- Privacy Policy

Home » What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and Writing Guide

What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Definition:
Hypothesis is an educated guess or proposed explanation for a phenomenon, based on some initial observations or data. It is a tentative statement that can be tested and potentially proven or disproven through further investigation and experimentation.
Hypothesis is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments and the collection and analysis of data. It is an essential element of the scientific method, as it allows researchers to make predictions about the outcome of their experiments and to test those predictions to determine their accuracy.
Types of Hypothesis
Types of Hypothesis are as follows:
Research Hypothesis
A research hypothesis is a statement that predicts a relationship between variables. It is usually formulated as a specific statement that can be tested through research, and it is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is a statement that assumes there is no significant difference or relationship between variables. It is often used as a starting point for testing the research hypothesis, and if the results of the study reject the null hypothesis, it suggests that there is a significant difference or relationship between variables.
Alternative Hypothesis
An alternative hypothesis is a statement that assumes there is a significant difference or relationship between variables. It is often used as an alternative to the null hypothesis and is tested against the null hypothesis to determine which statement is more accurate.
Directional Hypothesis
A directional hypothesis is a statement that predicts the direction of the relationship between variables. For example, a researcher might predict that increasing the amount of exercise will result in a decrease in body weight.
Non-directional Hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis is a statement that predicts the relationship between variables but does not specify the direction. For example, a researcher might predict that there is a relationship between the amount of exercise and body weight, but they do not specify whether increasing or decreasing exercise will affect body weight.
Statistical Hypothesis
A statistical hypothesis is a statement that assumes a particular statistical model or distribution for the data. It is often used in statistical analysis to test the significance of a particular result.
Composite Hypothesis
A composite hypothesis is a statement that assumes more than one condition or outcome. It can be divided into several sub-hypotheses, each of which represents a different possible outcome.
Empirical Hypothesis
An empirical hypothesis is a statement that is based on observed phenomena or data. It is often used in scientific research to develop theories or models that explain the observed phenomena.
Simple Hypothesis
A simple hypothesis is a statement that assumes only one outcome or condition. It is often used in scientific research to test a single variable or factor.
Complex Hypothesis
A complex hypothesis is a statement that assumes multiple outcomes or conditions. It is often used in scientific research to test the effects of multiple variables or factors on a particular outcome.
Applications of Hypothesis
Hypotheses are used in various fields to guide research and make predictions about the outcomes of experiments or observations. Here are some examples of how hypotheses are applied in different fields:
- Science : In scientific research, hypotheses are used to test the validity of theories and models that explain natural phenomena. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a particular variable on a natural system, such as the effects of climate change on an ecosystem.
- Medicine : In medical research, hypotheses are used to test the effectiveness of treatments and therapies for specific conditions. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a new drug on a particular disease.
- Psychology : In psychology, hypotheses are used to test theories and models of human behavior and cognition. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a particular stimulus on the brain or behavior.
- Sociology : In sociology, hypotheses are used to test theories and models of social phenomena, such as the effects of social structures or institutions on human behavior. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of income inequality on crime rates.
- Business : In business research, hypotheses are used to test the validity of theories and models that explain business phenomena, such as consumer behavior or market trends. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a new marketing campaign on consumer buying behavior.
- Engineering : In engineering, hypotheses are used to test the effectiveness of new technologies or designs. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the efficiency of a new solar panel design.
How to write a Hypothesis
Here are the steps to follow when writing a hypothesis:
Identify the Research Question
The first step is to identify the research question that you want to answer through your study. This question should be clear, specific, and focused. It should be something that can be investigated empirically and that has some relevance or significance in the field.
Conduct a Literature Review
Before writing your hypothesis, it’s essential to conduct a thorough literature review to understand what is already known about the topic. This will help you to identify the research gap and formulate a hypothesis that builds on existing knowledge.
Determine the Variables
The next step is to identify the variables involved in the research question. A variable is any characteristic or factor that can vary or change. There are two types of variables: independent and dependent. The independent variable is the one that is manipulated or changed by the researcher, while the dependent variable is the one that is measured or observed as a result of the independent variable.
Formulate the Hypothesis
Based on the research question and the variables involved, you can now formulate your hypothesis. A hypothesis should be a clear and concise statement that predicts the relationship between the variables. It should be testable through empirical research and based on existing theory or evidence.
Write the Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is the opposite of the alternative hypothesis, which is the hypothesis that you are testing. The null hypothesis states that there is no significant difference or relationship between the variables. It is important to write the null hypothesis because it allows you to compare your results with what would be expected by chance.
Refine the Hypothesis
After formulating the hypothesis, it’s important to refine it and make it more precise. This may involve clarifying the variables, specifying the direction of the relationship, or making the hypothesis more testable.
Examples of Hypothesis
Here are a few examples of hypotheses in different fields:
- Psychology : “Increased exposure to violent video games leads to increased aggressive behavior in adolescents.”
- Biology : “Higher levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere will lead to increased plant growth.”
- Sociology : “Individuals who grow up in households with higher socioeconomic status will have higher levels of education and income as adults.”
- Education : “Implementing a new teaching method will result in higher student achievement scores.”
- Marketing : “Customers who receive a personalized email will be more likely to make a purchase than those who receive a generic email.”
- Physics : “An increase in temperature will cause an increase in the volume of a gas, assuming all other variables remain constant.”
- Medicine : “Consuming a diet high in saturated fats will increase the risk of developing heart disease.”
Purpose of Hypothesis
The purpose of a hypothesis is to provide a testable explanation for an observed phenomenon or a prediction of a future outcome based on existing knowledge or theories. A hypothesis is an essential part of the scientific method and helps to guide the research process by providing a clear focus for investigation. It enables scientists to design experiments or studies to gather evidence and data that can support or refute the proposed explanation or prediction.
The formulation of a hypothesis is based on existing knowledge, observations, and theories, and it should be specific, testable, and falsifiable. A specific hypothesis helps to define the research question, which is important in the research process as it guides the selection of an appropriate research design and methodology. Testability of the hypothesis means that it can be proven or disproven through empirical data collection and analysis. Falsifiability means that the hypothesis should be formulated in such a way that it can be proven wrong if it is incorrect.
In addition to guiding the research process, the testing of hypotheses can lead to new discoveries and advancements in scientific knowledge. When a hypothesis is supported by the data, it can be used to develop new theories or models to explain the observed phenomenon. When a hypothesis is not supported by the data, it can help to refine existing theories or prompt the development of new hypotheses to explain the phenomenon.
When to use Hypothesis
Here are some common situations in which hypotheses are used:
- In scientific research , hypotheses are used to guide the design of experiments and to help researchers make predictions about the outcomes of those experiments.
- In social science research , hypotheses are used to test theories about human behavior, social relationships, and other phenomena.
- I n business , hypotheses can be used to guide decisions about marketing, product development, and other areas. For example, a hypothesis might be that a new product will sell well in a particular market, and this hypothesis can be tested through market research.
Characteristics of Hypothesis
Here are some common characteristics of a hypothesis:
- Testable : A hypothesis must be able to be tested through observation or experimentation. This means that it must be possible to collect data that will either support or refute the hypothesis.
- Falsifiable : A hypothesis must be able to be proven false if it is not supported by the data. If a hypothesis cannot be falsified, then it is not a scientific hypothesis.
- Clear and concise : A hypothesis should be stated in a clear and concise manner so that it can be easily understood and tested.
- Based on existing knowledge : A hypothesis should be based on existing knowledge and research in the field. It should not be based on personal beliefs or opinions.
- Specific : A hypothesis should be specific in terms of the variables being tested and the predicted outcome. This will help to ensure that the research is focused and well-designed.
- Tentative: A hypothesis is a tentative statement or assumption that requires further testing and evidence to be confirmed or refuted. It is not a final conclusion or assertion.
- Relevant : A hypothesis should be relevant to the research question or problem being studied. It should address a gap in knowledge or provide a new perspective on the issue.
Advantages of Hypothesis
Hypotheses have several advantages in scientific research and experimentation:
- Guides research: A hypothesis provides a clear and specific direction for research. It helps to focus the research question, select appropriate methods and variables, and interpret the results.
- Predictive powe r: A hypothesis makes predictions about the outcome of research, which can be tested through experimentation. This allows researchers to evaluate the validity of the hypothesis and make new discoveries.
- Facilitates communication: A hypothesis provides a common language and framework for scientists to communicate with one another about their research. This helps to facilitate the exchange of ideas and promotes collaboration.
- Efficient use of resources: A hypothesis helps researchers to use their time, resources, and funding efficiently by directing them towards specific research questions and methods that are most likely to yield results.
- Provides a basis for further research: A hypothesis that is supported by data provides a basis for further research and exploration. It can lead to new hypotheses, theories, and discoveries.
- Increases objectivity: A hypothesis can help to increase objectivity in research by providing a clear and specific framework for testing and interpreting results. This can reduce bias and increase the reliability of research findings.
Limitations of Hypothesis
Some Limitations of the Hypothesis are as follows:
- Limited to observable phenomena: Hypotheses are limited to observable phenomena and cannot account for unobservable or intangible factors. This means that some research questions may not be amenable to hypothesis testing.
- May be inaccurate or incomplete: Hypotheses are based on existing knowledge and research, which may be incomplete or inaccurate. This can lead to flawed hypotheses and erroneous conclusions.
- May be biased: Hypotheses may be biased by the researcher’s own beliefs, values, or assumptions. This can lead to selective interpretation of data and a lack of objectivity in research.
- Cannot prove causation: A hypothesis can only show a correlation between variables, but it cannot prove causation. This requires further experimentation and analysis.
- Limited to specific contexts: Hypotheses are limited to specific contexts and may not be generalizable to other situations or populations. This means that results may not be applicable in other contexts or may require further testing.
- May be affected by chance : Hypotheses may be affected by chance or random variation, which can obscure or distort the true relationship between variables.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write a Great Hypothesis
Hypothesis Definition, Format, Examples, and Tips
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Amy Morin, LCSW, is a psychotherapist and international bestselling author. Her books, including "13 Things Mentally Strong People Don't Do," have been translated into more than 40 languages. Her TEDx talk, "The Secret of Becoming Mentally Strong," is one of the most viewed talks of all time.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/VW-MIND-Amy-2b338105f1ee493f94d7e333e410fa76.jpg)
Verywell / Alex Dos Diaz
- The Scientific Method
Hypothesis Format
Falsifiability of a hypothesis.
- Operationalization
Hypothesis Types
Hypotheses examples.
- Collecting Data
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. It is a preliminary answer to your question that helps guide the research process.
Consider a study designed to examine the relationship between sleep deprivation and test performance. The hypothesis might be: "This study is designed to assess the hypothesis that sleep-deprived people will perform worse on a test than individuals who are not sleep-deprived."
At a Glance
A hypothesis is crucial to scientific research because it offers a clear direction for what the researchers are looking to find. This allows them to design experiments to test their predictions and add to our scientific knowledge about the world. This article explores how a hypothesis is used in psychology research, how to write a good hypothesis, and the different types of hypotheses you might use.
The Hypothesis in the Scientific Method
In the scientific method , whether it involves research in psychology, biology, or some other area, a hypothesis represents what the researchers think will happen in an experiment. The scientific method involves the following steps:
- Forming a question
- Performing background research
- Creating a hypothesis
- Designing an experiment
- Collecting data
- Analyzing the results
- Drawing conclusions
- Communicating the results
The hypothesis is a prediction, but it involves more than a guess. Most of the time, the hypothesis begins with a question which is then explored through background research. At this point, researchers then begin to develop a testable hypothesis.
Unless you are creating an exploratory study, your hypothesis should always explain what you expect to happen.
In a study exploring the effects of a particular drug, the hypothesis might be that researchers expect the drug to have some type of effect on the symptoms of a specific illness. In psychology, the hypothesis might focus on how a certain aspect of the environment might influence a particular behavior.
Remember, a hypothesis does not have to be correct. While the hypothesis predicts what the researchers expect to see, the goal of the research is to determine whether this guess is right or wrong. When conducting an experiment, researchers might explore numerous factors to determine which ones might contribute to the ultimate outcome.
In many cases, researchers may find that the results of an experiment do not support the original hypothesis. When writing up these results, the researchers might suggest other options that should be explored in future studies.
In many cases, researchers might draw a hypothesis from a specific theory or build on previous research. For example, prior research has shown that stress can impact the immune system. So a researcher might hypothesize: "People with high-stress levels will be more likely to contract a common cold after being exposed to the virus than people who have low-stress levels."
In other instances, researchers might look at commonly held beliefs or folk wisdom. "Birds of a feather flock together" is one example of folk adage that a psychologist might try to investigate. The researcher might pose a specific hypothesis that "People tend to select romantic partners who are similar to them in interests and educational level."
Elements of a Good Hypothesis
So how do you write a good hypothesis? When trying to come up with a hypothesis for your research or experiments, ask yourself the following questions:
- Is your hypothesis based on your research on a topic?
- Can your hypothesis be tested?
- Does your hypothesis include independent and dependent variables?
Before you come up with a specific hypothesis, spend some time doing background research. Once you have completed a literature review, start thinking about potential questions you still have. Pay attention to the discussion section in the journal articles you read . Many authors will suggest questions that still need to be explored.
How to Formulate a Good Hypothesis
To form a hypothesis, you should take these steps:
- Collect as many observations about a topic or problem as you can.
- Evaluate these observations and look for possible causes of the problem.
- Create a list of possible explanations that you might want to explore.
- After you have developed some possible hypotheses, think of ways that you could confirm or disprove each hypothesis through experimentation. This is known as falsifiability.
In the scientific method , falsifiability is an important part of any valid hypothesis. In order to test a claim scientifically, it must be possible that the claim could be proven false.
Students sometimes confuse the idea of falsifiability with the idea that it means that something is false, which is not the case. What falsifiability means is that if something was false, then it is possible to demonstrate that it is false.
One of the hallmarks of pseudoscience is that it makes claims that cannot be refuted or proven false.
The Importance of Operational Definitions
A variable is a factor or element that can be changed and manipulated in ways that are observable and measurable. However, the researcher must also define how the variable will be manipulated and measured in the study.
Operational definitions are specific definitions for all relevant factors in a study. This process helps make vague or ambiguous concepts detailed and measurable.
For example, a researcher might operationally define the variable " test anxiety " as the results of a self-report measure of anxiety experienced during an exam. A "study habits" variable might be defined by the amount of studying that actually occurs as measured by time.
These precise descriptions are important because many things can be measured in various ways. Clearly defining these variables and how they are measured helps ensure that other researchers can replicate your results.
Replicability
One of the basic principles of any type of scientific research is that the results must be replicable.
Replication means repeating an experiment in the same way to produce the same results. By clearly detailing the specifics of how the variables were measured and manipulated, other researchers can better understand the results and repeat the study if needed.
Some variables are more difficult than others to define. For example, how would you operationally define a variable such as aggression ? For obvious ethical reasons, researchers cannot create a situation in which a person behaves aggressively toward others.
To measure this variable, the researcher must devise a measurement that assesses aggressive behavior without harming others. The researcher might utilize a simulated task to measure aggressiveness in this situation.
Hypothesis Checklist
- Does your hypothesis focus on something that you can actually test?
- Does your hypothesis include both an independent and dependent variable?
- Can you manipulate the variables?
- Can your hypothesis be tested without violating ethical standards?
The hypothesis you use will depend on what you are investigating and hoping to find. Some of the main types of hypotheses that you might use include:
- Simple hypothesis : This type of hypothesis suggests there is a relationship between one independent variable and one dependent variable.
- Complex hypothesis : This type suggests a relationship between three or more variables, such as two independent and dependent variables.
- Null hypothesis : This hypothesis suggests no relationship exists between two or more variables.
- Alternative hypothesis : This hypothesis states the opposite of the null hypothesis.
- Statistical hypothesis : This hypothesis uses statistical analysis to evaluate a representative population sample and then generalizes the findings to the larger group.
- Logical hypothesis : This hypothesis assumes a relationship between variables without collecting data or evidence.
A hypothesis often follows a basic format of "If {this happens} then {this will happen}." One way to structure your hypothesis is to describe what will happen to the dependent variable if you change the independent variable .
The basic format might be: "If {these changes are made to a certain independent variable}, then we will observe {a change in a specific dependent variable}."
A few examples of simple hypotheses:
- "Students who eat breakfast will perform better on a math exam than students who do not eat breakfast."
- "Students who experience test anxiety before an English exam will get lower scores than students who do not experience test anxiety."
- "Motorists who talk on the phone while driving will be more likely to make errors on a driving course than those who do not talk on the phone."
- "Children who receive a new reading intervention will have higher reading scores than students who do not receive the intervention."
Examples of a complex hypothesis include:
- "People with high-sugar diets and sedentary activity levels are more likely to develop depression."
- "Younger people who are regularly exposed to green, outdoor areas have better subjective well-being than older adults who have limited exposure to green spaces."
Examples of a null hypothesis include:
- "There is no difference in anxiety levels between people who take St. John's wort supplements and those who do not."
- "There is no difference in scores on a memory recall task between children and adults."
- "There is no difference in aggression levels between children who play first-person shooter games and those who do not."
Examples of an alternative hypothesis:
- "People who take St. John's wort supplements will have less anxiety than those who do not."
- "Adults will perform better on a memory task than children."
- "Children who play first-person shooter games will show higher levels of aggression than children who do not."
Collecting Data on Your Hypothesis
Once a researcher has formed a testable hypothesis, the next step is to select a research design and start collecting data. The research method depends largely on exactly what they are studying. There are two basic types of research methods: descriptive research and experimental research.
Descriptive Research Methods
Descriptive research such as case studies , naturalistic observations , and surveys are often used when conducting an experiment is difficult or impossible. These methods are best used to describe different aspects of a behavior or psychological phenomenon.
Once a researcher has collected data using descriptive methods, a correlational study can examine how the variables are related. This research method might be used to investigate a hypothesis that is difficult to test experimentally.
Experimental Research Methods
Experimental methods are used to demonstrate causal relationships between variables. In an experiment, the researcher systematically manipulates a variable of interest (known as the independent variable) and measures the effect on another variable (known as the dependent variable).
Unlike correlational studies, which can only be used to determine if there is a relationship between two variables, experimental methods can be used to determine the actual nature of the relationship—whether changes in one variable actually cause another to change.
The hypothesis is a critical part of any scientific exploration. It represents what researchers expect to find in a study or experiment. In situations where the hypothesis is unsupported by the research, the research still has value. Such research helps us better understand how different aspects of the natural world relate to one another. It also helps us develop new hypotheses that can then be tested in the future.
Thompson WH, Skau S. On the scope of scientific hypotheses . R Soc Open Sci . 2023;10(8):230607. doi:10.1098/rsos.230607
Taran S, Adhikari NKJ, Fan E. Falsifiability in medicine: what clinicians can learn from Karl Popper [published correction appears in Intensive Care Med. 2021 Jun 17;:]. Intensive Care Med . 2021;47(9):1054-1056. doi:10.1007/s00134-021-06432-z
Eyler AA. Research Methods for Public Health . 1st ed. Springer Publishing Company; 2020. doi:10.1891/9780826182067.0004
Nosek BA, Errington TM. What is replication ? PLoS Biol . 2020;18(3):e3000691. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3000691
Aggarwal R, Ranganathan P. Study designs: Part 2 - Descriptive studies . Perspect Clin Res . 2019;10(1):34-36. doi:10.4103/picr.PICR_154_18
Nevid J. Psychology: Concepts and Applications. Wadworth, 2013.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

