
Explore millions of high-quality primary sources and images from around the world, including artworks, maps, photographs, and more.
Explore migration issues through a variety of media types
- Part of The Streets are Talking: Public Forms of Creative Expression from Around the World
- Part of The Journal of Economic Perspectives, Vol. 34, No. 1 (Winter 2020)
- Part of Cato Institute (Aug. 3, 2021)
- Part of University of California Press
- Part of Open: Smithsonian National Museum of African American History & Culture
- Part of Indiana Journal of Global Legal Studies, Vol. 19, No. 1 (Winter 2012)
- Part of R Street Institute (Nov. 1, 2020)
- Part of Leuven University Press
- Part of UN Secretary-General Papers: Ban Ki-moon (2007-2016)
- Part of Perspectives on Terrorism, Vol. 12, No. 4 (August 2018)
- Part of Leveraging Lives: Serbia and Illegal Tunisian Migration to Europe, Carnegie Endowment for International Peace (Mar. 1, 2023)
- Part of UCL Press
Harness the power of visual materials—explore more than 3 million images now on JSTOR.
Enhance your scholarly research with underground newspapers, magazines, and journals.
Explore collections in the arts, sciences, and literature from the world’s leading museums, archives, and scholars.

Peer Reviewed and Primary Research
- Peer Review--What is it?
- Scholarly Journal vs. Magazine
- Finding Peer-Reviewed Articles
- Databases for finding Articles with Primary Research
Reading an Article Citation
Taucar, Christopher Edward . "Standards of judicial review of administrative bodies: The consideration of citizen participation." Canadian Public Administration 53 , no. 1 (March 2010): 67-86
Author. " Article Title." Journal Name Volume, Issue ( Date): Pages

1. Connect to New Refworks 2. Create an Account 3. Create a New Folder 4. Search Databases for articles 5. Export your article citation to Refworks 6. You may also download the article PDF to your computer and then upload it in Refworks. 7. Create your Bibliography
- Refworks Libguide
Databases for locating Peer Reviewed Articles
Below is a selection of frequently used library subscription databases for finding primary research in peer-reviewed journals. For more library databases please see the alphabetical list at http://library.rwu.edu
- Academic Search Complete This link opens in a new window Multi-disciplinary academic database covering scholarly journals, newspapers, and more. An excellent place to begin your research.
- Criminal Justice Abstracts This link opens in a new window Index of the criminology literature. Topics include crime trends, prevention projects, corrections, juvenile delinquency, police, courts, offenders, victims, and sentencing.
- ERIC This link opens in a new window The Education Resources Information Center (ERIC), sponsored by the Institute of Education Sciences (IES) of the U.S. Department of Education, produces the world's premier database index of journal and non-journal education literature.
- ERIC - Ebsco Interface This link opens in a new window Index and abstracts of educational journals and other materials a since 1966. Use this version of ERIC to link to RWU library journal subscriptions not available in the U.S. Department of Educations ERIC interface.
- PsycINFO This link opens in a new window Covers psychology and related disciplines with full-text linking to PsycArticles and other e-journal providers as available.
- Materials Science & Engineering Collection This link opens in a new window Databases include: ANTE (Abstracts in New Technologies and Engineering), ASCE Civil Engineering Abstracts, Earthquake Engineering Abstracts, Environmental Engineering Abstracts, Mechanical & Transportation Engineering Abstracts.
- Biological Sciences This link opens in a new window Indexes a wide variety of biology journals.
- ASFA: Aquatic Sciences and Fisheries Abstracts (ASFA) This link opens in a new window Database covering the aquatic sciences including aquaculture, marine biology, oceanography, fisheries, limnology, and more.
- Sociological Abstracts This link opens in a new window Indexes the international literature in sociology and related disciplines in the social and behavioral sciences. Links to full-text as available.
- << Previous: Finding Peer-Reviewed Articles
- Last Updated: Feb 14, 2024 1:31 PM
- URL: https://rwu.libguides.com/peer-reviewed
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Trending Articles
- Global burden of 288 causes of death and life expectancy decomposition in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. GBD 2021 Causes of Death Collaborators. Lancet. 2024. PMID: 38582094
- Identifying and Characterizing a Novel Peritrophic Matrix Protein (MdPM-17) Associated With Antibacterial Response From the Housefly, Musca domestica (Diptera: Muscidae). Wang Y, et al. J Insect Sci. 2020. PMID: 33347588 Free PMC article.
- Pharmacotherapy for adults with overweight and obesity: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Shi Q, et al. Lancet. 2024. PMID: 38582569
- Gut bacteria-driven homovanillic acid alleviates depression by modulating synaptic integrity. Zhao M, et al. Cell Metab. 2024. PMID: 38582087
- Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Bray F, et al. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024. PMID: 38572751
Latest Literature
- Am J Clin Nutr (2)
- J Am Coll Cardiol (15)
- J Biol Chem (2)
- J Neurosci (1)
- Nat Commun (44)
- Nature (42)
- Oncogene (1)
NCBI Literature Resources
MeSH PMC Bookshelf Disclaimer
The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited.
Finding Scholarly Articles: Home

What's a Scholarly Article?
Your professor has specified that you are to use scholarly (or primary research or peer-reviewed or refereed or academic) articles only in your paper. What does that mean?
Scholarly or primary research articles are peer-reviewed , which means that they have gone through the process of being read by reviewers or referees before being accepted for publication. When a scholar submits an article to a scholarly journal, the manuscript is sent to experts in that field to read and decide if the research is valid and the article should be published. Typically the reviewers indicate to the journal editors whether they think the article should be accepted, sent back for revisions, or rejected.
To decide whether an article is a primary research article, look for the following:
- The author’s (or authors') credentials and academic affiliation(s) should be given;
- There should be an abstract summarizing the research;
- The methods and materials used should be given, often in a separate section;
- There are citations within the text or footnotes referencing sources used;
- Results of the research are given;
- There should be discussion and conclusion ;
- With a bibliography or list of references at the end.
Caution: even though a journal may be peer-reviewed, not all the items in it will be. For instance, there might be editorials, book reviews, news reports, etc. Check for the parts of the article to be sure.
You can limit your search results to primary research, peer-reviewed or refereed articles in many databases. To search for scholarly articles in HOLLIS , type your keywords in the box at the top, and select Catalog&Articles from the choices that appear next. On the search results screen, look for the Show Only section on the right and click on Peer-reviewed articles . (Make sure to login in with your HarvardKey to get full-text of the articles that Harvard has purchased.)
Many of the databases that Harvard offers have similar features to limit to peer-reviewed or scholarly articles. For example in Academic Search Premier , click on the box for Scholarly (Peer Reviewed) Journals on the search screen.
Review articles are another great way to find scholarly primary research articles. Review articles are not considered "primary research", but they pull together primary research articles on a topic, summarize and analyze them. In Google Scholar , click on Review Articles at the left of the search results screen. Ask your professor whether review articles can be cited for an assignment.
A note about Google searching. A regular Google search turns up a broad variety of results, which can include scholarly articles but Google results also contain commercial and popular sources which may be misleading, outdated, etc. Use Google Scholar through the Harvard Library instead.
About Wikipedia . W ikipedia is not considered scholarly, and should not be cited, but it frequently includes references to scholarly articles. Before using those references for an assignment, double check by finding them in Hollis or a more specific subject database .
Still not sure about a source? Consult the course syllabus for guidance, contact your professor or teaching fellow, or use the Ask A Librarian service.
- Last Updated: Oct 3, 2023 3:37 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.harvard.edu/FindingScholarlyArticles
Harvard University Digital Accessibility Policy

