- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide

Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Paper
Definition:
Research Paper is a written document that presents the author’s original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue.
It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new knowledge or insights to a particular field of study, and to demonstrate the author’s understanding of the existing literature and theories related to the topic.
Structure of Research Paper
The structure of a research paper typically follows a standard format, consisting of several sections that convey specific information about the research study. The following is a detailed explanation of the structure of a research paper:
The title page contains the title of the paper, the name(s) of the author(s), and the affiliation(s) of the author(s). It also includes the date of submission and possibly, the name of the journal or conference where the paper is to be published.
The abstract is a brief summary of the research paper, typically ranging from 100 to 250 words. It should include the research question, the methods used, the key findings, and the implications of the results. The abstract should be written in a concise and clear manner to allow readers to quickly grasp the essence of the research.
Introduction
The introduction section of a research paper provides background information about the research problem, the research question, and the research objectives. It also outlines the significance of the research, the research gap that it aims to fill, and the approach taken to address the research question. Finally, the introduction section ends with a clear statement of the research hypothesis or research question.
Literature Review
The literature review section of a research paper provides an overview of the existing literature on the topic of study. It includes a critical analysis and synthesis of the literature, highlighting the key concepts, themes, and debates. The literature review should also demonstrate the research gap and how the current study seeks to address it.
The methods section of a research paper describes the research design, the sample selection, the data collection and analysis procedures, and the statistical methods used to analyze the data. This section should provide sufficient detail for other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the research, using tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate the data. The findings should be presented in a clear and concise manner, with reference to the research question and hypothesis.
The discussion section of a research paper interprets the findings and discusses their implications for the research question, the literature review, and the field of study. It should also address the limitations of the study and suggest future research directions.
The conclusion section summarizes the main findings of the study, restates the research question and hypothesis, and provides a final reflection on the significance of the research.
The references section provides a list of all the sources cited in the paper, following a specific citation style such as APA, MLA or Chicago.
How to Write Research Paper
You can write Research Paper by the following guide:
- Choose a Topic: The first step is to select a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. Brainstorm ideas and narrow down to a research question that is specific and researchable.
- Conduct a Literature Review: The literature review helps you identify the gap in the existing research and provides a basis for your research question. It also helps you to develop a theoretical framework and research hypothesis.
- Develop a Thesis Statement : The thesis statement is the main argument of your research paper. It should be clear, concise and specific to your research question.
- Plan your Research: Develop a research plan that outlines the methods, data sources, and data analysis procedures. This will help you to collect and analyze data effectively.
- Collect and Analyze Data: Collect data using various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments. Analyze data using statistical tools or other qualitative methods.
- Organize your Paper : Organize your paper into sections such as Introduction, Literature Review, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion. Ensure that each section is coherent and follows a logical flow.
- Write your Paper : Start by writing the introduction, followed by the literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and follows the required formatting and citation styles.
- Edit and Proofread your Paper: Review your paper for grammar and spelling errors, and ensure that it is well-structured and easy to read. Ask someone else to review your paper to get feedback and suggestions for improvement.
- Cite your Sources: Ensure that you properly cite all sources used in your research paper. This is essential for giving credit to the original authors and avoiding plagiarism.
Research Paper Example
Note : The below example research paper is for illustrative purposes only and is not an actual research paper. Actual research papers may have different structures, contents, and formats depending on the field of study, research question, data collection and analysis methods, and other factors. Students should always consult with their professors or supervisors for specific guidelines and expectations for their research papers.
Research Paper Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health among Young Adults
Abstract: This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults. A literature review was conducted to examine the existing research on the topic. A survey was then administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Introduction: Social media has become an integral part of modern life, particularly among young adults. While social media has many benefits, including increased communication and social connectivity, it has also been associated with negative outcomes, such as addiction, cyberbullying, and mental health problems. This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults.
Literature Review: The literature review highlights the existing research on the impact of social media use on mental health. The review shows that social media use is associated with depression, anxiety, stress, and other mental health problems. The review also identifies the factors that contribute to the negative impact of social media, including social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Methods : A survey was administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The survey included questions on social media use, mental health status (measured using the DASS-21), and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis.
Results : The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Discussion : The study’s findings suggest that social media use has a negative impact on the mental health of young adults. The study highlights the need for interventions that address the factors contributing to the negative impact of social media, such as social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Conclusion : In conclusion, social media use has a significant impact on the mental health of young adults. The study’s findings underscore the need for interventions that promote healthy social media use and address the negative outcomes associated with social media use. Future research can explore the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health. Additionally, longitudinal studies can investigate the long-term effects of social media use on mental health.
Limitations : The study has some limitations, including the use of self-report measures and a cross-sectional design. The use of self-report measures may result in biased responses, and a cross-sectional design limits the ability to establish causality.
Implications: The study’s findings have implications for mental health professionals, educators, and policymakers. Mental health professionals can use the findings to develop interventions that address the negative impact of social media use on mental health. Educators can incorporate social media literacy into their curriculum to promote healthy social media use among young adults. Policymakers can use the findings to develop policies that protect young adults from the negative outcomes associated with social media use.
References :
- Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2019). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study. Preventive medicine reports, 15, 100918.
- Primack, B. A., Shensa, A., Escobar-Viera, C. G., Barrett, E. L., Sidani, J. E., Colditz, J. B., … & James, A. E. (2017). Use of multiple social media platforms and symptoms of depression and anxiety: A nationally-representative study among US young adults. Computers in Human Behavior, 69, 1-9.
- Van der Meer, T. G., & Verhoeven, J. W. (2017). Social media and its impact on academic performance of students. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 16, 383-398.
Appendix : The survey used in this study is provided below.
Social Media and Mental Health Survey
- How often do you use social media per day?
- Less than 30 minutes
- 30 minutes to 1 hour
- 1 to 2 hours
- 2 to 4 hours
- More than 4 hours
- Which social media platforms do you use?
- Others (Please specify)
- How often do you experience the following on social media?
- Social comparison (comparing yourself to others)
- Cyberbullying
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
- Have you ever experienced any of the following mental health problems in the past month?
- Do you think social media use has a positive or negative impact on your mental health?
- Very positive
- Somewhat positive
- Somewhat negative
- Very negative
- In your opinion, which factors contribute to the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Social comparison
- In your opinion, what interventions could be effective in reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Education on healthy social media use
- Counseling for mental health problems caused by social media
- Social media detox programs
- Regulation of social media use
Thank you for your participation!
Applications of Research Paper
Research papers have several applications in various fields, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Research papers contribute to the advancement of knowledge by generating new insights, theories, and findings that can inform future research and practice. They help to answer important questions, clarify existing knowledge, and identify areas that require further investigation.
- Informing policy: Research papers can inform policy decisions by providing evidence-based recommendations for policymakers. They can help to identify gaps in current policies, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and inform the development of new policies and regulations.
- Improving practice: Research papers can improve practice by providing evidence-based guidance for professionals in various fields, including medicine, education, business, and psychology. They can inform the development of best practices, guidelines, and standards of care that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- Educating students : Research papers are often used as teaching tools in universities and colleges to educate students about research methods, data analysis, and academic writing. They help students to develop critical thinking skills, research skills, and communication skills that are essential for success in many careers.
- Fostering collaboration: Research papers can foster collaboration among researchers, practitioners, and policymakers by providing a platform for sharing knowledge and ideas. They can facilitate interdisciplinary collaborations and partnerships that can lead to innovative solutions to complex problems.
When to Write Research Paper
Research papers are typically written when a person has completed a research project or when they have conducted a study and have obtained data or findings that they want to share with the academic or professional community. Research papers are usually written in academic settings, such as universities, but they can also be written in professional settings, such as research organizations, government agencies, or private companies.
Here are some common situations where a person might need to write a research paper:
- For academic purposes: Students in universities and colleges are often required to write research papers as part of their coursework, particularly in the social sciences, natural sciences, and humanities. Writing research papers helps students to develop research skills, critical thinking skills, and academic writing skills.
- For publication: Researchers often write research papers to publish their findings in academic journals or to present their work at academic conferences. Publishing research papers is an important way to disseminate research findings to the academic community and to establish oneself as an expert in a particular field.
- To inform policy or practice : Researchers may write research papers to inform policy decisions or to improve practice in various fields. Research findings can be used to inform the development of policies, guidelines, and best practices that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- To share new insights or ideas: Researchers may write research papers to share new insights or ideas with the academic or professional community. They may present new theories, propose new research methods, or challenge existing paradigms in their field.
Purpose of Research Paper
The purpose of a research paper is to present the results of a study or investigation in a clear, concise, and structured manner. Research papers are written to communicate new knowledge, ideas, or findings to a specific audience, such as researchers, scholars, practitioners, or policymakers. The primary purposes of a research paper are:
- To contribute to the body of knowledge : Research papers aim to add new knowledge or insights to a particular field or discipline. They do this by reporting the results of empirical studies, reviewing and synthesizing existing literature, proposing new theories, or providing new perspectives on a topic.
- To inform or persuade: Research papers are written to inform or persuade the reader about a particular issue, topic, or phenomenon. They present evidence and arguments to support their claims and seek to persuade the reader of the validity of their findings or recommendations.
- To advance the field: Research papers seek to advance the field or discipline by identifying gaps in knowledge, proposing new research questions or approaches, or challenging existing assumptions or paradigms. They aim to contribute to ongoing debates and discussions within a field and to stimulate further research and inquiry.
- To demonstrate research skills: Research papers demonstrate the author’s research skills, including their ability to design and conduct a study, collect and analyze data, and interpret and communicate findings. They also demonstrate the author’s ability to critically evaluate existing literature, synthesize information from multiple sources, and write in a clear and structured manner.
Characteristics of Research Paper
Research papers have several characteristics that distinguish them from other forms of academic or professional writing. Here are some common characteristics of research papers:
- Evidence-based: Research papers are based on empirical evidence, which is collected through rigorous research methods such as experiments, surveys, observations, or interviews. They rely on objective data and facts to support their claims and conclusions.
- Structured and organized: Research papers have a clear and logical structure, with sections such as introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. They are organized in a way that helps the reader to follow the argument and understand the findings.
- Formal and objective: Research papers are written in a formal and objective tone, with an emphasis on clarity, precision, and accuracy. They avoid subjective language or personal opinions and instead rely on objective data and analysis to support their arguments.
- Citations and references: Research papers include citations and references to acknowledge the sources of information and ideas used in the paper. They use a specific citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Peer-reviewed: Research papers are often peer-reviewed, which means they are evaluated by other experts in the field before they are published. Peer-review ensures that the research is of high quality, meets ethical standards, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
- Objective and unbiased: Research papers strive to be objective and unbiased in their presentation of the findings. They avoid personal biases or preconceptions and instead rely on the data and analysis to draw conclusions.
Advantages of Research Paper
Research papers have many advantages, both for the individual researcher and for the broader academic and professional community. Here are some advantages of research papers:
- Contribution to knowledge: Research papers contribute to the body of knowledge in a particular field or discipline. They add new information, insights, and perspectives to existing literature and help advance the understanding of a particular phenomenon or issue.
- Opportunity for intellectual growth: Research papers provide an opportunity for intellectual growth for the researcher. They require critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, which can help develop the researcher’s skills and knowledge.
- Career advancement: Research papers can help advance the researcher’s career by demonstrating their expertise and contributions to the field. They can also lead to new research opportunities, collaborations, and funding.
- Academic recognition: Research papers can lead to academic recognition in the form of awards, grants, or invitations to speak at conferences or events. They can also contribute to the researcher’s reputation and standing in the field.
- Impact on policy and practice: Research papers can have a significant impact on policy and practice. They can inform policy decisions, guide practice, and lead to changes in laws, regulations, or procedures.
- Advancement of society: Research papers can contribute to the advancement of society by addressing important issues, identifying solutions to problems, and promoting social justice and equality.
Limitations of Research Paper
Research papers also have some limitations that should be considered when interpreting their findings or implications. Here are some common limitations of research papers:
- Limited generalizability: Research findings may not be generalizable to other populations, settings, or contexts. Studies often use specific samples or conditions that may not reflect the broader population or real-world situations.
- Potential for bias : Research papers may be biased due to factors such as sample selection, measurement errors, or researcher biases. It is important to evaluate the quality of the research design and methods used to ensure that the findings are valid and reliable.
- Ethical concerns: Research papers may raise ethical concerns, such as the use of vulnerable populations or invasive procedures. Researchers must adhere to ethical guidelines and obtain informed consent from participants to ensure that the research is conducted in a responsible and respectful manner.
- Limitations of methodology: Research papers may be limited by the methodology used to collect and analyze data. For example, certain research methods may not capture the complexity or nuance of a particular phenomenon, or may not be appropriate for certain research questions.
- Publication bias: Research papers may be subject to publication bias, where positive or significant findings are more likely to be published than negative or non-significant findings. This can skew the overall findings of a particular area of research.
- Time and resource constraints: Research papers may be limited by time and resource constraints, which can affect the quality and scope of the research. Researchers may not have access to certain data or resources, or may be unable to conduct long-term studies due to practical limitations.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
- How to write a research paper
Last updated
11 January 2024
Reviewed by
With proper planning, knowledge, and framework, completing a research paper can be a fulfilling and exciting experience.
Though it might initially sound slightly intimidating, this guide will help you embrace the challenge.
By documenting your findings, you can inspire others and make a difference in your field. Here's how you can make your research paper unique and comprehensive.
- What is a research paper?
Research papers allow you to demonstrate your knowledge and understanding of a particular topic. These papers are usually lengthier and more detailed than typical essays, requiring deeper insight into the chosen topic.
To write a research paper, you must first choose a topic that interests you and is relevant to the field of study. Once you’ve selected your topic, gathering as many relevant resources as possible, including books, scholarly articles, credible websites, and other academic materials, is essential. You must then read and analyze these sources, summarizing their key points and identifying gaps in the current research.
You can formulate your ideas and opinions once you thoroughly understand the existing research. To get there might involve conducting original research, gathering data, or analyzing existing data sets. It could also involve presenting an original argument or interpretation of the existing research.
Writing a successful research paper involves presenting your findings clearly and engagingly, which might involve using charts, graphs, or other visual aids to present your data and using concise language to explain your findings. You must also ensure your paper adheres to relevant academic formatting guidelines, including proper citations and references.
Overall, writing a research paper requires a significant amount of time, effort, and attention to detail. However, it is also an enriching experience that allows you to delve deeply into a subject that interests you and contribute to the existing body of knowledge in your chosen field.
- How long should a research paper be?
Research papers are deep dives into a topic. Therefore, they tend to be longer pieces of work than essays or opinion pieces.
However, a suitable length depends on the complexity of the topic and your level of expertise. For instance, are you a first-year college student or an experienced professional?
Also, remember that the best research papers provide valuable information for the benefit of others. Therefore, the quality of information matters most, not necessarily the length. Being concise is valuable.
Following these best practice steps will help keep your process simple and productive:
1. Gaining a deep understanding of any expectations
Before diving into your intended topic or beginning the research phase, take some time to orient yourself. Suppose there’s a specific topic assigned to you. In that case, it’s essential to deeply understand the question and organize your planning and approach in response. Pay attention to the key requirements and ensure you align your writing accordingly.
This preparation step entails
Deeply understanding the task or assignment
Being clear about the expected format and length
Familiarizing yourself with the citation and referencing requirements
Understanding any defined limits for your research contribution
Where applicable, speaking to your professor or research supervisor for further clarification
2. Choose your research topic
Select a research topic that aligns with both your interests and available resources. Ideally, focus on a field where you possess significant experience and analytical skills. In crafting your research paper, it's crucial to go beyond summarizing existing data and contribute fresh insights to the chosen area.
Consider narrowing your focus to a specific aspect of the topic. For example, if exploring the link between technology and mental health, delve into how social media use during the pandemic impacts the well-being of college students. Conducting interviews and surveys with students could provide firsthand data and unique perspectives, adding substantial value to the existing knowledge.
When finalizing your topic, adhere to legal and ethical norms in the relevant area (this ensures the integrity of your research, protects participants' rights, upholds intellectual property standards, and ensures transparency and accountability). Following these principles not only maintains the credibility of your work but also builds trust within your academic or professional community.
For instance, in writing about medical research, consider legal and ethical norms, including patient confidentiality laws and informed consent requirements. Similarly, if analyzing user data on social media platforms, be mindful of data privacy regulations, ensuring compliance with laws governing personal information collection and use. Aligning with legal and ethical standards not only avoids potential issues but also underscores the responsible conduct of your research.
3. Gather preliminary research
Once you’ve landed on your topic, it’s time to explore it further. You’ll want to discover more about available resources and existing research relevant to your assignment at this stage.
This exploratory phase is vital as you may discover issues with your original idea or realize you have insufficient resources to explore the topic effectively. This key bit of groundwork allows you to redirect your research topic in a different, more feasible, or more relevant direction if necessary.
Spending ample time at this stage ensures you gather everything you need, learn as much as you can about the topic, and discover gaps where the topic has yet to be sufficiently covered, offering an opportunity to research it further.
4. Define your research question
To produce a well-structured and focused paper, it is imperative to formulate a clear and precise research question that will guide your work. Your research question must be informed by the existing literature and tailored to the scope and objectives of your project. By refining your focus, you can produce a thoughtful and engaging paper that effectively communicates your ideas to your readers.
5. Write a thesis statement
A thesis statement is a one-to-two-sentence summary of your research paper's main argument or direction. It serves as an overall guide to summarize the overall intent of the research paper for you and anyone wanting to know more about the research.
A strong thesis statement is:
Concise and clear: Explain your case in simple sentences (avoid covering multiple ideas). It might help to think of this section as an elevator pitch.
Specific: Ensure that there is no ambiguity in your statement and that your summary covers the points argued in the paper.
Debatable: A thesis statement puts forward a specific argument––it is not merely a statement but a debatable point that can be analyzed and discussed.
Here are three thesis statement examples from different disciplines:
Psychology thesis example: "We're studying adults aged 25-40 to see if taking short breaks for mindfulness can help with stress. Our goal is to find practical ways to manage anxiety better."
Environmental science thesis example: "This research paper looks into how having more city parks might make the air cleaner and keep people healthier. I want to find out if more green spaces means breathing fewer carcinogens in big cities."
UX research thesis example: "This study focuses on improving mobile banking for older adults using ethnographic research, eye-tracking analysis, and interactive prototyping. We investigate the usefulness of eye-tracking analysis with older individuals, aiming to spark debate and offer fresh perspectives on UX design and digital inclusivity for the aging population."
6. Conduct in-depth research
A research paper doesn’t just include research that you’ve uncovered from other papers and studies but your fresh insights, too. You will seek to become an expert on your topic––understanding the nuances in the current leading theories. You will analyze existing research and add your thinking and discoveries. It's crucial to conduct well-designed research that is rigorous, robust, and based on reliable sources. Suppose a research paper lacks evidence or is biased. In that case, it won't benefit the academic community or the general public. Therefore, examining the topic thoroughly and furthering its understanding through high-quality research is essential. That usually means conducting new research. Depending on the area under investigation, you may conduct surveys, interviews, diary studies, or observational research to uncover new insights or bolster current claims.
7. Determine supporting evidence
Not every piece of research you’ve discovered will be relevant to your research paper. It’s important to categorize the most meaningful evidence to include alongside your discoveries. It's important to include evidence that doesn't support your claims to avoid exclusion bias and ensure a fair research paper.
8. Write a research paper outline
Before diving in and writing the whole paper, start with an outline. It will help you to see if more research is needed, and it will provide a framework by which to write a more compelling paper. Your supervisor may even request an outline to approve before beginning to write the first draft of the full paper. An outline will include your topic, thesis statement, key headings, short summaries of the research, and your arguments.
9. Write your first draft
Once you feel confident about your outline and sources, it’s time to write your first draft. While penning a long piece of content can be intimidating, if you’ve laid the groundwork, you will have a structure to help you move steadily through each section. To keep up motivation and inspiration, it’s often best to keep the pace quick. Stopping for long periods can interrupt your flow and make jumping back in harder than writing when things are fresh in your mind.
10. Cite your sources correctly
It's always a good practice to give credit where it's due, and the same goes for citing any works that have influenced your paper. Building your arguments on credible references adds value and authenticity to your research. In the formatting guidelines section, you’ll find an overview of different citation styles (MLA, CMOS, or APA), which will help you meet any publishing or academic requirements and strengthen your paper's credibility. It is essential to follow the guidelines provided by your school or the publication you are submitting to ensure the accuracy and relevance of your citations.
11. Ensure your work is original
It is crucial to ensure the originality of your paper, as plagiarism can lead to serious consequences. To avoid plagiarism, you should use proper paraphrasing and quoting techniques. Paraphrasing is rewriting a text in your own words while maintaining the original meaning. Quoting involves directly citing the source. Giving credit to the original author or source is essential whenever you borrow their ideas or words. You can also use plagiarism detection tools such as Scribbr or Grammarly to check the originality of your paper. These tools compare your draft writing to a vast database of online sources. If you find any accidental plagiarism, you should correct it immediately by rephrasing or citing the source.
12. Revise, edit, and proofread
One of the essential qualities of excellent writers is their ability to understand the importance of editing and proofreading. Even though it's tempting to call it a day once you've finished your writing, editing your work can significantly improve its quality. It's natural to overlook the weaker areas when you've just finished writing a paper. Therefore, it's best to take a break of a day or two, or even up to a week, to refresh your mind. This way, you can return to your work with a new perspective. After some breathing room, you can spot any inconsistencies, spelling and grammar errors, typos, or missing citations and correct them.
- The best research paper format
The format of your research paper should align with the requirements set forth by your college, school, or target publication.
There is no one “best” format, per se. Depending on the stated requirements, you may need to include the following elements:
Title page: The title page of a research paper typically includes the title, author's name, and institutional affiliation and may include additional information such as a course name or instructor's name.
Table of contents: Include a table of contents to make it easy for readers to find specific sections of your paper.
Abstract: The abstract is a summary of the purpose of the paper.
Methods : In this section, describe the research methods used. This may include collecting data, conducting interviews, or doing field research.
Results: Summarize the conclusions you drew from your research in this section.
Discussion: In this section, discuss the implications of your research. Be sure to mention any significant limitations to your approach and suggest areas for further research.
Tables, charts, and illustrations: Use tables, charts, and illustrations to help convey your research findings and make them easier to understand.
Works cited or reference page: Include a works cited or reference page to give credit to the sources that you used to conduct your research.
Bibliography: Provide a list of all the sources you consulted while conducting your research.
Dedication and acknowledgments : Optionally, you may include a dedication and acknowledgments section to thank individuals who helped you with your research.
- General style and formatting guidelines
Formatting your research paper means you can submit it to your college, journal, or other publications in compliance with their criteria.
Research papers tend to follow the American Psychological Association (APA), Modern Language Association (MLA), or Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS) guidelines.
Here’s how each style guide is typically used:
Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS):
CMOS is a versatile style guide used for various types of writing. It's known for its flexibility and use in the humanities. CMOS provides guidelines for citations, formatting, and overall writing style. It allows for both footnotes and in-text citations, giving writers options based on their preferences or publication requirements.
American Psychological Association (APA):
APA is common in the social sciences. It’s hailed for its clarity and emphasis on precision. It has specific rules for citing sources, creating references, and formatting papers. APA style uses in-text citations with an accompanying reference list. It's designed to convey information efficiently and is widely used in academic and scientific writing.
Modern Language Association (MLA):
MLA is widely used in the humanities, especially literature and language studies. It emphasizes the author-page format for in-text citations and provides guidelines for creating a "Works Cited" page. MLA is known for its focus on the author's name and the literary works cited. It’s frequently used in disciplines that prioritize literary analysis and critical thinking.
To confirm you're using the latest style guide, check the official website or publisher's site for updates, consult academic resources, and verify the guide's publication date. Online platforms and educational resources may also provide summaries and alerts about any revisions or additions to the style guide.
Citing sources
When working on your research paper, it's important to cite the sources you used properly. Your citation style will guide you through this process. Generally, there are three parts to citing sources in your research paper:
First, provide a brief citation in the body of your essay. This is also known as a parenthetical or in-text citation.
Second, include a full citation in the Reference list at the end of your paper. Different types of citations include in-text citations, footnotes, and reference lists.
In-text citations include the author's surname and the date of the citation.
Footnotes appear at the bottom of each page of your research paper. They may also be summarized within a reference list at the end of the paper.
A reference list includes all of the research used within the paper at the end of the document. It should include the author, date, paper title, and publisher listed in the order that aligns with your citation style.
10 research paper writing tips:
Following some best practices is essential to writing a research paper that contributes to your field of study and creates a positive impact.
These tactics will help you structure your argument effectively and ensure your work benefits others:
Clear and precise language: Ensure your language is unambiguous. Use academic language appropriately, but keep it simple. Also, provide clear takeaways for your audience.
Effective idea separation: Organize the vast amount of information and sources in your paper with paragraphs and titles. Create easily digestible sections for your readers to navigate through.
Compelling intro: Craft an engaging introduction that captures your reader's interest. Hook your audience and motivate them to continue reading.
Thorough revision and editing: Take the time to review and edit your paper comprehensively. Use tools like Grammarly to detect and correct small, overlooked errors.
Thesis precision: Develop a clear and concise thesis statement that guides your paper. Ensure that your thesis aligns with your research's overall purpose and contribution.
Logical flow of ideas: Maintain a logical progression throughout the paper. Use transitions effectively to connect different sections and maintain coherence.
Critical evaluation of sources: Evaluate and critically assess the relevance and reliability of your sources. Ensure that your research is based on credible and up-to-date information.
Thematic consistency: Maintain a consistent theme throughout the paper. Ensure that all sections contribute cohesively to the overall argument.
Relevant supporting evidence: Provide concise and relevant evidence to support your arguments. Avoid unnecessary details that may distract from the main points.
Embrace counterarguments: Acknowledge and address opposing views to strengthen your position. Show that you have considered alternative arguments in your field.
7 research tips
If you want your paper to not only be well-written but also contribute to the progress of human knowledge, consider these tips to take your paper to the next level:
Selecting the appropriate topic: The topic you select should align with your area of expertise, comply with the requirements of your project, and have sufficient resources for a comprehensive investigation.
Use academic databases: Academic databases such as PubMed, Google Scholar, and JSTOR offer a wealth of research papers that can help you discover everything you need to know about your chosen topic.
Critically evaluate sources: It is important not to accept research findings at face value. Instead, it is crucial to critically analyze the information to avoid jumping to conclusions or overlooking important details. A well-written research paper requires a critical analysis with thorough reasoning to support claims.
Diversify your sources: Expand your research horizons by exploring a variety of sources beyond the standard databases. Utilize books, conference proceedings, and interviews to gather diverse perspectives and enrich your understanding of the topic.
Take detailed notes: Detailed note-taking is crucial during research and can help you form the outline and body of your paper.
Stay up on trends: Keep abreast of the latest developments in your field by regularly checking for recent publications. Subscribe to newsletters, follow relevant journals, and attend conferences to stay informed about emerging trends and advancements.
Engage in peer review: Seek feedback from peers or mentors to ensure the rigor and validity of your research. Peer review helps identify potential weaknesses in your methodology and strengthens the overall credibility of your findings.
- The real-world impact of research papers
Writing a research paper is more than an academic or business exercise. The experience provides an opportunity to explore a subject in-depth, broaden one's understanding, and arrive at meaningful conclusions. With careful planning, dedication, and hard work, writing a research paper can be a fulfilling and enriching experience contributing to advancing knowledge.
How do I publish my research paper?
Many academics wish to publish their research papers. While challenging, your paper might get traction if it covers new and well-written information. To publish your research paper, find a target publication, thoroughly read their guidelines, format your paper accordingly, and send it to them per their instructions. You may need to include a cover letter, too. After submission, your paper may be peer-reviewed by experts to assess its legitimacy, quality, originality, and methodology. Following review, you will be informed by the publication whether they have accepted or rejected your paper.
What is a good opening sentence for a research paper?
Beginning your research paper with a compelling introduction can ensure readers are interested in going further. A relevant quote, a compelling statistic, or a bold argument can start the paper and hook your reader. Remember, though, that the most important aspect of a research paper is the quality of the information––not necessarily your ability to storytell, so ensure anything you write aligns with your goals.
Research paper vs. a research proposal—what’s the difference?
While some may confuse research papers and proposals, they are different documents.
A research proposal comes before a research paper. It is a detailed document that outlines an intended area of exploration. It includes the research topic, methodology, timeline, sources, and potential conclusions. Research proposals are often required when seeking approval to conduct research.
A research paper is a summary of research findings. A research paper follows a structured format to present those findings and construct an argument or conclusion.
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 21 December 2023
Last updated: 16 December 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 12 May 2023
Last updated: 15 February 2024
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 18 May 2023
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 10 April 2023
Last updated: 20 December 2023
Latest articles
Related topics.
- 10 research paper
Log in or sign up
Get started for free
How To Write A Research Paper
Step-By-Step Tutorial With Examples + FREE Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | March 2024
For many students, crafting a strong research paper from scratch can feel like a daunting task – and rightly so! In this post, we’ll unpack what a research paper is, what it needs to do , and how to write one – in three easy steps. 🙂
Overview: Writing A Research Paper
What (exactly) is a research paper.
- How to write a research paper
- Stage 1 : Topic & literature search
- Stage 2 : Structure & outline
- Stage 3 : Iterative writing
- Key takeaways
Let’s start by asking the most important question, “ What is a research paper? ”.
Simply put, a research paper is a scholarly written work where the writer (that’s you!) answers a specific question (this is called a research question ) through evidence-based arguments . Evidence-based is the keyword here. In other words, a research paper is different from an essay or other writing assignments that draw from the writer’s personal opinions or experiences. With a research paper, it’s all about building your arguments based on evidence (we’ll talk more about that evidence a little later).
Now, it’s worth noting that there are many different types of research papers , including analytical papers (the type I just described), argumentative papers, and interpretative papers. Here, we’ll focus on analytical papers , as these are some of the most common – but if you’re keen to learn about other types of research papers, be sure to check out the rest of the blog .
With that basic foundation laid, let’s get down to business and look at how to write a research paper .

