7 Best Business Plan Software for Startups in 2024

- Resources for Planning a Business
- Best Business Plan Software
Last Updated: January 23, 2024 By TRUiC Team
Launching a new startup is an exciting yet challenging endeavor. Crafting a comprehensive business plan is a critical first step for any founder to outline their vision, objectives, and strategy. It acts as a roadmap to help guide important decisions and next steps as a company grows.
With so many options available, finding the right business planning tool can be daunting. The best software should be affordable, user-friendly, and offer a robust set of features to aid in financial modeling, strategic planning, and more.
In this review, we'll explore some of the top business plan software solutions designed specifically for entrepreneurs. We'll compare capabilities, ease of use, templates and resources, integrations, pricing, and more. Whether you’re looking to create an investor-ready plan or simply organize your strategy, choosing the right tool can help you get started on the right foot.
Best Business Plan Software for Startups: LivePlan

Top Business Plan Software Solutions
In this review, we'll look at seven of the best business plan software platforms — discussing their pros, cons, features, pricing, and more — so you can decide which one is right for your startup.
Best Business Plan Software for Startups 2024:
- LivePlan - Best Overall
- Bizplan - Easiest to Use
- Enloop - Best Automation Features
- PlanGuru - Best Financial Forecasting
- IdeaBuddy - Best for Idea Validation
- iPlanner - Best for Nonprofits
- Wise Business Plans - Best Professional Services
The following tools all have their own great features. Based on its affordable pricing and usability, LivePlan is our top business plan software choice for startups.
Try LivePlan today or continue reading to explore your options!
Best Business Plan Software: LivePlan
LivePlan is the overall best business plan tool, offering a large number of features at an affordable price.
Visit LivePlan
1. LivePlan - $15/month to $30/month
We love LivePlan overall because it offers great value at an affordable cost. The software lets you quickly create a business plan from anywhere in the world using what is arguably the best business plan software available on the market. It does everything better than its competition and costs way less.
What’s more, the online “cloud-based” platform is easy to use and you are under no contract or obligation to keep paying for the service. Even better, if you decide to stop service for whatever reason, Palo Alto Software, the makers of LivePlan, will keep your account active and data preserved for at least a year should you decide to reactivate your account later.
- Create an unlimited number of business plans
- A forecast feature for those less mathematically inclined. Plug in data, and it will generate charts, graphs, figures, and even the profit and loss, balance sheet, and cash flow statements
- 500+ business plan templates spanning all major industries
- Real-time financial data tracking
- Performance dashboards track sales and budgeting
- Create one-page pitch plans for potential investors
- Milestone scheduling feature — Some people will use it when working with others on their plan; it will let you assign milestones to people.
- Low-cost annual plans
- Affordable pay-as-you-go plans
- No cancellation fees
- Data saved for 12-months, even after cancellation
- Clean, modern platform
- Cloud-based; works on any business machine (Linus, Windows, Mac)
- Integrates with Quickbooks and Xero to import your data easily
- Knowledgeable customer support to get help with your plan
- No valuation capabilities
- Templates built on Palo Alto Software’s earlier software Business Plan Pro require some modifications to be used on LivePlan
Insider Information
Talking to the nice people at LivePlan we learned some inside information that we wanted to share with our readers.
Here's what we learned:
- LivePlan has been used by contestants on ABC's hit show "Shark Tank" to win over angel investors to help them get their ideas and businesses funded.
- Accountants use LivePlan as an added-value service to sell to their clients.
- Businesses continue using LivePlan because of a feature called “Dashboard” which lets you manually enter your actuals or pull actuals from Quickbooks online to do comparative forecasting and analysis.
- LivePlan helps with business continuity planning (BCP).
- LivePlan executives use LivePlan to make important business decisions.
- "Dashboard" does profit and loss, cash flow, and balance sheet reports and lets you compare and contrast your actuals from your forecasts to be able to show to investors.
- LivePlan lets you create business plans in 1/5th the time it takes using templates.
Customer Reviews
LivePlan receives great feedback from customers. LivePlan reviews average 4.5 stars out of 5 on GetApp. LivePlan is an easy company for us to recommend for the best business plan software.

2. Bizplan - $29/month, $249/year, $349 lifetime
Bizplan rates high on our list because they offer a lifetime plan that gets you "forever access" to their business plan software. As an added bonus, you also receive free access to Startup Courses and LaunchRock, a landing page builder.
- Easy, "fill-in-the-blanks" plan builder
- Publish your business plan online
- Unlimited business plans
- Bizplan takes care of the financials
- Cloud-based (use any browser on any computer)
- Options to add more graphics and photos
- Low-cost yearly plans
- Create unlimited business plans
- Xero to import your data easily
- Excellent and responsive customer support (email/chat/phone)
- Free access to Startup.com and LaunchRock.com
- Discount at Fundable.com (connect with lenders and investors)
- Can't export in Word
- Doesn't currently integrate with QuickBooks
- No free trial
- No third-party app integrations
Talking with BizPlan insiders, we learned that the premise behind BizPlan is to help startups easily create professional business plans to give them a leg-up with lenders and investors.
Here's what else we learned:
- BizPlan's does all your financial calculations for you.
- BizPlan strives to be an all-in-one solution for Startups needing funding.
- BizPlan is constantly making improvements to its software.
BizPlan receives great feedback from customers. BizPlan reviews average 4.4 stars out of 5 on GetApp. Still a relatively new option, BizPlan already has over 30,000 satisfied customers. As their platform grows, we wouldn’t be surprised to see them integrate even more valuable features. Keep a close eye on this one.

3. Enloop - Free to $39.95/month
If you’re looking to try before you buy, Enloop is a strong choice as one of the only business planning software tools with a free trial.
- User-friendly platform
- Compare your financials against your industry's performance
- Bank ready financial statements (Profit and Loss, Balance Sheet, Cash flow)
- Lets multiple team members work on a business plan
- 36-Month detailed financial reports
- Sync date and text into your business plan
- Real-time performance rating
- Generated business plan Pass/Fail report
- Multiple currency formatting
- Seven-day free trial (no credit card required)
- Advanced financial ratios
- Financial projections
- Video tutorials to help you with the writing process
- No phone or chat support, just a "contact us" form.
- Three business plan limit per account
- Doesn't integrate with QuickBooks or Xero
- No financial forecasts beyond 36-months
- No 30-day money-back guarantee
We learned that the premise behind Enloop is to make business planning easier for entrepreneurs. Enloop achieves this by making software simple to navigate through and takes risks off the table with their no credit card needed seven-day free trial. Their business plan creation software offers financial forecasting features for up to 36 months.
- Enloop utilizes 16 financial ratios to get your business ready for investors.
- Enloop offers some sample business plans that are easy to modify.
- Enloop's performance score increases as you create your detailed plan.
- A new business or small businesses benefit the most from Enloop's solutions.
Enloop receives fair feedback from customers. Enloop's reviews average 3 stars out of 5 on PCMag. Enloop's main complaint is its lack of instructional text for writing mission statements and other key sections. What they rank high on is their efficiency and the speed at which the software lets you write a business plan.
Even beyond the free version, Enloop Basic is just $9.95/month ($6/month when paid annually), so they’re one of the least expensive tools for writing a business plan.

4. PlanGuru - $99/month to $299/month
PlanGuru is a good option if you’re looking for considerably more robust software that offers quite a bit more. The most notable feature we like is the valuation tool, only present on the desktop version of the software. PlanGuru lets you calculate the valuation of your business using three different methods. No other business plan software offers this that we know of.
PlanGuru also offers budgeting, forecasting, and performance tools to help you put together a business plan. In the main, PlanGuru allows you to get a custom-tailored three financial statement budget model up and running out of QuickBooks or Xero in a matter of minutes. PlanGuru's business plan writing software takes you through a setup process where it asks you questions such as:
- What's the first month of your fiscal year?
- How many historical years do you want to import?
And, once you answer these questions, PlanGuru then generates a model for you that you can then populate with your historical data if you have it. Then you can go through PlanGuru's 20+ projection methods.
Some financial data projection methods include:
- Expenses, like payroll, etc.
- Balance sheet items, like accounts receivable, accounts payable, crude expenses, prepaid expenses, loans, etc.
These are only a few of the features the business plan software offers. Here are some more.
- Budgeting/Forecasting Software
- Analytics Service for Financial Performance & KPIs
- Valuation calculations (desktop software only)
- Desktop and cloud-based options
- Free 14-day trial and 30-day money-back guarantee
- Great customer support and knowledgeable sales staff
- Lower-cost yearly plans offered
- Advanced financial calculations
- Business valuation calculations
- No contracts
- Integrates with QuickBooks and Xero
- Costlier than LivePlan and most other business plan software options
- Additional cost per user can add up quickly
The great thing about PlanGuru is that the only thing you have to worry about is the income statement and balance sheet projections because the cash flow statement is automatically generated.
Then once you have the cash flow statement, income statement, and balance sheet in place, you can then lock down the budget.
- PlanGuru's desktop version has three different types of valuation methods that calculate the worth of your business.
- PlanGuru has some really nice reporting tools that pull together your financial statements into table formats, say, for the bank, line-by-line.
- PlanGuru also has some nice charts, graphs, scorecards, and some easily digestible reports that can help you visualize how your company is performing.
- Exports to Excel, PDF, and Word documents --and, there's even a tool that lets you create customized reports.
- You can print your plan off too to show partners, lenders, and investors.
- PlanGuru now offers a cloud-based version of its software, though it will take some time to catch up to the rich features offered by the current desktop software version.
- With PlanGuru you also get free updates, bug fixes, and new releases as they become available.
Important Note: These tools are important because investors may want to see not only historical performance but also projections.

5. IdeaBuddy - Free to $35/month
IdeaBuddy makes our list because of what's behind their approach. IdeaBuddy focuses on helping entrepreneurs develop their idea first, then share it, and then refine it into a plan. If you have a business idea and don't know what to do next, IdeaBuddy could be what you're looking for in a business plan software.
- Single-page business plan pitch (Idea plan)
- Clean modern design platform combined with great financial tools
- Marketing plan for selling and promoting your products
- Market overview plan where you create targeted customer profiles, identify your competition and calculate the market potential
- Business plan creation that includes forecasting performance and cash flow projections
- A proprietary algorithm calculates a final score for your idea providing recommendations for improvement after you complete "Story Mode"
- Idea Journal, that is an internal business plan for you to show potential investors
- A lifetime plan costs only $178
- Great for developing ideas
- Great for doing market research
- Pay-as-you-go plans offered
- Email-only customer service
- Software lag time issues
- Fewer software options than most other small business options
IdeaBuddy has some great features that are fantastic from idea conceptualization down to cost projections and the laying out of steps to take to start a business. We would have liked, however, to been given more KPIs that would notify us of tasks, help with idea validation, and help us measure other objectives to better monitor the health of our business. Another thing lacking was the design of the finished plan--it contained some noticeable structural issues.
IdeaBuddy has received some outstanding customer reviews on GetApp. IdeaBuddy has earned a 4.6-star rating out of 5 possible stars.

6. iPlanner - Starts at $55/year
iPlanner is a comprehensive business plan software that has been aiding entrepreneurs since 2007, providing a robust framework for developing business plans, models, and financial forecasts online.
- Unlimited Team Members & Collaboration
- A La Carte Pricing Model vs Packages
- Discounts for Serial Entrepreneurs & Business Coaches
- Solid amount of industry knowledge and experience.
- They've got two trademarked business planning services, Startup Framework™ and Strategy Designer™
- All of their business planning packages allow you to have unlimited collaborators and assign people three different roles: Project Owners, Advisors, and Viewers.
- Their Startup Framework software has a business modeling section where you can design a business model canvas and strategize as much as you need before diving into your plan.
- Doesn't have a month-to-month option for either of their services. Their Strategy Designer is payable only annually, while their Startup Framework is available for 3-month, 6-month, or 12-month payments.
- They don't offer refunds
- Their website is pretty old school and tough to navigate.
- Unlike other business planning software, iPlanner doesn't offer a free version or trial. However, you can take a tour of their Startup Framework software or view a demo of the Strategy Designer to get a feel for them.
iPlanner's Business Planning Software
If a simple framework is all you're looking for, iPlanner can help you out. They don't have many bells and whistles, but at these price points, they offer a good value for nonprofits and corporations.

7. Wise Business Plans - Pricing by Request
Wise business plans website is a little confusing to navigate, and pricing is by request only, which can get frustrating. They do have a lot of options for different kinds of business plans for various types of business types, which makes them versatile. They also have business building and funding options as well. And, if you wish to establish business credit, they offer net-30 accounts that get reported to Equifax business.
- Claim to be the only business plan company to write for Fortune 100 and 500 companies
- Business formation services
- Business license searches
- EIN services
- Digital marketing services
- Business website design and branding
- Has a lot of helpful information
- Helpful options for forming your business
- Options to help after you start your business
- Helps small businesses establish business credit
- Not an actual business plan software
- Expensive by comparison
- Website is difficult to navigate
- Pricing is by request only
- Limited products and features
- Turnaround is one month
- Requires some work on your end

Business Plan Software Pros and Cons
- By using business plan software providers, you’ll be able to create a solid outline for your business. Although some of the options above are better than others, each will walk you through from start to finish.
- No matter how you look at it, business plan software is cost-effective. As long as you actually use the tool, you’ll generate significantly more value than you’re spending on monthly subscription fees.
- If you spend the time to create a solid plan, you’re much more likely to hold yourself accountable. Think of planning software like an accountability buddy for entrepreneurship.
- Your business plan tool will help set realistic financial goals, and most can also keep your bottom line in check by integrating your accounting software.
- Business planning software enables you to collaborate with partners, mentors and investors.
- Some of the business plan tools don’t offer support and can have slightly buggy features. That said, if you’re serious about writing a solid plan, go with a tool that’s constantly updated and well made.
- Although some business plan tools have a collaboration feature, none of them can review it when you’re done. All business planning tools lack a human touch.
How to Choose the Right Business Plan Software
With the array of business planning tools available, it can be daunting to select the right one for your needs. Here are some tips for choosing a business plan software solution:
- Consider your skill level – Opt for software like a wizard-guided template if you are less experienced in writing plans. Choose more advanced software with greater flexibility once you know what you are doing. Look for drag-and-drop tools to easily organize sections.
- Determine your budget – Prices range from free to several hundred dollars. Know how much you can spend before shopping.
- Compare features – Look for software with the specific tools you need, like financial projections, sample text, customizable templates, and more.
- Evaluate the financial tool capabilities – The software should provide extensive financial tools like forecasting, modeling, projections, and dashboards to streamline financial planning.
- Check reviews and ratings – Get feedback from other users about their experience with the software. High reviews indicate easier, more user-friendly software.
Which Is the Best Business Plan Software?
You know the unique requirements of your startup better than we do. These are all quality services that offer business planning software tools for entrepreneurs like you. Feel free to read over our full reviews if you’d like to know more about any of them or even visit the websites directly.
In general, we do prefer LivePlan because they have a huge library of business plan templates, and we love their convenient dashboard. They're the planning software that is most likely to help you via customer support, continue updating their tool, and figure out ways to make your business experience better. Enjoy!
What is the purpose of a business plan?
The purpose of a business plan is to provide a structured outline and roadmap for a business's goals, strategies, and operations. It serves as a guide for decision-making, resource allocation, and management.
Furthermore, it can be a crucial tool for attracting investors, securing loans, and ensuring that all stakeholders have a clear understanding of the business's direction and objectives.
What does business plan software do?
Business plan software assists entrepreneurs and businesses in creating, organizing, and refining their business plans. It provides tools, templates, and guidance to streamline the planning process.
Features often include financial forecasting, market analysis, visual aids like charts and graphs, collaboration capabilities, and even integration with other business tools. This software aims to simplify the task of creating a thorough and professional business plan.
How do you write a business plan?
To write a business plan, start by writing an executive summary that provides an overview of your business idea, products/services, market opportunity, and projected growth. Outline your company description, industry analysis, target customers, competitive advantage, marketing and sales plans, operations, management team, and financial projections.
How long should a business plan be?
The length can vary based on the complexity of the business, its stage, and its intended audience. In general, it might range from 15-50 pages. However, the key is to ensure that the plan is comprehensive yet concise.
For many situations, especially when seeking investment, a more detailed one is preferable. Yet, for internal purposes or for businesses at very early stages, a shorter, more concise plan might suffice.
Are there business plan templates on Word?
Yes, Microsoft Word has business plan templates you can download and customize. The templates provide section headings, instructions, sample text, and tables to input your specific business information.
What is Palo Alto Software?
Palo Alto Software is a company that's been around since the late 1980s. They created business management software for startups and existing businesses. The software has since been updated and rebranded as LivePlan and today happens to be one of the most sought-after business plan software available in the marketplace.
Individual Business Plan Reviews
Featured articles.

What Is a Business Plan?

Lean Startup Business Plan Guide

How to Write a Business Plan
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
5 Best Business Plan Software in 2022

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
When you’re starting a business, developing a strong business plan will be one of the first steps you take. Your business plan will cover everything from a detailed explanation of your products or services and pricing model to at least three years of financial projections—plus much more. Therefore, whether you’re not sure how to get started or you’re just looking to make the process easier, you may want to turn to business plan software for help.
In this guide, we'll break down five of the best business plan software options—discussing their pros, cons, features, pricing, and more—so you have all the information you need to decide which solution is right for your small business.
Looking for tools to help grow your business?
Tell us where you're at in your business journey, and we'll direct you to the experience that fits.
on Nerdwallet's secure site
The 5 best business plan software options
The right business plan software will make the process of writing your business plan much simpler. Like many business software solutions, however, there are a number of different business plan software options out there—each of which has a unique set of features, user experience, and price.
This being said, if you're looking for a place to start your search for the best business plan software, you can explore the five top options below:
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
1. LivePlan
Best overall business plan software.
If you want template-rich, modern-feeling business plan software, then LivePlan may be the right pick for you. LivePlan excels with their user interface, which feels updated and slick, and also offers intuitive, easy-to-use features and options.
Their step-by-step instruction will help you kick things off from the beginning, and you can take advantage of their online learning center to continue to gain business skills.
Affordable plans, including pay-as-you-go option
No long-term contracts or cancellation fee; 60-day money-back guarantee
Modern, intuitive interface; cloud-based, can be used on Mac, PC, as well as tablets
Ability to create unlimited plans in one account; over 500 customizable templates
Variety of business resources including video tutorials, step-by-step instruction, and general customer support
Limited integration options
Challenging to enter your own financial modeling projections
Can be difficult to learn
Ability to create an unlimited number of business plans on one account
More than 500 business plan templates spanning various industries
Integration with Xero and QuickBooks Online
Real-time tracking of financial data with accounting integrations
Ability to export your business plan to Word or PDF
Expert advice and step-by-step instruction included
Performance dashboards for tracking against budgets and sales goals
Ability to create and export a one-page pitch executive summary
Annual plan: $15 per month, billed every 12 months
Six-month plan: $18 per month, billed every six months
Pay-as-you-go plan: $20 per month, billed once every month
2. GoSmallBiz
Best for multiple business management tools in one platform.
Next on our list of the best business plan software options is GoSmallBiz, which is much more than just a business plan software. With GoSmallBiz, you have access to business continuity planning software with features that cover creating a roadmap, working through business and legal forms, building a website, and more.
In this way, GoSmallBiz is great for startups or newer businesses looking to access multiple business management tools through one platform.
Unlimited business consultation and extensive library of online resources
Multiple business tools in one software
Website consultation analysis and business assessment
Industry-specific business plan templates with emphasis on financial projections and statements
Expensive monthly cost compared to alternatives
Limited business plan features
Entire business plan can only be exported to Microsoft Word
Outdated interface
Industry-specific business plan templates with step-by-step building wizard
Ability to create financial statements and projections
Free website hosting and website builder
Customer relationship manager with integration with MailChimp
Digital marketing dashboard with social media and Google Analytics integrations
HR document builder
Corporate minutes writer
Business documents library
Business courses library
Unlimited business consultation
$39 per month, no contracts, free cancellation
Best for simple, fast business plan creation.
If you're looking for free business plan software, Enloop will be one of your closest options—they offer an all-inclusive seven-day free trial, no credit card required. Additionally, unlike some of the other options on our list, Enloop is strictly dedicated to business plan creation, including automated text writing, financial forecast comparisons, and a real-time performance score that tracks your progress.
This being said, if you'd prefer the most straightforward, fast, and simple way to write your business plan, Enloop will be a platform worth considering.
Simple and straightforward software, solely dedicated to business plan creation
Seven-day free trial
Automatic text generation available to streamline the writing process
Affordable plans with annual discount option
Limited additional educational resources
Only one template option
No integration options
Ability to create three business plans with customizable text, images, tables, charts, and over 100 currency symbols and formats
Includes automatic text generation for each plan section that you can then customize
Automatically generated financial statements
Includes financial performance comparison analysis (using three ratios with Detailed plan and 16 with Performance plan)
Real-time performance score to track your progress
Ability to invite users to edit (two with Detailed plan, five with Performance plan)
Pass/fail report and certificate to help you identify issues with your plan
Free plan: Seven-day free trial with no credit card required
Detailed plan: $19.95 per month or $11 per month, paid annually
Performance plan: $39.95 per month, or $24 per month, paid annually
Best for startups looking to acquire funding or find investors.
Part of the Startups.com suite, Bizplan gets top marks for their user interface—it’s intuitive, easy to use, and modern. You’ll work with a step-by-step business plan builder to get exactly what you’d like from your business plan. It may remind you of a modern website builder, since it has drag-and-drop tools to build templates.
Moreover, for one subscription fee, you have access to all of the tools in the Startups.com network, including self-guided courses, how-to guides, masterclass videos, and more. All in all, with a direct connection to Fundable, Bizplan is a top business plan software option for startups looking to acquire funding and find investors.
Subscription gives you access to all Startups.com tools
Lifetime access subscription option
User-friendly drag-and-drop business plan builder
Excellent educational resources
Connection to Fundable great for businesses looking for capital
No free trial
No templates based on industry
No mobile access
Drag-and-drop templates for business plan building
Financial command center to track all business financials in one place
Unlimited account collaborators
Ability to share business plan online with investors
Online resources including self-guided courses, masterclass videos, how-to guides, mentorship access
Unlimited software use for Fundable, Launchrock, and Startups.com
Monthly plan: $29 per month
Annual plan: $20.75 per month, billed at $249 per year
Lifetime access: $349 one-time fee
5. PlanGuru
Best for financial planning and budgeting.
Finally, for some of the strongest financial features among business plan software options, including budgeting and forecasting, you might check out PlanGuru. Whereas the other solutions we've reviewed were first and foremost focused on writing a business plan, PlanGuru is dedicated to business financial planning —providing the tools you need to create budgets, financial forecasts, reports, and more.
Therefore, if you need a software solution that can streamline the financial piece of your business planning processes, PlanGuru will certainly have the most to offer.
Extensive financial tools and detailed forecasting, budgeting, and reporting capabilities
Substantial library of resources
Cloud-based and desktop options
14-day free trial and 30-day money-back guarantee
Expensive, especially for additional users
Only focuses on the financial aspect of business planning; no templates or tools for basic business plan writing
Difficult to use without prior financial knowledge
Cloud-based version of software, as well as locally installed Windows version (desktop version has a few more features)
Works with QuickBooks Online, Xero, and Excel
Budgeting and forecasting for up to 10 years
Over 20 standard forecasting methods
Formula builder to create custom methods
Ratios and KPIs
Dashboard and reporting tools
Help guides, video tutorials, knowledgebase, and live U.S.-based customer support
14-day free trial
$99 per month (additional users $29 per month)
$899 per year (additional users $299 per year)
What to look for in business plan software
Ultimately, it's up to you to decide, which, if any, of the best business plan software solutions on our list is right for your business.
So, if you're trying to figure out how to choose between the various options out there, it might be helpful to compare your top choices based on the following criteria:
Features: As we've seen different business plan software solutions offer different features. You'll want to look carefully at the feature list of any software and determine what features are most important for your business needs. Do you need an extensive library of templates with detailed customization? Would you prefer software that includes an online learning center for business skills? Are you looking for a solution that combines business plan writing with other tasks? It may be useful to list out your ideal feature set, so you can compare individual software plans to that list.
Price: Although you might be able to find some free business plan software options (or at the very least, free trials), in most cases, you'll need to pay a subscription fee to access the platform you choose. Therefore, you'll want to think about what your budget is for this business tool and what type of software is most cost-effective for your needs.
User experience: User experience can vary widely among different business plan software options. You’ll find some programs that are newer or have been recently updated. Others might have the kind of interfaces that felt new years ago but are now pretty out of date—and, subsequently, make them a little harder to use. The right user experience for your needs is genuinely a matter of opinion and comfort—nevertheless, it's worth testing thoroughly testing out a platform to ensure that it can truly work for you before investing in a monthly or annual subscription.
The bottom line
There's no doubt that properly crafting your business plan is important for the future growth and success of your small business. Luckily, the right business plan software should make the process much simpler.
This being said, whether you opt for one of the best business plan software options listed here, or another platform entirely, you'll want to take the time to compare multiple solutions and ensure you choose the one that's right for your business.
As we mentioned, it can be helpful to think about the features you're looking for, your budget, and your user-experience preferences ahead of time—that way, you'll have a set of criteria in mind as you explore different solutions.
Ultimately, perhaps the best thing you can do to find the right software is to actually test out the platforms themselves—either by using a free trial or a money-back guarantee.
This article originally appeared on JustBusiness, a subsidiary of NerdWallet.
On a similar note...

Home > Business > Business Startup
- 5 Best Business Plan Software and Tools in 2023 for Your Small Business

Data as of 3 /13/23 . Offers and availability may vary by location and are subject to change.

We are committed to sharing unbiased reviews. Some of the links on our site are from our partners who compensate us. Read our editorial guidelines and advertising disclosure .
A business plan can do a lot for your business. It can help you secure investors or other funding. It can give your company direction. It can keep your finances healthy. But, if we’re being honest, it can also be a pain to write.
Luckily, you don’t have to start from scratch or go it alone. Business plan software and services can help you craft a professional business plan, like our top choice LivePlan , which provides templates, guidance, and more.
You’ve got quite a few choices for business plan help, so we’re here to help you narrow things down. Let’s talk about the best business plan tools out there.
- LivePlan : Best overall
- BizPlanBuilder : Most user-friendly
- Wise Business Plans : Best professional service
- Business Sorter : Best for internal plans
- GoSmallBiz.com : Most extra features
- Honorable mentions
Business plan software 101
The takeaway, business plan software faq, compare the best business plan software.
By signing up I agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
LivePlan: Best overall business plan software
Data as of 3 /13/23 . Offers and availability may vary by location and are subject to change. *With annual billing
LivePlan has been our favorite business plan software for a while now, despite the stiff competition.
There’s a lot to like about LivePlan. It has pretty much all the features you could want from your business plan software. LivePlan gives you step-by-step instructions for writing your plan, helps you create financial reports, lets you compare your business’s actual financials to your plan’s goals, and much more. And if you ever need inspiration, it includes hundreds of sample business plans that can guide your writing.
LivePlan software pricing
But the best part? You get all that (and more) at a very competitive price. (You can choose from annual, six-month, or monthly billing.) While LivePlan isn’t quite the cheapest business plan builder out there, it’s not too far off either. And if comes with a 60-day money back guarantee. So there’s no risk in trying LivePlan out for yourself.
With a great balance of features and cost, LivePlan offers the best business plan solution for most businesses.
BizPlanBuilder: Most user-friendly
Need something easy to use? BizPlanBuilder fits the bill.
BizPlanBuilder doesn’t have a flashy, modern user interface―but it does have a very clear, intuitive one. You’ll be able to see your plan’s overall structure at a glance, so you can quickly navigate from your title page to your market trend section to that paragraph on your core values. And as you write, you’ll use a text editor that looks a whole lot like the word processing programs you’re already familiar with.
BizPlanBuilder software pricing
Data effective 3/13/23. At publishing time, amounts, rates, and requirements are current but are subject to change. Offers may not be available in all areas.
BizPlanBuilder also offers lots of helpful guidance for actually writing your plan. It gives you pre-written text, in which you just have to fill in relevant details. It offers explanations for what information you need to include in each section of your plan and way. It even gives you helpful tips from experts, so you’ll have all the information you need to plan like a pro.
So if you want planning software with almost no learning curve, you’ll like BizPlanBuilder.
Wise Business Plans: Best professional service
- Custom quote
Unlike all the other companies on this list, Wise Business Plans doesn’t offer software. Instead, it offers professional business plan writing services―meaning someone does all the hard work for you.
Now, you might think that sounds expensive―and you’re probably right (you have to request a custom quote for your plan). But there’s a lot to be said for expertise, and Wise Business Plans has plenty of that. Your business plan will get written by an experienced writer (with an MBA, no less). They’ll get information from you, do their own research, and then write your plan. You get one free revision, and you can always pay for more.
Wise Business Plans service pricing
Your end result will be a polished, entirely original business plan. (You can even get printed copies.) And best of all, you won’t have to spend your precious time working on the plan yourself. Wise Business Plans takes care of all the hard parts, and makes your business look good while doing it. Sounds like a service worth paying for, right?
Put simply, if you want the most professional business plan possible, we recommend using Wise Business Plans’s writing service.
Business Sorter: Best for internal plans
Many businesses need plans to show to people outside the company (to get financing, for example). But what if you just need a plan for internal use? In that case, we suggest Business Sorter.
Business Sorter uses a unique card-based method to help you craft the perfect business plan. (You can watch a demo video to see how it works.) You’ll plan some of the usual things, like finances and marketing. But Business Sorter also lets you make plans for specific teams and team members. It also emphasizes more internal matters, like operations, that might get overlooked in a business plan for outsiders.
Business Sorter software pricing
After you’ve made your business plan, Business Sorter also helps you stay accountable to it. You can create tasks, give them deadlines, and assign them to team members―giving you basic project management tools to make sure your business plans become business actions. (Oh, and did we mention that Business Sorter has the lowest starting prices of any software on this list?)
It all adds up to a business plan software that works great for internal planning.
GoSmallBiz: Most extra features
Want to get way more than just business planning software? Then you probably want GoSmallBiz.
See, GoSmallBiz offers business plan software as part of its service―but it’s just one part of a much bigger whole. You also get everything from discounts on legal services to a website builder to a CRM (customer relationship manager) to business document templates. And more. In other words, you get just about everything you need to get your startup off the ground.
GoSmallBiz software pricing
Don’t worry though―you still get all the business planning help you need. GoSmallBiz gives you business plan templates, step-by-step instructions, and the ability to create financial projections. And if you get stuck, GoSmallBiz will put you in touch with experts who can offer advice.
If you want business planning and much, much more, give GoSmallBiz a try.
- PlanGuru : Best financial forecasting
- EnLoop : Cheapest tool for startups
We recommend the software above for most business planning needs. Some businesses, though, might be interested in these more specialized planning software.
Honorable mention software pricing
Planguru: best financial forecasting features.

PlanGuru is pretty pricey compared to our other picks, but you might find its forecasting features worth paying for. It has more forecasting methods than other software (over 20) plus it lets you forecast up to 10 years.
EnLoop: Cheapest tool for startups

EnLoop doesn’t have our favorite features or interface, but it does have really, really low pricing plus a seven-day free trial. It's the most affordable software for startup business planning and still provides all the essential features like financial analysis, team collaboration, charting, and more.
Data as of 3 /13/23 . Offers and availability may vary by location and are subject to change. * With annual billing
Several of our previous favorite planning software, including BusinessPlanPro and StratPad, seem to have gone out of business.
A business plan is a written, living document that tells the story of your business and what you plan to do with it. It serves as the source of truth for you—the business owner—as well as potential partners, employees, and investors, but it also serves as a roadmap of what you want your business to be.
Why you need a business plan
While some small-business owners don’t see the point of creating a formal business plan, it can have some concrete benefits for your business. For example, one 2016 study found that business owners with written plans are more successful than those that don’t. 1
Still too vague? Then let’s get specific.
If you ever seek business funding (from, say, banks, angel investors , or venture capitalists ), you’ll have to prove that your business deserves the money you want. A formal business plan―complete with financial data and projections―gives you a professional document you can use to make your case. (In fact, most potential investors will expect you to have a business plan ready.)
Even if you’re not seeking funding right now, a business plan can help your business. A formal plan can guide your business’s direction and decision making. It can keep your business accountable (by, for example, seeing if your business meets the financial projections you included). And a formal plan offers a great way to make sure your team stays on the same page.
What to include in your business plan
Not all business plans are created equal. To make a really useful business plan, you’ll want to include a number of elements:
- Basic information about your business
- Your products/services
- Market and industry analysis
- What makes your business competitive
- Strategies and upcoming plans
- Your team (and your team’s background)
- Current financial status
- Financial and market projections
- Executive summary
Of course, you can include more or fewer elements―whatever makes sense for your business. Just make sure your business plan is comprehensive (but not overwhelming).
How business plan software can help
With so many elements to include, business plan creation can take a while. Business plan software tries to speed things up.
Most business plan software will include prompts for each section. In some cases, you can just fill in your business’s specific information, and the software will write the text for you. In other cases, the software will give you specific guidance and examples, helping you write the text yourself.
Plus, business plan software can help you stay organized. You’ll usually get intuitive menus that let you quickly flip through sections. So rather than endlessly scrolling through a long document in a word processor, you can quickly find your way around your plan. Some software even lets you drag and drop sections to reorganize your plan.
Sounds way easier than just staring at a blank page and trying to start from scratch, right?
Choosing business plan software
To find the right business plan builder for your business, you’ll want to compare features. For example, would you rather write your own text, getting prompts and advice from your software? Or would you rather go with a fill-in-the-blank method?
Likewise, think about the elements you need. If your plan will have a heavy focus on finances, you’ll want to choose business plan software with robust financial projection features. If you care more about market and competitor analysis, look for software that can help with that research.
You may also want to find business plan software that integrates with your business accounting software . Some plan builders will import data from Xero, QuickBooks, etc. to quickly generate your financial data and projections.
And of course, you’ll want to compare prices. After all, you always want to end up with software that fits your business budget.
The right business plan software can make your life easier. With LivePlan ’s wide breadth of features and online learning tools, you can’t go wrong. Plus, BizPlanBuilder 's one-time pricing makes it easy to invest while Business Sorter has a low starting cost. And if you're business is looking to grow, GoSmallBiz and Wise Business Plans will scale with you.
But of course, different companies have different needs. So shop around until you find the software that’s best for you and your business.
Now that you've got a business plan, take a look at our checklist for starting a small business. It can help you make sure you have everything else you need to get your startup off to a good start!
Related content
- 7 Steps to Build a Successful Project Management Sales Plan
- Best Project Management Software and Tools in 2023
- 4 Cost Management Techniques for Small Businesses
Creating a business plan can take anywhere from a couple hours to several weeks. Your timeline will depend on things like the elements you choose to include, whether you use software or hire a writing service, and how much research goes into your plan.
That said, much of the business plan software out there brags that it can help you create a fairly detailed plan in a few hours. So if you’re going the software route, that can help you set your expectations.
If you want to get the most out of your business plan, you should update it on a regular basis―at least annually. That way, you can continually refer to it to inform your company’s strategies and direction.
At the very least, you should update your business plan before you start looking for a new round of funding (whether that’s with investors or lenders).
Thanks to business plan software, you can easily write your own business plan rather than pay someone to do it for you. And in most cases, software will cost you less than a professional business plan service.
There are some times you might want to go with a service though. If time is tight, you might find that it’s worth the cost of a service. Or if you’ve got big investor meetings on the horizon, you might want the expertise and polish that a professional service can offer.
Ultimately, you’ll have to decide for yourself whether business plan software or a business plan service will work better for your company.
Methodology
We ranked business plan software and tools based on features, pricing and plans, and connections to project management and other services. The value of each plan and service, along with what it offers, was a big consideration in our rankings, and we looked to see if what was offered was useful to small businesses or just extra. The final thing we looked at was the ease of use of the software to see if it's too complex for small businesses.
At Business.org, our research is meant to offer general product and service recommendations. We don't guarantee that our suggestions will work best for each individual or business, so consider your unique needs when choosing products and services.
Sources 1. Harvard Business Review, “ Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed .” Accessed March 13, 2023.