The Craft of Writing a Strong Hypothesis

Table of Contents
Writing a hypothesis is one of the essential elements of a scientific research paper. It needs to be to the point, clearly communicating what your research is trying to accomplish. A blurry, drawn-out, or complexly-structured hypothesis can confuse your readers. Or worse, the editor and peer reviewers.
A captivating hypothesis is not too intricate. This blog will take you through the process so that, by the end of it, you have a better idea of how to convey your research paper's intent in just one sentence.
What is a Hypothesis?
The first step in your scientific endeavor, a hypothesis, is a strong, concise statement that forms the basis of your research. It is not the same as a thesis statement , which is a brief summary of your research paper .
The sole purpose of a hypothesis is to predict your paper's findings, data, and conclusion. It comes from a place of curiosity and intuition . When you write a hypothesis, you're essentially making an educated guess based on scientific prejudices and evidence, which is further proven or disproven through the scientific method.
The reason for undertaking research is to observe a specific phenomenon. A hypothesis, therefore, lays out what the said phenomenon is. And it does so through two variables, an independent and dependent variable.
The independent variable is the cause behind the observation, while the dependent variable is the effect of the cause. A good example of this is “mixing red and blue forms purple.” In this hypothesis, mixing red and blue is the independent variable as you're combining the two colors at your own will. The formation of purple is the dependent variable as, in this case, it is conditional to the independent variable.
Different Types of Hypotheses

Types of hypotheses
Some would stand by the notion that there are only two types of hypotheses: a Null hypothesis and an Alternative hypothesis. While that may have some truth to it, it would be better to fully distinguish the most common forms as these terms come up so often, which might leave you out of context.
Apart from Null and Alternative, there are Complex, Simple, Directional, Non-Directional, Statistical, and Associative and casual hypotheses. They don't necessarily have to be exclusive, as one hypothesis can tick many boxes, but knowing the distinctions between them will make it easier for you to construct your own.
1. Null hypothesis
A null hypothesis proposes no relationship between two variables. Denoted by H 0 , it is a negative statement like “Attending physiotherapy sessions does not affect athletes' on-field performance.” Here, the author claims physiotherapy sessions have no effect on on-field performances. Even if there is, it's only a coincidence.
2. Alternative hypothesis
Considered to be the opposite of a null hypothesis, an alternative hypothesis is donated as H1 or Ha. It explicitly states that the dependent variable affects the independent variable. A good alternative hypothesis example is “Attending physiotherapy sessions improves athletes' on-field performance.” or “Water evaporates at 100 °C. ” The alternative hypothesis further branches into directional and non-directional.
- Directional hypothesis: A hypothesis that states the result would be either positive or negative is called directional hypothesis. It accompanies H1 with either the ‘<' or ‘>' sign.
- Non-directional hypothesis: A non-directional hypothesis only claims an effect on the dependent variable. It does not clarify whether the result would be positive or negative. The sign for a non-directional hypothesis is ‘≠.'
3. Simple hypothesis
A simple hypothesis is a statement made to reflect the relation between exactly two variables. One independent and one dependent. Consider the example, “Smoking is a prominent cause of lung cancer." The dependent variable, lung cancer, is dependent on the independent variable, smoking.
4. Complex hypothesis
In contrast to a simple hypothesis, a complex hypothesis implies the relationship between multiple independent and dependent variables. For instance, “Individuals who eat more fruits tend to have higher immunity, lesser cholesterol, and high metabolism.” The independent variable is eating more fruits, while the dependent variables are higher immunity, lesser cholesterol, and high metabolism.
5. Associative and casual hypothesis
Associative and casual hypotheses don't exhibit how many variables there will be. They define the relationship between the variables. In an associative hypothesis, changing any one variable, dependent or independent, affects others. In a casual hypothesis, the independent variable directly affects the dependent.
6. Empirical hypothesis
Also referred to as the working hypothesis, an empirical hypothesis claims a theory's validation via experiments and observation. This way, the statement appears justifiable and different from a wild guess.
Say, the hypothesis is “Women who take iron tablets face a lesser risk of anemia than those who take vitamin B12.” This is an example of an empirical hypothesis where the researcher the statement after assessing a group of women who take iron tablets and charting the findings.
7. Statistical hypothesis
The point of a statistical hypothesis is to test an already existing hypothesis by studying a population sample. Hypothesis like “44% of the Indian population belong in the age group of 22-27.” leverage evidence to prove or disprove a particular statement.
Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis
Writing a hypothesis is essential as it can make or break your research for you. That includes your chances of getting published in a journal. So when you're designing one, keep an eye out for these pointers:
- A research hypothesis has to be simple yet clear to look justifiable enough.
- It has to be testable — your research would be rendered pointless if too far-fetched into reality or limited by technology.
- It has to be precise about the results —what you are trying to do and achieve through it should come out in your hypothesis.
- A research hypothesis should be self-explanatory, leaving no doubt in the reader's mind.
- If you are developing a relational hypothesis, you need to include the variables and establish an appropriate relationship among them.
- A hypothesis must keep and reflect the scope for further investigations and experiments.
Separating a Hypothesis from a Prediction
Outside of academia, hypothesis and prediction are often used interchangeably. In research writing, this is not only confusing but also incorrect. And although a hypothesis and prediction are guesses at their core, there are many differences between them.
A hypothesis is an educated guess or even a testable prediction validated through research. It aims to analyze the gathered evidence and facts to define a relationship between variables and put forth a logical explanation behind the nature of events.
Predictions are assumptions or expected outcomes made without any backing evidence. They are more fictionally inclined regardless of where they originate from.
For this reason, a hypothesis holds much more weight than a prediction. It sticks to the scientific method rather than pure guesswork. "Planets revolve around the Sun." is an example of a hypothesis as it is previous knowledge and observed trends. Additionally, we can test it through the scientific method.
Whereas "COVID-19 will be eradicated by 2030." is a prediction. Even though it results from past trends, we can't prove or disprove it. So, the only way this gets validated is to wait and watch if COVID-19 cases end by 2030.
Finally, How to Write a Hypothesis

Quick tips on writing a hypothesis
1. Be clear about your research question
A hypothesis should instantly address the research question or the problem statement. To do so, you need to ask a question. Understand the constraints of your undertaken research topic and then formulate a simple and topic-centric problem. Only after that can you develop a hypothesis and further test for evidence.
2. Carry out a recce
Once you have your research's foundation laid out, it would be best to conduct preliminary research. Go through previous theories, academic papers, data, and experiments before you start curating your research hypothesis. It will give you an idea of your hypothesis's viability or originality.
Making use of references from relevant research papers helps draft a good research hypothesis. SciSpace Discover offers a repository of over 270 million research papers to browse through and gain a deeper understanding of related studies on a particular topic. Additionally, you can use SciSpace Copilot , your AI research assistant, for reading any lengthy research paper and getting a more summarized context of it. A hypothesis can be formed after evaluating many such summarized research papers. Copilot also offers explanations for theories and equations, explains paper in simplified version, allows you to highlight any text in the paper or clip math equations and tables and provides a deeper, clear understanding of what is being said. This can improve the hypothesis by helping you identify potential research gaps.
3. Create a 3-dimensional hypothesis
Variables are an essential part of any reasonable hypothesis. So, identify your independent and dependent variable(s) and form a correlation between them. The ideal way to do this is to write the hypothetical assumption in the ‘if-then' form. If you use this form, make sure that you state the predefined relationship between the variables.
In another way, you can choose to present your hypothesis as a comparison between two variables. Here, you must specify the difference you expect to observe in the results.
4. Write the first draft
Now that everything is in place, it's time to write your hypothesis. For starters, create the first draft. In this version, write what you expect to find from your research.
Clearly separate your independent and dependent variables and the link between them. Don't fixate on syntax at this stage. The goal is to ensure your hypothesis addresses the issue.
5. Proof your hypothesis
After preparing the first draft of your hypothesis, you need to inspect it thoroughly. It should tick all the boxes, like being concise, straightforward, relevant, and accurate. Your final hypothesis has to be well-structured as well.
Research projects are an exciting and crucial part of being a scholar. And once you have your research question, you need a great hypothesis to begin conducting research. Thus, knowing how to write a hypothesis is very important.
Now that you have a firmer grasp on what a good hypothesis constitutes, the different kinds there are, and what process to follow, you will find it much easier to write your hypothesis, which ultimately helps your research.
Now it's easier than ever to streamline your research workflow with SciSpace Discover . Its integrated, comprehensive end-to-end platform for research allows scholars to easily discover, write and publish their research and fosters collaboration.
It includes everything you need, including a repository of over 270 million research papers across disciplines, SEO-optimized summaries and public profiles to show your expertise and experience.
If you found these tips on writing a research hypothesis useful, head over to our blog on Statistical Hypothesis Testing to learn about the top researchers, papers, and institutions in this domain.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. what is the definition of hypothesis.
According to the Oxford dictionary, a hypothesis is defined as “An idea or explanation of something that is based on a few known facts, but that has not yet been proved to be true or correct”.
2. What is an example of hypothesis?
The hypothesis is a statement that proposes a relationship between two or more variables. An example: "If we increase the number of new users who join our platform by 25%, then we will see an increase in revenue."
3. What is an example of null hypothesis?
A null hypothesis is a statement that there is no relationship between two variables. The null hypothesis is written as H0. The null hypothesis states that there is no effect. For example, if you're studying whether or not a particular type of exercise increases strength, your null hypothesis will be "there is no difference in strength between people who exercise and people who don't."
4. What are the types of research?
• Fundamental research
• Applied research
• Qualitative research
• Quantitative research
• Mixed research
• Exploratory research
• Longitudinal research
• Cross-sectional research
• Field research
• Laboratory research
• Fixed research
• Flexible research
• Action research
• Policy research
• Classification research
• Comparative research
• Causal research
• Inductive research
• Deductive research
5. How to write a hypothesis?
• Your hypothesis should be able to predict the relationship and outcome.
• Avoid wordiness by keeping it simple and brief.
• Your hypothesis should contain observable and testable outcomes.
• Your hypothesis should be relevant to the research question.
6. What are the 2 types of hypothesis?
• Null hypotheses are used to test the claim that "there is no difference between two groups of data".
• Alternative hypotheses test the claim that "there is a difference between two data groups".
7. Difference between research question and research hypothesis?
A research question is a broad, open-ended question you will try to answer through your research. A hypothesis is a statement based on prior research or theory that you expect to be true due to your study. Example - Research question: What are the factors that influence the adoption of the new technology? Research hypothesis: There is a positive relationship between age, education and income level with the adoption of the new technology.
8. What is plural for hypothesis?
The plural of hypothesis is hypotheses. Here's an example of how it would be used in a statement, "Numerous well-considered hypotheses are presented in this part, and they are supported by tables and figures that are well-illustrated."
9. What is the red queen hypothesis?
The red queen hypothesis in evolutionary biology states that species must constantly evolve to avoid extinction because if they don't, they will be outcompeted by other species that are evolving. Leigh Van Valen first proposed it in 1973; since then, it has been tested and substantiated many times.
10. Who is known as the father of null hypothesis?
The father of the null hypothesis is Sir Ronald Fisher. He published a paper in 1925 that introduced the concept of null hypothesis testing, and he was also the first to use the term itself.
11. When to reject null hypothesis?
You need to find a significant difference between your two populations to reject the null hypothesis. You can determine that by running statistical tests such as an independent sample t-test or a dependent sample t-test. You should reject the null hypothesis if the p-value is less than 0.05.
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, what is a hypothesis and how do i write one.
General Education

Think about something strange and unexplainable in your life. Maybe you get a headache right before it rains, or maybe you think your favorite sports team wins when you wear a certain color. If you wanted to see whether these are just coincidences or scientific fact, you would form a hypothesis, then create an experiment to see whether that hypothesis is true or not.
But what is a hypothesis, anyway? If you’re not sure about what a hypothesis is--or how to test for one!--you’re in the right place. This article will teach you everything you need to know about hypotheses, including:
- Defining the term “hypothesis”
- Providing hypothesis examples
- Giving you tips for how to write your own hypothesis
So let’s get started!