Overview: The 3-Stage Process
While there are, of course, many potential approaches you can take to write a research paper, there are typically three stages to the writing process. So, in this tutorial, we’ll present a straightforward three-step process that we use when working with students at Grad Coach.
These three steps are:
- Finding a research topic and reviewing the existing literature
- Developing a provisional structure and outline for your paper, and
- Writing up your initial draft and then refining it iteratively
Let’s dig into each of these.
Need a helping hand?
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature
As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question . More specifically, that’s called a research question , and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What’s important to understand though is that you’ll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources – for example, journal articles, government reports, case studies, and so on. We’ll circle back to this in a minute.
The first stage of the research process is deciding on what your research question will be and then reviewing the existing literature (in other words, past studies and papers) to see what they say about that specific research question. In some cases, your professor may provide you with a predetermined research question (or set of questions). However, in many cases, you’ll need to find your own research question within a certain topic area.
Finding a strong research question hinges on identifying a meaningful research gap – in other words, an area that’s lacking in existing research. There’s a lot to unpack here, so if you wanna learn more, check out the plain-language explainer video below.
Once you’ve figured out which question (or questions) you’ll attempt to answer in your research paper, you’ll need to do a deep dive into the existing literature – this is called a “ literature search ”. Again, there are many ways to go about this, but your most likely starting point will be Google Scholar .
If you’re new to Google Scholar, think of it as Google for the academic world. You can start by simply entering a few different keywords that are relevant to your research question and it will then present a host of articles for you to review. What you want to pay close attention to here is the number of citations for each paper – the more citations a paper has, the more credible it is (generally speaking – there are some exceptions, of course).

Ideally, what you’re looking for are well-cited papers that are highly relevant to your topic. That said, keep in mind that citations are a cumulative metric , so older papers will often have more citations than newer papers – just because they’ve been around for longer. So, don’t fixate on this metric in isolation – relevance and recency are also very important.
Beyond Google Scholar, you’ll also definitely want to check out academic databases and aggregators such as Science Direct, PubMed, JStor and so on. These will often overlap with the results that you find in Google Scholar, but they can also reveal some hidden gems – so, be sure to check them out.
Once you’ve worked your way through all the literature, you’ll want to catalogue all this information in some sort of spreadsheet so that you can easily recall who said what, when and within what context. If you’d like, we’ve got a free literature spreadsheet that helps you do exactly that.

Step 2: Develop a structure and outline
With your research question pinned down and your literature digested and catalogued, it’s time to move on to planning your actual research paper .
It might sound obvious, but it’s really important to have some sort of rough outline in place before you start writing your paper. So often, we see students eagerly rushing into the writing phase, only to land up with a disjointed research paper that rambles on in multiple
Now, the secret here is to not get caught up in the fine details . Realistically, all you need at this stage is a bullet-point list that describes (in broad strokes) what you’ll discuss and in what order. It’s also useful to remember that you’re not glued to this outline – in all likelihood, you’ll chop and change some sections once you start writing, and that’s perfectly okay. What’s important is that you have some sort of roadmap in place from the start.

At this stage you might be wondering, “ But how should I structure my research paper? ”. Well, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution here, but in general, a research paper will consist of a few relatively standardised components:
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Methodology
Let’s take a look at each of these.
First up is the introduction section . As the name suggests, the purpose of the introduction is to set the scene for your research paper. There are usually (at least) four ingredients that go into this section – these are the background to the topic, the research problem and resultant research question , and the justification or rationale. If you’re interested, the video below unpacks the introduction section in more detail.
The next section of your research paper will typically be your literature review . Remember all that literature you worked through earlier? Well, this is where you’ll present your interpretation of all that content . You’ll do this by writing about recent trends, developments, and arguments within the literature – but more specifically, those that are relevant to your research question . The literature review can oftentimes seem a little daunting, even to seasoned researchers, so be sure to check out our extensive collection of literature review content here .
With the introduction and lit review out of the way, the next section of your paper is the research methodology . In a nutshell, the methodology section should describe to your reader what you did (beyond just reviewing the existing literature) to answer your research question. For example, what data did you collect, how did you collect that data, how did you analyse that data and so on? For each choice, you’ll also need to justify why you chose to do it that way, and what the strengths and weaknesses of your approach were.
Now, it’s worth mentioning that for some research papers, this aspect of the project may be a lot simpler . For example, you may only need to draw on secondary sources (in other words, existing data sets). In some cases, you may just be asked to draw your conclusions from the literature search itself (in other words, there may be no data analysis at all). But, if you are required to collect and analyse data, you’ll need to pay a lot of attention to the methodology section. The video below provides an example of what the methodology section might look like.
By this stage of your paper, you will have explained what your research question is, what the existing literature has to say about that question, and how you analysed additional data to try to answer your question. So, the natural next step is to present your analysis of that data . This section is usually called the “results” or “analysis” section and this is where you’ll showcase your findings.
Depending on your school’s requirements, you may need to present and interpret the data in one section – or you might split the presentation and the interpretation into two sections. In the latter case, your “results” section will just describe the data, and the “discussion” is where you’ll interpret that data and explicitly link your analysis back to your research question. If you’re not sure which approach to take, check in with your professor or take a look at past papers to see what the norms are for your programme.
Alright – once you’ve presented and discussed your results, it’s time to wrap it up . This usually takes the form of the “ conclusion ” section. In the conclusion, you’ll need to highlight the key takeaways from your study and close the loop by explicitly answering your research question. Again, the exact requirements here will vary depending on your programme (and you may not even need a conclusion section at all) – so be sure to check with your professor if you’re unsure.
Step 3: Write and refine
Finally, it’s time to get writing. All too often though, students hit a brick wall right about here… So, how do you avoid this happening to you?
Well, there’s a lot to be said when it comes to writing a research paper (or any sort of academic piece), but we’ll share three practical tips to help you get started.
First and foremost , it’s essential to approach your writing as an iterative process. In other words, you need to start with a really messy first draft and then polish it over multiple rounds of editing. Don’t waste your time trying to write a perfect research paper in one go. Instead, take the pressure off yourself by adopting an iterative approach.
Secondly , it’s important to always lean towards critical writing , rather than descriptive writing. What does this mean? Well, at the simplest level, descriptive writing focuses on the “ what ”, while critical writing digs into the “ so what ” – in other words, the implications. If you’re not familiar with these two types of writing, don’t worry! You can find a plain-language explanation here.
Last but not least, you’ll need to get your referencing right. Specifically, you’ll need to provide credible, correctly formatted citations for the statements you make. We see students making referencing mistakes all the time and it costs them dearly. The good news is that you can easily avoid this by using a simple reference manager . If you don’t have one, check out our video about Mendeley, an easy (and free) reference management tool that you can start using today.
Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are:
- To choose a research question and review the literature
- To plan your paper structure and draft an outline
- To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing
Remember, this is just a b ig-picture overview of the research paper development process and there’s a lot more nuance to unpack. So, be sure to grab a copy of our free research paper template to learn more about how to write a research paper.
You Might Also Like:

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
What Is a Research Paper?
- An Introduction to Punctuation
Olivia Valdes was the Associate Editorial Director for ThoughtCo. She worked with Dotdash Meredith from 2017 to 2021.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Olivia-Valdes_WEB1-1e405fc799d9474e9212215c4f21b141.jpg)
- B.A., American Studies, Yale University
A research paper is a common form of academic writing . Research papers require students and academics to locate information about a topic (that is, to conduct research ), take a stand on that topic, and provide support (or evidence) for that position in an organized report.
The term research paper may also refer to a scholarly article that contains the results of original research or an evaluation of research conducted by others. Most scholarly articles must undergo a process of peer review before they can be accepted for publication in an academic journal.
Define Your Research Question
The first step in writing a research paper is defining your research question . Has your instructor assigned a specific topic? If so, great—you've got this step covered. If not, review the guidelines of the assignment. Your instructor has likely provided several general subjects for your consideration. Your research paper should focus on a specific angle on one of these subjects. Spend some time mulling over your options before deciding which one you'd like to explore more deeply.
Try to choose a research question that interests you. The research process is time-consuming, and you'll be significantly more motivated if you have a genuine desire to learn more about the topic. You should also consider whether you have access to all of the resources necessary to conduct thorough research on your topic, such as primary and secondary sources .
Create a Research Strategy
Approach the research process systematically by creating a research strategy. First, review your library's website. What resources are available? Where will you find them? Do any resources require a special process to gain access? Start gathering those resources—especially those that may be difficult to access—as soon as possible.
Second, make an appointment with a reference librarian . A reference librarian is nothing short of a research superhero. He or she will listen to your research question, offer suggestions for how to focus your research, and direct you toward valuable sources that directly relate to your topic.
Evaluate Sources
Now that you've gathered a wide array of sources, it's time to evaluate them. First, consider the reliability of the information. Where is the information coming from? What is the origin of the source? Second, assess the relevance of the information. How does this information relate to your research question? Does it support, refute, or add context to your position? How does it relate to the other sources you'll be using in your paper? Once you have determined that your sources are both reliable and relevant, you can proceed confidently to the writing phase.
Why Write Research Papers?
The research process is one of the most taxing academic tasks you'll be asked to complete. Luckily, the value of writing a research paper goes beyond that A+ you hope to receive. Here are just some of the benefits of research papers.
- Learning Scholarly Conventions: Writing a research paper is a crash course in the stylistic conventions of scholarly writing. During the research and writing process, you'll learn how to document your research, cite sources appropriately, format an academic paper, maintain an academic tone, and more.
- Organizing Information: In a way, research is nothing more than a massive organizational project. The information available to you is near-infinite, and it's your job to review that information, narrow it down, categorize it, and present it in a clear, relevant format. This process requires attention to detail and major brainpower.
- Managing Time: Research papers put your time management skills to the test. Every step of the research and writing process takes time, and it's up to you to set aside the time you'll need to complete each step of the task. Maximize your efficiency by creating a research schedule and inserting blocks of "research time" into your calendar as soon as you receive the assignment.
- Exploring Your Chosen Subject: We couldn't forget the best part of research papers—learning about something that truly excites you. No matter what topic you choose, you're bound to come away from the research process with new ideas and countless nuggets of fascinating information.
The best research papers are the result of genuine interest and a thorough research process. With these ideas in mind, go forth and research. Welcome to the scholarly conversation!
- What Is a Literature Review?
- How to Narrow the Research Topic for Your Paper
- 10 Places to Research Your Paper
- How to Write a Research Paper That Earns an A
- What Is a Senior Thesis?
- Research in Essays and Reports
- Documentation in Reports and Research Papers
- An Introduction to Academic Writing
- How to Organize Research Notes
- Writing an Annotated Bibliography for a Paper
- Why Archaeology Topics Are Great Options for Research Papers
- What Is a Bibliography?
- 5 Steps to Writing a Position Paper
- Abstract Writing for Sociology
- How to Develop a Research Paper Timeline
- Writing a Paper about an Environmental Issue

How to Write a Research Paper
Use the links below to jump directly to any section of this guide:
Research Paper Fundamentals
How to choose a topic or question, how to create a working hypothesis or thesis, common research paper methodologies, how to gather and organize evidence , how to write an outline for your research paper, how to write a rough draft, how to revise your draft, how to produce a final draft, resources for teachers .
It is not fair to say that no one writes anymore. Just about everyone writes text messages, brief emails, or social media posts every single day. Yet, most people don't have a lot of practice with the formal, organized writing required for a good academic research paper. This guide contains links to a variety of resources that can help demystify the process. Some of these resources are intended for teachers; they contain exercises, activities, and teaching strategies. Other resources are intended for direct use by students who are struggling to write papers, or are looking for tips to make the process go more smoothly.
The resources in this section are designed to help students understand the different types of research papers, the general research process, and how to manage their time. Below, you'll find links from university writing centers, the trusted Purdue Online Writing Lab, and more.
What is an Academic Research Paper?
"Genre and the Research Paper" (Purdue OWL)
There are different types of research papers. Different types of scholarly questions will lend themselves to one format or another. This is a brief introduction to the two main genres of research paper: analytic and argumentative.
"7 Most Popular Types of Research Papers" (Personal-writer.com)
This resource discusses formats that high school students commonly encounter, such as the compare and contrast essay and the definitional essay. Please note that the inclusion of this link is not an endorsement of this company's paid service.
How to Prepare and Plan Out Writing a Research Paper
Teachers can give their students a step-by-step guide like these to help them understand the different steps of the research paper process. These guides can be combined with the time management tools in the next subsection to help students come up with customized calendars for completing their papers.
"Ten Steps for Writing Research Papers" (American University)
This resource from American University is a comprehensive guide to the research paper writing process, and includes examples of proper research questions and thesis topics.
"Steps in Writing a Research Paper" (SUNY Empire State College)
This guide breaks the research paper process into 11 steps. Each "step" links to a separate page, which describes the work entailed in completing it.
How to Manage Time Effectively
The links below will help students determine how much time is necessary to complete a paper. If your sources are not available online or at your local library, you'll need to leave extra time for the Interlibrary Loan process. Remember that, even if you do not need to consult secondary sources, you'll still need to leave yourself ample time to organize your thoughts.
"Research Paper Planner: Timeline" (Baylor University)
This interactive resource from Baylor University creates a suggested writing schedule based on how much time a student has to work on the assignment.
"Research Paper Planner" (UCLA)
UCLA's library offers this step-by-step guide to the research paper writing process, which also includes a suggested planning calendar.
There's a reason teachers spend a long time talking about choosing a good topic. Without a good topic and a well-formulated research question, it is almost impossible to write a clear and organized paper. The resources below will help you generate ideas and formulate precise questions.
"How to Select a Research Topic" (Univ. of Michigan-Flint)
This resource is designed for college students who are struggling to come up with an appropriate topic. A student who uses this resource and still feels unsure about his or her topic should consult the course instructor for further personalized assistance.
"25 Interesting Research Paper Topics to Get You Started" (Kibin)
This resource, which is probably most appropriate for high school students, provides a list of specific topics to help get students started. It is broken into subsections, such as "paper topics on local issues."
"Writing a Good Research Question" (Grand Canyon University)
This introduction to research questions includes some embedded videos, as well as links to scholarly articles on research questions. This resource would be most appropriate for teachers who are planning lessons on research paper fundamentals.
"How to Write a Research Question the Right Way" (Kibin)
This student-focused resource provides more detail on writing research questions. The language is accessible, and there are embedded videos and examples of good and bad questions.
It is important to have a rough hypothesis or thesis in mind at the beginning of the research process. People who have a sense of what they want to say will have an easier time sorting through scholarly sources and other information. The key, of course, is not to become too wedded to the draft hypothesis or thesis. Just about every working thesis gets changed during the research process.
CrashCourse Video: "Sociology Research Methods" (YouTube)
Although this video is tailored to sociology students, it is applicable to students in a variety of social science disciplines. This video does a good job demonstrating the connection between the brainstorming that goes into selecting a research question and the formulation of a working hypothesis.
"How to Write a Thesis Statement for an Analytical Essay" (YouTube)
Students writing analytical essays will not develop the same type of working hypothesis as students who are writing research papers in other disciplines. For these students, developing the working thesis may happen as a part of the rough draft (see the relevant section below).
"Research Hypothesis" (Oakland Univ.)
This resource provides some examples of hypotheses in social science disciplines like Political Science and Criminal Justice. These sample hypotheses may also be useful for students in other soft social sciences and humanities disciplines like History.
When grading a research paper, instructors look for a consistent methodology. This section will help you understand different methodological approaches used in research papers. Students will get the most out of these resources if they use them to help prepare for conversations with teachers or discussions in class.
"Types of Research Designs" (USC)
A "research design," used for complex papers, is related to the paper's method. This resource contains introductions to a variety of popular research designs in the social sciences. Although it is not the most intuitive site to read, the information here is very valuable.
"Major Research Methods" (YouTube)
Although this video is a bit on the dry side, it provides a comprehensive overview of the major research methodologies in a format that might be more accessible to students who have struggled with textbooks or other written resources.
"Humanities Research Strategies" (USC)
This is a portal where students can learn about four methodological approaches for humanities papers: Historical Methodologies, Textual Criticism, Conceptual Analysis, and the Synoptic method.
"Selected Major Social Science Research Methods: Overview" (National Academies Press)
This appendix from the book Using Science as Evidence in Public Policy , printed by National Academies Press, introduces some methods used in social science papers.
"Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper: 6. The Methodology" (USC)
This resource from the University of Southern California's library contains tips for writing a methodology section in a research paper.
How to Determine the Best Methodology for You
Anyone who is new to writing research papers should be sure to select a method in consultation with their instructor. These resources can be used to help prepare for that discussion. They may also be used on their own by more advanced students.
"Choosing Appropriate Research Methodologies" (Palgrave Study Skills)
This friendly and approachable resource from Palgrave Macmillan can be used by students who are just starting to think about appropriate methodologies.
"How to Choose Your Research Methods" (NFER (UK))
This is another approachable resource students can use to help narrow down the most appropriate methods for their research projects.
The resources in this section introduce the process of gathering scholarly sources and collecting evidence. You'll find a range of material here, from introductory guides to advanced explications best suited to college students. Please consult the LitCharts How to Do Academic Research guide for a more comprehensive list of resources devoted to finding scholarly literature.
Google Scholar
Students who have access to library websites with detailed research guides should start there, but people who do not have access to those resources can begin their search for secondary literature here.
"Gathering Appropriate Information" (Texas Gateway)
This resource from the Texas Gateway for online resources introduces students to the research process, and contains interactive exercises. The level of complexity is suitable for middle school, high school, and introductory college classrooms.
"An Overview of Quantitative and Qualitative Data Collection Methods" (NSF)
This PDF from the National Science Foundation goes into detail about best practices and pitfalls in data collection across multiple types of methodologies.
"Social Science Methods for Data Collection and Analysis" (Swiss FIT)
This resource is appropriate for advanced undergraduates or teachers looking to create lessons on research design and data collection. It covers techniques for gathering data via interviews, observations, and other methods.
"Collecting Data by In-depth Interviewing" (Leeds Univ.)
This resource contains enough information about conducting interviews to make it useful for teachers who want to create a lesson plan, but is also accessible enough for college juniors or seniors to make use of it on their own.
There is no "one size fits all" outlining technique. Some students might devote all their energy and attention to the outline in order to avoid the paper. Other students may benefit from being made to sit down and organize their thoughts into a lengthy sentence outline. The resources in this section include strategies and templates for multiple types of outlines.
"Topic vs. Sentence Outlines" (UC Berkeley)
This resource introduces two basic approaches to outlining: the shorter topic-based approach, and the longer, more detailed sentence-based approach. This resource also contains videos on how to develop paper paragraphs from the sentence-based outline.
"Types of Outlines and Samples" (Purdue OWL)
The Purdue Online Writing Lab's guide is a slightly less detailed discussion of different types of outlines. It contains several sample outlines.
"Writing An Outline" (Austin C.C.)
This resource from a community college contains sample outlines from an American history class that students can use as models.
"How to Structure an Outline for a College Paper" (YouTube)
This brief (sub-2 minute) video from the ExpertVillage YouTube channel provides a model of outline writing for students who are struggling with the idea.
"Outlining" (Harvard)
This is a good resource to consult after completing a draft outline. It offers suggestions for making sure your outline avoids things like unnecessary repetition.
As with outlines, rough drafts can take on many different forms. These resources introduce teachers and students to the various approaches to writing a rough draft. This section also includes resources that will help you cite your sources appropriately according to the MLA, Chicago, and APA style manuals.
"Creating a Rough Draft for a Research Paper" (Univ. of Minnesota)
This resource is useful for teachers in particular, as it provides some suggested exercises to help students with writing a basic rough draft.
Rough Draft Assignment (Duke of Definition)
This sample assignment, with a brief list of tips, was developed by a high school teacher who runs a very successful and well-reviewed page of educational resources.
"Creating the First Draft of Your Research Paper" (Concordia Univ.)
This resource will be helpful for perfectionists or procrastinators, as it opens by discussing the problem of avoiding writing. It also provides a short list of suggestions meant to get students writing.
Using Proper Citations
There is no such thing as a rough draft of a scholarly citation. These links to the three major citation guides will ensure that your citations follow the correct format. Please consult the LitCharts How to Cite Your Sources guide for more resources.
Chicago Manual of Style Citation Guide
Some call The Chicago Manual of Style , which was first published in 1906, "the editors' Bible." The manual is now in its 17th edition, and is popular in the social sciences, historical journals, and some other fields in the humanities.
APA Citation Guide
According to the American Psychological Association, this guide was developed to aid reading comprehension, clarity of communication, and to reduce bias in language in the social and behavioral sciences. Its first full edition was published in 1952, and it is now in its sixth edition.
MLA Citation Guide
The Modern Language Association style is used most commonly within the liberal arts and humanities. The MLA Style Manual and Guide to Scholarly Publishing was first published in 1985 and (as of 2008) is in its third edition.
Any professional scholar will tell you that the best research papers are made in the revision stage. No matter how strong your research question or working thesis, it is not possible to write a truly outstanding paper without devoting energy to revision. These resources provide examples of revision exercises for the classroom, as well as tips for students working independently.
"The Art of Revision" (Univ. of Arizona)
This resource provides a wealth of information and suggestions for both students and teachers. There is a list of suggested exercises that teachers might use in class, along with a revision checklist that is useful for teachers and students alike.
"Script for Workshop on Revision" (Vanderbilt University)
Vanderbilt's guide for leading a 50-minute revision workshop can serve as a model for teachers who wish to guide students through the revision process during classtime.
"Revising Your Paper" (Univ. of Washington)
This detailed handout was designed for students who are beginning the revision process. It discusses different approaches and methods for revision, and also includes a detailed list of things students should look for while they revise.
"Revising Drafts" (UNC Writing Center)
This resource is designed for students and suggests things to look for during the revision process. It provides steps for the process and has a FAQ for students who have questions about why it is important to revise.
Conferencing with Writing Tutors and Instructors
No writer is so good that he or she can't benefit from meeting with instructors or peer tutors. These resources from university writing, learning, and communication centers provide suggestions for how to get the most out of these one-on-one meetings.
"Getting Feedback" (UNC Writing Center)
This very helpful resource talks about how to ask for feedback during the entire writing process. It contains possible questions that students might ask when developing an outline, during the revision process, and after the final draft has been graded.
"Prepare for Your Tutoring Session" (Otis College of Art and Design)
This guide from a university's student learning center contains a lot of helpful tips for getting the most out of working with a writing tutor.
"The Importance of Asking Your Professor" (Univ. of Waterloo)
This article from the university's Writing and Communication Centre's blog contains some suggestions for how and when to get help from professors and Teaching Assistants.
Once you've revised your first draft, you're well on your way to handing in a polished paper. These resources—each of them produced by writing professionals at colleges and universities—outline the steps required in order to produce a final draft. You'll find proofreading tips and checklists in text and video form.
"Developing a Final Draft of a Research Paper" (Univ. of Minnesota)
While this resource contains suggestions for revision, it also features a couple of helpful checklists for the last stages of completing a final draft.
Basic Final Draft Tips and Checklist (Univ. of Maryland-University College)
This short and accessible resource, part of UMUC's very thorough online guide to writing and research, contains a very basic checklist for students who are getting ready to turn in their final drafts.
Final Draft Checklist (Everett C.C.)
This is another accessible final draft checklist, appropriate for both high school and college students. It suggests reading your essay aloud at least once.
"How to Proofread Your Final Draft" (YouTube)
This video (approximately 5 minutes), produced by Eastern Washington University, gives students tips on proofreading final drafts.
"Proofreading Tips" (Georgia Southern-Armstrong)
This guide will help students learn how to spot common errors in their papers. It suggests focusing on content and editing for grammar and mechanics.
This final set of resources is intended specifically for high school and college instructors. It provides links to unit plans and classroom exercises that can help improve students' research and writing skills. You'll find resources that give an overview of the process, along with activities that focus on how to begin and how to carry out research.
"Research Paper Complete Resources Pack" (Teachers Pay Teachers)
This packet of assignments, rubrics, and other resources is designed for high school students. The resources in this packet are aligned to Common Core standards.
"Research Paper—Complete Unit" (Teachers Pay Teachers)
This packet of assignments, notes, PowerPoints, and other resources has a 4/4 rating with over 700 ratings. It is designed for high school teachers, but might also be useful to college instructors who work with freshmen.
"Teaching Students to Write Good Papers" (Yale)
This resource from Yale's Center for Teaching and Learning is designed for college instructors, and it includes links to appropriate activities and exercises.
"Research Paper Writing: An Overview" (CUNY Brooklyn)
CUNY Brooklyn offers this complete lesson plan for introducing students to research papers. It includes an accompanying set of PowerPoint slides.
"Lesson Plan: How to Begin Writing a Research Paper" (San Jose State Univ.)
This lesson plan is designed for students in the health sciences, so teachers will have to modify it for their own needs. It includes a breakdown of the brainstorming, topic selection, and research question process.
"Quantitative Techniques for Social Science Research" (Univ. of Pittsburgh)
This is a set of PowerPoint slides that can be used to introduce students to a variety of quantitative methods used in the social sciences.
- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 1913 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 40,305 quotes across 1913 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
Need something? Request a new guide .
How can we improve? Share feedback .
LitCharts is hiring!

