Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center


PHILOSOPHY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY: IT’S IMPACT ON RECENT DEVELOPMENT

In the contemporary society, science and technology are very much dominating in all part of the world, because the world is running with faster than ever before. The social and cultural values are shifting towards techno innovative. The philosophy will play a greater extent to understating the basic ethical and moral issues and crisis in science and technology of the global society. The science and technology as socially embedded enterprises, which change the intellectual paradigms. Philosophy of science is a new shift of epistemology in the light of emergency of technology and science. In the analytical philosophy the science and technological poses a new challenge in development and destruction are central issues in the modern debates. An enquiry into epistemological status of technological statement and technological statements are to be demarcated from scientific statement. The development of ethics of technology as a new system started as sub discipline of philosophy. The fundamental frame work on science and technology jobs are crucial in the given examples of the honesty, sincerity, truthfulness…etc. philosophy will deal all parts of science and technology and show the proper direction practically which will eradicate some issues change the society and lead into development and justify all part of the people and all areas
Related Papers
Technology and Society studies
Piet Ankiewicz
International Journal of …
GABRIELE CORNELLI , Márcio Rojas
Born to enable its creators to fulfill their needs, scientific technique has always played a significant role in human civilization. This is the context in which we glimpse the advent of modern technoscience, which has significantly contributed to the increment of human control over nature. This study aims to analyze, under the focus of bioethics, reflections on the philosophy of science as they relate to the neutrality of science and converge with epistemic rationality, as well as to relate those reflections to the process of making decisions in the administration of technoscience. The study has raised doubts about the capacity of technoscientific knowledge to legitimize and justify the decisions within the ambit of the national science and technology systems, thus signaling the need for promoting a link between technoscientific self-regulation and bioethic hetero-regulation.
Blackwell Pub.
CHALLENGES FACING PHILOSOPHY IN UNITED …
Laszlo Ropolyi
World Journal of Advanced Research and Reviews
BRUNO RICCARDI
The many years of epistemological discussion involving scientific culture, in the search for the primary role to be assigned to technology or science, has not yet reached a definitive synthesis. In the present technological era, marked by the continuous flourishing and converging of knowledge from one discipline into the other, this distinction has little meaning, if anything, it is a matter of assigning to both the fundamental role that together can and must fulfill for the man who is, or should be, both the creator and the sole beneficiary. In this article we briefly are going to review the prerogatives assigned by scientists and philosophers to the two activities over the centuries, finally arriving at the proposal to transfer the achievements of science and technology from utilitarian use to the exclusive benefit of industry, social use for the fundamental benefit of man.
Sara Baranzoni , Simone Belli
The Role of Technology in Science: Philosophical Perspectives
Sven Hansson
RELATED PAPERS
Toko Paving Block Murah
America Latina Hoy Revista De Ciencias Sociales
Soraia Marcelino Vieira
Bulletin du centre d’études médiévales d’Auxerre | BUCEMA
Dominique Iogna-Prat
Neuroscience
Nature communications
Alexey Zozulya
Narasimman Sundararajan
Chemical Physics
Jannis Samios
Debates em Psiquiatria
Marcelo Allevato
Jarvas zungumbia
Salud Mental
Gloria Benitez-King
Anja van Heelsum
I Made Samudra
Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
Melaku Alemu
Astroparticle Physics
N. Randazzo
International Journal of Astrobiology
Manfred Cuntz
Atherosclerosis
Rosalia Rodriguez Rodriguez
Geosciences
Gemma Musacchio
Kwartalnik Prawa Podatkowego
Jan Kowalski
Open Journal of Renewable Energy and Sustainable Development
Abu hussen Ahmed
Journal of the Neurological Sciences
Pusat Pelatihan Digital Marketing Jogjakarta
Pelatihan Digital Marketing
FEMS Microbiology Letters
Juan Pablo Paez Gonzalez
Majalah Ilmiah Pengkajian Industri
wahyu garinas
María Gabriela Paraje
See More Documents Like This
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

How Political Transitions Affect Science, Technology, and Innovation Policies
Those interested in science, technology, and innovation policy (STIP) would be remiss to remove politics from the policy. With 49 percent of the world’s population heading to election polls this year, it is a real possibility that government transitions will upend countries’ current STIP trajectories. Interested stakeholders seeking metrics to track those priorities may want to read a recent article in Quantitative Science Studies , titled, “ The Policy is Dead, Long Live the Policy—Revealing Science Technology and Innovation Policy Priorities and Government Transitions via Network Analysis .” Colombian research partners Julián D. Cortés and María Catalina Ramírez Cajiao analyzed how frequent and enmeshed research topics were in public funding research calls (RC) in Colombia from 2007 to 2022. Since the funding for these RCs came from public sources, they could serve as one indicator of government priorities. The researchers found that, alongside a general increase in research field diversity and density, several research fields such as drug discovery and conservation, “Maintained their higher strategic relevance despite the government in office.” If generalized, methods such as network analysis may be helpful for analysts to track science, technology, and innovation priorities across different periods of government and identify which research sectors are politicized.
