point and condense it into a concise statement that captures its essence. Avoid going into too much detail or providing new information. Focus on the core message of each point.
- Use bullet points or numbered lists: If applicable, present your main points as a list. This can help readers grasp the key arguments quickly and easily. Bullet points or numbered lists also create a visual break in the text, making it more reader-friendly.
- Order your main points strategically: Arrange your main points in a logical order that reinforces the flow of your essay. Consider prioritizing the most impactful or strongest evidence first.
- Avoid repetition: While summarizing your main points, be mindful of avoiding repetition. Restate each point in a way that adds value and emphasizes its significance without redundantly restating the exact same information.
By effectively summarizing your main points, you provide a concise overview of your essay’s key arguments and reinforce the foundation of your thesis.
Paraphrase Your Thesis Statement
Paraphrasing your thesis statement is an essential aspect of restating your thesis effectively. It involves expressing the main idea of your essay in a different way, using different words and sentence structures. Here are some strategies to help you paraphrase your thesis statement:
Change the sentence structure: Instead of using the same sentence structure as your original thesis statement, try rearranging the words and sentence structure to create a fresh and engaging restatement.
Example: Original thesis: “Climate change is a global problem that requires immediate action.” Paraphrased restatement: “Urgent measures are necessary to address the worldwide issue of climate change.”
Use synonyms and alternative words: Replace specific terms in your thesis statement with synonyms or related words. This not only helps avoid repetition but also adds depth and clarity to your restatement.
Example: Original thesis: “Education is crucial for societal progress.” Paraphrased restatement: “The advancement of societies heavily relies on the importance of education.”
Maintain the core message: While paraphrasing your thesis statement, ensure that the main idea or message remains intact. The restatement should still convey the central argument of your essay.
Example: Original thesis: “The government should implement stricter regulations on the usage of plastic to reduce environmental pollution.” Paraphrased restatement: “To combat environmental pollution, it is imperative for the government to enforce more stringent regulations regarding plastic consumption.”
By effectively paraphrasing your thesis statement, you provide a fresh perspective on your argument while staying true to the core message of your essay.
Connect Your Thesis to a Larger Idea or Context
Connecting your thesis to a larger idea or context helps emphasize the broader significance of your argument. It allows readers to understand the relevance and implications of your thesis statement in a broader context. Here are some strategies to help you connect your thesis to a larger idea or context:
Highlight the broader impact: Discuss how your thesis statement relates to a larger societal, cultural, or academic issue. Explain why understanding or addressing your thesis statement is essential in the larger scheme of things.
Example: Original thesis: “The portrayal of women in media perpetuates harmful stereotypes.” Restatement connected to a larger context: “Challenging the portrayal of women in media is an integral part of the ongoing fight for gender equality and empowering women.”
Provide historical or current examples: Demonstrate how your thesis statement connects to historical events, current affairs, or prominent figures. This highlights the relevance of your argument in a larger and recognizable context.
Example: Original thesis: “Corruption undermines the integrity of democratic systems.” Restatement connected to a larger context: “Throughout history, instances of corruption have been notorious for eroding trust in democratic institutions and fostering public disillusionment.”
Discuss the wider implications: Analyze the consequences or wider implications of your thesis statement beyond the scope of your essay. This helps readers understand the significance of your argument and its potential impact.
Example: Original thesis: “Automation in the workforce necessitates the need for reskilling and upskilling.” Restatement connected to a larger context: “The rapid advancement of automation technology not only requires individuals to adapt and acquire new skills but also poses significant challenges for educational institutions and policymakers in preparing the workforce of the future.”
By connecting your thesis to a larger idea or context, you demonstrate the broader relevance and impact of your argument, providing a deeper understanding for your readers.
Adding New Information or Ideas
While restating your thesis, you may want to introduce new information or ideas that support or expand upon your original argument. This can help enrich your restatement and provide further insight for your readers. Here are some strategies to add new information or ideas when restating your thesis:
- Present additional evidence: Introduce new evidence or examples that strengthen your argument and support your thesis statement. This shows that your original thesis is well-founded and backed by solid evidence.
- Include relevant statistics or research findings: Incorporate relevant statistics or research findings that further validate your thesis statement. This adds credibility and demonstrates a deep understanding of your topic.
- Discuss alternative perspectives: Address counterarguments or opposing viewpoints and explain how your thesis statement still holds strong despite these alternatives. This showcases critical thinking and strengthens the overall persuasiveness of your argument.
- Propose future implications or areas for further exploration: Suggest possible future developments or areas for further research and analysis related to your thesis statement. This expands the scope of your argument and encourages further engagement with the topic.
- Connect to current events or trends: Relate your thesis statement to ongoing current events or emerging trends. By highlighting the relevance of your argument to contemporary issues, you make your restatement more relatable and impactful.
Remember to integrate new information or ideas seamlessly into your restatement, ensuring they enhance and build upon your original thesis in a cohesive and logical manner.
Changing the Stance of Your Thesis
Sometimes, it can be effective to restate your thesis by presenting a different perspective or changing the stance of your original argument. This adds complexity and nuance to your restatement, engaging readers with a fresh viewpoint. Here are some strategies for changing the stance of your thesis:
- Acknowledge counterarguments: Address opposing viewpoints or critiques of your original thesis statement. Show that you have considered alternative perspectives and are open to a balanced discussion.
- Present a different angle: Introduce a related but contrasting aspect of your topic. This allows you to present a new interpretation or highlight a lesser-known aspect, challenging conventional thinking.
- Offer a qualified stance: Adjust the certainty or absoluteness of your thesis statement. Use words and phrases like “it is probable,” “it is likely,” or “there may be exceptions” to indicate a more nuanced or conditional stance.
- Explore the limitations: Discuss the limitations or constraints of your original thesis statement. This demonstrates critical thinking and an understanding of the complexities involved in your topic.
By changing the stance of your thesis, you demonstrate intellectual flexibility and engage readers with a thought-provoking restatement that encourages further exploration and discussion.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Restating Your Thesis
Restating a thesis statement is a crucial step in effectively summarizing your main argument and reinforcing its significance. However, there are some common mistakes that should be avoided in order to maintain clarity and coherence. Here are some pitfalls to steer clear of when restating your thesis:
- Repetition of the exact same words: While restating your thesis, strive to express the main idea using different words and sentence structures. Repetition can make your restatement sound monotonous and redundant.
- Adding new information or ideas: Remember that restating your thesis is about summarizing and reaffirming your original argument, rather than introducing new information or ideas. Avoid incorporating unrelated or irrelevant content in your restatement.
- Changing the meaning of your thesis: Ensure that the restatement maintains the same core message or main argument as your original thesis statement. Avoid altering the meaning or taking a completely different stance without proper justification.
- Being too vague or general: Avoid being overly broad or generic when restating your thesis. Aim to provide a concise and specific restatement that accurately captures the main focus of your essay.
- Not addressing the main points of your essay: Your restatement should reflect the key points and supporting arguments discussed in your essay. Neglecting to encompass these important elements can weaken the overall effectiveness of your restatement.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can successfully restate your thesis statement in a manner that reinforces your main argument while maintaining clarity and coherence.
Sociology Research Topics Ideas
Importance of Computer in Nursing Practice Essay
History Research Paper Topics For Students
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy. We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related emails.
Latest Articles
In today’s digital era, the fusion of artificial intelligence (AI) with academic writing has revolutionized how students approach essay composition....
Using Artificial Intelligence (AI) in education is changing how things are taught and learned in standard ways. With its ability...
The advancement of artificial intelligence has made it increasingly common for essays and articles to be written by AI. But...
I want to feel as happy, as your customers do, so I'd better order now
We use cookies on our website to give you the most relevant experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits. By clicking “Accept All”, you consent to the use of ALL the cookies. However, you may visit "Cookie Settings" to provide a controlled consent.