Reference management. Clean and simple.
Types of research papers
Analytical research paper
Argumentative or persuasive paper, definition paper, compare and contrast paper, cause and effect paper, interpretative paper, experimental research paper, survey research paper, frequently asked questions about the different types of research papers, related articles.
There are multiple different types of research papers. It is important to know which type of research paper is required for your assignment, as each type of research paper requires different preparation. Below is a list of the most common types of research papers.
➡️ Read more: What is a research paper?
In an analytical research paper you:
- pose a question
- collect relevant data from other researchers
- analyze their different viewpoints
You focus on the findings and conclusions of other researchers and then make a personal conclusion about the topic. It is important to stay neutral and not show your own negative or positive position on the matter.
The argumentative paper presents two sides of a controversial issue in one paper. It is aimed at getting the reader on the side of your point of view.
You should include and cite findings and arguments of different researchers on both sides of the issue, but then favor one side over the other and try to persuade the reader of your side. Your arguments should not be too emotional though, they still need to be supported with logical facts and statistical data.
Tip: Avoid expressing too much emotion in a persuasive paper.
The definition paper solely describes facts or objective arguments without using any personal emotion or opinion of the author. Its only purpose is to provide information. You should include facts from a variety of sources, but leave those facts unanalyzed.
Compare and contrast papers are used to analyze the difference between two:
Make sure to sufficiently describe both sides in the paper, and then move on to comparing and contrasting both thesis and supporting one.
Cause and effect papers are usually the first types of research papers that high school and college students write. They trace probable or expected results from a specific action and answer the main questions "Why?" and "What?", which reflect effects and causes.
In business and education fields, cause and effect papers will help trace a range of results that could arise from a particular action or situation.
An interpretative paper requires you to use knowledge that you have gained from a particular case study, for example a legal situation in law studies. You need to write the paper based on an established theoretical framework and use valid supporting data to back up your statement and conclusion.
This type of research paper basically describes a particular experiment in detail. It is common in fields like:
Experiments are aimed to explain a certain outcome or phenomenon with certain actions. You need to describe your experiment with supporting data and then analyze it sufficiently.
This research paper demands the conduction of a survey that includes asking questions to respondents. The conductor of the survey then collects all the information from the survey and analyzes it to present it in the research paper.
➡️ Ready to start your research paper? Take a look at our guide on how to start a research paper .
In an analytical research paper, you pose a question and then collect relevant data from other researchers to analyze their different viewpoints. You focus on the findings and conclusions of other researchers and then make a personal conclusion about the topic.
The definition paper solely describes facts or objective arguments without using any personal emotion or opinion of the author. Its only purpose is to provide information.
Cause and effect papers are usually the first types of research papers that high school and college students are confronted with. The answer questions like "Why?" and "What?", which reflect effects and causes. In business and education fields, cause and effect papers will help trace a range of results that could arise from a particular action or situation.
This type of research paper describes a particular experiment in detail. It is common in fields like biology, chemistry or physics. Experiments are aimed to explain a certain outcome or phenomenon with certain actions.

- Search This Site All UCSD Sites Faculty/Staff Search Term
- Contact & Directions
- Climate Statement
- Cognitive Behavioral Neuroscience
- Cognitive Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Adjunct Faculty
- Non-Senate Instructors
- Researchers
- Psychology Grads
- Affiliated Grads
- New and Prospective Students
- Honors Program
- Experiential Learning
- Programs & Events
- Psi Chi / Psychology Club
- Prospective PhD Students
- Current PhD Students
- Area Brown Bags
- Colloquium Series
- Anderson Distinguished Lecture Series
- Speaker Videos
- Undergraduate Program
- Academic and Writing Resources
Writing Research Papers
- Research Paper Structure
Whether you are writing a B.S. Degree Research Paper or completing a research report for a Psychology course, it is highly likely that you will need to organize your research paper in accordance with American Psychological Association (APA) guidelines. Here we discuss the structure of research papers according to APA style.
Major Sections of a Research Paper in APA Style
A complete research paper in APA style that is reporting on experimental research will typically contain a Title page, Abstract, Introduction, Methods, Results, Discussion, and References sections. 1 Many will also contain Figures and Tables and some will have an Appendix or Appendices. These sections are detailed as follows (for a more in-depth guide, please refer to " How to Write a Research Paper in APA Style ”, a comprehensive guide developed by Prof. Emma Geller). 2
What is this paper called and who wrote it? – the first page of the paper; this includes the name of the paper, a “running head”, authors, and institutional affiliation of the authors. The institutional affiliation is usually listed in an Author Note that is placed towards the bottom of the title page. In some cases, the Author Note also contains an acknowledgment of any funding support and of any individuals that assisted with the research project.
One-paragraph summary of the entire study – typically no more than 250 words in length (and in many cases it is well shorter than that), the Abstract provides an overview of the study.
Introduction
What is the topic and why is it worth studying? – the first major section of text in the paper, the Introduction commonly describes the topic under investigation, summarizes or discusses relevant prior research (for related details, please see the Writing Literature Reviews section of this website), identifies unresolved issues that the current research will address, and provides an overview of the research that is to be described in greater detail in the sections to follow.
What did you do? – a section which details how the research was performed. It typically features a description of the participants/subjects that were involved, the study design, the materials that were used, and the study procedure. If there were multiple experiments, then each experiment may require a separate Methods section. A rule of thumb is that the Methods section should be sufficiently detailed for another researcher to duplicate your research.
What did you find? – a section which describes the data that was collected and the results of any statistical tests that were performed. It may also be prefaced by a description of the analysis procedure that was used. If there were multiple experiments, then each experiment may require a separate Results section.
What is the significance of your results? – the final major section of text in the paper. The Discussion commonly features a summary of the results that were obtained in the study, describes how those results address the topic under investigation and/or the issues that the research was designed to address, and may expand upon the implications of those findings. Limitations and directions for future research are also commonly addressed.
List of articles and any books cited – an alphabetized list of the sources that are cited in the paper (by last name of the first author of each source). Each reference should follow specific APA guidelines regarding author names, dates, article titles, journal titles, journal volume numbers, page numbers, book publishers, publisher locations, websites, and so on (for more information, please see the Citing References in APA Style page of this website).
Tables and Figures
Graphs and data (optional in some cases) – depending on the type of research being performed, there may be Tables and/or Figures (however, in some cases, there may be neither). In APA style, each Table and each Figure is placed on a separate page and all Tables and Figures are included after the References. Tables are included first, followed by Figures. However, for some journals and undergraduate research papers (such as the B.S. Research Paper or Honors Thesis), Tables and Figures may be embedded in the text (depending on the instructor’s or editor’s policies; for more details, see "Deviations from APA Style" below).
Supplementary information (optional) – in some cases, additional information that is not critical to understanding the research paper, such as a list of experiment stimuli, details of a secondary analysis, or programming code, is provided. This is often placed in an Appendix.
Variations of Research Papers in APA Style
Although the major sections described above are common to most research papers written in APA style, there are variations on that pattern. These variations include:
- Literature reviews – when a paper is reviewing prior published research and not presenting new empirical research itself (such as in a review article, and particularly a qualitative review), then the authors may forgo any Methods and Results sections. Instead, there is a different structure such as an Introduction section followed by sections for each of the different aspects of the body of research being reviewed, and then perhaps a Discussion section.
- Multi-experiment papers – when there are multiple experiments, it is common to follow the Introduction with an Experiment 1 section, itself containing Methods, Results, and Discussion subsections. Then there is an Experiment 2 section with a similar structure, an Experiment 3 section with a similar structure, and so on until all experiments are covered. Towards the end of the paper there is a General Discussion section followed by References. Additionally, in multi-experiment papers, it is common for the Results and Discussion subsections for individual experiments to be combined into single “Results and Discussion” sections.
Departures from APA Style
In some cases, official APA style might not be followed (however, be sure to check with your editor, instructor, or other sources before deviating from standards of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association). Such deviations may include:
- Placement of Tables and Figures – in some cases, to make reading through the paper easier, Tables and/or Figures are embedded in the text (for example, having a bar graph placed in the relevant Results section). The embedding of Tables and/or Figures in the text is one of the most common deviations from APA style (and is commonly allowed in B.S. Degree Research Papers and Honors Theses; however you should check with your instructor, supervisor, or editor first).
- Incomplete research – sometimes a B.S. Degree Research Paper in this department is written about research that is currently being planned or is in progress. In those circumstances, sometimes only an Introduction and Methods section, followed by References, is included (that is, in cases where the research itself has not formally begun). In other cases, preliminary results are presented and noted as such in the Results section (such as in cases where the study is underway but not complete), and the Discussion section includes caveats about the in-progress nature of the research. Again, you should check with your instructor, supervisor, or editor first.
- Class assignments – in some classes in this department, an assignment must be written in APA style but is not exactly a traditional research paper (for instance, a student asked to write about an article that they read, and to write that report in APA style). In that case, the structure of the paper might approximate the typical sections of a research paper in APA style, but not entirely. You should check with your instructor for further guidelines.
Workshops and Downloadable Resources
- For in-person discussion of the process of writing research papers, please consider attending this department’s “Writing Research Papers” workshop (for dates and times, please check the undergraduate workshops calendar).
Downloadable Resources
- How to Write APA Style Research Papers (a comprehensive guide) [ PDF ]
- Tips for Writing APA Style Research Papers (a brief summary) [ PDF ]
- Example APA Style Research Paper (for B.S. Degree – empirical research) [ PDF ]
- Example APA Style Research Paper (for B.S. Degree – literature review) [ PDF ]
Further Resources
How-To Videos
- Writing Research Paper Videos
APA Journal Article Reporting Guidelines
- Appelbaum, M., Cooper, H., Kline, R. B., Mayo-Wilson, E., Nezu, A. M., & Rao, S. M. (2018). Journal article reporting standards for quantitative research in psychology: The APA Publications and Communications Board task force report . American Psychologist , 73 (1), 3.
- Levitt, H. M., Bamberg, M., Creswell, J. W., Frost, D. M., Josselson, R., & Suárez-Orozco, C. (2018). Journal article reporting standards for qualitative primary, qualitative meta-analytic, and mixed methods research in psychology: The APA Publications and Communications Board task force report . American Psychologist , 73 (1), 26.
External Resources
- Formatting APA Style Papers in Microsoft Word
- How to Write an APA Style Research Paper from Hamilton University
- WikiHow Guide to Writing APA Research Papers
- Sample APA Formatted Paper with Comments
- Sample APA Formatted Paper
- Tips for Writing a Paper in APA Style
1 VandenBos, G. R. (Ed). (2010). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (6th ed.) (pp. 41-60). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
2 geller, e. (2018). how to write an apa-style research report . [instructional materials]. , prepared by s. c. pan for ucsd psychology.
Back to top
- Formatting Research Papers
- Using Databases and Finding References
- What Types of References Are Appropriate?
- Evaluating References and Taking Notes
- Citing References
- Writing a Literature Review
- Writing Process and Revising
- Improving Scientific Writing
- Academic Integrity and Avoiding Plagiarism
- Writing Research Papers Videos

How to Write a Research Paper: Parts of the Paper
- Choosing Your Topic
- Citation & Style Guides This link opens in a new window
- Critical Thinking
- Evaluating Information
- Parts of the Paper
- Writing Tips from UNC-Chapel Hill
- Librarian Contact
Parts of the Research Paper Papers should have a beginning, a middle, and an end. Your introductory paragraph should grab the reader's attention, state your main idea, and indicate how you will support it. The body of the paper should expand on what you have stated in the introduction. Finally, the conclusion restates the paper's thesis and should explain what you have learned, giving a wrap up of your main ideas.
1. The Title The title should be specific and indicate the theme of the research and what ideas it addresses. Use keywords that help explain your paper's topic to the reader. Try to avoid abbreviations and jargon. Think about keywords that people would use to search for your paper and include them in your title.
2. The Abstract The abstract is used by readers to get a quick overview of your paper. Typically, they are about 200 words in length (120 words minimum to 250 words maximum). The abstract should introduce the topic and thesis, and should provide a general statement about what you have found in your research. The abstract allows you to mention each major aspect of your topic and helps readers decide whether they want to read the rest of the paper. Because it is a summary of the entire research paper, it is often written last.
3. The Introduction The introduction should be designed to attract the reader's attention and explain the focus of the research. You will introduce your overview of the topic, your main points of information, and why this subject is important. You can introduce the current understanding and background information about the topic. Toward the end of the introduction, you add your thesis statement, and explain how you will provide information to support your research questions. This provides the purpose and focus for the rest of the paper.
4. Thesis Statement Most papers will have a thesis statement or main idea and supporting facts/ideas/arguments. State your main idea (something of interest or something to be proven or argued for or against) as your thesis statement, and then provide your supporting facts and arguments. A thesis statement is a declarative sentence that asserts the position a paper will be taking. It also points toward the paper's development. This statement should be both specific and arguable. Generally, the thesis statement will be placed at the end of the first paragraph of your paper. The remainder of your paper will support this thesis.
Students often learn to write a thesis as a first step in the writing process, but often, after research, a writer's viewpoint may change. Therefore a thesis statement may be one of the final steps in writing.
Examples of Thesis Statements from Purdue OWL
5. The Literature Review The purpose of the literature review is to describe past important research and how it specifically relates to the research thesis. It should be a synthesis of the previous literature and the new idea being researched. The review should examine the major theories related to the topic to date and their contributors. It should include all relevant findings from credible sources, such as academic books and peer-reviewed journal articles. You will want to:
- Explain how the literature helps the researcher understand the topic.
- Try to show connections and any disparities between the literature.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
More about writing a literature review. . .
6. The Discussion The purpose of the discussion is to interpret and describe what you have learned from your research. Make the reader understand why your topic is important. The discussion should always demonstrate what you have learned from your readings (and viewings) and how that learning has made the topic evolve, especially from the short description of main points in the introduction.Explain any new understanding or insights you have had after reading your articles and/or books. Paragraphs should use transitioning sentences to develop how one paragraph idea leads to the next. The discussion will always connect to the introduction, your thesis statement, and the literature you reviewed, but it does not simply repeat or rearrange the introduction. You want to:
- Demonstrate critical thinking, not just reporting back facts that you gathered.
- If possible, tell how the topic has evolved over the past and give it's implications for the future.
- Fully explain your main ideas with supporting information.
- Explain why your thesis is correct giving arguments to counter points.
7. The Conclusion A concluding paragraph is a brief summary of your main ideas and restates the paper's main thesis, giving the reader the sense that the stated goal of the paper has been accomplished. What have you learned by doing this research that you didn't know before? What conclusions have you drawn? You may also want to suggest further areas of study, improvement of research possibilities, etc. to demonstrate your critical thinking regarding your research.
- << Previous: Evaluating Information
- Next: Research >>
- Last Updated: Feb 13, 2024 8:35 AM
- URL: https://libguides.ucc.edu/research_paper
- U.S. Locations
- UMGC Europe
- Learn Online
- Find Answers
- 855-655-8682
- Current Students
Online Guide to Writing and Research
The research process, explore more of umgc.
- Online Guide to Writing
Structuring the Research Paper
Formal research structure.
These are the primary purposes for formal research:
enter the discourse, or conversation, of other writers and scholars in your field
learn how others in your field use primary and secondary resources
find and understand raw data and information

For the formal academic research assignment, consider an organizational pattern typically used for primary academic research. The pattern includes the following: introduction, methods, results, discussion, and conclusions/recommendations.
Usually, research papers flow from the general to the specific and back to the general in their organization. The introduction uses a general-to-specific movement in its organization, establishing the thesis and setting the context for the conversation. The methods and results sections are more detailed and specific, providing support for the generalizations made in the introduction. The discussion section moves toward an increasingly more general discussion of the subject, leading to the conclusions and recommendations, which then generalize the conversation again.
Sections of a Formal Structure
The introduction section.
Many students will find that writing a structured introduction gets them started and gives them the focus needed to significantly improve their entire paper.
Introductions usually have three parts:
presentation of the problem statement, the topic, or the research inquiry
purpose and focus of your paper
summary or overview of the writer’s position or arguments
In the first part of the introduction—the presentation of the problem or the research inquiry—state the problem or express it so that the question is implied. Then, sketch the background on the problem and review the literature on it to give your readers a context that shows them how your research inquiry fits into the conversation currently ongoing in your subject area.
In the second part of the introduction, state your purpose and focus. Here, you may even present your actual thesis. Sometimes your purpose statement can take the place of the thesis by letting your reader know your intentions.
The third part of the introduction, the summary or overview of the paper, briefly leads readers through the discussion, forecasting the main ideas and giving readers a blueprint for the paper.
The following example provides a blueprint for a well-organized introduction.
Example of an Introduction
Entrepreneurial Marketing: The Critical Difference
In an article in the Harvard Business Review, John A. Welsh and Jerry F. White remind us that “a small business is not a little big business.” An entrepreneur is not a multinational conglomerate but a profit-seeking individual. To survive, he must have a different outlook and must apply different principles to his endeavors than does the president of a large or even medium-sized corporation. Not only does the scale of small and big businesses differ, but small businesses also suffer from what the Harvard Business Review article calls “resource poverty.” This is a problem and opportunity that requires an entirely different approach to marketing. Where large ad budgets are not necessary or feasible, where expensive ad production squanders limited capital, where every marketing dollar must do the work of two dollars, if not five dollars or even ten, where a person’s company, capital, and material well-being are all on the line—that is, where guerrilla marketing can save the day and secure the bottom line (Levinson, 1984, p. 9).
By reviewing the introductions to research articles in the discipline in which you are writing your research paper, you can get an idea of what is considered the norm for that discipline. Study several of these before you begin your paper so that you know what may be expected. If you are unsure of the kind of introduction your paper needs, ask your professor for more information. The introduction is normally written in present tense.
THE METHODS SECTION
The methods section of your research paper should describe in detail what methodology and special materials if any, you used to think through or perform your research. You should include any materials you used or designed for yourself, such as questionnaires or interview questions, to generate data or information for your research paper. You want to include any methodologies that are specific to your particular field of study, such as lab procedures for a lab experiment or data-gathering instruments for field research. The methods section is usually written in the past tense.
THE RESULTS SECTION
How you present the results of your research depends on what kind of research you did, your subject matter, and your readers’ expectations.
Quantitative information —data that can be measured—can be presented systematically and economically in tables, charts, and graphs. Quantitative information includes quantities and comparisons of sets of data.
Qualitative information , which includes brief descriptions, explanations, or instructions, can also be presented in prose tables. This kind of descriptive or explanatory information, however, is often presented in essay-like prose or even lists.
There are specific conventions for creating tables, charts, and graphs and organizing the information they contain. In general, you should use them only when you are sure they will enlighten your readers rather than confuse them. In the accompanying explanation and discussion, always refer to the graphic by number and explain specifically what you are referring to; you can also provide a caption for the graphic. The rule of thumb for presenting a graphic is first to introduce it by name, show it, and then interpret it. The results section is usually written in the past tense.
THE DISCUSSION SECTION
Your discussion section should generalize what you have learned from your research. One way to generalize is to explain the consequences or meaning of your results and then make your points that support and refer back to the statements you made in your introduction. Your discussion should be organized so that it relates directly to your thesis. You want to avoid introducing new ideas here or discussing tangential issues not directly related to the exploration and discovery of your thesis. The discussion section, along with the introduction, is usually written in the present tense.
THE CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS SECTION
Your conclusion ties your research to your thesis, binding together all the main ideas in your thinking and writing. By presenting the logical outcome of your research and thinking, your conclusion answers your research inquiry for your reader. Your conclusions should relate directly to the ideas presented in your introduction section and should not present any new ideas.
You may be asked to present your recommendations separately in your research assignment. If so, you will want to add some elements to your conclusion section. For example, you may be asked to recommend a course of action, make a prediction, propose a solution to a problem, offer a judgment, or speculate on the implications and consequences of your ideas. The conclusions and recommendations section is usually written in the present tense.
Key Takeaways
- For the formal academic research assignment, consider an organizational pattern typically used for primary academic research.
- The pattern includes the following: introduction, methods, results, discussion, and conclusions/recommendations.
Mailing Address: 3501 University Blvd. East, Adelphi, MD 20783 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License . © 2022 UMGC. All links to external sites were verified at the time of publication. UMGC is not responsible for the validity or integrity of information located at external sites.
Table of Contents: Online Guide to Writing
Chapter 1: College Writing
How Does College Writing Differ from Workplace Writing?
What Is College Writing?
Why So Much Emphasis on Writing?
Chapter 2: The Writing Process
Doing Exploratory Research
Getting from Notes to Your Draft
Introduction
Prewriting - Techniques to Get Started - Mining Your Intuition
Prewriting: Targeting Your Audience
Prewriting: Techniques to Get Started
Prewriting: Understanding Your Assignment
Rewriting: Being Your Own Critic
Rewriting: Creating a Revision Strategy
Rewriting: Getting Feedback
Rewriting: The Final Draft
Techniques to Get Started - Outlining
Techniques to Get Started - Using Systematic Techniques
Thesis Statement and Controlling Idea
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Freewriting
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Summarizing Your Ideas
Writing: Outlining What You Will Write
Chapter 3: Thinking Strategies
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone: Style Through Vocabulary and Diction
Critical Strategies and Writing
Critical Strategies and Writing: Analysis
Critical Strategies and Writing: Evaluation
Critical Strategies and Writing: Persuasion
Critical Strategies and Writing: Synthesis
Developing a Paper Using Strategies
Kinds of Assignments You Will Write
Patterns for Presenting Information
Patterns for Presenting Information: Critiques
Patterns for Presenting Information: Discussing Raw Data
Patterns for Presenting Information: General-to-Specific Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Problem-Cause-Solution Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Specific-to-General Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Summaries and Abstracts
Supporting with Research and Examples
Writing Essay Examinations
Writing Essay Examinations: Make Your Answer Relevant and Complete
Writing Essay Examinations: Organize Thinking Before Writing
Writing Essay Examinations: Read and Understand the Question
Chapter 4: The Research Process
Planning and Writing a Research Paper
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Ask a Research Question
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Cite Sources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Collect Evidence
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Decide Your Point of View, or Role, for Your Research
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Draw Conclusions
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Find a Topic and Get an Overview
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Manage Your Resources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Outline
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Survey the Literature
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Work Your Sources into Your Research Writing
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Human Resources
Research Resources: What Are Research Resources?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Electronic Resources
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Print Resources
Structuring the Research Paper: Formal Research Structure
Structuring the Research Paper: Informal Research Structure
The Nature of Research
The Research Assignment: How Should Research Sources Be Evaluated?
The Research Assignment: When Is Research Needed?
The Research Assignment: Why Perform Research?
Chapter 5: Academic Integrity
Academic Integrity
Giving Credit to Sources
Giving Credit to Sources: Copyright Laws
Giving Credit to Sources: Documentation
Giving Credit to Sources: Style Guides
Integrating Sources
Practicing Academic Integrity
Practicing Academic Integrity: Keeping Accurate Records
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Paraphrasing Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Quoting Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Summarizing Your Sources
Types of Documentation
Types of Documentation: Bibliographies and Source Lists
Types of Documentation: Citing World Wide Web Sources
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - APA Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - CSE/CBE Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - Chicago Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - MLA Style
Types of Documentation: Note Citations
Chapter 6: Using Library Resources
Finding Library Resources
Chapter 7: Assessing Your Writing
How Is Writing Graded?
How Is Writing Graded?: A General Assessment Tool
The Draft Stage
The Draft Stage: The First Draft
The Draft Stage: The Revision Process and the Final Draft
The Draft Stage: Using Feedback
The Research Stage
Using Assessment to Improve Your Writing
Chapter 8: Other Frequently Assigned Papers
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Article and Book Reviews
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Reaction Papers
Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Adapting the Argument Structure
Writing Arguments: Purposes of Argument
Writing Arguments: References to Consult for Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Anticipate Active Opposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Determine Your Organization
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Develop Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Introduce Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - State Your Thesis or Proposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Write Your Conclusion
Writing Arguments: Types of Argument
Appendix A: Books to Help Improve Your Writing
Dictionaries
General Style Manuals
Researching on the Internet
Special Style Manuals
Writing Handbooks
Appendix B: Collaborative Writing and Peer Reviewing
Collaborative Writing: Assignments to Accompany the Group Project
Collaborative Writing: Informal Progress Report
Collaborative Writing: Issues to Resolve
Collaborative Writing: Methodology
Collaborative Writing: Peer Evaluation
Collaborative Writing: Tasks of Collaborative Writing Group Members
Collaborative Writing: Writing Plan
General Introduction
Peer Reviewing
Appendix C: Developing an Improvement Plan
Working with Your Instructor’s Comments and Grades
Appendix D: Writing Plan and Project Schedule
Devising a Writing Project Plan and Schedule
Reviewing Your Plan with Others
By using our website you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about how we use cookies by reading our Privacy Policy .
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Saudi J Anaesth
- v.13(Suppl 1); 2019 Apr
Writing the title and abstract for a research paper: Being concise, precise, and meticulous is the key
Milind s. tullu.
Department of Pediatrics, Seth G.S. Medical College and KEM Hospital, Parel, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
This article deals with formulating a suitable title and an appropriate abstract for an original research paper. The “title” and the “abstract” are the “initial impressions” of a research article, and hence they need to be drafted correctly, accurately, carefully, and meticulously. Often both of these are drafted after the full manuscript is ready. Most readers read only the title and the abstract of a research paper and very few will go on to read the full paper. The title and the abstract are the most important parts of a research paper and should be pleasant to read. The “title” should be descriptive, direct, accurate, appropriate, interesting, concise, precise, unique, and should not be misleading. The “abstract” needs to be simple, specific, clear, unbiased, honest, concise, precise, stand-alone, complete, scholarly, (preferably) structured, and should not be misrepresentative. The abstract should be consistent with the main text of the paper, especially after a revision is made to the paper and should include the key message prominently. It is very important to include the most important words and terms (the “keywords”) in the title and the abstract for appropriate indexing purpose and for retrieval from the search engines and scientific databases. Such keywords should be listed after the abstract. One must adhere to the instructions laid down by the target journal with regard to the style and number of words permitted for the title and the abstract.
Introduction
This article deals with drafting a suitable “title” and an appropriate “abstract” for an original research paper. Because the “title” and the “abstract” are the “initial impressions” or the “face” of a research article, they need to be drafted correctly, accurately, carefully, meticulously, and consume time and energy.[ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 ] Often, these are drafted after the complete manuscript draft is ready.[ 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 9 , 10 , 11 ] Most readers will read only the title and the abstract of a published research paper, and very few “interested ones” (especially, if the paper is of use to them) will go on to read the full paper.[ 1 , 2 ] One must remember to adhere to the instructions laid down by the “target journal” (the journal for which the author is writing) regarding the style and number of words permitted for the title and the abstract.[ 2 , 4 , 5 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 12 ] Both the title and the abstract are the most important parts of a research paper – for editors (to decide whether to process the paper for further review), for reviewers (to get an initial impression of the paper), and for the readers (as these may be the only parts of the paper available freely and hence, read widely).[ 4 , 8 , 12 ] It may be worth for the novice author to browse through titles and abstracts of several prominent journals (and their target journal as well) to learn more about the wording and styles of the titles and abstracts, as well as the aims and scope of the particular journal.[ 5 , 7 , 9 , 13 ]
The details of the title are discussed under the subheadings of importance, types, drafting, and checklist.
Importance of the title
When a reader browses through the table of contents of a journal issue (hard copy or on website), the title is the “ first detail” or “face” of the paper that is read.[ 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 13 ] Hence, it needs to be simple, direct, accurate, appropriate, specific, functional, interesting, attractive/appealing, concise/brief, precise/focused, unambiguous, memorable, captivating, informative (enough to encourage the reader to read further), unique, catchy, and it should not be misleading.[ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 9 , 12 ] It should have “just enough details” to arouse the interest and curiosity of the reader so that the reader then goes ahead with studying the abstract and then (if still interested) the full paper.[ 1 , 2 , 4 , 13 ] Journal websites, electronic databases, and search engines use the words in the title and abstract (the “keywords”) to retrieve a particular paper during a search; hence, the importance of these words in accessing the paper by the readers has been emphasized.[ 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 12 , 14 ] Such important words (or keywords) should be arranged in appropriate order of importance as per the context of the paper and should be placed at the beginning of the title (rather than the later part of the title, as some search engines like Google may just display only the first six to seven words of the title).[ 3 , 5 , 12 ] Whimsical, amusing, or clever titles, though initially appealing, may be missed or misread by the busy reader and very short titles may miss the essential scientific words (the “keywords”) used by the indexing agencies to catch and categorize the paper.[ 1 , 3 , 4 , 9 ] Also, amusing or hilarious titles may be taken less seriously by the readers and may be cited less often.[ 4 , 15 ] An excessively long or complicated title may put off the readers.[ 3 , 9 ] It may be a good idea to draft the title after the main body of the text and the abstract are drafted.[ 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]
Types of titles
Titles can be descriptive, declarative, or interrogative. They can also be classified as nominal, compound, or full-sentence titles.
Descriptive or neutral title
This has the essential elements of the research theme, that is, the patients/subjects, design, interventions, comparisons/control, and outcome, but does not reveal the main result or the conclusion.[ 3 , 4 , 12 , 16 ] Such a title allows the reader to interpret the findings of the research paper in an impartial manner and with an open mind.[ 3 ] These titles also give complete information about the contents of the article, have several keywords (thus increasing the visibility of the article in search engines), and have increased chances of being read and (then) being cited as well.[ 4 ] Hence, such descriptive titles giving a glimpse of the paper are generally preferred.[ 4 , 16 ]
Declarative title
This title states the main finding of the study in the title itself; it reduces the curiosity of the reader, may point toward a bias on the part of the author, and hence is best avoided.[ 3 , 4 , 12 , 16 ]
Interrogative title
This is the one which has a query or the research question in the title.[ 3 , 4 , 16 ] Though a query in the title has the ability to sensationalize the topic, and has more downloads (but less citations), it can be distracting to the reader and is again best avoided for a research article (but can, at times, be used for a review article).[ 3 , 6 , 16 , 17 ]
From a sentence construct point of view, titles may be nominal (capturing only the main theme of the study), compound (with subtitles to provide additional relevant information such as context, design, location/country, temporal aspect, sample size, importance, and a provocative or a literary; for example, see the title of this review), or full-sentence titles (which are longer and indicate an added degree of certainty of the results).[ 4 , 6 , 9 , 16 ] Any of these constructs may be used depending on the type of article, the key message, and the author's preference or judgement.[ 4 ]
Drafting a suitable title
A stepwise process can be followed to draft the appropriate title. The author should describe the paper in about three sentences, avoiding the results and ensuring that these sentences contain important scientific words/keywords that describe the main contents and subject of the paper.[ 1 , 4 , 6 , 12 ] Then the author should join the sentences to form a single sentence, shorten the length (by removing redundant words or adjectives or phrases), and finally edit the title (thus drafted) to make it more accurate, concise (about 10–15 words), and precise.[ 1 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 9 ] Some journals require that the study design be included in the title, and this may be placed (using a colon) after the primary title.[ 2 , 3 , 4 , 14 ] The title should try to incorporate the Patients, Interventions, Comparisons and Outcome (PICO).[ 3 ] The place of the study may be included in the title (if absolutely necessary), that is, if the patient characteristics (such as study population, socioeconomic conditions, or cultural practices) are expected to vary as per the country (or the place of the study) and have a bearing on the possible outcomes.[ 3 , 6 ] Lengthy titles can be boring and appear unfocused, whereas very short titles may not be representative of the contents of the article; hence, optimum length is required to ensure that the title explains the main theme and content of the manuscript.[ 4 , 5 , 9 ] Abbreviations (except the standard or commonly interpreted ones such as HIV, AIDS, DNA, RNA, CDC, FDA, ECG, and EEG) or acronyms should be avoided in the title, as a reader not familiar with them may skip such an article and nonstandard abbreviations may create problems in indexing the article.[ 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 9 , 12 ] Also, too much of technical jargon or chemical formulas in the title may confuse the readers and the article may be skipped by them.[ 4 , 9 ] Numerical values of various parameters (stating study period or sample size) should also be avoided in the titles (unless deemed extremely essential).[ 4 ] It may be worthwhile to take an opinion from a impartial colleague before finalizing the title.[ 4 , 5 , 6 ] Thus, multiple factors (which are, at times, a bit conflicting or contrasting) need to be considered while formulating a title, and hence this should not be done in a hurry.[ 4 , 6 ] Many journals ask the authors to draft a “short title” or “running head” or “running title” for printing in the header or footer of the printed paper.[ 3 , 12 ] This is an abridged version of the main title of up to 40–50 characters, may have standard abbreviations, and helps the reader to navigate through the paper.[ 3 , 12 , 14 ]
Checklist for a good title
Table 1 gives a checklist/useful tips for drafting a good title for a research paper.[ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 12 ] Table 2 presents some of the titles used by the author of this article in his earlier research papers, and the appropriateness of the titles has been commented upon. As an individual exercise, the reader may try to improvise upon the titles (further) after reading the corresponding abstract and full paper.
Checklist/useful tips for drafting a good title for a research paper
Some titles used by author of this article in his earlier publications and remark/comment on their appropriateness

