

Quantitative and Qualitative Research
- I NEED TO . . .
What is Quantitative Research?
- What is Qualitative Research?
- Quantitative vs Qualitative
- Step 1: Accessing CINAHL
- Step 2: Create a Keyword Search
- Step 3: Create a Subject Heading Search
- Step 4: Repeat Steps 1-3 for Second Concept
- Step 5: Repeat Steps 1-3 for Quantitative Terms
- Step 6: Combining All Searches
- Step 7: Adding Limiters
- Step 8: Save Your Search!
- What Kind of Article is This?
- More Research Help This link opens in a new window
Quantitative methodology is the dominant research framework in the social sciences. It refers to a set of strategies, techniques and assumptions used to study psychological, social and economic processes through the exploration of numeric patterns . Quantitative research gathers a range of numeric data. Some of the numeric data is intrinsically quantitative (e.g. personal income), while in other cases the numeric structure is imposed (e.g. ‘On a scale from 1 to 10, how depressed did you feel last week?’). The collection of quantitative information allows researchers to conduct simple to extremely sophisticated statistical analyses that aggregate the data (e.g. averages, percentages), show relationships among the data (e.g. ‘Students with lower grade point averages tend to score lower on a depression scale’) or compare across aggregated data (e.g. the USA has a higher gross domestic product than Spain). Quantitative research includes methodologies such as questionnaires, structured observations or experiments and stands in contrast to qualitative research. Qualitative research involves the collection and analysis of narratives and/or open-ended observations through methodologies such as interviews, focus groups or ethnographies.
Coghlan, D., Brydon-Miller, M. (2014). The SAGE encyclopedia of action research (Vols. 1-2). London, : SAGE Publications Ltd doi: 10.4135/9781446294406
What is the purpose of quantitative research?
The purpose of quantitative research is to generate knowledge and create understanding about the social world. Quantitative research is used by social scientists, including communication researchers, to observe phenomena or occurrences affecting individuals. Social scientists are concerned with the study of people. Quantitative research is a way to learn about a particular group of people, known as a sample population. Using scientific inquiry, quantitative research relies on data that are observed or measured to examine questions about the sample population.
Allen, M. (2017). The SAGE encyclopedia of communication research methods (Vols. 1-4). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, Inc doi: 10.4135/9781483381411
How do I know if the study is a quantitative design? What type of quantitative study is it?
Quantitative Research Designs: Descriptive non-experimental, Quasi-experimental or Experimental?
Studies do not always explicitly state what kind of research design is being used. You will need to know how to decipher which design type is used. The following video will help you determine the quantitative design type.
- << Previous: I NEED TO . . .
- Next: What is Qualitative Research? >>
- Last Updated: Dec 8, 2023 10:05 PM
- URL: https://libguides.uta.edu/quantitative_and_qualitative_research
University of Texas Arlington Libraries 702 Planetarium Place · Arlington, TX 76019 · 817-272-3000
- Internet Privacy
- Accessibility
- Problems with a guide? Contact Us.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- What Is Quantitative Research? | Definition & Methods
What Is Quantitative Research? | Definition & Methods
Published on 4 April 2022 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on 10 October 2022.
Quantitative research is the process of collecting and analysing numerical data. It can be used to find patterns and averages, make predictions, test causal relationships, and generalise results to wider populations.
Quantitative research is the opposite of qualitative research , which involves collecting and analysing non-numerical data (e.g. text, video, or audio).
Quantitative research is widely used in the natural and social sciences: biology, chemistry, psychology, economics, sociology, marketing, etc.
- What is the demographic makeup of Singapore in 2020?
- How has the average temperature changed globally over the last century?
- Does environmental pollution affect the prevalence of honey bees?
- Does working from home increase productivity for people with long commutes?
Table of contents
Quantitative research methods, quantitative data analysis, advantages of quantitative research, disadvantages of quantitative research, frequently asked questions about quantitative research.
You can use quantitative research methods for descriptive, correlational or experimental research.
- In descriptive research , you simply seek an overall summary of your study variables.
- In correlational research , you investigate relationships between your study variables.
- In experimental research , you systematically examine whether there is a cause-and-effect relationship between variables.
Correlational and experimental research can both be used to formally test hypotheses , or predictions, using statistics. The results may be generalised to broader populations based on the sampling method used.
To collect quantitative data, you will often need to use operational definitions that translate abstract concepts (e.g., mood) into observable and quantifiable measures (e.g., self-ratings of feelings and energy levels).
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Once data is collected, you may need to process it before it can be analysed. For example, survey and test data may need to be transformed from words to numbers. Then, you can use statistical analysis to answer your research questions .
Descriptive statistics will give you a summary of your data and include measures of averages and variability. You can also use graphs, scatter plots and frequency tables to visualise your data and check for any trends or outliers.
Using inferential statistics , you can make predictions or generalisations based on your data. You can test your hypothesis or use your sample data to estimate the population parameter .
You can also assess the reliability and validity of your data collection methods to indicate how consistently and accurately your methods actually measured what you wanted them to.
Quantitative research is often used to standardise data collection and generalise findings . Strengths of this approach include:
- Replication
Repeating the study is possible because of standardised data collection protocols and tangible definitions of abstract concepts.
- Direct comparisons of results
The study can be reproduced in other cultural settings, times or with different groups of participants. Results can be compared statistically.
- Large samples
Data from large samples can be processed and analysed using reliable and consistent procedures through quantitative data analysis.
- Hypothesis testing
Using formalised and established hypothesis testing procedures means that you have to carefully consider and report your research variables, predictions, data collection and testing methods before coming to a conclusion.
Despite the benefits of quantitative research, it is sometimes inadequate in explaining complex research topics. Its limitations include:
- Superficiality
Using precise and restrictive operational definitions may inadequately represent complex concepts. For example, the concept of mood may be represented with just a number in quantitative research, but explained with elaboration in qualitative research.
- Narrow focus
Predetermined variables and measurement procedures can mean that you ignore other relevant observations.
- Structural bias
Despite standardised procedures, structural biases can still affect quantitative research. Missing data , imprecise measurements or inappropriate sampling methods are biases that can lead to the wrong conclusions.
- Lack of context
Quantitative research often uses unnatural settings like laboratories or fails to consider historical and cultural contexts that may affect data collection and results.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to test a hypothesis by systematically collecting and analysing data, while qualitative methods allow you to explore ideas and experiences in depth.
In mixed methods research , you use both qualitative and quantitative data collection and analysis methods to answer your research question .
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organisations.
Operationalisation means turning abstract conceptual ideas into measurable observations.
For example, the concept of social anxiety isn’t directly observable, but it can be operationally defined in terms of self-rating scores, behavioural avoidance of crowded places, or physical anxiety symptoms in social situations.
Before collecting data , it’s important to consider how you will operationalise the variables that you want to measure.
Reliability and validity are both about how well a method measures something:
- Reliability refers to the consistency of a measure (whether the results can be reproduced under the same conditions).
- Validity refers to the accuracy of a measure (whether the results really do represent what they are supposed to measure).
If you are doing experimental research , you also have to consider the internal and external validity of your experiment.
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2022, October 10). What Is Quantitative Research? | Definition & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved 29 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/introduction-to-quantitative-research/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Quantitative Methods
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
Quantitative methods emphasize objective measurements and the statistical, mathematical, or numerical analysis of data collected through polls, questionnaires, and surveys, or by manipulating pre-existing statistical data using computational techniques . Quantitative research focuses on gathering numerical data and generalizing it across groups of people or to explain a particular phenomenon.
Babbie, Earl R. The Practice of Social Research . 12th ed. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Cengage, 2010; Muijs, Daniel. Doing Quantitative Research in Education with SPSS . 2nd edition. London: SAGE Publications, 2010.
Need Help Locating Statistics?
Resources for locating data and statistics can be found here:
Statistics & Data Research Guide
Characteristics of Quantitative Research
Your goal in conducting quantitative research study is to determine the relationship between one thing [an independent variable] and another [a dependent or outcome variable] within a population. Quantitative research designs are either descriptive [subjects usually measured once] or experimental [subjects measured before and after a treatment]. A descriptive study establishes only associations between variables; an experimental study establishes causality.
Quantitative research deals in numbers, logic, and an objective stance. Quantitative research focuses on numeric and unchanging data and detailed, convergent reasoning rather than divergent reasoning [i.e., the generation of a variety of ideas about a research problem in a spontaneous, free-flowing manner].
Its main characteristics are :
- The data is usually gathered using structured research instruments.
- The results are based on larger sample sizes that are representative of the population.
- The research study can usually be replicated or repeated, given its high reliability.
- Researcher has a clearly defined research question to which objective answers are sought.
- All aspects of the study are carefully designed before data is collected.
- Data are in the form of numbers and statistics, often arranged in tables, charts, figures, or other non-textual forms.
- Project can be used to generalize concepts more widely, predict future results, or investigate causal relationships.
- Researcher uses tools, such as questionnaires or computer software, to collect numerical data.
The overarching aim of a quantitative research study is to classify features, count them, and construct statistical models in an attempt to explain what is observed.
Things to keep in mind when reporting the results of a study using quantitative methods :
- Explain the data collected and their statistical treatment as well as all relevant results in relation to the research problem you are investigating. Interpretation of results is not appropriate in this section.
- Report unanticipated events that occurred during your data collection. Explain how the actual analysis differs from the planned analysis. Explain your handling of missing data and why any missing data does not undermine the validity of your analysis.
- Explain the techniques you used to "clean" your data set.
- Choose a minimally sufficient statistical procedure ; provide a rationale for its use and a reference for it. Specify any computer programs used.
- Describe the assumptions for each procedure and the steps you took to ensure that they were not violated.
- When using inferential statistics , provide the descriptive statistics, confidence intervals, and sample sizes for each variable as well as the value of the test statistic, its direction, the degrees of freedom, and the significance level [report the actual p value].
- Avoid inferring causality , particularly in nonrandomized designs or without further experimentation.
- Use tables to provide exact values ; use figures to convey global effects. Keep figures small in size; include graphic representations of confidence intervals whenever possible.
- Always tell the reader what to look for in tables and figures .
NOTE: When using pre-existing statistical data gathered and made available by anyone other than yourself [e.g., government agency], you still must report on the methods that were used to gather the data and describe any missing data that exists and, if there is any, provide a clear explanation why the missing data does not undermine the validity of your final analysis.
Babbie, Earl R. The Practice of Social Research . 12th ed. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Cengage, 2010; Brians, Craig Leonard et al. Empirical Political Analysis: Quantitative and Qualitative Research Methods . 8th ed. Boston, MA: Longman, 2011; McNabb, David E. Research Methods in Public Administration and Nonprofit Management: Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches . 2nd ed. Armonk, NY: M.E. Sharpe, 2008; Quantitative Research Methods. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Singh, Kultar. Quantitative Social Research Methods . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2007.
Basic Research Design for Quantitative Studies
Before designing a quantitative research study, you must decide whether it will be descriptive or experimental because this will dictate how you gather, analyze, and interpret the results. A descriptive study is governed by the following rules: subjects are generally measured once; the intention is to only establish associations between variables; and, the study may include a sample population of hundreds or thousands of subjects to ensure that a valid estimate of a generalized relationship between variables has been obtained. An experimental design includes subjects measured before and after a particular treatment, the sample population may be very small and purposefully chosen, and it is intended to establish causality between variables. Introduction The introduction to a quantitative study is usually written in the present tense and from the third person point of view. It covers the following information:
- Identifies the research problem -- as with any academic study, you must state clearly and concisely the research problem being investigated.
- Reviews the literature -- review scholarship on the topic, synthesizing key themes and, if necessary, noting studies that have used similar methods of inquiry and analysis. Note where key gaps exist and how your study helps to fill these gaps or clarifies existing knowledge.
- Describes the theoretical framework -- provide an outline of the theory or hypothesis underpinning your study. If necessary, define unfamiliar or complex terms, concepts, or ideas and provide the appropriate background information to place the research problem in proper context [e.g., historical, cultural, economic, etc.].
Methodology The methods section of a quantitative study should describe how each objective of your study will be achieved. Be sure to provide enough detail to enable the reader can make an informed assessment of the methods being used to obtain results associated with the research problem. The methods section should be presented in the past tense.
- Study population and sampling -- where did the data come from; how robust is it; note where gaps exist or what was excluded. Note the procedures used for their selection;
- Data collection – describe the tools and methods used to collect information and identify the variables being measured; describe the methods used to obtain the data; and, note if the data was pre-existing [i.e., government data] or you gathered it yourself. If you gathered it yourself, describe what type of instrument you used and why. Note that no data set is perfect--describe any limitations in methods of gathering data.
- Data analysis -- describe the procedures for processing and analyzing the data. If appropriate, describe the specific instruments of analysis used to study each research objective, including mathematical techniques and the type of computer software used to manipulate the data.
Results The finding of your study should be written objectively and in a succinct and precise format. In quantitative studies, it is common to use graphs, tables, charts, and other non-textual elements to help the reader understand the data. Make sure that non-textual elements do not stand in isolation from the text but are being used to supplement the overall description of the results and to help clarify key points being made. Further information about how to effectively present data using charts and graphs can be found here .
- Statistical analysis -- how did you analyze the data? What were the key findings from the data? The findings should be present in a logical, sequential order. Describe but do not interpret these trends or negative results; save that for the discussion section. The results should be presented in the past tense.
Discussion Discussions should be analytic, logical, and comprehensive. The discussion should meld together your findings in relation to those identified in the literature review, and placed within the context of the theoretical framework underpinning the study. The discussion should be presented in the present tense.
- Interpretation of results -- reiterate the research problem being investigated and compare and contrast the findings with the research questions underlying the study. Did they affirm predicted outcomes or did the data refute it?
- Description of trends, comparison of groups, or relationships among variables -- describe any trends that emerged from your analysis and explain all unanticipated and statistical insignificant findings.
- Discussion of implications – what is the meaning of your results? Highlight key findings based on the overall results and note findings that you believe are important. How have the results helped fill gaps in understanding the research problem?
- Limitations -- describe any limitations or unavoidable bias in your study and, if necessary, note why these limitations did not inhibit effective interpretation of the results.
Conclusion End your study by to summarizing the topic and provide a final comment and assessment of the study.
- Summary of findings – synthesize the answers to your research questions. Do not report any statistical data here; just provide a narrative summary of the key findings and describe what was learned that you did not know before conducting the study.
- Recommendations – if appropriate to the aim of the assignment, tie key findings with policy recommendations or actions to be taken in practice.
- Future research – note the need for future research linked to your study’s limitations or to any remaining gaps in the literature that were not addressed in your study.
Black, Thomas R. Doing Quantitative Research in the Social Sciences: An Integrated Approach to Research Design, Measurement and Statistics . London: Sage, 1999; Gay,L. R. and Peter Airasain. Educational Research: Competencies for Analysis and Applications . 7th edition. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Merril Prentice Hall, 2003; Hector, Anestine. An Overview of Quantitative Research in Composition and TESOL . Department of English, Indiana University of Pennsylvania; Hopkins, Will G. “Quantitative Research Design.” Sportscience 4, 1 (2000); "A Strategy for Writing Up Research Results. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper." Department of Biology. Bates College; Nenty, H. Johnson. "Writing a Quantitative Research Thesis." International Journal of Educational Science 1 (2009): 19-32; Ouyang, Ronghua (John). Basic Inquiry of Quantitative Research . Kennesaw State University.
Strengths of Using Quantitative Methods
Quantitative researchers try to recognize and isolate specific variables contained within the study framework, seek correlation, relationships and causality, and attempt to control the environment in which the data is collected to avoid the risk of variables, other than the one being studied, accounting for the relationships identified.
Among the specific strengths of using quantitative methods to study social science research problems:
- Allows for a broader study, involving a greater number of subjects, and enhancing the generalization of the results;
- Allows for greater objectivity and accuracy of results. Generally, quantitative methods are designed to provide summaries of data that support generalizations about the phenomenon under study. In order to accomplish this, quantitative research usually involves few variables and many cases, and employs prescribed procedures to ensure validity and reliability;
- Applying well established standards means that the research can be replicated, and then analyzed and compared with similar studies;
- You can summarize vast sources of information and make comparisons across categories and over time; and,
- Personal bias can be avoided by keeping a 'distance' from participating subjects and using accepted computational techniques .
Babbie, Earl R. The Practice of Social Research . 12th ed. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Cengage, 2010; Brians, Craig Leonard et al. Empirical Political Analysis: Quantitative and Qualitative Research Methods . 8th ed. Boston, MA: Longman, 2011; McNabb, David E. Research Methods in Public Administration and Nonprofit Management: Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches . 2nd ed. Armonk, NY: M.E. Sharpe, 2008; Singh, Kultar. Quantitative Social Research Methods . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2007.
Limitations of Using Quantitative Methods
Quantitative methods presume to have an objective approach to studying research problems, where data is controlled and measured, to address the accumulation of facts, and to determine the causes of behavior. As a consequence, the results of quantitative research may be statistically significant but are often humanly insignificant.
Some specific limitations associated with using quantitative methods to study research problems in the social sciences include:
- Quantitative data is more efficient and able to test hypotheses, but may miss contextual detail;
- Uses a static and rigid approach and so employs an inflexible process of discovery;
- The development of standard questions by researchers can lead to "structural bias" and false representation, where the data actually reflects the view of the researcher instead of the participating subject;
- Results provide less detail on behavior, attitudes, and motivation;
- Researcher may collect a much narrower and sometimes superficial dataset;
- Results are limited as they provide numerical descriptions rather than detailed narrative and generally provide less elaborate accounts of human perception;
- The research is often carried out in an unnatural, artificial environment so that a level of control can be applied to the exercise. This level of control might not normally be in place in the real world thus yielding "laboratory results" as opposed to "real world results"; and,
- Preset answers will not necessarily reflect how people really feel about a subject and, in some cases, might just be the closest match to the preconceived hypothesis.
Research Tip
Finding Examples of How to Apply Different Types of Research Methods
SAGE publications is a major publisher of studies about how to design and conduct research in the social and behavioral sciences. Their SAGE Research Methods Online and Cases database includes contents from books, articles, encyclopedias, handbooks, and videos covering social science research design and methods including the complete Little Green Book Series of Quantitative Applications in the Social Sciences and the Little Blue Book Series of Qualitative Research techniques. The database also includes case studies outlining the research methods used in real research projects. This is an excellent source for finding definitions of key terms and descriptions of research design and practice, techniques of data gathering, analysis, and reporting, and information about theories of research [e.g., grounded theory]. The database covers both qualitative and quantitative research methods as well as mixed methods approaches to conducting research.
SAGE Research Methods Online and Cases
- << Previous: Qualitative Methods
- Next: Insiderness >>
- Last Updated: May 1, 2024 9:25 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions
Quantitative Research
What is Quantitative Research?
Quantitative research is the methodology which researchers use to test theories about people’s attitudes and behaviors based on numerical and statistical evidence. Researchers sample a large number of users (e.g., through surveys) to indirectly obtain measurable, bias-free data about users in relevant situations.
“Quantification clarifies issues which qualitative analysis leaves fuzzy. It is more readily contestable and likely to be contested. It sharpens scholarly discussion, sparks off rival hypotheses, and contributes to the dynamics of the research process.” — Angus Maddison, Notable scholar of quantitative macro-economic history
- Transcript loading…
See how quantitative research helps reveal cold, hard facts about users which you can interpret and use to improve your designs.
Use Quantitative Research to Find Mathematical Facts about Users
Quantitative research is a subset of user experience (UX) research . Unlike its softer, more individual-oriented “counterpart”, qualitative research , quantitative research means you collect statistical/numerical data to draw generalized conclusions about users’ attitudes and behaviors . Compare and contrast quantitative with qualitative research, below:
Qualitative Research
You Aim to Determine
The “what”, “where” & “when” of the users’ needs & problems – to help keep your project’s focus on track during development
The “why” – to get behind how users approach their problems in their world
Highly structured (e.g., surveys) – to gather data about what users do & find patterns in large user groups
Loosely structured (e.g., contextual inquiries) – to learn why users behave how they do & explore their opinions
Number of Representative Users
Ideally 30+
Often around 5
Level of Contact with Users
Less direct & more remote (e.g., analytics)
More direct & less remote (e.g., usability testing to examine users’ stress levels when they use your design)
Statistically
Reliable – if you have enough test users
Less reliable, with need for great care with handling non-numerical data (e.g., opinions), as your own opinions might influence findings
Quantitative research is often best done from early on in projects since it helps teams to optimally direct product development and avoid costly design mistakes later. As you typically get user data from a distance—i.e., without close physical contact with users—also applying qualitative research will help you investigate why users think and feel the ways they do. Indeed, in an iterative design process quantitative research helps you test the assumptions you and your design team develop from your qualitative research. Regardless of the method you use, with proper care you can gather objective and unbiased data – information which you can complement with qualitative approaches to build a fuller understanding of your target users. From there, you can work towards firmer conclusions and drive your design process towards a more realistic picture of how target users will ultimately receive your product.