5202 W Douglas Corrigan Way Salt Lake City, UT 84116
Accounting & Payroll
Point of Sale
Payment Processing
Inventory Management
Human Resources
Other Services
Best Small Business Loans
Best Inventory Management Software
Best Small Business Accounting Software
Best Payroll Software
Best Mobile Credit Card Readers
Best POS Systems
Best Tax Software
Stay updated on the latest products and services anytime anywhere.
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Disclaimer: The information featured in this article is based on our best estimates of pricing, package details, contract stipulations, and service available at the time of writing. All information is subject to change. Pricing will vary based on various factors, including, but not limited to, the customer’s location, package chosen, added features and equipment, the purchaser’s credit score, etc. For the most accurate information, please ask your customer service representative. Clarify all fees and contract details before signing a contract or finalizing your purchase.
Our mission is to help consumers make informed purchase decisions. While we strive to keep our reviews as unbiased as possible, we do receive affiliate compensation through some of our links. This can affect which services appear on our site and where we rank them. Our affiliate compensation allows us to maintain an ad-free website and provide a free service to our readers. For more information, please see our Privacy Policy Page . |
© Business.org 2023 All Rights Reserved.
#1 Business Plan Software for Early-Stage Startups
Cuttles is a fully interactive and guided business plan software that helps entrepreneurs build, understand and grow their business.
Get ready to meet investors with confidence
Our web app has all the features and in-app guides you need to create a startup pitch, write a business plan, define a startup team, do budgets and financial projections. It’s simpler, faster and more impactful than ever to start a business.
Trusted and used by startup teams at
Join our Cuttles Perks program and save up to $500.000 on startup tools.
We've partnered up with the greatest SaaS giants to give you the best possible startup deals & tools to kickoff your startup journey
More than 30.000 entrepreneurs grow their startups using Cuttles
Read what some of our happy customers have to say
When you’re building a startup there are lots of things you need to figure out and keeping your plan and investor material clearly defined shouldn’t be an extra task to keep you away from building a great product. While it's a sinuous task to write a business plan, Cuttles makes the process of thinking, sketching and writing your business plan seamless. We were able to get our plan ready in a couple of days easily and without issues.

We’ve been missing a tool like Cuttles for years! All our work is usually stuck within folders, within other folders and it’s hard to have a one-stop-shop with all the details of each of our startups. Plus, these changes almost come on a weekly basis! So having an always up-to-date link to the BP is such a nice feature. No more little hacks and workarounds, now business ideas have a home of their own!
Creating something from nothing is hard. Building a startup requires a huge amount of work and that's where Cuttles helps. The versatile and well-organized startup builder is a solution to many of the problems that founders face day by day. It is a must-have tool for every entrepreneur, and especially those in the early-stages.
Cuttles has so amazing UX and design that I immediately felt like I had help. There were prompts and tasks given to make me think critically about my startup business. And it felt fun without being childish. If you are just starting your business and aren't an MBA try Cuttles. It's easy to use and comes with high-quality exportable templates
The Cuttles team and their first-hand experience of successful start-ups and working with aspiring entrepreneurs has manage to built an amazing startup plan software. The Canvas forces one to succinctly summarise one’s business pitch, the Budget tool provides a powerful but easy to use interface to construct a detailed budget that includes cash flow projections and metrics that investors will require. The Business Plan follows the same ethos of stepwise guidance. A set of task that we thought would take months to complete were shortened to a few weeks. Cuttles is a wonderful resource that we would unequivocally recommend.
Finally business plan software with great UX and a painless process - 10/10 will always recommend! Absolutely love it. The guide will help you in every aspect of your plan, this was such a huge help for us! I've tried most apps out there including LivePlan, Bizplan, and Upmetrics, and found them all either frustrating or missing something critical. The Cuttles web app simplifies the tedious task of thinking what to write in a business plan, a pitch deck, and more. It comes with a great examples, super helpful tips, and very and documentation.
Cuttles is on a mission to help startups and SMEs succeed by providing them the tools needed for a smoother startup journey. That's pretty cool! Starting a company, hiring your team and closing funding should be easy, so startups can focus their energy on what's really important; innovation and growth. Together with Cuttles, we can help startups accelerate their growth and relevance in the market.
Building a business is hard work and you need digital solutions that can make everyday life easier as an early-stage founder. Cuttles is a guided and personalized startup builder that helps you with planning, budgeting, and presenting your startup to investors. Their business plan tool helps you write your plan in a fraction of the time. That’s why we’re so proud to partner with a cool SaaS startup planning tool like Cuttles . We share the same goal – to help you!
Trusted and mentioned by
Hi everyone.
I'm Christian, CEO here at Cuttles.
There are few things as rewarding as building your own business. It's fun, challenging, and can create a deep sense of meaning and purpose, which, these days, most of us desperately desire. But knowing where to begin and how to move forward can be tough.
We may have a dream and see the big picture, but where do we go from there?
A recent finding shows that 63% of people in their twenties would like to start their own business and are drawn to experience life as entrepreneurs. Most, however, never get any further. It’s hard to know precisely how to go about it, and for that reason most aspiring entrepreneurs never dare take the first plunge. This doesn’t come as a big surprise. Building a business is a high-risk mission and there’s no certainty it will work out in the end. All we really have to rely on is our motivation and our willingness to do the work.
For early-stage founders, that work includes business planning. After all, an idea is, well - just an idea. It is how you execute that idea that will define your outcome and create a business.
So, what do you think when I say business planning? Let’s face it. For most of us, business planning kind of sucks. Who wants to sit around and write a plan when you could be building, marketing, selling?
But what if I told you that 90% of startups fail and that 56% do so because of poor business planning – or no planning at all?
It’s not the act of writing a business plan that does the trick, it’s the work you do in the process. Doing the research, understanding the problem you’re trying to solve and empathizing with the people you solve it for. It's the making sure your business and your business model are well thought out, assessing the risks, and through that becoming more sure that your idea is worth pursuing and using it to build a product and a startup that your customers won’t just like, but that they need.
However, the urgency of planning your startup, doesn’t take away the tediousness and time it takes.
That’s why we built Cuttles. We want to change business planning for good, by making it simple and easy to start, build and grow your business. By removing the hassle of business planning for you, we create time and space for you to do what you do best: Create lasting change for your customers. And although we’re not quite there yet, we work tirelessly to revolutionize business planning to make it simple, fast, and fun to plan and share your startup and get the funding you need to grow.
Get startup smart in our academy
We’re not just a powerful business plan app and great startup deals. We also want to train, inspire and empower startups to create more game changing solutions.
Top Courses
Top resources.
Free Startup Business Plan Templates and Examples
By Joe Weller | May 6, 2020
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, we’ve rounded up a variety of the top, professionally designed startup business plan templates, all of which are free to download in PDF, Word, and Excel formats.
Included on this page, you’ll find a one-page startup business plan template , a business plan outline template for startups , a startup business planning template with a timeline , and a sample startup business plan .
Startup Business Plan Template

Download Startup Business Plan Template - Word
Word | Smartsheet
This startup business plan template contains the essential components you need to convey your business idea and strategy to investors and stakeholders, but you can customize this template to fit your needs. The template provides room to include an executive summary, a financial overview, a marketing strategy, details on product or service offerings, and more.
One-Page Startup Business Plan Template
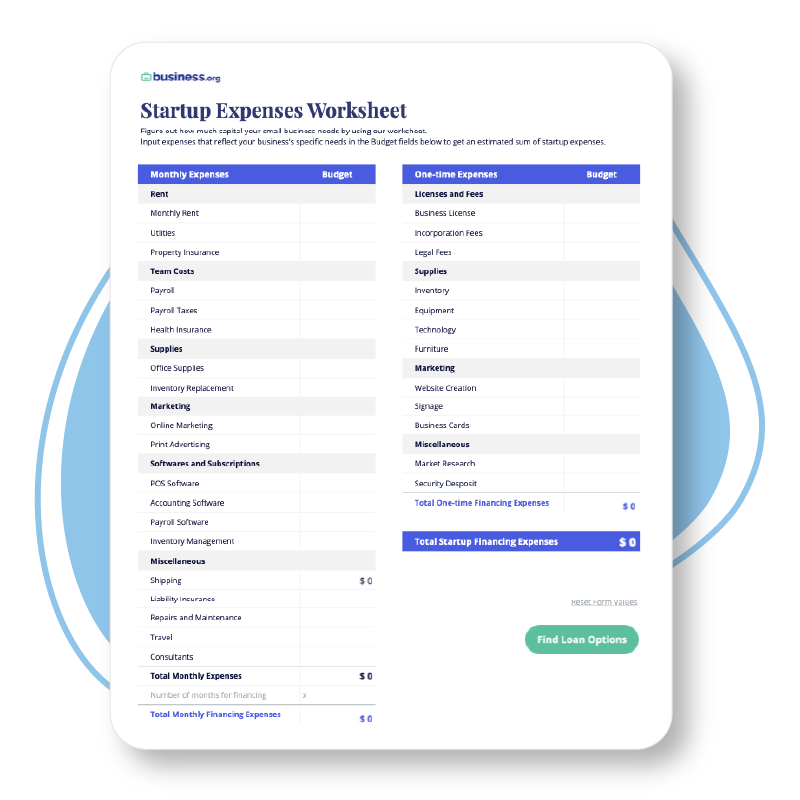
Download One-Page Startup Business Plan Template
Excel | Word | PDF
This one-page business plan is ideal for startup companies that want to document and organize key business concepts. The template offers an easy-to-scan layout that’s ideal for investors and stakeholders. Use this plan to create a high-level view of your business idea and as a reference as you flesh out a more detailed roadmap for your business.
For additional resources, visit " Free One-Page Business Plan Templates with a Quick How-To Guide ."
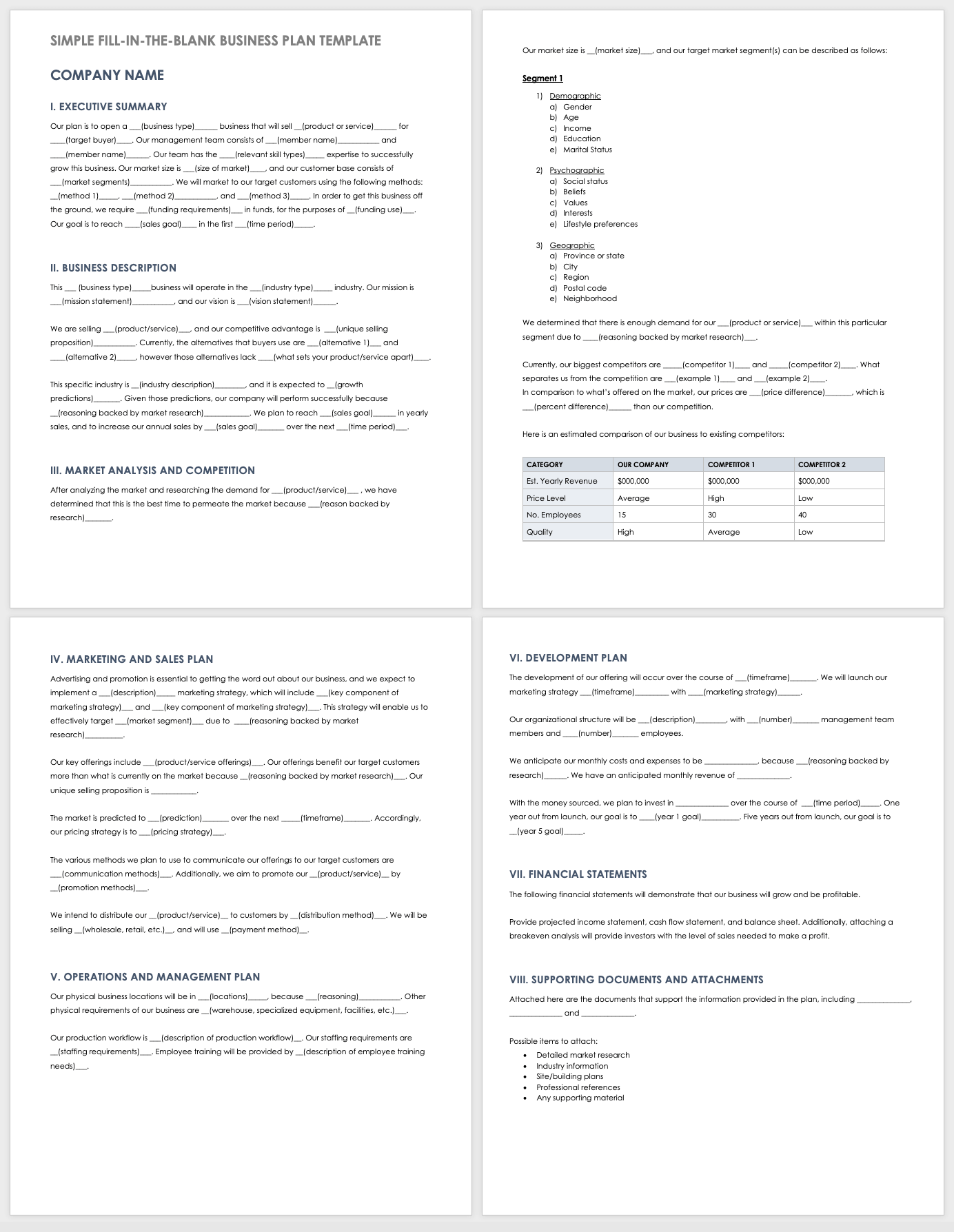
Simple Fill-In-the-Blank Business Plan Template for Startups
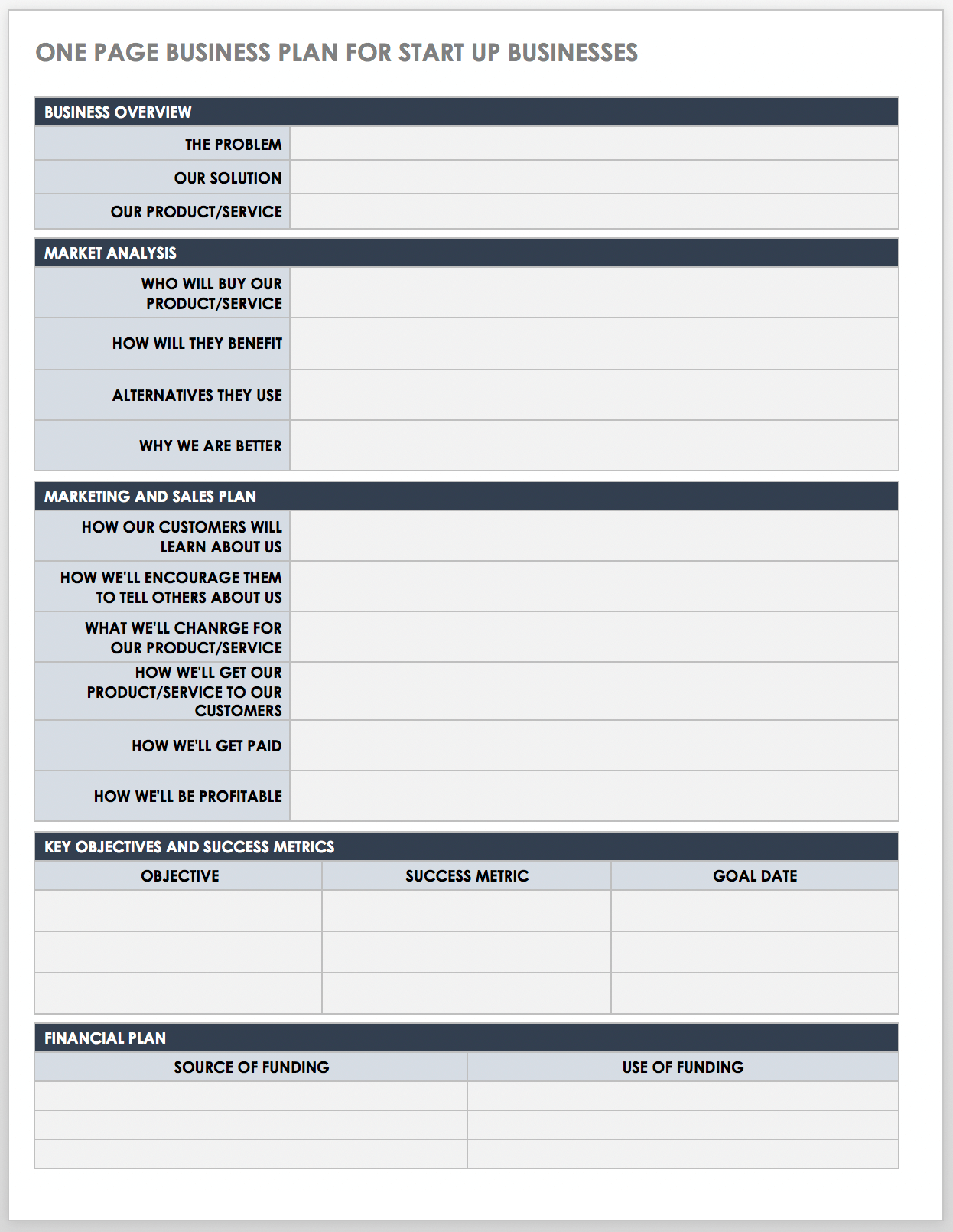
Download Simple Fill-in-the-Blank Business Plan Template for Startups
This comprehensive fill-in-the-blank business plan template is designed to guide entrepreneurs through the process of building a startup business plan. This template comes with a customizable cover page and table of contents, and each section includes sample content that you can modify to fit the needs of your business. For more fill-in business templates, read our "Free Fill-In-the-Blank Business Plan Templates" article.
Lean Business Plan Template for Startups

Download Lean Business Plan Template for Startups
This Lean business plan template takes a traditional business plan outline and extracts the most essential elements. Use this template to outline your company and industry overview, convey the problem you are solving, identify customer segments, highlight key performance metrics, and list a timeline of key activities.
Business Plan Outline Template for Startups

Download Business Plan Outline Template for Startups
You can use this business plan outline as a basis to create your own business plan. This template contains all the elements of a traditional business plan, including a title page, a table of contents, and information on what to include in each section. Simplify or expand this outline based on the size and needs of your startup business.
Startup Business Planning Template with Timeline
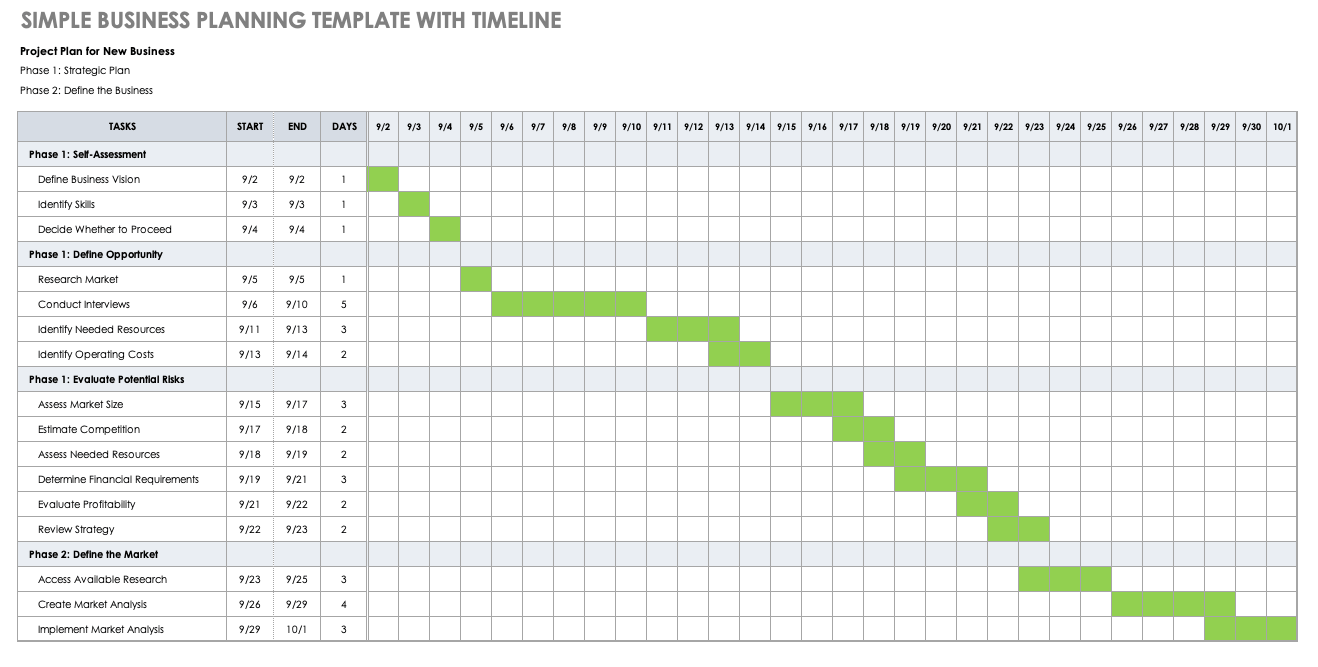
Download Startup Business Planning Template with Timeline
Excel | Smartsheet
As you create your business plan, this business planning template doubles as a schedule and timeline to track the progress of key activities. This template enables you to break down your plan into phases and provides space to include key tasks and dates for each task. For a visual timeline, shade in the cells according to each task’s start and end dates. The timeline ensures that your plan stays on track.
Business Plan Rubric Template for Startups
Download Business Plan Rubric Template for Startups
Excel | Word | PDF | Smartsheet
If you’re starting a business and want to keep all your ducks in a row, use this rubric to evaluate and score each aspect of your startup business plan. You can tailor this template to the needs of your specific business, and can also highlight areas of your plan that require improvement or expansion. Use this template as a tool to make sure your plan is clear, articulate, and organized. A sharp, insightful, well thought-out plan will definitely get the attention of potential investors and partners.
For additional resources to help support your business planning efforts, check out “Free Startup Plan, Budget, and Cost Templates.”
What’s the Best Business Plan Template for Startups?
The template you choose for your startup business depends on a number of factors, including the size and specific needs of your company. Moreover, as your business grows and your objectives change, you will need to adjust your plan (and possibly your choice of template) accordingly.
Some entrepreneurs find it useful to use a Lean business plan template design in order to jot down a business concept and see if it’s feasible before pursuing it further. Typically one to three pages, a Lean business plan template encourages you to highlight core ideas and strategic activities and remain focused on key points.
Other entrepreneurs prefer a template with a more traditional business plan design, which allows you to go into greater detail and ensure you include every detail. A traditional plan can range from 10 to 100 pages and cover both the high-level and granular particulars of your overall concept, objectives, and strategy.
There is no one-size-fits-all solution, but the following section outlines the minimum that your business plan template should include in order to gain buy-in from potential investors.
What to Include in a Startup Business Plan
Whether you choose to use a template to develop your startup business plan or decide to write one from scratch, you need to include the following elements:
- An overview of your company and the industry in which it operates
- The problem you are solving and the proposed solution
- A description of your product or service offerings, including key features
- The existing alternatives that customers use and your competitive advantage
- The target customer segments and the channels you will use to reach them
- The cost structure and revenue streams associated with your business
- A financial plan, including sales and revenue projections (ideally 3-5 years)
- If applicable, the financial requirements to get your business running, including how you will source and allocate funds
Each of the following sections provides an example of a business plan that you can use for reference as you develop your own.
One-Page Lean Business Plan Example
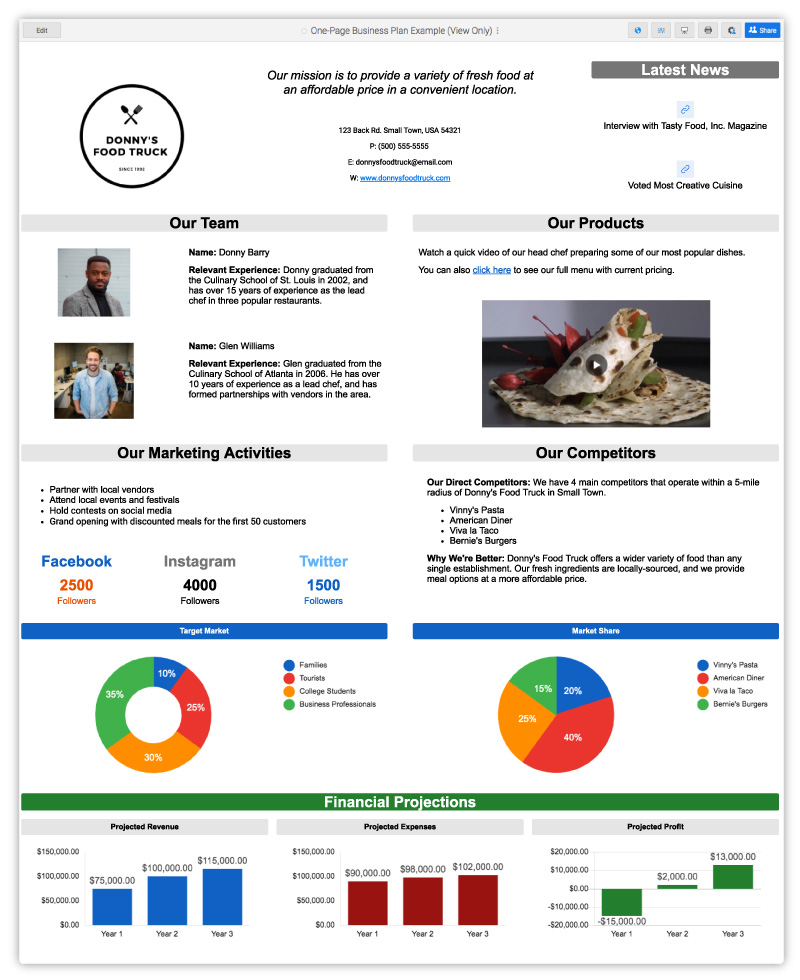
This Lean business plan example displays a visually appealing and scannable one-page illustration of a business plan. It conveys the key strategies you need to meet your main objectives. Each element of this concise plan provides stakeholders and potential investors with links to resources that support and expand upon the plan’s details, and it can also serve as an investor pitch deck.
Startup Business Plan Sample
This business plan sample contains all the aspects of a standard business plan. Using a fictional food truck business as the basis for a startup business plan, this sample will give you all the ideas you need to make your plan outstanding.
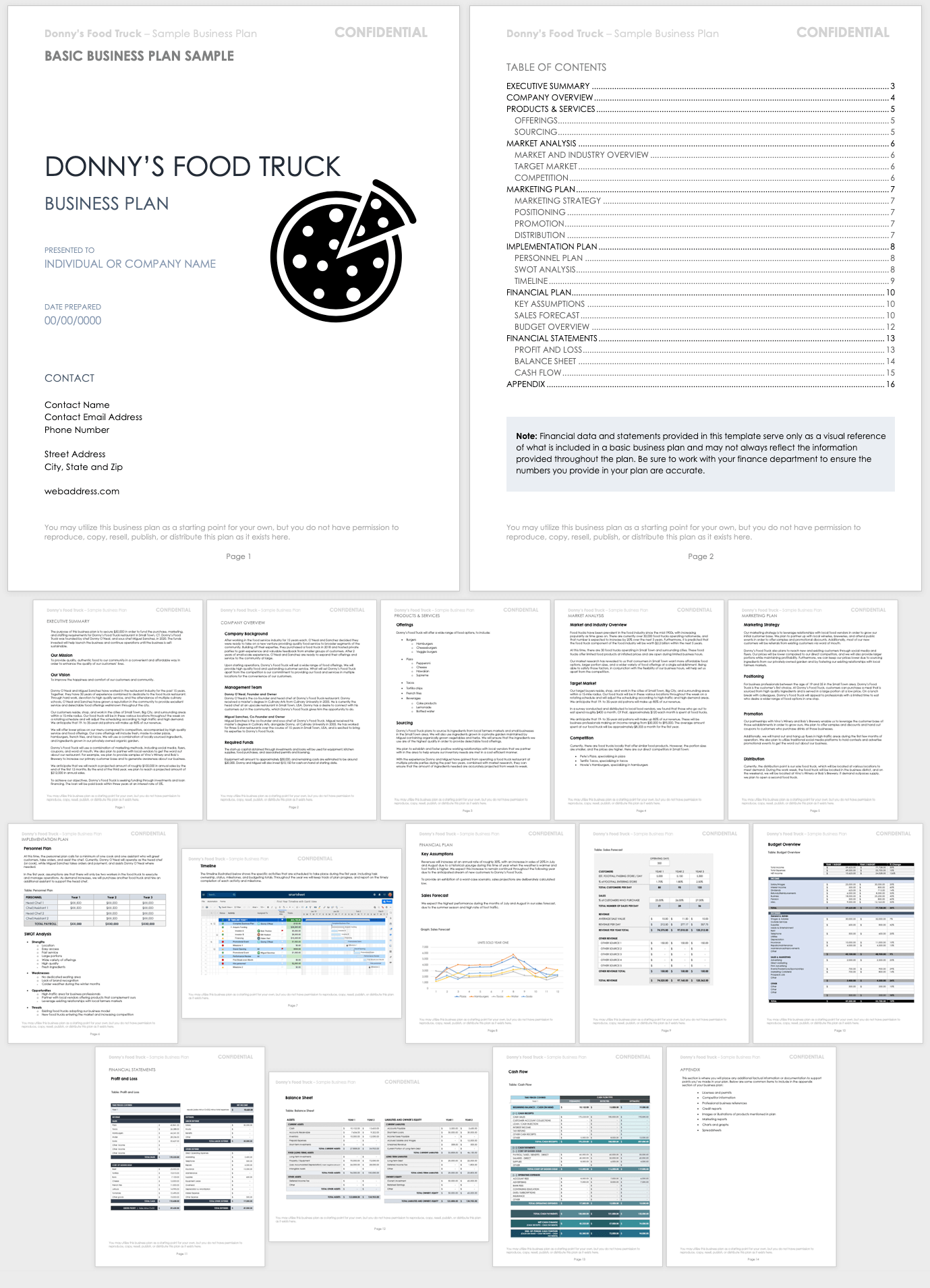
Download Startup Business Plan Sample - PDF
When the time comes that you need more space to lay out your goals and strategies, choose from our variety of free simple business plan templates . You can learn how to write a successful simple business plan here .
Visit this free non-profit business plan template roundup or of you are looking for a business plan template by file type, visit our pages dedicated specifically to Microsoft Excel , Microsoft Word , and Adobe PDF business plan templates. Read our articles offering free 30-60-90-day business plan templates to find more tailored options.
Top 10 Tips to Create a Startup Business Plan
Putting together a business plan can be overwhelming and time consuming, especially if you aren’t sure where to begin. Below, we share tips you can use to help simplify the process of developing a startup business plan of your own.
- Use a business plan template, or begin with a business plan outline that provides all the elements of a standard plan to get your ideas down on paper in a structured manner. (You can choose from the selection of templates above.)
- Remove sections from your outline that aren’t relevant or that aren’t necessary to launch and operate your business.
- Compile the data you have gathered on your business and industry, including research on your target market and product or service offerings, details on the competitive landscape, and a financial plan that anticipates the next three to five years. Use that information to fill in the sections of your plan outline.
- Get input and feedback from team members (e.g., finance, marketing, sales) and subject matter experts to ensure that the information you’ve included in the plan is accurate.
- Make certain that the objectives of your plan align with marketing, sales, and financial goals to ensure that all team members are moving in the same direction.
- Although this section of the plan comes first, write the executive summary last to provide an overview of the key points in your business plan.
- Prepare a pitch deck for potential clients, partners, or investors with whom you plan to meet in order to share vital information about your business, including what sets you apart and the direction you are headed.
- Who are the founders and management executives, and what relevant experience do they bring to the table?
- What is the problem you are solving, and how is your solution better than what currently exists?
- What’s the size of the market, and how much market share do you plan to capture?
- What are the trends in your market, and how are you applying them to your business?
- Who are your direct competitors, and what is your competitive advantage?
- What are the key features of your product or service that set it apart from alternative offerings, and what features do you plan to add in the future?
- What are the potential risks associated with your business, and how do you plan to address them?
- How much money do you need to get your business running, and how do you plan to source it?
- With the money you source, how do you plan to use it to scale your business?
- What are the key performance metrics associated with your business, and how will you know when you’re successful?
- Revisit and modify your plan on a regular basis as your goals and strategies evolve.
- Use a work collaboration tool that keeps key information across teams in one place, allows you to track plan progress, and captures updates in real time.
Successfully Implement Your Startup Business Plan with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
What stage is your business at?
Tell us and we’ll match you with a special LivePlan discount:
New Business Idea
Startup Phase
Established Business
Enter your email address to unlock it.
Please enter a valid email address
We care about your privacy. See our Privacy Policy .
Real business plans to inspire you

Launch and grow faster with a lean startup business plan
- #1 business plan software for startups at any stage
- Ideal for entrepreneurs seeking loans or investment
See how LivePlan works

Start planning for $20 per month
Rated 4.8 out of 5

Trusted by 1 million+ entrepreneurs like you
Rated 4.9 out of 5
Build a Lean Business Plan in under 60 minutes

Build a lean business plan in under 60 minutes
Clarify your ideas.
Outline your vision, the problems your startup solves, and other details. LivePlan helps you organize this information so you can better understand how your business model works.
Test your assumptions
Use financial forecasting and benchmarking tools to evaluate potential revenue and expenses. This helps you determine which products or ideas are most likely to bring success.

Be ready for every question an investor will ask
Your one—page lean business plan doubles as an investor pitch.
Get a field-tested pitch template
LivePlan was designed by entrepreneurs who have raised millions pitching both VCs and angel investors.
Build error—proof financials
Built-in forecasting software helps you create accurate financial projections. The data is then pulled into your pitch automatically and displayed as charts and graphs.
Write a detailed business plan faster with step-by-step guidance

Simple forecasting and budgeting
Just enter details about how you plan to make money. LivePlan uses built–in financial formulas to project your cash flow.

