- 212 best farm names

How to Write a Business Plan (Plus Examples & Templates)
May 24, 2021
Have you ever wondered how to write a business plan step by step? Mike Andes, told us:
This guide will help you write a business plan to impress investors.
Throughout this process, we’ll get information from Mike Andes, who started Augusta Lawn Care Services when he was 12 and turned it into a franchise with over 90 locations. He has gone on to help others learn how to write business plans and start businesses. He knows a thing or two about writing business plans!
We’ll start by discussing the definition of a business plan. Then we’ll discuss how to come up with the idea, how to do the market research, and then the important elements in the business plan format. Keep reading to start your journey!
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is simply a road map of what you are trying to achieve with your business and how you will go about achieving it. It should cover all elements of your business including:
- Finding customers
- Plans for developing a team
- Competition
- Legal structures
- Key milestones you are pursuing
If you aren’t quite ready to create a business plan, consider starting by reading our business startup guide .
Get a Business Idea
Before you can write a business plan, you have to have a business idea. You may see a problem that needs to be solved and have an idea how to solve it, or you might start by evaluating your interests and skills.
Mike told us, “The three things I suggest asking yourself when thinking about starting a business are:
- What am I good at?
- What would I enjoy doing?
- What can I get paid for?”

If all three of these questions don’t lead to at least one common answer, it will probably be a much harder road to success. Either there is not much market for it, you won’t be good at it, or you won’t enjoy doing it.
As Mike told us, “There’s enough stress starting and running a business that if you don’t like it or aren’t good at it, it’s hard to succeed.”
If you’d like to hear more about Mike’s approach to starting a business, check out our YouTube video
Conduct Market Analysis
Market analysis is focused on establishing if there is a target market for your products and services, how large the target market is, and identifying the demographics of people or businesses that would be interested in the product or service. The goal here is to establish how much money your business concept can make.
Product and Service Demand

A search engine is your best friend when trying to figure out if there is demand for your products and services. Personally, I love using presearch.org because it lets you directly search on a ton of different platforms including Google, Youtube, Twitter, and more. Check out the screenshot for the full list of search options.
With quick web searches, you can find out how many competitors you have, look through their reviews, and see if there are common complaints about the competitors. Bad reviews are a great place to find opportunities to offer better products or services.
If there are no similar products or services, you may have stumbled upon something new, or there may just be no demand for it. To find out, go talk to your most honest friend about the idea and see what they think. If they tell you it’s dumb or stare at you vacantly, there’s probably no market for it.
You can also conduct a survey through social media to get public opinion on your idea. Using Facebook Business Manager , you could get a feel for who would be interested in your product or service.
I ran a quick test of how many people between 18-65 you could reach in the U.S. during a week. It returned an estimated 700-2,000 for the total number of leads, which is enough to do a fairly accurate statistical analysis.
Identify Demographics of Target Market
Depending on what type of business you want to run, your target market will be different. The narrower the demographic, the fewer potential customers you’ll have. If you did a survey, you’ll be able to use that data to help define your target audience. Some considerations you’ll want to consider are:
- Other Interests
- Marital Status
- Do they have kids?
Once you have this information, it can help you narrow down your options for location and help define your marketing further. One resource that Mike recommended using is the Census Bureau’s Quick Facts Map . He told us,
“It helps you quickly evaluate what the best areas are for your business to be located.”
How to Write a Business Plan

Now that you’ve developed your idea a little and established there is a market for it, you can begin writing a business plan. Getting started is easier with the business plan template we created for you to download. I strongly recommend using it as it is updated to make it easier to create an action plan.
Each of the following should be a section of your business plan:
- Business Plan Cover Page
- Table of Contents
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Description of Products and Services
SWOT Analysis
- Competitor Data
- Competitive Analysis
- Marketing Expenses Strategy
Pricing Strategy
- Distribution Channel Assessment
- Operational Plan
- Management and Organizational Strategy
- Financial Statements and/or Financial Projections
We’ll look into each of these. Don’t forget to download our free business plan template (mentioned just above) so you can follow along as we go.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 1. Create a Cover Page
The first thing investors will see is the cover page for your business plan. Make sure it looks professional. A great cover page shows that you think about first impressions.
A good business plan should have the following elements on a cover page:
- Professionally designed logo
- Company name
- Mission or Vision Statement
- Contact Info
Basically, think of a cover page for your business plan like a giant business card. It is meant to capture people’s attention but be quickly processed.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 2. Create a Table of Contents
Most people are busy enough that they don’t have a lot of time. Providing a table of contents makes it easy for them to find the pages of your plan that are meaningful to them.
A table of contents will be immediately after the cover page, but you can include it after the executive summary. Including the table of contents immediately after the executive summary will help investors know what section of your business plan they want to review more thoroughly.
Check out Canva’s article about creating a table of contents . It has a ton of great information about creating easy access to each section of your business plan. Just remember that you’ll want to use different strategies for digital and hard copy business plans.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 3. Write an Executive Summary

An executive summary is where your business plan should catch the readers interest. It doesn’t need to be long, but should be quick and easy to read.
Mike told us,
How long should an executive summary bein an informal business plan?
For casual use, an executive summary should be similar to an elevator pitch, no more than 150-160 words, just enough to get them interested and wanting more. Indeed has a great article on elevator pitches . This can also be used for the content of emails to get readers’ attention.
It consists of three basic parts:
- An introduction to you and your business.
- What your business is about.
- A call to action
Example of an informal executive summary
One of the best elevator pitches I’ve used is:
So far that pitch has achieved a 100% success rate in getting partnerships for the business.
What should I include in an executive summary for investors?
Investors are going to need a more detailed executive summary if you want to secure financing or sell equity. The executive summary should be a brief overview of your entire business plan and include:
- Introduction of yourself and company.
- An origin story (Recognition of a problem and how you came to solution)
- An introduction to your products or services.
- Your unique value proposition. Make sure to include intellectual property.
- Where you are in the business life cycle
- Request and why you need it.
Successful business plan examples
The owner of Urbanity told us he spent 2 months writing a 75-page business plan and received a $250,000 loan from the bank when he was 23. Make your business plan as detailed as possible when looking for financing. We’ve provided a template to help you prepare the portions of a business plan that banks expect.
Here’s the interview with the owner of Urbanity:
When to write an executive summary?
Even though the summary is near the beginning of a business plan, you should write it after you complete the rest of a business plan. You can’t talk about revenue, profits, and expected expenditures if you haven’t done the market research and created a financial plan.
What mistakes do people make when writing an executive summary?
Business owners commonly go into too much detail about the following items in an executive summary:
- Marketing and sales processes
- Financial statements
- Organizational structure
- Market analysis
These are things that people will want to know later, but they don’t hook the reader. They won’t spark interest in your small business, but they’ll close the deal.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 4. Company Description
Every business plan should include a company description. A great business plan will include the following elements while describing the company:
- Mission statement
- Philosophy and vision
- Company goals
Target market
- Legal structure
Let’s take a look at what each section includes in a good business plan.
Mission Statement
A mission statement is a brief explanation of why you started the company and what the company’s main focus is. It should be no more than one or two sentences. Check out HubSpot’s article 27 Inspiring Mission Statement for a great read on informative and inspiring mission and vision statements.
Company Philosophy and Vision

The company philosophy is what drives your company. You’ll normally hear them called core values. These are the building blocks that make your company different. You want to communicate your values to customers, business owners, and investors as often as possible to build a company culture, but make sure to back them up.
What makes your company different?
Each company is different. Your new business should rise above the standard company lines of honesty, integrity, fun, innovation, and community when communicating your business values. The standard answers are corporate jargon and lack authenticity.
Examples of core values
One of my clients decided to add a core values page to their website. As a tech company they emphasized the values:
- Prioritize communication.
- Never stop learning.
- Be transparent.
- Start small and grow incrementally.
These values communicate how the owner and the rest of the company operate. They also show a value proposition and competitive advantage because they specifically focus on delivering business value from the start. These values also genuinely show what the company is about and customers recognize the sincerity. Indeed has a great blog about how to identify your core values .
What is a vision statement?
A vision statement communicate the long lasting change a business pursues. The vision helps investors and customers understand what your company is trying to accomplish. The vision statement goes beyond a mission statement to provide something meaningful to the community, customer’s lives, or even the world.
Example vision statements
The Alzheimer’s Association is a great example of a vision statement:
A world without Alzheimer’s Disease and other dementia.
It clearly tells how they want to change the world. A world without Alzheimers might be unachievable, but that means they always have room for improvement.
Business Goals
You have to measure success against goals for a business plan to be meaningful. A business plan helps guide a company similar to how your GPS provides a road map to your favorite travel destination. A goal to make as much money as possible is not inspirational and sounds greedy.
Sure, business owners want to increase their profits and improve customer service, but they need to present an overview of what they consider success. The goals should help everyone prioritize their work.
How far in advance should a business plan?
Business planning should be done at least one year in advance, but many banks and investors prefer three to five year business plans. Longer plans show investors that the management team understands the market and knows the business is operating in a constantly shifting market. In addition, a plan helps businesses to adjust to changes because they have already considered how to handle them.
Example of great business goals
My all time-favorite long-term company goals are included in Tesla’s Master Plan, Part Deux . These goals were written in 2016 and drive the company’s decisions through 2026. They are the reason that investors are so forgiving when Elon Musk continually fails to meet his quarterly and annual goals.
If the progress aligns with the business plan investors are likely to continue to believe in the company. Just make sure the goals are reasonable or you’ll be discredited (unless you’re Elon Musk).

You did target market research before creating a business plan. Now it’s time to add it to the plan so others understand what your ideal customer looks like. As a new business owner, you may not be considered an expert in your field yet, so document everything. Make sure the references you use are from respectable sources.
Use information from the specific lender when you are applying for lending. Most lenders provide industry research reports and using their data can strengthen the position of your business plan.
A small business plan should include a section on the external environment. Understanding the industry is crucial because we don’t plan a business in a vacuum. Make sure to research the industry trends, competitors, and forecasts. I personally prefer IBIS World for my business research. Make sure to answer questions like:
- What is the industry outlook long-term and short-term?
- How will your business take advantage of projected industry changes and trends?
- What might happen to your competitors and how will your business successfully compete?
Industry resources
Some helpful resources to help you establish more about your industry are:
- Trade Associations
- Federal Reserve
- Bureau of Labor Statistics
Legal Structure
There are five basic types of legal structures that most people will utilize:
- Sole proprietorships
- Limited Liability Companies (LLC)
Partnerships
Corporations.
- Franchises.
Each business structure has their pros and cons. An LLC is the most common legal structure due to its protection of personal assets and ease of setting up. Make sure to specify how ownership is divided and what roles each owner plays when you have more than one business owner.
You’ll have to decide which structure is best for you, but we’ve gathered information on each to make it easier.
Sole Proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is the easiest legal structure to set up but doesn’t protect the owner’s personal assets from legal issues. That means if something goes wrong, you could lose both your company and your home.
To start a sole proprietorship, fill out a special tax form called a Schedule C . Sole proprietors can also join the American Independent Business Alliance .
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
An LLC is the most common business structure used in the United States because an LLC protects the owner’s personal assets. It’s similar to partnerships and corporations, but can be a single-member LLC in most states. An LLC requires a document called an operating agreement.
Each state has different requirements. Here’s a link to find your state’s requirements . Delaware and Nevada are common states to file an LLC because they are really business-friendly. Here’s a blog on the top 10 states to get an LLC.
Partnerships are typically for legal firms. If you choose to use a partnership choose a Limited Liability Partnership. Alternatively, you can just use an LLC.
Corporations are typically for massive organizations. Corporations have taxes on both corporate and income tax so unless you plan on selling stock, you are better off considering an LLC with S-Corp status . Investopedia has good information corporations here .

There are several opportunities to purchase successful franchises. TopFranchise.com has a list of companies in a variety of industries that offer franchise opportunities. This makes it where an entrepreneur can benefit from the reputation of an established business that has already worked out many of the kinks of starting from scratch.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 5. Products and Services
This section of the business plan should focus on what you sell, how you source it, and how you sell it. You should include:
- Unique features that differentiate your business products from competitors
- Intellectual property
- Your supply chain
- Cost and pricing structure
Questions to answer about your products and services
Mike gave us a list of the most important questions to answer about your product and services:
- How will you be selling the product? (in person, ecommerce, wholesale, direct to consumer)?
- How do you let them know they need a product?
- How do you communicate the message?
- How will you do transactions?
- How much will you be selling it for?
- How many do you think you’ll sell and why?
Make sure to use the worksheet on our business plan template .
How to Write a Business Plan Step 6. Sales and Marketing Plan
The marketing and sales plan is focused on the strategy to bring awareness to your company and guides how you will get the product to the consumer. It should contain the following sections:
SWOT Analysis stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Not only do you want to identify them, but you also want to document how the business plans to deal with them.
Business owners need to do a thorough job documenting how their service or product stacks up against the competition.
If proper research isn’t done, investors will be able to tell that the owner hasn’t researched the competition and is less likely to believe that the team can protect its service from threats by the more well-established competition. This is one of the most common parts of a presentation that trips up business owners presenting on Shark Tank .
SWOT Examples

Examples of strengths and weaknesses could be things like the lack of cash flow, intellectual property ownership, high costs of suppliers, and customers’ expectations on shipping times.
Opportunities could be ways to capitalize on your strengths or improve your weaknesses, but may also be gaps in the industry. This includes:
- Adding offerings that fit with your current small business
- Increase sales to current customers
- Reducing costs through bulk ordering
- Finding ways to reduce inventory
- And other areas you can improve
Threats will normally come from outside of the company but could also be things like losing a key member of the team. Threats normally come from competition, regulations, taxes, and unforeseen events.
The management team should use the SWOT analysis to guide other areas of business planning, but it absolutely has to be done before a business owner starts marketing.
Include Competitor Data in Your Business Plan
When you plan a business, taking into consideration the strengths and weaknesses of the competition is key to navigating the field. Providing an overview of your competition and where they are headed shows that you are invested in understanding the industry.
For smaller businesses, you’ll want to search both the company and the owners names to see what they are working on. For publicly held corporations, you can find their quarterly and annual reports on the SEC website .
What another business plans to do can impact your business. Make sure to include things that might make it attractive for bigger companies to outsource to a small business.
Marketing Strategy
The marketing and sales part of business plans should be focused on how you are going to make potential customers aware of your business and then sell to them.
If you haven’t already included it, Mike recommends:
“They’ll want to know about Demographics, ages, and wealth of your target market.”
Make sure to include the Total addressable market . The term refers to the value if you captured 100% of the market.
Advertising Strategy
You’ll explain what formats of advertising you’ll be using. Some possibilities are:
- Online: Facebook and Google are the big names to work with here.
- Print : Print can be used to reach broad groups or targeted markets. Check out this for tips .
- Radio : iHeartMedia is one of the best ways to advertise on the radio
- Cable television : High priced, hard to measure ROI, but here’s an explanation of the process
- Billboards: Attracting customers with billboards can be beneficial in high traffic areas.
You’ll want to define how you’ll be using each including frequency, duration, and cost. If you have the materials already created, including pictures or links to the marketing to show creative assets.
Mike told us “Most businesses are marketing digitally now due to Covid, but that’s not always the right answer.”
Make sure the marketing strategy will help team members or external marketing agencies stay within the brand guidelines .

This section of a business plan should be focused on pricing. There are a ton of pricing strategies that may work for different business plans. Which one will work for you depends on what kind of a business you run.
Some common pricing strategies are:
- Value-based pricing – Commonly used with home buying and selling or other products that are status symbols.
- Skimming pricing – Commonly seen in video game consoles, price starts off high to recoup expenses quickly, then reduces over time.
- Competition-based pricing – Pricing based on competitors’ pricing is commonly seen at gas stations.
- Freemium services – Commonly used for software, where there is a free plan, then purchase options for more functionality.
HubSpot has a great calculator and blog on pricing strategies.
Beyond explaining what strategy your business plans to use, you should include references for how you came to this pricing strategy and how it will impact your cash flow.
Distribution Plan
This part of a business plan is focused on how the product or service is going to go through the supply chain. These may include multiple divisions or multiple companies. Make sure to include any parts of the workflow that are automated so investors can see where cost savings are expected and when.
Supply Chain Examples
For instance, lawn care companies would need to cover aspects such as:
- Suppliers for lawn care equipment and tools
- Any chemicals or treatments needed
- Repair parts for sprinkler systems
- Vehicles to transport equipment and employees
- Insurance to protect the company vehicles and people.
Examples of Supply Chains
These are fairly flat supply chains compared to something like a clothing designer where the clothes would go through multiple vendors. A clothing company might have the following supply chain:
- Raw materials
- Shipping of raw materials
- Converting of raw materials to thread
- Shipping thread to produce garments
- Garment producer
- Shipping to company
- Company storage
- Shipping to retail stores
There have been advances such as print on demand that eliminate many of these steps. If you are designing completely custom clothing, all of this would need to be planned to keep from having business disruptions.
The main thing to include in the business plan is the list of suppliers, the path the supply chain follows, the time from order to the customer’s home, and the costs associated with each step of the process.
According to BizPlanReview , a business plan without this information is likely to get rejected because they have failed to research the key elements necessary to make sales to the customer.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 7. Company Organization and Operational Plan
This part of the business plan is focused on how the business model will function while serving customers. The business plan should provide an overview of how the team will manage the following aspects:
Quality Control
- Legal environment
Let’s look at each for some insight.
Production has already been discussed in previous sections so I won’t go into it much. When writing a business plan for investors, try to avoid repetition as it creates a more simple business plan.
If the organizational plan will be used by the team as an overview of how to perform the best services for the customer, then redundancy makes more sense as it communicates what is important to the business.

Quality control policies help to keep the team focused on how to verify that the company adheres to the business plan and meets or exceeds customer expectations.
Quality control can be anything from a standard that says “all labels on shirts can be no more than 1/16″ off center” to a defined checklist of steps that should be performed and filled out for every customer.
There are a variety of organizations that help define quality control including:
- International Organization for Standardization – Quality standards for energy, technology, food, production environments, and cybersecurity
- AICPA – Standard defined for accounting.
- The Joint Commission – Healthcare
- ASHRAE – HVAC best practices
You can find lists of the organizations that contribute most to the government regulation of industries on Open Secrets . Research what the leaders in your field are doing. Follow their example and implement it in your quality control plan.
For location, you should use information from the market research to establish where the location will be. Make sure to include the following in the location documentation.
- The size of your location
- The type of building (retail, industrial, commercial, etc.)
- Zoning restrictions – Urban Wire has a good map on how zoning works in each state
- Accessibility – Does it meet ADA requirements?
- Costs including rent, maintenance, utilities, insurance and any buildout or remodeling costs
- Utilities – b.e.f. has a good energy calculator .
Legal Environment
The legal requirement section is focused on defining how to meet the legal requirements for your industry. A good business plan should include all of the following:
- Any licenses and/or permits that are needed and whether you’ve obtained them
- Any trademarks, copyrights, or patents that you have or are in the process of applying for
- The insurance coverage your business requires and how much it costs
- Any environmental, health, or workplace regulations affecting your business
- Any special regulations affecting your industry
- Bonding requirements, if applicable
Your local SBA office can help you establish requirements in your area. I strongly recommend using them. They are a great resource.
Your business plan should include a plan for company organization and hiring. While you may be the only person with the company right now, down the road you’ll need more people. Make sure to consider and document the answers to the following questions:
- What is the current leadership structure and what will it look like in the future?
- What types of employees will you have? Are there any licensing or educational requirements?
- How many employees will you need?
- Will you ever hire freelancers or independent contractors?
- What is each position’s job description?
- What is the pay structure (hourly, salaried, base plus commission, etc.)?
- How do you plan to find qualified employees and contractors?
One of the most crucial parts of a business plan is the organizational chart. This simply shows the positions the company will need, who is in charge of them and the relationship of each of them. It will look similar to this:

Our small business plan template has a much more in-depth organizational chart you can edit to include when you include the organizational chart in your business plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 8. Financial Statements
No business plan is complete without financial statements or financial projections. The business plan format will be different based on whether you are writing a business plan to expand a business or a startup business plan. Let’s dig deeper into each.
Provide All Financial Income from an Existing Business
An existing business should use their past financial documents including the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement to find trends to estimate the next 3-5 years.
You can create easy trendlines in excel to predict future revenue, profit and loss, cash flow, and other changes in year-over-year performance. This will show your expected performance assuming business continues as normal.
If you are seeking an investment, then the business is probably not going to continue as normal. Depending on the financial plan and the purpose of getting financing, adjustments may be needed to the following:
- Higher Revenue if expanding business
- Lower Cost of Goods Sold if purchasing inventory with bulk discounts
- Adding interest if utilizing financing (not equity deal)
- Changes in expenses
- Addition of financing information to the cash flow statement
- Changes in Earnings per Share on the balance sheet
Financial modeling is a challenging subject, but there are plenty of low-cost courses on the subject. If you need help planning your business financial documentation take some time to watch some of them.
Make it a point to document how you calculated all the changes to the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement in your business plan so that key team members or investors can verify your research.
Financial Projections For A Startup Business Plan
Unlike an existing business, a startup doesn’t have previous success to model its future performance. In this scenario, you need to focus on how to make a business plan realistic through the use of industry research and averages.
Mike gave the following advice in his interview:
Financial Forecasting Mistakes
One of the things a lot of inexperienced people use is the argument, “If I get one percent of the market, it is worth $100 million.” If you use this, investors are likely to file the document under bad business plan examples.
Let’s use custom t-shirts as an example.
Credence Research estimated in 2018 there were 11,334,800,000 custom t-shirts sold for a total of $206.12 Billion, with a 6% compound annual growth rate.
With that data, you can calculate that the industry will grow to $270 Billion in 2023 and that the average shirt sold creates $18.18 in revenue.
Combine that with an IBIS World estimate of 11,094 custom screen printers and that means even if you become an average seller, you’ll get .009% of the market.
Here’s a table for easier viewing of that information.

The point here is to make sure your business proposal examples make sense.
You’ll need to know industry averages such as cost of customer acquisition, revenue per customer, the average cost of goods sold, and admin costs to be able to create accurate estimates.
Our simple business plan templates walk you through most of these processes. If you follow them you’ll have a good idea of how to write a business proposal.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 9. Business Plan Example of Funding Requests
What is a business plan without a plan on how to obtain funding?
The Small Business Administration has an example for a pizza restaurant that theoretically needed nearly $20k to make it through their first month.
In our video, How to Start a $500K/Year T-Shirt Business (Pt. 1 ), Sanford Booth told us he needed about $200,000 to start his franchise and broke even after 4 months.
Freshbooks estimates it takes on average 2-3 years for a business to be profitable, which means the fictitious pizza company from the SBA could need up to $330k to make it through that time and still pay their bills for their home and pizza shop.
Not every business needs that much to start, but realistically it’s a good idea to assume that you need a fairly large cushion.
Ways to get funding for a small business
There are a variety of ways to cover this. the most common are:
- Bootstrapping – Using your savings without external funding.
- Taking out debt – loans, credit cards
- Equity, Seed Funding – Ownership of a percentage of the company in exchange for current funds
- Crowdsourcing – Promising a good for funding to create the product
Keep reading for more tips on how to write a business plan.
How funding will be used
When asking for business financing make sure to include:
- How much to get started?
- What is the minimum viable product and how soon can you make money?
- How will the money be spent?
Mike emphasized two aspects that should be included in every plan,
How to Write a Business Plan Resources
Here are some links to a business plan sample and business plan outline.
- Sample plan
It’s also helpful to follow some of the leading influencers in the business plan writing community. Here’s a list:
- Wise Plans – Shares a lot of information on starting businesses and is a business plan writing company.
- Optimus Business Plans – Another business plan writing company.
- Venture Capital – A venture capital thread that can help give you ideas.
How to Write a Business Plan: What’s Next?
We hope this guide about how to write a simple business plan step by step has been helpful. We’ve covered:
- The definition of a business plan
- Coming up with a business idea
- Performing market research
- The critical components of a business plan
- An example business plan
In addition, we provided you with a simple business plan template to assist you in the process of writing your startup business plan. The startup business plan template also includes a business model template that will be the key to your success.
Don’t forget to check out the rest of our business hub .
Have you written a business plan before? How did it impact your ability to achieve your goals?
80% of businesses fail... Learn how not to.
Learn from business failures and successes in 5 min or less. The stories, frameworks, and tactics that will make you a 10x better founder.
Brandon Boushy
Related articles
34 Interview Questions to Ask a Business Owner
- Origination of the business
- Processes and challenges during the startup stage
- Operations questions
- Financial questions
- Marketing questions
- Fun questions
Types of interviews you might have with small business owners
Hiring interviews (h), subject matter expert interviews (sme), business investment interviews (bi), company profile interviews (cp).

Questions to ask business owners during covid
"what are your policies on ppe involving covid", 2. "if someone in the workplace is diagnosed with covid, what should we expect to happen".
- Super cautious. (I have a friend that has been quarantined 8 times since Covid started due to potential exposure.)
- Follow local recommendations (Most prevalent)
- Blatantly disregarding the local recommendations ( I have another friend who has had 6 people out with "pneumonia" in the last month, and all continued working while sick.)

Many Business Owners Answer Questions About Their Inspiration
3. what were you doing before you started (insert company name) (sme, bi, cp), 4. how did you come up with the idea for (insert business name) (h, sme, bi, cp).

Business Formation and Process Questions to Ask a Business Owner
5. do you have a business plan (bi, cp), 6. did you start the business as a sole proprietorship, corporation, or llc (bi, cp), 7. what were your startup costs (sme, bi, cp), 8. follow-up questions to ask entrepreneurs- can you break down the costs for us.

9. Another followup: How do government regulations and startup costs create a barrier to entry in your field?
10. how did you fund your small business (h, sme, bi, cp), 11. do you have other outstanding business debts what are they, 12. what will the funding you are requesting be used for, 13. what were some challenges you faced when creating your product (sme, bi, cp), 14. how do you select vendors for your companies (h, sme, bi, cp), 15. follow-up question: once you’ve selected a vendor how do you verify they are performing up to those standards, questions to ask entrepreneurs about equipment computer systems (sme, cp), 17. what software do you use to track your inventory and sales, 18. what is the most profitable piece of equipment for your business, 19. where are the best places to buy equipment, 20. what software can't you live without, operations questions to ask a company about their business, 21. what does a normal day at your company look like (h, cp), 22. how do you manage customer relationships (h, bi, cp).

23. How do you delegate tasks? (H, SME, CP)
Financial questions to ask the owner of a company (bi), 24. what was last year's net profit, 25. what was the change in your cash flow last quarter, 26. what was year-over-year sales growth, 27. do you have enough cash to continue operations and service additional debt, marketing questions you might be asked as a business owner, 28. what social media channels get the best results, 29. what are your favorite marketing tools to use, 30. what percent of revenue do you spend on marketing, 31. what unique marketing strategies do you use to drive results, fun questions to ask business owners.

32.What are your favorite books?
33.who are your favorite entrepreneurs to follow , 34. what are some business opportunities today that you wish someone would tackle.
21 Unique Business Ideas for 2024
Unique business ideas across sectors and industries are waiting to be discovered. These businesses might cater to niche markets, invent and sell new products, or offer a traditional service in a new way.
Finding the right unique business idea can be a balancing act. You want to be different enough to stand out from the crowd, but not so different that there’s no market for your product or service. We’ll discuss the unique small business ideas that hit that sweet spot.
[su_note note_color="#dbeafc"] Click on any of the links below to jump straight to the section you want to learn more about, or just continue reading.
Top 21 Unique Business Ideas 2024
Unique service business ideas, unique cleaning business ideas, unique business ideas for small towns, unique online business ideas, unique business ideas for students, unique brick-and-mortar shop ideas, unique business ideas from home, unique business development ideas.
- Finding the Right Unique Small Business Idea [/su_note]
- Dog walking business
- Fingerprinting business
- Personal chef
- Remote cleaning business
- Ewaste collection and recycling
- Window cleaning business
- Flower shop
- Mobile veterinary services
- Specialty food store
- Virtual interior designer
- Online bakery
- Voiceover business
- Transcription business
- Pet sitting services
- AI book business
- Axe throwing business
- Sensory deprivation tank business
- Drone photography
- Furniture restoration business
- Custom treehouse business
You’ll find more information on each of these small business ideas, along with more unusual business ideas, in the article below.

1. Dog Walking
• Average Annual Revenue: $34K+ • Average Profit Margins: 16% • Startup Costs: $500-$5K • Time to Revenue: 3+ months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.7% • Best For: Animal lovers and experts, pet owners, people who like working outdoors
High demand puts a dog walking business among the best small business ideas for animal lovers to start in 2024. As of 2023, 65.1 million households in the U.S. own at least one dog, and many of those need help taking care of them. That’s a lot of potential customers for your new business venture.
Another plus of dog walking is the potentially low startup costs compared to other businesses. You can set up a profile on a site like Rover and start providing services locally right away with a very small budget.
2. Fingerprinting
• Average Annual Revenue: $132K+ • Average Profit Margins: 9.1% • Startup Costs: $500-$250K • Time to Revenue: 6-18 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: -0.6% • Best For: People with high professionalism, a commitment to security, and strong organization skills and attention to detail
Fingerprinting is another unique business idea with a potentially low initial investment.
These services have a broader customer base than many people realize, from criminal investigations to employment background checks and security clearances. If you’re able to attract customers and are skilled at providing customer service, fingerprinting can be a very lucrative business.
Dan Jurkowitsch is an expert in this unique niche market. He teaches people how to use this business model to start successful businesses. Hear his advice in this podcast interview:
3. Personal Chef Services
• Average Annual Revenue: $129K • Average Profit Margins: 51.7% • Startup Costs: $500-$5K • Time to Revenue: 1-6 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 0.9% • Best For: Culinary experts like chefs, cooks, and bakers with strong customer service skills
Being a personal chef is a great business idea for chefs who want to avoid the stress and high startup costs of food trucks and restaurants.
Since you work one-on-one with customers, it’s much less hectic and demanding, and you won’t need a brick-and-mortar space.
Connecting with your target audience is often the trickiest part of starting a personal chef business. Having an online presence for your business, including a website and a strong social media following, can be the best way to grow small businesses in this niche.
You can even expand this online presence into another revenue stream by offering online courses in cooking techniques or connecting your chef services to an online store selling ingredients or cooking supplies.