The Abstract
The details of the abstract are discussed under the subheadings of importance, types, drafting, and checklist.
Importance of the abstract
The abstract is a summary or synopsis of the full research paper and also needs to have similar characteristics like the title. It needs to be simple, direct, specific, functional, clear, unbiased, honest, concise, precise, self-sufficient, complete, comprehensive, scholarly, balanced, and should not be misleading.[ 1 , 2 , 3 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 13 , 17 ] Writing an abstract is to extract and summarize (AB – absolutely, STR – straightforward, ACT – actual data presentation and interpretation).[ 17 ] The title and abstracts are the only sections of the research paper that are often freely available to the readers on the journal websites, search engines, and in many abstracting agencies/databases, whereas the full paper may attract a payment per view or a fee for downloading the pdf copy.[ 1 , 2 , 3 , 7 , 8 , 10 , 11 , 13 , 14 ] The abstract is an independent and stand-alone (that is, well understood without reading the full paper) section of the manuscript and is used by the editor to decide the fate of the article and to choose appropriate reviewers.[ 2 , 7 , 10 , 12 , 13 ] Even the reviewers are initially supplied only with the title and the abstract before they agree to review the full manuscript.[ 7 , 13 ] This is the second most commonly read part of the manuscript, and therefore it should reflect the contents of the main text of the paper accurately and thus act as a “real trailer” of the full article.[ 2 , 7 , 11 ] The readers will go through the full paper only if they find the abstract interesting and relevant to their practice; else they may skip the paper if the abstract is unimpressive.[ 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 13 ] The abstract needs to highlight the selling point of the manuscript and succeed in luring the reader to read the complete paper.[ 3 , 7 ] The title and the abstract should be constructed using keywords (key terms/important words) from all the sections of the main text.[ 12 ] Abstracts are also used for submitting research papers to a conference for consideration for presentation (as oral paper or poster).[ 9 , 13 , 17 ] Grammatical and typographic errors reflect poorly on the quality of the abstract, may indicate carelessness/casual attitude on part of the author, and hence should be avoided at all times.[ 9 ]
Types of abstracts
The abstracts can be structured or unstructured. They can also be classified as descriptive or informative abstracts.
Structured and unstructured abstracts
Structured abstracts are followed by most journals, are more informative, and include specific subheadings/subsections under which the abstract needs to be composed.[ 1 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 13 , 17 , 18 ] These subheadings usually include context/background, objectives, design, setting, participants, interventions, main outcome measures, results, and conclusions.[ 1 ] Some journals stick to the standard IMRAD format for the structure of the abstracts, and the subheadings would include Introduction/Background, Methods, Results, And (instead of Discussion) the Conclusion/s.[ 1 , 2 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 17 , 18 ] Structured abstracts are more elaborate, informative, easy to read, recall, and peer-review, and hence are preferred; however, they consume more space and can have same limitations as an unstructured abstract.[ 7 , 9 , 18 ] The structured abstracts are (possibly) better understood by the reviewers and readers. Anyway, the choice of the type of the abstract and the subheadings of a structured abstract depend on the particular journal style and is not left to the author's wish.[ 7 , 10 , 12 ] Separate subheadings may be necessary for reporting meta-analysis, educational research, quality improvement work, review, or case study.[ 1 ] Clinical trial abstracts need to include the essential items mentioned in the CONSORT (Consolidated Standards Of Reporting Trials) guidelines.[ 7 , 9 , 14 , 19 ] Similar guidelines exist for various other types of studies, including observational studies and for studies of diagnostic accuracy.[ 20 , 21 ] A useful resource for the above guidelines is available at www.equator-network.org (Enhancing the QUAlity and Transparency Of health Research). Unstructured (or non-structured) abstracts are free-flowing, do not have predefined subheadings, and are commonly used for papers that (usually) do not describe original research.[ 1 , 7 , 9 , 10 ]
The four-point structured abstract: This has the following elements which need to be properly balanced with regard to the content/matter under each subheading:[ 9 ]
Background and/or Objectives: This states why the work was undertaken and is usually written in just a couple of sentences.[ 3 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 12 , 13 ] The hypothesis/study question and the major objectives are also stated under this subheading.[ 3 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 12 , 13 ]
Methods: This subsection is the longest, states what was done, and gives essential details of the study design, setting, participants, blinding, sample size, sampling method, intervention/s, duration and follow-up, research instruments, main outcome measures, parameters evaluated, and how the outcomes were assessed or analyzed.[ 3 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 17 ]
Results/Observations/Findings: This subheading states what was found, is longer, is difficult to draft, and needs to mention important details including the number of study participants, results of analysis (of primary and secondary objectives), and include actual data (numbers, mean, median, standard deviation, “P” values, 95% confidence intervals, effect sizes, relative risks, odds ratio, etc.).[ 3 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 17 ]
Conclusions: The take-home message (the “so what” of the paper) and other significant/important findings should be stated here, considering the interpretation of the research question/hypothesis and results put together (without overinterpreting the findings) and may also include the author's views on the implications of the study.[ 3 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 17 ]
The eight-point structured abstract: This has the following eight subheadings – Objectives, Study Design, Study Setting, Participants/Patients, Methods/Intervention, Outcome Measures, Results, and Conclusions.[ 3 , 9 , 18 ] The instructions to authors given by the particular journal state whether they use the four- or eight-point abstract or variants thereof.[ 3 , 14 ]
Descriptive and Informative abstracts
Descriptive abstracts are short (75–150 words), only portray what the paper contains without providing any more details; the reader has to read the full paper to know about its contents and are rarely used for original research papers.[ 7 , 10 ] These are used for case reports, reviews, opinions, and so on.[ 7 , 10 ] Informative abstracts (which may be structured or unstructured as described above) give a complete detailed summary of the article contents and truly reflect the actual research done.[ 7 , 10 ]
Drafting a suitable abstract
It is important to religiously stick to the instructions to authors (format, word limit, font size/style, and subheadings) provided by the journal for which the abstract and the paper are being written.[ 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 13 ] Most journals allow 200–300 words for formulating the abstract and it is wise to restrict oneself to this word limit.[ 1 , 2 , 3 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 22 ] Though some authors prefer to draft the abstract initially, followed by the main text of the paper, it is recommended to draft the abstract in the end to maintain accuracy and conformity with the main text of the paper (thus maintaining an easy linkage/alignment with title, on one hand, and the introduction section of the main text, on the other hand).[ 2 , 7 , 9 , 10 , 11 ] The authors should check the subheadings (of the structured abstract) permitted by the target journal, use phrases rather than sentences to draft the content of the abstract, and avoid passive voice.[ 1 , 7 , 9 , 12 ] Next, the authors need to get rid of redundant words and edit the abstract (extensively) to the correct word count permitted (every word in the abstract “counts”!).[ 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 13 ] It is important to ensure that the key message, focus, and novelty of the paper are not compromised; the rationale of the study and the basis of the conclusions are clear; and that the abstract is consistent with the main text of the paper.[ 1 , 2 , 3 , 7 , 9 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 17 , 22 ] This is especially important while submitting a revision of the paper (modified after addressing the reviewer's comments), as the changes made in the main (revised) text of the paper need to be reflected in the (revised) abstract as well.[ 2 , 10 , 12 , 14 , 22 ] Abbreviations should be avoided in an abstract, unless they are conventionally accepted or standard; references, tables, or figures should not be cited in the abstract.[ 7 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 13 ] It may be worthwhile not to rush with the abstract and to get an opinion by an impartial colleague on the content of the abstract; and if possible, the full paper (an “informal” peer-review).[ 1 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 11 , 17 ] Appropriate “Keywords” (three to ten words or phrases) should follow the abstract and should be preferably chosen from the Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) list of the U.S. National Library of Medicine ( https://meshb.nlm.nih.gov/search ) and are used for indexing purposes.[ 2 , 3 , 11 , 12 ] These keywords need to be different from the words in the main title (the title words are automatically used for indexing the article) and can be variants of the terms/phrases used in the title, or words from the abstract and the main text.[ 3 , 12 ] The ICMJE (International Committee of Medical Journal Editors; http://www.icmje.org/ ) also recommends publishing the clinical trial registration number at the end of the abstract.[ 7 , 14 ]
Checklist for a good abstract
Table 3 gives a checklist/useful tips for formulating a good abstract for a research paper.[ 1 , 2 , 3 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 17 , 22 ]
Checklist/useful tips for formulating a good abstract for a research paper
Concluding Remarks
This review article has given a detailed account of the importance and types of titles and abstracts. It has also attempted to give useful hints for drafting an appropriate title and a complete abstract for a research paper. It is hoped that this review will help the authors in their career in medical writing.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgement
The author thanks Dr. Hemant Deshmukh - Dean, Seth G.S. Medical College & KEM Hospital, for granting permission to publish this manuscript.

- Master Your Homework
- Do My Homework
The Difference Between a Research Paper and Manuscript
The research paper and manuscript are two distinct forms of academic writing that have many similarities, but also some key differences. This article will explore the main points of distinction between a research paper and a manuscript by examining their purpose, format, content organization, structure and length. Additionally, this article will provide an overview of the major components that compose both papers in order to further clarify any potential confusion for readers regarding these two genres. Finally, implications for writers when choosing one type over another will be discussed in detail with specific reference to areas such as audience appeal and marketability.
I. Introduction
Ii. definition of a research paper, iii. definition of a manuscript, iv. comparison between research papers and manuscripts, v. types of manuscripts, vi. variations in publication requirements for different genres of research papers and manuscripts, vii. conclusion.
When embarking on a scholarly writing journey, it is important to understand the distinction between two types of publications: research paper and manuscript.
- Research Paper : A research paper typically follows an academic format for presenting evidence in support of an argument. It may include data from primary sources such as surveys or interviews conducted by the author themselves, or secondary sources such as books or articles which analyze existing findings. Research papers generally draw upon more than one source when constructing their arguments.
A manuscript , however, can be thought of as more creative than its counterpart. While still containing factual information based on rigorous research methods and thorough analysis, manuscripts often contain narrative elements that help bring stories to life through vivid descriptions and engaging characters. Manuscripts also tend to focus much less heavily on citing other works; rather they are used primarily for conveying ideas in a compelling manner while providing background detail necessary for readers’ understanding.
A Research Paper Research papers are extended scholarly works that explore a specific topic in depth. They generally require an extensive research process, which may involve interviews and surveys as well as traditional library sources such as books or journal articles. These papers typically include the following:
The goal is to present evidence-based conclusions on the selected issue or topic; this will help inform and educate readers about it.
Manuscript vs Research Paper . Manuscripts can be quite similar to research papers, but they focus more narrowly on presenting work created by the author (as opposed to what has already been published). They often emphasize creativity rather than scientific inquiry, though manuscripts can certainly include both components depending on their intended audience and purpose. Manuscripts also usually have less stringent formatting requirements compared to formal research papers – while there may still be elements such as titles pages, these are not always necessary if submitting them in creative writing forums or contests where different rules apply.
Understanding a Manuscript A manuscript is an unpublished work, typically by one or more authors and can be in any medium such as handwritten, typed on a computer or created digitally. It differs from the traditional research paper because it does not need to include source citations; however it should still contain original thought and analysis. While manuscripts may follow established conventions for their form (ie poetry has specific styles), they are also highly creative works meant to draw out emotion.
Distinguishing Characteristics of Manuscripts – A unique product of creativity – Usually involves some level of personal reflection & insight – May have special formatting requirements depending on genre/type – Can take many forms including: book chapters, essays, stories, plays & poems – Not peer reviewed like research papers
In the world of academia, research papers and manuscripts occupy vastly different roles. Though both are written pieces that display an author’s findings or ideas, there is a great disparity in their individual characteristics.
- Scope : Research papers typically cover large amounts of information on a given subject matter; they often take much longer to write than manuscripts. Manuscripts may be shorter but should still present relevant data needed to support any conclusions made by the author.
- Audience : Research papers usually target specialists within a certain field who have advanced knowledge about what constitutes quality work in their specific discipline. On the other hand, manuscripts focus more heavily on general readership and aim to make complex topics easier for non-experts to understand.
There are several distinct types of manuscripts that authors may submit to journals for publication. These include research papers, review articles, and short reports.
- Research Papers : The most common type of manuscript submitted is the research paper . This typically includes an introduction section that outlines the purpose or hypothesis of the experiment followed by a discussion on related work from other authors in this field. Research methods used to carry out experiments should be detailed including how data was collected and analyzed. Finally, results should be presented in graphs and tables with associated interpretations before moving onto a conclusion section.
- Review Articles : A review article , also known as survey paper or literature review provides readers with a comprehensive summary of all significant studies pertaining to particular areas within a given topic while discussing recent developments such as trends, patterns, controversies etc., Such papers aim at helping scientists keep up-to-date with advances in their field.
Research papers and manuscripts are two different types of written works used to convey information. They both require a high level of accuracy, but they differ in their structure and publication requirements.
- A research paper is an academic piece that focuses on the analysis or interpretation of data collected from relevant sources.
- It should include an abstract summarizing your study’s main points; introduction to the topic, thesis statement, body paragraphs with evidence-based claims supported by research; discussion section for drawing conclusions; endnotes or footnotes providing additional information about cited resources.
In summary, this paper has presented a comprehensive comparison between the two major forms of academic writing: research papers and manuscripts. It is clear that both formats have their advantages and disadvantages when it comes to effectively conveying scholarly work, yet they are very distinct from one another in terms of purpose and structure. While research papers focus on presenting findings or conclusions through an empirical approach, manuscripts provide authors with opportunities to explore theoretical questions and ideas through more creative means.
It is important for aspiring scholars to understand the differences between these two mediums before deciding which format best fits their project objectives. Each form requires different levels of time investment as well as unique challenges during composition. For those wishing to present new knowledge in an innovative way without being bound by strict guidelines may find greater success with manuscript submissions; however if providing quantitative data-driven evidence is desired then a research paper might be better suited.
- Research Paper : Focuses primarily on empirical investigation & reporting results
- Manuscript : Explores theoretical concepts & presents alternative views
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Write down your thoughts and shred them to relieve anger, researchers say
Writing negative reactions on paper and shredding it or scrunching and throwing in the bin eliminates angry feelings, study finds
Since time immemorial humans have tried to devise anger management techniques.
In ancient Rome, the Stoic philosopher Seneca believed “my anger is likely to do me more harm than your wrong” and offered avoidance tips in his AD45 work De Ira (On Anger).
More modern methods include a workout on the gym punchbag or exercise bike. But the humble paper shredder may be a more effective – and accessible – way to decompress, according to research.
A study in Japan has found that writing down your reaction to a negative incident on a piece of paper and then shredding it, or scrunching it into a ball and throwing it in the bin, gets rid of anger.
“We expected that our method would suppress anger to some extent,” said Nobuyuki Kawai, lead researcher of the study at Nagoya University. “However, we were amazed that anger was eliminated almost entirely.”
The study, published in Scientific Reports on Nature , builds on research on the association between the written word and anger reduction as well as studies showing how interactions with physical objects can control a person’s mood. For instance, those wanting revenge on an ex-partner may burn letters or destroy gifts.
Researchers believe the shredder results may be related to the phenomenon of “backward magical contagion”, which is the belief that actions taken on an object associated with a person can affect the individuals themselves. In this case, getting rid of the negative physical entity, the piece of paper, causes the original emotion to also disappear.
This is a reversal of “magical contagion” or “celebrity contagion” – the belief that the “essence” of an individual can be transferred through their physical possessions.
Fifty student participants were asked to write brief opinions about an important social problem, such as whether smoking in public should be outlawed. Evaluators then deliberately scored the papers low on intelligence, interest, friendliness, logic, and rationality. For good measure, evaluators added insulting comments such as: “I cannot believe an educated person would think like this. I hope this person learns something while at the university.”
The wound-up participants then wrote down their angry thoughts on the negative feedback on a piece of paper. One group was told to either roll up the paper and throw it in a bin or keep it in a file on their desk. A second group was told to shred the paper, or put it in a plastic box.
Anger levels of the individuals who discarded their paper in the bin or shredded it returned to their initial state, while those who retained a hard copy of the paper experienced only a small decrease in their overall anger.
Researchers concluded that “the meaning (interpretation) of disposal plays a critical role” in reducing anger.
“This technique could be applied in the moment by writing down the source of anger as if taking a memo and then throwing it away,” said Kawai.
Along with its practical benefits, this discovery may shed light on the origins of the Japanese cultural tradition known as hakidashisara ( hakidashi sara refers to a dish or plate) at the Hiyoshi shrine in Kiyosu, just outside Nagoya. Hakidashisara is an annual festival where people smash small discs representing things that make them angry. The study’s findings may explain the feeling of relief that participants report after leaving the festival, the paper concluded.

Fridge magnets can be cool aid to holiday memory recall, study finds

Want to skip that Christmas party? The host probably won’t mind, study shows

‘Succession syndrome’ prevalent among wealthy households, psychiatrists warn

Drugs and alcohol do not make you more creative, research finds

Why being rude to the waiter (or other staff) is the worst strategy

Authors of original dating profiles rated more attractive, research finds

I fear my children are overexposed to technology. Experts say I’m right to worry

I used to be ashamed of being a fangirl. Now I see how joyous and creative it was

Autistic scholar Temple Grandin: ‘The education system is screening out visual thinkers’
Human neurons transplanted into rats to help study brain disorders
Most viewed.
AI Index Report
Welcome to the seventh edition of the AI Index report. The 2024 Index is our most comprehensive to date and arrives at an important moment when AI’s influence on society has never been more pronounced. This year, we have broadened our scope to more extensively cover essential trends such as technical advancements in AI, public perceptions of the technology, and the geopolitical dynamics surrounding its development. Featuring more original data than ever before, this edition introduces new estimates on AI training costs, detailed analyses of the responsible AI landscape, and an entirely new chapter dedicated to AI’s impact on science and medicine.
Read the 2024 AI Index Report
The AI Index report tracks, collates, distills, and visualizes data related to artificial intelligence (AI). Our mission is to provide unbiased, rigorously vetted, broadly sourced data in order for policymakers, researchers, executives, journalists, and the general public to develop a more thorough and nuanced understanding of the complex field of AI.
The AI Index is recognized globally as one of the most credible and authoritative sources for data and insights on artificial intelligence. Previous editions have been cited in major newspapers, including the The New York Times, Bloomberg, and The Guardian, have amassed hundreds of academic citations, and been referenced by high-level policymakers in the United States, the United Kingdom, and the European Union, among other places. This year’s edition surpasses all previous ones in size, scale, and scope, reflecting the growing significance that AI is coming to hold in all of our lives.
Steering Committee Co-Directors

Ray Perrault
Steering committee members.