550+ sample plans to inspire you
Plus hundreds of detailed examples and Lean Planning tutorials.

Automatic charts and graphs
Visual elements helps investors see the story behind the numbers.
Get a document that's polished and professional
- Customize your plan with 10 different document themes
- Download your plan as a PDF or Word doc or share it online
- Print your plan to get a clean, hard copy document

Get insights to make the right decisions
Should you boost your ad spend? Or maybe focus on reducing churn? LivePlan's Dashboard gives you real-time insights that make these types of decisions much easier.
Hit your goals faster by tracking your progress
Compare the projections in your plan to your actual financials at–a–glance. Monitor your revenue, scrutinize your expenses, and make adjustments to ensure you reach your goals.
A simpler, more visual way to handle budgeting
All calculations are done for you with built-in formulas, so you can quickly build visual reports and summaries that show what your financial data really means.

Join over 1 million entrepreneurs who created their business plans with LivePlan
Our customers give liveplan 5 out of 5 stars.
Software is professional and user-friendly. Highly recommend to any Entrepreneur. Would not be where I am today without LivePlan.
Mar. 15, 2024
I've been using LivePlan to help me write top-tier business plans over the last 2 years. A prominent business plan writing company referred me to this site to help me produce the best business plans, to collaboratively support their clients. I've consistently had the best customer service, whether by email or live chat. Rapid responses that are helpful and this is one of the "hand-down" best platforms if you're looking for high-quality products and services - and AMAZING customer service. The price of the plan subscription is a tiny drop in the ocean compared to the results I've had with business plans created through LivePlan. Thank you for the products and services here that help me present well
Feb. 29, 2024
I've used Liveplan for two projects and I have been happy with both experiences. I've needed support twice and both experiences were quickly resolved using the chat function. I'd highly recommend Liveplan to anyone wanting to get serious about new projects. They have great customer support, and it can be a vital tool to anyone wanting to build something from the ground up.
Feb. 20, 2024
I needed a business plan for a government grant and the platform helped me tremendously. It was super organized with all the touchpoints I had to fill and the AI for improving the texts was also amazing. I did a finance plan a well and I had no clue beforehand in how to do it and that was excellent and everything I needed to submit a full case! I finished my plan and submitted it. I will definitely use it again for when i need another business plan. Thank you
Feb. 3, 2024
Extremely user friendly. I appreciated how intuitive it was and useful when I got stuck or when wanting to rephrase sections - AI was a true support for me then
Sep. 26, 2023
LivePlan helps put your ideas and beliefs on paper in a professional & organized manner. It guides you through planning, organizing, and monitoring your plan.
Sep. 2, 2023
I didn't only get value for the money paid but also got the best customer service experience as well. And of course, I'm sticking to LivePlan forever.
IsefConsult
Aug. 14, 2023
Using LivePlan since March 2015, I've created precise financial plans and business strategies for ventures of all sizes. It's the perfect tool for rapid evaluation, eliminating the risk of spreadsheet errors.
Jul. 7, 2023
It's a great Financial planning software. It can also sync with Xero and Quickbooks.
Jun. 17, 2023
If you are looking to create a Business Plan then don't waste any time, buy LivePlan as it will make your life so much easier and save you days of work!
Jun. 28, 2022
A great tool for entrepreneurs with non-finance backgrounds. We all have business ideas but long-term planning is a challenge. LivePlan makes it simple and easy.
Jun. 24, 2022
I had put off writing a plan because I dreaded the research and didn't really know what I was doing. Because of you, I now have a comprehensive, professional-looking business plan.
May 24, 2022
Overall experience with LivePlan is awesome. Very informative and easy to read. Plans come with templates and other examples you can use to build your plan.
Deonta from Texas
May 11, 2022
The best part for me is the feeling of confidence it gave me. It really made me feel like my goals and even dreams were actually possible to reach.
Mar. 29, 2022
LivePlan was a lifesaver when starting our business! It helped us make a business plan and financial projections to show others, and everyone was blown away.
The Silver Fern Shop
Jan. 27, 2022
Software Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Software Company Business Plan
You’ve come to the right place to create your Software Company business plan.
We have helped over 1,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create software business plans and many have used them to start or grow their software companies.
Below is a software business plan template to help you create each section of your own Software Company business plan.
Executive Summary
Business overview.
SimpleBooks Inc. is a new accounting software company located in Seattle, Washington. We produce an accounting product that helps small and medium-sized businesses with all of their accounting tasks. Some of these features we provide in our software include bookkeeping, tracking cash flow, reconciling bank accounts, and creating/managing financial reports.
SimpleBooks Inc. is founded by Edward Jameson, who has been a developer for 20 years. He created this software based on the complaints that his wife had of the accounting software she was using. He initially created the software to help his wife’s business but decided to expand the product and sell it to other local small and medium-sized businesses with similar accounting needs.
Product Offering
SimpleBooks Inc. produces accounting software that helps small and medium-sized businesses with all their accounting needs. We offer an extensive list of features, including the following:
- Bookkeeping
- Reconciling bank accounts
- Cash flow tracking and management
- Accounts receivable
- Income and expenses tracking
- Invoice and payment processing
- Mileage tracking
- Receipt capture
- Bill management
- Tax deductions
- Inventory management
- Employee expenses tracking
- Business analytics
- Project profitability
- Time tracking
- Financial report generation
Customer Focus
SimpleBooks Inc. will primarily target businesses in the Seattle, Washington area. The software is designed for smaller businesses, so most of our clientele will include businesses with less than 500 employees.
Management Team
SimpleBooks Inc. is founded by Edward Jameson, who has been a developer for 20 years. He has substantial experience creating software for large companies and has been very successful in his career. He initially built the company’s accounting software to help his wife’s business, but decided to expand the product and sell it to other small businesses in the area.
Success Factors
SimpleBooks Inc. will be able to achieve success by offering the following competitive advantages:
- Edward Jameson has been extremely successful working in the software industry and will be able to use experience to create the best products for our target market.
- Edward knows many of the local leaders, business managers, and other influencers within Seattle, Washington and will use those connections to establish an initial clientbase.
- SimpleBooks Inc.’s products are designed with small businesses in mind and will be curated to help the particular accounting needs of this target demographic.
Financial Highlights
SimpleBooks Inc. is seeking a total funding of $500,000 of debt capital to launch. The breakout of the funding is below:
- Office design/build: $100,000
- Software development: $150,000
- Three months of overhead expenses (payroll, rent, utilities): $150,000
- Marketing costs: $50,000
- Working capital: $50,000
The following graph below outlines the pro forma financial projections for SimpleBooks Inc.:
Company Overview
Who is simplebooks inc..
SimpleBooks Inc. is a new accounting software company located in Seattle, Washington. We produce an accounting software product that helps small and medium-sized businesses with all of their accounting tasks. We offer three tiers of features. Our basic tier only offers basic accounting functions while our advanced tier offers an extensive list of features for larger and more complex businesses. Some of these features include bookkeeping, tracking cash flow, reconciling bank accounts, and creating/managing financial reports.
SimpleBooks Inc. is founded by Edward Jameson, who has been a developer for 20 years. His wife is an accountant who was very unhappy with other accounting software products. Other accounting software can be overwhelming to use, unintuitive, and are geared toward large organizations and enterprises. Edward knew of her complaints and developed an accounting software geared towards her small business. Edward’s wife has been successfully using the software for nearly a year, so Edward is confident that this product can help other small and medium-sized businesses with similar accounting needs.
SimpleBooks Inc.’s History
After developing the software for his wife’s company, Edward Jameson did a thorough market analysis to see how well his software would do if he sold it to other local small businesses. Once his market analysis was complete, Edward incorporated SimpleBooks Inc. as an S corporation.
Since incorporation, the company has achieved the following milestones:
- Located a potential office space and signed a Letter of Intent to lease it
- Developed the company’s name, logo, and website
- Determined equipment and necessary supplies
- Began recruiting key employees
SimpleBooks Inc.’s Services
SimpleBooks Inc. produces accounting software that helps small and medium-sized businesses with all their accounting needs. Clients interested in our software can purchase one of three plans: basic, intermediate, or advanced. Our most basic plan will offer just the essential bookkeeping and accounting functions that most businesses need and only allow up to three users per account. Our intermediate plan will offer more features and allow up to seven users per account. Our most advanced plan will offer an extensive suite of accounting features and allow up to twenty users per account. All plans are charged on a monthly basis, with our basic plan being the cheapest option and advanced option being the most expensive.
Some of the functions and features included in our software products include:
Industry Analysis
According to market research, the global software industry is expected to grow substantially over the next five years. Nearly every business uses some form of software to automate its processes and increase efficiency and accuracy. Therefore, demand remains high and the industry continues to grow and expand.
Business software includes project management software, communication software, customer relationship management software, and accounting software. Accounting software is particularly popular as it significantly improves accuracy and efficiency when handling all things related to accounting. Good accounting software can help a business keep detailed tracking of all its finances, and prevent a business from bleeding money or losing track of funds.
Business software companies can succeed by providing competitive features, multiple plans and products, and keeping their products affordable. They will also succeed if they can make products that work for both small businesses and large enterprises. A company that can provide this type of software will remain competitive in the global market and see rising demand from its clientele.
Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market.
SimpleBooks Inc. will primarily target businesses in the Seattle, Washington area. The software is designed for smaller businesses, so most of our clientele will include solopreneurs, small businesses, and medium businesses with less than 500 employees. We hope to eventually branch out and serve clients located beyond the Seattle area.
Customer Segmentation
SimpleBooks Inc. will primarily target the following customer profiles:
- Solopreneurs
- Small businesses
- Medium-sized businesses
Competitive Analysis
Direct and indirect competitors.
SimpleBooks Inc. will face competition from other companies with similar business profiles. A description of each competitor company is below.
QuickBooks is one of the most popular accounting programs out there. It provides businesses with everything a business needs for its accounting department, including tracking income and expenses, managing cash flow, and helping with taxes. Clients can choose one of four monthly plans depending on the features they need and how large their accounting department is. Plans are charged on a monthly basis and include quick and helpful support and app integration.
Xero is a powerful accounting software for companies of all sizes. Clients who have Xero can pay bills, manage payroll, claim expenses, send invoices, and track inventory. They offer three tiers to choose from, including a very affordable basic plan and other plans that offer extensive features. They also provide specialized features for small businesses and for businesses in particular industries.
Freshbooks is a popular accounting software with businesses of all sizes in mind. They offer numerous features that vary depending on if you are a freelancer, a business with contractors, or a business with employees. Some of these features include managing expenses and receipts, tracking mileage and time, invoicing, and generating financial reports. They offer three tiers of plans but also create custom plans for businesses with complex and unique accounting needs.
Competitive Advantage
SimpleBooks Inc. will be able to offer the following advantages over the competition:
- Management: Edward Jameson has been extremely successful working in the software industry and will be able to use his previous experience to create the best products and experience for his clients. His unique qualifications will serve customers in a much more sophisticated manner than SimpleBooks Inc.’s competitors.
- Relationships: Edward knows many of the local leaders, business managers, and other influencers within Seattle, Washington. With his 10 years of experience and good relationships with business leaders in the area, he will be able to develop an initial client base.
- Small business focus: While our competitors do offer features for small and medium sized businesses, their products are designed with large enterprises in mind. This can make their products feel overwhelming and unintuitive. SimpleBooks Inc.’s products are designed specifically for small and medium businesses with fewer than 500 employees.
Marketing Plan
Brand & value proposition.
SimpleBooks Inc. will offer a unique value proposition to its clientele:
- Service built on long-term relationships
- A focus on helping small businesses succeed
- Affordable pricing
- Excellent customer service
Promotions Strategy
The marketing strategy for SimpleBooks Inc. is as follows:
Referral Marketing
SimpleBooks Inc. will invest heavily in a social media advertising campaign. Edward will create the company’s social media accounts and invest in ads on all social media platforms. He will use targeted marketing to appeal to the target demographics.
Social Media SimpleBooks Inc. will invest heavily in a social media advertising campaign. Edward will create the company’s social media accounts and invest in ads on all social media platforms. He will use targeted marketing to appeal to the target demographics.
Website/SEO
SimpleBooks Inc. will invest in developing a professional website that displays all of the features of our accounting software. It will also invest heavily in SEO so that the brand’s website will appear at the top of search engine results.
Direct Mail
SimpleBooks Inc. will blanket businesses with direct mail pieces. These pieces will provide general information on SimpleBooks Inc., offer discounts, and/or provide other incentives for companies to try out our accounting software.
SimpleBooks Inc.’s pricing will be on par with competitors so clients feel they receive great value when purchasing our software.
Operations Plan
The following will be the operations plan for SimpleBooks Inc.: Operation Functions:
- Edward Jameson will be the Owner and CEO of the company. He will oversee all the operations and executive functions of the company. In the beginning, he will also provide customer support and development support until he hires several other developers and customer support professionals.
- Edward will employ an experienced assistant to help with various administrative duties around the office.
- Edward will also hire several developers to develop, improve, and maintain the company’s software products.
- Edward will also hire a solid sales team to sell our products to potential clients. As the company grows, he will also hire a team that is solely dedicated to customer service.
Milestones:
SimpleBooks Inc. will have the following milestones completed in the next six months.
- 5/2023 – Finalize lease agreement
- 6/2023 – Design and build out SimpleBooks Inc.
- 7/2023 – Hire and train initial staff
- 8/2023 – Kickoff of promotional campaign
- 9/2023 – Launch SimpleBooks Inc.
- 10/2023 – Reach break-even
SimpleBooks Inc. is founded by Edward Jameson, who has been a developer for 20 years. His wife is an accountant who was very unhappy with other accounting software products. Other accounting software can be overwhelming to use, unintuitive, and are geared toward large organizations and enterprises. Edward knew of her complaints and developed an accounting software geared towards her small business. Edward’s wife has been successfully using the software for nearly a year, so Edward is confident that this product can help other small and medium-sized businesses with similar accounting needs.
Financial Plan
Key revenue & costs.
The key revenues for SimpleBooks Inc. will come from the monthly fees that are charged to clients for using the software. There are three tiers that clients can choose from. The option that each client chooses will determine how much revenue the company makes.
The major cost drivers for the company include the lease, salaries, overhead, development costs, and marketing expenses.
Funding Requirements and Use of Funds
SimpleBooks Inc. is seeking a total funding of $500,000 of debt capital to launch. The funding will be dedicated to office design, software development, marketing, and working capital. Specifically, these funds will be used as follows:
Key Assumptions
The following outlines the key assumptions required in order to achieve the revenue and cost numbers in the financials and pay off the startup business loan.
- Number of clients:
- Annual rent: $30,000
Financial Projections
Income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, software company business plan faqs, what is a software company business plan.
A software company business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your software company business. Among other things, it outlines your business concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections.
You can easily complete your Software Company business plan using our Software Company Business Plan Template here .
What are the Main Types of Software Company Businesses?
There are a number of different kinds of software company businesses , some examples include: Open source, Client-specific, Programming services, and System services.
How Do You Get Funding for Your Software Company Business Plan?
Software Company businesses are often funded through small business loans. Personal savings, credit card financing and angel investors are also popular forms of funding.
What are the Steps To Start a Software Company Business?
Starting a software company business can be an exciting endeavor. Having a clear roadmap of the steps to start a business will help you stay focused on your goals and get started faster.
1. Develop A Software Company Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed software company business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast.
2. Choose Your Legal Structure - It's important to select an appropriate legal entity for your software company business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your software company business is in compliance with local laws.
3. Register Your Software Company Business - Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your software company business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
4. Identify Financing Options - It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your software company business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
5. Choose a Location - Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
6. Hire Employees - There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
7. Acquire Necessary Software Company Equipment & Supplies - In order to start your software company business, you'll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
8. Market & Promote Your Business - Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your software company business. This includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising.
Learn more about how to start a successful software company business:
- How to Start a Software Company Business
We earn commissions if you shop through the links below. Read more
Software Company
Back to All Business Ideas
How to Start a Software Company
Written by: Carolyn Young
Carolyn Young is a business writer who focuses on entrepreneurial concepts and the business formation. She has over 25 years of experience in business roles, and has authored several entrepreneurship textbooks.
Edited by: David Lepeska
David has been writing and learning about business, finance and globalization for a quarter-century, starting with a small New York consulting firm in the 1990s.
Published on May 31, 2022 Updated on April 3, 2024

Investment range
$3,550 - $8,100
Revenue potential
$130,000 - $520,000p.a.
Time to build
0 – 3 months
Profit potential
$117,000 - $156,000p.a.
Industry trend
If you’re a software developer, congratulations — your industry is going through the roof!
The US software market has more than doubled in the last decade and shows no signs of slowing down. If you think you have the “next big thing” in software, or want to develop software for others, you could start your own software company and haul in serious dough in a booming market.
But before you put on your developer’s hat, you’ll need to learn the business side of things. Fortunately, this step-by-step guide has all the business bases covered and will prepare you to launch a successful software company.
Looking to register your business? A limited liability company (LLC) is the best legal structure for new businesses because it is fast and simple.
Form your business immediately using ZenBusiness LLC formation service or hire one of the Best LLC Services .
Step 1: Decide if the Business Is Right for You
Pros and cons.
Starting a software company has pros and cons to consider before deciding if it’s right for you.
- Massive Market – The US software industry is worth nearly $430 billion
- Good Money – Hundreds per hour to develop software
- Ridiculous Potential – Create the next big tech tool and the sky’s the limit!
- Education Required – Specialized skills are necessary to develop software
- Crowded Market – Lots of big players in the software industry
Software industry trends
Industry size and growth.
- Industry size and past growth – The US software publishing industry is worth $427.9 billion in 2022 after more than doubling in the last decade.(( https://www.ibisworld.com/industry-statistics/market-size/software-publishing-united-states/ ))
- Growth forecast – The US software publishing industry is projected to expand 4.1% in 2022.
- Number of businesses – In 2022, 15,452 software publishing businesses are operating in the US.(( https://www.ibisworld.com/industry-statistics/number-of-businesses/software-publishing-united-states/ ))
- Number of people employed – In 2022, the US software publishing industry employs 865,580 people.(( https://www.ibisworld.com/industry-statistics/employment/software-publishing-united-states/ ))

Trends and challenges
Trends in the software industry include:
- Low-code and no-code software development products are becoming more popular, which allow software developers to handle the process more easily.
- Thanks to Big Data, data management software is in high demand.
Challenges in the software industry:
- As technology evolves, developers often struggle to keep up with new trends.
- Because software is such a huge industry, it’s becoming more and more competitive, which means software companies must find a way to stand out.

Demand hotspots
- Most popular states – T he most popular states for software developers are Washington, California, and Oregon . (( https://www.zippia.com/software-developer-jobs/best-states/ ))
- Least popular states – The least popular states for software developers are Alaska, Hawaii, and Oklahoma.
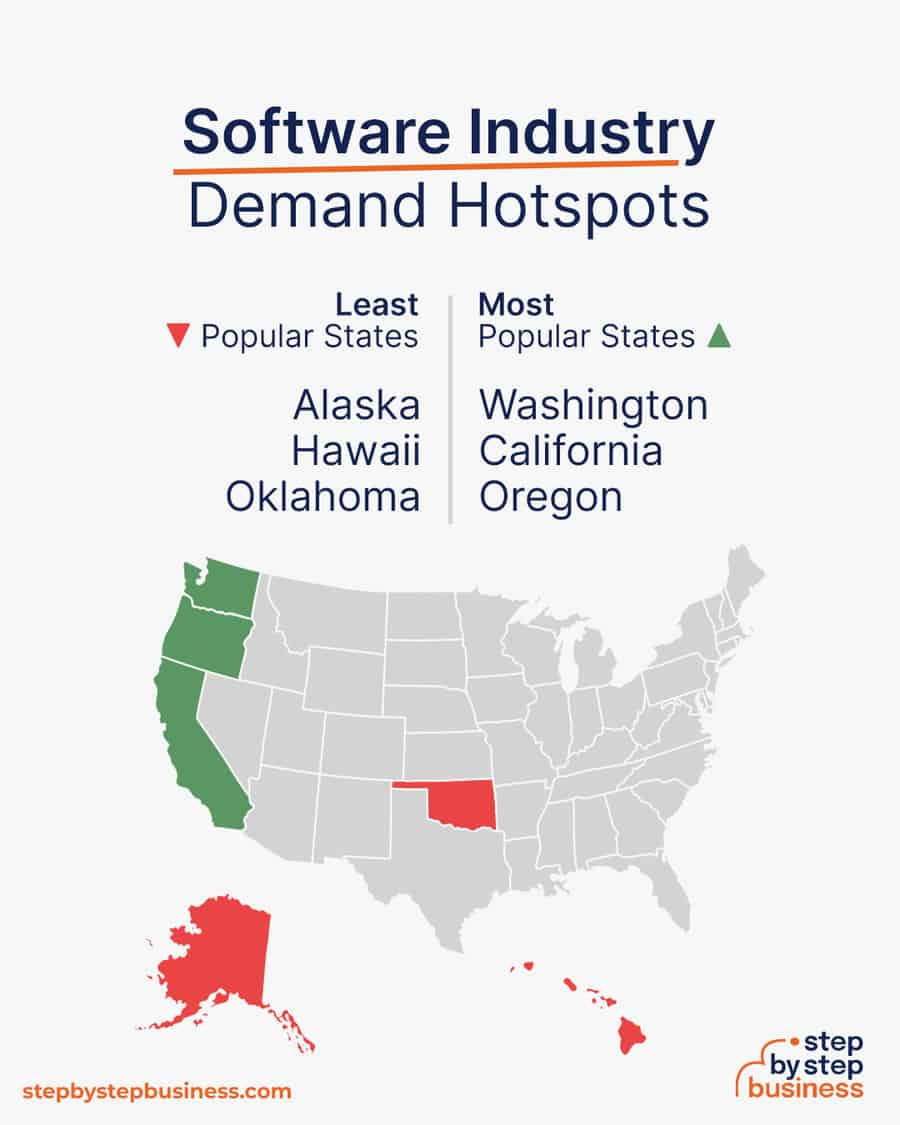
What kind of people work in software?
- Gender – 20.7% of software developers are female, while 79.3% are male.(( https://www.zippia.com/software-developer-jobs/demographics/ ))
- Average level of education – The average software developer has a bachelor’s degree.
- Average age -The average software developer in the US is 39.5 years old.
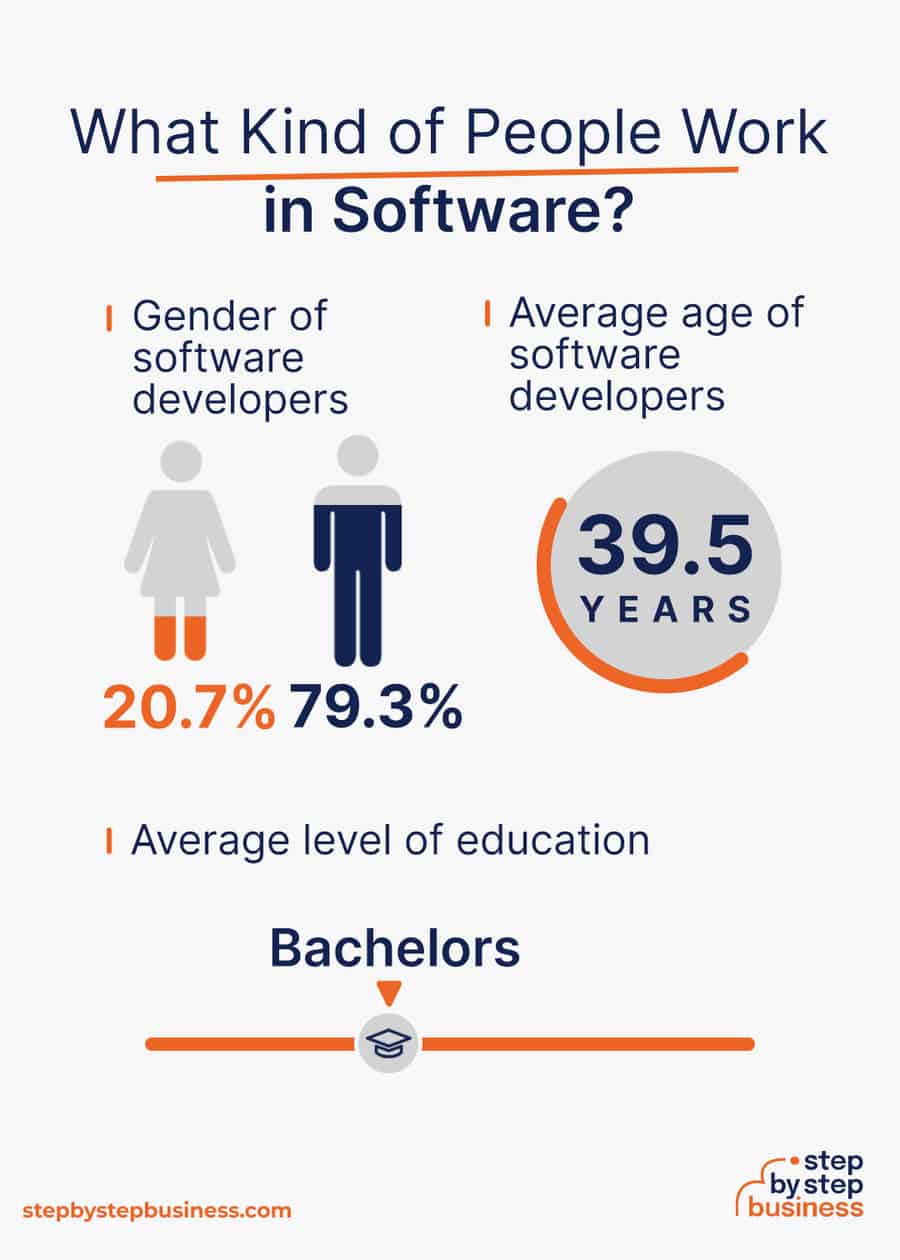
How much does it cost to start a software business?
Startup costs for a software company range from $3,500 to $8,000. Costs include a computer, programs for development projects, and a website.
If you’re not already a software developer, you can get an online software engineering degree from a place like SNHU .
How much can you earn from a software business?
Software development companies charge about $250 per hour, sometimes more, for developing software to a company’s specifications. If you’re going to develop software to be sold directly to consumers or businesses, you’ll likely charge a monthly subscription fee. This is the software as a service (SaaS) model, and subscriptions cost anywhere from $10 to $400 per month, or even more.
These calculations assume you’re going to start with the first option, charging $250 per hour. Your profit margin should be about 90%. In your first year or two, you could work from home for 10 hours a week, bringing in $130,000 in annual revenue. This would mean $117,000 in profit, assuming that 90% margin.
As your company gains traction, you could work 40 hours a week. At this stage, you’d rent a commercial space and hire staff, reducing your profit margin to around 30%. With annual revenue of $520,000, you’d make an outstanding profit of $156,000.
If you get to the point where you’re developing software to sell directly to consumers, the sky’s the limit to how much you can make if your products are successful.
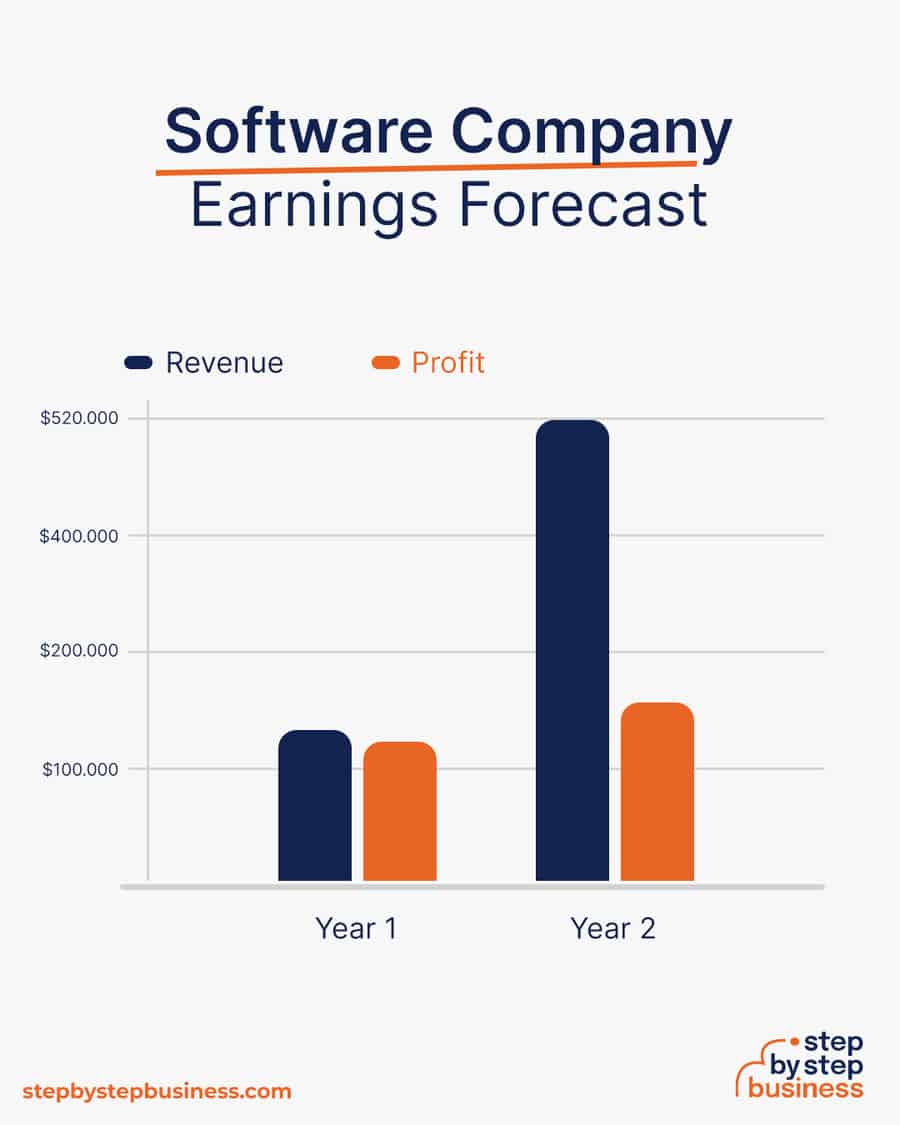
What barriers to entry are there?
There are a few barriers to entry for a software company. Your biggest challenges will be:
- The education necessary to be a software developer
- Facing a market that is crowded with software development companies
Related Business Ideas

How to Start a Live Scan Fingerprinting Business

How to Start a 3D Printing Business

How to Start a Cryptocurrency Business
Step by Step Business values real-life experience above all. Through our Entrepreneur Spotlight Series , we interview business leaders from diverse industries, providing readers with firsthand insights.
Read our interview with InvoZone’s CEO for essential insights on navigating the software industry successfully.
Dive into the world of low-code/no-code and gain insights for your entrepreneurial path from Jesus Vargas .
Gain insights on thriving in software development and remote team management from Nikita Sviridenko’s interview.
Read our interview with Alex Duchenchuk to learn how Moai Team is reshaping the landscape of AI and big data, and what it means for the future of tech.
Unlock insights into nearshore software development and staff augmentation – read our interview with Brett from BairesDev now !
Unlock insights into AI’s transformative role in software development by reading our interview with Jonathan Harel, VP R&D of Fine.dev .
Step 2: Hone Your Idea
Now that you know what’s involved in starting a software company, it’s a good idea to hone your concept in preparation to enter a competitive market.
Market research will give you the upper hand, even if you’re already positive that you have a perfect product or service. Conducting market research is important, because it can help you understand your customers better, who your competitors are, and your business landscape.
Why? Identify an opportunity
Research software companies in your area to examine their products and services, price points, and customer reviews. You’re looking for a market gap to fill. For instance, maybe the market is missing a company that offers a software solution for financial management, or a custom delivery app software company.
You might consider targeting a niche market by specializing in a certain aspect of your industry, such as software for retailers or software products for startup companies.
This could jumpstart your word-of-mouth marketing and attract clients right away.
What? Determine your products or services
You’ll probably start out by developing software solutions for businesses and charge an hourly rate for software engineering. For example, if someone wants to start a delivery service similar to DoorDash, you’ll develop the software for them. You can also offer web development and mobile app development.
Later, you may want to develop your own proprietary software that you can sell, such as business management software. When you do so, you might want to start with a minimum viable product (MVP), which is a basic version of your product that you can use to test the market and then determine features to add based on customer feedback.
How much should you charge for software?
Hourly rates for a software development company are about $250. Your profit margin when you’re working by yourself should be about 90%.
Once you know your costs, you can use this Step By Step profit margin calculator to determine your mark-up and final price points. Remember, the prices you use at launch should be subject to change if warranted by the market.
Who? Identify your target market
Your target market will be businesses or aspiring entrepreneurs. You can connect with both on LinkedIn or find business owners on Google and Yelp and call them directly.
Where? Choose your business premises
In the early stages, you may want to run your business from home to keep costs low. But as your business grows, you’ll likely need to hire workers for various roles and may need to rent out an office. You can find commercial space to rent in your area on sites such as Craigslist , Crexi , and Instant Offices .
When choosing a commercial space, you may want to follow these rules of thumb:
- Central location accessible via public transport
- Ventilated and spacious, with good natural light
- Flexible lease that can be extended as your business grows
- Ready-to-use space with no major renovations or repairs needed

