Reference management. Clean and simple.

How to write a thesis statement + examples

What is a thesis statement?
Is a thesis statement a question, how do you write a good thesis statement, how do i know if my thesis statement is good, examples of thesis statements, helpful resources on how to write a thesis statement, frequently asked questions about writing a thesis statement, related articles.
A thesis statement is the main argument of your paper or thesis.
The thesis statement is one of the most important elements of any piece of academic writing . It is a brief statement of your paper’s main argument. Essentially, you are stating what you will be writing about.
You can see your thesis statement as an answer to a question. While it also contains the question, it should really give an answer to the question with new information and not just restate or reiterate it.
Your thesis statement is part of your introduction. Learn more about how to write a good thesis introduction in our introduction guide .
A thesis statement is not a question. A statement must be arguable and provable through evidence and analysis. While your thesis might stem from a research question, it should be in the form of a statement.
Tip: A thesis statement is typically 1-2 sentences. For a longer project like a thesis, the statement may be several sentences or a paragraph.
A good thesis statement needs to do the following:
- Condense the main idea of your thesis into one or two sentences.
- Answer your project’s main research question.
- Clearly state your position in relation to the topic .
- Make an argument that requires support or evidence.
Once you have written down a thesis statement, check if it fulfills the following criteria:
- Your statement needs to be provable by evidence. As an argument, a thesis statement needs to be debatable.
- Your statement needs to be precise. Do not give away too much information in the thesis statement and do not load it with unnecessary information.
- Your statement cannot say that one solution is simply right or simply wrong as a matter of fact. You should draw upon verified facts to persuade the reader of your solution, but you cannot just declare something as right or wrong.
As previously mentioned, your thesis statement should answer a question.
If the question is:
What do you think the City of New York should do to reduce traffic congestion?
A good thesis statement restates the question and answers it:
In this paper, I will argue that the City of New York should focus on providing exclusive lanes for public transport and adaptive traffic signals to reduce traffic congestion by the year 2035.
Here is another example. If the question is:
How can we end poverty?
A good thesis statement should give more than one solution to the problem in question:
In this paper, I will argue that introducing universal basic income can help reduce poverty and positively impact the way we work.
- The Writing Center of the University of North Carolina has a list of questions to ask to see if your thesis is strong .
A thesis statement is part of the introduction of your paper. It is usually found in the first or second paragraph to let the reader know your research purpose from the beginning.
In general, a thesis statement should have one or two sentences. But the length really depends on the overall length of your project. Take a look at our guide about the length of thesis statements for more insight on this topic.
Here is a list of Thesis Statement Examples that will help you understand better how to write them.
Every good essay should include a thesis statement as part of its introduction, no matter the academic level. Of course, if you are a high school student you are not expected to have the same type of thesis as a PhD student.
Here is a great YouTube tutorial showing How To Write An Essay: Thesis Statements .


Thesis Statements
What this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can craft or refine one for your draft.
Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence near the beginning of your paper (most often, at the end of the first paragraph) that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I create a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis” that presents a basic or main idea and an argument that you think you can support with evidence. Both the argument and your thesis are likely to need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following :
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question. If the prompt isn’t phrased as a question, try to rephrase it. For example, “Discuss the effect of X on Y” can be rephrased as “What is the effect of X on Y?”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is likely to be “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s okay to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on contemporary communication, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: “Discuss the impact of social media on public awareness.” Looking back at your notes, you might start with this working thesis:
Social media impacts public awareness in both positive and negative ways.
You can use the questions above to help you revise this general statement into a stronger thesis.
- Do I answer the question? You can analyze this if you rephrase “discuss the impact” as “what is the impact?” This way, you can see that you’ve answered the question only very generally with the vague “positive and negative ways.”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not likely. Only people who maintain that social media has a solely positive or solely negative impact could disagree.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? No. What are the positive effects? What are the negative effects?
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? No. Why are they positive? How are they positive? What are their causes? Why are they negative? How are they negative? What are their causes?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? No. Why should anyone care about the positive and/or negative impact of social media?
After thinking about your answers to these questions, you decide to focus on the one impact you feel strongly about and have strong evidence for:
Because not every voice on social media is reliable, people have become much more critical consumers of information, and thus, more informed voters.
This version is a much stronger thesis! It answers the question, takes a specific position that others can challenge, and it gives a sense of why it matters.
Let’s try another. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
You begin to analyze your thesis:
- Do I answer the question? No. The prompt asks you to analyze some aspect of the novel. Your working thesis is a statement of general appreciation for the entire novel.
Think about aspects of the novel that are important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
- Do I answer the question? Yes!
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not really. This contrast is well-known and accepted.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? It’s getting there–you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation. However, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? Not yet. Compare scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions and anything else that seems interesting.
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?”
After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A. 2015. The St. Martin’s Handbook , 8th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Ramage, John D., John C. Bean, and June Johnson. 2018. The Allyn & Bacon Guide to Writing , 8th ed. New York: Pearson.
Ruszkiewicz, John J., Christy Friend, Daniel Seward, and Maxine Hairston. 2010. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers , 9th ed. Boston: Pearson Education.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- Write my thesis
- Thesis writers
- Buy thesis papers
- Bachelor thesis
- Master's thesis
- Thesis editing services
- Thesis proofreading services
- Buy a thesis online
- Write my dissertation
- Dissertation proposal help
- Pay for dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help online
- Buy dissertation online
- Cheap dissertation
- Dissertation editing services
- Write my research paper
- Buy research paper online
- Pay for research paper
- Research paper help
- Order research paper
- Custom research paper
- Cheap research paper
- Research papers for sale
- Thesis subjects
- How It Works
How Long Should a Thesis Statement Be?