Finding Primary Research Articles in the Sciences: Advanced Search-Databases
- Advanced Search-Databases
- Primary vs. Secondary
- Analyzing a Primary Research Article
- MLA, APA, and Chicago Style
Most databases have an advanced search feature. Below is the typical advanced search screen for an Ebsco database. Other databases may look slightly different but should have the same features.
Below are the steps that will give you the best results for this class and assignment:
1. Check the box for Full Text (gives you only full articles, rather than just abstracts). 2. Check the box for Scholarly (Peer Reviewed) Journals. 3. Enter a date range in Published Date (enter the date requirements of this assignment). 4. The final step is to enter your search terms in the search boxes at the top.
Once you have a list of results, you can start examining them to see if they meet the requirements of your assignment and chosen topic. To view the full text, look for the PDF Full Text or HTML Full text icons.
Recommended Databases
To get started, choose one of the databases below. Once you log in, enter your search terms to start looking for primary articles.
- Link to all Polk State College Library databases
Advanced Search
Step 1: Type in your search terms. This example uses: Diet OR nutrition
Step 2: Select your limits. In this example: Full text, Research Article, Published Date, and Peer Reviewed
Step 3: Search

Have questions or not finding what you need? Use the Ask a Librarian to get assistance with searching.
Search Topic Ideas (example topic: nutrition)
Here are some additional terminology ideas to help narrow your search. Putting a phrase in quotations keeps the words together. But if you are not finding enough results, try removing the quotations or adding synonymous terms with OR.
"Mediterranean diet"
"dash diet" OR "dietary approaches to stop hypertension"
"gluten free diet"
vegan OR vegetarian OR plant-based
"Ready-to-Use Therapeutic Food"
malnutrition or undernutrition or undernourishment
"nutrition education"
"school lunches"
"fast food" or fast-food
"processed foods"
"health food" OR "healthy eating"
"personalized nutrition"
"micronutrient deficiencies"
Other places to search (example topic: nutrition)
Some peer reviewed journals are open access, which means anyone can access them for free.
Nutrients is a peer-reviewed and open access journal
There is a special issue on Eating Habits and Health among College and University Students
The Journal of Nutrition is not open access, but many of the articles are free or unlocked. This is also a peer reviewed journal. I can tell this by going to the About section on the journal's webpage.
Questions? Use Ask a Librarian
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Primary vs. Secondary >>
- Last Updated: Feb 19, 2024 11:55 AM
- URL: https://libguides.polk.edu/primaryresearch
Polk State College is committed to equal access/equal opportunity in its programs, activities, and employment. For additional information, visit polk.edu/compliance .
- Primary Sources
- Primary Source Repositories @ USC
- Large Primary Source Databases
- Newspapers & Magazines
- Topical Primary Source Collections
- Visual Primary Source Collections
- Multimedia Primary Source Collections
- Electronically available Rare Books & Rare Book Collections
- Electronically available Maps
- Electronically available Manuscripts
- Search Strategies
- Evaluating Primary Sources
- Research Award This link opens in a new window
- Documentaries
- Information for Faculty
- Teaching with Primary Sources
Frequently used large Primary Source Databases
Adam Matthew - Primary Sources for Teaching and Research Adam Matthew publishes unique primary source collections from archives around the world. USC has access to a vast amount of Ada Matthew's collections.
Gale Primary Sources - Archives Unbound Archives Unbound presents topically-focused digital collections of historical documents that support the research and study needs of scholars, researchers, and students at the college and university level. A multi-disciplinary resource, collections cover a broad range of topics from the Middle Ages forward-from Witchcraft to World War II to twentieth-century political history. Particular strengths include U.S. foreign policy; U.S. civil rights; global affairs and colonial studies; and modern history. Collections are chosen based on requests from scholars, archivists, and students.
Sabin Americana - History of the Americas 1500-1926
Artstor Artstor provides faculty and students with a complete image resource in a wide array of subjects with the breath and depth to add context and examine influences beyond the confines of your discipline.
All database descriptions provided here derived from the database providers themselves.
Large primary source collections covering a range of topics and time periods
These mega-sites are good places to start your search for primary sources
- Digital History Online An American history site developed to support the teaching of American History in K-12 schools and colleges and is supported by the College of Education at the University of Houston.
- Digital Public Library of America (DPLA) Digitized collections from libraries, archives, and museums including art, books, manuscripts, etc.
- Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History Dates covered: 1493-present more... less... A nonprofit organization supporting the study of American history through a wide range of programs and resources for students, teachers, scholars, and history enthusiasts throughout the nation. Topics covered include the Founding Era; Slavery and Abolition; Civil War Era; Abraham Lincoln; Westward Expansion; Immigration; Early 20th Century; Great Depression and World War II; and America 1945-present
- History Matters A gateway to online primary source collections. Click the link on the website to enter the database.
- << Previous: Digitized Primary Sources
- Next: Newspapers & Magazines >>
- Last Updated: Jan 11, 2024 2:25 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/primarysources
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- Primary Research | Definition, Types, & Examples
Primary Research | Definition, Types, & Examples
Published on January 14, 2023 by Tegan George . Revised on January 12, 2024.
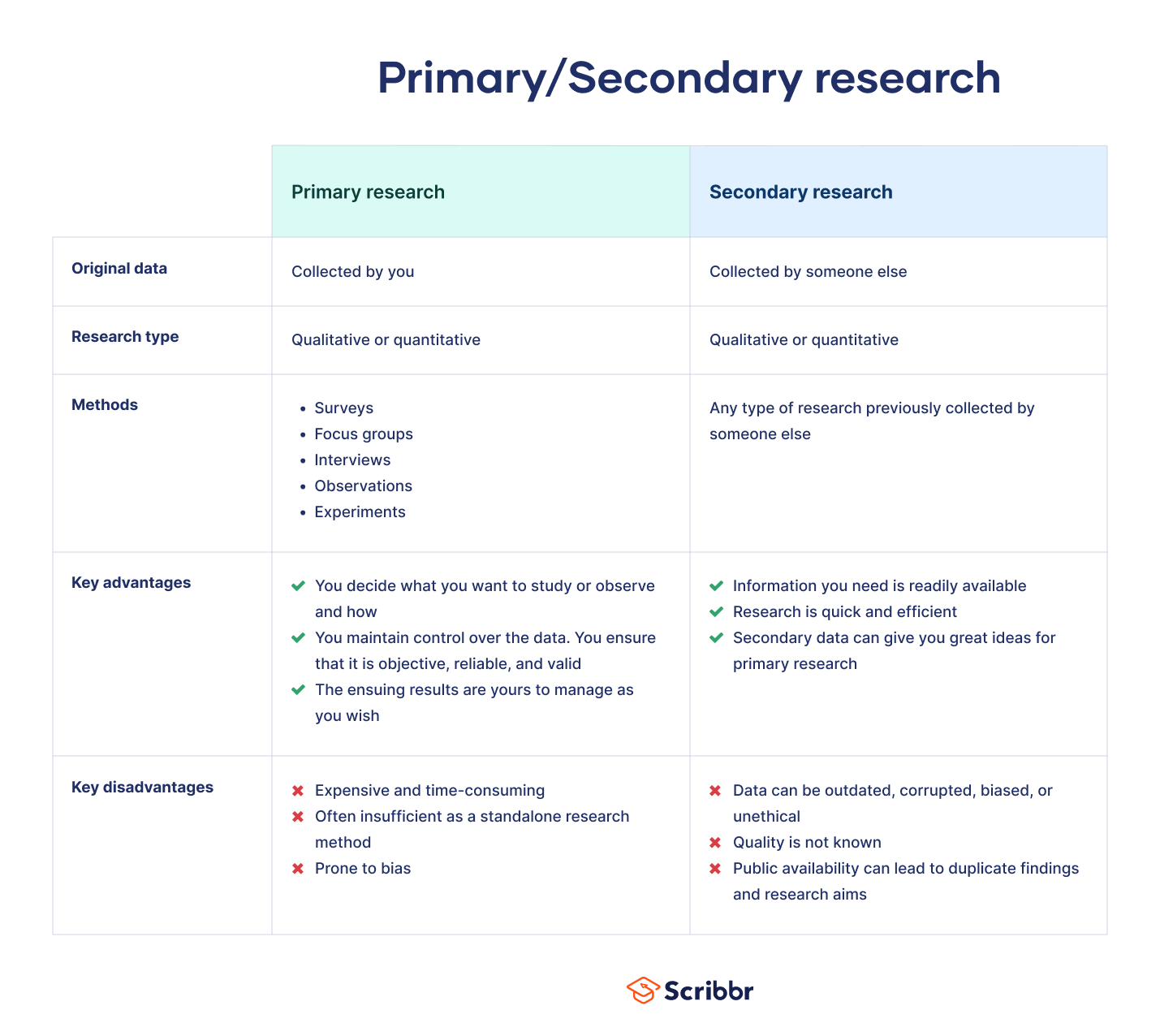
Primary research is a research method that relies on direct data collection , rather than relying on data that’s already been collected by someone else. In other words, primary research is any type of research that you undertake yourself, firsthand, while using data that has already been collected is called secondary research .
Primary research is often used in qualitative research , particularly in survey methodology, questionnaires, focus groups, and various types of interviews . While quantitative primary research does exist, it’s not as common.
Table of contents
When to use primary research, types of primary research, examples of primary research, advantages and disadvantages of primary research, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions.
Primary research is any research that you conduct yourself. It can be as simple as a 2-question survey, or as in-depth as a years-long longitudinal study . The only key is that data must be collected firsthand by you.