Step 3: Brainstorm a Software Company Name
Your business name is your business identity, so choose one that encapsulates your objectives, services, and mission in just a few words. You probably want a name that’s short and easy to remember, since much of your business, and your initial business in particular, will come from word-of-mouth referrals.
Here are some ideas for brainstorming your business name:
- Short, unique, and catchy names tend to stand out
- Names that are easy to say and spell tend to do better
- Name should be relevant to your product or service offerings
- Ask around — family, friends, colleagues, social media — for suggestions
- Including keywords, such as “software” or “software development”, boosts SEO
- Name should allow for expansion, for ex: “NextGen Tech” over “HealthSoft Solutions”
- Avoid location-based names that might hinder future expansion
- Use online tools like the Step by Step Business Name Generator . Just type in a few keywords and hit “generate” and you’ll have dozens of suggestions at your fingertips.
Once you’ve got a list of potential names, visit the website of the US Patent and Trademark Office to make sure they are available for registration and check the availability of related domain names using our Domain Name Search tool. Using “.com” or “.org” sharply increases credibility, so it’s best to focus on these.
Find a Domain
Powered by GoDaddy.com
Finally, make your choice among the names that pass this screening and go ahead with domain registration and social media account creation. Your business name is one of the key differentiators that sets your business apart. Once you pick your company name, and start with the branding, it is hard to change the business name. Therefore, it’s important to carefully consider your choice before you start a business entity.
Step 4: Create a Software Company Business Plan
Every business needs a plan. This will function as a guidebook to take your startup through the launch process and maintain focus on your key goals. A business plan also enables potential partners and investors to better understand your company and its vision:
- Executive Summary: Summarize your software company’s mission, highlighting the innovative software solutions you plan to offer and your strategies to address specific market needs.
- Business Overview: Describe the focus of your software company, including the development of custom software applications, mobile apps, or SaaS (Software as a Service) products.
- Product and Services: Detail the range of software products and services offered, like cloud-based solutions, enterprise software, or customer relationship management (CRM) systems.
- Market Analysis: Evaluate the demand for software solutions in your target markets, identifying key industries or consumer segments.
- Competitive Analysis: Assess the landscape of competing software companies, highlighting your products’ unique features, user experience, or technological innovation.
- Sales and Marketing: Outline your strategy for reaching potential customers, using methods like digital marketing, trade shows, or partnerships with technology firms.
- Management Team: Highlight the expertise of your management team in software development, project management, and business strategy.
- Operations Plan: Describe the software development lifecycle in your company, including design, development, testing, and deployment processes.
- Financial Plan: Provide an overview of the financial aspects, such as startup costs, revenue models (e.g., subscriptions, licenses), and funding strategies.
- Appendix: Include supplementary documents like technical specifications, market research data, or key partnership agreements that support your business plan.
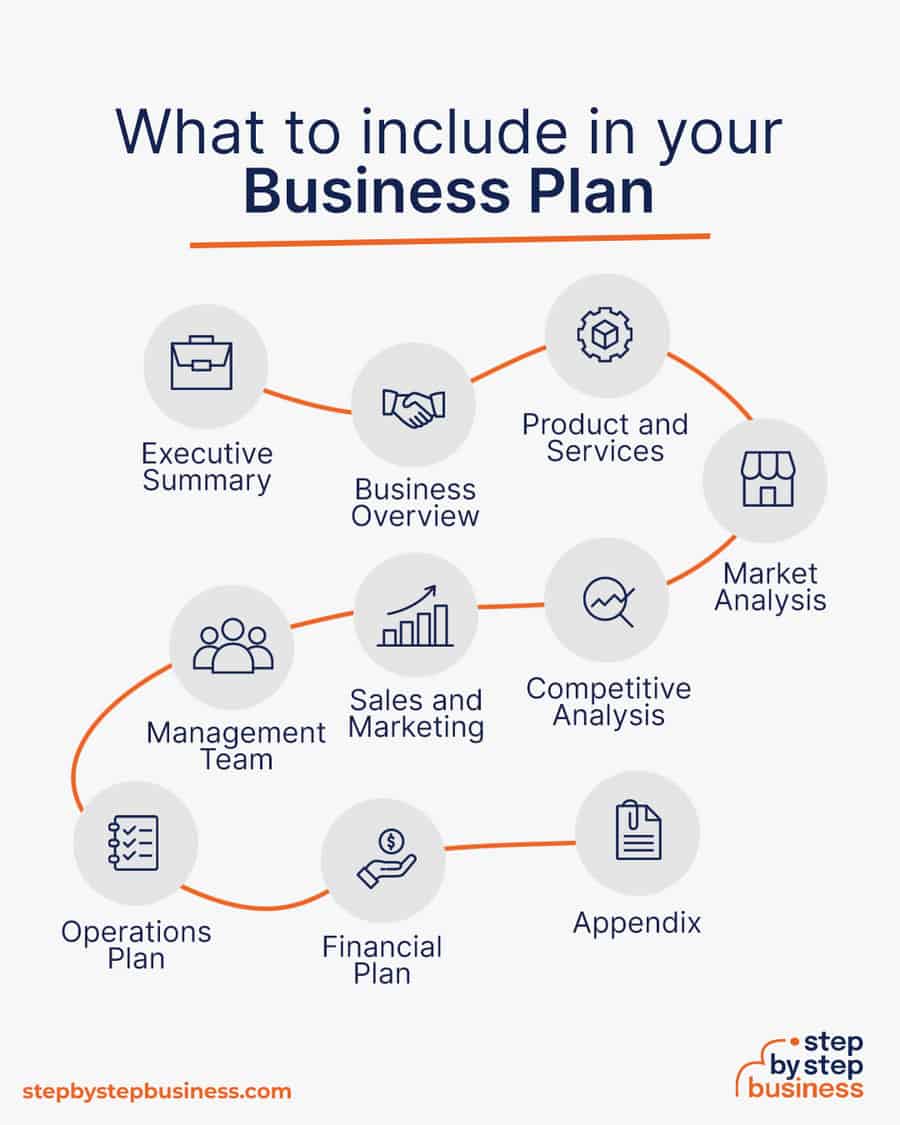
If you’ve never created a business plan, it can be an intimidating task. You might consider hiring a business plan specialist to create a top-notch business plan for you.
Step 5: Register Your Business
Registering your business is an absolutely crucial step — it’s the prerequisite to paying taxes, raising capital, opening a bank account, and other guideposts on the road to getting a business up and running.
Plus, registration is exciting because it makes the entire process official. Once it’s complete, you’ll have your own business!
Choose where to register your company
Your business location is important because it can affect taxes, legal requirements, and revenue. Most people will register their business in the state where they live, but if you’re planning to expand, you might consider looking elsewhere, as some states could offer real advantages when it comes to software companies.
If you’re willing to move, you could really maximize your business! Keep in mind, it’s relatively easy to transfer your business to another state.
Choose your business structure
Business entities come in several varieties, each with its pros and cons. The legal structure you choose for your software company will shape your taxes, personal liability, and business registration requirements, so choose wisely.
Here are the main options:
- Sole Proprietorship – The most common structure for small businesses makes no legal distinction between company and owner. All income goes to the owner, who’s also liable for any debts, losses, or liabilities incurred by the business. The owner pays taxes on business income on his or her personal tax return.
- General Partnership – Similar to a sole proprietorship, but for two or more people. Again, owners keep the profits and are liable for losses. The partners pay taxes on their share of business income on their personal tax returns.
- Limited Liability Company (LLC) – Combines the characteristics of corporations with those of sole proprietorships or partnerships. Again, the owners are not personally liable for debts.
- C Corp – Under this structure, the business is a distinct legal entity and the owner or owners are not personally liable for its debts. Owners take profits through shareholder dividends, rather than directly. The corporation pays taxes, and owners pay taxes on their dividends, which is sometimes referred to as double taxation.
- S Corp – An S-Corporation refers to the tax classification of the business but is not a business entity. An S-Corp can be either a corporation or an LLC , which just need to elect to be an S-Corp for tax status. In an S-Corp, income is passed through directly to shareholders, who pay taxes on their share of business income on their personal tax returns.
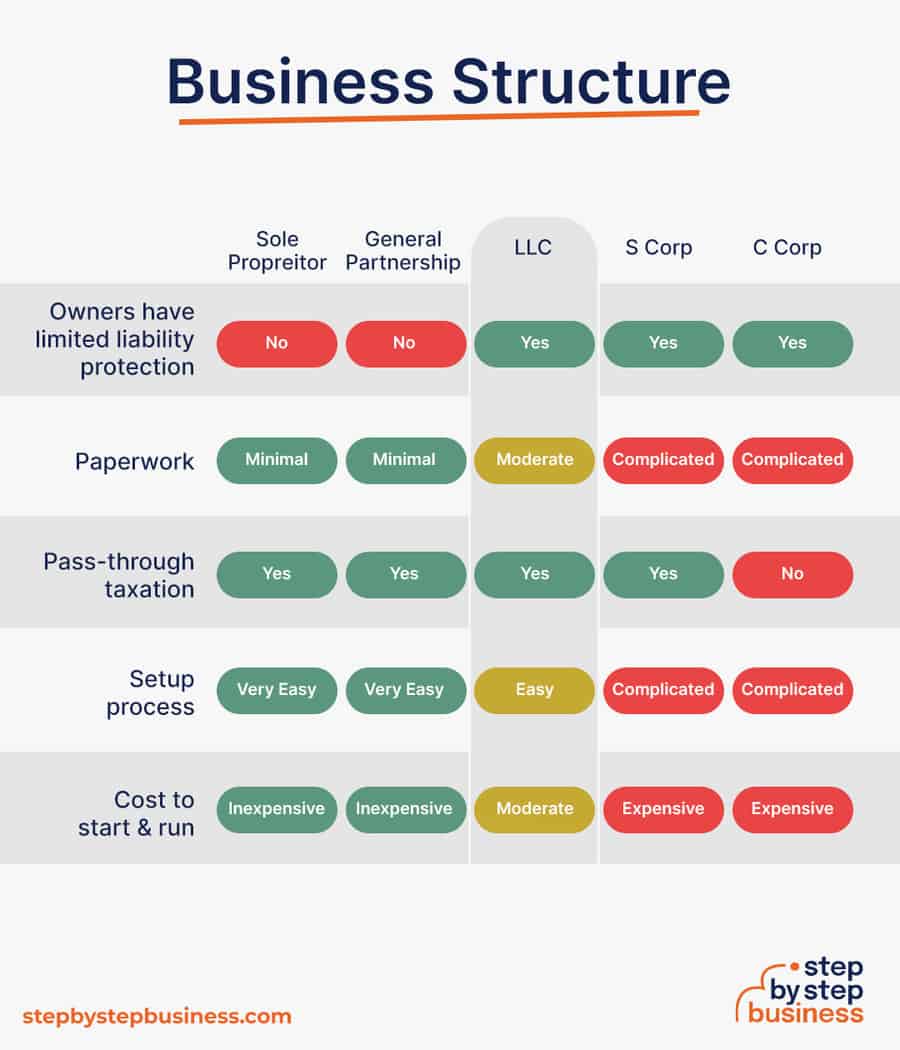
We recommend that new business owners choose LLC as it offers liability protection and pass-through taxation while being simpler to form than a corporation. You can form an LLC in as little as five minutes using an online LLC formation service. They will check that your business name is available before filing, submit your articles of organization , and answer any questions you might have.
Form Your LLC
Choose Your State
We recommend ZenBusiness as the Best LLC Service for 2024

Step 6: Register for Taxes
The final step before you’re able to pay taxes is getting an Employer Identification Number , or EIN. You can file for your EIN online or by mail or fax: visit the IRS website to learn more. Keep in mind, if you’ve chosen to be a sole proprietorship you can simply use your social security number as your EIN.
Once you have your EIN, you’ll need to choose your tax year. Financially speaking, your business will operate in a calendar year (January–December) or a fiscal year, a 12-month period that can start in any month. This will determine your tax cycle, while your business structure will determine which taxes you’ll pay.
The IRS website also offers a tax-payers checklist , and taxes can be filed online.
It is important to consult an accountant or other professional to help you with your taxes to ensure you’re completing them correctly.
Step 7: Fund your Business
Securing financing is your next step and there are plenty of ways to raise capital:
- Bank loans: This is the most common method but getting approved requires a rock-solid business plan and strong credit history.
- SBA-guaranteed loans: The Small Business Administration can act as guarantor, helping gain that elusive bank approval via an SBA-guaranteed loan .
- Government grants: A handful of financial assistance programs help fund entrepreneurs. Visit Grants.gov to learn which might work for you.
- Venture capital: Venture capital investors take an ownership stake in exchange for funds, so keep in mind that you’d be sacrificing some control over your business. This is generally only available for businesses with high growth potential.
- Angel investors: Reach out to your entire network in search of people interested in investing in early-stage startups in exchange for a stake. Established angel investors are always looking for good opportunities.
- Friends and Family: Reach out to friends and family to provide a business loan or investment in your concept. It’s a good idea to have legal advice when doing so because SEC regulations apply.
- Crowdfunding: Websites like Kickstarter and Indiegogo offer an increasingly popular low-risk option, in which donors fund your vision. Entrepreneurial crowdfunding sites like Fundable and WeFunder enable multiple investors to fund your business.
- Personal: Self-fund your business via your savings or the sale of property or other assets.
Bank and SBA loans are probably the best option, other than friends and family, for funding a software business. You might also try crowdfunding if you have an innovative concept.
If you have a unique idea for a software that you can develop to put on the market, you may be able to attract angel investors or venture capital. Tech startups are considered very investable because they have the potential for huge growth.
Step 8: Apply for Business Licenses/Permits
Starting a software business requires obtaining a number of licenses and permits from local, state, and federal governments.
Federal regulations, licenses, and permits associated with starting your business include doing business as (DBA), health licenses and permits from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration ( OSHA ), trademarks, copyrights, patents, and other intellectual properties, as well as industry-specific licenses and permits.
You may also need state-level and local county or city-based licenses and permits. The license requirements and how to obtain them vary, so check the websites of your state, city, and county governments or contact the appropriate person to learn more.
You could also check this SBA guide for your state’s requirements, but we recommend using MyCorporation’s Business License Compliance Package . They will research the exact forms you need for your business and state and provide them to ensure you’re fully compliant.
This is not a step to be taken lightly, as failing to comply with legal requirements can result in hefty penalties.
If you feel overwhelmed by this step or don’t know how to begin, it might be a good idea to hire a professional to help you check all the legal boxes.
Step 9: Open a Business Bank Account
Before you start making money, you’ll need a place to keep it, and that requires opening a bank account .
Keeping your business finances separate from your personal account makes it easy to file taxes and track your company’s income, so it’s worth doing even if you’re running your software business as a sole proprietorship. Opening a business bank account is quite simple, and similar to opening a personal one. Most major banks offer accounts tailored for businesses — just inquire at your preferred bank to learn about their rates and features.
Banks vary in terms of offerings, so it’s a good idea to examine your options and select the best plan for you. Once you choose your bank, bring in your EIN (or Social Security Number if you decide on a sole proprietorship), articles of incorporation, and other legal documents and open your new account.
Step 10: Get Business Insurance
Business insurance is an area that often gets overlooked yet it can be vital to your success as an entrepreneur. Insurance protects you from unexpected events that can have a devastating impact on your business.
Here are some types of insurance to consider:
- General liability: The most comprehensive type of insurance, acting as a catch-all for many business elements that require coverage. If you get just one kind of insurance, this is it. It even protects against bodily injury and property damage.
- Business Property: Provides coverage for your equipment and supplies.
- Equipment Breakdown Insurance: Covers the cost of replacing or repairing equipment that has broken due to mechanical issues.
- Worker’s compensation: Provides compensation to employees injured on the job.
- Property: Covers your physical space, whether it is a cart, storefront, or office.
- Commercial auto: Protection for your company-owned vehicle.
- Professional liability: Protects against claims from a client who says they suffered a loss due to an error or omission in your work.
- Business owner’s policy (BOP): This is an insurance plan that acts as an all-in-one insurance policy, a combination of the above insurance types.
Step 11: Prepare to Launch
As opening day nears, prepare for launch by reviewing and improving some key elements of your business.
Essential software and tools
Being an entrepreneur often means wearing many hats, from marketing to sales to accounting, which can be overwhelming. Fortunately, many websites and digital tools are available to help simplify many business tasks.
You may want to use project management software such as Azure DevOps , Zoho , or FunctionFox , to manage your projects, workflows, and collaboration.
- Popular web-based accounting programs for smaller businesses include Quickbooks , Freshbooks , and Xero .
- If you’re unfamiliar with basic accounting, you may want to hire a professional, especially as you begin. The consequences for filing incorrect tax documents can be harsh, so accuracy is crucial.
Develop your website
Website development is crucial because your site is your online presence and needs to convince prospective clients of your expertise and professionalism.
You can create your own website using website builders . This route is very affordable, but figuring out how to build a website can be time-consuming. If you lack tech-savvy, you can hire a web designer or developer to create a custom website for your business.
Your clients are unlikely to find your website, however, unless you follow Search Engine Optimization ( SEO ) practices. Regularly update content with industry insights and success stories to engage visitors and improve search engine rankings.
To thrive in the competitive tech industry, a software company must employ strategic and innovative marketing approaches. Here are the most effective ones:
- Content Marketing – Create valuable and informative content (blogs, whitepapers, webinars) that addresses customer pain points and showcases your software’s unique features.
- Social Media Engagement – Actively engage with your audience on platforms like LinkedIn, Twitter, and Facebook to build community and brand awareness.
- Email Marketing – Use targeted email campaigns to nurture leads and keep your audience informed about updates, offers, and industry insights.
- Customer Testimonials and Case Studies – Share success stories and testimonials to build trust and demonstrate the impact of your software.
- Partnerships and Collaborations – Collaborate with other businesses or influencers in your industry to reach new audiences and add credibility.
- Free Trials and Demonstrations – Offer free trials or live demonstrations to let potential customers experience your software firsthand.
- Paid Advertising – Invest in targeted ads on search engines and social media to reach a wider audience quickly.
- Trade Shows and Conferences – Participate in industry events to network, build relationships, and showcase your software.
- User Experience and Feedback – Continuously improve the user experience based on customer feedback and stay responsive to their needs.
Focus on USPs
Unique selling propositions, or USPs, are the characteristics of a product or service that sets it apart from the competition. Customers today are inundated with buying options, so you’ll have a real advantage if they are able to quickly grasp how your software company meets their needs or wishes. It’s wise to do all you can to ensure your USPs stand out on your website and in your marketing and promotional materials, stimulating buyer desire.
Global pizza chain Domino’s is renowned for its USP: “Hot pizza in 30 minutes or less, guaranteed.” Signature USPs for your software business could be:
- Custom software for your hot startup
- Streamlined management software to keep your business running smoothly
- Manage your finances with our custom software solutions

You may not like to network or use personal connections for business gain. But your personal and professional networks likely offer considerable untapped business potential. Maybe that Facebook friend you met in college is now running a software business, or a LinkedIn contact of yours is connected to dozens of potential clients. Maybe your cousin or neighbor has been working in software for years and can offer invaluable insight and industry connections.
The possibilities are endless, so it’s a good idea to review your personal and professional networks and reach out to those with possible links to or interest in software. You’ll probably generate new customers or find companies with which you could establish a partnership.
Step 12: Build Your Team
If you’re starting out small from a home office, you may not need any employees. But as your business grows, you will likely need workers to fill various roles. Potential positions for a software business include:
- Software Engineers – assist with software development
- General Manager – scheduling, accounting
- Marketing Lead – SEO strategies, social media
At some point, you may need to hire all of these positions or simply a few, depending on the size and needs of your business. You might also hire multiple workers for a single role or a single worker for multiple roles, again depending on need.
Free-of-charge methods to recruit employees include posting ads on popular platforms such as LinkedIn, Facebook, or Jobs.com. You might also consider a premium recruitment option, such as advertising on Indeed , Glassdoor , or ZipRecruiter . Further, if you have the resources, you could consider hiring a recruitment agency to help you find talent.
Step 13: Run a Software Company – Start Making Money!
As a software developer, you know how in demand your services are. The software industry in the US has taken off in the last decade, more than doubling to reach well over $400 billion. Your own software company could open up a world of opportunity for you and allow you to build great software solutions for businesses all over the world. You could even grow your company into the next Microsoft!
You’ve added business knowledge to your resume now, so it’s time to get to work and launch your successful software company.
- Software Business FAQs
For software companies, the sky’s the limit in terms of profitability. Software is a massive and growing industry, so if you’re a developer, there’s plenty of opportunity.
Software development companies charge about $250 per hour, sometimes more, for developing software to a company’s specification. If you’re going to develop software that you’ll sell directly to consumers or businesses, you’ll generally charge a monthly subscription fee of $10 to $400 or more.
Starting a software company can be challenging due to the competitive nature of the industry, the need for technical expertise, and the ever-evolving technology landscape. However, with careful planning, market research, and a solid business strategy, it is possible to overcome these challenges and build a successful software company.
To protect intellectual property and ensure data security in your software company, it is crucial to implement several measures. These include obtaining appropriate patents or copyrights for your software, implementing strict access controls and encryption methods, regularly updating security protocols, conducting thorough employee training on data protection, and employing robust backup and disaster recovery systems.
To differentiate your software company from competitors, you can focus on various strategies. This includes providing a unique and innovative software solution that solves a specific problem or meets an underserved market demand. Additionally, offering exceptional customer support, continuous software updates and improvements, competitive pricing, and cultivating a strong brand identity can help set your company apart in the market.
The future of software is incredibly promising. Advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and automation are expected to play a significant role in shaping the industry. Software will continue to permeate various sectors, from healthcare to finance, with increased focus on cybersecurity, cloud computing, and mobile applications. Additionally, emerging technologies such as blockchain, Internet of Things (IoT), and virtual reality (VR) present new opportunities for software development and integration.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Decide if the Business Is Right for You
- Hone Your Idea
- Brainstorm a Software Company Name
- Create a Software Company Business Plan
- Register Your Business
- Register for Taxes
- Fund your Business
- Apply for Business Licenses/Permits
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Get Business Insurance
- Prepare to Launch
- Build Your Team
- Run a Software Company - Start Making Money!
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Featured resources.

15 Software Business Ideas
Carolyn Young
Published on June 16, 2022
The global software industry is worth a massive $600 billion and projected to expand nearly a third by 2027. For software developers and engineers,t ...

15 SaaS Business Ideas for Startups
Published on June 8, 2022
The global market for SaaS, or software as a service, has exploded in recent years, expanding nearly seven-fold since 2015 to reach a whopping $208b ...
No thanks, I don't want to stay up to date on industry trends and news.
Let's get in touch
Kindly fill out the form below, and our team will get back to your inquiries ASAP.
Required(*)
Email Address
I'm interested in:
Please fill all the required fields!
*By submitting this form, you have read and agreed to Orient Software's Term of Use and Privacy Statement
+84 28 3812 0101
OTHER ENQUIRIES
7 Elements to Successfully Write a Tech Startup Business Plan

Vy Le | 18/05/2023

When it comes to starting a tech business, having a well-crafted tech business plan is crucial to attract investors and succeed in the competitive market landscape. A business plan outlines your company’s vision, strategy, and financial plan over time, giving potential investors insight into your business model and growth potential.
However, writing a tech startup business plan can be a daunting task, especially for new entrepreneurs that lack experience in the tech industry. In this article, we’ll provide you with a comprehensive guide on writing a tech startup business plan that will impress investors and help you succeed in the fast-paced tech startup world.
What is a Tech Startup Business Plan?

A tech startup business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines the goals, objectives, and strategies of a technology-based startup company. It is a crucial tool that helps entrepreneurs in the tech industry to define and organize their ideas, demonstrate the feasibility of their business concept, and present a clear plan for how they intend to build and grow their company.
Generally, most business plans typically include a summary of the company history, the problem it is solving, the target audience, competitive analysis, the marketing and sales strategy, the development strategy, and the financial plan. Also, such a document may include details about the management team, operations, and product development roadmap.
Particularly for the technology sector, the tech startup business plan also includes more specialized elements. Specifically, it is important to focus on the e-commerce technology trends being developed and how it addresses a gap or problem in the market while building such a document. This includes details such as the software or hardware being constructed, the technology stack being used, its technical architecture, and how it will improve or disrupt existing technology solutions.
Overall, a well-crafted business plan can help secure funding from potential investors or lenders, attract top talent, and ultimately guide the company toward success.
10 Core Questions to Answer When Conducting a Tech Startup Business Plan
For a tech startup business to build a good business plan, keep in your mind these questions and find the answers for yourself along the way. Answering these questions will help your startup team formulate a clear and compelling business plan/business idea, which can be used to guide the tech startup founder toward success.
1. Which product or service does your tech startup offer?
2. What is the team structure, and who are the key members?
3. Who is your target audience for the product or service?
4. Who are the competitors?
5. What are your competitive advantages?
6. What is your marketing strategy, and how do you leverage marketing channels?
7. What is your sales plan, and how do you leverage sales channels?
8. What is your financial plan, including projections for revenue, expenses, and funding needed?
9. What are the risks and challenges the business may face?
10. What is your timeline for product development, launch, and growth?
3 Reasons Why You Need a Technology Startup Business Plan
But why do businesses compose a tech startup business plan at the beginning of the software development process? There must be reasons. Check them out now!

Providing a Blueprint for Success
According to a Harvard Business Review study , startups that write a detailed business plan have a 16% chance to achieve viability than businesses that don’t. This metric proves the usefulness of this action.
By systematizing the business idea into a complete tech startup business plan, you give the business itself and each team member a clear picture of the company’s goals, vision, and strategies. While people are a prerequisite for an organization’s success, understanding the product’s direction will help each individual in the development team structure closely link together throughout the software development process and shorten product completion time.
Raising Capital from Investors
In the tech industry, startups often require significant amounts of capital to fund product development, hire staff, and invest in marketing and sales efforts. Raising such funds from investors is often necessary for startups’ future growth and success.
However, among the hundreds of thousands of startups out there, what sets your business apart from all of them? It is a specific technology startup business plan that is well-written to demonstrate.
Prospective investors and venture capitalists do not spend their money arbitrarily on poorly invested projects because, ultimately, they care about the return on investment (ROI). Investors are usually drawn to companies that understand their market and have a plan to tackle the market gap, and a well-curated business plan can make a tech startup stand out from the crowd.
Attract Top Talent
Suppose you don’t intend to use outsourced software development services to quickly build a development team of professionals and want to recruit developers for your startup yourself . A tech startup business plan can help in this situation.
A technology startup business plan can showcase the unique features of the business and its competitive advantage in a crowded market. Therefore, it can become a valuable tool for convincing top talent to join the team, especially if the company’s plans align with professionals’ aspirations and career goals.
7 Essential Elements to Write a Business Plan for Your Tech Startup
Your business idea can be good. But to easily realize it and stick to the outlined roadmap, you must present them in a systematic document. To do this, don’t skip the seven key elements to conduct a tech startup business plan below.

Executive Summary
The executive summary is the most critical component of a tech startup business plan as it gives the reader a first-hand look at your product/service. An executive summary is a brief overview of your entire tech startup business plan, providing context for the reader and summarizing all the key points. It is usually the first section of the business plan and is customized to reflect the company’s goals, values, and unique selling points in a way that inspires the reader’s confidence in the startup.
An excellent executive summary in a software startup business plan typically includes the general situation of the target market or related industry based on conducted market research and an overview of the software solution you offer. Other information, such as unique value proposition (UVP), competitors in the same segment, and the company’s goal, can also be included in the executive summary as an optional option.
The advice is not to write the executive summary too long and vague, lacking focus on the main ideas. It is recommended to keep it within two pages to optimize visual efficiency and avoid boring the reader. Use the executive summary as an opportunity to showcase your tech startup’s strengths before diving into the details later on.
Company Description
If the executive summary is the section that presents all the overview data about your product or service, the company description in a technology startup business plan is the part that gives the reader a clearer view of your entire tech startup, or what we call a company overview.
This section should provide a clear understanding of the business to potential partners or customers and inspire confidence in the startup . There are many primary elements that make up a complete company description. So, it will be hard if tech startup founders don’t start small. Draft fundamental ideas and gradually develop them into complete content until they meet all the needs of a business plan.
Here are some main elements to consider when writing a company description: tech company’s name, company history, business model, vision, mission, legal structure (whether it is a sole proprietorship, partnership, LLC, or corporation.), management team structure (each role and responsibilities) and competitive advantage.
Target Market Research
By doing target market research, a tech startup is able to figure out three key elements for a tech startup’s business plan. These are the total addressable market (TAM), technology market trends, target customer groups, and competitor analysis.
- The total addressable market (TAM) is the target market’s total size that helps assess potential future revenue streams and justify the business case.
- Market trends help tech startups stay up to date with market demand, ever-changing information technology, and changes in perspective customers’ behavior.
- Target audience gives tech startups a better understanding of their potential customers by gathering demographic, geographic, and behavior factors.
- The competitor analysis section of your business plan helps tech company in identifying their direct competitors and understand their own strengths and weaknesses to promote competitive advantage better.
Target market research not only benefits the startup company but also shows your investment and determination in the product or service.
Product/Service Line
It’s time to be more descriptive of the product or service your company offers rather than just general, like in the executive summary. Because the purpose of a startup business plan is generally still to introduce products to potential customers, this section should be written carefully and go into detail to demonstrate the product’s uniqueness and promising growth potentials.
Some elements to consider when writing a business plan include:
- Product or service explanation: This includes key features and benefits, how it works, and how it is different from other solutions in the market.
- Value proposition: Clearly stating how your product fulfills a customer need and backing it up with evidence.
- Product development: Providing a product development roadmap by outlining your timeline and steps to achieve further development goals.
Team Structure
The team structure is an essential part of a tech startup business plan. It gives investors and stakeholders insight into the management team’s ability to execute the business plan and the team’s capacity to bring the idea to fruition.
In this part of the business plan, it is vital to highlight the leadership team and their roles. Start by introducing your founders and executive team and describe their previous experience and expertise with a proven track record that makes them qualified to lead the company. For investors to easily visualize the development team of your startup business, using a graphic, such as an organizational chart, can help.
Next, outline the roles and responsibilities of each member of your team , including any advisors or board members. Remember to describe carefully how each team member will contribute and cooperate to the successful company and how their respective skill sets complement, and experience are relevant to the tech industry.
Goals and plans for the future of the leadership team and development team members can also be written in the business plan as a supplement. For example, you expect to expand your team within one year by hiring additional staff or bringing on new partners or investors. All must be written in a clear, concise, and focused manner.
Marketing and Sales Plan
A product or service with good quality is only part of it when marketing and sales plans are exactly the activities that bring users and profits to the company. The marketing and sales plan section of a tech startup business plan will serve as a critical component that outlines how your company plans to acquire and retain customers, generate revenue, and achieve sustainable growth.
Regarding the marketing strategy, since you have already defined the target audience in the target market research section of the business plan, you only need to briefly repeat this section to once again help investors develop a comprehensive understanding of your ideal customer and their buying behavior. Next, don’t forget to differentiate your product or service from competitors and effectively manage your marketing plan by describing your unique value proposition. Consider using social media advertising, SEO, content marketing, email marketing, and public relations as tactics to reach your audience and successfully execute a marketing plan.
After your marketing efforts, it’s time to build your business plan and a suitable sales strategy. The basic elements of sales strategies adopted by many startups include sales approach, pricing strategy, sales channels, and sales team structure, which provides a clear path for converting leads into paying customers.
To measure the success of your marketing and sales efforts, track progress, and make data-driven decisions, you should identify key performance indicators (KPIs) such as website traffic, conversion rates, customer acquisition cost, and revenue generated.
Financial Projections
Running out of cash is one of the primary reasons why many businesses fail. Building a financial plan right from the start will make it easier to manage expenses and manage risks for your software solution. There is no fixed financial plan of the business plan as each startup has different business orientations and goals.
However, one of the most vital aspects of this section is the sales forecast, which details how your company plans to generate revenue, including the sales channels you will use, your pricing strategy, and your projected customer acquisition rate.
The cash flow statement and the balance sheet are also important elements in a basic financial plan. The balance sheet provides a snapshot of the company’s financial health and helps you make informed decisions about your operations and growth strategies. The cash flow statement identifies how much money you expect to have on hand each month, taking into account both revenue and expense forecasts.
Final Thought

As for business plans, there is no single startup business plan template that is a perfect fit for your project since there is no startup like any other in the technology market. Each startup has different characteristics and different product businesses. Some companies set up a business plan to raise capital for a banking product . Meanwhile, there are companies that are working on human resources software.
So, start a business plan from small things. Take note of all your ideas on paper and discuss them in turn with the development team is Orient Software ’s advice.
With years of experience in the field of information technology, Orient is confident of having the ability to advise you on all problematic aspects of the industry. Contact us for more details !
Content Map
Related articles.

Deciphering Project Management Tools: Airtable Vs. Jira Comparison
Here is what you need to know to choose between Airtable and Jira - two popular project management tools.
Quynh Pham | 05/04/2024
Ten Programming Languages for Web Development in 2024
Øyvind Forsbak | 09/02/2024
Best Cloud Certifications: Which Ones Are in High Demand and Why?
Tan Dang | 24/01/2024
Salesforce Service Cloud Vs. Sales Cloud: The Comparison
Shannon Jackson-Barnes | 25/12/2023
Assemble a Competent Web Development Team: Roles, Skills, and Qualities
Hieu Nguyen | 18/12/2023
Disclose the Astonishing Use Cases of Robotic Process Automation in Healthcare
Trung Tran | 19/10/2023
Why Outsource Web Application Development? - All the Practical Benefits to Take Action
Trung Tran | 06/08/2023

The Ultimate Handbook on Source Code Management Tools
Source code management tools are the tools that facilitate effective communication and management of a codebase in a team of multiple developers.
Quynh Pham | 02/04/2024

CRM System Implementation: Step by Step Toward Success
For beginners, this is a CRM implementation guide - discussing the crucial steps involved in setting up an effective CRM system for your business.
Trung Tran | 25/12/2023

The Basics of Application Performance Management Software
Find out what application performance management software is, how it works, and the key features to look for when choosing this specific type of software.
Shannon Jackson-Barnes | 22/12/2023

Benefits of CRM Software: 7 Ways CRM Software Help You Reach Your Goals
Boosting sales revenue, enhancing customer retention and satisfaction, and automation are only some of the benefits of CRM software.
Quynh Pham | 09/12/2023
Looking for an IT partner?
Contact us today for a free quote within 3 business days


500+ business plans and financial models
How To Create A SaaS Business Plan In 11 Steps: Full Guide
- November 17, 2023
- Fundraising

Software as a service (SaaS) is the fastest-growing market segment of the past 5 years: the overall spend per company on SaaS products was up +50% in 2021 compared to 2018!
Yet, SaaS do require significant upfront investment before they can turn out a profit. Whether you are raising capital or applying for a grant, you will need a solid business plan for your SaaS startup.
Whilst every business is unique, we strongly recommend to follow a clear structure vetted by dozens of high-profile VC firms globally. Having a powerful and clear business plan will maximise your chances of raising capital from potential investors.
In this article we walk you through the 14 sections you must have in your SaaS business plan.
No te: If you are looking for a pitch deck instead, read our guide here . Although business plans and pitch decks are similar, they are also very different in their format. If you aren’t sure what is best for you, we recommend to read our article on the key differences between business plans and pitch decks .
SaaS Business Plan: The Template
If you are creating a business plan for your SaaS startup, we recommend you follow the following structure:
- Executive Summary
- The Problem
- The Solution
- Market Opportunity
- Competitive Landscape
- Business Model
- Intellectual Property
- Marketing Strategy
- Financial Plan

1. Executive Summary
The executive summary is the introduction of your SaaS business plan. This is a section you should spend a lot of time on as it’s the first impression investors will have when looking at your business plan.
The executive summary should fit in 2 pages maximum . Make it to the point, concise, and make sure to answer the following questions:
- What is the problem you want to solve?
- What is your solution?
- Who are the co-founders behind the project?
- Do you have early traction?
- What are you asking for (capital from investors, government grant application, etc.)?
Expert-built financial model templates for tech startups
2. The Problem
This is the “why” of your business. Explain in this section what is the problem you are trying to solve.
The greatest businesses are solving big problems, yet they aren’t necessarily obvious . For instance, if your SaaS startup aims to solve the pain points of HR administrative tasks (human errors, low digitalisation, time-consuming, etc.) make it clear here. Not everyone is knowledgeable about companies’ support functions processes, let alone HR.
Ideally you would list the 2/3 friction points you aim to fix. For instance, digitalisation usually fixes multiple problems at once: it is fast, seamless and accessible (vs. slow, prone to errors and non-readily available / accessible solutions).
3. The Solution
Your startup builds and commercialises a product and/or a service which solves the problem explained earlier.
This section should not explain in detail your product nor how it works. Instead, it should focus on the benefits for your customers .
Ideally, you should compare the pain points explained on section 2 (the Problem) to the benefits your solution brings to your customers. That way, it is crystal clear to investors your solution really adds value to potential customers .
4. Market Opportunity
Here, you need to clearly identify 2 very important metrics:
- Market size : how big is your market?
- Market growth: how fast does your market grow?
If you are operating in a niche market, chances are that you will face some challenges: the information might not be publicly available. In any case, you should be able to make a high-level estimation of your market. Read our article on market sizing and how to estimate TAM, SAM and SOM for your startup .
When looking for these metrics, you have multiple sources of information: public reports, specialised press, etc. Even public companies publish press releases and annual reports including some of their proprietary market estimates so be sure to look there too.