Based on a literature review of STIP evaluations in Europe, Cortés and Cajiao found that the most common methods for those evaluations included, “Descriptive statistics, context, documents, and case studies.” In addition to expanding methods of analysis, Cortés and Cajiao sought to expand the research geography to lower- and middle-income countries, which they considered to be an often-highlighted but rarely addressed research gap. Cortés and Cajiao reviewed public RC data oriented toward research in Colombia’s Ministry of STI open data portal and RC digital archive. Next, they coded research fields by manually reviewing each document for what fields each RC would support. They standardized research fields by utilizing the All Science Journal Classification Codes (ASJC) . For example, ASJC considers “Insect Science,” “Plant Science,” and “Soil Science,” as one overall topic, “Life Sciences.” Cortés and Cajiao did this analysis by year and matched RC priorities with periods of government (four years).
The authors also utilized co-word analysis first introduced by Callon et al. (1983) to visualize clusters of ASJC topics in trios. According to Cortés and Cajiao, “if a given RC has three ASJC, those ASJC (nodes) are collocated (linked) given that all of them are contained in the same RC.”
Figure 1: ASJC co-occurrence network ( Bastian, Heymann, and Jacomy, 2009 ; Callon et al., 1983 ; DNP, 2021 )
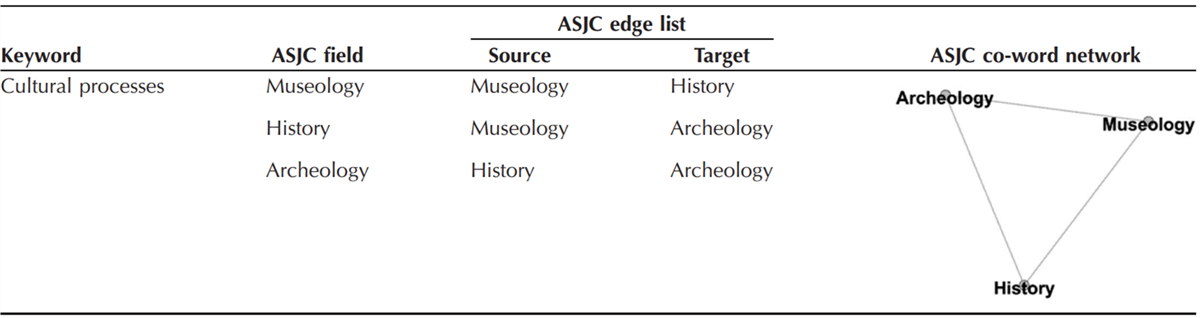
Research fields that were frequently part of ASJC co-word networks received high “Betweenness Centrality Scores,” which meant that they were research fields of interest. In contrast, research fields with lower scores may have more marginal or limited attention.