Erik Brynjolfsson

John Etchemendy

Katrina Ligett

Terah Lyons

James Manyika

Juan Carlos Niebles

Vanessa Parli

Yoav Shoham

Russell Wald
Staff members.

Loredana Fattorini

Nestor Maslej
Letter from the co-directors.
A decade ago, the best AI systems in the world were unable to classify objects in images at a human level. AI struggled with language comprehension and could not solve math problems. Today, AI systems routinely exceed human performance on standard benchmarks.
Progress accelerated in 2023. New state-of-the-art systems like GPT-4, Gemini, and Claude 3 are impressively multimodal: They can generate fluent text in dozens of languages, process audio, and even explain memes. As AI has improved, it has increasingly forced its way into our lives. Companies are racing to build AI-based products, and AI is increasingly being used by the general public. But current AI technology still has significant problems. It cannot reliably deal with facts, perform complex reasoning, or explain its conclusions.
AI faces two interrelated futures. First, technology continues to improve and is increasingly used, having major consequences for productivity and employment. It can be put to both good and bad uses. In the second future, the adoption of AI is constrained by the limitations of the technology. Regardless of which future unfolds, governments are increasingly concerned. They are stepping in to encourage the upside, such as funding university R&D and incentivizing private investment. Governments are also aiming to manage the potential downsides, such as impacts on employment, privacy concerns, misinformation, and intellectual property rights.
As AI rapidly evolves, the AI Index aims to help the AI community, policymakers, business leaders, journalists, and the general public navigate this complex landscape. It provides ongoing, objective snapshots tracking several key areas: technical progress in AI capabilities, the community and investments driving AI development and deployment, public opinion on current and potential future impacts, and policy measures taken to stimulate AI innovation while managing its risks and challenges. By comprehensively monitoring the AI ecosystem, the Index serves as an important resource for understanding this transformative technological force.
On the technical front, this year’s AI Index reports that the number of new large language models released worldwide in 2023 doubled over the previous year. Two-thirds were open-source, but the highest-performing models came from industry players with closed systems. Gemini Ultra became the first LLM to reach human-level performance on the Massive Multitask Language Understanding (MMLU) benchmark; performance on the benchmark has improved by 15 percentage points since last year. Additionally, GPT-4 achieved an impressive 0.97 mean win rate score on the comprehensive Holistic Evaluation of Language Models (HELM) benchmark, which includes MMLU among other evaluations.
Although global private investment in AI decreased for the second consecutive year, investment in generative AI skyrocketed. More Fortune 500 earnings calls mentioned AI than ever before, and new studies show that AI tangibly boosts worker productivity. On the policymaking front, global mentions of AI in legislative proceedings have never been higher. U.S. regulators passed more AI-related regulations in 2023 than ever before. Still, many expressed concerns about AI’s ability to generate deepfakes and impact elections. The public became more aware of AI, and studies suggest that they responded with nervousness.
Ray Perrault Co-director, AI Index
Our Supporting Partners

Analytics & Research Partners

Stay up to date on the AI Index by subscribing to the Stanford HAI newsletter.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Partisan divides over K-12 education in 8 charts

K-12 education is shaping up to be a key issue in the 2024 election cycle. Several prominent Republican leaders, including GOP presidential candidates, have sought to limit discussion of gender identity and race in schools , while the Biden administration has called for expanded protections for transgender students . The coronavirus pandemic also brought out partisan divides on many issues related to K-12 schools .
Today, the public is sharply divided along partisan lines on topics ranging from what should be taught in schools to how much influence parents should have over the curriculum. Here are eight charts that highlight partisan differences over K-12 education, based on recent surveys by Pew Research Center and external data.
Pew Research Center conducted this analysis to provide a snapshot of partisan divides in K-12 education in the run-up to the 2024 election. The analysis is based on data from various Center surveys and analyses conducted from 2021 to 2023, as well as survey data from Education Next, a research journal about education policy. Links to the methodology and questions for each survey or analysis can be found in the text of this analysis.
Most Democrats say K-12 schools are having a positive effect on the country , but a majority of Republicans say schools are having a negative effect, according to a Pew Research Center survey from October 2022. About seven-in-ten Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents (72%) said K-12 public schools were having a positive effect on the way things were going in the United States. About six-in-ten Republicans and GOP leaners (61%) said K-12 schools were having a negative effect.
About six-in-ten Democrats (62%) have a favorable opinion of the U.S. Department of Education , while a similar share of Republicans (65%) see it negatively, according to a March 2023 survey by the Center. Democrats and Republicans were more divided over the Department of Education than most of the other 15 federal departments and agencies the Center asked about.
In May 2023, after the survey was conducted, Republican lawmakers scrutinized the Department of Education’s priorities during a House Committee on Education and the Workforce hearing. The lawmakers pressed U.S. Secretary of Education Miguel Cardona on topics including transgender students’ participation in sports and how race-related concepts are taught in schools, while Democratic lawmakers focused on school shootings.
Partisan opinions of K-12 principals have become more divided. In a December 2021 Center survey, about three-quarters of Democrats (76%) expressed a great deal or fair amount of confidence in K-12 principals to act in the best interests of the public. A much smaller share of Republicans (52%) said the same. And nearly half of Republicans (47%) had not too much or no confidence at all in principals, compared with about a quarter of Democrats (24%).
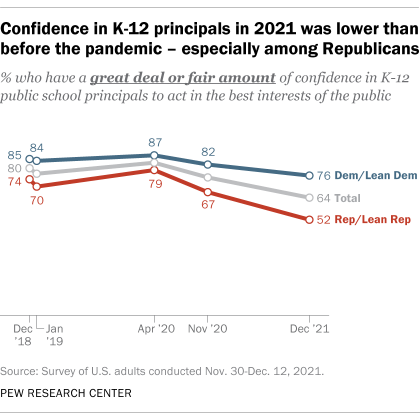
This divide grew between April 2020 and December 2021. While confidence in K-12 principals declined significantly among people in both parties during that span, it fell by 27 percentage points among Republicans, compared with an 11-point decline among Democrats.
Democrats are much more likely than Republicans to say teachers’ unions are having a positive effect on schools. In a May 2022 survey by Education Next , 60% of Democrats said this, compared with 22% of Republicans. Meanwhile, 53% of Republicans and 17% of Democrats said that teachers’ unions were having a negative effect on schools. (In this survey, too, Democrats and Republicans include independents who lean toward each party.)
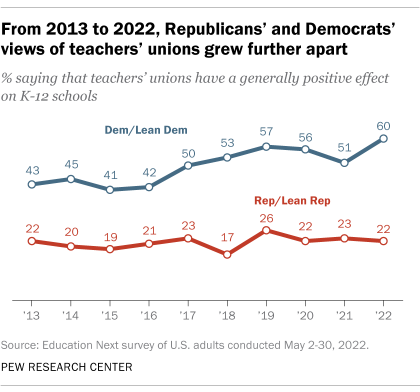
The 38-point difference between Democrats and Republicans on this question was the widest since Education Next first asked it in 2013. However, the gap has exceeded 30 points in four of the last five years for which data is available.
Republican and Democratic parents differ over how much influence they think governments, school boards and others should have on what K-12 schools teach. About half of Republican parents of K-12 students (52%) said in a fall 2022 Center survey that the federal government has too much influence on what their local public schools are teaching, compared with two-in-ten Democratic parents. Republican K-12 parents were also significantly more likely than their Democratic counterparts to say their state government (41% vs. 28%) and their local school board (30% vs. 17%) have too much influence.
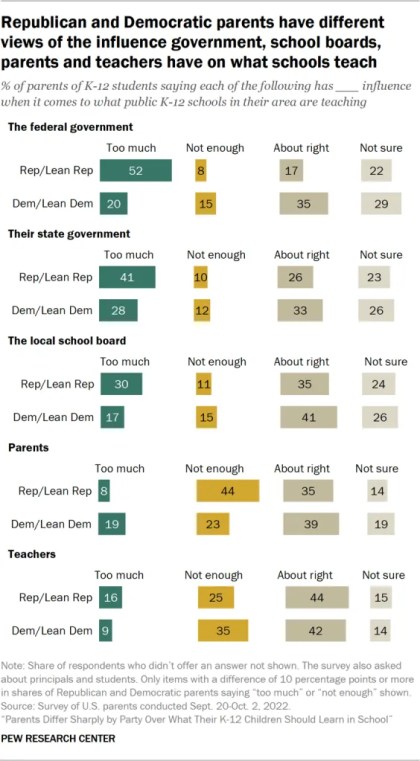
On the other hand, more than four-in-ten Republican parents (44%) said parents themselves don’t have enough influence on what their local K-12 schools teach, compared with roughly a quarter of Democratic parents (23%). A larger share of Democratic parents – about a third (35%) – said teachers don’t have enough influence on what their local schools teach, compared with a quarter of Republican parents who held this view.
Republican and Democratic parents don’t agree on what their children should learn in school about certain topics. Take slavery, for example: While about nine-in-ten parents of K-12 students overall agreed in the fall 2022 survey that their children should learn about it in school, they differed by party over the specifics. About two-thirds of Republican K-12 parents said they would prefer that their children learn that slavery is part of American history but does not affect the position of Black people in American society today. On the other hand, 70% of Democratic parents said they would prefer for their children to learn that the legacy of slavery still affects the position of Black people in American society today.
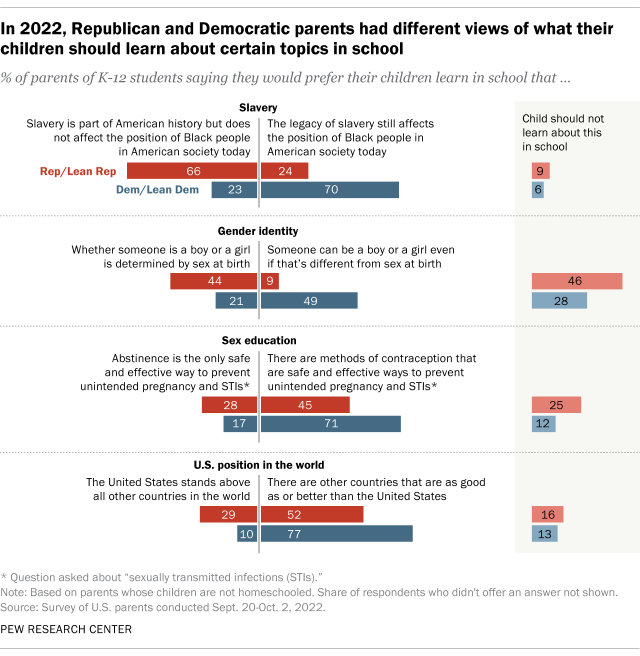
Parents are also divided along partisan lines on the topics of gender identity, sex education and America’s position relative to other countries. Notably, 46% of Republican K-12 parents said their children should not learn about gender identity at all in school, compared with 28% of Democratic parents. Those shares were much larger than the shares of Republican and Democratic parents who said that their children should not learn about the other two topics in school.
Many Republican parents see a place for religion in public schools , whereas a majority of Democratic parents do not. About six-in-ten Republican parents of K-12 students (59%) said in the same survey that public school teachers should be allowed to lead students in Christian prayers, including 29% who said this should be the case even if prayers from other religions are not offered. In contrast, 63% of Democratic parents said that public school teachers should not be allowed to lead students in any type of prayers.
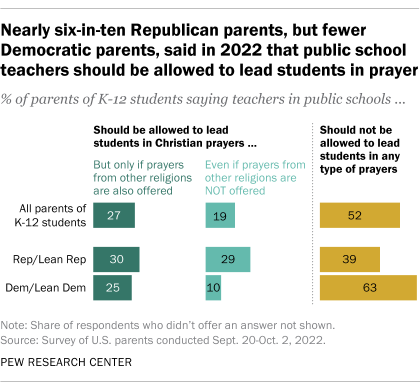
In June 2022, before the Center conducted the survey, the Supreme Court ruled in favor of a football coach at a public high school who had prayed with players at midfield after games. More recently, Texas lawmakers introduced several bills in the 2023 legislative session that would expand the role of religion in K-12 public schools in the state. Those proposals included a bill that would require the Ten Commandments to be displayed in every classroom, a bill that would allow schools to replace guidance counselors with chaplains, and a bill that would allow districts to mandate time during the school day for staff and students to pray and study religious materials.
Mentions of diversity, social-emotional learning and related topics in school mission statements are more common in Democratic areas than in Republican areas. K-12 mission statements from public schools in areas where the majority of residents voted Democratic in the 2020 general election are at least twice as likely as those in Republican-voting areas to include the words “diversity,” “equity” or “inclusion,” according to an April 2023 Pew Research Center analysis .
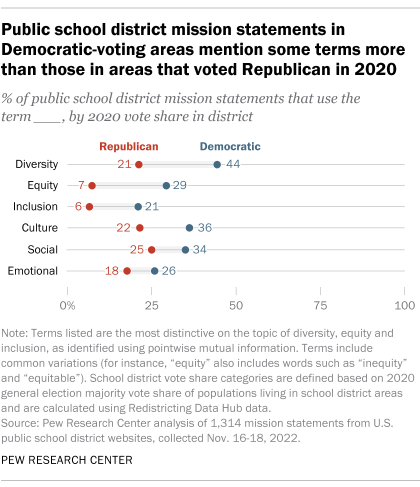
Also, about a third of mission statements in Democratic-voting areas (34%) use the word “social,” compared with a quarter of those in Republican-voting areas, and a similar gap exists for the word “emotional.” Like diversity, equity and inclusion, social-emotional learning is a contentious issue between Democrats and Republicans, even though most K-12 parents think it’s important for their children’s schools to teach these skills . Supporters argue that social-emotional learning helps address mental health needs and student well-being, but some critics consider it emotional manipulation and want it banned.
In contrast, there are broad similarities in school mission statements outside of these hot-button topics. Similar shares of mission statements in Democratic and Republican areas mention students’ future readiness, parent and community involvement, and providing a safe and healthy educational environment for students.
- Education & Politics
- Partisanship & Issues
- Politics & Policy
About 1 in 4 U.S. teachers say their school went into a gun-related lockdown in the last school year
About half of americans say public k-12 education is going in the wrong direction, what public k-12 teachers want americans to know about teaching, what’s it like to be a teacher in america today, race and lgbtq issues in k-12 schools, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy

World-first “Cybercrime Index” ranks countries by cybercrime threat level
Following three years of intensive research, an international team of researchers have compiled the first ever ‘World Cybercrime Index’, which identifies the globe’s key cybercrime hotspots by ranking the most significant sources of cybercrime at a national level.
The Index, published today in the journal PLOS ONE , shows that a relatively small number of countries house the greatest cybercriminal threat. Russia tops the list, followed by Ukraine, China, the USA, Nigeria, and Romania. The UK comes in at number eight.

‘The research that underpins the Index will help remove the veil of anonymity around cybercriminal offenders, and we hope that it will aid the fight against the growing threat of profit-driven cybercrime,’ Dr Bruce said.
‘We now have a deeper understanding of the geography of cybercrime, and how different countries specialise in different types of cybercrime.’
‘By continuing to collect this data, we’ll be able to monitor the emergence of any new hotspots and it is possible early interventions could be made in at-risk countries before a serious cybercrime problem even develops.’
The data that underpins the Index was gathered through a survey of 92 leading cybercrime experts from around the world who are involved in cybercrime intelligence gathering and investigations. The survey asked the experts to consider five major categories of cybercrime*, nominate the countries that they consider to be the most significant sources of each of these types of cybercrime, and then rank each country according to the impact, professionalism, and technical skill of its cybercriminals.

Co-author Associate Professor Jonathan Lusthaus , from the University of Oxford’s Department of Sociology and Oxford School of Global and Area Studies, said cybercrime has largely been an invisible phenomenon because offenders often mask their physical locations by hiding behind fake profiles and technical protections.
'Due to the illicit and anonymous nature of their activities, cybercriminals cannot be easily accessed or reliably surveyed. They are actively hiding. If you try to use technical data to map their location, you will also fail, as cybercriminals bounce their attacks around internet infrastructure across the world. The best means we have to draw a picture of where these offenders are actually located is to survey those whose job it is to track these people,' Dr Lusthaus said.
Figuring out why some countries are cybercrime hotspots, and others aren't, is the next stage of the research. There are existing theories about why some countries have become hubs of cybercriminal activity - for example, that a technically skilled workforce with few employment opportunities may turn to illicit activity to make ends meet - which we'll be able to test against our global data set. Dr Miranda Bruce Department of Sociology, University of Oxford and UNSW Canberra
Co-author of the study, Professor Federico Varese from Sciences Po in France, said the World Cybercrime Index is the first step in a broader aim to understand the local dimensions of cybercrime production across the world.
‘We are hoping to expand the study so that we can determine whether national characteristics like educational attainment, internet penetration, GDP, or levels of corruption are associated with cybercrime. Many people think that cybercrime is global and fluid, but this study supports the view that, much like forms of organised crime, it is embedded within particular contexts,’ Professor Varese said.
The World Cybercrime Index has been developed as a joint partnership between the University of Oxford and UNSW and has also been funded by CRIMGOV , a European Union-supported project based at the University of Oxford and Sciences Po. The other co-authors of the study include Professor Ridhi Kashyap from the University of Oxford and Professor Nigel Phair from Monash University.
The study ‘Mapping the global geography of cybercrime with the World Cybercrime Index’ has been published in the journal PLOS ONE .
*The five major categories of cybercrime assessed by the study were:
1. Technical products/services (e.g. malware coding, botnet access, access to compromised systems, tool production).
2. Attacks and extortion (e.g. denial-of-service attacks, ransomware).
3. Data/identity theft (e.g. hacking, phishing, account compromises, credit card comprises).
4. Scams (e.g. advance fee fraud, business email compromise, online auction fraud).
5. Cashing out/money laundering (e.g. credit card fraud, money mules, illicit virtual currency platforms).
DISCOVER MORE
- Support Oxford's research
- Partner with Oxford on research
- Study at Oxford
- Research jobs at Oxford
You can view all news or browse by category
This paper is in the following e-collection/theme issue:
Published on 23.4.2024 in Vol 26 (2024)
This is a member publication of University of Oxford (Jisc)
Empowering School Staff to Support Pupil Mental Health Through a Brief, Interactive Web-Based Training Program: Mixed Methods Study
Authors of this article:

Original Paper
- Emma Soneson 1, 2 , PhD ;
- Emma Howarth 3 , PhD ;
- Alison Weir 4, 5 , MA, MSc ;
- Peter B Jones 2 * , PhD ;
- Mina Fazel 1 * , DM
1 Department of Psychiatry, University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom
2 Department of Psychiatry, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom
3 School of Psychology, University of East London, London, United Kingdom
4 Faculty of Education, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom
5 Howard Community Academy, Anglian Learning multi-academy trust, Bury St Edmunds, United Kingdom
*these authors contributed equally
Corresponding Author:
Emma Soneson, PhD
Department of Psychiatry
University of Oxford
Warneford Lane
Oxford, OX3 7JX
United Kingdom
Phone: 44 1865 613127
Email: [email protected]
Background: Schools in the United Kingdom and elsewhere are expected to protect and promote pupil mental health. However, many school staff members do not feel confident in identifying and responding to pupil mental health difficulties and report wanting additional training in this area.
Objective: We aimed to explore the feasibility of Kognito’s At-Risk for Elementary School Educators , a brief, interactive web-based training program that uses a simulation-based approach to improve school staff’s knowledge and skills in supporting pupil mental health.
Methods: We conducted a mixed methods, nonrandomized feasibility study of At-Risk for Elementary School Educators in 6 UK primary schools. Our outcomes were (1) school staff’s self-efficacy and preparedness to identify and respond to pupil mental health difficulties, (2) school staff’s identification of mental health difficulties and increased risk of mental health difficulties, (3) mental health support for identified pupils (including conversations about concerns, documentation of concerns, in-class and in-school support, and referral and access to specialist mental health services), and (4) the acceptability and practicality of the training. We assessed these outcomes using a series of questionnaires completed at baseline (T1), 1 week after the training (T2), and 3 months after the training (T3), as well as semistructured qualitative interviews. Following guidance for feasibility studies, we assessed quantitative outcomes across time points by comparing medians and IQRs and analyzed qualitative data using reflexive thematic analysis.
Results: A total of 108 teachers and teaching assistants (TAs) completed T1 questionnaires, 89 (82.4%) completed T2 questionnaires, and 70 (64.8%) completed T3 questionnaires; 54 (50%) completed all 3. Eight school staff members, including teachers, TAs, mental health leads, and senior leaders, participated in the interviews. School staff reported greater confidence and preparedness in identifying and responding to mental health difficulties after completing the training. The proportion of pupils whom they identified as having mental health difficulties or increased risk declined slightly over time (median T1 =10%; median T2 =10%; median T3 =7.4%), but findings suggested a slight increase in accuracy compared with a validated screening measure (the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire). In-school mental health support outcomes for identified pupils improved after the training, with increases in formal documentation and communication of concerns as well as provision of in-class and in-school support. Referrals and access to external mental health services remained constant. The qualitative findings indicated that school staff perceived the training as useful, practical, and acceptable.
Conclusions: The findings suggest that brief, interactive web-based training programs such as At-Risk for Elementary School Educators are a feasible means to improve the identification of and response to mental health difficulties in UK primary schools. Such training may help address the high prevalence of mental health difficulties in this age group by helping facilitate access to care and support.
Introduction
In recent years, there has been an increased emphasis on the role of schools in supporting children’s mental health [ 1 - 3 ]. This enhanced focus has been driven in large part by an apparent increase in mental health difficulties (including behavioral, social, and emotional difficulties) present in school-aged populations [ 4 - 6 ]—a concern that became increasingly prominent in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic and the associated school closures and social distancing measures [ 7 , 8 ]. There is also a growing recognition of the many unique advantages of using the school setting to promote and protect pupil mental health [ 9 ]. First, most lifetime disorders begin during the schooling years [ 10 ], which suggests that schools may be an ideal setting for early identification and intervention. Second, schools have access to most children, meaning that they are an important component of any public health approach to address child mental health difficulties [ 11 - 14 ]. Third, schools benefit from prolonged engagement with pupils, which can facilitate the implementation of mental health promotion and prevention strategies as well as support and interventions for pupils with identified mental health needs [ 12 ]. Finally, mental health support in schools is often more accessible to families than other types of support [ 15 ].
However, while school staff are increasingly expected to support children’s mental health [ 1 ], many do not feel prepared to do so [ 16 - 19 ] due in part to receiving limited training and supervision in this area [ 20 ]. Therefore, improving school staff’s confidence and preparedness are important considerations for supporting them in taking an expanded role in pupil mental health [ 21 ]. Most schools offer some form of mental health training [ 22 , 23 ], but many staff members believe that they could benefit from additional training [ 18 - 20 , 24 - 26 ]. One area where staff training may be particularly beneficial is the identification of and first response to pupils who have mental health difficulties or who are believed to be at increased risk of developing them. However, although there is evidence suggesting that school staff, parents, and practitioners see such training as an acceptable, feasible, and potentially useful way to support pupil mental health [ 20 , 27 - 29 ], empirical evidence for the effectiveness of such training is limited and focuses primarily on intermediate outcomes (eg, staff knowledge and confidence) rather than downstream outcomes (eg, accurate identification, access to support, and mental health outcomes) [ 30 , 31 ]. Furthermore, there are several potential barriers to implementing training programs in schools, including time, cost, and resource requirements [ 28 ].
At-Risk for Elementary School Educators : A Brief, Interactive Web-Based Training
Training programs that address these barriers may be beneficial for supporting schools in identifying and responding to pupil mental health difficulties. Brief, interactive web-based training programs are a particularly promising avenue as they have the potential to be more affordable, flexible, and scalable than other training formats. One such training is At-Risk for Elementary School Educators (hereinafter, At-Risk ), a virtual simulation-based program developed by the American company Kognito [ 32 ]. The program, which has been completed by >125,000 teachers in the United States, aims to improve pupil mental health by “[building] awareness, knowledge, and skills about mental health, and [preparing] users to lead real-life conversations with pupils, parents, and caregivers about their concerns and available support” [ 33 ].
The program addresses many common implementation barriers to school-based mental health training. For example, At-Risk only requires approximately 1 hour to complete, which is much shorter than many other available training programs [ 31 , 34 ]. This comparatively low time commitment may address the concern that training programs are overly time intensive and, thus, make the training more feasible for busy schools [ 28 , 34 , 35 ]. The web-based format of At-Risk may also address concerns about school-based mental health programs being resource intensive [ 28 ]. Nearly all school mental health training programs documented in the literature are face-to-face sessions led by external facilitators [ 34 , 36 ], with only a few examples of web-based training [ 37 - 39 ]. For schools with limited budgets, programs requiring external facilitators can prove unsustainable and have limited scalability. In terms of financial resources, the costs of At-Risk vary depending on the number of licenses purchased, but the maximum cost is approximately £22 (US $30) per user, a price point that is feasible for many UK schools. In the United States, there have been many examples of bulk purchases at the district or state level that have made the training even more affordable per teacher. In many areas, the training is even free at point of use due to state- or district-wide licensing agreements [ 40 ].
To date, 3 randomized studies have examined the effectiveness and acceptability of At-Risk among samples of American teachers [ 17 , 41 ] and teachers in training [ 42 ] across school years. Each study found high satisfaction ratings, with between 75% and 85% of participants rating the training as useful, well constructed, relevant, and easy to use, and nearly all (88%-95%) reporting that they would recommend it to colleagues. The training also improved teachers’ self-rated preparedness, self-efficacy, and likelihood of identifying and discussing concerns about pupils’ mental health and referring them to appropriate support when needed. These improvements were reflected in the teachers’ behaviors—compared with teachers in the control group , those who completed At-Risk self-reported significantly more helping behaviors (eg, identifying psychological distress, discussing concerns with pupils and parents, and consulting with parents about options for care and support) and gatekeeping behaviors (ie, connecting pupils with care and support) after the training and at 3 months after the training. The findings of these studies indicate that At-Risk may help improve teachers’ ability to identify and respond to pupil mental health needs and lead to positive behavior change in terms of discussing concerns and facilitating access to care and support.
At-Risk in a UK Context: Considerations for Transportability
These 3 studies suggest that At-Risk may be a promising intervention for improving children’s mental health; however, there is still much to be learned about the training’s effectiveness, feasibility, and acceptability. Furthermore, to date, no evaluation of the training has been conducted outside the United States. There is increasing focus on the influence of context on the effectiveness of complex interventions [ 43 - 48 ], and while some interventions have shown success in terms of transportability [ 48 ], other interventions that have evidence of effectiveness in one context have demonstrated null or even negative effects in another [ 46 ]. Furthermore, information that could inform “transportability” is often not collected as part of evaluations [ 44 ], making it difficult to determine the likelihood of success in a new setting.
There are many contextual differences between the United States and the United Kingdom that could mean that school-based interventions developed in one country may not translate well to the other. Cross-country differences in education systems and (mental) health services are particularly relevant to this study. Differences in the education system include the length and content of initial teacher training, the number and roles of teaching assistants (TAs), and school funding structures. There are also key differences in the structure and availability of school-based mental health provision. In the United States, schools often have staff whose sole or at least main responsibility is mental health, such as school psychologists. While these roles are becoming more common in the United Kingdom with the implementation of the Green Paper recommendations [ 1 ], in most UK primary schools, mental health is included within the broader roles of the special educational needs coordinator (SENCo) and pastoral team. Finally, differences in the wider health care systems across the countries also mean that the process and outcomes of external referrals to specialist mental health services vary across settings, another fact that may influence the transportability of school-based interventions such as At-Risk.
Given these uncertainties regarding intervention transportability, additional evaluation of At-Risk is needed to understand whether it is a potentially useful and feasible tool to improve the identification of and response to mental health difficulties in UK primary schools. To explore the potential value of the training in this new context, we conducted a mixed methods feasibility study of At-Risk in 6 UK primary schools covering pupils aged 4 to 11 years . We aimed to examine the influence of At-Risk on staff confidence and preparedness, identification of pupils with mental health difficulties or increased risk of developing mental health difficulties, mental health support outcomes for identified children, and intervention acceptability and practicality.
Study Design
We used a mixed methods, nonrandomized, pretest-posttest study design to explore the feasibility of At-Risk in UK primary schools. While feasibility studies are acknowledged as a key stage of intervention design and evaluation [ 49 , 50 ], there is no universally agreed-upon definition of a feasibility study [ 50 , 51 ]. Therefore, we focused on 3 criteria from the guidance by Bowen et al [ 52 ]: acceptability, practicality, and limited effectiveness testing.
Intervention: At-Risk for Elementary School Educators
At-Risk is a web-based training that is delivered individually and requires only a log-in and internet connection. Using a simulation-based teaching model, the training aims to (1) improve mental health awareness and knowledge, (2) empower users to approach pupils about what they have noticed, (3) impart skills to have meaningful conversations with pupils and parents, and (4) train users to refer pupils to further support. The diagram in Figure 1 illustrates how the training might lead to improved mental health outcomes for pupils.
The simulation begins with an introduction by a virtual coach, who defines and explains how to recognize the warning signs of psychological distress and specific mental health difficulties and provides guidance and practical advice for discussing and acting upon concerns. Users then practice 2 virtual scenarios. The first scenario involves a fifth-grade (UK Year 6; ages of 10-11 years) teacher speaking with the parent of a pupil showing signs of behavioral difficulties. The second involves a third-grade (UK Year 4; ages of 8-9 years) teacher speaking with a pupil showing signs of emotional difficulties. During the conversations, users choose what to say via drop-down menus organized into categories (eg, “bring up concerns” or “ask a question”) and phrases (eg, “Mia sometimes seems a little agitated in class”). Throughout the conversation, users receive feedback through a “comfort bar” (based on how the pupil or parent perceives the conversation), opportunities to “see” the thoughts of the pupil or parent, and suggestions from the virtual coach.
Importantly, there is no one “right” way to conduct the conversations, and several approaches can lead to a positive outcome. Throughout the conversation, users can “undo” actions to backtrack after receiving an undesirable response or to explore what the response would have been had they chosen another option. At the end of each conversation, the pupil or parent provides feedback on the conversation. The training finishes with a short segment on connecting pupils with further support.
For this feasibility study, we used an unmodified version of the training (ie, the standard training designed for American schools, not tailored to the UK context) provided free of cost by Kognito. The potential need for adaptation and tailoring was an important consideration that we explicitly examined as part of our exploration of the acceptability and practicality of At-Risk in this new setting.