5. Competitive Landscape
How fragmented is your market.
Are there 3 big players sharing 90% market share or thousands of small players? Here, refer to public market reports and your own understanding of the competitive landscape.
A few questions you could ask yourself, among others:
- Who are your competitors?
- Are they local, regional, national or global?
- Do they have mobile and/or desktop applications?
Where do you position yourself vs. competition?
Is your solution a game changer other competitors don’t have (yet)? Do you have competitors with similar products/services?
Ideally, you would create a small table with, for each type of competitors (e.g. global diversified companies, small pure players, etc.) the main characteristics they share or not. For instance, do they all a global presence? Do they have a on-premise or a SaaS solution? Do they offer both a desktop and mobile app, or just desktop? What is their relative price positioning (expensive vs. accessible)?
6. Business Model
This section is very important. Now that we have clearly identified the problem you are solving and the benefits of your solution, let’s have a closer look at your product.
This is where you clearly explain 2 key things:
How does your product work?
Explain what your product is and how it works. For instance, is it a desktop and/or a mobile SaaS application? Who is it for exactly (is this a FP&A application only for CFOs or a Slack-like collaboration tool for any type of user)?
Pricing model
SaaS businesses have different types of pricing models: per-user, per-usage, flat-tiered, etc. For a full list of the different pricing models, refer to this great article here .
7. Intellectual Property
This section is optional: only include it if you already have a MVP. If so, you have a strong argument for product-driven investors which will give a lot of credit to your tech.
Be careful not to go into too many specifics though: investors aren’t always engineer by training. Do not put things like the programming language you have chosen (e.g. React, Python) or the database provider (PostgreSQL, MongoDB).
Instead, include things such as:
- whether you have a white-labelled solution or a proprietary back-end / database
- how many full time front/back-end engineers you have
- how much you invested already in your tech

8. Marketing Strategy
This section explains how you acquire customers .
Are you selling a SaaS solution to B2B customers? Or is this a B2C product? This will determine whether you have an inbound or outbound acquisition strategy, or both:
- Inbound acquisition : fully digital acquisition. It can be either paid (paid ads e.g. Google Ads) or organic (content, SEO). Essentially, you convert customers from leads who land on your landing page. This strategy is most common for B2C SaaS businesses
- Outbound acquisition : you acquire customers thanks to your sales team who contact potential customers via phone, emailing or in-person sales efforts. This strategy is very common for B2B SaaS businesses
Once you have clearly explained your acquisition strategy and what tools you are using (e.g. Google Ads for paid search, Instagram and/or newsletter for content), ideally you can show, among others:
- Your average Customer Acquisition Cost (only if you have early traction)
- The number of sales people you have today
- How many customers your sales people close per month in average
- Your monthly paid ads budget
- The number of followers you have on social media
- Your newsletter count

The roadmap tells investors where you are going and how is product going to evolve in the future. You can either keep it high-level (e.g. your long-term strategy) or more detailed (e.g. the pipeline of the near-future product features).
Investors do not just invest in your product as it is today. For example, you might only have developed a MVP with limited features for early-adopters while your product could be tweaked and serve a much larger customer base in the future.
Note: if you choose to include your product pipeline, keep it very simple. Your SaaS business plan isn’t your product manager’s presentation to engineers. Instead of features, focus on the additional benefits and customer segments you might target as such. For instance, if you plan to launch a messaging feature, focus on the fact it will open new growth opportunities (e.g. network effects).
In this section you should focus on the people behind the company. Unlike in the executive summary, the team section of your SaaS business plan should not be limited to the cofounding or management team.
Instead, you should explain the current organisational structure of your company, the different teams, who they report to and their relative size.
For the people, keep it short. Keep biography to a minimum and only to key people (cofounders and management team). As rule of thumb, 5 lines per team member are enough, 10 a maximum.
When it comes to biographies, only include what is relevant: name, position, years of experience and/or previous companies is more than enough.
What about advisors?
Do you have angel investors with significant experience who advise you on strategy? Do you have a PhD who acts as advisor to your SaaS startup (on regulation and market access matters for instance)?
Any advisor should also be included here, with the same level of detail as for the management team.
Demonstrating in your SaaS business plan that not only team members but also experts are advising and/or sitting on your board is a strong selling point.
Note: add a clickable link to the respective Linkedin profiles so investors can refer to a more exhaustive resume for your team members (if relevant)
11. Financial Plan
Along with your product and the team, this section is highly important. Unfortunately, many startups overlook the importance of financial projections in their SaaS business plan.
Think about your audience: investors (venture capital firms or angel investors) are financially literate individuals . As such, they invest in your business to generate returns. Logically, they care a lot about your financials and more especially, the expected financial performance of your business .
Do not expect investors to make up their own plan for your startup if you haven’t. As CEO, founder or entrepreneur alike, you should have a clear idea of where you are going .
As rule of thumb, the more advanced your startup is, the more granularity you should include here. Pre-seed startups might keep it short (1 slide) yet we recommend seed and Series A+ startups to include 2 slides instead.
Common SaaS metrics you should include in your financial plan slide are:
- Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)
- ARPU and ARPPU
- LTV and CAC
For a complete list of the 8 most important metrics for SaaS businesses, refer to our article here .
SaaS Financial Model
Download an expert-built 5-year Excel financial model for your pitch deck
Privacy Overview

How to Write a Winning Software Company Business Plan + Template

Creating a business plan is essential for any business, but it can be especially helpful for software businesses who want to improve their strategy and raise funding.
A well-crafted business plan not only outlines the vision for your company but also documents a step-by-step roadmap of how you will accomplish it. To create an effective business plan, you must first understand the components that are essential to its success.
This article provides an overview of the key elements that every software business owner should include in their business plan.
Download the Ultimate Business Plan Template
What is a Software Business Plan?
A software business plan is a formal written document that describes your company’s business strategy and its feasibility. It documents the reasons you will be successful, your areas of competitive advantage, and it includes information about your team members. Your business plan is a key document that will convince investors and lenders (if needed) that you are positioned to become a successful venture.
Why Write a Software Business Plan?
A software business plan is required for banks and investors. The document is a clear and concise guide of your business idea and the steps you will take to make it profitable.
Entrepreneurs can also use this as a roadmap when starting their new company or venture, especially if they are inexperienced in starting a business.
Writing an Effective Software Business Plan
The following are the key components of a successful software business plan:
Executive Summary
The executive summary of a software business plan is a one- to two-page overview of your entire business plan. It should summarize the main points, which will be presented in full in the rest of your business plan.
- Start with a one-line description of your software company
- Provide a short summary of the key points in each section of your business plan, which includes information about your company’s management team, industry analysis, competitive analysis, and financial forecast among others.
Company Description
This section should include a brief history of your company. Include a short description of how your company started, and provide a timeline of milestones your company has achieved.
If you are just starting your software business, you may not have a long company history. Instead, you can include information about your professional experience in this industry and how and why you conceived your new venture. If you have worked for a similar company before or have been involved in an entrepreneurial venture before starting your software firm, mention this.
You will also include information about your chosen software business model and how, if applicable, it is different from other companies in your industry.
Industry Analysis
The industry or market analysis is an important component of a software business plan. Conduct thorough market research to determine industry trends and document the size of your market.
Questions to answer include:
- What part of the software industry are you targeting?
- How big is the market?
- What trends are happening in the industry right now (and if applicable, how do these trends support the success of your company)?
You should also include sources for the information you provide, such as published research reports and expert opinions.
Customer Analysis
This section should include a list of your target audience(s) with demographic and psychographic profiles (e.g., age, gender, income level, profession, job titles, interests). You will need to provide a profile of each customer segment separately, including their needs and wants.
For example, a software business’s customers may include small, medium, and enterprise businesses. Each of these customer segments will have different needs and wants.
You can include information about how your customers make the decision to buy from you as well as what keeps them buying from you.
Develop a strategy for targeting those customers who are most likely to buy from you, as well as those that might be influenced to buy your products or software services with the right marketing.
Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis helps you determine how your product or service will be different from competitors, and what your unique selling proposition (USP) might be that will set you apart in this industry.
For each competitor, list their strengths and weaknesses. Next, determine your areas of competitive differentiation and/or advantage; that is, in what ways are you different from and ideally better than your competitors.
Below are sample competitive advantages your software business may have:
- Superior customer service
- Strong brand recognition
- Proven track record of success
- Robust product feature set
- Well-funded and experienced management team
- Innovative technology
- Scalable business model
- Strategic partnerships or alliances
- Favorable locations
- Access to important resources, like talent or capital
Keep in mind that your competitive advantages will change over time as your business grows and as new competitors enter the market. It is important to regularly review and update.
Marketing Plan
This part of the business plan is where you determine and document your marketing plan. . Your plan should be clearly laid out, including the following 4 Ps.
- Product/Service : Detail your product/service offerings here. Document their features and benefits.
- Price : Document your pricing strategy here. In addition to stating the prices for your products/services, mention how your pricing compares to your competition.
- Place : Where will your customers find you? What channels of distribution (e.g., partnerships) will you use to reach them if applicable?
- Promotion : How will you reach your target customers? For example, you may use social media, write blog posts, create an email marketing campaign, use pay-per-click advertising, or launch a direct mail campaign. Or you may promote your software business via a mix of these channels.

Operations Plan
This part of your software business plan should include the following information:
- How will you deliver your product/service to customers? For example, will you do it in person or over the phone only?
- What infrastructure, equipment, and resources are needed to operate successfully? How can you meet those requirements within budget constraints?
The operations plan is where you also need to include your company’s business policies. You will want to establish policies related to everything from customer service to pricing, to the overall brand image you are trying to present.
Finally, and most importantly, your Operations Plan will outline the milestones your company hopes to achieve within the next five years. Create a chart that shows the key milestone(s) you hope to achieve each quarter for the next four quarters, and then each year for the following four years. Examples of milestones for a software business include reaching $X in sales. Other examples include acquiring X number of customers or launching a new product line.
Management Team
List your team members here including their names and titles, as well as their expertise and experience relevant to your specific software industry. Include brief biography sketches for each team member.
Particularly if you are seeking funding, the goal of this section is to convince investors and lenders that your team has the expertise and experience to execute on your plan. If you are missing key team members, document the roles and responsibilities you plan to hire for in the future.
Financial Plan
Here you will include a summary of your complete and detailed financial plan (your full financial projections go in the Appendix).
This includes the following three financial statements:
Income Statement
Your income statement should include:
- Revenue : how much revenue you generate.
- Cost of Goods Sold : These are your direct costs associated with generating revenue. This includes labor costs, as well as the cost of any equipment and supplies used to deliver the product/service offering.
- Net Income (or loss) : Once expenses and revenue are totaled and deducted from each other, this is the net income or loss.
Sample Income Statement for a Startup Software Business
Balance sheet.
Include a balance sheet that shows your assets, liabilities, and equity. Your balance sheet should include:
- Assets : All of the things you own (including cash).
- Liabilities : This is what you owe against your company’s assets, such as accounts payable or loans.
- Equity : The worth of your business after all liabilities and assets are totaled and deducted from each other.
Sample Balance Sheet for a Startup Software Business
Cash flow statement.
Include a cash flow statement showing how much cash comes in, how much cash goes out and a net cash flow for each year. The cash flow statement should include cash flow from:
- Investments
Below is a sample of a projected cash flow statement for a startup software company.
Sample Cash Flow Statement for a Startup Software Business
You will also want to include an appendix section which will include:
- Your complete financial projections
- A complete list of your company’s business policies and procedures related to the rest of the business plan (marketing, operations, etc.)
- Any other documentation which supports what you included in the body of your business plan.
Write a Winning Business Plan for Your Software Company
Writing a good business plan gives you the advantage of being fully prepared to launch and/or grow your software company. It not only outlines your business vision but also provides a step-by-step process of how you are going to accomplish it.
A business plan is a critical document for any new software company. If you are seeking funding, your business plan will be a key component of your pitch to investors .
Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With our Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Other Helpful Articles
How to Write a Winning Tech Company Business Plan (+ Template)

How to Start a Software Company

ON THIS PAGE
How To Start a Software Company
How to start a software company faqs, additional resources in the software publishing industry.
Starting a software company can be very profitable. With proper planning, execution and hard work, you can enjoy great success. Below you will learn the keys to launching a successful software company.
Importantly, a crucial step in starting a software company is to complete your business plan. To help you out, you should download Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template here.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here
15 Steps To Start a Software Company
- Choose the Name for Your Software Company
- Develop Your Software Company Business Plan
- Choose the Legal Structure for Your Software Company
- Secure Startup Funding for Your Software Company (If Needed)
- Secure a Location for Your Business
- Register Your Software Company With the IRS
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Get the Required Business Licenses and Permits
- Get Business Insurance for Your Software Company
- Buy or Lease the Right Software Company Business Equipment
- Develop Your Software Company Marketing Materials
- Purchase and Setup the Software Needed to Run Your Software Company
- Start Building Your Team
- Open for Business
1. Choose the Name for Your Software Company
The first step to starting your own software company is to choose your business’ name.
This is a very important choice since your company name is your brand and will last for the lifetime of your business. Ideally you choose a name that is meaningful and memorable. Here are some tips for choosing a name for your software company:
- Make sure the name is available. Check your desired name against trademark databases and your state’s list of registered business names to see if it’s available. Also check to see if a suitable domain name is available.
- Keep it simple. The best names are usually ones that are easy to remember, pronounce and spell.
- Think about marketing. Come up with a name that reflects the desired brand and/or focus of your software company.
2. Develop Your Software Company Business Plan
One of the most important steps in starting a software company is to develop your business plan. The purpose of a business plan is to ensure that you fully understand your market and your software business strategy. The plan also provides you with a roadmap to follow and if needed, to present to funding sources to raise capital for your business.
Your software publishing business plan should include the following sections:
- Executive Summary – this section should summarize your entire business plan so readers can quickly understand the key details of your software company.
- Company Overview – this section tells the reader about the history of your software company and what type of software company you operate. For example, are you an enterprise software company or a software as a service company?
- Industry Analysis – here you will document key information about the software industry. Conduct market research and document how big the industry is and what trends are affecting it.
- Customer Analysis – in this section, you will document who your ideal or target customers are and their demographics. For example, do they have a specific job title or work in a particular industry?
- Competitive Analysis – here you will document the key direct and indirect competitors you will face and how you will build competitive advantage.
- Marketing Plan – your marketing plan should address the 4Ps: Product, Price, Promotions and Place.
- Product : Determine and document what products/services you will offer
- Prices : Document the prices of your products/services
- Place : Where will your business be located and how will that location help you increase sales?
- Promotions : What promotional methods will you use to attract customers to your software company? For example, you might decide to use pay-per-click advertising, public relations, search engine optimization and/or social media marketing.
- Operations Plan – here you will determine the key processes you will need to run your business operations. You will also determine your staffing needs. Finally, in this section of your plan, you will create a projected growth timeline showing the milestones you hope to achieve in the coming years.
- Management Team – this section details the background of your company’s management team.
- Financial Plan – finally, the financial plan answers questions including the following:
- What startup costs will you incur?
- How will your software company make money?
- What are your projected sales and expenses for the next five years?
- Do you need to raise funding to launch your business?
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
3. choose the legal structure for your software company.
Next you need to choose a legal structure for your software company and register it and your business name with the Secretary of State in each state where you operate your software business. Below are the five most common legal structures:
1) Sole Proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is a business entity in which the owner of the software company and the business are the same legal person. The owner of a sole proprietorship is responsible for all debts and obligations of the business. There are no formalities required to establish a sole proprietorship, and it is easy to set up and operate. The main advantage of a sole proprietorship is that it is simple and inexpensive to establish. The main disadvantage is that the owner is liable for all debts and obligations of the business.
2) Partnerships
A partnership is a legal structure that is popular among small businesses. It is an agreement between two or more people who want to start a software company together. The partners share in the profits and losses of the business.
The advantages of a partnership are that it is easy to set up, and the partners share in the profits and losses of the business. The disadvantages of a partnership are that the partners are jointly liable for the debts of the business, and disagreements between partners can be difficult to resolve.
3) Limited Liability Company (LLC)
A limited liability company, or LLC, is a type of business entity that provides limited liability to its owners. This means that the owners of an LLC are not personally responsible for the debts and liabilities of the business. The advantages of an LLC for a software company include flexibility in management, pass-through taxation (avoids double taxation as explained below), and limited personal liability. The disadvantages of an LLC include lack of availability in some states and self-employment taxes.
4) C Corporation
A C Corporation is a business entity that is separate from its owners. It has its own tax ID and can have shareholders. The main advantage of a C Corporation for a software company is that it offers limited liability to its owners. This means that the owners are not personally responsible for the debts and liabilities of the business. The disadvantage is that C Corporations are subject to double taxation. This means that the corporation pays taxes on its profits, and the shareholders also pay taxes on their dividends.
5) S Corporation
An S Corporation is a type of corporation that provides its owners with limited liability protection and allows them to pass their business income through to their personal income tax returns, thus avoiding double taxation. There are several limitations on S Corporations including the number of shareholders they can have among others.
Once you register your software company, your state will send you your official “Articles of Incorporation.” You will need this among other documentation when establishing your banking account (see below). We recommend that you consult an attorney in determining which legal structure is best suited for your company.
4. Secure Startup Funding for Your Software Company (If Needed)
In developing your software company business plan, you might have determined that you need to raise funding to launch your business. If so, the main sources of funding for a software business to consider are venture capital funds, personal savings, family and friends, credit card financing, bank loans, crowdfunding and angel investors. Angel investors are individuals who provide capital to early-stage businesses. Angel investors typically will invest in a software company that they believe has high potential for growth.
5. Secure a Location for Your Business
You have some flexibility in deciding whether you want to secure an office space for your software company, build a remote team, or a combination of the two.
If you choose to buy or rent a physical location, consider:
- Driving around to find the right areas while looking for “for lease” signs
- Contacting a commercial real estate agent
- Doing commercial real estate searches online
- Telling others about your needs and seeing if someone in your network has a connection that can help you find the right space
6. Register Your Software Company With the IRS
Next, you need to register your business with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) which will result in the IRS issuing you an Employer Identification Number (EIN).
Most banks will require you to have an EIN in order to open up an account. In addition, in order to hire employees, you will need an EIN since that is how the IRS tracks your payroll tax payments.
Note that if you are a sole proprietor without employees, you generally do not need to get an EIN. Rather, you would use your social security number (instead of your EIN) as your taxpayer identification number.
If you’d like to quickly and easily complete your business plan, download Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template and complete your plan and financial model in hours.
7. Open a Business Bank Account
It is important to establish a bank account in your software company’s name. This process is fairly simple and involves the following steps:
- Identify and contact the bank you want to use
- Gather and present the required documents (generally include your company’s Articles of Incorporation, driver’s license or passport, and proof of address)
- Complete the bank’s application form and provide all relevant information
- Meet with a banker to discuss your business needs and establish a relationship with them
8. Get a Business Credit Card
You should get a business credit card for your software company to help you separate personal and business expenses.
You can either apply for a business credit card through your bank or apply for one through a credit card company.
When you’re applying for a business credit card, you’ll need to provide some information about your business. This includes the name of your business, the address of your business, and the type of business you’re running. You’ll also need to provide some information about yourself, including your name, Social Security number, and date of birth.
Once you’ve been approved for a business credit card, you’ll be able to use it to make purchases for your business. You can also use it to build your credit history which could be very important in securing loans and getting credit lines for your business in the future.
9. Get the Required Business Licenses and Permits
Every state, county and city has different business license and permit requirements.
Nearly all states, counties and/or cities have license requirements including:
- General Business License – A business license is typically required to operate a business in a particular state. The requirements and fees for a business license vary by state, so it is important to research the requirements in your state. Some common requirements for a business license include having a registered name for your company and filing articles of incorporation.
- Sales Tax License – A sales tax license is typically required to collect and remit sales tax in a particular state. The requirements and fees for a sales tax license vary by state, so it is important to research the requirements in your state. Some common requirements for a sales tax license include registering with the state department of revenue and applying for a seller’s permit.
Depending on where you launch your software company, you will have to obtain the necessary state, county and/or city licenses.
10. Get Business Insurance for Your Software Company
Some common types of insurance to consider include:
- General Liability Insurance – General liability insurance is a type of insurance that provides coverage for a business in the event that it is sued for negligence or other wrongful acts. This type of insurance can help protect a software company from lawsuits related to product liability, property damage, or personal injury.
- Errors and Omissions Insurance – Errors and omissions insurance, also known as professional liability insurance, is a type of insurance that provides coverage for a business in the event that it is sued for negligence or other wrongful acts. This type of insurance can help protect a software company from lawsuits related to software development, consulting, or other professional services.
- Product Liability Insurance – Product liability insurance is a type of insurance that provides coverage for a business in the event that its products cause harm to consumers. This type of insurance can help protect a software company from lawsuits related to product defects, design flaws, or improper instructions.
- Workers’ Compensation Insurance – Workers’ compensation insurance is a type of insurance that provides coverage for a business in the event that an employee is injured while working. This type of insurance can help protect a software company from lawsuits related to workplace accidents.
Find an insurance agent, tell them about your business and its needs, and they will recommend policies that fit those needs.
11. Buy or Lease the Right Software Company Business Equipment
To start, a software company really only needs reliable computers and basic office supplies. If you are opening a physical location for your software company, you might also need desks and other office furniture for your team, as well as reception furniture. If you plan to do many virtual meetings, be sure to invest in a decent webcam.
12. Develop Your Software Company Marketing Materials
Marketing materials will be required to attract and retain customers to your software company.
The key marketing materials you will need are as follows:
- Logo – Spend some time developing a good logo for your software company. Your logo will be printed on company stationery, business cards, marketing materials, and may even be seen when users load your products. The right logo can increase customer trust and awareness of your brand.
- Website – Likewise, a professional software company website provides potential customers with information about the products and/or services you offer, your company’s history, and contact information. Importantly, remember that the look and feel of your website will affect how your target market perceives you.
- Social Media Accounts – Establish social media accounts in your company’s name. Accounts on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn and/or other social media networks will help customers and others find and interact with your software company.
13. Purchase and Setup the Software Needed to Run Your Software Company
Your team will need a good software development platform. This can be something like Microsoft Visual Studio, Eclipse, or Xcode. The company also needs a good source code control system, like Git or Subversion. Finally, the company will need some good software development tools, like a compiler, an editor, and a debugger.
Slack is another popular tool among software development teams that allows members to keep in touch and help to build workplace morale among virtual workers. You should also explore bookkeeping and payroll software.
14. Start Building Your Team
Your team should be composed of individuals with the necessary skills and experience to help you build your product and grow your company. When assembling your team, it’s important to find people who share your vision and are passionate about your product.
It is a good idea to hire at least one product manager who can be responsible for creating and managing your product roadmap, defining product features, and coordinating development efforts
Any software development business relies on having a strong development team. You will need software engineers to actually design, build, and maintain the products you create. Likewise, your should plan on hiring sales and marketing team members to spread awareness about your products and make sales.
15. Open for Business
You are now ready to open your software company. If you followed the steps above, you should be in a great position to build a successful business. Below are answers to frequently asked questions that might further help you.
How to Finish Your Software Company Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Click here to finish your business plan today.
Is It Hard To Start a Software Company?
Yes, it can be hard to start a software company. One of the biggest hurdles will be coming up with a great idea for software that people will want to use. Attempting to raise money needed to start a software development company can also be difficult. Owning a software company can also be a lot of fun and a rewarding experience, however, and the steps we have outlined above will help put you on the path to success. Just be sure to understand the needs of your particular business before you begin.
How Can I Start a Software Company With No Experience?
One of the most important things you can do to start a new software company with no experience is research. Look into the software industry as a whole, as well as how much it typically costs and the time needed to develop software. You might also consider connecting with experienced software development business owners who can give you their insights into the dos and don't of opening and running a successful software company.
What Type of Software Company Is Most Profitable?
There is no easy answer to this question, as the profitability of a software company depends on a variety of factors, including the type of software it produces, the size and location of the market it targets, and the level of competition it faces. However, some types of software companies are more likely to be profitable than others.
Generally speaking, an enterprise software development business can charge more for its products as the target market is often large organizations. Companies that make custom software may also charge more since they create tailor-made solutions for their customers, which often requires more resources and time than selling a premade software product.
How Much Does It Cost To Start a Software Company?
The amount you will need to spend to start a software development business will depend on the type of company you want to create, the services you offer, and the location where you plan to operate.
You will need to pay for office space, computers, software, and marketing materials. You may also need to hire employees or contractors. It is important to remember that you will also need to pay taxes on your income, so make sure you have enough money set aside to cover your expenses.
Startup costs for software companies range from $30,000 to $150,000 depending on the business scale.
What Are the Ongoing Expenses for a Software Company?
One of the biggest expenses for any software company is employee salaries. You'll need to pay your employees a livable wage in order to keep them happy and productive. In addition, you'll also need to budget for things like office supplies, marketing, and of course, taxes. Key expenses include:
- Wages – Over a third of revenue is comprised of wages.
- Purchases, Research and Development – Over 10% of software publishing revenue is spent for purchases, research and development.
- Other – The other costs in the software publishing industry comprise marketing costs, depreciation, rent, office supplies, furniture, etc.
How Does a Software Company Make Money?
There are a few ways that a software company can make money. The most common way is to sell licenses to the software that they create. This can be a one-time purchase or a fee charged on a subscription basis. In the case of SaaS, customers often pay a regular fee to access software over the internet instead of installing it on a local device. Another way to make money is to create add-on products or services that complement the software. These could be additional features or support plans.
Is Owning a Software Company Profitable?
The answer to this question largely depends on the specific industry and market conditions. However, in general, companies that produce and sell software can be quite profitable. The key is to have a unique and valuable product that meets the needs of your customers.
How Much Do Software Publishing Operators Make?
A software publisher earns an average of $61,000.
Why Do Software Companies Fail?
One of the main reasons software companies fail is that they do not have a clear vision and strategy. A company without a clear vision will lack focus and direction, which can lead to missed opportunities and failure. Additionally, a lack of strategy can doom a company to failure because it means they are not taking the necessary steps to succeed. Other reasons software companies fail include poor marketing, inadequate funding, and no customer base.
How Big Is the Software Publishing Industry?
There are 7,737 software companies in the U.S. and they generated $192.7 billion in revenue last year. This shows an annual growth rate of 3.6% in the past 5 years.
What Are the Key Segments of the Software Publishing Industry?
The main segments of the industry are Application software publishing and System software publishing. Other product segments include re-sale of computer hardware and software, Information technology technical consulting services, custom application design and development, and information technology-related training services.
What External Factors Affect the Software Publishing Industry?
A number of factors affect the performance of the software publishing industry. These drivers include:
- Private Investment in Computers and Software - When the demand for computers increases, the software publishing industry is positively affected. This year, investment in computers and software is expected to rise.
- Number of Mobile Internet Connections - An increase in the use of mobile internet connections make mobile devices more vulnerable to viruses, thus also increasing the need for security software and improving industry revenue. The number of mobile internet connections continues to increase.
- Corporate Profit - When the profit of companies rises, they tend to upgrade IT systems which involves purchases of new software.
- Demand From Video Games - An increase in sales from video games benefits the software publishers. This year, demand for video games will increase.
- Government Consumption and Investment - Government spending benefits the software publishing industry and it is increasing this year.
- Percentage of Households With at Least One Computer - An increase in the number of PC owners means there’s also higher demand for software. The percentage of households with at least one computer is increasing today.
- Per Capita Disposable Income - An increase in consumers’ per capita disposable income indicates that there is a high chance that they will purchase new software for personal use or entertainment.
Who Are the Key Competitors in the Software Publishing Industry?
Oracle Corp.
Microsoft Corporation
International Business Machines Corp.
What Are the Key Customer Segments in the Software Publishing Industry?
The largest customer segment in the software publishing industry is businesses. Households then make up about a third of all customers and government entities make up a small portion.
For additional information on the software publishing market, consider these industry resources:
- The Software & Information Industry Association: www.siia.net
- US Census Bureau: www.census.gov
- The Entertainment Software Association: www.theesa.com
- US Bureau of Labor Statistics: www.bls.gov
- Software Mavericks: www.softwaremavericks.com
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success.
Click here to see how Growthink’s business plan writing services can create your business plan for you.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

How to Write a Tech Startup Business Plan to Win Investors
You have a great business idea. Now you’re doing the hard part: raising capital.
With a failure rate of 63% in the tech startup industry, you need to have a highly compelling business idea and go-to-market strategy to win over investors.
We’re going to make writing a startup business plan really simple by providing you with a step-by-step guide along with a business plan template you can use to build startup business plan that wins investors.
What is a tech startup business plan?
Why do you need a technology startup business plan.
- 1. Executive summary
- 2. Market opportunity
- 3. Product or service overview
- 4. Marketing and sales strategy
- 5. Team and management structure
- 6. Key milestones
- 7. Financial plan
Sample tech startup business plan [template]
A technology startup business plan is a document that is used to outline the goals, strategies, and objectives of a new tech startup business. This document is often used to secure funding from investors and to help the business leaders form a unified sense of identity and purpose.
The business plan should include information on the products or services offered by the startup, the market opportunity, the business model, the team, the financial projections, and the risks and challenges associated with the business. A tech startup’s business plan should generally address three major areas of the business:
As a startup moves through various stages of growth, the business plan should be updated with new information and forward-looking goals. In this way it can serve as a “source of truth” for all of the startup’s stakeholders.
A business plan is an essential tool for any tech startup. It provides a road map for your business, helping you to define and communicate the company’s vision, goals, and strategies. Having a singular document that acts as a single source of truth for the business will help to keep the startup’s core leadership team unified and provides guidance on how to navigate the often-complex world of starting and growing a business.
You can utilize your startup business plan to secure funding and partnerships. A well-crafted business plan can also help you attract and retain top talent.
In summary, you need a technology startup business plan to:
- Unify the startup’s leadership team
- Secure funding and partnerships
- Attract top talent
- Act as a guide for navigating starting a business
This article will act as a guide for writing a business plan for tech startup founders.
7 key components of tech startup business plan
You know you need a business plan for your tech startup. You know generally what should be included. But, now you need to actually get to writing. We’re going to try to make this as easy as possible by outlining the 7 key components your technology startup business plan should have.
If you’re looking for a real shortcut, make sure you download our easy tech startup business plan template. Included in it you’ll find a sample business plan and an outline of what we’ll cover below.
Stick with me if you’re looking for a more detailed explanation of each of the 7 components.
- Executive summary
First up is an executive summary. This brief section should provide some context to readers as they begin to read your business plan. It’s your opportunity to share, at a high level, your business idea.
At a minimum, this section should outline what your business is, the general market you target or industry you are in, and what your products or services are. Optionally, you can include some information about your business’s history, bios of key members of your leadership team, competitive advantages, key customer benefits, and your company’s goals. How detailed you get with this section is up to you. Use this as an opportunity to provide an overview before you get into more detail in the other sections of your business plan.
- Market opportunity
This is where you will start to go into more detail about your business. Starting with the market opportunity allows you to paint the picture of the why _behind your tech startup before you go into the _what . Ultimately, you can only sell the feasibility of your business by backing it up data on who your potential customers will be. This section will help to inform the marketing strategy and sales plan later in the startup business plan document.
Take the time in this section to walk through the research you have done on your audience. To start, you should have data points on the following:
- Demographic data for your target market (age, gender, income, occupation, location)
- Main pain points of your target market
- Values and interests of your target market
- Needs and wants of your target market
It can also be compelling to provide some information on how your products or services will stand out from the competition. Consider answering the following questions in this section:
- Who are your main competitors?
- How will your products or services meet the market’s needs better than the competitors?
- Will your products or services be able to reach a currently unreached audience?
- How will you differentiate yourself from the competition within your target market?
All of this data should back up what the real market opportunity is for your business. Make sure this market opportunity is realistic and achievable. This should lead well into our next section which will cover in more detail the products or services your tech startup will offer to the market.
- Product or service overview
After you have outlined the market opportunity your business will take advantage of, it’s time to provide more details on the exact products or services that you will offer to your market.
Each product or service you include in this section should have a corresponding functional and technical description. The functional description should aim to outline to a layperson what the product or service is, what it does, and how it will be used. The technical description should outline the technologies each product or service utilizes or what technology has been developed specifically for the new business. It’s appropriate to go into detail here to give potential investors more confidence in your product or service.
It’s also important to include information on how the products or services will ultimately benefit customers and what problem they will solve for customers. If you have more than one product or service, make sure to outline this information for each one.
- Marketing and sales strategy
The marketing and sales strategy section of a technology startup business plan should include a description of the target market, the company's marketing and sales objectives, the strategies and tactics that will be used to reach these objectives, the key marketing and sales metrics that will be used to measure progress, and the budget for marketing and sales activities. In short, it should outline your business’s marketing and sales plan.

Starting with the objectives, you should outline specifically what you are trying to achieve with your marketing and sales efforts both in the short term (likely for launch) and long term. Each of your objectives should align with your overarching business goals and make sense for the market you outlined earlier in your business plan. Be realistic here. It’s better to estimate low and over deliver than to overestimate your success.
As you outline the strategies and tactics you will use to achieve your objectives, consider both the what _and the who_:
- (What) What tactics will you employ to achieve your goals?
- (What) What marketing tools do you need to achieve your goals?
- (What) What marketing channels will you use?
- (Who) Will the marketing work be done internally?
- (Who) Will you hire freelancers or a CMO to help implement the work at hand?
- (Who) Will you need a sales team right away?
- (Who) How will marketing and sales work together to achieve your goals?
Your marketing and sales strategy should be backed up by the market opportunity information you provided earlier. The strategies and tactics should be aiming to reach your target market.
Next, outline the metrics that will be used to measure marketing and sales progress. You should include specifically when these metrics will be measured and who will be held accountable for them.
Finally, include a marketing and sales budget in this section. The budget should be broken down by channel and tactic, so that dollars can be accurately tracked and attributed to results.
- Team and management structure
Up next is the team and management structure part of the business plan. To start, provide an overview of the startup’s organizational and management structure. Providing a graphical representation of the reporting structure can be helpful.
This can then lead into an overview of who owns or manages each of the key sectors of the business (CEO, CTO, CMO, etc.). It’s a good practice to provide a bio of each of the members of the leadership team, including their education, work history, and relevant expertise. Along with their bio, provide a description of their role and responsibilities within the organization.

