- Library databases
- Library website

Evidence-Based Research: Evidence Types
Introduction.
Not all evidence is the same, and appraising the quality of the evidence is part of evidence-based practice research. The hierarchy of evidence is typically represented as a pyramid shape, with the smaller, weaker and more abundant research studies near the base of the pyramid, and systematic reviews and meta-analyses at the top with higher validity but a more limited range of topics.
Several versions of the evidence pyramid have evolved with different interpretations, but they are all comprised of the types of evidence discussed on this page. Walden's Nursing 6052 Essentials of Evidence-Based Practice class currently uses a simplified adaptation of the Johns Hopkins model .
Evidence Levels:
Level I: Experimental, randomized controlled trial (RCT), systematic review RTCs with or without meta-analysis
Level II: Quasi-experimental studies, systematic review of a combination of RCTs and quasi-experimental studies, or quasi-experimental studies only, with or without meta-analysis
Level III: Nonexperimental, systematic review of RCTs, quasi-experimental with/without meta-analysis, qualitative, qualitative systematic review with/without meta-synthesis (see Daly 2007 for a sample qualitative hierarchy)
Level IV : Respected authorities’ opinions, nationally recognized expert committee or consensus panel reports based on scientific evidence
Level V: Literature reviews, quality improvement, program evaluation, financial evaluation, case reports, nationally recognized expert(s) opinion based on experiential evidence
Systematic review
What is a systematic review.
A systematic review is a type of publication that addresses a clinical question by analyzing research that fits certain explicitly-specified criteria. The criteria for inclusion is usually based on research from clinical trials and observational studies. Assessments are done based on stringent guidelines, and the reviews are regularly updated. These are usually considered one of the highest levels of evidence and usually address diagnosis and treatment questions.
Benefits of Systematic Reviews
Systematic reviews refine and reduce large amounts of data and information into one document, effectively summarizing the evidence to support clinical decisions. Since they are typically undertaken by a entire team of experts, they can take months or even years to complete, and must be regularly updated. The teams are usually comprised of content experts, an experienced searcher, a bio-statistician, and a methodologist. The team develops a rigorous protocol to thoroughly locate, identify, extract, and analyze all of the evidence available that addresses their specific clinical question.
As systematic reviews become more frequently published, concern over quality led to the PRISMA Statement to establish a minimum set of items for reporting in systematic reviews and meta-analyses.
Many systematic reviews also contain a meta-analysis.
What is a Meta-Analysis?
Meta-analysis is a particular type of systematic review that focuses on selecting and reviewing quantitative research. Researchers conducting a meta-analysis combine the results of several independent studies and reviews to produce a synthesis where possible. These publications aim to assist in making decisions about a particular therapy.
Benefits of Meta-Analysis
A meta-analysis synthesizes large amounts of data using a statistical examination. This type of analysis provides for some control between studies and generalized application to the population.
To learn how to find systematic reviews in the Walden Library, please see the Levels of Evidence Pyramid page:
- Levels of Evidence Pyramid: Systematic Reviews
Further reading
- Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions *updated 2022
Guidelines & summaries
Practice guidelines.
A practice guideline is a systematically-developed statement addressing common patient health care decisions in specific clinical settings and circumstances. They should be valid, reliable, reproducible, clinically applicable, clear and flexible. Documentation must be included and referenced. Practice guidelines may come from organizations, associations, government entities, and hospitals/health systems.
ECRI Guidelines Trust
Best Evidence Topics
Best evidence topics are sometimes referred to as Best BETs. These topics are developed and supported for situations or setting when the high levels of evidence don't fit or are unavailable. They originated from emergency medicine providers' need to conduct rapid evidence-based clinical decisions.
Critically-Appraised Topics
Critically-appraised topics are a standardized one- to two-page summary of the evidence supporting a clinical question. They include a critique of the literature and statement of relevant results. They can be found online in many repositories.
To learn how to find critically-appraised topics in the Walden Library, please see the Levels of Evidence Pyramid page:
- Levels of Evidence Pyramid: Critically-Appraised Topics
Critically-Appraised Articles
Critically-appraised articles are individual articles by authors that evaluate and synopsize individual research studies. ACP Journal Club is the most well known grouping of titles that include critically appraised articles.
To learn how to find critically-appraised articles in the Walden Library, please see the Levels of Evidence Pyramid page:
- Levels of Evidence Pyramid: Critically-Appraised Articles
Randomized controlled trial
A randomized controlled trial (RCT) is a clinical trial in which participants are randomly assigned to either the treatment group or control group. This random allocation of participants helps to reduce any possible selection bias and makes the RCT a high level of evidence. Having a control group, which receives no treatment or a placebo treatment, to compare the treatment group against allows researchers to observe the potential efficacy of the treatment when other factors remain the same. Randomized controlled trials are quantitative studies and are often the only studies included in systematic reviews.
To learn how to find randomize controlled trials, please see our CINAHL & MEDLINE help pages:
- CINAHL Search Help: Randomized Controlled Trials
- MEDLINE Search Help: Randomized Controlled Trials
Cohort study
A cohort study is an observational longitudinal study that analyzes risk factors and outcomes by following a group (cohort) that share a common characteristic or experience over a period of time.
Cohort studies can be retrospective, looking back over time at data that has already been collected, or can be prospective, following a group forward into the future and collecting data along the way.
While cohort studies are considered a lower level of evidence than randomized controlled trials, they may be the only way to study certain factors ethically. For example, researchers may follow a cohort of people who are tobacco smokers and compare them to a cohort of non-smokers looking for outcomes. That would be an ethical study. It would be highly unethical, however, to design a randomized controlled trial in which one group of participants are forced to smoke in order to compare outcomes.
To learn how to find cohort studies, please see our CINAHL and MEDLINE help pages:
- CINAHL Search Help: Cohort Studies
- MEDLINE Search Help: Cohort Studies
Case-controlled studies
Case-controlled studies are a type of observational study that looks at patients who have the same disease or outcome. The cases are those who have the disease or outcome while the controls do not. This type of study evaluates the relationship between diseases and exposures by retrospectively looking back to investigate what could potentially cause the disease or outcome.
To learn how to find case-controlled studies, please see our CINAHL and MEDLINE help pages:
- CINAHL Search Help: Case Studies
- MEDLINE Search Help: Case Studies
Background information & expert opinion
Background information and expert opinion can be found in textbooks or medical books that provide basic information on a topic. They can be helpful to make sure you understand a topic and are familiar with terms associated with it.
To learn about accessing background information, please see the Levels of Evidence Pyramid page:
- Levels of Evidence Pyramid: Background Information & Expert Opinion
- Previous Page: Levels of Evidence Pyramid
- Next Page: CINAHL Search Help
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
- Open access
- Published: 27 May 2020
How to use and assess qualitative research methods
- Loraine Busetto ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9228-7875 1 ,
- Wolfgang Wick 1 , 2 &
- Christoph Gumbinger 1
Neurological Research and Practice volume 2 , Article number: 14 ( 2020 ) Cite this article
706k Accesses
280 Citations
85 Altmetric
Metrics details
This paper aims to provide an overview of the use and assessment of qualitative research methods in the health sciences. Qualitative research can be defined as the study of the nature of phenomena and is especially appropriate for answering questions of why something is (not) observed, assessing complex multi-component interventions, and focussing on intervention improvement. The most common methods of data collection are document study, (non-) participant observations, semi-structured interviews and focus groups. For data analysis, field-notes and audio-recordings are transcribed into protocols and transcripts, and coded using qualitative data management software. Criteria such as checklists, reflexivity, sampling strategies, piloting, co-coding, member-checking and stakeholder involvement can be used to enhance and assess the quality of the research conducted. Using qualitative in addition to quantitative designs will equip us with better tools to address a greater range of research problems, and to fill in blind spots in current neurological research and practice.
The aim of this paper is to provide an overview of qualitative research methods, including hands-on information on how they can be used, reported and assessed. This article is intended for beginning qualitative researchers in the health sciences as well as experienced quantitative researchers who wish to broaden their understanding of qualitative research.
What is qualitative research?
Qualitative research is defined as “the study of the nature of phenomena”, including “their quality, different manifestations, the context in which they appear or the perspectives from which they can be perceived” , but excluding “their range, frequency and place in an objectively determined chain of cause and effect” [ 1 ]. This formal definition can be complemented with a more pragmatic rule of thumb: qualitative research generally includes data in form of words rather than numbers [ 2 ].
Why conduct qualitative research?
Because some research questions cannot be answered using (only) quantitative methods. For example, one Australian study addressed the issue of why patients from Aboriginal communities often present late or not at all to specialist services offered by tertiary care hospitals. Using qualitative interviews with patients and staff, it found one of the most significant access barriers to be transportation problems, including some towns and communities simply not having a bus service to the hospital [ 3 ]. A quantitative study could have measured the number of patients over time or even looked at possible explanatory factors – but only those previously known or suspected to be of relevance. To discover reasons for observed patterns, especially the invisible or surprising ones, qualitative designs are needed.
While qualitative research is common in other fields, it is still relatively underrepresented in health services research. The latter field is more traditionally rooted in the evidence-based-medicine paradigm, as seen in " research that involves testing the effectiveness of various strategies to achieve changes in clinical practice, preferably applying randomised controlled trial study designs (...) " [ 4 ]. This focus on quantitative research and specifically randomised controlled trials (RCT) is visible in the idea of a hierarchy of research evidence which assumes that some research designs are objectively better than others, and that choosing a "lesser" design is only acceptable when the better ones are not practically or ethically feasible [ 5 , 6 ]. Others, however, argue that an objective hierarchy does not exist, and that, instead, the research design and methods should be chosen to fit the specific research question at hand – "questions before methods" [ 2 , 7 , 8 , 9 ]. This means that even when an RCT is possible, some research problems require a different design that is better suited to addressing them. Arguing in JAMA, Berwick uses the example of rapid response teams in hospitals, which he describes as " a complex, multicomponent intervention – essentially a process of social change" susceptible to a range of different context factors including leadership or organisation history. According to him, "[in] such complex terrain, the RCT is an impoverished way to learn. Critics who use it as a truth standard in this context are incorrect" [ 8 ] . Instead of limiting oneself to RCTs, Berwick recommends embracing a wider range of methods , including qualitative ones, which for "these specific applications, (...) are not compromises in learning how to improve; they are superior" [ 8 ].
Research problems that can be approached particularly well using qualitative methods include assessing complex multi-component interventions or systems (of change), addressing questions beyond “what works”, towards “what works for whom when, how and why”, and focussing on intervention improvement rather than accreditation [ 7 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 ]. Using qualitative methods can also help shed light on the “softer” side of medical treatment. For example, while quantitative trials can measure the costs and benefits of neuro-oncological treatment in terms of survival rates or adverse effects, qualitative research can help provide a better understanding of patient or caregiver stress, visibility of illness or out-of-pocket expenses.
How to conduct qualitative research?
Given that qualitative research is characterised by flexibility, openness and responsivity to context, the steps of data collection and analysis are not as separate and consecutive as they tend to be in quantitative research [ 13 , 14 ]. As Fossey puts it : “sampling, data collection, analysis and interpretation are related to each other in a cyclical (iterative) manner, rather than following one after another in a stepwise approach” [ 15 ]. The researcher can make educated decisions with regard to the choice of method, how they are implemented, and to which and how many units they are applied [ 13 ]. As shown in Fig. 1 , this can involve several back-and-forth steps between data collection and analysis where new insights and experiences can lead to adaption and expansion of the original plan. Some insights may also necessitate a revision of the research question and/or the research design as a whole. The process ends when saturation is achieved, i.e. when no relevant new information can be found (see also below: sampling and saturation). For reasons of transparency, it is essential for all decisions as well as the underlying reasoning to be well-documented.
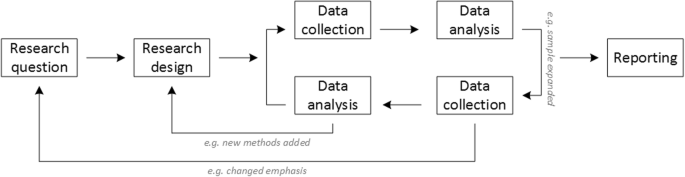
Iterative research process
While it is not always explicitly addressed, qualitative methods reflect a different underlying research paradigm than quantitative research (e.g. constructivism or interpretivism as opposed to positivism). The choice of methods can be based on the respective underlying substantive theory or theoretical framework used by the researcher [ 2 ].
Data collection
The methods of qualitative data collection most commonly used in health research are document study, observations, semi-structured interviews and focus groups [ 1 , 14 , 16 , 17 ].
Document study
Document study (also called document analysis) refers to the review by the researcher of written materials [ 14 ]. These can include personal and non-personal documents such as archives, annual reports, guidelines, policy documents, diaries or letters.
Observations
Observations are particularly useful to gain insights into a certain setting and actual behaviour – as opposed to reported behaviour or opinions [ 13 ]. Qualitative observations can be either participant or non-participant in nature. In participant observations, the observer is part of the observed setting, for example a nurse working in an intensive care unit [ 18 ]. In non-participant observations, the observer is “on the outside looking in”, i.e. present in but not part of the situation, trying not to influence the setting by their presence. Observations can be planned (e.g. for 3 h during the day or night shift) or ad hoc (e.g. as soon as a stroke patient arrives at the emergency room). During the observation, the observer takes notes on everything or certain pre-determined parts of what is happening around them, for example focusing on physician-patient interactions or communication between different professional groups. Written notes can be taken during or after the observations, depending on feasibility (which is usually lower during participant observations) and acceptability (e.g. when the observer is perceived to be judging the observed). Afterwards, these field notes are transcribed into observation protocols. If more than one observer was involved, field notes are taken independently, but notes can be consolidated into one protocol after discussions. Advantages of conducting observations include minimising the distance between the researcher and the researched, the potential discovery of topics that the researcher did not realise were relevant and gaining deeper insights into the real-world dimensions of the research problem at hand [ 18 ].
Semi-structured interviews
Hijmans & Kuyper describe qualitative interviews as “an exchange with an informal character, a conversation with a goal” [ 19 ]. Interviews are used to gain insights into a person’s subjective experiences, opinions and motivations – as opposed to facts or behaviours [ 13 ]. Interviews can be distinguished by the degree to which they are structured (i.e. a questionnaire), open (e.g. free conversation or autobiographical interviews) or semi-structured [ 2 , 13 ]. Semi-structured interviews are characterized by open-ended questions and the use of an interview guide (or topic guide/list) in which the broad areas of interest, sometimes including sub-questions, are defined [ 19 ]. The pre-defined topics in the interview guide can be derived from the literature, previous research or a preliminary method of data collection, e.g. document study or observations. The topic list is usually adapted and improved at the start of the data collection process as the interviewer learns more about the field [ 20 ]. Across interviews the focus on the different (blocks of) questions may differ and some questions may be skipped altogether (e.g. if the interviewee is not able or willing to answer the questions or for concerns about the total length of the interview) [ 20 ]. Qualitative interviews are usually not conducted in written format as it impedes on the interactive component of the method [ 20 ]. In comparison to written surveys, qualitative interviews have the advantage of being interactive and allowing for unexpected topics to emerge and to be taken up by the researcher. This can also help overcome a provider or researcher-centred bias often found in written surveys, which by nature, can only measure what is already known or expected to be of relevance to the researcher. Interviews can be audio- or video-taped; but sometimes it is only feasible or acceptable for the interviewer to take written notes [ 14 , 16 , 20 ].
Focus groups
Focus groups are group interviews to explore participants’ expertise and experiences, including explorations of how and why people behave in certain ways [ 1 ]. Focus groups usually consist of 6–8 people and are led by an experienced moderator following a topic guide or “script” [ 21 ]. They can involve an observer who takes note of the non-verbal aspects of the situation, possibly using an observation guide [ 21 ]. Depending on researchers’ and participants’ preferences, the discussions can be audio- or video-taped and transcribed afterwards [ 21 ]. Focus groups are useful for bringing together homogeneous (to a lesser extent heterogeneous) groups of participants with relevant expertise and experience on a given topic on which they can share detailed information [ 21 ]. Focus groups are a relatively easy, fast and inexpensive method to gain access to information on interactions in a given group, i.e. “the sharing and comparing” among participants [ 21 ]. Disadvantages include less control over the process and a lesser extent to which each individual may participate. Moreover, focus group moderators need experience, as do those tasked with the analysis of the resulting data. Focus groups can be less appropriate for discussing sensitive topics that participants might be reluctant to disclose in a group setting [ 13 ]. Moreover, attention must be paid to the emergence of “groupthink” as well as possible power dynamics within the group, e.g. when patients are awed or intimidated by health professionals.
Choosing the “right” method
As explained above, the school of thought underlying qualitative research assumes no objective hierarchy of evidence and methods. This means that each choice of single or combined methods has to be based on the research question that needs to be answered and a critical assessment with regard to whether or to what extent the chosen method can accomplish this – i.e. the “fit” between question and method [ 14 ]. It is necessary for these decisions to be documented when they are being made, and to be critically discussed when reporting methods and results.
Let us assume that our research aim is to examine the (clinical) processes around acute endovascular treatment (EVT), from the patient’s arrival at the emergency room to recanalization, with the aim to identify possible causes for delay and/or other causes for sub-optimal treatment outcome. As a first step, we could conduct a document study of the relevant standard operating procedures (SOPs) for this phase of care – are they up-to-date and in line with current guidelines? Do they contain any mistakes, irregularities or uncertainties that could cause delays or other problems? Regardless of the answers to these questions, the results have to be interpreted based on what they are: a written outline of what care processes in this hospital should look like. If we want to know what they actually look like in practice, we can conduct observations of the processes described in the SOPs. These results can (and should) be analysed in themselves, but also in comparison to the results of the document analysis, especially as regards relevant discrepancies. Do the SOPs outline specific tests for which no equipment can be observed or tasks to be performed by specialized nurses who are not present during the observation? It might also be possible that the written SOP is outdated, but the actual care provided is in line with current best practice. In order to find out why these discrepancies exist, it can be useful to conduct interviews. Are the physicians simply not aware of the SOPs (because their existence is limited to the hospital’s intranet) or do they actively disagree with them or does the infrastructure make it impossible to provide the care as described? Another rationale for adding interviews is that some situations (or all of their possible variations for different patient groups or the day, night or weekend shift) cannot practically or ethically be observed. In this case, it is possible to ask those involved to report on their actions – being aware that this is not the same as the actual observation. A senior physician’s or hospital manager’s description of certain situations might differ from a nurse’s or junior physician’s one, maybe because they intentionally misrepresent facts or maybe because different aspects of the process are visible or important to them. In some cases, it can also be relevant to consider to whom the interviewee is disclosing this information – someone they trust, someone they are otherwise not connected to, or someone they suspect or are aware of being in a potentially “dangerous” power relationship to them. Lastly, a focus group could be conducted with representatives of the relevant professional groups to explore how and why exactly they provide care around EVT. The discussion might reveal discrepancies (between SOPs and actual care or between different physicians) and motivations to the researchers as well as to the focus group members that they might not have been aware of themselves. For the focus group to deliver relevant information, attention has to be paid to its composition and conduct, for example, to make sure that all participants feel safe to disclose sensitive or potentially problematic information or that the discussion is not dominated by (senior) physicians only. The resulting combination of data collection methods is shown in Fig. 2 .
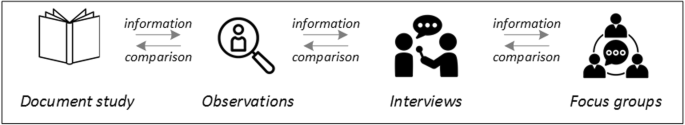
Possible combination of data collection methods
Attributions for icons: “Book” by Serhii Smirnov, “Interview” by Adrien Coquet, FR, “Magnifying Glass” by anggun, ID, “Business communication” by Vectors Market; all from the Noun Project
The combination of multiple data source as described for this example can be referred to as “triangulation”, in which multiple measurements are carried out from different angles to achieve a more comprehensive understanding of the phenomenon under study [ 22 , 23 ].
Data analysis
To analyse the data collected through observations, interviews and focus groups these need to be transcribed into protocols and transcripts (see Fig. 3 ). Interviews and focus groups can be transcribed verbatim , with or without annotations for behaviour (e.g. laughing, crying, pausing) and with or without phonetic transcription of dialects and filler words, depending on what is expected or known to be relevant for the analysis. In the next step, the protocols and transcripts are coded , that is, marked (or tagged, labelled) with one or more short descriptors of the content of a sentence or paragraph [ 2 , 15 , 23 ]. Jansen describes coding as “connecting the raw data with “theoretical” terms” [ 20 ]. In a more practical sense, coding makes raw data sortable. This makes it possible to extract and examine all segments describing, say, a tele-neurology consultation from multiple data sources (e.g. SOPs, emergency room observations, staff and patient interview). In a process of synthesis and abstraction, the codes are then grouped, summarised and/or categorised [ 15 , 20 ]. The end product of the coding or analysis process is a descriptive theory of the behavioural pattern under investigation [ 20 ]. The coding process is performed using qualitative data management software, the most common ones being InVivo, MaxQDA and Atlas.ti. It should be noted that these are data management tools which support the analysis performed by the researcher(s) [ 14 ].
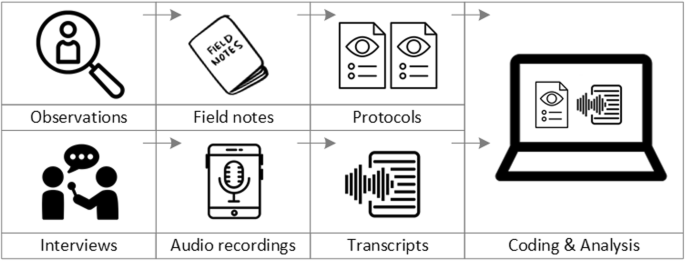
From data collection to data analysis
Attributions for icons: see Fig. 2 , also “Speech to text” by Trevor Dsouza, “Field Notes” by Mike O’Brien, US, “Voice Record” by ProSymbols, US, “Inspection” by Made, AU, and “Cloud” by Graphic Tigers; all from the Noun Project
How to report qualitative research?