Recruitment
We originally sought to purposively sample 5 primary schools from Cambridgeshire or Norfolk that (1) had a higher-than-average proportion of pupils eligible for free school meals or (2) were located in an area in the top tertile of deprivation as measured using the Index of Multiple Deprivation [ 53 ], which we calculated with the publicly available Schools, pupils and their characteristics data [ 54 ]. We emailed headteachers, SENCos, and mental health leads from 131 candidate schools in September and October 2019 about participating in the study. To increase recruitment, we contacted additional schools in January 2020 for a study start date of March 2020. However, the study was suspended in March 2020 due to the in-person school closures associated with the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. As some of the participating schools dropped out due to the pandemic, we reopened recruitment for a January 2021 study start date. In this round, we did not restrict participation by the 2 deprivation criteria described previously (ie, free school meal eligibility and Index of Multiple Deprivation), so any UK-based mainstream primary school was eligible to participate. The January 2021 start date was again delayed by the pandemic, but there was no subsequent recruitment.
Teachers and TAs
Schools were responsible for recruiting individual teachers and TAs to participate in the training. We encouraged schools to invite all teachers and TAs to participate, but schools made a variety of decisions in this regard. Three schools (schools D, E, and F) had all staff complete the training during inset (in-service training) days or other designated times, 2 schools (schools A and C) had staff volunteer to participate, and 1 school (school B) selected 2 to 3 staff members in each year group to participate.
Measures and Materials
School characteristics.
The characteristics of the participating schools, including school type, school sex (ie, whether they were single or mixed sex), urbanicity, head count, area-level deprivation, level of free school meal eligibility, ethnic composition, and proportion of pupils with special educational needs, were obtained from publicly available data from the Department for Education [ 54 , 55 ].
Teacher and TA Identification Form
The purpose of the Teacher and TA Identification Form ( Multimedia Appendix 1 ) was to understand which pupils participants would identify as having mental health difficulties or an increased risk of developing mental health difficulties. As systematic reviews in this area have identified no suitable questionnaires [ 28 , 30 ], we developed a bespoke questionnaire, which was reviewed by a school staff advisory group to ensure accuracy and relevance. The questionnaire begins with instructions, including explanations and examples of what is meant by “mental health difficulties or risk for mental health difficulties.” Full definitions are provided in Multimedia Appendix 1 , but in brief, “mental health difficulties” are described as “behavioural and social-emotional problems” regardless of formal diagnosis, and “risk for mental health difficulties” is described as experiences that increase the chance of a child developing mental health difficulties in the future.
For all pupils in their class, participants first indicated whether they thought a pupil had mental health difficulties or increased risk. If yes, they answered 9 subsequent questions about mental health support outcomes. The first four outcomes were about communication of concerns, namely whether they had (1) formally documented their concerns with the school, (2) communicated concerns to the SENCo, pastoral care lead, or mental health lead, (3) communicated concerns to another member of the school staff, or (4) communicated concerns to the child or their parents. The next five outcomes pertained to the provision of mental health support, namely whether the pupil (5) received in-class support; (6) received in-school support or had an in-house support plan; (7) had documented social, emotional, and mental health (SEMH) status (a type of special educational need focused on mental health difficulties); (8) had been referred to external mental health services; or (9) had access to external mental health services.
Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire
The teacher-report Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ) [ 56 - 59 ] served as the comparator for findings about teachers’ and TAs’ identification of pupils. The SDQ includes 25 positive and negative psychological attributes across 5 scales: emotional symptoms, conduct problems, hyperactivity/inattention, peer relationship problems, and prosocial behavior. The first 4 scales add up to a Total Difficulties Score (0-40, with higher scores representing greater difficulties). The SDQ has demonstrated acceptable psychometric properties in primary school samples [ 60 ]. It is important to note that the SDQ is not an exact comparator as it measures a narrower concept than the Teacher and TA Identification Form (which also includes increased risk ). However, this comparison could potentially yield valuable information regarding feasibility .
Pre- and Posttraining Surveys
Kognito uses pre- and posttraining surveys to assess their training. These surveys (based on the validated Gatekeeper Behavior Scale [ 61 ]) explore teachers’ self-efficacy in identifying and responding to mental health difficulties and whether their attitudes, self-efficacy, or practice have changed since completing the At-Risk training. The posttraining survey also includes questions on perceptions of the training’s impact. We independently (ie, with no input from Kognito) reviewed the merits of these questionnaires and decided to use them in this study because (1) they covered relevant and useful concepts related to our aims and (2) using them increased comparability to the other 3 US-based studies of At-Risk . We slightly adapted the surveys to make them more relevant to the UK context ( Multimedia Appendix 2 ).
Interview Schedules
For the pretraining interviews with SENCos and mental health leads, we developed a topic guide about current practice ( Multimedia Appendix 3 ) with the specific purpose of creating Mental Health Resource Maps for each school (refer to the Procedures section). The main topics pertained to formal and informal procedures for when staff members suspect that a child might have mental health difficulties or increased risk, as well as the types of support available.
For the posttraining interviews with teachers, TAs, and strategic stakeholders (ie, those with key leadership roles, including senior leadership teams [SLTs], school governors, and SENCos and mental health leads), we developed 3 separate topic guides ( Multimedia Appendix 3 ), which were informed by our research questions, systematic reviews [ 28 , 30 ], and the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research [ 62 , 63 ]. For teachers and TAs who completed At-Risk and strategic stakeholders, interview topics included the acceptability of the training, the practicality of implementing it in schools, the utility of further refinement and testing, possible harms associated with the training (if any), and suggestions for adaptations. For teachers and TAs who did not complete the training, topics included reasons for not completing it, barriers to acceptability and practicality, and suggestions for adaptations.
Interviews With SENCos and Mental Health Leads
We conducted a pretraining interview with each school’s SENCo or mental health lead to develop a “Mental Health Resource Map” with information on referral processes and available support. These maps served an ethical purpose by ensuring that pupils identified as potentially having mental health difficulties would have the best possible chance of being linked to care and support.
Completing At-Risk
Schools’ timelines for the study varied due to the pandemic and other commitments. School D completed the training in December 2020; school E completed the training in March 2021; schools B, C, and F completed the training in May 2021; and school A completed the training in June 2021. At baseline (T1), participants completed a Teacher and TA Identification Form and the pretraining survey. They then completed the At-Risk training. We encouraged schools to designate specific time for the training, which 3 schools (schools D, E, and F) did. One week after training (T2), participants were asked to complete a second Teacher and TA Identification Form and the posttraining survey. Three months after the training or at the end of the school year (whichever came first; T3), participants completed a third Teacher and TA Identification Form as well as SDQs for all pupils. All questionnaires were completed on the University of Cambridge Qualtrics platform (Qualtrics International Inc).
Feedback Provision
After T2, we provided all SENCos and mental health leads but not teachers or TAs with feedback regarding which children had been identified as having mental health difficulties or increased risk. After T3, we provided SDQ scores for each child as well as whole-class distributions (where available). This feedback was provided to ensure the ethical conduct of the study.
Interviews With Teachers, TAs, and Strategic Stakeholders
We aimed to recruit at least 3 teachers or TAs who completed the training per school, 3 to 5 teachers or TAs who had not completed the training across all schools, and up to 3 strategic stakeholders per school for posttraining semistructured interviews. Schools contacted staff members directly with an invitation to complete a virtual interview.
Quantitative Outcomes
Analytical samples.
For the main analysis, participants were included if they (1) completed at least the pretraining (T1) questionnaires and the training itself and (2) had what we judged to be a typical number of children they regularly worked with. For the latter criterion, given that the average UK primary school class size is approximately 27 to 28 pupils [ 64 ], we excluded teachers and TAs who worked with <10 children (as we suspected this would not be a random selection of pupils and would therefore influence aggregate identification rates) and those who worked with >60 children (as we believed that it would be difficult for a teacher or TA to know >2 classes’ worth of children well enough to make accurate judgments about their mental health).
Teacher and TA Self-Efficacy and Preparedness
To assess teachers’ and TAs’ preparedness, self-efficacy, and perceptions of training impact, we calculated the absolute and relative frequencies of responses to the pre- and posttraining surveys. Participants were eligible for inclusion in this analysis only if they had pretraining (T1) data.
Identification Outcomes
On the basis of the Teacher and TA Identification Forms, we calculated the number and percentage of pupils in each class whom teachers and TAs perceived as having mental health difficulties or increased risk at each time point. We summarized these across all participants using medians and IQRs.
We then calculated SDQ scores, which we compared with responses from the Teacher and TA Identification Form by calculating (1) the median and IQR for the percentage of children identified by participants who did not have elevated SDQ scores and (2) the median and IQR for the percentage of children with elevated SDQ scores who were not identified by participants. To be included in these analyses, participants had to have completed all 3 time points. For the first outcome, they had to have completed an SDQ for all children they identified in the Teacher and TA Identification Form . For the second outcome, they had to have completed SDQs for at least 80% of their class. Where it was possible to match pupil IDs between teachers and TAs, we pooled SDQ data such that, if one participant did not meet the inclusion criteria themselves, they could still be included if the SDQ data were available from another staff member working with the same children.
Mental Health Support Outcomes
Finally, for each time point, we calculated medians and IQRs for the proportion of identified children with each of the 9 mental health support outcomes (refer to the Teacher and TA Identification Form section for the outcomes) .
Sensitivity Analyses
We also conducted 2 post hoc sensitivity analyses. The first sensitivity analysis excluded all participants from school D. When we prepared feedback for school D (the first school to complete the training), we learned that most participants at the school had misinterpreted the Teacher and TA Identification Form. We edited the form and instructions accordingly to address this issue, but therefore, school D participants completed a slightly different form than the other schools. The second sensitivity analysis was a complete case analysis intended to explore observed differences in outcomes according to whether participants had completed all 3 time points. For the analysis of outcomes pertaining to preparedness, self-efficacy, and perceptions of training impact, we included all participants who completed the surveys at least at T1 and T2.
Statistical Analysis
For all quantitative outcomes, we focused on preliminary, descriptive comparisons across the 3 time points and did not perform any formal hypothesis testing. This aligns with established recommendations for feasibility studies, which generally lack the statistical power necessary for a clear interpretation of hypothesis-testing results [ 65 - 68 ]. We conducted all quantitative analyses in R (version 4.0.3; R Foundation for Statistical Computing) [ 69 ] except for the comparison of Teacher and TA Identification Forms and SDQ scores, for which we used Microsoft Excel (Microsoft Corp). We created all plots using the ggplot2 [ 70 ] and likert packages [ 71 ]. To score the SDQs, we used the freely available R code on the Youthinmind website [ 72 ].
Qualitative Outcomes
We considered 3 analysis approaches for the interview and qualitative questionnaire data: content analysis [ 73 ], framework analysis [ 74 ], and reflexive thematic analysis [ 75 , 76 ]. We initially decided to use content analysis for the survey comments and reflexive thematic analysis for the interviews; however, as we familiarized ourselves with the data, we realized that there was significant overlap between the survey comments and interviews and decided that analyzing them separately was not a useful distinction. As our main aim was to generate insights into the program and its future potential, we decided to use the 6-phase reflexive thematic analysis by Braun and Clarke [ 76 ] for all qualitative data due to its flexibility and ability to generate themes both inductively and deductively. ES developed the initial themes, and MF and EH helped clarify and enrich them. ES and MF worked together to name and refine the themes before the final write-up. We managed and coded all qualitative data in ATLAS.ti (version 9.1.3; ATLAS.ti Scientific Software Development GmbH) and additionally created manual thematic maps to better visualize and understand patterns between our data.
Ethical Considerations
This study was approved by the University of Cambridge Psychology Research Ethics Committee (PRE 2019.076). We obtained active informed consent from all teachers and TAs who took part in the study. We used an opt-out model for parental consent whereby parents received (directly from the schools via their preferred communication routes) an information sheet detailing study aims, procedures, how data would be used, and the right to opt their child out of participation. Parents had 2 weeks to opt their child out of the study by returning a hard copy of the opt-out form or emailing or calling the school. Schools kept track of all opt-outs and instructed teachers and TAs not to include these children in their forms. All quantitative data were collected using anonymous pupil and staff identifiers generated by the participating schools, and all qualitative data were deidentified before analysis, with identifiable information stored on secure servers at the University of Cambridge. Teachers and TAs received £20 (approximately US $28) vouchers for completing the training and questionnaires for at least 2 of the 3 time points and an additional £10 (approximately US $14) for taking part in an interview. School staff members who created the anonymous identifiers received £10 (approximately US $14) vouchers to thank them for their time.
Participants
A total of 6 schools participated in this study (Table S1 in Multimedia Appendix 4 [ 40 ]). Among these 6 schools, there were 4 (67%) from Cambridgeshire and 1 (17%) each from Greater London and Merseyside; 5 (83%) were located in urban areas and 1 (17%) was located in a rural area. All but 1 school (5/6, 83%) were situated in areas of above-average deprivation, and 50% (3/6) of the schools had a higher-than-average proportion of pupils eligible for free school meals. In total, 67% (4/6) of the schools had a high proportion of White pupils (>80%), and 33% (2/6) of the schools were more diverse, with approximately 20% of pupils from Black, Black British, Caribbean, or African backgrounds (school B) or Asian or Asian British backgrounds (school E).
A total of 108 teachers and TAs completed the T1 questionnaires and the training itself, 89 (82.4%) completed the T2 questionnaires, and 70 (64.8%) completed the T3 questionnaires ( Table 1 ), with 54 (50%) having completed all 3. After excluding those teachers and TAs who did not meet the inclusion criteria for the analyses, the final analytical samples were as follows:
- Main analysis of identification and mental health support outcomes: n=97 at T1, n=75 at T2, and n=57 at T3.
- Main analysis of preparedness, self-efficacy, and training impact outcomes: n=107 at T1 and n=83 at T2.
- Main analysis comparing identification outcomes with SDQ scores: n=28 and n=25 (refer to the following section).
- Complete case sensitivity analysis: n=51 at T1, T2, and T3.
- Sensitivity analysis excluding all teachers and TAs from school D: n=70 at T1, n=54 at T2, and n=41 at T3.
Compared with the 2019-2020 national workforce statistics for teachers and TAs working in state-funded nursery and primary schools [ 77 ], our sample had a similar proportion of women (81/89, 91% in our sample vs 90.9% nationally) and a slightly higher proportion of White staff members (82/89, 92% in our sample vs 90.5% nationally).
A total of 7.4% (8/108) of school staff members from 67% (4/6) of the schools completed an interview ( Table 2 ).
a N=89 because this information was collected only at T2.
b N NA =4 (number with missing data for this question).
c Percentages add up to >100 because some participants had multiple roles.
d SENCo: special educational needs coordinator.
e N NA =7 (number with missing data for this question).
a PSHE: Personal, Social, Health and Economic.
b SENCo: special educational needs coordinator.
c TA: teaching assistant.
d HLTA: higher-level teaching assistant.
Pretest-posttest changes suggested that participating in the training was beneficial for the staff and that they had positive perceptions of the training. Findings regarding preparedness ( Figure 2 ) suggest improvements across all domains of recognizing and acting upon concerns about pupils’ mental health, particularly in terms of using key communication strategies and working with parents. Findings regarding self-efficacy ( Figure 3 ) suggest that participants were more confident in their abilities to discuss their concerns about pupils’ mental health after the training than before. Again, the largest changes were observed in discussing concerns with parents and applying key communication strategies. Finally, findings regarding teachers’ and TAs’ perceptions of the impact of applying the skills of the training ( Figure 4 ) suggest that they were generally positive about the possible effects of the training on pupil outcomes (ie, attendance and academic success), teacher-pupil rapport, and the classroom environment. The results from the complete case analysis ( Multimedia Appendix 5 ) were nearly identical to those of the main analysis (all differences were ≤3 percentage points in magnitude).

In terms of how many pupils were identified as having mental health difficulties or increased risk, participants identified similar proportions of their pupils before and immediately after the training and then fewer over time. The median percentage of pupils whom participants believed had mental health difficulties or increased risk was 10% (IQR 6.7%-18.2%) at T1, 10% (IQR 4.5%-16.7%) at T2, and 7.4% (IQR 5.0%-16.7%) at T3. The directions of change were similar for both sensitivity analyses (whereby teachers and TAs identified fewer children over time), with slight differences. For the sensitivity analysis excluding school D ( Multimedia Appendix 6 ), the percentages were slightly (approximately 2 percentage points) higher. For the complete case analysis, the decrease was also notable 1 week after the training, decreasing from 10% (IQR 6.7%-17.3%) at T1 to 8% (IQR 3.9%-16.7%) at T2 and 7.4% (IQR 5.7%-16.7%) at T3.
In terms of the accuracy of identification, it seems that teachers and TAs became slightly more accurate over time in comparison to pupils’ SDQ scores (although it is important to acknowledge the limitations described in the Methods section regarding questionnaire comparability). The median percentage of children identified by participants who did not have elevated SDQ scores was 40% (IQR 0%-50%) at T1, 27.2% (IQR 0%-50%) at T2, and 25% (IQR 0%-50%) at T3. The median percentage of children with elevated SDQ scores who were not identified by participants was 68.8% (IQR 42.9%-87.5%) at T1, 66.7% (IQR 50%-88.2%) at T2, and 57.1% (IQR 33.3%-87.5%) at T3. In the sensitivity analysis excluding school D, the results were similar (typically within 5 percentage points); one small difference was that the median percentage of children identified by teachers and TAs who did not have elevated SDQ scores was 0% (IQR 0%-50%) at T2. The results of the complete case analysis were identical to those of the main analysis.
Overall, the findings suggest that the training may be beneficial for facilitating conversations and access to school-based support (but not external support) for pupils with identified mental health difficulties or increased risk. Figure 5 presents the findings for the 9 mental health support outcomes among identified children across the 3 study time points. As with before the training, there was typically a wide variation in outcomes.
A comparison across time points suggests that participants formally documented their concerns and spoke with the SENCo, pastoral lead, or mental health lead for a greater proportion of identified pupils after the training than before. For example, at T1, teachers and TAs documented concerns for a median of 50% (IQR 0%-100%) of identified pupils; this increased to 56.3% (IQR 4.2%-100%) at T2 and 75.7% (IQR 0%-100%) at T3. The equivalent statistics for speaking with the SENCo, pastoral lead, or mental health lead were a median of 66.7% (IQR 16.7%-100%) at T1, 75% (IQR 50.0%-100%) at T2, and 95.5% (IQR 50.0%-100%) at T3. There was no change in speaking with another staff member, but this was because nearly all participants did so across all time points. Finally, the percentage of pupils whom teachers and TAs spoke with (or whose parents they spoke with) also increased after the training, with a median of 33.3% (IQR 0%-87.5%) at T1, 61.9% (IQR 0%-100%) at T2, and 50% (IQR 0%-100%) at T3.
A comparison across time points also suggests increases in school-based support for identified children after the training compared with before. The median percentage of pupils identified by teachers and TAs who received in-class support increased from 75% (IQR 35.4%-100%) at T1 to 100% at T2 and T3 (IQR 50%-100% and 66.7%-100%, respectively). There was a more modest increase in the receipt of in-school support or in-house support plans, with a median of 40% (IQR 0%-71.4%) of identified pupils receiving them at T1 compared with 50% at T2 and T3 (IQR 3.6%-100% and 8.3%-81.4%, respectively). There was very little change in documented SEMH status or referral or access to specialist mental health services. For each of these outcomes, the median percentage of identified pupils was 0% across time points.
The findings from the sensitivity analyses were similar to those of the main analysis in terms of direction, although improvements across time in the complete case analysis ( Multimedia Appendix 5 ) tended to be more modest than for the main analysis.