Primary research is often used to supplement or strengthen existing secondary research. It is usually exploratory in nature, concerned with examining a research question where no preexisting knowledge exists. It is also sometimes called original research for this reason.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Primary research can take many forms, but the most common types are:
- Surveys and questionnaires
- Observational studies
- Interviews and focus groups
Surveys and questionnaires collect information about a group of people by asking them questions and analyzing the results. They are a solid choice if your research topic seeks to investigate something about the characteristics, preferences, opinions, or beliefs of a group of people.
Surveys and questionnaires can take place online, in person, or through the mail. It is best to have a combination of open-ended and closed-ended questions, and how the questions are phrased matters. Be sure to avoid leading questions, and ask any related questions in groups, starting with the most basic ones first.
Observational studies are an easy and popular way to answer a research question based purely on what you, the researcher, observes. If there are practical or ethical concerns that prevent you from conducting a traditional experiment , observational studies are often a good stopgap.
There are three types of observational studies: cross-sectional studies , cohort studies, and case-control studies. If you decide to conduct observational research, you can choose the one that’s best for you. All three are quite straightforward and easy to design—just beware of confounding variables and observer bias creeping into your analysis.
Similarly to surveys and questionnaires, interviews and focus groups also rely on asking questions to collect information about a group of people. However, how this is done is slightly different. Instead of sending your questions out into the world, interviews and focus groups involve two or more people—one of whom is you, the interviewer, who asks the questions.
There are 3 main types of interviews:
- Structured interviews ask predetermined questions in a predetermined order.
- Unstructured interviews are more flexible and free-flowing, proceeding based on the interviewee’s previous answers.
- Semi-structured interviews fall in between, asking a mix of predetermined questions and off-the-cuff questions.
While interviews are a rich source of information, they can also be deceptively challenging to do well. Be careful of interviewer bias creeping into your process. This is best mitigated by avoiding double-barreled questions and paying close attention to your tone and delivery while asking questions.
Alternatively, a focus group is a group interview, led by a moderator. Focus groups can provide more nuanced interactions than individual interviews, but their small sample size means that external validity is low.
Primary research can often be quite simple to pursue yourself. Here are a few examples of different research methods you can use to explore different topics.
Primary research is a great choice for many research projects, but it has distinct advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages of primary research
Advantages include:
- The ability to conduct really tailored, thorough research, down to the “nitty-gritty” of your topic . You decide what you want to study or observe and how to go about doing that.
- You maintain control over the quality of the data collected, and can ensure firsthand that it is objective, reliable , and valid .
- The ensuing results are yours, for you to disseminate as you see fit. You maintain proprietary control over what you find out, allowing you to share your findings with like-minded individuals or those conducting related research that interests you for replication or discussion purposes.
Disadvantages of primary research
Disadvantages include:
- In order to be done well, primary research can be very expensive and time consuming. If you are constrained in terms of time or funding, it can be very difficult to conduct your own high-quality primary research.
- Primary research is often insufficient as a standalone research method, requiring secondary research to bolster it.
- Primary research can be prone to various types of research bias . Bias can manifest on the part of the researcher as observer bias , Pygmalion effect , or demand characteristics . It can occur on the part of participants as a Hawthorne effect or social desirability bias .
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Chi square goodness of fit test
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
The 3 main types of primary research are:
Exploratory research aims to explore the main aspects of an under-researched problem, while explanatory research aims to explain the causes and consequences of a well-defined problem.
There are several methods you can use to decrease the impact of confounding variables on your research: restriction, matching, statistical control and randomization.
In restriction , you restrict your sample by only including certain subjects that have the same values of potential confounding variables.
In matching , you match each of the subjects in your treatment group with a counterpart in the comparison group. The matched subjects have the same values on any potential confounding variables, and only differ in the independent variable .
In statistical control , you include potential confounders as variables in your regression .
In randomization , you randomly assign the treatment (or independent variable) in your study to a sufficiently large number of subjects, which allows you to control for all potential confounding variables.
A questionnaire is a data collection tool or instrument, while a survey is an overarching research method that involves collecting and analyzing data from people using questionnaires.
When conducting research, collecting original data has significant advantages:
- You can tailor data collection to your specific research aims (e.g. understanding the needs of your consumers or user testing your website)
- You can control and standardize the process for high reliability and validity (e.g. choosing appropriate measurements and sampling methods )
However, there are also some drawbacks: data collection can be time-consuming, labor-intensive and expensive. In some cases, it’s more efficient to use secondary data that has already been collected by someone else, but the data might be less reliable.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2024, January 12). Primary Research | Definition, Types, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/primary-research/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, data collection | definition, methods & examples, observer bias | definition, examples, prevention, what is qualitative research | methods & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Main Navigation Menu
Peer-review and primary research.
- Getting Started With Peer-Reviewed Literature
Primary Research
Identifying a primary research article.
- Finding Peer-Reviewed Journal Articles
- Finding Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs)
- Evaluating Scholarly Articles
- Google Scholar
- Tips for Reading Journal Articles
STEM Librarian