Protocols of qualitative research can be published separately and in advance of the study results. However, the aim is not the same as in RCT protocols, i.e. to pre-define and set in stone the research questions and primary or secondary endpoints. Rather, it is a way to describe the research methods in detail, which might not be possible in the results paper given journals’ word limits. Qualitative research papers are usually longer than their quantitative counterparts to allow for deep understanding and so-called “thick description”. In the methods section, the focus is on transparency of the methods used, including why, how and by whom they were implemented in the specific study setting, so as to enable a discussion of whether and how this may have influenced data collection, analysis and interpretation. The results section usually starts with a paragraph outlining the main findings, followed by more detailed descriptions of, for example, the commonalities, discrepancies or exceptions per category [ 20 ]. Here it is important to support main findings by relevant quotations, which may add information, context, emphasis or real-life examples [ 20 , 23 ]. It is subject to debate in the field whether it is relevant to state the exact number or percentage of respondents supporting a certain statement (e.g. “Five interviewees expressed negative feelings towards XYZ”) [ 21 ].
How to combine qualitative with quantitative research?
Qualitative methods can be combined with other methods in multi- or mixed methods designs, which “[employ] two or more different methods [ …] within the same study or research program rather than confining the research to one single method” [ 24 ]. Reasons for combining methods can be diverse, including triangulation for corroboration of findings, complementarity for illustration and clarification of results, expansion to extend the breadth and range of the study, explanation of (unexpected) results generated with one method with the help of another, or offsetting the weakness of one method with the strength of another [ 1 , 17 , 24 , 25 , 26 ]. The resulting designs can be classified according to when, why and how the different quantitative and/or qualitative data strands are combined. The three most common types of mixed method designs are the convergent parallel design , the explanatory sequential design and the exploratory sequential design. The designs with examples are shown in Fig. 4 .
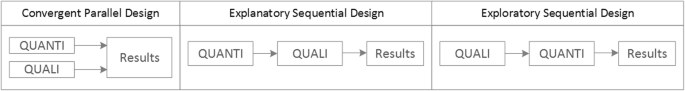
Three common mixed methods designs
In the convergent parallel design, a qualitative study is conducted in parallel to and independently of a quantitative study, and the results of both studies are compared and combined at the stage of interpretation of results. Using the above example of EVT provision, this could entail setting up a quantitative EVT registry to measure process times and patient outcomes in parallel to conducting the qualitative research outlined above, and then comparing results. Amongst other things, this would make it possible to assess whether interview respondents’ subjective impressions of patients receiving good care match modified Rankin Scores at follow-up, or whether observed delays in care provision are exceptions or the rule when compared to door-to-needle times as documented in the registry. In the explanatory sequential design, a quantitative study is carried out first, followed by a qualitative study to help explain the results from the quantitative study. This would be an appropriate design if the registry alone had revealed relevant delays in door-to-needle times and the qualitative study would be used to understand where and why these occurred, and how they could be improved. In the exploratory design, the qualitative study is carried out first and its results help informing and building the quantitative study in the next step [ 26 ]. If the qualitative study around EVT provision had shown a high level of dissatisfaction among the staff members involved, a quantitative questionnaire investigating staff satisfaction could be set up in the next step, informed by the qualitative study on which topics dissatisfaction had been expressed. Amongst other things, the questionnaire design would make it possible to widen the reach of the research to more respondents from different (types of) hospitals, regions, countries or settings, and to conduct sub-group analyses for different professional groups.
How to assess qualitative research?
A variety of assessment criteria and lists have been developed for qualitative research, ranging in their focus and comprehensiveness [ 14 , 17 , 27 ]. However, none of these has been elevated to the “gold standard” in the field. In the following, we therefore focus on a set of commonly used assessment criteria that, from a practical standpoint, a researcher can look for when assessing a qualitative research report or paper.
Assessors should check the authors’ use of and adherence to the relevant reporting checklists (e.g. Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR)) to make sure all items that are relevant for this type of research are addressed [ 23 , 28 ]. Discussions of quantitative measures in addition to or instead of these qualitative measures can be a sign of lower quality of the research (paper). Providing and adhering to a checklist for qualitative research contributes to an important quality criterion for qualitative research, namely transparency [ 15 , 17 , 23 ].
Reflexivity
While methodological transparency and complete reporting is relevant for all types of research, some additional criteria must be taken into account for qualitative research. This includes what is called reflexivity, i.e. sensitivity to the relationship between the researcher and the researched, including how contact was established and maintained, or the background and experience of the researcher(s) involved in data collection and analysis. Depending on the research question and population to be researched this can be limited to professional experience, but it may also include gender, age or ethnicity [ 17 , 27 ]. These details are relevant because in qualitative research, as opposed to quantitative research, the researcher as a person cannot be isolated from the research process [ 23 ]. It may influence the conversation when an interviewed patient speaks to an interviewer who is a physician, or when an interviewee is asked to discuss a gynaecological procedure with a male interviewer, and therefore the reader must be made aware of these details [ 19 ].
Sampling and saturation
The aim of qualitative sampling is for all variants of the objects of observation that are deemed relevant for the study to be present in the sample “ to see the issue and its meanings from as many angles as possible” [ 1 , 16 , 19 , 20 , 27 ] , and to ensure “information-richness [ 15 ]. An iterative sampling approach is advised, in which data collection (e.g. five interviews) is followed by data analysis, followed by more data collection to find variants that are lacking in the current sample. This process continues until no new (relevant) information can be found and further sampling becomes redundant – which is called saturation [ 1 , 15 ] . In other words: qualitative data collection finds its end point not a priori , but when the research team determines that saturation has been reached [ 29 , 30 ].
This is also the reason why most qualitative studies use deliberate instead of random sampling strategies. This is generally referred to as “ purposive sampling” , in which researchers pre-define which types of participants or cases they need to include so as to cover all variations that are expected to be of relevance, based on the literature, previous experience or theory (i.e. theoretical sampling) [ 14 , 20 ]. Other types of purposive sampling include (but are not limited to) maximum variation sampling, critical case sampling or extreme or deviant case sampling [ 2 ]. In the above EVT example, a purposive sample could include all relevant professional groups and/or all relevant stakeholders (patients, relatives) and/or all relevant times of observation (day, night and weekend shift).
Assessors of qualitative research should check whether the considerations underlying the sampling strategy were sound and whether or how researchers tried to adapt and improve their strategies in stepwise or cyclical approaches between data collection and analysis to achieve saturation [ 14 ].
Good qualitative research is iterative in nature, i.e. it goes back and forth between data collection and analysis, revising and improving the approach where necessary. One example of this are pilot interviews, where different aspects of the interview (especially the interview guide, but also, for example, the site of the interview or whether the interview can be audio-recorded) are tested with a small number of respondents, evaluated and revised [ 19 ]. In doing so, the interviewer learns which wording or types of questions work best, or which is the best length of an interview with patients who have trouble concentrating for an extended time. Of course, the same reasoning applies to observations or focus groups which can also be piloted.
Ideally, coding should be performed by at least two researchers, especially at the beginning of the coding process when a common approach must be defined, including the establishment of a useful coding list (or tree), and when a common meaning of individual codes must be established [ 23 ]. An initial sub-set or all transcripts can be coded independently by the coders and then compared and consolidated after regular discussions in the research team. This is to make sure that codes are applied consistently to the research data.
Member checking
Member checking, also called respondent validation , refers to the practice of checking back with study respondents to see if the research is in line with their views [ 14 , 27 ]. This can happen after data collection or analysis or when first results are available [ 23 ]. For example, interviewees can be provided with (summaries of) their transcripts and asked whether they believe this to be a complete representation of their views or whether they would like to clarify or elaborate on their responses [ 17 ]. Respondents’ feedback on these issues then becomes part of the data collection and analysis [ 27 ].
Stakeholder involvement
In those niches where qualitative approaches have been able to evolve and grow, a new trend has seen the inclusion of patients and their representatives not only as study participants (i.e. “members”, see above) but as consultants to and active participants in the broader research process [ 31 , 32 , 33 ]. The underlying assumption is that patients and other stakeholders hold unique perspectives and experiences that add value beyond their own single story, making the research more relevant and beneficial to researchers, study participants and (future) patients alike [ 34 , 35 ]. Using the example of patients on or nearing dialysis, a recent scoping review found that 80% of clinical research did not address the top 10 research priorities identified by patients and caregivers [ 32 , 36 ]. In this sense, the involvement of the relevant stakeholders, especially patients and relatives, is increasingly being seen as a quality indicator in and of itself.
How not to assess qualitative research
The above overview does not include certain items that are routine in assessments of quantitative research. What follows is a non-exhaustive, non-representative, experience-based list of the quantitative criteria often applied to the assessment of qualitative research, as well as an explanation of the limited usefulness of these endeavours.
Protocol adherence
Given the openness and flexibility of qualitative research, it should not be assessed by how well it adheres to pre-determined and fixed strategies – in other words: its rigidity. Instead, the assessor should look for signs of adaptation and refinement based on lessons learned from earlier steps in the research process.
Sample size
For the reasons explained above, qualitative research does not require specific sample sizes, nor does it require that the sample size be determined a priori [ 1 , 14 , 27 , 37 , 38 , 39 ]. Sample size can only be a useful quality indicator when related to the research purpose, the chosen methodology and the composition of the sample, i.e. who was included and why.
Randomisation
While some authors argue that randomisation can be used in qualitative research, this is not commonly the case, as neither its feasibility nor its necessity or usefulness has been convincingly established for qualitative research [ 13 , 27 ]. Relevant disadvantages include the negative impact of a too large sample size as well as the possibility (or probability) of selecting “ quiet, uncooperative or inarticulate individuals ” [ 17 ]. Qualitative studies do not use control groups, either.
Interrater reliability, variability and other “objectivity checks”
The concept of “interrater reliability” is sometimes used in qualitative research to assess to which extent the coding approach overlaps between the two co-coders. However, it is not clear what this measure tells us about the quality of the analysis [ 23 ]. This means that these scores can be included in qualitative research reports, preferably with some additional information on what the score means for the analysis, but it is not a requirement. Relatedly, it is not relevant for the quality or “objectivity” of qualitative research to separate those who recruited the study participants and collected and analysed the data. Experiences even show that it might be better to have the same person or team perform all of these tasks [ 20 ]. First, when researchers introduce themselves during recruitment this can enhance trust when the interview takes place days or weeks later with the same researcher. Second, when the audio-recording is transcribed for analysis, the researcher conducting the interviews will usually remember the interviewee and the specific interview situation during data analysis. This might be helpful in providing additional context information for interpretation of data, e.g. on whether something might have been meant as a joke [ 18 ].
Not being quantitative research
Being qualitative research instead of quantitative research should not be used as an assessment criterion if it is used irrespectively of the research problem at hand. Similarly, qualitative research should not be required to be combined with quantitative research per se – unless mixed methods research is judged as inherently better than single-method research. In this case, the same criterion should be applied for quantitative studies without a qualitative component.
The main take-away points of this paper are summarised in Table 1 . We aimed to show that, if conducted well, qualitative research can answer specific research questions that cannot to be adequately answered using (only) quantitative designs. Seeing qualitative and quantitative methods as equal will help us become more aware and critical of the “fit” between the research problem and our chosen methods: I can conduct an RCT to determine the reasons for transportation delays of acute stroke patients – but should I? It also provides us with a greater range of tools to tackle a greater range of research problems more appropriately and successfully, filling in the blind spots on one half of the methodological spectrum to better address the whole complexity of neurological research and practice.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
Endovascular treatment
Randomised Controlled Trial
Standard Operating Procedure
Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research
Philipsen, H., & Vernooij-Dassen, M. (2007). Kwalitatief onderzoek: nuttig, onmisbaar en uitdagend. In L. PLBJ & H. TCo (Eds.), Kwalitatief onderzoek: Praktische methoden voor de medische praktijk . [Qualitative research: useful, indispensable and challenging. In: Qualitative research: Practical methods for medical practice (pp. 5–12). Houten: Bohn Stafleu van Loghum.
Chapter Google Scholar
Punch, K. F. (2013). Introduction to social research: Quantitative and qualitative approaches . London: Sage.
Kelly, J., Dwyer, J., Willis, E., & Pekarsky, B. (2014). Travelling to the city for hospital care: Access factors in country aboriginal patient journeys. Australian Journal of Rural Health, 22 (3), 109–113.
Article Google Scholar
Nilsen, P., Ståhl, C., Roback, K., & Cairney, P. (2013). Never the twain shall meet? - a comparison of implementation science and policy implementation research. Implementation Science, 8 (1), 1–12.
Howick J, Chalmers I, Glasziou, P., Greenhalgh, T., Heneghan, C., Liberati, A., Moschetti, I., Phillips, B., & Thornton, H. (2011). The 2011 Oxford CEBM evidence levels of evidence (introductory document) . Oxford Center for Evidence Based Medicine. https://www.cebm.net/2011/06/2011-oxford-cebm-levels-evidence-introductory-document/ .
Eakin, J. M. (2016). Educating critical qualitative health researchers in the land of the randomized controlled trial. Qualitative Inquiry, 22 (2), 107–118.
May, A., & Mathijssen, J. (2015). Alternatieven voor RCT bij de evaluatie van effectiviteit van interventies!? Eindrapportage. In Alternatives for RCTs in the evaluation of effectiveness of interventions!? Final report .
Google Scholar
Berwick, D. M. (2008). The science of improvement. Journal of the American Medical Association, 299 (10), 1182–1184.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Christ, T. W. (2014). Scientific-based research and randomized controlled trials, the “gold” standard? Alternative paradigms and mixed methodologies. Qualitative Inquiry, 20 (1), 72–80.
Lamont, T., Barber, N., Jd, P., Fulop, N., Garfield-Birkbeck, S., Lilford, R., Mear, L., Raine, R., & Fitzpatrick, R. (2016). New approaches to evaluating complex health and care systems. BMJ, 352:i154.
Drabble, S. J., & O’Cathain, A. (2015). Moving from Randomized Controlled Trials to Mixed Methods Intervention Evaluation. In S. Hesse-Biber & R. B. Johnson (Eds.), The Oxford Handbook of Multimethod and Mixed Methods Research Inquiry (pp. 406–425). London: Oxford University Press.
Chambers, D. A., Glasgow, R. E., & Stange, K. C. (2013). The dynamic sustainability framework: Addressing the paradox of sustainment amid ongoing change. Implementation Science : IS, 8 , 117.
Hak, T. (2007). Waarnemingsmethoden in kwalitatief onderzoek. In L. PLBJ & H. TCo (Eds.), Kwalitatief onderzoek: Praktische methoden voor de medische praktijk . [Observation methods in qualitative research] (pp. 13–25). Houten: Bohn Stafleu van Loghum.
Russell, C. K., & Gregory, D. M. (2003). Evaluation of qualitative research studies. Evidence Based Nursing, 6 (2), 36–40.
Fossey, E., Harvey, C., McDermott, F., & Davidson, L. (2002). Understanding and evaluating qualitative research. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry, 36 , 717–732.
Yanow, D. (2000). Conducting interpretive policy analysis (Vol. 47). Thousand Oaks: Sage University Papers Series on Qualitative Research Methods.
Shenton, A. K. (2004). Strategies for ensuring trustworthiness in qualitative research projects. Education for Information, 22 , 63–75.
van der Geest, S. (2006). Participeren in ziekte en zorg: meer over kwalitatief onderzoek. Huisarts en Wetenschap, 49 (4), 283–287.
Hijmans, E., & Kuyper, M. (2007). Het halfopen interview als onderzoeksmethode. In L. PLBJ & H. TCo (Eds.), Kwalitatief onderzoek: Praktische methoden voor de medische praktijk . [The half-open interview as research method (pp. 43–51). Houten: Bohn Stafleu van Loghum.
Jansen, H. (2007). Systematiek en toepassing van de kwalitatieve survey. In L. PLBJ & H. TCo (Eds.), Kwalitatief onderzoek: Praktische methoden voor de medische praktijk . [Systematics and implementation of the qualitative survey (pp. 27–41). Houten: Bohn Stafleu van Loghum.
Pv, R., & Peremans, L. (2007). Exploreren met focusgroepgesprekken: de ‘stem’ van de groep onder de loep. In L. PLBJ & H. TCo (Eds.), Kwalitatief onderzoek: Praktische methoden voor de medische praktijk . [Exploring with focus group conversations: the “voice” of the group under the magnifying glass (pp. 53–64). Houten: Bohn Stafleu van Loghum.
Carter, N., Bryant-Lukosius, D., DiCenso, A., Blythe, J., & Neville, A. J. (2014). The use of triangulation in qualitative research. Oncology Nursing Forum, 41 (5), 545–547.
Boeije H: Analyseren in kwalitatief onderzoek: Denken en doen, [Analysis in qualitative research: Thinking and doing] vol. Den Haag Boom Lemma uitgevers; 2012.
Hunter, A., & Brewer, J. (2015). Designing Multimethod Research. In S. Hesse-Biber & R. B. Johnson (Eds.), The Oxford Handbook of Multimethod and Mixed Methods Research Inquiry (pp. 185–205). London: Oxford University Press.
Archibald, M. M., Radil, A. I., Zhang, X., & Hanson, W. E. (2015). Current mixed methods practices in qualitative research: A content analysis of leading journals. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 14 (2), 5–33.
Creswell, J. W., & Plano Clark, V. L. (2011). Choosing a Mixed Methods Design. In Designing and Conducting Mixed Methods Research . Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications.
Mays, N., & Pope, C. (2000). Assessing quality in qualitative research. BMJ, 320 (7226), 50–52.
O'Brien, B. C., Harris, I. B., Beckman, T. J., Reed, D. A., & Cook, D. A. (2014). Standards for reporting qualitative research: A synthesis of recommendations. Academic Medicine : Journal of the Association of American Medical Colleges, 89 (9), 1245–1251.
Saunders, B., Sim, J., Kingstone, T., Baker, S., Waterfield, J., Bartlam, B., Burroughs, H., & Jinks, C. (2018). Saturation in qualitative research: Exploring its conceptualization and operationalization. Quality and Quantity, 52 (4), 1893–1907.
Moser, A., & Korstjens, I. (2018). Series: Practical guidance to qualitative research. Part 3: Sampling, data collection and analysis. European Journal of General Practice, 24 (1), 9–18.
Marlett, N., Shklarov, S., Marshall, D., Santana, M. J., & Wasylak, T. (2015). Building new roles and relationships in research: A model of patient engagement research. Quality of Life Research : an international journal of quality of life aspects of treatment, care and rehabilitation, 24 (5), 1057–1067.
Demian, M. N., Lam, N. N., Mac-Way, F., Sapir-Pichhadze, R., & Fernandez, N. (2017). Opportunities for engaging patients in kidney research. Canadian Journal of Kidney Health and Disease, 4 , 2054358117703070–2054358117703070.
Noyes, J., McLaughlin, L., Morgan, K., Roberts, A., Stephens, M., Bourne, J., Houlston, M., Houlston, J., Thomas, S., Rhys, R. G., et al. (2019). Designing a co-productive study to overcome known methodological challenges in organ donation research with bereaved family members. Health Expectations . 22(4):824–35.
Piil, K., Jarden, M., & Pii, K. H. (2019). Research agenda for life-threatening cancer. European Journal Cancer Care (Engl), 28 (1), e12935.
Hofmann, D., Ibrahim, F., Rose, D., Scott, D. L., Cope, A., Wykes, T., & Lempp, H. (2015). Expectations of new treatment in rheumatoid arthritis: Developing a patient-generated questionnaire. Health Expectations : an international journal of public participation in health care and health policy, 18 (5), 995–1008.
Jun, M., Manns, B., Laupacis, A., Manns, L., Rehal, B., Crowe, S., & Hemmelgarn, B. R. (2015). Assessing the extent to which current clinical research is consistent with patient priorities: A scoping review using a case study in patients on or nearing dialysis. Canadian Journal of Kidney Health and Disease, 2 , 35.
Elsie Baker, S., & Edwards, R. (2012). How many qualitative interviews is enough? In National Centre for Research Methods Review Paper . National Centre for Research Methods. http://eprints.ncrm.ac.uk/2273/4/how_many_interviews.pdf .
Sandelowski, M. (1995). Sample size in qualitative research. Research in Nursing & Health, 18 (2), 179–183.
Sim, J., Saunders, B., Waterfield, J., & Kingstone, T. (2018). Can sample size in qualitative research be determined a priori? International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 21 (5), 619–634.