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Writing a Paper: Conclusions
Writing a conclusion.
A conclusion is an important part of the paper; it provides closure for the reader while reminding the reader of the contents and importance of the paper. It accomplishes this by stepping back from the specifics in order to view the bigger picture of the document. In other words, it is reminding the reader of the main argument. For most course papers, it is usually one paragraph that simply and succinctly restates the main ideas and arguments, pulling everything together to help clarify the thesis of the paper. A conclusion does not introduce new ideas; instead, it should clarify the intent and importance of the paper. It can also suggest possible future research on the topic.
An Easy Checklist for Writing a Conclusion
It is important to remind the reader of the thesis of the paper so he is reminded of the argument and solutions you proposed.
Think of the main points as puzzle pieces, and the conclusion is where they all fit together to create a bigger picture. The reader should walk away with the bigger picture in mind.
Make sure that the paper places its findings in the context of real social change.
Make sure the reader has a distinct sense that the paper has come to an end. It is important to not leave the reader hanging. (You don’t want her to have flip-the-page syndrome, where the reader turns the page, expecting the paper to continue. The paper should naturally come to an end.)
No new ideas should be introduced in the conclusion. It is simply a review of the material that is already present in the paper. The only new idea would be the suggesting of a direction for future research.
Conclusion Example
As addressed in my analysis of recent research, the advantages of a later starting time for high school students significantly outweigh the disadvantages. A later starting time would allow teens more time to sleep--something that is important for their physical and mental health--and ultimately improve their academic performance and behavior. The added transportation costs that result from this change can be absorbed through energy savings. The beneficial effects on the students’ academic performance and behavior validate this decision, but its effect on student motivation is still unknown. I would encourage an in-depth look at the reactions of students to such a change. This sort of study would help determine the actual effects of a later start time on the time management and sleep habits of students.
Related Webinar
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Thesis Statements
- Next Page: Writer's Block
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.

How to Restate a Thesis Statement: Examples & Tips
What is the most important part of any essay or research paper? Of course, it’s the thesis statement —a sentence that expresses the paper’s main idea and guides the readers through your arguments.
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!
But where do you place the thesis? You’ve probably answered, “in the introduction.” However, that’s not all of it—you also need to restate the thesis statement in the conclusion. Moreover, it should be paraphrased using a more diverse vocabulary.

If you’re unsure about how to restate a thesis, this article by Custom-Writing.org will be helpful for you. Here, you will find:
- various rephrasing strategies,
- a step-by-step guide,
- the most actionable thesis restatement tips.
- ✍️ Thesis Restatement Definition
- ✅ Step-By-Step Guide
- 💡 Rephrasing Strategies
- 📋 Example Sentences
- 🖼️ How to Reframe
- ✨ Bonus Tips
🔍 References
✍️ what is a restated thesis.
A restated thesis is a reworded and restructured version of the original statement. It is presented in a conclusion or any other part of the essay requiring a recap of the paper’s main idea. It shouldn’t repeat the thesis statement word for word: instead, it’s better to focus on its content.
Why Restating Your Thesis Is Necessary
For a solid, effective academic work, a restated thesis in a conclusion is a must. Here’s why:
- A restated thesis helps reintroduce your central argument, thus enhancing its perceived significance.
- A correctly restated main claim makes the transition to the implications smoother.
- A paraphrased thesis restatement signals the readers about the wrap-up of your paper.
✅ How to Restate a Thesis Step by Step
Now, let’s dwell on the restatement process in more detail. We recommend you follow the steps we described below. It will help you make your paraphrased thesis effective without undermining your persuasive arguments.
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour
💡 How to Rephrase a Thesis: Different Strategies
You can approach the restatement of thesis in several ways. Here are the best strategies that will make your argument effective and easily understood.

How to Restate a Claim by Substituting Synonyms
English is a language rich in synonyms, so you’ll hardly experience any trouble finding suitable substitutes for the words you’ve used in the original thesis. You can also try out an online reword generator or thesis statement maker to get different versions of your central claim.
For instance, imagine that this is your thesis:
People of color have achieved pronounced success in the fight for their civil rights and equality in the USA over the last century,
You may experiment with synonyms as freely as you want. Here are some variants:
- The 20-century civil rights movement gave many rights and freedoms to the minorities in the United States.
- The situation with racial equality improved significantly over the past 100 years, giving racial minorities a strong voice in American society.
Restating Your Thesis by Altering the Sentence Structure
The syntax is also a rich source of inspiration for thesis changes. If the original statement is compound, divide it into several shorter sentences. If you’ve used several simple sentences in the first version, consider combining them into one longer statement.
Receive a plagiarism-free paper tailored to your instructions. Cut 15% off your first order!
Here is an example of altering the thesis’ structure without changing the main points:
In the original version, we started by focusing on diabetes. In the reworded thesis, we presented the numbers as the first piece of data. This way, we’re directing the reader’s attention to the gravity of the problem.
How to Restate Your Thesis by Changing the Tense
In most cases, the original thesis statement uses future or present tense. It helps to inform the readers about what they are about to read. For instance, it can start with an introductory phrase:
I will argue that homework should be canceled to give students more free time and ease the burden of high school studies.
In this example, the thesis statement is written in the present tense. It links to the general statistics of time students spend on their homework. You can transform this statement into a past-tense sentence in the conclusion, showing that your argument has been proven.
The presented evidence showed that students benefited from homework cancellation and had more quality time for their hobbies and relaxation.
Restating a Thesis by Shortening or Lengthening It
The length of your thesis statement also matters. You may present it in a shorter way at the beginning of your paper, focusing only on the gist of your research question. Later on, once the arguments are laid out and explained in detail, you can present a more extended version of the initially formulated problem.
Get an originally-written paper according to your instructions!
In this restates thesis example, we have extended the original idea, explaining what “assigned seating” and “school bullying” mean. This way, the reworded version could embrace the evidence discussed in the argumentative essay’s body.
Restating a Thesis by Linking It to the Research Problem
The strategy we’re about to describe is suitable for use in research paper writing. You will need to tie the thesis statement to the problem you’ve outlined in the introduction, linking it to the issue you’re examining.
For instance, in an essay on child obesity in the USA, you can restate the thesis as follows:
Although preventive healthcare has witnessed much advancement in the past decade, evidence proves that child obesity is still on the rise, with alarming annual increase rates.
📋 How to Restate a Thesis: Example Sentences
Now, let’s examine how to rephrase a sentence in practice. Have a look at these examples:
Example # 1
Here, we expanded the thesis statement by making it longer and adding some details.
Here, we have changed the sentence structure by switching the first and second parts. The first example focuses on the legalization of marijuana, while the second version starts by mentioning the rising rates of teenage weed consumption.
In this example, we’ve changed the thesis statement’s tense from future to past, showing how an intention transformed into a completed task.
🖼️ How to Reframe a Reworded Thesis?
Once you’ve approached the conclusion paragraph of your work, it’s time to think about reframing your main claim. It’s important not to duplicate the introductory thesis because its role in the final section is different. Here are some workable reframing suggestions:
- Reword the original thesis and put it at the beginning of your conclusion. It will bring the focus back to your initial research purpose.
- Enumerate the central claims you’ve focused on. They can be compiled from topic sentences used in the body paragraphs.
- After restating the thesis, you can dwell on the broader significance of the problem you’ve examined. Make a logically related call to action based on the cited evidence. You can also mention your study’s limitations and clarify what additional research is needed.
✨ Bonus Thesis Statement Tips
Now, it’s time to give you a bonus for careful reading: our tried-and-tested tips for good thesis rewriting. Check them out:
As you can see, rephrasing a thesis statement requires effort. Using extensive vocabulary and syntax will help you restructure the content and retain its meaning. And, of course, make sure to follow our tips!
Further reading:
- Best Thesis Statement Examples with Expert Comments
- How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper: Examples & Tips
- How to Write a 5-Paragraph Essay: Outline, Examples, & Writing Steps
- What Are the 5 Different Types of Essays? A Complete Guide
❓ How to Restate Thesis in Conclusion FAQs
Restatement of your thesis involves restructuring and changing the vocabulary originally used in the introduction. However, the altered thesis should preserve your work’s meaning and central message.
You will typically need a reworded thesis in a conclusion paragraph. This part of your essay or research paper should wrap up everything you’ve said and summarize your claims in different words.
When composing your essay conclusion paragraph, it is vital to reword your thesis statement initially presented in the introduction. This strategy will help you make the conclusion sound non-redundant while preserving the original main idea.
When restating the claim, you do the same work as when you reword the thesis. You need to change the wording and syntax while preserving the overall meaning of the original claim.
A good example is as follows: “children should wear uniforms at school.” The reworded thesis would contain the same meaning rephrased in your own words: “Uniforms are recommended for all students.”
- Writing the Conclusion: Indiana University Bloomington
- Writing Introductory and Concluding Paragraphs: University of Minnesota
- How to Restate a Thesis Statement: Classroom: Synonym
- Writing a Paper: Conclusions: Walden University
- Conclusions: Purdue University
- Ending the Essay: Conclusions: Harvard University
- Thesis Statements: University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