What Is a Hypothesis?
Merriam Webster defines a hypothesis as “an assumption or concession made for the sake of argument.” In other words, a hypothesis is an educated guess . Scientists make a reasonable assumption--or a hypothesis--then design an experiment to test whether it’s true or not. Keep in mind that in science, a hypothesis should be testable. You have to be able to design an experiment that tests your hypothesis in order for it to be valid.
As you could assume from that statement, it’s easy to make a bad hypothesis. But when you’re holding an experiment, it’s even more important that your guesses be good...after all, you’re spending time (and maybe money!) to figure out more about your observation. That’s why we refer to a hypothesis as an educated guess--good hypotheses are based on existing data and research to make them as sound as possible.
Hypotheses are one part of what’s called the scientific method . Every (good) experiment or study is based in the scientific method. The scientific method gives order and structure to experiments and ensures that interference from scientists or outside influences does not skew the results. It’s important that you understand the concepts of the scientific method before holding your own experiment. Though it may vary among scientists, the scientific method is generally made up of six steps (in order):
- Observation
- Asking questions
- Forming a hypothesis
- Analyze the data
- Communicate your results
You’ll notice that the hypothesis comes pretty early on when conducting an experiment. That’s because experiments work best when they’re trying to answer one specific question. And you can’t conduct an experiment until you know what you’re trying to prove!
Independent and Dependent Variables
After doing your research, you’re ready for another important step in forming your hypothesis: identifying variables. Variables are basically any factor that could influence the outcome of your experiment . Variables have to be measurable and related to the topic being studied.
There are two types of variables: independent variables and dependent variables. I ndependent variables remain constant . For example, age is an independent variable; it will stay the same, and researchers can look at different ages to see if it has an effect on the dependent variable.
Speaking of dependent variables... dependent variables are subject to the influence of the independent variable , meaning that they are not constant. Let’s say you want to test whether a person’s age affects how much sleep they need. In that case, the independent variable is age (like we mentioned above), and the dependent variable is how much sleep a person gets.
Variables will be crucial in writing your hypothesis. You need to be able to identify which variable is which, as both the independent and dependent variables will be written into your hypothesis. For instance, in a study about exercise, the independent variable might be the speed at which the respondents walk for thirty minutes, and the dependent variable would be their heart rate. In your study and in your hypothesis, you’re trying to understand the relationship between the two variables.
Elements of a Good Hypothesis
The best hypotheses start by asking the right questions . For instance, if you’ve observed that the grass is greener when it rains twice a week, you could ask what kind of grass it is, what elevation it’s at, and if the grass across the street responds to rain in the same way. Any of these questions could become the backbone of experiments to test why the grass gets greener when it rains fairly frequently.
As you’re asking more questions about your first observation, make sure you’re also making more observations . If it doesn’t rain for two weeks and the grass still looks green, that’s an important observation that could influence your hypothesis. You'll continue observing all throughout your experiment, but until the hypothesis is finalized, every observation should be noted.
Finally, you should consult secondary research before writing your hypothesis . Secondary research is comprised of results found and published by other people. You can usually find this information online or at your library. Additionally, m ake sure the research you find is credible and related to your topic. If you’re studying the correlation between rain and grass growth, it would help you to research rain patterns over the past twenty years for your county, published by a local agricultural association. You should also research the types of grass common in your area, the type of grass in your lawn, and whether anyone else has conducted experiments about your hypothesis. Also be sure you’re checking the quality of your research . Research done by a middle school student about what minerals can be found in rainwater would be less useful than an article published by a local university.

Writing Your Hypothesis
Once you’ve considered all of the factors above, you’re ready to start writing your hypothesis. Hypotheses usually take a certain form when they’re written out in a research report.
When you boil down your hypothesis statement, you are writing down your best guess and not the question at hand . This means that your statement should be written as if it is fact already, even though you are simply testing it.
The reason for this is that, after you have completed your study, you'll either accept or reject your if-then or your null hypothesis. All hypothesis testing examples should be measurable and able to be confirmed or denied. You cannot confirm a question, only a statement!
In fact, you come up with hypothesis examples all the time! For instance, when you guess on the outcome of a basketball game, you don’t say, “Will the Miami Heat beat the Boston Celtics?” but instead, “I think the Miami Heat will beat the Boston Celtics.” You state it as if it is already true, even if it turns out you’re wrong. You do the same thing when writing your hypothesis.
Additionally, keep in mind that hypotheses can range from very specific to very broad. These hypotheses can be specific, but if your hypothesis testing examples involve a broad range of causes and effects, your hypothesis can also be broad.

The Two Types of Hypotheses
Now that you understand what goes into a hypothesis, it’s time to look more closely at the two most common types of hypothesis: the if-then hypothesis and the null hypothesis.
#1: If-Then Hypotheses
First of all, if-then hypotheses typically follow this formula:
If ____ happens, then ____ will happen.
The goal of this type of hypothesis is to test the causal relationship between the independent and dependent variable. It’s fairly simple, and each hypothesis can vary in how detailed it can be. We create if-then hypotheses all the time with our daily predictions. Here are some examples of hypotheses that use an if-then structure from daily life:
- If I get enough sleep, I’ll be able to get more work done tomorrow.
- If the bus is on time, I can make it to my friend’s birthday party.
- If I study every night this week, I’ll get a better grade on my exam.
In each of these situations, you’re making a guess on how an independent variable (sleep, time, or studying) will affect a dependent variable (the amount of work you can do, making it to a party on time, or getting better grades).
You may still be asking, “What is an example of a hypothesis used in scientific research?” Take one of the hypothesis examples from a real-world study on whether using technology before bed affects children’s sleep patterns. The hypothesis read s:
“We hypothesized that increased hours of tablet- and phone-based screen time at bedtime would be inversely correlated with sleep quality and child attention.”
It might not look like it, but this is an if-then statement. The researchers basically said, “If children have more screen usage at bedtime, then their quality of sleep and attention will be worse.” The sleep quality and attention are the dependent variables and the screen usage is the independent variable. (Usually, the independent variable comes after the “if” and the dependent variable comes after the “then,” as it is the independent variable that affects the dependent variable.) This is an excellent example of how flexible hypothesis statements can be, as long as the general idea of “if-then” and the independent and dependent variables are present.
#2: Null Hypotheses
Your if-then hypothesis is not the only one needed to complete a successful experiment, however. You also need a null hypothesis to test it against. In its most basic form, the null hypothesis is the opposite of your if-then hypothesis . When you write your null hypothesis, you are writing a hypothesis that suggests that your guess is not true, and that the independent and dependent variables have no relationship .
One null hypothesis for the cell phone and sleep study from the last section might say:
“If children have more screen usage at bedtime, their quality of sleep and attention will not be worse.”
In this case, this is a null hypothesis because it’s asking the opposite of the original thesis!
Conversely, if your if-then hypothesis suggests that your two variables have no relationship, then your null hypothesis would suggest that there is one. So, pretend that there is a study that is asking the question, “Does the amount of followers on Instagram influence how long people spend on the app?” The independent variable is the amount of followers, and the dependent variable is the time spent. But if you, as the researcher, don’t think there is a relationship between the number of followers and time spent, you might write an if-then hypothesis that reads:
“If people have many followers on Instagram, they will not spend more time on the app than people who have less.”
In this case, the if-then suggests there isn’t a relationship between the variables. In that case, one of the null hypothesis examples might say:
“If people have many followers on Instagram, they will spend more time on the app than people who have less.”
You then test both the if-then and the null hypothesis to gauge if there is a relationship between the variables, and if so, how much of a relationship.

4 Tips to Write the Best Hypothesis
If you’re going to take the time to hold an experiment, whether in school or by yourself, you’re also going to want to take the time to make sure your hypothesis is a good one. The best hypotheses have four major elements in common: plausibility, defined concepts, observability, and general explanation.
#1: Plausibility
At first glance, this quality of a hypothesis might seem obvious. When your hypothesis is plausible, that means it’s possible given what we know about science and general common sense. However, improbable hypotheses are more common than you might think.
Imagine you’re studying weight gain and television watching habits. If you hypothesize that people who watch more than twenty hours of television a week will gain two hundred pounds or more over the course of a year, this might be improbable (though it’s potentially possible). Consequently, c ommon sense can tell us the results of the study before the study even begins.
Improbable hypotheses generally go against science, as well. Take this hypothesis example:
“If a person smokes one cigarette a day, then they will have lungs just as healthy as the average person’s.”
This hypothesis is obviously untrue, as studies have shown again and again that cigarettes negatively affect lung health. You must be careful that your hypotheses do not reflect your own personal opinion more than they do scientifically-supported findings. This plausibility points to the necessity of research before the hypothesis is written to make sure that your hypothesis has not already been disproven.
#2: Defined Concepts
The more advanced you are in your studies, the more likely that the terms you’re using in your hypothesis are specific to a limited set of knowledge. One of the hypothesis testing examples might include the readability of printed text in newspapers, where you might use words like “kerning” and “x-height.” Unless your readers have a background in graphic design, it’s likely that they won’t know what you mean by these terms. Thus, it’s important to either write what they mean in the hypothesis itself or in the report before the hypothesis.
Here’s what we mean. Which of the following sentences makes more sense to the common person?
If the kerning is greater than average, more words will be read per minute.
If the space between letters is greater than average, more words will be read per minute.
For people reading your report that are not experts in typography, simply adding a few more words will be helpful in clarifying exactly what the experiment is all about. It’s always a good idea to make your research and findings as accessible as possible.

Good hypotheses ensure that you can observe the results.
#3: Observability
In order to measure the truth or falsity of your hypothesis, you must be able to see your variables and the way they interact. For instance, if your hypothesis is that the flight patterns of satellites affect the strength of certain television signals, yet you don’t have a telescope to view the satellites or a television to monitor the signal strength, you cannot properly observe your hypothesis and thus cannot continue your study.
Some variables may seem easy to observe, but if you do not have a system of measurement in place, you cannot observe your hypothesis properly. Here’s an example: if you’re experimenting on the effect of healthy food on overall happiness, but you don’t have a way to monitor and measure what “overall happiness” means, your results will not reflect the truth. Monitoring how often someone smiles for a whole day is not reasonably observable, but having the participants state how happy they feel on a scale of one to ten is more observable.
In writing your hypothesis, always keep in mind how you'll execute the experiment.
#4: Generalizability
Perhaps you’d like to study what color your best friend wears the most often by observing and documenting the colors she wears each day of the week. This might be fun information for her and you to know, but beyond you two, there aren’t many people who could benefit from this experiment. When you start an experiment, you should note how generalizable your findings may be if they are confirmed. Generalizability is basically how common a particular phenomenon is to other people’s everyday life.
Let’s say you’re asking a question about the health benefits of eating an apple for one day only, you need to realize that the experiment may be too specific to be helpful. It does not help to explain a phenomenon that many people experience. If you find yourself with too specific of a hypothesis, go back to asking the big question: what is it that you want to know, and what do you think will happen between your two variables?

Hypothesis Testing Examples
We know it can be hard to write a good hypothesis unless you’ve seen some good hypothesis examples. We’ve included four hypothesis examples based on some made-up experiments. Use these as templates or launch pads for coming up with your own hypotheses.
Experiment #1: Students Studying Outside (Writing a Hypothesis)
You are a student at PrepScholar University. When you walk around campus, you notice that, when the temperature is above 60 degrees, more students study in the quad. You want to know when your fellow students are more likely to study outside. With this information, how do you make the best hypothesis possible?
You must remember to make additional observations and do secondary research before writing your hypothesis. In doing so, you notice that no one studies outside when it’s 75 degrees and raining, so this should be included in your experiment. Also, studies done on the topic beforehand suggested that students are more likely to study in temperatures less than 85 degrees. With this in mind, you feel confident that you can identify your variables and write your hypotheses:
If-then: “If the temperature in Fahrenheit is less than 60 degrees, significantly fewer students will study outside.”
Null: “If the temperature in Fahrenheit is less than 60 degrees, the same number of students will study outside as when it is more than 60 degrees.”
These hypotheses are plausible, as the temperatures are reasonably within the bounds of what is possible. The number of people in the quad is also easily observable. It is also not a phenomenon specific to only one person or at one time, but instead can explain a phenomenon for a broader group of people.
To complete this experiment, you pick the month of October to observe the quad. Every day (except on the days where it’s raining)from 3 to 4 PM, when most classes have released for the day, you observe how many people are on the quad. You measure how many people come and how many leave. You also write down the temperature on the hour.
After writing down all of your observations and putting them on a graph, you find that the most students study on the quad when it is 70 degrees outside, and that the number of students drops a lot once the temperature reaches 60 degrees or below. In this case, your research report would state that you accept or “failed to reject” your first hypothesis with your findings.
Experiment #2: The Cupcake Store (Forming a Simple Experiment)
Let’s say that you work at a bakery. You specialize in cupcakes, and you make only two colors of frosting: yellow and purple. You want to know what kind of customers are more likely to buy what kind of cupcake, so you set up an experiment. Your independent variable is the customer’s gender, and the dependent variable is the color of the frosting. What is an example of a hypothesis that might answer the question of this study?
Here’s what your hypotheses might look like:
If-then: “If customers’ gender is female, then they will buy more yellow cupcakes than purple cupcakes.”
Null: “If customers’ gender is female, then they will be just as likely to buy purple cupcakes as yellow cupcakes.”
This is a pretty simple experiment! It passes the test of plausibility (there could easily be a difference), defined concepts (there’s nothing complicated about cupcakes!), observability (both color and gender can be easily observed), and general explanation ( this would potentially help you make better business decisions ).