Quantitative analysis helps you test your assumptions and establish clearer views of your users in their various contexts.
Quantitative Research Methods You Can Use to Guide Optimal Designs
There are many quantitative research methods, and they help uncover different types of information on users. Some methods, such as A/B testing, are typically done on finished products, while others such as surveys could be done throughout a project’s design process. Here are some of the most helpful methods:
A/B testing – You test two or more versions of your design on users to find the most effective. Each variation differs by just one feature and may or may not affect how users respond. A/B testing is especially valuable for testing assumptions you’ve drawn from qualitative research. The only potential concerns here are scale—in that you’ll typically need to conduct it on thousands of users—and arguably more complexity in terms of considering the statistical significance involved.
Analytics – With tools such as Google Analytics, you measure metrics (e.g., page views, click-through rates) to build a picture (e.g., “How many users take how long to complete a task?”).
Desirability Studies – You measure an aspect of your product (e.g., aesthetic appeal) by typically showing it to participants and asking them to select from a menu of descriptive words. Their responses can reveal powerful insights (e.g., 78% associate the product/brand with “fashionable”).
Surveys and Questionnaires – When you ask for many users’ opinions, you will gain massive amounts of information. Keep in mind that you’ll have data about what users say they do, as opposed to insights into what they do . You can get more reliable results if you incentivize your participants well and use the right format.
Tree Testing – You remove the user interface so users must navigate the site and complete tasks using links alone. This helps you see if an issue is related to the user interface or information architecture.
Another powerful benefit of conducting quantitative research is that you can keep your stakeholders’ support with hard facts and statistics about your design’s performance—which can show what works well and what needs improvement—and prove a good return on investment. You can also produce reports to check statistics against different versions of your product and your competitors’ products.
Most quantitative research methods are relatively cheap. Since no single research method can help you answer all your questions, it’s vital to judge which method suits your project at the time/stage. Remember, it’s best to spend appropriately on a combination of quantitative and qualitative research from early on in development. Design improvements can be costly, and so you can estimate the value of implementing changes when you get the statistics to suggest that these changes will improve usability. Overall, you want to gather measurements objectively, where your personality, presence and theories won’t create bias.
Learn More about Quantitative Research
Take our User Research course to see how to get the most from quantitative research.
See how quantitative research methods fit into your design research landscape .
This insightful piece shows the value of pairing quantitative with qualitative research .
Find helpful tips on combining quantitative research methods in mixed methods research .
Questions related to Quantitative Research
Qualitative and quantitative research differ primarily in the data they produce. Quantitative research yields numerical data to test hypotheses and quantify patterns. It's precise and generalizable. Qualitative research, on the other hand, generates non-numerical data and explores meanings, interpretations, and deeper insights. Watch our video featuring Professor Alan Dix on different types of research methods.
This video elucidates the nuances and applications of both research types in the design field.
In quantitative research, determining a good sample size is crucial for the reliability of the results. William Hudson, CEO of Syntagm, emphasizes the importance of statistical significance with an example in our video.
He illustrates that even with varying results between design choices, we need to discern whether the differences are statistically significant or products of chance. This ensures the validity of the results, allowing for more accurate interpretations. Statistical tools like chi-square tests can aid in analyzing the results effectively. To delve deeper into these concepts, take William Hudson’s Data-Driven Design: Quantitative UX Research Course .
Quantitative research is crucial as it provides precise, numerical data that allows for high levels of statistical inference. Our video from William Hudson, CEO of Syntagm, highlights the importance of analytics in examining existing solutions.
Quantitative methods, like analytics and A/B testing, are pivotal for identifying areas for improvement, understanding user behaviors, and optimizing user experiences based on solid, empirical evidence. This empirical nature ensures that the insights derived are reliable, allowing for practical improvements and innovations. Perhaps most importantly, numerical data is useful to secure stakeholder buy-in and defend design decisions and proposals. Explore this approach in our Data-Driven Design: Quantitative Research for UX Research course and learn from William Hudson’s detailed explanations of when and why to use analytics in the research process.
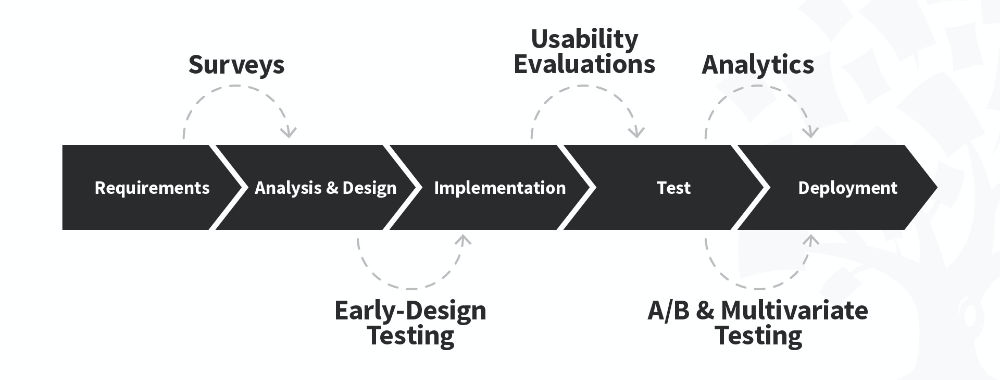
After establishing initial requirements, statistical data is crucial for informed decisions through quantitative research. William Hudson, CEO of Syntagm, sheds light on the role of quantitative research throughout a typical project lifecycle in this video:
During the analysis and design phases, quantitative research helps validate user requirements and understand user behaviors. Surveys and analytics are standard tools, offering insights into user preferences and design efficacy. Quantitative research can also be used in early design testing, allowing for optimal design modifications based on user interactions and feedback, and it’s fundamental for A/B and multivariate testing once live solutions are available.
To write a compelling quantitative research question:
Create clear, concise, and unambiguous questions that address one aspect at a time.
Use common, short terms and provide explanations for unusual words.
Avoid leading, compound, and overlapping queries and ensure that questions are not vague or broad.
According to our video by William Hudson, CEO of Syntagm, quality and respondent understanding are vital in forming good questions.
He emphasizes the importance of addressing specific aspects and avoiding intimidating and confusing elements, such as extensive question grids or ranking questions, to ensure participant engagement and accurate responses. For more insights, see the article Writing Good Questions for Surveys .
Survey research is typically quantitative, collecting numerical data and statistical analysis to make generalizable conclusions. However, it can also have qualitative elements, mainly when it includes open-ended questions, allowing for expressive responses. Our video featuring the CEO of Syntagm, William Hudson, provides in-depth insights into when and how to effectively utilize surveys in the product or service lifecycle, focusing on user satisfaction and potential improvements.
He emphasizes the importance of surveys in triangulating data to back up qualitative research findings, ensuring we have a complete understanding of the user's requirements and preferences.
Descriptive research focuses on describing the subject being studied and getting answers to questions like what, where, when, and who of the research question. However, it doesn’t include the answers to the underlying reasons, or the “why” behind the answers obtained from the research. We can use both f qualitative and quantitative methods to conduct descriptive research. Descriptive research does not describe the methods, but rather the data gathered through the research (regardless of the methods used).
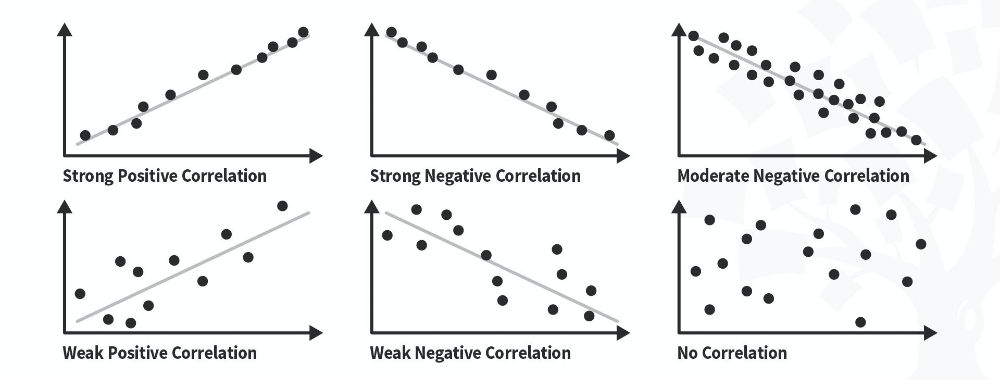
When we use quantitative research and gather numerical data, we can use statistical analysis to understand relationships between different variables. Here’s William Hudson, CEO of Syntagm with more on correlation and how we can apply tests such as Pearson’s r and Spearman Rank Coefficient to our data.
This helps interpret phenomena such as user experience by analyzing session lengths and conversion values, revealing whether variables like time spent on a page affect checkout values, for example.
Random Sampling: Each individual in the population has an equitable opportunity to be chosen, which minimizes biases and simplifies analysis.
Systematic Sampling: Selecting every k-th item from a list after a random start. It's simpler and faster than random sampling when dealing with large populations.
Stratified Sampling: Segregate the population into subgroups or strata according to comparable characteristics. Then, samples are taken randomly from each stratum.
Cluster Sampling: Divide the population into clusters and choose a random sample.
Multistage Sampling: Various sampling techniques are used at different stages to collect detailed information from diverse populations.
Convenience Sampling: The researcher selects the sample based on availability and willingness to participate, which may only represent part of the population.
Quota Sampling: Segment the population into subgroups, and samples are non-randomly selected to fulfill a predetermined quota from each subset.
These are just a few techniques, and choosing the right one depends on your research question, discipline, resource availability, and the level of accuracy required. In quantitative research, there isn't a one-size-fits-all sampling technique; choosing a method that aligns with your research goals and population is critical. However, a well-planned strategy is essential to avoid wasting resources and time, as highlighted in our video featuring William Hudson, CEO of Syntagm.
He emphasizes the importance of recruiting participants meticulously, ensuring their engagement and the quality of their responses. Accurate and thoughtful participant responses are crucial for obtaining reliable results. William also sheds light on dealing with failing participants and scrutinizing response quality to refine the outcomes.
The 4 types of quantitative research are Descriptive, Correlational, Causal-Comparative/Quasi-Experimental, and Experimental Research. Descriptive research aims to depict ‘what exists’ clearly and precisely. Correlational research examines relationships between variables. Causal-comparative research investigates the cause-effect relationship between variables. Experimental research explores causal relationships by manipulating independent variables. To gain deeper insights into quantitative research methods in UX, consider enrolling in our Data-Driven Design: Quantitative Research for UX course.
The strength of quantitative research is its ability to provide precise numerical data for analyzing target variables.This allows for generalized conclusions and predictions about future occurrences, proving invaluable in various fields, including user experience. William Hudson, CEO of Syntagm, discusses the role of surveys, analytics, and testing in providing objective insights in our video on quantitative research methods, highlighting the significance of structured methodologies in eliciting reliable results.
To master quantitative research methods, enroll in our comprehensive course, Data-Driven Design: Quantitative Research for UX .
This course empowers you to leverage quantitative data to make informed design decisions, providing a deep dive into methods like surveys and analytics. Whether you’re a novice or a seasoned professional, this course at Interaction Design Foundation offers valuable insights and practical knowledge, ensuring you acquire the skills necessary to excel in user experience research. Explore our diverse topics to elevate your understanding of quantitative research methods.
Literature on Quantitative Research
Here’s the entire UX literature on Quantitative Research by the Interaction Design Foundation, collated in one place:
Learn more about Quantitative Research
Take a deep dive into Quantitative Research with our course User Research – Methods and Best Practices .
How do you plan to design a product or service that your users will love , if you don't know what they want in the first place? As a user experience designer, you shouldn't leave it to chance to design something outstanding; you should make the effort to understand your users and build on that knowledge from the outset. User research is the way to do this, and it can therefore be thought of as the largest part of user experience design .
In fact, user research is often the first step of a UX design process—after all, you cannot begin to design a product or service without first understanding what your users want! As you gain the skills required, and learn about the best practices in user research, you’ll get first-hand knowledge of your users and be able to design the optimal product—one that’s truly relevant for your users and, subsequently, outperforms your competitors’ .
This course will give you insights into the most essential qualitative research methods around and will teach you how to put them into practice in your design work. You’ll also have the opportunity to embark on three practical projects where you can apply what you’ve learned to carry out user research in the real world . You’ll learn details about how to plan user research projects and fit them into your own work processes in a way that maximizes the impact your research can have on your designs. On top of that, you’ll gain practice with different methods that will help you analyze the results of your research and communicate your findings to your clients and stakeholders—workshops, user journeys and personas, just to name a few!
By the end of the course, you’ll have not only a Course Certificate but also three case studies to add to your portfolio. And remember, a portfolio with engaging case studies is invaluable if you are looking to break into a career in UX design or user research!
We believe you should learn from the best, so we’ve gathered a team of experts to help teach this course alongside our own course instructors. That means you’ll meet a new instructor in each of the lessons on research methods who is an expert in their field—we hope you enjoy what they have in store for you!
All open-source articles on Quantitative Research
Best practices for qualitative user research.

- 3 years ago
Card Sorting

Understand the User’s Perspective through Research for Mobile UX

- 11 mths ago
7 Simple Ways to Get Better Results From Ethnographic Research

Question Everything

Tree Testing
Adding Quality to Your Design Research with an SSQS Checklist
- 8 years ago
How to Fit Quantitative Research into the Project Lifecycle
Why and When to Use Surveys

Correlation in User Experience
First-Click Testing

What to Test

Rating Scales in UX Research: The Ultimate Guide

Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this page , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share Knowledge, Get Respect!
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this page.
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
Quantitative Methods
- Living reference work entry
- First Online: 11 June 2021
- Cite this living reference work entry

- Juwel Rana 2 , 3 , 4 ,
- Patricia Luna Gutierrez 5 &
- John C. Oldroyd 6
364 Accesses
1 Citations
Quantitative analysis ; Quantitative research methods ; Study design
Quantitative method is the collection and analysis of numerical data to answer scientific research questions. Quantitative method is used to summarize, average, find patterns, make predictions, and test causal associations as well as generalizing results to wider populations. It allows us to quantify effect sizes, determine the strength of associations, rank priorities, and weigh the strength of evidence of effectiveness.
Introduction
This entry aims to introduce the most common ways to use numbers and statistics to describe variables, establish relationships among variables, and build numerical understanding of a topic. In general, the quantitative research process uses a deductive approach (Neuman 2014 ; Leavy 2017 ), extrapolating from a particular case to the general situation (Babones 2016 ).
In practical ways, quantitative methods are an approach to studying a research topic. In research, the...
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Institutional subscriptions
Babones S (2016) Interpretive quantitative methods for the social sciences. Sociology. https://doi.org/10.1177/0038038515583637
Balnaves M, Caputi P (2001) Introduction to quantitative research methods: an investigative approach. Sage, London
Book Google Scholar
Brenner PS (2020) Understanding survey methodology: sociological theory and applications. Springer, Boston
Google Scholar
Creswell JW (2014) Research design: qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches. Sage, London
Leavy P (2017) Research design. The Gilford Press, New York
Mertens W, Pugliese A, Recker J (2018) Quantitative data analysis, research methods: information, systems, and contexts: second edition. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-102220-7.00018-2
Neuman LW (2014) Social research methods: qualitative and quantitative approaches. Pearson Education Limited, Edinburgh
Treiman DJ (2009) Quantitative data analysis: doing social research to test ideas. Jossey-Bass, San Francisco
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Public Health, School of Health and Life Sciences, North South University, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Department of Biostatistics and Epidemiology, School of Health and Health Sciences, University of Massachusetts Amherst, MA, USA
Department of Research and Innovation, South Asia Institute for Social Transformation (SAIST), Dhaka, Bangladesh
Independent Researcher, Masatepe, Nicaragua
Patricia Luna Gutierrez
School of Behavioral and Health Sciences, Australian Catholic University, Fitzroy, VIC, Australia
John C. Oldroyd
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Juwel Rana .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton, FL, USA
Ali Farazmand
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Rana, J., Gutierrez, P.L., Oldroyd, J.C. (2021). Quantitative Methods. In: Farazmand, A. (eds) Global Encyclopedia of Public Administration, Public Policy, and Governance. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-31816-5_460-1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-31816-5_460-1
Received : 31 January 2021
Accepted : 14 February 2021
Published : 11 June 2021
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-31816-5
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-31816-5
eBook Packages : Springer Reference Economics and Finance Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Quantitative Research: What It Is, Practices & Methods
Quantitative research involves analyzing and gathering numerical data to uncover trends, calculate averages, evaluate relationships, and derive overarching insights. It’s used in various fields, including the natural and social sciences. Quantitative data analysis employs statistical techniques for processing and interpreting numeric data.
Research designs in the quantitative realm outline how data will be collected and analyzed with methods like experiments and surveys. Qualitative methods complement quantitative research by focusing on non-numerical data, adding depth to understanding. Data collection methods can be qualitative or quantitative, depending on research goals. Researchers often use a combination of both approaches to gain a comprehensive understanding of phenomena.
What is Quantitative Research?
Quantitative research is a systematic investigation of phenomena by gathering quantifiable data and performing statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques. Quantitative research collects statistically significant information from existing and potential customers using sampling methods and sending out online surveys , online polls , and questionnaires , for example.
One of the main characteristics of this type of research is that the results can be depicted in numerical form. After carefully collecting structured observations and understanding these numbers, it’s possible to predict the future of a product or service, establish causal relationships or Causal Research , and make changes accordingly. Quantitative research primarily centers on the analysis of numerical data and utilizes inferential statistics to derive conclusions that can be extrapolated to the broader population.
An example of a quantitative research study is the survey conducted to understand how long a doctor takes to tend to a patient when the patient walks into the hospital. A patient satisfaction survey can be administered to ask questions like how long a doctor takes to see a patient, how often a patient walks into a hospital, and other such questions, which are dependent variables in the research. This kind of research method is often employed in the social sciences, and it involves using mathematical frameworks and theories to effectively present data, ensuring that the results are logical, statistically sound, and unbiased.
Data collection in quantitative research uses a structured method and is typically conducted on larger samples representing the entire population. Researchers use quantitative methods to collect numerical data, which is then subjected to statistical analysis to determine statistically significant findings. This approach is valuable in both experimental research and social research, as it helps in making informed decisions and drawing reliable conclusions based on quantitative data.
Quantitative Research Characteristics
Quantitative research has several unique characteristics that make it well-suited for specific projects. Let’s explore the most crucial of these characteristics so that you can consider them when planning your next research project:

- Structured tools: Quantitative research relies on structured tools such as surveys, polls, or questionnaires to gather quantitative data . Using such structured methods helps collect in-depth and actionable numerical data from the survey respondents, making it easier to perform data analysis.
- Sample size: Quantitative research is conducted on a significant sample size representing the target market . Appropriate Survey Sampling methods, a fundamental aspect of quantitative research methods, must be employed when deriving the sample to fortify the research objective and ensure the reliability of the results.
- Close-ended questions: Closed-ended questions , specifically designed to align with the research objectives, are a cornerstone of quantitative research. These questions facilitate the collection of quantitative data and are extensively used in data collection processes.
- Prior studies: Before collecting feedback from respondents, researchers often delve into previous studies related to the research topic. This preliminary research helps frame the study effectively and ensures the data collection process is well-informed.
- Quantitative data: Typically, quantitative data is represented using tables, charts, graphs, or other numerical forms. This visual representation aids in understanding the collected data and is essential for rigorous data analysis, a key component of quantitative research methods.
- Generalization of results: One of the strengths of quantitative research is its ability to generalize results to the entire population. It means that the findings derived from a sample can be extrapolated to make informed decisions and take appropriate actions for improvement based on numerical data analysis.
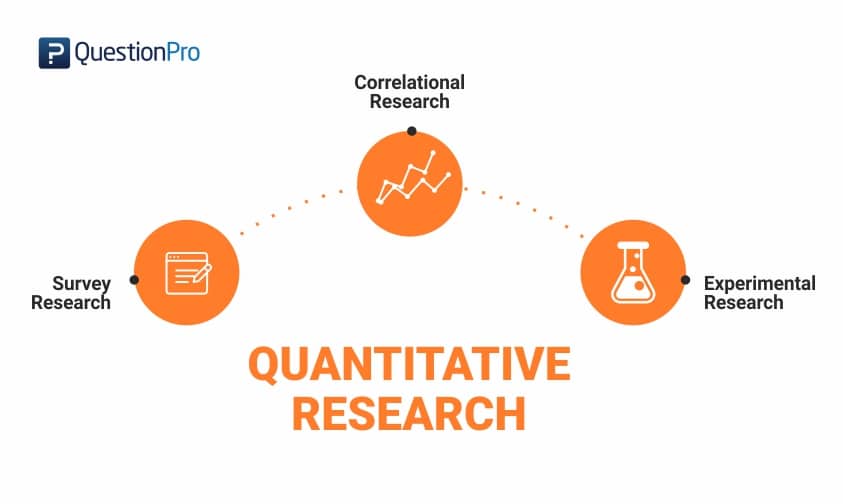
Quantitative Research Methods
Quantitative research methods are systematic approaches used to gather and analyze numerical data to understand and draw conclusions about a phenomenon or population. Here are the quantitative research methods:
- Primary quantitative research methods
- Secondary quantitative research methods
Primary Quantitative Research Methods
Primary quantitative research is the most widely used method of conducting market research. The distinct feature of primary research is that the researcher focuses on collecting data directly rather than depending on data collected from previously done research. Primary quantitative research design can be broken down into three further distinctive tracks and the process flow. They are:
A. Techniques and Types of Studies
There are multiple types of primary quantitative research. They can be distinguished into the four following distinctive methods, which are:
01. Survey Research
Survey Research is fundamental for all quantitative outcome research methodologies and studies. Surveys are used to ask questions to a sample of respondents, using various types such as online polls, online surveys, paper questionnaires, web-intercept surveys , etc. Every small and big organization intends to understand what their customers think about their products and services, how well new features are faring in the market, and other such details.
By conducting survey research, an organization can ask multiple survey questions , collect data from a pool of customers, and analyze this collected data to produce numerical results. It is the first step towards collecting data for any research. You can use single ease questions . A single-ease question is a straightforward query that elicits a concise and uncomplicated response.
This type of research can be conducted with a specific target audience group and also can be conducted across multiple groups along with comparative analysis . A prerequisite for this type of research is that the sample of respondents must have randomly selected members. This way, a researcher can easily maintain the accuracy of the obtained results as a huge variety of respondents will be addressed using random selection.
Traditionally, survey research was conducted face-to-face or via phone calls. Still, with the progress made by online mediums such as email or social media, survey research has also spread to online mediums.There are two types of surveys , either of which can be chosen based on the time in hand and the kind of data required:
Cross-sectional surveys: Cross-sectional surveys are observational surveys conducted in situations where the researcher intends to collect data from a sample of the target population at a given point in time. Researchers can evaluate various variables at a particular time. Data gathered using this type of survey is from people who depict similarity in all variables except the variables which are considered for research . Throughout the survey, this one variable will stay constant.
- Cross-sectional surveys are popular with retail, SMEs, and healthcare industries. Information is garnered without modifying any parameters in the variable ecosystem.
- Multiple samples can be analyzed and compared using a cross-sectional survey research method.
- Multiple variables can be evaluated using this type of survey research.
- The only disadvantage of cross-sectional surveys is that the cause-effect relationship of variables cannot be established as it usually evaluates variables at a particular time and not across a continuous time frame.
Longitudinal surveys: Longitudinal surveys are also observational surveys , but unlike cross-sectional surveys, longitudinal surveys are conducted across various time durations to observe a change in respondent behavior and thought processes. This time can be days, months, years, or even decades. For instance, a researcher planning to analyze the change in buying habits of teenagers over 5 years will conduct longitudinal surveys.
- In cross-sectional surveys, the same variables were evaluated at a given time, and in longitudinal surveys, different variables can be analyzed at different intervals.
- Longitudinal surveys are extensively used in the field of medicine and applied sciences. Apart from these two fields, they are also used to observe a change in the market trend analysis , analyze customer satisfaction, or gain feedback on products/services.
- In situations where the sequence of events is highly essential, longitudinal surveys are used.
- Researchers say that when research subjects need to be thoroughly inspected before concluding, they rely on longitudinal surveys.
02. Correlational Research
A comparison between two entities is invariable. Correlation research is conducted to establish a relationship between two closely-knit entities and how one impacts the other, and what changes are eventually observed. This research method is carried out to give value to naturally occurring relationships, and a minimum of two different groups are required to conduct this quantitative research method successfully. Without assuming various aspects, a relationship between two groups or entities must be established.
Researchers use this quantitative research design to correlate two or more variables using mathematical analysis methods. Patterns, relationships, and trends between variables are concluded as they exist in their original setup. The impact of one of these variables on the other is observed, along with how it changes the relationship between the two variables. Researchers tend to manipulate one of the variables to attain the desired results.
Ideally, it is advised not to make conclusions merely based on correlational research. This is because it is not mandatory that if two variables are in sync that they are interrelated.
Example of Correlational Research Questions :
- The relationship between stress and depression.
- The equation between fame and money.
- The relation between activities in a third-grade class and its students.
03. Causal-comparative Research
This research method mainly depends on the factor of comparison. Also called quasi-experimental research , this quantitative research method is used by researchers to conclude the cause-effect equation between two or more variables, where one variable is dependent on the other independent variable. The independent variable is established but not manipulated, and its impact on the dependent variable is observed. These variables or groups must be formed as they exist in the natural setup. As the dependent and independent variables will always exist in a group, it is advised that the conclusions are carefully established by keeping all the factors in mind.
Causal-comparative research is not restricted to the statistical analysis of two variables but extends to analyzing how various variables or groups change under the influence of the same changes. This research is conducted irrespective of the type of relationship that exists between two or more variables. Statistical analysis plan is used to present the outcome using this quantitative research method.
Example of Causal-Comparative Research Questions:
- The impact of drugs on a teenager. The effect of good education on a freshman. The effect of substantial food provision in the villages of Africa.
04. Experimental Research
Also known as true experimentation, this research method relies on a theory. As the name suggests, experimental research is usually based on one or more theories. This theory has yet to be proven before and is merely a supposition. In experimental research, an analysis is done around proving or disproving the statement. This research method is used in natural sciences. Traditional research methods are more effective than modern techniques.
There can be multiple theories in experimental research. A theory is a statement that can be verified or refuted.
After establishing the statement, efforts are made to understand whether it is valid or invalid. This quantitative research method is mainly used in natural or social sciences as various statements must be proved right or wrong.
- Traditional research methods are more effective than modern techniques.
- Systematic teaching schedules help children who struggle to cope with the course.
- It is a boon to have responsible nursing staff for ailing parents.
B. Data Collection Methodologies
The second major step in primary quantitative research is data collection. Data collection can be divided into sampling methods and data collection using surveys and polls.
01. Data Collection Methodologies: Sampling Methods
There are two main sampling methods for quantitative research: Probability and Non-probability sampling .
Probability sampling: A theory of probability is used to filter individuals from a population and create samples in probability sampling . Participants of a sample are chosen by random selection processes. Each target audience member has an equal opportunity to be selected in the sample.
There are four main types of probability sampling:
- Simple random sampling: As the name indicates, simple random sampling is nothing but a random selection of elements for a sample. This sampling technique is implemented where the target population is considerably large.
- Stratified random sampling: In the stratified random sampling method , a large population is divided into groups (strata), and members of a sample are chosen randomly from these strata. The various segregated strata should ideally not overlap one another.
- Cluster sampling: Cluster sampling is a probability sampling method using which the main segment is divided into clusters, usually using geographic segmentation and demographic segmentation parameters.
- Systematic sampling: Systematic sampling is a technique where the starting point of the sample is chosen randomly, and all the other elements are chosen using a fixed interval. This interval is calculated by dividing the population size by the target sample size.
Non-probability sampling: Non-probability sampling is where the researcher’s knowledge and experience are used to create samples. Because of the researcher’s involvement, not all the target population members have an equal probability of being selected to be a part of a sample.
There are five non-probability sampling models:
- Convenience sampling: In convenience sampling , elements of a sample are chosen only due to one prime reason: their proximity to the researcher. These samples are quick and easy to implement as there is no other parameter of selection involved.
- Consecutive sampling: Consecutive sampling is quite similar to convenience sampling, except for the fact that researchers can choose a single element or a group of samples and conduct research consecutively over a significant period and then perform the same process with other samples.
- Quota sampling: Using quota sampling , researchers can select elements using their knowledge of target traits and personalities to form strata. Members of various strata can then be chosen to be a part of the sample as per the researcher’s understanding.
- Snowball sampling: Snowball sampling is conducted with target audiences who are difficult to contact and get information. It is popular in cases where the target audience for analysis research is rare to put together.
- Judgmental sampling: Judgmental sampling is a non-probability sampling method where samples are created only based on the researcher’s experience and research skill .
02. Data collection methodologies: Using surveys & polls
Once the sample is determined, then either surveys or polls can be distributed to collect the data for quantitative research.
Using surveys for primary quantitative research
A survey is defined as a research method used for collecting data from a pre-defined group of respondents to gain information and insights on various topics of interest. The ease of survey distribution and the wide number of people it can reach depending on the research time and objective makes it one of the most important aspects of conducting quantitative research.
Fundamental levels of measurement – nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio scales
Four measurement scales are fundamental to creating a multiple-choice question in a survey. They are nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio measurement scales without the fundamentals of which no multiple-choice questions can be created. Hence, it is crucial to understand these measurement levels to develop a robust survey.
Use of different question types
To conduct quantitative research, close-ended questions must be used in a survey. They can be a mix of multiple question types, including multiple-choice questions like semantic differential scale questions , rating scale questions , etc.
Survey Distribution and Survey Data Collection
In the above, we have seen the process of building a survey along with the research design to conduct primary quantitative research. Survey distribution to collect data is the other important aspect of the survey process. There are different ways of survey distribution. Some of the most commonly used methods are:
- Email: Sending a survey via email is the most widely used and effective survey distribution method. This method’s response rate is high because the respondents know your brand. You can use the QuestionPro email management feature to send out and collect survey responses.
- Buy respondents: Another effective way to distribute a survey and conduct primary quantitative research is to use a sample. Since the respondents are knowledgeable and are on the panel by their own will, responses are much higher.
- Embed survey on a website: Embedding a survey on a website increases a high number of responses as the respondent is already in close proximity to the brand when the survey pops up.
- Social distribution: Using social media to distribute the survey aids in collecting a higher number of responses from the people that are aware of the brand.
- QR code: QuestionPro QR codes store the URL for the survey. You can print/publish this code in magazines, signs, business cards, or on just about any object/medium.
- SMS survey: The SMS survey is a quick and time-effective way to collect a high number of responses.
- Offline Survey App: The QuestionPro App allows users to circulate surveys quickly, and the responses can be collected both online and offline.
Survey example
An example of a survey is a short customer satisfaction (CSAT) survey that can quickly be built and deployed to collect feedback about what the customer thinks about a brand and how satisfied and referenceable the brand is.
Using polls for primary quantitative research
Polls are a method to collect feedback using close-ended questions from a sample. The most commonly used types of polls are election polls and exit polls . Both of these are used to collect data from a large sample size but using basic question types like multiple-choice questions.
C. Data Analysis Techniques
The third aspect of primary quantitative research design is data analysis . After collecting raw data, there must be an analysis of this data to derive statistical inferences from this research. It is important to relate the results to the research objective and establish the statistical relevance of the results.
Remember to consider aspects of research that were not considered for the data collection process and report the difference between what was planned vs. what was actually executed.
It is then required to select precise Statistical Analysis Methods , such as SWOT, Conjoint, Cross-tabulation, etc., to analyze the quantitative data.
- SWOT analysis: SWOT Analysis stands for the acronym of Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threat analysis. Organizations use this statistical analysis technique to evaluate their performance internally and externally to develop effective strategies for improvement.
- Conjoint Analysis: Conjoint Analysis is a market analysis method to learn how individuals make complicated purchasing decisions. Trade-offs are involved in an individual’s daily activities, and these reflect their ability to decide from a complex list of product/service options.
- Cross-tabulation: Cross-tabulation is one of the preliminary statistical market analysis methods which establishes relationships, patterns, and trends within the various parameters of the research study.
- TURF Analysis: TURF Analysis , an acronym for Totally Unduplicated Reach and Frequency Analysis, is executed in situations where the reach of a favorable communication source is to be analyzed along with the frequency of this communication. It is used for understanding the potential of a target market.
Inferential statistics methods such as confidence interval, the margin of error, etc., can then be used to provide results.
Secondary Quantitative Research Methods
Secondary quantitative research or desk research is a research method that involves using already existing data or secondary data. Existing data is summarized and collated to increase the overall effectiveness of the research.
This research method involves collecting quantitative data from existing data sources like the internet, government resources, libraries, research reports, etc. Secondary quantitative research helps to validate the data collected from primary quantitative research and aid in strengthening or proving, or disproving previously collected data.
The following are five popularly used secondary quantitative research methods:
- Data available on the internet: With the high penetration of the internet and mobile devices, it has become increasingly easy to conduct quantitative research using the internet. Information about most research topics is available online, and this aids in boosting the validity of primary quantitative data.
- Government and non-government sources: Secondary quantitative research can also be conducted with the help of government and non-government sources that deal with market research reports. This data is highly reliable and in-depth and hence, can be used to increase the validity of quantitative research design.
- Public libraries: Now a sparingly used method of conducting quantitative research, it is still a reliable source of information, though. Public libraries have copies of important research that was conducted earlier. They are a storehouse of valuable information and documents from which information can be extracted.
- Educational institutions: Educational institutions conduct in-depth research on multiple topics, and hence, the reports that they publish are an important source of validation in quantitative research.
- Commercial information sources: Local newspapers, journals, magazines, radio, and TV stations are great sources to obtain data for secondary quantitative research. These commercial information sources have in-depth, first-hand information on market research, demographic segmentation, and similar subjects.
Quantitative Research Examples
Some examples of quantitative research are:
- A customer satisfaction template can be used if any organization would like to conduct a customer satisfaction (CSAT) survey . Through this kind of survey, an organization can collect quantitative data and metrics on the goodwill of the brand or organization in the customer’s mind based on multiple parameters such as product quality, pricing, customer experience, etc. This data can be collected by asking a net promoter score (NPS) question , matrix table questions, etc. that provide data in the form of numbers that can be analyzed and worked upon.
- Another example of quantitative research is an organization that conducts an event, collecting feedback from attendees about the value they see from the event. By using an event survey , the organization can collect actionable feedback about the satisfaction levels of customers during various phases of the event such as the sales, pre and post-event, the likelihood of recommending the organization to their friends and colleagues, hotel preferences for the future events and other such questions.
What are the Advantages of Quantitative Research?
There are many advantages to quantitative research. Some of the major advantages of why researchers use this method in market research are:
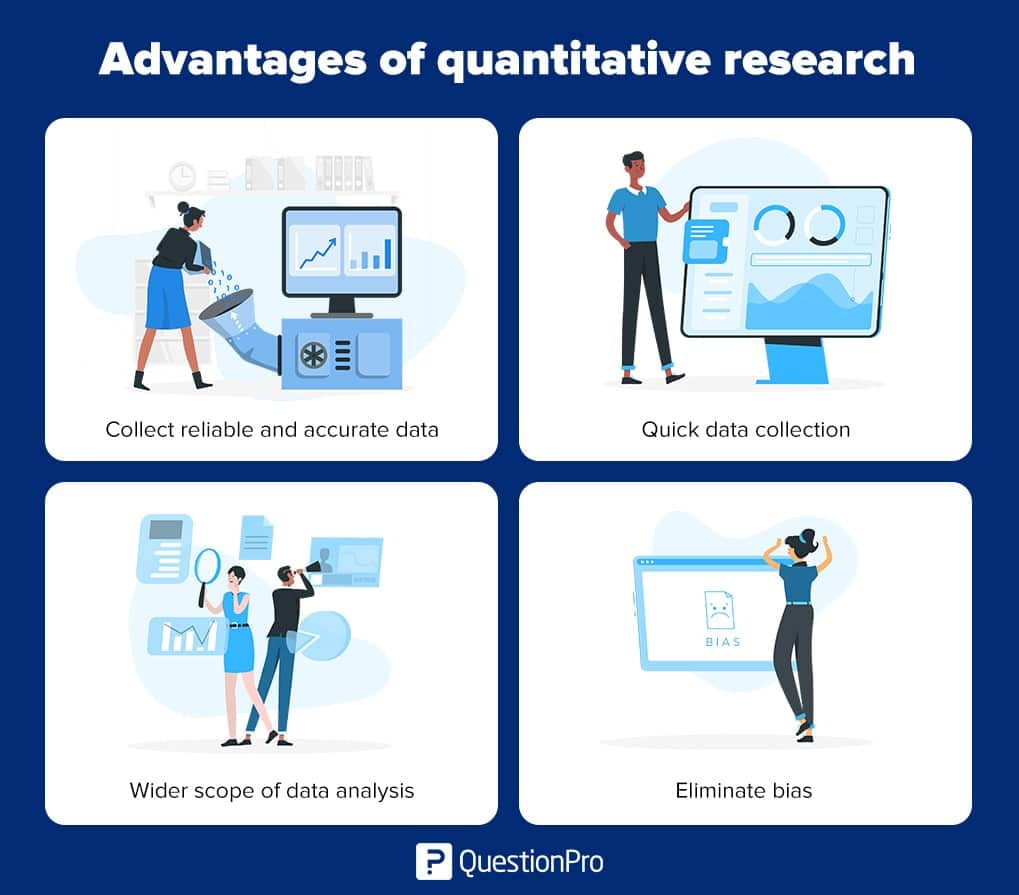
Collect Reliable and Accurate Data:
Quantitative research is a powerful method for collecting reliable and accurate quantitative data. Since data is collected, analyzed, and presented in numbers, the results obtained are incredibly reliable and objective. Numbers do not lie and offer an honest and precise picture of the conducted research without discrepancies. In situations where a researcher aims to eliminate bias and predict potential conflicts, quantitative research is the method of choice.
Quick Data Collection:
Quantitative research involves studying a group of people representing a larger population. Researchers use a survey or another quantitative research method to efficiently gather information from these participants, making the process of analyzing the data and identifying patterns faster and more manageable through the use of statistical analysis. This advantage makes quantitative research an attractive option for projects with time constraints.
Wider Scope of Data Analysis:
Quantitative research, thanks to its utilization of statistical methods, offers an extensive range of data collection and analysis. Researchers can delve into a broader spectrum of variables and relationships within the data, enabling a more thorough comprehension of the subject under investigation. This expanded scope is precious when dealing with complex research questions that require in-depth numerical analysis.
Eliminate Bias:
One of the significant advantages of quantitative research is its ability to eliminate bias. This research method leaves no room for personal comments or the biasing of results, as the findings are presented in numerical form. This objectivity makes the results fair and reliable in most cases, reducing the potential for researcher bias or subjectivity.
In summary, quantitative research involves collecting, analyzing, and presenting quantitative data using statistical analysis. It offers numerous advantages, including the collection of reliable and accurate data, quick data collection, a broader scope of data analysis, and the elimination of bias, making it a valuable approach in the field of research. When considering the benefits of quantitative research, it’s essential to recognize its strengths in contrast to qualitative methods and its role in collecting and analyzing numerical data for a more comprehensive understanding of research topics.
Best Practices to Conduct Quantitative Research
Here are some best practices for conducting quantitative research:

- Differentiate between quantitative and qualitative: Understand the difference between the two methodologies and apply the one that suits your needs best.
- Choose a suitable sample size: Ensure that you have a sample representative of your population and large enough to be statistically weighty.
- Keep your research goals clear and concise: Know your research goals before you begin data collection to ensure you collect the right amount and the right quantity of data.
- Keep the questions simple: Remember that you will be reaching out to a demographically wide audience. Pose simple questions for your respondents to understand easily.
Quantitative Research vs Qualitative Research
Quantitative research and qualitative research are two distinct approaches to conducting research, each with its own set of methods and objectives. Here’s a comparison of the two:

Quantitative Research
- Objective: The primary goal of quantitative research is to quantify and measure phenomena by collecting numerical data. It aims to test hypotheses, establish patterns, and generalize findings to a larger population.
- Data Collection: Quantitative research employs systematic and standardized approaches for data collection, including techniques like surveys, experiments, and observations that involve predefined variables. It is often collected from a large and representative sample.
- Data Analysis: Data is analyzed using statistical techniques, such as descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, and mathematical modeling. Researchers use statistical tests to draw conclusions and make generalizations based on numerical data.
- Sample Size: Quantitative research often involves larger sample sizes to ensure statistical significance and generalizability.
- Results: The results are typically presented in tables, charts, and statistical summaries, making them highly structured and objective.
- Generalizability: Researchers intentionally structure quantitative research to generate outcomes that can be helpful to a larger population, and they frequently seek to establish causative connections.
- Emphasis on Objectivity: Researchers aim to minimize bias and subjectivity, focusing on replicable and objective findings.
Qualitative Research
- Objective: Qualitative research seeks to gain a deeper understanding of the underlying motivations, behaviors, and experiences of individuals or groups. It explores the context and meaning of phenomena.
- Data Collection: Qualitative research employs adaptable and open-ended techniques for data collection, including methods like interviews, focus groups, observations, and content analysis. It allows participants to express their perspectives in their own words.
- Data Analysis: Data is analyzed through thematic analysis, content analysis, or grounded theory. Researchers focus on identifying patterns, themes, and insights in the data.
- Sample Size: Qualitative research typically involves smaller sample sizes due to the in-depth nature of data collection and analysis.
- Results: Findings are presented in narrative form, often in the participants’ own words. Results are subjective, context-dependent, and provide rich, detailed descriptions.
- Generalizability: Qualitative research does not aim for broad generalizability but focuses on in-depth exploration within a specific context. It provides a detailed understanding of a particular group or situation.
- Emphasis on Subjectivity: Researchers acknowledge the role of subjectivity and the researcher’s influence on the Research Process . Participant perspectives and experiences are central to the findings.
Researchers choose between quantitative and qualitative research methods based on their research objectives and the nature of the research question. Each approach has its advantages and drawbacks, and the decision between them hinges on the particular research objectives and the data needed to address research inquiries effectively.
Quantitative research is a structured way of collecting and analyzing data from various sources. Its purpose is to quantify the problem and understand its extent, seeking results that someone can project to a larger population.
Companies that use quantitative rather than qualitative research typically aim to measure magnitudes and seek objectively interpreted statistical results. So if you want to obtain quantitative data that helps you define the structured cause-and-effect relationship between the research problem and the factors, you should opt for this type of research.
At QuestionPro , we have various Best Data Collection Tools and features to conduct investigations of this type. You can create questionnaires and distribute them through our various methods. We also have sample services or various questions to guarantee the success of your study and the quality of the collected data.
Quantitative research is a systematic and structured approach to studying phenomena that involves the collection of measurable data and the application of statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques for analysis.
Quantitative research is characterized by structured tools like surveys, substantial sample sizes, closed-ended questions, reliance on prior studies, data presented numerically, and the ability to generalize findings to the broader population.
The two main methods of quantitative research are Primary quantitative research methods, involving data collection directly from sources, and Secondary quantitative research methods, which utilize existing data for analysis.
1.Surveying to measure employee engagement with numerical rating scales. 2.Analyzing sales data to identify trends in product demand and market share. 4.Examining test scores to assess the impact of a new teaching method on student performance. 4.Using website analytics to track user behavior and conversion rates for an online store.
1.Differentiate between quantitative and qualitative approaches. 2.Choose a representative sample size. 3.Define clear research goals before data collection. 4.Use simple and easily understandable survey questions.
MORE LIKE THIS

Taking Action in CX – Tuesday CX Thoughts
Apr 30, 2024

QuestionPro CX Product Updates – Quarter 1, 2024
Apr 29, 2024


NPS Survey Platform: Types, Tips, 11 Best Platforms & Tools
Apr 26, 2024
User Journey vs User Flow: Differences and Similarities
Other categories.
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Employee Exit Interviews
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
Market Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Quantitative Research
Try Qualtrics for free
Your ultimate guide to quantitative research.
12 min read You may be already using quantitative research and want to check your understanding, or you may be starting from the beginning. Here’s an exploration of this research method and how you can best use it for maximum effect for your business.
You may be already using quantitative research and want to check your understanding, or you may be starting from the beginning. Here’s an exploration of this research method and how you can best use it for maximum effect for your business.
What is quantitative research?
Quantitative is the research method of collecting quantitative data – this is data that can be converted into numbers or numerical data, which can be easily quantified, compared, and analyzed.
Quantitative research deals with primary and secondary sources where data is represented in numerical form. This can include closed-question poll results, statistics, and census information or demographic data .
Quantitative data tends to be used when researchers are interested in understanding a particular moment in time and examining data sets over time to find trends and patterns.
To collect numerical data, surveys are often employed as one of the main research methods to source first-hand information in primary research . Quantitative research can also come from third-party research studies .
Quantitative research is widely used in the realms of social sciences, such as biology, chemistry, psychology, economics, sociology, and marketing .
Research teams collect data that is significant to proving or disproving a hypothesis research question – known as the research objective. When they collect quantitative data, researchers will aim to use a sample size that is representative of the total population of the target market they’re interested in.
Then the data collected will be manually or automatically stored and compared for insights.
Free eBook: The ultimate guide to conducting market research
Quantitative vs qualitative research
While the quantitative research definition focuses on numerical data, qualitative research is defined as data that supplies non-numerical information.
Quantitative research focuses on the thoughts, feelings, and values of a participant , to understand why people act in the way they do . They result in data types like quotes, symbols, images, and written testimonials.
These data types tell researchers subjective information, which can help us assign people into categories, such as a participant’s religion, gender , social class, political alignment, likely favored products to buy, or their preferred training learning style.
For this reason, qualitative research is often used in social research, as this gives a window into the behavior and actions of people.
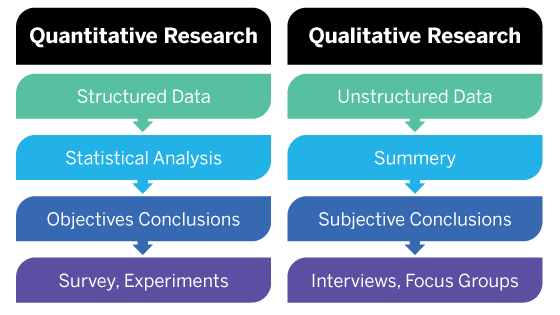
In general, if you’re interested in measuring something or testing a hypothesis, use quantitative methods. If you want to explore ideas, thoughts, and meanings, use qualitative methods.
However, quantitative and qualitative research methods are both recommended when you’re looking to understand a point in time, while also finding out the reason behind the facts.
Quantitative research data collection methods
Quantitative research methods can use structured research instruments like:
- Surveys : A survey is a simple-to-create and easy-to-distribute research method , which helps gather information from large groups of participants quickly. Traditionally, paper-based surveys can now be made online, so costs can stay quite low.
Quantitative questions tend to be closed questions that ask for a numerical result, based on a range of options, or a yes/no answer that can be tallied quickly.
- Face-to-face or phone interviews: Interviews are a great way to connect with participants , though they require time from the research team to set up and conduct.
Researchers may also have issues connecting with participants in different geographical regions . The researcher uses a set of predefined close-ended questions, which ask for yes/no or numerical values.
- Polls: Polls can be a shorter version of surveys , used to get a ‘flavor’ of what the current situation is with participants. Online polls can be shared easily, though polls are best used with simple questions that request a range or a yes/no answer.
Quantitative data is the opposite of qualitative research, another dominant framework for research in the social sciences, explored further below.
Quantitative data types
Quantitative research methods often deliver the following data types:
- Test Scores
- Percent of training course completed
- Performance score out of 100
- Number of support calls active
- Customer Net Promoter Score (NPS)
When gathering numerical data, the emphasis is on how specific the data is, and whether they can provide an indication of what ‘is’ at the time of collection. Pre-existing statistical data can tell us what ‘was’ for the date and time range that it represented
Quantitative research design methods (with examples)
Quantitative research has a number of quantitative research designs you can choose from:
Descriptive
This design type describes the state of a data type is telling researchers, in its native environment. There won’t normally be a clearly defined research question to start with. Instead, data analysis will suggest a conclusion , which can become the hypothesis to investigate further.
Examples of descriptive quantitative design include:
- A description of child’s Christmas gifts they received that year
- A description of what businesses sell the most of during Black Friday
- A description of a product issue being experienced by a customer
Correlational
This design type looks at two or more data types, the relationship between them, and the extent that they differ or align. This does not look at the causal links deeper – instead statistical analysis looks at the variables in a natural environment.
Examples of correlational quantitative design include:
- The relationship between a child’s Christmas gifts and their perceived happiness level
- The relationship between a business’ sales during Black Friday and the total revenue generated over the year
- The relationship between a customer’s product issue and the reputation of the product
Causal-Comparative/Quasi-Experimental
This design type looks at two or more data types and tries to explain any relationship and differences between them, using a cause-effect analysis. The research is carried out in a near-natural environment, where information is gathered from two groups – a naturally occurring group that matches the original natural environment, and one that is not naturally present.
This allows for causal links to be made, though they might not be correct, as other variables may have an impact on results.
Examples of causal-comparative/quasi-experimental quantitative design include:
- The effect of children’s Christmas gifts on happiness
- The effect of Black Friday sales figures on the productivity of company yearly sales
- The effect of product issues on the public perception of a product
Experimental Research
This design type looks to make a controlled environment in which two or more variables are observed to understand the exact cause and effect they have. This becomes a quantitative research study, where data types are manipulated to assess the effect they have. The participants are not naturally occurring groups, as the setting is no longer natural. A quantitative research study can help pinpoint the exact conditions in which variables impact one another.
Examples of experimental quantitative design include:
- The effect of children’s Christmas gifts on a child’s dopamine (happiness) levels
- The effect of Black Friday sales on the success of the company
- The effect of product issues on the perceived reliability of the product
Quantitative research methods need to be carefully considered, as your data collection of a data type can be used to different effects. For example, statistics can be descriptive or correlational (or inferential). Descriptive statistics help us to summarize our data, while inferential statistics help infer conclusions about significant differences.
Advantages of quantitative research
- Easy to do : Doing quantitative research is more straightforward, as the results come in numerical format, which can be more easily interpreted.
- Less interpretation : Due to the factual nature of the results, you will be able to accept or reject your hypothesis based on the numerical data collected.
- Less bias : There are higher levels of control that can be applied to the research, so bias can be reduced , making your data more reliable and precise.
Disadvantages of quantitative research
- Can’t understand reasons: Quantitative research doesn’t always tell you the full story, meaning you won’t understand the context – or the why, of the data you see, why do you see the results you have uncovered?
- Useful for simpler situations: Quantitative research on its own is not great when dealing with complex issues. In these cases, quantitative research may not be enough.
How to use quantitative research to your business’s advantage
Quantitative research methods may help in areas such as:
- Identifying which advert or landing page performs better
- Identifying how satisfied your customers are
- How many customers are likely to recommend you
- Tracking how your brand ranks in awareness and customer purchase intent
- Learn what consumers are likely to buy from your brand.
6 steps to conducting good quantitative research
Businesses can benefit from quantitative research by using it to evaluate the impact of data types. There are several steps to this:
- Define your problem or interest area : What do you observe is happening and is it frequent? Identify the data type/s you’re observing.
- Create a hypothesis : Ask yourself what could be the causes for the situation with those data types.
- Plan your quantitative research : Use structured research instruments like surveys or polls to ask questions that test your hypothesis.
- Data Collection : Collect quantitative data and understand what your data types are telling you. Using data collected on different types over long time periods can give you information on patterns.
- Data analysis : Does your information support your hypothesis? (You may need to redo the research with other variables to see if the results improve)
- Effectively present data : Communicate the results in a clear and concise way to help other people understand the findings.
How Qualtrics products can enhance & simplify the quantitative research process
The Qualtrics XM system gives you an all-in-one, integrated solution to help you all the way through conducting quantitative research. From survey creation and data collection to statistical analysis and data reporting, it can help all your internal teams gain insights from your numerical data.
Quantitative methods are catered to your business through templates or advanced survey designs. While you can manually collect data and conduct data analysis in a spreadsheet program, this solution helps you automate the process of quantitative research, saving you time and administration work.
Using computational techniques helps you to avoid human errors, and participant results come in are already incorporated into the analysis in real-time.
Our key tools, Stats IQ™ and Driver IQ™ make analyzing numerical data easy and simple. Choose to highlight key findings based on variables or highlight statistically insignificant findings. The choice is yours.
Some examples of your workspace in action, using drag and drop to create fast data visualizations quickly:
Related resources
Market intelligence 10 min read, marketing insights 11 min read, ethnographic research 11 min read, qualitative vs quantitative research 13 min read, qualitative research questions 11 min read, qualitative research design 12 min read, primary vs secondary research 14 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?