If you’re a student, you’ve heard about a formal essay: a factual, research-based paper written in 3rd person. Most students have to produce dozens of them during their educational career. Writing a formal essay may not be the easiest task. But fear not: our custom-writing team is here to guide...

Rhetorical analysis is never a simple task. This essay type requires you to analyze rhetorical devices in a text and review them from different perspectives. Such an assignment can be a part of an AP Lang exam or a college home task. Either way, you will need a solid outline...

Narrative essays are unlike anything you wrote throughout your academic career. Instead of writing a formal paper, you need to tell a story. Familiar elements such as evidence and arguments are replaced with exposition and character development. The importance of writing an outline for an essay like this is hard...

Discourse is the way people talk about any specific topic. It’s also the way in which language is used to convey social and historical meanings. Discourse analysis is the process that helps to understand the underlying message of what is being said. Sounds interesting? Keep reading to learn more. This in...

A précis is a brief synopsis of a written piece. It is used to summarize and analyze a text’s main points. If you need to write a précis for a research paper or the AP Lang exam, you’ve come to the right place. In this comprehensive guide by Custom-Writing.org, you’ll...

A synthesis essay requires you to work with multiple sources. You combine the information gathered from them to present a well-rounded argument on a topic. Are you looking for the ultimate guide on synthesis essay writing? You’ve come to the right place! In this guide by our custom writing team,...

Do you know how to make your essay stand out? One of the easiest ways is to start your introduction with a catchy hook. A hook is a phrase or a sentence that helps to grab the reader’s attention. After reading this article by Custom-Writing.org, you will be able to...

A critical analysis essay is an academic paper that requires a thorough examination of theoretical concepts and ideas. It includes a comparison of facts, differentiation between evidence and argument, and identification of biases. Crafting a good paper can be a daunting experience, but it will be much easier if you...

Critical thinking is the process of evaluating and analyzing information. People who use it in everyday life are open to different opinions. They rely on reason and logic when making conclusions about certain issues. A critical thinking essay shows how your thoughts change as you research your topic. This type...

Process analysis is an explanation of how something works or happens. Want to know more? Read the following article prepared by our custom writing specialists and learn about: process analysis and its typesa process analysis outline tipsfree examples and other tips that might be helpful for your college assignment So,...

A visual analysis essay is an academic paper type that history and art students often deal with. It consists of a detailed description of an image or object. It can also include an interpretation or an argument that is supported by visual evidence. In this article, our custom writing experts...

Want to know how to write a reflection paper for college or school? To do that, you need to connect your personal experiences with theoretical knowledge. Usually, students are asked to reflect on a documentary, a text, or their experience. Sometimes one needs to write a paper about a lesson...

Get Started
Take the first step and invest in your future.

Online Programs
Offering flexibility & convenience in 51 online degrees & programs.

Prairie Stars
Featuring 15 intercollegiate NCAA Div II athletic teams.

Find your Fit
UIS has over 85 student and 10 greek life organizations, and many volunteer opportunities.

Arts & Culture
Celebrating the arts to create rich cultural experiences on campus.

Give Like a Star
Your generosity helps fuel fundraising for scholarships, programs and new initiatives.

Bragging Rights
UIS was listed No. 1 in Illinois and No. 3 in the Midwest in 2023 rankings.
- Quick links Applicants & Students Important Apps & Links Alumni Faculty and Staff Community Admissions How to Apply Cost & Aid Tuition Calculator Registrar Orientation Visit Campus Academics Register for Class Programs of Study Online Degrees & Programs Graduate Education International Student Services Study Away Student Support Bookstore UIS Life Dining Diversity & Inclusion Get Involved Health & Wellness COVID-19 United in Safety Residence Life Student Life Programs UIS Connection Important Apps UIS Mobile App Advise U Canvas myUIS i-card Balance Pay My Bill - UIS Bursar Self-Service Email Resources Bookstore Box Information Technology Services Library Orbit Policies Webtools Get Connected Area Information Calendar Campus Recreation Departments & Programs (A-Z) Parking UIS Newsroom The Observer Connect & Get Involved Update your Info Alumni Events Alumni Networks & Groups Volunteer Opportunities Alumni Board News & Publications Featured Alumni Alumni News UIS Alumni Magazine Resources Order your Transcripts Give Back Alumni Programs Career Development Services & Support Accessibility Services Campus Services Campus Police Facilities & Services Registrar Faculty & Staff Resources Website Project Request Web Services Training & Tools Academic Impressions Career Connect CSA Reporting Cybersecurity Training Faculty Research FERPA Training Website Login Campus Resources Newsroom Campus Calendar Campus Maps i-Card Human Resources Public Relations Webtools Arts & Events UIS Performing Arts Center Visual Arts Gallery Event Calendar Sangamon Experience Center for Lincoln Studies ECCE Speaker Series Community Engagement Center for State Policy and Leadership Illinois Innocence Project Innovate Springfield Central IL Nonprofit Resource Center NPR Illinois Community Resources Child Protection Training Academy Office of Electronic Media University Archives/IRAD Institute for Illinois Public Finance
Request Info