Results and Implications
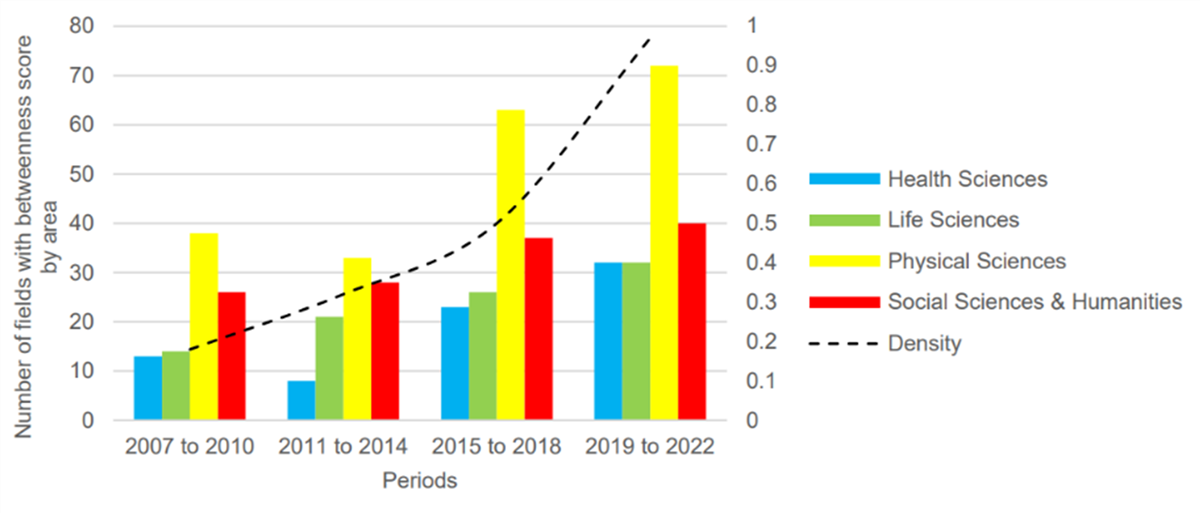
From 2007 to 2022, the number of research fields in Colombia’s RCs increased. Despite changes in Colombia’s government, Physical Sciences retained its position as the top field with its high betweenness score compared the other top fields of Life, Health, and Social Sciences. Health Sciences topics are on an upward trend ever since an apparent dip in priority during the 2011–2014 government period, catching up to Life Sciences based on their betweenness scores. Despite these findings, Cortés and Cajiao caution that their research does “Not integrate the effects of STIP priority fluctuations and research/innovation outputs, nor the amount of funding by fields in the same framework.” They noted that although the Health Sciences sector’s betweenness score was not particularly impressive compared to other top fields, its research growth rate surpassed Physical, Life, and Social Sciences.
Figure 2: Number of fields Cortés and Cajiao identified in RCs with betweenness centrality score by area (left y-axis) and network density score (right y-axis) by period
Related Search Content
October 28, 2019
A Policymaker’s Guide to the “Techlash”—What It Is and Why It’s a Threat to Growth and Progress
April 30, 2019
A Policymaker’s Guide to Blockchain
October 5, 2020
The Impact of China’s Production Surge on Innovation in the Global Solar Photovoltaics Industry
Green finance reform and application intensity of chemical fertilizer and pesticide: policy evidence from China
- Circular Economy and Sustainable Development
- Published: 01 April 2024
Cite this article
- Jianjun Miao 1 ,
- Xinming Wang 1 , 3 ,
- Chao Hua ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7144-4472 1 &
- Jingwei Han 2
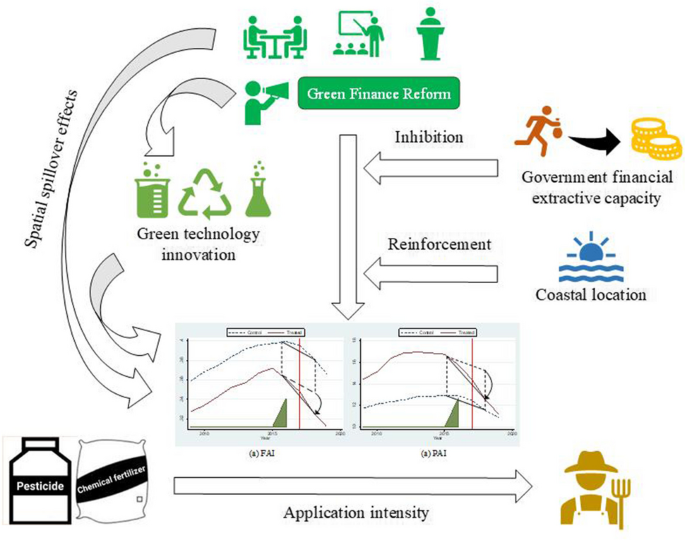
The environmental hazards resulting from the excessive application of pesticides and fertilizers have been an inevitable agricultural production issue in various countries around the world. New technologies and policies are constantly trying to improve their application efficiency. This paper utilizes panel data of the provincial level in China from 2009 to 2019 to empirically study the effect of green finance reform policies on the chemical fertilizer application intensity (FAI) and pesticide application intensity (PAI). Standard difference-in-differences (DID), synthetic DID, difference-in-difference-in differences (DDD), and spatial DID models are constructed for specific empirical analysis. The findings can be concluded as follows: (1) A unit of the green finance reform policy reduces FAI by 0.0144 and PAI by 1.7921 by promoting green technology innovation. (2) Government financial extractive capacity hinders the reduction effect of green finance on PAI. (3) Coastal geographical location is conducive to reducing PAI through green finance reform. (4) FAI and PAI show positive spatial autocorrelations, and the influence of green finance reform overflows to surrounding areas. The research results can provide policy references for countries around the world to promote the green development of agriculture and reduce environmental pollution.