Research Methods and Design
- Action Research
- Case Study Design
- Literature Review
- Quantitative Research Methods
- Qualitative Research Methods
- Mixed Methods Study
- Indigenous Research and Ethics This link opens in a new window
- Identifying Empirical Research Articles This link opens in a new window
- Research Ethics and Quality
- Data Literacy
- Get Help with Writing Assignments
Quantitative research methods
a method of research that relies on measuring variables using a numerical system, analyzing these measurements using any of a variety of statistical models, and reporting relationships and associations among the studied variables. For example, these variables may be test scores or measurements of reaction time. The goal of gathering this quantitative data is to understand, describe, and predict the nature of a phenomenon, particularly through the development of models and theories. Quantitative research techniques include experiments and surveys.
SAGE Research Methods Videos
What are the strengths of quantitative research.
Professor Norma T. Mertz briefly discusses qualitative research and how it has changed since she entered the field. She emphasizes the importance of defining a research question before choosing a theoretical approach to research.
This is just one segment in a series about quantitative methods. You can find additional videos in our SAGE database, Research Methods:
Videos covering research methods and statistics
Further Reading
- << Previous: Literature Review
- Next: Qualitative Research Methods >>
- Last Updated: Feb 6, 2024 9:20 AM
CityU Home - CityU Catalog