Experiment #3: Backyard Bird Feeders (Integrating Multiple Variables and Rejecting the If-Then Hypothesis)
While watching your backyard bird feeder, you realized that different birds come on the days when you change the types of seeds. You decide that you want to see more cardinals in your backyard, so you decide to see what type of food they like the best and set up an experiment.
However, one morning, you notice that, while some cardinals are present, blue jays are eating out of your backyard feeder filled with millet. You decide that, of all of the other birds, you would like to see the blue jays the least. This means you'll have more than one variable in your hypothesis. Your new hypotheses might look like this:
If-then: “If sunflower seeds are placed in the bird feeders, then more cardinals will come than blue jays. If millet is placed in the bird feeders, then more blue jays will come than cardinals.”
Null: “If either sunflower seeds or millet are placed in the bird, equal numbers of cardinals and blue jays will come.”
Through simple observation, you actually find that cardinals come as often as blue jays when sunflower seeds or millet is in the bird feeder. In this case, you would reject your “if-then” hypothesis and “fail to reject” your null hypothesis . You cannot accept your first hypothesis, because it’s clearly not true. Instead you found that there was actually no relation between your different variables. Consequently, you would need to run more experiments with different variables to see if the new variables impact the results.
Experiment #4: In-Class Survey (Including an Alternative Hypothesis)
You’re about to give a speech in one of your classes about the importance of paying attention. You want to take this opportunity to test a hypothesis you’ve had for a while:
If-then: If students sit in the first two rows of the classroom, then they will listen better than students who do not.
Null: If students sit in the first two rows of the classroom, then they will not listen better or worse than students who do not.
You give your speech and then ask your teacher if you can hand out a short survey to the class. On the survey, you’ve included questions about some of the topics you talked about. When you get back the results, you’re surprised to see that not only do the students in the first two rows not pay better attention, but they also scored worse than students in other parts of the classroom! Here, both your if-then and your null hypotheses are not representative of your findings. What do you do?
This is when you reject both your if-then and null hypotheses and instead create an alternative hypothesis . This type of hypothesis is used in the rare circumstance that neither of your hypotheses is able to capture your findings . Now you can use what you’ve learned to draft new hypotheses and test again!
Key Takeaways: Hypothesis Writing
The more comfortable you become with writing hypotheses, the better they will become. The structure of hypotheses is flexible and may need to be changed depending on what topic you are studying. The most important thing to remember is the purpose of your hypothesis and the difference between the if-then and the null . From there, in forming your hypothesis, you should constantly be asking questions, making observations, doing secondary research, and considering your variables. After you have written your hypothesis, be sure to edit it so that it is plausible, clearly defined, observable, and helpful in explaining a general phenomenon.
Writing a hypothesis is something that everyone, from elementary school children competing in a science fair to professional scientists in a lab, needs to know how to do. Hypotheses are vital in experiments and in properly executing the scientific method . When done correctly, hypotheses will set up your studies for success and help you to understand the world a little better, one experiment at a time.

What’s Next?
If you’re studying for the science portion of the ACT, there’s definitely a lot you need to know. We’ve got the tools to help, though! Start by checking out our ultimate study guide for the ACT Science subject test. Once you read through that, be sure to download our recommended ACT Science practice tests , since they’re one of the most foolproof ways to improve your score. (And don’t forget to check out our expert guide book , too.)
If you love science and want to major in a scientific field, you should start preparing in high school . Here are the science classes you should take to set yourself up for success.
If you’re trying to think of science experiments you can do for class (or for a science fair!), here’s a list of 37 awesome science experiments you can do at home

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
What Is A Research (Scientific) Hypothesis? A plain-language explainer + examples
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020
If you’re new to the world of research, or it’s your first time writing a dissertation or thesis, you’re probably noticing that the words “research hypothesis” and “scientific hypothesis” are used quite a bit, and you’re wondering what they mean in a research context .
“Hypothesis” is one of those words that people use loosely, thinking they understand what it means. However, it has a very specific meaning within academic research. So, it’s important to understand the exact meaning before you start hypothesizing.
Research Hypothesis 101
- What is a hypothesis ?
- What is a research hypothesis (scientific hypothesis)?
- Requirements for a research hypothesis
- Definition of a research hypothesis
- The null hypothesis
What is a hypothesis?
Let’s start with the general definition of a hypothesis (not a research hypothesis or scientific hypothesis), according to the Cambridge Dictionary:
Hypothesis: an idea or explanation for something that is based on known facts but has not yet been proved.
In other words, it’s a statement that provides an explanation for why or how something works, based on facts (or some reasonable assumptions), but that has not yet been specifically tested . For example, a hypothesis might look something like this:
Hypothesis: sleep impacts academic performance.
This statement predicts that academic performance will be influenced by the amount and/or quality of sleep a student engages in – sounds reasonable, right? It’s based on reasonable assumptions , underpinned by what we currently know about sleep and health (from the existing literature). So, loosely speaking, we could call it a hypothesis, at least by the dictionary definition.
But that’s not good enough…
Unfortunately, that’s not quite sophisticated enough to describe a research hypothesis (also sometimes called a scientific hypothesis), and it wouldn’t be acceptable in a dissertation, thesis or research paper . In the world of academic research, a statement needs a few more criteria to constitute a true research hypothesis .
What is a research hypothesis?
A research hypothesis (also called a scientific hypothesis) is a statement about the expected outcome of a study (for example, a dissertation or thesis). To constitute a quality hypothesis, the statement needs to have three attributes – specificity , clarity and testability .
Let’s take a look at these more closely.
Need a helping hand?
Hypothesis Essential #1: Specificity & Clarity
A good research hypothesis needs to be extremely clear and articulate about both what’ s being assessed (who or what variables are involved ) and the expected outcome (for example, a difference between groups, a relationship between variables, etc.).
Let’s stick with our sleepy students example and look at how this statement could be more specific and clear.
Hypothesis: Students who sleep at least 8 hours per night will, on average, achieve higher grades in standardised tests than students who sleep less than 8 hours a night.
As you can see, the statement is very specific as it identifies the variables involved (sleep hours and test grades), the parties involved (two groups of students), as well as the predicted relationship type (a positive relationship). There’s no ambiguity or uncertainty about who or what is involved in the statement, and the expected outcome is clear.
Contrast that to the original hypothesis we looked at – “Sleep impacts academic performance” – and you can see the difference. “Sleep” and “academic performance” are both comparatively vague , and there’s no indication of what the expected relationship direction is (more sleep or less sleep). As you can see, specificity and clarity are key.

Hypothesis Essential #2: Testability (Provability)
A statement must be testable to qualify as a research hypothesis. In other words, there needs to be a way to prove (or disprove) the statement. If it’s not testable, it’s not a hypothesis – simple as that.
For example, consider the hypothesis we mentioned earlier:
Hypothesis: Students who sleep at least 8 hours per night will, on average, achieve higher grades in standardised tests than students who sleep less than 8 hours a night.
We could test this statement by undertaking a quantitative study involving two groups of students, one that gets 8 or more hours of sleep per night for a fixed period, and one that gets less. We could then compare the standardised test results for both groups to see if there’s a statistically significant difference.
Again, if you compare this to the original hypothesis we looked at – “Sleep impacts academic performance” – you can see that it would be quite difficult to test that statement, primarily because it isn’t specific enough. How much sleep? By who? What type of academic performance?
So, remember the mantra – if you can’t test it, it’s not a hypothesis 🙂

Defining A Research Hypothesis
You’re still with us? Great! Let’s recap and pin down a clear definition of a hypothesis.
A research hypothesis (or scientific hypothesis) is a statement about an expected relationship between variables, or explanation of an occurrence, that is clear, specific and testable.
So, when you write up hypotheses for your dissertation or thesis, make sure that they meet all these criteria. If you do, you’ll not only have rock-solid hypotheses but you’ll also ensure a clear focus for your entire research project.
What about the null hypothesis?
You may have also heard the terms null hypothesis , alternative hypothesis, or H-zero thrown around. At a simple level, the null hypothesis is the counter-proposal to the original hypothesis.
For example, if the hypothesis predicts that there is a relationship between two variables (for example, sleep and academic performance), the null hypothesis would predict that there is no relationship between those variables.
At a more technical level, the null hypothesis proposes that no statistical significance exists in a set of given observations and that any differences are due to chance alone.
And there you have it – hypotheses in a nutshell.
If you have any questions, be sure to leave a comment below and we’ll do our best to help you. If you need hands-on help developing and testing your hypotheses, consider our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the research journey.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

16 Comments
Very useful information. I benefit more from getting more information in this regard.
Very great insight,educative and informative. Please give meet deep critics on many research data of public international Law like human rights, environment, natural resources, law of the sea etc
In a book I read a distinction is made between null, research, and alternative hypothesis. As far as I understand, alternative and research hypotheses are the same. Can you please elaborate? Best Afshin
This is a self explanatory, easy going site. I will recommend this to my friends and colleagues.
Very good definition. How can I cite your definition in my thesis? Thank you. Is nul hypothesis compulsory in a research?
It’s a counter-proposal to be proven as a rejection
Please what is the difference between alternate hypothesis and research hypothesis?
It is a very good explanation. However, it limits hypotheses to statistically tasteable ideas. What about for qualitative researches or other researches that involve quantitative data that don’t need statistical tests?
In qualitative research, one typically uses propositions, not hypotheses.
could you please elaborate it more
I’ve benefited greatly from these notes, thank you.
This is very helpful
well articulated ideas are presented here, thank you for being reliable sources of information
Excellent. Thanks for being clear and sound about the research methodology and hypothesis (quantitative research)
I have only a simple question regarding the null hypothesis. – Is the null hypothesis (Ho) known as the reversible hypothesis of the alternative hypothesis (H1? – How to test it in academic research?
this is very important note help me much more
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- What Is Research Methodology? Simple Definition (With Examples) - Grad Coach - […] Contrasted to this, a quantitative methodology is typically used when the research aims and objectives are confirmatory in nature. For example,…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples
How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples
Published on 6 May 2022 by Shona McCombes .
A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested by scientific research. If you want to test a relationship between two or more variables, you need to write hypotheses before you start your experiment or data collection.
Table of contents
What is a hypothesis, developing a hypothesis (with example), hypothesis examples, frequently asked questions about writing hypotheses.
A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. It is a tentative answer to your research question that has not yet been tested. For some research projects, you might have to write several hypotheses that address different aspects of your research question.
A hypothesis is not just a guess – it should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations, and statistical analysis of data).
Variables in hypotheses
Hypotheses propose a relationship between two or more variables . An independent variable is something the researcher changes or controls. A dependent variable is something the researcher observes and measures.
In this example, the independent variable is exposure to the sun – the assumed cause . The dependent variable is the level of happiness – the assumed effect .
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Step 1: ask a question.
Writing a hypothesis begins with a research question that you want to answer. The question should be focused, specific, and researchable within the constraints of your project.
Step 2: Do some preliminary research
Your initial answer to the question should be based on what is already known about the topic. Look for theories and previous studies to help you form educated assumptions about what your research will find.
At this stage, you might construct a conceptual framework to identify which variables you will study and what you think the relationships are between them. Sometimes, you’ll have to operationalise more complex constructs.
Step 3: Formulate your hypothesis
Now you should have some idea of what you expect to find. Write your initial answer to the question in a clear, concise sentence.
Step 4: Refine your hypothesis
You need to make sure your hypothesis is specific and testable. There are various ways of phrasing a hypothesis, but all the terms you use should have clear definitions, and the hypothesis should contain:
- The relevant variables
- The specific group being studied
- The predicted outcome of the experiment or analysis
Step 5: Phrase your hypothesis in three ways
To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if … then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable.
In academic research, hypotheses are more commonly phrased in terms of correlations or effects, where you directly state the predicted relationship between variables.
If you are comparing two groups, the hypothesis can state what difference you expect to find between them.
Step 6. Write a null hypothesis
If your research involves statistical hypothesis testing , you will also have to write a null hypothesis. The null hypothesis is the default position that there is no association between the variables. The null hypothesis is written as H 0 , while the alternative hypothesis is H 1 or H a .
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
A hypothesis is not just a guess. It should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations, and statistical analysis of data).
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (‘ x affects y because …’).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses. In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, May 06). How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 29 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/hypothesis-writing/
Is this article helpful?

Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, operationalisation | a guide with examples, pros & cons, what is a conceptual framework | tips & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples.
Research Hypothesis: Elements, Format, Types