Download references
Acknowledgements
no external funding.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Neurology, Heidelberg University Hospital, Im Neuenheimer Feld 400, 69120, Heidelberg, Germany
Loraine Busetto, Wolfgang Wick & Christoph Gumbinger
Clinical Cooperation Unit Neuro-Oncology, German Cancer Research Center, Heidelberg, Germany
Wolfgang Wick
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
LB drafted the manuscript; WW and CG revised the manuscript; all authors approved the final versions.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Loraine Busetto .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Busetto, L., Wick, W. & Gumbinger, C. How to use and assess qualitative research methods. Neurol. Res. Pract. 2 , 14 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42466-020-00059-z
Download citation
Received : 30 January 2020
Accepted : 22 April 2020
Published : 27 May 2020
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s42466-020-00059-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Qualitative research
- Mixed methods
- Quality assessment
Neurological Research and Practice
ISSN: 2524-3489
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Criteria for Good Qualitative Research: A Comprehensive Review
- Regular Article
- Open access
- Published: 18 September 2021
- Volume 31 , pages 679–689, ( 2022 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article
- Drishti Yadav ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2974-0323 1
77k Accesses
28 Citations
72 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
This review aims to synthesize a published set of evaluative criteria for good qualitative research. The aim is to shed light on existing standards for assessing the rigor of qualitative research encompassing a range of epistemological and ontological standpoints. Using a systematic search strategy, published journal articles that deliberate criteria for rigorous research were identified. Then, references of relevant articles were surveyed to find noteworthy, distinct, and well-defined pointers to good qualitative research. This review presents an investigative assessment of the pivotal features in qualitative research that can permit the readers to pass judgment on its quality and to condemn it as good research when objectively and adequately utilized. Overall, this review underlines the crux of qualitative research and accentuates the necessity to evaluate such research by the very tenets of its being. It also offers some prospects and recommendations to improve the quality of qualitative research. Based on the findings of this review, it is concluded that quality criteria are the aftereffect of socio-institutional procedures and existing paradigmatic conducts. Owing to the paradigmatic diversity of qualitative research, a single and specific set of quality criteria is neither feasible nor anticipated. Since qualitative research is not a cohesive discipline, researchers need to educate and familiarize themselves with applicable norms and decisive factors to evaluate qualitative research from within its theoretical and methodological framework of origin.
Similar content being viewed by others

Good Qualitative Research: Opening up the Debate

What is Qualitative in Research
Patrik Aspers & Ugo Corte
What is Qualitative in Qualitative Research
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
“… It is important to regularly dialogue about what makes for good qualitative research” (Tracy, 2010 , p. 837)
To decide what represents good qualitative research is highly debatable. There are numerous methods that are contained within qualitative research and that are established on diverse philosophical perspectives. Bryman et al., ( 2008 , p. 262) suggest that “It is widely assumed that whereas quality criteria for quantitative research are well‐known and widely agreed, this is not the case for qualitative research.” Hence, the question “how to evaluate the quality of qualitative research” has been continuously debated. There are many areas of science and technology wherein these debates on the assessment of qualitative research have taken place. Examples include various areas of psychology: general psychology (Madill et al., 2000 ); counseling psychology (Morrow, 2005 ); and clinical psychology (Barker & Pistrang, 2005 ), and other disciplines of social sciences: social policy (Bryman et al., 2008 ); health research (Sparkes, 2001 ); business and management research (Johnson et al., 2006 ); information systems (Klein & Myers, 1999 ); and environmental studies (Reid & Gough, 2000 ). In the literature, these debates are enthused by the impression that the blanket application of criteria for good qualitative research developed around the positivist paradigm is improper. Such debates are based on the wide range of philosophical backgrounds within which qualitative research is conducted (e.g., Sandberg, 2000 ; Schwandt, 1996 ). The existence of methodological diversity led to the formulation of different sets of criteria applicable to qualitative research.
Among qualitative researchers, the dilemma of governing the measures to assess the quality of research is not a new phenomenon, especially when the virtuous triad of objectivity, reliability, and validity (Spencer et al., 2004 ) are not adequate. Occasionally, the criteria of quantitative research are used to evaluate qualitative research (Cohen & Crabtree, 2008 ; Lather, 2004 ). Indeed, Howe ( 2004 ) claims that the prevailing paradigm in educational research is scientifically based experimental research. Hypotheses and conjectures about the preeminence of quantitative research can weaken the worth and usefulness of qualitative research by neglecting the prominence of harmonizing match for purpose on research paradigm, the epistemological stance of the researcher, and the choice of methodology. Researchers have been reprimanded concerning this in “paradigmatic controversies, contradictions, and emerging confluences” (Lincoln & Guba, 2000 ).
In general, qualitative research tends to come from a very different paradigmatic stance and intrinsically demands distinctive and out-of-the-ordinary criteria for evaluating good research and varieties of research contributions that can be made. This review attempts to present a series of evaluative criteria for qualitative researchers, arguing that their choice of criteria needs to be compatible with the unique nature of the research in question (its methodology, aims, and assumptions). This review aims to assist researchers in identifying some of the indispensable features or markers of high-quality qualitative research. In a nutshell, the purpose of this systematic literature review is to analyze the existing knowledge on high-quality qualitative research and to verify the existence of research studies dealing with the critical assessment of qualitative research based on the concept of diverse paradigmatic stances. Contrary to the existing reviews, this review also suggests some critical directions to follow to improve the quality of qualitative research in different epistemological and ontological perspectives. This review is also intended to provide guidelines for the acceleration of future developments and dialogues among qualitative researchers in the context of assessing the qualitative research.
The rest of this review article is structured in the following fashion: Sect. Methods describes the method followed for performing this review. Section Criteria for Evaluating Qualitative Studies provides a comprehensive description of the criteria for evaluating qualitative studies. This section is followed by a summary of the strategies to improve the quality of qualitative research in Sect. Improving Quality: Strategies . Section How to Assess the Quality of the Research Findings? provides details on how to assess the quality of the research findings. After that, some of the quality checklists (as tools to evaluate quality) are discussed in Sect. Quality Checklists: Tools for Assessing the Quality . At last, the review ends with the concluding remarks presented in Sect. Conclusions, Future Directions and Outlook . Some prospects in qualitative research for enhancing its quality and usefulness in the social and techno-scientific research community are also presented in Sect. Conclusions, Future Directions and Outlook .
For this review, a comprehensive literature search was performed from many databases using generic search terms such as Qualitative Research , Criteria , etc . The following databases were chosen for the literature search based on the high number of results: IEEE Explore, ScienceDirect, PubMed, Google Scholar, and Web of Science. The following keywords (and their combinations using Boolean connectives OR/AND) were adopted for the literature search: qualitative research, criteria, quality, assessment, and validity. The synonyms for these keywords were collected and arranged in a logical structure (see Table 1 ). All publications in journals and conference proceedings later than 1950 till 2021 were considered for the search. Other articles extracted from the references of the papers identified in the electronic search were also included. A large number of publications on qualitative research were retrieved during the initial screening. Hence, to include the searches with the main focus on criteria for good qualitative research, an inclusion criterion was utilized in the search string.
From the selected databases, the search retrieved a total of 765 publications. Then, the duplicate records were removed. After that, based on the title and abstract, the remaining 426 publications were screened for their relevance by using the following inclusion and exclusion criteria (see Table 2 ). Publications focusing on evaluation criteria for good qualitative research were included, whereas those works which delivered theoretical concepts on qualitative research were excluded. Based on the screening and eligibility, 45 research articles were identified that offered explicit criteria for evaluating the quality of qualitative research and were found to be relevant to this review.
Figure 1 illustrates the complete review process in the form of PRISMA flow diagram. PRISMA, i.e., “preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses” is employed in systematic reviews to refine the quality of reporting.
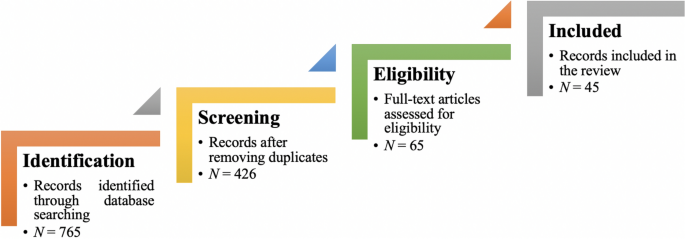
PRISMA flow diagram illustrating the search and inclusion process. N represents the number of records
Criteria for Evaluating Qualitative Studies
Fundamental criteria: general research quality.
Various researchers have put forward criteria for evaluating qualitative research, which have been summarized in Table 3 . Also, the criteria outlined in Table 4 effectively deliver the various approaches to evaluate and assess the quality of qualitative work. The entries in Table 4 are based on Tracy’s “Eight big‐tent criteria for excellent qualitative research” (Tracy, 2010 ). Tracy argues that high-quality qualitative work should formulate criteria focusing on the worthiness, relevance, timeliness, significance, morality, and practicality of the research topic, and the ethical stance of the research itself. Researchers have also suggested a series of questions as guiding principles to assess the quality of a qualitative study (Mays & Pope, 2020 ). Nassaji ( 2020 ) argues that good qualitative research should be robust, well informed, and thoroughly documented.
Qualitative Research: Interpretive Paradigms
All qualitative researchers follow highly abstract principles which bring together beliefs about ontology, epistemology, and methodology. These beliefs govern how the researcher perceives and acts. The net, which encompasses the researcher’s epistemological, ontological, and methodological premises, is referred to as a paradigm, or an interpretive structure, a “Basic set of beliefs that guides action” (Guba, 1990 ). Four major interpretive paradigms structure the qualitative research: positivist and postpositivist, constructivist interpretive, critical (Marxist, emancipatory), and feminist poststructural. The complexity of these four abstract paradigms increases at the level of concrete, specific interpretive communities. Table 5 presents these paradigms and their assumptions, including their criteria for evaluating research, and the typical form that an interpretive or theoretical statement assumes in each paradigm. Moreover, for evaluating qualitative research, quantitative conceptualizations of reliability and validity are proven to be incompatible (Horsburgh, 2003 ). In addition, a series of questions have been put forward in the literature to assist a reviewer (who is proficient in qualitative methods) for meticulous assessment and endorsement of qualitative research (Morse, 2003 ). Hammersley ( 2007 ) also suggests that guiding principles for qualitative research are advantageous, but methodological pluralism should not be simply acknowledged for all qualitative approaches. Seale ( 1999 ) also points out the significance of methodological cognizance in research studies.
Table 5 reflects that criteria for assessing the quality of qualitative research are the aftermath of socio-institutional practices and existing paradigmatic standpoints. Owing to the paradigmatic diversity of qualitative research, a single set of quality criteria is neither possible nor desirable. Hence, the researchers must be reflexive about the criteria they use in the various roles they play within their research community.
Improving Quality: Strategies
Another critical question is “How can the qualitative researchers ensure that the abovementioned quality criteria can be met?” Lincoln and Guba ( 1986 ) delineated several strategies to intensify each criteria of trustworthiness. Other researchers (Merriam & Tisdell, 2016 ; Shenton, 2004 ) also presented such strategies. A brief description of these strategies is shown in Table 6 .
It is worth mentioning that generalizability is also an integral part of qualitative research (Hays & McKibben, 2021 ). In general, the guiding principle pertaining to generalizability speaks about inducing and comprehending knowledge to synthesize interpretive components of an underlying context. Table 7 summarizes the main metasynthesis steps required to ascertain generalizability in qualitative research.
Figure 2 reflects the crucial components of a conceptual framework and their contribution to decisions regarding research design, implementation, and applications of results to future thinking, study, and practice (Johnson et al., 2020 ). The synergy and interrelationship of these components signifies their role to different stances of a qualitative research study.

Essential elements of a conceptual framework
In a nutshell, to assess the rationale of a study, its conceptual framework and research question(s), quality criteria must take account of the following: lucid context for the problem statement in the introduction; well-articulated research problems and questions; precise conceptual framework; distinct research purpose; and clear presentation and investigation of the paradigms. These criteria would expedite the quality of qualitative research.
How to Assess the Quality of the Research Findings?
The inclusion of quotes or similar research data enhances the confirmability in the write-up of the findings. The use of expressions (for instance, “80% of all respondents agreed that” or “only one of the interviewees mentioned that”) may also quantify qualitative findings (Stenfors et al., 2020 ). On the other hand, the persuasive reason for “why this may not help in intensifying the research” has also been provided (Monrouxe & Rees, 2020 ). Further, the Discussion and Conclusion sections of an article also prove robust markers of high-quality qualitative research, as elucidated in Table 8 .
Quality Checklists: Tools for Assessing the Quality
Numerous checklists are available to speed up the assessment of the quality of qualitative research. However, if used uncritically and recklessly concerning the research context, these checklists may be counterproductive. I recommend that such lists and guiding principles may assist in pinpointing the markers of high-quality qualitative research. However, considering enormous variations in the authors’ theoretical and philosophical contexts, I would emphasize that high dependability on such checklists may say little about whether the findings can be applied in your setting. A combination of such checklists might be appropriate for novice researchers. Some of these checklists are listed below:
The most commonly used framework is Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ) (Tong et al., 2007 ). This framework is recommended by some journals to be followed by the authors during article submission.
Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR) is another checklist that has been created particularly for medical education (O’Brien et al., 2014 ).
Also, Tracy ( 2010 ) and Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP, 2021 ) offer criteria for qualitative research relevant across methods and approaches.
Further, researchers have also outlined different criteria as hallmarks of high-quality qualitative research. For instance, the “Road Trip Checklist” (Epp & Otnes, 2021 ) provides a quick reference to specific questions to address different elements of high-quality qualitative research.
Conclusions, Future Directions, and Outlook
This work presents a broad review of the criteria for good qualitative research. In addition, this article presents an exploratory analysis of the essential elements in qualitative research that can enable the readers of qualitative work to judge it as good research when objectively and adequately utilized. In this review, some of the essential markers that indicate high-quality qualitative research have been highlighted. I scope them narrowly to achieve rigor in qualitative research and note that they do not completely cover the broader considerations necessary for high-quality research. This review points out that a universal and versatile one-size-fits-all guideline for evaluating the quality of qualitative research does not exist. In other words, this review also emphasizes the non-existence of a set of common guidelines among qualitative researchers. In unison, this review reinforces that each qualitative approach should be treated uniquely on account of its own distinctive features for different epistemological and disciplinary positions. Owing to the sensitivity of the worth of qualitative research towards the specific context and the type of paradigmatic stance, researchers should themselves analyze what approaches can be and must be tailored to ensemble the distinct characteristics of the phenomenon under investigation. Although this article does not assert to put forward a magic bullet and to provide a one-stop solution for dealing with dilemmas about how, why, or whether to evaluate the “goodness” of qualitative research, it offers a platform to assist the researchers in improving their qualitative studies. This work provides an assembly of concerns to reflect on, a series of questions to ask, and multiple sets of criteria to look at, when attempting to determine the quality of qualitative research. Overall, this review underlines the crux of qualitative research and accentuates the need to evaluate such research by the very tenets of its being. Bringing together the vital arguments and delineating the requirements that good qualitative research should satisfy, this review strives to equip the researchers as well as reviewers to make well-versed judgment about the worth and significance of the qualitative research under scrutiny. In a nutshell, a comprehensive portrayal of the research process (from the context of research to the research objectives, research questions and design, speculative foundations, and from approaches of collecting data to analyzing the results, to deriving inferences) frequently proliferates the quality of a qualitative research.
Prospects : A Road Ahead for Qualitative Research
Irrefutably, qualitative research is a vivacious and evolving discipline wherein different epistemological and disciplinary positions have their own characteristics and importance. In addition, not surprisingly, owing to the sprouting and varied features of qualitative research, no consensus has been pulled off till date. Researchers have reflected various concerns and proposed several recommendations for editors and reviewers on conducting reviews of critical qualitative research (Levitt et al., 2021 ; McGinley et al., 2021 ). Following are some prospects and a few recommendations put forward towards the maturation of qualitative research and its quality evaluation:
In general, most of the manuscript and grant reviewers are not qualitative experts. Hence, it is more likely that they would prefer to adopt a broad set of criteria. However, researchers and reviewers need to keep in mind that it is inappropriate to utilize the same approaches and conducts among all qualitative research. Therefore, future work needs to focus on educating researchers and reviewers about the criteria to evaluate qualitative research from within the suitable theoretical and methodological context.
There is an urgent need to refurbish and augment critical assessment of some well-known and widely accepted tools (including checklists such as COREQ, SRQR) to interrogate their applicability on different aspects (along with their epistemological ramifications).
Efforts should be made towards creating more space for creativity, experimentation, and a dialogue between the diverse traditions of qualitative research. This would potentially help to avoid the enforcement of one's own set of quality criteria on the work carried out by others.
Moreover, journal reviewers need to be aware of various methodological practices and philosophical debates.
It is pivotal to highlight the expressions and considerations of qualitative researchers and bring them into a more open and transparent dialogue about assessing qualitative research in techno-scientific, academic, sociocultural, and political rooms.
Frequent debates on the use of evaluative criteria are required to solve some potentially resolved issues (including the applicability of a single set of criteria in multi-disciplinary aspects). Such debates would not only benefit the group of qualitative researchers themselves, but primarily assist in augmenting the well-being and vivacity of the entire discipline.
To conclude, I speculate that the criteria, and my perspective, may transfer to other methods, approaches, and contexts. I hope that they spark dialog and debate – about criteria for excellent qualitative research and the underpinnings of the discipline more broadly – and, therefore, help improve the quality of a qualitative study. Further, I anticipate that this review will assist the researchers to contemplate on the quality of their own research, to substantiate research design and help the reviewers to review qualitative research for journals. On a final note, I pinpoint the need to formulate a framework (encompassing the prerequisites of a qualitative study) by the cohesive efforts of qualitative researchers of different disciplines with different theoretic-paradigmatic origins. I believe that tailoring such a framework (of guiding principles) paves the way for qualitative researchers to consolidate the status of qualitative research in the wide-ranging open science debate. Dialogue on this issue across different approaches is crucial for the impending prospects of socio-techno-educational research.
Amin, M. E. K., Nørgaard, L. S., Cavaco, A. M., Witry, M. J., Hillman, L., Cernasev, A., & Desselle, S. P. (2020). Establishing trustworthiness and authenticity in qualitative pharmacy research. Research in Social and Administrative Pharmacy, 16 (10), 1472–1482.
Article Google Scholar
Barker, C., & Pistrang, N. (2005). Quality criteria under methodological pluralism: Implications for conducting and evaluating research. American Journal of Community Psychology, 35 (3–4), 201–212.
Bryman, A., Becker, S., & Sempik, J. (2008). Quality criteria for quantitative, qualitative and mixed methods research: A view from social policy. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 11 (4), 261–276.
Caelli, K., Ray, L., & Mill, J. (2003). ‘Clear as mud’: Toward greater clarity in generic qualitative research. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 2 (2), 1–13.
CASP (2021). CASP checklists. Retrieved May 2021 from https://casp-uk.net/casp-tools-checklists/
Cohen, D. J., & Crabtree, B. F. (2008). Evaluative criteria for qualitative research in health care: Controversies and recommendations. The Annals of Family Medicine, 6 (4), 331–339.
Denzin, N. K., & Lincoln, Y. S. (2005). Introduction: The discipline and practice of qualitative research. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), The sage handbook of qualitative research (pp. 1–32). Sage Publications Ltd.
Google Scholar
Elliott, R., Fischer, C. T., & Rennie, D. L. (1999). Evolving guidelines for publication of qualitative research studies in psychology and related fields. British Journal of Clinical Psychology, 38 (3), 215–229.
Epp, A. M., & Otnes, C. C. (2021). High-quality qualitative research: Getting into gear. Journal of Service Research . https://doi.org/10.1177/1094670520961445
Guba, E. G. (1990). The paradigm dialog. In Alternative paradigms conference, mar, 1989, Indiana u, school of education, San Francisco, ca, us . Sage Publications, Inc.
Hammersley, M. (2007). The issue of quality in qualitative research. International Journal of Research and Method in Education, 30 (3), 287–305.
Haven, T. L., Errington, T. M., Gleditsch, K. S., van Grootel, L., Jacobs, A. M., Kern, F. G., & Mokkink, L. B. (2020). Preregistering qualitative research: A Delphi study. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 19 , 1609406920976417.
Hays, D. G., & McKibben, W. B. (2021). Promoting rigorous research: Generalizability and qualitative research. Journal of Counseling and Development, 99 (2), 178–188.
Horsburgh, D. (2003). Evaluation of qualitative research. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 12 (2), 307–312.
Howe, K. R. (2004). A critique of experimentalism. Qualitative Inquiry, 10 (1), 42–46.
Johnson, J. L., Adkins, D., & Chauvin, S. (2020). A review of the quality indicators of rigor in qualitative research. American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education, 84 (1), 7120.
Johnson, P., Buehring, A., Cassell, C., & Symon, G. (2006). Evaluating qualitative management research: Towards a contingent criteriology. International Journal of Management Reviews, 8 (3), 131–156.
Klein, H. K., & Myers, M. D. (1999). A set of principles for conducting and evaluating interpretive field studies in information systems. MIS Quarterly, 23 (1), 67–93.
Lather, P. (2004). This is your father’s paradigm: Government intrusion and the case of qualitative research in education. Qualitative Inquiry, 10 (1), 15–34.
Levitt, H. M., Morrill, Z., Collins, K. M., & Rizo, J. L. (2021). The methodological integrity of critical qualitative research: Principles to support design and research review. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 68 (3), 357.
Lincoln, Y. S., & Guba, E. G. (1986). But is it rigorous? Trustworthiness and authenticity in naturalistic evaluation. New Directions for Program Evaluation, 1986 (30), 73–84.
Lincoln, Y. S., & Guba, E. G. (2000). Paradigmatic controversies, contradictions and emerging confluences. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), Handbook of qualitative research (2nd ed., pp. 163–188). Sage Publications.
Madill, A., Jordan, A., & Shirley, C. (2000). Objectivity and reliability in qualitative analysis: Realist, contextualist and radical constructionist epistemologies. British Journal of Psychology, 91 (1), 1–20.
Mays, N., & Pope, C. (2020). Quality in qualitative research. Qualitative Research in Health Care . https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119410867.ch15
McGinley, S., Wei, W., Zhang, L., & Zheng, Y. (2021). The state of qualitative research in hospitality: A 5-year review 2014 to 2019. Cornell Hospitality Quarterly, 62 (1), 8–20.
Merriam, S., & Tisdell, E. (2016). Qualitative research: A guide to design and implementation. San Francisco, US.
Meyer, M., & Dykes, J. (2019). Criteria for rigor in visualization design study. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 26 (1), 87–97.