Students often ask how long should a thesis statement be when given a paper to write. This article addresses frequently asked questions concerning thesis statements and other relevant issues. We will answer several questions, including how many words in a thesis and how long should a thesis statement be.
How Long is a Thesis Statement, and Where Should it Be?
How long can a thesis statement be and not be, how long should a thesis statement be for a high school student, how many sentences are in a thesis statement, how long should a thesis paper be, how long is a thesis supposed to be for high school essay, how long are thesis statements for college essays, what is the length of a typical thesis statement for professional research papers, how long does a thesis paper have to be.
How long is a thesis paper that determines many things and has brought about several questions like how many words should a thesis statement be? It should not be too long, thirty to forty words at the most. As a rule, your thesis statement should reflect your knowledge and the scope of the essay you are writing. Whether you are writing an analytical research paper or an essay, the thesis statement should be in the introduction part. Your thesis should be at the beginning of the paper, preferably in the first paragraph.
A too-short thesis statement won’t give the sufficient information an audience needs, while one too long will be offering too much. This is something to keep in mind when researching; how long should a thesis statement be? Regardless of how long your essay or research paper is, your thesis statement should explain your position in short sentences. That means it should be convincing enough to get your audience interested in your point of view. Your thesis statement should not exceed one paragraph, whether you’re writing a school essay or an in-depth research paper.
If you’re writing a paper in high school, your thesis shouldn’t be more than two sentences long. Your teacher doesn’t expect you to have an extremely elaborate thesis statement as a high school student. So, one or two short sentences indicating your essay’s aim should be more than enough. Knowing how many sentences are in a thesis statement helps ensure you don’t overdo it.
How many sentences should a thesis statement depend on what type of paper you are writing? A thesis statement should normally be no more than two sentences long unless you are writing a very long paper. Your thesis statement should be short and straight to the point, declaring your specific position on the topic you’re writing on.
A good thesis will strike the right balance between not having a flat thesis and not giving too much information. How many sentences are in a thesis determines how many should be in a thesis statement?
A thesis paper is usually forty pages long, but it varies significantly from project to project and from one expertise level to another. This number includes texts, figures, and a list of references, but it doesn’t include appendices. Also, don’t take these generalizations on how long should a thesis be too seriously, especially if you’re working on a labor-intensive project.
How Many Words is a Thesis?
How long a thesis is usually around eighty to a hundred thousand words long, depending on the topic’s depth. At the master’s or college level, a thesis fluctuates between fifteen and twenty thousand words. However, research journals ask for articles no more than three to five thousand words. After knowing how long is a thesis, the next question is, how long should your thesis statement be?
Your thesis in high school should be short, depending on what topic you are working on. It is better to contain one concise sentence, clearly stating your thoughts on the topic. It is this thought you’ll expound on later in the essay. Always ask your teacher or instructor for clarity on how long is a thesis statement.
A college thesis statement’s length depends on how many sentences is a thesis and how many points a writer mentions. It should contain at least two clauses, an independent clause, your opinion, and a dependent clause, the reasons. It would help if you aimed for a single sentence at least two lines long, or at most forty words long.
A typical thesis statement for professional research papers is usually no more than fifty words long. However, thesis statements don’t exactly have an exact word count, but most experts advise staying within that range. Once you know how long are thesis papers, you’ll have an idea of how long a thesis statement should be.
A single sentence clearly stating your position is great, but it may be hard to compress all your thoughts into one sentence. Thus, if you can’t do one sentence, you can keep it to two, four at the most, lines in a paragraph.
Your thesis paper has to be as long as the instructions say; there is no one-rule-fits-all answer to this question. If you’re writing a thesis paper in college, it wouldn’t be as long as writing a Ph.D. thesis paper . A thesis length is at least three thousand words and at most a hundred thousand. How long should a thesis be in an essay is a common question for people new to writing professional research papers.
Your thesis statement may be short or long, depending on your academic level. While there is no one rule on how long is a thesis statement supposed to be, experts advise 20-50 words. Long or short, your thesis should clearly state your paper’s aim in one to four lines; leave out irrelevant words. If you need professional help writing your thesis, you can contact our expert team to give you the best services.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Developing a Thesis Statement
Many papers you write require developing a thesis statement. In this section you’ll learn what a thesis statement is and how to write one.
Keep in mind that not all papers require thesis statements . If in doubt, please consult your instructor for assistance.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement . . .
- Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic.
- Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper.
- Is focused and specific enough to be “proven” within the boundaries of your paper.
- Is generally located near the end of the introduction ; sometimes, in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or in an entire paragraph.
- Identifies the relationships between the pieces of evidence that you are using to support your argument.
Not all papers require thesis statements! Ask your instructor if you’re in doubt whether you need one.
Identify a topic
Your topic is the subject about which you will write. Your assignment may suggest several ways of looking at a topic; or it may name a fairly general concept that you will explore or analyze in your paper.
Consider what your assignment asks you to do
Inform yourself about your topic, focus on one aspect of your topic, ask yourself whether your topic is worthy of your efforts, generate a topic from an assignment.
Below are some possible topics based on sample assignments.
Sample assignment 1
Analyze Spain’s neutrality in World War II.
Identified topic
Franco’s role in the diplomatic relationships between the Allies and the Axis
This topic avoids generalities such as “Spain” and “World War II,” addressing instead on Franco’s role (a specific aspect of “Spain”) and the diplomatic relations between the Allies and Axis (a specific aspect of World War II).
Sample assignment 2
Analyze one of Homer’s epic similes in the Iliad.
The relationship between the portrayal of warfare and the epic simile about Simoisius at 4.547-64.
This topic focuses on a single simile and relates it to a single aspect of the Iliad ( warfare being a major theme in that work).
Developing a Thesis Statement–Additional information
Your assignment may suggest several ways of looking at a topic, or it may name a fairly general concept that you will explore or analyze in your paper. You’ll want to read your assignment carefully, looking for key terms that you can use to focus your topic.
Sample assignment: Analyze Spain’s neutrality in World War II Key terms: analyze, Spain’s neutrality, World War II
After you’ve identified the key words in your topic, the next step is to read about them in several sources, or generate as much information as possible through an analysis of your topic. Obviously, the more material or knowledge you have, the more possibilities will be available for a strong argument. For the sample assignment above, you’ll want to look at books and articles on World War II in general, and Spain’s neutrality in particular.
As you consider your options, you must decide to focus on one aspect of your topic. This means that you cannot include everything you’ve learned about your topic, nor should you go off in several directions. If you end up covering too many different aspects of a topic, your paper will sprawl and be unconvincing in its argument, and it most likely will not fulfull the assignment requirements.
For the sample assignment above, both Spain’s neutrality and World War II are topics far too broad to explore in a paper. You may instead decide to focus on Franco’s role in the diplomatic relationships between the Allies and the Axis , which narrows down what aspects of Spain’s neutrality and World War II you want to discuss, as well as establishes a specific link between those two aspects.
Before you go too far, however, ask yourself whether your topic is worthy of your efforts. Try to avoid topics that already have too much written about them (i.e., “eating disorders and body image among adolescent women”) or that simply are not important (i.e. “why I like ice cream”). These topics may lead to a thesis that is either dry fact or a weird claim that cannot be supported. A good thesis falls somewhere between the two extremes. To arrive at this point, ask yourself what is new, interesting, contestable, or controversial about your topic.
As you work on your thesis, remember to keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times . Sometimes your thesis needs to evolve as you develop new insights, find new evidence, or take a different approach to your topic.
Derive a main point from topic
Once you have a topic, you will have to decide what the main point of your paper will be. This point, the “controlling idea,” becomes the core of your argument (thesis statement) and it is the unifying idea to which you will relate all your sub-theses. You can then turn this “controlling idea” into a purpose statement about what you intend to do in your paper.
Look for patterns in your evidence
Compose a purpose statement.
Consult the examples below for suggestions on how to look for patterns in your evidence and construct a purpose statement.
- Franco first tried to negotiate with the Axis
- Franco turned to the Allies when he couldn’t get some concessions that he wanted from the Axis
Possible conclusion:
Spain’s neutrality in WWII occurred for an entirely personal reason: Franco’s desire to preserve his own (and Spain’s) power.
Purpose statement
This paper will analyze Franco’s diplomacy during World War II to see how it contributed to Spain’s neutrality.
- The simile compares Simoisius to a tree, which is a peaceful, natural image.
- The tree in the simile is chopped down to make wheels for a chariot, which is an object used in warfare.
At first, the simile seems to take the reader away from the world of warfare, but we end up back in that world by the end.
This paper will analyze the way the simile about Simoisius at 4.547-64 moves in and out of the world of warfare.
Derive purpose statement from topic
To find out what your “controlling idea” is, you have to examine and evaluate your evidence . As you consider your evidence, you may notice patterns emerging, data repeated in more than one source, or facts that favor one view more than another. These patterns or data may then lead you to some conclusions about your topic and suggest that you can successfully argue for one idea better than another.
For instance, you might find out that Franco first tried to negotiate with the Axis, but when he couldn’t get some concessions that he wanted from them, he turned to the Allies. As you read more about Franco’s decisions, you may conclude that Spain’s neutrality in WWII occurred for an entirely personal reason: his desire to preserve his own (and Spain’s) power. Based on this conclusion, you can then write a trial thesis statement to help you decide what material belongs in your paper.
Sometimes you won’t be able to find a focus or identify your “spin” or specific argument immediately. Like some writers, you might begin with a purpose statement just to get yourself going. A purpose statement is one or more sentences that announce your topic and indicate the structure of the paper but do not state the conclusions you have drawn . Thus, you might begin with something like this:
- This paper will look at modern language to see if it reflects male dominance or female oppression.
- I plan to analyze anger and derision in offensive language to see if they represent a challenge of society’s authority.
At some point, you can turn a purpose statement into a thesis statement. As you think and write about your topic, you can restrict, clarify, and refine your argument, crafting your thesis statement to reflect your thinking.
As you work on your thesis, remember to keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times. Sometimes your thesis needs to evolve as you develop new insights, find new evidence, or take a different approach to your topic.
Compose a draft thesis statement
If you are writing a paper that will have an argumentative thesis and are having trouble getting started, the techniques in the table below may help you develop a temporary or “working” thesis statement.
Begin with a purpose statement that you will later turn into a thesis statement.
Assignment: Discuss the history of the Reform Party and explain its influence on the 1990 presidential and Congressional election.
Purpose Statement: This paper briefly sketches the history of the grassroots, conservative, Perot-led Reform Party and analyzes how it influenced the economic and social ideologies of the two mainstream parties.
Question-to-Assertion
If your assignment asks a specific question(s), turn the question(s) into an assertion and give reasons why it is true or reasons for your opinion.
Assignment : What do Aylmer and Rappaccini have to be proud of? Why aren’t they satisfied with these things? How does pride, as demonstrated in “The Birthmark” and “Rappaccini’s Daughter,” lead to unexpected problems?
Beginning thesis statement: Alymer and Rappaccinni are proud of their great knowledge; however, they are also very greedy and are driven to use their knowledge to alter some aspect of nature as a test of their ability. Evil results when they try to “play God.”
Write a sentence that summarizes the main idea of the essay you plan to write.
Main idea: The reason some toys succeed in the market is that they appeal to the consumers’ sense of the ridiculous and their basic desire to laugh at themselves.
Make a list of the ideas that you want to include; consider the ideas and try to group them.
- nature = peaceful
- war matériel = violent (competes with 1?)
- need for time and space to mourn the dead
- war is inescapable (competes with 3?)
Use a formula to arrive at a working thesis statement (you will revise this later).
- although most readers of _______ have argued that _______, closer examination shows that _______.
- _______ uses _______ and _____ to prove that ________.
- phenomenon x is a result of the combination of __________, __________, and _________.
What to keep in mind as you draft an initial thesis statement
Beginning statements obtained through the methods illustrated above can serve as a framework for planning or drafting your paper, but remember they’re not yet the specific, argumentative thesis you want for the final version of your paper. In fact, in its first stages, a thesis statement usually is ill-formed or rough and serves only as a planning tool.
As you write, you may discover evidence that does not fit your temporary or “working” thesis. Or you may reach deeper insights about your topic as you do more research, and you will find that your thesis statement has to be more complicated to match the evidence that you want to use.
You must be willing to reject or omit some evidence in order to keep your paper cohesive and your reader focused. Or you may have to revise your thesis to match the evidence and insights that you want to discuss. Read your draft carefully, noting the conclusions you have drawn and the major ideas which support or prove those conclusions. These will be the elements of your final thesis statement.
Sometimes you will not be able to identify these elements in your early drafts, but as you consider how your argument is developing and how your evidence supports your main idea, ask yourself, “ What is the main point that I want to prove/discuss? ” and “ How will I convince the reader that this is true? ” When you can answer these questions, then you can begin to refine the thesis statement.
Refine and polish the thesis statement
To get to your final thesis, you’ll need to refine your draft thesis so that it’s specific and arguable.
- Ask if your draft thesis addresses the assignment
- Question each part of your draft thesis
- Clarify vague phrases and assertions
- Investigate alternatives to your draft thesis
Consult the example below for suggestions on how to refine your draft thesis statement.
Sample Assignment
Choose an activity and define it as a symbol of American culture. Your essay should cause the reader to think critically about the society which produces and enjoys that activity.
- Ask The phenomenon of drive-in facilities is an interesting symbol of american culture, and these facilities demonstrate significant characteristics of our society.This statement does not fulfill the assignment because it does not require the reader to think critically about society.
Drive-ins are an interesting symbol of American culture because they represent Americans’ significant creativity and business ingenuity.
Among the types of drive-in facilities familiar during the twentieth century, drive-in movie theaters best represent American creativity, not merely because they were the forerunner of later drive-ins and drive-throughs, but because of their impact on our culture: they changed our relationship to the automobile, changed the way people experienced movies, and changed movie-going into a family activity.
While drive-in facilities such as those at fast-food establishments, banks, pharmacies, and dry cleaners symbolize America’s economic ingenuity, they also have affected our personal standards.
While drive-in facilities such as those at fast- food restaurants, banks, pharmacies, and dry cleaners symbolize (1) Americans’ business ingenuity, they also have contributed (2) to an increasing homogenization of our culture, (3) a willingness to depersonalize relationships with others, and (4) a tendency to sacrifice quality for convenience.
This statement is now specific and fulfills all parts of the assignment. This version, like any good thesis, is not self-evident; its points, 1-4, will have to be proven with evidence in the body of the paper. The numbers in this statement indicate the order in which the points will be presented. Depending on the length of the paper, there could be one paragraph for each numbered item or there could be blocks of paragraph for even pages for each one.
Complete the final thesis statement
The bottom line.
As you move through the process of crafting a thesis, you’ll need to remember four things:
- Context matters! Think about your course materials and lectures. Try to relate your thesis to the ideas your instructor is discussing.
- As you go through the process described in this section, always keep your assignment in mind . You will be more successful when your thesis (and paper) responds to the assignment than if it argues a semi-related idea.
- Your thesis statement should be precise, focused, and contestable ; it should predict the sub-theses or blocks of information that you will use to prove your argument.
- Make sure that you keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times. Change your thesis as your paper evolves, because you do not want your thesis to promise more than your paper actually delivers.
In the beginning, the thesis statement was a tool to help you sharpen your focus, limit material and establish the paper’s purpose. When your paper is finished, however, the thesis statement becomes a tool for your reader. It tells the reader what you have learned about your topic and what evidence led you to your conclusion. It keeps the reader on track–well able to understand and appreciate your argument.