Primary research or a primary study refers to a research article that is an author’s original research that is almost always published in a peer-reviewed journal. A primary study reports on the details, methods and results of a research study. These articles often have a standard structure of a format called IMRAD, referring to sections of an article: Introduction, Methods, Results and Discussion. Primary research studies will start with a review of the previous literature, however, the rest of the article will focus on the authors’ original research. Literature reviews can be published in peer-reviewed journals, however, they are not primary research.
Primary studies are part of primary sources but should not be mistaken for primary documents. Primary documents are usually original sources such as a letter, a diary, a speech or an autobiography. They are a first person view of an event or a period. Typically, if you are a Humanities major, you will be asked to find primary documents for your paper however, if you are in Social Sciences or the Sciences you are most likely going to be asked to find primary research studies. If you are unsure, ask your professor or a librarian for help.
A primary research or study is an empirical research that is published in peer-reviewed journals. Some ways of recognizing whether an article is a primary research article when searching a database:
1. The abstract includes a research question or a hypothesis, methods and results.

2. Studies can have tables and charts representing data findings.

3. The article includes a section for "methods” or “methodology” and "results".

4. Discussion section indicates findings and discusses limitations of the research study, and suggests further research.

5. Check the reference section because it will refer you to the studies and works that were consulted. You can use this section to find other studies on that particular topic.

The following are not to be confused with primary research articles:
- Literature reviews
- Meta-analyses or systematic reviews (these studies make conclusions based on research on many other studies)
- << Previous: Getting Started With Peer-Reviewed Literature
- Next: Finding Peer-Reviewed Journal Articles >>
- Last Updated: Feb 15, 2024 2:45 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.ucmo.edu/peerreview
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Anaesth
- v.60(9); 2016 Sep
Literature search for research planning and identification of research problem
Anju grewal.
Department of Anaesthesiology, Dayanand Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India
Hanish Kataria
1 Department of Surgery, Government Medical College and Hospital, Chandigarh, India
2 Department of Cardiac Anaesthesia, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India
Literature search is a key step in performing good authentic research. It helps in formulating a research question and planning the study. The available published data are enormous; therefore, choosing the appropriate articles relevant to your study in question is an art. It can be time-consuming, tiring and can lead to disinterest or even abandonment of search in between if not carried out in a step-wise manner. Various databases are available for performing literature search. This article primarily stresses on how to formulate a research question, the various types and sources for literature search, which will help make your search specific and time-saving.
INTRODUCTION
Literature search is a systematic and well-organised search from the already published data to identify a breadth of good quality references on a specific topic.[ 1 ] The reasons for conducting literature search are numerous that include drawing information for making evidence-based guidelines, a step in the research method and as part of academic assessment.[ 2 ] However, the main purpose of a thorough literature search is to formulate a research question by evaluating the available literature with an eye on gaps still amenable to further research.
Research problem[ 3 ] is typically a topic of interest and of some familiarity to the researcher. It needs to be channelised by focussing on information yet to be explored. Once we have narrowed down the problem, seeking and analysing existing literature may further straighten out the research approach.
A research hypothesis[ 4 ] is a carefully created testimony of how you expect the research to proceed. It is one of the most important tools which aids to answer the research question. It should be apt containing necessary components, and raise a question that can be tested and investigated.
The literature search can be exhaustive and time-consuming, but there are some simple steps which can help you plan and manage the process. The most important are formulating the research questions and planning your search.
FORMULATING THE RESEARCH QUESTION
Literature search is done to identify appropriate methodology, design of the study; population sampled and sampling methods, methods of measuring concepts and techniques of analysis. It also helps in determining extraneous variables affecting the outcome and identifying faults or lacunae that could be avoided.
Formulating a well-focused question is a critical step for facilitating good clinical research.[ 5 ] There can be general questions or patient-oriented questions that arise from clinical issues. Patient-oriented questions can involve the effect of therapy or disease or examine advantage versus disadvantage for a group of patients.[ 6 ]
For example, we want to evaluate the effect of a particular drug (e.g., dexmedetomidine) for procedural sedation in day care surgery patients. While formulating a research question, one should consider certain criteria, referred as ‘FINER’ (F-Feasible, I-Interesting, N-Novel, E-Ethical, R-Relevant) criteria.[ 5 ] The idea should be interesting and relevant to clinical research. It should either confirm, refute or add information to already done research work. One should also keep in mind the patient population under study and the resources available in a given set up. Also the entire research process should conform to the ethical principles of research.
The patient or study population, intervention, comparison or control arm, primary outcome, timing of measurement of outcome (PICOT) is a well-known approach for framing a leading research question.[ 7 , 8 ] Dividing the questions into key components makes it easy and searchable. In this case scenario:
- Patients (P) – What is the important group of patients? for example, day care surgery
- Intervention (I) – What is the important intervention? for example, intravenous dexmedetomidine
- Comparison (C) – What is the important intervention of comparison? for example, intravenous ketamine
- Outcome (O) – What is the effect of intervention? for example, analgesic efficacy, procedural awareness, drug side effects
- Time (T) – Time interval for measuring the outcome: Hourly for first 4 h then 4 hourly till 24 h post-procedure.
Multiple questions can be formulated from patient's problem and concern. A well-focused question should be chosen for research according to significance for patient interest and relevance to our knowledge. Good research questions address the lacunae in available literature with an aim to impact the clinical practice in a constructive manner. There are limited outcome research and relevant resources, for example, electronic database system, database and hospital information system in India. Even when these factors are available, data about existing resources is not widely accessible.[ 9 ]
TYPES OF MEDICAL LITERATURE
(Further details in chapter ‘Types of studies and research design’ in this issue).
Primary literature
Primary sources are the authentic publication of an expert's new evidence, conclusions and proposals (case reports, clinical trials, etc) and are usually published in a peer-reviewed journal. Preliminary reports, congress papers and preprints also constitute primary literature.[ 2 ]
Secondary literature
Secondary sources are systematic review articles or meta-analyses where material derived from primary source literature are infererred and evaluated.[ 2 ]
Tertiary literature
Tertiary literature consists of collections that compile information from primary or secondary literature (eg., reference books).[ 2 ]