Conclusions

- Request Info Request info for.... Undergraduate/Graduate Online Study Away Continuing & Professional Education International Student Services General Inquiries
Some say the conclusion is the most difficult section of the paper to write because it’s hard to come up with something else to say after you’ve covered your main points. But imagine meeting someone without saying good bye or having a gourmet meal without the joy of a fine dessert. Having an anticlimactic conclusion, or no conclusion at all, brings forth that same lame effect in your paper.
The conclusion is the section in the paper where everything comes together as one; it is where all the ideas join together to query, agitate, and persuade. With a strong conclusion, the audience will be certain your paper has a well-meaning purpose, and that it wasn’t just a cluster of ideas put together loosely. The conclusion is perhaps the most important part of your paper, and the one your reader will ponder about the most.
Keep in Mind
- Restate your thesis statement but do not repeat it verbatim
- Relate the ideas in the text to the actual world and how these will affect our future
- Pose questions and point at areas of exploration to encourage more research and scrutiny on behalf of other researchers
- Tell your reader why the points of view you just expressed in your work are not only necessary to expose, but also, why these are so important to discuss
- Remind the reader of the course of action to be taken after reading the paper
- Compose your conclusion so that it is in balance to the rest of your paper – it should be similar in length to your introduction.
NOTE: It is important that you write an entirely new paragraph for your conclusion. Do not simply copy and paste your introduction and change a few words here and there. You need to adequately summarize what is in your paper to give closure to your argument, and what is in your introduction probably doesn’t provide that closure. Remember that a conclusion serves a separate purpose.
Below, we have included a sample prompt with its introduction, followed by one unsuccessful and one successful conclusion. Read on to see how these examples can inform your approach to conclusions the next time you have to write a paper!
Instructions
Evaluate the role of genre in selling European films to British audiences since 2000. Answer with reference to ONE or MORE of the films studied in this course.
Introduction
While there are several components one must consider when evaluating whether to sell a European film to British audiences, the genre of a film plays a significant role since a movie with strong ties to a particular genre will theoretically be easier to market than those with multiple genres. Many distributors will choose one genre and focus on those traits during the advertising campaign. This can clearly be seen with Good Bye Lenin (2003); UGC Cinemas focused on the comedic aspect and left out the drama initially to draw in more audiences. According to the UK Film Council, Good Bye Lenin was categorized in two genres: comedy and drama. Despite UGC Cinemas executing its focus on comedy, both genres for this film played a role in selling this film to viewers: comedy played an important role for distributors to sell the film through the trailer, drama was more thoroughly explored through the reviews, and by the time the film was sold on DVD, both the dramatic and comedic elements were represented on the DVD cover to bridge the gap identified between the trailer and reviews.
Unsuccessful Conclusion
As previously stated, there are many different components to think about when considering which European film to sell to British audiences, and genre remains a critical factor in selling these films. With Good Bye Lenin , UGC Cinemas may have initially focused on the comedic genre, but later, when it became apparent the dramatic was more thoroughly explored through the reviews, elements of the dramatic and comedic were well represented on the DVD cover, which all shows genre has a vital role in determining how to market film to British audiences.
Why is this conclusion unsuccessful?
- If you compare the language from the introduction, you can see there are many similar word constructions and phrases. This conclusion was likely copied and pasted from the introduction.
- The conclusion does not encourage action, further thought, and does not apply knowledge to a real world situation.
- This conclusion does not leave the reader with something new to think about; it simply restates ideas.
- When comparing the introduction and this conclusion, the conclusion is much shorter than the introduction, hinting that balance may be off.
Successful Conclusion
According to the UK Film Council’s website, in 2003, 106 out of 426 films released were sorted as being a comedy as its primary genre while only 18 out of those 106 films were listed as only comedy without any other genres. Given this information, having multiple genres along with comedy is extremely common. However, the practice of only focusing on one particular genre when advertising a movie can potentially limit the audiences that distributors are drawing in. With films like Good Bye Lenin, it can come as surprise to audiences who viewed the trailer to go to a theater and watch a more dramatic film than they previously anticipated. Nowadays, blending genres has become a common practice in film and literature. Audiences are interested in films and books with multiple genres, and distributors may benefit from portraying both genres in their trailers like they did with Good Bye Lenin ’s DVD cover. For now, especially with foreign language films, we can expect one genre to be more highly advertised than another if the film features more than one genre. However, by looking up reviews of the film, one can gain a more accurate perception of the film’s genre, even if the reviews are more likely to cast a negative light on the film.
Why is this conclusion successful?
- This conclusion offers a potential problem, avenues for further exploration, and a temporary solution.
- The conclusion opens with new and relevant information.
- When comparing the introduction and this conclusion, the two paragraphs seem to be more balanced.
- Contains real world context.
UK Film Council. “2003 UK Genre List.” British Film Institute , 22 Feb. 2012, http://industry.bfi.org.uk/genre
How can I restate a thesis statement effectively?

This is the second of three chapters about Thesis Restatements . To complete this reader, read each chapter carefully and then unlock and complete our materials to check your understanding.
– Introduce four tips for writing effective thesis restatements
– Explore the four elements of a thesis restatement
– Provide guidance on restating a thesis restatement using paraphrasing techniques
Chapter 1: Why are concluding thesis restatements important?
Chapter 2: How can I restate a thesis statement effectively?
Chapter 3: Can I see example academic thesis restatements?
Before you begin reading...
- video and audio texts
- knowledge checks and quizzes
- skills practices, tasks and assignments
In Chapter 1 of this short reader we introduced the basic elements of a concluding paragraph and compared the introductory thesis statement with the concluding thesis restatement . In Chapter 2, we next attempt to deconstruct and reconstruct some example thesis restatements to exemplify how these elements can be written most effectively. This exemplification can be broken down into four tips. Continue reading to learn about how to apply these simple tips to your own writing.
Tip 1: Include the Elements
As was mentioned at the end of Chapter 1, there are four key elements that build a thesis statement – and these same elements can be used to build thesis restatements too. The first is the inclusion of task language. The task language provided in the table below works to inform the reader of both the format of the assignment ( essay , dissertation , etc) and its type ( discuss , evaluate , etc.). From this information, an experienced reader should then be able to predict the likely structure of the essay based on their experience:
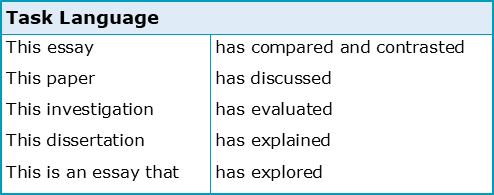
The second and third aspects are usually constructed from the topic of the essay and its key arguments. While the topic is simple as it’s often taken directly from the essay question, the writer’s key arguments are somewhat more complex as they’re drawn from the body-paragraph main ideas – as outlined in the essay’s topic sentences . As can be seen in the following table, however, these aspects are straightforward enough to write once the body section is complete (a thesis restatement should not be written before this stage):

When writing a thesis restatement, students should also remember to provide their main ideas in the same order as presented in the body section of their essay, also including stance (writer opinion) as the fourth element wherever required:
Tip 2: Paraphrase the Thesis Statement
While it’s important that the meaning of the original thesis is restated by the writer in the concluding paragraph , this doesn’t mean that precisely the same words should be used. In fact, doing so might appear lazy or repetitive to the reader. Instead, writers should use a wide variety of techniques to help them restate their thesis in different words and linguistic structures.