Writing Process and Structure
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Getting Started with Your Paper
Interpreting Writing Assignments from Your Courses
Generating Ideas for
Creating an Argument
Thesis vs. Purpose Statements
Architecture of Arguments
Working with Sources
Quoting and Paraphrasing Sources
Using Literary Quotations
Citing Sources in Your Paper
Drafting Your Paper
Generating Ideas for Your Paper
Introductions
Paragraphing
Developing Strategic Transitions
Conclusions
Revising Your Paper
Peer Reviews
Reverse Outlines
Revising an Argumentative Paper
Revision Strategies for Longer Projects
Finishing Your Paper
Twelve Common Errors: An Editing Checklist
How to Proofread your Paper
Writing Collaboratively
Collaborative and Group Writing
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
How to Write a Strong Thesis Statement: 4 Steps + Examples

What’s Covered:
What is the purpose of a thesis statement, writing a good thesis statement: 4 steps, common pitfalls to avoid, where to get your essay edited for free.
When you set out to write an essay, there has to be some kind of point to it, right? Otherwise, your essay would just be a big jumble of word salad that makes absolutely no sense. An essay needs a central point that ties into everything else. That main point is called a thesis statement, and it’s the core of any essay or research paper.
You may hear about Master degree candidates writing a thesis, and that is an entire paper–not to be confused with the thesis statement, which is typically one sentence that contains your paper’s focus.
Read on to learn more about thesis statements and how to write them. We’ve also included some solid examples for you to reference.
Typically the last sentence of your introductory paragraph, the thesis statement serves as the roadmap for your essay. When your reader gets to the thesis statement, they should have a clear outline of your main point, as well as the information you’ll be presenting in order to either prove or support your point.
The thesis statement should not be confused for a topic sentence , which is the first sentence of every paragraph in your essay. If you need help writing topic sentences, numerous resources are available. Topic sentences should go along with your thesis statement, though.
Since the thesis statement is the most important sentence of your entire essay or paper, it’s imperative that you get this part right. Otherwise, your paper will not have a good flow and will seem disjointed. That’s why it’s vital not to rush through developing one. It’s a methodical process with steps that you need to follow in order to create the best thesis statement possible.
Step 1: Decide what kind of paper you’re writing
When you’re assigned an essay, there are several different types you may get. Argumentative essays are designed to get the reader to agree with you on a topic. Informative or expository essays present information to the reader. Analytical essays offer up a point and then expand on it by analyzing relevant information. Thesis statements can look and sound different based on the type of paper you’re writing. For example:
- Argumentative: The United States needs a viable third political party to decrease bipartisanship, increase options, and help reduce corruption in government.
- Informative: The Libertarian party has thrown off elections before by gaining enough support in states to get on the ballot and by taking away crucial votes from candidates.
- Analytical: An analysis of past presidential elections shows that while third party votes may have been the minority, they did affect the outcome of the elections in 2020, 2016, and beyond.
Step 2: Figure out what point you want to make
Once you know what type of paper you’re writing, you then need to figure out the point you want to make with your thesis statement, and subsequently, your paper. In other words, you need to decide to answer a question about something, such as:
- What impact did reality TV have on American society?
- How has the musical Hamilton affected perception of American history?
- Why do I want to major in [chosen major here]?
If you have an argumentative essay, then you will be writing about an opinion. To make it easier, you may want to choose an opinion that you feel passionate about so that you’re writing about something that interests you. For example, if you have an interest in preserving the environment, you may want to choose a topic that relates to that.
If you’re writing your college essay and they ask why you want to attend that school, you may want to have a main point and back it up with information, something along the lines of:
“Attending Harvard University would benefit me both academically and professionally, as it would give me a strong knowledge base upon which to build my career, develop my network, and hopefully give me an advantage in my chosen field.”
Step 3: Determine what information you’ll use to back up your point
Once you have the point you want to make, you need to figure out how you plan to back it up throughout the rest of your essay. Without this information, it will be hard to either prove or argue the main point of your thesis statement. If you decide to write about the Hamilton example, you may decide to address any falsehoods that the writer put into the musical, such as:
“The musical Hamilton, while accurate in many ways, leaves out key parts of American history, presents a nationalist view of founding fathers, and downplays the racism of the times.”
Once you’ve written your initial working thesis statement, you’ll then need to get information to back that up. For example, the musical completely leaves out Benjamin Franklin, portrays the founding fathers in a nationalist way that is too complimentary, and shows Hamilton as a staunch abolitionist despite the fact that his family likely did own slaves.
Step 4: Revise and refine your thesis statement before you start writing
Read through your thesis statement several times before you begin to compose your full essay. You need to make sure the statement is ironclad, since it is the foundation of the entire paper. Edit it or have a peer review it for you to make sure everything makes sense and that you feel like you can truly write a paper on the topic. Once you’ve done that, you can then begin writing your paper.
When writing a thesis statement, there are some common pitfalls you should avoid so that your paper can be as solid as possible. Make sure you always edit the thesis statement before you do anything else. You also want to ensure that the thesis statement is clear and concise. Don’t make your reader hunt for your point. Finally, put your thesis statement at the end of the first paragraph and have your introduction flow toward that statement. Your reader will expect to find your statement in its traditional spot.
If you’re having trouble getting started, or need some guidance on your essay, there are tools available that can help you. CollegeVine offers a free peer essay review tool where one of your peers can read through your essay and provide you with valuable feedback. Getting essay feedback from a peer can help you wow your instructor or college admissions officer with an impactful essay that effectively illustrates your point.

Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

It appears you have javascript disabled. Please enable javascript to get the full experience of gustavus.edu
Tips on writing a thesis statement: composing compelling thesis statements.
College-level courses demand a solid grasp of writing concepts, and some students arrive at Intro to Composition unprepared to write a high-quality essay. Teachers tend to give a bit more slack at the high school level, but college professors are often much more exacting. That’s why excellent writing skills are crucial to the majority of college courses — even outside the English department.
One of the most important elements to master is the thesis statement. A strong thesis statement is at the root of all writing, from op-eds to research papers. It’s an essential element of any persuasive piece; something we look for without even thinking about it. A convincing, attention-grabbing thesis statement keeps the reader engaged — and lets them know where the piece is headed.
Having a few tips and tricks in your toolbox can help you to make a convincing academic argument every time.
What is a Thesis Statement?
First, the basics. A thesis statement is a sentence or two that states the main idea of a writing assignment. It also helps to control the ideas presented within the paper. However, it is not merely a topic. It often reflects a claim or judgment that a writer has made about a reading or personal experience. For instance: Tocqueville believed that the domestic role most women held in America was the role that gave them the most power, an idea that many would hotly dispute today.
Every assignment has a question or prompt. It’s important that your thesis statement answers the question. For the above thesis statement, the question being answered might be something like this: Why was Tocqueville wrong about women? If your thesis statement doesn’t answer a question, you’ll need to rework your statement.
Where Will I Use Thesis Statements?
Writing an exceptional thesis statement is a skill you’ll need both now and in the future, so you’ll want to be confident in your ability to create a great one. Whether in academic, professional, or personal writing, a strong thesis statement enhances the clarity, effectiveness, and impact of the overall message. Here are some real-world examples that demonstrate the importance of composing an outstanding thesis statement:
- Academic writing. The success of academic research papers depends on an exceptional thesis statement. Along with establishing the focus of the paper, it also provides you with direction in terms of research. The thesis sets a clear intention for your essay, helping the reader understand the argument you’re presenting and why the evidence and analysis support it.
- Persuasive writing. Persuasive writing depends on an excellent thesis statement that clearly defines the author’s position. Your goal is to persuade the audience to agree with your thesis. Setting an explicit stance also provides you with a foundation on which to build convincing arguments with relevant evidence.
- Professional writing. In the business and marketing world, a sound thesis statement is required to communicate a project’s purpose. Thesis statements not only outline a project’s unique goals but can also guide the marketing team in creating targeted promotional strategies.
Where Do Thesis Statements Go?
A good practice is to put the thesis statement at the end of your introduction so you can use it to lead into the body of your paper. This allows you, as the writer, to lead up to the thesis statement instead of diving directly into the topic. Placing your thesis here also sets you up for a brief mention of the evidence you have to support your thesis, allowing readers a preview of what’s to come.
A good introduction conceptualizes and anticipates the thesis statement, so ending your intro with your thesis makes the most sense. If you place the thesis statement at the beginning, your reader may forget or be confused about the main idea by the time they reach the end of the introduction.
What Makes a Strong Thesis Statement?
A quality thesis statement is designed to both inform and compel. Your thesis acts as an introduction to the argument you’ll be making in your paper, and it also acts as the “hook”. Your thesis should be clear and concise, and you should be ready with enough evidence to support your argument.
There are several qualities that make for a powerful thesis statement, and drafting a great one means considering all of them:
A strong thesis makes a clear argument .
A thesis statement is not intended to be a statement of fact, nor should it be an opinion statement. Making an observation is not sufficient — you should provide the reader with a clear argument that cohesively summarizes the intention of your paper.
Originality is important when possible, but stick with your own convictions. Taking your paper in an already agreed-upon direction doesn’t necessarily make for compelling reading. Writing a thesis statement that presents a unique argument opens up the opportunity to discuss an issue in a new way and helps readers to get a new perspective on the topic in question. Again, don’t force it. You’ll have a harder time trying to support an argument you don’t believe yourself.
A strong thesis statement gives direction .
If you lack a specific direction for your paper, you’ll likely find it difficult to make a solid argument for anything. Your thesis statement should state precisely what your paper will be about, as a statement that’s overly general or makes more than one main point can confuse your audience.
A specific thesis statement also helps you focus your argument — you should be able to discuss your thesis thoroughly in the allotted word count. A thesis that’s too broad won’t allow you to make a strong case for anything.
A strong thesis statement provides proof.
Since thesis statements present an argument, they require support. All paragraphs of the essay should explain, support, or argue with your thesis. You should support your thesis statement with detailed evidence that will interest your readers and motivate them to continue reading the paper.
Sometimes it is useful to mention your supporting points in your thesis. An example of this could be: John Updike's Trust Me is a valuable novel for a college syllabus because it allows the reader to become familiar with his writing and provides themes that are easily connected to other works. In the body of your paper, you could write a paragraph or two about each supporting idea. If you write a thesis statement like this, it will often help you to keep control of your ideas.
A strong thesis statement prompts discussion .
Your thesis statement should stimulate the reader to continue reading your paper. Many writers choose to illustrate that the chosen topic is controversial in one way or another, which is an effective way to pull in readers who might agree with you and those who don’t!
The ultimate point of a thesis statement is to spark interest in your argument. This is your chance to grab (and keep) your reader’s attention, and hopefully, inspire them to continue learning about the topic.
Testing Your Thesis Statement
Because your thesis statement is vital to the quality of your paper, you need to ensure that your thesis statement posits a cohesive argument. Once you’ve come up with a working thesis statement, ask yourself these questions to further refine your statement:
- Is it interesting ? If your thesis is dull, consider clarifying your argument or revising it to make a connection to a relatable issue. Again, your thesis statement should draw the reader into the paper.
- Is it specific enough ? If your thesis statement is too broad, you won’t be able to make a persuasive argument. If your thesis contains words like “positive” or “effective”, narrow it down. Tell the reader why something is “positive”. What in particular makes something “effective”?
- Does it answer the question ? Review the prompt or question once you’ve written your working thesis and be sure that your thesis statement directly addresses the given question.
- Does my paper successfully support my thesis statement ? If you find that your thesis statement and the body of your paper don’t mesh well, you’re going to have to change one of them. But don’t worry too much if this is the case — writing is intended to be revised and reworked.
- Does my thesis statement present the reader with a new perspective? Is it a fresh take on an old idea? Will my reader learn something from my paper? If your thesis statement has already been widely discussed, consider if there’s a fresh angle to take before settling.
- Finally, am I happy with my thesis ? If not, you may have difficulty writing your paper. Composing an essay about an argument you don’t believe in can be more difficult than taking a stand for something you believe in.
Quick Tips for Writing Thesis Statements
If you’re struggling to come up with a thesis statement, here are a few tips you can use to help:
- Know the topic. The topic should be something you know or can learn about. It is difficult to write a thesis statement, let alone a paper, on a topic that you know nothing about. Reflecting on personal experience and/or researching your thesis topic thoroughly will help you present more convincing information about your statement.
- Brainstorm. If you are having trouble beginning your paper or writing your thesis, take a piece of paper and write down everything that comes to mind about your topic. Did you discover any new ideas or connections? Can you separate any of the things you jotted down into categories? Do you notice any themes? Think about using ideas generated during this process to shape your thesis statement and your paper.
- Phrase the topic as a question. If your topic is presented as a statement, rephrasing it as a question can make it easier to develop a thesis statement.
- Limit your topic. Based on what you know and the required length of your final paper, limit your topic to a specific area. A broad scope will generally require a longer paper, while a narrow scope can be sufficiently proven by a shorter paper.
Writing Thesis Statements: Final Thoughts
The ability to compose a strong thesis statement is a skill you’ll use over and over again during your college days and beyond. Compelling persuasive writing is important, whether you’re writing an academic essay or putting together a professional pitch.
If your thesis statement-writing skills aren’t already strong, be sure to practice before diving into college-level courses that will test your skills. If you’re currently looking into colleges, Gustavus Adolphus offers you the opportunity to refine your writing skills in our English courses and degree program . Explore Gustavus Adolphus’ undergraduate majors here .
- Learning Tips
- Exam Guides
- School Life
How Long is a Thesis Statement: Write Good Thesis Sentences
- by Judy Jeni
- January 26, 2024