Acceptability and Practicality
Quantitative findings.
Quantitative data from the posttraining survey showed that participants were generally positive about the training. Of the 83 participants who completed the survey, 53 (64%) rated it as “good” and 13 (16%) rated it as “very good.” An additional 17% (14/83) rated it as “fair,” 2% (2/83) rated it as “poor”, and 1% (1/83) as “very poor.” A total of 84% (70/83) of the teachers and TAs said that the scenarios in the training were relevant to them. Finally, most participants (74/83, 89%) would recommend the training to other educators.
Qualitative Findings
Qualitative data also suggested that school staff generally found the training practical and acceptable. We generated three themes from our survey and interview data:
- Individual fit: positive perceptions, self-efficacy, and change.
- Institutional fit: alignment with school values and context.
- Taking it forward: improvements and implementation.
Additional findings on possible harms are presented in Multimedia Appendix 7 .
Individual Fit: Positive Perceptions, Self-Efficacy, and Change
In general, participants perceived the program to be a “good fit” with their personal philosophies and practice. Regarding the training itself, many appreciated the included scenarios, particularly in terms of their relevance to their practice. The format of the training—primarily that it was web-based and required active role-play—was also viewed as useful, engaging, and novel and might have contributed to its perceived usefulness. For example, one teacher commented:
The interactive elements of the training were brilliant and something which I have never encountered before! [Survey respondent (SR) 56; school E]
One teacher and well-being lead described:
I think it definitely made you think. [...] you had to really think about what was being said and the response that you would give, reflecting back on sort of the knowledge that they’d given you beforehand, so I thought that was good. [Interviewee 1]
Other participants suggested that opportunities to practice skills during the training improved the likelihood of using those skills in day-to-day practice.
Participants also believed that they had learned a lot from the training, especially in terms of skills and strategies. These included but were not limited to the skills within the At-Risk “EASING” strategy (check your Emotions, Ask for permission, be Specific, use I statements, keep it Neutral, and show Genuine curiosity). Importantly, there was evidence that participants had also applied new skills. Several participants described having new conversations with pupils or parents facilitated by the skills and strategies from the training. For example, one teacher described:
It was that permission thing [...] I wanted to ask [a child] about his home life [...] and kind of he just cried and didn’t want to speak about it anymore, and then when I asked him if we were OK to talk about it, he said, “Actually no, because I think I’m going to cry again,” so then we left it. And then he came to me the following week, and [...] said, “Can we talk about it now?” [...] so actually me asking that, it was the wrong time for him to talk about it, he wasn’t ready, he would have just been emotional, and wouldn’t have been able to get his words out, and actually the week after, him coming to me and saying, “Can we have a little chat,” works perfectly [...] And now we’re more aware of his situation. [Interviewee 2]
This skill seems to have enabled this pupil to have this conversation with the teacher in a manner (in terms of time, place, and identified person) that suited him. Other participants provided similar examples, referencing how skills from the training had facilitated better outcomes.
However, it is important to note that the perceived usefulness of the training varied. Most notably, some participants indicated that their previous training or role made the training less impactful. Illustratively, when asked how the training had impacted their practice, one TA responded:
Having previously received similar training, due to my role, I do not have any recent cases where the training would have changed the way I carried out discussions. [SR 60; school E]
Institutional Fit: Alignment With School Values and Context
Sustainable school-based programs should also align with the values of the school more broadly. Participants often referenced the importance of schools’ prioritization of pupil mental health. For example, one teacher described:
[Mental health is] a conversation which is constantly ongoing and trying to constantly better our practices and make sure we’re looking after them as best as we can and spotting things as best we can as well. [Interviewee 3]
This description demonstrates how prioritizing mental health can promote the critical evaluation of related school practices as well as the additional provision of training opportunities. In many cases, support from the SLT led to formal recognition of pupil mental health within school policies or plans. One strategic stakeholder explained:
I think because our school have well-being and mental health as such a focus, SLT are very supportive of doing things like this and they’re very accommodating. So when I said we had the training and people were going to have to take part in the training, it was very flexible, although they had other ones lined up, they were quite happy to move things around to make things work. And I think, the fact it is such a priority in our school definitely makes that easier. [Interviewee 1]
In this school, mental health and well-being were one of three main school priorities. As indicated previously, direction setting from the SLT is key to ensuring momentum and impetus. However, as others noted, it is important that support from the SLT is genuine rather than being “just another tick box” (Interviewee 4) exercise.
Another facet of institutional fit pertained to the practical aspects of the training. Schools are time- and resource-limited settings, so mental health training needs to fit within this context. The format of At-Risk, especially its flexibility and relatively low time requirements, was viewed as beneficial, with comments such as “For the amount of time [...] I got a huge amount from it” (Interviewee 4). Others made direct comparisons with other training courses. For example, one higher-level TA had previously completed a 1-day, in-person training course with a similar purpose to that of At-Risk. While she preferred the in-person training, she listed the benefits of both types:
[In the in-person training] you can then query and question to your trainer, so you’ve got that interaction, so that obviously isn’t there, is it, on the computer one. [...] if I was looking from a management point of view, I would say, budgetary, I’m sure it’s cheaper [...] to use [At-Risk], not just cheaper as in [...] money, [...] but also cheaper in time [...] So probably if I was looking [...] with my management hat on, I would say the computer-based [training] would get the same message, or similar message, across for a wider audience for probably a cheaper cost. [Interviewee 7]
In terms of efficiency, this participant highlighted the favorable input-to-output ratio of At-Risk , which could allow more staff members to participate in training. This quote also highlights that schools could use At-Risk flexibly. For example, schools might assign staff members to different training programs based on their roles and previous experience, with more intensive, in-person training for staff members with more significant mental health roles and At-Risk for those with fewer responsibilities or less experience.
Taking It Forward: Improvements and Implementation
Participants offered key insights into how to take the training forward in terms of both changes to the training itself and how best to implement it, primarily by tailoring it to the UK context. In terms of language, there was some reference to the American accent, but more so, participants highlighted the need to adapt some of the terminology and signposting resources to reflect UK support systems. They also made suggestions about additional training that could be useful with different topics (such as bullying) and age groups (particularly for younger children).
In addition to improvements and adaptations to the training itself, participants illustrated the importance of implementation. A common theme was that, to maximize impact, the training should include follow-up discussions or live workshopping. One teacher suggested:
I think some kind of “live” element to conclude the training—to have a “real” person to ask questions to as part of a group video chat could have been useful. Also, maybe to ask advice about particular scenarios that we may have found ourselves in in the past. [SR 56; school E]
By facilitating greater engagement and critical thinking, a live element could enhance the impact of the training and potentially make At-Risk more acceptable to those who generally prefer face-to-face training. Participants indicated that someone internal, for example, the SENCo, would be best placed to lead a live element and would enable staff to practice role-playing based on situations and scenarios specific to each school.
There was also wide acknowledgment that any training had to lie within a strong support system. This began with having a clear referral pathway for identified concerns, which was viewed as important for facilitating access to support. In some cases, teachers and TAs were able to find new ways to support children after completing the training. However, in many cases, participants—and strategic stakeholders in particular—explained that support had not always been readily available. For example, one strategic stakeholder recounted what happened after the training:
A lot of them are people saying to me, “What are you going to do about it?” about different children. And I, because some of our support staff don’t know the sort of route for getting extra support, or they’re really shocked to find actually there’s nothing out there for these children...it’s about what we can do in school, and I think people have been really quite shocked about that. You know, they just presume I can make a phone call and these children will get face-to-face counselling. [Interviewee 5]
This shows the importance of embedding the training within a wider support system, including collaboration with external agencies. However, many interviewees referenced the systemic issues that schools face in helping pupils access specialist support, particularly in terms of the high thresholds and long waiting lists that exist for many external services. While schools may be able to provide beneficial support for children, particularly for those with lower-level difficulties, this indicates an ongoing area of need for schools and their pupils.
Summary of Findings
This study offers the first UK evidence for Kognito’s At-Risk for Elementary School Educators , extending findings from 3 US-based trials and providing needed evidence regarding the potential utility, acceptability, and practicality of brief, interactive web-based mental health training for school staff. Overall, the findings showed that At-Risk is a feasible means of improving the identification of and response to pupil mental health difficulties in UK primary schools. Quantitative findings showed that staff preparedness and self-efficacy in identifying and responding to mental health difficulties increased after the training. Identification rates did not increase (and, in fact, decreased at the 3-month follow-up), but there was some suggestion that teachers’ and TAs’ identification became slightly more accurate in comparison with SDQ scores. Crucially, for those pupils identified as having mental health difficulties or increased risk, in-school mental health support outcomes (ie, documentation or discussion of concerns, conversations with pupils and parents, and in-class and in-school support) increased after the training, but more “downstream” outcomes (ie, documented SEMH status and referral and access to external mental health services) did not. Qualitative findings indicated that participants generally found the training acceptable and practical, with many explaining how they intended to use or had already used the skills they learned to improve their practice. Participants also suggested several useful improvements for the training and its implementation, including making it more relevant to the United Kingdom, adding more scenarios, and including a live element in the implementation of the training.
Findings regarding confidence and preparedness reflect those of the 3 US-based studies of At-Risk [ 17 , 41 , 42 ] and the wider literature surrounding teacher mental health training [ 31 ]. In general, mental health training seems to be effective in improving staff confidence. For example, 2 Australian-based studies [ 37 , 78 ] found that secondary school teachers who completed training felt more confident discussing their concerns and helping pupils with their mental health. Another UK-based study of a psychoeducational training program to improve recognition of depression in secondary schools [ 79 ] found significant pretest-posttest improvements in teacher confidence in their knowledge of symptoms, ability to recognize symptoms, and knowledge about how to speak with pupils about their mental health. However, not all studies have shown an impact, with a prominent UK-based study of mental health first aid training finding no effect on educators’ confidence in helping pupils with their mental health [ 80 ].
The general decrease in the proportion of pupils identified as having mental health difficulties or increased risk stands in contrast to previous studies of At-Risk , which found that school staff identified significantly more pupils of concern after completing the training [ 17 , 41 ]. Evidence of the effect of other training programs on identification is extremely limited [ 30 , 31 , 36 ], and differences in context, training content and delivery, baseline knowledge, and outcome measurement make it difficult to compare findings across studies. Two vignette-based studies showed little effect of either mental health first aid [ 78 ] or psychoeducational [ 81 ] training on identification (although each study also reported high recognition of difficulties before the training), whereas studies focused on real-world identification have shown mixed results [ 79 , 82 ]. However, changes in the proportion of identified pupils must be contextualized within the accuracy of identification. There are consequences of both over- and underidentification [ 83 , 84 ], most notably in terms of inefficient allocation of limited mental health support resources. While comparison with the SDQ suggested that there was some improvement in terms of the accuracy of identification following the training, underidentification remained a substantial challenge, with between one-half and two-thirds of pupils with elevated SDQ scores remaining unidentified by teachers and TAs. The underidentification of children with mental health difficulties in educational settings, particularly for children with internalizing as opposed to externalizing problems [ 85 ], has been well documented in the literature [ 30 ], and it is likely that a combination of identification models is required to address this challenge [ 27 , 29 ].
Promisingly, the training appeared to be useful in terms of connecting pupils with care and support, an outcome not frequently measured in other studies [ 30 , 31 , 34 ]. First, the findings suggested that participants had conversations about or documented concerns for a greater proportion of identified pupils following the training, which reflects findings from previous studies of At-Risk [ 17 , 41 ]. This is a rather unique outcome in the literature as other training evaluations have found no difference between training and control groups in terms of conversations with pupils and colleagues [ 78 ]. Importantly, this study went beyond conversations to include outcomes pertaining to in-school and external support. The increases in in-class and in-school support for identified pupils reflect findings of the UK-based study by Kidger et al [ 80 ] of mental health first aid training and the Australian-based pilot study by Parker et al [ 37 ] of a web-based training program, each of which found a positive effect of the training on helping behaviors. Although in-class and in-school support seemed to increase following the training, it is notable that referrals and access to specialist services did not. There are several plausible explanations for this finding. For example, it is likely that school staff were already aware of children with the most severe mental health difficulties and were confident and able to support newly identified pupils—who might have had lower-level mental health difficulties—within the school setting. However, if the training did lead to the identification of children who might benefit from specialist care, there are many barriers to accessing such support (eg, availability and long waiting lists) that might have influenced these outcomes, as reflected in both the qualitative interviews and the wider literature [ 23 , 86 ].
In addition, quantitative and qualitative findings suggested that the program was a good fit for individuals and schools, which aligns with previous research on the acceptability and perceived need for mental health training for school staff [ 18 , 20 , 27 - 29 , 87 , 88 ]. The training’s format seemed to be a key contributor to its feasibility. With a few exceptions [ 37 , 39 , 89 ], the web-based simulation-based format of At-Risk is unique among training programs and is well aligned with teachers’ preferences. For example, in their focus group study of UK secondary school teachers, Shelemy et al [ 20 ] found that participants wanted engaging, interactive, and concise training that included practical strategies and illustrative case studies, all of which are central to At-Risk . While the authors found that teachers disagreed over the usefulness of web-based training, it is possible that these concerns would have decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic as staff became more accepting of web-based opportunities to learn.
Qualitative findings also demonstrated the importance of school context and culture, which have been highlighted in previous research [ 27 ]. In particular, participants noted the importance of school culture in adopting mental health interventions into regular practice. In their systematic review, Moore et al [ 90 ] identified school culture, values, and policies as key facilitators of sustaining mental health interventions. A related area of focus was support from the SLT. This support is a well-recognized factor contributing to intervention success and sustainability for several reasons, including these leaders’ practical role in communicating about interventions and allocating specific time and resources to them [ 43 , 90 , 91 ]. However, it is important to recognize that mental health training for school staff may be even more needed and impactful in schools where mental health is not as much of a priority.
Limitations
Our mixed methods approach, wide range of outcomes, and diverse sample of participating schools offer rich information regarding the feasibility of At-Risk in the United Kingdom. These strengths notwithstanding, there are also several limitations to consider when interpreting the findings. The nonrandomized design, while common for feasibility studies, prevents any conclusions regarding causality and also limits the exploration of other factors that may have influenced outcomes (eg, providing teachers and TAs with the Mental Health Resource Maps or SENCos and mental health leads with feedback on identified pupils). In terms of recruitment and retention, the study had 50% (54/108) attrition. Several factors may have influenced this, including the increased pressure on school staff due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the timing of the study within the school year, and the requirement to communicate with participants only via the study link person. While we tried to explore the effect of attrition through a complete case sensitivity analysis, we lacked important information on the characteristics of those who dropped out as this information was collected only at T2. Furthermore, we were only able to recruit 8 staff members for the posttraining interviews, which was far below our recruitment target. Low participation rates could again be due to several factors, including the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic or competing priorities. Of note, we were not able to recruit anyone who did not complete the training, any headteachers, or any staff from 2 of the schools (schools A and D). This could mean that we lack viewpoints that may be important for understanding the feasibility and utility of the training.
There were also limitations associated with the study measures. While the Teacher and TA Identification Form was informed by the literature and reviewed by our primary school staff advisory group, its validity and reliability are unknown. In addition, the questionnaire only measured mental health support outcomes for those pupils identified as having mental health difficulties or increased risk. Therefore, we do not have information on those who were not identified. The measure is also based on teacher and TA reports and so may not have complete information about all types of support that pupils receive. Another important limitation pertains to the comparator used to assess the identification outcomes. To understand the potential utility of the training program, it is important to have a robust comparator. While we chose to use the teacher-report SDQ, it would also have been interesting to compare identification outcomes with parent-rated mental health difficulties, particularly in light of the low interrater agreement of common measures of child mental health difficulties [ 92 ]. An even stronger comparator would be to assess the teacher and TA identification outcomes against a clinical interview; however, this was not feasible in this study.
Finally, at the time of writing, At-Risk is currently not available for use as Kognito restructures its offerings. This demonstrates a trend that unfortunately is a common occurrence in the field of mental health, whereby many evidence-based digital tools are not available to potential end users [ 93 ]. Nonetheless, the learnings from this feasibility study offer rich information on what type of content and format may be useful for training programs in this area and, as such, can support further development and evaluation in the field.
Implications for Practice
Studies have consistently demonstrated that school staff would appreciate additional training on how best to support pupil mental health [ 18 , 20 , 87 , 88 ]. However, to be scalable, such programs must be realistic in terms of time, cost, and resource requirements [ 28 , 90 , 91 ]. Contextualized within the wider literature on school-based mental health interventions, the findings from this study suggest that mental health training is a feasible option for upskilling school staff to identify and respond to pupil mental health difficulties. They further highlight several specific factors that might positively contribute to feasibility and scalability, many of which are reflected in the broader literature on mental health training [ 20 , 28 ]. For example, teachers and TAs appreciated that the training actively engaged them in learning and applying new skills and that it used realistic examples to demonstrate the real-world applicability of the training, whereas school leaders identified the relatively low time and cost requirements and flexibility as key factors that could make the training feasible for their school context.
However, this is not to say that there are no implementation barriers associated with At-Risk or similar training programs. While the resources required to implement At-Risk are relatively low compared with other training programs, they must still be considered within the context of other school priorities. As demonstrated in the interviews and the wider literature [ 3 , 43 , 90 , 91 ], support from school leadership is essential for securing the time and budget required to implement a training such as At-Risk , and in schools where mental health is not a priority, there are likely to be many barriers to implementation . Even in schools with strong support from the leadership team, it may be difficult to find the requisite budget, time, and human resources to devote to the training. Finally, as is the case with any school-based mental health intervention, it is important that schools do not take sole responsibility for pupils’ mental health. Active partnership between schools and mental health services is key to ensuring that schools feel empowered and supported in this role [ 21 , 90 , 94 ]. While the schools in this study worked hard to support pupils as best they could, interviewees expressed frustration about the difficulty of accessing external support for children who could benefit from it. This is not an uncommon theme in the wider literature surrounding school-based interventions [ 20 , 23 , 91 ] and is a key consideration for scaling up training programs.
Implications for Future Research
The promising findings of this study suggest that additional research is needed to explore the role of scalable mental health training in supporting schools to protect and promote children’s mental health. On the basis of gaps in the literature, particular areas of interest include training for primary school staff (as most are focused on secondary school staff), web-based training (as opposed to traditional time- and resource-intensive in-person training), and training that takes a “whole school approach” by including all school staff members (rather than only teachers). This final area is especially interesting as findings from this study and others [ 27 ] have highlighted stakeholders’ preference that training programs include all school staff members. While our study jointly analyzed findings for teachers and TAs, future research would do well to consider how the unique roles and perspectives of these professionals—as well as other staff members within the school setting—might influence outcomes. Furthermore, future research should be more inclusive about their choice of outcomes, as too often evaluations of school staff training programs have focused on intermediate outcomes such as knowledge or confidence [ 31 ] without considering more “downstream” outcomes such as access to support. Finally, as demonstrated in our study, there is great value in using mixed methods approaches and including information about wider issues of feasibility and implementation, and studies that take this broader lens can help identify programs that are scalable, sustainable, and effective.
Conclusions
School staff would welcome additional mental health training to enable them to respond to pupil mental health difficulties, but there are many barriers to implementing such training at scale. Therefore, training programs that have relatively low time and resource requirements have great potential to fulfill an unmet need in schools. This mixed methods feasibility study showed that At-Risk for Elementary School Educators —an example of a brief, interactive web-based training program—is a feasible means of empowering school staff to accurately identify and respond to pupil mental health difficulties and increased risk.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Professor Paul Ramchandani for his input in the design of this study, the Cambridge Mental Health in Schools Advisory Group for sharing their views and advice throughout the study, and the staff at the 6 schools that took part in this study for their time and effort. This study was funded by the UK Research and Innovation Emerging Minds network (grant ES/S004726/2), and the training was provided to the schools free of cost by Kognito. ES was funded by a Gates Cambridge Scholarship (grant OPP1144) for the duration of the study. MF is funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) Oxford and Thames Valley Applied Research Collaboration at the Oxford Health National Health Service (NHS) Foundation Trust. PBJ is funded by the NIHR (grant 0616-20003). All research in the Cambridge Department of Psychiatry is supported by the NIHR Applied Research Collaboration East of England and the Cambridge Biomedical Research Centre at the Cambridgeshire and Peterborough NHS Foundation Trust. The views expressed are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR, the Department of Health and Social Care, or the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
Data Availability
The data sets generated during and analyzed during this study are not publicly available due to restrictions associated with our ethics approvals but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
Kognito is a for-profit company. After reviewing their questionnaires on preparedness and self-efficacy and having found them rigorous and unbiased, we independently decided to include them as outcomes in our study. Kognito had no role in the study design, analysis, or publication. PBJ was a scientific advisory board member for MSD. All other authors declare no other conflicts of interest.
Teacher and Teaching Assistant Identification Form.
Kognito pre- and posttraining surveys.
Interview topic guides.
School characteristics.
Results from complete case sensitivity analysis.
Results from the sensitivity analysis excluding school D.
Quantitative and qualitative findings pertaining to the potential harms of At-Risk.
- Transforming children and young people's mental health provision: a green paper. Department of Health and Department for Education, United Kingdom Government. Dec 2017. URL: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/5a823518e5 274a2e87dc1b56/Transforming_children_and_young_people_s_mental_health_provision.pdf [accessed 2024-03-25]
- Future in mind: promoting, protecting and improving our children and young people’s mental health and wellbeing. National Health Service England. URL: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/5a80b26bed915d74e33fbe3c/Childrens_Mental _Health.pdf [accessed 2024-03-25]
- Promoting children and young people's mental health and wellbeing. Office for Health Improvement and Disparities and Department for Education, United Kingdom Government. Mar 20, 2015. URL: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/promoting-children-and-young-peoples-emotional-health-and-wellbeing [accessed 2024-03-25]
- Newlove-Delgado T, Williams T, Robertson K, McManus S, Sadler K, Vizard T, et al. Mental health of children and young people in England 2021 - wave 2 follow up to the 2017 survey. National Health Service Digital. 2021. URL: https://openac cess.city.ac.uk/id/eprint/28718/ [accessed 2024-03-25]
- Vizard T, Sadler K, Ford T, Newlove-Delgado T, McManus S, Marcheselli F, et al. Mental health of children and young people in England, 2020. National Health Service Digital. Oct 22, 2020. URL: https://www.infocoponline.es/pdf/mhcyp _2020_rep.pdf [accessed 2024-03-25]
- Pitchforth J, Fahy K, Ford T, Wolpert M, Viner RM, Hargreaves DS. Mental health and well-being trends among children and young people in the UK, 1995-2014: analysis of repeated cross-sectional national health surveys. Psychol Med. Jun 2019;49(8):1275-1285. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Newlove-Delgado T, McManus S, Sadler K, Thandi S, Vizard T, Cartwright C, et al. Child mental health in England before and during the COVID-19 lockdown. Lancet Psychiatry. May 2021;8(5):353-354. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Creswell C, Shum A, Pearcey S, Skripkauskaite S, Patalay P, Waite P. Young people's mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. Aug 2021;5(8):535-537. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Fazel M, Hoagwood K, Stephan S, Ford T. Mental health interventions in schools 1: mental health interventions in schools in high-income countries. Lancet Psychiatry. Oct 2014;1(5):377-387. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, Jin R, Merikangas KR, Walters EE. Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. Jun 2005;62(6):593-602. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Greenberg MT, Domitrovich CE, Weissberg RP, Durlak JA. Social and emotional learning as a public health approach to education. Future Child. 2017;27(1):13-32. [ CrossRef ]
- Humphrey N, Wigelsworth M. Making the case for universal school-based mental health screening. Emot Behav Difficulties. 2016;21(1):22-42. [ CrossRef ]
- Kutcher S, Wei Y. School mental health: a necessary component of youth mental health policy and plans. World Psychiatry. Jun 2020;19(2):174-175. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Fazel M, Soneson E. Current evidence and opportunities in child and adolescent public mental health: a research review. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. Dec 2023;64(12):1699-1719. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Stephan SH, Weist M, Kataoka S, Adelsheim S, Mills C. Transformation of children's mental health services: the role of school mental health. Psychiatr Res. Oct 2007;58(10):1330-1338. [ CrossRef ]
- Day L, Blades R, Spence C, Ronicle J. Mental health services and schools link pilots: evaluation brief. Department for Education, United Kingdom Government. Feb 2017. URL: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/5a817dfaed915d74 e33fe812/Evaluation_of_the_MH_services_and_schools_link_pilots-RB.pdf [accessed 2024-03-25]
- Long MW, Albright G, McMillan J, Shockley KM, Price OA. Enhancing educator engagement in school mental health care through digital simulation professional development. J Sch Health. Sep 2018;88(9):651-659. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Rothì DM, Leavey G, Best R. On the front-line: teachers as active observers of pupils’ mental health. Teach Teach Educ. Jul 2008;24(5):1217-1231. [ CrossRef ]
- Mazzer KR, Rickwood DJ. Teachers' role breadth and perceived efficacy in supporting student mental health. Adv Sch Ment Health Promot. 2015;8(1):29-41. [ CrossRef ]
- Shelemy L, Harvey K, Waite P. Supporting students’ mental health in schools: what do teachers want and need? Emot Behav Difficulties. 2019;24(1):100-116. [ CrossRef ]
- Fazel M, Soneson E, Sellars E, Butler G, Stein A. Partnerships at the interface of education and mental health services: the utilisation and acceptability of the provision of specialist liaison and teacher skills training. Int J Environ Res Public Health. Feb 24, 2023;20(5):4066. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Marshall L, Wishart R, Dunatchik A, Smith N. Supporting mental health in schools and colleges: quantitative survey. Department for Education, United Kingdom Government. Aug 2017. URL: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/5a82e5bb40f0b6230269d46c/Supporting_Mental-Health_survey_report.pdf [accessed 2024-03-25]
- Sharpe H, Ford T, Lereya ST, Owen C, Viner RM, Wolpert M. Survey of schools' work with child and adolescent mental health across England: a system in need of support. Child Adolesc Ment Health. Sep 2016;21(3):148-153. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Danby G, Hamilton P. Addressing the ‘elephant in the room’. The role of the primary school practitioner in supporting children’s mental well-being. Pastor Care Educ. 2016;34(2):90-103. [ CrossRef ]
- Reinke WM, Stormont M, Herman KC, Puri R, Goel N. Supporting children's mental health in schools: teacher perceptions of needs, roles, and barriers. Sch Psychol Q. 2011;26(1):1-13. [ CrossRef ]
- Kidger J, Gunnell D, Biddle L, Campbell R, Donovan J. Part and parcel of teaching? Secondary school staff's views on supporting student emotional health and well-being. Br Educ Res J. Jan 02, 2013;36(6):919-935. [ CrossRef ]
- Soneson E, Burn AM, Anderson JK, Humphrey A, Jones PB, Fazel M, et al. Determining stakeholder priorities and core components for school-based identification of mental health difficulties: a Delphi study. J Sch Psychol. Apr 2022;91:209-227. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Soneson E, Howarth E, Ford T, Humphrey A, Jones PB, Thompson Coon J, et al. Feasibility of school-based identification of children and adolescents experiencing, or at-risk of developing, mental health difficulties: a systematic review. Prev Sci. Jul 2020;21(5):581-603. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Childs-Fegredo J, Burn AM, Duschinsky R, Humphrey A, Ford T, Jones PB, et al. Acceptability and feasibility of early identification of mental health difficulties in primary schools: a qualitative exploration of UK school staff and parents’ perceptions. Sch Ment Health. Nov 18, 2020;13:143-159. [ CrossRef ]
- Anderson JK, Ford T, Soneson E, Coon JT, Humphrey A, Rogers M, et al. A systematic review of effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of school-based identification of children and young people at risk of, or currently experiencing mental health difficulties. Psychol Med. Sep 13, 2018;49(1):9-19. [ CrossRef ]
- Yamaguchi S, Foo JC, Nishida A, Ogawa S, Togo F, Sasaki T. Mental health literacy programs for school teachers: a systematic review and narrative synthesis. Early Interv Psychiatry. Feb 2020;14(1):14-25. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kognito homepage. Kognito. URL: https://kognito.com/ [accessed 2024-03-26]
- At-risk for elementary school educators. Kognito. URL: https://kognito.com/products/at-risk-for-elementary-schools [accessed 2024-03-25]
- Anderson M, Werner-Seidler A, King C, Gayed A, Harvey SB, O’Dea B. Mental health training programs for secondary school teachers: a systematic review. Sch Ment Health. Oct 3, 2018;11:489-508. [ CrossRef ]
- Ekornes S. Teacher perspectives on their role and the challenges of inter-professional collaboration in mental health promotion. Sch Ment Health. Mar 17, 2015;7:193-211. [ CrossRef ]
- Ohrt JH, Deaton JD, Linich K, Guest JD, Wymer B, Sandonato B. Teacher training in K–12 student mental health: a systematic review. Psychol Sch. Mar 03, 2020;57(5):833-846. [ CrossRef ]
- Parker BL, Anderson M, Batterham PJ, Gayed A, Subotic-Kerry M, Achilles MR, et al. Examining the preliminary effectiveness and acceptability of a web-based training program for Australian secondary school teachers: pilot study of the BEAM (building educators' skills in adolescent mental health) program. JMIR Ment Health. Oct 22, 2021;8(10):e29989. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- McVey G, Gusella J, Tweed S, Ferrari M. A controlled evaluation of web-based training for teachers and public health practitioners on the prevention of eating disorders. Eat Disord. 2009;17(1):1-26. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Pereira CA, Wen CL, Miguel EC, Polanczyk GV. A randomised controlled trial of a web-based educational program in child mental health for schoolteachers. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. Aug 2015;24(8):931-940. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kognito At-Risk in PK-12. Oklahoma Department of Mental Health and Substance Abuse Services. URL: https://oklahoma.gov/odmhsas/trainings/training-institute/at-risk-pk-12.html [accessed 2024-03-14]
- Albright G, Fazel M, Khalid N, McMillan J, Hilty D, Shockley K, et al. High school educator training by simulation to address emotional and behavioral concerns in school settings: a randomized study. J Technol Behav Sci. 2022;7(3):277-289. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Greif Green J, Levine RS, Oblath R, Corriveau KH, Holt MK, Albright G. Pilot evaluation of preservice teacher training to improve preparedness and confidence to address student mental health. Evid Based Pract Child Adolesc Ment Health. 2020;5(1):42-52. [ CrossRef ]
- Domitrovich CE, Bradshaw CP, Poduska JM, Hoagwood K, Buckley JA, Olin S, et al. Maximizing the implementation quality of evidence-based preventive interventions in schools: a conceptual framework. Adv Sch Ment Health Promot. Jul 2008;1(3):6-28. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Bonell C, Prost A, Melendez-Torres GJ, Davey C, Hargreaves JR. Will it work here? A realist approach to local decisions about implementing interventions evaluated as effective elsewhere. J Epidemiol Community Health. Jan 2021;75(1):46-50. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Domitrovich CE, Greenberg MT. The study of implementation: current findings from effective programs that prevent mental disorders in school-aged children. J Educ Psychol Consult. 2000;11(2):193-221. [ CrossRef ]
- Evans RE, Craig P, Hoddinott P, Littlecott H, Moore L, Murphy S, et al. When and how do 'effective' interventions need to be adapted and/or re-evaluated in new contexts? The need for guidance. J Epidemiol Community Health. Jun 2019;73(6):481-482. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Gardner F, Montgomery P, Knerr W. Transporting evidence-based parenting programs for child problem behavior (age 3-10) between countries: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2016;45(6):749-762. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Leijten P, Melendez-Torres GJ, Knerr W, Gardner F. Transported versus homegrown parenting interventions for reducing disruptive child behavior: a multilevel meta-regression study. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. Jul 2016;55(7):610-617. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Craig P, Dieppe P, Macintyre S, Michie S, Nazareth I, Petticrew M. Developing and evaluating complex interventions: the new medical research Council guidance. BMJ. Sep 29, 2008;337:a1655. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Moore L, Hallingberg B, Wight D, Turley R, Segrott J, Craig P, et al. Exploratory studies to inform full-scale evaluations of complex public health interventions: the need for guidance. J Epidemiol Community Health. Oct 2018;72(10):865-866. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Eldridge SM, Lancaster GA, Campbell MJ, Thabane L, Hopewell S, Coleman CL, et al. Defining feasibility and pilot studies in preparation for randomised controlled trials: development of a conceptual framework. PLoS One. 2016;11(3):e0150205. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Bowen DJ, Kreuter M, Spring B, Cofta-Woerpel L, Linnan L, Weiner D, et al. How we design feasibility studies. Am J Prev Med. May 2009;36(5):452-457. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- McLennan D, Noble S, Noble M, Plunkett E, Wright G, Gutacker N. The English indices of deprivation 2019: technical report. Ministry of Housing, Communities and Local Government, United Kingdom Government. Sep 2019. URL: https://dera.ioe.ac.uk/34259/1/IoD2019_Technical_Report.pdf [accessed 2024-03-25]
- Schools, pupils and their characteristics: January 2019. Department for Education, United Kingdom Government. Jun 2019. URL: https://www.gov.uk/government/statistics/schools-pupils-and-their-characteristics-january-2019 [accessed 2024-03-25]
- Special educational needs in England: January 2019. Department for Education, United Kingdom Government. Jul 4, 2019. URL: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/5d1c91cce5274a08df3d35bd/SEN_2019_Text.docx.pdf [accessed 2024-03-25]
- Goodman R. The Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire: a research note. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. Jul 07, 1997;38(5):581-586. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Goodman R. The extended version of the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire as a guide to child psychiatric caseness and consequent burden. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. Jul 1999;40(5):791-799. [ CrossRef ]
- Goodman R, Ford T, Simmons H, Gatward R, Meltzer H. Using the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ) to screen for child psychiatric disorders in a community sample. Br J Psychiatry. Dec 02, 2000;177(6):534-539. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Goodman R, Meltzer H, Bailey V. The Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire: a pilot study on the validity of the self-report version. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. Sep 12, 1998;7(3):125-130. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Stone LL, Otten R, Engels RC, Vermulst AA, Janssens JM. Psychometric properties of the parent and teacher versions of the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire for 4- to 12-year-olds: a review. Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev. Sep 2010;13(3):254-274. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Albright GL, Davidson J, Goldman R, Shockley KM, Timmons-Mitchell J. Development and validation of the Gatekeeper Behavior Scale. Crisis. Jul 2016;37(4):271-280. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Damschroder LJ, Aron DC, Keith RE, Kirsh SR, Alexander JA, Lowery JC. Fostering implementation of health services research findings into practice: a consolidated framework for advancing implementation science. Implement Sci. Aug 07, 2009;4:50. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Lyon AR, Bruns EJ. From evidence to impact: joining our best school mental health practices with our best implementation strategies. School Ment Health. Mar 1, 2019;11(1):106-114. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Schools, pupils and their characteristics: January 2020. Department for Education, United Kingdom Government. Jun 25, 2020. URL: https://www.gov.uk/government/statistics/schools-pupils-and-their-characteristics-january-2020 [accessed 2024-03-25]
- Eldridge SM, Chan CL, Campbell MJ, Bond CM, Hopewell S, Thabane L, et al. CONSORT 2010 statement: extension to randomised pilot and feasibility trials. BMJ. Oct 24, 2016;355:i5239. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Wilson DT, Walwyn RE, Brown J, Farrin AJ, Brown SR. Statistical challenges in assessing potential efficacy of complex interventions in pilot or feasibility studies. Stat Methods Med Res. Jun 2016;25(3):997-1009. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Lancaster GA, Dodd S, Williamson PR. Design and analysis of pilot studies: recommendations for good practice. J Eval Clin Pract. May 2004;10(2):307-312. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Thabane L, Ma J, Chu R, Cheng J, Ismaila A, Rios LP, et al. A tutorial on pilot studies: the what, why and how. BMC Med Res Methodol. Jan 06, 2010;10:1. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- R: a language and environment for statistical computing. The Comprehensive R Archive Network. Feb 10, 2015. URL: https://www.gbif.org/tool/81287/r-a-language-and-environment-for-statistical-computing [accessed 2024-03-25]
- Wickham H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. New York, NY. Springer; 2009.
- Bryer J, Speerschneider K. Analysis and visualization of Likert based items. GitHub. URL: http://github.com/jbryer/likert
- YouthinMind homepage. YouthinMind. URL: https://youthinmind.com/ [accessed 2024-03-26]
- Hsieh HF, Shannon SE. Three approaches to qualitative content analysis. Qual Health Res. Nov 2005;15(9):1277-1288. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Gale NK, Heath G, Cameron E, Rashid S, Redwood S. Using the framework method for the analysis of qualitative data in multi-disciplinary health research. BMC Med Res Methodol. Sep 18, 2013;13:117. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual Res Psychol. 2006;3(2):77-101. [ CrossRef ]
- Braun V, Clarke V. Thematic Analysis: A Practical Guide. Thousand Oaks, CA. SAGE Publications; 2021.
- School workforce in England. United Kingdom Government. Jun 8, 2023. URL: https://explore-education-statistics.service .gov.uk/find-statistics/school-workforce-in-england [accessed 2024-03-14]
- Jorm AF, Kitchener BA, Sawyer MG, Scales H, Cvetkovski S. Mental health first aid training for high school teachers: a cluster randomized trial. BMC Psychiatry. Jun 24, 2010;10:51. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Moor S, Maguire A, McQueen H, Wells EJ, Elton R, Wrate R, et al. Improving the recognition of depression in adolescence: can we teach the teachers? J Adolesc. Feb 2007;30(1):81-95. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kidger J, Stone T, Tilling K, Brockman R, Campbell R, Ford T, et al. A pilot cluster randomised controlled trial of a support and training intervention to improve the mental health of secondary school teachers and students - the WISE (Wellbeing in Secondary Education) study. BMC Public Health. Oct 06, 2016;16(1):1060. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Vieira MA, Gadelha AA, Moriyama TS, Bressan RA, Bordin IA. Evaluating the effectiveness of a training program that builds teachers' capability to identify and appropriately refer middle and high school students with mental health problems in Brazil: an exploratory study. BMC Public Health. Feb 28, 2014;14:210. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- McLaughlin RJ, Holcomb JD, Jibaja-Rusth ML, Webb J. Teacher ratings of student risk for substance use as a function of specialized training. J Drug Educ. 1993;23(1):83-95. [ CrossRef ]
- Soneson E, Childs-Fegredo J, Anderson JK, Stochl J, Fazel M, Ford T, et al. Acceptability of screening for mental health difficulties in primary schools: a survey of UK parents. BMC Public Health. Dec 22, 2018;18(1):1404. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Levitt JM, Saka N, Hunter Romanelli L, Hoagwood K. Early identification of mental health problems in schools: the status of instrumentation. J Sch Psychol. Apr 2007;45(2):163-191. [ CrossRef ]
- Loades ME, Mastroyannopoulou K. Teachers' recognition of children's mental health problems. Child Adolesc Ment Health. Sep 2010;15(3):150-156. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Anderson JK, Howarth E, Vainre M, Jones PB, Humphrey A. A scoping literature review of service-level barriers for access and engagement with mental health services for children and young people. Child Youth Serv Rev. Jun 2017;77:164-176. [ CrossRef ]
- Moon J, Williford A, Mendenhall A. Educators' perceptions of youth mental health: implications for training and the promotion of mental health services in schools. Child Youth Serv Rev. Feb 2017;73:384-391. [ CrossRef ]
- Graham A, Phelps R, Maddison C, Fitzgerald R. Supporting children’s mental health in schools: teacher views. Teach Teach. 2011;17(4):479-496. [ CrossRef ]
- Atkins MS, Graczyk PA, Frazier SL, Abdul-Adil J. Toward a new model for promoting urban children's mental health: accessible, effective, and sustainable school-based mental health services. Sch Psychol Rev. 2003;32(4):503-514. [ CrossRef ]
- Moore A, Stapley E, Hayes D, Town R, Deighton J. Barriers and facilitators to sustaining school-based mental health and wellbeing interventions: a systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. Mar 17, 2022;19(6):3587. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Gee B, Wilson J, Clarke T, Farthing S, Carroll B, Jackson C, et al. Review: delivering mental health support within schools and colleges - a thematic synthesis of barriers and facilitators to implementation of indicated psychological interventions for adolescents. Child Adolesc Ment Health. Feb 2021;26(1):34-46. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Fält E, Wallby T, Sarkadi A, Salari R, Fabian H. Agreement between mothers', fathers', and teachers' ratings of behavioural and emotional problems in 3-5-year-old children. PLoS One. Nov 01, 2018;13(11):e0206752. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Bear HA, Ayala Nunes L, DeJesus J, Liverpool S, Moltrecht B, Neelakantan L, et al. Determination of markers of successful implementation of mental health apps for young people: systematic review. J Med Internet Res. Nov 09, 2022;24(11):e40347. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Durbin K, Harmon S. We are on the same team: child psychiatry and the school system. JAACAP Connect. 2020;7(1):32-36. [ CrossRef ]
Abbreviations
Edited by T Leung; submitted 24.02.23; peer-reviewed by E Widnall, B Fernandes, J Burns, K Cohen; comments to author 27.08.23; accepted 01.03.24; published 23.04.24.
©Emma Soneson, Emma Howarth, Alison Weir, Peter B Jones, Mina Fazel. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (https://www.jmir.org), 23.04.2024.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work, first published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research, is properly cited. The complete bibliographic information, a link to the original publication on https://www.jmir.org/, as well as this copyright and license information must be included.
Asking the better questions that unlock new answers to the working world's most complex issues.
Trending topics
AI insights
EY podcasts
EY webcasts
Operations leaders
Technology leaders
Marketing and growth leaders
Cybersecurity and privacy leaders
Risk leaders
EY Center for Board Matters
EY helps clients create long-term value for all stakeholders. Enabled by data and technology, our services and solutions provide trust through assurance and help clients transform, grow and operate.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Strategy, transaction and transformation consulting
Technology transformation
Tax function operations
Climate change and sustainability services
EY Ecosystems
Supply chain and operations
EY Partner Ecosystem
Explore Services
We bring together extraordinary people, like you, to build a better working world.
Experienced professionals
MBA and advanced-degree students
Student and entry level programs
Contract workers
EY-Parthenon careers
Discover how EY insights and services are helping to reframe the future of your industry.
Case studies
Energy and resources
How data analytics can strengthen supply chain performance
13-Jul-2023 Ben Williams
How Takeda harnessed the power of the metaverse for positive human impact
26-Jun-2023 Edwina Fitzmaurice
Banking and Capital Markets
How cutting back infused higher quality in transaction monitoring
11-Jul-2023 Ron V. Giammarco
At EY, our purpose is building a better working world. The insights and services we provide help to create long-term value for clients, people and society, and to build trust in the capital markets.
EY is now carbon negative
19-Sep-2022 Carmine Di Sibio
Our commitment to audit quality
13-Nov-2023 Julie A. Boland
No results have been found
Recent Searches

