- Home |
- About |
- Contact Us |
- Privacy |
- Copyright |
- Shop |
- 🔍 Search Site
- Easter Color By Number Sheets
- Printable Easter Dot to Dot
- Easter Worksheets for kids
- Kindergarten
- All Generated Sheets
- Place Value Generated Sheets
- Addition Generated Sheets
- Subtraction Generated Sheets
- Multiplication Generated Sheets
- Division Generated Sheets
- Money Generated Sheets
- Negative Numbers Generated Sheets
- Fraction Generated Sheets
- Place Value Zones
- Number Bonds
- Addition & Subtraction
- Times Tables
- Fraction & Percent Zones
- All Calculators
- Fraction Calculators
- Percent calculators
- Area & Volume Calculators
- Age Calculator
- Height Calculator
- Roman Numeral Calculator
- Coloring Pages
- Fun Math Sheets
- Math Puzzles
- Mental Math Sheets
- Online Times Tables
- Online Addition & Subtraction
- Math Grab Packs
- All Math Quizzes
- 1st Grade Quizzes
- 2nd Grade Quizzes
- 3rd Grade Quizzes
- 4th Grade Quizzes
- 5th Grade Quizzes
- 6th Grade Math Quizzes
- Place Value
- Rounding Numbers
- Comparing Numbers
- Number Lines
- Prime Numbers
- Negative Numbers
- Roman Numerals
- Subtraction
- Add & Subtract
- Multiplication
- Fraction Worksheets
- Learning Fractions
- Fraction Printables
- Percent Worksheets & Help
- All Geometry
- 2d Shapes Worksheets
- 3d Shapes Worksheets
- Shape Properties
- Geometry Cheat Sheets
- Printable Shapes
- Coordinates
- Measurement
- Math Conversion
- Statistics Worksheets
- Bar Graph Worksheets
- Venn Diagrams
- All Word Problems
- Finding all possibilities
- Logic Problems
- Ratio Word Problems
- All UK Maths Sheets
- Year 1 Maths Worksheets
- Year 2 Maths Worksheets
- Year 3 Maths Worksheets
- Year 4 Maths Worksheets
- Year 5 Maths Worksheets
- Year 6 Maths Worksheets
- All AU Maths Sheets
- Kindergarten Maths Australia
- Year 1 Maths Australia
- Year 2 Maths Australia
- Year 3 Maths Australia
- Year 4 Maths Australia
- Year 5 Maths Australia
- Meet the Sallies
- Certificates

Explore 2d Shapes Worksheets
Welcome to the Math Salamanders Explore 2d Shapes worksheets for kids. Here you will find a range of printable geometry worksheets, which will help your child to learn the properties of 2d shapes and develop their geometric reasoning skills.
For full functionality of this site it is necessary to enable JavaScript.
Here are the instructions how to enable JavaScript in your web browser .
Explore 2d Shapes
The worksheets you find on this page have all been developed to try to help children get a better understanding of what 2d shapes are all about.
In particular, many children still find it hard to realize that a square is also a rectangle which is also a parallelogram which is also a quadrilateral which is also a polygon.
So one of the main development points of these sheets is to get children to know their shapes really well, and to understand what properties they have.
The other aim of these sheets is to try to get children to prove or demonstrate why a particular statement might be always true, sometimes true or never true in the context of geometry.
Reasoning is a key element in mathematics which is often neglected, and really gets children to think about their beliefs and why they think what they do.
Using these sheets will help your child to:
- know the properties of a range of 2d shapes;
- recognise that some shapes can also be described as being other shapes; e.g. a square is also a rhombus;
- recognise and understand right angles, parallel lines, lines of symmetry;
- develop their geometric reasoning skills.
Can You Draw It? Worksheets
The worksheets here involve children applying their knowledge and understanding to explore 2d shapes.
They are a great way to stretch the more able learners, or get children to think hard about the properties shapes have.
Although the sheets in this section are aimed at 3rd grade, they could easily be used by older children.
2d Shapes - Can you draw it?
- 2d Shapes - Can you draw it 1
- PDF version
- 2d Shapes - Can you draw it 2
Explore 2D Shapes Worksheets
All the sheets in this section involve saying whether a given statement is Always, Sometimes, or Never True.
There is also a section for children to explain the reasoning behind their thinking for each answer.
The worksheets have been split up into grades, starting with 3rd grade.
The grades provide a rough guide to where the children have developed enough skills to answer the questions.
However, you can use the worksheets with older children or even adults, to get them to develop their reasoning skills and explore 2d shapes.
With some sheets, there is a UK version of the sheet because of the difference in terminology of the word 'trapezium' and 'trapezoid'.
All of the other sheets can be used by anyone!
- Exploring 2d Shapes Sheet 1
- Exploring 2d Shapes Sheet 2
- Exploring 2d Shapes Sheet 3
- Exploring 2d Shapes Sheet 4
- Exploring 2d Shapes Sheet 4 UK version
- UK version Answers
- Exploring 2d Shapes Sheet 5
- Exploring 2d Shapes Sheet 5 UK Version
- UK Version Answers
- Exploring 2d Shapes Sheet 6
- Exploring 2d Shapes Sheet 7
Other Geometry Worksheets
- More 2d Shapes Worksheets
- Looking for some printable 2d shape worksheets?
- Need some symmetry worksheets?
- Looking for sheets about the properties of 2d shapes?
We have a huge selection of printable 2d shape worksheets for a range of abilities.
Using the link below will take you to our 2d shapes worksheet page where you will find a selection of our worksheets on 2d shapes for a variety of grades from kindergarten upwards.
If you are looking for 3d shape worksheets then you have found the right place.
All of our printable 3d shape worksheets from the website have been put onto the webpage below.
We have a wide selection of 3d shape sheets to cater for a range of grades and abilities.
There are sheets suitable from children age from kindergarten and up.
At Kindergarten level, the focus is on recognising 3d shapes and 2d shapes.
At 1st grade, we start identifying specific types of 3d shapes such as cones or prisms.
At 2nd grade we are beginning to name the shapes and count some of their faces.
At 3rd grade the focus turns to identifying properties such as faces, edges and vertices. We also start investigating the links between 3d shapes and their nets.
Symmetry Worksheets
Here is our selection of free printable symmetry worksheets for 2nd and 3rd grade.
The sheets are all graded in order from easiest to hardest.
- learn how to reflect simple shapes in a horizontal or vertical mirror line;
- learn how to reflect simple shapes in 2 mirror lines.
All the free printable geometry worksheets in this section support Elementary Math Benchmarks.
- Symmetry Worksheets - Block Symmetry
Geometry Nets Worksheets
On this page you will find information and worksheets about nets.
The worksheets consist of identifying and matching the net that matches the correct 3d shape.
- Geometry Nets Information and Worksheets
Geometry Riddles
Here you will find our free printable geometry riddles from 1st to 5th grade.
These riddles are all about problem solving with 2d shapes.
Using these riddles will help your child to:
- develop their geometry skills;
- develop their understanding of geometric language;
- apply their geometric knowledge to solve problems.
All the geometry riddles in this section support elementary math benchmarks.
- Geometry Worksheets (Riddles)
How to Print or Save these sheets 🖶
Need help with printing or saving? Follow these 3 steps to get your worksheets printed perfectly!
- How to Print support
Return to Geometry Hub page
Return from Explore 2d Shapes Worksheets to Math Salamanders Homepage
Math-Salamanders.com
The Math Salamanders hope you enjoy using these free printable Math worksheets and all our other Math games and resources.
We welcome any comments about our site or worksheets on the Facebook comments box at the bottom of every page.
New! Comments
TOP OF PAGE
© 2010-2024 Math Salamanders Limited. All Rights Reserved.
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Policy
One to one maths interventions built for KS4 success
Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons now available
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
This topic is relevant for:

Here we will learn about 2D shapes, including symmetry, perimeter, area, circles, sectors, arcs and angles in polygons.
There are also 2D shapes worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
What are 2D shapes?
2D shapes are flat shapes which only have two dimensions; length and width.
Some examples of common 2D shapes names are triangles, rectangles, pentagons, hexagons, heptagons, octagons, nonagons, decagons and circles.
We can solve problems involving 2D shapes using a variety of methods.
Polygons are 2D shapes made from straight lines. You will deal with two different types of polygons.
Regular polygons
Regular polygons have specific properties. They have all sides of equal length and all interior angles are equal.
Examples of basic 2D shapes that are regular polygons are equilateral triangles and squares.
Irregular polygons
Irregular shapes (or polygons) do not have all equal sides and do not have all equal angles . When the number of sides is unknown, we describe this shape as an \textbf{n-gon} where the number of sides is given as \textbf{n}.
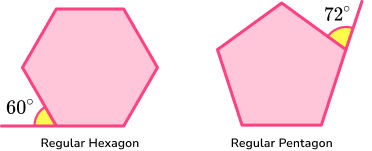
You will also need to be able to solve problems involving angles in polygons. The angles in a polygon can help determine whether a polygon is regular, a specific type of polygon or to determine how many sides a polygon has. You need to be familiar with interior and exterior angles of polygons.
Interior angles are angles that are contained within the polygon.
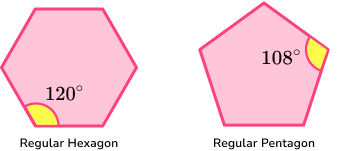
The sum of interior angles of any polygon can be calculated using the formula,
Sum of interior angles = (n-2) \times 180
where n represents the number of sides.
Exterior angles are supplementary to the interior angle. This means that the sum of the interior and exterior angles at a vertex always equals 180^{o}. We can use this property to find either the interior angle, or exterior angle at a vertex.
For any polygon the sum of exterior angles of a polygon 360^{o}.
Step-by-step guide: Polygons
Symmetry is when a line is drawn through a shape to make one side of the line a reflection of the other. It is a property of a 2D polygon or 3D polyhedron.
There are two different types of symmetry that you need to be aware of. Lines of symmetry and rotational symmetry .
For example, a rectangle has two lines of symmetry
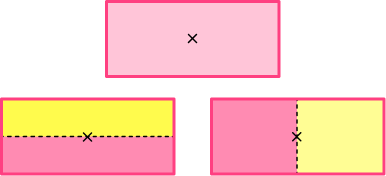
and has order 2 rotational symmetry.
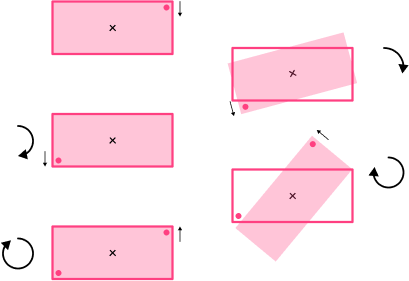
Step-by-step guide: Symmetry
Area is a measure of how much space there is inside of a 2 dimensional shape.
Here are formulae we need to remember to calculate the area of certain 2D shapes.
These are seen in the table below.
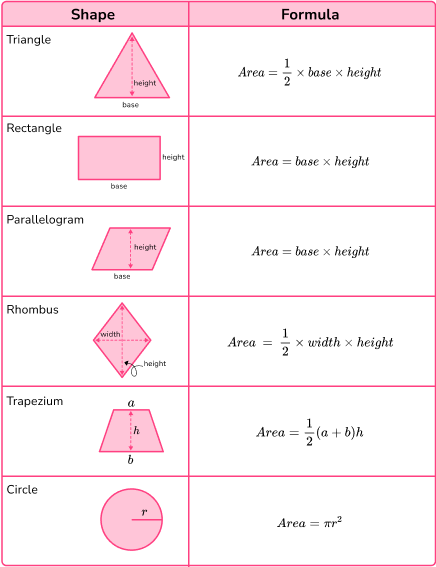
Step-by-step guide: How to work out area
The perimeter is the total distance around the outside of a 2D shape.
For example, let’s find the perimeter of the triangle.
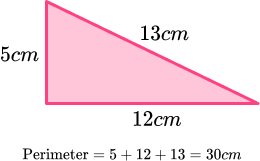
For example, let’s find the perimeter of the rectangle.
The opposite sides of a rectangle are equal, a and b are the side lengths.
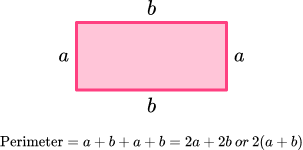
For example, let’s find the perimeter of the circle.
The perimeter of a circle is known as the circumference of a circle.
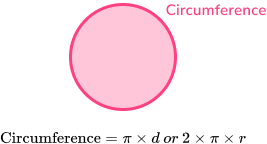
The circumference of this circle is
Step-by-step guide: How to work out perimeter
- Circles, sectors and arcs
Circles are round plane figures whose boundaries consist of points equidistant from a fixed point (the centre of the circle).
As well as the area and circumference of a circle we can also work out the following.
Step-by-step guide: Circles, sectors and arcs
- Parts of a circle
The parts of a circle have specific names and properties which you need to know for all circle related questions. An important fact to remember is that the radius of a circle is half of its diameter.
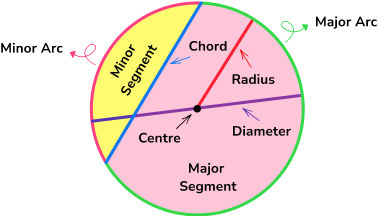
Step-by-step guide: Parts of a circle
- Area of a sector
The area of a sector is part of the area of a circle.
It can be found by using the formula \frac{\theta}{360} \times \pi r^{2}.
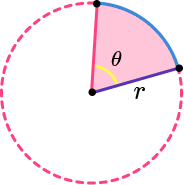
For example,
The area of this sector is
Step-by-step guide: Area of a sector
See also: Sector of a circle
The arc of a circle is part of the circle’s circumference.
It’s length can be found using the formula \frac{\theta}{360} \times \pi d.
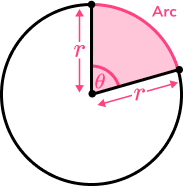
The arc length of this sector is
Step-by-step guide: Arc length
See also: Arc of a circle
- Perimeter of a sector
To find the perimeter of a sector you need to find the arc length and then add it to the two straight sides which are both radii (i.e. the length around the outside of the sector).
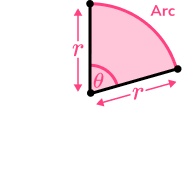
The perimeter of this sector is
Step-by-step guide: Perimeter of a sector
- Segment of a circle
A segment of a circle is created by an arc length and a chord.
You may have to find its area using a combination of mathematical rules such as trigonometry or Pythagoras’ theorem.
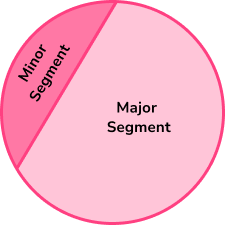
Step-by-step guide: Segment of a circle
- Equation of a circle
The equation of a circle (at GCSE) can be given in the form below
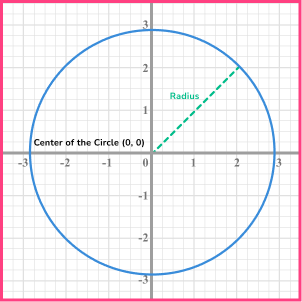
Step-by-step guide: Equation of a circle
How to use 2D shapes
We can use 2D shapes in lots of different ways.
We will learn about:
Explain how to use 2D shapes