A thesis statement identifies the discussion topic by including the points being discussed in your paper. You will place your thesis statement in the introduction. We use the thesis statement to draw the attention of the reader to continue to explore the topic.
The thesis statement will establish the direction of the whole paper. Furthermore, this thesis will take a stand to justify further action. It will narrow down the topic to a particular focus for investigation.
A thesis statement can limit what you want to write about. It is a platform where you will be informing your reader what you intend to cover in the paragraph body.
In this context, all the paragraphs in the essay should support, explain, or argue in the same direction as your thesis.
How Long is a Thesis Statement?
For one to understand the length of the thesis statement, it is sensible to know the type of essay you are crafting. For example, it is not reasonable to use a short statement on a short essay or a long one for a long essay.
When you are writing your thesis statement, it is critical to keep the word count of the essay. The word count will determine the length of the essay.
A thesis statement should only be one sentence long and not more than that because it needs to be succinct and clear. No matter the number of points or clauses you want to argue out, the thesis statement must be just a single statement.
Therefore, you need to compress all the clauses into a single sentence that takes a stand on what you are writing about.
Also, the length of the statement depends on the type of essay you are writing. Typically, the ideal scenario calls for a one-sentence statement. However, it can be a challenge for one to find a concise way of putting it in a single sentence.
The whole scenario needs a lot of thought and detailed scrutiny.

In the case of more extended essays, you will have to write a longer thesis statement.
That becomes useful as one should offer a detailed explanation of the topic to the audience, promoting the statement to appear long.
Also, the type of language used will dictate the length of the thesis statement.
The main goal in this situation is to capture the key ideas and arguments of your topic.
As such, you should express using words concisely. You should try to keep the thesis statement short as you capture the main ideas well.
Another aspect that determines the length of the thesis statement is how the author balances the general ideas and particular topic elements. You can keep your thesis statement to be specific by expressing your ideas well.
How to Write a Good Thesis Statement

A good thesis statement will sum up your central point about your essay paper. This statement will appear at the end of the introduction.
Whoever the type of your essay can make your thesis seem different. It should give the main idea of what you want to put across.
Writing a thesis statement will require proof and not a statement of facts.
The author must support the thesis statement with clear evidence to motivate the audience to continue reading it.
It becomes helpful to mention the supporting points in your thesis.
So, how do you come up with a good essay statement? It should happen as soon as you decide on your essay topic. The correct essay statement should offer direction to your essay.
There are two styles of thesis statements. It could be informative or persuasive. When you are composing an informative thesis, you should declare your intentions and guide the audience to the end.
When you are handing a persuasive thesis, it usually contains an opinion and offers the reason why the opinion is valid. Use the following variable when writing a good thesis statement:
1. Know the Topic
The topic is a basic idea of your paper. This topic has a few words or phrases that summarize the paper’s subject. If you are crafting an essay, ensure that your topic becomes as specific as possible.
Generally, the topic should cover something that you can learn about. It can be hard to write a thesis statement on something that you lack an understanding of. You should reflect on your personal experience to help you to discover your topic.
2. Begin with a Question

Your assignment should have a question, right? Suppose it lacks, try to include one. It should cover what you want to find out concerning your topic.
For example, when you are writing an argumentative essay, the question may prompt you to take sides, as given in the below example.
Has the game app been a threat to the social well-being of kids? Look at more examples by exploring some unique thesis statements about social media , another topic that is common in college essay writing.
3. Write Your Initial Answer
After performing initial research, you should now formulate a tentative answer to your question. Give a simple answer at this stage because it will guide the process of writing and researching.
If you are writing an argumentative essay, the answer should take sides to help the audience understand your position. For example:
The gaming app has a more positive impact on kids than negatives.
4. Limit Your Topic
The author should limit the topic based on the length of the final paper. It is helpful to limit the topic to a particular area. A longer paper will cover a broader scope and vice versa.
In our guide to writing good college essays , we explained how to get a good topic. This is the topic that will guide your thesis statement.
5. State the Main Idea
You should know what you are trying to prove or state about your topic. Also, understand what you want to persuade the reader to believe. As you state your opinion, it is important to express one major idea.
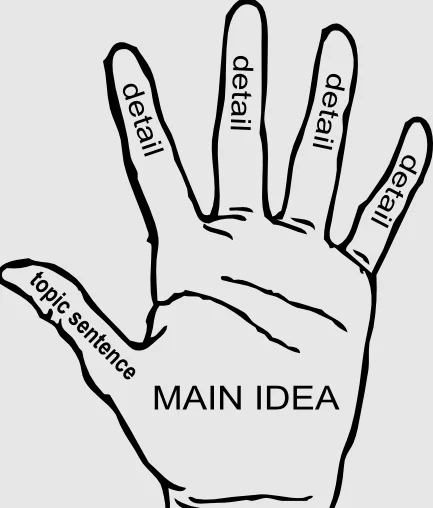
Again, you should name the topic as you assert something particular about it. Furthermore, you should take a stance on a particular issue which you can support with reasons and facts. Do not be shy to take a position.
6. Develop an Answer
At this stage, you need to convince your reader to believe that this is your answer. You should give a detailed answer as you read more about the topic and write.
The final thesis statement should summarize your overall arguments. The answer should be based on the thesis or the theme you are writing. But be keen to know the difference between thesis and theme so that you can know how to handle each.
7. Acknowledge any Opposing Viewpoint
A good thesis statement should acknowledge that there is also another side of an argument. The author should also include an opposing viewpoint to the thesis statement.
You should also write down what a different person who may disagree with your position should say.

How to Write a Thesis Statement with a Simple Guide

At the heart of every great piece of writing lies the thesis statement - a compact yet powerful sentence that sets the course for your entire work. Though brief, it's a powerhouse, encapsulating the core message of your essay.
In this article, we'll explain how to create a strong thesis statement, offering expert insights and practical tips to help you master this essential skill. Along the way, we'll illustrate key concepts with clear examples, ensuring you're equipped to tackle your writing challenges head-on. And should you ever find yourself in need of assistance, don't hesitate to reach out - ' Write my thesis ' - we're here to help you succeed.