Graphical Abstract
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
Abadi BJ (2018) The determinants of cucumber farmers’ pesticide use behavior in central Iran: implications for the pesticide use management. J Clean Prod 205:1069–1081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.09.147
Article Google Scholar
Abadie A, Diamond A, Hainmueller J (2010) Synthetic control methods for comparative case studies: estimating the effect of California’s tobacco control program. J Am Stat Assoc 105(490):493–505. https://doi.org/10.1198/jasa.2009.ap08746
Article CAS Google Scholar
Acemoglu D, Robinson JA (2012) Why nations fail: the origins of power, prosperity and poverty. Crown Publishers, New York
Google Scholar
Achilladelis B, Schwarzkopf A, Cines M (1987) A study of innovation in the pesticide industry: analysis of the innovation record of an industrial sector. Res Policy 16(2–4):175–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/0048-7333(87)90030-8
Adnan N, Nordin SM, Anwar A (2020) Transition pathways for Malaysian paddy farmers to sustainable agricultural practices: an integrated exhibiting tactics to adopt Green fertilizer. Land Use Policy 90:104255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2019.104255
Ali P, Kabir M, Haque SS, Qin XH, Nasrin S, Landis D, Holmquist B, Ahmed N (2020) Farmer’s behavior in pesticide use: insights study from smallholder and intensive agricultural farms in Bangladesh. Sci Total Environ 747:141160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141160
Arkhangelsky D, Athey S, Hirshberg DA, Imbens GW, Wager S (2021) Synthetic difference-in-differences. Am Econ Rev 111(12):4088–4118. http://www.nber.org/papers/w25532 . Accessed July 2021
Ataei P, Gholamrezai S, Movahedi R, Aliabadi V (2021) An analysis of farmers’ intention to use green pesticides: the application of the extended theory of planned behavior and health belief model. J Rural Stud 81:374–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2020.11.003
Athukorala W, Lee BL, Wilson C, Fujii H, Managi S (2023) Measuring the impact of pesticide exposure on farmers’ health and farm productivity. Economic Analysis and Policy 77:851–862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eap.2022.12.007
Barman A, De PK, Chakraborty AK, Lim CP, Das R (2023) Optimal pricing policy in a three-layer dual-channel supply chain under government subsidy in green manufacturing. Math Comput Simul 204:401–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matcom.2022.08.008
Chang KW, Liu LL, Luo D, Xing K (2023) The impact of green technology innovation on carbon dioxide emissions: the role of local environmental regulations. J Environ Manage 340:117990. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.117990
Chen K, Bian R (2023) Green financing and renewable resources for China’s sustainable growth: assessing macroeconomic industry impact. Resources Policy. 85(Part A):103927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2023.103927
Chen JD, Huang SS, Shen ZY, Song ML, Zhu ZH (2022) Impact of sulfur dioxide emissions trading pilot scheme on pollution emissions intensity: a study based on the synthetic control method. Energy Policy 161:112730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2021.112730
Chen X, Xing LR, Wang K, Zhang Y, Han XQ (2023) Nonlinear effects of internet development on chemical fertilizer application intensity: macro evidence from China. J Clean Prod 386:135794. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.135794
China Agricultural Green Development Report (2021) China Agricultural Press. China Agricultural Green Development Research Association. http://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id =7105272110. Accessed 24 July 2021
Deng HY, Zheng WY, Shen ZY, Štreimikienė D (2023) Does fiscal expenditure promote green agricultural productivity gains: an investigation on corn production. Appl Energy 334:120666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2023.120666
Dong SM, Ren GX, Xue YY, Liu K (2023) How does green innovation affect air pollution? An analysis of 282 Chinese cities. Atmos Pollut Res 14(9):101863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2023.101863
Du K, Li P, Yan Z (2019) Do green technology innovations contribute to carbon dioxide emission reduction? Empirical evidence from patent data. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 146:297–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2019.06.010
Fang GC, Gao ZY, Wang L, Tian LX (2022) How does green innovation drive urban carbon emission efficiency? —Evidence from the Yangtze River Economic Belt. J Clean Prod 375:134196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134196
Feng YD, Zou LH, Yuan HX, Dai L (2022) The spatial spillover effects and impact paths of financial agglomeration on green development: evidence from 285 prefecture-level cities in China. J Clean Prod 340:130816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130816
Ferman B (2020) Inference in differences-in-differences: how much should we trust in independent clusters? MPRA Paper 93746. University Library of Munich, Germany. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1909.01782
Book Google Scholar
Gong HQ, Guo Y, Wu JC, Wu HJ, Nkebiwe PM, Pu ZX, Feng G, Jiao XQ (2022) Synergies in sustainable phosphorus use and greenhouse gas emissions mitigation in China: perspectives from the entire supply chain from fertilizer production to agricultural use. Sci Total Environ 838(Part 2):155997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155997