Area of 2D shapes worksheet
Get your free 2D shapes worksheet of 20+ area of 2D shapes questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
2D shapes examples
Example 1: regular / irregular polygons.
The shape ABCDE below is made from two scalene triangles, and one isosceles triangle. M is a midpoint on the line CD . AM is a line of symmetry.
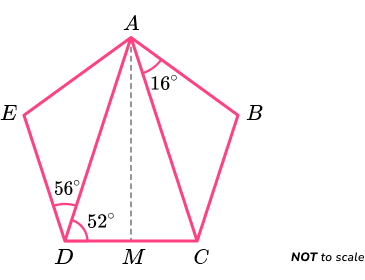
Determine what type of polygon ABCDE is and determine if it is regular or irregular.
- State / calculate the number of sides of the polygon.
The polygon ABCDE has 5 sides so it is a type of pentagon.
2 Determine the size of the angles / side lengths within the polygon.
As triangle ACD is isosceles and AM is a line of symmetry, angle ACD = angle ADC = 52^{o}.
As the sum of angles in a triangle is 180^{o},
angle CAD = 180-(52+52)=76^{o}.
As AM is a line of symmetry, triangles ABC and ACD must be congruent, sharing the same angles and side lengths. This means that,
- Angle BCA = angle ADE =56^{o}
- Angle DAE = angle CAB =16^{o}
Again, as the sum of angles in a triangle total 180^{o},
angle AED = 180-(56+16)=108^{o}.
This is the same for angle ABC as it is symmetrical to angle AED and therefore equal.
We now have all of the following angles,
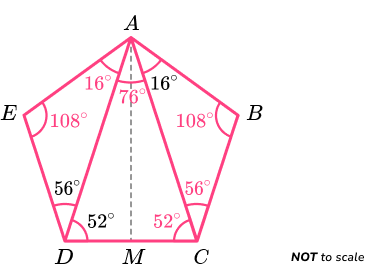
3 Recognise the other properties of the polygon.
For a pentagon to be regular, all of the interior angles must be the same and side lengths must be the same.
Furthermore, as the interior angle sum of a pentagon is 540^{o}, each interior angle of a regular pentagon is equal to
Adding the angles at each vertex together, we have
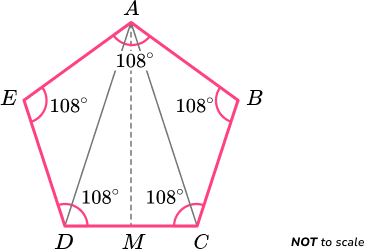
Each interior angle of the polygon ABCDE is equal to 108^{o}.
However, the triangles AED and ABC are scalene. Therefore, AB has a different length to BC .
The interior angles are equal but the side lengths are not equal.
The polygon is an irregular pentagon.
Example 2: types of quadrilateral
Determine what type of quadrilateral ABCD is below.
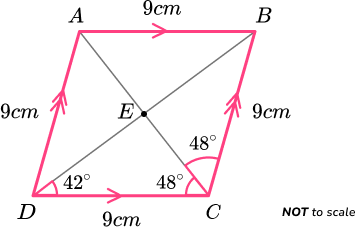
Determine the size of the angles / side lengths within the quadrilateral.
All four side lengths are equal to 9cm with two pairs of parallel sides.
Angle BCD = 48+48=96^o and so ABCD cannot be a square.
CDE is a triangle. As the sum of angles in a triangle total 180^{o},
angle CED = 180-(42+48)=90^{o}.
Labelling this on the diagram, we have
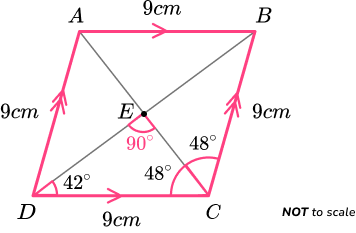
Recognise the other properties of the polygon.
As vertically opposite angles are equal, angle AED = angle CED = 90^{o}.
As the sum of angles on a straight line total 180^{o},
Angle AED = 180-90=90^{o}.
This is also true for angle BEC .
We therefore have the diagonals intersecting at 90 degrees.
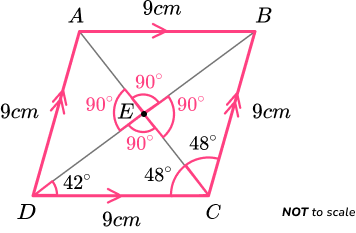
ABCD is a rhombus.
Remember: The properties of a rhombus are,
- Four equal sides
- Opposing sides are parallel
- Two opposing pairs of equal angles
- Diagonals bisect each other at 90 degrees
- Two lines of symmetry
- Rotational symmetry of order 2
Example 3: symmetry
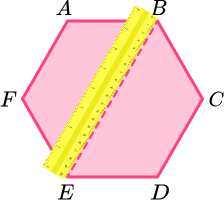
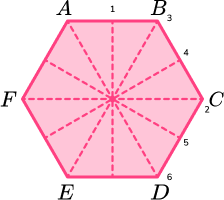
State the number of lines of symmetry for a regular hexagon.
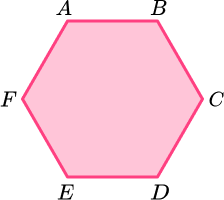
Locate the centre of the 2D shape.
To locate the centre of a shape with an even number of vertices, draw a pair of straight lines connecting two opposing vertices.
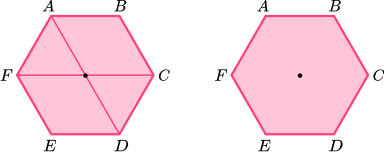
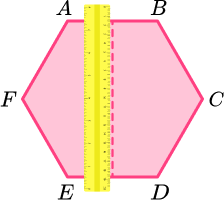
Use a ruler to visualise a horizontal and/or vertical line of symmetry through the centre of the shape.
The regular hexagon has a vertical line of symmetry.
The regular hexagon has a horizontal line of symmetry.
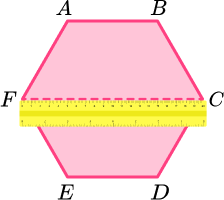
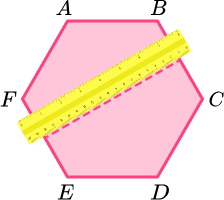
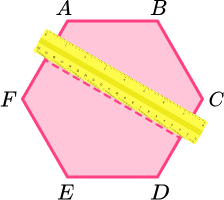
Continue to rotate the ruler around 180 degrees over the centre point to cover all sides and vertices.
Line of symmetry 3.
Line of symmetry 4.
Line of symmetry 5.
Line of symmetry 6.
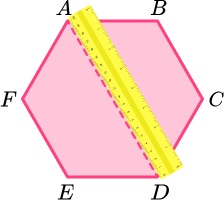
A regular hexagon has 6 lines of symmetry.
Example 4: area of an isosceles triangle
Calculate the area of the triangle below.
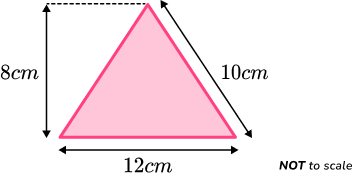
Identify the base and perpendicular height of the triangle.
The two values that are perpendicular to one another are the 12cm along the base, and the vertical height of 8cm.
The 10cm is not required to find the area of this triangle.
Write the area formula.
The area of a triangle formula is,
\text{Area of a triangle}=\cfrac{\text{base }\times\text{height}}{2}.
Substitute known values into the area formula.
As the base = 12cm and the height = 8cm, we have
\text{Area of a triangle }=\cfrac{12\times{8}}{2}.
Solve the equation.
Write the answer, including the units.
As the units of length are in centimetres, the units of area are square centimetres.
The area of the triangle is 48cm^{2}.
Example 5: circumference of a circle
Calculate the circumference of a circle with a radius of 4cm. Write your answer correct to 2 decimal places.
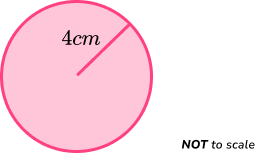
Find the radius or diameter of the circle.
The radius of the circle is 4cm.
Use the relevant formula to calculate the circumference of the circle.
The formula for the circumference of a circle (C) in terms of the radius (r) is
Substituting r=4 into the formula, we have
\begin{aligned} C&=2\times\pi\times{4} \\\\ &=8\times\pi \\\\ &=8\pi \\\\ &=25.13274123 \\\\ &=25.13\text{ (2dp)} \end{aligned}
Give your answer clearly with the correct units.
The circumference of the circle is 25.13cm \ (2dp).
Example 6: perimeter of compound shapes – real life problem
A car park needs a new boundary fence installing. A sketch of the car park is given below.
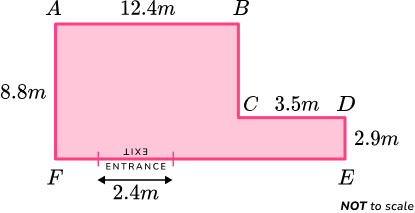
Determine the length of the boundary wall (the car park entrance/exit must not be included in this value).
Add all the side lengths.
A few of the side lengths are missing and so we need to calculate these lengths first.
As AF = 8.8m and DE = 2.9m, the length of BC can be calculated by subtracting DE from AF ,
8.8-2.9 = 5.9m.
As AB = 12.4m and CD = 3.5m, the length of EF can be calculated by adding AB and CD together,
12.4+3.5=15.9m.
Writing these two measurements onto the diagram, we have
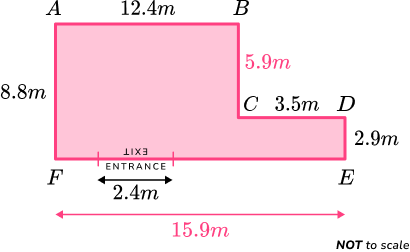
The perimeter is the sum of the side lengths and so we have the sum,
12.4+5.9+3.5+2.9+15.9+8.8=49.4m.
Note: For an L shape, this is the same as doubling the sum of the height and the width ((8.8+15.9)\times{2}=49.4m).
Write the final answer with the correct units.
As we need to calculate the boundary excluding the entrance/exit, we need to subtract the width of the entrance from the total perimeter.
49.4-2.4=47m
The perimeter of the car park excluding the entrance/exit is 47m.
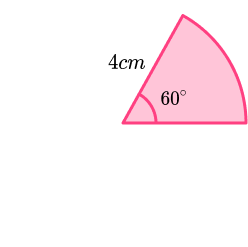
Example 7: area of a sector
A circular cake is cut into 8 equal slices as shown below.
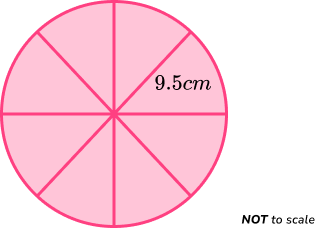
Calculate the area of the top of one slice of cake.
Find the length of the radius \textbf{r} .
The radius r = 9.5cm.
Find the size of the angle creating the sector
The angle of the sector is one eighth of a full turn. As a full turn is 360 degrees,
360\div{8}=45.
The angle of the sector is 45^{o}.
Substitute the value of the radius and the angle into the formula for the area of a sector.
The formula for the area of the sector is
\text{Area of a sector }=\frac{\theta}{360}\times\pi{r}^{2}
where \theta is the angle of the sector, and r is the radius of the overall circle.
Substituting \theta=45^{o} and r = 9.5cm, we have
\begin{aligned} \text{Area of a sector }&=\frac{45}{360}\times\pi\times{9.5}^{2} \\\\ &=\frac{1}{8}\times\pi\times{90.25} \\\\ &=11.28125\pi \\\\ &=35.44109212 \\\\ &=35.44\text{cm}^{2}\text{ (2dp)} \end{aligned}
Clearly state your answer.
The area of the top of the cake slice is 35.44cm^{2}.
Example 8: equation of a circle
Determine the equation of the unit circle, centred at the origin.
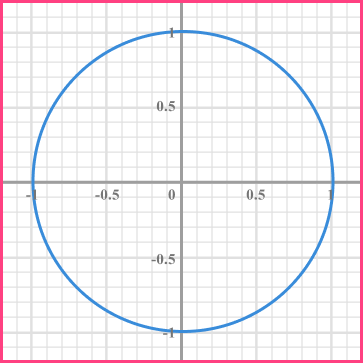
Write the general equation of a circle.
The general equation of a circle is x^{2}+y^{2}=r^{2}.
State any variables you know.
The radius of the unit circle is 1. We can also see this as the centre of the circle lies at the point (0,0) and a coordinate on the circumference of the circle is (1,0), giving us a radius of 1.
Substitute any values you know into the equation.
Substituting r=1 into the equation of a circle, we have
x^{2}+y^{2}=1^{2}.
Use the information you have to solve the problem.
Evaluating 1^{2} we get 1^{2}=1 \times 1=1.
Clearly state the answer.
The equation of the unit circle, centred at the origin is x^{2}+y^{2}=1.
Common misconceptions
- Rotational symmetry/lines of symmetry
Lines of symmetry are often confused with rotational symmetry. A line of symmetry on a two-dimensional shape divides the shape equally into two symmetrical pieces. Rotational symmetry is the number of times a shape fits into itself when rotated around its centre.
- Confusing perimeter with area
Remember, perimeter is distance around the outside of a shape, whilst area is the space inside the shape.
- Angles properties
Ensure you have a good understanding of the different types of angles (for example, acute angles and right angles) along with how to calculate angles in polygons and angles in parallel lines. Getting these confused can lead to misconceptions when problem solving.
Practice 2D shapes questions
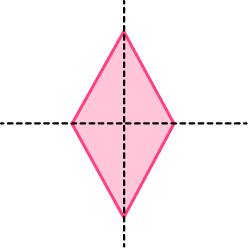
1. Which of the following shapes has 2 lines of symmetry and rotational symmetry order 2.
Parallelogram