METHODS OF LITERATURE SEARCH
There are various methods of literature search that are used alone or in combination [ Table 1 ]. For past few decades, searching the local as well as national library for books, journals, etc., was the usual practice and still physical literature exploration is an important component of any systematic review search process.[ 10 , 11 ] With the advancement of technology, the Internet is now the gateway to the maze of vast medical literature.[ 12 ] Conducting a literature review involves web-based search engines, i.e., Google, Google Scholar, etc., [ Table 2 ], or using various electronic research databases to identify materials that describe the research topic or those homologous to it.[ 13 , 14 ]
Methods of literature search

Web based methods of literature search

The various databases available for literature search include databases for original published articles in the journals [ Table 2 ] and evidence-based databases for integrated information available as systematic reviews and abstracts [ Table 3 ].[ 12 , 14 ] Most of these are not freely available to the individual user. PubMed ( http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/ ) is the largest available resource since 1996; however, a large number of sources now provide free access to literature in the biomedical field.[ 15 ] More than 26 million citations from Medline, life science journals and online books are included in PubMed. Links to the full-text material are included in citations from PubMed Central and publisher web sites.[ 16 ] The choice of databases depends on the subject of interest and potential coverage by the different databases. Education Resources Information Centre is a free online digital library of education research and information sponsored by the Institute of Education Sciences of the U.S. Department of Education, available at http://eric.ed.gov/ . No one database can search all the medical literature. There is need to search several different databases. At a minimum, PubMed or Medline, Embase and the Cochrane central trials Registry need to be searched. When searching these databases, emphasis should be given to meta-analysis, systematic reviews randomised controlled trials and landmark studies.
Electronic source of Evidence-Based Database

Time allocated to the search needs attention as exploring and selecting data are early steps in the research method and research conducted as part of academic assessment have narrow timeframes.[ 17 ] In Indian scenario, limited outcome research and accessibility to data leads to less thorough knowledge of nature of research problem. This results in the formulation of the inappropriate research question and increases the time to literature search.
TYPES OF SEARCH
Type of search can be described in different forms according to the subject of interest. It increases the chances of retrieving relevant information from a search.
Translating research question to keywords
This will provide results based on any of the words specified; hence, they are the cornerstone of an effective search. Synonyms/alternate terms should be considered to elicit further information, i.e., barbiturates in place of thiopentone. Spellings should also be taken into account, i.e., anesthesia in place of anaesthesia (American and British). Most databases use controlled word-stock to establish common search terms (or keywords). Some of these alternative keywords can be looked from database thesaurus.[ 4 ] Another strategy is combining keywords with Boolean operators. It is important to keep a note of keywords and methods used in exploring the literature as these will need to be described later in the design of search process.
‘Medical Subject Heading (MeSH) is the National Library of Medicine's controlled hierarchical vocabulary that is used for indexing articles in PubMed, with more specific terms organised underneath more general terms’.[ 17 ] This provides a reliable way to retrieve citations that use different terminology for identical ideas, as it indexes articles based on content. Two features of PubMed that can increase yield of specific articles are ‘Automatic term mapping’ and ‘automatic term explosion’.[ 4 ]
For example, if the search keyword is heart attack, this term will match with MeSH transcription table heading and then explode into various subheadings. This helps to construct the search by adding and selecting MeSH subheadings and families of MeSH by use of hyperlinks.[ 4 ]
We can set limits to a clinical trial for retrieving higher level of evidence (i.e., randomised controlled clinical trial). Furthermore, one can browse through the link entitled ‘Related Articles’. This PubMed feature searches for similar citations using an intricate algorithm that scans titles, abstracts and MeSH terms.[ 4 ]
Phrase search
This will provide pages with only the words typed in the phrase, in that exact order and with no words in between them.
Boolean operators
AND, OR and NOT are the three Boolean operators named after the mathematician George Boole.[ 18 ] Combining two words using ‘AND’ will fetch articles that mention both the words. Using ‘OR’ will widen the search and fetch more articles that mention either subject. While using the term ‘NOT’ to combine words will fetch articles containing the first word but not the second, thus narrowing the search.
Filters can also be used to refine the search, for example, article types, text availability, language, age, sex and journal categories.
Overall, the recommendations for methodology of literature search can be as below (Creswell)[ 19 ]
- Identify keywords and use them to search articles from library and internet resources as described above
- Search several databases to search articles related to your topic
- Use thesaurus to identify terms to locate your articles
- Find an article that is similar to your topic; then look at the terms used to describe it, and use them for your search
- Use databases that provide full-text articles (free through academic libraries, Internet or for a fee) as much as possible so that you can save time searching for your articles
- If you are examining a topic for the first time and unaware of the research on it, start with broad syntheses of the literature, such as overviews, summaries of the literature on your topic or review articles
- Start with the most recent issues of the journals, and look for studies about your topic and then work backward in time. Follow-up on references at the end of the articles for more sources to examine
- Refer books on a single topic by a single author or group of authors or books that contain chapters written by different authors
- Next look for recent conference papers. Often, conference papers report the latest research developments. Contact authors of pertinent studies. Write or phone them, asking if they know of studies related to your area of interest
- The easy access and ability to capture entire articles from the web make it attractive. However, check these articles carefully for authenticity and quality and be cautious about whether they represent systematic research.
The whole process of literature search[ 20 ] is summarised in Figure 1 .

Process of literature search
Literature search provides not only an opportunity to learn more about a given topic but provides insight on how the topic was studied by previous analysts. It helps to interpret ideas, detect shortcomings and recognise opportunities. In short, systematic and well-organised research may help in designing a novel research.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.
- Books, eBooks & Articles
- Databases A-Z
- Primary Sources
- E-Audiobooks
- Videos & Images
- Online Videos
- Images & Artwork
- More resources
- Research Guides
- Library Instruction
- Request Research Guide
- Interlibrary Loan
- Books on Reserve
- Research Assistance
- Writing Lab
- Online Tutoring
- Group Study Sessions
- Turabian/Chicago
- Other Citing Styles
Service Alert

Finding Primary Articles in PubMed: Home
- APA Citations
Finding Primary Articles in PubMed
From the library homepage -- library.surry.edu (opens in new window) -- click on Find Articles .