The most helpful techniques are listed for students below:
- alter the grammar
- alter the sentence structure
- change the order of information
- change the word order
- modify the word forms
- use antonyms and synonyms

Students should remember, of course, that it’s not necessary to paraphrase every word. Names, collocates and subject-specific words should be maintained, as can small grammatical words such as prepositions and determiners .
Tip 3: Be Specific and Concise
An effective thesis restatement should always be specific and concise . Specificity is critical as being vague will only confuse your reader or lead them to believe that you’re as unsure about your topic as they are. Likewise, overwritten text may be tiring for the reader and will use up your limited word count . To see this in action, take a look at the two example thesis restatements below and see why example A has the best balance of specificity and concision:

Tip 4: Edit Carefully
Finally, remember to check every aspect of your essay carefully for grammar and spelling errors before submission, including your concluding thesis restatement. Should a reader spot too many errors in your writing, their confidence in your argumentation will be reduced (and so too may your grade).
To reference this reader:
Academic Marker (2022) Thesis Restatements . Available at: https://academicmarker.com/essay-writing/concluding-paragraphs/thesis-restatements/ (Accessed: Date Month Year).
- Harvard University Writing Center
- University of North Carolina Writing Center
- University of New England
Downloadables
Once you’ve completed all three chapters in this short reader about Thesis Restatements , you might then wish to download our Chapter Worksheets to check your progress or print for your students. These professional PDF worksheets can be easily accessed for only a few Academic Marks .
Chapter 1 explores the topic: Why are concluding thesis restatements important? Our Chapter 1 Worksheet (containing guidance, activities and answer keys) can be accessed here at the click of a button.
Chapter 2 explores the topic: How can I restate a thesis statement effectively? Our Chapter 2 Worksheet (containing guidance, activities and answer keys) can be accessed here at the click of a button.
Chapter 3 explores the topic: Can I see example academic thesis restatements? Our Chapter 3 Worksheet (containing guidance, activities and answer keys) can be accessed here at the click of a button.
To save yourself 2 Marks , click on the button below to gain unlimited access to all of our Thesis Restatements Chapter Worksheets. This All-in-1 Pack includes every chapter, activity and answer key related to this topic in one handy and professional PDF.
Collect Academic Marks
- 100 Marks for joining
- 25 Marks for daily e-learning
- 100-200 for feedback/testimonials
- 100-500 for referring your colleages/friends
Thesis Conclusion: Making Your Research Paper Outstanding
A thesis conclusion summarizes your dissertation and highlights the scope for further research. Learn what it is and how to write it.
Imagine yourself in a cooking competition and you made a delightful gourmet dish, all your efforts blended in with the spices and the aroma spreading around the kitchen. You beam with pride that you made the best dish of your life but fail to recognize that you haven’t presented it well and your opponents win the competition. It’s because in the end, not only the dish, even the presentation matters for you to stand out from the crowd.
A thesis conclusion is something similar to that where a researcher summarizes his work and puts in references for future studies. It is the ending note or a type of presentation, like our above example, that is really important as this distinguishes an average research paper from an outstanding one.
In this article, we are going to learn about the thesis conclusion , how to write it, examples of a good thesis conclusion, and things to avoid while writing one.
What exactly is meant by Thesis Conclusion?
A thesis conclusion, which summarizes the findings and offers suggestions for further research, is an important part of a research report. It is a chance for the author to make an impact on the reader and highlight the importance of their research.
The most important facts should be highlighted in a well-structured, succinct conclusion. Along with addressing the study’s shortcomings and outlining its wider implications, the thesis conclusion should also offer doable and realistic recommendations for further research.
Good conclusions avoid typical errors including overgeneralizing, repeating information and introducing new information. They should be distinct and clear in their writing, utilize powerful and persuasive language, and make the conclusion stand out.
Though writing a thesis conclusion is a daunting task, it is an essential part of your research as the conclusion is where you bring together all the fine threads of research work that you did for your paper, and presenting it in a unique yet simple manner is where the challenge lies. Therefore, it is important for every researcher to know the prominence of a thesis conclusion and how to write an effective one.
How long should a Thesis Conclusion be?
The length of a thesis conclusion can vary from researcher to researcher but basically, it depends on the discipline, the detailed requirements of the written thesis, and the content that has to be included in order to make it stand apart. However, as a general guideline, a thesis conclusion should be about 5-10% of the total word count of the thesis. For example, if your thesis is 10,000 words long, your conclusion should be around 500-1000 words.
It’s important to keep in mind that the conclusion should be crisp and should solely focus on summarizing and interpreting the key findings and contributions of the research rather than focusing on the word count and extending it unnecessarily.
It’s also essential to check with your academic supervisor or department chief to know the guidelines that are being followed at your University to see if they have specific requirements or recommendations for the length of the conclusion.
Things to Avoid in the Thesis Conclusion
When writing a thesis conclusion, it’s important to avoid certain mistakes that one may tend to make which can impact your overall work. Here are some things to avoid in your thesis conclusion:
New Information
Don’t introduce new information that hasn’t been discussed in the main body of your thesis. The conclusion should summarize and reiterate the main points of your thesis, not introduce new ones.
Unsubstantiated Claims
Avoid making statements that can’t be backed up with evidence from your research. Your conclusion should be based on the findings and analysis presented in your thesis.
Avoid Generalizations
Be specific in your conclusions and avoid making broad generalizations that aren’t supported by your research. Your conclusion should reflect the nuances and complexities of your research.
Avoid Personal Opinions
Your thesis should be based on the objectives of the research and its analysis, so avoid injecting your personal opinions into the conclusion.
No Apologies
Don’t apologize for any shortcomings or limitations of your research. Instead, focus on the strengths and contributions of your work.
While it’s important to summarize your key findings and conclusions, avoid simply repeating what you’ve already said in the main body of your thesis. Instead, highlight the main takeaways and implications of your research.
Make sure your conclusions are clear and unambiguous. Avoid using vague or imprecise language that can be interpreted in different ways.
6 Steps to Write an Effective Thesis
Composing a thesis conclusion is an essential step in the research process. It should include a final assessment of your work and a summary of the key aspects of your research. The procedures for writing a thesis conclusion are as follows:
- Restate the thesis: Reinforce your thesis at the beginning of your conclusion. This will serve to remind your reader of the key point or inquiry you were trying to answer.
- Summarize your research points: Briefly summarize your research’s primary ideas by writing a few phrases. The main conclusions, findings, or justifications from your thesis should be included here.
- Interpreting the outcomes: In light of your research question and thesis statement, interpret the findings of your study. Describe what your study adds to the field and its consequences.
- Discuss the study limitations: Distinguish any limitations you may be aware of. Recognize any problems or restrictions in your research and offer solutions for future research.
- Make suggestions: Based on your findings, suggest more research or policy implications. Describe how your research can advance the industry and impact daily practice.
- Finish with a powerful statement: Make a strong remark at the end of your conclusion to highlight the importance of your study. This can be a concluding thought or a call to action that leaves an impact on your reader.
Examples of Thesis Conclusion:
Here are a few examples of thesis conclusions to help give you an idea of what they might look like:
In conclusion, our study has shown that there is a direct link between physical activity and better mental health in people. The findings suggest that regular exercise can enhance general well-being by easing the symptoms of anxiety and despair. However, much more research is needed in this area to understand the mechanisms underlying this link completely. Future research should concentrate on examining the long-term impact of physical activity on mental health and creating efficient treatments for those with mental health problems.
To summarize, this thesis investigated the connection between teenage females’ use of social media and body image dissatisfaction. The results indicate that being exposed to idealized photos on social media may have a negative effect on one’s perception of one’s physique, resulting in higher degrees of discontent and lower levels of self-esteem. It’s crucial to remember that social media can also be a potent instrument for encouraging a good perception of one’s body and self-acceptance. Future studies should concentrate on discovering efficient social media marketing tactics that will encourage body positivity and lessen detrimental effects on body image.
In conclusion, this study determined whether mindfulness-based therapies could help college students with their stress and anxiety symptoms. The findings imply that mindfulness training can be useful for this population’s stress management and mental health enhancement. Future research should concentrate on examining the long-term impacts of mindfulness instruction and coming up with solutions to increase the accessibility of these interventions for individuals who need them.
These are some of the examples of thesis conclusions made using the steps mentioned above. These examples help you frame an appropriate thesis conclusion and present it in a way that justifies the research.
On an endnote, crafting a thesis conclusion includes giving your research findings serious thought, reflecting critically on your own work, and summarizing your main ideas in a clear, straightforward manner. These components will help you create an engaging conclusion that will leave a long-lasting impression on your reader.
Make scientifically accurate infographics in minutes
As a scientist, you might be in a plight to amplify your research work and make it presentable for your readers. But did you know, not just the depth of your research and data can work wonders? Readers love to visualize the content and skim through the concepts and this can be made possible when you sign up for Mind the Graph. The library of scientifically accurate science figures is present across topics and can be accessed in minutes, enriching the quality of your research paper.