A parallelogram has no lines of symmetry and rotational symmetry order 2.
A square has 4 lines of symmetry and rotational symmetry order 4.
A kite has 1 line of symmetry and no rotational symmetry.
2. The rectangle has a perimeter of 42cm. Find x.
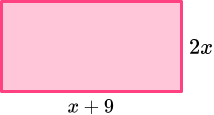
Form an equation for the perimeter.
Solve the equation, to find x=4.
3. Find the area of the isosceles triangle.
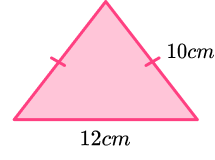
This is an isosceles triangle. We can split it vertically to form two identical triangles with base 6cm, and hypotenuse 10cm.
We then use Pythagoras’ theorem to find the height of the triangle.
Then we can use the formulae for the area of a triangle, and multiply the height by the base (remembering to use the base as 12cm for the area of the whole triangle) then divide by 2.
4. The sector has an area of \frac{27}{2} \pi cm^2, Find the perimeter in terms of \pi.
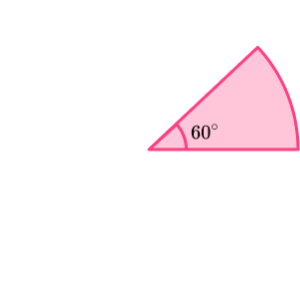
To find the perimeter of the sector we need to calculate the arc length. To do this we need to know the diameter of the sector.
We can work backwards using the formula for the area of a sector to find the radius to help us find the diameter.
Substituting in what we know,
Now we can calculate the arc length. If the radius is 9cm, the diameter must be 18cm.
For the total perimeter we need to add the two radii to the arc length.
5. What is the sum of the interior angles of a pentagon?
6. A regular polygon has an interior angle of 165^{\circ}. How many sides does it have?
The interior and exterior angle of a polygon sum to 180^{\circ}. We can find the exterior angle using this fact.
To find out the number of sides we then do,
2D shapes GCSE questions
1. The hexagon ABCDEF has one line of symmetry.
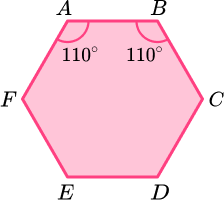
Angle FAB = angle ABC = 110^{\circ}.
Angle AFE = angle BCD .
Angle FED = angle CDE .
Angle CDE : angle BCD = 3 : 2.
Find the size of angle AFE .
Indicating sum of angles is 720^{\circ} or 540^{\circ} if line of symmetry used to form a pentagon.
Finding the sum of AFE and FED is 250^{\circ}.
Use of ratio 3:2 or sight of 3x and 2x.
Finding x=50.
Angle AFE = 100^{\circ}.
2. The perimeter of the rectangle is twice the perimeter of the isosceles triangle.
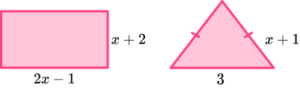
Find the area of the rectangle.
Correct expression for perimeter of rectangle or triangle,
Forming an equation linking the perimeters.
For example, 6x+2=2(2x+5) or equivalent.
Solving equation to get x=4.
Correctly substituted into length and width of rectangle.
Area given as 42cm^{2}.
3. The sector has a perimeter 25cm and radius 6cm.
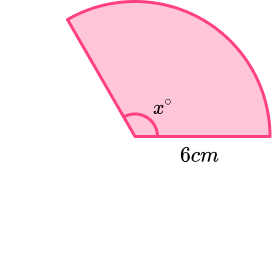
Find the size of angle x. Give your answer to 3 significant figures.
Sight of arc length given as 13cm.
Process to use formula \frac{x}{360} \times 2 \times \pi \times 6=13
Learning checklist
You have now learned how to:
- Identify lines of symmetry and order of rotational symmetry in 2D shapes
- How to work out the perimeter
- Work out the area of triangles, quadrilaterals and circles
- Work out the area of compound shapes
- Identify and apply circle definitions and properties
- Calculate the circumference of a circle
- Calculate the area and arc length of a sector
- Distinguish between regular and irregular polygon
The next lessons are
- Pythagoras theorem
Still stuck?
Prepare your KS4 students for maths GCSEs success with Third Space Learning. Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons delivered by expert maths tutors.

Find out more about our GCSE maths tuition programme.
Privacy Overview

Visual maths worksheets, each maths worksheet is differentiated and visual.
Properties of Shapes Worksheets
KS1 and KS2 Maths Worksheets / Properties of Shapes Worksheets
Our Properties of Shapes worksheets are designed to help students learn the basic properties and fundamental characteristics of shapes, including angles, quadrilaterals, 2D and 3D shapes, nets and parts of a circle. With these worksheets, students can identify different shapes based on their characteristics and use them in problem-solving scenarios. Our Properties of Shape PDF printable worksheets also provide a solid foundation for the introduction of more advanced topics concepts such as symmetry and unity, which are necessary for students as they move towards secondary school. All our resources are developed by teachers and come with answer sheets.
A 2D shape is a flat shape that has only two dimensions - length and width, with no thickness or depth, that is the reason why it is called a two-dimensional shape . For example, a sheet of paper is two-dimensional in shape. It consists of a length and a width but does not have any depth or height. Some common 2D shapes are squares, rectangles, triangles, circles, and hexagons. Let us learn more about 2D geometric shapes , the difference between 2D and 3D shapes, along with some 2D shapes examples on this page.
What are 2D Shapes?
In geometry, 2D shapes (2 dimensional shapes) can be defined as plane figures that are completely flat and have only two dimensions - length and width. They do not have any thickness and can be measured only by the two dimensions. In comparison to these, a 3D (three-dimensional) shape has three dimensions - length, width, and height. For example, a dice is three-dimensional because it consists of a length, a width, and a height. Some common 3D shapes are cuboids, cones, pyramids, and cylinders.
2D Shapes Definition
A polygon is a 2 dimensional shape made up of straight line segments which are connected with each other, thus giving it a closed shape. A circle, square, rectangle, and triangle are some examples of two-dimensional shapes and these shapes can be drawn on paper. All the 2 dimensional shapes have sides, vertices (corners), and interior angles, except for the circle, which is a curved figure. 2D shapes with at least three straight sides are called polygons and these include triangles, squares, and quadrilaterals . The figure given below shows a list of 2D shapes that we commonly come across.

Types of 2D Shapes - Regular and Irregular 2D Shapes
A 2D shape can be classified as regular or irregular based on the length and the interior angles :
- A 2 dimensional shape (2D shape) is said to be regular if all its sides are equal in length and all its interior angles measure the same.
- A two dimensional shape (2D shape) is irregular if all the sides are of unequal length and all its angles are of unequal measures.
Observe the following figure which shows the difference between regular and irregular two dimensional shapes. It shows a list of 2d shapes.

Difference Between 2D and 3D Shapes
The following table shows a comparison between 2D and 3D shapes.
Properties of 2D Shapes
2-D shapes are flat and can be drawn on a sheet of paper. There are different types of regular and irregular two dimensional shapes like a circle, triangle, square, rectangle, pentagon, and hexagon. Let us learn about a few of them along with their properties.
2D Shapes Names
There are many 2d shapes in geometry. However, a few of them are commonly seen around us and are discussed below. Here is a list of 2D shapes examples along with their properties.
A circle is a closed 2 Dimensional shape made up of a curved line with no corners or edges. Some real-life examples of the circle are coins, wheels, and pizzas. A circle consists of various parts like the radius, diameter, circumference, and so on.
Properties of a Circle
Observe the properties of a circle to identify it as a two-dimensional shape.
- Circles are completely round and made up of a single curved line.
- The circumference is the length of the boundary of the circle.
- The radius is the distance from the center of the circle to the boundary of the circle.
- The diameter is a line segment that goes straight across the circle, through the center. It is the longest possible line that can be drawn inside a circle and is twice the length of the radius.
Observe the following figure to see the different parts of a circle.

A triangle is a 2 dimensional shape with three sides and three vertices (corners).
Properties of a Triangle
Observe the properties of a triangle to identify it as a two dimensional shape.
- A triangle is a closed shape with 3 sides, 3 vertices and 3 angles.
- It is a polygon whose interior angles add up to 180°.
Some real-life examples of a triangle are traffic signs, pyramids, and nachos. The following figure shows the sides and vertices of a triangle.

A square is a 2 dimensional shape with four equal sides and each angle is equal to 90˚. Some of the real-life examples of a square are: a loaf of bread and a chessboard.
Properties of a Square
Observe the properties of the given square PQSR to identify it as a 2D shape.
- All four sides are equal, i.e., side PQ = QS = RS = PR
- Side PQ is parallel to RS.
- Side PR is parallel to QS.
- All four internal angles measure 90 ̊.

A rectangle is a 2D shape with four sides in which the opposite sides are equal and parallel, and all the four angles measure 90 ̊. Some of the real-life examples of a rectangle are table tops, blackboards, cardboard, etc.
Properties of a Rectangle
Observe the properties of the given rectangle ABCD to identify it as a 2D shape.
- Side AB = DC
- Side AD = BC
- Side AB is parallel to DC.
- Side AD is parallel to BC.
- All four angles measure 90 ̊.