Guo LL, Li HJ, Cao XX, Cao AD, Huang MJ (2021) Effect of agricultural subsidies on the use of chemical fertilizer. J Environ Manage 299:113621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113621
Guo JB, Li C, Xu XB, Sun MX, Zhang LX (2022a) Farmland scale and chemical fertilizer use in rural China: new evidence from the perspective of nutrient elements. J Clean Prod 376:134278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134278
Guo LL, Li HJ, Cao AD, Gong XT (2022b) The effect of rising wages of agricultural labor on pesticide application in China. Environ Impact Assess Rev 95:106809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2022.106809
Guo ZD, Chen XQ, Zhang YW (2022c) Impact of environmental regulation perception on farmers’ agricultural green production technology adoption: a new perspective of social capital. Technol Soc 71:102085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2022.102085
Haggblade S, Hazell P (1989) Agricultural technology and farm-nonfarm growth linkages. Agric Econ 3(4):345–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/0169-5150(89)90008-X
Han X, Wang Y, Yu WL, Xia XL (2023) Coupling and coordination between green finance and agricultural green development: evidence from China. Finan Res Lett 58(Part A):104221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.frl.2023.104221
Hasan MK, Kumar L (2021) Yield trends and variabilities explained by climatic change in coastal and non-coastal areas of Bangladesh. Sci Total Environ 795:148814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148814
Hua C, Miao JJ, Liu WP, Du G, Wang X (2021) The impact mechanism of industrial agglomeration on energy efficiency-evidence from producer service industry in China. Energy Sources Part B 16(8):740–758. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567249.2021.1966132
Huang Y, Luo X, Tang L, Yu W (2020) The power of habit: does production experience lead to pesticide overuse? Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:25287–25296. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08961-4
Huang YM, Chen C, Lei LJ, Zhang YP (2022) Impacts of green finance on green innovation: a spatial and nonlinear perspective. J Clean Prod 365:132548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132548
Irfan M, Razzaq A, Sharif A, Yang XD (2022) Influence mechanism between green finance and green innovation: exploring regional policy intervention effects in China. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 182:121882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2022.121882
Ju XT, Gu BJ, Wu YY, Galloway JN (2016) Reducing China’s fertilizer use by increasing farm size. Glob Environ Chang 41:26–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2016.08.005
Kong GW, Wang S, Wang YN (2022) Fostering firm productivity through green finance: evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in China. Econ Model 115:105979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econmod.2022.105979
Li HJ, Yuan KH, Cao AD, Zhao XM, Guo LL (2022) The role of crop insurance in reducing pesticide use: evidence from rice farmers in China. J Environ Manage 306:114456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114456
Li M, Chen Q, Yang L, Zhang Y, Jiang JL, Deng SP, Wan JZ, Fan TT, Long T, Zhang ST, Lin YS (2023) Contaminant characterization at pesticide production sites in the Yangtze River Delta: residue, distribution, and environmental risk. Sci Total Environ 860:160156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160156
Liu S, Wang YK (2023) Green innovation effect of pilot zones for green finance reform: evidence of quasi natural experiment. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 186(Part A):122079. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2022.122079
Liu M, Xu Z, Su F, Tao R (2012) Rural tax reform and the extractive capacity of local state in China. China Econ Rev 23(1):190–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chieco.2011.10.002
Mao H, Zhou L, Ying RY, Pan D (2021) Time preferences and green agricultural technology adoption: field evidence from rice farmers in China. Land Use Policy 109:105627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2021.105627
Marsala RZ, Capri E, Russo E, Bisagni M, Colla R, Lucini L, Gallo A, Suciu NA (2020) First evaluation of pesticides occurrence in groundwater of Tidone Valley, an area with intensive viticulture. Sci Total Environ 736:139730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139730
Mellaku MT, Sebsibe AS (2022) Potential of mathematical model-based decision making to promote sustainable performance of agriculture in developing countries: a review article. Heliyon 8(2):e08968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e08968
Ok M, Hogarh JN, Vb PJ (2020) Environmental risk assessment of pesticides currently applied in Ghana. Chemosphere 254:126845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126845
Peng WC, Lu SB, Lu WJ (2022) Green financing for the establishment of renewable resources under carbon emission regulation. Renewable Energy 199:1210–1225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2022.08.140
Raihan A, Muhtasim DA, Farhana S, Pavel MI, Faruk O, Rahman M, Mahmood A (2022) Nexus between carbon emissions, economic growth, renewable energy use, urbanization, industrialization, technological innovation, and forest area towards achieving environmental sustainability in Bangladesh. Energy and Clim Chang 3:100080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egycc.2022.100080