When a proposition is formulated for empirical testing, we call it a hypothesis. Almost all studies begin with one or more hypotheses.
Let’s Understand Research Hypothesis.
What is a hypothesis.
A hypothesis, specifically a research hypothesis, is formulated to predict an assumed relationship between two or more variables of interest.
If we reasonably guess that a relationship exists between the variables of interest, we first state it as a hypothesis and then test it in the field.
Hypotheses are stated in terms of the particular dependent and independent variables that are going to be used in the study.
Research Hypothesis Definition
A research hypothesis is a conjectural statement, a logical supposition, a reasonable guess, and an educated prediction about the nature of the relationship between two or more variables that we expect to happen in our study.
Unless you are creating an exploratory study, your hypothesis should always explain what you expect to happen during your experiment or research.
Remember, a hypothesis does not have to be correct. While the hypothesis predicts what the researchers expect to see, the research aims to determine whether this guess is right or wrong.
When experimenting, researchers might explore different factors to determine which ones might contribute to the outcome.
In many cases, researchers may find that the results of an experiment do not support the original hypothesis. When writing up these results, the researchers might suggest other options that should be explored in future studies.
Elements of a Good Hypothesis
Regardless of the type of hypothesis, the goal of a good hypothesis is to help explain the focus and direction of the experiment or research. As such, a good hypothesis will
- State the purpose of the research.
- Identify which variables are to be used.
A good hypothesis;
- Needs to be logical.
- Must be precise in language.
- It should be testable with research or experimentation.
A hypothesis is usually written in a form where it proposes that if something is done, then something will occur.
Finally, when you are trying to come up with a good hypothesis for your research or experiments, ask yourself the following questions:
- Is your hypothesis based on any previous research on a topic?
- Can your hypothesis be tested?
- Does your hypothesis include independent and dependent variables?
Before you come up with a specific hypothesis, spend some time doing background research on your topic.
Once you have completed a literature review, start thinking of potential questions you still have. Pay attention to the discussion section in the journal articles you read. Many authors will suggest questions that still need to be explored.
Basic Format of a Good Hypothesis
A hypothesis often follows a basic format of “If {this happens}, then {this will happen}.” One way to structure your hypothesis is to describe what will happen to the dependent variable if you change the independent variable.
The basic format might be:
“If {these changes are made to a certain independent variable}, then we will observe {a change in a specific dependent variable}.”
A few examples:
- Students who eat breakfast will perform better on a math test than students who do not eat breakfast.
- Students who experience test anxiety before an exam get higher scores than students who do not experience test anxiety.
- Drivers who talk on their mobile phones while driving will be more likely to make errors when driving than those who do not talk on the phone.
- People with high exposure to ultraviolet light will have a higher frequency of skin cancer than those who do not have such exposure.
Look at the last example.
Here is the independent variable (exposure to ultraviolet light)) is specified, and the dependent variable (skin cancer) is also specified.
Notice also that this research hypothesis specifies a direction in that it predicts that people exposed to ultraviolet light will have a higher risk of cancer.
This is not always the case. Research hypotheses can also specify a difference without saying which group will be better or higher than the other.
For example, one might formulate a hypothesis of the type: ‘Religion does not make any significant difference in the performance of cultural activities.’
In general, however, it is considered a better hypothesis if you can specify a direction.
Research hypotheses serve several important functions. The most important one is to direct and guide the research.
A few of the other functions of the research hypothesis are enumerated below:
- A research hypothesis indicates the major independent variables to be included in the study;
- A research hypothesis suggests the type of data that must be collected and the type of analysis that must be conducted to measure the relationship;
- A research hypothesis identifies facts that are relevant and that are not;
- A research hypothesis suggests the type of research design to be employed.
Types of Research Hypothesis
Two types of research hypotheses are;
- Descriptive hypothesis.
- Relational hypothesis.
Descriptive Hypotheses
Descriptive hypotheses are propositions that typically state some variables’ existence, size, form, or distribution.
These hypotheses are formulated in the form of statements in which we assign variables to cases.
For example,
- The prevalence of contraceptive use among currently married women in India exceeds 60%.
In this example, the case is ‘currently married women,’ and the variable is ‘prevalence of contraceptives.’ As a second example,
- The public universities are currently experiencing budget difficulties.
Here,’ public universities’ is the case, and ‘budget difficulties’ is the variable.
- The National Board of Revenue claims that over 15% of potential taxpayers falsify in their income tax returns.
- At most, 75% of the pre-school children in community A have a protein-deficient diet.
- The average sales in a superstore exceed taka 25 lac per month.
- Smoking increases the risk of lung cancer.
- The average longevity of women is higher among females than among males.
- Gainfully employed women tend to have lower than average fertility.
- Women with child loss experience will have higher fertility than those who do not have such experiences.
All examples of descriptive hypotheses.
It is important to note that the Descriptive hypothesis does not always have variables that can be designated as independent or dependent.
Relational Hypotheses
Relational hypotheses, on the other hand, are statements that describe the relationship between variables concerning some cases.
- Communities with many modern facilities will have a higher rate of contraception than communities with few modern facilities.
In this instance, the case is ‘communities,’ and the variables are ‘rate of contraception’ and ‘modern facilities.’
Similarly, “People who use chewing tobacco have a higher risk of oral carcinoma than people who have never used chewing tobacco” is a relational hypothesis.
A relational hypothesis is again of two types: correlational hypothesis and the causal hypothesis.
A correlational hypothesis states that variables occur in some predictable relationships without implying that one variable causes the other to change or take on different values.
Here is an example of a co-relational hypothesis:
- Males are more efficient than their female counterparts in typing.
In making such a statement, we do not claim that sex (male-female) as a variable influences the other variable,’ typing efficiency’ (less efficient-more efficient). Here is one more example of a correlational hypothesis:
- Saving habit is more pronounced among Christians than the people of other religions.
Once again, religion is not believed to be a factor in saving habits, although a positive relationship has been observed.
Look at the following example:
- The participation of women in household decision making increases with age, their level of education, and the number of surviving children.
Here too, women’s education, several surviving children, or education does not guarantee their decision-making autonomy.
With causal hypotheses (also called explanatory hypotheses), on the other hand, there is an implication that a change in one variable causes a change or leads to an effect on the other variable.
A causal variable is typically called an independent variable, and the other is the dependent variable. It is important to note that the term “cause” roughly means “help make happen.” So, the independent variable need not be the sole reason for the existence of or change in the dependent variable. Here are some examples of causal hypotheses:
- An increase in family income leads to an increase in the income saved.
- Exposure of mothers to mass media increases their knowledge of malnutrition among their children.
- An offer of a discount in a department store enhances the sales volume.
- Chewing tobacco increases the risk of oral carcinoma.
- Goat farming contributes to poverty alleviation of rural people.
- The utilization of child welfare clinics is the lowest in those clinics in which the clinic personnel are poorly motivated to provide preventive services.
- An increase in bank interest rate encourages the customers for increased savings.
In the above example, we have ample reasons to believe that one variable (family income and savings, misuse of credit, and farm size) has a bearing on the other variable.
We cite two more examples to illustrate the hypothesis, general objective, ultimate objective, and a few specific objectives.
General objective:
- To compare the complications of acceptors of laparoscopic sterilization and mini-laparotomy among American women.
Research hypothesis:
- The risk of complications is higher in the mini-laparotomy method of sterilization than in laparoscopic sterilization.
Specific objectives:
- To assess the complications of laparoscopic sterilization and mini-laparotomy.
- To assess service providers’ knowledge and perception regarding the complications, preferences, and convenience of the two methods.
Ultimate Objectives:
- To introduce and popularize the laparoscopic female sterilization method in the National Family Planning Program to reduce the rapid population growth rate.
In a study designed to examine the living and working conditions of the overseas migrant workers from India and the pattern of remittances from overseas migrant workers, the general objective, specific objectives, and the ultimate objective were formulated as follows:
- To examine the living and working conditions of the overseas migrant workers from India.”
- Characteristics of migrant workers by significant migration channels;
- Countries of destination;
- The occupational skill of the workers;
- Pattern and procedures of remittances;
- Impact of remittances on government revenue;
- Better utilization of remittances.
Ultimate objective:
- To suggest ways and means to minimize the differences in the policy adopted by the public and private sectors in their recruitment process in the interest of the workers;
- To ascertain the possible exploitation of the workers by the private agencies and suggest remedies for such exploitation.
- Private agencies, in most cases, exploit migrant workers.
What are the elements of a good hypothesis?
A good hypothesis should state the purpose of the research, identify which variables are to be used, be logical, precise in language, and be testable with research or experimentation.
How is a hypothesis typically structured?
A hypothesis often follows a basic format of “If {this happens}, then {this will happen}.” It proposes that if something is done, then a specific outcome will occur.
What is a Descriptive hypothesis?
Descriptive hypotheses are propositions that typically state some variables’ existence, size, form, or distribution. They are formulated in the form of statements in which variables are assigned to cases.
What distinguishes a Relational hypothesis?
Relational hypotheses describe the relationship between variables concerning some cases. They can be correlational, where variables occur in a predictable relationship without implying causation, or causal, where a change in one variable causes a change in another.
What is the difference between a correlational hypothesis and a causal hypothesis?
A correlational hypothesis states that variables occur in some predictable relationships without implying that one variable causes the other to change. A causal hypothesis, on the other hand, implies that a change in one variable causes a change or leads to an effect on the other variable.
What are the two main types of research hypotheses?
The two main types of research hypotheses are Descriptive hypothesis and Relational hypothesis
What is a hypothesis in the context of academic research?
A hypothesis is a statement about an expected relationship between variables or an explanation of an occurrence that is clear, specific, and testable.
How does a research hypothesis differ from a general hypothesis?
A research hypothesis is more specific and clear about what’s being assessed and the expected outcome. It must also be testable, meaning there should be a way to prove or disprove it.
What are the essential attributes of a good research hypothesis?
A good research hypothesis should have specificity, clarity, and testability.
Why is testability crucial for a research hypothesis?
Testability ensures that empirical research can prove or disproven the hypothesis. If a statement isn’t testable, it doesn’t qualify as a research hypothesis.
What is the null hypothesis?
The null hypothesis is the counter-proposal to the original hypothesis. It predicts that there is no relationship between the variables in question.
How can one ensure that a hypothesis is clear and specific?
A hypothesis should clearly identify the variables involved, the parties involved, and the expected relationship type, leaving no ambiguity about its intent or meaning.
Why is it essential to avoid value judgments in a research hypothesis?
Value judgments are subjective and not appropriate for a hypothesis. A research hypothesis should strive to be objective, avoiding personal opinions.
What is the basic definition of a hypothesis in research?
A research hypothesis is a statement about an expected relationship between variables, or an explanation of an occurrence, that is clear, specific, and testable.
While a general hypothesis is an idea or explanation based on known facts but not yet proven, a research hypothesis is a clear, specific, and testable statement about the expected outcome of a study.
What are the essential characteristics of a good research hypothesis?
A good research hypothesis should possess specificity, clarity, and testability. It should clearly define what’s being assessed and the expected outcome, and it must be possible to prove or disprove the statement through experimentation.
How can one ensure that a hypothesis is testable?
A hypothesis is testable if there’s a possibility to prove both its truth and falsity. The results of the hypothesis should be reproducible, and it should be specific enough to allow for clear testing procedures.
What is the difference between a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis?
The null hypothesis proposes that no statistical significance exists in a set of observations, suggesting any differences are due to chance alone. The alternative hypothesis, on the other hand, predicts a relationship between the variables of the study and states that the results are significant to the research topic.
How should one formulate an effective research hypothesis?
To formulate an effective research hypothesis, one should state the problem clearly, use an ‘if-then’ statement structure, define the variables as dependent or independent, and scrutinize the hypothesis to ensure it meets the criteria of specificity, clarity, and testability.
What are some types of hypotheses in research?
Types of hypotheses include simple, complex, directional, non-directional, associative and causal, empirical, and statistical hypotheses. Each type serves a specific purpose and is used based on the nature of the research question or problem.

Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- How To Write A Hypothesis
How to Write a Hypothesis: Types and Tips to Remember
Many people might not know what a hypothesis is, the purpose of a hypothesis or where a hypothesis is needed. A hypothesis is a statement that explains the research’s predictions and the reasons behind the research. It is an “educated guess” of the final result of the research problem and is written for an academic research paper. A good hypothesis is carefully stated as a key aspect of the scientific method, yet even the simplest ones can be difficult to explain.
If you are unaware of the process of writing a hypothesis, we are here to help you with all your queries. Read the article and learn how to write a hypothesis for your academic paper/thesis.
Table of Contents
What is a hypothesis.
- Simple Hypothesis
- Complex Hypothesis
- Null Hypothesis
- Alternative Hypothesis
- Logical Hypothesis
- Empirical Hypothesis
- Statistical Hypothesis
Writing a Good Hypothesis – Points to Remember
- How to Write a Hypothesis
Frequently Asked Questions on How to Write a Hypothesis
A hypothesis is prepared in the early stages of a research project. Based on the preliminary research observations, a hypothesis is framed. It is the prediction of the end result of the research problem. For example, suppose you have observed that the plants grow up better with regular watering. In that case, your hypothesis can be “Plants grow better with regular watering”. Once you have got your hypothesis, you can begin the experiments required to support and prove it.
A hypothesis must include variables. It can be some events, objects or concepts which are to be observed and tested for your research experiments. There are two kinds of variables – dependent variables and independent variables. The independent variables are the ones which can be modified in the experiment, and the dependent variables are the ones which can only be observed.
Hypotheses are a crucial part of the research paper since they influence the direction and arrangement of the research methods. The readers will want to know if the hypothesis was proven right or wrong, and therefore it must be mentioned clearly in the introduction or the abstract of the paper.
Types of Hypotheses
Depending on the nature of the research and the findings, the hypothesis can be categorised into one or more of the seven major categories.
1. Simple Hypothesis
A simple hypothesis states the relationship between the two variables (dependent and independent variables).
2. Complex Hypothesis
A complex hypothesis entails the existence of a relationship between two or more variables. It can be two dependent variables and one independent variable or vice versa.
3. Null Hypothesis
A null hypothesis is a statement that states that the variables have no relationship.
4. Alternative Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is the polar opposite of the alternative hypothesis. It states that the two variables under study have a link (one variable has an effect on the other).
5. Logical Hypothesis
In the absence of verifiable proof, a logical hypothesis indicates a relationship between variables. Assertions are based on inference or logic rather than evidence.
6. Empirical Hypothesis
An empirical hypothesis, often known as a “working hypothesis,” is one that is being researched right now. Empirical hypotheses, unlike logical assumptions, are supported by evidence.
7. Statistical Hypothesis
When you test a sample of a population and then use the collected statistical evidence to draw conclusions about the full population, you’ve generated a statistical hypothesis. You test a section of it and then make an educated guess about the rest based on the results.
A good hypothesis is written following the same format and guidelines. To write a good hypothesis, the below-mentioned information has to be added.
Causes and Effects: A hypothesis always includes a cause-and-effect relationship where one variable causes another to change or not change, depending on the type of hypothesis.
Measurable Prediction: Other than logical hypotheses, most hypotheses are designed to be tested. Before you commit to any hypothesis, make sure that it is experimented. Select a testable hypothesis involving an independent variable over which you can have complete control.
Dependent and Independent Variables: You can define the type of variables of your research for the readers.
Language used in a Hypothesis: Make sure to write the hypothesis in simple and clear language.
Adhere to Ethics: Before conducting your research, keep an eye on what you are experimenting with. Those hypotheses which are objectionable, questionable or taboo can be avoided unless they are absolutely necessary.
How to Write a Hypothesis?
A good hypothesis can be written in the following six steps.
Asking a Question
Arousing curiosity in the minds of the readers can be a good way to start a hypothesis. It would make the readers think about the topic critically.
Conducting a Preliminary Research
Before writing the hypothesis, it is essential to get background information regarding the topic. The preliminary research can be done through various web searches, reading books, etc.
Defining the Variables
After you have decided on your hypothesis, you can now decide on your variables. Keep in mind that the independent variables are the ones over which you have complete control and accordingly decide the limits of your hypothesis.
Writing the Hypothesis in the “if-then” Statement
While writing a hypothesis, keep in mind that it must be written in an “if-then” format statement which is a reliable method of expressing the causes and effects. A simple example would be, “If we water the plants daily, then they might grow really well.”
Collection of Adequate Data to Back the Hypothesis
A hypothesis is written to reach the conclusion of the research. After writing the hypothesis, the experiments can be conducted. See to it that you collect the adequate data needed to support the hypothesis.
Writing with Confidence
After you have collected enough data, you can start writing the hypothesis. Make sure you write confidently, without any errors. It would be good to get your writing counter-checked by an expert if you are not confident about it.
What is a hypothesis?
A hypothesis is a statement that explains the research’s predictions and the reasons behind the research. It is written based on various observations.
Why is a hypothesis important?
A hypothesis is important in an academic paper because it explains the result of the research problem. It will help the researcher, as well as the audience, to stay focused and not deviate from the main idea.
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing is a tool for making statistical inferences about the population data. It is an analysis tool that tests assumptions and determines how likely something is within a given standard of accuracy. Hypothesis testing provides a way to verify whether the results of an experiment are valid.
A null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis are set up before performing the hypothesis testing. This helps to arrive at a conclusion regarding the sample obtained from the population. In this article, we will learn more about hypothesis testing, its types, steps to perform the testing, and associated examples.
What is Hypothesis Testing in Statistics?
Hypothesis testing uses sample data from the population to draw useful conclusions regarding the population probability distribution . It tests an assumption made about the data using different types of hypothesis testing methodologies. The hypothesis testing results in either rejecting or not rejecting the null hypothesis.
Hypothesis Testing Definition
Hypothesis testing can be defined as a statistical tool that is used to identify if the results of an experiment are meaningful or not. It involves setting up a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis. These two hypotheses will always be mutually exclusive. This means that if the null hypothesis is true then the alternative hypothesis is false and vice versa. An example of hypothesis testing is setting up a test to check if a new medicine works on a disease in a more efficient manner.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is a concise mathematical statement that is used to indicate that there is no difference between two possibilities. In other words, there is no difference between certain characteristics of data. This hypothesis assumes that the outcomes of an experiment are based on chance alone. It is denoted as \(H_{0}\). Hypothesis testing is used to conclude if the null hypothesis can be rejected or not. Suppose an experiment is conducted to check if girls are shorter than boys at the age of 5. The null hypothesis will say that they are the same height.
Alternative Hypothesis
The alternative hypothesis is an alternative to the null hypothesis. It is used to show that the observations of an experiment are due to some real effect. It indicates that there is a statistical significance between two possible outcomes and can be denoted as \(H_{1}\) or \(H_{a}\). For the above-mentioned example, the alternative hypothesis would be that girls are shorter than boys at the age of 5.
Hypothesis Testing P Value
In hypothesis testing, the p value is used to indicate whether the results obtained after conducting a test are statistically significant or not. It also indicates the probability of making an error in rejecting or not rejecting the null hypothesis.This value is always a number between 0 and 1. The p value is compared to an alpha level, \(\alpha\) or significance level. The alpha level can be defined as the acceptable risk of incorrectly rejecting the null hypothesis. The alpha level is usually chosen between 1% to 5%.
Hypothesis Testing Critical region
All sets of values that lead to rejecting the null hypothesis lie in the critical region. Furthermore, the value that separates the critical region from the non-critical region is known as the critical value.
Hypothesis Testing Formula
Depending upon the type of data available and the size, different types of hypothesis testing are used to determine whether the null hypothesis can be rejected or not. The hypothesis testing formula for some important test statistics are given below:
- z = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\). \(\overline{x}\) is the sample mean, \(\mu\) is the population mean, \(\sigma\) is the population standard deviation and n is the size of the sample.
- t = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{s}{\sqrt{n}}}\). s is the sample standard deviation.
- \(\chi ^{2} = \sum \frac{(O_{i}-E_{i})^{2}}{E_{i}}\). \(O_{i}\) is the observed value and \(E_{i}\) is the expected value.
We will learn more about these test statistics in the upcoming section.
Types of Hypothesis Testing
Selecting the correct test for performing hypothesis testing can be confusing. These tests are used to determine a test statistic on the basis of which the null hypothesis can either be rejected or not rejected. Some of the important tests used for hypothesis testing are given below.
Hypothesis Testing Z Test
A z test is a way of hypothesis testing that is used for a large sample size (n ≥ 30). It is used to determine whether there is a difference between the population mean and the sample mean when the population standard deviation is known. It can also be used to compare the mean of two samples. It is used to compute the z test statistic. The formulas are given as follows:
- One sample: z = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\).
- Two samples: z = \(\frac{(\overline{x_{1}}-\overline{x_{2}})-(\mu_{1}-\mu_{2})}{\sqrt{\frac{\sigma_{1}^{2}}{n_{1}}+\frac{\sigma_{2}^{2}}{n_{2}}}}\).
Hypothesis Testing t Test
The t test is another method of hypothesis testing that is used for a small sample size (n < 30). It is also used to compare the sample mean and population mean. However, the population standard deviation is not known. Instead, the sample standard deviation is known. The mean of two samples can also be compared using the t test.
- One sample: t = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{s}{\sqrt{n}}}\).
- Two samples: t = \(\frac{(\overline{x_{1}}-\overline{x_{2}})-(\mu_{1}-\mu_{2})}{\sqrt{\frac{s_{1}^{2}}{n_{1}}+\frac{s_{2}^{2}}{n_{2}}}}\).
Hypothesis Testing Chi Square
The Chi square test is a hypothesis testing method that is used to check whether the variables in a population are independent or not. It is used when the test statistic is chi-squared distributed.
One Tailed Hypothesis Testing
One tailed hypothesis testing is done when the rejection region is only in one direction. It can also be known as directional hypothesis testing because the effects can be tested in one direction only. This type of testing is further classified into the right tailed test and left tailed test.
Right Tailed Hypothesis Testing
The right tail test is also known as the upper tail test. This test is used to check whether the population parameter is greater than some value. The null and alternative hypotheses for this test are given as follows:
\(H_{0}\): The population parameter is ≤ some value
\(H_{1}\): The population parameter is > some value.
If the test statistic has a greater value than the critical value then the null hypothesis is rejected
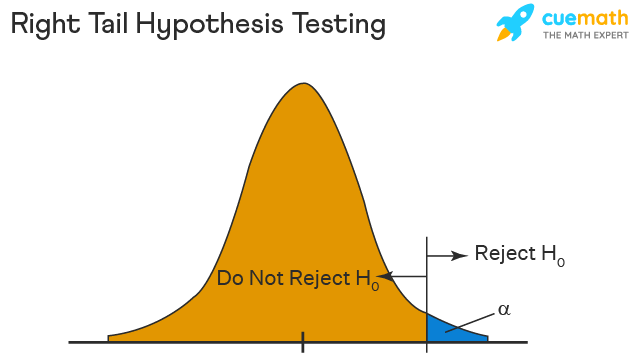
Left Tailed Hypothesis Testing
The left tail test is also known as the lower tail test. It is used to check whether the population parameter is less than some value. The hypotheses for this hypothesis testing can be written as follows:
\(H_{0}\): The population parameter is ≥ some value
\(H_{1}\): The population parameter is < some value.
The null hypothesis is rejected if the test statistic has a value lesser than the critical value.
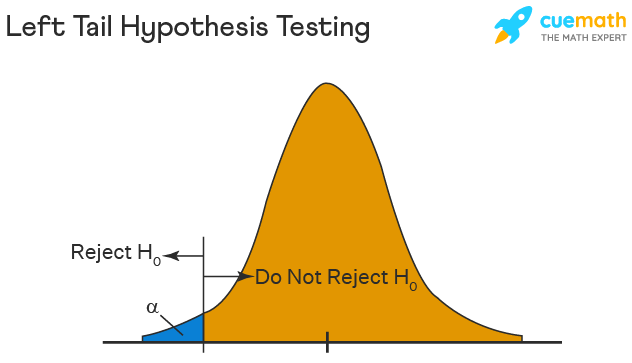
Two Tailed Hypothesis Testing
In this hypothesis testing method, the critical region lies on both sides of the sampling distribution. It is also known as a non - directional hypothesis testing method. The two-tailed test is used when it needs to be determined if the population parameter is assumed to be different than some value. The hypotheses can be set up as follows:
\(H_{0}\): the population parameter = some value
\(H_{1}\): the population parameter ≠ some value
The null hypothesis is rejected if the test statistic has a value that is not equal to the critical value.
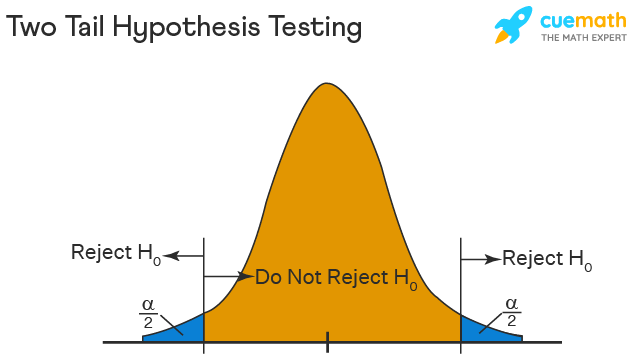
Hypothesis Testing Steps
Hypothesis testing can be easily performed in five simple steps. The most important step is to correctly set up the hypotheses and identify the right method for hypothesis testing. The basic steps to perform hypothesis testing are as follows:
- Step 1: Set up the null hypothesis by correctly identifying whether it is the left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed hypothesis testing.
- Step 2: Set up the alternative hypothesis.
- Step 3: Choose the correct significance level, \(\alpha\), and find the critical value.
- Step 4: Calculate the correct test statistic (z, t or \(\chi\)) and p-value.
- Step 5: Compare the test statistic with the critical value or compare the p-value with \(\alpha\) to arrive at a conclusion. In other words, decide if the null hypothesis is to be rejected or not.
Hypothesis Testing Example
The best way to solve a problem on hypothesis testing is by applying the 5 steps mentioned in the previous section. Suppose a researcher claims that the mean average weight of men is greater than 100kgs with a standard deviation of 15kgs. 30 men are chosen with an average weight of 112.5 Kgs. Using hypothesis testing, check if there is enough evidence to support the researcher's claim. The confidence interval is given as 95%.
Step 1: This is an example of a right-tailed test. Set up the null hypothesis as \(H_{0}\): \(\mu\) = 100.
Step 2: The alternative hypothesis is given by \(H_{1}\): \(\mu\) > 100.
Step 3: As this is a one-tailed test, \(\alpha\) = 100% - 95% = 5%. This can be used to determine the critical value.
1 - \(\alpha\) = 1 - 0.05 = 0.95
0.95 gives the required area under the curve. Now using a normal distribution table, the area 0.95 is at z = 1.645. A similar process can be followed for a t-test. The only additional requirement is to calculate the degrees of freedom given by n - 1.
Step 4: Calculate the z test statistic. This is because the sample size is 30. Furthermore, the sample and population means are known along with the standard deviation.
z = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\).
\(\mu\) = 100, \(\overline{x}\) = 112.5, n = 30, \(\sigma\) = 15
z = \(\frac{112.5-100}{\frac{15}{\sqrt{30}}}\) = 4.56
Step 5: Conclusion. As 4.56 > 1.645 thus, the null hypothesis can be rejected.
Hypothesis Testing and Confidence Intervals
Confidence intervals form an important part of hypothesis testing. This is because the alpha level can be determined from a given confidence interval. Suppose a confidence interval is given as 95%. Subtract the confidence interval from 100%. This gives 100 - 95 = 5% or 0.05. This is the alpha value of a one-tailed hypothesis testing. To obtain the alpha value for a two-tailed hypothesis testing, divide this value by 2. This gives 0.05 / 2 = 0.025.
Related Articles:
- Probability and Statistics
- Data Handling
Important Notes on Hypothesis Testing
- Hypothesis testing is a technique that is used to verify whether the results of an experiment are statistically significant.
- It involves the setting up of a null hypothesis and an alternate hypothesis.
- There are three types of tests that can be conducted under hypothesis testing - z test, t test, and chi square test.
- Hypothesis testing can be classified as right tail, left tail, and two tail tests.
Examples on Hypothesis Testing
- Example 1: The average weight of a dumbbell in a gym is 90lbs. However, a physical trainer believes that the average weight might be higher. A random sample of 5 dumbbells with an average weight of 110lbs and a standard deviation of 18lbs. Using hypothesis testing check if the physical trainer's claim can be supported for a 95% confidence level. Solution: As the sample size is lesser than 30, the t-test is used. \(H_{0}\): \(\mu\) = 90, \(H_{1}\): \(\mu\) > 90 \(\overline{x}\) = 110, \(\mu\) = 90, n = 5, s = 18. \(\alpha\) = 0.05 Using the t-distribution table, the critical value is 2.132 t = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{s}{\sqrt{n}}}\) t = 2.484 As 2.484 > 2.132, the null hypothesis is rejected. Answer: The average weight of the dumbbells may be greater than 90lbs
- Example 2: The average score on a test is 80 with a standard deviation of 10. With a new teaching curriculum introduced it is believed that this score will change. On random testing, the score of 38 students, the mean was found to be 88. With a 0.05 significance level, is there any evidence to support this claim? Solution: This is an example of two-tail hypothesis testing. The z test will be used. \(H_{0}\): \(\mu\) = 80, \(H_{1}\): \(\mu\) ≠ 80 \(\overline{x}\) = 88, \(\mu\) = 80, n = 36, \(\sigma\) = 10. \(\alpha\) = 0.05 / 2 = 0.025 The critical value using the normal distribution table is 1.96 z = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\) z = \(\frac{88-80}{\frac{10}{\sqrt{36}}}\) = 4.8 As 4.8 > 1.96, the null hypothesis is rejected. Answer: There is a difference in the scores after the new curriculum was introduced.
- Example 3: The average score of a class is 90. However, a teacher believes that the average score might be lower. The scores of 6 students were randomly measured. The mean was 82 with a standard deviation of 18. With a 0.05 significance level use hypothesis testing to check if this claim is true. Solution: The t test will be used. \(H_{0}\): \(\mu\) = 90, \(H_{1}\): \(\mu\) < 90 \(\overline{x}\) = 110, \(\mu\) = 90, n = 6, s = 18 The critical value from the t table is -2.015 t = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{s}{\sqrt{n}}}\) t = \(\frac{82-90}{\frac{18}{\sqrt{6}}}\) t = -1.088 As -1.088 > -2.015, we fail to reject the null hypothesis. Answer: There is not enough evidence to support the claim.
go to slide go to slide go to slide