A Quick Guide to Quantitative Research in the Social Sciences
(12 reviews)
Christine Davies, Carmarthen, Wales
Copyright Year: 2020
Last Update: 2021
Publisher: University of Wales Trinity Saint David
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Jennifer Taylor, Assistant Professor, Texas A&M University-Corpus Christi on 4/18/24
This resource is a quick guide to quantitative research in the social sciences and not a comprehensive resource. It provides a VERY general overview of quantitative research but offers a good starting place for students new to research. It... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
This resource is a quick guide to quantitative research in the social sciences and not a comprehensive resource. It provides a VERY general overview of quantitative research but offers a good starting place for students new to research. It offers links and references to additional resources that are more comprehensive in nature.
Content Accuracy rating: 4
The content is relatively accurate. The measurement scale section is very sparse. Not all types of research designs or statistical methods are included, but it is a guide, so details are meant to be limited.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 4
The examples were interesting and appropriate. The content is up to date and will be useful for several years.
Clarity rating: 5
The text was clearly written. Tables and figures are not referenced in the text, which would have been nice.
Consistency rating: 5
The framework is consistent across chapters with terminology clearly highlighted and defined.
Modularity rating: 5
The chapters are subdivided into section that can be divided and assigned as reading in a course. Most chapters are brief and concise, unless elaboration is necessary, such as with the data analysis chapter. Again, this is a guide and not a comprehensive text, so sections are shorter and don't always include every subtopic that may be considered.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
The guide is well organized. I appreciate that the topics are presented in a logical and clear manner. The topics are provided in an order consistent with traditional research methods.
Interface rating: 5
The interface was easy to use and navigate. The images were clear and easy to read.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
I did not notice any grammatical errors.
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
The materials are not culturally insensitive or offensive in any way.
I teach a Marketing Research course to undergraduates. I would consider using some of the chapters or topics included, especially the overview of the research designs and the analysis of data section.
Reviewed by Tiffany Kindratt, Assistant Professor, University of Texas at Arlington on 3/9/24
The text provides a brief overview of quantitative research topics that is geared towards research in the fields of education, sociology, business, and nursing. The author acknowledges that the textbook is not a comprehensive resource but offers... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 3 see less
The text provides a brief overview of quantitative research topics that is geared towards research in the fields of education, sociology, business, and nursing. The author acknowledges that the textbook is not a comprehensive resource but offers references to other resources that can be used to deepen the knowledge. The text does not include a glossary or index. The references in the figures for each chapter are not included in the reference section. It would be helpful to include those.
Overall, the text is accurate. For example, Figure 1 on page 6 provides a clear overview of the research process. It includes general definitions of primary and secondary research. It would be helpful to include more details to explain some of the examples before they are presented. For instance, the example on page 5 was unclear how it pertains to the literature review section.
In general, the text is relevant and up-to-date. The text includes many inferences of moving from qualitative to quantitative analysis. This was surprising to me as a quantitative researcher. The author mentions that moving from a qualitative to quantitative approach should only be done when needed. As a predominantly quantitative researcher, I would not advice those interested in transitioning to using a qualitative approach that qualitative research would enhance their research—not something that should only be done if you have to.
Clarity rating: 4
The text is written in a clear manner. It would be helpful to the reader if there was a description of the tables and figures in the text before they are presented.
Consistency rating: 4
The framework for each chapter and terminology used are consistent.
Modularity rating: 4
The text is clearly divided into sections within each chapter. Overall, the chapters are a similar brief length except for the chapter on data analysis, which is much more comprehensive than others.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 4
The topics in the text are presented in a clear and logical order. The order of the text follows the conventional research methodology in social sciences.
I did not encounter any interface issues when reviewing this text. All links worked and there were no distortions of the images or charts that may confuse the reader.
Grammatical Errors rating: 3
There are some grammatical/typographical errors throughout. Of note, for Section 5 in the table of contents. “The” should be capitalized to start the title. In the title for Table 3, the “t” in typical should be capitalized.
Cultural Relevance rating: 4
The examples are culturally relevant. The text is geared towards learners in the UK, but examples are relevant for use in other countries (i.e., United States). I did not see any examples that may be considered culturally insensitive or offensive in any way.
I teach a course on research methods in a Bachelor of Science in Public Health program. I would consider using some of the text, particularly in the analysis chapter to supplement the current textbook in the future.
Reviewed by Finn Bell, Assistant Professor, University of Michigan, Dearborn on 1/3/24
For it being a quick guide and only 26 pages, it is very comprehensive, but it does not include an index or glossary. read more
For it being a quick guide and only 26 pages, it is very comprehensive, but it does not include an index or glossary.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
As far as I can tell, the text is accurate, error-free and unbiased.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
This text is up-to-date, and given the content, unlikely to become obsolete any time soon.
The text is very clear and accessible.
The text is internally consistent.
Given how short the text is, it seems unnecessary to divide it into smaller readings, nonetheless, it is clearly labelled such that an instructor could do so.
The text is well-organized and brings readers through basic quantitative methods in a logical, clear fashion.
Easy to navigate. Only one table that is split between pages, but not in a way that is confusing.
There were no noticeable grammatical errors.
The examples in this book don't give enough information to rate this effectively.
This text is truly a very quick guide at only 26 double-spaced pages. Nonetheless, Davies packs a lot of information on the basics of quantitative research methods into this text, in an engaging way with many examples of the concepts presented. This guide is more of a brief how-to that takes readers as far as how to select statistical tests. While it would be impossible to fully learn quantitative research from such a short text, of course, this resource provides a great introduction, overview, and refresher for program evaluation courses.
Reviewed by Shari Fedorowicz, Adjunct Professor, Bridgewater State University on 12/16/22
The text is indeed a quick guide for utilizing quantitative research. Appropriate and effective examples and diagrams were used throughout the text. The author clearly differentiates between use of quantitative and qualitative research providing... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
The text is indeed a quick guide for utilizing quantitative research. Appropriate and effective examples and diagrams were used throughout the text. The author clearly differentiates between use of quantitative and qualitative research providing the reader with the ability to distinguish two terms that frequently get confused. In addition, links and outside resources are provided to deepen the understanding as an option for the reader. The use of these links, coupled with diagrams and examples make this text comprehensive.
The content is mostly accurate. Given that it is a quick guide, the author chose a good selection of which types of research designs to include. However, some are not provided. For example, correlational or cross-correlational research is omitted and is not discussed in Section 3, but is used as a statistical example in the last section.
Examples utilized were appropriate and associated with terms adding value to the learning. The tables that included differentiation between types of statistical tests along with a parametric/nonparametric table were useful and relevant.
The purpose to the text and how to use this guide book is stated clearly and is established up front. The author is also very clear regarding the skill level of the user. Adding to the clarity are the tables with terms, definitions, and examples to help the reader unpack the concepts. The content related to the terms was succinct, direct, and clear. Many times examples or figures were used to supplement the narrative.
The text is consistent throughout from contents to references. Within each section of the text, the introductory paragraph under each section provides a clear understanding regarding what will be discussed in each section. The layout is consistent for each section and easy to follow.
The contents are visible and address each section of the text. A total of seven sections, including a reference section, is in the contents. Each section is outlined by what will be discussed in the contents. In addition, within each section, a heading is provided to direct the reader to the subtopic under each section.
The text is well-organized and segues appropriately. I would have liked to have seen an introductory section giving a narrative overview of what is in each section. This would provide the reader with the ability to get a preliminary glimpse into each upcoming sections and topics that are covered.
The book was easy to navigate and well-organized. Examples are presented in one color, links in another and last, figures and tables. The visuals supplemented the reading and placed appropriately. This provides an opportunity for the reader to unpack the reading by use of visuals and examples.
No significant grammatical errors.
The text is not offensive or culturally insensitive. Examples were inclusive of various races, ethnicities, and backgrounds.
This quick guide is a beneficial text to assist in unpacking the learning related to quantitative statistics. I would use this book to complement my instruction and lessons, or use this book as a main text with supplemental statistical problems and formulas. References to statistical programs were appropriate and were useful. The text did exactly what was stated up front in that it is a direct guide to quantitative statistics. It is well-written and to the point with content areas easy to locate by topic.
Reviewed by Sarah Capello, Assistant Professor, Radford University on 1/18/22
The text claims to provide "quick and simple advice on quantitative aspects of research in social sciences," which it does. There is no index or glossary, although vocabulary words are bolded and defined throughout the text. read more
The text claims to provide "quick and simple advice on quantitative aspects of research in social sciences," which it does. There is no index or glossary, although vocabulary words are bolded and defined throughout the text.
The content is mostly accurate. I would have preferred a few nuances to be hashed out a bit further to avoid potential reader confusion or misunderstanding of the concepts presented.
The content is current; however, some of the references cited in the text are outdated. Newer editions of those texts exist.
The text is very accessible and readable for a variety of audiences. Key terms are well-defined.
There are no content discrepancies within the text. The author even uses similarly shaped graphics for recurring purposes throughout the text (e.g., arrow call outs for further reading, rectangle call outs for examples).
The content is chunked nicely by topics and sections. If it were used for a course, it would be easy to assign different sections of the text for homework, etc. without confusing the reader if the instructor chose to present the content in a different order.
The author follows the structure of the research process. The organization of the text is easy to follow and comprehend.
All of the supplementary images (e.g., tables and figures) were beneficial to the reader and enhanced the text.
There are no significant grammatical errors.
I did not find any culturally offensive or insensitive references in the text.
This text does the difficult job of introducing the complicated concepts and processes of quantitative research in a quick and easy reference guide fairly well. I would not depend solely on this text to teach students about quantitative research, but it could be a good jumping off point for those who have no prior knowledge on this subject or those who need a gentle introduction before diving in to more advanced and complex readings of quantitative research methods.
Reviewed by J. Marlie Henry, Adjunct Faculty, University of Saint Francis on 12/9/21
Considering the length of this guide, this does a good job of addressing major areas that typically need to be addressed. There is a contents section. The guide does seem to be organized accordingly with appropriate alignment and logical flow of... read more
Considering the length of this guide, this does a good job of addressing major areas that typically need to be addressed. There is a contents section. The guide does seem to be organized accordingly with appropriate alignment and logical flow of thought. There is no glossary but, for a guide of this length, a glossary does not seem like it would enhance the guide significantly.
The content is relatively accurate. Expanding the content a bit more or explaining that the methods and designs presented are not entirely inclusive would help. As there are different schools of thought regarding what should/should not be included in terms of these designs and methods, simply bringing attention to that and explaining a bit more would help.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 3
This content needs to be updated. Most of the sources cited are seven or more years old. Even more, it would be helpful to see more currently relevant examples. Some of the source authors such as Andy Field provide very interesting and dynamic instruction in general, but they have much more current information available.
The language used is clear and appropriate. Unnecessary jargon is not used. The intent is clear- to communicate simply in a straightforward manner.
The guide seems to be internally consistent in terms of terminology and framework. There do not seem to be issues in this area. Terminology is internally consistent.
For a guide of this length, the author structured this logically into sections. This guide could be adopted in whole or by section with limited modifications. Courses with fewer than seven modules could also logically group some of the sections.
This guide does present with logical organization. The topics presented are conceptually sequenced in a manner that helps learners build logically on prior conceptualization. This also provides a simple conceptual framework for instructors to guide learners through the process.
Interface rating: 4
The visuals themselves are simple, but they are clear and understandable without distracting the learner. The purpose is clear- that of learning rather than visuals for the sake of visuals. Likewise, navigation is clear and without issues beyond a broken link (the last source noted in the references).
This guide seems to be free of grammatical errors.
It would be interesting to see more cultural integration in a guide of this nature, but the guide is not culturally insensitive or offensive in any way. The language used seems to be consistent with APA's guidelines for unbiased language.
Reviewed by Heng Yu-Ku, Professor, University of Northern Colorado on 5/13/21
The text covers all areas and ideas appropriately and provides practical tables, charts, and examples throughout the text. I would suggest the author also provides a complete research proposal at the end of Section 3 (page 10) and a comprehensive... read more
The text covers all areas and ideas appropriately and provides practical tables, charts, and examples throughout the text. I would suggest the author also provides a complete research proposal at the end of Section 3 (page 10) and a comprehensive research study as an Appendix after section 7 (page 26) to help readers comprehend information better.
For the most part, the content is accurate and unbiased. However, the author only includes four types of research designs used on the social sciences that contain quantitative elements: 1. Mixed method, 2) Case study, 3) Quasi-experiment, and 3) Action research. I wonder why the correlational research is not included as another type of quantitative research design as it has been introduced and emphasized in section 6 by the author.
I believe the content is up-to-date and that necessary updates will be relatively easy and straightforward to implement.
The text is easy to read and provides adequate context for any technical terminology used. However, the author could provide more detailed information about estimating the minimum sample size but not just refer the readers to use the online sample calculators at a different website.
The text is internally consistent in terms of terminology and framework. The author provides the right amount of information with additional information or resources for the readers.
The text includes seven sections. Therefore, it is easier for the instructor to allocate or divide the content into different weeks of instruction within the course.
Yes, the topics in the text are presented in a logical and clear fashion. The author provides clear and precise terminologies, summarizes important content in Table or Figure forms, and offers examples in each section for readers to check their understanding.
The interface of the book is consistent and clear, and all the images and charts provided in the book are appropriate. However, I did encounter some navigation problems as a couple of links are not working or requires permission to access those (pages 10 and 27).
No grammatical errors were found.
No culturally incentive or offensive in its language and the examples provided were found.
As the book title stated, this book provides “A Quick Guide to Quantitative Research in Social Science. It offers easy-to-read information and introduces the readers to the research process, such as research questions, research paradigms, research process, research designs, research methods, data collection, data analysis, and data discussion. However, some links are not working or need permissions to access them (pages 10 and 27).
Reviewed by Hsiao-Chin Kuo, Assistant Professor, Northeastern Illinois University on 4/26/21, updated 4/28/21
As a quick guide, it covers basic concepts related to quantitative research. It starts with WHY quantitative research with regard to asking research questions and considering research paradigms, then provides an overview of research design and... read more
As a quick guide, it covers basic concepts related to quantitative research. It starts with WHY quantitative research with regard to asking research questions and considering research paradigms, then provides an overview of research design and process, discusses methods, data collection and analysis, and ends with writing a research report. It also identifies its target readers/users as those begins to explore quantitative research. It would be helpful to include more examples for readers/users who are new to quantitative research.
Its content is mostly accurate and no bias given its nature as a quick guide. Yet, it is also quite simplified, such as its explanations of mixed methods, case study, quasi-experimental research, and action research. It provides resources for extended reading, yet more recent works will be helpful.
The book is relevant given its nature as a quick guide. It would be helpful to provide more recent works in its resources for extended reading, such as the section for Survey Research (p. 12). It would also be helpful to include more information to introduce common tools and software for statistical analysis.
The book is written with clear and understandable language. Important terms and concepts are presented with plain explanations and examples. Figures and tables are also presented to support its clarity. For example, Table 4 (p. 20) gives an easy-to-follow overview of different statistical tests.
The framework is very consistent with key points, further explanations, examples, and resources for extended reading. The sample studies are presented following the layout of the content, such as research questions, design and methods, and analysis. These examples help reinforce readers' understanding of these common research elements.
The book is divided into seven chapters. Each chapter clearly discusses an aspect of quantitative research. It can be easily divided into modules for a class or for a theme in a research method class. Chapters are short and provides additional resources for extended reading.
The topics in the chapters are presented in a logical and clear structure. It is easy to follow to a degree. Though, it would be also helpful to include the chapter number and title in the header next to its page number.
The text is easy to navigate. Most of the figures and tables are displayed clearly. Yet, there are several sections with empty space that is a bit confusing in the beginning. Again, it can be helpful to include the chapter number/title next to its page number.
Grammatical Errors rating: 4
No major grammatical errors were found.
There are no cultural insensitivities noted.
Given the nature and purpose of this book, as a quick guide, it provides readers a quick reference for important concepts and terms related to quantitative research. Because this book is quite short (27 pages), it can be used as an overview/preview about quantitative research. Teacher's facilitation/input and extended readings will be needed for a deeper learning and discussion about aspects of quantitative research.
Reviewed by Yang Cheng, Assistant Professor, North Carolina State University on 1/6/21
It covers the most important topics such as research progress, resources, measurement, and analysis of the data. read more
It covers the most important topics such as research progress, resources, measurement, and analysis of the data.
The book accurately describes the types of research methods such as mixed-method, quasi-experiment, and case study. It talks about the research proposal and key differences between statistical analyses as well.
The book pinpointed the significance of running a quantitative research method and its relevance to the field of social science.
The book clearly tells us the differences between types of quantitative methods and the steps of running quantitative research for students.
The book is consistent in terms of terminologies such as research methods or types of statistical analysis.
It addresses the headlines and subheadlines very well and each subheading should be necessary for readers.
The book was organized very well to illustrate the topic of quantitative methods in the field of social science.
The pictures within the book could be further developed to describe the key concepts vividly.
The textbook contains no grammatical errors.
It is not culturally offensive in any way.
Overall, this is a simple and quick guide for this important topic. It should be valuable for undergraduate students who would like to learn more about research methods.
Reviewed by Pierre Lu, Associate Professor, University of Texas Rio Grande Valley on 11/20/20
As a quick guide to quantitative research in social sciences, the text covers most ideas and areas. read more
As a quick guide to quantitative research in social sciences, the text covers most ideas and areas.
Mostly accurate content.
As a quick guide, content is highly relevant.
Succinct and clear.
Internally, the text is consistent in terms of terminology used.
The text is easily and readily divisible into smaller sections that can be used as assignments.
I like that there are examples throughout the book.
Easy to read. No interface/ navigation problems.
No grammatical errors detected.
I am not aware of the culturally insensitive description. After all, this is a methodology book.
I think the book has potential to be adopted as a foundation for quantitative research courses, or as a review in the first weeks in advanced quantitative course.
Reviewed by Sarah Fischer, Assistant Professor, Marymount University on 7/31/20
It is meant to be an overview, but it incredibly condensed and spends almost no time on key elements of statistics (such as what makes research generalizable, or what leads to research NOT being generalizable). read more
It is meant to be an overview, but it incredibly condensed and spends almost no time on key elements of statistics (such as what makes research generalizable, or what leads to research NOT being generalizable).
Content Accuracy rating: 1
Contains VERY significant errors, such as saying that one can "accept" a hypothesis. (One of the key aspect of hypothesis testing is that one either rejects or fails to reject a hypothesis, but NEVER accepts a hypothesis.)
Very relevant to those experiencing the research process for the first time. However, it is written by someone working in the natural sciences but is a text for social sciences. This does not explain the errors, but does explain why sometimes the author assumes things about the readers ("hail from more subjectivist territory") that are likely not true.
Clarity rating: 3
Some statistical terminology not explained clearly (or accurately), although the author has made attempts to do both.
Very consistently laid out.
Chapters are very short yet also point readers to outside texts for additional information. Easy to follow.
Generally logically organized.
Easy to navigate, images clear. The additional sources included need to linked to.
Minor grammatical and usage errors throughout the text.
Makes efforts to be inclusive.
The idea of this book is strong--short guides like this are needed. However, this book would likely be strengthened by a revision to reduce inaccuracies and improve the definitions and technical explanations of statistical concepts. Since the book is specifically aimed at the social sciences, it would also improve the text to have more examples that are based in the social sciences (rather than the health sciences or the arts).
Reviewed by Michelle Page, Assistant Professor, Worcester State University on 5/30/20
This text is exactly intended to be what it says: A quick guide. A basic outline of quantitative research processes, akin to cliff notes. The content provides only the essentials of a research process and contains key terms. A student or new... read more
This text is exactly intended to be what it says: A quick guide. A basic outline of quantitative research processes, akin to cliff notes. The content provides only the essentials of a research process and contains key terms. A student or new researcher would not be able to use this as a stand alone guide for quantitative pursuits without having a supplemental text that explains the steps in the process more comprehensively. The introduction does provide this caveat.
Content Accuracy rating: 3
There are no biases or errors that could be distinguished; however, it’s simplicity in content, although accurate for an outline of process, may lack a conveyance of the deeper meanings behind the specific processes explained about qualitative research.
The content is outlined in traditional format to highlight quantitative considerations for formatting research foundational pieces. The resources/references used to point the reader to literature sources can be easily updated with future editions.
The jargon in the text is simple to follow and provides adequate context for its purpose. It is simplified for its intention as a guide which is appropriate.
Each section of the text follows a consistent flow. Explanation of the research content or concept is defined and then a connection to literature is provided to expand the readers understanding of the section’s content. Terminology is consistent with the qualitative process.
As an “outline” and guide, this text can be used to quickly identify the critical parts of the quantitative process. Although each section does not provide deeper content for meaningful use as a stand alone text, it’s utility would be excellent as a reference for a course and can be used as an content guide for specific research courses.
The text’s outline and content are aligned and are in a logical flow in terms of the research considerations for quantitative research.
The only issue that the format was not able to provide was linkable articles. These would have to be cut and pasted into a browser. Functional clickable links in a text are very successful at leading the reader to the supplemental material.
No grammatical errors were noted.
This is a very good outline “guide” to help a new or student researcher to demystify the quantitative process. A successful outline of any process helps to guide work in a logical and systematic way. I think this simple guide is a great adjunct to more substantial research context.
Table of Contents
- Section 1: What will this resource do for you?
- Section 2: Why are you thinking about numbers? A discussion of the research question and paradigms.
- Section 3: An overview of the Research Process and Research Designs
- Section 4: Quantitative Research Methods
- Section 5: the data obtained from quantitative research
- Section 6: Analysis of data
- Section 7: Discussing your Results
Ancillary Material
About the book.
This resource is intended as an easy-to-use guide for anyone who needs some quick and simple advice on quantitative aspects of research in social sciences, covering subjects such as education, sociology, business, nursing. If you area qualitative researcher who needs to venture into the world of numbers, or a student instructed to undertake a quantitative research project despite a hatred for maths, then this booklet should be a real help.
The booklet was amended in 2022 to take into account previous review comments.
About the Contributors
Christine Davies , Ph.D
Contribute to this Page
Quantitative research
Affiliation.
- 1 Faculty of Health and Social Care, University of Hull, Hull, England.
- PMID: 25828021
- DOI: 10.7748/ns.29.31.44.e8681
This article describes the basic tenets of quantitative research. The concepts of dependent and independent variables are addressed and the concept of measurement and its associated issues, such as error, reliability and validity, are explored. Experiments and surveys – the principal research designs in quantitative research – are described and key features explained. The importance of the double-blind randomised controlled trial is emphasised, alongside the importance of longitudinal surveys, as opposed to cross-sectional surveys. Essential features of data storage are covered, with an emphasis on safe, anonymous storage. Finally, the article explores the analysis of quantitative data, considering what may be analysed and the main uses of statistics in analysis.
Keywords: Experiments; measurement; nursing research; quantitative research; reliability; surveys; validity.
- Biomedical Research / methods*
- Double-Blind Method
- Evaluation Studies as Topic
- Longitudinal Studies
- Randomized Controlled Trials as Topic
- United Kingdom
Research Methodologies
Quantitative research methodologies.
- Qualitative Research Methodologies
- Systematic Reviews
- Finding Articles by Methodology
- Design Your Research Project
Library Help
What is quantitative research.
Quantitative methodologies use statistics to analyze numerical data gathered by researchers to answer their research questions. Quantitative methods can be used to answer questions such as:
- What are the relationships between two or more variables?
- What factors are at play in an environment that might affect the behavior or development of the organisms in that environment?
Quantitative methods can also be used to test hypotheses by conducting quasi-experimental studies or designing experiments.
Independent and Dependent Variables
In quantitative research, a variable is something (an intervention technique, a pharmaceutical, a temperature, etc.) that changes. There are two kinds of variables: independent variables and dependent variables . In the simplest terms, the independent variable is whatever the researchers are using to attempt to make a change in their dependent variable.
* This is a real, repeatable experiment you can try on your plants.
Correlational
Researchers will compare two sets of numbers to try and identify a relationship (if any) between two things.
- Köse S., & Murat, M. (2021). Examination of the relationship between smartphone addiction and cyberchondria in adolescents. Archives of Psychiatric Nursing, 35(6): 563-570.
- Pilger et al. (2021). Spiritual well-being, religious/spiritual coping and quality of life among the elderly undergoing hemodialysis: a correlational study. Journal of Religion, Spirituality & Aging, 33(1): 2-15.
Descriptive
Researchers will attempt to quantify a variety of factors at play as they study a particular type of phenomenon or action. For example, researchers might use a descriptive methodology to understand the effects of climate change on the life cycle of a plant or animal.
- Lakshmi, E. (2021). Food consumption pattern and body mass index of adolescents: A descriptive study. International Journal of Nutrition, Pharmacology, Neurological Diseases, 11(4), 293–297.
- Lin, J., Singh, S., Sha, L., Tan, W., Lang, D., Gašević, D., & Chen, G. (2022). Is it a good move? Mining effective tutoring strategies from human–human tutorial dialogues. Future Generation Computer Systems, 127, 194–207.
Experimental
To understand the effects of a variable, researchers will design an experiment where they can control as many factors as possible. This can involve creating control and experimental groups. The experimental group will be exposed to the variable to study its effects. The control group provides data about what happens when the variable is absent. For example, in a study about online teaching, the control group might receive traditional face-to-face instruction while the experimental group would receive their instruction virtually.
- Jinzhang Jia, Yinuo Chen, Guangbo Che, Jinchao Zhu, Fengxiao Wang, & Peng Jia. (2021). Experimental study on the explosion characteristics of hydrogen-methane premixed gas in complex pipe networks. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 1–11.
- Sasaki, R. et al. (2021). Effects of cryotherapy applied at different temperatures on inflammatory pain during the acute phase of arthritis in rats. Physical Therapy, 101(2), 1–9.
Quasi-Experimental/Quasi-Comparative
Researchers will attempt to determine what (if any) effect a variable can have. These studies may have multiple independent variables (causes) and multiple dependent variables (effects), but this can complicate researchers' efforts to find out if A can cause B or if X, Y, and Z are also playing a role.
- Jafari, A., Alami, A., Charoghchian, E., Delshad Noghabi, A., & Nejatian, M. (2021). The impact of effective communication skills training on the status of marital burnout among married women. BMC Women’s Health, 21(1), 1-10.
- Phillips, S. W., Kim, D.-Y., Sobol, J. J., & Gayadeen, S. M. (2021). Total recall?: A quasi-experimental study of officer’s recollection in shoot - don’t shoot simulators. Police Practice and Research, 22(3), 1229–1240.
Surveys can be considered a quantitative methodology if the researchers require their respondents to choose from pre-determined responses.
- Harries et al. (2021). Effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on medical students: A multicenter quantitative study. BMC Medical Education, 21(14), 1-8.
- Call : 801.863.8840
- Text : 801.290.8123
- In-Person Help
- Email a Librarian
- Make an Appointment
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Qualitative Research Methodologies >>
- Last Updated: Apr 30, 2024 1:49 PM
- URL: https://uvu.libguides.com/methods
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research Methods & Data Analysis
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
What is the difference between quantitative and qualitative?
The main difference between quantitative and qualitative research is the type of data they collect and analyze.
Quantitative research collects numerical data and analyzes it using statistical methods. The aim is to produce objective, empirical data that can be measured and expressed in numerical terms. Quantitative research is often used to test hypotheses, identify patterns, and make predictions.
Qualitative research , on the other hand, collects non-numerical data such as words, images, and sounds. The focus is on exploring subjective experiences, opinions, and attitudes, often through observation and interviews.
Qualitative research aims to produce rich and detailed descriptions of the phenomenon being studied, and to uncover new insights and meanings.
Quantitative data is information about quantities, and therefore numbers, and qualitative data is descriptive, and regards phenomenon which can be observed but not measured, such as language.
What Is Qualitative Research?
Qualitative research is the process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting non-numerical data, such as language. Qualitative research can be used to understand how an individual subjectively perceives and gives meaning to their social reality.
Qualitative data is non-numerical data, such as text, video, photographs, or audio recordings. This type of data can be collected using diary accounts or in-depth interviews and analyzed using grounded theory or thematic analysis.
Qualitative research is multimethod in focus, involving an interpretive, naturalistic approach to its subject matter. This means that qualitative researchers study things in their natural settings, attempting to make sense of, or interpret, phenomena in terms of the meanings people bring to them. Denzin and Lincoln (1994, p. 2)
Interest in qualitative data came about as the result of the dissatisfaction of some psychologists (e.g., Carl Rogers) with the scientific study of psychologists such as behaviorists (e.g., Skinner ).
Since psychologists study people, the traditional approach to science is not seen as an appropriate way of carrying out research since it fails to capture the totality of human experience and the essence of being human. Exploring participants’ experiences is known as a phenomenological approach (re: Humanism ).
Qualitative research is primarily concerned with meaning, subjectivity, and lived experience. The goal is to understand the quality and texture of people’s experiences, how they make sense of them, and the implications for their lives.
Qualitative research aims to understand the social reality of individuals, groups, and cultures as nearly as possible as participants feel or live it. Thus, people and groups are studied in their natural setting.
Some examples of qualitative research questions are provided, such as what an experience feels like, how people talk about something, how they make sense of an experience, and how events unfold for people.
Research following a qualitative approach is exploratory and seeks to explain ‘how’ and ‘why’ a particular phenomenon, or behavior, operates as it does in a particular context. It can be used to generate hypotheses and theories from the data.
Qualitative Methods
There are different types of qualitative research methods, including diary accounts, in-depth interviews , documents, focus groups , case study research , and ethnography.
The results of qualitative methods provide a deep understanding of how people perceive their social realities and in consequence, how they act within the social world.
The researcher has several methods for collecting empirical materials, ranging from the interview to direct observation, to the analysis of artifacts, documents, and cultural records, to the use of visual materials or personal experience. Denzin and Lincoln (1994, p. 14)
Here are some examples of qualitative data:
Interview transcripts : Verbatim records of what participants said during an interview or focus group. They allow researchers to identify common themes and patterns, and draw conclusions based on the data. Interview transcripts can also be useful in providing direct quotes and examples to support research findings.
Observations : The researcher typically takes detailed notes on what they observe, including any contextual information, nonverbal cues, or other relevant details. The resulting observational data can be analyzed to gain insights into social phenomena, such as human behavior, social interactions, and cultural practices.
Unstructured interviews : generate qualitative data through the use of open questions. This allows the respondent to talk in some depth, choosing their own words. This helps the researcher develop a real sense of a person’s understanding of a situation.
Diaries or journals : Written accounts of personal experiences or reflections.
Notice that qualitative data could be much more than just words or text. Photographs, videos, sound recordings, and so on, can be considered qualitative data. Visual data can be used to understand behaviors, environments, and social interactions.
Qualitative Data Analysis
Qualitative research is endlessly creative and interpretive. The researcher does not just leave the field with mountains of empirical data and then easily write up his or her findings.
Qualitative interpretations are constructed, and various techniques can be used to make sense of the data, such as content analysis, grounded theory (Glaser & Strauss, 1967), thematic analysis (Braun & Clarke, 2006), or discourse analysis.
For example, thematic analysis is a qualitative approach that involves identifying implicit or explicit ideas within the data. Themes will often emerge once the data has been coded.
Key Features
- Events can be understood adequately only if they are seen in context. Therefore, a qualitative researcher immerses her/himself in the field, in natural surroundings. The contexts of inquiry are not contrived; they are natural. Nothing is predefined or taken for granted.
- Qualitative researchers want those who are studied to speak for themselves, to provide their perspectives in words and other actions. Therefore, qualitative research is an interactive process in which the persons studied teach the researcher about their lives.
- The qualitative researcher is an integral part of the data; without the active participation of the researcher, no data exists.
- The study’s design evolves during the research and can be adjusted or changed as it progresses. For the qualitative researcher, there is no single reality. It is subjective and exists only in reference to the observer.
- The theory is data-driven and emerges as part of the research process, evolving from the data as they are collected.
Limitations of Qualitative Research
- Because of the time and costs involved, qualitative designs do not generally draw samples from large-scale data sets.
- The problem of adequate validity or reliability is a major criticism. Because of the subjective nature of qualitative data and its origin in single contexts, it is difficult to apply conventional standards of reliability and validity. For example, because of the central role played by the researcher in the generation of data, it is not possible to replicate qualitative studies.
- Also, contexts, situations, events, conditions, and interactions cannot be replicated to any extent, nor can generalizations be made to a wider context than the one studied with confidence.
- The time required for data collection, analysis, and interpretation is lengthy. Analysis of qualitative data is difficult, and expert knowledge of an area is necessary to interpret qualitative data. Great care must be taken when doing so, for example, looking for mental illness symptoms.
Advantages of Qualitative Research
- Because of close researcher involvement, the researcher gains an insider’s view of the field. This allows the researcher to find issues that are often missed (such as subtleties and complexities) by the scientific, more positivistic inquiries.
- Qualitative descriptions can be important in suggesting possible relationships, causes, effects, and dynamic processes.
- Qualitative analysis allows for ambiguities/contradictions in the data, which reflect social reality (Denscombe, 2010).
- Qualitative research uses a descriptive, narrative style; this research might be of particular benefit to the practitioner as she or he could turn to qualitative reports to examine forms of knowledge that might otherwise be unavailable, thereby gaining new insight.
What Is Quantitative Research?
Quantitative research involves the process of objectively collecting and analyzing numerical data to describe, predict, or control variables of interest.
The goals of quantitative research are to test causal relationships between variables , make predictions, and generalize results to wider populations.
Quantitative researchers aim to establish general laws of behavior and phenomenon across different settings/contexts. Research is used to test a theory and ultimately support or reject it.
Quantitative Methods
Experiments typically yield quantitative data, as they are concerned with measuring things. However, other research methods, such as controlled observations and questionnaires , can produce both quantitative information.
For example, a rating scale or closed questions on a questionnaire would generate quantitative data as these produce either numerical data or data that can be put into categories (e.g., “yes,” “no” answers).
Experimental methods limit how research participants react to and express appropriate social behavior.
Findings are, therefore, likely to be context-bound and simply a reflection of the assumptions that the researcher brings to the investigation.
There are numerous examples of quantitative data in psychological research, including mental health. Here are a few examples:
Another example is the Experience in Close Relationships Scale (ECR), a self-report questionnaire widely used to assess adult attachment styles .
The ECR provides quantitative data that can be used to assess attachment styles and predict relationship outcomes.
Neuroimaging data : Neuroimaging techniques, such as MRI and fMRI, provide quantitative data on brain structure and function.
This data can be analyzed to identify brain regions involved in specific mental processes or disorders.
For example, the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) is a clinician-administered questionnaire widely used to assess the severity of depressive symptoms in individuals.
The BDI consists of 21 questions, each scored on a scale of 0 to 3, with higher scores indicating more severe depressive symptoms.
Quantitative Data Analysis
Statistics help us turn quantitative data into useful information to help with decision-making. We can use statistics to summarize our data, describing patterns, relationships, and connections. Statistics can be descriptive or inferential.
Descriptive statistics help us to summarize our data. In contrast, inferential statistics are used to identify statistically significant differences between groups of data (such as intervention and control groups in a randomized control study).
- Quantitative researchers try to control extraneous variables by conducting their studies in the lab.
- The research aims for objectivity (i.e., without bias) and is separated from the data.
- The design of the study is determined before it begins.
- For the quantitative researcher, the reality is objective, exists separately from the researcher, and can be seen by anyone.
- Research is used to test a theory and ultimately support or reject it.
Limitations of Quantitative Research
- Context: Quantitative experiments do not take place in natural settings. In addition, they do not allow participants to explain their choices or the meaning of the questions they may have for those participants (Carr, 1994).
- Researcher expertise: Poor knowledge of the application of statistical analysis may negatively affect analysis and subsequent interpretation (Black, 1999).
- Variability of data quantity: Large sample sizes are needed for more accurate analysis. Small-scale quantitative studies may be less reliable because of the low quantity of data (Denscombe, 2010). This also affects the ability to generalize study findings to wider populations.
- Confirmation bias: The researcher might miss observing phenomena because of focus on theory or hypothesis testing rather than on the theory of hypothesis generation.
Advantages of Quantitative Research
- Scientific objectivity: Quantitative data can be interpreted with statistical analysis, and since statistics are based on the principles of mathematics, the quantitative approach is viewed as scientifically objective and rational (Carr, 1994; Denscombe, 2010).
- Useful for testing and validating already constructed theories.
- Rapid analysis: Sophisticated software removes much of the need for prolonged data analysis, especially with large volumes of data involved (Antonius, 2003).
- Replication: Quantitative data is based on measured values and can be checked by others because numerical data is less open to ambiguities of interpretation.
- Hypotheses can also be tested because of statistical analysis (Antonius, 2003).
Antonius, R. (2003). Interpreting quantitative data with SPSS . Sage.
Black, T. R. (1999). Doing quantitative research in the social sciences: An integrated approach to research design, measurement and statistics . Sage.
Braun, V. & Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology . Qualitative Research in Psychology , 3, 77–101.
Carr, L. T. (1994). The strengths and weaknesses of quantitative and qualitative research : what method for nursing? Journal of advanced nursing, 20(4) , 716-721.
Denscombe, M. (2010). The Good Research Guide: for small-scale social research. McGraw Hill.
Denzin, N., & Lincoln. Y. (1994). Handbook of Qualitative Research. Thousand Oaks, CA, US: Sage Publications Inc.
Glaser, B. G., Strauss, A. L., & Strutzel, E. (1968). The discovery of grounded theory; strategies for qualitative research. Nursing research, 17(4) , 364.
Minichiello, V. (1990). In-Depth Interviewing: Researching People. Longman Cheshire.
Punch, K. (1998). Introduction to Social Research: Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches. London: Sage
Further Information
- Designing qualitative research
- Methods of data collection and analysis
- Introduction to quantitative and qualitative research
- Checklists for improving rigour in qualitative research: a case of the tail wagging the dog?
- Qualitative research in health care: Analysing qualitative data
- Qualitative data analysis: the framework approach
- Using the framework method for the analysis of
- Qualitative data in multi-disciplinary health research
- Content Analysis
- Grounded Theory
- Thematic Analysis
- Open access
- Published: 01 May 2024
Hospital performance evaluation indicators: a scoping review
- Shirin Alsadat Hadian ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1443-1990 1 ,
- Reza Rezayatmand ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9907-3597 2 ,
- Nasrin Shaarbafchizadeh ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7104-2214 3 ,
- Saeedeh Ketabi ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6778-5645 4 &
- Ahmad Reza Pourghaderi ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2682-2160 5
BMC Health Services Research volume 24 , Article number: 561 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Hospitals are the biggest consumers of health system budgets and hence measuring hospital performance by quantitative or qualitative accessible and reliable indicators is crucial. This review aimed to categorize and present a set of indicators for evaluating overall hospital performance.
We conducted a literature search across three databases, i.e., PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science, using possible keyword combinations. We included studies that explored hospital performance evaluation indicators from different dimensions.
We included 91 English language studies published in the past 10 years. In total, 1161 indicators were extracted from the included studies. We classified the extracted indicators into 3 categories, 14 subcategories, 21 performance dimensions, and 110 main indicators. Finally, we presented a comprehensive set of indicators with regard to different performance dimensions and classified them based on what they indicate in the production process, i.e., input, process, output, outcome and impact.
The findings provide a comprehensive set of indicators at different levels that can be used for hospital performance evaluation. Future studies can be conducted to validate and apply these indicators in different contexts. It seems that, depending on the specific conditions of each country, an appropriate set of indicators can be selected from this comprehensive list of indicators for use in the performance evaluation of hospitals in different settings.
Peer Review reports
Healthcare is complex [ 1 ] and a key sector [ 2 ] that is now globally faced with problems of rising costs, lack of service efficiency, competition, and equity as well as responsiveness to users [ 3 ]. One estimate by the WHO has shown a yearly waste of approximately 20–40% of total healthcare resources because of inefficiency [ 4 ]. European countries have spent on average 9.6% of their gross domestic product (GDP) on healthcare in 2017 and 9.92% in 2019. Germany, France, and Sweden reported the highest healthcare expenditures in Europe in 2018 (between 10.9% and 11.5% of GDP) [ 5 ]. In the U.S., healthcare spending consumes 18% of the GDP, which is likely to eclipse $6 trillion by 2027 [ 6 ].
Hospitals, as the biggest consumers of health system budgets [ 7 ], are the major part of the health system [ 8 ]. In many countries 50–80% of the health sector budget is dedicated to hospitals [ 8 , 9 ]. As a result, hospital performance analysis is becoming a routine task for every hospital manager. On the one hand, hospital managers worldwide are faced with difficult decisions regarding cost reduction, increasing service efficiency, and equity [ 10 ]. On the other hand, measuring hospital efficiency is an issue of interest among researchers because patients demand high-quality care at lower expenses [ 11 ].
To address the above mentioned need to measure hospital performance, implementing an appropriate hospital performance evaluation system is crucial in any hospital. In doing so, hospital administrators use various tools to analyse and monitor hospital activities [ 1 ], which need well-defined objectives, standards and quantitative indicators [ 12 ]. The latter are used to evaluate care provided to patients both quantitatively and qualitatively and are often related to input, output, processes, and outcomes. These indicators can be used for continuous quality improvement by monitoring, benchmarking, and prioritizing activities [ 13 ]. These parameters are developed to improve health outcomes and to provide comparative information for monitoring and managing and formulating policy objectives within and across health services [ 12 ]. Studies thus far have used their own set of indicators while evaluating hospital performance, which could be context dependent. In addition, those studies have mostly used a limited set of indicators that focus on few dimensions (2–6 dimensions) of hospital performance [ 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 ].
Therefore, comprehensive knowledge of potential indicators that can be used for hospital performance evaluation is necessary. It would help choose appropriate indicators when evaluating hospital performance in different contexts. It would also help researchers extend the range of analysis to evaluate performance from a wider perspective by considering more dimensions of performance. Although performance is a very commonly used term, it has several definitions [ 19 , 20 ], yet, it is often misunderstood [ 21 ]. Therefore, some researchers have expressed confusion about the related terms and considered them interchangeable. These terms are effectiveness, efficiency, productivity, quality, flexibility, creativity, sustainability, evaluation, and piloting [ 21 , 22 , 23 ]. Thus, this scoping review aimed to categorize and present a comprehensive set of indicators that can be used as a suitable set for hospital performance evaluation at any needed level of analysis, i.e., clinical, para-clinical, logistical, or departmental, and relate those indicators to the appropriate performance dimensions. The uniqueness of this paper is that it provides its readers with a comprehensive collection of indicators that have been used in different performance analysis studies.
Materials and methods
We conducted a scoping review of a body of literature. The scoping review can be of particular use when the topic has not yet been extensively reviewed or has a complex or heterogeneous nature. This type of review is commonly undertaken to examine the extent, range, and nature of research activity in a topic area; determine the value and potential scope and cost of undertaking a full systematic review; summarize and disseminate research findings; and identify research gaps in the existing literature. As a scoping review provides a rigorous and transparent method for mapping areas of research, it can be used as a standalone project or as a preliminary step to a systematic review [ 24 ]. While a systematic review (qualitative or quantitative) usually addresses a narrow topic/scope and is a method for integrating or comparing findings from previous studies [ 25 ].
In our study, we used the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) Checklist following the methods outlined by Arksey and O’Malley [ 26 ] and Tricco [ 27 ]. A systematic search for published and English-language literature on hospital performance evaluation models was conducted, using three databases, i.e., PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science, from 2013 to January 2023. Initially, the identified keywords were refined and validated by a team of experts. Then, a combination of vocabularies was identified by the authors through a brainstorming process. The search strategy was formulated using Boolean operators. The title and abstract of the formulas were searched in the online databases. The search query for each database is presented in Table 1 .
In the screening process, relevant references related to hospital performance evaluation were screened and abstracted into researcher-developed Microsoft® Excel forms by dual independent reviewers and conflicting information was provided by other reviewers.
The inclusion criteria were as follows: focused only on the hospital setting, available full text and written in English. We excluded studies that focused on health organization indicators, not specifically on hospital indicators; articles without appropriate data (only focused on models and not indicators; or qualitative checklist questionnaires); and articles that focused only on clinical or disease-related indicators, not hospital performance dimensions, and provided very general items as indicators, not the domains of the indicators themselves. Then, a PRISMA-ScR Checklist was used to improve transparency in our review [ 28 ].
To extract the data, researcher-developed Microsoft® Excel forms (data tables) were designed. The following data were subsequently extracted into Microsoft®Excel for synthesis and evaluation: title, author, article year, country, indicator category, study environment (number of hospitals studied), study time frame, indicator name, number of indicators, indicator level (hospital level, department level), evaluation perspective (performance, productivity, efficiency, effectiveness, quality, cost, safety, satisfaction, etc. ) , study type (quantitative or qualitative), indicator subtype (input (structure), process, output (result), outcome and impact), and other explanations. To create a descriptive summary of the results that address the objectives of this scoping review, numerical summarization was also used.
The purpose of creating the main category and the evaluation perspective section was to develop them and create new categories, which focused on the type of indicators related to the performance term. For example, in the “Category” section, the names of the departments or wards of the hospital (such as hospital laboratories, pharmacies, clinical departments, and warehouses) and in the “Evaluation perspective” section, various terms related to the evaluation of hospital performance were extracted. These two types were used after extracting their information under the title “performance dimension”.
The indicators’ levels were collected to determine the level of performance evaluation with the relevant index. Some indicators were used to evaluate the performance of the entire hospital, some were used to evaluate the performance of hospital departments, and some were used to evaluate the performance at the level of a specific project. For example, several indicators (such as bed occupancy ratio, length of stay, and waiting time) were used to evaluate the performance of the entire hospital, and other indicators (such as laboratory department indicators, energy consumption indicators, and neonatal department indicators) were used only to measure the performance of specific departments. This sections were used under the title “category”. The “category” and “indicator’s name” sections were defined according to the results of the “subcategory” section.
The subtypes of indicators (input (structure), process, output(result), outcome and impact) were defined based on the chain model, and each of the selected indicators was linked to it (Appendix 1 ). As a result of the chain model, inputs were used to carry out activities, activities led to the delivery of services or products (outputs). The outputs started to bring about change (outcomes), and eventually, this (hopefully) contributed to the impact [ 29 ]. The classification of the set of input, process, output, outcome and impact indicators was such that readers could access these categories if necessary according to their chosen evaluation models. The term was used under the title “Indicators by types”.
The type of study was considered quantitative or qualitative for determining whether an indicator was able to perform calculations. In this way, readers can choose articles that use quantitative or qualitative indicators to evaluate hospital performance.
We included 91 full-text studies (out of 7475) in English published between 2013 and January 2023 (Fig. 1 ), approximately 40% of which were published between 2020 and 2023. More than 20% of the retrieved studies were conducted in Iran and USA.
Study selection and data abstraction
Study characteristic
As shown in Table 2 , in 85% of the reviewed studies, a number of hospitals (1 to 3828 hospitals, 13,221 hospitals in total) were evaluated. More than 90% of the studies used a quantitative approach. In more than 70% of the studies, hospital evaluation occurred at the department level, which can also be divided into three levels: administrative, clinical ward, and paramedical department. In addition, the administrative departments consist of 13 departments, including financial management [ 48 , 55 , 61 , 67 , 68 , 80 , 83 , 109 , 113 ], supply chain management and warehouse [ 15 , 43 , 84 ], value-based purchasing [ 33 , 85 ], human resource management [ 97 , 101 ], medical equipment [ 32 , 87 ], health information management department [ 90 ], information systems [ 106 ], nutritional assessment [ 93 ], energy management [ 30 , 45 , 92 ], facility management [ 52 , 53 ], building sustainability and resilience [ 35 ], research activities [ 44 ], and education [ 107 ].