Shen ZY, Wang SK, Boussemart JP, Hao Y (2022) Digital transition and green growth in Chinese agriculture. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 181:121742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2022.121742
Sundhar S, Shakila RJ, Shalini R, Aanand S, Jayakumar N (2023) Spatial distribution and seasonal variation of pesticide residues in the sediment, seawater, and edible seaweeds: environmental and human health risk assessment. Mar Pollut Bull 194(Part B):115435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2023.115435
Tan SJ, Xie DT, Ni JP, Chen FX, Ni CS, Shao JG, Zhu D, Wang S, Lei P, Zhao GY, Zhang SC, Deng H (2022) Characteristics and influencing factors of chemical fertilizer and pesticide applications by farmers in hilly and mountainous areas of Southwest. China Ecol Indic 143:109346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109346
Wang Y, Zhu YC, Zhang SX, Wang YQ (2018) What could promote farmers to replace chemical fertilizers with organic fertilizers? J Clean Prod 199:882–890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.07.222
Wang WK, Li K, Liu Y, Lian JY, Hong S (2022a) A system dynamics model analysis for policy impacts on green agriculture development: a case of the Sichuan Tibetan Area. J Clean Prod 371:133562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133562
Wang X, Hua C, Miao J (2022b) The spatial effect of factor market distortion on green agriculture development in China. Energy Sources Part A: Recover Utilization and Environ Eff 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2022.2027579
Xia D, Zhang MJ, Yu Q, Tu Y (2019) Developing a framework to identify barriers of green technology adoption for enterprises. Resour Conserv Recycl 143:99–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.12.022
Yalamalle VR, Tomar BS, Shabeer AK, Ahammed TP (2019) Seed soak method for application of plant protectants for increasing pesticide use efficiency, healthy crop and higher yield in garlic (Allium sativum L.). Sci Hortic 257:108703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2019.108703
Yu J, Liu P, Fu DH, Shi XP (2023) How do power shortages affect CO2 emission intensity? Firm-Level Evid China Energy 282:128927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2023.128927
Zhang T (2023) Can green finance policies affect corporate financing? Evidence from China’s green finance innovation and reform pilot zones. J Clean Prod 419:138289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.138289
Zhang JX, Yu JL, Chen Y (2011) Investment problems of China rural human capital. J Northeast Agric Univ (Engl Ed) 18(4):77–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-8104(12)60029-4
Zhang YJ, Gao W, Luan HA, Tang JW, Li RN, Li MY, Zhang HZ, Huang SW (2022a) Effects of a decade of organic fertilizer substitution on vegetable yield and soil phosphorus pools, phosphatase activities, and the microbial community in a greenhouse vegetable production system. J Integr Agric 21(7):2119–2133. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(21)63715-2
Zhang ZH, Zhang GX, Su B (2022b) The spatial impacts of air pollution and socio-economic status on public health: empirical evidence from China. Socioecon Plann Sci 83:101167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seps.2021.101167
Zhang SW, Li YX, Jiang LS, Han W, Zhao Y, Jiang XM, Li J, Shi WZ, Zhang XL (2023a) Organic fertilizer facilitates the soil microplastic surface degradation and enriches the diversity of bacterial biofilm. J Hazard Mater 459:132139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.132139
Zhang ZH, Wang J, Feng C, Chen X (2023b) Do pilot zones for green finance reform and innovation promote energy savings? Evid China Energy Econ 124:106763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2023.106763
Zhang H, Duan Y, Yang J, Han ZL, Wang HY (2023c) Can green finance improve China’s haze pollution reduction? The role of energy efficiency. Environ Dev 45:100833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envdev.2023.100833
Zhao LG, Wang DM, Wang XY, Zhang ZJ (2023) Impact of green finance on total factor productivity of heavily polluting enterprises: evidence from green finance reform and innovation pilot zone. Econ Anal Policy 79:765–785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eap.2023.06.045
Zhou M (2022) The impact of green finance on high-quality economic development in China. J Soc Sci Harbin Normal Univ [In Chinese] 02:71–75
Zhu W, QI LX, WANG RM (2022) The relationship between farm size and fertilizer use efficiency: evidence from China. J Integr Agric 21(1):273–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(21)63724-3
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for comments received by anonymous reviewers.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Economics and Management, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing, 211106, Jiangsu, People’s Republic of China
Jianjun Miao, Xinming Wang & Chao Hua
Institute of Food Economics, Nanjing University of Finance and Economics, Nanjing, 210023, Jiangsu, People’s Republic of China
Jingwei Han
Nantong Normal College, Nantong, 226010, Jiangsu, People’s Republic of China
Xinming Wang
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar

Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Xinming Wang and Jianjun Miao. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Chao Hua. Jianjun Miao and Jingwei Han were responsible for data investigation, review and editing. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Chao Hua .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval.