Book a Free Trial Class
FAQs on Hypothesis Testing
What is hypothesis testing.
Hypothesis testing in statistics is a tool that is used to make inferences about the population data. It is also used to check if the results of an experiment are valid.
What is the z Test in Hypothesis Testing?
The z test in hypothesis testing is used to find the z test statistic for normally distributed data . The z test is used when the standard deviation of the population is known and the sample size is greater than or equal to 30.
What is the t Test in Hypothesis Testing?
The t test in hypothesis testing is used when the data follows a student t distribution . It is used when the sample size is less than 30 and standard deviation of the population is not known.
What is the formula for z test in Hypothesis Testing?
The formula for a one sample z test in hypothesis testing is z = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\) and for two samples is z = \(\frac{(\overline{x_{1}}-\overline{x_{2}})-(\mu_{1}-\mu_{2})}{\sqrt{\frac{\sigma_{1}^{2}}{n_{1}}+\frac{\sigma_{2}^{2}}{n_{2}}}}\).
What is the p Value in Hypothesis Testing?
The p value helps to determine if the test results are statistically significant or not. In hypothesis testing, the null hypothesis can either be rejected or not rejected based on the comparison between the p value and the alpha level.
What is One Tail Hypothesis Testing?
When the rejection region is only on one side of the distribution curve then it is known as one tail hypothesis testing. The right tail test and the left tail test are two types of directional hypothesis testing.
What is the Alpha Level in Two Tail Hypothesis Testing?
To get the alpha level in a two tail hypothesis testing divide \(\alpha\) by 2. This is done as there are two rejection regions in the curve.
- Machine Learning Tutorial
- Data Analysis Tutorial
- Python - Data visualization tutorial
- Machine Learning Projects
- Machine Learning Interview Questions
- Machine Learning Mathematics
- Deep Learning Tutorial
- Deep Learning Project
- Deep Learning Interview Questions
- Computer Vision Tutorial
- Computer Vision Projects
- NLP Project
- NLP Interview Questions
- Statistics with Python
- 100 Days of Machine Learning
- Data Analysis with Python
Introduction to Data Analysis
- What is Data Analysis?
- Data Analytics and its type
- How to Install Numpy on Windows?
- How to Install Pandas in Python?
- How to Install Matplotlib on python?
- How to Install Python Tensorflow in Windows?
Data Analysis Libraries
- Pandas Tutorial
- NumPy Tutorial - Python Library
- Data Analysis with SciPy
- Introduction to TensorFlow
Data Visulization Libraries
- Matplotlib Tutorial
- Python Seaborn Tutorial
- Plotly tutorial
- Introduction to Bokeh in Python
Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
- Univariate, Bivariate and Multivariate data and its analysis
- Measures of Central Tendency in Statistics
- Measures of spread - Range, Variance, and Standard Deviation
- Interquartile Range and Quartile Deviation using NumPy and SciPy
- Anova Formula
- Skewness of Statistical Data
- How to Calculate Skewness and Kurtosis in Python?
- Difference Between Skewness and Kurtosis
- Histogram | Meaning, Example, Types and Steps to Draw
- Interpretations of Histogram
- Quantile Quantile plots
- What is Univariate, Bivariate & Multivariate Analysis in Data Visualisation?
- Using pandas crosstab to create a bar plot
- Exploring Correlation in Python
- Mathematics | Covariance and Correlation
- Factor Analysis | Data Analysis
- Data Mining - Cluster Analysis
- MANOVA Test in R Programming
- Python - Central Limit Theorem
- Probability Distribution Function
- Probability Density Estimation & Maximum Likelihood Estimation
- Exponential Distribution in R Programming - dexp(), pexp(), qexp(), and rexp() Functions
- Mathematics | Probability Distributions Set 4 (Binomial Distribution)
- Poisson Distribution - Definition, Formula, Table and Examples
- P-Value: Comprehensive Guide to Understand, Apply, and Interpret
- Z-Score in Statistics
- How to Calculate Point Estimates in R?
- Confidence Interval
- Chi-square test in Machine Learning
Understanding Hypothesis Testing
Data preprocessing.
- ML | Data Preprocessing in Python
- ML | Overview of Data Cleaning
- ML | Handling Missing Values
- Detect and Remove the Outliers using Python
Data Transformation
- Data Normalization Machine Learning
- Sampling distribution Using Python
Time Series Data Analysis
- Data Mining - Time-Series, Symbolic and Biological Sequences Data
- Basic DateTime Operations in Python
- Time Series Analysis & Visualization in Python
- How to deal with missing values in a Timeseries in Python?
- How to calculate MOVING AVERAGE in a Pandas DataFrame?
- What is a trend in time series?
- How to Perform an Augmented Dickey-Fuller Test in R
- AutoCorrelation
Case Studies and Projects
- Top 8 Free Dataset Sources to Use for Data Science Projects
- Step by Step Predictive Analysis - Machine Learning
- 6 Tips for Creating Effective Data Visualizations
Hypothesis testing involves formulating assumptions about population parameters based on sample statistics and rigorously evaluating these assumptions against empirical evidence. This article sheds light on the significance of hypothesis testing and the critical steps involved in the process.
What is Hypothesis Testing?
Hypothesis testing is a statistical method that is used to make a statistical decision using experimental data. Hypothesis testing is basically an assumption that we make about a population parameter. It evaluates two mutually exclusive statements about a population to determine which statement is best supported by the sample data.
Example: You say an average height in the class is 30 or a boy is taller than a girl. All of these is an assumption that we are assuming, and we need some statistical way to prove these. We need some mathematical conclusion whatever we are assuming is true.
Defining Hypotheses
Key Terms of Hypothesis Testing
- P-value: The P value , or calculated probability, is the probability of finding the observed/extreme results when the null hypothesis(H0) of a study-given problem is true. If your P-value is less than the chosen significance level then you reject the null hypothesis i.e. accept that your sample claims to support the alternative hypothesis.
- Test Statistic: The test statistic is a numerical value calculated from sample data during a hypothesis test, used to determine whether to reject the null hypothesis. It is compared to a critical value or p-value to make decisions about the statistical significance of the observed results.
- Critical value : The critical value in statistics is a threshold or cutoff point used to determine whether to reject the null hypothesis in a hypothesis test.
- Degrees of freedom: Degrees of freedom are associated with the variability or freedom one has in estimating a parameter. The degrees of freedom are related to the sample size and determine the shape.
Why do we use Hypothesis Testing?
Hypothesis testing is an important procedure in statistics. Hypothesis testing evaluates two mutually exclusive population statements to determine which statement is most supported by sample data. When we say that the findings are statistically significant, thanks to hypothesis testing.
One-Tailed and Two-Tailed Test
One tailed test focuses on one direction, either greater than or less than a specified value. We use a one-tailed test when there is a clear directional expectation based on prior knowledge or theory. The critical region is located on only one side of the distribution curve. If the sample falls into this critical region, the null hypothesis is rejected in favor of the alternative hypothesis.
One-Tailed Test
There are two types of one-tailed test:
Two-Tailed Test
A two-tailed test considers both directions, greater than and less than a specified value.We use a two-tailed test when there is no specific directional expectation, and want to detect any significant difference.
What are Type 1 and Type 2 errors in Hypothesis Testing?
In hypothesis testing, Type I and Type II errors are two possible errors that researchers can make when drawing conclusions about a population based on a sample of data. These errors are associated with the decisions made regarding the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.
How does Hypothesis Testing work?
Step 1: define null and alternative hypothesis.
We first identify the problem about which we want to make an assumption keeping in mind that our assumption should be contradictory to one another, assuming Normally distributed data.
Step 2 – Choose significance level
Step 3 – Collect and Analyze data.
Gather relevant data through observation or experimentation. Analyze the data using appropriate statistical methods to obtain a test statistic.
Step 4-Calculate Test Statistic
The data for the tests are evaluated in this step we look for various scores based on the characteristics of data. The choice of the test statistic depends on the type of hypothesis test being conducted.
There are various hypothesis tests, each appropriate for various goal to calculate our test. This could be a Z-test , Chi-square , T-test , and so on.
- Z-test : If population means and standard deviations are known. Z-statistic is commonly used.
- t-test : If population standard deviations are unknown. and sample size is small than t-test statistic is more appropriate.
- Chi-square test : Chi-square test is used for categorical data or for testing independence in contingency tables
- F-test : F-test is often used in analysis of variance (ANOVA) to compare variances or test the equality of means across multiple groups.
We have a smaller dataset, So, T-test is more appropriate to test our hypothesis.
T-statistic is a measure of the difference between the means of two groups relative to the variability within each group. It is calculated as the difference between the sample means divided by the standard error of the difference. It is also known as the t-value or t-score.
Step 5 – Comparing Test Statistic:
In this stage, we decide where we should accept the null hypothesis or reject the null hypothesis. There are two ways to decide where we should accept or reject the null hypothesis.
Method A: Using Crtical values
Comparing the test statistic and tabulated critical value we have,
- If Test Statistic>Critical Value: Reject the null hypothesis.
- If Test Statistic≤Critical Value: Fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Note: Critical values are predetermined threshold values that are used to make a decision in hypothesis testing. To determine critical values for hypothesis testing, we typically refer to a statistical distribution table , such as the normal distribution or t-distribution tables based on.
Method B: Using P-values
We can also come to an conclusion using the p-value,
Note : The p-value is the probability of obtaining a test statistic as extreme as, or more extreme than, the one observed in the sample, assuming the null hypothesis is true. To determine p-value for hypothesis testing, we typically refer to a statistical distribution table , such as the normal distribution or t-distribution tables based on.
Step 7- Interpret the Results
At last, we can conclude our experiment using method A or B.
Calculating test statistic
To validate our hypothesis about a population parameter we use statistical functions . We use the z-score, p-value, and level of significance(alpha) to make evidence for our hypothesis for normally distributed data .
1. Z-statistics:
When population means and standard deviations are known.
- μ represents the population mean,
- σ is the standard deviation
- and n is the size of the sample.
2. T-Statistics
T test is used when n<30,
t-statistic calculation is given by:
- t = t-score,
- x̄ = sample mean
- μ = population mean,
- s = standard deviation of the sample,
- n = sample size
3. Chi-Square Test
Chi-Square Test for Independence categorical Data (Non-normally distributed) using:
- i,j are the rows and columns index respectively.
Real life Hypothesis Testing example
Let’s examine hypothesis testing using two real life situations,
Case A: D oes a New Drug Affect Blood Pressure?
Imagine a pharmaceutical company has developed a new drug that they believe can effectively lower blood pressure in patients with hypertension. Before bringing the drug to market, they need to conduct a study to assess its impact on blood pressure.
- Before Treatment: 120, 122, 118, 130, 125, 128, 115, 121, 123, 119
- After Treatment: 115, 120, 112, 128, 122, 125, 110, 117, 119, 114
Step 1 : Define the Hypothesis
- Null Hypothesis : (H 0 )The new drug has no effect on blood pressure.
- Alternate Hypothesis : (H 1 )The new drug has an effect on blood pressure.
Step 2: Define the Significance level
Let’s consider the Significance level at 0.05, indicating rejection of the null hypothesis.
If the evidence suggests less than a 5% chance of observing the results due to random variation.
Step 3 : Compute the test statistic
Using paired T-test analyze the data to obtain a test statistic and a p-value.
The test statistic (e.g., T-statistic) is calculated based on the differences between blood pressure measurements before and after treatment.
t = m/(s/√n)
- m = mean of the difference i.e X after, X before
- s = standard deviation of the difference (d) i.e d i = X after, i − X before,
- n = sample size,
then, m= -3.9, s= 1.8 and n= 10
we, calculate the , T-statistic = -9 based on the formula for paired t test
Step 4: Find the p-value
The calculated t-statistic is -9 and degrees of freedom df = 9, you can find the p-value using statistical software or a t-distribution table.
thus, p-value = 8.538051223166285e-06
Step 5: Result
- If the p-value is less than or equal to 0.05, the researchers reject the null hypothesis.
- If the p-value is greater than 0.05, they fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Conclusion: Since the p-value (8.538051223166285e-06) is less than the significance level (0.05), the researchers reject the null hypothesis. There is statistically significant evidence that the average blood pressure before and after treatment with the new drug is different.
Python Implementation of Hypothesis Testing
Let’s create hypothesis testing with python, where we are testing whether a new drug affects blood pressure. For this example, we will use a paired T-test. We’ll use the scipy.stats library for the T-test.
Scipy is a mathematical library in Python that is mostly used for mathematical equations and computations.
We will implement our first real life problem via python,
In the above example, given the T-statistic of approximately -9 and an extremely small p-value, the results indicate a strong case to reject the null hypothesis at a significance level of 0.05.
- The results suggest that the new drug, treatment, or intervention has a significant effect on lowering blood pressure.
- The negative T-statistic indicates that the mean blood pressure after treatment is significantly lower than the assumed population mean before treatment.
Case B : Cholesterol level in a population
Data: A sample of 25 individuals is taken, and their cholesterol levels are measured.
Cholesterol Levels (mg/dL): 205, 198, 210, 190, 215, 205, 200, 192, 198, 205, 198, 202, 208, 200, 205, 198, 205, 210, 192, 205, 198, 205, 210, 192, 205.
Populations Mean = 200
Population Standard Deviation (σ): 5 mg/dL(given for this problem)
Step 1: Define the Hypothesis
- Null Hypothesis (H 0 ): The average cholesterol level in a population is 200 mg/dL.
- Alternate Hypothesis (H 1 ): The average cholesterol level in a population is different from 200 mg/dL.
As the direction of deviation is not given , we assume a two-tailed test, and based on a normal distribution table, the critical values for a significance level of 0.05 (two-tailed) can be calculated through the z-table and are approximately -1.96 and 1.96.
Step 4: Result
Since the absolute value of the test statistic (2.04) is greater than the critical value (1.96), we reject the null hypothesis. And conclude that, there is statistically significant evidence that the average cholesterol level in the population is different from 200 mg/dL
Limitations of Hypothesis Testing
- Although a useful technique, hypothesis testing does not offer a comprehensive grasp of the topic being studied. Without fully reflecting the intricacy or whole context of the phenomena, it concentrates on certain hypotheses and statistical significance.
- The accuracy of hypothesis testing results is contingent on the quality of available data and the appropriateness of statistical methods used. Inaccurate data or poorly formulated hypotheses can lead to incorrect conclusions.
- Relying solely on hypothesis testing may cause analysts to overlook significant patterns or relationships in the data that are not captured by the specific hypotheses being tested. This limitation underscores the importance of complimenting hypothesis testing with other analytical approaches.
Hypothesis testing stands as a cornerstone in statistical analysis, enabling data scientists to navigate uncertainties and draw credible inferences from sample data. By systematically defining null and alternative hypotheses, choosing significance levels, and leveraging statistical tests, researchers can assess the validity of their assumptions. The article also elucidates the critical distinction between Type I and Type II errors, providing a comprehensive understanding of the nuanced decision-making process inherent in hypothesis testing. The real-life example of testing a new drug’s effect on blood pressure using a paired T-test showcases the practical application of these principles, underscoring the importance of statistical rigor in data-driven decision-making.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. what are the 3 types of hypothesis test.
There are three types of hypothesis tests: right-tailed, left-tailed, and two-tailed. Right-tailed tests assess if a parameter is greater, left-tailed if lesser. Two-tailed tests check for non-directional differences, greater or lesser.
2.What are the 4 components of hypothesis testing?
Null Hypothesis ( ): No effect or difference exists. Alternative Hypothesis ( ): An effect or difference exists. Significance Level ( ): Risk of rejecting null hypothesis when it’s true (Type I error). Test Statistic: Numerical value representing observed evidence against null hypothesis.
3.What is hypothesis testing in ML?
Statistical method to evaluate the performance and validity of machine learning models. Tests specific hypotheses about model behavior, like whether features influence predictions or if a model generalizes well to unseen data.
4.What is the difference between Pytest and hypothesis in Python?
Pytest purposes general testing framework for Python code while Hypothesis is a Property-based testing framework for Python, focusing on generating test cases based on specified properties of the code.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- data-science
- Data Science
- Machine Learning

Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

Hypothesis Testing in Statistics – Short Notes + PPT
“Truth can be stated in a thousand different ways, yet each one can be true…” Swami Vivekananda
What is ‘Test of Hypothesis’?
Ø Test of Hypothesis (Hypothesis Testing) is a process of testing of the significance regarding the parameters of the population on the basis of sample drawn from it. Ø Test of hypothesis is also called as ‘Test of Significance’. Ø J. Neyman and E.S. Pearson initiated the practice of testing of hypothesis in statistics.
What is the purpose of Hypothesis Testing?
Ø The main purpose of hypothesis testing is to help the researcher in reaching a conclusion regarding the population by examining a sample taken from that population. Ø The hypothesis testing does not provide proof for the hypothesis. Ø The test only indicates whether the hypothesis is supported or not supported by the available data.
What is Hypothesis?
Ø Hypothesis is a statement about one or more populations.
Ø It is a statement about the parameters of the population about which the statement is made.
Ø Example:
$ A doctor hypothesized: “The drug ‘X’ is ineffective in 99% of cases of which it is used”.
$ “The average pass percentage of central university degree programme is 98”.
Ø Through the hypothesis testing the researcher or investigator can determine whether or not such statements are compatible with the available data.
Types of Hypothesis
Ø There are TWO types of hypothesis.
(A). Research Hypothesis
(B). Statistical Hypothesis
(A). Research Hypothesis
Ø Research Hypothesis is “a tentative solution for the problem being investigated”.
Ø It is the supposition (guess) that motivates the research.
Ø In research, the researcher determines whether or not their supposition can be supported through scientific investigation.
Ø The research hypothesis directly leads to statistical hypothesis.
(B). Statistical Hypothesis
Details of the Statistical hypothesis are discussed in the “Steps or Components in Testing of Statistical Hypothesis”.
Steps / Components in Testing of Statistical Hypothesis:
Ø The statistical hypothesis testing consists of following Steps / Components
(1). Data (variable)
(2). Statistical Hypothesis
(3). Test Statistic
(4). Decision Rule
(5). Significance Level
(6). Statistical Decision
(7). p – Value
(1). Data (variable)
Ø Data is the information collected from the population.
Ø It may be the observation of a natural phenomenon, Result of an experiment, Data from a survey or a secondary data.
Ø The nature of data determines the type of statistical test to be selected.
Ø All the features of the data such as continuous, discontinuous, quantitative or qualitative etc. matters in the process of hypothesis testing.
(2). Statistical Hypothesis
Ø Statistical hypothesis is a statement about the population which we want to verify on the basis of information available from the sample.
Ø A statistical hypothesis is stated in such a way that they may be evaluated by appropriate statistical techniques.
Ø There are TWO types of statistical hypothesizes:
(a). Null hypothesis
(b). Alternative hypothesis
(a). Null Hypothesis
Ø The Null hypothesis is the hypothesis to be tested by test statistic.
Ø Null hypothesis is denoted as H 0 .
Ø Usually the null hypothesis stated as the ‘Hypothesis of No Difference’.
Ø The statement is created complementary to the conclusion that the researcher is seeking to reach through his research.
Ø Usually stated in the negative terms of the original research hypothesis.
Ø Example: The drug ‘X’ DO NOT induces apoptosis in cancerous cells.
Ø In the statistical testing process, the null hypothesis is either:
$ Rejected
$ Not rejected (Fail to be rejected / accepted)
Ø If the null hypothesis is not rejected, we say that the data on which the test is based do not provide sufficient evidence to cause the rejection of null hypothesis.
Ø If the null hypothesis is rejected in the testing process, we say that the data at hand are not compatible with the null hypothesis but are supportive for some other hypothesis (commonly called as alternative hypothesis).
(b). Alternative Hypothesis
Ø Alternate hypothesis is created in a negative meaning of the null hypothesis.
Ø It is denoted as H 1 or H A .
Ø Usually the alternative hypothesis and research hypothesis are the same.
Ø Example: The drug ‘X’ induces apoptosis in cancerous cells.
How to state the statistical hypothesis?
Ø The null hypothesis should contain an equality sign (=, ≤ or ≥).
Ø Example: The population mean (μ) is not 100.
$ H0: μ = 100
$ H1: μ ≠ 100
Ø Example: The population means is greater than 100.
$ H0: μ ≤ 100
$ H1: μ > 100
Ø Example: The population mean is less than 100.
$ H0: μ ≥ 100
$ H1: μ < 100
Things to remember when constructing the Null Hypothesis:
$ What you expected to conclude with the study should be placed in the alternative hypothesis.
$ The null hypothesis should contain a statement of equality (=, ≤, ≥).
$ The null hypothesis is the hypothesis to be tested.
$ The null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis should be complementary.
(3). Test Statistic
Ø Test statistic is the statistic computed from the data sample.
Ø There are many possible values that the test statistic can adopt.
Ø Test value of the statistic depends on the nature of the sample.
Ø The test statistic is the decision maker in hypothesis testing.
Ø Decision is to reject or not reject the null hypothesis.
Ø General formula for test statistic: (applicable to most of the test statistic but not to all)
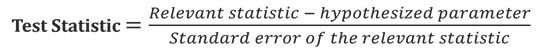
x̄ : mean
μ0 : hypothesized value of population mean
σ/√n : Standard error
(4). Decision Rule
Ø All the possible values that the test statistic can assume are points on the horizontal axis of a graph of the distribution of the test statistic.
Ø The values are divided into two groups:
1. Values of the rejection region
2. Values of the non-rejection region
Ø The decision rule tell us to reject the null hypothesis if the values of the test statistic that we compute from our sample is one of the values in the rejection region and not to reject the null hypothesis if the computed values of the test statistic is on the values in the non-rejection region.
(5) Significance Level
Ø Level of significance is the probability of rejecting a true null hypothesis in the statistical testing procedure.
Ø The level of significance is a probability value and it is denoted as ‘α’.
Ø The significance level decide the decision value to go the rejection region or to the non-rejection region.
Ø Due to the ‘Level of significance’ the test statistic is often called as ‘Significance Test’.
Ø If we reject a true null hypothesis we are committed an error.
Ø Thus, you have to ensure that the probability of rejecting a true null hypothesis is very small.
Ø Thus, we select a small value of α to ensure the probability of rejecting a true null hypothesis is very less.
Ø The frequently used α values are 0.01 (99%), 0.05 (95%).
Ø Explanation : if we select 0.01 (99%) as the significance level, it means that we are 99% confident in our decision but still there is 1% change for our decision being false.
(6). Statistical Decision
Ø It is the decision of rejecting or not rejecting the null hypothesis.
Ø We reject the null hypothesis if the computed value of the test statistic is fall in the rejection region.
Ø We will NOT reject the null hypothesis if the computed value falls in the non-rejection region.
Ø Conclusion:
Ø If we reject H 0 , we conclude that H A is true.
Ø If we fail to reject H 0 , we conclude that the H 0 may be true.
Ø When a null hypothesis is not rejected one should not say that the null hypothesis accepted but we say that null hypothesis is not rejected.
Ø We usually avoid the usage ‘accept’, because we may have committed a type II error.
Learn more: Statistical Errors (Type I and Type II Errors)
(7). p-Value
Ø p-value is the smallest value of α for which we can reject a null hypothesis.
Ø A p-value is the probability that the computed value for a test statistic is at least as extreme as specified value of the test statistic when the null hypothesis is true.
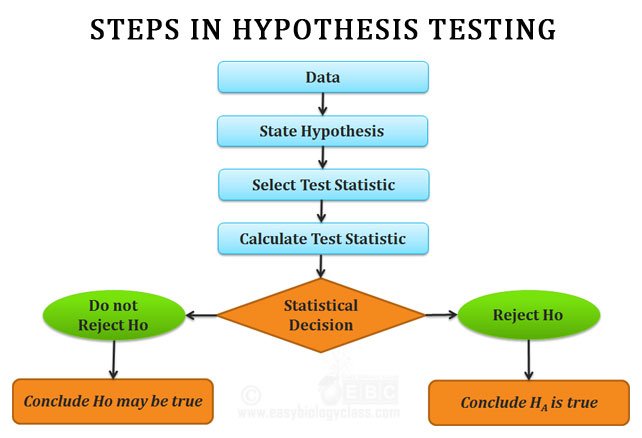
Daniel, W.W., 1999. Biostatistics: A foundation for analysis in the health sciences 9th edition. John Wiley & Sons inc.: USA.
Khan, I.A. and Khanum, A., 2012, Fundamentals of Biostatistics, 3rd edition (revised), Ukaaz Publications, Hyderabad, India.
Kothari, C.R., 2004. Research methodology: Methods and techniques. New Age International, India.
<<< Back to Statistics Note Papte
Do you have any Queries? Please leave me a COMMENT in the Comments Section below. I will be Happy to Read your Comments and Reply.
Download the PPT of this Topic
Hypothesis Testing PPT (Tips and Procedure of Statistical Significance Test)
You might also like…
@. Introduction to Biostatistics
@. Data Collection Methods in Statistics
@. Difference between Type I and Type II Errors
@. Biostatistics PPTs.
More Lecture Notes from Easy Biology Class…
Botany Zoology Biochemistry Genetics Cell & Molecular Biology Biotechnology Physiology & Endocrinology Plant Physiology Microbiology Immunology Embryology Ecology Evolution Biophysics Research Methodology Biostatistics Chemistry for Biologists Physics for Biologists
Browse more in Easy Biology Class…
Lecture Notes Biology PPTs Video Tutorials Biology MCQ Question Bank Difference between Practical Aids Mock Tests (Online) Biology Exams
Related posts:
- Principles of Experimental Designs in Statistics – Replication, Randomization & Local Control
- Types of Experimental Designs in Statistics (RBD, CRD, LSD, Factorial Designs)
- Difference between Primary and Secondary Data
- MCQ on Hypothesis Testing in Statistics
- What is Data in Statistics?
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Privacy Overview

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Definition: Hypothesis is an educated guess or proposed explanation for a phenomenon, based on some initial observations or data. It is a tentative statement that can be tested and potentially proven or disproven through further investigation and experimentation. Hypothesis is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments ...
Functions of Hypothesis. Following are the functions performed by the hypothesis: Hypothesis helps in making an observation and experiments possible. It becomes the start point for the investigation. Hypothesis helps in verifying the observations. It helps in directing the inquiries in the right direction.
5. Phrase your hypothesis in three ways. To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if…then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable. If a first-year student starts attending more lectures, then their exam scores will improve.
Hypothesis is a testable statement that explains what is happening or observed. It proposes the relation between the various participating variables. Hypothesis is also called Theory, Thesis, Guess, Assumption, or Suggestion. Hypothesis creates a structure that guides the search for knowledge. In this article, we will learn what is hypothesis ...
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. It is a preliminary answer to your question that helps guide the research process. Consider a study designed to examine the relationship between sleep deprivation and test ...
3. Simple hypothesis. A simple hypothesis is a statement made to reflect the relation between exactly two variables. One independent and one dependent. Consider the example, "Smoking is a prominent cause of lung cancer." The dependent variable, lung cancer, is dependent on the independent variable, smoking. 4.
Merriam Webster defines a hypothesis as "an assumption or concession made for the sake of argument.". In other words, a hypothesis is an educated guess. Scientists make a reasonable assumption--or a hypothesis--then design an experiment to test whether it's true or not.
Examples. A research hypothesis, in its plural form "hypotheses," is a specific, testable prediction about the anticipated results of a study, established at its outset. It is a key component of the scientific method. Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding.
A research hypothesis (also called a scientific hypothesis) is a statement about the expected outcome of a study (for example, a dissertation or thesis). To constitute a quality hypothesis, the statement needs to have three attributes - specificity, clarity and testability. Let's take a look at these more closely.
Step 5: Phrase your hypothesis in three ways. To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if … then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable. If a first-year student starts attending more lectures, then their exam scores will improve.
Here are some good research hypothesis examples: "The use of a specific type of therapy will lead to a reduction in symptoms of depression in individuals with a history of major depressive disorder.". "Providing educational interventions on healthy eating habits will result in weight loss in overweight individuals.".
A proposition (or hypothesis) that two events are related cannot be tested in the same way as a law of nature can be tested. An example would be to see if some drug is effective to treat a given medical condition. Even if there is a strong correlation that indicates that this is the case, some samples would still not fit the hypothesis.
Types of hypotheses include simple, complex, directional, non-directional, associative and causal, empirical, and statistical hypotheses. Each type serves a specific purpose and is used based on the nature of the research question or problem. The research hypothesis is a logical supposition and an educated prediction of the assumed relationship ...
0 and an alternative hypothesis H 1. For example: H 0: = 0 versus 6= 0: More generally, consider a parameter space . We consider H 0: 2 0 versus H 1: 2 1 where 0 \ 1 = ;. If 0 consists of a single point, we call this a simple null hypothesis. If 0 consists of more than one point, we call this a composite null hypothesis. Example 1 X 1;:::;X n ...
There are 5 main steps in hypothesis testing: State your research hypothesis as a null hypothesis and alternate hypothesis (H o) and (H a or H 1 ). Collect data in a way designed to test the hypothesis. Perform an appropriate statistical test. Decide whether to reject or fail to reject your null hypothesis. Present the findings in your results ...
Types of Hypothesis. The hypothesis can be broadly classified into different types. They are: Simple Hypothesis. A simple hypothesis is a hypothesis that there exists a relationship between two variables. One is called a dependent variable, and the other is called an independent variable. Complex Hypothesis.
1. Simple Hypothesis. A simple hypothesis states the relationship between the two variables (dependent and independent variables). 2. Complex Hypothesis. A complex hypothesis entails the existence of a relationship between two or more variables. It can be two dependent variables and one independent variable or vice versa.
The alternative hypothesis (H a) is the other answer to your research question. It claims that there's an effect in the population. Often, your alternative hypothesis is the same as your research hypothesis. In other words, it's the claim that you expect or hope will be true. The alternative hypothesis is the complement to the null hypothesis.
Hypothesis testing is a tool for making statistical inferences about the population data. It is an analysis tool that tests assumptions and determines how likely something is within a given standard of accuracy. Hypothesis testing provides a way to verify whether the results of an experiment are valid. A null hypothesis and an alternative ...
In hypothesis testing, we quantify our uncertainty by asking whether it is likely that data came from a particular distribution. We will focus on the following common type of hypothesis testing scenario: I The data Y come from some distribution f(Yj ), with parameter . I There are two possibilities for : either = 0, or 6= 0.
Note: The p-value is the probability of obtaining a test statistic as extreme as, or more extreme than, the one observed in the sample, assuming the null hypothesis is true. To determine p-value for hypothesis testing, we typically refer to a statistical distribution table , such as the normal distribution or t-distribution tables based on.
Ø Test of Hypothesis (Hypothesis Testing) is a process of testing of the significance regarding the parameters of the population on the basis of sample drawn from it. Ø Test of hypothesis is also called as 'Test of Significance'. Ø J. Neyman and E.S. Pearson initiated the practice of testing of hypothesis in statistics.