Click on the letter P or scroll through the list until you see PubMed . To limit to full text articles, click on the PubMed Central link in the PubMed description.

Type in a search for your topic. Press Enter or click the Search button.

You will retrieve a list of articles. To limit to primary research articles, click on Clinical Trial or click More to select other type of trials and original research studies.

You may also limit your article results to Free full text either on the left or you can scan below the article results for Free Article or Free PMC Article .

If the article is available for free, you will see a link to access the article in the upper right of the screen. If you can't find the article text, email Alan Unsworth, Research Librarian , to see if the article may be obtained .

- Next: APA Citations >>
- Last Updated: Nov 9, 2023 2:07 PM
- URL: https://library.surry.edu/pubmed
Identifying Primary and Secondary Research Articles
- Primary and Secondary

Primary Research Articles
Primary research articles report on a single study. In the health sciences, primary research articles generally describe the following aspects of the study:
- The study's hypothesis or research question
- Some articles will include information on how participants were recruited or identified, as well as additional information about participants' sex, age, or race/ethnicity
- A "methods" or "methodology" section that describes how the study was performed and what the researchers did
- Results and conclusion section
Secondary Research Articles
Review articles are the most common type of secondary research article in the health sciences. A review article is a summary of previously published research on a topic. Authors who are writing a review article will search databases for previously completed research and summarize or synthesize those articles, as opposed to recruiting participants and performing a new research study.
Specific types of review articles include:
- Systematic Reviews
- Meta-Analysis
- Narrative Reviews
- Integrative Reviews
- Literature Reviews
Review articles often report on the following:
- The hypothesis, research question, or review topic
- Databases searched-- authors should clearly describe where and how they searched for the research included in their reviews
- Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis should provide detailed information on the databases searched and the search strategy the authors used.Selection criteria-- the researchers should describe how they decided which articles to include
- A critical appraisal or evaluation of the quality of the articles included (most frequently included in systematic reviews and meta-analysis)
- Discussion, results, and conclusions
Determining Primary versus Secondary Using the Database Abstract
Information found in PubMed, CINAHL, Scopus, and other databases can help you determine whether the article you're looking at is primary or secondary.
Primary research article abstract
- Note that in the "Objectives" field, the authors describe their single, individual study.
- In the materials and methods section, they describe the number of patients included in the study and how those patients were divided into groups.
- These are all clues that help us determine this abstract is describing is a single, primary research article, as opposed to a literature review.
- Primary Article Abstract

Secondary research/review article abstract
- Note that the words "systematic review" and "meta-analysis" appear in the title of the article
- The objectives field also includes the term "meta-analysis" (a common type of literature review in the health sciences)
- The "Data Source" section includes a list of databases searched
- The "Study Selection" section describes the selection criteria
- These are all clues that help us determine that this abstract is describing a review article, as opposed to a single, primary research article.
- Secondary Research Article

- Primary vs. Secondary Worksheet
Full Text Challenge
Can you determine if the following articles are primary or secondary?
- Last Updated: Feb 17, 2024 5:25 PM
- URL: https://library.usfca.edu/primary-secondary
2130 Fulton Street San Francisco, CA 94117-1080 415-422-5555
- Facebook (link is external)
- Instagram (link is external)
- Twitter (link is external)
- YouTube (link is external)
- Consumer Information
- Privacy Statement
- Web Accessibility
Copyright © 2022 University of San Francisco
NUR 3165 - Nursing Research
- Nursing Databases
- Research Article Basics
- - Practice 1
Finding Primary Research Articles - Overview
- - Practice 2
- Quantitative/Qualitative/Mixed Methods
- - Practice 3
- How to Find Full Text Articles
- Terminology
There are several ways to locate primary research articles as you will see in the following practice exercises (see next page). Here are some tips to consider while looking for original research studies:
Tip #1 - Incorporate subject headings into your search
Subject headings are terms that are part of a controlled vocabulary used to describe the contents tagged inside the article record. These terms can be found in each of the CINAHL Detailed Records under Major Subjects and Minor Subjects. So, if you see the ultimate article, look to see what terms it is tagged with and add them to the search in the appropriate line if relevant. For example,(MH "Emergency Service") is the medical subject heading used for Emergency Department!
To search for possible subject headings, try putting a keyword in a new search and check the Suggest Subject Terms box. The asterisk covers any number of characters (i.e., nurs* yields nurse, nurses, and nurses at the same time). Quotation marks around two or more terms searches them as a phrase.

Try it out! Place the term Hospital Acquired Infection in CINAHL, check the Suggest Subject Terms box and click search to see the subject heading for this term!

Tip #2 - Check the research article box
Databases like CINAHL allow you to select Research Article to retrieve research articles in your search.
Tip #3 - Sections of the Research Article to look for
When reading an article, make sure to look inside the abstract (and the full text) and scan for sections contained in many primary research studies such as Introduction, Participants, Methods, Results and Discussion! Look at those sections to see if the researchers are working directly with the participants and conducting original research.
See the next section for additional tips!
- << Previous: - Practice 1
- Next: - Practice 2 >>
- Last Updated: Mar 11, 2024 4:30 PM
- URL: https://guides.ucf.edu/NUR3165a
Educator Resources