The clinical wards consisted of 8 wards, namely, emergency departments (EDs) [ 16 , 39 , 56 , 57 , 69 , 70 , 89 ], surgery departments [ 58 , 62 , 63 , 91 , 102 ], intensive care units (ICUs) [ 47 , 64 , 65 ], operating rooms (ORs) [ 38 , 88 , 108 ], surgical intensive care units (SICUs) [ 111 ], obstetrics and gynecology department [ 59 ], neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) [ 74 , 103 ] and quality of care [ 18 , 31 , 40 , 50 , 72 , 92 , 95 , 112 ] indicators. The paramedical departments consisted of 3 departments, pharmacy [ 60 , 76 , 98 ], laboratory and blood bank [ 37 , 42 , 43 , 49 ], and outpatient assessment [ 86 ] indicators.
With regard to data categorization, firstly, a total of 1204 indicators in 91 studies were extracted and after detailed examination, 43 indices (such as hospital ownership, level of care, admission process, and personal discipline) were removed due to their generality and impossibility of calculation in the hospital environment. Then, 1161 performance indicators were entered in this research and were categorized based on the performance criteria (more details about the indicators can be found in Appendix 1 ). Secondly, 145 functional dimensions, including divisions based on different departments and units of the hospital, were defined according to several focus group discussions with 5 health experts. Then, re-categorization and functional summarization were performed, after which 21 performance dimensions were finalized.
As shown in Table 4 , the 21 performance dimensions were divided into three parts: category, subcategory, and related indicators. Additionally, according to the hospital levels, there were three categories: ‘organizational management’, ‘clinical management’, and ‘administrative management’. Then, according to the type of indicators, fifteen subcategories were defined for the 110 selected main indicators.
Performance dimensions
The ‘productivity’ dimension focuses on indicators reflecting the macro-performance of the hospital, considering that this index is more effective and efficient. The ‘efficiency’ dimension focuses on general performance indicators for the optimal use of resources to create optimal output in the hospital. The ‘effectiveness’ dimension is a general performance indicator with an outcome view. The ‘speed’ dimension focuses on the indicators that show attention to the service delivery time and the speed of the procedures. The ‘development’ dimension focuses on matters related to employees’ and students’ training and related training courses. In terms of ‘safety’ dimension, there were issues related to patient safety, unwanted and harmful events, and hospital infections.
The “quality of work life” dimension emphasizes matters related to personnel volume and work conditions. The ‘quality’ dimension is related to the quality of service provided in different parts of the hospital and possible complications in improving the quality of services. The ‘satisfaction’ dimension focuses on the satisfaction of patients, employees, and their complaints. The ‘innovation’ dimension relates to the research process and its output. The ‘appropriateness’ dimension involves proper service from clinical departments, pharmaceutical services, and patient treatment. The ‘evaluation’ dimension focuses on the indicators related to the assessment scores of the para-clinical departments of the hospital.
The ‘profitability’ dimension focuses on the overall output indicators for income and profitability. The ‘cost’ dimension focuses on indicators related to general expenditures and the average cost per bed and patient and budgeting. The ‘economy’ dimension is related to financial rates and their indicators. The ‘coherence’ dimension emphasizes the indicators related to the continuity of the service delivery process. The ‘patient-centeredness’ dimension focuses on the indicators related to the patient’s experience of the facility, environment, treatment processes, communications, and relevant support for the patient. The ‘equity’ dimension studies indicators related to social and financial justice and life expectancy. The ‘relationship’ dimension evaluates the process of consultations and discussions required during the patients’ care provided by the treatment team. The ‘sustainability’ dimension focuses on indicators related to energy standards. The ‘flexibility’ dimension focuses on the hospital’s response to the crisis.
According to Table 4 , most studies focused on ‘efficiency’, ‘productivity’, ‘safety’ and ‘effectiveness’ as performance dimensions in 54, 53, 38 and 37 studies, respectively (40–70% of studies). In the ‘efficiency’ subcategory, resource management, supportive unit assessment, and human resource management indicators were the first to third most common indicators used in 26, 23 and 22 studies, respectively (approximately 25% of the studies).
In addition, for the ‘efficiency’ dimension, ‘medical staff numbers’, ‘emergency department bed numbers’, and ‘nonmedical staff numbers’ were reported in 16, 13, and 11 studies, respectively (between 20 and 30% of the studies). For the ‘productivity’ subcategory, ‘bed utilization rate’ and ‘service delivery and treatment’ were reported in 50% and 20% of the studies, respectively (46 and 19 out of 91).
Additionally, for the ‘productivity’ dimension, the ‘length of stay’ indicator was used more than others and reported in approximately 80% of the studies (43 out of 53), followed by the ‘bed occupancy rate’ in approximately 40% of the studies (21 out of 53). The ‘bed turnover ratio’ and ‘hospitalization rate’ were also reported in 12 studies. Furthermore, for ‘safety’ dimensions, all indicators were in the ‘patient safety’ subcategory, which has been reported in 38 studies, and ‘complications’, ‘accidents or adverse events’, and ‘incidents or errors rates’ were the most concentrated indicators by researchers in 13, 12, and 11 studies, respectively. The performance dimension of ‘effectiveness’ was presented in 37 studies (40%), with only two indicators, ‘mortality rate’ in 29 studies and ‘readmission rate’ in 23 studies.
Performance categories
Considering the three categories shown in Table 4 , ‘organizational management’ indicators were more commonly used among the other two categories (‘clinical’ and ‘administrative’) and were present in more than 85% of the studies (78 out of 91). Two categories, ‘clinical management’ and ‘administrative management’, were reported in 62 and 51 studies, respectively.
Performance subcategories
Considering the 14 subcategories shown in Table 4 , both the ‘bed utilization rate’ and ‘patient safety’ indicators were mentioned in 46 studies and were more common among the other subcategories. The second most common indicator of the ‘financial management’ subcategory was reported in 38 studies. At the third level, both the ‘human resource management’ and ‘time management’ indicators were presented in 31 studies. The ‘paramedical’ subcategory indicators were presented in less than 10% of the studies [ 60 , 96 , 97 , 98 , 106 , 113 ].
Performance indicators
According to the indicator columns in Table 3 , the most used indicators in reviewed studies were the length of stay, mortality rate, and readmission rate in 47%, 32%, and 25% of studies, respectively. Bed occupancy rate and non-personnel costs were reported in 23% of studies. Additionally, among the 110 indicators, 16 indicators, namely, the lab cancellation rate, exam-physician ratios, number of coded diagnoses, number of medical records, laboratory sample/report intervals, medical information request time, safety standards in the archives, nutritional risk screening, imaging quality control failures, errors in medical reports, average impact factor, nutritional measures, laboratory scoring, imaging inspection, discharge process and emergency response rate, were reported in less than 1% of the studies.
The classification of the indicators in Table 4 was performed based on the chain model, which included the input, process, output, outcome and impact. The assignment of the indicators to each category was performed according to the experts’ opinions. For instance, the number of publications by academic member of an academic hospital and the average impact factor of those publications were considered outcome indicators. As depicted in the Table 4 , most studies (80%) focused more on output indicators. Additionally, fifteen studies focused on introducing and extracting some of the input, process, output, outcome and impact indicators; among those, only one study [ 96 ] has examined the input, process, output and impact indicators simultaneously.
Additionally, in approximately 42% (36 out of 91) of the studies, the indicators’ definitions, formulas, or descriptions have been illustrated, while less than 10% of the studies have defined measuring units, standard or benchmark units for all studied indicators [ 15 , 43 , 45 , 51 , 52 , 57 , 67 ].
Overall, nine studies related to hospital performance evaluation were conducted using systematic review methodologies (five systematic reviews [ 16 , 29 , 30 , 56 , 113 ], two literature reviews [ 79 , 80 ], one narrative review [ 98 ] and one brief review [ 92 ]). Most of these studies focused on extracting performance indicators from one or more hospital departments (e.g., the emergency department) [ 16 , 56 ], hospital laboratory and radiology information systems [ 106 ], supply chain performance [ 29 ], resources and financial results and activity [ 113 ], hospital water consumption [ 30 ], and the pharmaceutical sector [ 98 ]. Other reviews included a three-step process to review, evaluate and rank these hospital indicators in a systematic approach [ 16 ], or to evaluate performance indicator models to create an interactive network and visualize the causal relationships between performance indicators [ 79 ]; moreover, some have focused on the importance of indicators to ensure adequate coverage of the relevant areas of health care services to be evaluated [ 92 ].
Only one scoping review aimed to identify current assessments of hospital performance and compared quality measures from each method in the context of the six qualitative domains of STEEEP (safety, timeliness, effectiveness, efficiency, equity, and patient-centeredness) of the Institute of Medicine (IOM) in accordance with Donabedian’s framework and formulating policy recommendations [ 115 ].
In addition, 21 studies divided performance indicators into 2 to 6 dimensions of performance. Also, the reviewed studies included 2–40 indicators in zero [ 29 , 30 , 98 ] to 6 domains [ 34 ]. Moreover, none of the studies have tried to comprehensively summarize and categorize the performance indicators in several categories, focusing on all the indicators reflecting the performance of the entire hospital organization, or the indicators of administrative units or clinical departments.
In this scoping review, a unique set of hospital performance evaluation indicators related to the various performance dimensions was categorized from 91 studies over the past ten years.
Similarly, in a study, 19 performance dimensions, 32 sub-dimensions, and 138 indicators were extracted from only six studies. Those dimensions were described by all studies included in the review, but only three studies specified the relevant indicators, and the list provided for all possible indicators was not comprehensive. Also, despite current review, there was no classification of indicators based on the hospital levels: managerial, clinical, or organizational levels [ 116 ]. Another study has similarly investigated the performance evaluation indicators of the hospital in such a way that among 42 studies, 111 indicators were presented in the four categories: input, output, outcome, and impact. But, there was no classification of indicators based on performance dimensions and hospital levels [ 117 ].
In this study, the importance of categorized indicators, for the first time to our knowledge, was determined based on their frequency of use in the published literature (Appendix 2 ). The ‘Organizational management’ indicators were the most common compared with the other two categories (‘clinical’ and ‘administrative’). It could be because of the fact that the indicators such as ‘bed occupancy rate’, ‘average length of stay’, ‘mortality rate’, ‘hospital infection rate’, and ‘patient safety’ are easier to be registered in hospital software compared to other indicators, and also they better reflect the overall performance of hospital. Thus, researchers are more interested in using these indicators.
Considering 14 subcategories, indicators related to three subcategories i.e. bed utilization, patient safety and financial management are the most frequent used indicators for hospital performance evaluation. It reflects the need of hospital managers to increase the profitability of hospital in one hand, and to control cost on the other hand. As a results, researchers have paid special attention to ‘cost income’, ‘profitability’, ‘economic’, etc., as indicators for evaluating hospital performance.
When considering indicators by type, more studies have focused on output indicators, while input indicators were the least common used. This might be because of the fact that at hospital level, it is difficult for managers to change those inputs such as ‘beds’, ‘human resources’, ‘equipment and facilities’. In addition, due to the complexity of interdepartmental relationships in hospitals, process indicators seemed to provide more variety for analysis than input indicators, so they were more often used. As mentioned above, output indicators were the most used indicators for hospital performance evaluation due to their ease of calculation and interpretation.
The main purpose of this paper was to identify a comprehensive set of indicators that can be used to evaluate hospital performance in various hospital settings by being distilled into a smaller and more related set of indicators for every hospital or department setting. future studies could be designed to validate each set of indicators in any specific context. In addition, they could investigate the relationship between the indicators and their outcomes of interest and the performance dimension each could address. This will enable hospital managers to build their own set of indicators for performance evaluation both at organization or at department level. Also it should be mentioned that.
Although some previous studies have provided definitions for each indicator and determined the standard criteria for them, this was not done in this study because the focus of this study was to provide a collection of all the indicators used in hospital performance evaluation, which resulted in the identification of more than a thousand indicators without limiting to specific country or context. So while preparing a smaller set of indicators, specific conditions of each country, such as the type of health system and its policy, the type of financing system, and the structure of services, should be taken into account to select appropriate indicators.
In addition, although it is important to examine the scope of each article to compare the list of indicators and the relationships between the dimensions of the hospital in terms of size and type and between the number and type of selected indicators, this was considered beyond the scope of this review due to the high number of indicators, which made the abovementioned investigations impossible. Future studies could do that while working with a smaller set of indicators.
This review aimed to categorize and present a comprehensive set of indicators for evaluating overall hospital performance in a systematic way. 1161 hospital performance indicators were drawn from 91 studies over the past ten years. They then were summarized into 110 main indicators, and categorized into three categories: 14 subcategories, and 21 performance dimensions This scoping review also highlighted the most frequent used indicators in performance evaluation studies which could reflect their importance for that purpose. The results of this review help hospital managers to build their own set of indicators for performance evaluation both at organization or at department level with regard to various performance dimensions.
As the results of this review was not limited to any specific country or context, specific conditions of each country, such as the type of health system and its policy, the type of financing system, and the structure of services, should be taken into account while selecting appropriate indicators as a smaller set of indicators for hospital performance evaluation in specific context.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Gross domestic product
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews
Emergency departments
Intensive care unit
Operating room
Surgical intensive care unit
Neonatal intensive care unit
Readmission rate
Quality Control
Medication use evaluation
safety, timeliness, effectiveness, efficiency, equity, and patient-centeredness
Institute of Medicine
Abdullah A, Ahmad S, Athar MA, Rajpoot N, Talib F. Healthcare performance management using integrated FUCOM-MARCOS approach: the case of India. Int J Health Plann Manage. 2022;37(5):2635–68.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Pestana M, Pereira R, Moro S. Improving health care management in hospitals through a productivity dashboard. J Med Syst. 2020;44(4):87.
Amos D. A practical framework for performance measurement of facilities management services in developing countries’ public hospitals. J Facil Manag. 2022;20(5):713–31.
Article Google Scholar
Ahmed S, Hasan MZ, MacLennan M, Dorin F, Ahmed MW, Hasan MM, et al. Measuring the efficiency of health systems in Asia: a data envelopment analysis. BMJ Open. 2019;9(3):e022155.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Mitkova Z, Doneva M, Gerasimov N, Tachkov K, Dimitrova M, Kamusheva M, et al. Analysis of healthcare expenditures in Bulgaria. Healthc. 2022;10(2):274.
Patrinely JR, Walker SH, Glassman GE, Davis MJ, Abu-Ghname A, Khan U, et al. The importance of financial metrics in physician funding and performance evaluation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2021;147:1213–8.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Buathong S, Bangchokdee S. The use of the performance measures in Thai public hospitals. ASIAN Rev Acc. 2017;25(4):472–85.
Google Scholar
Imani A, Alibabayee R, Golestani M, Dalal K. Key indicators affecting hospital efficiency: a systematic review. Front Public Heal. 2022;10:830102.
Mahdiyan S, Dehghani A, Tafti AD, Pakdaman M, Askari R. Hospitals’ efficiency in Iran: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Educ Health Promot. 2019;8(1):126.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Amos D, Musa ZN, Au-Yong CP. Performance measurement of facilities management services in Ghana’s public hospitals. Build Res Inf. 2020;48(2):218–38.
Feibert DC, Andersen B, Jacobsen P. Benchmarking healthcare logistics processes–a comparative case study of Danish and US hospitals. Total Qual Manag Bus Excell. 2019;30(1–2):108–34.
Gün I, Yilmaz F, Şenel IK. Efficiency analysis of health systems in world bank countries. Arch Heal Sci Res. 2021;8(2):147–52.
Breyer JZ, Giacomazzi J, Kuhmmer R, Lima KM, Hammes LS, Ribeiro RA, et al. Hospital quality indicators: a systematic review. Int J Health Care Qual Assur. 2019;32(2):474–87.
Regragui H, Sefiani N, Azzouzi H. Improving performance through measurement: the application of BSC and AHP in healthcare organization. In: Equipe De Recherche, Ingénierie, Innovation Et Management Des Systèmes Industriels, Université Abdelmalek Saadi. Tanger, Morocco: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc; 2018. p. 51–6.
Ghozali MT, Latifah DN, Darayani A. Analysis of Drug Supply Management of the Pharmacy Warehouse of Prof. Dr. Soerojo Mental Health Hospital, Magelang, Indonesia. Clin Schizophr Relat Psychoses. 2021;15:1–6.
Etu EE, Monplaisir L, Aguwa C, Arslanturk S, Masoud S, Markevych I, et al. Identifying indicators influencing emergency department performance during a medical surge: a consensus-based modified fuzzy Delphi approach. PLoS ONE. 2022;17(4 April):e0265101.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Lin C-Y, Shih F-C, Ho Y-H. Applying the balanced scorecard to build service performance measurements of medical institutions: An AHP-DEMATEL approach. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20(2):1022.
Backman C, Vanderloo S, Forster AJ. Measuring and improving quality in university hospitals in Canada: the collaborative for excellence in healthcare quality. Health Policy (New York). 2016;120(9):982–6.
Ghalem Â, Okar C, Chroqui R, Semma E. Performance: A concept to define. In: Performance: A concept to define. LOGISTIQUA 2016; 2016. p. 1–13.
Sonnentag S, Frese M. Performance Concepts and Performance Theory. In 2005. p. 1–25.
Tangen S. Demystifying productivity and performance. Int J Prod Perform Manag. 2005;54:34–46.
Elena-Iuliana I, Maria C. Organizational Performance – A Concept That Self-Seeks To Find Itself. Ann - Econ Ser Constantin Brancusi Univ Fac Econ. 2016;4(4):179–83.
Riratanaphong C, Van der Voordt T, Sarasoja A. Performance Measurement in the context of CREM and FM. In: Per Anker Jensen, Theo Van der Voordt CC, editor. The added value of facilities management: concepts, findings and perspectives. Lyngby Denmark: Polyteknisk Forlag; 2012. p. 1–21.
Pham M, Rajić A, Greig J, Sargeant J, Papadopoulos A, Mcewen S. A scoping review of scoping reviews: advancing the approach and enhancing the consistency. Res Synth Methods. 2014;5:371–85.
Chaney M. So you want to write a narrative review article? J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2021;35:3045–9.
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8(1):19–32.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(7):467–73.
Tricco A, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien K, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(7):467–73.
Dolatabad AH, Mahdiraji HA, Babgohari AZ, Garza-Reyes JA, Ai A. Analyzing the key performance indicators of circular supply chains by hybrid fuzzy cognitive mapping and Fuzzy DEMATEL: evidence from healthcare sector. Environ Dev Sustain. 2022;1–27.
Batista KJM, da Silva SR, Rabbani ERK, Zlatar T. Systematic review of indicators for the assessment of water consumption rates at hospitals. Water Supply. 2020;20(2):373–82.
Beta G, Role D, Berloviene D, Balkena Z. PATIENTS’ SATISFICATION AS THE QUALITY INDICATOR OF NURSING. In: Lubkina V, Kaupuzs A, Znotina D, editors. SOCIETY INTEGRATION EDUCATION, VOL VI: PUBLIC HEALTH AND SPORT, RESEARCHES IN ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT FOR SUSTAINABLE EDUCATION. 2020. p. 79–88.
Bhardwaj P, Joshi NK, Singh P, Suthar P, Joshi V, Jain YK, et al. Competence-based assessment of biomedical equipment management and maintenance system (e-Upkaran) using benefit evaluation framework. CUREUS J Med Sci. 2022;14(10):e30579.
Cheon O, Song M, Mccrea AM, Meier KJ. Health care in America: the relationship between subjective and objective assessments of hospitals. Int PUBLIC Manag J. 2021;24(5):596–622.
Craig KJT, McKillop MM, Huang HT, George J, Punwani ES, Rhee KB. US hospital performance methodologies: a scoping review to identify opportunities for crossing the quality chasm. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020;20(1):640.
Cristiano S, Ulgiati S, Gonella F. Systemic sustainability and resilience assessment of health systems, addressing global societal priorities: Learnings from a top nonprofit hospital in a bioclimatic building in Africa. Renew Sustain ENERGY Rev. 2021;141:110765.
Dadi D, Introna V, Santolamazza A, Salvio M, Martini C, Pastura T, et al. Private Hospital Energy Performance Benchmarking Using Energy Audit Data: An Italian Case Study. Energies. 2022;15(3):1–16.
Dawande PP, Wankhade RS, Akhtar FI, Noman O. Turnaround time: an efficacy measure for medical laboratories. CUREUS J Med Sci. 2022;14(9):e28824.
De Sousa LR, Mazzo A, De Almeida ACF, Tonello C, Lourençone LFM. Evaluation of quality indicators in the management of an operating room at a tertiary-level hospital. Med. 2022;55(1):1–8.
Drynda S, Schindler W, Slagman A, Pollmanns J, Horenkamp-Sonntag D, Schirrmeister W, et al. Evaluation of outcome relevance of quality indicators in the emergency department (ENQuIRE): study protocol for a prospective multicentre cohort study. BMJ Open. 2020;10(9):e038776.
Fekri O, Manukyan E, Klazinga N. Appropriateness, effectiveness and safety of care delivered in Canadian hospitals: a longitudinal assessment on the utility of publicly reported performance trend data between 2012–2013 and 2016–2017. BMJ Open. 2020;10(6):e035447.
Galloa AJO, Ramírez CA. Evaluating Colombian public hospitals productivity during 2004–2015. A luenberger-indicator approach. Rev Gerenc Y Polit Salud. 2020;19:1–23.
Gebreyes M, Sisay A, Tegen D, Asnake A, Wolde M. Evaluation of laboratory performance, associated factors and staff awareness towards achieving turnaround time in tertiary hospitals, Ethiopia. Ethiop J Health Sci. 2020;30(5):767–76.
Gnanaraj J, Kulkarni RG, Sahoo D, Abhishekh B. Assessment of the Key Performance Indicator Proposed by NABH in the Blood Centre of a Tertiary Health Care Hospital in Southern India. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2022;39:308–16.
Horenberg F, Lungu DA, Nuti S. Measuring research in the big data era: the evolution of performance measurement systems in the Italian teaching hospitals. Health Policy (New York). 2020;124(12):1387–94.
Hwang DK, Cho J, Moon J. Feasibility study on energy audit and data driven analysis procedure for building energy efficiency: bench-marking in Korean hospital buildings. Energies. 2019;14(15):3006.
Jaskova D. Efficiency of management, processes in a private hospital. Entrep Sustain Issues. 2021;9(1):436–46.
Jebraeily M, Valizadeh MA, Rahimi B, Saeidi S. The development of a clinical dashboard for monitoring of key performance indicators in ICU. J Iran Med Counc. 2022;5(2):308–17.
Kang Y, Kim M, Jung K. The equity of health care spending in South Korea: testing the impact of publicness. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(5):1775.
Abou Tarieh RR, Zayyat R, Naoufal RN, Samaha HR. A case study exploring the impact of JCI standards implementation on staff productivity and motivation at the laboratory and blood bank. Heal Sci Rep. 2022;5(1):e497.
Kadoic N, Simic D, Mesaric J, Redep NB. Measuring quality of public hospitals in croatia using a multi-criteria Approach. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18:19.
Khalilabad T, Amir N, Asl P, Raeissi Shali M, Niknam N. Assessment of clinical and paraclinical departments of military hospitals based on the Pabon Lasso Model. J Educ Health Promot. 2020;9:1–6.
Lai JHK, Hou H, Edwards DJ, Yuen PL. An analytic network process model for hospital facilities management performance evaluation. Facilities. 2022;40(5–6):333–52.
Lai J, Yuen PL. Identification, classification and shortlisting of performance indicators for hospital facilities management. Facilities. 2021;39(1–2):4–18.
Lin CS, Chiu CM, Huang YC, Lang HC, Chen MS. Evaluating the operational efficiency and quality of Tertiary hospitals in Taiwan: the application of the EBITDA Indicator to the DEA Method and TOBIT Regression. Healthcare. 2022;10(1):58.
Matos R, Ferreira D, Pedro MI. Economic analysis of portuguese public hospitals through the construction of quality, efficiency, access, and financial related composite indicators. Soc Indic Res. 2021;157(1):361–92.
Morisod K, Luta X, Marti J, Spycher J, Malebranche M, Bodenmann P. Measuring health equity in emergency care using routinely collected data: a systematic review. Heal Equity. 2021;5(1):801–17.
Nik Hisamuddin R, Tuan Hairulnizam TK. Developing key performance indicators for emergency department of teaching hospitals: a mixed fuzzy Delphi and nominal group technique approach. Malays J Med Sci. 2022;29(2):114–25.
Ramírez Calazans A, Paredes Esteban RM, Grijalva Estrada OB, Ibarra Rodríguez MR. Assessment of quality indicators in pediatric major outpatient surgery. Influence of the COVID-19 pandemic. Cir Pediatr. 2023;36(1):17–21.
PubMed Google Scholar
Shaqura II, Gholami M, Akbari Sari A. Assessment of public hospitals performance in Gaza governorates using the Pabón Lasso Model. Int J Health Plann Manage. 2021;36(4):1223–35.
Al-Jazairi AS, Alnakhli AO. Quantifying clinical pharmacist activities in a tertiary care hospital using key performance indicators. Hosp Pharm. 2021;56(4):321–7.
Aloh HE, Onwujekwe OE, Aloh OG, Nweke CJ. Is bed turnover rate a good metric for hospital scale efficiency? A measure of resource utilization rate for hospitals in Southeast Nigeria. Cost Eff Resour Alloc. 2020;18(1):1–8.
Bari S, Incorvia J, Ahearn O, Dara L, Sharma S, Varallo J, et al. Building safe surgery knowledge and capacity in Cambodia: a mixed-methods evaluation of an innovative training and mentorship intervention. Glob Health Action. 2021;14(1):1998996.
Bari S, Incorvia J, Iverson KR, Bekele A, Garringer K, Ahearn O, et al. Surgical data strengthening in Ethiopia: results of a Kirkpatrick framework evaluation of a data quality intervention. Glob Health Action. 2021;14(1):1–11.
Bastos LSL, Hamacher S, Zampieri FG, Cavalcanti AB, Salluh JIF, Bozza FA. Structure and process associated with the efficiency of intensive care units in low-resource settings: an analysis of the CHECKLIST-ICU trial database. J Crit Care. 2020;59:118–23.
Bastos LSL, Wortel SA, de Keizer NF, Bakhshi-Raiez F, Salluh JIF, Dongelmans DA, et al. Comparing continuous versus categorical measures to assess and benchmark intensive care unit performance. J Crit Care. 2022;70:154063.
Kocisova K, Hass-Symotiuk M, Kludacz-Alessandri M. Use of the dea method to verify the performance model for hospitals. E M Ekon A Manag. 2018;21(4):125–40.
Lee D, Yu S, Yoon SN. Analysis of hospital management based on the characteristics of hospitals: focusing on financial indicators. Glob Bus Financ Rev. 2019;24(3):1–13.
Mirzaei A, Tabibi SJ, Nasiripour AA, Riahi L. Evaluating the feasibility of financial variables of health: A hospital administrator’s viewpoint. Galen Med J. 2016;5(1):25–30.
Middleton S, Gardner G, Gardner A, Considine J, FitzGerald G, Christofis L, et al. Are service and patient indicators different in the presence or absence of nurse practitioners? The EDPRAC cohort study of Australian emergency departments. BMJ Open. 2019;9(7):e024529.
Nobakht S, Jahangiri K, Hajinabi K. Correlation of performance indicators and productivity: A cross sectional study of emergency departments in Tehran, Iran during year 2016. Trauma Mon. 2018;23(5):1–6.
Nuti S, Grillo Ruggieri T, Podetti S. Do university hospitals perform better than general hospitals? A comparative analysis among Italian regions. BMJ Open. 2016;6(8):e011426.
Petrovic GM, Vukovic M, Vranes AJ. The impact of accreditation on health care quality in hospitals. Vojnosanit Pregl. 2018;75(8):803–8.
Pirani N, Zahiri M, Engali KA, Torabipour A. Hospital efficiency measurement before and after health sector evolution plan in Southwest of Iran: a DEA-panel data study. Acta Inf Med. 2018;26(2):106–10.
Profit J, Gould JB, Bennett M, Goldstein BA, Draper D, Phibbs CS, et al. The association of level of care with NICU quality. Pediatrics. 2016;137(3):44–51.
Rahimi H, Bahmaei J, Shojaei P, Kavosi Z, Khavasi M. Developing a strategy map to improve public hospitals performance with balanced scorecard and dematel approach. Shiraz E Med J. 2018;19(7):1–12.
Ahmed S, Hasan MZ, Laokri S, Jannat Z, Ahmed MW, Dorin F, et al. Technical efficiency of public district hospitals in Bangladesh: a data envelopment analysis. COST Eff Resour Alloc. 2019;17:17.
Rahman MH, Tumpa TJ, Ali SM, Paul SK. A grey approach to predicting healthcare performance. Meas J Int Meas Confed. 2019;134:307–25.
Sajadi HS, Sajadi ZS, Sajadi FA, Hadi M, Zahmatkesh M. The comparison of hospitals’ performance indicators before and after the Iran’s hospital care transformations plan. J Educ Health Promot. 2017;6:89.
Si S-L, You X-Y, Liu H-C, Huang J. Identifying key performance indicators for holistic hospital management with a modified DEMATEL approach. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017;14(8): 934.
Váchová L, Hajdíková T. Evaluation of Czech hospitals performance using MCDM methods. In: A SI, G WS, C D, editors. Department of exact methods, faculty of management, university of economics, Prague, Jarošovská 1117, Jindřichuv Hradec, vol. 37701. Czech Republic: Newswood Limited; 2017. p. 732–5.
Xenos P, Yfantopoulos J, Nektarios M, Polyzos N, Tinios P, Constantopoulos A. Efficiency and productivity assessment of public hospitals in Greece during the crisis period 2009–2012. Cost Eff Resour Alloc. 2017;15(1):6.
Zhang L, Liu R, Jiang S, Luo G, Liu H-C. Identification of key performance indicators for hospital management using an extended hesitant linguistic DEMATEL Approach. Healthc (Basel Switzerland). 2019;8(1):7.
Aksezer CS. A nonparametric approach for optimal reliability allocation in health services. Int J Qual Reliab Manag. 2016;33(2):284–94.
Cagliano AC, Grimaldi S, Rafele C. Assessing warehouse centralization and outsourcing in the healthcare sector: an Italian case study. In: Department of Management and Production Engineering, Politecnico Di Torino, Corso Duca Degli Abruzzi 24, Torino, 10129. Italy: AIDI - Italian Association of Industrial Operations Professors; 2017. p. 244–50.
Cefalu MS, Elliott MN, Setodji CM, Cleary PD, Hays RD. Hospital quality indicators are not unidimensional: a reanalysis of Lieberthal and Comer. Health Serv Res. 2019;54(2):502–8.
Gao H, Chen H, Feng J, Qin X, Wang X, Liang S, et al. Balanced scorecard-based performance evaluation of Chinese county hospitals in underdeveloped areas. J Int Med Res. 2018;46(5):1947–62.
Gonnelli V, Satta F, Frosini F, Iadanza E. Evidence-based approach to medical equipment maintenance monitoring. In: V HEO, V J, editors. University of Florence, Dept. of Information Engineering. Florence, Italy: Springer; 2017. p. 258–61.
Helkio P, Aantaa R, Virolainen P, Tuominen R. Productivity benchmarks for operative service units. ACTA Anaesthesiol Scand. 2016;60(4):450–6.
Khalifa M, Zabani I. Developing emergency room key performance indicators: What to measure and why should we measure it? J. M, A. H, P. G, A. K, M.S. H, editors. Vol. 226. King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Center, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia: IOS Press BV; 2016. p. 179–182.
Ajami S, Ebadsichani A, Tofighi S, Tavakoli N. Medical records department and balanced scorecard approach. J Educ Health Promot. 2013;2:7.
Bosse G, Mtatifikolo F, Abels W, Strosing C, Breuer J-P, Spies C. Immediate outcome indicators in perioperative care: a controlled intervention study on quality improvement in hospitals in Tanzania. PLoS One. 2013;8(6):e65428.
Hung K-Y, Jerng J-S. Time to have a paradigm shift in health care quality measurement. J Formos Med Assoc. 2014;113(10):673–9.
Jeejeebhoy KN, Keller H, Gramlich L, Allard JP, Laporte M, Duerksen DR, et al. Nutritional assessment: comparison of clinical assessment and objective variables for the prediction of length of hospital stay and readmission. Am J Clin Nutr. 2015;101(5):956–65.
Kittelsen SAC, Anthun KS, Goude F, Huitfeldt IMS, Häkkinen U, Kruse M, et al. Costs and quality at the hospital level in the nordic countries. Heal Econ (United Kingdom). 2015;24:140–63.
Koné Péfoyo AJ, Wodchis WP. Organizational performance impacting patient satisfaction in Ontario hospitals: a multilevel analysis. BMC Res Notes. 2013;6: 509.
Li CH, Yu CH. Performance evaluation of public non-profit hospitals using a BP Artificial neural network: the case of Hubei Province in China. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2013;10(8):3619–33.
Liu K, Jain S, Shi J. Physician performance assessment using a composite quality index. Stat Med. 2013;32(15):2661–80.
Lloyd GF, Bajorek B, Barclay P, Goh S. Narrative review: Status of key performance indicators in contemporary hospital pharmacy practice. J Pharm Pract Res. 2015;45(4):396–403.
Mehrtak M, Yusefzadeh H, Jaafaripooyan E. Pabon Lasso and data envelopment analysis: a complementary approach to hospital performance measurement. Glob J Health Sci. 2014;6(4):107–16.
Mohammadi M, Ziapoor A, Mahboubi M, Faroukhi A, Amani N, Pour FH, et al. Performance evaluation of hospitals under supervision of Kermanshah medical sciences using pabonlasoty diagram of a five-year period (2008–2012). Life Sci J. 2014;11:77–81 ( 1 SPECL. ISSUE) ).
Niaksu O, Zaptorius J. Applying operational research and data mining to performance based medical personnel motivation system. In: Vilnius University, Institute of Mathematics and Informatics. Lithuania: IOS; 2014. p. 63–70.
Córdoba S, Caballero I, Navalón R, Martínez-Sánchez D, Martínez-Morán C, Borbujo J. Analysis of the surgical activity in the dermatology department of Fuenlabrada University Hospital, Madrid, Spain, between 2005 and 2010: determination of the standard operating times. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2013;104(2):141–7.
Profit J, Kowalkowski MA, Zupancic JAF, Pietz K, Richardson P, Draper D, et al. Baby-MONITOR: a composite indicator of NICU Quality. Pediatrics. 2014;134(1):74–82.
Rabar D, Pap N. Evaluation of crotia’s regional hospital effiency: an application of data envelopment analysis . Bacher U, Barkovic D, Dernoscheg KH, LamzaMaronic M, Matic B, Runzheimer B, editors. Interdisciplinary Management Research IX. 2013;9:649–59.
Ramos MCA, da Cruz LP, Kishima VC, Pollara WM, de Lira ACO, Couttolenc BF. Performance evaluation of hospitals that provide care in the public health system, Brazil. Rev Saude Publica. 2015;49:1–9.
Schuers M, Joulakian MB, Griffon N, Pachéco J, Périgard C, Lepage E, et al. In: S IN, de PM AM, editors. Quality indicators from laboratory and radiology information systems. A. G. Volume 216. France: IOS; 2015. pp. 212–6. Department of Biomedical Informatics, Rouen University Hospital, Rouen Cedex, 76031,.
Tabrizi JS, Saadati M, Sadeghi-Bazargani H, Ebadi A, Golzari SEJ. Developing indicators to improve educational governance in hospitals. Clin Gov. 2014;19(2):117–25.
Costa A Jr, aS., Leão LE, Novais MA, Zucchi P. An assessment of the quality indicators of operative and non-operative times in a public university hospital. Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2015;13(4):594–9.
Coyne JS, Helton J. How prepared are US hospitals for the affordable care act? A financial condition analysis of US hospitals in 2011. J Health Care Finance. 2015;41(3).
Davis P, Milne B, Parker K, Hider P, Lay-Yee R, Cumming J, et al. Efficiency, effectiveness, equity (E-3). Evaluating hospital performance in three dimensions. Health Policy (New York). 2013;112(1–2):19–27.
Flatow VH, Ibragimova N, Divino CM, Eshak DSA, Twohig BC, Bassily-Marcus AM, et al. Quality outcomes in the surgical intensive care unit after electronic health record implementation. Appl Clin Inf. 2015;6(4):611–8.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Fonseca JRS, Ramos RMP, Santos AMP, Fonseca APSS. Policy effects on the quality of public health care: evaluating Portuguese public hospitals’ quality through customers’ views. Cent Eur J Public Policy. 2015;9(2):122–40.
Hadji B, Meyer R, Melikeche S, Escalon S, Degoulet P. Assessing the Relationships Between Hospital Resources and Activities: A Systematic Review. J Med Syst. 2014;38(10):1–21.
Hajduová Z, Herbrik G, Beslerová S. Application of DEA in the environment of Slovak hospitals. Invest Manag Financ Innov. 2015;12(4):148–53.
Thomas Craig KJ, McKillop MM, Huang HT, George J, Punwani ES, Rhee KB. U.S. hospital performance methodologies: a scoping review to identify opportunities for crossing the quality chasm. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020;20(1):640.
Carini E, Gabutti I, Frisicale EM, Di Pilla A, Pezzullo AM, de Waure C, et al. Assessing hospital performance indicators. What dimensions? Evidence from an umbrella review. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020;20(1):1038.
Rasi V, Delgoshaee B, Maleki M. Identification of common indicators of hospital performance evaluation models: a scoping review. J Educ Health Promot. 2020;9(1):63.
Xenos P, Yfantopoulos J, Nektarios M, Polyzos N, Tinios P, Constantopoulos A. Efficiency and productivity assessment of public hospitals in Greece during the crisis period 2009–2012. COST Eff Resour Alloc. 2017;15:15.
Shaqura II, Gholami M, Sari AA. Evaluation of performance at Palestinian public hospitals using Pabon Lasso model. Int J Health Plann Manage. 2021;36(3):896–910.
Li J, Seale H, Ray P, Wang Q, Yang P, Li S, et al. E-Health preparedness assessment in the context of an influenza pandemic: a qualitative study in China. BMJ Open. 2013;3(3):e002293.
Huang C-Y, Lai C-H. Effects of internal branding management in a hospital context. Serv Ind J. 2021;41(15–16):985–1006.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the support of the Vice Chancellor for Research of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences.
The present article is part of the result of a doctoral thesis approved by Isfahan University of Medical Sciences with code 55657 (IR.MUI.NUREMA.REC.1401.005), without financial source.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Student Research Committee, School of Management and Medical Information Sciences, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran
Shirin Alsadat Hadian
Health Management and Economics Research Center, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran
Reza Rezayatmand
Hospital Management Research Center, Health Management Research Institute, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
Nasrin Shaarbafchizadeh
Department of Management, Faculty of Administrative Sciences and Economics, University of Isfahan, Isfahan, Iran
Saeedeh Ketabi
School of Public Health and Preventive Medicine, Monash University, Victoria, Australia
Ahmad Reza Pourghaderi
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Shirin Alsadat Hadian and Reza Rezayatmans and Saeedeh Ketabi: Study conceptualization and design. Acquisition of data: Shirin Alsadat Hadian, Reza Rezayatmand. Analysis and interpretation of data: Shirin Alsadat Hadian, Reza Rezayatmand, Nasrin Shaarbafchizadeh, Saeedeh Ketabi. Drafting of the manuscript: Shirin Alsadat Hadian, Reza Rezayatmand. Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: Reza Rezayatmand, Nasrin Shaarbafchizadeh, Saeedeh Ketabi, Ahmad Reza Pourghaderi.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Reza Rezayatmand .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1., supplementary material 2., supplementary material 3., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Hadian, S.A., Rezayatmand, R., Shaarbafchizadeh, N. et al. Hospital performance evaluation indicators: a scoping review. BMC Health Serv Res 24 , 561 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-10940-1
Download citation
Received : 03 January 2024
Accepted : 02 April 2024
Published : 01 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-10940-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Performance evaluation
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Published: 30 April 2024
Developing more useful equity measurements for flood-risk management
- Adam B. Pollack ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6642-0591 1 ,
- Casey Helgeson ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5333-9954 2 , 3 ,
- Carolyn Kousky 4 &
- Klaus Keller ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5451-8687 1
Nature Sustainability ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
- Climate-change policy
- Natural hazards
Decision-makers increasingly invoke equity to motivate, design, implement and evaluate strategies for managing flood risks. Unfortunately, there is little guidance on how analysts can develop measurements that support these tasks. Here we analyse how equity can be defined and measured by surveying 167 peer-reviewed publications that explicitly state an interest in equity in the context of flood-risk management. Our main result is a taxonomy that systematizes how equity has been, and can be, defined and measured in flood-risk research. The taxonomy embodies how equity is a pluralistic and unavoidably ethical concept. Despite this, we find that most quantitative studies fail to motivate or defend critical value judgements on which their findings depend. We also find that studies often include only a single equity measurement. This practice can overlook important trade-offs between competing perspectives on equity. For example, the few studies that employ distinct principles show that conclusions about equity depend on which principle underlies a specific measurement and how that principle is operationalized. We draw on our analysis to suggest practices for developing more useful equity indicators and performing more comprehensive quantitative equity assessments in the broader context of environmental risks.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
111,21 € per year
only 9,27 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Data availability
All data and materials used in the analysis are freely and permanently available via Zenodo 115 . This analysis was tested and confirmed for reproducibility by S. Baboolal on 11 July 2023. If you have any issues reproducing the results, please contact the corresponding author on the GitHub repository.
Code availability
All code used in the analysis are freely and permanently available via Zenodo 115 . This analysis was tested and confirmed for reproducibility by S. Baboolal on 11 July 2023. If you have any issues reproducing the results, please contact the corresponding author on the GitHub repository.
Čapek, S. M. The ‘Environmental Justice’ frame: a conceptual discussion and an application. Soc. Probl. 40 , 5–24 (1993).
Article Google Scholar
Bullard, R. The legacy of American apartheid and environmental racism. J. Civil Rights Econ. Dev. 9 , 445–474 (1994).
Google Scholar
Cutter, S. L. Race, class and environmental justice. Prog. Hum. Geogr. 19 , 111–122 (1995).
Bullard, R. D. Dismantling environmental racism in the USA. Local Environ. 4 , 5–19 (1999).
Brulle, R. J. & Pellow, D. N. Environmental justice: human health and environmental inequalities. Annu. Rev. Public Health 27 , 103–124 (2006).
Schlosberg, D. Defining Environmental Justice: Theories, Movements, and Nature (Oxford Univ. Press, 2007).
Mohai, P., Pellow, D. & Roberts, J. T. Environmental justice. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 34 , 405–430 (2009).
Walker, C. & Burningham, K. Flood risk, vulnerability and environmental justice: evidence and evaluation of inequality in a UK context. Crit. Soc. Policy 31 , 216–240 (2011).
Schlosberg, D. Theorising environmental justice: the expanding sphere of a discourse. Env. Polit. 22 , 37–55 (2013).
Banzhaf, S., Ma, L. & Timmins, C. Environmental justice: the economics of race, place, and pollution. J. Econ. Perspect. 33 , 185–208 (2019).
McDermott, M., Mahanty, S. & Schreckenberg, K. Examining equity: a multidimensional framework for assessing equity in payments for ecosystem services. Environ. Sci. Policy 33 , 416–427 (2013).
Liao, K.-H., Chan, J. K. H. & Huang, Y.-L. Environmental justice and flood prevention: the moral cost of floodwater redistribution. Landsc. Urban Plan. 189 , 36–45 (2019).
Shi, L. et al. Roadmap towards justice in urban climate adaptation research. Nat. Clim. Change 6 , 131–137 (2016).
Siders, A. R. Social justice implications of US managed retreat buyout programs. Clim. Change 152 , 239–257 (2019).
Johnson, C., Penning-Rowsell, E. & Parker, D. Natural and imposed injustices: the challenges in implementing ‘fair’ flood risk management policy in England. Geogr. J. 173 , 374–390 (2007).
Kaminsky, T. An Act to Amend the Environmental Conservation Law, the Public Service Law, the Public Authorities Law, the Labor Law and the Community Risk and Resiliency Act, in Relation to Establishing the New York State Climate Leadership and Community Protection Act Bill Number: S6599 (The New York State Senate, 2019).
Climate and Equitable Jobs Act Bill SB2408 (Illinois General Assembly, 2021).
National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. Communities, Climate Change, and Health Equity—State-Level Implementation: Proceedings of a Workshop—in Brief (The National Academies Press, 2022).
Executive Office of the President. Advancing racial equity and support for underserved communities through the Federal Government. Fed. Regist . 86 , 7009–7013 (2021).
Executive Office of the President. Tackling the climate crisis at home and abroad. Fed. Regist . 86 , 7619–7633 (2021).
Diezmartínez, C. V. & Short Gianotti, A. G. US cities increasingly integrate justice into climate planning and create policy tools for climate justice. Nat. Commun. 13 , 5763 (2022).
Executive Order 45. One NYC Equity Review (The City of New York Office of the Mayor, 2019).
City Agencies’ Strategies for Equity (2022) (Equity NYC, 2022).
Executive Order No. 1-20 (City of Philadelphia Office of the Mayor, 2020).
Racial Equity Action Plans (City of Philadelphia, 2022).
Interim Implementation Guidance for the Justice40 Initiative (M-21-28) (Executive Office of the President, 2021).
FEMA Equity Action Plan (Federal Emergency Management Agency, 2022).
Executive Order 13985 Equity Action Plan (EPA, 2022).
HUD Equity Action Plan (Department of Housing and Urban Development, 2022).
Study to Identify Methods to Assess Equity: Report to the President (Office of Management and Budget, 2021).
Coggins, S. et al. Empirical assessment of equity and justice in climate adaptation literature: a systematic map. Environ. Res. Lett. 16 , 073003 (2021).
Seigerman, C. K. et al. Operationalizing equity for integrated water resources management. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 59 , 281–298 (2022).
Jafino, B. A., Kwakkel, J. H. & Taebi, B. Enabling assessment of distributive justice through models for climate change planning: a review of recent advances and a research agenda. WIREs Clim. Change 12 , e721 (2021).
Jafino, B. A., Kwakkel, J. H. & Klijn, F. Evaluating the distributional fairness of alternative adaptation policies: a case study in Vietnam’s upper Mekong Delta. Clim. Change 173 , 17 (2022).
Kraan, C. M., Hino, M., Niemann, J., Siders, A. R. & Mach, K. J. Promoting equity in retreat through voluntary property buyout programs. J. Environ. Stud. Sci. 11 , 481–492 (2021).
Sovacool, B. K., Newell, P., Carley, S. & Fanzo, J. Equity, technological innovation and sustainable behaviour in a low-carbon future. Nat. Hum. Behav. 6 , 326–337 (2022).
Hino, M. & Nance, E. Five ways to ensure flood-risk research helps the most vulnerable. Nature 595 , 27–29 (2021).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Fletcher, S et al. Equity in water resources planning: a path forward for decision support modelers. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manage. 148 , 02522005 (2022).
Rudge, K. Leveraging critical race theory to produce equitable climate change adaptation. Nat. Clim. Change 13 , 623–631 (2023).
Markanday, A., Galarraga, I. & Markandya, A. A critical review of cost-benefit analysis for climate change adaptation in cities. Clim. Change Econ. 10 , 1950014 (2019).
Eakin, H., Parajuli, J., Yogya, Y., Hernández, B. & Manheim, M. Entry points for addressing justice and politics in urban flood adaptation decision making. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 51 , 1–6 (2021).
Alexander, M., Doorn, N. & Priest, S. Bridging the legitimacy gap—translating theory into practical signposts for legitimate flood risk governance. Reg. Environ. Change 18 , 397–408 (2018).
Elliott, K. C. A Tapestry of Values: An Introduction to Values in Science (Oxford Univ. Press, 2017).
Cash, D. W. & Belloy, P. G. Salience, credibility and legitimacy in a rapidly shifting world of knowledge and action. Sustain. Sci. Pract. Policy 12 , 7376 (2020).
Cash, D. W. et al. Knowledge systems for sustainable development. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 100 , 8086–8091 (2003).
Bistline, J., Budolfson, M. & Francis, B. Deepening transparency about value-laden assumptions in energy and environmental modelling: improving best practices for both modellers and non-modellers. Clim. Policy 21 , 1–15 (2021).
Smith, A. B. U.S. billion-dollar weather and climate disasters, 1980 - present (NCEI accession 0209268). NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information https://doi.org/10.25921/STKW-7W73 (2020).
Historical Flood Risk and Costs (FEMA, 2022).
Building Resilient Infrastructure and Communities FY 2021 Subapplication and Selection Status (FEMA, 2022).
Flood Mitigation Assistance Fiscal Year 2021 Subapplication Status (FEMA, 2022).
Gotham, K. F. Reinforcing inequalities: the impact of the CDBG Program on post-Katrina rebuilding. Hous. Policy Debate 24 , 192–212 (2014).
Vilá, O., Smith, G., Cutts, B., Gyawali, S. & Bhattarai, S. Equity in FEMA hazard mitigation assistance programs: the role of state hazard mitigation officers. Environ. Sci. Policy 136 , 632–641 (2022).
Albert, C. et al. Planning nature-based solutions: principles, steps, and insights. Ambio 50 , 1446–1461 (2021).
Rudge, K. Participatory climate adaptation planning in New York City: analyzing the role of community-based organizations. Urban Clim. 40 , 101018 (2021).
Shi, L. et al. Equitable buyouts? Learning from state, county, and local floodplain management programs. Clim. Change 174 , 29 (2022).
Fussell, E. The long term recovery of New Orleans’ population after Hurricane Katrina. Am. Behav. Sci. 59 , 1231–1245 (2015).
Matthews, V. et al. Differential mental health impact six months after extensive river flooding in rural Australia: a cross-sectional analysis through an equity lens. Front. Public Health 7 , 367 (2019).
Jonkman, S. N., Maaskant, B., Boyd, E. & Levitan, M. L. Loss of life caused by the flooding of New Orleans after Hurricane Katrina: analysis of the relationship between flood characteristics and mortality. Risk Anal. 29 , 676–698 (2009).
Bessette, D. L. et al. Building a values-informed mental model for New Orleans climate risk management. Risk Anal. 37 , 1993–2004 (2017).
Kind, J., Wouter Botzen, W. J. & Aerts, J. C. J. H. Accounting for risk aversion, income distribution and social welfare in cost‐benefit analysis for flood risk management. WIREs Clim. Change 8 , e446 (2017).
Thaler, T. & Hartmann, T. Justice and flood risk management: reflecting on different approaches to distribute and allocate flood risk management in Europe. Nat. Hazards 83 , 129–147 (2016).
Dundon, L. A. & Camp, J. S. Climate justice and home-buyout programs: renters as a forgotten population in managed retreat actions. J. Environ. Stud. Sci . 11 , 420–433 (2021).
Objective 1.3 - Achieve Equitable Outcomes for Those We Serve (FEMA, 2021).
Rittel, H. W. J. & Webber, M. M. Dilemmas in a general theory of planning. Policy Sci. 4 , 155–169 (1973).
Lamont, J. & Favor, C. Distributive justice. The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (ed. Zalta, E. N.) https://plato.stanford.edu/archives/win2017/entries/justice-distributive/ (Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University, 2017).
Environmental Indicators: Better Coordination is Needed to Develop Environmental Indicator Sets that Inform Decisions GAO-05-52 (US Government Accountability Office, 2004).
Key Indicator Systems: Experiences of Other National and Subnational Systems Offer Insights for the United States GAO-11-396 (US Government Accountability Office, 2011).
Main Economic Indicators (OECD, 2023).
Informing Our Nation: Improving How to Understand and Assess the USA’s Position and Progress GAO-05-1 (US Government Accountability Office, 2004).
Alonso, W. & Starr, P. The Politics of Numbers (Russell Sage Foundation, 1987).
WDI - Economy (The World Bank, 2018).
Know Your Risk for Heart Disease (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2023).
Ciullo, A., Kwakkel, J. H., De Bruijn, K. M., Doorn, N. & Klijn, F. Efficient or fair? Operationalizing ethical principles in flood risk management: a case study on the Dutch–German Rhine. Risk Anal. 40 , 1844–1862 (2020).
Dennig, F. Climate change and the re-evaluation of cost-benefit analysis. Clim. Change 151 , 43–54 (2018).
Elliott, J. R., Loughran, K. & Brown, P. L. Divergent residential pathways from flood-prone areas: how neighborhood inequalities are shaping urban climate adaptation. Soc. Probl. 70 , 869–892 (2021).
Tate, E., Strong, A., Kraus, T. & Xiong, H. Flood recovery and property acquisition in Cedar Rapids, Iowa. Nat. Hazards 80 , 2055–2079 (2016).
Fletcher, C. S., Rambaldi, A. N., Lipkin, F. & McAllister, R. R. J. Economic, equitable, and affordable adaptations to protect coastal settlements against storm surge inundation. Reg. Environ. Change. 16 , 1023–1034 (2016).
Apgar, J. M. et al. Identifying opportunities to improve governance of aquatic agricultural systems through participatory action research. Ecol. Soc . https://www.jstor.org/stable/26270053 (2017).
Merz, B., Kreibich, H., Schwarze, R. & Thieken, A. Review article “Assessment of economic flood damage”. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 10 , 1697–1724 (2010).
Pollack, A. B., Sue Wing, I. & Nolte, C. Aggregation bias and its drivers in large scale flood loss estimation: a Massachusetts case study. J. Flood Risk Manage . 15 , e12851 (2022).
de Moel, H., Bouwer, L. M. & Aerts, J. C. J. H. Uncertainty and sensitivity of flood risk calculations for a dike ring in the south of the Netherlands. Sci. Total Environ. 473–474 , 224–234 (2014).
Aerts, J. C. J. H. et al. Climate adaptation. Evaluating flood resilience strategies for coastal megacities. Science 344 , 473–475 (2014).
Kron, W. Flood risk = hazard • values • vulnerability. Water Int. 30 , 58–68 (2005).
Keller, K., Helgeson, C. & Srikrishnan, V. Climate risk management. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci . 49 , 95–116 (2021).
BCA Reference Guide (FEMA, 2009).
Mobini, S., Becker, P., Larsson, R. & Berndtsson, R. Systemic inequity in urban flood exposure and damage compensation. Water 12 , 3152 (2020).
Turnham, J. et al. Housing Recovery on the Gulf Coast, Phase II: Results of Property Owner Survey in Louisiana, Mississippi, and Texas (HUD User, 2011).
Simpson, N. P. et al. A framework for complex climate change risk assessment. One Earth 4 , 489–501 (2021).
Tate, E., Rahman, M. A., Emrich, C. T. & Sampson, C. C. Flood exposure and social vulnerability in the United States. Nat. Hazards 106 , 435–457 (2021).
Emrich, C. T., Tate, E., Larson, S. E. & Zhou, Y. Measuring social equity in flood recovery funding. Environ. Hazards 19 , 228–250 (2020).
Pallathadka, A., Sauer, J., Chang, H. & Grimm, N. B. Urban flood risk and green infrastructure: who is exposed to risk and who benefits from investment? A case study of three U.S. cities. Landsc. Urban Plan. 223 , 104417 (2022).
Zoll, D. Climate adaptation as a racial project: an analysis of color-blind flood resilience efforts in Austin, Texas. Environ. Justice 14 , 288–297 (2021).
Linscott, G., Rishworth, A., King, B. & Hiestand, M. P. Uneven experiences of urban flooding: examining the 2010 Nashville flood. Nat. Hazards 110 , 629–653 (2022).
Bosisio, A. & Moreno-Jiménez, A. Spatially disaggregated assessment of environmental inequalities among vulnerable groups due to urban rainstorm flooding. Appl. Spat. Anal. Policy 15 , 1263–1285 (2022).
Debbage, N. Multiscalar spatial analysis of urban flood risk and environmental justice in the Charlanta megaregion, USA. Anthropocene 28 , 100226 (2019).
Montgomery, M. C. & Chakraborty, J. Assessing the environmental justice consequences of flood risk: a case study in Miami, Florida. Environ. Res. Lett. 10 , 095010 (2015).
Gourevitch, J. D. et al. Spatial targeting of floodplain restoration to equitably mitigate flood risk. Glob. Environ. Change 61 , 102050 (2020).
Frontuto, V., Dalmazzone, S., Salcuni, F. & Pezzoli, A. Risk aversion, inequality and economic evaluation of flood damages: a case study in Ecuador. Sustain. Sci. Pract. Policy 12 , 10068 (2020).
Kind, J., Wouter Botzen, W. J. & Aerts, J. C. J. Social vulnerability in cost-benefit analysis for flood risk management. Environ. Dev. Econ. 25 , 115–134 (2020).
Halsnæs, K., Kaspersen, P. S. & Drews, M. Key drivers and economic consequences of high‑end climate scenarios: uncertainties and risks. Clim. Res. 64 , 85–98 (2015).
Markanday, A., Markandya, A., de Murieta, E. S. & Galarraga, I. Accounting for the effects of employment, equity, and risk aversion in cost–benefit analysis: an application to an adaptation project. J. Benefit Cost Anal. 12 , 313–334 (2021).
Palagi, E., Coronese, M., Lamperti, F. & Roventini, A. Climate change and the nonlinear impact of precipitation anomalies on income inequality. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 119 , e2203595119 (2022).
Chetty, R., Hendren, N., Kline, P., Saez, E. & Turner, N. Is the United States still a land of opportunity? Recent trends in intergenerational mobility. Am. Econ. Rev. 104 , 141–147 (2014).
Bakkensen, L. A. & Barrage, L. Going underwater? Flood risk belief heterogeneity and coastal home price dynamics. Rev. Financ. Stud. 35 , 3666–3709 (2022).
Principles of Environmental Justice (United Church of Christ, 2017).
Noonan, D. S. & Sadiq, A.-A. A. Flood risk management: exploring the impacts of the community rating system program on poverty and income inequality. Risk Anal. 38 , 489–503 (2018).
Huang, X. & Wang, C. Estimates of exposure to the 100-year floods in the conterminous United States using national building footprints. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 50 , 101731 (2020).
Messager, M. L., Ettinger, A. K., Murphy-Williams, M. & Levin, P. S. Fine-scale assessment of inequities in inland flood vulnerability. Appl. Geogr. 133 , 102492 (2021).
Bakkensen, L. A., Fox-Lent, C., Read, L. K. & Linkov, I. Validating resilience and vulnerability indices in the context of natural disasters. Risk Anal. 37 , 982–1004 (2017).
Spielman, S. E. et al. Evaluating social vulnerability indicators: criteria and their application to the Social Vulnerability Index. Nat. Hazards 100 , 417–436 (2020).
Kuhlicke, C. et al. Spinning in circles? A systematic review on the role of theory in social vulnerability, resilience and adaptation research. Glob. Environ. Change 80 , 102672 (2023).
Helgeson, C., Nicholas, R. E., Keller, K., Forest, C. E. & Tuana, N. Attention to values helps shape convergence research. Clim. Change 170 , 17 (2022).
Goal 1 - Instill Equity as a Foundation of Emergency Management (FEMA, 2021).
Anderson, E. S. What is the point of equality? Ethics 109 , 287–337 (1999).
Pollack, A. abpoll/equity_meas: V1.1.0. Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8139215 (2023).
The Pandas Development Team. pandas-dev/pandas: Pandas (v1.5.2). Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7344967 (2022).
Collaborative Data Science (Plotly Technologies, 2015).
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank D. Spiegelman for an annotated bibliography of several key references; C. Bacon, M. Budolfson, C. Cooper, J. Doss-Gollin, A. Giang, B. Kopp, J. Kwakkel, C. Little, R. Nicholas, C. Nolte, Y. Romitti, V. Srikrishnan and N. Tuana for reading an earlier version of the manuscript and offering helpful feedback; A. Alipour, S. Baboolal, P. Hegde, X. Huang, M. May, S. Roth, S. Sreenivasan, N. Tebyanian and H. Ye for conversations and support. We also thank S. Baboolal for confirming code reproducibility and S. Wishbone for invaluable inputs. All authors acknowledge funding from the Megalopolitan Coastal Transformation Hub (MACH) under NSF award ICER-2103754. A.B.P. and K.K. acknowledge funding from Dartmouth College.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Thayer School of Engineering, Dartmouth College, Hanover, NH, USA
Adam B. Pollack & Klaus Keller
Earth and Environmental Systems Institute, Penn State University, State College, PA, USA
Casey Helgeson
Department of Philosophy, Penn State University, State College, PA, USA
Environmental Defense Fund, Philadelphia, PA, USA
Carolyn Kousky
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
A.B.P., C.H., C.K. and K.K. conceptualized the project, developed the methodology, and reviewed and edited the manuscript. A.B.P. conducted investigations, performed formal analysis and administered the project. A.B.P. and C.H. performed visualization. C.K. and K.K. acquired funding and supervised the project. A.B.P. wrote the original draft of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Adam B. Pollack .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information.
Nature Sustainability thanks Danny Otto and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information.
Supplementary Text and Table 1.
Reporting Summary
Rights and permissions.
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Pollack, A.B., Helgeson, C., Kousky, C. et al. Developing more useful equity measurements for flood-risk management. Nat Sustain (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-024-01345-3
Download citation
Received : 15 September 2023
Accepted : 10 April 2024
Published : 30 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-024-01345-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.