Monrouxe, L. V., & Rees, C. E. (2020). When I say… quantification in qualitative research. Medical Education, 54 (3), 186–187.
Morrow, S. L. (2005). Quality and trustworthiness in qualitative research in counseling psychology. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 52 (2), 250.
Morse, J. M. (2003). A review committee’s guide for evaluating qualitative proposals. Qualitative Health Research, 13 (6), 833–851.
Nassaji, H. (2020). Good qualitative research. Language Teaching Research, 24 (4), 427–431.
O’Brien, B. C., Harris, I. B., Beckman, T. J., Reed, D. A., & Cook, D. A. (2014). Standards for reporting qualitative research: A synthesis of recommendations. Academic Medicine, 89 (9), 1245–1251.
O’Connor, C., & Joffe, H. (2020). Intercoder reliability in qualitative research: Debates and practical guidelines. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 19 , 1609406919899220.
Reid, A., & Gough, S. (2000). Guidelines for reporting and evaluating qualitative research: What are the alternatives? Environmental Education Research, 6 (1), 59–91.
Rocco, T. S. (2010). Criteria for evaluating qualitative studies. Human Resource Development International . https://doi.org/10.1080/13678868.2010.501959
Sandberg, J. (2000). Understanding human competence at work: An interpretative approach. Academy of Management Journal, 43 (1), 9–25.
Schwandt, T. A. (1996). Farewell to criteriology. Qualitative Inquiry, 2 (1), 58–72.
Seale, C. (1999). Quality in qualitative research. Qualitative Inquiry, 5 (4), 465–478.
Shenton, A. K. (2004). Strategies for ensuring trustworthiness in qualitative research projects. Education for Information, 22 (2), 63–75.
Sparkes, A. C. (2001). Myth 94: Qualitative health researchers will agree about validity. Qualitative Health Research, 11 (4), 538–552.
Spencer, L., Ritchie, J., Lewis, J., & Dillon, L. (2004). Quality in qualitative evaluation: A framework for assessing research evidence.
Stenfors, T., Kajamaa, A., & Bennett, D. (2020). How to assess the quality of qualitative research. The Clinical Teacher, 17 (6), 596–599.
Taylor, E. W., Beck, J., & Ainsworth, E. (2001). Publishing qualitative adult education research: A peer review perspective. Studies in the Education of Adults, 33 (2), 163–179.
Tong, A., Sainsbury, P., & Craig, J. (2007). Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): A 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. International Journal for Quality in Health Care, 19 (6), 349–357.
Tracy, S. J. (2010). Qualitative quality: Eight “big-tent” criteria for excellent qualitative research. Qualitative Inquiry, 16 (10), 837–851.
Download references
Open access funding provided by TU Wien (TUW).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Informatics, Technische Universität Wien, 1040, Vienna, Austria
Drishti Yadav
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Drishti Yadav .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Yadav, D. Criteria for Good Qualitative Research: A Comprehensive Review. Asia-Pacific Edu Res 31 , 679–689 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-021-00619-0
Download citation
Accepted : 28 August 2021
Published : 18 September 2021
Issue Date : December 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-021-00619-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Qualitative research
- Evaluative criteria
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types and Guide
Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types and Guide
Table of Contents

Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a type of research methodology that focuses on exploring and understanding people’s beliefs, attitudes, behaviors, and experiences through the collection and analysis of non-numerical data. It seeks to answer research questions through the examination of subjective data, such as interviews, focus groups, observations, and textual analysis.
Qualitative research aims to uncover the meaning and significance of social phenomena, and it typically involves a more flexible and iterative approach to data collection and analysis compared to quantitative research. Qualitative research is often used in fields such as sociology, anthropology, psychology, and education.
Qualitative Research Methods

Qualitative Research Methods are as follows:
One-to-One Interview
This method involves conducting an interview with a single participant to gain a detailed understanding of their experiences, attitudes, and beliefs. One-to-one interviews can be conducted in-person, over the phone, or through video conferencing. The interviewer typically uses open-ended questions to encourage the participant to share their thoughts and feelings. One-to-one interviews are useful for gaining detailed insights into individual experiences.
Focus Groups
This method involves bringing together a group of people to discuss a specific topic in a structured setting. The focus group is led by a moderator who guides the discussion and encourages participants to share their thoughts and opinions. Focus groups are useful for generating ideas and insights, exploring social norms and attitudes, and understanding group dynamics.
Ethnographic Studies
This method involves immersing oneself in a culture or community to gain a deep understanding of its norms, beliefs, and practices. Ethnographic studies typically involve long-term fieldwork and observation, as well as interviews and document analysis. Ethnographic studies are useful for understanding the cultural context of social phenomena and for gaining a holistic understanding of complex social processes.
Text Analysis
This method involves analyzing written or spoken language to identify patterns and themes. Text analysis can be quantitative or qualitative. Qualitative text analysis involves close reading and interpretation of texts to identify recurring themes, concepts, and patterns. Text analysis is useful for understanding media messages, public discourse, and cultural trends.
This method involves an in-depth examination of a single person, group, or event to gain an understanding of complex phenomena. Case studies typically involve a combination of data collection methods, such as interviews, observations, and document analysis, to provide a comprehensive understanding of the case. Case studies are useful for exploring unique or rare cases, and for generating hypotheses for further research.
Process of Observation
This method involves systematically observing and recording behaviors and interactions in natural settings. The observer may take notes, use audio or video recordings, or use other methods to document what they see. Process of observation is useful for understanding social interactions, cultural practices, and the context in which behaviors occur.
Record Keeping
This method involves keeping detailed records of observations, interviews, and other data collected during the research process. Record keeping is essential for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the data, and for providing a basis for analysis and interpretation.
This method involves collecting data from a large sample of participants through a structured questionnaire. Surveys can be conducted in person, over the phone, through mail, or online. Surveys are useful for collecting data on attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors, and for identifying patterns and trends in a population.
Qualitative data analysis is a process of turning unstructured data into meaningful insights. It involves extracting and organizing information from sources like interviews, focus groups, and surveys. The goal is to understand people’s attitudes, behaviors, and motivations
Qualitative Research Analysis Methods
Qualitative Research analysis methods involve a systematic approach to interpreting and making sense of the data collected in qualitative research. Here are some common qualitative data analysis methods:
Thematic Analysis
This method involves identifying patterns or themes in the data that are relevant to the research question. The researcher reviews the data, identifies keywords or phrases, and groups them into categories or themes. Thematic analysis is useful for identifying patterns across multiple data sources and for generating new insights into the research topic.
Content Analysis
This method involves analyzing the content of written or spoken language to identify key themes or concepts. Content analysis can be quantitative or qualitative. Qualitative content analysis involves close reading and interpretation of texts to identify recurring themes, concepts, and patterns. Content analysis is useful for identifying patterns in media messages, public discourse, and cultural trends.
Discourse Analysis
This method involves analyzing language to understand how it constructs meaning and shapes social interactions. Discourse analysis can involve a variety of methods, such as conversation analysis, critical discourse analysis, and narrative analysis. Discourse analysis is useful for understanding how language shapes social interactions, cultural norms, and power relationships.
Grounded Theory Analysis
This method involves developing a theory or explanation based on the data collected. Grounded theory analysis starts with the data and uses an iterative process of coding and analysis to identify patterns and themes in the data. The theory or explanation that emerges is grounded in the data, rather than preconceived hypotheses. Grounded theory analysis is useful for understanding complex social phenomena and for generating new theoretical insights.
Narrative Analysis
This method involves analyzing the stories or narratives that participants share to gain insights into their experiences, attitudes, and beliefs. Narrative analysis can involve a variety of methods, such as structural analysis, thematic analysis, and discourse analysis. Narrative analysis is useful for understanding how individuals construct their identities, make sense of their experiences, and communicate their values and beliefs.
Phenomenological Analysis
This method involves analyzing how individuals make sense of their experiences and the meanings they attach to them. Phenomenological analysis typically involves in-depth interviews with participants to explore their experiences in detail. Phenomenological analysis is useful for understanding subjective experiences and for developing a rich understanding of human consciousness.
Comparative Analysis
This method involves comparing and contrasting data across different cases or groups to identify similarities and differences. Comparative analysis can be used to identify patterns or themes that are common across multiple cases, as well as to identify unique or distinctive features of individual cases. Comparative analysis is useful for understanding how social phenomena vary across different contexts and groups.
Applications of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research has many applications across different fields and industries. Here are some examples of how qualitative research is used:
- Market Research: Qualitative research is often used in market research to understand consumer attitudes, behaviors, and preferences. Researchers conduct focus groups and one-on-one interviews with consumers to gather insights into their experiences and perceptions of products and services.
- Health Care: Qualitative research is used in health care to explore patient experiences and perspectives on health and illness. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with patients and their families to gather information on their experiences with different health care providers and treatments.
- Education: Qualitative research is used in education to understand student experiences and to develop effective teaching strategies. Researchers conduct classroom observations and interviews with students and teachers to gather insights into classroom dynamics and instructional practices.
- Social Work : Qualitative research is used in social work to explore social problems and to develop interventions to address them. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with individuals and families to understand their experiences with poverty, discrimination, and other social problems.
- Anthropology : Qualitative research is used in anthropology to understand different cultures and societies. Researchers conduct ethnographic studies and observe and interview members of different cultural groups to gain insights into their beliefs, practices, and social structures.
- Psychology : Qualitative research is used in psychology to understand human behavior and mental processes. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with individuals to explore their thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
- Public Policy : Qualitative research is used in public policy to explore public attitudes and to inform policy decisions. Researchers conduct focus groups and one-on-one interviews with members of the public to gather insights into their perspectives on different policy issues.
How to Conduct Qualitative Research
Here are some general steps for conducting qualitative research:
- Identify your research question: Qualitative research starts with a research question or set of questions that you want to explore. This question should be focused and specific, but also broad enough to allow for exploration and discovery.
- Select your research design: There are different types of qualitative research designs, including ethnography, case study, grounded theory, and phenomenology. You should select a design that aligns with your research question and that will allow you to gather the data you need to answer your research question.
- Recruit participants: Once you have your research question and design, you need to recruit participants. The number of participants you need will depend on your research design and the scope of your research. You can recruit participants through advertisements, social media, or through personal networks.
- Collect data: There are different methods for collecting qualitative data, including interviews, focus groups, observation, and document analysis. You should select the method or methods that align with your research design and that will allow you to gather the data you need to answer your research question.
- Analyze data: Once you have collected your data, you need to analyze it. This involves reviewing your data, identifying patterns and themes, and developing codes to organize your data. You can use different software programs to help you analyze your data, or you can do it manually.
- Interpret data: Once you have analyzed your data, you need to interpret it. This involves making sense of the patterns and themes you have identified, and developing insights and conclusions that answer your research question. You should be guided by your research question and use your data to support your conclusions.
- Communicate results: Once you have interpreted your data, you need to communicate your results. This can be done through academic papers, presentations, or reports. You should be clear and concise in your communication, and use examples and quotes from your data to support your findings.
Examples of Qualitative Research
Here are some real-time examples of qualitative research:
- Customer Feedback: A company may conduct qualitative research to understand the feedback and experiences of its customers. This may involve conducting focus groups or one-on-one interviews with customers to gather insights into their attitudes, behaviors, and preferences.
- Healthcare : A healthcare provider may conduct qualitative research to explore patient experiences and perspectives on health and illness. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with patients and their families to gather information on their experiences with different health care providers and treatments.
- Education : An educational institution may conduct qualitative research to understand student experiences and to develop effective teaching strategies. This may involve conducting classroom observations and interviews with students and teachers to gather insights into classroom dynamics and instructional practices.
- Social Work: A social worker may conduct qualitative research to explore social problems and to develop interventions to address them. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with individuals and families to understand their experiences with poverty, discrimination, and other social problems.
- Anthropology : An anthropologist may conduct qualitative research to understand different cultures and societies. This may involve conducting ethnographic studies and observing and interviewing members of different cultural groups to gain insights into their beliefs, practices, and social structures.
- Psychology : A psychologist may conduct qualitative research to understand human behavior and mental processes. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with individuals to explore their thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
- Public Policy: A government agency or non-profit organization may conduct qualitative research to explore public attitudes and to inform policy decisions. This may involve conducting focus groups and one-on-one interviews with members of the public to gather insights into their perspectives on different policy issues.
Purpose of Qualitative Research
The purpose of qualitative research is to explore and understand the subjective experiences, behaviors, and perspectives of individuals or groups in a particular context. Unlike quantitative research, which focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis, qualitative research aims to provide in-depth, descriptive information that can help researchers develop insights and theories about complex social phenomena.
Qualitative research can serve multiple purposes, including:
- Exploring new or emerging phenomena : Qualitative research can be useful for exploring new or emerging phenomena, such as new technologies or social trends. This type of research can help researchers develop a deeper understanding of these phenomena and identify potential areas for further study.
- Understanding complex social phenomena : Qualitative research can be useful for exploring complex social phenomena, such as cultural beliefs, social norms, or political processes. This type of research can help researchers develop a more nuanced understanding of these phenomena and identify factors that may influence them.
- Generating new theories or hypotheses: Qualitative research can be useful for generating new theories or hypotheses about social phenomena. By gathering rich, detailed data about individuals’ experiences and perspectives, researchers can develop insights that may challenge existing theories or lead to new lines of inquiry.
- Providing context for quantitative data: Qualitative research can be useful for providing context for quantitative data. By gathering qualitative data alongside quantitative data, researchers can develop a more complete understanding of complex social phenomena and identify potential explanations for quantitative findings.
When to use Qualitative Research
Here are some situations where qualitative research may be appropriate:
- Exploring a new area: If little is known about a particular topic, qualitative research can help to identify key issues, generate hypotheses, and develop new theories.
- Understanding complex phenomena: Qualitative research can be used to investigate complex social, cultural, or organizational phenomena that are difficult to measure quantitatively.
- Investigating subjective experiences: Qualitative research is particularly useful for investigating the subjective experiences of individuals or groups, such as their attitudes, beliefs, values, or emotions.
- Conducting formative research: Qualitative research can be used in the early stages of a research project to develop research questions, identify potential research participants, and refine research methods.
- Evaluating interventions or programs: Qualitative research can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions or programs by collecting data on participants’ experiences, attitudes, and behaviors.

Characteristics of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is characterized by several key features, including:
- Focus on subjective experience: Qualitative research is concerned with understanding the subjective experiences, beliefs, and perspectives of individuals or groups in a particular context. Researchers aim to explore the meanings that people attach to their experiences and to understand the social and cultural factors that shape these meanings.
- Use of open-ended questions: Qualitative research relies on open-ended questions that allow participants to provide detailed, in-depth responses. Researchers seek to elicit rich, descriptive data that can provide insights into participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Sampling-based on purpose and diversity: Qualitative research often involves purposive sampling, in which participants are selected based on specific criteria related to the research question. Researchers may also seek to include participants with diverse experiences and perspectives to capture a range of viewpoints.
- Data collection through multiple methods: Qualitative research typically involves the use of multiple data collection methods, such as in-depth interviews, focus groups, and observation. This allows researchers to gather rich, detailed data from multiple sources, which can provide a more complete picture of participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Inductive data analysis: Qualitative research relies on inductive data analysis, in which researchers develop theories and insights based on the data rather than testing pre-existing hypotheses. Researchers use coding and thematic analysis to identify patterns and themes in the data and to develop theories and explanations based on these patterns.
- Emphasis on researcher reflexivity: Qualitative research recognizes the importance of the researcher’s role in shaping the research process and outcomes. Researchers are encouraged to reflect on their own biases and assumptions and to be transparent about their role in the research process.
Advantages of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research offers several advantages over other research methods, including:
- Depth and detail: Qualitative research allows researchers to gather rich, detailed data that provides a deeper understanding of complex social phenomena. Through in-depth interviews, focus groups, and observation, researchers can gather detailed information about participants’ experiences and perspectives that may be missed by other research methods.
- Flexibility : Qualitative research is a flexible approach that allows researchers to adapt their methods to the research question and context. Researchers can adjust their research methods in real-time to gather more information or explore unexpected findings.
- Contextual understanding: Qualitative research is well-suited to exploring the social and cultural context in which individuals or groups are situated. Researchers can gather information about cultural norms, social structures, and historical events that may influence participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Participant perspective : Qualitative research prioritizes the perspective of participants, allowing researchers to explore subjective experiences and understand the meanings that participants attach to their experiences.
- Theory development: Qualitative research can contribute to the development of new theories and insights about complex social phenomena. By gathering rich, detailed data and using inductive data analysis, researchers can develop new theories and explanations that may challenge existing understandings.
- Validity : Qualitative research can offer high validity by using multiple data collection methods, purposive and diverse sampling, and researcher reflexivity. This can help ensure that findings are credible and trustworthy.
Limitations of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research also has some limitations, including:
- Subjectivity : Qualitative research relies on the subjective interpretation of researchers, which can introduce bias into the research process. The researcher’s perspective, beliefs, and experiences can influence the way data is collected, analyzed, and interpreted.
- Limited generalizability: Qualitative research typically involves small, purposive samples that may not be representative of larger populations. This limits the generalizability of findings to other contexts or populations.
- Time-consuming: Qualitative research can be a time-consuming process, requiring significant resources for data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
- Resource-intensive: Qualitative research may require more resources than other research methods, including specialized training for researchers, specialized software for data analysis, and transcription services.
- Limited reliability: Qualitative research may be less reliable than quantitative research, as it relies on the subjective interpretation of researchers. This can make it difficult to replicate findings or compare results across different studies.
- Ethics and confidentiality: Qualitative research involves collecting sensitive information from participants, which raises ethical concerns about confidentiality and informed consent. Researchers must take care to protect the privacy and confidentiality of participants and obtain informed consent.
Also see Research Methods
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide
Qualitative research as evidence: expanding the paradigm for evidence-based healthcare
Affiliation.
- 1 Nuffield Department of Primary Care Health Sciences, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK.
- PMID: 30850372
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjebm-2018-111131
Keywords: critical appraisal; patient experience; qualitative health research.
- Evidence-Based Practice* / methods
- Qualitative Research*

Key Concepts in Qualitative Research
Qualitative studies, as we learned earlier in this course, use an inductive method. Meaning, they seek to understand a phenomenon, and then use an emergency design that evolves as the research takes place in order to finally produce a theory. Qualitative designs are also subjective and use an analysis of words to understand the meaning of viewpoints and realities of the participants.
- Definition of Qualitative Methodology
- Assumptions of Qualitative Methods
- Types of Qualitative Studies
- Population and Samples
- Common Data Collection Methods
- Data Analyses
- Common Statistical Analyses
Objectives:
- Define qualitative research methodology.
- Describe the foundational assumptions of qualitative methods.
- Understand the types of qualitative studies.
- Describe sampling in qualitative research.
- Describe the common data collection methods and data analyses in qualitative research.
- Define mixed methods research.
Qualitative Research Methodology
A key concept is to remember that qualitative research is generally not generalizable, as we are not testing a hypothesis and not making inferences based on data. However, in qualitative research, it is often revolving around the concept of transferability. Transferability is established by providing evidence that the research study’s findings could be applicable to other contexts, situations, times, and populations.
Foundational Assumptions of Qualitative Methods.
The overarching assumptions in qualitative methodology include:
- Truth is fluid. Meaning, it is flexible and holistic.
- Some aspects of humanity and the human experience is best examined with qualitative methods so that we can have a deeper understanding of a person’s experience and viewpoints.
In general, qualitative design (methodology):
- Is flexible and capable to changing as the study progresses, depending on what is learned during the data collection.
- It often uses various data collection strategies in order to collect rich data.
- Is holistic in nature, with the goal of understanding of the whole.
- Researchers are involved, reflexive, and can interact with participants during data collection.
Types of qualitative studies
The common types of qualitative research include:
Phenomenology: the lived experiences; useful to learn about the human experience.
Grounded Theory: to discover the process; often a social process in nursing.
Ethnography: to describe a culture; used commonly in nursing to describe cultures (Brown, 2017).
Historical: a retrospective examination of events to explain and understand (Schmidt & Brown, 2019).
Case Study: a comprehensive investigation of individuals or groups of people to gain insight into a specific situation (Brown, 2017).
Sampling in Qualitative Research
Sample sizes in qualitative research are often much smaller than quantitative research. Remember, we are not generalizing findings to a larger population, so the sample size can be very small.
One of the reasons samples are smaller is because each participant contributes a large amount of data in the form of a narrative. The narrative (words) is then analyzed for themes (thematic analysis) and this takes a lot of time.
Data saturation involves sampling until no new information is obtained and redundancy is achieved. This can vary the sample size, depending on various factors. Data quality can absolutely affect the sample size. If participants are insightful and can share their narrative well, then saturation may be achieved with a relatively small sample.
Common Data Collection Methods and Data Analyses in Qualitative Research
Types of data collection methods in qualitative research include:
Self-Reports : These can include unstructured interviews that begin with a general question, and then subsequent questions are guided by the initial answers. Researchers utilize a general topic guide so that the interviews progress.
Focus Group Interviews : As above, but in a group setting when opinions and experiences are solicited simultaneously. The researcher/interviewer acts as moderator to keep conversation progressing.
Open-Ended Questions in a Survey : Participants can fill in a narrative as they wish. This sometimes elicits information that may not have been obtained in an in-person interview.
Personal Diaries : A standard data course in historical research.
Observations : The aim of observational is to understand the behaviors and experiences of people as they occur. The researcher participates in whatever group is being studies, which often elicits insights that would have eluded more passive or concealed observers.
Next are commonly used data analysis strategies used in qualitative methods. The intent is to introduce terms and how these relate to qualitative analysis.
Coding : line by line coding of the transcript is done to identify reappearing concepts in the data (Schmidt & Brown, 2019). Coding is the process of labeling and organizing your qualitative data to identify different themes and the relationships between them. When coding, you assign labels to words or phrases that represent important (and recurring) themes in each response.