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual communication in science.
Unlock Your Creativity
Create infographics, presentations and other scientifically-accurate designs without hassle — absolutely free for 7 days!
About Sowjanya Pedada
Sowjanya is a passionate writer and an avid reader. She holds MBA in Agribusiness Management and now is working as a content writer. She loves to play with words and hopes to make a difference in the world through her writings. Apart from writing, she is interested in reading fiction novels and doing craftwork. She also loves to travel and explore different cuisines and spend time with her family and friends.
Content tags
English Studies
This website is dedicated to English Literature, Literary Criticism, Literary Theory, English Language and its teaching and learning.
Restate Your Thesis Statement
Restating your thesis means repeating your claim or repeating your position. It serves several purposes.
Why Restate Your Thesis in the Conclusion of the Essay?
Table of Contents
Restate your thesis means repeating your claim or repeating your position. It serves several purposes as given below.
- Recapitulation of the Central Argument : Restating the thesis or main idea in the conclusion .
- Reiteration of the Key Point : Summarizing the main point or argument and emphasizing its significance.
- Final Emphasis on the Thesis : Reinforcing the main idea or thesis to leave a lasting impression on the reader.
- Reaffirmation of the Core Message : Reiterating the central message or theme explored throughout the paper.
- Closure with a Thesis Reminder : Reminding the reader of the thesis statement to provide a sense of closure.
- Highlighting the Central Claim : Drawing attention to the primary claim made in the essay or research paper.
- Reemphasizing the Main Idea : Restating the main concept or idea to reinforce its importance.
- Revisiting the Thesis Statement : Returning to the original thesis statement to restate it in a concise manner.
- Recapping the Main Argument : Summarizing the main argument made in the body of the paper.
- Restating the Core Proposition : Paraphrasing the central proposition or hypothesis in the conclusion.
Examples of Restate Your Thesis Statement in the Conclusion
Process to restate thesis statement step by step.
- Review Your Thesis Statement : Before you can restate your thesis, make sure you clearly understand what your thesis statement is. Go back to your introduction and read the original thesis statement carefully.
- Avoid Repetition : Your goal is to restate your thesis, not just repeat it verbatim. You should use different words and phrasing while retaining the original meaning. This shows your ability to reiterate your point in a fresh way.
- Summarize Your Main Points : In the body of your essay or paper, you’ve likely presented supporting arguments or evidence. Briefly summarize these main points. This will help contextualize your thesis restatement and remind the reader of the evidence you’ve presented.
- Synthesize Your Argument : Once you’ve summarized your main points, bring them together to reinforce your thesis. Explain how these points collectively support your thesis statement. This helps tie your entire argument together.
- Use Transition Phrases : To smoothly transition into your thesis restatement, use transitional phrases such as “In conclusion,” “To sum up,” or “In summary.” These signal to the reader that you’re wrapping up your argument.
- Rephrase Your Thesis Statement : Now, restate your thesis statement using different words and phrasing. Make it clear and concise. Avoid introducing new ideas or arguments at this point. You’re simply reemphasizing your main point.
- Highlight the Significance : After restating your thesis, briefly mention why it’s important or what it means in the broader context of your topic. This helps the reader understand the significance of your argument.
- Leave a Lasting Impression : Craft your thesis restatement in a way that leaves a strong impression on the reader. You want them to remember your main point after they’ve finished reading.
- Avoid New Information : Resist the urge to introduce new information or arguments in your conclusion. Your conclusion should recap what you’ve already discussed, not introduce new ideas.
- Proofread and Revise : Like any other part of your paper, your thesis restatement should be free of grammatical errors and typos. Take a moment to proofread and make any necessary revisions.
- Check for Coherence : Ensure that your thesis restatement flows logically from the points you’ve summarized. It should feel like a natural conclusion to your essay or paper.
- Consider Your Audience : Think about your target audience and the overall tone of your paper. Tailor your thesis restatement to match the tone and style of your writing.
- Practice Conciseness : Keep your restated thesis statement concise and to the point. You don’t need to repeat all the details; just focus on the core message.
- End with a Thoughtful Closing Sentence : After restating your thesis, end your conclusion with a closing sentence that provides a sense of closure and finality to your essay or paper.
Remember that the purpose of restating your thesis is to remind the reader of your main argument and leave them with a clear understanding of your position. It should tie everything together and leave a strong impression.
Suggested Readings
- Graff, Gerald, and Cathy Birkenstein. They Say / I Say : The Moves That Matter in Academic Writing. 4th ed., W.W. Norton & Company, 2018.
- Langan, John. College Writing Skills with Readings . 9th ed., McGraw-Hill Education, 2017.
- Ramage, John D. et al. The Allyn & Bacon Guide to Writing . 8th ed., Pearson, 2016.
- Strunk Jr., William, and E.B. White. The Elements of Style . 4th ed., Longman, 1999.
Related posts:
- Essay Type-3
- Background Information
- Informative Thesis Statement
- Reflective Essay: How to Write it
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