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent to publish
All the authors have seen the manuscript and approved to submit to the journal for future publish.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ilhan Ozturk
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
• Green finance reform reduces pesticide and fertilizer application intensity.
• Green technology innovation is an intermediary factor.
• Government financial extracting hinders reducing pesticide application intensity.
• Coastal geographical location supports reducing pesticide application intensity.
• Negative spatial spillover effects of the policy are verified.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Miao, J., Wang, X., Hua, C. et al. Green finance reform and application intensity of chemical fertilizer and pesticide: policy evidence from China. Environ Sci Pollut Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33113-3
Download citation
Received : 10 November 2023
Accepted : 24 March 2024
Published : 01 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33113-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Green finance reform
- Chemical fertilizer
- Pesticide, Difference-in-Differences model
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Operating Systems
Title: aios: llm agent operating system.
Abstract: The integration and deployment of large language model (LLM)-based intelligent agents have been fraught with challenges that compromise their efficiency and efficacy. Among these issues are sub-optimal scheduling and resource allocation of agent requests over the LLM, the difficulties in maintaining context during interactions between agent and LLM, and the complexities inherent in integrating heterogeneous agents with different capabilities and specializations. The rapid increase of agent quantity and complexity further exacerbates these issues, often leading to bottlenecks and sub-optimal utilization of resources. Inspired by these challenges, this paper presents AIOS, an LLM agent operating system, which embeds large language model into operating systems (OS) as the brain of the OS, enabling an operating system "with soul" -- an important step towards AGI. Specifically, AIOS is designed to optimize resource allocation, facilitate context switch across agents, enable concurrent execution of agents, provide tool service for agents, and maintain access control for agents. We present the architecture of such an operating system, outline the core challenges it aims to resolve, and provide the basic design and implementation of the AIOS. Our experiments on concurrent execution of multiple agents demonstrate the reliability and efficiency of our AIOS modules. Through this, we aim to not only improve the performance and efficiency of LLM agents but also to pioneer for better development and deployment of the AIOS ecosystem in the future. The project is open-source at this https URL .
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Abstract. The study reports on an investigation about the impact of science-technology-society (STS) instruction on middle school student understanding of the nature of science (NOS) and attitudes toward science compared to students taught by the same teacher using traditional textbook-oriented instruction.
Kim (2008) focused on the perspectives and viewpoints of elementary students studying ecosystem STS issues in a Korean classroom. The intended purpose of this study was to acquire the significance of Science, Technology, Society, and Environment (STSE) knowledge in the form of children's knowledge of the environment.
course of science and technology. This collection offers a broad, deep, and accessible set of essays on the interplay between science, technology, and society. It re ects a very broad range of disciplines and an international group of contributors. Science and technology studies (STS), from its birth in the 1960 s, has
This paper shows data science's potential for disruptive innovation in science, industry, policy, and people's lives. We present how data science impacts science and society at large in the coming years, including ethical problems in managing human behavior data and considering the quantitative expectations of data science economic impact. We introduce concepts such as open science and e ...
ABSTRACT. Artificial intelligence may greatly increase the efficiency of the existing economy. But it may have an even larger impact by serving as a new general-purpose "method of invention" that can reshape the nature of the innovation process and the organization of R&D.
3. Science and t echnology play an increasing role in e veryday life and. progress in modern science and technology occurs quickly, both in specific. subjects and because of the opening up of new ...
This editorial essay was prepared by John H. ''Jack'' Marburger for a workshop on the ''science of science and innovation policy'' held in 2009 that was the basis for this special issue. It is published posthumously. Linking the words ''science,'' ''technology,'' and ''innovation,'' may suggest that we know
Science and technology are concepts. of primary importance dealing with a practical application that. something entirely new can be done, or so that something can be done. in a completely new way ...
The paradigm of new techno-economic innovation principles was based on the factory as the center of production, mechanization, the importance of productivity, and the existence of local networks. Understanding Innovation and Technology: Key Definitions and Concepts 7. The second major shift into a new economic paradigm started in 1829 and was ...