sorry, we can ' t preview this file
Data from: an interactive r-based custom quantification program for quantitative analysis of triacylglycerols in bovine milk.
[Note: Title updated 2024-04-23]
Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) experiment data files for bovine milk lipid extracts, standards, and blanks, in mzML format. For use with "An Open-Source R-Based Workflow for Qualitative and Quantitative Lipidomics of Bovine Milk". Chromatography used a fast (10 minute) non-aqueous reversed-phase UHPLC separation. MS analysis was performed on a ThermoScientific QExactive Orbitrap high-resolution, accurate-mass mass spectrometer operated in electrospray ionization (ESI) mode.
Resources in this dataset:
- Resource Title: Bovine Milk Data acquired 06/10/21 File Name: ByrdwellData_Milk_061021.zip Resource Description: Sequence of runs containing 10 Blanks, 30 Standards (6 Levels x 5 replicates), and 48 Bovine Milk extracts, as follows: 2 Cows, 3 feeding periods, 2 days (samples) per feeding period, 4 replicates for 24 samples per cow x 2 cows. 88 runs (separate data files) altogether. All files originally in proprietary .RAW format converted to .mzML. Data obtained on ThermoScientific QExactive orbitrap high-resolution, accurate-mass mass spectrometer.
Agricultural Research Service, Base funds
Data contact name, data contact email, intended use, temporal extent start date, temporal extent end date.
- Not specified
Geographic Coverage
Geographic location - description, iso topic category, national agricultural library thesaurus terms, omb bureau code.
- 005:18 - Agricultural Research Service
OMB Program Code
- 005:040 - National Research
ARS National Program Number
Pending citation, public access level, preferred dataset citation, usage metrics.
- Agricultural, veterinary and food sciences
- Animal production
- Food sciences
- Food chemistry and food sensory science