4. Remote Cleaning
• Average Annual Revenue: $74K+ • Average Profit Margins: 6.7% • Startup Costs: $500-$30K • Time to Revenue: 1-6 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.2% • Best For: System-driven and organized entrepreneurs who are tech-savvy with strong digital marketing skills
Offering cleaning services may not be a unique business idea on its own, but it is when you run that company completely remotely. You can set up an online booking system, hire remote team members, and run a cleaning business without ever setting foot in a customer’s home.
Neel Parekh launched his cleaning company, MaidThis, in 2013. Today, it brings in an average revenue of $166,000 per month using a 100% remote business model. Learn how Neel started and grew this unique business idea in the interview below:
5. E-Waste Collection and Recycling
• Average Annual Revenue: $5.7M+ • Average Profit Margins: 2.9% • Startup Costs: $100K-$3.5M • Time to Revenue: 6-18 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.9% • Best For: People who like physical work, entrepreneurs passionate about sustainability and the environment
Electronic waste, also known as e-waste, has been a growing problem over the past decade. Roughly 6.9 million tons are generated in the United States alone each year, of which only about 17% is properly recycled. Part of the problem is that many people don’t know how to properly dispose of electronics or lack services in their area to do so.
This makes an e-waste recycling service both a unique business idea with potentially high demand and a much-needed service to safeguard our natural resources.
This is another unique small business idea that could be done remotely. Kyle Landwehr started a junk removal business and has turned those systems into six-figure remote trash hauling businesses through the Junk Academy. Find out more in this podcast interview:
6. Window Cleaning
• Average Annual Revenue: $64K • Average Profit Margins: 8.8% • Startup Costs: $200-$5K • Time to Revenue: 3+ months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 0.9% • Best For: Detail-oriented and hands-on entrepreneurs who excel at customer service
One way to stand out with a cleaning services business is to focus on a niche. Window cleaning can be an extremely profitable option because it’s a relatively untapped niche with a potentially wide customer base.
Both residential and commercial customers have a need for window cleaning services. This is also something many people can’t do themselves, particularly for multi-story buildings.
On The Spot Window Cleaning has grown to a $45,000-a-month business since its founding in 1998. Learn how owner Jeremiah Hickey started and grew this small business idea in his podcast interview:

7. Flower Shop
• Average Annual Revenue: $262K+ • Average Profit Margins: 5.4% • Startup Costs: $100,000-$3.5M • Time to Revenue: 6-18 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 2.8% • Best For: Gardeners, florists, and other plant care professionals, creative entrepreneurs with a green thumb
A flower shop is among the best small-town business ideas. People everywhere love getting beautiful, sweet-smelling flower arrangements as a gift, but smaller towns often don’t have local businesses that provide the service.
Small business owners in the floral niche also have several options to add revenue streams. For example, you could sell herbs, potted plants, seeds, bulbs, and gardening supplies. You can also expand your customer base by selling edible flowers to local restaurants or partnering with other small businesses in the gift niche.
It doesn’t take much experience or business savvy to start a flower business. Dylan Capshaw started a flower business online when he was only 16. He’s since expanded it into a unique business, Stemistry, that combines a flower shop with a cafe. Hear his story in this podcast interview:
8. Mobile Veterinary Services
• Average Annual Revenue: $72K • Average Profit Margins: 11.5% • Startup Costs: $1K-$100K • Time to Revenue: 6-18 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.1% • Best For: Veterinarians, dog breeders and trainers, and other animal care experts
Being a veterinarian isn’t necessarily a unique business in its own right, but it is once you put it on wheels!
This is an innovative business idea for a small town or rural area. Pet owners in lower-population areas often have to travel a long distance to access vet care. Mobile services go to them, making transactions more lucrative because you’re giving customers much-needed convenience.
Granted, this unique business idea isn’t for everyone. You’ll need extensive training in animal healthcare. For those who already have this training, though, a mobile business model can be a great way to start a successful business venture.
9. Specialty Food Store
• Average Annual Revenue: $9.3M+ • Average Profit Margins: 1.8% • Startup Costs: $100K-$3.5M • Time to Revenue: 6-18 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 0.8% • Best For: Foodies, cooks, and food service professionals with strong organization and inventory management skills
People who live in small towns still enjoy unique food, but it can be hard to come by outside of large cities. This is why a specialty food store is an excellent small business idea for small-town entrepreneurs.
Successful business owners in the specialty food niche need to be responsive to customer demands. The key is to find out what items are missing from your local markets and fill that gap.
Communicating with locals, both in person and through social media, is a great way to predict which specialty foods will fly off the shelf in your town.

10. Virtual Interior Design
• Average Annual Revenue: $168K+ • Average Profit Margins: 10.6% • Startup Costs: $1K-$100K • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.2% • Best For: Designers, artists, and creative entrepreneurs, real estate industry and home staging professionals
The expansion of virtual tools has created lots of opportunities for unusual business ideas, one being virtual interior design. Designers in this niche use virtual design software to make furnishing and decoration recommendations completely remotely.
Having a website and a strong social media presence is crucial for success as a virtual designer. You can demonstrate your authority and aesthetic with an online portfolio, virtual design workshops, or online courses that teach interior design basics.
11. Online Bakery Business
• Average Annual Revenue: $1.52M • Average Profit Margins: 5.4% • Startup Costs: $100-$3M • Time to Revenue: 1-6 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.1% • Best For: Cooks, bakers, and food experts who are system-driven, organized, and tech-literate
Similar to a cupcake food truck business or bakery catering service, an online bakery business can be a great way to profit from your baking skills without the expense of a brick-and-mortar space.
Instead of buying products at a bakery, customers order their baked goods through an online interface and then get products delivered, either through the mail or local delivery.
Along with lower expenses, this mode allows the business owner to work at their own pace. It’s also easier to control inventory when you’re preparing baked goods to order rather than trying to anticipate the demands of hungry customers.
12. Voiceover Business
• Average Annual Revenue: $73K+ • Average Profit Margins: 3.7% • Startup Costs: $100-$500 • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 9.12% • Best For: Actors, singers, and performers who are patient, detail-focused, and excel at time management
If you’ve ever been told that you have a great voice for radio, then a voiceover business should be on your list of top small business ideas.
Voiceover artists take on a range of assignments, from voicing characters in cartoons and video games to reading audiobooks or content for apps like GPS systems. The main skills you’ll need are a clear speaking voice and the ability to read from a script.
The easiest way to start an online business in voice acting is to sign up for a freelance platform focused on the craft. Snap Recordings , Filmless , and Voice123 are among the most popular sites for building a career in this industry.

13. Transcription Business
• Average Annual Revenue: $25K+ • Average Profit Margins: 9% • Startup Costs: $0-$5K • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.9% • Best For: Good listeners with fast typing skills
Students need a business with low startup costs—and it doesn’t get any lower than 0. While some new transcription business owners pay for advertising to attract customers, you can start for free by taking jobs through sites like TranscribeMe or Rev .
If you can type at a speed of at least 60 words per minute, transcription can be a good business idea. You can also find free and low-cost software to make the job easier. Typically, transcriptionists work at their own pace, so this is also an easy business to schedule around your classes and other activities.
14. Pet Sitting Services
• Average Annual Revenue: $34K+ • Average Profit Margins: 16% • Startup Costs: $500-$5K • Time to Revenue: 3+ months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.7% • Best For: Animal lovers, pet owners, people who are patient, organized, and great communicators
Many students need to fit their small business ideas around studying and homework time. This is what can make pet sitting a perfect fit. While you’ll need to feed and care for the animals, a lot of your work is just keeping an eye on them—basically, you can get paid for hanging out with cats and dogs.
Building your client base can be the tricky part of getting started in this niche business. Many small business owners in the pet sitting niche build a client list through websites like Rover , Wag! , and PetSitter . You can also connect with clients through social media sites like Nextdoor.
15. AI Book Business
• Average Annual Revenue: Unknown • Average Profit Margins: 23.3% • Startup Costs: $500-$5K • Time to Revenue: 1-3 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 7.80% • Best For: Strong editors with knowledge of generative AI and digital marketing skills
Generative artificial intelligence (AI) has opened up a host of new business ideas. Using AI to generate books is one way to leverage this new technology into a lucrative business opportunity.
The key to success with an AI book business is knowing how to identify your target audience and market to them effectively. That’s how Joe Popelas made over $1M in his first year selling AI-generated books. Hear his story and advice in this podcast interview:

16. Axe Throwing Business
• Average Annual Revenue: $454K • Average Profit Margins: 9.91% • Startup Costs: $100K-$3.5M • Time to Revenue: 6-18 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.9% • Best For: Outgoing and fun-loving entrepreneurs with strong system-building and marketing skills
If you want to provide your area with a unique entertainment option, starting an axe-throwing establishment can be both a very fun and an extremely profitable business opportunity. Originating in Canada, this is a relatively new industry that’s skyrocketed in popularity over the past decade.
Along with charging customers for axe-throwing sessions, you can expand your revenue streams by hosting tournaments, selling memberships, or having an on-site shop that sells refreshments and merchandise.
17. Sensory Deprivation Tank Business
• Average Annual Revenue: $1.1M+ • Average Profit Margins: 12.07% • Startup Costs: $100K-$3.5M • Time to Revenue: 6-18 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.1% • Best For: Wellness-oriented entrepreneurs with strong customer service and marketing skills
First developed in the 1950s, sensory deprivation tanks (also known as flotation tanks or isolation tanks) have seen substantial growth in popularity in recent years. They can help people unplug from the distractions of modern life, so it’s no surprise that so many of them have popped up across the United States since 2020.
Ryan Duey’s transformative experience in a float tank led him to open his own flotation therapy spa, Capitol Floats. He’s since built on that business by making and selling his own cold plunge tanks and sensory deprivation tanks. Hear how he built his business in this podcast interview:
18. Cat Cafe
• Average Annual Revenue: $865K+ • Average Profit Margins: 5.8% • Startup Cost: $1K-$100K • Time to Revenue: 3+ months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.2% • Best For: Animal lovers, baristas and food service professionals
Some of the top unique businesses are twists on old classics. Cat cafes are one example of this, putting a new spin on the classic coffee shop.
Connecting with other businesses is a critical first step to opening a cat cafe. Primarily, you’ll need an animal partner that can provide well-socialized cats for guests to interact with (and adopt, if they fall in love with a floof during their visit).
Cat cafes can set up multiple revenue streams to increase their odds of success. This can include selling merchandise and pet-friendly snacks in addition to the typical cafe offerings. They can also charge an entrance fee for the cat space.

19. Drone Photography and Videography
• Average Annual Revenue: $50K • Average Profit Margins: 7.3% • Startup Costs: $1K-$10K • Time to Revenue: 1-6 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 0.3% • Best For: Photographers and visual artists, tech-literate and creative entrepreneurs
Drone photography is a relatively new industry, and that’s part of what makes it a good small business idea. While the market for photography services can be crowded, most photographers can’t take overhead shots. Offering that unique service can help a new small business owner stand out in their local market.
This niche business in the photography industry is often in high demand as a B2B business. For instance, real estate industry professionals use drone photography to sell their properties, while advertising professionals use it in commercials and other marketing materials.
Mile High Productions built a strong customer base of real estate agents, earning an average revenue of $35,000 a month. Learn how it grew in this YouTube interview:
20. Furniture Restoration and Flipping
• Average Annual Revenue: $111K+ • Average Profit Margins: 1.9% • Startup Costs: $100K-$3.5M • Time to Revenue: 6-18 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: 6.55% • Best For: Woodworkers, interior designers, creative entrepreneurs who like working with their hands
Furniture restoration is among the best home business ideas for makers, tinkerers, and other hands-on entrepreneurs. It lets you make a living from breathing new life into old things, which makes it sustainable and eco-friendly, as well.
The best business plan for a furniture restoration business often includes multiple services. You can restore pieces for clients or buy, fix up, and flip old furniture you find at thrift stores, flea markets, and antique stores.
Jennifer Beck started in furniture retail sales, then built on her passion for restoration into her own business with Saved By Design. Learn how she got started in this podcast interview:
21. Custom Treehouse Business
• Average Annual Revenue: $696K+ • Average Profit Margins: 3.4% • Startup Costs: $1K-$100K • Time to Revenue: 1-6 months • Annual Market Growth Rate: -1.3% • Best For: Carpenters, designers, and construction professionals with strong customer service and communication skills
Treehouses aren’t just for kids anymore. From unique Airbnbs to fun home offices and entertainment spaces, there are a variety of reasons people add custom treehouses to their properties.
You don’t have to only build treehouses, either. Often, business owners in this niche market build other backyard spaces for customers, like decks and sheds.
Anthony and Jamie Taylor-Weber and started their innovative business, Outdoor Office, from their home garage. Now, it brings in a revenue of $1.2M a year. See how they did it in this YouTube interview:
Having a unique business concept doesn’t need to mean you’re inventing a completely new thing from scratch. Here are some tips on ways to turn any concept into a unique business idea.
Take Your Business on the Road
Convenience is king in the modern world. Taking your product or service straight to customers can give you a definite leg up on your competition.
Mobile vet services are one example of this, and you can apply the concept to just about any niche. From food trucks to mobile clothing boutiques or hair salons, there’s a way to take just about any type of business on the road.
This approach has benefits for business owners as well as customers. It often costs less to start, for one thing, and has lower overhead expenses compared to brick-and-mortar shops. It also makes any type of business super-scalable—just buy another truck for the fleet, and you’ve effectively doubled your capacity.
Combine Compatible Ideas in New Ways
One of the businesses referenced above is Stemistry, a combination flower shop and coffee shop. By bringing these concepts together, Dylan Capshaw expanded his revenue streams and target audience.
A cat cafe is another example of this. People love cafes, and they love playing with pets—so why not put the two together into one place?
You can take the same approach with other business ideas. This can be a way to put a new spin on a familiar concept, or it can add profitability to a new idea that may take a while to gain traction otherwise.
Share Independent Research and Education Resources
You might think that teaching other people about your industry is counterproductive for growing business revenue. After all, if your customers know how to do things themselves, why would they pay you?
But think about it: most people know how to clean a home, but cleaning businesses are still very profitable.
Providing educational resources, like online courses, white papers, infographics, or how-to videos, establishes your authority in your industry. You can also use these as an additional revenue stream or as marketing materials to attract new customers.
Finding the Right Unique Small Business Idea
This list of unusual business ideas certainly isn’t comprehensive. There are unique business ideas not yet implemented in every industry. Now it’s time for you to go out and find the right one for you.
What is your favorite unique business idea? Let us know in the comments!
53 Best Franchises to Own in 2024
Are you looking for franchise opportunities? These are the best franchises to own in 2024. Most of these profitable franchises are household names, but there are a few surprises on the list, including cheap franchises to open.
We’ll help you find the top franchises of 2024!
[su_note note_color="#dbeafc"] If you want to jump ahead, just click any of the links to find a franchise for small business owners.
UpFlip Featured Franchises
- Where to Research Franchise Opportunities
- The 6 Best Franchises to Own
Start Your Own Business Under These Franchise Owners
Other great franchise businesses by industry, franchising definitions, can you get rich owning a franchise.
UpFlip has partnered with companies that specifically believe in providing business owners with the franchise tools they need to become profitable franchises. Some of our favorite franchises are:
- Wise Coatings
- Brown’s Pressure Washing
We’ll discuss these first.
#1. Wise Coatings
Brandon Vaughn started Wise Coatings with just $15,000. The majority was spent on marketing and learning how to work with the coating materials. There are currently 8 franchises and 140 applicants (and growing). The company helps with the marketing and systems you need to run the business right. This franchise opportunity requires:
• Franchise Fee : $50,000 • Total Investment : $117,400-$160,000 (including 3 months working capital) • Space Needed : 100-2,000 square feet • Employees : 2-4 employees (suggested) • Territories : Discounts for buying more than 1 • Franchising Funding Assistance : Yes, through Benetrends. Learn how to qualify .
Check out our interview with Brandon below.
#2. MaidThis
Neel Parekh started MaidThis in 2013 and today the company makes over $166K per month. They have 17 franchisees and are helping many small business owners start running a remote cleaning company.
• Franchise Fee : $39,000 • Total Investment : $50,400-$72,650 • Royalty Fee: 7% • Space Needed : 100-2,000 square feet • Employees : Work it yourself or hire employees. • Territories : You can buy more than one territory if they are available in your area. • Franchising Funding Assistance : Yes, through third-party financing services.
Check out our interview with Neel below.
Learn more about starting a remote cleaning business here .
#3. Brown’s Pressure Washing
Brown’s Pressure Washing is a franchise opportunity that UpFlip and Joshua Brown have created to help you start a turnkey pressure washing business. The licensing fee includes the video courses, website, boot camp, contract, territory, systems manuals, brand license, and access to the 24/7 online community. There’s also a 10% royalty that covers weekly coaching and admin support.
• Licensing Fee : $ 20,000 • Total Investment : $50,000-$100,000 • Royalty Fee: 10% • Space Needed : 100-2,000 square feet • Employees : Hire employees or subcontractors to do the cleaning • Territories : You can buy more than one territory if they are available in your area • Franchising Funding Assistance : Yes, through third-party financing services
Check out the free training for a sneak peek of what’s to come.
#4. Spray-Net
Carmelo started Spray-Net because he realized the painting industry needed modernization to speed up the process of painting. They have 40 franchisees and own patents on the process so nobody else can offer it.
• Franchise Fee : $45,000 • Total Investment : $170,825-$241,825 • Royalty Fee: 8% • Space Needed : 100-2,000 square feet • Employees : Hire employees or subcontractors to do the cleaning. • Territories : You can buy more than one territory if they are available in your area. • Franchising Funding Assistance : Yes, through third-party financing services.
Learn more about starting a painting franchise below.
#5. EverLine
EverLine Coatings is a Canadian company started by John Evans. They repair parking lots and the average franchise owner is making nearly $900K in the first year.
• Franchise Fee : $49,500 • Total Investment : $164,744-$332,443 • Royalty Fee: 9% or $500 per territory+ 3%—whichever is greater • Space Needed : 100-2,000 square feet • Employees : Hire employees to provide the services • Territories : You can buy more than one territory if they are available in your area • Franchising Funding Assistance : Yes, through third-party financing services.
Research Franchise Opportunities
Using the four ranking lists below, we researched franchise opportunities to establish which ones were the most attractive.
- Vetted Biz Most Profitable Franchises - Top 20
- Vetted Biz Most Popular Franchises - Top 20
- Franchise Direct Top 100
- Entrepreneur Top 500
To simplify the process, we reduced the top 100 and top 500 lists to just the top 20, then compared the franchises that appeared on each list.
What Are the Best Franchises to Own?

The best franchise to own will vary based on the demographics in your area, the franchises available, and the amount you have to invest. Based on a review of the various franchise opportunities and how ranking sites rate the franchises, I would start by considering:
- The UPS Store : Ranked Top 20 in 4 Different Lists
- Dunkin’ : Ranked Top 20 in 4 Different Lists
- Ace Hardware : Top 20 in 3 Different Lists
- Domino’s : Ranked Top 20 in 3 Different Lists
- Wendy’s : Ranked Top 20 in 3 Different Lists
- McDonald’s : Ranked Top 20 in 3 Different Lists
#6. UPS Store
If you’re wondering what is the #1 franchise to own, consider United Parcel Service (UPS) Store. UPS Store franchises are ranked #4 by Entrepreneur, #2 for profitability, #16 for popularity, and #17 by Franchise Direct. It is one of two franchises that are top-rated in all four expert lists and is not in the food industry (which many people will consider a positive). A UPS Store requires:
• Franchise Fee : $9,500 to $30K • Startup Costs : $80K-$510K • Liquid Assets : $75K
These are low-cost franchises with high profit. Learn more about UPS Store franchises .
#7. Dunkin’
I love donuts and coffee! How about you? Compared to some of the other major franchises in the fast food industry, Dunkin’ franchises are one of the cheapest franchises to start. You can get into a franchise for:
• Franchise Fee : $1K to $90K • Total Investment : $121K to $1.8M • Minimum Net Worth : $500K • Royalty Fee : 5.9% • Advertising Royalty : 2.5%
Learn more about Dunkin’ franchises .
#8. Ace Hardware
If you have a passion for hardware, you should consider Ace Hardware one of the best small business franchises. It’s ranked best in its category by Entrepreneur (7th overall), 9th by Franchise Direct, and 18th in the list of popular franchises. Their main qualifications are net worth, a solid reputation, and commitment to operational excellence. Check out their business-friendly requirements:
• Franchise Fee : none • Total Investment : $650K to $1M • Liquidity : $250K • Net Worth : $400K • Royalty Fee : none
Get more information from Ace Hardware .
#9. Domino’s

This pizza joint is the 7th most popular franchise, 12th most profitable, and ranked 8th by Franchise Direct in the top franchises 2022 list. There’s a catch, though. You can’t buy a franchise unless you work for the company. 95% of the Domino’s store location owners started working in a store. If you want to get into this franchise business model, go get a job as a GM or find a business partner that already works for the parent company.
• Franchise Fee : $0-$10K • Total Investment : $107K to $683K • Liquidity : $75K • Net Worth : $250K • Royalty Fee : 10.5-13.5%
The strategy of requiring franchisees to work for the company before buying a franchise makes this one of the best franchises to own for beginners. Find out more from Domino’s .
Check out their franchise promo video below.
#10. Wendy’s
The most expensive fast food restaurant is in the Top 20 on Entrepreneur, Franchise Direct, and the most popular franchise list. If you want to join the ranks of Wendy’s franchise owners, you’ll need:
• Franchise Fee : $50K • Investment : $330K-$3.7M • Net Worth : $1M • Liquid Cash : $500K
Find out more about Wendy’s franchise opportunities .
#11. McDonald’s
The world’s largest real estate owner uses the franchise business model and serves fast food. McD’s requires:
• Franchise Fee : $45K • Liquid Cash : $100K • Initial Investment : $1.4M- $2.5M • Royalty : 4% royalty • Advertising : Royalty: 4% or more
It’s not cheap to get into these profitable franchises, but they have the most proven business model on the planet. In fact, many other profitable franchise opportunities like Chipotle have replicated their business model with great success. Find out more about getting a McDonald’s franchise .

Next, we’ll cover franchises that made at least two of the lists. These include:
- Burger King
- Hampton by Hilton
- Jersey Mike's
- Snap-on tools
#12. Burger King

Burger King ranks among the most popular franchises globally, with more than 19,000 franchise locations around the world. Franchisees have the option of a traditional Burger King restaurant or an institutional or non-traditional location, such as within a college, corporate, or medical campus, or within a convenience store or rest area.
• Franchise Fee : $50,000 • Initial Investment : $1.7M-$4.2M • Net Worth : $1.5M • Royalty : 4.5% • Marketing Fee : 4%
Learn how to open your own Burger King franchise .
#13. Culver’s
Known for its butter burgers and frozen custard, Culver’s is among the most profitable franchises in the restaurant sector. It’s a great choice for hands-on owner-operators and has a high loan success ratio compared to other fast food franchises. The company is actively looking to expand, with 871 locations across 26 states as of early 2023.
• Franchise Fee : $55,000 • Total Investment : $2.3M-$5.8M • Net Worth : $1.25M • Royalty Fee : 4% • Advertising Fee : 2.5%
Get all the info to start a Culver’s franchise .
Check out their franchise video below.
#14. Hampton by Hilton
Ranked #9 on Entrepreneur’s Franchise 500 list, Hampton by Hilton is a leading hotel franchise, with 2,200 locations in the United States and more than 250 internationally. As a trusted name in hospitality, Hilton’s established brand name is a plus for prospective franchisees. Like many hotel businesses, however, it does have a relatively high initial investment and franchise fee, which may be an impediment to owning a franchise for some entrepreneurs.
• Franchise Fee : $75,000 • Total Investment : $7.6M-$20.6M • Royalty Fee : 6% • Advertising Fee : 4%
Read this Hampton by Hilton franchise information to get started.
#15. Jersey Mike’s
Jersey Mike’s is one of the top franchises for both popularity and profitability, ranked #3 on the Franchise 500 list for 2023 and with an impressive 74:1 SBA Loan Success Ratio. Franchisees get a built-in roadmap with full corporate support, excellent brand recognition, and a high success rate. If you want to be your own boss while serving fresh store-cooked roast beef on freshly-baked bread, Jersey Mike’s could be the right business opportunity for you.
• Franchise Fee : $18,500 • Initial Investment : $194,035-$954,611 • Liquid Cash : $100,000 • Royalty Fee : 6.5% • Ad Royalty : 5%
Learn more about starting a Jersey Mike’s franchise .

This popular fast food chain takes the top spot on Franchise Direct’s Top 100 franchises in 2022, in large part because of their strong franchisee support and the high financial stability of their parent company, YUM! Brands, Inc. KFC also offers business loan support for minority franchisees, guaranteeing 25% of the principal, up to $3 million per loan. The company’s active investment in diversity and inclusion puts them among the best franchise opportunities for diverse franchisees.
• Franchise Fee : $45,000 • Initial Investment : $1.4M-$3.1M • Net Worth : $1.5M • Royalty : 4-5% • Advertising : 5%
Get the info to start your own KFC franchise .
#17. Pizza Hut
Pizza Hut is an excellent business opportunity for franchisees who want to open multiple locations. They require owners opening new franchises to commit to at least two locations, with the end goal of owning five. Since Pizza Hut already holds a significant share of the American market, it’s possible to grow a successful franchise quickly and scale this success across multiple locations.
• Franchise Fee : $25,000 • Minimum Investment : $367,000-$2M • Net Worth : $700,000 ($350,000 liquid assets) • Royalty : 6% • Ad Royalty : 4.75%
Learn more about Pizza Hut franchises .
#18. Snap-on Tools
As the #1 tool franchise in the United States, Snap-on Tools is a trusted name among automotive repair professionals. The steady demand for automotive tools, combined with their proven track record of guaranteed quality, puts this among the best franchise opportunities for hands-on owners. The initial startup costs are very reasonable, especially given the size and reputation of the company.
• Franchise Fee : $8,000-$16,000 • Total Investment : $201,433-$465,436 • Discount for veterans : $20,000 off startup inventory cost • Net Worth : $38,126 • Royalty : $135/month
Get all the Snap-on franchise information to start your own.
Check out the Snap-on Tools franchise introduction video.
#19. Taco Bell
Taco Bell takes the #1 spot on the Franchise 500 list because it’s among the most profitable franchises to start. It’s under the same YUM! Brands, Inc. umbrella as KFC, and franchisees enjoy the same extensive business support and high brand recognition that sets them up to succeed.
• Franchise Fee : $25,000-$45,000 • Initial Investment : $575,600-$3.3M • Net Worth : $5M • Royalty : 5.5% • Ad Royalty : 4.25%
Get more information from Taco Bell .
#20. Subway

If you want to own your own business in the quick service restaurant industry, a Subway franchise is the most popular way to go about it. The brand has more than 44,000 locations across 100 countries, and that wide reach translates to high financial stability and a proven business model for franchisees to follow.
• Franchise Fee : $15,000 • Minimum Investment : $140,050-$342,400 • Liquid Assets : $30,000-$90,000 • Royalty : 8% • Ad Royalty : 4.5%
Learn more with this Subway franchise information .
#21. Wingstop
As a Wingstop franchise owner, you’ll join a network of more than 1,700 locations worldwide with an average unit volume of $1.59 million, among the highest sales per square foot in the industry.
• Franchise Fee : $20,000 • Total Investment : $315,310-$948,080 • Net Worth : $1.2M • Royalty : 6% • Ad Royalty : 6%
Start your own Wingstop franchise .
If all of these are a bit out of your price range, check out our blog about the cheapest franchises to start .
#22. 7-Eleven
Ranked #2 on Franchise Direct’s list, 7-Eleven is one of the most popular convenience stores in the world. With more than 80,000 locations, it’s an established brand customers know no matter where you want to open a business. That’s also good news when it comes to franchisee support and the company’s financial outlook.
• Franchise Fee : Varies by store ($0-$1M) • Minimum Initial Investment : $125,250 • Internal financing : Up to 65% of franchise fee • Royalty : Varies based on gross profit • Advertising Royalty : 1%
Learn more about opening a 7-Eleven franchise .
#23. Ameriprise
Ameriprise is among the most profitable franchises you can start in 2024. As one of the largest banks in the United States, Ameriprise offers franchise owners a loyal customer base, high brand recognition, and low ongoing fees. Owners also get equity ownership opportunities, mentorship, and turnkey marketing service.
• Franchise Fee : $1,500 • Minimum Investment : $11,434-$127,565 • Monthly Association Fee : $290 • Required : FINRA Series 7 and Series 63 or 66
If you can pass the Finra exams , this would be one of the best franchises to own under $100K.
Get more Ameriprise franchise information .