Finding Primary Sources for Teachers and Students
Finding primary sources.
Primary Sources from DocsTeach Thousands of online primary source documents from the National Archives to bring the past to life as classroom teaching tools.
National Archives Catalog Find online primary source materials for classroom & student projects from the National Archive's online catalog (OPA).
Beginning Research Activities Student activities designed to help you navigate the National Archives resources and web site.
Online Exhibits Exhibits featuring online documents, photos and primary sources from the National Archives
Our Documents 100 Milestone Documents of American History
Getting Started with Research How to start researching records at the National Archives. Finding your topic, identifying records, planning a visit, and more.
Online Research Tools & Aids Introduction to catalogs, databases, and other online resources.
Citing Primary Sources Citing Records in the National Archives of the United States
Articles & Databases
Explore our collection of hundreds of online resources and databases. Use our free online content to help with your research, whether it's finding a single article, tracing a family tree, learning a new language, or anything in between.
Featured Resources
.css-1t84354{transition-property:var(--nypl-transition-property-common);transition-duration:var(--nypl-transition-duration-fast);transition-timing-function:var(--nypl-transition-easing-ease-out);cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;outline:2px solid transparent;outline-offset:2px;color:var(--nypl-colors-ui-link-primary);text-decoration-style:dotted;text-decoration-thickness:1px;text-underline-offset:2px;}.css-1t84354:hover,.css-1t84354[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:var(--nypl-colors-ui-link-secondary);text-decoration-style:dotted;text-decoration-thickness:1px;}.chakra-ui-dark .css-1t84354:hover:not([data-theme]),.chakra-ui-dark .css-1t84354[data-hover]:not([data-theme]),[data-theme=dark] .css-1t84354:hover:not([data-theme]),[data-theme=dark] .css-1t84354[data-hover]:not([data-theme]),.css-1t84354:hover[data-theme=dark],.css-1t84354[data-hover][data-theme=dark]{color:var(--nypl-colors-dark-ui-link-secondary);}.css-1t84354:focus,.css-1t84354[data-focus]{box-shadow:var(--nypl-shadows-outline);}.chakra-ui-dark .css-1t84354:not([data-theme]),[data-theme=dark] .css-1t84354:not([data-theme]),.css-1t84354[data-theme=dark]{color:var(--nypl-colors-dark-ui-link-primary);}.css-1t84354:visited{color:var(--nypl-colors-ui-link-tertiary);}.chakra-ui-dark .css-1t84354:visited:not([data-theme]),[data-theme=dark] .css-1t84354:visited:not([data-theme]),.css-1t84354:visited[data-theme=dark]{color:var(--nypl-colors-dark-ui-link-tertiary);}.css-1t84354 a:hover,.css-1t84354 a[data-hover]{color:var(--nypl-colors-ui-link-secondary);}.css-1t84354 screenreaderOnly{clip:rect(1px, 1px, 1px, 1px);height:1px;overflow:hidden;position:absolute!important;width:1px;word-wrap:normal;} Start Your Research
Not sure where to begin? From primary sources to scholarly articles, start your research with resources chosen by our expert librarians.
Homework Help
Discover the wide range of learning resources the Library has to offer students of all ages, from chemistry and history to English and math.
Newspapers and Magazines
Browse popular contemporary and historic publications including The New York Times , People magazine, and Sports Illustrated among others.
World Languages
Read e-books, newspapers, and more in languages including Spanish, Chinese, Russian, and French.
African American Studies
Explore a variety of academic, historic, and cultural resources curated by the Schomburg Center for Research in Black Culture.
Performing Arts
Find materials about theatre, film, dance, music, and recorded sound selected by The New York Public Library for the Performing Arts.
New York City History
Uncover primary and secondary sources about the five boroughs, including neighborhood data, historic photos, newspaper archives, and more.
Trace ancestry information and family trees through public records, historical documents, and other genealogical archives.
Job Search and Career Development
Whether you’re looking for a new job or changing careers, these resources will help you find training tutorials, resume guides, and more.
Most Popular
.css-1t84354{transition-property:var(--nypl-transition-property-common);transition-duration:var(--nypl-transition-duration-fast);transition-timing-function:var(--nypl-transition-easing-ease-out);cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;outline:2px solid transparent;outline-offset:2px;color:var(--nypl-colors-ui-link-primary);text-decoration-style:dotted;text-decoration-thickness:1px;text-underline-offset:2px;}.css-1t84354:hover,.css-1t84354[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:var(--nypl-colors-ui-link-secondary);text-decoration-style:dotted;text-decoration-thickness:1px;}.chakra-ui-dark .css-1t84354:hover:not([data-theme]),.chakra-ui-dark .css-1t84354[data-hover]:not([data-theme]),[data-theme=dark] .css-1t84354:hover:not([data-theme]),[data-theme=dark] .css-1t84354[data-hover]:not([data-theme]),.css-1t84354:hover[data-theme=dark],.css-1t84354[data-hover][data-theme=dark]{color:var(--nypl-colors-dark-ui-link-secondary);}.css-1t84354:focus,.css-1t84354[data-focus]{box-shadow:var(--nypl-shadows-outline);}.chakra-ui-dark .css-1t84354:not([data-theme]),[data-theme=dark] .css-1t84354:not([data-theme]),.css-1t84354[data-theme=dark]{color:var(--nypl-colors-dark-ui-link-primary);}.css-1t84354:visited{color:var(--nypl-colors-ui-link-tertiary);}.chakra-ui-dark .css-1t84354:visited:not([data-theme]),[data-theme=dark] .css-1t84354:visited:not([data-theme]),.css-1t84354:visited[data-theme=dark]{color:var(--nypl-colors-dark-ui-link-tertiary);}.css-1t84354 a:hover,.css-1t84354 a[data-hover]{color:var(--nypl-colors-ui-link-secondary);}.css-1t84354 screenreaderonly{clip:rect(1px, 1px, 1px, 1px);height:1px;overflow:hidden;position:absoluteimportant;width:1px;word-wrap:normal;} novelny resources.
NOVELny Resources are available to all New Yorkers without a password as long as one is in New York State, via a NY driver or non-driver ID if not currently in New York State and/or via a Library Card.
A searchable, digitized archive -- from the first date of publication to the last three to five years -- of major scholarly journals in many academic fields.
Access to this resource has been temporarily expanded to NYPL cardholders working from home, courtesy of JSTOR.
Ancestry Library Edition
Access billions of names in thousands of genealogical databases including Census and Vital Records, birth, marriage and death notices, the Social Security Death Index, Passenger lists and naturalizations, Military and Holocaust Records, City Directories, New York Emigrant Savings Bank records, and African American and Native American Records. Library version of Ancestry.com.
***PLEASE NOTE THAT TEMPORARY REMOTE ACCESS TO THIS DATABASE HAS BEEN TERMINATED.***
Biotechnology
- Library vs. Google
- Background Reading
- Keyword Searching
- Evaluating Sources
Primary Research Articles
- Citing Sources
- Need more help?
How Can I Find Primary Research Articles?
Many of the recommended databases in this subject guide contain primary research articles (also known as empirical articles or research studies). Search in databases like ScienceDirect , MEDLINE , and Health Source: Nursing/Academic Edition .
Primary Research Articles: How Will I Know One When I See One?
Primary Research Articles To conduct and publish an experiment or research study, an author or team of authors designs an experiment, gathers data, then analyzes the data and discusses the results of the experiment. A published experiment or research study will therefore look very different from other types of articles (newspaper stories, magazine articles, essays, etc.) found in our library databases. The following guidelines will help you recognize a primary research article, written by the researchers themselves and published in a scholarly journal.
Structure of a Primary Research Article Typically, a primary research article has the following sections:
- The author summarizes her article
- The author discusses the general background of her research topic; often, she will present a literature review, that is, summarize what other experts have written on this particular research topic
- The author describes the study she designed and conducted
- The author presents the data she gathered during her experiment
- The author offers ideas about the importance and implications of her research findings, and speculates on future directions that similar research might take
- The author gives a References list of sources she used in her paper
The structure of the article will often be clearly shown with headings: Introduction, Method, Results, Discussion.
A primary research article will almost always contains statistics, numerical data presented in tables. Also, primary research articles are written in very formal, very technical language.
- << Previous: Evaluating Sources
- Next: Citing Sources >>
- Last Updated: Nov 21, 2023 1:35 PM
- URL: https://libguides.umgc.edu/biotechnology
ENGL 103 King: Find articles
- Assignment review
- Topic to Keywords
- Find articles
- Citing sources
- Research & Writing Help
In the research process: ARTICLES
Searching library databases.
Dolphin and Anchor Symbol Aldus Manutius Beta Phi Mu Information Literacy Librarian
General Databases:
Academic Search Ultimate offers access to an unprecedented collection of resources including journals, magazines, reports, books, and videos. Many are peer-reviewed and full-text. Subjects range from astronomy to zoology.
- MasterFILE Premier This link opens in a new window Provides abstracts and indexing for 2,650 general periodicals. Full text of articles for nearly 2,000 periodicals, and 5,000 full text Magill Book Reviews.
Library databases
Library d atabases: A-Z list and by subject
Differences between popular magazines and scholarly journals
- Popular Magazines Vs. Scholarly Journals
- << Previous: Find books
- Next: Citing sources >>
- Last Updated: Apr 8, 2024 10:35 AM
- URL: https://libraryguides.salisbury.edu/King103