What Is a Thesis Statement
Let's break down what is a thesis statement in an essay. It's essentially the heart of your academic paper, condensed into a single, powerful sentence. Usually tucked at the end of your introduction, it serves as a guidepost for your readers, giving them a peek into what lies ahead.
Crafting a solid thesis statement isn't just about summarizing your main idea. It's about taking a stand on your chosen topic and setting the tone for your entire piece. Picture it as the hub around which all your arguments and evidence orbit, providing clarity and direction for both you and your readers.
But here's the kicker: a strong thesis statement isn't wishy-washy. It's a bold, specific, and debatable claim that grabs attention and lays the groundwork for what's to come in your paper or essay.
Characteristics of a robust thesis statement:
- Clearly communicates the main idea of the paper.
- Focuses sharply on a specific aspect or angle of the topic.
- Makes a strong, assertive statement rather than posing a question.
- Succinctly summarizes the core argument of the paper.
- Provides readers with a clear roadmap of what to expect in the paper.
- Takes a clear stance or position on the topic.
- Offers a preview of the supporting arguments that will be explored.
- Maintains an academic and objective tone throughout.
- Typically positioned near the conclusion of the introductory paragraph.
- May adapt or refine as research and analysis progress.
- Essential for ensuring the strength and effectiveness of the academic paper.
If you're struggling with crafting your thesis, you're not alone. Many students find it challenging. But fear not – if you're ever stuck and thinking, 'Where to pay someone to write my paper ?', – consider reaching out to our expert help for guidance.
Want to Unlock the Power of Thesis Statement Ideas?
Secure your academic success with our custom-crafted thesis statements and elevate your research to the next level!
10 Tips for Writing a Thesis Statement
Often confused with a topic sentence, which starts a paragraph, the thesis statement shares the role of introducing the main idea that unfolds in the subsequent discussion. Here are the tips that will help your statement capture the essence of your entire paper.
- Ensure your thesis is clear and to the point, presenting your main argument straightforwardly.
- Address a particular aspect of the topic for a focused and targeted argument.
- State your thesis as a clear declaration rather than a question to assert a definite position.
- Keep it brief, capturing the essence of your argument without unnecessary detail.
- Provide a preview of the main points or arguments to be explored in your paper.
- Clearly express your position on the topic, whether supporting, refuting, or analyzing an idea.
- Maintain a formal and unbiased tone, avoiding emotional language in your thesis.
- According to the essay format rules, position your thesis near the end of the introduction to set the stage for the discussion.
- Recognize that your thesis may evolve as you delve deeper into research and analysis, adjusting to new insights.
- Regularly review and refine your thesis statement to ensure it aligns with the evolving content of your paper.
How to Write a Thesis Statement Step by Step
Now that we've covered the fundamental tips for how to write a thesis statement let's delve into a step-by-step guide for creating one. If you're interested in hiring a professional to write my personal statement , our help is just one click away.
.webp)
Step 1: Topic Selection
When selecting a topic for your thesis statement, it's crucial to choose something that genuinely interests you. This will keep you motivated throughout the research and writing process. Consider the scope of your topic; it should be neither too broad nor too narrow. Ask yourself:
- What topics within my field of study am I genuinely passionate about?
- Is the topic manageable within the scope of a thesis, or is it too broad or narrow?
- How does my chosen topic contribute to the existing knowledge or debates in my field?
- Are there any recent developments or emerging trends related to this topic that I can explore?
Step 2: Research and Analysis
As you gather information, critically analyze and evaluate each source's credibility, reliability, and relevance to your thesis. Look for patterns, connections, and gaps in the existing literature that you can address in your thesis. Consider these points:
- What are the key concepts, theories, or arguments related to my topic?
- What existing research, studies, or literature can I draw upon to support my thesis?
- Are there any conflicting viewpoints or gaps in the literature that I need to address?
- How can I critically analyze and evaluate the sources I find to ensure their relevance and credibility?
- Are there any methodologies or approaches that I can employ to further investigate my topic and gather new insights?
Step 3: Identify a Position
After selecting a topic and conducting thorough research, the next step is to identify a clear position or argument that you will defend in your thesis statement. For example, for a topic on healthcare policy, you could identify a position regarding the effectiveness of a particular healthcare reform initiative supported by evidence from your research. Or, in a literary analysis thesis, you might take a position on the interpretation of a novel's themes or characters, drawing on textual evidence to support your argument. In each case, you might want to consider the following:
- What evidence or data from my research supports a particular viewpoint on the topic?
- Are there any counterarguments or alternative perspectives that I need to address in my thesis statement?
- How does my chosen position contribute to the broader conversation or understanding of the topic within my field of study?
- Does my thesis statement clearly and concisely communicate my stance on the topic while leaving room for further exploration and argumentation in the thesis?
Step 4: Formulate a Debatable Statement
Once you've identified your position, the next step is to craft a thesis statement that presents this position in a debatable and compelling manner. You might want to avoid vague or broad statements that lack clarity or focus. Also, anticipate potential objections or alternative perspectives to your position.
- Non-Debatable Statement: Climate change is happening.
- Debatable Statement: Human activities are the primary drivers of climate change, and urgent action is needed to mitigate its impact.
- Non-Debatable Statement: Education is important.
- Debatable Statement: The traditional classroom setting is becoming obsolete in the digital age, challenging the efficacy of traditional teaching methods.
Step 5: Provide Scope and Direction
After formulating a debatable thesis statement, it's essential to provide clarity on the scope and direction of your thesis. This step helps readers understand what to expect and guides your research and writing process.
- If your thesis statement is about the impact of technology on education, you might specify that your research will focus on the use of educational apps in primary schools.
- For a thesis on mental health stigma, you could outline that your research will explore the portrayal of mental illness in the media and its influence on public perceptions.
- If your thesis statement concerns the effectiveness of a specific marketing strategy, you might indicate that your analysis will concentrate on its implementation in a particular industry.
Types of Thesis Statements
Writing a thesis statement can take different forms depending on the essay's purpose. Here are common types according to our custom essay service :
- Argumentative : Asserts a position on a controversial topic and provides reasons or evidence to support it. Example : 'The government should implement stricter gun control laws to reduce instances of mass shootings and protect public safety.'
- Analytical : Breaks down a topic into its component parts and evaluates them. Example : 'Through an analysis of symbolism and character development, Shakespeare's 'Hamlet' explores the theme of moral decay in society.'
- Explanatory : Explains the significance or meaning of a subject. Example : 'The Industrial Revolution had a profound impact on society by transforming economies, social structures, and daily life.'
- Comparative : Compares two or more subjects to highlight similarities or differences. Example : 'Although both cats and dogs make great pets, dogs require more attention and maintenance due to their higher energy levels and need for exercise.'
- Cause and Effect : Identifies the relationship between actions and outcomes. Example : 'The widespread use of smartphones has led to decreased face-to-face social interaction among young adults, resulting in feelings of loneliness and isolation.'
- Descriptive : Provides an overview or description of a topic. Example : 'The Gothic architecture of Notre Dame Cathedral in Paris exemplifies the intricate craftsmanship and religious symbolism of the medieval era.'
- Narrative : Tells a story or recounts a sequence of events. Example : 'My journey to overcome adversity and pursue higher education is a testament to the resilience of the human spirit.'
Now that you've mastered creating a thesis statement, are you ready to tackle the full academic paper—the thesis? If not, let our thesis writing service take the wheel and steer you clear of any trouble.
Good Thesis Statement Examples
In this section, let’s take a look at ten examples of effective thesis statements across various subjects:
.webp)
- Literature: 'In George Orwell's '1984,' the oppressive surveillance state serves as a cautionary tale about the dangers of unchecked governmental power.'
- History: 'The Civil Rights Movement of the 1960s marked a significant turning point in American history, challenging systemic racism and paving the way for greater social equality.'
- Science: 'The theory of evolution by natural selection, proposed by Charles Darwin, remains the most comprehensive explanation for the diversity of life on Earth.'
- Social Sciences: 'The gender pay gap persists due to a combination of systemic discrimination, occupational segregation, and implicit bias in hiring and promotion practices.'
- Education: 'Implementing inclusive classroom practices, such as differentiated instruction and universal design for learning, is essential for meeting the diverse needs of students with varying abilities.'
- Environmental Studies: 'Transitioning to renewable energy sources is crucial for mitigating the impacts of climate change and ensuring a sustainable future for generations to come.'
- Psychology: 'The prevalence of mental health disorders among adolescents underscores the need for early intervention programs and destigmatization efforts in schools and communities.'
- Business: 'Corporate social responsibility initiatives not only benefit society and the environment but also contribute to long-term profitability and brand reputation.'
- Health Sciences: 'Access to affordable healthcare is a fundamental human right, and implementing universal healthcare systems can address disparities in healthcare access and outcomes.'
- Technology: 'The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence poses ethical dilemmas regarding privacy, job displacement, and the potential for autonomous decision-making by machines.'
In-Text Examples
Now, let’s focus on the role of a thesis statement in guiding your paper's direction. Check out the highlighted statements in the analytical essay example that shape the overall argument.
In the realm of environmental science, the discourse surrounding climate change has become increasingly urgent. As we grapple with the consequences of human activity on the planet, understanding the mechanisms driving climate change and identifying actionable solutions has never been more critical. In the face of mounting evidence pointing to human-induced climate change as a pressing global issue, it is imperative that societies worldwide prioritize the adoption of renewable energy sources and implement stringent environmental policies to curb greenhouse gas emissions and safeguard the future of our planet.
In recent years, the proliferation of online learning platforms has revolutionized the landscape of education, offering students unprecedented access to resources and opportunities for self-directed learning. Within the domain of mathematics education, these platforms have garnered particular attention for their potential to enhance learning outcomes and facilitate personalized instruction. As traditional classroom settings grapple with challenges such as limited resources and varying student needs, online learning platforms offer a promising alternative for delivering tailored instruction and supporting individualized learning trajectories. By leveraging interactive tutorials, adaptive assessments, and real-time feedback mechanisms, these platforms aim to engage students more effectively and address gaps in understanding.
Your thesis isn't just a statement—it's the engine that drives your essay forward. It keeps your writing focused and engaging, drawing your reader in and keeping them interested. Knowing how to write a good thesis statement gives you the power to express yourself effectively, making your ideas resonate with your audience.
So, let's remember the crucial role a solid thesis plays in making our writing stand out. It's the secret weapon that can take your assignments from good to great.
Need a Perfect Thesis Statement?
Set up your research paper for greatness by entrusting your thesis statement to our expert writers
How Long Should a Strong Thesis Statement Be?
How do i begin a thesis statement, related articles.
.webp)
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to content

- Home – AI for Research

How long should a thesis statement be?
Writing a good and efficient thesis statement is an important skill for students and researchers to acquire. Although everyone is in agreement that research statements should be concise, there seems to be little guidance with regards to their optimal length. So, exactly how long should a thesis statement be? Well , it depends … is the boring but correct answer.
To get at the question, let’s dissect the following:
● How does the nature of the paper impact the length of your thesis statement?
● How specific should your thesis statement be?
● Where in a paper or essay does a thesis statement belong?
How does the nature of the paper you are writing impact the length of your statement?
A rule of thumb is to always craft a thesis statement that reflects your knowledge and the scope of the paper you are writing. A broad thesis that ties together a limited number of thoughts in a fairly short paper should be concise, a sentence or two at most. But if you are involved in an in-depth professional discourse where your thesis interacts with other detailed arguments in a rich dialogue, the thesis statement can be three or four sentences long. In other words, a complex argument requires more words. Joe Haley, who used to work as a writing instructor at Johns Hopkins University, illustrates this well by contrasting the difference in scope between these two theses statements about Jane Austen’s Pride and Prejudice
- In Jane Austen’s Pride and Prejudice , gossip is an important but morally ambiguous tool for shaping characters’ opinions of each other.
- As the aforementioned critics have noted, the prevalence of gossip in Jane Austen’s oeuvre does indeed reflect the growing prominence of an explicitly-delineated private sphere in nineteenth-century British society. However, in contrast with these critics’ general conclusions about Austen and class, which tend to identify her authorial voice directly with the bourgeois mores shaping her appropriation of the bildungsroman , the ambiguity of this communicative mode in Pride and Prejudice suggests that when writing at the height of her authorial powers, at least, Austen is capable of skepticism and even self-critique. For what is the narrator of her most celebrated novel if not its arch-gossip par excellence ?
Both statements are fine, the size is ultimately determined by the aim and scope of your paper and how much knowledge you have of the topic.
How specific should your thesis statement be?
Whether you happen to be writing an analytical, expository or argumentative paper, you need the thesis statement to frame the topic you are covering and for it to declare your specific position on the topic at hand. It is important for the thesis statement to make it clear to the reader what you are arguing for without unnecessary exposition. It is all about striking the right balance between not having a flat and trivial thesis and not imparting too much extraneous information.
Although it’s impossible to put a specific number on it, most experts advise staying in a range between 25-50 words for a thesis statement. Try to keep it to a single sentence, if you can, preferably to three or four lines in a paragraph. You should certainly not exceed a single paragraph. Make sure every word in your thesis statement is purposeful. Remove all vague or unnecessary words.
Where in a paper or essay does a thesis statement belong?
Irrespective of whether you are writing an essay or an analytical research paper, the thesis statement always belongs in the beginning, preferably in the first paragraph. It helps the reader understand the purpose of the paper and the intentions of the author.
Some final advice!
Take time to really think about how you compose your thesis statement. Do it right and it can be an invaluable map that guides the reader.
Treat the writing process as an act of discovery. Don’t worry if your thesis statement changes as you are writing, just remember to revise the thesis statement to reflect where you have ended up in your journey.
You may also like
Formatting Tips: How to Italicize Text Using LaTeX
Learn how to italicize text using LaTeX and enhance your academic writing. Discover the benefits of LaTeX for formatting and collaborating on complex projects. Click here for tips and insights.