#24. Best Western Inn
Becoming a Best Western franchise owner gives you a voice in the company operations and the backing of a powerful global brand, while still maintaining full control over the property management and enjoying a low fee structure that lets you keep more of what you earn.
• Franchise Fee : $54,000-$94,000 • Initial Investment : $505,050-$10.3M • Royalty : 5%
Check out this Best Western franchise information .
#25. Choice Hotels International Inn
The franchisee-first focus of Choice Hotels puts them among the most profitable franchise companies in the hospitality sector, with over $7.8 billion in reservations across more than 7,100 franchise locations worldwide in 2021.
• Franchise Fee : $15,000-$60,000 • Initial Investment : $118,825-$26.3M • Liquid Cash : $1M • Royalty : 5-6% • Ad Royalty : 2.5-3.5%
Ready to get started? Read this Choice Hotels franchise information .
#26. InterContinental Hotels and Resorts (IHG)

The hotels under the IHG umbrella range from the well-known Holiday Inn and Regent brands to the boutique upscale experience of Hotel Indigo, Crowne Plaza, and Staybridge Suites. While it has the potential to be a very profitable franchising business, the high startup cost can be an obstacle to owning a franchise for some.
• Franchise Fee : $100,000 • Initial Investment : $81.2M-$118.3M • Royalty : 6%
Find out more about IHG franchise opportunities .
#27. Marriott International
Marriott is the world’s largest travel franchise, with 30 brands and more than 8,300 properties across 138 countries and territories. It’s also one of the most profitable franchise options for global franchisees, though like other hospitality franchises it can be costly to start.
• Franchise Fee : $120,000 • Total Investment : $82.9M-$136.8M • Room Sales Royalty : 6% • Food and Beverage Royalty : 3%
Learn more about Marriott franchises .
Check out the Marriot franchise promotional video below.
#28. Red Roof Inn
Red Roof Inn’s 90% franchisee satisfaction speaks to the support you’ll get as an owner. This profitable franchise opportunity comes with access to proprietary software, purchasing co-ops, and extensive marketing and branding materials, with lower startup costs than most hospitality franchises.
• Franchise Fee : $30,000 • Minimum Investment : $203,500 • Royalty : 4.5% • Ad Royalty : 4%
Here's all the pertinent Red Roof Inn franchise information you need to get started.
#29. Super 8

Another hotel franchise with a comparatively affordable financial requirement is Super 8 by Wyndham. It’s the world’s largest economy hotel brand, with more than 2,600 locations across four continents.
• Franchise Fee : $25,000 • Initial Investment : $221,026-$5.4M • Royalty : 5.5% • Ad Royalty : 3%
Find out more with this Super 8 franchise information .
Professional Services
#30. allstate insurance.
As an Allstate franchisee, you don’t just profit from your revenue, but also own equity in the business. The variety of product offerings gives agency owners lots of flexibility to maximize their earnings, and you don’t need prior insurance experience to get started.
• Franchise Fee : none • Licensing Fee : none • Liquid Cash : $100,000 • Veteran Discount : 25%
Get all the details: AllState Insurance franchise information .
Check out AllState’s franchise video below.
#31. CENTURY 21
Real estate agents can be their own boss by opening a Century 21 franchise. New franchisees receive comprehensive training to become licensed experts in the real estate market, so you don’t need to be an experienced realtor to start.
• Franchise Fee : $0-$25,000 • Total Investment : $24,700-$271,950 • Net Worth : $150,000 • Royalty : 6% • Ad Royalty : .5%
Start your own Century 21 franchise .
#32. RE/MAX

RE/MAX is a perennial presence on Entrepreneur’s list of top franchises to own, as well as one of the fastest-growing franchises for 9 consecutive years. For real estate agents, opening a franchise puts you in a network of more than 140,000 agents around the world and gives you access to a high commission concept that makes it easy to scale your profits.
• Franchise Fee : $17,500-$35,000 • Initial Investment : $43,000-$236,500
Learn how to start a RE/MAX franchise .
#33. H&R Block
Finding an H&R Block franchise for sale in your area secures you an exclusive territory that can range from a city neighborhood to an entire town. New franchisees receive extensive training on tax preparation, as well as strong ongoing support in marketing, lease negotiations, and other areas.
• Franchise Fee : $2,500 • Initial Investment : $31,557-$157,898 • Royalty Fee : 30%
Get started with this H&R Block franchise information .
#34. Jackson Hewitt
Another top franchise for tax professionals, Jackson Hewitt is among the largest in-person tax services in the U.S., and franchisees benefit from that established brand as well as corporate support and training.
• Franchise Fee : $7,500 • Initial Investment : $49,200-$81,805 • Net Worth : $100,000 • Royalty : 5-15% • Ad Royalty : 6.5%
Learn more: Jackson Hewitt franchises .
Gas Station and Automotive

#35. Chevron
Compared to other gas stations, Chevron franchises show a high loan success rate, which is proof of its profitability. Franchisees get ongoing support with all aspects of the business as well as multiple revenue streams to profit from.
• Initial Investment : $1.5M-$2.5M • Liquid Cash : $500,000
Read more about Chevron Franchises .
#36. Circle K
A Circle K franchise can be operated as a convenience store only, or you can add a gas station or quick-serve restaurant. That flexibility is one of the main advantages of becoming an owner.
• Franchise Fee : $25,000 • Initial Investment : $268,500-$2M • Net Worth : $500,000 • Royalty : 2.5-5.5 • Ad Royalty : 1.5%
Get the details on starting your own Circle K franchise .
Learn about owning a Circle-K below.
#37. Christian Brothers Automotive
Most people rely on their cars, giving an automotive repair franchise a built-in customer base. The company’s balanced work model, 2:1 franchisee support, and community focus are other advantages of becoming an owner.
• Franchise Fee : $135,000 franchise fee • Initial Investment : $520,250-$640,400 initial investment • Net Worth : $250,000 • Discount for Veterans : 10% off franchise fee • Ad Royalty : $10,000 per year
Learn how to start a Christian Brothers Automotive franchise .

#38. Bimbo Bakeries
Bimbo Bakeries offers a unique opportunity for owners to become distributors for the largest commercial baking company in the United States. It can have low startup costs for a food business, too, depending on which franchise model you go with.
• Franchise Fee : $8,000-$500,000 • Initial Investment : $14,000-$606,000
Become a Bimbo Bakeries distributor .
#39. Chick-fil- A
New franchisees for Chick-fil-A get 3-4 weeks of hybrid training and can expand beyond a single store once they’ve established themselves as an owner, making it easy to both get started and scale your profits over time.
• Franchise Fee : $10,000 • Initial Investment : $219,055-$2.9M • Ad Royalty : 3.25%
Ready to start your own Chick-fil-A franchise ? information
#40. Little Caesars
Little Caesars has a proven business model of pizza take-out and delivery and is actively seeking to expand its brand, both in the U.S. and internationally.
• Franchise Fee : $20,000 • Initial Investment : $221,000-$654,000 • Liquid Cash : $50,000 • Royalty : 6% • Ad Royalty : 3%
Learn how to open a Little Caesars franchise .
Learn more about Little Caesars franchises in the video below.
#41. Tim Hortons
Tim Hortons has long been Canada’s favorite coffee shop, and the brand’s expansion into the U.S. market means ample franchises for sale for coffee and food lovers looking for a profitable opportunity.
• Franchise Fee : $25,000-$50,000 • Initial Investment : $94,000-$2.1M • Liquid Assets : $500,000 • Royalty : 6% • Ad Royalty : 4%
Starting a Tim Hortons franchise is straightforward with the right info.
#42. Popeyes Louisiana Kitchen

The Louisiana-style flavors served from a Popeyes kitchen are a popular alternative to other fast food. Franchisees benefit from being part of a strong and growing brand, with extensive business support for owners.
• Franchise Fee : $2,500-$50,000 • Initial Investment : $109,500-$3.5M • Net Worth : $1M • Royalty : 5% • Ad Royalty : 4%
Learn more about Popeyes franchises .
#43. European Wax Center
With more than 750 locations in the United States, European Wax Center has grown into one of the largest beauty franchises in the country. Roughly two-thirds of their owners have multiple locations, making it a business franchise with high revenue growth potential.
• Franchise Fee : $45,000 • Initial Investment : $349,600-$553,950 • Net Worth : $1M • Royalty : 6% • Ad Royalty : 3%
Discover how to open a European Wax Center franchise .
#44. Great Clips

Great Clips is both the largest and fastest-growing haircutting brand worldwide, with a recession-proof business model that puts them among the top franchise organizations as a smart investment.
• Franchise Fee : $20,000 • Initial Investment : $178,400-$376,900 • Net Worth : $300,000-$1M • Royalty : 6% • Ad Royalty : 5%
This Great Clips franchise information is all you need to get started.
Watch this testimonial from a Great Clips owner.
#45. Sport Clips
Another top haircutting brand, Sport Clips has more than 1,800 locations open or in development and aims to expand further, opening up ample franchise opportunities for new owners.
• Franchise Fee : $30,000-$69,500 • Initial Investment : $266,300-$439,500 • Net Worth : $400,000 • Royalty : 6% • Ad Royalty : 5%
Learn more: Sport Clips franchise information .
Cleaning Businesses
For those who wonder what franchise can you open for $10,000, look to cleaning franchises!
Note that even the cheapest franchises to open cost more than our cleaning course by millionaire housekeeper Chris Mondragon. Get the exact recipe he used to make $1.5 million last year, and you could make money in the cleaning industry without all the ongoing royalties you’d pay the best cleaning franchises.
#46. Coverall
Coverall provides on-demand commercial cleaning across the U.S. and Canada. Franchisees get a proven business roadmap and the backing of a well-regarded brand when they sign their franchise agreement.
• Franchise Fee : $15,570-$40,320 • Initial Investment : $18,613-$51,392 • Royalty : 5%
Start your own Coverall franchise .
Watch Coverall’s franchise video.
#47. The Maids
As the exclusive partner of the famous Mr. Clean brand, The Maids offers cleaning services for residences and small businesses.
• Franchise Fee : $12K • Initial Investment : $10K to $80K • Royalty : 3.9% to 6.9%
Learn more about opening a franchise with The Maids .
#48. Jan-Pro

Jan-Pro is the #1 cleaning franchise, specializing in cleaning and disinfecting of spaces like schools, daycares, and healthcare facilities. Franchisees provide a necessary service under a trusted and established brand name.
• Franchise Fee : $2,520-$44,000 • Total Investment : $4,830-$58,070 • Royalty : 10% • Ad Royalty : 1%
Get all the details to open a Jan-Pro franchise .
#49. Augusta Lawn Care Services
Mike Andes is a brilliant entrepreneur who founded Augusta Lawn Care Services when he was a teenager, and today it’s one of the top 500 franchises in the U.S. and Canada. Their franchise opportunities offer low barriers to entry and flat fees instead of the standard percentage model. Here’s what it takes to become an Augusta Franchise:
• Franchise Fee: $6,999-$25,000 • Total Investment: $12,999-$82,500 • Royalty Fee: $699-$1.2K/mo. • Space Needed: 100-2,000 square feet • Employees: Solopreneur or hire other employees when starting a franchise • Territories: You can buy more than one territory if they are available in your area • Franchising Funding Assistance: Yes, through the Franchise Forgiveness Model
Learn more about starting a lawn care franchise below.
We have 16 more cleaning franchises for you to consider.
Work It! Twerk It!

#50. Anytime Fitness
Anytime Fitness is the first gym to have a presence on all 7 continents, with more than $87 billion in revenue worldwide and a new member joining every minute. Their simple onboarding and 360-degree support are other perks for franchisees.
• Franchise Fee : $42,500 • Total Investment : $381,575-$783,897 • Net Worth : $350,000 • Royalty : $699/month • Ad Royalty : $600/month
This Anytime Fitness franchise information will help you get started.
Learn what it’s like to own an Anytime Fitness below.
#51. Jazzercise
Jazzercise is one of the best franchises to own under $25K. Combined with their solid reputation and high profitability, it’s one of the best and most accessible franchise opportunities for active entrepreneurs.
• Franchise Fee : $1,250 • Initial Investment : $2,445-$21,775 • Royalty : 20%
Read more: Jazzercise franchise information .
#52. Orangetheory Fitness
This contemporary fitness studio uses scientifically-backed workout routines and a tried-and-true business model, with comprehensive corporate training and support for owners.
• Franchise Fee : $59,950 • Initial Investment : $589,129-$1.6M • Royalty : 8%
Here's all you need to know: Orangetheory Fitness franchise info .
#53. Planet Fitness

The judgment-free zone promised by Planet Fitness is a big selling point for their brand, as evidenced by their growth to 17 million members across 2,400 locations.
• Franchise Fee : $20,000 • Total Investment : $1.6M-$4.9M • Net Worth : $3M • Royalty : 7% • Ad Royalty : 9%
Learn more about opening a Planet Fitness franchise .
Franchises are a reliable way to start your own business, but there are some unique terms you’ll need to understand when comparing franchise opportunities. We’ll cover each definition to help you evaluate each franchise opportunity more thoroughly.
A franchisor is an organization that owns the intellectual property (IP) and the brand name. They license the IP to other business owners in exchange for a franchise fee. They may also have other fees and requirements you have to follow to run a franchise under their business name.

A franchisee is a business owner that has purchased the rights to use the business name, processes, and strategies from the franchisor. They will normally need to:
- Pay an initial franchise fee
- Prove the ability to pay the initial investment (startup costs plus operating costs until the franchise makes a profit)
- Undergo comprehensive training
- Pay ongoing marketing fees and royalty fees
Franchise Fee
When you buy a franchise, you’ll have to pay for the rights to use the intellectual property. This includes both an initial franchise fee and ongoing payments.
If you haven’t found a franchise that works for you yet, we have some other resources for you!
Check out these resources if you want to find more information on the best franchises to start.
- UpFlip's Franchise Buying Guide : Learn about the process of buying and why the cheapest franchises to start are not always the best.
- Reddit : If you search the best franchises to own Reddit, you’ll find lots of conversations about low cost franchise opportunities, experiences, and other input. Plus you can tell how much authority the person has by analyzing their Karma. It’s free of the paid placement and intentional bias of many search engines which is important when it comes to your money.
Plenty of people get rich buying a franchise location. Some only cost a few thousand dollars to get started, and once those costs are recouped, owners can make a great living. Just make sure you research
What area of the franchise business model would you like us to explore next?
nice work https://binarychemist.com/
My Name is PRETTY NGOMANE. A south African female. Aspiring to do farming. And finding a home away from home for the differently abled persons in their daily needs.
Become a business owner in less than 90 days
Start your 10-day free trial of the UpFlip Academy and learn how to start your own business from scratch.
Get business advice straight to your Inbox

- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans for April 2024 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How To Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices

Investment Company Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Investment Company Business Plan
Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 1,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their investment companies. On this page, we will first give you some background information with regards to the importance of business planning. We will then go through an investment company business plan template step-by-step so you can create your plan today.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
What is an Investment Company Business Plan?
A business plan provides a snapshot of your investment company as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It explains your business goals and your strategy for reaching them. It also includes market research to support your plans.
Why You Need a Business Plan for an Investment Company
If you’re looking to start an investment company, or grow your existing investment company, you need a business plan. A business plan will help you raise funding, if needed, and plan out the growth of your investment company in order to improve your chances of success. Your business plan is a living document that should be updated annually as your company grows and changes.
Sources of Funding for Investment Companies
With regards to funding, the main sources of funding for an investment company are bank loans and angel investors. With regards to bank loans, banks will want to review your business plan and gain confidence that you will be able to repay your loan and interest. To acquire this confidence, the loan officer will not only want to confirm that your financials are reasonable, but they will also want to see a professional plan. Such a plan will give them the confidence that you can successfully and professionally operate a business. Investors, grants, personal investments, and bank loans are the most common funding paths for investment companies.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
How to write a business plan for an investment company.
If you want to start an investment company or expand your current one, you need a business plan. Below we detail what you should include in each section of your own business plan:
Executive Summary
Your executive summary provides an introduction to your business plan, but it is normally the last section you write because it provides a summary of each key section of your plan.
The goal of your Executive Summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the type of investment company you are operating and the status. For example, are you a startup, do you have an investment company that you would like to grow, or are you operating investment companies in multiple markets?
Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your business plan. For example, give a brief overview of the investment company industry. Discuss the type of investment company you are operating. Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target customers. Provide a snapshot of your marketing plan. Identify the key members of your team. And offer an overview of your financial plan.
Company Analysis
In your company analysis, you will detail the type of investment company you are operating.
For example, you might operate one of the following types of investment companies:
- Closed-End Funds Investment Company : this type of investment company issues a fixed number of shares through a single IPO to raise capital for its initial investments.
- Mutual Funds (Open-End Funds) Investment Company: this type of investment company is a diversified portfolio of pooled investor money that can issue an unlimited number of shares.
- Unit Investment Trusts (UITs) Investment Company: this type of investment company offers a fixed portfolio, generally of stocks and bonds, as redeemable units to investors for a specific period of time.
In addition to explaining the type of investment company you will operate, the Company Analysis section of your business plan needs to provide background on the business.
Include answers to question such as:
- When and why did you start the business?
- What milestones have you achieved to date? Milestones could include the number of investments made, number of client positive reviews, reaching X amount of clients invested for, etc.
- Your legal structure. Are you incorporated as an S-Corp? An LLC? A sole proprietorship? Explain your legal structure here.
Industry Analysis
In your industry analysis, you need to provide an overview of the investment industry.
While this may seem unnecessary, it serves multiple purposes.
First, researching the investment industry educates you. It helps you understand the market in which you are operating.
Secondly, market research can improve your strategy, particularly if your research identifies market trends.
The third reason for market research is to prove to readers that you are an expert in your industry. By conducting the research and presenting it in your plan, you achieve just that.
The following questions should be answered in the industry analysis section of your business plan:
- How big is the investment industry (in dollars)?
- Is the market declining or increasing?
- Who are the key competitors in the market?
- Who are the key suppliers in the market?
- What trends are affecting the industry?
- What is the industry’s growth forecast over the next 5 – 10 years?
- What is the relevant market size? That is, how big is the potential market for your investment company? You can extrapolate such a figure by assessing the size of the market in the entire country and then applying that figure to your local population.
Customer Analysis
The customer analysis section of your business plan must detail the customers you serve and/or expect to serve.
The following are examples of customer segments: companies or employees in specific industries, couples with double income, families with kids, small business owners, etc.
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will have a great impact on the type of investment company you operate. Clearly, couples with families and double income would respond to different marketing promotions than corporations, for example.
Try to break out your target customers in terms of their demographic and psychographic profiles. With regards to demographics, include a discussion of the ages, genders, locations and income levels of the customers you seek to serve.
Psychographic profiles explain the wants and needs of your target customers. The more you can understand and define these needs, the better you will do in attracting and retaining your customers.
Finish Your Investment Company Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Competitive Analysis
Your competitive analysis should identify the indirect and direct competitors your business faces and then focus on the latter.
Direct competitors are other investment companies.
Indirect competitors are other options that customers have to purchase from that aren’t direct competitors. This includes robo investors and advisors, company 401Ks, etc. You need to mention such competition as well.
With regards to direct competition, you want to describe the other investment companies with which you compete. Most likely, your direct competitors will be investment companies located very close to your location.
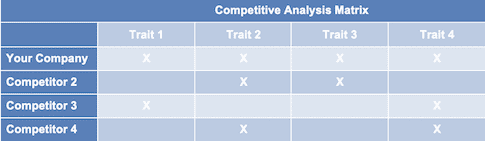
For each such competitor, provide an overview of their businesses and document their strengths and weaknesses. Unless you once worked at your competitors’ businesses, it will be impossible to know everything about them. But you should be able to find out key things about them such as:
- What types of clients do they serve?
- What type of investment company are they and what certifications do they have?
- What is their pricing (premium, low, etc.)?
- What are they good at?
- What are their weaknesses?
With regards to the last two questions, think about your answers from the customers’ perspective. And don’t be afraid to ask your competitors’ customers what they like most and least about them.
The final part of your competitive analysis section is to document your areas of competitive advantage. For example:
- Will you provide better investment strategies?
- Will you provide services that your competitors don’t offer?
- Will you provide better customer service?
- Will you offer better pricing?
Think about ways you will outperform your competition and document them in this section of your plan.
Marketing Plan
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P’s: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For an investment company, your marketing plan should include the following:
Product : In the product section, you should reiterate the type of company that you documented in your Company Analysis. Then, detail the specific products you will be offering. For example, in addition to an investment company, will you provide insurance products, website and app accessibility, quarterly or annual investment reviews, and any other services?
Price : Document the prices you will offer and how they compare to your competitors. Essentially in the product and price sub-sections of your marketing plan, you are presenting the services you offer and their prices.
Place : Place refers to the location of your company. Document your location and mention how the location will impact your success. For example, is your investment company located in a busy retail district, a business district, a standalone office, etc. Discuss how your location might be the ideal location for your customers.
Promotions : The final part of your investment company marketing plan is the promotions section. Here you will document how you will drive customers to your location(s). The following are some promotional methods you might consider:
- Advertising in local papers and magazines
- Commercials and billboards
- Reaching out to websites
- Social media marketing
- Local radio advertising
Operations Plan
While the earlier sections of your business plan explained your goals, your operations plan describes how you will meet them. Your operations plan should have two distinct sections as follows.
Everyday short-term processes include all of the tasks involved in running your investment company, including researching the stock market, keeping abreast of all investment industry knowledge, updating clients on any new activity, answering client phone calls and emails, networking to attract potential new clients.
Long-term goals are the milestones you hope to achieve. These could include the dates when you expect to land your Xth client, or when you hope to reach $X in revenue. It could also be when you expect to expand your investment business to a new city.

Management Team
To demonstrate your investment company’s ability to succeed, a strong management team is essential. Highlight your key players’ backgrounds, emphasizing those skills and experiences that prove their ability to grow a company.
Ideally you and/or your team members have direct experience in managing investment companies. If so, highlight this experience and expertise. But also highlight any experience that you think will help your business succeed.
If your team is lacking, consider assembling an advisory board. An advisory board would include 2 to 8 individuals who would act like mentors to your business. They would help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. If needed, look for advisory board members with experience in managing an investment company or successfully advised clients who have achieved a successful net worth.
Financial Plan
Your financial plan should include your 5-year financial statement broken out both monthly or quarterly for the first year and then annually. Your financial statements include your income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statements.
Income Statement : an income statement is more commonly called a Profit and Loss statement or P&L. It shows your revenues and then subtracts your costs to show whether you turned a profit or not.
In developing your income statement, you need to devise assumptions. For example, will you take on one new client at a time or multiple new clients? And will sales grow by 2% or 10% per year? As you can imagine, your choice of assumptions will greatly impact the financial forecasts for your business. As much as possible, conduct research to try to root your assumptions in reality.
Balance Sheets : Balance sheets show your assets and liabilities. While balance sheets can include much information, try to simplify them to the key items you need to know about. For instance, if you spend $50,000 on building out your investment company, this will not give you immediate profits. Rather it is an asset that will hopefully help you generate profits for years to come. Likewise, if a bank writes you a check for $50,000, you don’t need to pay it back immediately. Rather, that is a liability you will pay back over time.
In developing your Income Statement and Balance Sheets be sure to include several of the key costs needed in starting or growing an investment company:
- Cost of investor licensing..
- Cost of equipment and supplies
- Payroll or salaries paid to staff
- Business insurance
- Taxes and permits
- Legal expenses
Attach your full financial projections in the appendix of your plan along with any supporting documents that make your plan more compelling. For example, you might include your office location lease or list of clients that you have acquired.
Putting together a business plan for your investment company is a worthwhile endeavor. If you follow the template above, by the time you are done, you will truly be an expert. You will really understand the investment industry, your competition, and your customers. You will have developed a marketing plan and will really understand what it takes to launch and grow a successful investment company.
Investment Company Business Plan FAQs
What is the easiest way to complete my investment company business plan.
Growthink's Ultimate Business Plan Template allows you to quickly and easily complete your Investment Company Business Plan.
What is the Goal of a Business Plan's Executive Summary?
The goal of your Executive Summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the type of investment company you are operating and the status; for example, are you a startup, do you have an investment company that you would like to grow, or are you operating a chain of investment companies?
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your Investment Company business plan?
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success. Click here to hire someone to write a business plan for you from Growthink’s team.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates


Business Planning: Ultimate Guide to Writing a Business Plan for Investors

If you are planning to start, grow or sell a business, it is almost essential you have a plan of attack.
A traditional business plan is much more than a general list of things that you need to do.
An effective plan focuses on short-term and long-term business goals, with information that outlines how you intend to reach them.
A formal business plan will be one of the most valuable tools that you will use in raising capital from investors and for building and growing your business.
Like the businesses themselves, business plans come in many types and forms.
Oftentimes even established business owners and managers underestimate the effectiveness of a qualified business plan.
Some mistakenly think business plans are only used in the venture capital world of start-up finance.
This simply is not true. Enterprise planning is often required for anything from SBA lending and debt financing to internal planning and partnership qualification.
Many find they regularly refer to a previously-written business plan to ensure they stay on track and under budget.
A business plan can also help you establish a framework for your dream business, including structure and planning goals.
In addition, business planning is often a fluid process and a living document, with changes occurring mid-stream which means those best prepared have already done their homework and are prepared to pivot.
Crafting Your Business Plan(s)
Discovering a business idea, introductory page, executive summary, industry analysis, description of the venture, production or service plan, marketing plan, organization and management, assessment of risk, financial plan, start-up plan, internal plans, operations plans, growth plans, type 1 and type 2 business plans, type 3 and type 4 business plans, type 5 business plan, type 6 business plan, benefits of an outsourced business plan, business plan executive summary, financial statements & financial plan, how long should a business plan be, expert forecasting, market estimates from past data, common sense market estimations, porter’s five forces – industry, porter’s five forces, porter’s five forces – macroenvironmental factors, macroeconomic forces, legal/political forces, social & cultural forces, technological forces, demographic forces, global forces, porter’s five forces – scorecard, capital costs, economies of scale, brand loyalty, absolute cost advantages, customer switching costs, laws & regulation, summary of barriers to entry , defining market type boundaries, a recap of market boundaries , the importance of the tim, tam, sam, tm and som, scalable, high growth company, successful, mid-sized privately held businesses, lifestyle businesses, target marketing, time expectations as an entrepreneur, business plan writing, why write a business plan, standard evaluation and review, the business plan writing process, terms & conditions, pricing & cost of your business plan, business plans for financing, pro forma financial plans, marketing business plan.
You will essentially create two plans. The first is known as the internal or initial start-up business plan . This plan includes your company’s mission statement, product/service description, marketing strategy plan and initial start-up goals. Most importantly, the initial plan will also include a market analysis. Performing research on the market helps both internal managers understand whether the business concept or business idea is viable and worth pursuing and to attract investors.
If it is, the initial plan will morph into something suitable for angel investors, venture capitalists and private equity groups. Typically, your final secondary plan will incorporate the details in your initial start-up plan into a more finalized version ready for publication. InvestmentBank.com assists throughout this entire process.
How you go about your business plan process is dependent on the audience for which it will be created.
For example, if you will be seeking a business loan, you need to create business plan for bank loans . Conversely, if you are seeking investment capital in equity financing, you’ll most likely need a venture capital business plan . Regardless of the audience any typical business plan will generally include the following:
- A company description, including a description of your business and the products and/or services offered
- A detailed description of the target market and how they will best be served
- Information regarding the management team and key employees within the company
- Detailed information about cash flow and financial analysis, budget and market penetration
- An Executive Summary for a snapshot 30,000 foot view of all aspects of the business and how it will be successful
Discovering a business idea is the first step towards creating a business model hypothesis. Specifically, a business idea worth investigating further is a “proto-business model” – the embryo of a viable business model. The business idea is essentially your best guess that describes your Value Proposition (the thing you want to sell) and your Customer Segment(s) (the target customers you want to sell to). This is your initial pass at creating a viable Value Proposition – Customer Segment “fit”.
At a minimum, a business idea worth investigating further should have one or more Customer Segments and a corresponding Value Proposition to match each Customer Segment. Completing the following steps will validate that your business idea is worth investigating further.
- Identify Value Proposition – Customer Segment pairings. This step involves pinpointing the type and number of Customer Segment(s) your business is going to serve and what your business’s Value Proposition will be for each of those Customer Segments. This will create one or more Value Proposition – Customer Segment pairings.
- What your Customer Segment is trying to do (i.e. eat dinner, find a date, get in shape…). What are your Customer Segment’s problems (they are hungry and don’t want to cook, they can’t find a suitable boyfriend/girlfriend, they are out of shape…). What does your Customer Segment expect to gain from accomplishing whatever they want to do (eat a tasty meal, find a pleasant date, loose a few pounds and feel better)?
- What your company can offer your Customer Segment (i.e. a good quick meal, a matchmaking service, a place to work out…). How will your offer solve your Customer Segment’s problems? What benefits will your offer create for your Customer Segment? The best business solves real-world problems.
Business Plan Outline
A business plan may contain many types of information depending on the nature, size, and financing needs of the company. One general business plan template can be developed with the help of our JDs, MBAs and expert business planning professionals. While various institutions like the Small Business Administration (SBA) help provide guidelines, it is often best to get your detailed business plan drafted by professionals who know what it takes to get funded and what investors are looking for when they sift through thousands of plans.
This is the title or cover page. This page will contain the information of the names and addresses of business enterprise and entrepreneurs, a paragraph describing the nature of business, and the vision and mission statement of the company.
An executive summary of the comprehensive business plan report should be presented within four pages, summarizing the whole report and emphasizing on business purpose, industry analysis, market opportunity, key elements of the business, revenue, and planning.
This segment of a viable business plan will show the present conditions of the industry, in which the entrepreneur desires to enter. This section should include present and future outlook and demographic developments, analysis of competitors, market segmentation, and industry financial forecasts.
In this segment of the business plan a detailed picture of the venture should be outlined with particular reference to products, services, office equipment, machinery, personnel, size of business, and background of entrepreneurs.
This portion of the business plan is indeed an operational plan. The operational activities of manufacturing, trading and service business are different. So the operational plans of different types of enterprises will be different. For example operational plan of a manufacturing business may cover unique aspects such as manufacturing process,equipment, names of the providers of the raw materials and other inputs of the production process, and so on.
It includes market condition, market strategy, and future market prospect. The pricing, promotion, distribution, product forecasts, and controls should be evaluated carefully for the business plan.
This section includes forms of the ownership, identification of partners or major shareholders, the authority of the managers, management-team background, and the duties and responsibilities of members of the organization.
It is very important for any business plan to assess all the possible risks that may affect the enterprise, prior to starting the business. Assessment of risk must include evaluation of the weaknesses of the enterprise, latest technologies, and contingency plans.
This section shows financial viability of the business plan, in which the entrepreneur must prepare forecasted income statement, cash flow estimates, forecasted balance sheet, break-even analysis, and sources and usages of funds. This section will be scrutinized to determine the profitability and sustainability of the enterprise by the investors, such as the bankers or venture capitalists.
It contains all the backup materials such as legal documents, market research data, lease contracts, and price forecasts from suppliers.
These are the general contents of a business plan that are suggested by the experts, but these contents may vary from business to business. A good business plan should be comprehensive enough to provide a complete picture and understanding of the venture regarding its present status and future growth potential to the prospective investors and other interest groups.
Business Plan Types
Traditional business plans come in many types. They include strategic plans, expansion plans, investment plans, growth plans, operational plans, internal plans, annual plans, feasibility plans, product plans, and many more.
The various types of business plans will always matche the specific business situation. For instance, it is not necessary to add all the background information that is known already, while preparing a plan to use internally and not circulating it to financial institutions or investors. Investors always look for information on the description of the management team, while bankers always look for financial background or history of the company.
The various types of business plans are due to the specific case differences:
Start-up plan is the most standard plan that explains the steps for a developing new business. Start-up plans often include standard topics such as the organization, product or service offering, market place, business forecasts, strategy, management team, implementation milestones, and financial analysis. Sales forecast, profit and loss statement, cash flow statements, balance sheet, and probably a few other tables are included in the financial analysis.
First year monthly projections are shown in the start-up plan, which usually begins with an abstract and ends with appendix.
Click on the following link to learn more about how we approach startup investing .
Business plans that are not usually intended for external investors, financial institutions, or any other third parties are called Internal plans. A detailed description of the organization or the management team may not be included in it. Detailed financial projections like budgets and forecasts may or may not get included in Internal plans. Instead of presenting the whole business plan in the form of paragraph text, Internal plans display the main points in the form of bullet points in slides.
Operations plan can be referred to as Internal plan, which is also known as an annual plan. More detailed information on specific dates, implementation milestones, deadlines, and teams and managers responsibilities are given in Operations plan.
Strategic planning usually does not focus on specific responsibilities and detailed dates, rather it focuses on setting high priorities and high-level options and is also referred to as an internal plan. Unlike most other internal plans, it includes data in the form of bullet points in slides. Organization or management team descriptions are not included in it. Also, some of the financial information is not explained in detail and left while preparing strategic plans.
Some business plans focuses on specific areas of the business or a subcategory of the business, and these plans are referred to as a growth plan or an expansion plan or a new product plan. Depending on whether these business plans are linked to new investments or loan applications, they could be classified as internal plans or not. For instance, like a start-up plan developed for investors, an expansion plan that requires new investment would also have detailed description of the company and its management teams background data. These details will also be required for loan applications. But, these descriptions are skipped in an internal business plan, which is used to design the steps for growth or expansion that is funded internally within the organisation. Although, detailed financial projections might not be given, forecast of the sales as well as the expenses for the new business venture is at least included in more detail.
A very simple start-up plan is the feasibility plan, which include an abstract, mission statement, market analysis, keys to long-term success, and initial cost analysis, pricing, and projected expenses. Feasibility plans helps to analyze whether it is good to continue with a plan or not, to find if the business plan is worth continuing.
Writing a business plan is a highly collaborative affair between the entrepreneur(s) and the business plan writer. The more complex the plan is, the more both the entrepreneur(s) and the business plan writer will need to communicate and collaborate in order to produce a professional, marketable business plan. The business plans we write fall into six general categories. We will discuss each in detail below.
These are business plans for new companies that are 1) trying to raise startup capital to launch the business and 2) the business will serve a clearly defined target market with a service or product that already exists. These business plans are usually the least complex to write because the business models
The hourly fee for work over the project’s estimated number of hours is $20 per hour.
Type 1 and Type 2 business plans are written in five distinct units. Each unit reflects a progressive step in putting the business plan together. Before we can begin writing each unit, we must receive feedback to specific questions that we will send you concerning the topics covered in each specific unit. After we complete each of the first four units, we will send you a draft of that unit in a Microsoft Word document. You will then have the opportunity to review unit draft and critique or clarify it.
We will make any necessary changes needed for each unit draft. The fifth and final unit will be integrating the information in each of the previous four units into a final, complete business plan. You will then have the opportunity to review and critique that completed business plan draft. We will then correct any and all discrepancies in that final complete draft.
The entire business planning process of writing a Type 1 or Type 2 business plan depends upon our general workload and the speed with which you respond to our requests for information about your business. We estimate that either a Type 1 or Type 2 business plan will take generally 10 to 15 work days to complete (two to three weeks).
These are business plans for existing companies that are 1) trying to raise capital for a new business project or idea and 2) the business project is serving a clearly defined market with a service or product that already exists.
Type 3 and Type 4 business plans are written in six distinct units. Each unit reflects a progressive step in putting the business plan together. Before we can begin writing each unit, we must receive feedback to specific questions that we will send you concerning the topics covered in each specific unit. After we complete each of the first five units, we will send you a draft of that unit in a Microsoft Word document. You will then have the opportunity to review the draft of each unit and critique or clarify it. We will change or modify any discrepancies you have with the drafts of each unit. The final unit will be integrating the information in each of the five units into a final, complete business plan. You will then have the opportunity to review and critique that completed business plan draft. We will then correct any and all discrepancies in that final complete draft.
The entire process of writing a Type 3 or Type 4 business plan depends upon our general workload and the speed with which you respond to our requests for information about your business. We estimate that either a Type 3 or Type 4 business plan will take generally 15 to 20 work days to complete (three to four weeks).
These are business plans for classic startup companies that are trying to create new products or services to serve new or reimagined markets. These companies are usually looking to raise equity capital from angel investors and venture capital firms. These business plans are far more difficult to write because their business models are largely unproven.
Type 5 business plans are written in five distinct units. Each unit reflects a progressive step in putting the business plan together. Before we can begin writing each unit, we must receive feedback to specific questions that we will send you concerning the topics covered in each specific unit. After we complete each of the first four units, we will send you a draft of that unit in a Microsoft Word document. You will then have the opportunity to review unit draft and critique or clarify it. We will make any necessary changes needed for each unit draft. The fifth and final unit will be integrating the information in each of the previous four units into a final, complete business plan. You will then have the opportunity to review and critique that completed business plan draft. We will then correct any and all discrepancies in that final complete draft.
The entire process of writing a Type 5 business plan depends upon our general workload and the speed with which you respond to our requests for information about your business. Also, the novelty and newness of the industry you are entering and the market you will be serving are real wild card variables in terms of how much time the business plan will take to complete. We estimate that a Type 5 business plan will take generally 25 to 40 work days to complete (five to eight weeks).
These are business plans for existing companies that are attempting to create new products or services to serve new or reimagined markets. The markets these companies are trying to serve with their new products and services are either undefined or completely new. Usually these companies are seeking financing to raise equity capital (because these business projects are usually risky), but sometimes raising debt capital may be an options for them. These business plans are as difficult to write as Type 5 plans.
Type 6 business plans are written in six distinct units. Each unit reflects a progressive step in putting the business plan together. Before we can begin writing each unit, we must receive feedback to specific questions that we will send you concerning the topics covered in each specific unit. After we complete each of the first five units, we will send you a draft of that unit in a Microsoft Word document. You will then have the opportunity to review the draft of each unit and critique or clarify it. We will change or modify any discrepancies you have with the drafts of each unit. The final unit will be integrating the information in each of the five units into a final, complete business plan. You will then have the opportunity to review and critique that completed business plan draft. We will then correct any and all discrepancies in that final complete draft.
The entire process of writing a Type 6 business plan depends upon our general workload and the speed with which you respond to our requests for information about your business. Also, the novelty and newness of the industry you are entering and the target market you will be serving are real wild card variables (in terms of how much time the business plan will take to complete). We estimate that a Type 6 business plan will take generally 25 to 40 work days to complete (five to eight weeks).
Running a Business Is Tough, Especially Without a Business Plan
If you are running a business, it’s very important to have a business plan made up and it’s just as important to stick to your business plan once you create it. When you have a business plan you are setting objectives for yourself and you are establishing the priorities you have for your business. It also makes it much easier to reach the goals that you set for yourself as well which is always crucial in a business.
Think of your business plan as a map for your business, without this map you and the way you run your business are traveling blindly which is very dangerous. You want to have a clear idea of where your business is headed and where you want it to go and a business plan outlines what will steer you in the right direction.
Looking for a Loan?
If you are looking to get a loan for your business, you’re going to need a definite business plan. Most banks won’t even consider giving you a loan until they see a business plan. If you don’t have a business plan they’ll think of you as a risk since you don’t truly know where you want your business to go. When you present your business plan to a bank to get the loan you desire be sure that you go over what your business is all about and why you started it. You will also want to list for them what you see in the future of your business as well.
Looking for a Business Investment?
Having a business plan doesn’t mean that you will surely get the investment you desire but not having a business plan will surely mean you will not get the investment you desire. Investors need to know what exactly they are investing in and they will look to your business plan to understand what the idea of the business is, your businesses track records, the technology behind your business and of course yourself. You will absolutely not get a business investment without having a business plan because the investors won’t have anything to help them understand what your business is all about.
Have Business Partners?
A business plan is what defines your agreements that you have made with your business partners which means you’ll have a lot of issues if you don’t have a business plan if you are in this business with more than just yourself. A business plan is the only way to keep everything between you and your partners fair and it ensures that everyone knows what the ground rules are for the business and where each and every one of you stand.
Communicating with a Management Team Won’t Work Without a Business Plan
How can you and your management team effectively run your business without being able to see where you all want it to go? The answer is, you can’t. You can’t steer your business down the right path if nobody knows exactly where it should be going and your management team will feel the exact same way. There will be a lot of different problems that will come up during the day-to-day work and it will be very challenging for you to face them and communicate all of these problems when you or your management team don’t truly know where the problem falls under in the business plan.
Do you need a business valuation?
Whether you need to place a value on your business to sell it or for taxes, a business plan is an essential part in this. It’s always important to know what your business is worth even if you don’t plan on selling it at all, you may need to know what it’s worth when it comes to planning an estate or an unexpected divorce could come up. You always should know what your business is worth an a business plan will help you understand that and keep track of it.
When it comes to developing a business plan, many people believe that it’s too difficult or it’s just too time consuming to do but what those people don’t realize is that putting together a business plan will save you in many ways and you it will help your business in more ways than you can imagine.
Developing a business plan is not that much of a challenge and it will very valuable to you in the future. Nobody should ever try to do something big without planning it first and this includes running a business. You have all these business plans in your head so just lay those plan out on paper so you have tangible evidence of your business and what you want to do with it.
A business plan a very crucial part in creating and owning a business so take the time and effort in creating one and you will benefit from it much more than you think and you’re business will run much more smoothly.
A business plan’s executive summary section provides a round-up of the main points of your business plan. Although the summary will appear at the top of the final printed piece, the majority of business plan developers do not write the executive summary until the last moment. The summary forms the gateway to the remainder of the plan. If you do not write a business plan executive summary it well, your target audience will not read beyond the executive summary.
What should be included in an executive summary?
When a regular business plan is being written, the following should usually be incorporated into the opening paragraph of the executive summary:
• The name of the business • The location of the business • The service or product being offered • The aim of the plan
A further paragraph should underline significant points, for example projected profits and sales, profitability, unit sales, and keys to success. Give the details you need everyone to notice. This is also a sensible point at which to include a highlights chart, a bar chart depicting gross margin, profits before taxes and interest, and sales for the three years to come. These numbers must be explained and cited in the text.
Different summaries are required for different plans
Internal plans, for example annual or strategic plans, or operations plans, do not need such formal executive summaries. With such a plan, make its purpose obvious, and be certain that all the highlights are mentioned, but other details – such as the description of your service or product, and location – may not need to be repeated.
Be concise with your summary
If investment is what you are seeking, mention this in your executive summary, specifying the amount of investment required and the level of equity ownership that will be provided in return. It is also a good idea to include some highlights regarding your competitive advantage and your management team.
If it is a loan that you are looking for, say so in the executive summary, specifying the sum required. Do not include details of the loan.
What is the right length for an executive summary? There are differing views from experts about the ideal length of an executive summary. Some recommend taking only one or two pages, while others suggest a more in-depth approach, with the summary lasting for anything up to ten pages and including sufficient information to be used instead of the full plan. Although it was once common to write business plans of 50 or more pages, today’s lenders and investors expect a more focused, concise plan.
A single page is the perfect length for an executive summary. Keep everything brief, emphasizing the major aspects of your plan. You are not trying to explain every last detail, simply piquing your readers’ interest about the rest of the plan and encouraging them to read further.
Be careful not to confuse a summary memo with an executive summary. The executive summary is the opening section of a business plan, while a summary memo is a distinct publication, usually running to no more than five or ten pages; this is intended as a substitute for the full plan for the benefit of those who are not yet in a position to read the full plan.
In general, a financial plan is a set of steps or goals put together for the business which is intended to help attain and accomplish a final financial goal. It shows the future and current financial state of a business by using known variables to forecast future cash flows, asset values and withdrawal plans. The plan shows financial viability of the business plan, in which the entrepreneur must prepare forecasted income statement, cash flow estimates, forecasted balance sheet, break-even analysis, and sources and usages of funds.
Why is a financial plan important? Investors and bankers must have an incentive to invest in your business. Profitability gives them an incentive to invest. If your plan is weak and unorganized it will portray your business as unsustainable. Investors and banks will see you only as a risk and be unlikely to give the kind of capital needed for your business. For this reason you need to create a solid financial plan which will convince investors that your business is worth investing in.
Here at InvestmentBank.com we will design for you a financial plan intended to demonstrate to the bank and your investors that your business is sustainable and profitable. We cannot guarantee you the investments you are hoping for, but we can guarantee that if you don’t have a plan, you will also not receive your hopeful investments. Let us guide you in the planning process.
One core component of market analysis is market forecasting and proforma financial statement drafting. The future trends, characteristics, and numbers in your target market are projected in market analysis. In a standard analysis process, the projected number of potential customers is divided into segments.
Generally, market size is not the only factor that is determined, but the market value is also very important. For instance, small business customers spend around 4 times as much as the home office customer, even though they are 2.5 times smaller than their high-end home segment in terms of customer size. So, in terms of dollar value, the small business market is often considered very important.
Market value is calculated through simple mathematics. The number of potential customers in the market is multiplied by the average purchase per customer. Market value is calculated by taking the average number of customers in each segment over a period of time and then multiplied that figure by the average purchase per customer. In market analysis table, the other items are only subjective qualities that help with marketing. These points are allotted to people who are assigned in preparing marketing information.
Reality Checks Reality checks are always important for market forecast. Finding a way to check reality, while performing a forecast is essential. If you are able to estimate your total market value, then you would relate that figure to the estimate sales of all their competitors to check if the 2 figures relate to each other. The import and export value and production values are checked in an international market to find whether the annual shipments estimates appear to be somewhere in the same range as the estimated figures. To check your results with the forecast, you might also check for some given years with the vendors, who sold products to this market. Macroeconomic data can also be overlooked to confirm the size of this market compared to other markets with same characteristics.
Target Focus Review
Market analysis should help in the development of strategic market focus, which means selecting the key target markets. This is considered the critical foundation of strategy. We speak on this as market positioning and segmentation.
Company will not try to address the needs of all market segments under normal circumstances. While selecting target market segments, understand the inherent market differences, competitive advantage, keys to success, and strengths and weaknesses (SWOT analysis) of your organization. Everyone wants to focus on the best market segment, but the market segment with the maximum growth or the largest market segments, might not be necessarily the best one to address. The best market segment to address would be the one that matches your own company profile.
It is not a good idea to use page count as a gauge to determine the length of a business plan. A business plan with 20 pages of text alone can be considered to be longer than a 35-page plan which is well laid out with bullet points, helpful images of products or locations and charts that highlight vital projections.
In fact, a plan should be measured by its readability as well as the summary provided. If the business plan is prepared keeping these aspects in mind, the reader will be able to get an overall idea in about 15 minutes by quickly browsing through the key points.
Illustrations, headings, format and white space contribute to improving the appeal of the business plan. The summary section is a very important aspect of any business plan. The salient points of the business plan must be clearly visible to the reader as it is done in a presentation.
It is unfortunate that many people still tend to measure the worth of a business plan by the number of pages in it. In this connection, some of the key aspects to be kept in mind are as follows:
- Practical business plans prepared for internal use only can have five to ten pages
- Business plans of large companies may have hundreds of pages
A standard expansion or start-up plan prepared for presentation to outsiders can have 20 to 40 pages. However, it should be easy to read with text well spaced and have bullet point formatting, illustrations in the form of business charts and financial tables in the condensed form. The details of financial aspects can be organized in appendices.
However, the length of the business plan is decided by its nature and the purpose for which it is prepared. Some of the questions that can be considered when drafting out a business plan in order to decide on its length are:
- Should descriptions about the company as well as the management team be included as outsiders are likely to read the business plan?
- Should a standalone executive summary be provided for the business plan?Is there a need to incorporate plans, blueprints, drawings and detailed research?Is it an investment proposal?
- Should it be worded in such a way as to clear legal scrutiny?
The form of the business plan is actually decided by the requirement for which it is to be prepared.
Often, venture contests specify a limit of 30 pages or 40 pages at times, but rarely 50 pages, including the appendices that contain detailed financial statements, for a business plan. Some contestants make very bad options because of page restrictions and cram the content using thick texts and bold typefaces, making it worse and not better.
Most often, good plans have as many as 30 to 40 pages . The plans have 20 to 30 pages of text, excluding graphics to illustrate locations, menus, designs, etc. and appendices consisting of team leaders’ resumes, monthly financial projections, etc. Some pages may have to be included for standard financials. This calls for tables for sales, income and cash flow statement, balance sheet and personnel on a monthly basis. In the body of the plan, annual numbers may also have to be included.
It is not prudent to reduce the length of the plan by cutting down on helpful graphics. Readability is more important than the length. Making use of business charts to illustrate numbers makes it easier to understand. Make use of drawings and photographs to depict locations, sample menus and products. It is important to use as much illustration as possible. Finally, extra graphics such as clip art that are not relevant to the matter at hand may better be avoided.
Business Plan Market Forecast
Proper market forecasting helps provide budgetary allocation for coming market trends, innovative shifts and internal financial allocation. It is a key component of proforma financial statements and professional market research . Intelligent estimates are best backed by quality, time-intensive research. That’s where we come in. Rather than producing a business plan based on educated guesswork, we use a litany of some of the industry’s best market research tools available to some of the most prestigious universities. Many a business plan software tools can also aid in your research work. Typically business plan software also includes industry-specific templates, which can help with how you approach your niche or even the broader market.
Today’s technology provides access to large data-sets for current and past information. Obtaining the data is not difficult. We help to analyze, interpret and make qualitative assumptions about future trends. By using both qualitative and quantitative approaches we work to derive parallel data forecasts for future trends within your business, your industry and the market as a whole. The future may be uncertain, but with the help of expert modeling, it can be simplified, understood and, in some cases, accurately predicted.
Many business planners lack the luxury of funding a previously-published market forecast from which to glean relevant data. In many cases, free published forecasts can help to paint a meaningful picture. However, when professional forecasts are not forthcoming on market size, supply/demand metrics and potential company penetration, it is usually left up to thoughtful opinion and expert “reverse engineering” to determine any meaningful dribble from the data.
Without free forecasts, a business owners may feel forced to purchase expensive data sets, market research reports and published articles to determine helpful data about the potential of a business idea. Where we can, we utilize past relationships and access to thousands of reports through expensive subscriptions to find the data-set that best fits your business goals for the plan you may be crafting.
Apart from the more obvious sources like the Internet, library references and popular publications, we provide access to industry-specific reports and paid-for research studies not accessible to would-be entrepreneurs. We fully recognize that data forecasting is part art and part science, but we prefer to adhere to more quantitative methods so as to make your business plan as convincing and relevant as possible for its particular audience.
Extrapolation of past data with large populations and data-sets helps to provide reliable predictions about future trends and outcomes. Understanding past growth, market saturation and the competing forces that can impact a company’s success in market entrance are absolutely vital components of the marketing portion of your business plan. Past data is never a fail safe, but it can act as a healthy gauge of future trends in a marketplace.
When no relevant data on current conditions within your market can be found, we work with the available numbers to create plausible models that form convincing arguments for your particular plan goals.
Perhaps the greatest downfall of many potentially-successful business plans is the disconnect between gathered data, assumptions, external and internal market forces and projections. Without a common sense litmus test, many plans fail to deliver relevant metrics to help make business funding possible. Performing common sense tests often requires qualitative work outside the realms of the given data. Making phone calls to Chambers of Commerce, trade organizations and market reporting agencies to obtain a wider base and deeper foundation of information is extremely helpful when crafting assumptions.