An Overview of the Writing Process
Thesis statements, what this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can discover or refine one for your draft.
Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper .
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:.
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence somewhere in your first paragraph that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I get a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis,” a basic or main idea, an argument that you think you can support with evidence but that may need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following:
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question.
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough?
Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is, “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s o.k. to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on 19th-century America, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: Compare and contrast the reasons why the North and South fought the Civil War. You turn on the computer and type out the following:
The North and South fought the Civil War for many reasons, some of which were the same and some different.
This weak thesis restates the question without providing any additional information. You will expand on this new information in the body of the essay, but it is important that the reader know where you are heading. A reader of this weak thesis might think, “What reasons? How are they the same? How are they different?” Ask yourself these same questions and begin to compare Northern and Southern attitudes (perhaps you first think, “The South believed slavery was right, and the North thought slavery was wrong”). Now, push your comparison toward an interpretation—why did one side think slavery was right and the other side think it was wrong? You look again at the evidence, and you decide that you are going to argue that the North believed slavery was immoral while the South believed it upheld the Southern way of life. You write:
While both sides fought the Civil War over the issue of slavery, the North fought for moral reasons while the South fought to preserve its own institutions.
Now you have a working thesis! Included in this working thesis is a reason for the war and some idea of how the two sides disagreed over this reason. As you write the essay, you will probably begin to characterize these differences more precisely, and your working thesis may start to seem too vague. Maybe you decide that both sides fought for moral reasons, and that they just focused on different moral issues. You end up revising the working thesis into a final thesis that really captures the argument in your paper:
While both Northerners and Southerners believed they fought against tyranny and oppression, Northerners focused on the oppression of slaves while Southerners defended their own right to self-government.
Compare this to the original weak thesis. This final thesis presents a way of interpreting evidence that illuminates the significance of the question. Keep in mind that this is one of many possible interpretations of the Civil War—it is not the one and only right answer to the question . There isn’t one right answer; there are only strong and weak thesis statements and strong and weak uses of evidence.
Let’s look at another example. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
Why is this thesis weak? Think about what the reader would expect from the essay that follows: you will most likely provide a general, appreciative summary of Twain’s novel. The question did not ask you to summarize; it asked you to analyze. Your professor is probably not interested in your opinion of the novel; instead, she wants you to think about why it’s such a great novel— what do Huck’s adventures tell us about life, about America, about coming of age, about race relations, etc.? First, the question asks you to pick an aspect of the novel that you think is important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
Here’s a working thesis with potential: you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation; however, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal. Your reader is intrigued, but is still thinking, “So what? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?” Perhaps you are not sure yet, either. That’s fine—begin to work on comparing scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions. Eventually you will be able to clarify for yourself, and then for the reader, why this contrast matters. After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing the original version of this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find the latest publications on this topic. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial .
Anson, Chris M. and Robert A. Schwegler. The Longman Handbook for Writers. 2nd ed. New York: Longman, 2000.
Hairston, Maxine and John J. Ruszkiewicz. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers. 4th ed. New York: HarperCollins, 1996.
Lunsford, Andrea and Robert Connors. The St. Martin’s Handbook. 3rd ed. New York: St. Martin’s, 1995.
Rosen, Leonard J. and Laurence Behrens. The Allyn & Bacon Handbook. 3rd ed. Boston: Allyn & Bacon, 1997.
- Thesis Statements. Provided by : The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Located at : http://writingcenter.unc.edu/ . License : CC BY-NC-ND: Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives

Conclusions
What this handout is about.
This handout will explain the functions of conclusions, offer strategies for writing effective ones, help you evaluate conclusions you’ve drafted, and suggest approaches to avoid.
About conclusions
Introductions and conclusions can be difficult to write, but they’re worth investing time in. They can have a significant influence on a reader’s experience of your paper.
Just as your introduction acts as a bridge that transports your readers from their own lives into the “place” of your analysis, your conclusion can provide a bridge to help your readers make the transition back to their daily lives. Such a conclusion will help them see why all your analysis and information should matter to them after they put the paper down.
Your conclusion is your chance to have the last word on the subject. The conclusion allows you to have the final say on the issues you have raised in your paper, to synthesize your thoughts, to demonstrate the importance of your ideas, and to propel your reader to a new view of the subject. It is also your opportunity to make a good final impression and to end on a positive note.
Your conclusion can go beyond the confines of the assignment. The conclusion pushes beyond the boundaries of the prompt and allows you to consider broader issues, make new connections, and elaborate on the significance of your findings.
Your conclusion should make your readers glad they read your paper. Your conclusion gives your reader something to take away that will help them see things differently or appreciate your topic in personally relevant ways. It can suggest broader implications that will not only interest your reader, but also enrich your reader’s life in some way. It is your gift to the reader.
Strategies for writing an effective conclusion
One or more of the following strategies may help you write an effective conclusion:
- Play the “So What” Game. If you’re stuck and feel like your conclusion isn’t saying anything new or interesting, ask a friend to read it with you. Whenever you make a statement from your conclusion, ask the friend to say, “So what?” or “Why should anybody care?” Then ponder that question and answer it. Here’s how it might go: You: Basically, I’m just saying that education was important to Douglass. Friend: So what? You: Well, it was important because it was a key to him feeling like a free and equal citizen. Friend: Why should anybody care? You: That’s important because plantation owners tried to keep slaves from being educated so that they could maintain control. When Douglass obtained an education, he undermined that control personally. You can also use this strategy on your own, asking yourself “So What?” as you develop your ideas or your draft.
- Return to the theme or themes in the introduction. This strategy brings the reader full circle. For example, if you begin by describing a scenario, you can end with the same scenario as proof that your essay is helpful in creating a new understanding. You may also refer to the introductory paragraph by using key words or parallel concepts and images that you also used in the introduction.
- Synthesize, don’t summarize. Include a brief summary of the paper’s main points, but don’t simply repeat things that were in your paper. Instead, show your reader how the points you made and the support and examples you used fit together. Pull it all together.
- Include a provocative insight or quotation from the research or reading you did for your paper.
- Propose a course of action, a solution to an issue, or questions for further study. This can redirect your reader’s thought process and help them to apply your info and ideas to their own life or to see the broader implications.
- Point to broader implications. For example, if your paper examines the Greensboro sit-ins or another event in the Civil Rights Movement, you could point out its impact on the Civil Rights Movement as a whole. A paper about the style of writer Virginia Woolf could point to her influence on other writers or on later feminists.
Strategies to avoid
- Beginning with an unnecessary, overused phrase such as “in conclusion,” “in summary,” or “in closing.” Although these phrases can work in speeches, they come across as wooden and trite in writing.
- Stating the thesis for the very first time in the conclusion.
- Introducing a new idea or subtopic in your conclusion.
- Ending with a rephrased thesis statement without any substantive changes.
- Making sentimental, emotional appeals that are out of character with the rest of an analytical paper.
- Including evidence (quotations, statistics, etc.) that should be in the body of the paper.
Four kinds of ineffective conclusions
- The “That’s My Story and I’m Sticking to It” Conclusion. This conclusion just restates the thesis and is usually painfully short. It does not push the ideas forward. People write this kind of conclusion when they can’t think of anything else to say. Example: In conclusion, Frederick Douglass was, as we have seen, a pioneer in American education, proving that education was a major force for social change with regard to slavery.
- The “Sherlock Holmes” Conclusion. Sometimes writers will state the thesis for the very first time in the conclusion. You might be tempted to use this strategy if you don’t want to give everything away too early in your paper. You may think it would be more dramatic to keep the reader in the dark until the end and then “wow” them with your main idea, as in a Sherlock Holmes mystery. The reader, however, does not expect a mystery, but an analytical discussion of your topic in an academic style, with the main argument (thesis) stated up front. Example: (After a paper that lists numerous incidents from the book but never says what these incidents reveal about Douglass and his views on education): So, as the evidence above demonstrates, Douglass saw education as a way to undermine the slaveholders’ power and also an important step toward freedom.
- The “America the Beautiful”/”I Am Woman”/”We Shall Overcome” Conclusion. This kind of conclusion usually draws on emotion to make its appeal, but while this emotion and even sentimentality may be very heartfelt, it is usually out of character with the rest of an analytical paper. A more sophisticated commentary, rather than emotional praise, would be a more fitting tribute to the topic. Example: Because of the efforts of fine Americans like Frederick Douglass, countless others have seen the shining beacon of light that is education. His example was a torch that lit the way for others. Frederick Douglass was truly an American hero.
- The “Grab Bag” Conclusion. This kind of conclusion includes extra information that the writer found or thought of but couldn’t integrate into the main paper. You may find it hard to leave out details that you discovered after hours of research and thought, but adding random facts and bits of evidence at the end of an otherwise-well-organized essay can just create confusion. Example: In addition to being an educational pioneer, Frederick Douglass provides an interesting case study for masculinity in the American South. He also offers historians an interesting glimpse into slave resistance when he confronts Covey, the overseer. His relationships with female relatives reveal the importance of family in the slave community.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Douglass, Frederick. 1995. Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave, Written by Himself. New York: Dover.
Hamilton College. n.d. “Conclusions.” Writing Center. Accessed June 14, 2019. https://www.hamilton.edu//academics/centers/writing/writing-resources/conclusions .
Holewa, Randa. 2004. “Strategies for Writing a Conclusion.” LEO: Literacy Education Online. Last updated February 19, 2004. https://leo.stcloudstate.edu/acadwrite/conclude.html.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This article provides an effective technique for writing a conclusion adapted from Erika Eby's The College Student's Guide to Writing a Good Research Paper: 101 Easy Tips & Tricks to Make Your Work Stand Out.. While the thesis introduction starts out with broad statements about the topic, and then narrows it down to the thesis statement, a thesis conclusion does the same in the opposite order.
5. Don't apologize. When restarting the thesis, assume that you have proven it over the course of the paper and don't make apologies or hedge, which will weaken the conclusion and thus the paper. Avoid saying things like, "It seems like" or "It is possible that" in the restatement.
Your restatements will become more concise, compelling, and impactful, resonating with clarity, coherence, and conviction. In conclusion, the art of thesis restatement is not merely a technical skill but a powerful tool that can elevate your academic writing to new heights. Embrace it with confidence, implement the techniques learned, and watch ...
Address the limitations of your argument. The strategy you employ in writing a conclusion for your paper may depend upon a number of factors: The conventions of the discipline in which you are writing. The tone of your paper (whether your paper is analytical, argumentative, explanatory, etc.) Whether your paper is meant to be formal or informal.
Depending on the nature of your research paper, this might mean restating your thesis and arguments, or summarizing your overall findings. Argumentative paper: Restate your thesis and arguments. In an argumentative paper, you will have presented a thesis statement in your introduction, expressing the overall claim your paper argues for. In the ...
Therefore, as you restate the thesis, you should not make apologetic statements because they undermine your argument. Such statements, which you should avoid, include: "It appears that …. "It is possible that …". "It is my opinion that …". The only time when using such statements when restating your thesis might be okay is when ...
while the conclusion to a STEM paper could focus on questions for further study, the conclusion of a literature paper could include a quotation from your central text that can now be understood differently in light of what has been discussed in the paper. You should consult your instructor about expectations for conclusions in a particular
In some cases, this context may be different from the one established in your conclusion, and it may push slightly beyond the boundaries of the writing prompt. Structural Components Evolved Thesis. Many strong conclusions restate the thesis—in different language from the introduction—in the opening sentence.
Step 1: Answer your research question. Step 2: Summarize and reflect on your research. Step 3: Make future recommendations. Step 4: Emphasize your contributions to your field. Step 5: Wrap up your thesis or dissertation. Full conclusion example. Conclusion checklist. Other interesting articles.
Avoid incorporating unrelated or irrelevant content in your restatement. Changing the meaning of your thesis: Ensure that the restatement maintains the same core message or main argument as your original thesis statement. Avoid altering the meaning or taking a completely different stance without proper justification.
Writing a Conclusion. A conclusion is an important part of the paper; it provides closure for the reader while reminding the reader of the contents and importance of the paper. It accomplishes this by stepping back from the specifics in order to view the bigger picture of the document. In other words, it is reminding the reader of the main ...
Step #1. Reread the original thesis statement carefully. Step #2. Determine in which person it is written (1 st, 2 nd, or 3 rd) and preserve that point of view in the rewrite. Step #3. Outline all keywords and main points that should be present in the reworded thesis.
Here are effective steps on how to create an effective restated thesis statement: Step 1. Review your statement. Begin by revisiting your original phrase from the introduction of your argumentative essay. Ensure you understand the main argument or assertion you presented. Step 2.
Step 1: Return to your thesis. To begin your conclusion, signal that the essay is coming to an end by returning to your overall argument. Don't just repeat your thesis statement—instead, try to rephrase your argument in a way that shows how it has been developed since the introduction.. Example: Returning to the thesis Braille paved the way for dramatic cultural changes in the way blind ...
Ending with a rephrased thesis statement without any substantive changes. ... This conclusion just restates the thesis and is usually painfully short. It does not push the ideas forward. People write this kind of conclusion when they can't think of anything else to say. Example: In conclusion, Frederick Douglass was, as we have seen, a ...
Conclusions. Some say the conclusion is the most difficult section of the paper to write because it's hard to come up with something else to say after you've covered your main points. But imagine meeting someone without saying good bye or having a gourmet meal without the joy of a fine dessert. Having an anticlimactic conclusion, or no ...
Instead, writers should use a wide variety of techniques to help them restate their thesis in different words and linguistic structures. The most helpful techniques are listed for students below: alter the grammar. alter the sentence structure. change the order of information. change the word order. modify the word forms.
However, as a general guideline, a thesis conclusion should be about 5-10% of the total word count of the thesis. For example, if your thesis is 10,000 words long, your conclusion should be around 500-1000 words. It's important to keep in mind that the conclusion should be crisp and should solely focus on summarizing and interpreting the key ...
Examine the three steps of an effective conclusion: restatement of the thesis, review of the main points, and concluding device. Differentiate among Miller's (1946) ten concluding devices. In Section 11.1 "Why Conclusions Matter", we discussed the importance a conclusion has on a speech. In this section, we're going to examine the three ...
Practice Conciseness: Keep your restated thesis statement concise and to the point. You don't need to repeat all the details; just focus on the core message. End with a Thoughtful Closing Sentence: After restating your thesis, end your conclusion with a closing sentence that provides a sense of closure and finality to your essay or paper.
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
The conclusion pushes beyond the boundaries of the prompt and allows you to consider broader issues, make new connections, and elaborate on the significance of your findings. Your conclusion should make your readers glad they read your paper. Your conclusion gives your reader something to take away that will help them see things differently or ...
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.