After you have covered the leadership team, outline the other team members along with their roles and responsibilities. Following this, include some commentary on the team’s strengths and weaknesses as well as what gaps remain within the organization. If additional staffing is required, provide a hiring plan that includes a description of the role, salary, and strategy for recruitment.
End this section with an overview of the organization’s values. Paint a picture of what it’s really like to work for your company and how you build a sense of ownership and responsibility within the team. Highlight how you intend for the team to work together to accomplish the company’s goals.
- Key milestones
At this point in the business plan you have outlined the target market, products and services you will offer as well as the members of your team that will bring the company’s vision to life. In this section you’ll provide a timeline of the past and future milestones for your business. This will help to illustrate your startup’s growth path and how you intend to move forward.
Some key milestones to consider when writing this section:
- When business was founded.
- When the business was/will be launched publicly.
- When the business was/will be profitable.
- When the business reached/will reach funding milestones.
- When development project milestones were/will be reached.
- When marketing milestones were/will be reached.
- When key staff were/will be hired.
- Future product release dates.
You might consider showcasing this information in the form of a graphic like this:
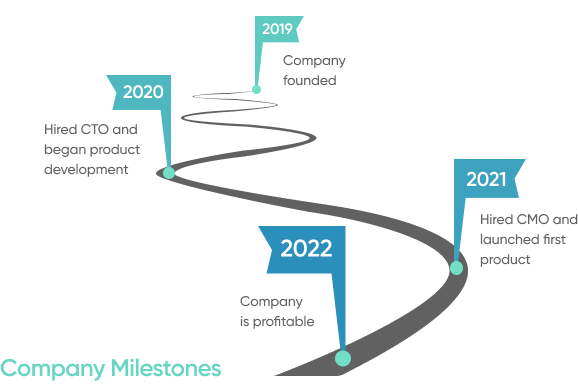
In addition to a company timeline, we recommend you include additional data in this section such as:
- Current number of employees and the number of employees projected in the future.
- The amount of revenue generated in the past and projected for the future
- Key clients or contracts that have been signed or that are in the works.
This section should clearly demonstrate your startup’s ability to grow from an idea into a business. Providing concrete dates and real data in this section will provide some validity to your startup and showcase what you’re able to accomplish.
- Financial plan
The final section of your technology startup business plan should be a financial plan. This is the section of the business plan that outlines how the business has been funded to date and how it will be financed moving forward.
There is no one way to write the financial plan section of a business plan, as the amount and type of information that needs to be included will vary depending on the business and the specific financial goals of the plan.
However, there are some basic elements that should be included in most financial plans. These include a pro forma income statement, balance sheet, sales forecast, and cash flow statement. The pro forma financial statements should be based on historical financial data, if available, and should include assumptions about future revenue and expenses. The financial plan should also include a discussion of the company's capital structure, including its debt and equity financing.
If you’re at a very early stage with your startup and seeking a modest amount of funding, it’s probably sufficient to air on the side of brevity. If you’re seeking series A, B, or C funding, you’ll likely need a very comprehensive financial summary along with a detailed plan on how the funding will be utilized to grow the business. Seek counsel from a business accountant if you’re unsure of how to provide adequate financial documentation.
We have walked through the 7 key elements of any tech startup business plan. Now we’re going to share a sample business plan template to help you get started with writing your own!
Innovation is critical to success in the software industry. The executive team of this startup believes they have the next big thing. They have developed a new software application that helps businesses manage their social media accounts more effectively. The software provides insights on when to post, what to post, and how to engage with customers. The software also allows businesses to track their social media analytics and see the return on investment for their social media campaigns.
The executive team has extensive experience in the software industry and believes this new product has the potential to be a game-changer for businesses. The team is seeking $1 million in seed funding to help with product development, marketing, and sales. The company plans to generate revenue through monthly subscription fees and by selling data analytics services to businesses.
The social media management software market is expected to grow from $9.3 billion in 2020 to $17.4 billion by 2025, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.2%. This growth is being driven by the increasing use of social media by businesses of all sizes and the need to effectively manage social media accounts to drive brand awareness and customer engagement.
The software application developed by the startup helps businesses manage their social media accounts more effectively. The software provides insights on when to post, what to post, and how to engage with customers. The software also allows businesses to track their social media analytics and see the return on investment for their social media campaigns.
The software is available on a monthly subscription basis and businesses can also purchase data analytics services to help them further understand their social media campaigns.
The company plans to generate awareness for the software through online and offline marketing campaigns. The team will target small businesses and medium businesses that are active on social media but do not have the resources to effectively manage their accounts.
The company will use a mix of paid and organic marketing to reach its target audience. For paid marketing, the company will use Google AdWords and Facebook Ads. For organic marketing, the company will use content marketing and social media outreach.
The company plans to sell the software on a monthly subscription basis. The team will offer a free trial to businesses to get them started with the software. Once the free trial expires, businesses will be charged a monthly subscription fee.
The executive team of the startup consists of experienced software professionals. The team has a proven track record of developing and marketing successful software products.
The company plans to hire a sales and marketing team to help generate awareness and drive sales of the software. The team will be based in the United States and will consist of sales and marketing professionals with experience in the software industry.
The company plans to achieve the following milestones over the next 12 months:
- Launch the software application
- Generate 500 paying customers
- Achieve $1 million in annual revenue
The company is seeking $1 million in seed funding to help with product development, marketing, and sales. The company plans to generate revenue through monthly subscription fees and by selling data analytics services to businesses.
The company projects the following financials for the next 12 months:
- Revenue: $1 million
- Expenses: $500,000
- Profit: $500,000
As a startup founder you know that having a software startup business plan on hand is critical to win over investors and get your business funded. However, no one wants to spend days writing a complicated it startup business plan. It’s much more important to focus on the day-to-day operation associated with building your tech startup.
To help save you time (but still create a winning startup business plan), we’ve outlined the 7 key components of any tech startup business plan:
As you tackle writing your own, make sure you refer back to this guide along with our template to ensure you’re writing a compelling business plan that is sure to win over investors!
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to content

- Try Tactyqal

The Ultimate Guide to Creating a Lean Startup Business Plan
Starting a business can be both thrilling and terrifying. On one hand, you have this brilliant idea and can’t wait to bring it into the world. But there’s also the nagging fear that your amazing concept might fall flat or fail to gain traction.
So how do you make sure your startup succeeds? The answer is charting out a solid business plan.
I know, I know. Just hearing the phrase “business plan” brings back bad memories of dry, long-winded documents from business school. But for startups, there’s a better way to plan out your venture – something called the lean startup business plan.
The lean startup approach focuses on streamlining the business planning process so you can start testing your idea faster, without getting bogged down with lengthy sections and financial projections you can’t possibly predict accurately at such an early stage.
In this beginner’s guide, I’ll walk you through exactly how to create a lean startup business plan template that helps you quickly validate your business idea with real-life customers.
What is a Lean Startup Business Plan?
First things first – let’s define what exactly the lean methodology means when applied to an entrepreneur’s business plan.
Put simply, a lean startup business plan is a streamlined, no-fluff version of a traditional business plan. It’s designed for speed and adaptability rather than comprehensiveness.
The lean startup movement first became popular around 2008. It emphasizes testing a product or service idea quickly, using a minimum viable product (MVP), and getting real user feedback before committing to long development and release cycles.
The key principles of lean startup are:
- Rapid build-test-learn loops
- Scientific testing with real customers from day one
- Iterating based on validated learning
Most new companies that take the lean approach never reach an official launch stage. Instead, they continuously test with and adapt to real customers – refining their MVP and pivoting directions based on evidence of what does or doesn’t get market traction.
So how does that tie in with writing a business plan?
Well, the traditional business plan model doesn’t fit the lean paradigm shift.
Lengthy, complex, intricate business plans take too much time to write. Attempting to project multiple years of expenses, sales, hiring, growth rates etc…..it’s all just guesswork when you haven’t started selling anything yet.
The lean startup business plan tosses unnecessary details out the window and instead focuses only on critical hypotheses and assumptions that must be tested as quickly as possible.
Investors like this approach because it shows you:
- Know what assumptions make or break your business
- Can test them quickly at low cost
- Will adapt based on real data
So if you’re an early stage startup looking for funding or entering an accelerator program like Y Combinator, a lean business plan is likely your best bet to showcase your entrepreneurial abilities.
Now the big question….
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup template pares down the typical business plan format to just the essential elements early-stage investors care about:
- Problem – What pain points will your product address? Why are those needs not being met?
- Solution – How will your product alleviate that pain better than alternatives? Why will customers buy from you over other options?
- Target market — Who has that specific problem and will buy your solution? ( Note: Be specific! “Everyone” is never the right answer.)
- Competition — Who else is tackling that customer problem? How is your solution fundamentally better or different?
- Key features – What’s the minimum feature set to address target customers’ needs on day one and provide value?
- Marketing & sales – What tactics will you use to reach early adopters? ( Note: For most startups, digital sales & marketing channels rule supreme. )
- Operations – Outline your core business processes. Don’t go into granular detail, just highlight how you’ll deliver value to customers.
- Milestones – What big assumptions will you test? Include timelines + costs to conduct experiments so you can demonstrate a logical thought process.
- Financials – Optional Breakdown high-level estimates only if useful. For the lean startup plan, elaborate projections are unnecessary and speculative. Focus everything on testing key assumptions.
You may have noticed one conspicuously absent item – the Executive Summary. We’re skipping it because unlike traditional business plans sent to various stakeholders, your lean startup plan has just one audience – startup investors.
And remember, the lean methodology is all about using real-life data instead of guesses and best-case scenarios. So even if some assumptions in your original lean business plan don’t pan out, that’s actually great news! It gives you hard evidence to adapt intelligently while developing your MVP.
Now that you know what the lean startup template includes at a high-level, let’s go through each of the core sections in more detail.
First and foremost, you need to spell out exactly what customer problem your startup aims to solve. (And yes, it needs to be an actual must-solve problem, not a nice-to-have).
Start by broadly describing the pain points your target customers face. Get tactical by including stats, data or quotes that showcase why this issue is so urgent for them.
Then explain how the problem ties into a larger trend in your target industry. Paint a big picture view of why common solutions up until now have failed to address this pain sufficiently.
Essentially, convincingly convey that there’s a pressing customer need ready for innovation.
You need to display beyond any doubt that you:
- Deeply understand your target customers’ challenges
- Can explain why those problems exist in the first place
- Will provide a compelling solution tailored to fix them
This sets the stage for why launching a startup to address this issue makes so much sense.
2. Solution
Now that you’ve framed the problem, shift gears into explaining your startup’s solution. Start by providing an overview of your product and how it alleviates target customer pains better than alternatives already on the market.
Then embellish with details on:
Product Benefits
How specifically will your product make customers’ lives easier? Don’t just describe product features or functionality. Speak directly to how you’ll empower them to achieve something that’s currently difficult, inconvenient or even impossible for them to accomplish on their own.
Competitive Advantage
What specifically sets your solution apart from potential competitor offerings and substitutes? Is it higher quality, better convenience, lower cost, less hassle, faster performance – or perhaps an innovative model that’s never been seen before in the market?
Highlight your startup’s special sauce that no one else can easily replicate. Explain barriers to entry that will hinder copycats.
Customer Incentive
Why will target users’ purchase from your brand over chasing other options? It usually comes down to believing you can deliver significantly MORE value than alternatives or solve an urgent pain nothing else currently satisfies. Make your case for why you fit one or both scenarios.
Scalability
Particularly if you are pursuing venture capital investors, explain how your business can rapidly scale up to tap a very large global market with your solution. Outline a blueprint for how you realistically grow from thousands to millions of customers in the coming years.
Remember, don’t drown potential investors in intricate details about every single product feature and technical specification. They care most about how your solution nails the value proposition trifecta:
- Targets an urgent customer problem
- Provides 10x+ better value over existing options
- Can scale to a very large market long term
If you can compellingly check all three boxes, you’ll spark investor interest even with limited hard evidence at such an early phase.
Of course, that doesn’t mean you won’t eventually need to back up your claims. However, the lean startup plan is more about framing hypotheses than definitive proof. We’ll cover how to demonstrate enough evidence to warrant launching experiments soon.
For now, stick to crafting an intriguing startup story that sets you up to start testing fundamental assumptions very soon after funding. There will be plenty of time to figure out minor product details once you validate solving a pressing problem for real paying customers.
3. Target Market
Up until now, I’ve used the term “target customer” quite loosely. But it’s time to get very specific on who those real-world people actually are for your startup.
Venture capital investors want to quantify the population size and traits of target buyer personas in precise detail. So you need to describe exact psychographic and demographic qualities of your beachhead market – the subset of overall customers you tackle first to gain a foothold quickly.
Start by explaining your total addressable market (TAM) – the entire population who could plausibly need and want your solution for the core problem it tackles. Depending on the ubiquity of that issue for consumers and/or businesses, the TAM could be very narrow or encompass hundreds of millions globally.
Then segment down from that full market to identify your specific beachhead target customer population. The ideal beachhead often has these characteristics:
- Suffers from the problem much more painfully than casual groups
- Has already tried existing solutions without sufficient success
- Has disposable income to purchase a premium solution for relief
- Is easy to access and serve operationally in early phases
- Isn’t incredibly price sensitive
- Can provide extensive feedback on the product
- Has influencer qualities to attract wider market segments
Nail down quantifiable population size estimates for this core beachhead subset. Combine publicly accessible data from existing market research reports with reasonable inferences or assumptions from adjacent industries.
But resist the founder’s tendency towards magical thinking – “If we nailed even just 1% of the market…!” Generic hypotheticals don’t sway experienced investors focused on tangible traction signals.
Paint a detailed demographic picture of exactly who fits the mold of a hot prospect customer for you in the beginning.
For B2C startups , call out relevant attributes like:
- Marital/family status
- Home ownership
For B2B startups , highlight qualities like:
- Industry vertical
- Company size
- Title seniority
- Annual revenue
- Tech adoption habits
Then outline statistical commonalities across your core beachhead buyers – what key similarities unite this subgroup vs. the entire population facing the problem?
Finally, convey TAM expansion opportunities once you solidify solutions tailored for that first niche. But defer outlining detailed ways to extend your reach right now since nailing product/market fit with just one segment is the critical prerequisite to win over adjacent groups.
Position your solution as optimized for an underserved niche ripe for disruption based on competitors failing to deliver adequate solutions. Then segue into how your distribution plan concentrated on this “low-hanging fruit” beachhead will purposefully evolve later to expand TAM reach long term.
4. Competition
What the competition section lacks by traditional business plan standards in length, it more than makes up for in strategic rigor.
The core question competitive analysis must answer:
Why are current solutions in the market failing to adequately alleviate your target customers’ pain?
Start by inventorying existing competitor products/services currently used by prospects experiencing this problem. List out the main options your target persona has for solving their struggles today, even if those solutions don’t perfectly fix the issue or fully satisfy them.
Then contrast point-by-point specifics on why your solution beats competitors, especially on the metrics most important to your target niche. Show how you will “disrupt the disruptors” because even pioneering products have limitations needing innovation.
Criteria to call out where you claim competitive advantage:
- Convenience
- Scale potential
- Business model innovation
Back up any bold claims of superiority with limited initial evidence beyond conjecture — data from beta user testing prototype versions, customer quotes from initial beachhead outreach, or precedents from analogs in adjacent markets.
Take care to focus specifically on competitors targeting the same early adopter beachhead market segment though. Details contrasting solutions for other peripherical segments are unnecessary right now.
Round out competitor analysis by itemizing macro trends almost certain to diminish prospects for legacy products over the next 5-10 years. These should make the rationale behind your startup now abundantly clear even to skeptics.
5. Key Features
Thus far you’ve made a case for:
- A pressing customer problem inadequately solved
- Your startup’s superior solution
- Quantified target beachhead market
Now it’s time to shift to specifics on the crucial product and feature details enabling your entire value proposition.
Remember – only include what’s absolutely necessary for launch based on addressing revealed target customer needs!
Err on the side of a minimal feature set early on. Describe additional functionality prospects request once you start serving initial customers.
Outline the critical set of features required to deploy a minimum viable product (MVP) with just enough core attributes to satisfy early adopters on day one.
Organize by:
Must-Have Features
What feature absolute “must-haves” must be ready for early adopters to provide enough value converting from current solutions?
Nice-To-Have Features
What would enhance perceived value but aren’t imperative to activate paying users? Defer these to later product milestones.
Future Features
Briefly mention functionality on the long-term roadmap to showcase platform potential.
Think of must-have features as the “walking version” of your product – unscalable manual processes providing baseline value perfect for testing with friendly early adopters.
Then nice-to-haves represent the “jogging version” – automating more of the workflow via technology – while future functionality serves as the “running version” enhanced for steep vertical scaling.
In conjunction with digital tools, brainstorm creative ways to manually deliver MVP experiences centered around must-haves. This showcases your determination to activate solutions for that first tiny niche even sans a fully built production-grade product.
Emphasize with investors that you respect their money enough to not waste it on premature optimizations. Your plan ensures you build and roadmap additional functionality responsibly IF AND ONLY IF initial feature experimentation proves substantial product/market fit warranting doubling down.
6. Marketing & Sales
Thus far you’ve covered the key value proposition and functionality your startup will offer. Now shift to tactical specifics on how you’ll connect your novel solution with that clearly defined target beachhead.
Start by breaking down your blended omni-channel market blueprint to cut through the noise and achieve conversion lift.
Here is an ideal framework pairing both scalable and targeted elements for seed-stage ventures:
Paid Digital Marketing
- Targeted Facebook/Instagram/TikTok Ads
- Search/Display Retargeting
- Streaming Radio Spots
- Industry Forum Sponsorships
- Highly-Targeted Content Marketing
Grassroots Outreach
- Beachhead Email Outreach
- Beachhead Calls/Texts
- Industry Event Networking
- Local University Campus Reps
- Early Adopter Referral Programs
Earned Media
- Contributed Articles
- Podcast Interviews
- Reviews / Testimonials
- Referral Partnerships
- PR Launches & Press Releases
The glaring omission? Sales team headcount.
Early on, founders must handle sales themselves to economize cash burn. Hiring reps too early risks overextending finances before ensuring product viability.
So spotlight your personal founder sales fit first. Play up hands-on selling experience within the specific market context you’re pursuing with this venture.
Then convey a scaling plan centered on refining and automating conversion funnel elements that empirically guide qualified leads to become delighted long-term customers.
The core funnel methodology goes:
- Broad-based brand awareness marketing → Baits wide audience
- Lead capturing mechanisms → Filters for buyers
- Consultative selling touchpoints → Focuses high-potential targets
- Frictionless conversion → Delivers ROI proof
If your business model doesn’t fit this framework, adapt concepts accordingly while sticking to the seed stage constraints of capital efficiency and lean experimentation.
7. Operations
By this point you’ve described WHAT your startup does and WHO it serves. Now it’s time to explain HOW you’ll deliver on ambitious promises to customers.
Start by simply framing core business processes required to get your product or service from raw inputs all the way through to solving target user pain points.
For physical products, that could involve flows like:
- Design concepts → Engineering specifications → Prototyping → Manufacturing → Quality assurance → Packaging → Distributing → Support
For software platforms:
- Product requisites → Cloud infrastructure → Coding → Version control → Usage analytics → Onboarding → Technical support
For services:
- Prospecting → Onboarding → Account Management → Delivery capacity → Quality control → Supplemental services → Support
You get the idea. Just define macro processes without diving into granular details. Those come through experimentation!
Primarily, concentrate operational details on two crucial pillars:
- Proprietary unfair advantages that supercharge efficiency to delight customers while maintaining profit margins despite tight costs. Common examples include algorithms, datasets, novel business model frameworks, or embedded industry experts.
- Partnerships or platforms enabling you to deliver baseline functionality matching incumbent competitors on day one. Don’t attempt to build everything end-to-end or innovate across every dimension from the start! Leverage existing commoditized solutions while you test differentiated value propositions focused on solving target customer problems 10x better.
Essentially, convey you grasp the key 20% inputs that drive 80% of customer value. If the processes seem complex, find ingenious ways to simplify. Position enhanced intricacies as optional add-ons once baseline product/market fit is proven vs. overbuilding the wrong advanced solution.
8. Milestones
The milestones section represents the culmination of everything you’ve documented thus far. Here, outline the step-by-step process for methodically testing the riskiest assumptions underlying your startup.
In conjunction with the experiment design, detail concrete metrics or signals indicating whether hypotheses prove true or false. Then estimate costs, durations, and resource requirements for rapid experiments.
Frame assumptions through statements structured like:
We believe [this capability] will result in [this customer reaction]
Then design tests around the ability to measure:
- behavioral changes
- sentiment improvements
- usage increases
- revenue lift
Common milestone tests to consider:
- Solution Viability – Manual then automated demonstrations quantifying interest
- Demand Validation – Willingness to prepay as a signal
- Market Sizing Accuracy – Applying proxies from analogous use cases
- Business Model Fit – Contrasting pricing sensitivity across customer segments
- Feature Prioritization – Gauging reactions to mockups or limited functionality
- Operational Scalability – Maximizing utilization before adding overhead
Combine testing both internally-facing operations and externally-visible customer experiences. But concentrate on product/solution related hypotheses first.
Beating competitors takes precedence over backend experimentation. Optimize business operations AFTER establishing winning customer value propositions.
The key is conveying to investors an empirical, metrics-driven approach centered on turning critical assumptions into facts or disproving them faster than incumbents hampered by legacies and red tape.
Cement belief you’ll double down on evidence proving repeatable formulas to acquire and monetize target niche segments. And quickly cut losses spending minimal capital if data suggests limited viability.
9. Financials
We’ve made it clear that traditional multi-year financial projections typical of standard business plans are counterproductive guesses for early stage startups.
However, seed investors still want to see back-of-napkin math you’ve done to quantify potential venture scale. So mock up top level metrics more as directional guidelines than definitive targets.
Take utmost care however NOT to pull imaginary hockey stick numbers from thin air. Founders claiming $100 million valuations on basic eCommerce stores face extreme investor skepticism…and deserve to!
Baseline financial model components should include:
- Estimated Customer Acquisition Costs Per Beachhead Channel
- Willingness-To-Pay Price Range For Target Personas
- Logical Volume Estimates Based On Analog Use Cases
- Assumed Conversion Rates Each Funnel Stage
- Operational Unit Economics At Various Scale Points
Use inherently bottom-up thinking grounded in realities of what combination of inputs would need to scale to hit specific 8-figure outcomes. Top-down abstract number picking lacks validity.
And remember, early-stage startup financial models serve more as instruments of learning than definitive targets. Adapt projections based on empirical evidence once live.
Concentrate everything on validating customer demand first. Defer advanced modeling of operational minutiae or elaborating hockey stick projections.
Getting REAL buyers is all that matters initially.
Bringing It All Together
Despite extending 3k+ words at this point, the lean startup methodology boils down to an elementary formula:
- Start by deeply understanding a pressing customer problem
- Design an innovative solution specifically addressing root causes
- Concentrate on dominating an underserved niche beachhead market segment
- Validate demand empirically through rapid testing
- Scale up deliberately only once achieving initial product/market fit
In that sense, think of the lean business plan format as more of an exercise in startup soul searching than a stuffy document.
It pushes founders to pressure test their value proposition, business model, and operational viability through the lens of target customers rather than theoretical academic assumptions.
You can’t survive let alone thrive in the brutally competitive startup game without getting inside the hearts and minds of actual buyers needing your solutions.
So escape the temptation to overly complicate initial planning with intricate spreadsheets and 40-page reports professional managers expect.
Instead, concentrate efforts on distilling explanations of the crucial assumptions requiring testing above all else before launch.
Then close your lean startup business plan with next step calls-to-action so readers clearly understand how you’ll leverage funding to start rapidly experimenting using the scientific method.
Now…go show the world what your brilliance is made of!
Related Posts

Partha Chakraborty
Partha Chakraborty is a venture capitalist turned entrepreneur with 17 years of experience. He has worked across India, China & Singapore. He is the founder of Tactyqal.com, a startup that guides other startup founders to find success. He loves to brainstorm new business ideas, and talk about growth hacking, and venture capital. In his spare time, he mentors young entrepreneurs to build successful startups.
You may also like

55 Art Business Ideas to Make Money from Your Creativity
- Startup business ideas

What is a Turnkey Site?
- Uncategorized
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Professional Services
- Creative & Design
- See all teams
- Project Management
- Workflow Management
- Task Management
- Resource Management
- See all use cases
Apps & Integrations
- Microsoft Teams
- See all integrations
Explore Wrike
- Book a Demo
- Take a Product Tour
- Start With Templates
- Customer Stories
- ROI Calculator
- Find a Reseller
- Mobile & Desktop Apps
- Cross-Tagging
- Kanban Boards
- Project Resource Planning
- Gantt Charts
- Custom Item Types
- Dynamic Request Forms
- Integrations
- See all features
Learn and connect
- Resource Hub
- Educational Guides
Become Wrike Pro
- Submit A Ticket
- Help Center
- Premium Support
- Community Topics
- Training Courses
- Facilitated Services
How to Write a Startup Business Plan
May 28, 2022 - 10 min read
A startup business plan is an outline of your ideas and strategies for what you’ll need to do to start, manage, and even complete your startup’s mission. Creating one might sound simple enough, but because it’s a startup’s roadmap for success, it can be a complex document to create.
Writing a business plan can make a world of difference for entrepreneurs who desire external funding. It involves determining your target customers, understanding what makes them tick, and figuring out how to reach them through marketing campaigns.
In this blog post, we’ve explained why you should have a startup business plan, different types of startup business plans, and we’ve included 12 of the most effective tips for writing a startup business plan. If you’re ready to start with now, we have a product launch template to get you started quickly.
What is a startup business plan?
A startup business plan is a written document that outlines your ideas and strategies for launching, managing, and eventually exiting your new venture.
A well-constructed business plan can be crucial to the success of any entrepreneurial endeavor . As you prepare your proposal, keep in mind that it will evolve as you learn more about your market.
To start, create an outline of the most important items you'd like feedback on before writing anything down officially.
Then ask yourself these questions:
- What do I want?
- Why does my company exist?
- How will I make money?
- What are my long-term goals?
A detailed business plan helps you set milestones for measuring success. You can share the plan with investors who may want some reassurance on the viability of their investment in your company.
The best way to create a successful startup business plan is by including everything in an organized and easy-to-read document — marketing strategies, financial projections, team bios, timelines, and more.
What is a lean startup business plan?
A lean startup business plan is a method for developing products that relies on iterative experimentation to reduce uncertainty.
It has been used by companies such as Google , Amazon, and Facebook in the early stages of their development, and involves testing your idea with real customers early in development.
Lean startups are less likely to fail because they have tested their product or service with live feedback from consumers. Doing this allows them to make changes quickly without wasting resources on something no one wants.
The goal is not to build an extensive business plan but rather a "lean" one that can be changed based on customer feedback and then re-evaluated in regular intervals until it reaches market potential — or fails.
A lean startup business plan is a strategy that focuses on getting a product in front of customers as quickly and cheaply as possible. Use the lean startup business plan to validate your ideas before wasting time and resources.
Why do you need a small startup business plan?
A small startup business plan is one of the most important steps in building a company. Apart from helping you to focus on company goals, it aids in obtaining feedback from potential partners and keeps the team on the same page.
The best thing about starting small? You can change course at any time! If you need help developing or tweaking your small startup business plan, use this guide for entrepreneurs to get started.
You've built a product and you're ready to take the next step, but what's your plan? First, you need a strategy in place. Do you know how much money it will cost, or where exactly that funding should come from? What about marketing strategies for getting customers in the door?

You’ll also need to find ways to retain them afterwards so they keep coming back again and again (and spending more).

Obtain external funding
If you want to get funding from lenders or investors, you need a startup business plan. Lenders want to make sure they're investing in a company that will last and grow.
A well-organized idea shows passion for its purpose and outlines clear goals for helping customers. At the same time, having an exit strategy is also important.
Making a plan for when things don’t pan out as desired lets investors understand how much value there can be while giving customers (and yourself) peace of mind.
Understand your target market
One key piece of your business plan is knowing how to conduct a market analysis. To do this, consider the industry, target market, and competitors.
Are there any market trends or competitor factors that can affect your business? Review them closely and get ready to make required changes to your business plan.
Prioritize high ROI strategies
In business, ROI is important. Any business that doesn’t generate as much cash as it burns is likely to fail.
With a startup business plan in place, the strategies with the highest ROI become crystal clear. You'll know exactly what to tackle first and how to prioritize the rest of your tasks.
Accelerate financial health
Business plans are not crystal balls, but they can help forecast your financial health. Planning for expenses is vital to keep operations steady and identify problems as soon as possible.
Cash flow projections can help you see if goals are achievable or highlight upcoming issues that need correction before it's too late.
How to write a small startup business plan
Use this guide for entrepreneurs to develop or tweak a startup business plan. By following this easy six-step process, you'll soon have a clear path to startup success.
1. Clarify the startup vision, mission, and values
The first step to writing a startup business plan is understanding the startup itself.
Once you know what your startup does, ask yourself why. What is the startup's mission? What problem will it help customers solve? The startup's mission statement helps define its reason for existing.
It’s usually expressed in a simple sentence, but can also be written as a short paragraph.
Try to answer these questions: What does your startup do? How will it make money? How quickly do you hope it will grow? Are there any significant milestones or deadlines that need to be met?
2. Outline the executive summary
Now that you have an idea for your startup, its mission, and a vision in mind, it's time to write your startup business plan executive summary.
Keep it simple and precise. Begin by writing a one-sentence startup business plan introduction that showcases the core customer need/pain point and how you propose to solve it.
3. Develop startup goals and milestones
Next, write down the milestones and goals for your startup business plan. This is a crucial step that many entrepreneurs forget when they're starting out.
Do you want to focus on getting new customers? Or attaining a specific revenue number? Without clear short-term goals, it can be hard to know how to prioritize startup tasks.
4. Write a company description
Answer the two fundamental questions — who are you and what will you do? Then, give an introduction to why you're in business.
Provide a summary of introspective goals, clarifying intangible aspects such as values or cultural philosophies. Make sure to mention:
- Proposed business structure (limited partnership, sole proprietorship, incorporated company, or a general partnership)
- Business model
- Business vision and mission statement
- Background information of your team members

5. Conduct market analysis
Choosing the right market is crucial to your organization’s success. There are different kinds of products and services that a business can offer and each has particular requirements for a successful market fit.
If you choose one that doesn't have a large enough customer base or is not profitable enough, your company may end up struggling for every sale.
Ensure that there is a clear market niche — an ideal audience of customers with a need or a pain point that your business can help solve.
6. Develop startup partnerships and resources
When you're launching a small startup, one of the most important things that your business needs is capital. There are several ways to get going on this front.
When thinking about sources of funding for startups , consider startup grants, startup loans, startup investors, and startup accelerators.
7. Write a startup marketing plan and startup budget
Your startup business plan is almost complete! All that's left is to create a startup marketing plan and budget. Your startup marketing plan will help you define your company’s target audience and brand image.
The startup budget is an integral part of any startup that helps you take the guesswork out of writing expenses.
Examples of startup business plans
Business plans differ based on the nature of the business, target market, competitive advantage, delivery of product/service, scope, and size.
Though the core business plan template remains the same, the content and flow change. Here is an example of an accounting firm's business plan:
Vision statement
At our company, ABC Accounting Services LLC, we work hard to provide the best service and build a strong team. Our vision is for this brand to be recognized as #1 throughout NYC by both smaller businesses and larger corporations.
Our values are reflected in all that we do: integrity (ethical behavior), service (giving top priority to clients' needs), excellence ("doing it right"), teamwork (working together).
Executive summary
ABC Accounting Services LLC is the premier accounting firm in New York City and will handle various financial services. We specialize in audits, bookkeeping, tax preparation/compliance work, and budgeting assistance with high-quality consulting.
Business structure
ABC Accounting Services LLC will be structured as an LLC — a Limited Liability Company in the state of New York. It will provide accounting, bookkeeping, taxation, auditing, and compliance-related services to small, medium, and large enterprises situated in New York City.
Marketing strategy and competitive advantages
Despite the fact that there are many established accounting services firms in our industry, we have a great chance of becoming successful because of the high demand for financial consulting.
Often, small businesses don't need full-time employees but would rather hire an accounting service provider like us to handle their bookkeeping and tax returns on time every year.
It is best to find a unique niche or carve out your own market in the financial consulting services industry. If you're able to create an identifiable brand identity for your accounting business, then you will likely see less competition from other firms.
Startup milestones
ABC Accounting Services LLC will focus on delivering an exceptional client experience to grow the business and expand market share.
Startup business plan template
Here's a template you can follow when creating your startup business plan:

Top tips for writing a startup business plan
The following tips will help you create a compelling startup business plan without getting overwhelmed.
Know your audience
To write an effective business plan, tailor your language and level of detail to match the audience reading it.
Have a simple and clear goal
If you have a goal of securing funding for your business, it will be an uphill task with lots of work and research.
Simplifying and breaking down bigger goals into smaller, actionable tasks will assist you in getting through them faster.
Spend time researching
Avoid assuming anything about your target audience, product/service, or the market need.
Spending adequate time and effort on research from primary and secondary sources will help you develop an accurate business plan.
Build a startup toolkit
The process of creation becomes easier if you have the right startup tools and software by your side. Pick the right ones that will help you in your journey.
Keep it precise
Short and easy-to-read business plans are best kept within 20 pages. If you have additional documents, consider adding them as appendices or provide a link if available online.
Ensure tonal consistency
Keep the tone consistent by having just one author write your startup business plan. Otherwise, be sure to edit it thoroughly before you finalize it.
Add reference points
All information regarding the market, your competitors, and your customers should reference authoritative data points.
Be ready to pivot
A business plan should be fluid and flexible. Think of it as an evolving document that will continue to change over time.
How to create a business plan with Wrike
A good business plan is a powerful tool and can be a key predictor of future progress, but simply filling in a startup business plan won’t help you achieve success. You need to create action steps with accountability that will help you reach your goals.
Wrike’s project management software can help your organization deliver successful projects and maximize individual and team productivity, and our product launch template can help you turn your startup business plan goals into actionable steps.
Start a free trial of Wrike today to see how it can help to simplify work, showcase progress to stakeholders, and achieve startup success.