Making wild guesses about targets, markets and industries without thoughtful research can be detrimental to fulfilling the goals of your particular business plan. BusinessPlanning.org helps to remove the guesswork and provide your business with relevant data from which to tell a compelling story.
Correctly identifying the structure and competitive dynamics of the industry you are proposing to enter will create a good general point of reference for judging whether you should enter it or not. If the general industry profile does not appear attractive to you, and you are planning to offer value propositions that have close industry substitutes, then this may be an important signal that your proposed venture may need to be reconsidered. But if the industry profile looks attractive, then this could be a sign that you are on to something.
A fantastic tool to analyze an industry that serves a Defined Existing Market is Porter’s Five Forces Model. Michael Porter is a professor at Harvard Business School and published this strategy model in his seminal work, Competitive Strategy . Porter’s model is powerful. It demonstrates how an industry’s attractiveness to either its current competitors or a new entrant is an amalgam of disparate, and sometimes contradictory, factors.
To help determine if your business idea will be worth the investment of time, money and energy, you will conduct two sequential analyses using the Five Forces Model. The first Five Forces analysis will be of the overall industry that you are contemplating to enter. The second Five Forces analysis will be of the particular market segment(s) you would be choosing to serve with your Value Proposition(s).
The figure below illustrates how Porter’s model works by focusing on the five forces that shape competition within an industry: 1) the risk of entry by potential competitors, 2) the intensity of the rivalry among established companies within an industry, 3) the bargaining power of suppliers, 4) the bargaining power of buyers, and 5) the similarity of substitutes to an industry’s value propositions.[1]
The main point of Porter’s Five Forces Model is as follows. The stronger that one of the five competitive forces becomes, the greater the overall competitive rivalry becomes within the industry. The more intense the competitive rivalry becomes, the harder it is for ventures within the industry to raise prices or maintain high prices to reap greater profits. The less in average profits that a firm in the industry is able to earn, the more intense the rivalry for customer demand is among the industry’s rival competitors.
The opposite is true also. The weaker that one of the five competitive forces becomes, the less intense the overall competitive rivalry among the industry’s firms is. If rivalry amongst the industry’s firms decreases, the easier it becomes for the industry’s competitors to raise either raise prices or reduce their cost structure (by lowering their value propositions’ quality) and ultimately earn higher profits. The higher the average level of industry profits, the less intense the rivalry for customer demand will be among the industry’s rival competitors.
The importance of each of the five forces is situationally dependent upon the unique facts and circumstances of each industry. For example, the overall threat of new market entrants might be insignificant in determining whether an entrepreneur wants to enter an industry in its growth phase, but it may be a paramount factor in a mature industry.
I developed another diagram (below) to show how the five forces within Porter’s model interact with each other. As you can see, four of the forces (risk of entry by potential competitors, bargaining power of suppliers, bargaining power of buyers, and threat of new entrants) each act upon the fifth force – the intensity of rivalry among the industry’s competitors. This means that if the bargaining power an industry’s buyers increases, the intensity of rivalry among industry competitors will increase. This causal relationship works in only one direction – a change in any of the forces ultimately either increases or decreases the intensity of rivalry among the industry’s competitors. Therefore a change in the intensity of rivalry will not cause change in one of the other four forces.
[1] Charles W. L. Hill and Gareth R. Jones, Strategic Management Theory , Eighth Edition, Houghton Mifflin Company, pg. 45, 2008.
Macroenvironmental forces are changes in the broader economic, political/legal, social, technological, demographic, and global forces beyond the industry being examined. Any one of these six forces can change or effect any one of an industry’s five internal competitive forces. In conducting an industry’s initial Five Forces analysis – which is a snapshot measurement of an industry’s present competitive environment – these macroenvironmental forces are automatically accounted for. They are already included because an industry’s competitive environment is an aggregate of these turbulent and often conflicting forces. But entrepreneurs and business owners must also make educated guesses about how macroenvironmental trends and forces will shape the industry’s attractiveness into the future, both in the short run and in the long run.
Below is a diagram that visually represents how each of these seven forces can affect an industry’s Five Forces as the future unfolds.
The Six Macroenvironmental Forces
The following is a detailed analysis of the seven macroenvironmental forces touched upon above.
Macroeconomic forces affect the general economic well-being of the nation or the region in which an industry operates. [1] The following are the major macroeconomic forces that can affect an industry’s ability to deliver an adequate economic return.
- The rate of growth for the economy. Economic expansions cause a general rise in aggregate consumer demand while recessions cause a general drop in aggregate consumer demand. Because aggregate demand for goods and services rises during economic expansions, an industry’s intensity of competitive rivalry, broadly speaking, will usually decline. The reason is that generally the market demand for an industry’s value propositions will cause an expansion in the industry’s revenue. Therefore its possible for the industry’s firms to generate revenue growth without fighting their competitive rivals for market share. Conversely, a decline in economic growth or a recession causes general aggregate demand to contract. This generally shrinks the amount of revenue an industry can earn and may cause price wars, consolidations and bankruptcies.
- Interest rates. Interest rates affect the cost of borrowing for consumers, thus affecting aggregate demand. Higher interest rates generally makes the cost of borrowing more expensive and can dampen demand for real estate and purchases of major assets (cars, durable goods). Ultimately, higher interest rates can lead to higher industry rivalry if the industry is directly or tangentially affected by borrowing costs. Higher interest rates also affect business’ cost of capital. High interest rates may restrict a business’s ability to invest in new equipment or facilities. On the other hand, low cost of capital makes it substantially easier for established businesses to borrow and invest into expanding their operations.
- Exchange rates. Exchange rates either make imports more or less expensive for domestic consumers and exports more or less expensive for foreign consumers of domestically produced value propositions. A weak dollar makes imported value propositions more expensive and domestically produced value propositions comparatively less expensive. A strong dollar makes foreign value propositions less expensive and domestic value propositions comparatively more expensive.
- Inflation/Deflation. Inflation is the decrease in the purchasing power of a nation’s currency over time. Inflation can destabilize an economy, slow economic growth, higher interest rates and increased currency volatility. [2] Increasing inflation makes business planning very difficult because the future becomes less predictable. Uncertainty makes companies unwilling to invest in growing their operations. On other side of the coin is deflation. Deflation is even more potentially damaging than inflation is. If the purchasing power of currency is increasing over time, firms and consumers will hoard their cash. This will causes a self-reinforcing cycle of low or negative economic growth. Usually the best inflation formula for stable economic growth is a low, steady inflation rate.
- Wage Levels. The price of labor from industry to industry can have a significant impacts on an industry’s costs of production. High or increasing industry labor costs can make substitute value propositions more attractive for the industry’s customers. Low or decreasing industry labor costs can make substitute value propositions less attractive for the industry’s customers.
- Level of Employment: High unemployment levels give firms greater leverage over their employees in keeping wage increases down or in actually decreasing labor costs to the firms in an industry. This can reduce the industry’s cost structure and thus raise the industry’s average profitability.
Legal and political forces are the results of changes in laws and regulations within the country your business operates in. [3] Political and legal developments can be both opportunities and threats. The following are the major legal and political changes that can impact the fortunes of industries.
- Current and Expected Levels of Taxation. High tax rates can affect the decisions of entrepreneurs to engage in business activities or reduce the ability of companies to reinvest profits in expansion. But often the most important effect of taxes are not the levels of taxation, but the different effective tax rates for different activities. For example, the oil and gas industry, ecommerce businesses and the video game industry get significant tax breaks that reduces their effective tax rate. This can raise or lower the attractiveness of getting into certain industries.
- Import/Export Quotas and Tariffs. Tariffs and import/export quotas affect the costs of value propositions imported into a country and those exported to other countries. Raising or lowering tariffs or trade quotas can cause demand for the value propositions of the industries affected to increase or decrease. An example of a broad change in trade quotas and tariffs was the implementation of the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA).
- Government Grants. Government grants are programs that can provide nascent industries with seed capital and resources. Governments (state, local and national) often provide businesses with financial support if the business pursues profit opportunities that align with a government’s policy goals. An example of a significant government grant program is the U.S. government’s Small Business Innovation Research grant (SBIR).
- War/Terrorism. War and terrorism can increase regulations and transaction costs associated with global travel or insurance. Wars can also saddle nations with large medical costs to society. Wars and anti-terrorism efforts can also increase military related contracting opportunities.
- Quid Pro Quo. Many industries try (and often succeed) in influencing politicians to enact laws that are favorable to their bottom line and create barriers of entry against potential competitors. A recent example of this was the influence the health care and pharmaceutical industries exerted upon the U.S. Congress during the passage of the Affordable Care Act in 2009.
- The Regulatory State. In the U.S., most of the regulations that affect business and the general public are promulgated through various government agencies. Often, small changes in regulations can lead to desired or unintended consequences for a number of industries. Here is a small sample of legal and regulatory issues that are managed by various state and federal agencies: environmental protection, corporate governance, intellectual property rights, employment law, criminal law, tort law, food & drug regulation, public health… In the United States (and most other industrialized countries), virtually every area of commerce is affected by government regulations and laws. For any given industry, changes in these regulations and laws can be either threats or opportunities.
Social forces are changes in the social mores and values of a society and how they affect any particular industry. Social changes can create both opportunities and threats for any industry.
- Social and cultural forces specifically refer to changes in the tastes, habits and cultural norms within a significant segment of a country’s population. One example of a social trend is the growth of the organic and local food movements in the U.S. over the last thirty years. The local and organic food movements have created an opportunity for some small farmers near large population centers, but this movement has also created a potential threat to large mono-agriculture farms.
- Cultural attitudes can shift drastically over time, rendering once commonplace habits and activities to no longer be widely accepted or tolerated. An example is the decline of smoking in the U.S. Smoking used to be tolerated in most indoor spaces forty years ago. Now it is either banned or highly frowned upon and the public has become very aware of the health risks smoking causes. This has led to a significant decline in the percentage of adults in the U.S. who smoke. Conversely, marijuana use, which was highly frowned upon by the majority of U.S. society over forty years ago, has become more widely accepted among the public. As a result, many state laws are changing to reflect this increased tolerance of marijuana use.
- Changes in what society considers fashionable are in a constant state of flux. Various fads and crazes rise and fall, sparking opportunities and threats for the industries that capitalize on these trends. Examples of changes in fashion, fads or crazes are: rock n roll in the 1960s, disco music in the 1970s, the Pet Rock, the Hula Hoop, Cabbage Patch Dolls…
Technological change is a primary driver of Schumpeter’s “perennial gale of creative destruction” among business ventures. Technological forces can render established, profitable value propositions obsolete virtually overnight and usher into existence exiting new business ventures. Because of the dual role technological change (both creative and destructive) plays in our society, it can be both an opportunity and a threat.
- Technological forces can cause industries to move through their life cycles more quickly. They can also disrupt an industry in the beginning or middle of its life cycle, rendering it obsolete or changing it so radically that most of the industry’s competitors cannot keep up. Essentially, technological change makes the life cycles of industries more volatile and unpredictable.
- Technological change can lower the barriers of entry for many industries. An example is the internet made it much easier for a potential retailer to sell products to its customers through a virtual storefront versus acquiring, stocking and running a brick and mortar facility. The lowering of barriers of entry tends to increase an industry’s intensity of rivalry, leading to both lower prices and industry profits.
- Technological forces can also reduce transaction costs. Reducing transaction costs is often destructive to the industries that thrive on them (auction houses being replaced by eBay or newspaper classifieds being replaced by Craigslist). Within an industry, a reduction in transaction costs driven by technological change usually leads to an increase in the industry’s intensity of competitive rivalry.
- Technological change can either reduce or increase customer switching costs. An example of how technological forces can reduce customer switching costs are instant price comparison applications on mobile devices. These give the consumers the ability to identify which retailers offer the same value propositions at the lowest prices. Technological forces can also increase customer switching costs. An example is Facebook or eBay. Both of these websites lock in users due to their network effects – alternative market choices do not present as much value because they are not as big.
- Technological forces can unleash changes in industries far removed from the industry in which the technology originated. An example of this is the Internet. The Internet has caused massive sea changes in industries only tangentially related to it such as retail, the news industry, book publishing, and matchmaking services (online dating).
Demographic forces are changes in the characteristics of a population of people. These characteristics can be sex, age, education, race, national origin, social class… Changes in demographics can present businesses with both opportunities and threats.
- Changes in a population’s age distribution can present both opportunities and threats. For example, in the U.S., the population of elderly people is growing more rapidly than the population as a whole. This presents an opportunity for industries who provide long term assisted living, the financial industry (reverse mortgages and retirement planning), and both the health and pharmaceutical industries. It also presents a threat to certain industries like funeral and burial providers (if the general population is living longer, it means people are dying at a slower rate).
- The rapid increase of the Hispanic population in the U.S. has led to an increase in Spanish speaking music, television and news in the U.S. This represents a growing opportunity for food and media companies that market to Latinos.
Global forces are changes that occur within and beyond the borders of the country a business is operating within and affect how a company can operate on the international stage. Global forces can present both opportunities and threats to an industry.
- The economic growth rates of other countries can play important roles in determining the demand for imports and exports. As barriers to trade fall, national economies become more subject to the winds of international commerce and capital flows. This international liberalization of trading agreements can allow domestic firms greater access to foreign markets. An example of the liberalization of international trade is the outsourcing trend over the last two decades from industrial economies in the west to developing economies in Asia.
- Climate change is another example of a global force. The long term changes to the world’s climate will profoundly shape countless industries in the decades to come. Climate change can offer both opportunities and threats to different industries. For example, the wine industry in France may have to experiment with new varietals due to changes in temperature and rainfall expected by scientists in the coming decades. Climate change also presents some industries with opportunities. One example is the shipping industry. The rapidly dwindling polar ice cap in the Arctic Ocean presents the possibility that new, more efficient shipping routes might become available.
[1] Charles W. L. Hill and Gareth R. Jones, Strategic Management Theory , Eighth Edition, Houghton Mifflin Company, pg. 66, 2008.
[2] Charles W. L. Hill and Gareth R. Jones, Strategic Management Theory , Eighth Edition, Houghton Mifflin Company, pg. 68, 2008.
[3] Charles W. L. Hill and Gareth R. Jones, Strategic Management Theory , Eighth Edition, Houghton Mifflin Company, pg. 70, 2008.
A good Five Forces analysis will cause you to sift through a lot of data, much of it conflicting and confusing. Below is a series of scorecards that try to condense the most important points from your Five Forces analysis and present them to you in an easily understandable format.
The scorecards rate the attractiveness of an industry’s five forces from the perspective of a new venture attempting to enter the industry . Each force gets its own scorecard. Each scorecard has the main factors that help determine the strength the force exerts upon the industry. A factor’s attractiveness is rated on a five category scale that ranges from Highly Unattractive, Mildly Unattractive, Neutral, Mildly Attractive, to Highly Attractive. For each factors’ rating, the top line (yellow) indicates the level of the factor’s level of attractiveness at present. The bottom line (green) is the entrepreneur’s rating of what he or she thinks each factors’ level of attractiveness will be in the future. The level of future attractiveness for a factor is determined by analyzing how macroenvironmental forces will affect the industry in the future.
Directly below is a hypothetical example scorecard of an industry’s intensity of rivalry:
Remember, none of this is exact science. There is no mathematical formula that determines whether you should enter an industry or not. The purpose of this exercise is to ensure that you, the entrepreneur, have thoroughly thought about the nature and future of the competitive environment you are proposing to jump into.
Force One: Intensity of Rivalry among Industry Competitors
Force Two: Risk of Entry by Potential Competitors
Force Three: The Bargaining Power of Buyers
Force Four: The Bargaining Power of Suppliers
Force Five: The Availability and Similarity of Substitutes to an Industry’s Value Propositions
And finally, the table below is a final snapshot evaluation of the industry’s attractiveness. To fill out this table, you should look at your ratings in the tables above as guidelines. The importance of the forces, and the factors that comprise them, will change from industry to industry. It will ultimately depend upon the unique facts and circumstances of each industry being evaluated. Therefore you will have to use your best judgment.
Overall Evaluation of Industry’s Attractiveness
Porter’s Five Forces – Risk of Entry
Profitable industries are like chum in the water for new competitors. The smell of money to be made will attract potential competitors to circle an industry, try to enter it and look for an easy meal. The only thing stopping a myriad of potential competitors from entering an industry are barriers to entry – a business version of a steel shark cage.
Profitable industries attract new market entrants – potential competitors. Potential competitors are companies that are not currently competing in an industry, but possess the ability to do so if they choose. Theoretically, if it cost nothing to form a company and enter an industry serving a profitable market, new firms would flood into that industry until the industry’s average profit margin shrank to zero. But we don’t live in a frictionless, theoretical world and different industries have wildly different levels of profitability. Barriers of entry are what discourages new companies from entering a profitable market and making a killing.
Barriers of entry benefit established companies within an industry by protecting them from new competition and preserving their profit margins. Low barriers of entry leave an industry wide open to new market entrants. The results to an industry with low barriers of entry are lower profits for the companies within that industry will inevitably result.
Therefore, established firms within an industry have great incentive to erect barriers of entry to keep the number of potential rivals to a minimum. Some barriers of entry are passive and a natural result of the industry’s operations. An example of this is economies of scale. But companies often take active steps to discourage new companies from entering their industries. Examples of this are when companies create brand loyalty or try to purposely raise their customers’ switching costs. The reason is simple – the more companies that enter the industry, the more difficult it is for established companies to maintain their market share and protect their profits.
The risk of entry by potential competitors is a function of the industry’s profitability and the height of its barriers to entry. The higher an industry’s average profit margin, the more enticing it is for new competitors to jump into the fray and wrestle market share from the incumbent companies. High barriers to entry can deter potential competitors from trying to enter an industry and serve its market segments. The higher the cost of entry into an industry, the weaker the competitive force (the risk of entry by potential competitors) is and generally translates into higher average industry profits. Important barriers to entry include the following:
Capital Requirements – If it takes a great amount of money or assets to enter the industry, this can be a significant barrier of entry for firms who wish to enter it. Usually industries with high fixed costs have high capital requirements (i.e. factories, warehouses, computing assets…).
Economies of Scale – Economies of scale is where the companies in an industry enjoy diminishing per unit costs for their value propositions as the volume produced increases.
Brand Loyalty – Consumers often have preferences for the value propositions offered by established companies due to familiarity and reputation.
Absolute Cost Advantages – Other entrants cannot hope to match the established firms within the industry’s cost structure. Absolute cost advantages arise from three sources: 1) possessing unique and critical resources (patents, trade secrets, or accumulated experience), 2) control of particular inputs of production (i.e. fertile farm land, a prime piece of commercial real estate…), 3) access to cheaper funds because existing companies represent lower risks than new entrants.
Customer Switching Costs – High customer switching costs occur when customers resist spending the time, money and energy to switch from the current supplier of a value proposition to one offered by a different company, even though that alternative value proposition may be of greater value.
Government Regulation – Government regulations, and the lack of them, can be a significant barrier of entry for potential new entrants into an industry. An example of this would be environmental regulations placed on coal mining companies and their operations.
We will now dig deeper into how to identify and analyze these potential barriers of entry, and ultimately understand how they affect the competitive rivalry within an industry.
Capital costs mean the startup costs of your business idea that must be incurred before you can commence operations. Basically, this is the total amount of money you need to spend (on equipment, employees, facilities, legal, accounting….) before you can hang your “Were Open!” sign in your shop window. For some asset intensive businesses, such as a full service health club or a golf course, initial capital costs can be extensive. For other businesses that use relatively few assets, such as an internet marketing business or a hotdog stand, initial capital costs can be relatively small.
For many aspiring entrepreneurs without a lot of financial resources, capital costs can be the most daunting barrier of entry of all. Many industries are able to maintain decent profit margins simply because the capital costs required to enter the industry are significant and insurmountable for many. Also, your time can be thought of as a capital asset too. Your investment of time in pursuing a business endeavor represents an opportunity cost on your part – you are giving up time that you could be working for someone else (and the income that entails) in exchange for pursuing your entrepreneurial ambitions. For example, it may take $100,000 and one year of full time work to create and open a business. If you had to give up a $50,000 per year job in order to pursue the endeavor, the real capital cost for you to start your business would be $150,000, not $100,000.
Another example of this would be opening a law practice. Legal services, in the United States, is a fragmented industry that has an average industry profit of 19.5%. This is a very attractive profit margin. Furthermore, the capital cost required to start a legal practice – purely from creating the actual legal services business – is relatively small. A lawyer needs a laptop, access to research materials, a place to meet clients, and some office equipment. This may cost as little as $10,000 in initial startup capital. But this does not represent the actual capital cost to start a law firm. To actually open a law firm and practice law, a lawyer would have needed to: 1) obtain a law degree (lets estimate $120,000), not work for three years while going to law school (lets estimate $150,000 for three cumulative years), get a state bar card ($3,500 for the test and the study course), and not work for three months while studying for the bar (lets estimate $12,500). Then, an only then, a lawyer could spend $10,000 on opening a legal practice. The real cost of this venture, both in absolute capital costs and opportunity costs, would be $296,000.
So the real capital cost of opening a law firm and practicing law (and being in an industry with an attractive 19.5% profit margin) may be at least nearly $300,000. This capital cost represents a serious barrier of entry to many people who would want to enter this industry, but balk at the $300,000 price tag that it requires.
Key Questions:
- What are the average total capital costs for entering the industry you proposing to enter?
- Is the average profit margin for the industry you are proposing to enter enough to service the capital costs required from a typical new market entrant?
Economies of scale arise when unit costs fall as a firm expands its output. In other words, the more of a value proposition a company produces, the less per unit the company pays to produce those value propositions. Sources of scale economies include 1) cost reductions gained by efficiently creating a massed produced output, 2) discounts on bulk purchases of raw materials, and 3) cost benefits gained from spreading production costs and marketing and advertising over a large production volume. Some industries benefit greatly from economies of scale (i.e. the beer industry, the auto industry…). Other industries do not enjoy economies of scale much at all (i.e. nail salons, massage therapy, dry cleaners…).
The following are examples of economies of scale: 1) when the creator of a product gets bulk discounts on the purchases of raw materials for their products, 2) spreading fixed production costs over a large production volume, 3) cost reductions through mass-producing a standardized output, 4) cost savings associated with spreading marketing and advertising costs over a large volume of output. Most manufacturing industries, such as pulp and paper products or textiles, are examples of industries with economies of scale. If economies of scale are a factor in an industry, then many small producers are at a disadvantage because their per-unit costs will be higher than that of their larger competitors.
An industry whose rivals have significant economies of scale creates powerful barriers to entry for an aspiring new entrant to overcome. First, the established firms will have a substantial cost advantage over a new rival. Second, because high economies of scale imply high fixed costs (equipment, facilities), it is critical that these companies protect their market share at all costs. If their sales volumes decrease, this can render them incapable of sustaining their high fixed costs.
Companies, who try to match the existing industry competitors’ economies of scale, must enter the industry as a large producer to overcome this problem. But to do so, it must raise enough capital (to purchase the necessary assets and facilities) to match its competitors’ economies of scale. This becomes another barrier of entry in itself. Furthermore, if a new company enters an industry with a large capital investment (to match current industry competitors’ economies of scale), the increased supply of products the new company brings to the market risks depressing prices and may trigger a price war with established industry competitors.
- Does the industry you propose to enter have significant economies of scale (where the per-unit costs for producing a good or service decrease significantly as the volume of production increases)?
- Does the industry you propose to enter have high fixed costs (equipment, facilities, or significant R&D requirements)?
- Do the suppliers of the industry you propose to enter give significant volume discounts and payment terms to large-volume buyers?
- Within the industry you are proposing to enter, do its company’s marketing and sales budgets increase, on a per unit basis, proportionally to sales of its value propositions, or do the costs of its company’s sales and marketing budgets decrease, on a per unit basis, with an increase in the sales volume of its value propositions?
Brand loyalty is when consumers develop and hold a preference for a particular company’s brand of value propositions. Significant brand loyalty makes it difficult for new market entrants to wrestle market share away from established industry brands. Examples of value propositions with strong brand loyalty are mass consumer products such as beer (Budweiser, Coors and Miller), soft drinks (Coca Cola and Pepsi), or tobacco products (Marlborough and Winston-Salem’s).
A company can also cultivate brand loyalty by developing innovative value propositions. Probably the most successful major company over the last decade that has leveraged innovative value propositions into brand loyalty has been Apple.
A venture may be able to sidestep an industry’s brand loyalty barriers of entry by entering the premium category of product markets. An example would be Dry Soda or small craft micro-brewers.
Significant brand loyalty makes it difficult for new entrants to take market share away from established industry brands. A company faces the daunting task of not only convincing consumers to buy its value propositions, but also to choose not to buy value propositions they already like and feel comfortable with.
- Are the value propositions in the industry you propose to enter highly branded?
- How strong is the brand loyalty in the industry you are proposing to enter?
Absolute Cost Advantages are when an established venture has an insurmountable cost advantage, meaning that new entrants cannot possibly hope to match the incumbent companies’ lower cost structure. Absolute cost advantages can arise from: 1) superior production operations and processes due to access to unique assets (i.e. patents, copyrights, or fertile farmland), 2) accumulated skill and expertise, 3) exclusive or relatively favorable control of their value propositions’ inputs (labor, materials, equipment, or management skill), and 4) access to cheaper capital due to their lower business risk when compared to a new market entrant. Also, access to superior distribution channels could be considered an absolute cost advantage. If established companies have absolute cost advantages, then the threat of entry as a competitive force will be weaker.
A new market entrant must be especially careful in attempting to directly compete with entrenched industry competitors that have absolute cost advantages. If a new entrant enters an industry where there are established competitors who have lower cost structures, the established firms can lower the price of their value propositions to eliminate the new entrant. This could erase any ability for the new market entrant to ever earn a profit. If this threat is credible, it can be a barrier of entry for new market entrants.
- Do the major competitors in the industry you are proposing to enter possess absolute cost advantages? If so, will you be able to acquire these absolute cost advantages before you begin directly competing with them?
- If the major competitors within the industry you are proposing to enter possess absolute cost advantages over your business idea, are there any steps or actions you can take to mitigate those absolute cost advantages?
Customer switching costs are the time, energy, and money necessary for them to switch from the value propositions offered by an established company to those of a new market entrant. If switching costs are high, customers will be unlikely to change even if the new product is superior to other market substitutes and alternatives. An example would be the switching costs associated with leaving the Microsoft Windows operating system or the QWERTY keyboard. Other value propositions in the market may be better/faster, but consumers often find themselves resistant to change because the time or hassle of switching to a better product or service proves prohibitive.
K ey Questions:
- In the industry you are proposing to enter, do the value propositions the industry produces have high switching costs? If they do, can you think of a way your business idea can mitigate this obstacle?
- If the industry you are proposing to enter doesn’t typically have high switching costs, can you think of a way for your business to raise the switching costs for your proposed value propositions?
Government regulations create politically and legally defined barriers of entry for many industries. Government regulations can increase barriers of entry for market entrants and potentially reduce competition. An example would be food safety regulations or anti-pollution laws. Also, in industries where economies of scale are a powerful force, the absence of regulations can lead to an intense concentration of market share in the hands of a few firms. This can create barriers of entry that are extremely difficult for a new market entrant to overcome. To sum up, high regulation within an industry usually leads to higher barriers of entry, but not always.
- Does the industry you propose to enter require government licenses or strict adherence to statutory codes (construction, health care, lending money, real estate rental, restaurant & food preparation…)?
- To what degree are the industry’s regulations beneficial to the incumbent industry competitors?
Below is a chart that summarizes how the six types of barriers of entry affects industry attractiveness from both the perspective of a new market entrant and an industry incumbent.
Estimating Market Size
Estimating the size of the market you want to enter is the first critical step in testing the feasibility of your business idea. This is a lot like cliff diving. If you are going to jump off a cliff into a pool of water far below, it’s a really good idea to know beforehand just how deep the water is. If you jump without finding out (or at least making an educated guess based on objective facts), you run the very real risk of getting hurt. Bad.
The first order of business in determining the sizes of the various market types for your business idea’s value proposition(s) is to correctly define the parameters of the market types you are trying to measure. This may sound rather simple, but it is honestly the hardest and most frustrating part of this process. Estimating a market size is the epitome of the phrase “garbage in – garbage out.” If you incorrectly define the boundaries of the type of market you are trying to size up, your entire estimate (and the basis for all of your future financial projections) won’t really be worth the paper it is printed on.
So, creating a quality market size estimate that’s based upon good, logical assumptions, is the first step in determining if your business idea can support a potentially successful business model. To make a quality market size estimate, you should roughly measure the size of each relevant market type for your business idea’s value propositions. By understanding the rough size of each of these market types, you can roughly gauge how much revenue (based upon your market share assumptions) your business idea could generate in the present and going forward into the future. Determining which market types to estimate the size of depends upon the type of market your business idea is attempting to serve. These general market types are Defined Exiting Markets, Cloned Markets, Re-segmented Markets, or a New Markets.
A market is a group of customers that have the willingness to buy a particular type of value proposition. When determining the size of the markets for your proposed business idea’s value proposition(s), you may use all or some combination of the following market type definitions.