Open coding : the grouping of data into main categories (Schmidt & Brown, 2019). With open coding, you break your data into discrete parts and create “codes” to label them. As its name would imply, open-coding is meant to open you up to new theoretical possibilities, as you first engage with your qualitative data.
Axial coding : after open coding is completed, the categories are analyzed (Schmidt & Brown, 2019). Axial coding is when the researcher begins to draw connections between ideas in their research.
There are some software programs that analyze qualitative data in transcripts to look for themes or commonly appearing concepts (Schmidt & Brown, 2019).
This can also be done manually by researchers. Some use index cards, tally marks, and other methods to note common themes/patterns (Leibold, 2020).
Mixed Methods Research
Finally, not all research is simply qualitative or quantitative. Research in which both types of methodology is utilized is called mixed-methods research . Mixed methods is a research approach whereby researchers collect and analyze both quantitative and qualitative data within the same study.
Growth of mixed methods research in nursing and healthcare has occurred at a time of internationally increasing complexity in healthcare delivery. Mixed methods research draws on potential strengths of both qualitative and quantitative methods, allowing researchers to explore diverse perspectives and uncover relationships that exist between the intricate layers of our multifaceted research questions. As providers and policy makers strive to ensure quality and safety for patients and families, researchers can use mixed methods to explore contemporary healthcare trends and practices across increasingly diverse practice settings (Shorten & Smith, 2017).
References & Attribution
“ Green check mark ” by rawpixel licensed CC0 .
Brown, S. J. (2017). Evidence-based nursing: The research-practice connection (4th ed.). Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Leibold, N. (2020). Research variables. Measures and Concepts Commonly Encountered in EBP. CC BY-NC
Schmidt, N. A. & Brown, J. M. (2019). Evidence-based practice for nurses: Appraisal and application of research (4th ed.). Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Shorten, A., & Smith, J. (2017). Mixed methods research: Expanding the evidence base. Evidence-Based Nursing, 20 , 74-75.
Evidence-Based Practice & Research Methodologies Copyright © by Tracy Fawns is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- Write for Us
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Volume 22, Issue 1
- How to appraise qualitative research
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- Calvin Moorley 1 ,
- Xabi Cathala 2
- 1 Nursing Research and Diversity in Care, School of Health and Social Care , London South Bank University , London , UK
- 2 Institute of Vocational Learning , School of Health and Social Care, London South Bank University , London , UK
- Correspondence to Dr Calvin Moorley, Nursing Research and Diversity in Care, School of Health and Social Care, London South Bank University, London SE1 0AA, UK; Moorleyc{at}lsbu.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1136/ebnurs-2018-103044
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
Introduction
In order to make a decision about implementing evidence into practice, nurses need to be able to critically appraise research. Nurses also have a professional responsibility to maintain up-to-date practice. 1 This paper provides a guide on how to critically appraise a qualitative research paper.
What is qualitative research?
- View inline
Useful terms
Some of the qualitative approaches used in nursing research include grounded theory, phenomenology, ethnography, case study (can lend itself to mixed methods) and narrative analysis. The data collection methods used in qualitative research include in depth interviews, focus groups, observations and stories in the form of diaries or other documents. 3
Authenticity
Title, keywords, authors and abstract.
In a previous paper, we discussed how the title, keywords, authors’ positions and affiliations and abstract can influence the authenticity and readability of quantitative research papers, 4 the same applies to qualitative research. However, other areas such as the purpose of the study and the research question, theoretical and conceptual frameworks, sampling and methodology also need consideration when appraising a qualitative paper.
Purpose and question
The topic under investigation in the study should be guided by a clear research question or a statement of the problem or purpose. An example of a statement can be seen in table 2 . Unlike most quantitative studies, qualitative research does not seek to test a hypothesis. The research statement should be specific to the problem and should be reflected in the design. This will inform the reader of what will be studied and justify the purpose of the study. 5
Example of research question and problem statement
An appropriate literature review should have been conducted and summarised in the paper. It should be linked to the subject, using peer-reviewed primary research which is up to date. We suggest papers with a age limit of 5–8 years excluding original work. The literature review should give the reader a balanced view on what has been written on the subject. It is worth noting that for some qualitative approaches some literature reviews are conducted after the data collection to minimise bias, for example, in grounded theory studies. In phenomenological studies, the review sometimes occurs after the data analysis. If this is the case, the author(s) should make this clear.
Theoretical and conceptual frameworks
Most authors use the terms theoretical and conceptual frameworks interchangeably. Usually, a theoretical framework is used when research is underpinned by one theory that aims to help predict, explain and understand the topic investigated. A theoretical framework is the blueprint that can hold or scaffold a study’s theory. Conceptual frameworks are based on concepts from various theories and findings which help to guide the research. 6 It is the researcher’s understanding of how different variables are connected in the study, for example, the literature review and research question. Theoretical and conceptual frameworks connect the researcher to existing knowledge and these are used in a study to help to explain and understand what is being investigated. A framework is the design or map for a study. When you are appraising a qualitative paper, you should be able to see how the framework helped with (1) providing a rationale and (2) the development of research questions or statements. 7 You should be able to identify how the framework, research question, purpose and literature review all complement each other.
There remains an ongoing debate in relation to what an appropriate sample size should be for a qualitative study. We hold the view that qualitative research does not seek to power and a sample size can be as small as one (eg, a single case study) or any number above one (a grounded theory study) providing that it is appropriate and answers the research problem. Shorten and Moorley 8 explain that three main types of sampling exist in qualitative research: (1) convenience (2) judgement or (3) theoretical. In the paper , the sample size should be stated and a rationale for how it was decided should be clear.
Methodology
Qualitative research encompasses a variety of methods and designs. Based on the chosen method or design, the findings may be reported in a variety of different formats. Table 3 provides the main qualitative approaches used in nursing with a short description.
Different qualitative approaches
The authors should make it clear why they are using a qualitative methodology and the chosen theoretical approach or framework. The paper should provide details of participant inclusion and exclusion criteria as well as recruitment sites where the sample was drawn from, for example, urban, rural, hospital inpatient or community. Methods of data collection should be identified and be appropriate for the research statement/question.
Data collection
Overall there should be a clear trail of data collection. The paper should explain when and how the study was advertised, participants were recruited and consented. it should also state when and where the data collection took place. Data collection methods include interviews, this can be structured or unstructured and in depth one to one or group. 9 Group interviews are often referred to as focus group interviews these are often voice recorded and transcribed verbatim. It should be clear if these were conducted face to face, telephone or any other type of media used. Table 3 includes some data collection methods. Other collection methods not included in table 3 examples are observation, diaries, video recording, photographs, documents or objects (artefacts). The schedule of questions for interview or the protocol for non-interview data collection should be provided, available or discussed in the paper. Some authors may use the term ‘recruitment ended once data saturation was reached’. This simply mean that the researchers were not gaining any new information at subsequent interviews, so they stopped data collection.
The data collection section should include details of the ethical approval gained to carry out the study. For example, the strategies used to gain participants’ consent to take part in the study. The authors should make clear if any ethical issues arose and how these were resolved or managed.
The approach to data analysis (see ref 10 ) needs to be clearly articulated, for example, was there more than one person responsible for analysing the data? How were any discrepancies in findings resolved? An audit trail of how the data were analysed including its management should be documented. If member checking was used this should also be reported. This level of transparency contributes to the trustworthiness and credibility of qualitative research. Some researchers provide a diagram of how they approached data analysis to demonstrate the rigour applied ( figure 1 ).
- Download figure
- Open in new tab
- Download powerpoint
Example of data analysis diagram.
Validity and rigour
The study’s validity is reliant on the statement of the question/problem, theoretical/conceptual framework, design, method, sample and data analysis. When critiquing qualitative research, these elements will help you to determine the study’s reliability. Noble and Smith 11 explain that validity is the integrity of data methods applied and that findings should accurately reflect the data. Rigour should acknowledge the researcher’s role and involvement as well as any biases. Essentially it should focus on truth value, consistency and neutrality and applicability. 11 The authors should discuss if they used triangulation (see table 2 ) to develop the best possible understanding of the phenomena.
Themes and interpretations and implications for practice
In qualitative research no hypothesis is tested, therefore, there is no specific result. Instead, qualitative findings are often reported in themes based on the data analysed. The findings should be clearly linked to, and reflect, the data. This contributes to the soundness of the research. 11 The researchers should make it clear how they arrived at the interpretations of the findings. The theoretical or conceptual framework used should be discussed aiding the rigour of the study. The implications of the findings need to be made clear and where appropriate their applicability or transferability should be identified. 12
Discussions, recommendations and conclusions
The discussion should relate to the research findings as the authors seek to make connections with the literature reviewed earlier in the paper to contextualise their work. A strong discussion will connect the research aims and objectives to the findings and will be supported with literature if possible. A paper that seeks to influence nursing practice will have a recommendations section for clinical practice and research. A good conclusion will focus on the findings and discussion of the phenomena investigated.
Qualitative research has much to offer nursing and healthcare, in terms of understanding patients’ experience of illness, treatment and recovery, it can also help to understand better areas of healthcare practice. However, it must be done with rigour and this paper provides some guidance for appraising such research. To help you critique a qualitative research paper some guidance is provided in table 4 .
Some guidance for critiquing qualitative research
- ↵ Nursing and Midwifery Council . The code: Standard of conduct, performance and ethics for nurses and midwives . 2015 https://www.nmc.org.uk/globalassets/sitedocuments/nmc-publications/nmc-code.pdf ( accessed 21 Aug 18 ).
- Barrett D ,
- Cathala X ,
- Shorten A ,
Patient consent for publication Not required.
Competing interests None declared.
Provenance and peer review Commissioned; internally peer reviewed.
Read the full text or download the PDF:
News alert: UC Berkeley has announced its next university librarian
Secondary menu
- Log in to your Library account
- Hours and Maps
- Connect from Off Campus
- UC Berkeley Home
Search form
Research methods--quantitative, qualitative, and more: evidence synthesis/systematic reviews.
- Quantitative Research
- Qualitative Research
- Data Science Methods (Machine Learning, AI, Big Data)
- Text Mining and Computational Text Analysis
- Evidence Synthesis/Systematic Reviews
- Get Data, Get Help!
About Evidence Synthesis and Systematic Reviews
According to the Royal Society, 'evidence synthesis' refers to the process of bringing together information from a range of sources and disciplines to inform debates and decisions on specific issues. They generally include a methodical and comprehensive literature synthesis focused on a well-formulated research question. Their aim is to identify and synthesize all of the scholarly research on a particular topic, including both published and unpublished studies. Evidence syntheses are conducted in an unbiased, reproducible way to provide evidence for practice and policy-making, as well as to identify gaps in the research. Evidence syntheses may also include a meta-analysis, a more quantitative process of synthesizing and visualizing data retrieved from various studies.
Evidence syntheses are much more time-intensive than traditional literature reviews and require a multi-person research team. See this PredicTER tool to get a sense of a systematic review timeline (one type of evidence synthesis). Before embarking on an evidence synthesis, it's important to clearly identify your reasons for conducting one.
(From the Cornell University Library Research Guide, A Guide to Evidence Synthesis )
Open Access Evidence Synthesis Resources
(From the Cornell University Library Research Guide, A Guide to Evidence Synthesis )
New content will be added by the Cornell University team to the list below as it becomes available. Browse our public Zotero library of evidence synthesis research here.
Training Materials:
The Evidence Synthesis Institute is a training program aimed at library staff supporting evidence syntheses in topics outside of the health sciences, and is fully funded by the Institute of Museum and Library Services (IMLS). The teaching slides from this institute are available here and are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License . Slides cover all aspects of the evidence synthesis process and much of the content is applicable to researchers as well as librarians.
Introduction to Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis : This Massive Open Online Course (MOOC), offered through Coursera, describes and provides instruction for completing all stages of systematic reviews and meta-analyses.
Cochrane Interactive Learning provides tutorials for performing systematic reviews on health-related topics. Module 1: Introduction to Conducting Systematic Reviews is free if you sign up for a Cochrane account.
INASP provides a free search strategies tutorial to teach users how to clearly define and describe a search topic, identify suitable search terms, pick the best platform(s) on which to search, and use tools and techniques to refine and modify your search.
Software Tools:
SR Toolbox : a web-based catalogue of tools that support various tasks within the systematic review and wider evidence synthesis process
Rayyan : Free article screening tool
Zotero : Free citation management tool
RawGraphs : Free tool for creating appealing graphs
Open Science Framework Preregistration : Free, open source resource for preregistering evidence synthesis protocols, with well-documented guidance on using the tool
SnowGlobe : Free tool for "snowballing" included resources (locating their citations, and those papers that have cited them).
Grey Literature:
[Grey literature includes reliable sources that may not necessarily have been published in a peer reviewed journal, such as government reports. PubMed is a good source for grey literature.] PubMed comprises more than 32 million citations for biomedical literature from MEDLINE, life science journals, and online books. Citations may include links to full text content from PubMed Central and publisher web sites. The PubMed Trainer's Toolkit contains instruction materials and short tutorials for navigating PubMed.
Is a Systematic Review for Me?
(From the University of California, San Francisco Library Research Guide, Systematic Reviews )
Systematic review - A systematic review synthesizes data from articles into a summary review which has the potential to make conclusions more certain. Systematic reviews are considered the highest level of evidence in evidence-based medicine (EBM) evidence pyramid . An overview of the systematic review process includes:
- Time Commitment : Typically 12–24 months from start to finish (may take longer)
- Team Requirement : Typically 3-5 people at minimum. You will need at least a primary reviewer and a secondary reviewer. Other roles to consider include a subject expert, methodologist/statistician, operations manager, and medical librarian.
- Topic : A significant question is being asked and answered. The topic is not the subject of a recent review and is not being worked on currently by others.
If this doesn't meet your needs, see " A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies ".
Grant, Maria J., and Andrew Booth. “A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies.” Health information and libraries journal 26.2 (2009): 91–108. Web.
For your reference, see these examples of a UCSF-authored systematic review , scoping review , and protocol .
Systematic Review Resource List
(From the University of California, San Francisco Library Research Guide, Systematic Reviews )
- PRISMA reporting guidelines - for systematic reviews ( PRISMA 2020 ), scoping reviews ( PRISMA-ScR ), searching ( PRISMA-S ) & more
Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework (2005) & Scoping studies: advancing the methodology (2010) - Scoping review frameworks & guidelines
Systematic review handbooks & guidelines - Duke University
Steps in the systematic review process - Stanford University
Searching for & publishing systematic review protocols - Stanford University
Screening software for systematic reviews - Cambridge University
Critical appraisal tools - Memorial Sloan Kettering Library
Covidence- A Tool for Systematic Reviews
If you do decide to do a systematic review, UC Berkeley licenses Covidence, a tool to help you. In Covidence, you can import citations , screen titles and abstracts , upload references , screen full text , create forms for critical appraisal , perform risk of bias tables , complete data extraction , and export a PRISMA flowchart summarizing your review process. As an institutional member, our users have priority access to Covidence support. To access Covidence using the UC Berkeley institutional account , start at this page and follow the instructions.
- << Previous: Text Mining and Computational Text Analysis
- Next: Get Data, Get Help! >>
- Last Updated: Apr 3, 2023 3:14 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.berkeley.edu/researchmethods
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Volume 25, Issue 1
- Critical appraisal of qualitative research: necessity, partialities and the issue of bias
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5660-8224 Veronika Williams ,
- Anne-Marie Boylan ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4597-1276 David Nunan
- Nuffield Department of Primary Care Health Sciences , University of Oxford, Radcliffe Observatory Quarter , Oxford , UK
- Correspondence to Dr Veronika Williams, Nuffield Department of Primary Care Health Sciences, University of Oxford, Oxford OX2 6GG, UK; veronika.williams{at}phc.ox.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjebm-2018-111132
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
- qualitative research
Introduction
Qualitative evidence allows researchers to analyse human experience and provides useful exploratory insights into experiential matters and meaning, often explaining the ‘how’ and ‘why’. As we have argued previously 1 , qualitative research has an important place within evidence-based healthcare, contributing to among other things policy on patient safety, 2 prescribing, 3 4 and understanding chronic illness. 5 Equally, it offers additional insight into quantitative studies, explaining contextual factors surrounding a successful intervention or why an intervention might have ‘failed’ or ‘succeeded’ where effect sizes cannot. It is for these reasons that the MRC strongly recommends including qualitative evaluations when developing and evaluating complex interventions. 6
Critical appraisal of qualitative research
Is it necessary.
Although the importance of qualitative research to improve health services and care is now increasingly widely supported (discussed in paper 1), the role of appraising the quality of qualitative health research is still debated. 8 10 Despite a large body of literature focusing on appraisal and rigour, 9 11–15 often referred to as ‘trustworthiness’ 16 in qualitative research, there remains debate about how to —and even whether to—critically appraise qualitative research. 8–10 17–19 However, if we are to make a case for qualitative research as integral to evidence-based healthcare, then any argument to omit a crucial element of evidence-based practice is difficult to justify. That being said, simply applying the standards of rigour used to appraise studies based on the positivist paradigm (Positivism depends on quantifiable observations to test hypotheses and assumes that the researcher is independent of the study. Research situated within a positivist paradigm isbased purely on facts and consider the world to be external and objective and is concerned with validity, reliability and generalisability as measures of rigour.) would be misplaced given the different epistemological underpinnings of the two types of data.
Given its scope and its place within health research, the robust and systematic appraisal of qualitative research to assess its trustworthiness is as paramount to its implementation in clinical practice as any other type of research. It is important to appraise different qualitative studies in relation to the specific methodology used because the methodological approach is linked to the ‘outcome’ of the research (eg, theory development, phenomenological understandings and credibility of findings). Moreover, appraisal needs to go beyond merely describing the specific details of the methods used (eg, how data were collected and analysed), with additional focus needed on the overarching research design and its appropriateness in accordance with the study remit and objectives.
Poorly conducted qualitative research has been described as ‘worthless, becomes fiction and loses its utility’. 20 However, without a deep understanding of concepts of quality in qualitative research or at least an appropriate means to assess its quality, good qualitative research also risks being dismissed, particularly in the context of evidence-based healthcare where end users may not be well versed in this paradigm.
How is appraisal currently performed?
Appraising the quality of qualitative research is not a new concept—there are a number of published appraisal tools, frameworks and checklists in existence. 21–23 An important and often overlooked point is the confusion between tools designed for appraising methodological quality and reporting guidelines designed to assess the quality of methods reporting. An example is the Consolidate Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ) 24 checklist, which was designed to provide standards for authors when reporting qualitative research but is often mistaken for a methods appraisal tool. 10
Broadly speaking there are two types of critical appraisal approaches for qualitative research: checklists and frameworks. Checklists have often been criticised for confusing quality in qualitative research with ‘technical fixes’ 21 25 , resulting in the erroneous prioritisation of particular aspects of methodological processes over others (eg, multiple coding and triangulation). It could be argued that a checklist approach adopts the positivist paradigm, where the focus is on objectively assessing ‘quality’ where the assumptions is that the researcher is independent of the research conducted. This may result in the application of quantitative understandings of bias in order to judge aspects of recruitment, sampling, data collection and analysis in qualitative research papers. One of the most widely used appraisal tools is the Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP) 26 and along with the JBI QARI (Joanna Briggs Institute Qualitative Assessment and Assessment Instrument) 27 presents examples which tend to mimic the quantitative approach to appraisal. The CASP qualitative tool follows that of other CASP appraisal tools for quantitative research designs developed in the 1990s. The similarities are therefore unsurprising given the status of qualitative research at that time.
Frameworks focus on the overarching concepts of quality in qualitative research, including transparency, reflexivity, dependability and transferability (see box 1 ). 11–13 15 16 20 28 However, unless the reader is familiar with these concepts—their meaning and impact, and how to interpret them—they will have difficulty applying them when critically appraising a paper.
The main issue concerning currently available checklist and framework appraisal methods is that they take a broad brush approach to ‘qualitative’ research as whole, with few, if any, sufficiently differentiating between the different methodological approaches (eg, Grounded Theory, Interpretative Phenomenology, Discourse Analysis) nor different methods of data collection (interviewing, focus groups and observations). In this sense, it is akin to taking the entire field of ‘quantitative’ study designs and applying a single method or tool for their quality appraisal. In the case of qualitative research, checklists, therefore, offer only a blunt and arguably ineffective tool and potentially promote an incomplete understanding of good ‘quality’ in qualitative research. Likewise, current framework methods do not take into account how concepts differ in their application across the variety of qualitative approaches and, like checklists, they also do not differentiate between different qualitative methodologies.
On the need for specific appraisal tools
Current approaches to the appraisal of the methodological rigour of the differing types of qualitative research converge towards checklists or frameworks. More importantly, the current tools do not explicitly acknowledge the prejudices that may be present in the different types of qualitative research.
Concepts of rigour or trustworthiness within qualitative research 31
Transferability: the extent to which the presented study allows readers to make connections between the study’s data and wider community settings, ie, transfer conceptual findings to other contexts.
Credibility: extent to which a research account is believable and appropriate, particularly in relation to the stories told by participants and the interpretations made by the researcher.
Reflexivity: refers to the researchers’ engagement of continuous examination and explanation of how they have influenced a research project from choosing a research question to sampling, data collection, analysis and interpretation of data.
Transparency: making explicit the whole research process from sampling strategies, data collection to analysis. The rationale for decisions made is as important as the decisions themselves.
However, we often talk about these concepts in general terms, and it might be helpful to give some explicit examples of how the ‘technical processes’ affect these, for example, partialities related to:
Selection: recruiting participants via gatekeepers, such as healthcare professionals or clinicians, who may select them based on whether they believe them to be ‘good’ participants for interviews/focus groups.