Yuvika Iyer
Yuvika is a freelance writer who specializes in recruitment and resume writing.
Related articles

How to Write a Business Case (With Example & Template)
A business plan is a straightforward document. In it, you’ll include market research, your overall goals for the business, and your strategies for achieving those goals. But what is a business case and why do you need one if a business plan outlines everything else? A business case takes a closer look at a specific problem and how you can solve it. Think of a business case as the reason you create a project you’re going to manage in the first place. The article provides a step-by-step guide on how to write a successful business case, including a checklist for identifying problems, researching solutions, and presenting to stakeholders. As a bonus, we’ll show you how to use Wrike to manage your product business cases with a requirements management template or implement them with a project scheduling template. What is a business case? A business case is a project you’ll assemble for identifying, addressing, and solving a specific business problem. The key to a business case is the change it creates in your business. Developing a business case starts with identifying a problem that needs a permanent solution. Without that lasting change, a business case is only an observation about what’s going wrong. A complete business case addresses how a company can alter its strategy to fix that problem. Front-to-back, a business case is a complete story. It has a beginning, a middle, and an end. It typically looks like this: Beginning: Someone identifies a problem within the business and presents the business case to the key decision-makers. Middle: With the project go-ahead, the company launches an internal team to address the business case and deliver results. End: The team delivers a presentation on the changes made and their long-term effects. In short, a business case is the story of a problem that needs solving. Examples of business cases The problem for many companies is that they can turn a blind eye to challenges that are right in front of their faces. This is even the case when the company has a compelling product to sell. Consider the example of Febreze. In the mid-1990s, a researcher at Procter & Gamble was working with hydroxypropyl beta-cyclodextrin. His wife noticed that his clothes no longer smelled like cigarettes, which was a frequent complaint. P&G had something of a miracle product on its hands. However, their approach was wrong. They initially marketed Febreze as a way to eliminate embarrassing smells. Predictably, the product flopped. But P&G stuck at it. They had a potential business case on their hands: a highly marketable product proved difficult to market. What was going wrong? Working on the business case from beginning to end provided the answer. After some focus group testing, P&G found out that few consumers recognized the nasty odors they were used to. Instead, they learned to use a different business case for Febreze: it was a cleaning product now, a way to make the house smell nice when the floors are vacuumed and the counters are wiped clean. They gave it its own pleasant smell and fashioned it into a cleaning product. And because it worked so well, so did the campaign. That’s an example of a business case overall. But let’s get specific: developing a business case is easier when you have a template to look at. Let’s build an example using a made-up company, ABC Widgets, and a hypothetical business case. Let’s call our business case example “Operation Super Widgets”: Business Case: ABC Widgets Section 1: Summary Briefly describe the problem and the opportunities. ABC Widgets’ latest widget, the Super Widget, is suffering from supply issues, requiring higher shipping costs to procure the necessary resources, and eating into profits. We need to switch to a new supplier to restore the viability of the Super Widget. Section 2: Project Scope This section should include the following: Financial appraisal of the situation. Super Widgets are now 20% more expensive to produce than in the year prior, resulting in -1% profits with each Super Widget sold. Business objectives. To get revenues back up, we need to restore profit margins on Cost Per Unit Sold for every Super Widget back to 2020 levels. Benefits/limitations. Restoring Cost Per Unit Sold will restore 5% of sagging revenues. However, we are limited to three choices for new Super Widget suppliers. Scope and impact. We will need to involve supply chain managers and Super Widget project management teams, which may temporarily reduce the number of widgets we’re able to produce, potentially resulting in $25,000 in lost revenue. Plan. Project Management Teams A and B will take the next two weeks to get quotes from suppliers and select one while integrating an immediate plan to bring in new Super Widget parts for manufacturing within four weeks. Organization. Team Member Sarah will take the lead on Operation Super Widget Profit. Both teams will report to Sarah. This is a bare-bones example of what a business case might look like, but it does hit on the key points: what’s the problem, how can you fix it, what’s the plan to fix it, and what will happen if you succeed? How do you write and develop a business case? When writing your own business case, the above example is a good guide to follow as you get started with the basics. But, once you’re more familiar with the nuts and bolts, it’s also worth being prepared for some potential roadblocks you could face along the way. Challenges of writing a good business case Why don’t more companies create a business case? It might come down to a lack of good communication. Many people don’t even know how to write a business case, let alone present one. “The idea may be great, but if it’s not communicated well, it won’t get any traction,” said Nancy Duarte, communication and author who wrote The HBR Guide to Persuasive Presentations. The key challenge, notes Duarte, is taking abstract business concepts (like lagging numbers) and turning them into an immediately recognizable problem. After all, if a company already had perfect awareness that it was making a mistake, it likely would find a way to stop the error in its tracks. A business case is challenging because it usually means you’ll have to persuade someone that change is needed. And change can be difficult. In a thriving business, it’s especially problematic because it’s easy to point to the bottom line and say that whatever the company is doing is already working. How do you present a business case? The tips and examples above give you some nice remedies for creating a business case without the typical problems. But you’ll still want to present a business case with the straightforward proposals and numbers you’d associate with any new project. Essentially, it all comes down to how well your business case can persuade the decision-makers. That’s why you shouldn’t just build a case off of raw numbers. The bottom line might be a compelling argument, but it’s not always what “clicks.” If you’re presenting a business case, you’re a salesperson. And not every sale is a matter of precise logic. It’s also about emotion—the story of why something’s gone wrong and what needs doing if you’re going to overcome it. The art of a good business case is the art of persuasion. Keep these specific points in mind as you craft one of your own: Point to an example of a bad business case and liken it to the present case. No one likes the idea of watching themselves walk into a mistake. Presenting an example of a business that made the same mistake your company is making and then translating it into the present moment is a compelling way to craft a business case that makes ears perk up. Build a narrative. Nancy Duarte pointed out that in one business case, a client convinced a CEO to follow through with a project by using simple illustrations. It’s not that the idea of adding illustrations to the business case was so great. It’s that the illustrations were able to tell a compelling story about why the case needed to go through. Distill the idea into an elevator pitch. Try this exercise: get your business case down to one sentence. If you can’t explain it any more simply than that, your business case might not be as memorable as it needs to be to sway decision-makers. Use analogies to drive the point home. Let’s say you discovered a problem in a growing business. Overall, revenues are good — but you’ve noticed an associated cost that has the potential to explode in the future and tank the business. But it’s not compelling to use dollars and cents when the business is doing so well. Instead, consider introducing the business case with a simple analogy: “Without repair, every leaky boat eventually sinks.” You now have their attention. Use the numbers to drive the point home, but not to make the point. If you’re presenting a business case to decision-makers, remember that it’s not only the logic of your argument that will convince people — it’s how persuasive you can be. Business case checklist Before you can check “learn how to write a business case” off your list, you have to know the essentials. Make sure you include the following elements in your business case checklist (and, of course, your business case itself): Reasons. This should be the most compelling part of your business case. You can tell a story here. And the most compelling stories start with a loss or a complication of some sort. What is the threat to the business that needs remedy? What are the reasons for moving forward? Potential courses of action. It’s not a complete story until we know the next chapter. A business case isn’t just about the problem — it’s about rectifying a problem through the solution. Recommend a few specific courses of action to help spur discussion about what to do next. Risks and benefits. Not every solution is going to be perfectly clean. There are going to be solutions with downsides. There are going to be costs along with the benefits. Make sure to include each of these to give a clear and complete picture. This is the time to manage expectations — but also the time to inspire action. Cost. What’s it going to cost to complete the project? The people making the decisions need to know the bottom line figure to assess which business cases to prioritize. Timeline. A good project isn’t only measured in dollars but in days, weeks, and months. What is the expected timeline for the business case? How quickly can the problem meet its solution? With every business case, specificity is key. A vague timeline won’t help — a timeline with specific weekly milestones looks more achievable. To make your business case more compelling, always look for the specific details that tie your story together. Business case template A business case template is a document that outlines the key elements of a business case in a structured format. By using a standardized template, companies can ensure that all relevant information is captured and shared in a clear and consistent manner. Depending on the size of your business and the scope of your project, your business case template can be as detailed or as simple as you like. For a smaller project, you can use a one-pager to get started, detailing the main points of your project, which include: Executive summary: An overview of your project, its goals, and the benefits of completing it for your business Team and stakeholders: A list of the relevant people involved in your project, and their contact information SWOT analysis: An analysis of how your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats weigh up against your competitors Risk analysis: An overview of the kind of risks that are involved with your project and how you may avoid them Budget and financial plan: Details of your budget and where you may secure financing for your project Project plan: A schedule of how you plan to implement your project and what tasks are involved Let's see what that might look like. Executive summary Team and stakeholders SWOT analysis Risk analysis Budget Project plan How to write a business case with Wrike Wrike’s project management software can step in and turn a business case from the seedling of an idea to a full-fledged initiative. The requirements management pre-built template can help you document and track project requirements in a structured manner. The template includes sections for capturing stakeholder requirements and business cases, as well as any constraints that may affect the project’s success. By using this template, you can ensure that all necessary requirements are identified and that potential issues are addressed early in the project planning process. If you want to move from the business case description to the actual implementation faster, consider using the project scheduling template. This template can help you create a detailed project timeline with milestones, identify task dependencies, and assign resources. By utilizing this template, you can ensure that the project is realistically achievable and meets all business needs, giving stakeholders confidence in the project’s success.

Operational Planning: How to Make an Operational Plan
Learn how to create an operational plan that will help your business succeed. Check out our guide to everything you need to know about operational planning.

What Is a PMIS and How Does it Work?
Discover how a PMIS can help your team deliver high-quality projects faster in this in-depth guide. Learn what is PMIS and how you can set one up.

Get weekly updates in your inbox!
You are now subscribed to wrike news and updates.
Let us know what marketing emails you are interested in by updating your email preferences here .
Sorry, this content is unavailable due to your privacy settings. To view this content, click the “Cookie Preferences” button and accept Advertising Cookies there.
Upmetrics AI Assistant: Simplifying Business Planning through AI-Powered Insights. Learn How
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai Pitch Deck Generator
Strategic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
- Sample Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Customers Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Small Business Tools
Strategic Canvas Templates
E-books, Guides & More
How to Start a SaaS Company (2024 Guide)
20 Min Read
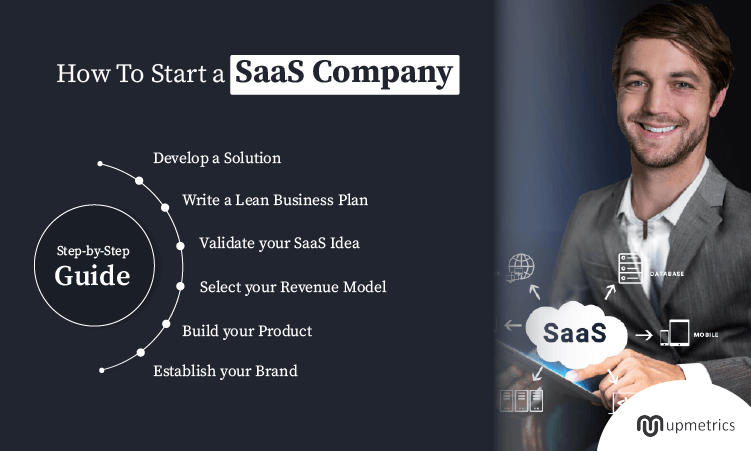
- Startup costs: $50,000-$150,000
- Industry trend: Growing
- Difficulty: Moderately difficult
- Profitability: 68-75%
- Time to build: 6–18 months
- Commitment: Full-time
From an era where it took hours at length to install software to an era where it takes a few minutes to avail of software services – the technology generation has come a long way.
As of 2023, the SaaS space is worth 195 billion dollars and it is expected to grow tremendously over the next few years. There is no better time than today to start your own SaaS business.
Whether you are a software developer with a solid technical foundation or a smart-witted entrepreneur wanting to capture their share in this thriving market, SaaS is perfect for you.
However, starting a SaaS business is not an easy task. It’s complicated and requires a series of trials, testing, and reiterations to get it right.
Well, we have your back. This step-by-step guide answers all your questions regarding how to start a SaaS company in great detail.
So simply, let’s dive right in.
What is a software as a service (SaaS) company?
SaaS companies are typically software-based companies offering their services through web-based applications or Internet browsers. Most SaaS companies charge a monthly or yearly subscription from their customers while there are other ways to generate revenue as well.
Unlike traditional software companies that have a slightly restrictive structure, SaaS business models offer a plentitude of opportunities with their flexible structure. These softwares are hosted over individual cloud servers making it easy to scale and deploy changes.
Wondering how much money will it cost you to set up a SaaS business? Well, read along.
How much money do you need to start a SaaS business?
The average cost to start a SaaS (software as a service) business in the US is anywhere between $50,500- $150,500 . Depending on the complexity of your SaaS business model, the costs can extend up to $500,000 .
These costs are highly influenced by factors such as development, legal, branding, and marketing costs.
Now before you start looking out for funds, let’s have a look at detailed steps that will help you start a SaaS company systematically.
Step-by-Step Guide to Start a SaaS Company
Table of contents.
- Develop a Solution for a Customer Problem
- Write a Lean Business Plan
- Validate Your SaaS Idea
- Select Your Revenue Generation Model
- Brainstorm a Name for Your SaaS Product
- Register Your Business
- Build Your Product
- Consider Your Funding Options
- Establish Your SaaS Brand
- Develop a Marketing Strategy
- Measuring Success with Metrics
1. Develop a Solution for a Customer Problem
“You don’t need a brilliant idea to start a business . You just need a customer with a problem and a solution to offer.”
To build a successful SaaS business, begin by identifying the problems around you. Pay attention to the personal and professional communication in your everyday life. Look at your own struggles with different products and services and see if there is an untapped market opportunity.
Another brilliant idea is to explore the ideas on Reddit and Quora channels to skim different sorts of problems. The overall idea is to find a problem worthy enough to get a SaaS solution built around it.
Now, while exploring potential solutions for the problem, you have one of these 3 ways to go around:
- Identify the gap in existing solutions and find a way to fix it.
- Talk with potential customers and identify their pain points.
- Leverage your understanding of the industry to devise a solution.
Don’t try to solve multiple problems all at once. Stick to a specific niche and develop a market around it.
2. Write a Lean Business Plan
Start by quickly translating your idea onto a paper by writing a lean business plan. Unlike traditional detailed plans, let’s keep it short for now.
Lean planning is an effective and easier way to get around when your SaaS idea is yet to be validated. This one-page pitch includes a quick overview of strategy, tactics, business model as well your SaaS business proposition.
Create a checklist and ensure that you answer the following questions in your SaaS lean plan.
- What problems will you solve with your SaaS product?
- What are the USPs of your SaaS company?
- What will be the cost of building and deploying a minimum viable product?
- Who is your target market or what different market segments will you target?
- Who are your competitors and what is your competitive edge?
- Who will be there on your SaaS team?
- What is the value proposition of your saas business and what are the milestones you plan to achieve?
- What will be your revenue model?

Write a lean business plan in no time
Get Upmetrics’ lean plan template, import data directly into the editor, and start editing using Upmetrics AI Assistant.
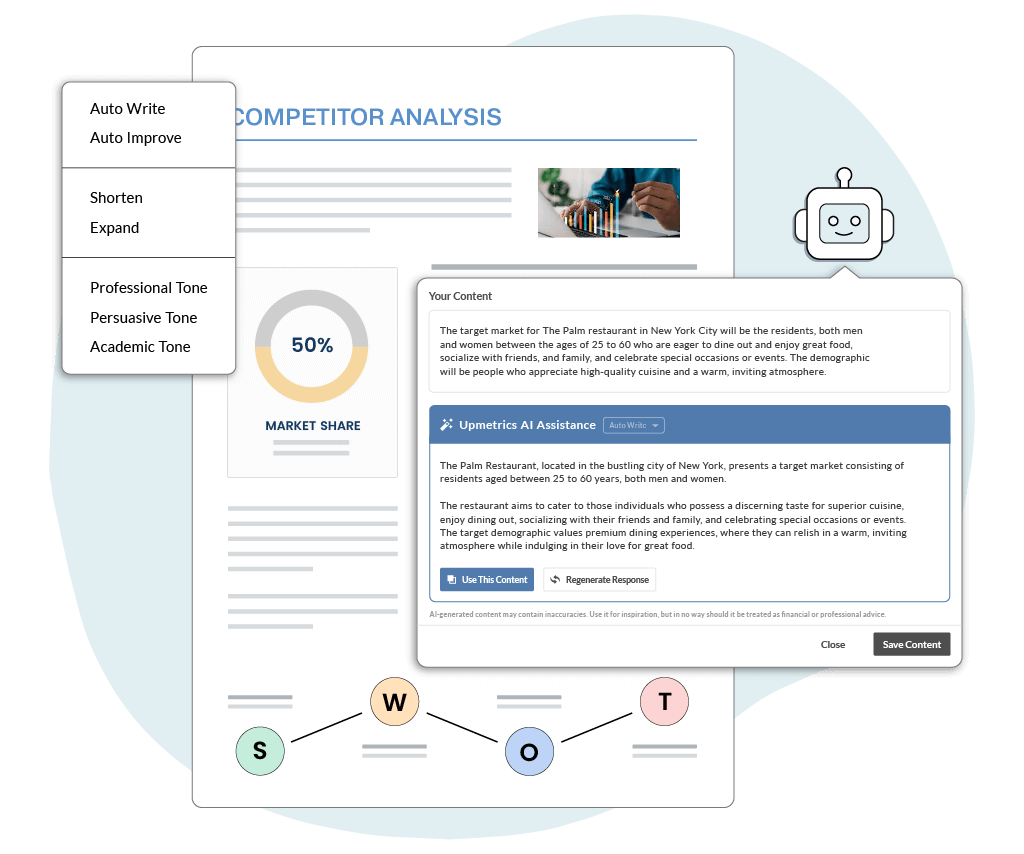
Start Planning Now
3. Validate Your SaaS Idea
After identifying the problem and devising a solution for it, it is now time to validate your SaaS idea. Take that lean plan and check if the assumptions you made are viable or not.
This step is important to understand if your idea has enough potential to make you money. Be realistic instead of diving right into the first idea that you consider to be best and pragmatic.
Here’s how you will validate your SaaS product idea:
Get to know your target customer
Getting to know your potential customer is perhaps the most important part of starting a SaaS company.
Gather a ton of primary data by talking to your potential customers directly. An easier way would be to design surveys and interviews in your target market. Run a search ad and launch a Kickstarter to collect realistic data for your SaaS company.
This step will help you understand whether or not the problem identified by you resonates with your potential customers and if your proposed solution is perfect for them. Moreover, this step will help evaluate the range within which you can price your SaaS products.
Conduct a competitive analysis
“To compete effectively, you must know your competition better than they know themselves.”
Competition is nothing to be afraid of. It’s in fact an indication that the problem you are attempting to solve is actually a realistic problem that demands a solution.
Conduct market research and identify the SaaS providers that will pose your SaaS business as a competition. Evaluate their SaaS products and identify where they fall short in fulfilling the customers’ wants.
Conduct a SWOT analysis and identify these SaaS companies’ strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Determine your competitive edge over these businesses and devise your software accordingly.
Create a minimum viable product
Creating an MVP is the easiest and most practical way of validating business ideas . It is the basic and simplest version of your product, focusing on one value proposition.
One huge mistake made by SaaS businesses is delaying the launch till they get their extensive product ready. Well, let’s break the bubble- your perfect SaaS product will never be ready.
Launching an MVP in the market will allow you to gather real-user feedback and accordingly make iterations to the product features and design. This will help you create a sustainable product that can beat other SaaS products in the market.
Here are a few things to keep in mind while launching your MVP:
- Keep your MVP extremely simple. Include bare minimum features that are extremely crucial for your SaaS application.
- Gather the feedback right from the beginning. Talk with your potential customers to understand what they like and dislike and what they want from your product.
- Don’t ignore the feedback if it’s not to your liking. Take it constructively and be prepared to change the idea if it doesn’t suit your audience.
If you don’t have the resources to create an MVP of your SaaS application, you can get the work done with wireframes, mockups, explainer videos, landing pages, and even paper sketches.
Leverage the data collected using MVP and use it resourcefully to build a product that people will actually pay for.
4. Select Your Revenue Generation Model
In this step, you will determine a way to make money by selling your SaaS software services. In simple terms, a pricing model to charge for your SaaS products.
SaaS businesses typically use one of these revenue generation models depending on their type of offerings and the target market.
Subscription-based pricing model
In the SaaS industry, SaaS subscriptions are the commonly used method of generating revenue. SaaS companies charge monthly or annual fee on their subscriptions and sometimes even quarterly. You can also offer a free trial before taking the commitment from users.
A subscription-based pricing model helps you retain a customer base for a longer time, given that you continue to provide effective solutions to their problem.
Tiered pricing
Tiered pricing is suitable for SaaS companies that can easily segment their users based on available features. In this method, you create different pricing plans ranging from one with the least features and support to the one with maximum features and support.
Customers get to select what level of features and support they require by choosing specific plans.
User-based pricing
Another method used by SaaS companies is to charge their services depending on number of users. For instance, $10 per user/ month.
This method is suited for SaaS companies that are targeting businesses of different sizes, i.e. small, medium, and large scale.
Flat pricing model
In this pricing model, SaaS businesses charge a flat fee in the beginning and offer lifetime access to the services. However, keep in mind, that this model will not give you recurring revenue.
Free pricing
Some SaaS companies offer their services for absolutely free and generate revenue by running ads on their platform. While your prospective customers would love free services, they may not like the invasive nature of ads and interruptions.
Depending on your SaaS business model, you can create a hybrid pricing strategy while keeping your target audience in mind.
It’s important to price your services within a range that is feasible for your potential customers.
5. Brainstorm a Name for Your SaaS Product
In the business world, a great name is a great asset. The success of your SaaS company might not entirely rely on a name, but it definitely plays a crucial role in building your brand image.
Choosing a name may seem like an easy task. But it isn’t. Here are a few things to keep in mind while brainstorming and finalizing your SaaS business name:
- Pick a simple and easy-to-spell name. Don’t go around messing with the spelling just to make it creative.
- Pick something that can be easily remembered and recalled.
- Choose a name that resonates with your SaaS product idea.
- The name should of course be unique. Check the state registry to ensure that there are no other businesses operating with the same name.
- Check the availability of domain names and social media handles before finalizing the name.
Brainstorm different ideas for the name using online name generators. And, don’t forget to get help from friends and family members to help finalize a suitable SaaS company name.
Want a Unique Name for your SaaS Company?
Generate a brandable and catchy business name in seconds with our free business name generator for saas company.
6. Register Your Business
It’s important to legally register your SaaS business by complying with the applicable state and federal rules. Now, the registration process may vary depending on the industry you are planning to enter. So check that with an expert or official pages to ensure complete compliance.
Select a business entity
A business entity is the legal identity of your SaaS company that dictates its liabilities, tax structure, and regulatory compliance. It separates you from the business making it a completely separate entity.
SaaS companies can choose between sole proprietorship, LLC, C.corp, partnership, or LLC partnership business structure models for their business.
Identify the pros and cons of each business structure before determining the ideal structure for your software company.
Also, consider how you want your company to look in front of investors and the public. This will help you pick a business entity that’s suitable for your idea.
While registering a business, consider getting a DBA (doing business as) name if you plan to operate your business with another name.
Apply for tax registration & business EIN
Comply with the state rules and apply for tax registration of your SaaS company. Also, get your EIN number from an Internal Revenue Service (IRS) portal.
Employer’s identification number (EIN) is like the social security number of your business giving it a unique identity. This unique number is essential while applying for a business bank account, filing taxes, officiating payrolls, and filling out an application for a business credit card.
7. Build Your Product
After validating your ideas and gathering feedback from MVP, it is now time for software development of your product. Select a development methodology and get your test models working.
To build your product and work on software development, you will need a team with technical expertise. At this stage, you have one of the following options to consider:
- Hire an in-house team- remote or on-site
- Hire freelancers/ agencies
It is recommended to keep the development process in-house instead of outsourcing it. Having an in-house team will allow you to have complete control over the development and its scope. You can rigorously monitor the quality and speed up the process to meet your requirements.
Instead of renting a commercial place, it is better to hire a remote team and individual software developer. This will help you save unnecessary expenses on lease and monthly rentals. Don’t be afraid to make overseas hires. Invest in collaboration and communication tools to allow a seamless flow of development process in your company.
Also, stop waiting for a perfect time. Start as soon as the MVP of your product is ready. Get your landing pages in line and start with light advertising. It’s recommended to start collecting contact information of your target customers and running targeted ads on them.
8. Consider Your Funding Options
Now comes the funding. You need funds to start software development and work on your SaaS company. The question is how much fund will you require and where will you acquire that funds from?
If you haven’t made the financial projections earlier, it is the perfect time to work on it. Get detailed projections for sales, revenue, startup costs, and overhead expenses to assess the flow of money in and out of the business.
Many SaaS companies venture into the market by bootstrapping their projects. And ideally, it’s the right way to do so. However, if you don’t have enough funds, here are a few options for you to consider:
- Angel investors
- Venture capital firms
It’s also a feasible option to get lending from friends and family instead of relying on angel investors right from the beginning. Doing so will have two advantages. Firstly, you will have complete control over the product and secondly lower liabilities.
However, venture capitalists and angel investors can offer an influx of cash that can prove to be beneficial in development and marketing activities.
Overall, assess your needs and understand the implications of each before pitching your plan to potential investors.
9. Establish Your SaaS Brand
The market is crowded with SaaS businesses trying to capture their share of the market. To stand tall in the competition, you need to create a remarkable brand with a solid competitive edge.
The first step in branding would be to determine the look and feel of your software product and your overall SaaS company. Begin by putting together the logo, colors, and designs that will dominate your SaaS software.
Ensure that the visual elements of your software align with the tone you want to establish in the market. For instance, if you want to come across as a functionally professional but quirky software brand, you need your user interface to align with that image.
Even the domain name is part of your branding strategy. Splurge a little and get a powerful domain name for your SaaS company. A short, simple, easy-to-spell .com extension will help you establish a solid presence right from the beginning.
Lastly, ensure that you have your core values, mission, and purpose clearly aligned. Having clarity in vision will help you create a compelling brand value in the minds of your target customers.
10. Develop a Marketing Strategy
Now, that your software is ready, what are your plans for customer acquisition? Even the most brilliant SaaS software needs to make its presence in the target market to start getting sales.
In this step, you will design your go-to-market strategy to market your SaaS software. Even if you are testing the product on early adopters, you do need a proper marketing plan to reach the target audience.
Wondering what makes a perfect marketing strategy? Well, answer these questions to get your answer:
- What will be your sales strategy and the sales channel?
- How much budget will you spare for marketing activities?
- What marketing tools will you use?
- Will you work on marketing in-house or hire an agency?
- What marketing channels can benefit you?
Now, you can choose a variety of marketing channels to build brand momentum in the market. From content marketing to paid Google adverts, email marketing, influencer marketing, and Social media- your marketing strategies can be as extensive as your budget and resources.
Understand that different marketing activities serve different purposes.
For instance, content marketing by writing educational and informative blogs can help establish your credibility as an expert in the market but not necessarily get you sales. Landing pages and Email adverts on the other hand are a perfect go-to-market strategy for converting your potential clients.
Ideally, you should do a bit of everything initially to figure out what might and might not work for you. Don’t sweat much about the marketing costs. This is an investment you make in increasing your outreach as a SaaS brand.
11. Measuring Success with Metrics
You successfully launched your SaaS company after conducting market research and a series of trials. But hey, this is not it.
In order to run a successful business, you need to consistently monitor and track the performance of your product and marketing activities.
Using the customer data, design customer surveys and understand what these people like and dislike about your product. Get an in-depth analysis
Gather the customer data and run surveys to understand customer satisfaction with apps, products, pricing, websites, and other factors. Dive a little deep to check if the customer is in tune with your value proposition and business offerings.
Now, use this data to measure your KPIs (key performance indicators) and enhance the effectiveness of your product and marketing strategies.
And, that’s pretty much everything to get you started. Now, read along and make sure to not make these mistakes while starting a SaaS company.
Key mistakes to avoid when building a successful SaaS company
Thousands of SaaS startups start every year. However, most software companies lack a solid foundation to withstand the dynamically changing market.
Here are a few mistakes you must avoid to set a strong foothold in the market.
1. Passive marketing
Don’t make a mistake like other SaaS entrepreneurs who skimp on marketing activities. Marketing is a costly affair- accept it.
Building an amazing product won’t bring you customers. Consistent, proactive marketing efforts will. Conduct a detailed market analysis and identify different strategies that might attract customers to your business.
SaaS businesses thrive in a competitive market space. Figure out a way to increase your marketing reach and also measure the performance of each activity to determine what works for you.
2. Focused on too many problems
Instead of solving all the problems in an ineffective way, stick to one customer problem and solve it efficiently.
Only solve one primary concern with your product. Build your SaaS features around that problem and focus on simplicity and ease. Having one core problem will help you market your SaaS solution effectively in the market.
3. Leaving behind security
Invest heavily in the security aspects of your SaaS application. Not only will you establish yourself as a credible business, but having well-built security will save you from major security breaches.
In many cases, negligence on your part can result in heavy fines and penalties from the government.
4. Undermining the importance of maintenance
The customer experience is of utmost importance for the SaaS business model. Maintaining software might not be at the top of your priorities until a significant issue pops up.
However, such untimely chaos will result in prolonged downtime of the SaaS application and extra costs, something that can be avoided by having a proactive maintenance plan in action.
5. Not accepting the change
Most SaaS startups fail because of their inability to change and adapt. If you plan to stay successful for decades, you need to be flexible.
Sometimes the strategies that worked for you initially might not work later on because of certain reasons. In such moments, it’s upon you to nourish your business outlook with a new approach.
Avoid these mistakes and keep yourself abreast with the changing market while starting a new SaaS company.
Related SaaS Business Resources
- SaaS Business Plan Template
- Cost to Build a SaaS Platform
Can you start a SaaS company with no technical background?
Absolutely, you can. Having technical expertise can be an added advantage when starting your own SaaS company. But it is not absolutely crucial.
Partner with the right people with a strong foundation of technical know-how. It’s ideal to have a Chief Technical Officer on board when the owner or the CEO lacks the stronghold on the technical front.
However, to get the right people on board, you must know at least the basics of technical aspects to understand the severity of the situation whenever a technical roadblock arises. It’s easier to acquire knowledge online and learn basic coding if you put your mind to it.
Lastly, consider acquiring a ready SaaS product from the market and getting it white-labeled for your SaaS startup.
Evaluate your options and enter this thriving marketplace with a stellar SaaS business idea.
The process of starting a SaaS company is time-consuming. From filtering the business ideas to developing an MVP to working on its development and marketing it to the right audience- it will take a whole lot of work on your end to set it right.
However, more important than anything, is to get started quickly. Get your product out there in the market- ASAP. Don’t wait to perfect the dreamy ideas while someone else captures the market with your idea.
Once the product is out test it, monitor it, iterate the changes, and keep refining it to sail through the tough waters of a competitive world.
The Quickest Way to turn a Business Idea into a Business Plan
Fill-in-the-blanks, AI-assistance, and automatic financials make it easy.

Frequently Asked Questions
How is saas different from traditional software.
SaaS and traditional software differ primarily in their method of delivery and pricing. SaaS is hosted over the cloud whereas traditional software is downloaded over desktop and PC devices. Further, SaaS generates revenue through monthly subscription fees, whereas traditional software companies charge a one-time flat fee to download their software.
How do I identify a target market for my SaaS product?
Begin by conducting thorough market research to understand the needs, pain points, and preferences of your potential customers. Draw a clear persona of your potential buyers to understand who will pay for your SaaS services. Also, dive deep into the market analysis to identify your potential competitors and your competitive edge.
Do I need a business plan for my SaaS startup?
Absolutely, yes. A business plan is essential regardless of whether you are starting a new SaaS startup or scaling the current SaaS model. However, instead of having a traditional 40-page plan, begin by writing a lean plan. Once your SaaS business idea is validated you can add detailed projections for finances and other details to your plan.
How do I create a financial model for my SaaS company?
Before launching your SaaS business, you need to determine the revenue model suitable for your particular target market. Most SaaS companies generate their revenue through subscription-based models by charging flat fees, tiered pricing, or user-based pricing fees.
Identify what pricing model will suit your customer and create a suitable hybrid mix.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when starting a SaaS company?
Here are a few mistakes you must avoid while starting a SaaS company:
- Solving too many problems.
- Not focusing on marketing activities.
- Leaving the aspect of security and maintenance unattended.
- Not identifying the right problem or target market mix.
About the Author

Shyam Dua is a seasoned tax professional with 40+ years of experience & a mentor at SCORE. He stands out due to his exceptional business planning skills. With a keen eye for detail and a strong financial acumen, Shyam crafts compelling business plans that pave the way to success. A CPA with a philanthropic heart, Shyam's strategic expertise, and dedication make him an invaluable asset in shaping thriving business ventures. Read more
Reach Your Goals with Accurate Planning
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates
5 Common Mistakes with Business Financial Projections
2 min. read
Updated April 19, 2024
I was glad to be asked about common mistakes with financial projections. I read about 100 business plans a year for angel investment and business plan competitions. Here are the most common mistakes I see in business forecasts.
- 1. Unrealistic profitability
Most of the business plans I see project profits too high, or profits too early. In the real world, startups choose growth or profits, not both. The plans I see are aimed at angel investment. And for that, the investors win on growth, not profitability. Think about it: If a startup is profitable early on, it doesn’t need investors.
- 2. Underestimated market expenses
Many successful tech businesses, especially software and web businesses, spend 30% or more of sales on marketing.
Don’t underestimate development expenses, testing, certifications, and expenses of regulations.
If you are selling physical products, don’t underestimate the impact of selling through channels. Distributors and retailers take their margins and often demand admin and co-promotion expenses. Distributors often pay very slowly, like six months or so after receiving the goods.
- 3. Applying a small percentage to a large market
That doesn’t work. Nobody gets half a percent of a $10 billion market. Instead, sales forecasts should be built on drivers as assumptions. Drivers might be web visits and conversions, emails sent, paid search terms, or, for physical products, channel assumptions such as distributors, chains, stores, and sales per store.
- 4. Large sales growth with a limited headcount increase
If you are going to sell $100 million in the fifth year, get a clue: you won’t do that with only $2 million in employee expenses. Divide your projected sales by your headcount, and compare that to industry benchmarks.
For most industries, $250,000 per employee is really good. If you are getting $2 million per employee, that doesn’t mean you’re going to be that efficient.
It means you don’t understand the business.
- 5. Confusing profit and cash
Having a profit doesn’t mean you’ll have cash in the bank. Good startup financial projections need to include cash flow. Always. For more on that, see points 4, 6,
Businesses selling to businesses (B2B) normally sell on account. A sale generates not money directly but money owed, to be paid later, which goes on the balance sheet as Accounts Receivable, or AR. Every dollar in AR shows up as sales in the P&L but not in cash.
Many plans underestimate the length of the sales cycle and expenses related to selling directly to enterprises.
Many plans underestimate the cash flow affect of inventory. Every dollar in inventory is a dollar that hasn’t yet shown up in the P&L but may have already affected cash balances.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.