Cybersecurity and Data Privacy: Ensuring Research Data Security
Ensure research data security and protect valuable findings. Learn about cybersecurity and data privacy best practices in this informative blog. Click to read more!
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Privacy Overview
Adding {{itemName}} to cart
Added {{itemName}} to cart

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
Can a Thesis Statement Be at the End of an Essay?
by Antony W
February 16, 2023

A thesis statement is the primary assertion that tells a reader the main point that you wish to explore in your essay. A good thesis is narrow, specific, and purposeful. It’s usually a sentence long, although it might stretch to two sentences in some cases. Given the significant role that it plays, can a thesis statement be at the end of an essay?
A thesis statement should appear immediately after the introduction paragraph of your essay. However, you can tweak the placement if you’re writing a narrative essay, in which case you can write it at the end of the paper. That’s because the narrative usually sets up your point or moral lesson.
We at Help for Assessment strongly recommend placing the thesis statement in the introduction. After all, that has always been the tradition and it’s best to stick to the format that your professor looks forward to see.
Moreover, we can’t reiterate enough just how significant being specific with your thesis statement is. Essay readers are smart enough to base their judgment of the paper on the construction of this statement, so make it so interesting that a reader will find it easy to make a guess about what to expect from the rest of the essay.
Can a Thesis Statement Be at the End of an Essay? (What You Should Know)
A thesis statement in an essay isn’t merely a topic. It’s a sentence that clearly states the primary idea of writing your essay. Every idea you will introduce and support with statistics and evidence will build upon what the thesis.
Generally, the statement demonstrates a very strong opinion that a writer has about a topic based on facts, personal experiences, or in-depth analysis.
It’s important to note that your professor wants to know exactly what an essay is about before reading it. So it doesn’t make sense to include the thesis statement at the end of an essay. The statement should appear in the introduction paragraph. It’s short, usually a complete sentence although it’s okay to stretch it into two sentences.
The statement that comes before the thesis statement is what introduces it, and the ideas that follow will not only explain but also support it. Given that its PURPOSE is to help readers recognize what is to follow, it would make little sense to include the thesis statement at eh very end of the essay.
Do Thesis Statements Really Vary?
A thesis statement will vary depending on the type of essay your instructor asks you to write. So it’s important to first check the assignment guidelines issued to you before you structure and write the essay.
For example:
- The thesis for an argumentative essay should clearly show your stance and state your opinion on an issue. Everything else you write in the body parts of the argumentative essay will support the statement.
- In the case of a compare and contrast essay, you will have to write the thesis in such a way that it shows how two issues are similar and different.
The variation is quite significant because it makes it quite easy for your target audience (you professor in this case) to reflect on the objective of the paper.
What Does a Good Thesis Statement Look Like?
Regardless of the type of essay your instructor asks you to write, you want to make sure your thesis statement draws in the attention of anyone who would be interested in writing your essay.
The statement should be interesting, short, and concise. It can even be controversial as with the case of an argumentative writing. That way, it can easily draw in the attention of the reader to the paper and give them the curiosity to keep reading.
You may have to write your thesis more than once to give it the sparkle that can easily draw in the attention of the reader. However, make sure that whatever you write not only makes sense but also matches the overall objective of your paper.
Perhaps the most important thing to keep in mind when writing your thesis is that it should instantly make a statement of purpose or reveal your point. Re-read it to make sure it meets this criterion. If it doesn’t, it’s likely too general and therefore would need revision.
Should Your Essay Ideas Tie Back to the Thesis Statement?
Each idea that you introduce in your essay should tie back to the thesis statement.
First, introduce your idea, making sure it relates to the topic under investigation. Second, provide sufficient information to support your idea, making sure that they idea is on its own paragraph. Lastly, tie back the idea to the thesis statement by demonstrating how well it answers the question.
One of the most important things to remember when writing an essay is that a thesis statement is not your research question. Rather, it’s a part of the essay that makes your primary assertion about your points of view on the topic under investigation.
Can I Tweak My Thesis Statement?
If your ideas change, particularly as you do your research, tweaking the thesis statement to match up what you find can go a long way to make it more precise and interesting to read.
You may have to change your thesis statement more than once, and that’s completely fine. Just make sure it reflects the ideas that you would like to present in the essay.
- How Can I Support a Claim in an Essay?
Final Thoughts
That’s it for the placement of a thesis statement in an essay.
Always make sure that the thesis statement you write for any essay appears only in the introduction paragraph. Doing so will make it easy for you to draw in the attention of your professor and get them to read the body of the essay to learn more about your arguments.
After all, the main objective of the statement is to provide a clear roadmap that you and your reader can use as a clear guide throughout the essay.
Related Reading
- How Long is a Short Essay?
- Can You End an Essay With a Quote?
- What is a Claim in an Essay and How Do You Make One?
- Can You Use Contraction in a College Essay?
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.

- Current Students
- Faculty & Staff
- Business & Community
- Course Schedule
- Academic & Career Programs
- Paying for College
- Student Support
- Developing Paragraphs
- Taking Notes
- Writing A Thesis
- Stress Management
- Time Management
- Critical Reading
- Writing An Effective Thesis Statement
- Where Should a Thesis Sta...
- Where Should a Thesis Statement Be Placed
A thesis statement is usually at the end of an introductory paragraph. The sentences that precede the sentence will introduce it, and the sentences that follow will support and explain it. Just as a topic sentence introduces and organizes a paragraph, a thesis statement helps readers recognize what is to follow.
For example, consider the following thesis statement:
The Battle of Vicksburg changed the course of the Civil War, leading to the success of the Union.
This statement defines the subject, limits it (one battle, not the entire Civil War), and sets up a cause and effect pattern for the essay that follows.
- Using Thesis Statements
- Informative
- Creating a Thesis Statement
- Summarizing the Thesis Statement
- Entries feed
- Comments feed
- WordPress.org
Search this Website
Start here. get there..

Main Address
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Healthy Happy Teacher
Helping hardworking teachers stay healthy and happy.
How Long Should Your Thesis Be? [Answered]
If you are a graduate student writing a Master’s thesis, you are probably wondering about the project’s length requirements.
Many of us face uncertainties regarding this, and understandably so. The length of a thesis influences the scope and area of your studies.
So, how long is a thesis? In this article, Healthy Happy Teacher walks you through all aspects of how long a masters degree thesis for graduate school should be. Because sometimes it’s just good to work on our mindsets and productivity!
Drop your deadline-driven anxiety at the door, and let’s take a look.
What is a Thesis?
First, it’s essential to define what a thesis is, as well as its function. A thesis is a long-form academic paper that proves a premise in the form of a thesis statement.
This is a statement that succinctly defines what your thesis paper is going to do. It can be featured as a preface, or it can be placed in your introductory paragraph, but it’s essential to refine it as concisely as possible.
A Point About Thesis Writing
Before you write the thesis itself, refining your thesis statement as concisely as possible is essential, as this will influence the research scope and, consequently, the length.
To that end, there are many common thesis statement mistakes you will want to avoid when writing yours. Often, a thesis statement needs to be clarified.
Remember, the reader must understand your paper’s purpose right from the get-go. This applies to you, the academic, as well. The more succinctly you refine your scope, the more efficient the project, giving you much more control over the length.
Another common mistake is when students make their statement too complex – you want to ensure that it isn’t too wordy or lengthy, as this can weaken the argument. The short, declarative sentence will beat a verbose, elongated approach any day.
Also, ensure your statement has a purpose and isn’t too obvious. That said, how long should the masters thesis that follows be?
The Length of A Thesis
Let’s get into the question of how long a thesis is.
In truth, there is no set rule for the length of a thesis.
In fact, according to various sources , the purpose of every thesis is different, and therefore so will the length of each one. Yes, it is unequivocally better to keep it as concise and impactful as possible, but it’s always better to make your point fully than cut it short to adhere to a page count.
That said, the average thesis length is around 50-80 pages. It’s not typical for a thesis to extend much beyond this.
Other factors will affect the length, too. Below is a common example:
The Complexity of the Proposition
Your paper might be particularly complex or have a few complicated components that need to be explored. It is better served by featuring a two-paragraph introduction before introducing the thesis. Also, consider the fact that no thesis statement, however concise, is complete the moment it is typed out. The thesis statement can be revised and restructured during the writing process.
As you will know by now, research reveals new avenues that can alter the paper’s trajectory. It is okay to revise your thesis accordingly.
Above all, allow yourself to explore every facet of your paper. There is no one-size-fits-all for dissertation papers. They are fluid, explorative, and above all, personal to you.
Determining The Length of Your Thesis
Other factors will determine the length of your thesis. Here are a few examples:
Guidelines From Your Institution
Your college or university will have its length standards, and you can find these out by contacting your professors or seeking out the guidelines in your academic database.
Every institution has these resources, so if you are uncertain, there is no shame in asking! Get in touch, and get your surefootedness.
Research Topic and Methodology
Again, theses are all different. Each will have its demands, research areas, and focal points. To this end, try not to focus on the theses of your peers too much, as their areas of study are likely to be completely different from your own.
It’s the equivalent of comparing your Chapter One to somebody else’s Chapter 12 – it’s simply not relevant. Focus on your project, collaborate with your professors, and allow the project to shape up how it needs to be the best it can be.
Your Supervisor’s Expectations
We touched on it already, but the expectations of your thesis supervisor are an essential element of the studying process. It’s always good to confer with your supervisor to clarify your premise and approach.
If needed, go through each research area with them. And, of course, take their guidance on board. This will have a positive impact on your thesis length.
Tips for Writing a Thesis of Appropriate Length
Need a few pointers about staying on track and within the length guidelines set out by your course and supervisor(s)? Here are a few ideas that will streamline any project and have worked for many of us at Healthy Happy Teacher!
Organizing your research and ideas
Organizing your research and ideas, preferably with post-it notes and colored markers, will inform you how long each piece of research will take and, consequently, give you a clearer picture of the length of your project.
Try laying out a plan for each section – subject to change, of course – and the project will start to shape up before you know it. Doing this also informs you where to explore ideas more thoroughly, showing you what work you must prioritize and ease the process!
Editing and revising to eliminate unnecessary content
Down the road comes editing and revising your content.
It is always wise to refer back to your thesis statement in this procedure, as this will inform you about what is the most relevant and clue you in about what is pertinent to proving your premise and what is not. Then you can edit accordingly.
Doing this is excellent, as it frees up space to explore other areas in more depth.
Maintaining focus on your research question
If you are concerned about your thesis being too long or short, always refer back to your thesis statement to maintain focus.
This will streamline your work and help you to avoid writing irrelevant content or going too far down a particular avenue.
Frequently Asked Questions
● what is the typical page count for a thesis.
Around 50 pages. But if you look online, it’s difficult to find consistency. If you are uncertain, check in with your academic institution, as this is the horse’s mouth!
● Is there a minimum or maximum length for a thesis?
Typically, there is a word limit, and it is not advisable to go above or beneath the required thesis length. But once again, this depends on your subject, study area, and your individual needs. It is worth booking an advice session with your tutor(s).
● Can a thesis be too long or too short?
It is possible for your thesis submission to be too long or two short. You should always stay within the standard as laid out by your course and supervisor.
● How can I make sure that my thesis is the appropriate length?
The critical factor in the research/writing process is fully exploring your subject. Once you get into it, you can cut down where needed or find other areas to explore for your final thesis.
Try not to fill the paper with irrelevant information and ‘waffle’, as this is unlikely to add to your results.
● What’s the difference between a thesis and a dissertation?
The main difference between a dissertation and a thesis is the degree program. Students who are completing a master’s degree program are required to write a thesis, whereas doctoral degree students are required to write a dissertation.
A PhD dissertation also requires doctoral candidates to create and expand upon an original research idea, whereas a masters thesis builds upon existing ideas.
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Disclosure, disclaimer & privacy policy
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases

Can a Thesis Statement Be a Question: Tips on Writing the Perfect Thesis Statement
You have probably struggled with your thesis statement when writing a research paper on whether the statement can be a question or not. And for many finding the perfect statement is one of the struggles in writing.
But in this blog, we’ll explore the formal and informal definitions of a thesis statement and then talk about whether or not it can be a question. It covers what your thesis statement should be as well as tips and tricks on how to write one.
After reading this post, you will be better placed to write your thesis statement and generally understand its structure.
Can a Thesis Statement Be a Question
Generally, your thesis statement cannot be a question because it essentially answers the question, “what is this paper about?” However, it’s a good idea to think of your thesis statement as a question, but it shouldn’t be an actual question.
New Service Alert !!!
We are now taking exams and courses
Your thesis statement is a declarative sentence that tells readers what you will discuss in your essay. If you have a question instead of a statement, it will be hard for people to know what your paper is about.
Further, the statement is a sentence in your essay providing your paper’s main idea. It is also the purpose or theme of your article and often appears near the beginning of your writing. This further shows that questions may not be the best if used as thesis statements.
Also see: Best thesis generator for your college paper
Thesis statements can be various, but they all have one thing in common; they state an opinion or position on a particular subject. Therefore, a thesis statement is not just a statement of fact. It is an assertion that you will prove with evidence from your research.
Further, a question does not present or state a fact or claim. Thus questions should appear in the body but not as a thesis statement.
Can You Ask a Question in a Thesis Statement
In most cases, you cannot ask a question in a thesis statement because it will not help your readers understand what your paper is about.
It is essential to understand a thesis statement to know why you cannot ask a question in it. A thesis statement is used when writing an academic paper and is usually found at the end of your introduction paragraph, which states what you will talk about in your essay. It can also be used as a summary or summary sentence for your paper.
Similarly, it is the central point of your paper. It states what you’re going to talk about and how you’re going to talk about it. In most cases, it’s a declarative sentence that tells your reader what your argument is without giving away the conclusion. Thus, it is the backbone of your essay and acts as your chance to tell the reader what you’ll talk about and why it’s crucial.
For these reasons, you cannot ask a question here because it will be more confusing. The general rule is to make it clear and concise, and questions do not provide this clarity or conciseness.
How to Write a Good Thesis Statement With Examples
The thesis statement is the most critical element of your essay. The statement tells your reader what to expect and why it’s worth reading.
A good thesis statement is clear, concise, and specific. It states your position on an issue but doesn’t overstate or understate it. It contains a word or phrase that will grab the attention of your reader and make them want to keep reading.
The following are some tips to help you craft a good statement;
Be clear and focused.
This means you should ensure your thesis statement clearly states the main idea of your paper without any ambiguity or vagueness. You should avoid using superlatives in your statement as they do not add anything substantial but make it more difficult for the reader to understand what you are trying to say.
Also, do not use phrases like “this paper argues” or “this paper will discuss” as they do not give much information about what is going on in the rest of your paper
Further, don’t try to cover everything in one sentence. Instead, choose one main idea and make it clear what that idea is. The thesis statement should not have several ideas or multiple points because doing so will confuse readers and make it difficult for them to follow your argumentation in the body paragraphs of your essay.
Make sure it’s a declarative sentence
A good thesis statement is a declarative sentence that clearly states what your paper is about. It must be specific enough to serve as an organizing principle for the article but not so narrow that it limits your ability to explore other ideas during research and writing.
For example, you can say dogs do not like milk rather than dogs may like milk.
Additionally, don’t use words like “I believe” or “I think.” Instead, come up with a fact that you want to prove. For example, if you’re writing about the effects of pollution on the environment, write something like “Air pollution is responsible for millions of deaths each year.”
Include appropriate keywords or phrases related to your topic
Your thesis statement should contain proper keywords or phrases related to your subject to help readers understand what they’ll learn from reading your essay.
Use short sentences, active verbs, and simple words in your thesis statement; they improve readability and make it easy for readers to understand your statement quickly.
For example, if the topic is factors contributing to dog illnesses, your statement may include keywords like dog illnesses.

In the age of cancel culture, shaming can be healthy for online communities – a political scientist explains when and how
Assistant Professor of Political Science, Loyola University Chicago
Disclosure statement
Jennifer Forestal has received funding from the National Endowment for the Humanities.
View all partners
“Cancel culture” has a bad reputation. There is growing anxiety over this practice of publicly shaming people online for violating social norms ranging from inappropriate jokes to controversial business practices .
Online shaming can be a wildly disproportionate response that violates the privacy of the shamed while offering them no good way to defend themselves. These consequences lead some critics to claim that online shaming creates a “ hate storm ” that destroys lives and reputations, leaves targets with “ permanent digital baggage ” and threatens the fundamental right to publicly express yourself in a democracy. As a result, some scholars have declared that online shaming is a “ moral wrong and social ill .”
But is online public shaming necessarily negative? I’m a political scientist who studies the relationship between digital technologies and democracy . In my research, I show how public shaming can be a valuable tool for democratic accountability . However, it is more likely to provide these positive effects within a clearly defined community whose members have many overlapping connections.
When shaming helps
Public shaming is a “ horizontal” form of social sanctioning , in which people hold one another responsible for violating social norms, rather than appealing to higher authorities to do so. This makes it especially useful in democratic societies , as well as in cases where the shamers face power imbalances or lack access to formal authorities that could hold the shamed accountable.
For example, public shaming can be an effective strategy for challenging corporate power and behavior or maintaining journalistic norms in the face of plagiarism . By harnessing social pressure , public shaming can both motivate people to change their behavior and deter future violations by others.
But public shaming generally needs to occur in a specific social context to have these positive effects. First, everyone involved must recognize shared social norms and the shamer’s authority to sanction violations of them. Second, the shamed must care about their reputation . And third, the shaming must be accompanied by the possibility of reintegration , allowing the shamed to atone and be welcomed back into the fold.
This means that public shaming is more likely to deliver accountability in clearly defined communities where members have many overlapping connections, such as schools where all the parents know one another .
In communal spaces where people frequently run into each other, like workplaces , it is more likely that they understand shared social norms and the obligations to follow them. In these environments, it is more likely that people care about what others think of them, and that they know how to apologize when needed so that they can be reintegrated in the community.
Communities that connect
Most online shamings, however, do not take place in this kind of positive social context. On the social platform X, previously known as Twitter, which hosts many high-profile public shamings, users generally lack many shared connections with one another. There is no singular “X community” with universally shared norms, so it is difficult for users to collectively sanction norm violations on the platform.
Moreover, reintegration for targets of shamings on X is nearly impossible, since it is not clear to what community they should apologize, or how they should do so. It should not be surprising, then, that most highly publicized X shamings – like those of PR executive Justine Sacco , who was shamed for a racist tweet in 2013, and Amy Cooper , the “Central Park Karen” – tend to degenerate into campaigns of harassment and stigmatization .
But just because X shamings often turn pathological does not mean all online shamings do. On Threadless , an online community and e-commerce site for artists and designers, users effectively use public shaming to police norms around intellectual property. Wikipedians’ use of public “reverts” – reversals of edits to entries – has helped enforce the encylopedia’s standards even with anonymous contributors. Likewise, Black Twitter has long used the practice of public shaming as an effective mechanism of accountability.
What sets these cases apart is their community structure. Shamings in these contexts are more productive because they occur within clearly defined groups in which members have more shared connections.
Acknowledging these differences in social context helps clarify why, for example, when a Reddit user was shamed by his subcommunity for posting an inappropriate photo, he accepted the rebuke, apologized and was welcomed back into the community. In contrast, those shamed on X often issue vague apologies before disengaging entirely.
Crossing online borders
There are still very real consequences of moving public shaming online. Unlike in most offline contexts, online shamings often play out on a massive scale that makes it more difficult for users to understand their connections with one another. Moreover, by creating opportunities to expand and overlap networks, the internet can blur community boundaries in ways that complicate the practice of public shaming and make it more likely to turn pathological.
For example, although the Reddit user was reintegrated into his community, the shaming soon spread to other subreddits, as well as national news outlets, which ultimately led him to delete his Reddit account altogether.
This example suggests that online public shaming is not straightforward. While shaming on X is rarely productive, the practice on other platforms, and in offline spaces characterized by clearly defined communities such as college campuses, can provide important public benefits.
Shaming, like other practices of a healthy democracy, is a tool whose value depends on how it’s used.
- Social media
- Social norms
- Public shaming
- Social media and democracy
- Cancel culture
- Online communities
- X (formerly Twitter)

Sydney Horizon Educators (Identified)

Senior Disability Services Advisor

Deputy Social Media Producer

Associate Professor, Occupational Therapy

GRAINS RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION CHAIRPERSON
Opening statements in Trump's historic trial set to begin Monday after tense day of jury selection
Opening statements are set to begin next week in Donald Trump’s historic criminal trial after the final members of the jury were seated Friday, following a dramatic day in which two prospective jurors broke down in tears, an appeals court judge rejected Trump's request for a stay, and a man set himself on fire in front of the courthouse.
“We’re going to have opening statements on Monday morning. This trial is starting,” Judge Juan Merchan said towards the end of the day, after successfully seating the remaining five alternate jurors that were needed.
The case — the first-ever criminal trial of a former president —will be heard by a panel of 12 jurors and a total of six alternates. It's expected to last roughly six weeks.
The five alternates ultimately selected Friday include an unemployed married woman who’s into art and described herself as not political, an audio professional, a contract specialist, a clothing company executive and a construction company project manager. It took four days of jury selection to find the 18 jurors.
Around the same time the judge declared, "we have our full panel" inside the courtroom in the early afternoon, a man set himself on fire outside the courthouse. The NYPD said the man, identified as Max Azzarello of Florida, later died. He appeared to have had pamphlets describing a conspiracy involving cryptocurrency that he threw around before setting himself ablaze, police said.
Later in the afternoon, Trump's attorneys were in a state appeals court trying again to get an emergency stay of the trial. Trump attorney Cliff Robert argued his client could not get a fair trial in Manhattan, which had been Trump's longtime home before moving to Florida after he was elected president in 2016.
Steven Wu of Manhattan District Attorney Alvin Bragg's office countered that "what the last week has shown is that the jury selection has worked."
"We have 18 ordinary New Yorkers who are ready to serve. It would be unfair to them and the public for this to be delayed further," he argued. The judge rejected Trump's stay request a short time later.
The jury selection process Friday was especially intense, some potential jurors breaking down in tears and others saying they were too anxious to serve.
The day began with the judge calling up the 22 remaining potential jurors from the previous pool of 96 to answer questions designed to indicate whether they could be fair and impartial about the divisive real estate mogul and presumptive Republican nominee for president.
The first of those potential jurors was dismissed after she said she didn’t think she could be fair. “I have really, really bad anxiety and people have found out where I am,” she told the judge. A short time later, two other potential jurors were dismissed after each told the judge that upon further reflection, “I don’t think I can be impartial.”
Other potential jurors included a married father who said he listens to a podcast called “Order of Man,” which is described on Apple’s website as discussions about “reclaiming what it means to be a man.” Some past guests of the podcast include people who’ve been outspoken in their support of Trump and were highly critical of the civil fraud case New York Attorney General Letitia James brought against the former president. The man, an audio specialist, was chosen as one of the alternates.
Another potential juror was a married fund manager who said he’d done “get-out-the-vote” work for former Secretary of State Hillary Clinton, Trump’s 2016 presidential opponent. Trump and his attorney Todd Blanche passed notes back and forth while that juror was speaking. He was later dismissed after being asked about a 2020 Facebook post where he apparently called Trump “the devil and a sociopath.”