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Harness the power of visual materials—explore more than 3 million images now on JSTOR. Enhance your scholarly research with underground newspapers, magazines, and journals. Explore collections in the arts, sciences, and literature from the world's leading museums, archives, and scholars. JSTOR is a digital library of academic journals ...
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions.
What is Database Search? Harvard Library licenses hundreds of online databases, giving you access to academic and news articles, books, journals, primary sources, streaming media, and much more. The contents of these databases are only partially included in HOLLIS. To make sure you're really seeing everything, you need to search in multiple places.
Databases for finding Articles with Primary Research; Reading an Article Citation. Taucar, Christopher Edward. "Standards of judicial review of administrative bodies: The consideration of citizen participation." ... Below is a selection of frequently used library subscription databases for finding primary research in peer-reviewed journals.
Moved Permanently. The document has moved here.
Advanced. Journal List. PubMed Central ® (PMC) is a free full-text archive of biomedical and life sciences journal literature at the U.S. National Institutes of Health's National Library of Medicine (NIH/NLM)
A published experiment or research study will therefore look very different from other types of articles (newspaper stories, magazine articles, essays, etc.) found in our library databases. The following guidelines will help you recognize a primary research article, written by the researchers themselves and published in a scholarly journal ...
Many of the databases that Harvard offers have similar features to limit to peer-reviewed or scholarly articles. For example in Academic Search Premier, click on the box for Scholarly (Peer Reviewed) Journals on the search screen. Review articles are another great way to find scholarly primary research articles. Review articles are not ...
You can use the library's databases to search for primary research articles. A research article will almost always be published in a peer-reviewed journal. Therefore, it is a good idea to limit your results to peer-reviewed articles. Click on the Advanced Search-Databases tab at the top of this guide for instructions.
Academic Search Complete (EBSCO) This link opens in a new window Academic Search Complete, designed specifically for academic institutions, is the world's most valuable and comprehensive scholarly, multi-disciplinary full-text database, with more than 5,300 full-text periodicals, including 4,400 peer-reviewed journals. In addition to full text, this database offers indexing and abstracts for ...
Provides access to over nearly 5,000 primary documents, as well as 185,000+ reference articles, over 613,000 periodical articles, and more than 73,000 images. This database covers themes, events, individuals and periods in U.S. history from pre-Colonial times to the present.
Primary research is any research that you conduct yourself. It can be as simple as a 2-question survey, or as in-depth as a years-long longitudinal study. The only key is that data must be collected firsthand by you. Primary research is often used to supplement or strengthen existing secondary research.
Search all biomedical databases provided by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), an agency of the U.S. National Library of Medicine at the NIH ... While these interactions have been well studied, a research team supported in part by NIH has made an unexpected discovery into how a key immune checkpoint works, with ...
A primary research or study is an empirical research that is published in peer-reviewed journals. Some ways of recognizing whether an article is a primary research article when searching a database: 1. The abstract includes a research question or a hypothesis, methods and results. 2. Studies can have tables and charts representing data findings. 3.
Abstract. Literature search is a key step in performing good authentic research. It helps in formulating a research question and planning the study. The available published data are enormous; therefore, choosing the appropriate articles relevant to your study in question is an art. It can be time-consuming, tiring and can lead to disinterest or ...
To limit to full text articles, click on the PubMed Central link in the PubMed description. Type in a search for your topic. Press Enter or click the Search button. You will retrieve a list of articles. To limit to primary research articles, click on Clinical Trial or click More to select other type of trials and original research studies.
A published experiment or research study will therefore look very different from other types of articles (newspaper stories, magazine articles, essays, etc.) found in our library databases. The following guidelines will help you recognize a primary research article, written by the researchers themselves and published in a scholarly journal ...
Determining Primary versus Secondary Using the Database Abstract. Information found in PubMed, CINAHL, Scopus, and other databases can help you determine whether the article you're looking at is primary or secondary. Primary research article abstract. Note that in the "Objectives" field, the authors describe their single, individual study.
Databases like CINAHL allow you to select Research Article to retrieve research articles in your search. Tip #3 - Sections of the Research Article to look for When reading an article, make sure to look inside the abstract (and the full text) and scan for sections contained in many primary research studies such as Introduction, Participants ...
Getting Started with Research How to start researching records at the National Archives. Finding your topic, identifying records, planning a visit, and more. Online Research Tools & AidsIntroduction to catalogs, databases, and other online resources. Citing Primary Sources Citing Records in the National Archives of the United States
Explore our collection of hundreds of online resources and databases. Use our free online content to help with your research, whether it's finding a single article, tracing a family tree, learning a new language, or anything in between. ... From primary sources to scholarly articles, start your research with resources chosen by our expert ...
A published experiment or research study will therefore look very different from other types of articles (newspaper stories, magazine articles, essays, etc.) found in our library databases. The following guidelines will help you recognize a primary research article, written by the researchers themselves and published in a scholarly journal ...
In the research process: ARTICLES. 1. Explore topic context & primary sources (the open web) 2. Learn the background (library catalog: books) 3. Discover scholarly conversations (library databases: journal articles) 4. Support your argument (source citation) 5. Rinse, repeat; drafts & revisions (research librarians, writing center)
This article is a systematic review which analyses research sources from the Scopus database. It extensively reviewed 2463 peer-reviewed published articles and focused explicitly on articles related to the WEF nexus that discussed pollution. ... The primary focus of this review article is to showcase the findings of WEF nexus studies regarding ...