- Examples: the car market (supplied by the car industry), the personal computer market (supplied by the personal computer industry), and the athletic shoe market (supplied by the athletic shoe industry).
- Examples: the total market for electric cars, the total market for tablet computers, the total market for running shoes.
- Examples: the market for electric cars in the United States sold through dealerships, the market for android compatible tablet computers sold through big box stores, the market for athletic shoes sold through e-commerce websites .
- The TM is comprised of one or more customer segments , each of which are offered a unique value proposition by your proposed business idea. For a comprehensive explanation of what comprises a customer segment, please refer to the following section.
- The TM is a measurement dependent upon the definition and size of the SAM (because it is a portion of the SAM), but independent of the SOM. Both the TM and the SOM are portions of the SAM that measure different things.
- Examples: Upper-middle class, educated, ecologically conscious automobile customers, early adopter electronics consumers who use their personal computers and laptops mostly for entertainment and not work, high school and college athletes who buy high performance running shoes to gain an edge on their competition.
- Like the TM, the SOM is dependent upon the definition and size of the SAM, but is independent of the TM. Both the TM and the SOM are portions of the SAM that measure different things.
- Examples: the portion of the market for electric cars sold in the United States through dealerships that your business idea can realistically capture, the portion of the android compatible tablet computer market in the United States sold though big box stores that your business idea can realistically capture, the portion of the market for high performance running shoes for athletes in the United States that are sold through ecommerce websites that your business idea can realistically capture.
For practical purposes, you can think of both the SOM and TM as a portions of the SAM, the SAM as a portion of the TAM, and the TAM as a portion of the TID. Both the SOM and TM are separate business concepts that measure different things. The SOM estimates your proposed value proposition’s penetration of the SAM. The TM estimates the size of the group of people for whom your proposed value proposition is specifically designed for.
I know, it’s a lot of acronyms to keep straight. But estimating the sizes of the TIM, TAM, SAM, TM and SOM are important for determining if the market size for your business idea’s value proposition(s) can support your entrepreneurial ambitions and business goals. The following are three generalizations – rule-of-thumb explanations – of what market sizes are necessary to support a particular business type, development path and outcome.
This type of company is usually entering a cloned, re-segmented, blue ocean or new market, or a defined existing market with a new product. They usually seek traditional angel investor and venture capital funding. Rapid scalability an achieving high market share is the key to this type of company. Often the founders of scalable, high growth companies have either an Initial Public Offering (IPO) or the sale of the company to a Fortune 500 corporation as their exit strategy .
These companies require a SAM large enough to support potential company EBITDA (after the company has successfully scaled its operations) of at least somewhere between $10 million to $20 million per year. Publically traded companies, on average, often trade for 10x their annual EBITDA or greater. This, depending upon the company’s industry and whether or not its founders and investors want it to have an IPO, would probably put the company’s valuation at greater than $100 million. A $100 million valuation is a safe rough estimate for whether a company will be able to both afford to go public and financially benefit from an IPO.
So, armed with these rough guidelines, to create a scalable, high growth company that proposes to enter an industry with a 10 percent average EBITDA and capture 10 percent of that industry’s market share, would need to at least generate $100 million per year in revenue ($10 million per year in EBITDA divided by the industry EBITDA average of 10 percent). To achieve this annual EBITDA target and a 10 percent SAM penetration, the overall SAM size would need to be $1 billion ($100 million per year in revenue divided by a 10 percent penetration of the market by the company).
This type of company can be entering a Defined Existing Market, Cloned Market, Re-segmented Market, or Blue Ocean Market. They do not enter New Markets with New Products due to the incredible amount of time, business risk and resources that would be required. These businesses usually seek capital from the founders, founders’ friends and family, non-bank lenders, bank and institutional lenders, and some angel investors. Rapid scalability is usually not a primary goal for these business ventures. They often prioritize strong, stable profits and cash flow for their owners above all else. Exit strategies for these companies’ founders include selling the company to a third party such as another privately held business or private equity group, passing on the business to heirs, or simply holding on to the business. These types of businesses often make excellent cash cows.
Successful, mid-sized privately held businesses are usually valued between $5 million and $50 million. These businesses, as a rough rule of thumb and depending upon the industry, are usually valued at 3x to 5x their average yearly EBITDA. So, a $30 million dollar privately held business would need an average yearly EBITDA of between $6 and $10 million per year ($6 million per year if the business valuation ratio would be 5x; $10 million if the business valuation ratio would be 3x).
Lifestyle businesses are undertaken by entrepreneurs who want to create their own jobs and/or to support the conscious lifestyle choices of the entrepreneur (hobbies, schedules, living location…). This type of company usually solely enters Defined Existing Markets. Many, if not most, of the entrepreneurs who start lifestyle businesses do not begin their business ventures with any particular exit strategy in mind. Instead, the primary financial goal of these entrepreneurs is usually to generate enough cash flow to support their lifestyle needs. These businesses usually seek capital from the founders, bootstrap financing, and the founders’ friends and family. Rapid scalability is usually not a primary goal for these business ventures.
The market size necessary to support a lifestyle business really depends upon the needs and wants of each individual entrepreneur. The variables used to determine a rough estimate of the minimum market size needed to support a lifestyle business are: 1) the entrepreneurs’ desired minimum yearly EBITDA (include the entrepreneurs’ salaries in with EBITDA), 2) the average EBITDA ratio for a firm competing within the industry you are proposing to enter, and 3) the entrepreneurs’ assumption of how much of their proposed business idea’s SAM they will be able to capture.
For example, if an entrepreneur’s goal is to earn at least $120,000 (in EBITDA and salary) from the lifestyle business per year, the average EBITDA ratio for the proposed business idea’s industry is 15 percent of annual revenue, and the entrepreneur assumes she can capture 10 percent of the SAM she proposes to enter, then the minimum necessary SAM size needed to support the business venture would be $8 million ($120,000 divided by a 15 percent EBITDA ratio divided by a 10 percent SAM penetration equals $8,000,000).
The following chart summarizes the rule-of-thumb market size needs of the business types analyzed above:
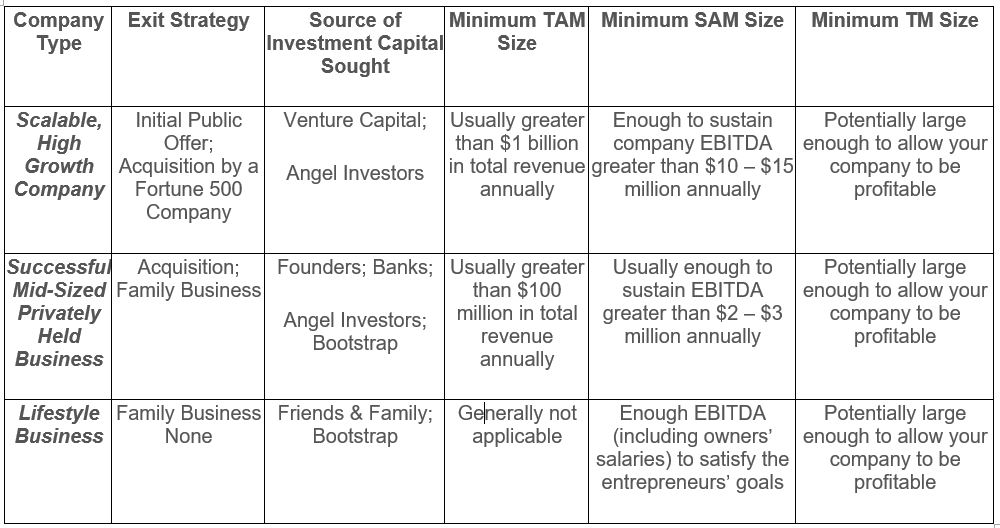
Targeting a specific audience is most effective strategy when creating a marketing campaign. The more specific of a customer base a campaign can reach, the more dollars per potential customer a campaign will make. This is why companies will allocate a large amount of resources in order to find the audience that they are looking for. By doing this, you can create a marketing budget as effectively as possible and maximize your results. Knowing or choosing exactly who you are getting your message to has proven to be the most effective method of forming a marketing campaign. Once you have identified your target audience, the hard part is figuring out how to reach it. Below, we will discuss ways to do so.
The goal of any marketing campaign is to give the most amount of information about a product or service to the prospective customer possible. The more the customer knows, the more likely they are to take action. The more that is known about that customer, the more likely it is that you can communicate that information effectively. Using information about your customer base will help you make connections that they can relate to and in turn, they will be more likely to respond to your campaigns call to action.
There are four main ways that are commonly used in identifying targeted markets.
Geographic: This includes the location, the geographical size and makeup of the area and other environmental factors such as climate.
Demographics: This includes age, gender, income, average family size, average education, and the types of jobs that are in the geographic area.
Psychographics: This involves factors such as the personality that you area tends to take on, what and how people behave that live in that area and also factors that will affect the way your potential customers will use your product or service. Will they use it often not so often? Is it a necessity or luxury?
Behaviors: This has more to do with how your potential customers will react to things such as price changes and price points, how they will react based on what information is given to them, and what types of marketing campaigns they are most likely to respond favorably to. All of these factors can be used to help determine how a population will respond to a specific marketing campaign. Likewise, you can a marketing campaign that will increase conversions based on the information gathered above.
One of the fundamentals of marketing focuses on the benefits to cost trade-off. Understanding how customers will weigh the potential benefits of a product or service versus the costs to obtain that product or service is critical when designing a marketing campaign. Ask yourself, how will your customer gain monetarily or in other ways from purchasing your product or service? Though it is not always achievable, satisfying this is the most effective ways to create sales.
To better understand how they will you this trade-off, ask yourself the following questions.
- How much will it save them? Is this a product that can potentially pay for itself?
- Are there any intangible benefits to this particular product or service that a customer may ignore or find appealing?
- Will this product or service save the customer money, time, effort, or resources?
- Will it increase the customer’s income, investments, future, or personal relationship will it reduce a customer’s expenses, taxes, liabilities, or work?
- Will it improve that customer’s abilities, productivity, appearance, confidence or peace of mind?
Understanding the effect that your product or service will have on the customer will serve as an invaluable tool when designing an effective marketing campaign.
As mentioned in the beginning, understanding, identifying and reaching a target audience is the most effective way creating a marketing campaign that will give you the best results possible relative to the budget and time you are allotted. Ignoring these factors can costs you money and can be the difference between a successful and unsuccessful marketing campaign.
It’s important to define the nature of your involvement, in both depth and scope, in the business you are founding. An entrepreneur’s involvement in his own business can range from being a full-time manager/employee (active ownership) to that of a hands-off investor (passive ownership).
An active owner materially participates in the day-to-day activities of the business. Most business owners and entrepreneurs actively participate in their businesses in some way, shape or form. Many work full-time in their businesses as employee/managers, drawing both a paycheck and profits (if there are any).
The definition of a passive owner is a little trickier to nail down. A passive business owner does not participate in the day-to-day activities of the business he or she owns. The IRS states that passive income can only come from two possible sources: rental activities or “ trade or business activities in which you do not materially participate .” Within the context of entrepreneurial endeavors some examples of passive income are:
- Earnings from a business from which you, an owner, are not required to be directly involved with (neither labor nor day-to-day management)
- Rent from either tangible personal property or real estate
- Royalties from intellectual property (patent, copyright, trademark…)
Receiving passive income is delightful. The hard part is usually accumulating enough assets in the first place to begin receiving passive income from them (rents or passive business activities). Examples, where an entrepreneur can derive passive income from her investments, are:
- A landlord rents an apartment building to tenants and uses a real estate management company to collect rents and make repairs.
- A passive investor invests capital into a partnership where others manage the business, and in return for his contribution of capital, the passive investor receives a portion of the business’s profits.
- An entrepreneur builds a successful business from scratch. She then hires a manager to manage the day-to-day affairs of the business. She then receives the profits from her business even though she is no longer actively involved in it.
Most entrepreneurs who start businesses have one of two basic plans for their involvement in their enterprises.
1. The entrepreneur(s) plan to be heavily involved in the lean startup plan and operations over a period of a couple of years. Then, at some undetermined point in the future, they plan to hire a manager and then run the company as a passive investment.
2. The entrepreneur(s) are essentially creating a job for themselves. They plan on working in the enterprise as an open-ended, long-term committment.
Starting and/or running a business is a complex and daunting task. Identifying both potential roadblocks and opportunities well in advance is essential for businesses of any size to outmaneuver the competition and gain a foothold as a dominant market leader. But over one-half of all new businesses will fail within five years of their founding. The vast majority of all new businesses never achieve the financial success originally envisioned by the founders. These new businesses and start-ups begin with energetic enthusiasm, but unfortunately, many business plans fall short due to various reasons: lack of capital, a flawed business strategy, unrealistic expectations, or they lack the people with the required skills and expertise to succeed.
Business plans may be required for any number of reasons. Here are a few of the most common business plan needs.
- To Obtain Debt Financing . A company may be required by a bank or other financial institution to provide a detailed, professional business plan in order to secure debt financing. Examples would be bank business loans or a line of credit.
- To Obtain Equity Financing . Start-ups and other new businesses often must sell equity (stock or membership units) to investors to raise capital for new business ventures. Investors can range from friends and family to angel investors to venture capital firms.
- For Internal Company Planning . Companies often need business plans to compare the relative viability between competing potential business projects. This can give those companies a clearer perspective on where to invest limited resources within the organization.
- Joint Ventures and Partnerships . When entering a strategic JV or partnership with another firm, a business plan works to outline the objectives of the two firms working in tangent.
- Mergers, Acquisitions and Corporate Divestiture . Detailed plans are needed when businesses change hands in order to help new owners see details in the industry and the enterprise itself. An expert plan can also serve as part of the marketing material to get the business sold.
The reasons for creating a business plan can be as varied as the businesses themselves. Each plan requires a unique approach to the industry you are in, the market you intend to serve, and your financial needs. That’s where we come in.
Creating a professional business plan can help mitigate these risks, raise capital from potential investors and put the company on the path to success. A good business plan helps to focus an entrepreneur’s mind on accomplishing the tasks necessary to make his or her business succeed. A business plan is not a static document. It is a logical series of informed assumptions that are relevant at the time the plan is written. As soon as market and industry conditions begin to change (which usually happens about five minutes after the plan is written), the plan begins becoming obsolete. For the entrepreneur, the value in the business plan isn’t necessarily the plan itself. Instead, its real value lies in the process – the research, thought and inquiry – in creating it.
We will work with you from start to finish to create a professional business plan that will help you accomplish your objectives. We will ask the necessary questions, help you find the answers, and organize your ideas into a coherent plan. From researching your market and industry to producing realistic, justifiable pro forma financial statements (cash flow, income statements & balance sheet), we will craft a document that can help you accomplish your business objectives.
So your business needs a plan. The question is, what kind of plan does it need? Please check out our business plan menu options and pricing here.
Business Plan Review & Evaluation
If you already have a business plan and would like to have it reviewed by a professional business plan consultant, then this is the right service for you. We will review and critique your business plan with an investor’s eye, scrutinizing it for financial errors, grammatical errors, and weak or unrealistic assumptions. We will also point out what you did right. Our business plan review service is an efficient and affordable way to ensure that your business plan is as good as it can be. Our business plan review services are provided at a substantial discount to our normal hourly rates. Depending on your needs and budget, we offer three levels of business plan review services:
– We will spend 2 and 1/2 hours reviewing your materials. We will then provide a written evaluation and critique your plan and financial model.
– We will spend 30 minutes consulting with you on the telephone, answering any questions you may have and offering additional guidance.
– Optional: if you have made any changes to your business plan, based upon the evaluations and critiques we made in our first examination of your materials, we can offer subsequent reviews of the improvements you have made to your plan. In these subsequent reviews, we will spend up to 2 hours examining your materials again.
– Flat Rate Price: $297 for first review; $147 for subsequent reviews
- Once you place your order, we will provide instructions for sending us your business plan. Your plan must be sent to us in Microsoft Word format so we can use the Track Changes feature).
- Your review will generally take place within 3-5 business days of you sending us your business plan.
- When our review of your business plan is complete, we will send you the redlined/track changes version of your business plan with our critiques and suggestions.
- After you receive your reviewed/critiqued version of your business plan, we will work with you to schedule a mutually convenient time for the telephone portion of the review service.
- Optional Subsequent Reviews: After you make changes to the critiqued version of your business plan that we sent you, you may send us your new version for further critiques/comments. Please allow 3-5 business days to complete the evaluation.
– All information you provide will be treated confidentially.
– Fees are payable in advance and are non-refundable. If you decide you no longer want a business plan review after you have made payment, we will provide an equivalent amount of consulting firm services of your choosing (3 hours for the Standard Evaluation and Review).
– Once you submit your plan for review, please allow two business days to schedule an initial discussion so that we can understand your needs and tailor our review for your specific situation. This allows us to make sure you get the most out of this process.
– Depending on our existing workload, please allow up to 5 business days for us to complete the review following this initial discussion.
– All reviews are provided on a best efforts basis. You are ultimately responsible for the accuracy of the information in your business plan (and related materials).
– You agree to defend, indemnify, and hold us harmless from and against all third party claims, losses, or damage which we incur and which arise from or are attributable to our role in this business plan review.
We believe that we have the most transparent and customer friendly pricing strategy on the market.
For someone writing their first business plan, even for simple small businesses, the process can take upwards of 100 hours of time. Often, it takes more than 200 hours . For complex business plans (business plans for unproven business models and undefined markets), the process can often take more than 400 hours. Because we have considerable experience and skill at writing plans, we estimate that, on average, that we can complete an average business plan (depending upon its type, audience and complexity) in the range of 30 to 120 hours.
The range between 30 and 120 hours depends upon three general factors that contribute to a business plan’s complexity. The first factor is whether the plan is for a new business or a business already in existence, The second factor is whether the business’s industry and market are well defined (for example: dry cleaners, dollar stores, organic vegetable farms, family restaurants…) or if the market or industry is new and untested. The third factor is who is the audience for the business plan: equity investors, debt lenders or the internal management of an existing business.
Note: unless your business idea is exploiting a new market or market niche, or offering customers a product or service that is radically different from what is currently offered to the market, then only on rare occasions will your business plan require longer than 70 hours to complete.
From three factors above, we can generally estimate the average number of hours the plan will take to complete, and therefore we can charge a base flat fee for the project. We Our base flat fee rates are the product of our estimated number of hours times our business plan writing hourly rate. For our business plan writing, we charge $75 per hour.
The business plans we produce fall into the following six general categories:
But often, due to unseen factors (a change in the business plan format scope and direction), a plan may take longer than the anticipated range. Often project extensions occur when it becomes necessary to modify or change the focus of the business plan due to unforeseeable factors (i.e. new market research, assumptions are proven wrong, the founders choose to shift or expand the scope of the business…). So, if your business plan takes longer than the anticipated number of hours to produce, we will charge you at only $20 per hour beyond the original estimated time frame.
This ensures the following:
– By using our pricing formula (flat fee plus $20 per hour beyond the estimated project timeframe) versus using only a fixed billable hour rate, we mitigate any incentive to “run the meter” and unnecessarily inflate the price of your solid business plan. Our goal is to maximize our income per hour for each plan that we produce. Therefore, if we end up going beyond the project’s estimated timeframe, this means we will be working at a significant discount ($20 per hour after the end of the project’s initial timeframe estimate).
– We use our pricing formula also gives us some measure of protection against unforeseen changes to the project’s scope or direction. Creating a lean business plan is a dynamic process. Information discovered or uncovered during the plan writing process can change the focus, scope and goals of the project. Also, by charging a modest hourly rate beyond a predetermined period, helps to focus and frame exactly what you want in your business plan.
– Ultimately, our system encourages both you and us to remain disciplined, efficient and to maximize the value of each other’s time.
For example: You task us with writing a Type 1 business plan. The project takes 50 hours to complete because the scope changed in the middle of the project. Under these circumstances, the final price for the project would be the Type 1 business plan flat fee ($2,250) plus $20 per hour for every hour spent on the project over 30 hours (20 hours x $20/hour = $400). Therefore, the final complete price for the project would be $2,650 ($2,250 + $400 = $2,650).
- One half (50%) of the project’s flat fee price is required to be paid up front.
- 30% of the project flat fee is due upon completion of the business plan’s Executive Summary (the last plan component to be completed).
- Upon completion of the business plan’s final draft and its approval by the client, the remaining 20% of the project’s flat fee is due plus any extra hourly charges if the project goes beyond its initially estimated time.
Preparing an expert business plan can be extremely time-consuming. While the process of mastering and completing your plan may be helpful in understanding the business dynamics, corporate strategy and overall financial and marketing model, it can take you away from operational support that is vital for day-to-day operations. That is where our business planning services come into play. We help business owners in crafting expert MBA-level business plans for internal management buy-in as well as external business funding needs.
Companies often create business plans to obtain financing from venture capitalists, private equity groups and angel investors. Your particular plan will be dependent on the industry you play in, the financing you are seeking to obtain and your overall strategy for execution. Finding the key strengths, knowing potential flaws and being conversant with competitive forces in the industry are only a few of the necessary components of your completed plan. In other words, a full SWOT analysis may be necessary.
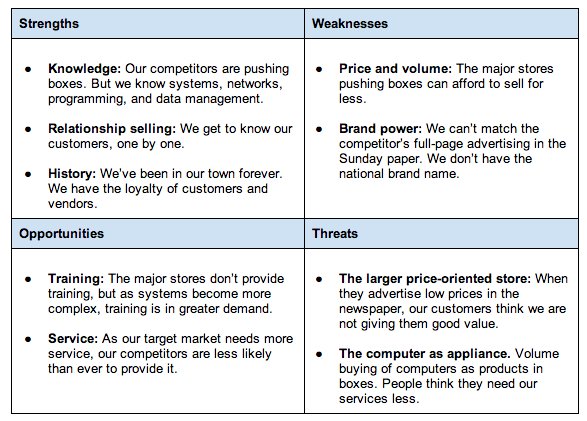
Regardless of whether you write a business plan yourself or outsource it to one of the expert members of our qualified MBA team, it is helpful to have a second pair of eyes to edit and provide constructive feedback. You plan and pitch will help to make or break your financing efforts. Don’t skimp on quality. You need to show off your financial health.
Being conversant in finance is certainly not a requirement to operate or be successful in business. Having great financials, including thoughtful projected and proforma financial statements is a must for any entrepreneur seeking to secure funding or internal management buy-in. We help to craft properly-structured financial plans for your business using historical data and realistic assumptions.
Obtain financing for your business with an professionally crafted financial plan as part of your overall strategy.
Business plans are great, but execution is the name of the game. Without a proper marketing plan coupled with flawless execution, your business may eventually disappear.
We work directly with the entrepreneurs themselves to craft detailed, specific and attainable goals and strategies to take your product or service to market. For the seasoned entrepreneur, this may be “old hat,” but having an expert business plan consultant in your corner is helpful to the proper execution of your overall strategy. While there are many business plan software providers on the market, you will still need the human-touch element to really make business plan sing.
If you are seeking funding from any number of sources or simply need help crafting a plan to help you take your business to the next level, we can help. Contact us today to find out more.
Related posts
10 real estate investment exit strategies to consider, investing in residential vs. commercial real estate: which is better, what is private equity real estate investing.
Investment Company Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Investment Company Business Plan
You’ve come to the right place to create your Investment Company business plan.
We have helped over 1,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans and many have used them to start or grow their Investment Companies.
Below is a template to help you create each section of your Investment Company business plan.
Executive Summary
Business overview.
NovaGrowth Investments is a startup investment company located in Aurora, Colorado. The company is founded by Thom Anderson, an investment broker from Colorado Springs, Colorado, who has amassed millions of dollars for his clients over ten years while working at Clear River Investments. Because Thom has gained an extensive following of clients who have already indicated they will follow him to his new investment company, he has made the initial steps into forming NovaGrowth Investments. Thom plans on recruiting a team of highly-qualified professionals to help manage the day-to-day operations of a premier investment company in every aspect of marketing and advising in the land acquisition investment company.
NovaGrowth Investments will provide a wide array of services for investors, in particular those related to the optimal attention and time needed to secure valuable investments on their behalf. Investors can feel confident and secure, knowing that Thom and his team are looking out for their interests in every aspect of the land acquisition process. What’s more, NovaGrowth offers customized guarantees of investment performance that are singular within the investment company industry.
Product Offering
The following are the services that NovaGrowth Investments will provide:
- Analysis and expansive vetting of land acquisition opportunities up to 5M acres
- Extensive market research that secures in-depth findings
- Consistent and competitive returns while managing risk effectively
- Full spectrum wealth management
- Comprehensive array of software tools/programs to capture critical intelligence
- Unique strategies tailored for each individual client
- “New investor” welcome package with goal-setting seminar included
- “Boots on the Ground” team of investment analysts who visit each location under consideration and offer a full report plus video capture of the land
- Oversight and management of each portfolio and customized suggestions
Customer Focus
NovaGrowth Investments will target individual investors. They will also target corporate investors who are seeking land acquisitions. They will target fast-growing companies known to be seeking additional tracts of land. NovaGrowth Investments will target industry partners (cattle ranchers, horse breeders, etc) that could benefit from land acquisition as an investment.
Management Team
NovaGrowth Investments will be owned and operated by Thom Anderson. He recruited Jackson Byers and Kylie Carlson to manage the day-to-day operations of the investment company and oversee human resources.
Thom Anderson is a graduate of Cambridge University in the U.K., where he graduated with an International Business bachelor’s degree. He spent five years in the U.K. sourcing land for a large investment firm as an entry-level investment advisor.
Upon his return to the U.S.,Thom obtained his investment broker’s license and was employed by Clear River Investments in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Within one year, Thom secured over 5M in investments for his clients and, within five years, he amassed over 25M in land acquisition investments on behalf of his clients.
Jackson Byers is a graduate of the University of Illinois, where he graduated with a master’s degree in Accounting. His former role at Clear River Investments was as the Associate Accountant, where he managed the normal business accounting processes for the firm. He will serve as the Staff Accountant in the startup company and will assist in overseeing the day-to-day operations of the firm.
Kylie Carlson was hired by Thom Anderson as his Assistant and worked for him at Clear River Investments for over ten years. Her new role will be the Human Resources Manager, overseeing personnel and the processes that are regulated and required by Colorado.
Success Factors
NovaGrowth Investments will be able to achieve success by offering the following competitive advantages:
- Friendly, knowledgeable, and highly-qualified team of NovaGrowth Investments
- “Boots on the Ground” team of investment analysts who visit each location under consideration and offer a full report plus video capture of the land.
- NovaGrowth Investments offers outstanding value for each client in both their management fees and land acquisition percentages. Their pricing denotes quality and value and their results continually substantiate it.
Financial Highlights
NovaGrowth Investments is seeking $200,000 in debt financing to launch its NovaGrowth Investments. The funding will be dedicated toward securing the office space and purchasing office equipment and supplies. Funding will also be dedicated toward three months of overhead costs to include payroll of the staff, rent, and marketing costs for the marketing costs. The breakout of the funding is below:
- Office space build-out: $20,000
- Office equipment, supplies, and materials: $10,000
- Three months of overhead expenses (payroll, rent, utilities): $150,000
- Marketing costs: $10,000
- Working capital: $10,000
The following graph outlines the financial projections for NovaGrowth Investments.
Company Overview
Who is novagrowth investments.
NovaGrowth Investments is a newly established, full-service investment company in Aurora, Colorado. NovaGrowth Investments will be the most reliable, effective and value-driven choice for private and commercial investors in Aurora and the surrounding communities. NovaGrowth Investments will provide a comprehensive menu of portfolio and land acquisition services for any potential investor to utilize. Their full-service approach includes a comprehensive seminar and helpful introductory information for first-time investors.
NovaGrowth Investments will be able to manage the investments and acquire new investments for their clients. The team of professionals are highly qualified and experienced in investment brokerage and land acquisitions. NovaGrowth Investments removes all headaches and issues of trying to locate safe and secure investments and ensures all issues are taken care of expeditiously while delivering the best customer service.
NovaGrowth Investments History
Thom Anderson is a graduate of Cambridge University in the U.K., where he graduated with an International Business bachelor’s degree. He spent five years in the U.K. sourcing land for a large investment firm as an entry-level investment advisor. Upon his return to the U.S.,Thom obtained his investment broker’s license and was employed by Clear River Investments in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Within one year, Thom secured over 5M in investments for his clients and, within five years, he amassed over 25M in land acquisition investments on behalf of his clients.
Since incorporation, NovaGrowth Investments has achieved the following milestones:
- Registered NovaGrowth Investments, LLC to transact business in the state of Colorado.
- Has a contract in place for a 10,000 square foot office at one of the midtown buildings
- Reached out to numerous contacts to sign on with NovaGrowth Investments.
- Began recruiting a staff of seven and four office personnel to work at NovaGrowth Investments
NovaGrowth Investments Services
The following will be the services NovaGrowth Investments will provide:
Industry Analysis
The investment company industry is expected to grow over the next five years to over $1.3 trillion. The growth will be driven by ongoing vast opportunities for individuals and organizations seeking to grow their wealth The growth will be driven by new technology that navigating the complexities of the financial markets The growth will be driven by an increase in the interest of individuals in “making their own way” in the world The growth will be driven by the stability of land ownership as an on-going and important element in investment portfolios.
Costs will likely be reduced as technology continues to advance, allowing better-informed acquisition interest and supplemental risk mitigation Costs will likely be reduced as younger investors, such as Gen Z and millennials, continue to express an interest and desire for land acquisition investments, which indicates an increased number of sellers will enter the market due to favorable conditions.
Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market.
NovaGrowth Investments will target those potential individual investors in Aurora, Colorado. They will target businesses with a track record of land investments or a need for land due to company growth. NovaGrowth Investments will target industry partners (cattle ranchers, horse breeders, etc) that could benefit from land acquisition as an investment.
Customer Segmentation
NovaGrowth Investments will primarily target the following customer profiles:
- Individual investors
- Businesses with a record of land investments or those seeking land due to internal growth
- Industry partners seeking additional land for livestock or farming purposes
Competitive Analysis
Direct and indirect competitors.
NovaGrowth Investments will face competition from other companies with similar business profiles. A description of each competitor company is below.
CapitalMax Advisors
CapitalMax Advisors is a startup investment company in Colorado Springs, Colorado. The owner, Barry Jackson, is a graduate of Purdue University and has been an investment advisor for over ten years. He recently launched Capital Max Advisors to meet what he coined, “The Great Asset Allocation” investment opportunities within the city of Colorado Springs. Barry has hired ten associates from his former employer’s company to seek investors who are primarily interested in asset allocation investments and the company is promising reduced portfolio management rates for the first six months of business.
CapitalMax Advisors is a full-service investment company with a strong following of investors who were delighted by Barry’s performance on their behalf at his former employer. The expectation is that CapitalMax Advisors will live up to their primary purpose, which is to oversee and direct asset allocation to maximize returns in substantial numbers.
WealthWise Investments
Owned by Tamara and Loren Downs, WealthWise Investments is known for it’s assertive actions on behalf of clients. The company was founded in 2010 and currently offers a diverse range of investment products and services. They specialize in ETFs, mutual funds, and alternative investments. WealthWise Investments is known for its expertise in risk management, technology-driven investment strategies, and statewide reach beyond it’s home city of Colorado Springs.
WealthWise Investments offers excellent services to clients; however, clients have noted publicly that the fees and service charges are high in tandem with the asset allocation gains. There have been two complaints noted with the state regulatory agencies. Meanwhile, Tamara and Loren Downs continue to employ efforts to bring technology-driven tools into the investment company that will trim staff and distribute higher rates on behalf of investors.
FinTech Capital Management
FinTech Capital Management is a five-year-old company located in Denver, Colorado. The focus of the company is on financial technology investments on behalf of their client investors. Currently, the company has recorded stable and growing levels of profitability and has been tagged as an investment management firm known for its expertise in mutual funds and retirement planning They offer a sizable range of investment strategies, including equity, fixed income, and asset allocation funds. They are tech-driven and focus on research-driven investment decisions to fulfill the goals of their clients in long-term wealth creation.
In addition to tech acquisitions, FinTech Capital Management is also directed toward senior investors, with brokerage, retirement planning, wealth management, and mutual funds in their services offered. They provide a range of investment options, from individual stocks and bonds to managed portfolios and retirement accounts, many of which are perfect for those investors who have amassed a sizable portfolio, but are becoming risk-averse as they age. FinTech Capital Management is owned by The Thurgood Family Trust with the Thurgood brothers, Jonathan and Regis, responsible for day-to-day management. It has been recently suggested that the firm may be sold if the right buyers were to approach.
Competitive Advantage
NovaGrowth Investments will be able to offer the following advantages over their competition:
Marketing Plan
Brand & value proposition.
NovaGrowth Investments will offer the unique value proposition to its clientele:
- Unique investment strategies tailored for each individual client
Promotions Strategy
The promotions strategy for NovaGrowth Investments is as follows:
Word of Mouth/Referrals
Thom Anderson has built up an extensive list of contacts over the years by providing exceptional service and expertise to former clients and potential investors. The contacts and clients will follow him to his new company and help spread the word of NovaGrowth Investments.
Professional Associations and Networking
The executives within NovaGrowth Investments will begin networking in professional associations and at events within the city-wide industry groups. This will bring the new startup into focus for other companies, providing a path to increased clients and strategic partnerships within the city.
Social Media Marketing
NovaGrowth Investments will target their primary and secondary audiences with a series of text announcements via social media. The announcements will be invitations to the opening of the company, with a champagne reception and information regarding the services available at NovaGrowth Investments. The social media announcements will continue for the three weeks prior to the launch of the company.
Website/SEO Marketing
NovaGrowth Investments will fully utilize their website. The website will be well organized, informative, and list the services that NovaGrowth Investments provides. The website will also list their contact information and biographies of the executive group. The website will engage in SEO marketing tactics so that anytime someone types in the Google or Bing search engine “Investment company” or “Investment opportunities near me,” NovaGrowth Investments will be listed at the top of the search results.
The pricing of NovaGrowth Investments will be moderate and on par with competitors so customers feel they receive excellent value when purchasing their services.
Operations Plan
The following will be the operations plan for NovaGrowth Investments. Operation Functions:
- Thom Anderson will be the owner and President of the company. He will oversee all staff and manage client relations. Thom has spent the past year recruiting the following staff:
- Jackson Byers will provide all client accounting, tax payments and monthly financial reporting. His title will be Staff Accountant.
- Kylie Carlson will provide all employee onboarding and oversight as she assumes the role of Human Resources Manager.
Milestones:
NovaGrowth Investments will have the following milestones completed in the next six months.
- 5/1/202X – Finalize contract to lease office space
- 5/15/202X – Finalize personnel and staff employment contracts for NovaGrowth Investments
- 6/1/202X – Finalize contracts for NovaGrowth Investments clients
- 6/15/202X – Begin networking at industry events
- 6/22/202X – Begin moving into NovaGrowth Investments office
- 7/1/202X – NovaGrowth Investments opens its doors for business
Financial Plan
Key revenue & costs.
The revenue drivers for NovaGrowth Investments are the fees they will charge to clients for their investment acquisition and portfolio management services.
The cost drivers will be the overhead costs required in order to staff NovaGrowth Investments. The expenses will be the payroll cost, rent, utilities, office supplies, and marketing materials.
Funding Requirements and Use of Funds
NovaGrowth Investments is seeking $200,000 in debt financing to launch its investment company. The funding will be dedicated toward securing the office space and purchasing office equipment and supplies. Funding will also be dedicated toward three months of overhead costs to include payroll of the staff, rent, and marketing costs for the print ads and association memberships. The breakout of the funding is below:
Key Assumptions
The following outlines the key assumptions required in order to achieve the revenue and cost numbers in the financials and in order to pay off the startup business loan.
- Number of Clients Per Month: 175
- Average Revenue per Month: $437,500
- Office Lease per Year: $100,000
Financial Projections
Income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, investment company business plan faqs, what is an investment company business plan.
An investment company business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your investment company business. Among other things, it outlines your business concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections.
You can easily complete your Investment Company business plan using our Investment Company Business Plan Template here .
What are the Main Types of Investment Company Businesses?
There are a number of different kinds of investment company businesses , some examples include: Closed-End Funds Investment Company, Mutual Funds (Open-End Funds) Investment Company, and Unit Investment Trusts (UITs) Investment Company.
How Do You Get Funding for Your Investment Company Business Plan?
Investment Company businesses are often funded through small business loans. Personal savings, credit card financing and angel investors are also popular forms of funding.
What are the Steps To Start an Investment Company Business?
Starting an investment company business can be an exciting endeavor. Having a clear roadmap of the steps to start a business will help you stay focused on your goals and get started faster.
1. Develop An Investment Company Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed investment company business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast.
2. Choose Your Legal Structure - It's important to select an appropriate legal entity for your investment company business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your investment company business is in compliance with local laws.
3. Register Your Investment Company Business - Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your investment company business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
4. Identify Financing Options - It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your investment company business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
5. Choose a Location - Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
6. Hire Employees - There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
7. Acquire Necessary Investment Company Equipment & Supplies - In order to start your investment company business, you'll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
8. Market & Promote Your Business - Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your investment company business. This includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising.
Learn more about how to start a successful investment company business:
- How to Start an Investment Company
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
14 Business Startup Costs Business Owners Need to Know