Area and Perimeter of 2D Shapes
The area of a 2D shape is the space enclosed within it. The perimeter of a 2D shape is the total length of its boundary. The following table shows the formulas that are used to calculate the area and perimeter of a few common 2D shapes:
Important Notes
Here are a few important notes that should be remembered while studying 2D shapes.
- Every 2D shape can be measured by its width and length.
- All the 2D shapes are completely flat.
2d Shapes Real Life Examples
A few real-life examples of 2d shapes are given below:
- A currency note which has the shape of a rectangle
- A chess board that has the shape of a square.
- A cookie in the shape of a circle.
- A honeycomb with little hexagons in it.
☛ Related Articles
- Geometric Shapes
- Plane Shapes
- Solid Shapes
- Visualizing Solid Shapes
- 2D and 3D Shapes Worksheets
2D Shapes Examples
Example 1: Does a rectangle come under the category of 2D shapes? The length of a rectangle is 32 m and the width is 20 m. Find the perimeter of this rectangle.
Solution : Yes, a rectangle comes under the category of 2D shapes. The length of the given rectangle = 32 m; width = 20 m
We know that the perimeter of a rectangle = 2 (length + width)
P = 2 (32 + 20) = 2 (52) = 2 × 52 = 104 m
Therefore, the perimeter of the rectangle is 104 m.
Example 2: Does a circle come under 2D shapes? Find the area of a circle whose radius is 6 cm.
Area of the circle = π × r 2
= 3.14 × 6 2
= 3.14 × 36
Therefore, the Area of the circle = 113.04 square cm
Example 3: Identify the 2D shapes from the following. Circle, rectangular box, Rubik's cube, hexagon
Among the given shapes, a circle and a hexagon are 2D shapes because they do not have any thickness or depth. A rectangular box and a Rubik's cube are 3D shapes because they have 3 dimensions, (length, width, and height).
go to slide go to slide go to slide

Book a Free Trial Class
Practice Questions on 2D Shapes
go to slide go to slide
FAQs on 2D Shapes
What are 2d shapes in maths.
A 2D (two-dimensional) shape can be defined as a plane figure that can be drawn on a flat surface. It has only two dimensions - length and width, with no thickness or depth. Some of the basic 2D shapes are rectangle, pentagon, quadrilateral, circle, triangles , square, octagon , and hexagon.
What are 2D Shapes and 3D Shapes?
A flat shape that has two dimensions - length and width, is a 2D shape, whereas, a shape that has three dimensions - length, width, and depth (height) is a 3D shape .
What are the Properties of 2D Shapes?
A 2D shape is a flat shape that can be drawn on a plane surface. As the name suggests, it has only two dimensions of length and width without any thickness. While some 2D shapes have sides and vertices, others are made up of curved lines.
How many 2D Shapes are there?
There are many different kinds of 2D shapes, like the rectangle, pentagon, quadrilateral, circle, triangle, square , octagon and hexagon . These are flat shapes that can be drawn on a flat surface.
How to find the Area of 2D Shapes?
The area of a 2D shape is the space occupied by it. Since there are different kinds of 2D shapes like circles, squares, rectangles, etc., there are different formulas used to find their areas. For example, the area of a circle can be calculated with the help of the formula, Area = πr 2 , where 'r' is the radius of the circle and (pi) π is a constant with a value of 22/7. The area of a square is calculated with the formula, Area = side × side. The area of 2D shapes is expressed in square units.
How to Teach 2D Shapes?
Teaching 2D shapes is easy if the concept is introduced in the early years. First of all, the names of the basic shapes can be made to learn. Then, the students should be asked to identify the names of the shapes from a list of 2d shapes. Another interesting way can be by asking them to spot the shapes around them.
Name the 2D Shapes around the House.
Some commonly seen 2d shapes that can be seen in the house are, the rectangular surface of a notebook (rectangle), the circular shape of a clock (circle), the circular shape of a pizza, a square-shaped window (square)
Is Circle a 2D Shape?
Yes, a circle is a 2D shape because it exists on a plane with no depth. It is a curved shape that has no corners or edges.
Which 2D Shape has 4 Sides?
A quadrilateral is a 2D shape that has four sides. For example, quadrilaterals like squares and rectangles are 2D shapes with 4 sides.
Is Oval 2D or 3D Shape?
Oval is a 2D shape because it exists on a plane and has no depth. It is a curved figure with no edges or corners.
- 4th Grade Math