Science, Technology and Society is a peer-reviewed journal that takes an interdisciplinary perspective, encouraging analyses whose approaches are drawn from a variety of disciplines such as history, sociology, philosophy, economics, political science and international relations, science policy involving innovation, foresight studies involving science and technology, technology management ...
Technological innovation is an element of the complex system of technology directed to satisfy needs, achieve goals, and solve problems of adopters. The origin and diffusion of technological ...
2. The wider science and technology convergence. Science is about discovering, understanding, explaining and predicting patterns in natural phenomena, producing more accurate explanations of how the natural world works (Bertolaso, Citation 2013; Robson & McCartan, Citation 2016), regardless of potential applications.It is the result of deep curiosity and its goal is the pursuit of knowledge ...
Teaching Science, Technology, and Society to Engineering Students: A Sixteen Year Journey. Haldun M. Özaktas. Engineering, Environmental Science. Science and Engineering Ethics. 2011. TLDR. The teaching philosophy and experiences of the instructor, challenges and solutions related to teaching a large class, and results of outcome measurements ...
Science & Technology Outlook 2021 IBM Research case study below, in Accelerated Discovery.) Now building on this data, scientific discovery is entering a new era, where AI, and increasingly quantum computing, is applied by communi-ties of discovery—in the hybrid cloud—to transform the scien-tific method and overcome long-standing bottlenecks.
The fundamental frame work on science and technology jobs are crucial in the given examples of the honesty, sincerity, truthfulness…etc. philosophy will deal all parts of science and technology and show the proper direction practically which will eradicate some issues change the society and lead into development and justify all part of the ...
from outside the traditional science powers of the US, EU and Japan: China now publishes more than any other country apart from the US (Table 1). Table 1: The rise of China in science Share of world scientific papers 2003 Share of world scientific papers 2013 Average annual growth rate in scientific papers 2003-13 US 26.8% 18.8% 7.0% EU 31.0% ...
View PDF View EPUB. 'Technology' is one of the keywords of our world, yet it is also one of the most confused. As an analytical category it seems necessary for our understanding of all of humanity's history, and indeed beyond. We are probably comfortable with asserting that humans have had technologies since the Palaeolithic, and a ...
A new research paper has found that calls for scientific research funding in Colombia increased over a 15-year period despite transitions in political control of the country's government. ... methods such as network analysis may be helpful for analysts to track science, technology, and innovation priorities across different periods of ...
Research Paper on Technology and Society - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. research paper on technology and society
View PDF Abstract: In addition to the advancements in deepfake generation, corresponding detection technologies need to continuously evolve to regulate the potential misuse of deepfakes, such as for privacy invasion and phishing attacks. This survey comprehensively reviews the latest developments in deepfake generation and detection, summarizing and analyzing the current state of the art in ...
Covers all areas of Environmental Science and related subjects. Publishes on the natural sciences, but also includes the impacts of legislation, regulation, and the economy on pollution control. Safeguards international and interdisciplinary character through a global network of editorial board members.
Green technology innovation is an intuitive factor that affects FAI and PAI, and the research and design process above provide theoretical analysis and literature support. The regression results in Table 4 indicate that green finance reform policy significantly reduces FAI and PAI by promoting green technology innovation.
Importance of technolog y in education. The role of technology in the field of education is four-. fold: it is included as a part of the curriculum, as an. instructional delivery system, as a ...
Research Paper - Science and Technology - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free.
Call for Papers Smart Grid Electricity Parameter Sensing Measurement and Self-supply Technology. Submission deadline: Monday, 30 September 2024 Expected Publication Month: March 2025 . With the continuous development of power Internet of Things and wireless sensor networks, intelligent sensing devices will be widely used in the power system.
View PDF Abstract: In the domain of data science, the predictive tasks of classification, regression, and imputation of missing values are commonly encountered challenges associated with tabular data. This research endeavors to apply Large Language Models (LLMs) towards addressing these predictive tasks. Despite their proficiency in comprehending natural language, LLMs fall short in dealing ...
View PDF HTML (experimental) Abstract: The integration and deployment of large language model (LLM)-based intelligent agents have been fraught with challenges that compromise their efficiency and efficacy. Among these issues are sub-optimal scheduling and resource allocation of agent requests over the LLM, the difficulties in maintaining context during interactions between agent and LLM, and ...
Abstract. Technological spillover—the transfer and use of knowledge between defense and civilian sectors—is desired by many countries. Indeed, in the context of intensifying US-China competition, both countries have pursued policies to encourage spillover in the hopes of gaining a technological advantage.