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
Deciding to start a business is exciting, but can also be daunting if you're a new entrepreneur. Calculating business startup costs, worrying about long-term profitability, securing startup funding — it can all be pretty stressful.
The question of costs is critical because the initial investment can be significant. A Kauffman Foundations study shows the average cost to be around $30,000, and costs tend to increase each year.
Fortunately, certain types of businesses, such as micro-businesses and home-based companies, have lower financial entry barriers. Here, we’ve put together a list of 14 different types of business startup costs you’ll need to consider when launching your company.

ZenBusiness
How to calculate the cost of starting a business
Drafting a business plan is the best way to estimate your business startup costs. Within your plan, the financial projections section should estimate your revenue, profit, and expenses for the next three to five years.
There are other resources to estimate your finances as well, such as the SBA’s startup costs worksheet . Templates will help you estimate your initial investment costs, so you know how much capital you should request when you seek startup funding.

Keep in mind that many of the business startup costs we list below are recurring. You'll need to cover these costs over a monthly, quarterly, or annual basis — think rent, office supplies, and payroll. Other expenses, like the incorporation fee or office furniture, are one-time costs.
When calculating your business startup costs, a good rule of thumb is to be able to cover six months’ worth of expenses upfront. So don’t count on your business’s revenue to start easing your costs until at least after that early period is over. You’ll want a cushion while you get your feet under you and work on attracting business.
>> MORE: Best business budgeting tools
14 business startup costs to plan for
Although this is a typical list of business startup costs, your actual startup expenses depend entirely upon your specific business and industry.
Here are some typical business startup costs to plan for:
1. Equipment: $10,000 to $125,000
Almost every business will need to finance equipment immediately. Equipment costs for startups can range anywhere from $10,000 to $125,000, depending on the industry and size of the company.
For example, if you’re starting your own moving or shipping company, you’ll need to finance a truck. If you’re opening a restaurant, you’ll need commercial-grade ovens, stoves, dishware, and cooking utensils. If you own a hair salon, you’ll need styling chairs. And nearly any business will require computers.
Of course, these costs range according to your industry and the size of your business. Hiring employees will incur additional costs, as you may need to secure individual equipment, as well.
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
2. Incorporation fees: Under $300
One of your first to-dos when setting up a business is to choose a business entity, which has tax, legal, and financial implications.
If you decide to incorporate your business or form a limited liability company, you’ll need to file articles of incorporation or articles of organization, respectively, with your state. The filing fee can range from $50 to as high as $725 depending on the state. However, the fee is under $300 in the majority of states.
Even if you’re not incorporating, you’ll probably need to apply for federal or state licensing or permits. The types of documentation you'll need will vary based on your industry and location. For example, businesses within the agriculture or aviation sectors require federal licensing. Service-based sectors may need to have trade-specific licenses. And retail companies will likely need sales tax licenses or permits.
3. Office space: $100 to $1,000 per employee per month
Paying for an office or retail space will be a sizeable portion of your fixed costs, whether you rent or buy. You might spend between $100 per employee per month up to $1,000 per employee per month — again, it will depend on the type of space you're using.
You can mitigate these costs if you work from home in the beginning, or look into coworking spaces — both ideal for smaller businesses. And if you own a service-based business, you can travel directly to clients to further decrease overhead costs.
4. Inventory: 17% to 25% of your total budget
If you’re in the retail, wholesale, manufacturing, or distribution sector, you'll likely need to secure inventory to sell, as soon as you possibly can.
Knowing how much inventory to carry can be tricky: If you have too much inventory, you risk spoilage or damage. If you have too little, you risk losing customers who won't wait for items on backorder. This is especially true for seasonal businesses where inventory can vary drastically year-round.
You should allocate between 17% to 25% of your budget to inventory, depending on your industry. When you’re first starting out, consider securing more inventory. You'll want to attract customers and generate as much revenue as you can in your company's early stages.
5. Marketing: Below 10% of your total budget (even 0%)
Marketing materials might include physical materials, like signs, banners, and business cards. You might also consider paid ads, as well as more creative options, like videos and giveaways, that might require you to hire a consultant or a video producer.
Courtney Barbee, COO at The Bookkeeper, recommends keeping overall marketing costs to a minimum. Specifically, strive to keep your ad materials under 10% of your budget.
The good news? You can do the bulk of your small business marketing, for free. Thanks to social media and other online marketing strategies, advertising costs are often much lower for small businesses just starting now than they would have been 20 years ago.
6. Website: Around $40 per month
When building your business website, you'll want it to look professional, be easy to navigate, and display information about your services, products, hours, and contact information.
Fortunately, services like Wix, Squarespace, and Weebly, make creating a website easy and cost-effective. These content management systems are sometimes free, but premium plans will come at a monthly or yearly subscription cost:
Wix : $13 to $39 per month for a premium plan.
Squarespace : $12 to $18 per month billed annually, or $26 billed month to month.
Weebly : $5 to $25 per month.
Wix and Weebly also offer basic, free website builders. If you’re relatively tech-savvy, it’s easy to build a website through one of these services, no coding background required. But if you’re not very familiar with computers, you may want to hire someone to build the website — which, of course, is an additional cost (although it might become a worthwhile investment).
7. Office furniture and supplies: 10% of your total budget
Office furniture and supplies add up fast. If you’re operating in a traditional nine-to-five office environment, then every employee will need a desk, a chair, a computer, and a phone. Add in break room appliances, small office supplies, and computer programs, like your accounting software, and you’ll reach a hefty sum.
Again, that sum varies depending on the tools your business needs to operate, and the number of employees you need to outfit. Nate Masterson, the marketing manager at Maple Holistics, estimates that the total cost for office furniture and supplies would be around $5,000. In all, though, Masterson recommends keeping your furniture and supply costs to approximately 10% of your budget.
8. Utilities: Around $2 per square foot of office space
In addition to the fixed costs of rent and a down payment, you’ll be responsible for paying the electric, gas, water, internet, and phone bills for your office space. According to Iota Communications, the average cost of utilities for commercial buildings is $2.10 per square foot.
If you intend to install HVAC units, that will incur an additional cost — usually a couple of thousand dollars, not including installation fees and upkeep.
9. Payroll: 25% to 50% of your total budget
You need to pay your employees, even in the early stages, where you’re not bringing in much revenue. Remember, payroll includes all of the following:
Commissions.
Overtime pay.
Paid time off.
Of course, payroll costs will vary across startups. Typically, an employee will cost 1.25x to 1.4x their salary. For example, an employee on a $40,000 salary will actually cost you around $54,000 after factoring in various payroll tax costs and insurance.
A conservative payroll budget could work if you’re a sole proprietor, or if you’re running a small enterprise and use mostly 1099 contractors — and either is a pretty likely scenario for most startups.
10. Professional consultants: Between $1,000 and $5,000 per year
It’s tempting to take a DIY approach for all your business operations. After all, who knows your business best? But working with experts and professionals can be worth the investment.
For example, certified public accountants can explain the different legal structures, help you choose an employee benefit program, and ensure you're fulfilling your responsibilities as an employer. When tax season rolls around, they’ll prepare your tax returns and help you save on your taxes.
You don't need to hire a full-time accountant either. But it’s often a good idea to consult with your accountant on a monthly, quarterly, or annual basis to review your financial statements, and for general financial guidance and advice. Consulting with an attorney regularly can also save you from major legal mistakes like failing to trademark your logo or developing relationships with vendors without a contract in place.
Every CPA and lawyer charges different hourly rates. Rates and additional fees vary depending on the number and level of difficulty involved in the tasks you need outsourced, the time it takes to complete your projects, and your consultant’s tenure. However, you can mitigate these costs by taking on some basic tasks yourself, only outsourcing the most complicated projects. There are even some options to get free business legal advice.
And with the help of good business accounting software, you can handle basic bookkeeping, like processing and managing payroll, creating and tracking invoices, and managing your business bank account.
According to SCORE , all told, the majority of small business owners spend between $1,000 and $5,000 per year on administration tasks, including accounting and legal fees. But as a startup — and by taking advantage of those cost-cutting tactics we mentioned — you’ll probably err on the lower end of that spectrum.
11. Insurance: Average of $1,200 per year
Your business needs the same protections you provide to your health, home, and car. There are many different kinds of business insurance , including protection from customers that file a lawsuit against you and disaster insurance for potential fires that can shut down your restaurant for weeks.
The type of insurance your startup needs is entirely dependent on your business, industry, number of employees, and other risk factors. For instance, a sole proprietor running an online business has far fewer insurance requirements than a construction company with several employees.
Here are a few essential forms of insurance you should look into to protect yourself, and policy costs vary according to several different factors:
General liability insurance : About $400 to $800 per year. Your industry’s risk will be the most significant factor influencing the cost of your policy.
Commercial property insurance: Anywhere from $300 to $2,500+, depending on the value of the property and its assets, and a risk factor dependent upon the nature of the business and the location of the property.
Workers compensation insurance : Approximately $0.75 to $2.74 per $100 of payroll, depending on the business’s size, location, payroll, and risk.
Errors and omissions insurance: Approximately $2,000 to $5,000 per year, depending on your business’s size, industry, location, revenue, legal history, and the quality of your contracts and employee training procedures.
12. Taxes: Variable, but 21% corporate tax rate
When planning your budget, determining the exact amount to allocate toward business taxes can be confusing. It depends on your revenue (which is difficult to predict), your deductible expenses, and your business entity.
Under current federal law, corporations pay a flat 21% corporate income tax. For pass-through entities, business income and losses pass through to the owners' personal tax returns. Pass-through entities can claim a 20% deduction on income before paying their business taxes.
But know that you can often save money and time by working with a CPA. A skilled CPA will determine what you can deduct so that you pay as little as possible.
13. Travel: Variable
Not every new entrepreneur needs to factor travel into their business startup costs. But if you have a consulting business or you visit your customers directly, you will be traveling a lot. You'll need to factor in the price of transportation, food, and lodging — multiply these costs if you have multiple employees traveling. Be mindful of how quickly those costs add up.
Try to keep total travel costs to an absolute minimum so that you can allocate your revenue toward bigger expenses, like payroll and rent. And to make some returns on all that time on the road or in the air, consider using a travel business credit card, which can earn you points and miles for every dollar you spend. If you do have to travel frequently, keep the nonessentials like business class tickets to a minimum.
14. Shipping: Variable
Service-based businesses can probably stop reading here. But if you’re in retail, you might be shipping products to customers. If so, you’ll need to factor shipping into your startup costs, including packing materials and postage. Depending on what you’re sending, these costs can reach into the thousands of dollars.
Services like Stamps.com can ease the burden of shipping costs on small business owners. With this service, you can print postage without having to buy a costly postage meter. If possible, you can secure free or low-cost shipping boxes from your shipping service of choice.
How to save on startup costs
The costs of starting a business can certainly add up, with many expenses being non-negotiable. Do your research before you splurge on high-ticket purchases, and recognize that there are ways to take care of some of these startup costs on the cheap.
For example, using software like QuickBooks can save on the costs of hiring a professional bookkeeper. Working from home or using a coworking space is a cost-effective alternative to leasing office space. And leveraging social media can mitigate your marketing costs.
Some costs are worth the investment. Don’t buy poor-quality equipment just because it’s cheaper — you’ll lose time and money making repairs and eventually need to purchase new equipment. Hire a legal or accounting expert if you’re confused. And make sure your website and advertising campaigns are professional-looking and effective.
Secure funding
If you've calculated your business startup costs and now feel overwhelmed, know that there are plenty of resources to help you find startup financing.
Your initial funding will likely come from a combination of debt and equity financing. But keep in mind that debt financing options — small-business loans — are relatively limited for brand-new businesses. Most lenders only feel comfortable offering loans to established companies with hard evidence of profitability, as well as healthy credit, which most startups simply don’t have yet.
Some lenders work with startup business owners, so don’t completely rule it out if you think it’s your best option. Check out more information on how to get a loan to start a business if you think debt financing is the right move for you.
» MORE: What is a business loan?
Get a business credit card
Once you’ve established a legal entity for your business, we recommend applying for a business credit card.
The application is simple, and a business credit card is usually easier to qualify for than a traditional business loan. Also, you typically gain access to a higher credit limit than your personal card. More importantly, a business credit of card keeps your personal and business finances separate — essential if you wish to maintain your personal liability protections after forming an LLC or corporation.
» MORE: What is a business credit card?
Just make sure you’re not maxing out your credit card or charging more than you can repay. Both can harm your credit score, which might hurt your chances of securing a small business loan down the line.
Start Your Dream Business
Frequently asked questions
1. what is the average cost to start a small business.
The cost of starting a small business depends on the type and size of the business you’re opening and your industry. For example, opening a McDonald’s franchise can cost you $1 million, while starting a social media consulting company may cost less than $10,000. The average cost will vary on a case-by-case basis.
2. How do you calculate startup costs?
The most straightforward method for calculating your startup costs is to use a budget template. Your budget will break down your startup costs and recurring expenses — rent, office supplies, payroll, and more.
It’s prudent to cover six months’ worth of expenses minimum upfront; this financial cushion will support you in your business’s early stages when your profit margins might be slim.
3. Are business startup costs tax-deductible?
While the IRS does not recognize startup costs as capital expenditures, they do state that you can deduct $5,000 of business startup and $5,000 of organizational costs paid or incurred after October 22, 2004, but only if your total startup costs are $50,000 or less.
You can review IRS Publication 535 or consult a business accountant for additional information.
4. What is considered a startup cost?
A startup cost is any expense incurred when starting a new business. Startup costs will include equipment, incorporation fees, insurance, taxes, and payroll.
Although startup costs will vary by your business type and industry — an expense for one company may not apply to another. For example, a brick-and-mortar business will need to pay to rent a separate business location, unlike a home-based online consulting company.
This article originally appeared on JustBusiness, a subsidiary of NerdWallet.
On a similar note...

Upmetrics AI Assistant: Simplifying Business Planning through AI-Powered Insights. Learn How
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai Pitch Deck Generator
Strategic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
- Sample Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Customer Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Small Business Tools
Strategic Planning Templates
E-books, Guides & More
- Sample Business Plans
Investment Company Business Plan
The possibility for substantial financial gains is one of the main advantages of an investment company. As the company expands and gains customers, it has the potential to generate large fees and commissions based on investment portfolios.
Are you looking for the same rewards? Then go on with planning everything first.
Need help writing a business plan for your investment company? You’re at the right place. Our investment company business plan template will help you get started.

Free Business Plan Template
Download our free business plan template now and pave the way to success. Let’s turn your vision into an actionable strategy!
- Fill in the blanks – Outline
- Financial Tables
How to Write An Investment Company Business Plan?
Writing an investment company business plan is a crucial step toward the success of your business. Here are the key steps to consider when writing a business plan:
1. Executive Summary
An executive summary is the first section planned to offer an overview of the entire business plan. However, it is written after the entire business plan is ready and summarizes each section of your plan.
Here are a few key components to include in your executive summary:
Introduce your Business:
Start your executive summary by briefly introducing your business to your readers.
Market Opportunity:
Products and services:.
Highlight the investment company services you offer your clients. The USPs and differentiators you offer are always a plus.
Marketing & Sales Strategies:
Financial highlights:, call to action:.
Ensure your executive summary is clear, concise, easy to understand, and jargon-free.
Say goodbye to boring templates
Build your business plan faster and easier with AI
Plans starting from $7/month

2. Business Overview
The business overview section of your business plan offers detailed information about your company. The details you add will depend on how important they are to your business. Yet, business name, location, business history, and future goals are some of the foundational elements you must consider adding to this section:
Business Description:
Describe your business in this section by providing all the basic information:
Describe what kind of investment company you run and the name of it. You may specialize in one of the following investment businesses:
- Mutual fund companies
- Venture capital funds
- Private equity funds
- Asset management companies
- Pension fund managers
- Describe the legal structure of your investment company, whether it is a sole proprietorship, LLC, partnership, or others.
- Explain where your business is located and why you selected the place.
Mission Statement:
Business history:.
If you’re an established investment company, briefly describe your business history, like—when it was founded, how it evolved over time, etc.
Future Goals:
This section should provide a thorough understanding of your business, its history, and its future plans. Keep this section engaging, precise, and to the point.
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section of your business plan should offer a thorough understanding of the industry with the target market, competitors, and growth opportunities. You should include the following components in this section.
Target market:
Start this section by describing your target market. Define your ideal customer and explain what types of services they prefer. Creating a buyer persona will help you easily define your target market to your readers.
Market size and growth potential:
Describe your market size and growth potential and whether you will target a niche or a much broader market.
Competitive Analysis:
Market trends:.
Analyze emerging trends in the industry, such as technology disruptions, changes in customer behavior or preferences, etc. Explain how your business will cope with all the trends.
Regulatory Environment:
Here are a few tips for writing the market analysis section of your investment company business plan:
- Conduct market research, industry reports, and surveys to gather data.
- Provide specific and detailed information whenever possible.
- Illustrate your points with charts and graphs.
- Write your business plan keeping your target audience in mind.
4. Products And Services
The product and services section should describe the specific services and products that will be offered to customers. To write this section should include the following:
Describe your services:
Mention the investment company services your business will offer. This list may include services like,
- Portfolio management
- Financial planning
- Investment research and analysis
- Wealth management
- Mutual funds and exchange-traded funds
Investment advisory services:
Additional services:.
In short, this section of your investment business plan must be informative, precise, and client-focused. By providing a clear and compelling description of your offerings, you can help potential investors and readers understand the value of your business.
5. Sales And Marketing Strategies
Writing the sales and marketing strategies section means a list of strategies you will use to attract and retain your clients. Here are some key elements to include in your sales & marketing plan:
Unique Selling Proposition (USP):
Define your business’s USPs depending on the market you serve, the equipment you use, and the unique services you provide. Identifying USPs will help you plan your marketing strategies.
Pricing Strategy:
Marketing strategies:, sales strategies:, customer retention:.
Overall, this section of your investment company business plan should focus on customer acquisition and retention.
Have a specific, realistic, and data-driven approach while planning sales and marketing strategies for your investment business, and be prepared to adapt or make strategic changes in your strategies based on feedback and results.
6. Operations Plan
The operations plan section of your business plan should outline the processes and procedures involved in your business operations, such as staffing requirements and operational processes. Here are a few components to add to your operations plan:
Staffing & Training:
Operational process:, equipment & software:.
Include the list of equipment and software required for investment business, such as servers & data storage, network equipment, trading platforms, customer relationship management software, portfolio management software, etc.
Adding these components to your operations plan will help you lay out your business operations, which will eventually help you manage your business effectively.
7. Management Team
The management team section provides an overview of your investment business’s management team. This section should provide a detailed description of each manager’s experience and qualifications, as well as their responsibilities and roles.
Founders/CEO:
Key managers:.
Introduce your management and key members of your team, and explain their roles and responsibilities.
Organizational structure:
Compensation plan:, advisors/consultants:.
Mentioning advisors or consultants in your business plans adds credibility to your business idea.
This section should describe the key personnel for your investment company, highlighting how you have the perfect team to succeed.
8. Financial Plan
Your financial plan section should provide a summary of your business’s financial projections for the first few years. Here are some key elements to include in your financial plan:
Profit & loss statement:
Cash flow statement:, balance sheet:, break-even point:.
Determine and mention your business’s break-even point—the point at which your business costs and revenue will be equal.
Financing Needs:
Be realistic with your financial projections, and make sure you offer relevant information and evidence to support your estimates.
9. Appendix
The appendix section of your plan should include any additional information supporting your business plan’s main content, such as market research, legal documentation, financial statements, and other relevant information.
- Add a table of contents for the appendix section to help readers easily find specific information or sections.
- In addition to your financial statements, provide additional financial documents like tax returns, a list of assets within the business, credit history, and more. These statements must be the latest and offer financial projections for at least the first three or five years of business operations
- Provide data derived from market research, including stats about the industry, user demographics, and industry trends.
- Include any legal documents such as permits, licenses, and contracts.
- Include any additional documentation related to your business plan, such as product brochures, marketing materials, operational procedures, etc.
Use clear headings and labels for each section of the appendix so that readers can easily find the necessary information.
Remember, the appendix section of your investment firm business plan should only include relevant and important information supporting your plan’s main content.
The Quickest Way to turn a Business Idea into a Business Plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
This sample investment company business plan will provide an idea for writing a successful investment company plan, including all the essential components of your business.
After this, if you still need clarification about writing an investment-ready business plan to impress your audience, download our investment company business plan pdf .
Related Posts
Bookkeeping Business Plan
Concierge Services Business Plan
How to make Perfect Business Outline
Simple Business Plan Template Example
What are Business Plan Components
How to Write Business Plan Appendix
Frequently asked questions, why do you need an investment company business plan.
A business plan is an essential tool for anyone looking to start or run a successful investment business. It helps to get clarity in your business, secures funding, and identifies potential challenges while starting and growing your business.
Overall, a well-written plan can help you make informed decisions, which can contribute to the long-term success of your investment company.
How to get funding for your investment company?
There are several ways to get funding for your investment company, but self-funding is one of the most efficient and speedy funding options. Other options for funding are:
Small Business Administration (SBA) loan
Crowdfunding, angel investors.
Apart from all these options, there are small business grants available, check for the same in your location and you can apply for it.
Where to find business plan writers for your investment company?
There are many business plan writers available, but no one knows your business and ideas better than you, so we recommend you write your investment company business plan and outline your vision as you have in your mind.
What is the easiest way to write your investment company business plan?
A lot of research is necessary for writing a business plan, but you can write your plan most efficiently with the help of any investment company business plan example and edit it as per your need. You can also quickly finish your plan in just a few hours or less with the help of our business plan software .
About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more
Plan your business in the shortest time possible
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates

Create a great Business Plan with great price.
- 400+ Business plan templates & examples
- AI Assistance & step by step guidance
- 4.8 Star rating on Trustpilot
Streamline your business planning process with Upmetrics .