Grade 4 Math: Exploring 2D Shapes with Printable Worksheets
Looking for engaging and educational worksheets to help your fourth-grade students learn about 2D shapes? Look no further! These printable worksheets are designed to reinforce Grade 4 math skills and introduce students to the world of 2D shapes. By exploring 2D Shapes with printable worksheets , your 4 th graders will become more active in recognizing and drawing shapes with their specified attributes like number of sides, angles, etc.
Whether you're a teacher looking for classroom resources or a parent wanting to support your child's learning at home, these worksheets are a great tool to have on hand. So, let’s get started!
Why are 2D shapes important for math learning?
2D shapes are important for math learning because they are the building blocks of geometry. Geometry is the branch of math that studies shapes, sizes, positions, and properties of space. Geometry helps us understand the world and solve problems involving shapes and measurements. For example, geometry can help us design buildings, create art, map the earth, and more.
BROWSE THE WEBSITE
Download free worksheets, 4th grade math topics.
- Number sense
Subtraction
Multiplication
- Mixed operations
- Variable expressions
- Coordinate plane
- Data and graphs
- Logical reasoning
- Patterns and sequences
- Units measurement
- Telling time
- Equivalent fractions
- Compare & order fractions
- Add & subtract fractions with like denominators
- Add & subtract fractions with unlike denominators
- Multiply fractions
- Add and subtract decimals
- Probabilities and statistics
- Triangles and quadrilaterals
- Geometric measurement
Start practice on Fourth Grade here
A brief overview of the definition, properties, and examples of common 2d shapes such as squares, rectangles, circles, triangles, and more.
To understand and explore our printable Grade 4 math 2d shapes worksheets interestingly, it will be important to have a brief overview of the definition, properties, and examples of common 2D shapes such as squares, rectangles, circles, triangles, and more .
What are 2D shapes?
2D shapes are shapes that have two dimensions: length and width. They are also called flat shapes because they lie on a flat surface. They have no thickness or depth. Some examples of 2D shapes are squares, rectangles, circles, triangles, pentagons, hexagons, octagons, and more.
Common properties of 2D shapes
Each 2D shape has properties that describe its features and characteristics. Some common properties of 2D shapes are:
- Sides: The straight or curved edges of a shape.
- Angles : The corners where two sides meet. Angles can be acute (less than 90 degrees), right (90 degrees), or obtuse (more than 90 degrees).
- Vertices : The points where two or more sides meet. Also called corners.
- Symmetry : The ability of a shape to be divided into two or more equal parts that match exactly when folded or flipped over a line or a point.
How can printable worksheets help 4th graders practice and master 2D shapes?
Printable worksheets are a great way to practice and master 2D shapes because they provide fun and engaging activities reinforcing 4 th Grade math learning. We can use printable worksheets to review what has been taught in class, to prepare for tests, or to challenge students with new problems.
These printable worksheets also allow students to work at their own pace and level and get instant feedback on their answers.
How to identify 2D shapes? Some tips and tricks on how to recognize and name 2D shapes by looking at their sides, angles, corners, and symmetry
One way to identify 2D shapes is by looking at their sides . You can count how many sides a shape has and what shape they are. For example;
- A square has four equal straight sides ,
- A rectangle has four straight sides with two pairs of equal length,
- A circle has one curved side ,
- A triangle has three straight sides , and so on.
Another way to identify 2D shapes is by looking at their angles . You can measure the angles of a shape using a protractor or estimate them by comparing them to right angles. For example,
- A square has four right angles ,
- A rectangle has four right angles ,
- A circle has no angles,
- A triangle has three angles that add up to 180 degrees, and so on.
A third way to identify 2D shapes is by looking at their vertice s. You can count how many vertices a shape has and where they are located. For example,
- A square has four vertices at its corners,
- A rectangle has four vertices at its corners,
- A circle has no vertices,
- A triangle has three vertices at its corners, and so on.
A fourth way to identify 2D shapes is by looking at their symmetry . You can check if a shape has a line or point symmetry by folding or flipping it over a line or point. For example,
- A square has four lines of symmetry and one point of symmetry ,
- A rectangle has two lines of symmetry and one point of symmetry ,
- A circle has infinite lines of symmetry and one point of symmetry ,
- A triangle has one or more lines of symmetry depending on its type (equilateral, isosceles, or scalene), and so on.
How to measure 2D shapes? A review of the concepts and formulas for finding the perimeter, area, and angles of different 2D shapes
- One way to measure 2D shapes is by finding their perimeter . The perimeter is the distance around the edge of a shape. To find the perimeter of a shape, add up the lengths of all its sides. For example, the perimeter of a square is 4 times the length of one side, the perimeter of a rectangle is 2 times the length plus 2 times the width, the perimeter of a circle is 2 times pi times the radius, and so on.
- Another way to measure 2D shapes is by finding their area . The area is the amount of space inside a shape. To find the area of a shape, use different formulas depending on the type of shape. For example, the area of a square is the length of one side squared, the area of a rectangle is the length times the width, the area of a circle is pi times the radius squared, the area of a triangle is half the base times the height, and so on.
- A third way to measure 2D shapes is by finding their angles . The angles of a shape are the measures of the turns between its sides. To find the angles of a shape, use a protractor or some rules and formulas depending on the type of shape. For example, the angles of a square are all 90 degrees, the angles of a rectangle are all 90 degrees, the angles of a circle are all 360 degrees, the angles of a triangle add up to 180 degrees, and so on.
Exploring Grade 4 two-dimensional shapes with printable worksheets: Samples of skills available in Mathskills4kids.com
Identifying 2d shapes.
Students will practice identifying and naming different 2D shapes, such as squares, rectangles, triangles, and circles.
This worksheet set is perfect for helping students develop their shape-recognition skills. Each worksheet features a variety of 2D shapes, and students are tasked with identifying and naming each shape . They will encounter common shapes such as squares, rectangles, triangles, and circles and more complex shapes like pentagons and hexagons.
By completing these worksheets, students will become more familiar with the characteristics of each shape and improve their ability to identify them in real-world objects.
Properties of 2D Shapes
Students will learn about the properties of different 2D shapes, including the number of sides, angles, and symmetry.
Understanding the properties of 2D shapes is an important skill for fourth-grade students to develop. In this worksheet set, students will learn about the number of sides, angles, and symmetry of various shapes. They can identify shapes based on these properties and understand how they relate to real-world objects.
By completing these worksheets, students will strengthen their knowledge of 2D shapes and improve their ability to analyze and classify them.
Sorting 2D shapes
Students will sort various 2D shapes based on their attributes, such as the number of sides or angles.
This activity will help students practice identifying and categorizing different 2D shapes. They will be given a set of shapes and asked to sort them into groups based on specific attributes, such as the number of sides or angles . This will help them develop their critical thinking and problem-solving skills and reinforce their understanding of shape properties.
By engaging in this hands-on activity, students will gain a deeper understanding of 2D shapes and improve their ability to analyze and classify them.
Drawing 2D Shapes
Students will practice drawing different 2D shapes using a ruler and protractor to ensure accuracy.
In this activity, students can practice their drawing skills by creating various 2D shapes. They will use a ruler to ensure straight lines and a protractor to measure and create accurate angles. This activity will help students improve their drawing abilities and reinforce their understanding of shape properties and measurements.
By engaging in this hands-on activity, students will develop their spatial reasoning skills and gain a deeper understanding of 2D shapes.
Problem-Solving with 2D Shapes
Students will solve word problems that involve 2D shapes, such as finding the perimeter or area of a shape.
This activity is designed to help students apply their knowledge of 2D shapes to real-world problem-solving situations. Students will develop their critical thinking and mathematical reasoning skills by solving word problems that involve finding the perimeter or area of a shape. They will also better understand how 2D shapes are used in practical situations.
This activity can be done individually or in small groups and can be fun and engaging for students to practice their math skills.
How to compare and classify 2D shapes? A fun activity on sorting and grouping 2D shapes based on their attributes and characteristics
One way to compare and classify 2D shapes is by sorting and grouping them based on their attributes and characteristics . You can use different criteria to sort and group shapes, such as:
- Number of sides : You can sort and group shapes by how many sides they have. For example, you can make groups of shapes with three sides (triangles), four sides (quadrilaterals), five sides (pentagons), six sides (hexagons), etc.
- Type of sides : You can sort and group shapes by what type of sides they have. For example, you can make groups of shapes with straight sides (polygons), curved sides (circles), or both (semi-circles).
- Length of sides : You can sort and group shapes by their sides' length. For example, you can make groups of shapes with equal sides (regular polygons), unequal sides (irregular polygons), or both (trapezoids).
- Type of angles : You can sort and group shapes by what type of angles they have. For example, you can make groups of shapes with right angles (rectangles), acute angles (acute triangles), obtuse angles (obtuse triangles), or both (scalene triangles).
- Number of vertices : You can sort and group shapes by their number of vertices. For example, you can make groups of shapes with three vertices (triangles), four vertices (quadrilaterals), five vertices (pentagons), six vertices (hexagons), etc.
- Type of symmetry : You can sort and group shapes by their symmetry type. For example, you can make groups of shapes with line symmetry (squares), point symmetry (circles), both (rectangles), or none (scalene triangles).
Bonus: Extra 2D shapes activities to reinforce 4 th graders' practice
If you are looking for extra engaging activities to help your students practice their 2D shapes skills, here is a compiled list of awesome web pages offering free and interactive 2D shapes games, puzzles, quizzes, and more. These activities are perfect for reinforcing what your students have learned in class or providing extra practice at home.
- [ Math Playground ] ( https://www.mathplayground.com/shape_patterns.html ): This web page has a cool game where students have to complete a pattern of 2D shapes by dragging and dropping the correct shape into an empty space. The game gets harder as the students progress, and they can choose from different difficulty levels. This game is great for developing spatial reasoning, logic skills, and 2D shapes recognition.
- [ SplashLearn ] ( https://www.splashlearn.com/math-games/2d-shapes ): This web page has various games covering different aspects of 2D shapes, such as identifying, naming, sorting, comparing, and classifying them. These colorful and interactive games provide feedback and hints to help the students. The games also adapt to the student's skill level, so they can challenge themselves and learn at their own pace.
- [Education.Com] ( https://www.education.com/games/geometry/ ): This web page has games teaching students about geometry concepts, including 2D shapes. The games are fun and engaging, covering topics such as angles, symmetry, area, perimeter, and more. The games also have different modes and options so that students can customize their learning experience.
Thank you for sharing the links of MathSkills4Kids.com with your loved ones. Your choice is greatly appreciated.
We hope you find this article useful and enjoyable for your 4th graders and learn something new about 2D shapes. This article introduces us to Mathskills4kids.com, and more links, which are great for reinforcing 4 th Grade 2D shapes knowledge and skills and making learning fun.
In this article, we have explored 2D shapes with printable worksheets that you can download and print for free. We have learned what 2D shapes are, how to identify and measure them, and how to compare and classify them.
Now it's your turn to practice and master Grade 4 Math 2D Shapes with Printable Worksheets for free. You will find different types of activities that will help you review and reinforce your learning.
You will also have fun solving puzzles, coloring pictures, drawing shapes, and more. Click the link below to download and print our Mathskills4kids Grade 4 math 2D shapes worksheets.
Have fun exploring 2D Shapes with Printable Worksheets !
WHAT’S THIS ALL ABOUT?
This is mathskills4kids.com a premium math quality website with original Math activities and other contents for math practice. We provide 100% free Math ressources for kids from Preschool to Grade 6 to improve children skills.
Measurement
Telling Time
Problem Solving
Data & Graphs
Kindergarten
First Grade
Second Grade
Third Grade
Fourth Grade
Fifth Grade
Sixth Grade
SUBSCRIBE TO OUR NEWSLETTER
Privacy policy.
Our team Don't Pass on to third parties any identifiable information about mathskills4kids.com users. Your email address and other information will NEVER be given or sold to a third party.
USE OF CONTENTS
Many contents are released for free but you're not allowed to share content directly (we advise sharing website links), don't use these contents on another website or for a commercial issue. You're supposed to protect downloaded content and take it for personal or classroom use. Special rule : Teachers can use our content to teach in class.
Want Better Math Grades?
✅ Unlimited Solutions
✅ Step-by-Step Answers
✅ Available 24/7
➕ Free Bonuses ($1085 value!)
On this page
- Introduction to Geometry
- Functions and Graphs
- 1. Introduction to Functions
- 2. Functions from Verbal Statements
- 3. Rectangular Coordinates
- 4. The Graph of a Function
- 4a. Domain and Range of a Function
- 4b. Domain and Range interactive applet
- 4c. Comparison calculator BMI - BAI
- 5. Graphing Using a Computer Algebra System
- 5a. Online graphing calculator (1): Plot your own graph (JSXGraph)
- 5b. Online graphing calculator (2): Plot your own graph (SVG)
- 6. Graphs of Functions Defined by Tables of Data
- 7. Continuous and Discontinuous Functions
- 8. Split Functions
- 9. Even and Odd Functions
Related Sections
Math Tutoring
Need help? Chat with a tutor anytime, 24/7.
Online Math Solver
Solve your math problem step by step!
IntMath Forum
Get help with your math queries:
2D Shapes in Geometry
What are 2d shapes in geometry.
2D shapes in geometry are two-dimensional shapes. They have length and width, but no depth. 2D shapes can be found in many different forms and can be used to construct objects in the real world, as well as in mathematics. 2D shapes are also known as polygons, and they can be regular or irregular.
2D shapes can be categorized into different types, including circles, squares, rectangles, triangles, trapezoids, parallelograms, rhombuses, and kites. Each type of 2D shape has its own set of properties and characteristics, which can be used to identify them.
Circles are round, two-dimensional shapes that have a radius, or distance from the center to the edge. Circles are important in geometry since they are used to measure angles and distances. The area of a circle is calculated using the formula A = pr 2 , where A is the area and r is the radius of the circle.
Circles can also be used to construct objects in the real world. For example, a wheel is a circular object that is used to move things from one place to another.
Squares are four-sided polygons that have all four sides equal in length and all four angles equal in measure. The area of a square is calculated using the formula A = s 2 , where A is the area and s is the length of one side of the square.
Squares are used to construct objects in the real world. For example, a cube is a three-dimensional object that is made up of six equal squares.
Triangles are three-sided polygons that have three sides of varying lengths and three angles of varying measure. The area of a triangle is calculated using the formula A = 1/2 bh, where A is the area, b is the base of the triangle, and h is the height of the triangle.
Triangles are also used to construct objects in the real world. For example, the roof of a house is typically made up of multiple triangles.
Practice Problems
1. Find the area of a circle with a radius of 5 cm.
Answer: A = pr 2 = p(5 cm) 2 = 78.5 cm 2
2. Find the area of a square with a side length of 6 cm.
Answer: A = s 2 = (6 cm) 2 = 36 cm 2
3. Find the area of a triangle with a base of 8 cm and a height of 10 cm.
Answer: A = 1/2 bh = 1/2 (8 cm)(10 cm) = 40 cm 2
4. Find the circumference of a circle with a radius of 7 cm.
Answer: C = 2pr = 2p(7 cm) = 43.98 cm
5. Find the perimeter of a square with a side length of 5 cm.
Answer: P = 4s = 4(5 cm) = 20 cm
6. Find the perimeter of a triangle with sides of length 8 cm, 10 cm, and 12 cm.
Answer: P = 8 cm + 10 cm + 12 cm = 30 cm
In this article, we discussed 2D shapes in geometry. These shapes can be categorized into different types, including circles, squares, rectangles, triangles, trapezoids, parallelograms, rhombuses, and kites. Each type of 2D shape has its own set of properties and characteristics, which can be used to identify them. We also practiced some problems related to finding the area and perimeter of different 2D shapes.
What is a 2D shape in geometry?
A 2D shape in geometry is a shape that has two dimensions, such as length and width. It is flat and can be measured and drawn on a plane.
What is the definition of 2D figures?
A 2D figure is a shape that has two dimensions, such as length and width. It is flat and can be measured and drawn on a plane.
How do you introduce 2D shapes?
When introducing 2D shapes, it is important to explain the basic concepts of geometry, such as points, lines, and angles, as well as the different types of 2D shapes, such as squares, circles, and triangles. It is also helpful to provide visuals, such as diagrams or images, to help students understand the concepts.
What are 2D shape properties?
2D shape properties describe the characteristics of a 2D shape, such as the number of sides, angles, and length of the sides. Additionally, properties such as perimeter, area, and symmetry can be used to further describe 2D shapes.
Problem Solver