Table of Contents
Related Articles

6 Min. Read
How to Forecast Sales for a Subscription Business

10 Min. Read
How to Create a Cash Flow Forecast

How to Create a Profit and Loss Forecast

2 Min. Read
How to Use These Common Business Ratios
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Small Business Trends
How to start a virtual assistant business.

If you buy something through our links, we may earn money from our affiliate partners. Learn more .
Starting a virtual assistant business is a great option for those wanting to start their own business. Having your own VA business enables you to set your own hours, work with different clients, and generate income. If you’re considering a virtual assistant business but aren’t sure what is a virtual assistant , how much do virtual assistants make when starting their own business? We’ll answer all those questions and more in this article.
What is a Virtual Assistant Business?
The virtual assistant industry has seen a boom over the last few years as more people have taken up the profession. A virtual assistant business offers specialized skills and services to business owners, ranging from general administrative tasks like scheduling appointments to customer relationship management and other services to busy professionals.
Is a Virtual Assistant Business Profitable?
Virtual assistants can generate significant income for themselves, but it depends on several factors such as hourly rate, working hours, number of clients, and more. In the US, the average salary for a virtual assistant is up to $20 an hour, but professionals can charge more or less depending on experience and availability.

Why You Should Start a Virtual Assistant Business
There are many reasons to start your own virtual assistant business. If you’re not sure how to start a virtual assistant business or why you should do it, here are just a few reasons why you should consider it:
- Low start-up costs. You can start a virtual assistant business with very little money. All you need is a computer, an internet connection, and some basic office supplies.
- Flexibility. You can work from anywhere in the world, and you can set your own hours. This is a great option for people who want to be their own boss and have a flexible work schedule.
- Variety of services. Virtual assistants can offer a wide variety of services, from administrative tasks to marketing and social media management. This means that you can find a niche that you are passionate about and that you are good at.
- High demand. The demand for virtual assistants is growing rapidly. This is because businesses are increasingly looking for ways to outsource non-core tasks to save money and time.
- Potential for high income. Virtual assistants can earn a good living. The average hourly rate for a virtual assistant is around $20. However, some virtual assistants can earn much more than that, depending on their skills and experience.
Starting a virtual assistant business is a great way to be your own boss and have a flexible work schedule. If you are interested in starting a virtual assistant business, do your research and take the necessary steps to get started.
Here are some additional tips for starting a successful virtual assistant business:
- Build a strong online presence. This includes having a professional website, being active on social media, and being listed in online directories.
- Network with other virtual assistants and business owners. This is a great way to learn from others and to find new clients.
- Offer high-quality services. This means being reliable, and efficient, and providing excellent customer service.
- Be organized and efficient. This will help you to manage your time effectively and to deliver high-quality work.
- Be patient and persistent. It takes time to build a successful virtual assistant business. Don’t get discouraged if you don’t see results immediately. Keep working hard and eventually, you will achieve your goals.
Starting a Virtual Assistant Business in 21 Simple Steps
Once you’re ready to be a virtual assistant, keep up the momentum and start setting up your business. We’ll walk you through how to create a successful virtual assistant business and how to become a virtual assistant for clients.

1. Choose a Niche
The first step to becoming a virtual assistant is to pick a niche for yourself. For example, some VA businesses only focus on administrative tasks, while others offer services like maintaining social media accounts, scheduling, and other ad-hoc tasks that a personal assistant might offer. Think about your skills and where you think you can offer the most value, and go from there.
2. Know Your Target Market
Once you’ve identified your niche, think about who your target market is. Are you going for a busy professional, such as a solopreneur or a real estate agent? Or would you instead offer VA services to a small business or company?
Many virtual assistants work as a personal assistant or as a virtual receptionist for businesses, while others work with multiple clients.
3. Create Business Plan
Developing a business plan involves more than just outlining services. It should include a detailed analysis of the potential market, a clear definition of your unique selling proposition, and an in-depth operational plan.
This plan should detail how you’ll manage daily operations, client communications, and service delivery. It’s also crucial to include a financial plan with a break-even analysis, cash flow projections, and a pricing strategy that balances competitiveness with profitability.
Your business becomes more official once you make a business plan, which consists of several elements:
- A business name, business license, and legal entity, if needed
- Information about who you’re targeting as your market
- How you plan on gaining new clients
- Marketing materials for your business
- Operating expenses
- Income targets
4. Set Up a Business Bank Account and Credit Card
Once you’ve come up with a business plan and a brand for your VA business, your next step is organizing income. A business bank account and credit card help separate your work money from your personal money and make filing taxes easier.
5. Consider Taking Our Business Insurance
Business insurance is an essential step because it protects you from liabilities and gives your business more security. It’s a cost-effective way to keep your business operating. It makes you look credible to potential clients, and it can help with marketing efforts.
6. Invest in the Relevant Tech
VA businesses need the right tech to offer their services to busy clients, which can vary depending on the type of tasks being completed. Some important equipment to consider includes:
- A second monitor/screen
- Good quality headphones
- Office chair
7. Sort Out Your Business Structure and Register
There are different business registration options and legal entities you can use to structure your business and pay for taxes.
- You can work as a sole/independent contractor and report your earnings to the IRS. For this option, you should work with a tax professional to understand how much state and federal taxes you’ll need to withhold
- You can register as an LLC and pay yourself a salary
- Another option is to register your business as a corporation, but that may have different tax implications depending on the state you are in

8. Plan a Marketing Strategy
Now that your business is up and running, it’s time to think about marketing yourself to small business owners and online businesses.
Make sure to highlight how virtual savvy you are, how you can offer value to business owners, and be clear about the services you offer. Look at elements of your business plan to define your marketing strategy and what channels will be best suited for your services.
9. Price Your Services
When hiring virtual assistants, most businesses tend to worry about costs – especially small businesses. Being upfront and competitive with your pricing will set you apart from other VA businesses.
Before pricing yourself, look at what others in your area are charging, especially those with a similar experience level. Some VA businesses start with a low hourly rate such as $15-20 an hour to entice small businesses and then raise prices once they gain an established client base. You can also charge flat fees and retainers for different services, and create pricing packages to appeal to different clients.
10. Create a Business Website
As a new business, establishing yourself is key – a website helps make that happen, and it can make the difference in landing your first client. You can create a sleek and simple website that showcases your services, and it can serve as your business card.
11. Market Your Business and Find Clients
Market your business through a variety of channels such as social media, paid ads, and local newspapers to reach as many people as possible. You can find virtual assistant jobs and apply to them on job sites as well to broaden your search for clients. Dedicate at least some time in the month to market to your current network and find new clients to build your business.
Marketing for a virtual assistant business should not only cover the basics like social media and local ads but also include networking strategies, building a referral system, and establishing partnerships with complementary businesses.
Utilize digital marketing tools such as SEO, content marketing, and email campaigns to reach a broader audience. Attend industry events and webinars to network with potential clients and peers.
Crafting a unique brand story and consistently sharing it across all platforms can significantly increase your visibility and appeal to your target market.
12. Search for Virtual Assistants
You can find virtual assistants to grow your network and extend your service offerings through third-party websites and LinkedIn. This way, you’ll have a strong connection with virtual assistants in different locations and areas to increase your coverage for clients and expand.

13. Invest in a Time Tracking Tool
Most virtual assistants start with hourly contracts, which is why time tracking tools are so useful. You’ll be able to bill clients with transparency, and also keep an eye on working hours, output, and how you can grow your business.
Some great time tracking tools include:
14. Ask for Reviews
Reviews are everything! Once you build up a solid base of customers and have regular work coming in, make sure to ask them for reviews! Glowing reviews can really make a difference in building your client base, so make sure to periodically ask. You can post reviews as testimonials on your website, on professional profiles for networking, and other channels as a marketing strategy.
15. Develop a Scalable Service Portfolio
As your virtual assistant business grows, consider diversifying your services. This can involve upskilling in areas like digital marketing, bookkeeping, or specialized administrative tasks. Offering a range of services not only attracts a broader client base but also provides opportunities for upselling to existing clients.
16. Implement Efficient Workflow Systems
Use project management and collaboration tools like Asana, Trello, or Slack to streamline workflows. Efficient systems save time and improve client satisfaction. Automating routine tasks with tools like Zapier can also increase productivity, allowing you to focus on more critical aspects of your business.
17. Focus on Client Relationship Management
Building strong relationships with clients is key to a successful virtual assistant business. Regular check-ins, personalized services, and understanding each client’s unique business needs can lead to long-term partnerships. Consider using CRM tools to manage client interactions and ensure a personalized approach to service delivery.
18. Continuous Professional Development
Stay updated with the latest trends and tools in the virtual assistant field. Regularly invest in training and certifications to enhance your skill set. This ongoing learning not only keeps you competitive but also allows you to offer more advanced services to clients.
19. Build a Strong Online Community
Create a community around your brand by engaging with followers on social media, starting a blog, or creating a newsletter. Share tips, industry insights, and personal experiences to establish yourself as a thought leader in the virtual assistant space.
20. Explore Collaboration Opportunities
Partner with other virtual assistants or freelancers to offer a wider range of services. Collaborations can lead to new client referrals and allow you to take on larger projects that require a diverse skill set.
21. Scale Your Business
As you build your services and grow your business, think about how you want to expand. Do you want to offer more personal assistants to businesses to increase coverage? Or do you want to grow your current client base and try to offer more services to entice them?
Scaling your business is about balancing capabilities with resources, and looking at what your clients are asking for and how you can provide them more value.
Virtual Assistant Services
There are many specialized services that virtual assistants offer, and different kinds of virtual assistant tasks depending on business needs. Here are some of the key virtual assistant services your business should be offering:
- Social media management and maintaining a social media presence: Handling and curating content across social media platforms to engage with the audience and promote brand visibility.
- Freelance writing: Providing writing services on a contract basis for various clients, publications, or businesses.
- Data entry: Entering, organizing, and managing data into databases, spreadsheets, or systems.
- Administrative support: Assisting with general office tasks, organizing files, scheduling appointments, and coordinating administrative duties.
- Answering and taking phone calls: Responding to incoming calls, providing information, and handling inquiries.
- Scheduling: Managing calendars, and appointments, and coordinating meetings for individuals or teams.
- Email management: Organizing, filtering, and responding to emails efficiently.
- Travel arrangements: Planning and coordinating travel logistics, including flights, accommodations, and transportation.
- Customer support: Assisting customers with inquiries, and issues, and providing solutions to ensure satisfaction.
- Community management: Engaging and interacting with online communities on behalf of a brand or organization.
- Digital marketing: Promoting products or services through various digital channels, such as social media, SEO, and email marketing.
- Project management: Overseeing and coordinating projects from planning to execution, ensuring successful completion within set timelines and budget.

What skills and qualifications do I need to become a virtual assistant?
To become a virtual assistant, you should possess strong organizational, communication, and time management skills. Familiarity with various software and online tools is also beneficial.
How do I determine my services and target market as a virtual assistant?
Assess your strengths, interests, and expertise to define the services you can offer. Identify your target market based on industries or professionals that align with your skills.
What equipment and software are necessary to start a virtual assistant business?
You’ll need a reliable computer, high-speed internet connection, and essential office software such as word processors, email clients, and project management tools.
How do I set my pricing and payment terms as a virtual assistant?
Research industry rates and consider your experience when setting prices. Define clear payment terms, including payment methods, due dates, and any upfront fees.
How can I market and promote my virtual assistant services?
Utilize social media platforms, create a professional website, and network within your target market. Offer free resources and showcase your expertise to attract potential clients.
What legal and financial aspects should I consider when starting a virtual assistant business?
Register your business, obtain necessary licenses, and review tax requirements for your location. Consider liability insurance to protect yourself from potential risks.
How do I establish strong client relationships and maintain professionalism?
Communicate promptly and effectively with clients. Be reliable, meet deadlines, and provide high-quality work. Respect confidentiality and handle client information with care.
Save money on shipping costs for your Amazon purchases. Plus, enjoy thousands of titles from Amazons video library with an Amazon Prime membership. Learn more and sign up for a free trial today.
Image: Depositphotos, Envato Elements

Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
© Copyright 2003 - 2024, Small Business Trends LLC. All rights reserved. "Small Business Trends" is a registered trademark.

The Ultimate Guide To Starting Your Own PC Building Business

Are you passionate about computers and looking to turn that passion into a profitable venture? Starting your own PC building business might just be the perfect fit for you. A PC building business entails designing, assembling, and selling custom-built personal computers.
To ensure its success you, of course, need to have a great understanding of the PC building business.
But to stand out in the PC market, which is estimated at $204.07 billion in 2024, you’ll require more than just technical prowess. You also need a deep understanding of the PC building market, a good business plan, an effective marketing strategy, and a strong brand among other strategies.
This comprehensive article will walk you through all the key steps while providing great tips on how to start a PC building business successfully. Let’s get started!
1. Conduct market research and identify the niche
Before diving headfirst into starting your custom PC business, it’s crucial to conduct thorough market research to understand the landscape and identify your niche.
Start by researching the demand for custom-built PCs in your niche market. Identify the types of customers who are interested in custom PCs. Are they gamers, content creators, professionals, or businesses? Also, analyze market demand and industry trends, like the popularity of certain components, gaming genres, or emerging technologies like VR or AI.
Then dive deep into understanding your target customers’ specific needs and preferences. What are they looking for in a custom PC? Is it high-performance gaming rigs, silent workstations, compact HTPCs, or something else entirely?
It’s also equally important that you understand the competitive landscape. So ensure you research existing custom PC builders. Identify their strengths, weaknesses, pricing strategies, and target demographics. Look for gaps or underserved segments in the market where you can differentiate your business and carve out a niche for yourself.
Then armed with that information, define your unique selling proposition (USP)—which helps you stand out from your competition. See how MAINGEAR mainly highlights their rear-side cable connectors.

Your USP could be your superior craftsmanship, personalized customer service, exclusive partnerships with component manufacturers, or innovative customization options.
2. Craft a comprehensive business plan
We can’t discuss how to start a PC building business without covering creating a great business plan since it serves as the roadmap for your building journey. Here are some of the key details you must include in your comprehensive business plan as a custom PC builder:
- Executive summary : Provide the key highlights of your business plan, including your goals, target market, USP, and financial projections.
- Product and service offerings : Outline the products and services you plan to offer, including the types of custom PCs, customization options, additional services (e.g., overclocking, system optimization, warranty support), and pricing strategies.
- Marketing strategy : Develop a comprehensive marketing strategy to promote your business and attract a loyal customer base. This may include online marketing tactics such as SEO, social media advertising, email campaigns, content marketing, as well as offline strategies like networking events and word-of-mouth referrals.
- Financial projections : Create detailed financial projections for your PC building business, including startup costs, operating expenses, revenue forecasts, and profit margins.
- Operational plan : Define the day-to-day operations of your business, including inventory management, order fulfillment, customer service, and post-sale support.
- Risk assessment and contingency plans : Identify potential risks and challenges that may affect your business, such as supply chain disruptions, changes in market conditions, or competitive threats. Then include contingency plans and mitigation strategies to minimize risks and ensure business continuity.
With a comprehensive business plan, you can demonstrate your readiness to investors, lenders, and other stakeholders. Additionally, it will guide your decisions, helping you confidently navigate any challenges you face.
3. Register your business
With your business plan in hand, it’s time to make things official by registering your business. This is essential when starting any sort of business, whether it’s an online business like a call center business or an offline business like a cleaning business .
Start by choosing a suitable business name and structure, whether a sole proprietorship, partnership, or LLC. Each structure has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of liability, taxation, and regulatory requirements, so choose wisely based on your specific circumstances.
Next, register your PC building business with the appropriate government authorities. The registration processes will vary based on your location and chosen business structure. So check with your local business registration office for guidance on the registration process in your area.
However, the process will typically involve filing registration forms, paying registration fees, and obtaining necessary licenses or permits to operate legally.
Additionally, consider trademarking your business name, logo, or any unique product designs or inventions to protect your intellectual property.
4. Source quality components and forge partnerships with suppliers
You’ll need to source a wide range of components to build high-quality custom computers tailored to your customers’ needs. Some of these components include RAM modules, solid-state drives (SSDs), hard disk drives (HDDs), central processing units (CPUs), graphics cards, motherboards, and cooling solutions.
To ensure you source quality components start by researching reputable component suppliers and distributors. Look for suppliers with a track record of reliability, quality, and customer satisfaction. Then consider factors like product selection, pricing, delivery times, return policies, and customer service.
You can use a platform like PC Builder to easily find the right supplier. Additionally, the platform offers building guides and gives feedback on the most compatible components for your PC.

While it’s tempting to prioritize price when sourcing components, quality should always be your top priority. Invest in high-quality components from trusted brands to ensure great performance, reliability, and product longevity, customer satisfaction.
A poorly built PC device will only lead to poor system performance and slow processing, which affects tasks like gaming, video editing, and web browsing. In fact, even the fastest web hosting platform cannot compensate for a poorly built PC device.
Over time, build strong relationships with your component suppliers by making repeat orders, communicating regularly, and providing feedback. Establishing a good relationship with your suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority access, and personalized support, which will give you a competitive advantage.
However, it’s also key to know when to diversify your supplier base to mitigate the risk of supply chain disruptions, shortages, or quality issues.
5. Build your brand and market your services
Once your products are ready for the market, it’s time to focus on building brand awareness and visibility.
Start by creating a professional website showcasing your services, portfolio of past builds, and customer testimonials.
Your website should be visually appealing, easy to navigate, and optimized for search engines to attract organic traffic and generate leads. Additionally, include helpful resources to show your customers how your products work or how well they work. For instance, you can record screen activities to prove your device is high-performing.
Digital Storm is a great example of an exceptional PC building business website. See how they use a clean design, images, product videos, consistent brand colors, and customer testimonials, among other design elements to capture potential customers’ attention.

You can also use guest blog posts , social media platforms, online forums, and key industry events to spread the word about your business and engage with potential customers. Besides sharing valuable content, consider offering special promotions or hosting giveaways, as shown below, to incentivize purchases and encourage repeat business.

Additionally, you can collaborate with tech influencers , bloggers, YouTubers, and streamers in the gaming and tech community to reach a wider audience and gain credibility.
6. Provide exceptional customer service and support
Providing exceptional customer service and support can set you apart from the competition. In fact, research shows that 80% of customers believe the experience a company provides is just as important as its products and services.
So how do you provide exceptional customer service and support? Here are a few effective ways:
- Expert recommendations : Offer expert recommendations and guidance to help customers make informed decisions about their custom PCs. Use your technical expertise to suggest the most suitable components, configurations, and customization options based on their needs. This will ensure they get the best value for their investment.
- Transparent communication : Keep your customers informed and updated throughout the PC building process. Provide regular updates on the status, any delays or issues encountered, and estimated completion times. Additionally, be transparent about pricing, component availability, and potential limitations to manage customer expectations effectively.
- Quality assurance : Conduct thorough quality assurance checks on each PC build to ensure that it meets the highest standards of performance, reliability, and aesthetics. This also enables you to address any issues or defects promptly before delivering the system to the customer.
- Post-sale support : Provide comprehensive post-sale support to assist customers with setup, installation, troubleshooting, and optimizing their custom PCs. You should also offer clear instructions, documentation, and tutorials on your website to guide customers through common tasks and issues they may encounter with their new systems.
- Warranty services : Reassure your customers they are making the right investment by offering generous warranties. Clearly communicate warranty terms and conditions, including coverage periods, repair or replacement policies, and any exclusions or limitations, to ensure transparency and accountability.
- Responsive communicatio n: Respond promptly to customer inquiries, feedback, and support requests through various channels, including phone, email, live chat, and social media. Quick responses demonstrate your commitment to customer satisfaction, which helps you easily earn their trust.
- Continuous improvement : Continuously seek customer feedback to identify areas for improvement and opportunities to enhance your custom PC building services. Then actively implement the changes to match customer expectations in the future.
Keep in mind, happy customers are more likely to return for future purchases, recommend your business to others, and contribute to your long-term success and growth.
Starting your own PC building business can be a rewarding and lucrative endeavor. While it’s not an easy task, like with any venture, it is not impossible.
By following our steps on how to start a PC building business, you can easily turn your dream of owning a successful PC building enterprise into a reality.
Start by conducting market research and identifying a niche. Then craft a business plan, register your business, source quality components, forge supplier partnerships, build your brand, market your services, and provide great customer service and support.
Above all stay adaptable, stay curious, and stay connected to keep building great PC products for your customers. Best of luck!
About the author
Nicholas Prins
I'm the founder of Launch Space. We work with global companies helping them scale lead generation through SEO and content marketing. Head over to the homepage to find out more.

How to Launch a Cafe Business

How to Start a Cleaning Business
Guest Post Guidelines
Business Blog Content Marketing Blog Entrepreneurship Blog General Blog
Software Review Software Comparison Lifetime Software Deals
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

UK startup lifts lid on plan to turn human waste into jet fuel
Low-cost airline Wizz Air puts in 525,000-tonne order for product of Firefly’s proposed refinery in Essex
Aircraft could one day take off on fuel made from human waste under plans revealed by Wizz Air and the British sustainable aviation company Firefly to build a commercial refinery in Essex.
Firefly, based in Bristol, said it had developed a process to convert treated sewage into sustainable aviation fuel , or SAF.
The low-cost airline Wizz said it was investing by placing an order – potentially worth hundreds of millions of pounds – for up to 525,000 tonnes of Firefly’s waste-based fuel over the next 15 years.
Firefly has now signed agreements with industrial partners for a pilot refinery in Harwich that would take “biosolids” from Anglian Water and turn it into aircraft fuel. Airlines will have to ensure that a minimum proportion of fuel burned is certified sustainable in the coming decade, with the EU mandating at least 20% SAF by 2035, and the UK expected soon to announce a mandatory 10% by 2030.
There are various ways of making SAF but most are much more expensive than normal kerosene jet fuel, with a limited supply of waste feedstocks such as used cooking oil.
Firefly’s chief operations officer, Paul Hilditch, said converted sewage should be cheaper and more abundant, providing up to 5% of airlines’ fuel needs in the UK. The process uses biosolids, the water industry term for the final product in the treatment process. “It’s crumbly – like compost or wet chocolate cake,” he said. “There’s millions of tonnes of the stuff. And it has no intrinsic value.”
The company has produced small test quantities of SAF that he said were “chemically indistinguishable” from jet fuel, with a residue that can be used as a soil enhancer. The fuel is still in a regulatory testing process, and Firefly is still to secure the investment it needs to build a full-scale factory.
However, its chief executive, James Hygate, said it was confident it could be delivering commercial supplies of SAF by 2028-29. He said the first facility in Harwich would serve London airports and there was potential for two more in the UK.
“We’re turning sewage into jet fuel and I can’t think of many things that are cooler than that,” he commented.
Wizz Air’s corporate and ESG officer, Yvonne Moynihan, said: “Alongside fleet renewal and operational efficiency, SAF plays a crucial role in reducing carbon emissions from aviation.”
She said Wizz’s investment in Firefly was a “perfect pair-up for a low-cost airline” and the carrier aspired to use 10% SAF across its entire operation by 2030, although it would need “a significant ramp-up of production and deployment”.
The UK government has said it expects five commercial plants to produce SAF in the UK to be under construction by 2025. However, campaigners have said even using human waste for aviation was not truly sustainable.
after newsletter promotion
Matt Finch, of the thinktank Transport & Environment UK, said sewage could also be used to make biomethane and there was direct competition for its use: “What’s the best use of this biomass hasn’t been clarified … It’s another conundrum.”
About 87% of UK water companies’ biosolids are currently spread on farmland. Cait Hewitt, of the Aviation Environment Foundation, said: “It’s not to be sniffed at, given that this is truly unavoidable waste, but not great either given it’s already in use as fertiliser.”
She said any test for the carbon credentials of alternative fuels should ask: “Has the producer done something to draw down additional CO 2 from the atmosphere? Otherwise it’s nothing near a net zero solution.”
Hilditch said the use of biosolids for muckspreading on farms was of low value, and the residue from the sewage-to-fuel process would still be available to improve soil.
Many other countries simply incinerated human waste, meaning that converting it to jet fuel could also have other benefits in terms of efficient disposal, he added. “It’s not just the UK of course. Anywhere in the world where there are people, there’s poo.”
- Airline industry
- Airline emissions
- Air transport
- Travel and transport
- Travel & leisure

Airlines hope that sustainable fuels will propel them to a guilt-free future

Airlines warn of higher fares as industry moves to net zero target

E-fuels: how big a niche can they carve out for cars?

Electric planes sound like a fantasy but they may be the future for short-haul in Australia

Airlines need to do more than plant trees to hit net zero, MPs told

‘They said we were eccentrics’: the UK team developing clean aviation fuel
Most viewed.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Start-Up Founder Sentenced to 18 Months in Prison for Fraud
Manish Lachwani, who founded the software start-up HeadSpin, is the latest tech entrepreneur to face time in prison in recent years.

By Erin Griffith
Reporting from San Francisco
Another start-up founder is going to prison for overstating his company’s performance to investors.
Manish Lachwani, who last year pleaded guilty to three counts of defrauding investors at his software start-up, HeadSpin, was sentenced to one and a half years in prison on Friday. He will also pay a fine of $1 million.
Government prosecutors said Mr. Lachwani, 48, deceived investors by inflating HeadSpin’s revenue nearly fourfold, making false claims about its customers and creating fake invoices to cover it up. His misrepresentations allowed him to raise $117 million in funding from top investment firms, valuing his start-up at $1.1 billion.
When HeadSpin’s board members found out about the behavior in 2020, they pushed Mr. Lachwani to resign and slashed the company’s valuation by two-thirds.
Mr. Lachwani is at least the fourth start-up founder in recent years to face serious consequences after taking Silicon Valley’s culture of hype too far. Other founders currently in prison for fraud include Sam Bankman-Fried of the cryptocurrency exchange FTX and Elizabeth Holmes and Ramesh Balwani of the blood testing start-up Theranos.
Trevor Milton, a founder of the electric vehicle company Nikola, was sentenced to prison in December for fraud. Michael Rothenberg, a venture capital investor who was recently convicted of 12 counts of fraud and money laundering, is set to be sentenced in June. And Changpeng Zhao, who founded the cryptocurrency exchange Binance and pleaded guilty to money laundering last year, is scheduled to be sentenced later this month.
Carlos Watson, the founder of the digital media outlet Ozy Media, and Charlie Javice, founder of the financial aid start-up Frank, have pleaded not guilty to fraud charges and face trials later this year.
Past generations of start-up founders rarely faced lasting consequences for their exaggerations. But the last decade’s low interest rates led to growing sums being poured into tech start-ups . Some founders used that environment to stretch the truth about what their technology could do or how their business performed.
The government has stepped up its investigations into such situations. The Justice Department said last month that its fraud division tried more than 100 white-collar crime cases over the last two years, which was a record. It also announced plans to beef up its program to pay whistle-blowers.
At Mr. Lachwani’s sentencing on Friday, his lawyer, John Hemann, argued for a lower sentence because — unlike other start-up frauds — HeadSpin’s business was a success and investors did not lose money.
“He wasn’t making up a product,” Mr. Hemann said of Mr. Lachwani. “He wasn’t selling snake oil.”
Judge Charles Breyer of California’s Northern District court said success was not a panacea for fraud. Silicon Valley’s tech founders and executives need to know that exaggerating to investors will result in incarceration, no matter how successful they are, he said.
“If you win, there are no serious consequences — that simply can’t be the law,” he said.
Addressing the judge, Mr. Lachwani broke down in tears several times. He apologized to the investors he misled and spoke of HeadSpin’s success. “HeadSpin just got very big, very fast,” he said.
Other government agencies are also investigating founders. On Wednesday, the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau accused Austin Allred, founder of BloomTech, a coding school that let students pay tuition by promising a portion of their future income, of violating the law by making false claims to customers.
In one claim, Mr. Allred said a “cohort” of BloomTech’s students had a 100 percent job placement rate, but the “cohort” consisted of one student, the agency said. The C.F.P.B fined BloomTech $164,000 and barred it from making loans.
Erin Griffith covers tech companies, start-ups and the culture of Silicon Valley from San Francisco. More about Erin Griffith
A Guide to Digital Safety
A few simple changes can go a long way toward protecting yourself and your information online..
A data breach into your health information can leave you feeling helpless. But there are steps you can take to limit the potential harm.
Don’t know where to start? These easy-to-follow tips and best practices will keep you safe with minimal effort.
Your email address has become a digital bread crumb that companies can use to link your activity across sites. Here’s how you can limit this .
Protect your most sensitive accounts by creating unique passwords and adding extra layers of verification .
There are stronger methods of two-factor authentication than text messages. Here are the pros and cons of each .
Do you store photos, videos and important documents in the cloud? Make sure you keep a copy of what you hold most dear .
Browser extensions are free add-ons that you can use to slow down or stop data collection. Here are a few to try.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Best Business Plan Software of 2024. Wrike: Best overall. Smartsheet: Best for goal management. LivePlan: Best for financial forecasting. Aha!: Best for roadmapping. Bizplan: Best for ...
Best Business Plan Software: LivePlan. LivePlan is the overall best business plan tool, offering a large number of features at an affordable price. Visit LivePlan. 1. LivePlan - $15/month to $30/month. We love LivePlan overall because it offers great value at an affordable cost.
Six-month plan: $18 per month, billed every six months. Pay-as-you-go plan: $20 per month, billed once every month. 2. GoSmallBiz. Best for multiple business management tools in one platform. Next ...
5 Best Business Plan Software and Tools in 2023 for Your Small Business. Entrepreneurs who write formal business plans are 16% more likely to achieve success than entrepreneurs who don't. 1 This software can help. Data as of 3/13/23. Offers and availability may vary by location and are subject to change.
10 steps to start a software as a service company. 1. Develop a solution for a problem. Before diving into pricing, branding, or building a team, it's important to make sure you have a clear problem to address and a solution that alleviates it. After all, if you're not solving a problem, you don't have a business.
Building a business is hard work and you need digital solutions that can make everyday life easier as an early-stage founder. Cuttles is a guided and personalized startup builder that helps you with planning, budgeting, and presenting your startup to investors. Their business plan tool helps you write your plan in a fraction of the time.
Writing a software company business plan is a crucial step toward the success of your business. Here are the key steps to consider when writing a business plan: 1. Executive Summary. An executive summary is the first section planned to offer an overview of the entire business plan. However, it is written after the entire business plan is ready ...
Download Startup Business Plan Template - Word. Word | Smartsheet. This startup business plan template contains the essential components you need to convey your business idea and strategy to investors and stakeholders, but you can customize this template to fit your needs. The template provides room to include an executive summary, a financial ...
Build a lean business plan in under 60 minutes. A traditional business plan isn't right for everyone. With LivePlan, you can create a lean one-page plan to: Clarify your ideas. Outline your vision, the problems your startup solves, and other details. LivePlan helps you organize this information so you can better understand how your business ...
A software company business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your software company business. Among other things, it outlines your business concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections.
Step 4: Create a Software Company Business Plan. Every business needs a plan. This will function as a guidebook to take your startup through the launch process and maintain focus on your key goals. A business plan also enables potential partners and investors to better understand your company and its vision:
An excellent executive summary in a software startup business plan typically includes the general situation of the target market or related industry based on conducted market research and an overview of the software solution you offer. Other information, such as unique value proposition (UVP), competitors in the same segment, and the company ...
Roadmap. Financial Plan. 1. Executive Summary. The executive summary is the introduction of your SaaS business plan. This is a section you should spend a lot of time on as it's the first impression investors will have when looking at your business plan. The executive summary should fit in 2 pages maximum.
The executive summary of a software business plan is a one- to two-page overview of your entire business plan. It should summarize the main points, which will be presented in full in the rest of your business plan. Start with a one-line description of your software company. Provide a short summary of the key points in each section of your ...
The 10 online business plan software solutions examined in this roundup —Atlas Business Solutions Ultimate Business Planner 5.0, Enloop, EquityNet, NetEkspert iPlanner.NET, OnePlace, Palo Alto ...
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P's: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a software company business plan, your marketing strategy should include the following: Product: In the product section, you should reiterate the type of software company that you documented in your company overview.
Importantly, a crucial step in starting a software company is to complete your business plan. To help you out, you should download Growthink's Ultimate Business Plan Template here. Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here. 15 Steps To Start a Software Company. Choose the Name for Your Software Company; Develop Your Software Company ...
The business plan should include information on the products or services offered by the startup, the market opportunity, the business model, the team, the financial projections, and the risks and challenges associated with the business. A tech startup's business plan should generally address three major areas of the business:
Put simply, a lean startup business plan is a streamlined, no-fluff version of a traditional business plan. It's designed for speed and adaptability rather than comprehensiveness. ... For software platforms: Product requisites → Cloud infrastructure → Coding → Version control → Usage analytics → Onboarding → Technical support; For ...
Keep it simple and precise. Begin by writing a one-sentence startup business plan introduction that showcases the core customer need/pain point and how you propose to solve it. 3. Develop startup goals and milestones. Next, write down the milestones and goals for your startup business plan.
The average cost to start a SaaS (software as a service) business in the US is anywhere between $50,500- $150,500. Depending on the complexity of your SaaS business model, the costs can extend up to $500,000. These costs are highly influenced by factors such as development, legal, branding, and marketing costs.
1. Executive summary. This short section introduces the business plan as a whole to the people who will be reading it, including investors, lenders, or other members of your team. Start with a sentence or two about your business, development goals, and why it will succeed. If you are seeking funding, summarise the basics of the financial plan.
I read about 100 business plans a year for angel investment and business plan competitions. Here are the most common mistakes I see in business forecasts. 1. Unrealistic profitability. Most of the business plans I see project profits too high, or profits too early. In the real world, startups choose growth or profits, not both.
1. Choose a Niche. The first step to becoming a virtual assistant is to pick a niche for yourself. For example, some VA businesses only focus on administrative tasks, while others offer services like maintaining social media accounts, scheduling, and other ad-hoc tasks that a personal assistant might offer.
Let's get started! 1. Conduct market research and identify the niche. Before diving headfirst into starting your custom PC business, it's crucial to conduct thorough market research to understand the landscape and identify your niche. Start by researching the demand for custom-built PCs in your niche market. Identify the types of customers ...
At the inaugural Bill Gross Business Plan Competition, aspiring entrepreneurs pitched start-up ideas to a panel of seasoned investors.In this version of Shark Tank, each team was made up of Caltech undergraduate and graduate students armed with scientific expertise and a vision of how next-generation technology will improve the world.. Fifteen student teams—selected as finalists from 80 ...
Markets on edge. Treasuries are up and S&P 500 futures are dropping as investors try to discern the rapidly developing situation in the Middle East. The market reaction was stronger initially when ...
The low-cost airline Wizz said it was investing by placing an order - potentially worth hundreds of millions of pounds - for up to 525,000 tonnes of Firefly's waste-based fuel over the next ...
Manish Lachwani, who founded the software start-up HeadSpin, is the latest tech entrepreneur to face time in prison in recent years. Listen to this article · 3:56 min Learn more Share full article