Trump appeared most interested in jurors whose answers offer ambiguity around their personal political views. When one prospective juror said they were a Fox News viewer, Trump cocked his head, then quickly conferred with his lawyer, Todd Blanche.
Another potential juror was a woman who became emotional as she disclosed she'd served two years in prison on drug-related charges, but said she could be "fair and impartial."
During a morning break, Merchan — who'd chided reporters on Thursday for disclosing too much information about potential jurors — said the woman had shared "very personal things about her life" and was "very brave." “I just wanted to encourage the press to please be kind. Please be kind to this person,” the judge said. He later dismissed her, saying she needed a certificate of release to be qualified for service going forward. On her way out, she cheerfully called out, "Good luck!"
Following that juror's departure, the DA's office began its individual questioning of the jurors. One woman, who'd disclosed that her father is lifelong friends with Trump ally turned critic Chris Christie, broke down in tears when prosecutor Susan Hoffinger asked her an innocuous question about the burden of proof in the case. "I feel so nervous and anxious right now. I’m sorry," she responded, bursting out into tears. "I thought I could do this," she said, adding "I wouldn’t want someone who feels this way to judge my case." She was dismissed.
Hoffinger's questioning was followed by Trump attorney Susan Necheles, who asked a potential juror who'd started their own business how she would assess a witness's credibility. The woman then asked to speak to the judge, saying she was "getting anxiety and self-doubt” from Necheles's line of questioning. She was dismissed.
Necheles later asked another woman — who previously said she was a victim of sexual assault — whether she would hold it against Trump that women outside this case have accused Trump of sexual assault. She said she would not have a problem setting those accusations aside but the judge ultimately excused her, saying, "It’s best to err on the side of caution."
Another man said he has some differences from Trump on his policies but thinks he's “usually awesome.” He was not chosen for the jury.
On his way into court in the morning, Trump again complained the case against him is "unfair," and that the partial gag order preventing him from lashing out at witnesses, prosecutors, court staffers and jurors is not "constitutional." "Everyone else can say whatever they want about me. They can say anything they want. They can continue to make up lies and everything else. They lie. They’re real scum. But you know what? I’m not allowed to speak," he told reporters.
Prosecutors this week asked the judge to fine Trump and hold him in contempt for social media posts that they said violate the gag order. A hearing on the matter is scheduled for Tuesday.
The m a in pa nel of 12 is made up of seven men and five women, including two lawyers, a teacher, a retired wealth manager, a product development manager, a security engineer, a software engineer, a speech therapist and a physical therapist. The foreman — the juror who essentially acts as the leader and spokesperson for the panel — is a married man who works in sales and gets his news from The New York Times, MSNBC and Fox News.
The lone alternate selected Thursday is a woman who works as an asset manager.
Trump vented about the speed of the process in a post on social media shortly after the final jurors were selected, claiming the judge is “‘railroading’ me, at breakneck speed, in order to completely satisfy his ‘friends’.”
Later in the day, Merchan held what's known as a Sandoval hearing . That's a type of hearing designed to let defendants know the scope of questions they could face from prosecutors on cross-examination so they can make informed decisions about whether to take the witness stand in their own defense.
Leaving court on Friday, Trump was asked whether he was still planning to testify and he said he was.
Manhattan District Attorney Alvin Bragg's office disclosed in a court filing that it would like to ask Trump about several items, among them the $464 million civil judgment against him and his company for fraud , the total $88 million verdicts and liability findings for sexual abuse and defamation in lawsuits brought by writer E. Jean Carroll and a number of other adverse court rulings over the past few years.
Trump has denied wrongdoing in all the cases and is appealing the fraud judgment and the Carroll verdicts.
Prosecutors said they want to be able to bring those findings up “to impeach the credibility of the defendant” if he takes the witness stand.
Discussing the findings in the fraud case, prosecutor Matthew Colangelo told the judge it was "hard to think of something that is more squarely in the wheelhouse” for the DA to ask Trump about "than a finding by a judge of persistent and repeated fraud and illegality."
Trump's attorney Emil Bove countered that prosecutors shouldn't be able to breach the topic at all because Trump's appeal is still pending. He made similar arguments over the DA's contention that they should be allowed to ask about a judge's finding that he was untruthful on the witness stand during the fraud trial and had violated a gag order in the case.
“Is it your position that because a case is being appealed or might be appealed, that therefore it can not be used?" Merchan asked the lawyer. "Not necessarily," Bove replied.
The judge said he'd issue his ruling on the dispute on Monday morning.
Trump said last week he “absolutely” plans to testify , but he is under no obligation to do so.
Asked by Necheles at the end of the day who the DA's first witness would be, prosecutor Joshua Steinglass said they wouldn't inform Trump's team of the person's identity until Sunday, given that Trump has been criticizing some witnesses on social media despite the partial gag order in the case. “And if that should be tweeted, that’ll be the last time we provide that courtesy,” Steinglass said.
Merchan called the DA's position "understandable" and told Necheles "I will not compel them to do anything."
Trump has pleaded not guilty to 34 counts of falsifying business records and faces up to four years in prison if he is convicted.
Bragg alleges that Trump falsified records to hide money he was paying his former lawyer Michael Cohen to reimburse him for $130,000 he paid adult film actor Stormy Daniels near the end of the 2016 presidential campaign. Daniels has claimed she had a sexual encounter with Trump in 2006. Trump has denied that he slept with Daniels, but he has acknowledged repaying Cohen.
The DA’s office also alleges that as part of a scheme to boost Trump, National Enquirer publisher American Media Inc. paid $150,000 to model and actor Karen McDougal , who appeared in Playboy magazine and claimed that she had a nine-month affair with Trump before he was elected president “in exchange for her agreement not to speak out about the alleged sexual relationship,” according to a statement of facts filed by Bragg.
Trump has also denied having a sexual relationship with McDougal.
Adam Reiss is a reporter and producer for NBC and MSNBC.
Lisa Rubin is an MSNBC legal correspondent and a former litigator.
Dareh Gregorian is a politics reporter for NBC News.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The short answer is: one or two sentences. The more i n-depth answer: as your writing evolves, and as you write longer papers, your thesis statement will typically be at least two, and often more, sentences. The thesis of a scholarly article may have three or four long sentences. The point is to write a well-formed statement that clearly sets ...
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
It is a brief statement of your paper's main argument. Essentially, you are stating what you will be writing about. Organize your papers in one place. Try Paperpile. No credit card needed. Get 30 days free. You can see your thesis statement as an answer to a question. While it also contains the question, it should really give an answer to the ...
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
Your thesis statement may be short or long, depending on your academic level. While there is no one rule on how long is a thesis statement supposed to be, experts advise 20-50 words. Long or short, your thesis should clearly state your paper's aim in one to four lines; leave out irrelevant words. If you need professional help writing your ...
A thesis statement is a very common component of an essay, particularly in the humanities. It usually comprises 1 or 2 sentences in the introduction of your essay, and should clearly and concisely summarize the central points of your academic essay. A thesis is a long-form piece of academic writing, often taking more than a full semester to ...
A thesis statement . . . Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic. Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper. Is focused and specific enough to be "proven" within the boundaries of your paper. Is generally located near the end ...
Thesis Statements. A thesis is the main claim you are making in an argument, similar to the hypothesis in a scientific experiment. It is what you are trying to prove or persuade your audience to believe or do. It's helpful to develop a working thesis to guide your composition process. "Working" is the operative word here; your ideas are ...
It is an attainable goal for many students. A thesis statement should concisely summarize the main point or claim of the paper while also addressing and showcasing the supportive evidence. It should be formulated clear and concise, without exceeding about a few sentences. The ideal length for a thesis statement is three sentences, as this ...
Step 4: Revise and refine your thesis statement before you start writing. Read through your thesis statement several times before you begin to compose your full essay. You need to make sure the statement is ironclad, since it is the foundation of the entire paper. Edit it or have a peer review it for you to make sure everything makes sense and ...
If you're struggling to come up with a thesis statement, here are a few tips you can use to help: Know the topic. The topic should be something you know or can learn about. It is difficult to write a thesis statement, let alone a paper, on a topic that you know nothing about. Reflecting on personal experience and/or researching your thesis ...
A thesis statement should only be one sentence long and not more than that because it needs to be succinct and clear. No matter the number of points or clauses you want to argue out, the thesis statement must be just a single statement. Therefore, you need to compress all the clauses into a single sentence that takes a stand on what you are writing about.
Types of Thesis Statements. Writing a thesis statement can take different forms depending on the essay's purpose. Here are common types according to our custom essay service:. Argumentative: Asserts a position on a controversial topic and provides reasons or evidence to support it.Example: 'The government should implement stricter gun control laws to reduce instances of mass shootings and ...
It is all about striking the right balance between not having a flat and trivial thesis and not imparting too much extraneous information. Although it's impossible to put a specific number on it, most experts advise staying in a range between 25-50 words for a thesis statement. Try to keep it to a single sentence, if you can, preferably to ...
Crafting a clear thesis statement can demonstrate all of the main points of your argument. Whether you create it personally or by using Avidnote, the impact is the same. Even if the paper has a length of several pages, the thesis statement should represent them. How long should a thesis statment be is an easy question, too.
1. Do make your thesis statement specific and concise. A strong thesis statement should be specific and concise, clearly stating the main argument or focus of your paper. Avoid vague or general ...
So it doesn't make sense to include the thesis statement at the end of an essay. The statement should appear in the introduction paragraph. It's short, usually a complete sentence although it's okay to stretch it into two sentences. The statement that comes before the thesis statement is what introduces it, and the ideas that follow will ...
A thesis statement is usually at the end of an introductory paragraph. The sentences that precede the sentence will introduce it, and the sentences that follow will support and explain it. Just as a topic sentence introduces and organizes a paragraph, a thesis statement helps readers recognize what is to follow. For example, consider the ...
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons: It gives your writing direction and focus. It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point. Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
A thesis is a long-form academic paper that proves a premise in the form of a thesis statement. This is a statement that succinctly defines what your thesis paper is going to do. It can be featured as a preface, or it can be placed in your introductory paragraph, but it's essential to refine it as concisely as possible.
Thesis statements can be various, but they all have one thing in common; they state an opinion or position on a particular subject. Therefore, a thesis statement is not just a statement of fact. It is an assertion that you will prove with evidence from your research. Further, a question does not present or state a fact or claim.
The length of a thesis statement depends on the type of essay you're writing and on its overall length. Naturally, you cannot write a lengthy thesis statement for a five paragraph essay. On the other hand, when your task is to write a longer dissertation-type paper, it is quite acceptable to expand your thesis statement accordingly.
The scale and speed of social media can change the dynamics of public shaming when it occurs online. Crossing online borders There are still very real consequences of moving public shaming online.
Opening statements are set to begin next week in Donald Trump's historic criminal trial after the final members of the jury were seated Friday, following a dramatic day in which two prospective ...