Data collection: poor interview guide with closed questions which encourage yes/no answers and/leading questions.
Reflexivity and transparency: where researchers may focus their analysis on preconceived ideas rather than ground their analysis in the data and do not reflect on the impact of this in a transparent way.
The lack of tailored, method-specific appraisal tools has potentially contributed to the poor uptake and use of qualitative research for informing evidence-based decision making. To improve this situation, we propose the need for more robust quality appraisal tools that explicitly encompass both the core design aspects of all qualitative research (sampling/data collection/analysis) but also considered the specific partialities that can be presented with different methodological approaches. Such tools might draw on the strengths of current frameworks and checklists while providing users with sufficient understanding of concepts of rigour in relation to the different types of qualitative methods. We provide an outline of such tools in the third and final paper in this series.
As qualitative research becomes ever more embedded in health science research, and in order for that research to have better impact on healthcare decisions, we need to rethink critical appraisal and develop tools that allow differentiated evaluations of the myriad of qualitative methodological approaches rather than continuing to treat qualitative research as a single unified approach.
- Williams V ,
- Boylan AM ,
- Lingard L ,
- Orser B , et al
- Brawn R , et al
- Van Royen P ,
- Vermeire E , et al
- Barker M , et al
- McGannon KR
- Dixon-Woods M ,
- Agarwal S , et al
- Greenhalgh T ,
- Dennison L ,
- Morrison L ,
- Conway G , et al
- Barrett M ,
- Mayan M , et al
- Lockwood C ,
- Santiago-Delefosse M ,
- Bruchez C , et al
- Sainsbury P ,
- ↵ CASP (Critical Appraisal Skills Programme). date unknown . http://www.phru.nhs.uk/Pages/PHD/CASP.htm .
- ↵ The Joanna Briggs Institute . JBI QARI Critical appraisal checklist for interpretive & critical research . Adelaide : The Joanna Briggs Institute , 2014 .
- Stephens J ,
Contributors VW and DN: conceived the idea for this article. VW: wrote the first draft. AMB and DN: contributed to the final draft. All authors approve the submitted article.
Competing interests None declared.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Correction notice This article has been updated since its original publication to include a new reference (reference 1.)
Read the full text or download the PDF:
Artificial intelligence in qualitative research methods
A one-day community-building gathering.
- Starts: 09:30, 26 April 2024
- Ends: 16:00, 26 April 2024
- Location: BI - campus Oslo, room: A2-Red 13
- Contact: Renate Kratochvil ([email protected])
The purpose of this event is to bring together qualitative researchers from different parts of Norway, other Nordic countries, and beyond. The main objective is to establish relationships, learn from each other, and build a community.
During the day, you will hear from some prestigious scholars, learn what others are working on, receive (and give) feedback on work in progress, and socialize with like-minded colleagues.
This year, our main focus will be on the utilization of AI and machine learning in qualitative research. The recent advancements in these technologies present an array of opportunities and challenges for qualitative researchers and their traditional skills, as they can automate the processes of data collection, analysis, and presentation of findings. Through this event, we aim to delve deeper into the current hype surrounding AI and its possible implications for qualitative research.
Established scholars, early career researchers, and PhD students from all parts of Norway, other Nordic countries, and beyond are welcome to attend.
Keynote speakers
Catherine Welch, Katharina Cepa, Heidi Karlsen and David Morgan.
Work in progress
If you want to receive feedback on your work in progress (any management topic), please share a document of up to 2,000 words by April 16th. We welcome both early-stage ideas and proposals, as well as more developed drafts.
Participation is free, coffee & tea will be served.
The event is organized jointly by BI Qualitative Research Forum (Renate Kratochvil, Davide Nicolini & Victor Renza) and NHH (Inger Stensaker, Vidya Oruganti).
Provisional Programme
Room: A2 - Red 13
- Key notes by Catherine Welch (Trinity), Katharina Cepa (VU), Heidi Karlsen (BI) & David Morgan (Portland, zoom)
- Research speed dating
- Feedback on participants papers (Round tables, any topic)
- AI Showcasing discussions
Share this article:
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Can J Hosp Pharm
- v.68(3); May-Jun 2015

Qualitative Research: Data Collection, Analysis, and Management
Introduction.
In an earlier paper, 1 we presented an introduction to using qualitative research methods in pharmacy practice. In this article, we review some principles of the collection, analysis, and management of qualitative data to help pharmacists interested in doing research in their practice to continue their learning in this area. Qualitative research can help researchers to access the thoughts and feelings of research participants, which can enable development of an understanding of the meaning that people ascribe to their experiences. Whereas quantitative research methods can be used to determine how many people undertake particular behaviours, qualitative methods can help researchers to understand how and why such behaviours take place. Within the context of pharmacy practice research, qualitative approaches have been used to examine a diverse array of topics, including the perceptions of key stakeholders regarding prescribing by pharmacists and the postgraduation employment experiences of young pharmacists (see “Further Reading” section at the end of this article).
In the previous paper, 1 we outlined 3 commonly used methodologies: ethnography 2 , grounded theory 3 , and phenomenology. 4 Briefly, ethnography involves researchers using direct observation to study participants in their “real life” environment, sometimes over extended periods. Grounded theory and its later modified versions (e.g., Strauss and Corbin 5 ) use face-to-face interviews and interactions such as focus groups to explore a particular research phenomenon and may help in clarifying a less-well-understood problem, situation, or context. Phenomenology shares some features with grounded theory (such as an exploration of participants’ behaviour) and uses similar techniques to collect data, but it focuses on understanding how human beings experience their world. It gives researchers the opportunity to put themselves in another person’s shoes and to understand the subjective experiences of participants. 6 Some researchers use qualitative methodologies but adopt a different standpoint, and an example of this appears in the work of Thurston and others, 7 discussed later in this paper.
Qualitative work requires reflection on the part of researchers, both before and during the research process, as a way of providing context and understanding for readers. When being reflexive, researchers should not try to simply ignore or avoid their own biases (as this would likely be impossible); instead, reflexivity requires researchers to reflect upon and clearly articulate their position and subjectivities (world view, perspectives, biases), so that readers can better understand the filters through which questions were asked, data were gathered and analyzed, and findings were reported. From this perspective, bias and subjectivity are not inherently negative but they are unavoidable; as a result, it is best that they be articulated up-front in a manner that is clear and coherent for readers.
THE PARTICIPANT’S VIEWPOINT
What qualitative study seeks to convey is why people have thoughts and feelings that might affect the way they behave. Such study may occur in any number of contexts, but here, we focus on pharmacy practice and the way people behave with regard to medicines use (e.g., to understand patients’ reasons for nonadherence with medication therapy or to explore physicians’ resistance to pharmacists’ clinical suggestions). As we suggested in our earlier article, 1 an important point about qualitative research is that there is no attempt to generalize the findings to a wider population. Qualitative research is used to gain insights into people’s feelings and thoughts, which may provide the basis for a future stand-alone qualitative study or may help researchers to map out survey instruments for use in a quantitative study. It is also possible to use different types of research in the same study, an approach known as “mixed methods” research, and further reading on this topic may be found at the end of this paper.
The role of the researcher in qualitative research is to attempt to access the thoughts and feelings of study participants. This is not an easy task, as it involves asking people to talk about things that may be very personal to them. Sometimes the experiences being explored are fresh in the participant’s mind, whereas on other occasions reliving past experiences may be difficult. However the data are being collected, a primary responsibility of the researcher is to safeguard participants and their data. Mechanisms for such safeguarding must be clearly articulated to participants and must be approved by a relevant research ethics review board before the research begins. Researchers and practitioners new to qualitative research should seek advice from an experienced qualitative researcher before embarking on their project.
DATA COLLECTION
Whatever philosophical standpoint the researcher is taking and whatever the data collection method (e.g., focus group, one-to-one interviews), the process will involve the generation of large amounts of data. In addition to the variety of study methodologies available, there are also different ways of making a record of what is said and done during an interview or focus group, such as taking handwritten notes or video-recording. If the researcher is audio- or video-recording data collection, then the recordings must be transcribed verbatim before data analysis can begin. As a rough guide, it can take an experienced researcher/transcriber 8 hours to transcribe one 45-minute audio-recorded interview, a process than will generate 20–30 pages of written dialogue.
Many researchers will also maintain a folder of “field notes” to complement audio-taped interviews. Field notes allow the researcher to maintain and comment upon impressions, environmental contexts, behaviours, and nonverbal cues that may not be adequately captured through the audio-recording; they are typically handwritten in a small notebook at the same time the interview takes place. Field notes can provide important context to the interpretation of audio-taped data and can help remind the researcher of situational factors that may be important during data analysis. Such notes need not be formal, but they should be maintained and secured in a similar manner to audio tapes and transcripts, as they contain sensitive information and are relevant to the research. For more information about collecting qualitative data, please see the “Further Reading” section at the end of this paper.
DATA ANALYSIS AND MANAGEMENT
If, as suggested earlier, doing qualitative research is about putting oneself in another person’s shoes and seeing the world from that person’s perspective, the most important part of data analysis and management is to be true to the participants. It is their voices that the researcher is trying to hear, so that they can be interpreted and reported on for others to read and learn from. To illustrate this point, consider the anonymized transcript excerpt presented in Appendix 1 , which is taken from a research interview conducted by one of the authors (J.S.). We refer to this excerpt throughout the remainder of this paper to illustrate how data can be managed, analyzed, and presented.
Interpretation of Data
Interpretation of the data will depend on the theoretical standpoint taken by researchers. For example, the title of the research report by Thurston and others, 7 “Discordant indigenous and provider frames explain challenges in improving access to arthritis care: a qualitative study using constructivist grounded theory,” indicates at least 2 theoretical standpoints. The first is the culture of the indigenous population of Canada and the place of this population in society, and the second is the social constructivist theory used in the constructivist grounded theory method. With regard to the first standpoint, it can be surmised that, to have decided to conduct the research, the researchers must have felt that there was anecdotal evidence of differences in access to arthritis care for patients from indigenous and non-indigenous backgrounds. With regard to the second standpoint, it can be surmised that the researchers used social constructivist theory because it assumes that behaviour is socially constructed; in other words, people do things because of the expectations of those in their personal world or in the wider society in which they live. (Please see the “Further Reading” section for resources providing more information about social constructivist theory and reflexivity.) Thus, these 2 standpoints (and there may have been others relevant to the research of Thurston and others 7 ) will have affected the way in which these researchers interpreted the experiences of the indigenous population participants and those providing their care. Another standpoint is feminist standpoint theory which, among other things, focuses on marginalized groups in society. Such theories are helpful to researchers, as they enable us to think about things from a different perspective. Being aware of the standpoints you are taking in your own research is one of the foundations of qualitative work. Without such awareness, it is easy to slip into interpreting other people’s narratives from your own viewpoint, rather than that of the participants.
To analyze the example in Appendix 1 , we will adopt a phenomenological approach because we want to understand how the participant experienced the illness and we want to try to see the experience from that person’s perspective. It is important for the researcher to reflect upon and articulate his or her starting point for such analysis; for example, in the example, the coder could reflect upon her own experience as a female of a majority ethnocultural group who has lived within middle class and upper middle class settings. This personal history therefore forms the filter through which the data will be examined. This filter does not diminish the quality or significance of the analysis, since every researcher has his or her own filters; however, by explicitly stating and acknowledging what these filters are, the researcher makes it easer for readers to contextualize the work.
Transcribing and Checking
For the purposes of this paper it is assumed that interviews or focus groups have been audio-recorded. As mentioned above, transcribing is an arduous process, even for the most experienced transcribers, but it must be done to convert the spoken word to the written word to facilitate analysis. For anyone new to conducting qualitative research, it is beneficial to transcribe at least one interview and one focus group. It is only by doing this that researchers realize how difficult the task is, and this realization affects their expectations when asking others to transcribe. If the research project has sufficient funding, then a professional transcriber can be hired to do the work. If this is the case, then it is a good idea to sit down with the transcriber, if possible, and talk through the research and what the participants were talking about. This background knowledge for the transcriber is especially important in research in which people are using jargon or medical terms (as in pharmacy practice). Involving your transcriber in this way makes the work both easier and more rewarding, as he or she will feel part of the team. Transcription editing software is also available, but it is expensive. For example, ELAN (more formally known as EUDICO Linguistic Annotator, developed at the Technical University of Berlin) 8 is a tool that can help keep data organized by linking media and data files (particularly valuable if, for example, video-taping of interviews is complemented by transcriptions). It can also be helpful in searching complex data sets. Products such as ELAN do not actually automatically transcribe interviews or complete analyses, and they do require some time and effort to learn; nonetheless, for some research applications, it may be a valuable to consider such software tools.
All audio recordings should be transcribed verbatim, regardless of how intelligible the transcript may be when it is read back. Lines of text should be numbered. Once the transcription is complete, the researcher should read it while listening to the recording and do the following: correct any spelling or other errors; anonymize the transcript so that the participant cannot be identified from anything that is said (e.g., names, places, significant events); insert notations for pauses, laughter, looks of discomfort; insert any punctuation, such as commas and full stops (periods) (see Appendix 1 for examples of inserted punctuation), and include any other contextual information that might have affected the participant (e.g., temperature or comfort of the room).
Dealing with the transcription of a focus group is slightly more difficult, as multiple voices are involved. One way of transcribing such data is to “tag” each voice (e.g., Voice A, Voice B). In addition, the focus group will usually have 2 facilitators, whose respective roles will help in making sense of the data. While one facilitator guides participants through the topic, the other can make notes about context and group dynamics. More information about group dynamics and focus groups can be found in resources listed in the “Further Reading” section.
Reading between the Lines
During the process outlined above, the researcher can begin to get a feel for the participant’s experience of the phenomenon in question and can start to think about things that could be pursued in subsequent interviews or focus groups (if appropriate). In this way, one participant’s narrative informs the next, and the researcher can continue to interview until nothing new is being heard or, as it says in the text books, “saturation is reached”. While continuing with the processes of coding and theming (described in the next 2 sections), it is important to consider not just what the person is saying but also what they are not saying. For example, is a lengthy pause an indication that the participant is finding the subject difficult, or is the person simply deciding what to say? The aim of the whole process from data collection to presentation is to tell the participants’ stories using exemplars from their own narratives, thus grounding the research findings in the participants’ lived experiences.
Smith 9 suggested a qualitative research method known as interpretative phenomenological analysis, which has 2 basic tenets: first, that it is rooted in phenomenology, attempting to understand the meaning that individuals ascribe to their lived experiences, and second, that the researcher must attempt to interpret this meaning in the context of the research. That the researcher has some knowledge and expertise in the subject of the research means that he or she can have considerable scope in interpreting the participant’s experiences. Larkin and others 10 discussed the importance of not just providing a description of what participants say. Rather, interpretative phenomenological analysis is about getting underneath what a person is saying to try to truly understand the world from his or her perspective.
Once all of the research interviews have been transcribed and checked, it is time to begin coding. Field notes compiled during an interview can be a useful complementary source of information to facilitate this process, as the gap in time between an interview, transcribing, and coding can result in memory bias regarding nonverbal or environmental context issues that may affect interpretation of data.
Coding refers to the identification of topics, issues, similarities, and differences that are revealed through the participants’ narratives and interpreted by the researcher. This process enables the researcher to begin to understand the world from each participant’s perspective. Coding can be done by hand on a hard copy of the transcript, by making notes in the margin or by highlighting and naming sections of text. More commonly, researchers use qualitative research software (e.g., NVivo, QSR International Pty Ltd; www.qsrinternational.com/products_nvivo.aspx ) to help manage their transcriptions. It is advised that researchers undertake a formal course in the use of such software or seek supervision from a researcher experienced in these tools.
Returning to Appendix 1 and reading from lines 8–11, a code for this section might be “diagnosis of mental health condition”, but this would just be a description of what the participant is talking about at that point. If we read a little more deeply, we can ask ourselves how the participant might have come to feel that the doctor assumed he or she was aware of the diagnosis or indeed that they had only just been told the diagnosis. There are a number of pauses in the narrative that might suggest the participant is finding it difficult to recall that experience. Later in the text, the participant says “nobody asked me any questions about my life” (line 19). This could be coded simply as “health care professionals’ consultation skills”, but that would not reflect how the participant must have felt never to be asked anything about his or her personal life, about the participant as a human being. At the end of this excerpt, the participant just trails off, recalling that no-one showed any interest, which makes for very moving reading. For practitioners in pharmacy, it might also be pertinent to explore the participant’s experience of akathisia and why this was left untreated for 20 years.
One of the questions that arises about qualitative research relates to the reliability of the interpretation and representation of the participants’ narratives. There are no statistical tests that can be used to check reliability and validity as there are in quantitative research. However, work by Lincoln and Guba 11 suggests that there are other ways to “establish confidence in the ‘truth’ of the findings” (p. 218). They call this confidence “trustworthiness” and suggest that there are 4 criteria of trustworthiness: credibility (confidence in the “truth” of the findings), transferability (showing that the findings have applicability in other contexts), dependability (showing that the findings are consistent and could be repeated), and confirmability (the extent to which the findings of a study are shaped by the respondents and not researcher bias, motivation, or interest).
One way of establishing the “credibility” of the coding is to ask another researcher to code the same transcript and then to discuss any similarities and differences in the 2 resulting sets of codes. This simple act can result in revisions to the codes and can help to clarify and confirm the research findings.
Theming refers to the drawing together of codes from one or more transcripts to present the findings of qualitative research in a coherent and meaningful way. For example, there may be examples across participants’ narratives of the way in which they were treated in hospital, such as “not being listened to” or “lack of interest in personal experiences” (see Appendix 1 ). These may be drawn together as a theme running through the narratives that could be named “the patient’s experience of hospital care”. The importance of going through this process is that at its conclusion, it will be possible to present the data from the interviews using quotations from the individual transcripts to illustrate the source of the researchers’ interpretations. Thus, when the findings are organized for presentation, each theme can become the heading of a section in the report or presentation. Underneath each theme will be the codes, examples from the transcripts, and the researcher’s own interpretation of what the themes mean. Implications for real life (e.g., the treatment of people with chronic mental health problems) should also be given.
DATA SYNTHESIS
In this final section of this paper, we describe some ways of drawing together or “synthesizing” research findings to represent, as faithfully as possible, the meaning that participants ascribe to their life experiences. This synthesis is the aim of the final stage of qualitative research. For most readers, the synthesis of data presented by the researcher is of crucial significance—this is usually where “the story” of the participants can be distilled, summarized, and told in a manner that is both respectful to those participants and meaningful to readers. There are a number of ways in which researchers can synthesize and present their findings, but any conclusions drawn by the researchers must be supported by direct quotations from the participants. In this way, it is made clear to the reader that the themes under discussion have emerged from the participants’ interviews and not the mind of the researcher. The work of Latif and others 12 gives an example of how qualitative research findings might be presented.
Planning and Writing the Report
As has been suggested above, if researchers code and theme their material appropriately, they will naturally find the headings for sections of their report. Qualitative researchers tend to report “findings” rather than “results”, as the latter term typically implies that the data have come from a quantitative source. The final presentation of the research will usually be in the form of a report or a paper and so should follow accepted academic guidelines. In particular, the article should begin with an introduction, including a literature review and rationale for the research. There should be a section on the chosen methodology and a brief discussion about why qualitative methodology was most appropriate for the study question and why one particular methodology (e.g., interpretative phenomenological analysis rather than grounded theory) was selected to guide the research. The method itself should then be described, including ethics approval, choice of participants, mode of recruitment, and method of data collection (e.g., semistructured interviews or focus groups), followed by the research findings, which will be the main body of the report or paper. The findings should be written as if a story is being told; as such, it is not necessary to have a lengthy discussion section at the end. This is because much of the discussion will take place around the participants’ quotes, such that all that is needed to close the report or paper is a summary, limitations of the research, and the implications that the research has for practice. As stated earlier, it is not the intention of qualitative research to allow the findings to be generalized, and therefore this is not, in itself, a limitation.
Planning out the way that findings are to be presented is helpful. It is useful to insert the headings of the sections (the themes) and then make a note of the codes that exemplify the thoughts and feelings of your participants. It is generally advisable to put in the quotations that you want to use for each theme, using each quotation only once. After all this is done, the telling of the story can begin as you give your voice to the experiences of the participants, writing around their quotations. Do not be afraid to draw assumptions from the participants’ narratives, as this is necessary to give an in-depth account of the phenomena in question. Discuss these assumptions, drawing on your participants’ words to support you as you move from one code to another and from one theme to the next. Finally, as appropriate, it is possible to include examples from literature or policy documents that add support for your findings. As an exercise, you may wish to code and theme the sample excerpt in Appendix 1 and tell the participant’s story in your own way. Further reading about “doing” qualitative research can be found at the end of this paper.
CONCLUSIONS
Qualitative research can help researchers to access the thoughts and feelings of research participants, which can enable development of an understanding of the meaning that people ascribe to their experiences. It can be used in pharmacy practice research to explore how patients feel about their health and their treatment. Qualitative research has been used by pharmacists to explore a variety of questions and problems (see the “Further Reading” section for examples). An understanding of these issues can help pharmacists and other health care professionals to tailor health care to match the individual needs of patients and to develop a concordant relationship. Doing qualitative research is not easy and may require a complete rethink of how research is conducted, particularly for researchers who are more familiar with quantitative approaches. There are many ways of conducting qualitative research, and this paper has covered some of the practical issues regarding data collection, analysis, and management. Further reading around the subject will be essential to truly understand this method of accessing peoples’ thoughts and feelings to enable researchers to tell participants’ stories.
Appendix 1. Excerpt from a sample transcript
The participant (age late 50s) had suffered from a chronic mental health illness for 30 years. The participant had become a “revolving door patient,” someone who is frequently in and out of hospital. As the participant talked about past experiences, the researcher asked:
- What was treatment like 30 years ago?