This tool combines the power of mathematical computation engine that excels at solving mathematical formulas with the power of GPT large language models to parse and generate natural language. This creates math problem solver thats more accurate than ChatGPT, more flexible than a calculator, and faster answers than a human tutor. Learn More.
Tips, tricks, lessons, and tutoring to help reduce test anxiety and move to the top of the class.
Email Address Sign Up
- 1st Grade Math
- 2nd Grade Math
- 3rd Grade Math
- 4th Grade Math
- 5th Grade Math
- 6th Grade Math
- 7th Grade Math
- 8th Grade Math
- Knowledge Base
- Math for kids
2D (Two Dimensional) Shapes
Created: January 9, 2024
Last updated: January 9, 2024
Discover the fascinating world of 2D shapes with Brighterly ! Our unique approach to teaching geometry helps children easily grasp the concepts of two-dimensional shapes while having fun. We focus on making learning enjoyable and interactive so that kids are excited to explore the various shapes, properties, and calculations associated with these essential mathematical figures.
What are 2D Shapes?
2D shapes are flat, two-dimensional objects that have length and width. They are also known as plane figures or plane shapes because they lie entirely in a single plane. Children are often introduced to 2D shapes in their early years of education, and understanding these shapes is crucial for building a strong foundation in geometry and other branches of mathematics.
In this engaging and informative post, we will delve into the captivating realm of 2D shapes. By exploring their unique properties and common examples, your child will not only gain a solid understanding of geometric concepts but also develop an appreciation for the beauty and relevance of mathematics in everyday life.
2D Shapes Names and Properties
There are several basic 2D shapes, each with its own unique properties. Let’s dive into each of them:
A circle is a beautifully symmetrical, round, closed figure in which all points are equidistant from a central point called the center. This equidistance is referred to as the radius, which serves as a crucial measurement in circle-related calculations. One fascinating aspect of circles is their circumference – the distance that encompasses the entire shape. The formula to determine the circumference is 2πr, where “r” represents the radius. In the world of geometry, circles hold a unique position due to their smooth, continuous curve and infinite lines of symmetry.
Triangles are intriguing polygons with three sides and three angles that come together to create various shapes. The fascinating world of triangles offers diverse classifications based on their sides (equilateral, isosceles, or scalene) and angles (acute, right, or obtuse). Equilateral triangles boast three equal sides, while isosceles triangles have two equal sides. In contrast, scalene triangles exhibit no equal sides. Triangles play a pivotal role in geometry as the simplest polygons and can be combined to create more complex shapes.
The square is an elegant four-sided polygon characterized by equal sides and four right angles (90 degrees). It holds a special place in geometry as it is both a rectangle and a rhombus. The area of a square, a measure of the space it occupies, is determined by squaring the length of one side (side^2). Squares exhibit remarkable symmetry, with four lines of symmetry dividing them into equal halves. Their simplicity and elegance make them a fundamental shape in geometry and design.
Rectangles are versatile four-sided polygons featuring opposite sides of equal length and four right angles. The area of a rectangle is calculated by multiplying its length and width, providing a simple yet effective measure of the space it occupies. Rectangles are unique due to their perfect balance of symmetry and flexibility. They have two lines of symmetry, making them less symmetrical than squares but more adaptable to various real-world applications, such as in architecture and design.
Pentagons are fascinating polygons with five sides and five angles. They can be regular, exhibiting equal sides and angles, or irregular, with varying sides and angles. Pentagons play a significant role in both geometry and nature, with the regular pentagon serving as the foundation for the dodecahedron, a Platonic solid. These five-sided wonders captivate the imagination and challenge the intellect, as they are the first polygons that cannot be regularly tessellated on a plane.
Octagons are striking polygons with eight sides and eight angles. They can be regular, characterized by equal sides and angles, or irregular, with sides and angles of different lengths and measures. Octagons possess intriguing properties and are often seen in everyday life, such as in stop signs and architecture. With their unique shape and a balance between symmetry and complexity, octagons offer a captivating subject for exploration in the world of 2D shapes.
Unveiling the Secrets of 2D Shapes Properties
Every 2D shape possesses its own unique properties, such as the number of sides, angles, and their measures. Some shapes also display lines of symmetry, which bisect the shape into two identical halves. Understanding the properties of each 2D shape is vital to mastering geometry and appreciating the inherent beauty and order in mathematics.
2D And 3D Shape Worksheets PDF
2D And 3D Shape Worksheets
2D 3D Shape Worksheets PDF
2D 3D Shape Worksheets
To deepen your understanding of 2D shapes, we recommend exploring the math worksheets offered by Brighterly. These worksheets have been designed to assist in learning and consolidating your knowledge on this topic.
Area and Perimeter of 2D Shapes
The area of a 2D shape represents the amount of space it occupies, while the perimeter refers to the total length of its boundaries. To excel in geometry, children need to learn and practice various formulas for calculating the area and perimeter of different 2D shapes. For instance, the area of a square is calculated by squaring the length of one side, while the perimeter is determined by multiplying the side length by 4. By mastering these calculations, children can enhance their problem-solving skills and develop a deeper understanding of geometric concepts.
Difference Between 2D and 3D Shapes
A key distinction between 2D and 3D shapes lies in their dimensionality. While 2D shapes are flat and possess only length and width, 3D shapes have length, width, and height (or depth), giving them a more substantial presence in the physical world. Examples of 3D shapes include cubes, spheres, and cylinders, which can be observed in everyday objects like dice, basketballs, and soda cans. Gaining an understanding of the differences between 2D and 3D shapes is vital for children to broaden their perspective on geometry and the world around them.
Solved Examples
To assist your child in grasping the concepts of 2D shapes more effectively, we have provided a variety of solved examples. These examples cover diverse topics, such as calculating area and perimeter, identifying shapes based on properties, and solving geometric problems. By studying these examples, children can hone their skills and gain the confidence to tackle even more challenging problems.
Sort 2D And 3D Shapes Worksheet
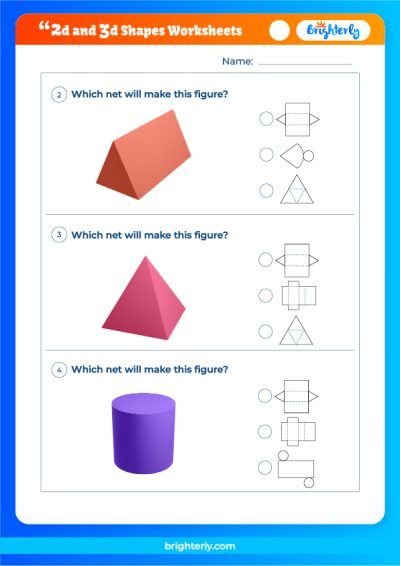
Sorting 2D And 3D Shapes Worksheet
Problems on Two Dimensional Shapes
The key to mastering 2D shapes is consistent practice. Encourage your child to work on a range of practice problems to improve their understanding of 2D shapes and their properties. These problems encompass various levels of difficulty, allowing children to progressively build their skills and confidence in geometry. As they work through the problems, your child will develop a strong foundation in 2D shapes that will serve them well in their mathematical journey.
Embracing the world of 2D shapes is an essential step in a child’s mathematical journey. Through a comprehensive understanding of these shapes, their properties, and the ability to calculate their area and perimeter, children can establish a robust foundation in geometry. This knowledge will prove invaluable in various aspects of life, from tackling everyday problems to pursuing advanced studies in mathematics or related fields.
At Brighterly, we are committed to making learning an enjoyable and engaging experience for children. We believe that by fostering a love for mathematics, we are empowering the next generation of problem solvers, critical thinkers, and innovative leaders. Explore our website for a wealth of resources, interactive activities, and captivating games designed to help your child excel in mathematics and beyond. With Brighterly by their side, your child’s future will undoubtedly shine Brighterly!
Frequently Asked Questions on Two Dimensional Shapes
What are some real-life examples of 2d shapes.
- Circles: coins, clock faces, and wheels
- Triangles: yield signs, pizza slices, and the Eiffel Tower
- Squares: chessboards, tiles, and windows
- Rectangles: doors, bricks, and smartphones
- Pentagons: the Pentagon building, home plate in baseball, and traffic signs
- Octagons: stop signs, and the shape of some tables
How can I help my child learn about 2D shapes?
- Use everyday objects to illustrate the different shapes.
- Encourage them to practice drawing the shapes.
- Play games and engage in activities that involve recognizing and categorizing shapes.
- Provide them with practice problems and puzzles involving 2D shapes.
Are there other types of polygons besides the ones mentioned in this article?
Yes, there are numerous other types of polygons, such as hexagons (6 sides), heptagons (7 sides), nonagons (9 sides), and decagons (10 sides). These shapes can also be regular (all sides and angles equal) or irregular (sides and angles not equal).
The information in this article was gathered from the following sources:
- Gov: National Center for Education Statistics
- BBC Bitesize: KS2 Maths
I am a seasoned math tutor with over seven years of experience in the field. Holding a Master’s Degree in Education, I take great joy in nurturing young math enthusiasts, regardless of their age, grade, and skill level. Beyond teaching, I am passionate about spending time with my family, reading, and watching movies. My background also includes knowledge in child psychology, which aids in delivering personalized and effective teaching strategies.
Problems with Geometry?
- Does your child struggle to master geometry lessons?
- Try lessons with an online tutor.
Kid’s grade
Is your child having trouble grasping the basics of geometry? An online tutor could provide the necessary support.