BEPS 2.0: as policies evolve, engagement is key
It remains to be seen whether the US will align its tax law with the OECD/G20’s global BEPS 2.0 rules. MNEs will feel the impact in 2024. Learn more.

How GenAI strategy can transform innovation
Companies considering or investing in a transformative GenAI strategy should tie generative artificial intelligence use cases to revenue, cost and expense. Learn more

Top five private equity trends for 2024
Read about the five key trends private equity firms will emphasize in 2024 as they create value
Select your location
close expand_more

How life insurers can provide differentiated retirement benefits

EY Americas Retirement Leader Principal, Ernst & Young LLP
Related topics
Benefits of integrating insurance products into a retirement plan (pdf), permanent life insurance and deferred income annuities with increasing income potential outperform investment-only approaches in our analysis..
- By 2030, gaps in investors’ retirement savings and needed protections are projected to exceed hundreds of trillions of dollars in the US.
- This presents an opportunity for insurance companies to better serve customers to bridge these chasms, through modified investment approaches.
A lthough facing challenges, the US life insurance and retirement industry has enormous potential to grow. Our analysis reveals insights on how best to capitalize on this opportunity.
EY researchers estimate that by 2030, there will be a $240 trillion retirement savings gap and a $160 trillion protection gap. Insurers are uniquely positioned to address these gaps with products that offer legacy protection, tax-deferred savings growth and guaranteed income for life.
In this article, we explore how two products can be used to meet investors’ savings and protection needs: permanent life insurance (PLI) and a deferred income annuity with increasing income potential (DIA with IIP), which represents deferred income annuities with persistency bonuses and non-guaranteed dividends. Can integrating PLI and a DIA with IIP into a retirement plan provide value beyond an investment-only strategy?
It is a complex question to answer. To judge the impact of PLI and DIAs with IIP, we analyzed five strategies, conducted across three different starting ages: 25, 35 and 45. For each strategy, our Monte Carlo analysis generated 1,000 scenarios based on randomized input from a range of factors, such as interest rates, inflation rates, equity returns and bond returns. The high-level results are shown in this summary article and elaborated upon in our full report.
Download the full report
The five strategies compared.
We examined a baseline of traditional investment strategies and then compared them against those that also factor in PLI and DIAs with IIP:

For strategies that include PLI and a DIA with IIP, the value of these products is included in the total financial assets and considered part of the fixed income allocation. Thus, for strategies where an investor allocates a portion of their wealth to an insurance product, the amount invested in bonds decreases compared to the investment-only strategy.
In our analysis, PLI cash value (accessed via surrenders or loans) are used to fund retirement income during periods of market volatility, allowing investors to avoid liquidating assets from their traditional investments that have fallen in value.
We divided the investor’s assets between the investments and the insurance products. Different product allocation combinations were simulated in increments of 10% of total annual savings for PLI and projected wealth at age 55 for DIA with IIP. Allocation percentages were capped at 60% for PLI and 30% for DIAs with IIP. For each allocation combination, we calculated the after tax retirement income that an investor can sustain in over 90% of the market return scenarios. We also calculated the legacy value at the end of the time horizon.
The benefit to investors
Following this methodology, strategies involving PLI and DIAs with IIP excelled overall against investment-only approaches — although the implications must be couched in a bit of nuance, depending on whether the investor is focused more on retirement income than legacy. Here are six key insights on how the strategies compare:
1. PLI + investments strategies outperform investment-only and term life + investments strategies.
PLI tends to provide superior returns over fixed income in long-run scenarios, while the term premium acts as a drag on portfolio performance. PLI loans act as a buffer against market volatility as well, improving returns since the investor does not have to sell and realize losses on investments.
2. DIA with IIP + investments strategies outperform other strategies in retirement income.
With DIAs with IIP + investments, the investor uses a portion of the balance to purchase the DIA with IIP and does not receive that balance upon death, boosting retirement income compared to other strategies. Projected legacy tends to be lower than PLI + investments but higher than the legacy from the investment-only strategy. The latter observation is a result of the DIA with IIP outperforming fixed income due to mortality credits and dividends.
3. Integrated strategies are more efficient than investment-only strategies.
For example, a strategy allocating 30% of annual savings to PLI and 30% of assets at age 55 to a DIA with IIP produced 5% higher retirement income and 19% more legacy than the investment-only strategy, because PLI and DIA with IIP both outperform fixed income.
4. For investors with a higher risk appetite, integrated strategies remain better.
We performed the same exercise described above, except that we calculated the retirement income (and legacy values) based on the amount that the investor can sustain in over 75% of the market return scenarios, reflecting the expectations of an investor with higher risk. Income and legacy do not improve as much, yet an integrated portfolio still provides benefits relative to an investment-only strategy.
5. Integrated strategies provide investors with the flexibility to focus on the financial outcomes most important to them: retirement income, legacy or a balance in between.
We found that PLI and a DIA with IIP mix well together, whether a person is focused on retirement income, legacy or a balance. Higher allocations to a DIA with IIP emphasize retirement income, while higher PLI boosts legacy protection. The right mix depends on the investor’s preferences.
6. Allocation up to 30% of annual savings to PLI and up to 30% of wealth at age 55 to DIA with IIP may be appropriate when optimizing retirement income and legacy value outcomes.
Results varied by investor starting age. But the projected retirement income and legacy values generally supported allocations of 10% to 30% to both PLI and DIAs with IIPs. An investor solely focused on maximizing legacy may still opt to allocate more to PLI, but when that allocation redirects too many assets away from equities, the reduction to retirement income can be substantial.
The results point to the value of PLI and DIAs with IIPs in a retirement plan: an integrated approach can give comfort and peace of mind to retirement investors by providing legacy protection, tax-deferred savings growth, and guaranteed income for life without sacrificing their present lifestyle. Insurers can use these products to strengthen their relationships with investors, seizing upon the possibilities in a marketplace that has proved challenging.
This article has been authored by Christopher Raham, Justin Singer, Ben Yahr, Ben Lee, and Annie E Mayer.
Investment-only approaches do not deliver as promising returns as those that are combined with PLI and DIAs with increasing income potential, an EY analysis shows, although there are distinctions to consider depending on whether more retirement income or legacy value is desired. Allocation levels should be approached with care.
About this article

- Connect with us
- Our locations
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Legal and privacy
- Accessibility
- Open Facebook profile
- Open X profile
- Open LinkedIn profile
- Open Youtube profile
EY refers to the global organization, and may refer to one or more, of the member firms of Ernst & Young Global Limited, each of which is a separate legal entity. Ernst & Young Global Limited, a UK company limited by guarantee, does not provide services to clients.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The purpose of a research paper is to present the results of a study or investigation in a clear, concise, and structured manner. Research papers are written to communicate new knowledge, ideas, or findings to a specific audience, such as researchers, scholars, practitioners, or policymakers. The primary purposes of a research paper are:
A research paper is a piece of academic writing that provides analysis, interpretation, and argument based on in-depth independent research. Research papers are similar to academic essays, but they are usually longer and more detailed assignments, designed to assess not only your writing skills but also your skills in scholarly research ...
A research paper provides an excellent opportunity to contribute to your area of study or profession by exploring a topic in depth.. With proper planning, knowledge, and framework, completing a research paper can be a fulfilling and exciting experience. Though it might initially sound slightly intimidating, this guide will help you embrace the challenge.
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature. As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question.More specifically, that's called a research question, and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What's important to understand though is that you'll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources - for ...
Definition. A research paper is a paper that makes an argument about a topic based on research and analysis. Any paper requiring the writer to research a particular topic is a research paper. Unlike essays, which are often based largely on opinion and are written from the author's point of view, research papers are based in fact.
A research paper is a common form of academic writing. Research papers require students and academics to locate information about a topic (that is, to conduct research ), take a stand on that topic, and provide support (or evidence) for that position in an organized report. The term research paper may also refer to a scholarly article that ...
Move 2. Research Context: a. Compare and contrast your findings with those of other published results. b. Explain any discrepancies and unexpected findings. c. State the limitations, weaknesses, and assumptions of your study. Move 3. Closing the paper: a. Summarize the answers to the research questions. b.
Learn to write a research paper step-by-step with a process that involves determining the research purpose and question in the early stages, finding sources, taking notes, creating an outline, and ...
A "research design," used for complex papers, is related to the paper's method. This resource contains introductions to a variety of popular research designs in the social sciences. Although it is not the most intuitive site to read, the information here is very valuable.
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about: Your overall research objectives and approach. Whether you'll rely on primary research or secondary research. Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects. Your data collection methods.
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
narrative table of contents that summarizes the flow of the rest of the paper. Below, see an example roadmap in which Cuevas (2019) succinctly outlines her argument. You may also see roadmaps that list the bodies of literature that the author will review, or key points from the study design and procedure.
Experimental research paper. This type of research paper basically describes a particular experiment in detail. It is common in fields like: biology. chemistry. physics. Experiments are aimed to explain a certain outcome or phenomenon with certain actions. You need to describe your experiment with supporting data and then analyze it sufficiently.
What is the significance of your results? - the final major section of text in the paper. The Discussion commonly features a summary of the results that were obtained in the study, describes how those results address the topic under investigation and/or the issues that the research was designed to address, and may expand upon the implications of those findings.
Writing Your Paper. Parts of the Research Paper. Papers should have a beginning, a middle, and an end. Your introductory paragraph should grab the reader's attention, state your main idea, and indicate how you will support it. The body of the paper should expand on what you have stated in the introduction. Finally, the conclusion restates the ...
Formal Research Structure. These are the primary purposes for formal research: enter the discourse, or conversation, of other writers and scholars in your field. learn how others in your field use primary and secondary resources. find and understand raw data and information. For the formal academic research assignment, consider an ...
Introduction. This article deals with drafting a suitable "title" and an appropriate "abstract" for an original research paper. Because the "title" and the "abstract" are the "initial impressions" or the "face" of a research article, they need to be drafted correctly, accurately, carefully, meticulously, and consume time and energy.[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10] Often, these ...
In shorter scientific papers, where the aim is to report the findings of a specific study, you might simply describe what you did in a methods section. In a longer or more complex research project, such as a thesis or dissertation , you will probably include a methodology section , where you explain your approach to answering the research ...
A Research Paper Research papers are extended scholarly works that explore a specific topic in depth. They generally require an extensive research process, which may involve interviews and surveys as well as traditional library sources such as books or journal articles. These papers typically include the following: Title page ; Abstract
A study in Japan has found that writing down your reaction to a negative incident on a piece of paper and then shredding it, or scrunching it into a ball and throwing it in the bin, gets rid of anger.
The AI Index report tracks, collates, distills, and visualizes data related to artificial intelligence (AI). Our mission is to provide unbiased, rigorously vetted, broadly sourced data in order for policymakers, researchers, executives, journalists, and the general public to develop a more thorough and nuanced understanding of the complex field ...
Pew Research Center conducted this analysis to provide a snapshot of partisan divides in K-12 education in the run-up to the 2024 election. The analysis is based on data from various Center surveys and analyses conducted from 2021 to 2023, as well as survey data from Education Next, a research journal about education policy.
Co-author of the study, Dr Miranda Bruce from the University of Oxford and UNSW Canberra said the study will enable the public and private sectors to focus their resources on key cybercrime hubs and spend less time and funds on cybercrime countermeasures in countries where the problem is not as significant. 'The research that underpins the Index will help remove the veil of anonymity around ...
Millions of Borderlands 3 players are now collectively listed as contributors to a peer reviewed scientific paper, after participating in a minigame that helped provide researchers with real-world ...
Compare your paper to billions of pages and articles with Scribbr's Turnitin-powered plagiarism checker. Run a free check ... But the type of research is only the first step: next, you have to make more concrete decisions about your research methods and the details of the study. Read more about creating a research design. Other interesting ...
1.Introduction. Greenwashing - "the dissemination of false or deceptive information regarding an organization's environmental strategies, goals, motivations, and actions" [1] - is gaining the attention of researchers, policymakers, and regulators.The charge of greenwashing is now levelled at various organizations, not only in academic studies, but in formal complaints [2], lawsuits [3 ...
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications. ... This study emphasizes the need ...
Step 4: Create a research design. The research design is a practical framework for answering your research questions. It involves making decisions about the type of data you need, the methods you'll use to collect and analyze it, and the location and timescale of your research. There are often many possible paths you can take to answering ...
Background: Schools in the United Kingdom and elsewhere are expected to protect and promote pupil mental health. However, many school staff members do not feel confident in identifying and responding to pupil mental health difficulties and report wanting additional training in this area. Objective: We aimed to explore the feasibility of Kognito's At-Risk for Elementary School Educators, a ...
Here are six key insights on how the strategies compare: 1. PLI + investments strategies outperform investment-only and term life + investments strategies. PLI tends to provide superior returns over fixed income in long-run scenarios, while the term premium acts as a drag on portfolio performance. PLI loans act as a buffer against market ...