- Umm—well it was pretty much they could do what they wanted with you because I was put into the er, the er kind of system er, I was just on
- endless section threes.
- Really…
- But what I didn’t realize until later was that if you haven’t actually posed a threat to someone or yourself they can’t really do that but I didn’t know
- that. So wh-when I first went into hospital they put me on the forensic ward ’cause they said, “We don’t think you’ll stay here we think you’ll just
- run-run away.” So they put me then onto the acute admissions ward and – er – I can remember one of the first things I recall when I got onto that
- ward was sitting down with a er a Dr XXX. He had a book this thick [gestures] and on each page it was like three questions and he went through
- all these questions and I answered all these questions. So we’re there for I don’t maybe two hours doing all that and he asked me he said “well
- when did somebody tell you then that you have schizophrenia” I said “well nobody’s told me that” so he seemed very surprised but nobody had
- actually [pause] whe-when I first went up there under police escort erm the senior kind of consultants people I’d been to where I was staying and
- ermm so er [pause] I . . . the, I can remember the very first night that I was there and given this injection in this muscle here [gestures] and just
- having dreadful side effects the next day I woke up [pause]
- . . . and I suffered that akathesia I swear to you, every minute of every day for about 20 years.
- Oh how awful.
- And that side of it just makes life impossible so the care on the wards [pause] umm I don’t know it’s kind of, it’s kind of hard to put into words
- [pause]. Because I’m not saying they were sort of like not friendly or interested but then nobody ever seemed to want to talk about your life [pause]
- nobody asked me any questions about my life. The only questions that came into was they asked me if I’d be a volunteer for these student exams
- and things and I said “yeah” so all the questions were like “oh what jobs have you done,” er about your relationships and things and er but
- nobody actually sat down and had a talk and showed some interest in you as a person you were just there basically [pause] um labelled and you
- know there was there was [pause] but umm [pause] yeah . . .
This article is the 10th in the CJHP Research Primer Series, an initiative of the CJHP Editorial Board and the CSHP Research Committee. The planned 2-year series is intended to appeal to relatively inexperienced researchers, with the goal of building research capacity among practising pharmacists. The articles, presenting simple but rigorous guidance to encourage and support novice researchers, are being solicited from authors with appropriate expertise.
Previous articles in this series:
Bond CM. The research jigsaw: how to get started. Can J Hosp Pharm . 2014;67(1):28–30.
Tully MP. Research: articulating questions, generating hypotheses, and choosing study designs. Can J Hosp Pharm . 2014;67(1):31–4.
Loewen P. Ethical issues in pharmacy practice research: an introductory guide. Can J Hosp Pharm. 2014;67(2):133–7.
Tsuyuki RT. Designing pharmacy practice research trials. Can J Hosp Pharm . 2014;67(3):226–9.
Bresee LC. An introduction to developing surveys for pharmacy practice research. Can J Hosp Pharm . 2014;67(4):286–91.
Gamble JM. An introduction to the fundamentals of cohort and case–control studies. Can J Hosp Pharm . 2014;67(5):366–72.
Austin Z, Sutton J. Qualitative research: getting started. C an J Hosp Pharm . 2014;67(6):436–40.
Houle S. An introduction to the fundamentals of randomized controlled trials in pharmacy research. Can J Hosp Pharm . 2014; 68(1):28–32.
Charrois TL. Systematic reviews: What do you need to know to get started? Can J Hosp Pharm . 2014;68(2):144–8.
Competing interests: None declared.
Further Reading
Examples of qualitative research in pharmacy practice.
- Farrell B, Pottie K, Woodend K, Yao V, Dolovich L, Kennie N, et al. Shifts in expectations: evaluating physicians’ perceptions as pharmacists integrated into family practice. J Interprof Care. 2010; 24 (1):80–9. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gregory P, Austin Z. Postgraduation employment experiences of new pharmacists in Ontario in 2012–2013. Can Pharm J. 2014; 147 (5):290–9. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Marks PZ, Jennnings B, Farrell B, Kennie-Kaulbach N, Jorgenson D, Pearson-Sharpe J, et al. “I gained a skill and a change in attitude”: a case study describing how an online continuing professional education course for pharmacists supported achievement of its transfer to practice outcomes. Can J Univ Contin Educ. 2014; 40 (2):1–18. [ Google Scholar ]
- Nair KM, Dolovich L, Brazil K, Raina P. It’s all about relationships: a qualitative study of health researchers’ perspectives on interdisciplinary research. BMC Health Serv Res. 2008; 8 :110. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pojskic N, MacKeigan L, Boon H, Austin Z. Initial perceptions of key stakeholders in Ontario regarding independent prescriptive authority for pharmacists. Res Soc Adm Pharm. 2014; 10 (2):341–54. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
Qualitative Research in General
- Breakwell GM, Hammond S, Fife-Schaw C. Research methods in psychology. Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage Publications; 1995. [ Google Scholar ]
- Given LM. 100 questions (and answers) about qualitative research. Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage Publications; 2015. [ Google Scholar ]
- Miles B, Huberman AM. Qualitative data analysis. Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage Publications; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Patton M. Qualitative research and evaluation methods. Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage Publications; 2002. [ Google Scholar ]
- Willig C. Introducing qualitative research in psychology. Buckingham (UK): Open University Press; 2001. [ Google Scholar ]
Group Dynamics in Focus Groups
- Farnsworth J, Boon B. Analysing group dynamics within the focus group. Qual Res. 2010; 10 (5):605–24. [ Google Scholar ]
Social Constructivism
- Social constructivism. Berkeley (CA): University of California, Berkeley, Berkeley Graduate Division, Graduate Student Instruction Teaching & Resource Center; [cited 2015 June 4]. Available from: http://gsi.berkeley.edu/gsi-guide-contents/learning-theory-research/social-constructivism/ [ Google Scholar ]
Mixed Methods
- Creswell J. Research design: qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches. Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage Publications; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
Collecting Qualitative Data
- Arksey H, Knight P. Interviewing for social scientists: an introductory resource with examples. Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage Publications; 1999. [ Google Scholar ]
- Guest G, Namey EE, Mitchel ML. Collecting qualitative data: a field manual for applied research. Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage Publications; 2013. [ Google Scholar ]
Constructivist Grounded Theory
- Charmaz K. Grounded theory: objectivist and constructivist methods. In: Denzin N, Lincoln Y, editors. Handbook of qualitative research. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage Publications; 2000. pp. 509–35. [ Google Scholar ]
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Online First
- Locum doctor working and quality and safety: a qualitative study in English primary and secondary care
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8129-8376 Jane Ferguson 1 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9325-3362 Gemma Stringer 2 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0696-480X Kieran Walshe 2 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2972-7911 Thomas Allen 3 , 4 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1621-8648 Christos Grigoroglou 3 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2958-915X Darren M Ashcroft 5 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6450-5815 Evangelos Kontopantelis 6 , 7
- 1 Health Services Management Centre, School of Social Policy , University of Birmingham , Birmingham , UK
- 2 Alliance Manchester Business School , University of Manchester , Manchester , UK
- 3 Manchester Centre for Health Economics, Division of Population Health, Health Services Research and Primary Care , University of Manchester , Manchester , UK
- 4 Danish Centre for Health Economics , University of Southern Denmark , Odense , Denmark
- 5 NIHR Greater Manchester Patient Safety Research Collaboration (PSRC), Division of Pharmacy and Optometry, Faculty of Biology Medicine and Health , University of Manchester , Manchester , UK
- 6 Division of Informatics, Imaging and Data Sciences , University of Manchester , Manchester , UK
- 7 NIHR School for Primary Care Research, Centre for Primary Care, Division of Population Health, Health Services Research and Primary Care , University of Manchester , Manchester , UK
- Correspondence to Dr Jane Ferguson, Health Services Management Centre, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, UK; j.ferguson.1{at}bham.ac.uk
Background The use of temporary doctors, known as locums, has been common practice for managing staffing shortages and maintaining service delivery internationally. However, there has been little empirical research on the implications of locum working for quality and safety. This study aimed to investigate the implications of locum working for quality and safety.
Methods Qualitative semi-structured interviews and focus groups were conducted with 130 participants, including locums, patients, permanently employed doctors, nurses and other healthcare professionals with governance and recruitment responsibilities for locums across primary and secondary healthcare organisations in the English NHS. Data were collected between March 2021 and April 2022. Data were analysed using reflexive thematic analysis and abductive analysis.
Results Participants described the implications of locum working for quality and safety across five themes: (1) ‘familiarity’ with an organisation and its patients and staff was essential to delivering safe care; (2) ‘balance and stability’ of services reliant on locums were seen as at risk of destabilisation and lacking leadership for quality improvement; (3) ‘discrimination and exclusion’ experienced by locums had negative implications for morale, retention and patient outcomes; (4) ‘defensive practice’ by locums as a result of perceptions of increased vulnerability and decreased support; (5) clinical governance arrangements, which often did not adequately cover locum doctors.
Conclusion Locum working and how locums were integrated into organisations posed some significant challenges and opportunities for patient safety and quality of care. Organisations should take stock of how they work with the locum workforce to improve not only quality and safety but also locum experience and retention.
- Health services research
- Patient safety
- Qualitative research
- Quality improvement
Data availability statement
No data are available.
This is an open access article distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Unported (CC BY 4.0) license, which permits others to copy, redistribute, remix, transform and build upon this work for any purpose, provided the original work is properly cited, a link to the licence is given, and indication of whether changes were made. See: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjqs-2023-016699
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
WHAT IS ALREADY KNOWN ON THIS TOPIC
Despite longstanding policy concerns about the implications of locum working for quality and safety, there has been little empirical research. Understanding how organisations engage, support and work with locums and how locum doctors integrate and interact with the complex and changing systems in which they work is essential if quality and safety are to be improved.
WHAT THIS STUDY ADDS
This qualitative study examines the perspectives of locums, patients and people who work with locums to identify the implications of temporary medical working for quality and safety.
HOW THIS STUDY MIGHT AFFECT RESEARCH, PRACTICE OR POLICY
Organisations should examine how they engage, support and work with locums. Organisations and locums need to reflect on whether their practices support a collective approach to patient safety and quality of care.
Introduction
Temporary doctors, often known as locums, are a vital resource that enable healthcare organisations to deliver care by flexing capacity and covering staffing gaps. In the United Kingdom, all doctors, other than those in their first year of training after qualifying, can work as a locum. Locum work can vary from very short-term (a single shift) to longer-term assignments (weeks, months or even sometimes years). Locums find work through various platforms, including locum agencies, online job platforms, professional networks or word of mouth. Locum agencies typically have some governance responsibilities (such as compliance with regulations and licensing requirements), but the extent of these responsibilities varies and the NHS in England has no oversight over how recruitment agencies operate. Despite concerns among policymakers, healthcare providers, professional associations and professional regulators about the implications of locum working for quality and safety and cost, 1–3 there is limited robust empirical research to evidence or support those concerns.
The workforce retention crisis is a significant challenge in healthcare internationally 4–6 and persistent understaffing poses a serious risk to patient safety. 7 8 In the UK, high doctor turnover has been linked to poorer service and health outcomes 9 and has led NHS trusts and general practices (GPs) to be ‘overly reliant’ 3 on temporary staff to fill rota gaps. 10 11 Expenditure on temporary staff in the NHS in England increased from £3.45 billion to £5.2 billion between 2021 and 2022. 3 12 The NHS Long Term Workforce Plan aims to reduce reliance on temporary staff and make substantive employment the most cost-effective and attractive option. 3 However, with the vacancy rate in the NHS projected to increase, 13 locums are likely to continue to be essential to maintaining service provision, especially in shortage specialities such as psychiatry. 14
An obvious implication of locum working is a reduced likelihood of organisational and team integration, 15 familiarity and a shared understanding of ‘the way things are done around here’. 16 Locums are likely to be less familiar with teams and other contextual factors relevant to providing safe and effective care 17 and more likely to be situated on the periphery of organisational structures, teams and governance systems 1 18 Teamwork represents a powerful process to improve patient care, 19 20 and trust, shared understanding, communication and collaboration have been associated with better patient outcomes. 21 22 The ability of healthcare teams to develop and maintain team situational awareness, or a shared perception, comprehension and subsequent projection of what is going on in complex and changing clinical environments, has been described as crucial for patient safety. 23 24 Through participation and working together, 25 teams gain an understanding of the roles, skills and competencies of others to demonstrate ‘collective competence’, 26 27 which is critical for healthcare delivery, 28 29 and existing research on locums suggests a need for better integration into teams to improve quality and safety. 30 31
Context matters for patient safety and quality improvement, 32 33 yet the limited evidence 17 relating to locums practice is largely ‘acontextual’ and tends to ignore the role of the organisation in the integration of temporary staff, focusing instead on the potential risks locums present as individual clinicians, 17 30 which is perhaps unsurprising given the liminal space locums occupy. In the UK, responsibility for the quality and safety of healthcare services is shared primarily between organisations and the individual professionals working within them. 34 Organisations are responsible for creating systems and environments that promote and protect clinical governance and enable all doctors to meet their professional obligations, while doctors are expected to participate in the systems and processes put in place by regulators and organisations to protect and improve patient care. 35 However, NHS trusts and primary care organisations procure the services of locum doctors without assuming the responsibilities normally associated with an employer–employee relationship 30 and locums often struggle to participate in teams and governance systems that were designed for doctors working in conventional employment relationships. 18 36
There is longstanding debate about the role of individual accountability in patient safety and how responsibility is distributed between organisations and individuals. 37 A systems approach reasons that adverse events are likely to occur as a result of system failures rather than individual failures, 38 and patients are protected from mistakes by well designed systems and environments that promote safety cultures. 39 But locums are often positioned at the periphery of these systems, 30 and doctors who are new to and also peripheral to organisations, and organisations who are inexperienced with and unsupportive of locums are unlikely to be able to perform optimally. 40
The aim of this research was to provide evidence on how locum working arrangements impact quality and safety and the implications of locum working for patients, locums and health service organisations in primary and secondary care in the English NHS. Locum doctors are an essential and growing part of the healthcare workforce 1 who have been largely ignored in healthcare workforce research. This research addresses a gap in the empirical evidence base on how locum doctor working arrangements affect quality and safety, and provides, for the first time, an in-depth exploration that includes perspectives from patients, locums and the people they work with.
Study design and setting
A qualitative semi-structured interview and focus group study was conducted with locums, people working with locums, and patients with experience of being treated by locums. Participants were purposively sampled through 11 organisations, including NHS trusts, primary care practices, statutory NHS bodies and locum agencies. Locum doctor participants were recruited through these organisations, locum recruitment agencies and networks. We used purposive, snowball and convenience sampling, drawing on intelligence from stakeholders, including our project advisory group, to identify and recruit organisations and participants. Patient participants were recruited through patient and contributor forums. The forum involved active partnership between patients and researchers in the research process to develop research which is relevant and useful to patient and public needs. Participant demographics were monitored to ensure representation across a broad range of roles in primary and secondary care and to increase diversity in terms of gender and ethnicity (see table 1 ).
- View inline
Characteristics of study participants
Data collection
Three semi-structured interview and focus group guides were developed for use with locums, people working with locums and patients with experience of being treated by locums (as shown in online supplemental files 1-3 ). Our previous review of the literature relating to quality and safety and locum work 17 informed the schedules as well as the initial coding and thematic development. Schedules were also refined and informed by our patient and public involvement (PPI) forum and our project advisory group. Each schedule was intended to explore locum doctor working arrangements with a particular focus on understanding how locum doctor working may affect the safety and quality of care and what strategies or systems organisations and individuals used to assure or improve quality and safety. The topic guides for locums and people working with locums also covered governance and support, the impact of the COVID pandemic and policies and initiatives used to support locums.
Supplemental material
Interviews and focus groups were transcribed verbatim by a professional transcription company and organised into codes and themes using the software package NVivo. 41 Reflexive thematic analysis (RTA) 42 was used and involved familiarisation with the data by reading and re-reading the transcripts and field notes; coding the dataset and collating all relevant data extracts; generating initial themes by examining the codes and collated data to identify significant broader patterns of meaning across the dataset; reviewing themes by questioning whether themes answered the research question and told a convincing story of the data and combining, splitting and discarding themes as necessary; defining and naming themes by developing a detailed analysis of each theme; and finally the analytical write up which positioned the analysis in relation to existing literature. 43 RTA acknowledges the active role of researchers in knowledge production and the researcher’s subjectivity as the analytic resource. 42 RTA recognises interpretive variability between researchers based on differences in their knowledge and skills, theoretical assumptions and differences in how they responded to the dataset is acknowledged and expected. 42 The research team worked reflexively discussing their personal biases and their potential impact on the research at regular meetings throughout the data collection and analysis period. Our PPI forum were also involved in data collection and analysis, and offered a form of triangulation to enhance rigour, challenge and alternative interpretations of the findings. 44 Analysis adopted a constructionist epistemology, in that while we acknowledged the importance of recurrence in generating themes, meaning and meaningfulness were the central criteria in the coding process. 42
After themes were developed, an abductive approach was taken to position findings against a background of existing theory and knowledge. 17 30 This provided a way of constructing empirically based theorisations without confining theory to predefined concepts. 45 This approach integrated inductive data-driven coding with deductive theory-driven interpretation; aiming to find a middle ground between inductive and deductive methods and the most logical solution and useful explanation for phenomena. 45
We conducted 130 interviews with 88 participants who worked in healthcare and 42 patients took part in focus groups and one-to-one interviews. Participants included locums, permanently employed doctors; nurses and other health professionals; medical directors/clinical leaders; responsible officers (ROs are accountable for local clinical governance processes and focus on the performance of doctors) and appraisers; leads for medical staffing and clinical governance and practice managers (see table 2 ). Three experienced qualitative researchers (JF, GS and KW) and two members of the PPI forum (MM and MS) carried out five focus groups with 30 patients, and JF and GS carried out 12 one-to-one interviews. Data were collected between March 2021 and April 2022 during the COVID pandemic using video conferencing software (n=126) or over the phone (n=4) at a time convenient to participants. Interviews and focus groups ranged in length from 23 to 171 min, with the average interview being 59 min.
Healthcare organisations and participant roles
Thematic framework
Our findings are presented under five broad and interrelated themes that examine how locum work relates to and impacts quality and safety: ‘familiarity’ with an organisation and its patients and staff; ‘balance and stability’ in services with lots of locums; ‘discrimination and exclusion’ towards locums and their effects; ‘defensive practice’ by locums; and the positioning of locums outside clinical governance arrangements.
Familiarity: knowing who, where and how
Locums described often working in unfamiliar environments, sometimes with minimal induction and varying levels of support. Unfamiliarity, lack of access to or other restrictions on computer systems, policies, procedures and buildings meant that locums were not always able to do their job safely, productively or effectively.
That’s probably the biggest sort of safety aspect that sticks in my mind, is that it is unbelievably frustrating to have to learn a whole new set of patients from day to day … when I was signed up to four different hospitals, plus the locum agencies, I very quickly realised that not only is it the fact that you don’t know the patients from day to day, if you’re chopping and changing site the whole time, then store cupboards are laid out differently, ways of contacting relevant staff members are different, you’ve got to recognise what code to put in to bleep someone that’s different at every single site. (Interview 23, locum, secondary care)
Locum working sometimes created extra work for permanent staff who were responsible for inducting, training and supervising locums. The amount of additional workload was dependent on contextual factors, such as the experience of the locum, organisational support and length of placement, access to systems and what terms and conditions locums or organisations had negotiated. Locum reliance on permanent staff meant that care could be delayed, partially completed or not completed at all, which sometimes caused resentment.
Some of the things that we don’t … like, for example, procedures of limited clinical value that we don’t refer in for, they won’t know about those in our areas … So they’ll do referrals that we then will get pulled on. They’ll maybe prescribe medications that are not first line medications within our own formulary. So we see quite a bit of that, you know, there’s quite a lot of tidying up to be done afterwards or work. They generate that. So whilst we meet the patient numbers, they create a lot of work for the rest of the team. (Interview 3, practice manager, primary care)
Locums mitigated risks related to working in unfamiliar environments by avoiding organisations considered chaotic or unsafe, working below their grade to avoid having responsibility in unfamiliar organisations where they may not be supported or included in the team or working in a limited number of organisations to increase familiarity.
Most locums take jobs, locum work below their grade. So a person who’s at a registrar level would take a locum work as an SHO (senior house officer), because they don't know the trust that well. (Interview 55, locum, secondary care)
However, lack of familiarity and discontinuity could at times be beneficial for patients and organisations as fresh perspectives offered by locums led to different routes of treatment or management, and could alter organisational cultures or practices.
So that [locum] doctor, through that line of questioning and not having any sort of prior history … ordered the right tests and didn’t feel constrained in that practice about what tests that they could order. And someone subsequently … because when you get referred to hospital, the consultant said that that doctor was very much on the ball. And, of course, that’s a change to lifelong medication. And literally within a month of the medication kicking in, it transformed my life. (Focus group A, patient 1)
Balance and stability
The balance between locum and permanent staff had implications for quality and safety, organisational leadership, long-term planning and governance. Locums were often employed to deliver immediate services and consequently were less likely to be involved in team and organisational development. Locums recognised that having ‘an NHS run by locums’ was detrimental to quality and safety, and some avoided organisations that were locum dependent for this reason. Well functioning established teams were regarded as better able to incorporate a small number of locums without being significantly impacted.
Locum work, my view on it is they’re there to fill a gap. They shouldn’t be relied upon to deliver a service Monday to Friday, day in, day out, week in, week out. And unfortunately my trust see it as that, though, that’s my worry that they feel they’re not just plugging a gap, they’re almost as a workforce … (Interview 84, lead GP, primary and secondary care)
Departments that were disproportionately locum dependent were often perceived to lack clinical leadership and direction. An absence of consistent medical leadership meant that quality improvement was slower or less likely to happen, and trusting relationships between staff were harder to establish.