After-School Math Program
Related math.
Understanding the basics of geometry is like learning a new language. We’re here at Brighterly to help simplify this language of shapes and sizes for our young learners. Today, we’re looking at a simple yet vital concept in geometry, the Straight Angle. What Is an Angle? Before we dive into straight angles, let’s first understand […]
Welcome to Brighterly’s math blog, where we make learning math a delightful experience for children! In this article, we will explore the concept of divisibility and provide you with clear definitions and practical examples to help you understand this fundamental mathematical concept. Divisibility is a term that frequently appears in the world of mathematics, especially […]
We write the number 16 in words as “sixteen”. It’s the count after fifteen. If you have sixteen crayons, it means you have fifteen crayons and add one more to them. Tens Ones 1 6 How to Write 16 in Words? The number 16 is written as ‘Sixteen’ in words. It has a ‘1’ in […]
We use cookies to help give you the best service possible. If you continue to use the website we will understand that you consent to the Terms and Conditions. These cookies are safe and secure. We will not share your history logs with third parties. Learn More

Or search by topic
Number and algebra
- The Number System and Place Value
- Calculations and Numerical Methods
- Fractions, Decimals, Percentages, Ratio and Proportion
- Properties of Numbers
- Patterns, Sequences and Structure
- Algebraic expressions, equations and formulae
- Coordinates, Functions and Graphs
Geometry and measure
- Angles, Polygons, and Geometrical Proof
- 3D Geometry, Shape and Space
- Measuring and calculating with units
- Transformations and constructions
- Pythagoras and Trigonometry
- Vectors and Matrices
Probability and statistics
- Handling, Processing and Representing Data
- Probability
Working mathematically
- Thinking mathematically
- Mathematical mindsets
- Cross-curricular contexts
- Physical and digital manipulatives
For younger learners
- Early Years Foundation Stage
Advanced mathematics
- Decision Mathematics and Combinatorics
- Advanced Probability and Statistics
Early Years Foundation Stage (EYFS)
Exploring 2D Shapes

Children often enjoy playing with long strings or ribbons and making and describing shapes. Adults could build on this by providing long loops of string or elastic to stimulate conversations about 2D shapes.
Encouraging mathematical thinking and reasoning:
The Mathematical Journey
Same and different:
- developing the use of language to compare, contrast and describe. For example: straight, wiggly, curved, rounded, pointy, bigger, smaller, longer, shorter, corner, like, different, side, curve
Recognising and labelling common shapes:
- making connections with shapes in their own environment and beginning to use names such as triangle, rectangle, square, corner, side...
- counting the sides and corners of the shapes they make
Describing position:
- using words such as on, inside, outside, under, left, right, above and below to describe position
Comparing sizes:
- beginning to use language such as bigger, smaller, longer and shorter to introduce ideas about measuring

- Shape searches in a series of photos or in books and drawings
- I-spy shapes games
- Using educational games that involve shape sorting or matching
- Building pictures from precut shapes or cutting shapes from coloured paper or magazines
- Painting on the ground or wall with big wallpaper brushes and water
- Using natural materials such as leaves, twigs and daisy chains to make shapes
- Printing with potato or sponge shapes
- Drawing shapes in the sand tray, with paints, through cornflour gloop or with a finger
- Riding wheeled toys through puddles and looking at the tracks
Download a PDF of this resource.

- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search
Properties of 2D shapes including problem solving
Subject: Mathematics
Age range: 7-11
Resource type: Worksheet/Activity
Last updated
6 October 2018
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest
smartboard and worksheets on properties of 2d shapes.
Creative Commons "Sharealike"
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
Empty reply does not make any sense for the end user
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Welcome to the Math Salamanders 2d Shapes Worksheets. We have a wide selection of worksheets on 2d shapes, including symmetry worksheets, naming 2d shapes, shape riddles and puzzles, and sheets about the properties of 2d shapes. There are a range of worksheets at different levels, suitable for children from Kindergarten and up.
Properties of shapes deal with the definitions of shapes and how shapes are classified. Additionally, we will use our knowledge of shapes to identify counterexamples, determine whether three lines of specified length can form a triangle, and solving problems by drawing diagrams.
Resources tagged with: 2D shapes and their properties Types All types Problems Articles Games Age range All ages 5 to 11 7 to 14 11 to 16 14 to 18 Challenge level There are 134 NRICH Mathematical resources connected to 2D shapes and their properties , you may find related items under Angles, polygons, and geometrical proof .
Sponge Sections. Age 7 to 11. Challenge Level. You have been given three shapes made out of sponge: a sphere, a cylinder and a cone. Your challenge is to find out how to cut them to make different shapes for printing.
Use these differentiated problem-solving worksheets to consolidate learning about 2D shapes and related vocabulary. The activities include use of multiplication tables facts up to the ten times table. Why not support pupils who are less confident about properties of 2D shapes by using these 2D Shape Posters display posters on your working wall.
2D Shapes Practice Questions - Corbettmaths. 5-a-day GCSE 9-1. 5-a-day Primary. 5-a-day Further Maths. Further Maths.
Worksheets. The worksheets here involve children applying their knowledge and understanding to explore 2d shapes. They are a great way to stretch the more able learners, or get children to think hard about the properties shapes have. Although the sheets in this section are aimed at 3rd grade, they could easily be used by older children.
2D shapes are flat shapes which only have two dimensions; length and width. Some examples of common 2D shapes names are triangles, rectangles, pentagons, hexagons, heptagons, octagons, nonagons, decagons and circles. We can solve problems involving 2D shapes using a variety of methods.
Preparing for Advanced Geometry: A solid understanding of the properties of 2D shapes prepares your students or child for further studies in geometry and makes the transition the higher levels much easier. Enhancing Problem-Solving Abilities: Beyond geometry, learning about 2D shapes improves students' problem-solving skills across various ...
Our Properties of Shapes worksheets are designed to help students learn the basic properties and fundamental characteristics of shapes, including angles, quadrilaterals, 2D and 3D shapes, nets and parts of a circle. With these worksheets, students can identify different shapes based on their characteristics and use them in problem-solving scenarios. Our Properties of Shape PDF printable ...
2D Shapes. A 2D shape is a flat shape that has only two dimensions - length and width, with no thickness or depth, that is the reason why it is called a two-dimensional shape. For example, a sheet of paper is two-dimensional in shape. It consists of a length and a width but does not have any depth or height. Some common 2D shapes are squares ...
This is great as it shows understanding of properties and language and has some problem solving. Explain Everything App and Shape Properties. Miss Kingsley and her lovely Year 1 class at Russell Scott Primary have been using the Explain Everything App to talk about the properties of 2D shape, what a great idea and some superb mathematical ...
These excellent properties of 2D Shapes pack include five worksheets that are ideal for teaching children the properties of 2D shapes. Including a wide range of activities, each resource is colourful and engaging and will help you swiftly teach your class about 2D shapes.Use the 2D shapes edges sorting activity to build your classes understanding and ability to identify the different ...
Playing with 2D Shape. Giving children chance to 'play around' with two-dimensional shapes gives them the freedom to explore spatial properties for themselves, thereby developing their understanding in a meaningful way. These activities offer contexts in which children can engage in this 'play'. Can you sort these triangles into three different ...
Understanding the properties of 2D shapes is an important skill for fourth-grade students to develop. In this worksheet set, students will learn about the number of sides, angles, and symmetry of various shapes. ... Problem-Solving with 2D Shapes. Students will solve word problems that involve 2D shapes, such as finding the perimeter or area of ...
These shapes can be categorized into different types, including circles, squares, rectangles, triangles, trapezoids, parallelograms, rhombuses, and kites. Each type of 2D shape has its own set of properties and characteristics, which can be used to identify them. We also practiced some problems related to finding the area and perimeter of ...
The names of 2D shapes are famous and you can use them in your day-to-day life. The famous 2D shapes names are: Circle: A circle is a familiar and widespread shape. It is without corners or angles and has a unique roundness. It has an unchanging radius and diameter. Square: A square is a shape having four equal sides.
Unveiling the Secrets of 2D Shapes Properties. Every 2D shape possesses its own unique properties, such as the number of sides, angles, and their measures. ... By mastering these calculations, children can enhance their problem-solving skills and develop a deeper understanding of geometric concepts. Difference Between 2D and 3D Shapes.
These 2D Shape Reasoning Challenges are the perfect activity for children to complete in order to challenge their understanding of 2D shapes and support making comparisons! An activity that further develops children's basic understanding of the properties of 2D shapes and supports them in recording full reasoning answers of comparison.
Exploring 2D Shapes. Age 3 to 5. Describing and comparing 2D shapes. Understanding the characteristics of 2D shapes. Children often enjoy playing with long strings or ribbons and making and describing shapes. Adults could build on this by providing long loops of string or elastic to stimulate conversations about 2D shapes. The Activity.
Properties of 2D shapes including problem solving. Subject: Mathematics. Age range: 7-11. Resource type: Worksheet/Activity. salma99. 4.48 139 reviews. ... docx, 1.11 MB notebook, 389.43 KB. smartboard and worksheets on properties of 2d shapes. Creative Commons "Sharealike" Reviews. 5 Something went wrong, please try again later. Stellwagen. 4 ...
Reasoning and Problem Solving - Draw 2D Shapes - Teaching Information. 1a.Mandip is drawing a square. Connect the dots to finish her shape. 1b. Jack is drawing a rectangle. Connect the dots to finish his shape. 2a. another rectangle that fits inside the given rectangle. 2b. another square that fits inside the given square.
Reasoning and Problem Solving -Recognise 2D and 3D Shapes Developing 1a. Jay is correct. Both of the shapes are triangles in different positions. 1b. Bella is incorrect. The first shape is a cylinder but the second shape is a sphere. 2a. Alia has put the square and the pyramid in the wrong places. They need to swa. 2b.