COMMENTS
Revised on June 22, 2023. Quantitative research is the process of collecting and analyzing numerical data. It can be used to find patterns and averages, make predictions, test causal relationships, and generalize results to wider populations. Quantitative research is the opposite of qualitative research, which involves collecting and analyzing ...
Quantitative research methods are used to observe events that affect a particular group of individuals, which is the sample population. In this type of research, diverse numerical data are collected through various methods and then statistically analyzed to aggregate the data, compare them, or show relationships among the data. ...
Quantitative research is used by social scientists, including communication researchers, to observe phenomena or occurrences affecting individuals. Social scientists are concerned with the study of people. Quantitative research is a way to learn about a particular group of people, known as a sample population.
Quantitative research is used in many different fields, including social sciences, business, engineering, and health sciences. It can be used to investigate a wide range of phenomena, from human behavior and attitudes to physical and biological processes. The purpose of quantitative research is to provide reliable and valid data that can be ...
Quantitative research is a research strategy that focuses on quantifying the collection and analysis of data. It is formed from a deductive approach where emphasis is placed on the testing of theory, shaped by empiricist and positivist philosophies.. Associated with the natural, applied, formal, and social sciences this research strategy promotes the objective empirical investigation of ...
Revised on 10 October 2022. Quantitative research is the process of collecting and analysing numerical data. It can be used to find patterns and averages, make predictions, test causal relationships, and generalise results to wider populations. Quantitative research is the opposite of qualitative research, which involves collecting and ...
Quantitative research methods are concerned with the planning, design, and implementation of strategies to collect and analyze data. Descartes, the seventeenth-century philosopher, suggested that how the results are achieved is often more important than the results themselves, as the journey taken along the research path is a journey of discovery. . High-quality quantitative research is ...
Quantitative methods emphasize objective measurements and the statistical, mathematical, or numerical analysis of data collected through polls, questionnaires, and surveys, or by manipulating pre-existing statistical data using computational techniques.Quantitative research focuses on gathering numerical data and generalizing it across groups of people or to explain a particular phenomenon.
Quantitative research is the methodology which researchers use to test theories about people's attitudes and behaviors based on numerical and statistical evidence. Researchers sample a large number of users (e.g., through surveys) to indirectly obtain measurable, bias-free data about users in relevant situations.
Quantitative method is the collection and analysis of numerical data to answer scientific research questions. Quantitative method is used to summarize, average, find patterns, make predictions, and test causal associations as well as generalizing results to wider populations.
INTRODUCTION. Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses.1,2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results.3,4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the ...
Quantitative research involves analyzing and gathering numerical data to uncover trends, calculate averages, evaluate relationships, and derive overarching insights. It's used in various fields, including the natural and social sciences. Quantitative data analysis employs statistical techniques for processing and interpreting numeric data.
Quantitative research data collection methods. Quantitative research methods can use structured research instruments like: Surveys: A survey is a simple-to-create and easy-to-distribute research method, which helps gather information from large groups of participants quickly. Traditionally, paper-based surveys can now be made online, so costs ...
The focus of this book is on using quantitative research methods to test hypotheses and build theory in political science, public policy and public administration. It is designed for advanced undergraduate courses, or introductory and intermediate graduate-level courses. The first part of the book introduces the scientific method, then covers ...
Mixed-methods research is a flexible approach, where the research design is determined by what we want to find out rather than by any predetermined epistemological position. In mixed-methods research, qualitative or quantitative components can predominate, or both can have equal status. 1.4. Units and variables.
This resource is intended as an easy-to-use guide for anyone who needs some quick and simple advice on quantitative aspects of research in social sciences, covering subjects such as education, sociology, business, nursing. If you area qualitative researcher who needs to venture into the world of numbers, or a student instructed to undertake a quantitative research project despite a hatred for ...
Quantitative research is relatively uncommon in socio-legal studies, which tend, on the whole, to make use of qualitative methodology or take a mixed methodological approach to empirical research. One exception to this was a large-scale randomised telephone survey carried out in the late 1990s in the United Kingdom. This produced some ...
This article describes the basic tenets of quantitative research. The concepts of dependent and independent variables are addressed and the concept of measurement and its associated issues, such as error, reliability and validity, are explored. Experiments and surveys - the principal research designs in quantitative research - are described ...
Quantitative research is a type of research that focuses on collecting and analyzing numerical data to answer research questions. There are two main methods used to conduct quantitative research: 1. Primary Method. There are several methods of primary quantitative research, each with its own strengths and limitations.
Quantitative methods can also be used to test hypotheses by conducting quasi-experimental studies or designing experiments. Independent and Dependent Variables In quantitative research, a variable is something (an intervention technique, a pharmaceutical, a temperature, etc.) that changes.
Quantitative research is often used to test hypotheses, identify patterns, and make predictions. Qualitative research, on the other hand, collects non-numerical data such as words, images, and sounds. The focus is on exploring subjective experiences, opinions, and attitudes, often through observation and interviews. ...
Scientific research: Quantitative data is used extensively in scientific research to test hypotheses and draw conclusions. For example, in biology, researchers might use quantitative data to measure the growth rate of cells or the effectiveness of a drug treatment.
In order to obtain results from the quantitative data collected, some form of analysis must be conducted. The most basic methods of exploring quantitative data are called statistics (Sheard, 2018). T he selected statistical analysis should align with the variables presented in the article and answer the research question(s) guiding the project ...
The term was used under the title "Indicators by types". The type of study was considered quantitative or qualitative for determining whether an indicator was able to perform calculations. In this way, readers can choose articles that use quantitative or qualitative indicators to evaluate hospital performance.
Bidirectional slope is widely used in geological and geomorphological research to describe the variations in terrain relative to a specific horizontal scale, also known as a baseline . It is a quantitative method for characterizing both the rate of change of roughness with spatial scale and the amplitude of roughness . The calculation of ...
Research priorities for quantitative equity assessments. Based on our analysis into how equity has been measured in flood-risk research, we have three main recommendations to advance the ...
[Note: Title updated 2024-04-23]Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) experiment data files for bovine milk lipid extracts, standards, and blanks, in mzML format. For use with "An Open-Source R-Based Workflow for Qualitative and Quantitative Lipidomics of Bovine Milk". Chromatography used a fast (10 minute) non-aqueous reversed-phase UHPLC separation. MS analysis was performed on a ...