If you get a department that is disproportionately locum dependent, then it stagnates, it doesn't progress. Things like implementation of new NICE guidance, for example, that sort of thing tends not to happen or happen less well, less quickly. (Interview 30, responsible officer, secondary care)
Discrimination and exclusion
Most locums described negative behaviours and attitudes from staff and some patients, which impacted their involvement, inclusion and experiences in organisations. Negative attitudes and behaviours towards locums could affect turnover, locum well-being, team dynamics and potentially patient safety. Perceived disparities between pay, workload, competence and organisational and team commitment between locums and permanent staff could be sources of resentment and influenced how locums were treated and viewed. This compromised staff communication and reduced the sharing of important patient information.
I guess like any temporary post really, you struggle to invest in them, don't necessarily see them as being part of the team. Not very positive about them, particularly junior staff, particularly in the acute trusts. We'd have locums refusing to come back because of the treatment of the midwives. (Interview 86, clinical lead, secondary care)
Negative perceptions of competency and safety meant that locums were often stigmatised, marginalised and excluded. The identity of locum intersected and overlapped with other identities and was described as ‘layering up’ with ethnicity and gender to further exacerbate discrimination.
Oh, doctors coming over from Germany. There was one locum … that administered a dose of something and the patient died, and then there’s this whole layer of extra negativity attached to locum doctors in general because of what one doctor did, and that doctor happened to be someone from a different ethnicity … As a UK born and qualified doctor I can see that those overseas get it but I can also see that I have experienced that as well. So yeah, it can layer up with the whole locum thing. (Interview 59, locum GP, primary care)
A sense of othering and being seen as less was particularly evident during the COVID pandemic when resources were limited. Some locums described how they were not afforded the same protections as permanent members of staff and were sometimes expected to take on riskier work.
I’ve worked in another practice where, because they live on locums and they live on ad hoc locums, you’re a piece of dirt under the shoe. You don’t get gloves, you didn’t have aprons, you didn’t have a face visor, you didn’t have safety specs, you have to ask for a mask. Not only are you not treated as a service provider, you’re not treated as a colleague, someone with knowledge. (Interview 44, locum GP)
Defensive practice by locums
Locums recognised that they were likely to be scapegoated if things went wrong, and some locums described being more likely to practice defensively. Defensive practice has been defined as deviation from standard practice to avoid litigation, complaints or criticism. 46 Participants reported instances of defensive practice which involved providing services (eg, tests, referrals) or avoiding high-risk decisions, usually to reduce the risk of adverse outcomes such as patient complaints or potential termination of contract at short notice. Locums described practicing defensively because they were attempting to practice as safely as possible in complex unfamiliar environments where they were professionally isolated and perceived negatively. Permanent members of staff could perceive that locums practiced defensively because they lacked confidence in their abilities. The diversion of resources away from more clinically relevant activities placed additional burden on teams, who were already facing significant workload challenges.
Being risk averse and practising defensive medicine usually means more tests, more referrals, whereas holding risk tends to be disadvantageous for you as a locum because what’s the benefit to you of not doing that. You’re benefiting the system by rationing resource, the patient won’t thank you. (Interview 35, locum GP)
Locums described avoiding making decisions when risks to employment or medical licenses were perceived as high. Locums felt they were more vulnerable to criticisms of their clinical competence and disempowered to make decisions. Others felt that some locums were simply avoiding work and evaded responsibility for patients by pushing work onto others or into the future.
You don’t interfere, very simple. Over time locums have learned that if you interfere, if you participate in the team, you participate in patient care, [and this] is when you get into trouble … Well most of the locums that I know will just say, okay, there’s already somebody else who’s made a decision, it’s not my job to make a decision, I just follow through. If things go wrong, call the senior person and be done with it, that’s the end of my role. Actually doing something to protect a patient is not important for a locum because the risk is too high. (Interview 55, locum, secondary care)
Locums fall outside clinical governance arrangements
Governance practices in relation to locums varied widely and were not generally regarded as being as robust in comparison to permanently employed doctors. Responsibility for involving locum doctors in performance feedback, supervision, educational opportunities, appraisal and quality improvement was unclear. While some organisations included locums in their governance activities, others regarded locum work as transactional; where the locum was there to provide a finite service and the organisation assumed no responsibilities for their performance, development or oversight. There were concerns that governance structures were modelled on and designed for permanently employed doctors and did not work for locums. When deficits in performance were undetected or unaddressed, doctor performance and patient safety could be jeopardised.
I think it’s a remote world. It’s like a cloud, you know, it’s like the cloud. We talk about the cloud when it comes to storing information. And I think locum world is a bit like that … And I don’t know the doctors anywhere like as much as I did when I was an RO in the NHS, I knew them all personally. If I used to have a problem, I used to get them in my office there and then, chat it all through, sort it. Can’t do that in locum world, it might take me four days to get hold of the doctor, some of them won’t respond immediately … They don’t know me and I don’t know them. (Interview 51, responsible officer, locum agency)
The absence of typical recruitment processes (involving meeting a doctor, carrying out an interview and following up on references) meant that healthcare organisations were reliant on partial information from locum agencies, which made it difficult to determine competency, scope of practice and suitability for a role. However, staff shortages and a requirement to meet safe staffing ratios meant that organisational leaders had little recourse of action if they were unsure about a doctor’s capability, which caused anxiety and frustration. This suggests that the provision of healthcare superseded ensuring safety standards and necessitated accepting one of two objectionable alternatives; accepting gaps in staffing that may jeopardise patient safety or accepting unknown doctors; each of which may compromise patient safety.
If a locum turns up and I have serious doubts about their ability to do the job to the required standard, I don’t have any recourse … And therefore I’m in a position where either I accept this locum or I don’t. There’s not much in the way of middle ground. Not accepting them is a really unpalatable choice because if I say look, I’m sorry, I don’t think you’re up to this, I think you should go home, that leaves me with a gap. (Interview 30, consultant and responsible officer, secondary care)
Similar governance and information sharing problems were described by locum agencies and NHS organisations; both described difficulties in gathering and sharing feedback. When concerns were raised, participants were often uncertain as to what happened to the information they provided and whether it was shared or acted on. Locums often did not get to hear about concerns raised about them, meaning learning opportunities were missed.
It would give you more confidence if you heard back. And sometimes I'll pick up the phone and you try to do the best you can to make sure this information gets passed on. But I just have this nagging doubt that I'm not always convinced it does. (Interview 30, responsible officer, secondary care)
There was also a perception from some locum agency responsible officers that while most locum doctors were excellent, there were some locums who were isolated and in need of organisational and professional support.
You have to accept that whilst within the agency world, 80 per cent of the doctors we place are excellent, and have no problems, and do a great job, perhaps 20 per cent are those that have shaken down to that 20 per cent in the agency world, because they’ve not succeeded in the NHS, they’ve not got a substantive place, they are lost souls. And they are less able to cope with the vicissitudes of busy clinical life and professional life within a large organisation such as the NHS. (Interview 47, responsible officer, locum agency)
Our findings provide some profound and concerning insights for patient safety and quality of care. The ways in which locums were recruited, inducted, deployed and integrated, and supported by organisations undoubtedly affected quality and safety. Our findings indicate that regardless of their level of experience, it was unlikely that locum doctors would be able to function optimally in unfamiliar environments; and organisations who had poor supportive infrastructure and governance mechanisms for locums were less likely to deliver high-quality safe services.
Locums were often regarded as organisational outsiders—positioned at the periphery of the team and the organisation. The implications of transience and peripheral participation were weaker relationships with organisations, teams, peers and patients, leading some to suggest locum working is better suited to experienced doctors. 47 Consistent with previous research, 48 frequent variation in process, systems and equipment, combined with disruption in relationships and a lack of mutual awareness of team skills and competencies, decreased collective competence, placed additional burden on the wider healthcare team and reduced patient safety. As others have found in research on safe staffing and nursing, 49 temporary staff are not effective substitutes for staff who regularly work in the organisation. Safe medical staffing is not just achieved by filling rota gaps, but also team composition and doctors’ familiarity with the team and organisation must be taken into account. Regulatory agencies should consider locum usage in their inspections and perhaps be particularly concerned when organisations have ‘services run on locums’.
Our research found, as others have, 18 that organisations and doctors sometimes struggled to meet their governance obligations and that governance activities differed based on contractual status and organisational policies and norms, with systems being less robust for locums. This research has highlighted that much still needs to be done to develop governance systems that promote and protect the interests of patients and create an environment which supports locum doctors in meeting their professional obligations.
More positively, locum doctors are a potentially valuable source of information about safety concerns, faulty systems or poor conduct. 50 Locums move between organisations, have broad systems knowledge and are perhaps better placed to identify some quality and safety issues than permanent doctors. However, findings indicate opportunities for shared learning were often missed. Locums recognised their precarity and vulnerability when offering second opinions, sharing improvement ideas or voicing safety concerns; meaning opinions were not always offered and concerns were not always raised. Failure to voice concerns is a persistent problem in healthcare, 51 and locums may be even less inclined to offer potentially valuable information about safety concerns because of their perceptions of unsupportive organisational climates.
Our findings shed light on how temporary doctors fit into the enduring debate 37 around how responsibility between organisational systems and individual professionals is distributed. Locums appear to represent a subsection of the medical profession for whom the wider paradigm shift from a focus on individual blame to a systems approach 52 appeared not to have been made. Locums were often not regarded as a part of the organisation, and therefore the system, and not afforded the same protections as permanent staff when things went wrong. Blaming locums when things go wrong and punishing or sanctioning individuals who make errors in contexts that were not designed to incorporate temporary workers may divert attention from understanding inadequately designed, poorly functioning systems, or indeed the individual practice of other doctors. While we should take into account systemic factors that impede locums from performing safely, we should expect high standards of healthcare professionals, be cognisant of individual agency and recognise the distinction between blaming someone and holding them responsible. 53
Strengths and limitations
This large qualitative study explores locum working and quality and safety in an under-researched, yet growing area of the medical workforce. However, sites were all based in England, which means caution should be taken when extrapolating findings. Similar research in other countries and contexts to understand more about locum doctor working and quality and safety is therefore important. It is possible that our sample may have been skewed towards locums, healthcare professionals and patients who had more negative perceptions and experiences, although accounts resonate with previous research 30 and patient perspectives were generally positive. Our data were collected during the COVID pandemic, which may have affected findings as there was a reduction in locum working during that time 10 11 ; it also meant we were unable to carry out observations, which would have strengthened our findings and mitigated some of the inherent limitations of interviews, such as recall bias. We used both one-to-one interviews and focus groups in data collection. Although flexibility in data collection meant that participants had the option to take part in an interview or a focus group, these methods are used for different reasons and produce different data. There may have been differences in what participants disclosed depending on the method
Our findings show that the way in which doctors who worked on a temporary basis were integrated into organisations posed some significant challenges and opportunities for patient safety and quality of care, and that both organisations and locums had a part to play in improvement. Doctors working as locums are a heterogeneous group with differing backgrounds, experiences, skills and capabilities that likely reflect the variability seen in the wider population of doctors. Locums are working in the same pressured and imperfect systems as other health workers; it is vital that systemic problems are not mistaken for problems about individuals and important to recognise that a locum is not a type of doctor but a way of working. Our findings are a call to action for organisations to take stock of how they engage, support and work with locums, and asks both locums and organisations to reflect on whether their practices support a collective approach to patient safety and quality of care.
Ethics statements
Patient consent for publication.
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
This study involves human participants and was approved by the Health Research Authority North West—Haydock Research Ethics Committee 20/NW/0386. Participants gave informed consent to participate in the study before taking part.
- General Medical Council
- NHS England
- World Health Organization
- Health Social Care Committee
- Harvey PR ,
- Trudgill NJ
- Bower P , et al
- Grigoroglou C ,
- Kontopantelis E , et al
- Shembavnekar N ,
- Bazeer N , et al
- Glatter R ,
- Papadakos P ,
- Ferguson J ,
- Schmutz JB ,
- DiazGranados D ,
- Dietz AS , et al
- Sutradhar R ,
- Jerath A , et al
- Oeppen RS , et al
- Pollack AH ,
- Mishra SR ,
- Apodaca C , et al
- McLaney E ,
- Morassaei S ,
- Hughes L , et al
- Firth-Cozens J
- Tazzyman A ,
- Walshe K , et al
- Pouwels KB ,
- van Hecke O , et al
- Aveling E-L ,
- Dixon-Woods M
- Blumenthal DM ,
- Olenski AR ,
- Tsugawa Y , et al
- QSR International Pty Ltd
- Stewart D ,
- Tierney T , et al
- Timmermans S
- Baungaard N ,
- Skovvang PL ,
- Assing Hvidt E , et al
- Lewis L , et al
- Liberati EG ,
- Tarrant C ,
- Willars J , et al
- Zaranko B ,
- Sanford NJ ,
- Kelly E , et al
- Martin GP ,
- Dixon-Woods M ,
- Aveling EL ,
- Campbell A , et al
- Karsh B-T ,
- Holden RJ ,
- Alper SJ , et al
Supplementary materials
Supplementary data.
This web only file has been produced by the BMJ Publishing Group from an electronic file supplied by the author(s) and has not been edited for content.
- Data supplement 1
- Data supplement 2
- Data supplement 3
- Data supplement 4
Twitter @janefergo, @@kieran_walshe
Contributors JF, KW, DA, TA and EK conceived the study. Recruitment was led by JF and supported by GS. JF, GS and KW conducted the interviews, reviewed and analysed the transcripts, and JF wrote the first version of the manuscript. Two members of the patient and public involvement (PPI) forum also assisted with focus groups. JF conducted data analysis with input from KW and GS, the PPI forum, and review by all authors. JF and KW were involved in initial critical review and revision of the manuscript, followed by all authors. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript. JF is the guarantor.
Funding This study was funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) Health and Social Care Delivery Research programme (NIHR128349), and the NIHR Greater Manchester Patient Safety Research Collaboration (PSRC). The views expressed are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the NIHR or the Department of Health and Social Care.
Competing interests None declared.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Supplemental material This content has been supplied by the author(s). It has not been vetted by BMJ Publishing Group Limited (BMJ) and may not have been peer-reviewed. Any opinions or recommendations discussed are solely those of the author(s) and are not endorsed by BMJ. BMJ disclaims all liability and responsibility arising from any reliance placed on the content. Where the content includes any translated material, BMJ does not warrant the accuracy and reliability of the translations (including but not limited to local regulations, clinical guidelines, terminology, drug names and drug dosages), and is not responsible for any error and/or omissions arising from translation and adaptation or otherwise.
Linked Articles
- Editorial Locums: threat or opportunity Richard Lilford BMJ Quality & Safety 2024; - Published Online First: 16 Apr 2024. doi: 10.1136/bmjqs-2023-016951
Read the full text or download the PDF:

COMMENTS
Qualitative research involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research. Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which involves collecting and ...
Abstract. This paper aims to provide an overview of the use and assessment of qualitative research methods in the health sciences. Qualitative research can be defined as the study of the nature of phenomena and is especially appropriate for answering questions of why something is (not) observed, assessing complex multi-component interventions ...
Qualitative research is a type of research that explores and provides deeper insights into real-world problems.[1] Instead of collecting numerical data points or intervene or introduce treatments just like in quantitative research, qualitative research helps generate hypotheses as well as further investigate and understand quantitative data. Qualitative research gathers participants ...
A qualitative evidence synthesis can be undertaken and integrated with a corresponding intervention review; or; Undertaken using a mixed-method design that integrates a qualitative evidence synthesis with an intervention review in a single protocol. Methods for qualitative evidence synthesis are complex and continue to develop.
As faculty who regularly teach introductory qualitative research methods course, ... Second, case studies address the full complexity of a research problem by incorporating multiple sources and types of evidence . Several research topics and questions indicate a case study as an appropriate approach. The key criterion is the bounded system, so ...
The major types of qualitative research designs are narrative research, phenomenological research, grounded theory research, ethnographic research, historical research, and case study research. ... This overview illustrates various qualitative methods and shows how these methods can be used to generate evidence that informs clinical practice ...
Not all evidence is the same, and appraising the quality of the evidence is part of evidence-based practice research.The hierarchy of evidence is typically represented as a pyramid shape, with the smaller, weaker and more abundant research studies near the base of the pyramid, and systematic reviews and meta-analyses at the top with higher validity but a more limited range of topics.
A qualitative evidence synthesis, or QES, is a type of systematic review that brings together the findings from primary qualitative research in a systematic way. The aim is to to arrive at new or enhanced understandings about the phenomenon under study/review. Methods for conducting QES have developed against a backdrop of increasing demand ...
This paper aims to provide an overview of the use and assessment of qualitative research methods in the health sciences. Qualitative research can be defined as the study of the nature of phenomena and is especially appropriate for answering questions of why something is (not) observed, assessing complex multi-component interventions, and focussing on intervention improvement. The most common ...
A qualitative evidence synthesis, or QES, is a type of systematic review that brings together the findings from primary qualitative research in a systematic way. A primary qualitative research study is one that uses a qualitative method of data collection and analysis.
The article is an attempt to show that a continuing issue in qualitative research methods is describing and justifying how qualitative data become "evidence" for a claim. Several models from the field of Confirmation Theory are developed and described within the context of a qualitative research example. It is argued that for the ...
Fundamental Criteria: General Research Quality. Various researchers have put forward criteria for evaluating qualitative research, which have been summarized in Table 3.Also, the criteria outlined in Table 4 effectively deliver the various approaches to evaluate and assess the quality of qualitative work. The entries in Table 4 are based on Tracy's "Eight big‐tent criteria for excellent ...
Qualitative Research. Qualitative research is a type of research methodology that focuses on exploring and understanding people's beliefs, attitudes, behaviors, and experiences through the collection and analysis of non-numerical data. It seeks to answer research questions through the examination of subjective data, such as interviews, focus groups, observations, and textual analysis.
About Research Methods. This guide provides an overview of research methods, how to choose and use them, and supports and resources at UC Berkeley. As Patten and Newhart note in the book Understanding Research Methods, "Research methods are the building blocks of the scientific enterprise. They are the "how" for building systematic knowledge.
Qualitative research as evidence: expanding the paradigm for evidence-based healthcare BMJ Evid Based Med. 2019 Oct;24(5):168-169. doi: 10.1136/bmjebm-2018-111131. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Authors ... Evidence-Based Practice* / methods Humans Qualitative Research* ...
A fourth issue is that the "implicit use of methods in qualitative research makes the field far less standardized than the quantitative ... which gradually or suddenly change due to the iteration of data, evidence and concepts. However, qualitative research generates understanding in the iterative process when the researcher gets closer to ...
A key concept is to remember that qualitative research is generally not generalizable, as we are not testing a hypothesis and not making inferences based on data. However, in qualitative research, it is often revolving around the concept of transferability. Transferability is established by providing evidence that the research study's ...
Useful terms. Some of the qualitative approaches used in nursing research include grounded theory, phenomenology, ethnography, case study (can lend itself to mixed methods) and narrative analysis. The data collection methods used in qualitative research include in depth interviews, focus groups, observations and stories in the form of diaries ...
Evidence syntheses are much more time-intensive than traditional literature reviews and require a multi-person research team. See this PredicTER tool to get a sense of a systematic review timeline (one type of evidence synthesis). Before embarking on an evidence synthesis, it's important to clearly identify your reasons for conducting one.
Qualitative evidence allows researchers to analyse human experience and provides useful exploratory insights into experiential matters and meaning, often explaining the 'how' and 'why'. As we have argued previously1, qualitative research has an important place within evidence-based healthcare, contributing to among other things policy on patient safety,2 prescribing,3 4 and ...
The JBI SUMARI is primarily designed for qualitative systematic review and employs a meta-aggregative method to synthesise qualitative evidence. One key characteristic of this approach is the ability to generate generalisable recommendations presented as a set of statements, which guide practitioners and policymakers (Aromataris, 2020 ).
INTRODUCTION. Qualitative research methods refer to techniques of investigation that rely on nonstatistical and nonnumerical methods of data collection, analysis, and evidence production. Qualitative research techniques provide a lens for learning about nonquantifiable phenomena such as people's experiences, languages, histories, and cultures.
To summarize our findings from the qualitative interviews regarding research question 2, our qualitative evidence suggests that packaging material played an important role in the consumption decision. Interestingly, the considerations regarding the packaging of apples and tomatoes were not very different, but for both products plastic packaging ...
Thorne (2009) has written eloquently on the challenges and complexities of the evidence-based movement for understanding the potential contributions of qualitative research and offers some sage advice that can help us identify a way forward here. Principally, that our challenge is not to try and convince that qualitative work reflects objective ...
The use of community health workers and peer supporters offer a way of ensuring the benefits of self-management support observed in the general population are shared by those in minoritized communities.The major databases were searched for existing qualitative evidence of participants' experiences and perspectives of self-management support for ...
This year, our main focus will be on the utilization of AI and machine learning in qualitative research. The recent advancements in these technologies present an array of opportunities and challenges for qualitative researchers and their traditional skills, as they can automate the processes of data collection, analysis, and presentation of ...
THE PARTICIPANT'S VIEWPOINT. What qualitative study seeks to convey is why people have thoughts and feelings that might affect the way they behave. Such study may occur in any number of contexts, but here, we focus on pharmacy practice and the way people behave with regard to medicines use (e.g., to understand patients' reasons for nonadherence with medication therapy or to explore ...
Background The use of temporary doctors, known as locums, has been common practice for managing staffing shortages and maintaining service delivery internationally. However, there has been little empirical research on the implications of locum working for quality and safety. This study aimed to investigate the implications of locum working for quality and safety. Methods Qualitative semi ...