- Capital Budgeting Process
- International Capital Budgeting
- NPV Calculation
- Expected NPV
- NPV Profile
- Initial Investment
- IRR Calculation
- Discount Rate
- Incremental IRR
- Normal Cash Flow
- Non-Normal Cash Flow
- Certainty Equivalent Cash Flow
- Cannibalization
- Terminal Cash Flow
- Equivalent Annual Cost
- Equivalent Annual Annuity
- Profitability Index
- Modified IRR
- Crossover Rate
- Capital Rationing
- Scenario Analysis
- Sensitivity Analysis
- Excel NPV Function
- Excel XNPV Function
- Excel IRR Function
- Excel XIRR Function
- Excel MIRR Function
Initial investment is the amount required to start a business or a project. It is also called initial investment outlay or simply initial outlay. It equals capital expenditures plus working capital requirement plus after-tax proceeds from assets disposed off or available for use elsewhere.
Capital budgeting decisions involve careful estimation of the initial investment outlay and future cash flows of a project. Correct estimation of these inputs helps in taking decisions that increase shareholders wealth.
Initial investment equals the amount needed for capital expenditures, such as machinery, tools, shipment and installation, etc.; plus any increase in working capital, minus any after tax cash flows from disposal of any old assets. Sunk costs are ignored because they are irrelevant.
Initial Investment = CapEx + ΔWC + D
Where, CapEx is capital expenditure , ∆WC is the change in working capital and D is the net cash flow from disposed asset.
Saindak Copper Company Ltd (SCCL) started a copper and gold exploration and extraction project in Baluchistan in 20X5. In 20X6-20X7, it incurred expenditure of $200 million on seismic studies of the area and $500 million on equipment, etc. In 20X8, the company abandoned the project due to disagreement with the government. Recently, a new business friendly government is sworn in. SCCL managing director believes the project needs reconsideration. The company's financial analyst and chief engineer estimate that $1,500 million worth of new equipment is needed to restart the project. Shipment and installation expenditures would amount to $200 million. Current assets must increase by $200 million and current liabilities by $90 million. The equipment purchased in 20X6-20X7 is no longer useful and is to be disposed of for after tax proceeds of $120 million. Find the initial investment outlay.
Initial investment = equipment purchase price + shipment and installation + increase in working capital − disposal inflows = $1,500 million + $200 million + ($200 million − $90 million) − $120 million = $1,690 million.
SCCL needs $1,690 million to restart the project. It needs to estimate future cash flows from the project, and calculate net present value and/or internal rate of return in order to decide whether to go ahead with the restart or not.
$200 million expenditure on the seismic studies is not part of the initial investment because it is a sunk cost.
by Obaidullah Jan, ACA, CFA and last modified on Mar 31, 2019
Related Topics
- Capital Expenditure
- Working Capital
- Sunk Costs vs Opportunity Costs
All Chapters in Finance
- Time Value of Money
- Cost of Capital
- Capital Structure
- Stock Valuation
- Risk and Return
- Exchange Rates
- Real Estate
- Financial Ratios
- Excel PV Function
- Corporate Finance
- Business Valuation
- Performance Measurement
- Primary & Secondary Market
Current Chapter
XPLAIND.com is a free educational website; of students, by students, and for students. You are welcome to learn a range of topics from accounting, economics, finance and more. We hope you like the work that has been done, and if you have any suggestions, your feedback is highly valuable. Let's connect!
Copyright © 2010-2024 XPLAIND.com
11.4 The Business Plan
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the different purposes of a business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a brief business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a full business plan
Unlike the brief or lean formats introduced so far, the business plan is a formal document used for the long-range planning of a company’s operation. It typically includes background information, financial information, and a summary of the business. Investors nearly always request a formal business plan because it is an integral part of their evaluation of whether to invest in a company. Although nothing in business is permanent, a business plan typically has components that are more “set in stone” than a business model canvas , which is more commonly used as a first step in the planning process and throughout the early stages of a nascent business. A business plan is likely to describe the business and industry, market strategies, sales potential, and competitive analysis, as well as the company’s long-term goals and objectives. An in-depth formal business plan would follow at later stages after various iterations to business model canvases. The business plan usually projects financial data over a three-year period and is typically required by banks or other investors to secure funding. The business plan is a roadmap for the company to follow over multiple years.
Some entrepreneurs prefer to use the canvas process instead of the business plan, whereas others use a shorter version of the business plan, submitting it to investors after several iterations. There are also entrepreneurs who use the business plan earlier in the entrepreneurial process, either preceding or concurrently with a canvas. For instance, Chris Guillebeau has a one-page business plan template in his book The $100 Startup . 48 His version is basically an extension of a napkin sketch without the detail of a full business plan. As you progress, you can also consider a brief business plan (about two pages)—if you want to support a rapid business launch—and/or a standard business plan.
As with many aspects of entrepreneurship, there are no clear hard and fast rules to achieving entrepreneurial success. You may encounter different people who want different things (canvas, summary, full business plan), and you also have flexibility in following whatever tool works best for you. Like the canvas, the various versions of the business plan are tools that will aid you in your entrepreneurial endeavor.
Business Plan Overview
Most business plans have several distinct sections ( Figure 11.16 ). The business plan can range from a few pages to twenty-five pages or more, depending on the purpose and the intended audience. For our discussion, we’ll describe a brief business plan and a standard business plan. If you are able to successfully design a business model canvas, then you will have the structure for developing a clear business plan that you can submit for financial consideration.
Both types of business plans aim at providing a picture and roadmap to follow from conception to creation. If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept.
The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, dealing with the proverbial devil in the details. Developing a full business plan will assist those of you who need a more detailed and structured roadmap, or those of you with little to no background in business. The business planning process includes the business model, a feasibility analysis, and a full business plan, which we will discuss later in this section. Next, we explore how a business plan can meet several different needs.
Purposes of a Business Plan
A business plan can serve many different purposes—some internal, others external. As we discussed previously, you can use a business plan as an internal early planning device, an extension of a napkin sketch, and as a follow-up to one of the canvas tools. A business plan can be an organizational roadmap , that is, an internal planning tool and working plan that you can apply to your business in order to reach your desired goals over the course of several years. The business plan should be written by the owners of the venture, since it forces a firsthand examination of the business operations and allows them to focus on areas that need improvement.
Refer to the business venture throughout the document. Generally speaking, a business plan should not be written in the first person.
A major external purpose for the business plan is as an investment tool that outlines financial projections, becoming a document designed to attract investors. In many instances, a business plan can complement a formal investor’s pitch. In this context, the business plan is a presentation plan, intended for an outside audience that may or may not be familiar with your industry, your business, and your competitors.
You can also use your business plan as a contingency plan by outlining some “what-if” scenarios and exploring how you might respond if these scenarios unfold. Pretty Young Professional launched in November 2010 as an online resource to guide an emerging generation of female leaders. The site focused on recent female college graduates and current students searching for professional roles and those in their first professional roles. It was founded by four friends who were coworkers at the global consultancy firm McKinsey. But after positions and equity were decided among them, fundamental differences of opinion about the direction of the business emerged between two factions, according to the cofounder and former CEO Kathryn Minshew . “I think, naively, we assumed that if we kicked the can down the road on some of those things, we’d be able to sort them out,” Minshew said. Minshew went on to found a different professional site, The Muse , and took much of the editorial team of Pretty Young Professional with her. 49 Whereas greater planning potentially could have prevented the early demise of Pretty Young Professional, a change in planning led to overnight success for Joshua Esnard and The Cut Buddy team. Esnard invented and patented the plastic hair template that he was selling online out of his Fort Lauderdale garage while working a full-time job at Broward College and running a side business. Esnard had hundreds of boxes of Cut Buddies sitting in his home when he changed his marketing plan to enlist companies specializing in making videos go viral. It worked so well that a promotional video for the product garnered 8 million views in hours. The Cut Buddy sold over 4,000 products in a few hours when Esnard only had hundreds remaining. Demand greatly exceeded his supply, so Esnard had to scramble to increase manufacturing and offered customers two-for-one deals to make up for delays. This led to selling 55,000 units, generating $700,000 in sales in 2017. 50 After appearing on Shark Tank and landing a deal with Daymond John that gave the “shark” a 20-percent equity stake in return for $300,000, The Cut Buddy has added new distribution channels to include retail sales along with online commerce. Changing one aspect of a business plan—the marketing plan—yielded success for The Cut Buddy.
Link to Learning
Watch this video of Cut Buddy’s founder, Joshua Esnard, telling his company’s story to learn more.
If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept. This version is used to interest potential investors, employees, and other stakeholders, and will include a financial summary “box,” but it must have a disclaimer, and the founder/entrepreneur may need to have the people who receive it sign a nondisclosure agreement (NDA) . The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, providing supporting details, and would be required by financial institutions and others as they formally become stakeholders in the venture. Both are aimed at providing a picture and roadmap to go from conception to creation.
Types of Business Plans
The brief business plan is similar to an extended executive summary from the full business plan. This concise document provides a broad overview of your entrepreneurial concept, your team members, how and why you will execute on your plans, and why you are the ones to do so. You can think of a brief business plan as a scene setter or—since we began this chapter with a film reference—as a trailer to the full movie. The brief business plan is the commercial equivalent to a trailer for Field of Dreams , whereas the full plan is the full-length movie equivalent.
Brief Business Plan or Executive Summary
As the name implies, the brief business plan or executive summary summarizes key elements of the entire business plan, such as the business concept, financial features, and current business position. The executive summary version of the business plan is your opportunity to broadly articulate the overall concept and vision of the company for yourself, for prospective investors, and for current and future employees.
A typical executive summary is generally no longer than a page, but because the brief business plan is essentially an extended executive summary, the executive summary section is vital. This is the “ask” to an investor. You should begin by clearly stating what you are asking for in the summary.
In the business concept phase, you’ll describe the business, its product, and its markets. Describe the customer segment it serves and why your company will hold a competitive advantage. This section may align roughly with the customer segments and value-proposition segments of a canvas.
Next, highlight the important financial features, including sales, profits, cash flows, and return on investment. Like the financial portion of a feasibility analysis, the financial analysis component of a business plan may typically include items like a twelve-month profit and loss projection, a three- or four-year profit and loss projection, a cash-flow projection, a projected balance sheet, and a breakeven calculation. You can explore a feasibility study and financial projections in more depth in the formal business plan. Here, you want to focus on the big picture of your numbers and what they mean.
The current business position section can furnish relevant information about you and your team members and the company at large. This is your opportunity to tell the story of how you formed the company, to describe its legal status (form of operation), and to list the principal players. In one part of the extended executive summary, you can cover your reasons for starting the business: Here is an opportunity to clearly define the needs you think you can meet and perhaps get into the pains and gains of customers. You also can provide a summary of the overall strategic direction in which you intend to take the company. Describe the company’s mission, vision, goals and objectives, overall business model, and value proposition.
Rice University’s Student Business Plan Competition, one of the largest and overall best-regarded graduate school business-plan competitions (see Telling Your Entrepreneurial Story and Pitching the Idea ), requires an executive summary of up to five pages to apply. 51 , 52 Its suggested sections are shown in Table 11.2 .
Are You Ready?
Create a brief business plan.
Fill out a canvas of your choosing for a well-known startup: Uber, Netflix, Dropbox, Etsy, Airbnb, Bird/Lime, Warby Parker, or any of the companies featured throughout this chapter or one of your choice. Then create a brief business plan for that business. See if you can find a version of the company’s actual executive summary, business plan, or canvas. Compare and contrast your vision with what the company has articulated.
- These companies are well established but is there a component of what you charted that you would advise the company to change to ensure future viability?
- Map out a contingency plan for a “what-if” scenario if one key aspect of the company or the environment it operates in were drastically is altered?
Full Business Plan
Even full business plans can vary in length, scale, and scope. Rice University sets a ten-page cap on business plans submitted for the full competition. The IndUS Entrepreneurs , one of the largest global networks of entrepreneurs, also holds business plan competitions for students through its Tie Young Entrepreneurs program. In contrast, business plans submitted for that competition can usually be up to twenty-five pages. These are just two examples. Some components may differ slightly; common elements are typically found in a formal business plan outline. The next section will provide sample components of a full business plan for a fictional business.
Executive Summary
The executive summary should provide an overview of your business with key points and issues. Because the summary is intended to summarize the entire document, it is most helpful to write this section last, even though it comes first in sequence. The writing in this section should be especially concise. Readers should be able to understand your needs and capabilities at first glance. The section should tell the reader what you want and your “ask” should be explicitly stated in the summary.
Describe your business, its product or service, and the intended customers. Explain what will be sold, who it will be sold to, and what competitive advantages the business has. Table 11.3 shows a sample executive summary for the fictional company La Vida Lola.
Business Description
This section describes the industry, your product, and the business and success factors. It should provide a current outlook as well as future trends and developments. You also should address your company’s mission, vision, goals, and objectives. Summarize your overall strategic direction, your reasons for starting the business, a description of your products and services, your business model, and your company’s value proposition. Consider including the Standard Industrial Classification/North American Industry Classification System (SIC/NAICS) code to specify the industry and insure correct identification. The industry extends beyond where the business is located and operates, and should include national and global dynamics. Table 11.4 shows a sample business description for La Vida Lola.
Industry Analysis and Market Strategies
Here you should define your market in terms of size, structure, growth prospects, trends, and sales potential. You’ll want to include your TAM and forecast the SAM . (Both these terms are discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis .) This is a place to address market segmentation strategies by geography, customer attributes, or product orientation. Describe your positioning relative to your competitors’ in terms of pricing, distribution, promotion plan, and sales potential. Table 11.5 shows an example industry analysis and market strategy for La Vida Lola.
Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis is a statement of the business strategy as it relates to the competition. You want to be able to identify who are your major competitors and assess what are their market shares, markets served, strategies employed, and expected response to entry? You likely want to conduct a classic SWOT analysis (Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats) and complete a competitive-strength grid or competitive matrix. Outline your company’s competitive strengths relative to those of the competition in regard to product, distribution, pricing, promotion, and advertising. What are your company’s competitive advantages and their likely impacts on its success? The key is to construct it properly for the relevant features/benefits (by weight, according to customers) and how the startup compares to incumbents. The competitive matrix should show clearly how and why the startup has a clear (if not currently measurable) competitive advantage. Some common features in the example include price, benefits, quality, type of features, locations, and distribution/sales. Sample templates are shown in Figure 11.17 and Figure 11.18 . A competitive analysis helps you create a marketing strategy that will identify assets or skills that your competitors are lacking so you can plan to fill those gaps, giving you a distinct competitive advantage. When creating a competitor analysis, it is important to focus on the key features and elements that matter to customers, rather than focusing too heavily on the entrepreneur’s idea and desires.
Operations and Management Plan
In this section, outline how you will manage your company. Describe its organizational structure. Here you can address the form of ownership and, if warranted, include an organizational chart/structure. Highlight the backgrounds, experiences, qualifications, areas of expertise, and roles of members of the management team. This is also the place to mention any other stakeholders, such as a board of directors or advisory board(s), and their relevant relationship to the founder, experience and value to help make the venture successful, and professional service firms providing management support, such as accounting services and legal counsel.
Table 11.6 shows a sample operations and management plan for La Vida Lola.
Marketing Plan
Here you should outline and describe an effective overall marketing strategy for your venture, providing details regarding pricing, promotion, advertising, distribution, media usage, public relations, and a digital presence. Fully describe your sales management plan and the composition of your sales force, along with a comprehensive and detailed budget for the marketing plan. Table 11.7 shows a sample marketing plan for La Vida Lola.
Financial Plan
A financial plan seeks to forecast revenue and expenses; project a financial narrative; and estimate project costs, valuations, and cash flow projections. This section should present an accurate, realistic, and achievable financial plan for your venture (see Entrepreneurial Finance and Accounting for detailed discussions about conducting these projections). Include sales forecasts and income projections, pro forma financial statements ( Building the Entrepreneurial Dream Team , a breakeven analysis, and a capital budget. Identify your possible sources of financing (discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis ). Figure 11.19 shows a template of cash-flow needs for La Vida Lola.
Entrepreneur In Action
Laughing man coffee.
Hugh Jackman ( Figure 11.20 ) may best be known for portraying a comic-book superhero who used his mutant abilities to protect the world from villains. But the Wolverine actor is also working to make the planet a better place for real, not through adamantium claws but through social entrepreneurship.
A love of java jolted Jackman into action in 2009, when he traveled to Ethiopia with a Christian humanitarian group to shoot a documentary about the impact of fair-trade certification on coffee growers there. He decided to launch a business and follow in the footsteps of the late Paul Newman, another famous actor turned philanthropist via food ventures.
Jackman launched Laughing Man Coffee two years later; he sold the line to Keurig in 2015. One Laughing Man Coffee café in New York continues to operate independently, investing its proceeds into charitable programs that support better housing, health, and educational initiatives within fair-trade farming communities. 55 Although the New York location is the only café, the coffee brand is still distributed, with Keurig donating an undisclosed portion of Laughing Man proceeds to those causes (whereas Jackman donates all his profits). The company initially donated its profits to World Vision, the Christian humanitarian group Jackman accompanied in 2009. In 2017, it created the Laughing Man Foundation to be more active with its money management and distribution.
- You be the entrepreneur. If you were Jackman, would you have sold the company to Keurig? Why or why not?
- Would you have started the Laughing Man Foundation?
- What else can Jackman do to aid fair-trade practices for coffee growers?
What Can You Do?
Textbooks for change.
Founded in 2014, Textbooks for Change uses a cross-compensation model, in which one customer segment pays for a product or service, and the profit from that revenue is used to provide the same product or service to another, underserved segment. Textbooks for Change partners with student organizations to collect used college textbooks, some of which are re-sold while others are donated to students in need at underserved universities across the globe. The organization has reused or recycled 250,000 textbooks, providing 220,000 students with access through seven campus partners in East Africa. This B-corp social enterprise tackles a problem and offers a solution that is directly relevant to college students like yourself. Have you observed a problem on your college campus or other campuses that is not being served properly? Could it result in a social enterprise?
Work It Out
Franchisee set out.
A franchisee of East Coast Wings, a chain with dozens of restaurants in the United States, has decided to part ways with the chain. The new store will feature the same basic sports-bar-and-restaurant concept and serve the same basic foods: chicken wings, burgers, sandwiches, and the like. The new restaurant can’t rely on the same distributors and suppliers. A new business plan is needed.
- What steps should the new restaurant take to create a new business plan?
- Should it attempt to serve the same customers? Why or why not?
This New York Times video, “An Unlikely Business Plan,” describes entrepreneurial resurgence in Detroit, Michigan.
- 48 Chris Guillebeau. The $100 Startup: Reinvent the Way You Make a Living, Do What You Love, and Create a New Future . New York: Crown Business/Random House, 2012.
- 49 Jonathan Chan. “What These 4 Startup Case Studies Can Teach You about Failure.” Foundr.com . July 12, 2015. https://foundr.com/4-startup-case-studies-failure/
- 50 Amy Feldman. “Inventor of the Cut Buddy Paid YouTubers to Spark Sales. He Wasn’t Ready for a Video to Go Viral.” Forbes. February 15, 2017. https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestreptalks/2017/02/15/inventor-of-the-cut-buddy-paid-youtubers-to-spark-sales-he-wasnt-ready-for-a-video-to-go-viral/#3eb540ce798a
- 51 Jennifer Post. “National Business Plan Competitions for Entrepreneurs.” Business News Daily . August 30, 2018. https://www.businessnewsdaily.com/6902-business-plan-competitions-entrepreneurs.html
- 52 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition . March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf
- 53 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition. March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf; Based on 2019 RBPC Competition Rules and Format April 4–6, 2019. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2019-RBPC-Competition-Rules%20-Format.pdf
- 54 Foodstart. http://foodstart.com
- 55 “Hugh Jackman Journey to Starting a Social Enterprise Coffee Company.” Giving Compass. April 8, 2018. https://givingcompass.org/article/hugh-jackman-journey-to-starting-a-social-enterprise-coffee-company/
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Michael Laverty, Chris Littel
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Entrepreneurship
- Publication date: Jan 16, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/11-4-the-business-plan
© Jan 4, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
How to Start a Business From Scratch in 6 Easy Steps
10 min. read
Updated April 30, 2024
Did you know that most of the world’s new businesses are bootstrapped ?
That’s right, most business owners do not launch with loans or outside investment but instead use their personal resources and savings to get up and running. They start from scratch and reinvest in the business as it gains traction.
And you can do the same.
Key Takeaways:
- Start with an idea that uses your experience, knowledge, or passion.
- Determine if there’s a need for your product or service.
- Create a plan and financial forecasts.
- Treat it like a side hustle until you get traction.
- What does it mean to start from scratch?
“Starting a business from scratch” does not mean:
- Using no money to launch your business.
- Getting no outside assistance.
- Inventing a business idea no one has done before.
Starting from scratch is about building a business from the ground up, using personal resources and minimal external financial support. The goal is to establish a sustainable business you control that satisfies a need in the market.
- Why start a business from scratch?
Here’s why starting from scratch might be the right approach for you:
- Risk reduction: Control your initial investment and expenses and scale gradually, allowing you to avoid overspending.
- Full control: With no outside investment or stakeholders to please, you can shape your business how you see fit.
- Proves your idea has real customers: Test your concept with customers early to help refine your offering and validate market demand.
- Fast decision-making: Quickly pivot to meet changing market demands without the red tape of larger organizations.
- Potentially makes future funding easier: You take the time to prove your business model and profitability before seeking funding. Your track record reduces investor and lender risk and can lead to better funding terms.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- 6 steps to start a new business from scratch
For this article, we will focus on the steps that take you from a budding business idea to generating sales.
For additional resources, check out our starting a business guide .
1. Start with an idea
Do some self-reflection and choose an idea you’re passionate about or one that uses your existing skills and experience.
This will make it far easier to execute and often requires less research, training, and upfront investment to get up and running than an idea completely new to you.
For example, service-based businesses, like accounting or consulting, often need just your time and expertise. If any cash is needed, it should be a small enough amount to fund yourself, giving you full control over the speed at which you grow your business.
As you explore possible ideas, create a one-page business plan to document how it could work.
It doesn’t have to be an official plan at this stage; just fill in what you can, mark any assumptions, and keep adding details throughout the rest of this process.
What businesses can you typically start from scratch?
While not an exhaustive list, here are a few potential ideas that can be started from scratch:
- Freelance Writing or Content Creation: Offer writing skills to businesses and online publications.
- Consulting Services: Share your professional management, marketing, or tech expertise.
- Handmade Crafts and Art: Sell your unique creations on platforms like Etsy or at local fairs.
- Tutoring: Offer either in-person or online.
- Web Design and Development: Build websites for small businesses or individuals.
- Virtual Assistant: Provide administrative support to businesses remotely.
- Landscaping and Gardening Services: Turn your love of plants into a business with basic gardening tools.
For more business options and a process to generate ideas, check out our guide on developing good business ideas .
2. Find product-market fit
Landing on an idea is not enough to create a viable business. You need to determine if you have initial product-market fit—that your business satisfies and is demanded by a large enough group of people.
This involves identifying your potential customers, understanding their motivations and needs, and determining whether they are willing to pay for your product or service. Additionally, spend time researching the market and understand who your competitors are.
At this stage, you don’t need a fully fleshed-out business. You just need enough of an idea to start speaking to potential customers.
This is where your one-page plan can be incredibly useful, as it helps you formalize enough information to have the working framework of a business. You can even add notes from your customer interviews to help adapt your plan.
Your goal, in this instance, is to:
- Hone in on pain points your potential customers have
- Verify that you can solve them
- Identify any gaps or issues with your idea
- (Bonus) Make initial sales
Keep in mind that you may find none of that. Your solution may not be needed or is missing key components. You may even be targeting the wrong audience and need to change course.
That’s completely okay! Most businesses don’t get things right the first time. Be willing to refine and iterate on your initial idea. Verify what works and what doesn’t, and make the right adjustments to create a sustainable business that customers really want.
3. Examine your resources
While I have this as the third step, you’ll likely be doing this throughout every stage of starting a business.
Start by evaluating your funding sources. Personal savings are ideal as they keep you in full control of your business. If needed, consider asking friends and family for small contributions, as they’ll likely be much more flexible about repayment than traditional lenders.
Next, consider if a partner could benefit your venture. Do they bring complementary skills, share the workload, or offer additional resources?
The right partner can fill crucial roles – like marketing or operations – allowing you to focus on your core strengths. They may even fill a necessary gap to get customers in the door.
Finally, don’t underestimate the power of your network. Reach out to former colleagues, industry peers, and mentors for advice, services, or referrals.
Why you need to know your available resources
Taking stock of your resources is the first step in understanding what is feasible for your business. It helps you determine whether you have enough cash, expertise, and support to meet your customers’ expectations.
For example, let’s say you want to launch an eCommerce website and have enough cash on hand to fulfill orders but require customers to pay for shipping. If you’re competing with similar businesses that offer free shipping, your lack of it could turn customers away.
Similarly, you have a solid understanding of product development and have already gotten pre-orders. But you have no idea how to set up an eCommerce site , keep track of orders, and ensure they actually ship.
In both circumstances, your resources fall short of the needs of your customers. You may have to explore funding ( it doesn’t have to be a loan ) and find a partner with the right skill set to get your site up and running.
4. Write a business plan and develop financial forecasts
At this point, you need to finalize your business plan and create initial forecasts .
If you’ve been using the one-page plan throughout the last few steps, then this shouldn’t be a time-consuming process. Your goal at this point is to clearly define:
- Business Model: Value proposition, customer segments, distribution channels, and revenue streams.
- Milestones: Set realistic goals (landing your first customer, scaling, etc.) with specific timelines and action steps to track progress.
For your forecasts, start by estimating your:
- Startup costs and ongoing expenses
- Revenue in the first year of operation
- Cash flow — how much money will be moving in and out of your business each month as you collect revenue and pay expenses
These numbers do not have to be perfect. You’ll likely be making educated guesses or using industry estimates. The point is to have something that you believe represents your business. It will help you maintain a healthy cash flow and understand what it will take to be profitable.
Remember, you don’t need to create an overly lengthy plan or complex financial statements. They’re your tools, so focus on usability – they should be flexible and evolve with your business, helping you make informed decisions.
Dedicate time ( at least monthly or quarterly) to reviewing and updating your plan and forecasts as you gather data to ensure your strategy aligns with real-world performance.
5. Protect your business
As a business owner, you must make your business legal and guard against liabilities. To keep things simple, we’ll assume you’re starting as a sole proprietorship for this article.
Check out our full guide to learn more about the specifics of each legal structure .
Necessary legal components for a simple startup:
- Business Registration: As a sole proprietor, you may not need to register your business with the state government if you do business under your legal name. However, if you operate under a name that’s not yours, you must file for a “Doing Business As” (DBA) name. This is often required to set up a business bank account.
- Licenses & Permits: Research local requirements for your specific business type. You may need a general business license, professional licenses, or specific permits (e.g., health and safety). Contact your city or county business office for details.
- Tax Registration: Report business income on your personal tax return. If you plan to hire employees, you’ll need to apply for an Employer Identification Number (EIN) from the IRS. Even without employees, an EIN can protect your personal information and may streamline certain business transactions. Check if you need to register for state sales tax collections.
- Insurance : Consider general liability insurance for accidents and negligence claims. Get professional liability (errors and omissions) insurance if you offer professional services.
- Contracts: Use written agreements for business partners and supplier or contractor transactions. This clarifies expectations, prevents disputes, and protects both parties. Contact a lawyer to review or help you write this documentation if needed.
6. Promote and run your business
At this point, you just need to run your business. You don’t need to go all in, either. Launch it as a side hustle until you hit the point where it can become your full-time focus.
Don’t overcomplicate it: Set up a simple website, payment system, and essential operational tools. You want to serve customers immediately and learn from real-world experience.
But unless you locked in pre-orders earlier in this process, you’ll need to market your business to do it.
Select marketing channels you believe will reach your target customers. Start small — you want to avoid overspending while you determine the right mix of marketing tactics. If you’re unsure where to start, paid social media ads (Facebook and Instagram), email campaigns, and local partnerships can be inexpensive options.
Stick to the budget you created, run small, easily measured marketing tests, and look for a positive return on investment (i.e., bringing in more revenue from sales than you spent on advertising).
Only consider increasing spending after you start bringing in customers.
- Continue to review and revise
You are on your way to running a sustainable business and may even have your first customers already!
Just don’t get too far ahead of yourself. You’re still proving that there is traction that can be repeated with multiple customers.
As you operate, review your plan and forecasts. Pay close attention to your cash flow and be willing to pivot if things aren’t working.
That’s the benefit of starting from scratch: You are in full control and can scale and spend at a pace that improves your chances of success.
If you haven’t yet, download a free one-page business plan template to document your idea. The earlier you begin developing the plan, the more useful it will be throughout the startup process.
Clarify your ideas and understand how to start your business with LivePlan
Kody Wirth is a content writer and SEO specialist for Palo Alto Software—the creator's of Bplans and LivePlan. He has 3+ years experience covering small business topics and runs a part-time content writing service in his spare time.
.png?format=auto)
Table of Contents
Related Articles

5 Min. Read
How to Start a Side Hustle

8 Min. Read
How Much Does it Cost to Start a Business?

11 Min. Read
7 Steps to Successfully Start a Business With No Money

2 Min. Read
What to Do Before Starting a Business
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Here are the divestment demands that student protestors are making

Adrian Florido
At the heart of the student protests overtaking college campuses are demands that their universities divest from companies that do business with Israel.
Copyright © 2024 NPR. All rights reserved. Visit our website terms of use and permissions pages at www.npr.org for further information.
NPR transcripts are created on a rush deadline by an NPR contractor. This text may not be in its final form and may be updated or revised in the future. Accuracy and availability may vary. The authoritative record of NPR’s programming is the audio record.
Mark Zuckerberg laid out 3 ways Meta will make money from its huge AI investments
- Mark Zuckerberg has become "more optimistic and ambitious" about Meta's ability to win in AI.
- The Meta CEO now plans to spend about $40 billion this year, largely on AI investments.
- He sees three ways AI can become a "massive business" for Meta in the next few years.

Mark Zuckerberg is now convinced that Meta is a top artificial-intelligence company, and he has even laid out how the technology will become a significant source of profit in the years ahead.
With the recent release of Llama 3 , Meta's latest AI model , Zuckerberg said he became "more optimistic and ambitious on AI" and his company's ability to deliver on the tech.
He made it clear during a Wednesday earnings call with analysts that he intended to "invest significantly more over the coming years to build even more advanced models and the largest-scale AI services in the world."
"With the latest models, we're not just building good AI models that are capable of building some new good social and commerce products," the CEO told analysts. "I actually think we're in a place where we've shown that we can build leading models and be the leading AI company in the world. And that opens up a lot of additional opportunities beyond just the ones that are the most obvious for us."
Heavy spending again
Such ambition doesn't come cheap. Meta increased its guidance on capital expenditure for this year, saying it now planned to spend between $35 billion and $40 billion, largely on AI investments. Its stock slumped 16% in after-hours trading.
The last time Zuckerberg got excited about a new technology — the metaverse — Meta spent wildly and freaked investors out. The stock collapsed and didn't recover until the company embarked on a "year of efficiency" marked by mass layoffs and a more business-minded CEO .
Zuckerberg on Wednesday made a concerted effort to head off Wall Street panic that his new AI enthusiasm is lacking in business acumen.
Related stories
He said he saw "several ways" generative AI could make money and laid out three specific paths to this becoming "a massive business" for Meta. Although he warned that getting there was a "long-term" prospect.
'Business messaging'
One of the ways AI can make money is by building up "business messaging" so that companies pay Meta for generative-AI tools, such as services that support automated interactions with users and customers. Zuckerberg envisions Meta's AI moving beyond just being a chatbot and becoming an AI "agent" that handles more complex tasks and processes multiple queries to solve user problems instead of coming back instantly with rote answers.
Zuckerberg said revenue from AI business messaging was "one of the nearer-term opportunities." While it may not become a reality this year, he said it was less than five years away. He explained that the immediate goal on this front was "getting many hundreds of millions or billions of people to use Meta AI as a core part of what they do."
Ads appearing in AI interactions
Another way generative AI could make money for Meta is by "introducing ads or paid content into AI interactions," as Zuckerberg said. Although brands and companies paying for products to show up in generative-AI results is not yet the standard for AI chatbots, Meta's entire business is effectively driven by selling digital advertising. Inserting ads into its social and messaging products is at the core of Meta as a company.
AI is already being more widely deployed by Meta in its newer "unconnected content" algorithm for social-media content recommendations, which Zuckerberg said was leading to more app engagement. That, in turn, leads to more people seeing more ads. He said that 30% of the content that Facebook users were seeing was recommended by AI, and the same applied to 50% of the content seen by Instagram users.
Selling access to AI models
A third distinct way Meta may make money from AI is by selling access to models as they get larger. "Enabling people to pay to use bigger AI models and access more compute," as Zuckerberg put it on Wednesday.
Right now, Llama 3 and Meta's other large language models are freely available to users and companies below a certain size threshold. Charging for access may be a move away from Meta's "open source" approach.
"So if the technology and products evolve in the way that we hope, each of those will unlock massive amounts of value for people and business for us over time," Zuckerberg said, adding, "I think it makes sense to go for it, and we're going to."
Watch: AI expert explains how to incorporate generative AI into your business strategy
- Main content
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.
- India Today
- Business Today
- Reader’s Digest
- Harper's Bazaar
- Brides Today
- Cosmopolitan
- Aaj Tak Campus
- India Today Hindi
Meta is spending around $40 billion on AI services and Mark Zuckerberg has a plan to earn it all back
Meta's massive $40 billion investment in ai services is part of a grand plan by ceo mark zuckerberg. despite costs exceeding initial estimates, zuckerberg is confident that the investment will pay off..
Listen to Story

During a call with analysts, Zuckerberg expressed his optimism about the potential of AI development, stating, "We've shown that we can build leading models and be the leading AI company in the world. And that opens up a lot of additional opportunities beyond just the most obvious ones for us," according to Business Insider.
Meta's Plan for Business Messaging with AI
Ads in ai interactions, charging for access to larger ai models.
A third avenue for AI monetisation is selling access to AI models as they grow larger and more complex. Currently, Meta offers access to its large language models, such as Llama 3, for free to users and companies below a certain size threshold. In the future, Meta may charge for access to larger models and more computing power, potentially deviating from its current open-source approach.
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Labor to fast-track foreign investment to help fund future industrial policy
Treasurer Jim Chalmers will set a target of 30 days to clear cases as he seeks money for build-to-rent and energy transition
- Follow our Australia news live blog for latest updates
- Get our morning and afternoon news emails , free app or daily news podcast
Foreign investment approvals will be made quicker but greater scrutiny will be placed on potential risks as Australia tries to balance economic and security interests, the treasurer, Jim Chalmers, will say on Wednesday.
The Treasury will set a target to process half of foreign investment cases needing approval within 30 days from next January, Chalmers will tell the Lowy Institute in Sydney. It will also seek more funds from abroad to support so-called build-to-rent housing ventures and the energy transition away from fossil fuels.
The budget will also set aside more funds to screen foreign investments in critical infrastructure, minerals and technology. Projects involving sensitive datasets and those to be located near defence sites will also be examined more closely “to ensure that all risks are identified, understood and can be managed”, he will say, according to a copy of his speech.
In an interview with the ABC’s 7.30 program on Tuesday, Chalmers denied the foreign investment reforms were at odds with comments by the trade minister, Don Farrell, in November that Australia was not proposing any changes regarding Chinese investment in critical minerals.
Chalmers said even after the changes, Australia’s foreign investment regime would remain “non-discriminatory”, with the same rules applying regardless of the source country. He said Australia welcomed investment that met the national interest and proposals must be screened “robustly”.
Sign up for Guardian Australia’s free morning and afternoon email newsletters for your daily news roundup
In his speech, Chalmers will say that the nation is facing challenges “vastly different” from a decade ago. These are marked by “heightened geostrategic competition, an international system under continuous pressure, demographic change, greater risk of major shocks to supply chains, and a restructuring of global trade from the net zero transformation”.
Australia’s economy has long relied on foreign investment to bolster the economy even as domestic sources, such as the $3.7tn superannuation industry, continue to grow.
Competition for funds and technology is likely to intensify as governments such as the US and Europe stump up many billions of dollars to foster decarbonisation industries including batteries and renewable energy, often to catch up with China’s advances.
According to Chalmers, the International Monetary Fund found 18,000 instances of subsidy intervention by China, the US and Europe between 2008 and 2021. It also identified a further 2,500 cases last year alone, with those three economic blocks accounting for about half.
Those trends supported the Albanese government’s so-called Future Made in Australia investments , including in critical minerals processing and solar photovoltaic panel production. The 14 May federal budget is likely to contain more funds for such projects.
“We can’t replicate or retrofit the approaches under way elsewhere,” Chalmers will say. “But it would be preposterously self-defeating to leave our policies unchanged in the face of all this industry policy taking shape and taking hold around us.”
Australia had to become “indispensable” to the global decarbonisation efforts. That could only happen, though, “if we align our economic and security interests more tightly, and only if we invest and engage, not just protect or retreat”.
after newsletter promotion
More money will go to the Treasury’s compliance team to “better monitor and enforce” conditions imposed on deals by the foreign investment review board. “This team will also support the use of my call-in power to review investments that come to pose a national security concern in time,” he will say.
The government will also release updated guidance about tax arrangements to ensure foreign companies pay their way.
Foreign investors will be allowed to buy established build-to-rent properties to foster demand and provide incentives to construct new projects.
Direct and portfolio foreign investment reached about $3.5tn in 2023.
As for the pending Future Made in Australia legislation, the government plans to set five key tests for its intervention, ranging from whether the investment is in an industry that the country can be competitive to its contribution “to an orderly path to net zero”.
Other tests include the boosting of skills and support to regional Australia, and whether it improves “Australia’s national security and economic resilience”.
But the private sector will have to play a key role in such investments and “deliver genuine value for money for government”.
- Foreign investment
- Australian economy
- Jim Chalmers (Australian politician)
- Australian politics
- Labor party
Most viewed
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Who Can Be Trusted for Retirement Advice? New Rules Strengthen Protections.
More investment professionals will be required to act in their customers’ best interest when providing advice about their retirement money.

By Tara Siegel Bernard
When you walk into a financial adviser’s office, you expect them to put your best interests above all else — in the same way a doctor would, rather than, say, a car salesman. But many people don’t realize that the rules financial professionals must follow vary, depending on where they work and what products they’re selling.
One of those federal regulations, which governs retirement plans, was just tightened: The Biden administration announced new rules on Tuesday that will require more financial professionals to adhere to a higher standard when providing financial advice about your retirement money.
Starting Sept. 23, investment professionals who hold themselves out as trusted advisers will be required to act as fiduciaries — that is, they can’t place their interests ahead of the investor — when customers pay them for advice on individual retirement accounts, 401(k)s and similar buckets of tax-advantaged dollars. The goal is to minimize conflicts of interest, or at least ensure that they aren’t influencing investment professionals’ advice that lines their pockets at the customers’ expense. The rule, which will be published in the Federal Register on Thursday, will be fully effective in September 2025.
The changes, issued by the Department of Labor, which oversees retirement plans, close loopholes that made it easier for many investment professionals to avoid fiduciary status — including, for example, when workers roll over their savings from a 401(k) plan to an individual retirement account. Those transactions, which totaled nearly $800 billion in 2022, weren’t always covered by these investor protections, even though these sums often amount to a person’s life savings.
“If you’re a retirement investor looking for help with how to manage your retirement investments, it’s only reasonable that you get advice that is prudent, loyal and doesn’t involve misleading you,” said Tim Hauser, deputy assistant secretary for program operations of the Employee Benefits Security Administration at the Labor Department. “It shouldn’t matter what product you’re recommending, and that’s what the rule does.”
This isn’t the first effort to update the federal retirement law known as ERISA , which was enacted in 1974 to oversee private pension plans before 401(k)s existed. Strengthening its protections has been the subject of intense debate for more than a decade, over three presidential administrations.
Indeed, critics (including financial industry stakeholders) say the new regulation — initially introduced in October — was rushed, but the Labor Department has been working on different versions since it introduced its first proposal in 2010 . The Obama administration issued a more stringent rule in 2016 , but the Trump administration hit the brakes before it was fully implemented . An appeals court later struck it down in 2018 . Agency officials said they took comments from the financial industry and others into account and made several changes that are reflected in the final rule . But Lisa M. Gomez, assistant secretary for Employee Benefits Security, said the investor protections remain. “There is nothing in these clarifications or changes that one should interpret as a watering down or a real change in position from the proposal,” she said on a media briefing call.
When the onus is on individuals to save and invest for a financially secure retirement, with money that must last through advanced age, investor protections are paramount. Still, individuals might be wondering why they aren’t entitled to fiduciary-level advice on all of their money, all of the time, regardless of what account it sits in or what type of product they’re investing in.
Here’s an overview of how the rules have changed and what it means for you — and how to find fiduciary-level professionals, regardless of the political climate.
What’s changed and where do these rules apply?
The regulation redefines who is considered an investment fiduciary. Before the changes, financial professionals had to meet a five-part test before they were held to that standard — and one part stated that the person making the recommendation must provide the advice on a regular basis. That means one-time recommendations were not necessarily included, which left 401(k) rollover guidance at risk.
The new rule aims to level the playing field for all financial professionals — including investment brokers and insurance salespeople — who describe themselves as trusted advisers when providing advice about your retirement money. It doesn’t matter whether they’re recommending mutual funds, stock investments, insurance products like annuities, illiquid real estate investments — it’s all covered. Investment brokers selling retirement plans to businesses would also be held to the fiduciary standard.
Why is fiduciary status important? What does it even mean?
Fiduciaries under the federal law known as ERISA must follow strict rules of conduct and avoid conflicts of interest. That means they can’t provide advice that affects their compensation, unless they meet certain conditions to ensure investors are protected. This includes putting policies in place to mitigate those conflicts. Investment professionals must also be upfront with customers about their roles as fiduciaries — if they have conflicts, and many do, they must now acknowledge their fiduciary status in writing.
That should go a long way in helping retirees who land in their offices, said Joe Peiffer, a founding partner of Peiffer Wolf Carr Kane Conway & Wise, a law firm in New Orleans. He said he has represented thousands of investors who have received poor advice, including from insurance salespeople who call themselves financial advisers when selling indexed annuity products and universal life policies — often with “disastrous” results.
“They’re exactly the kind of case that the new D.O.L. rule is trying to address,” he said, referring to the Department of Labor. “Because, currently, when we sue these ‘advisers,’ their response is that they are nothing more than insurance salesman that do not have a fiduciary duty.”
I want to work with someone who will always act in my best interest, on all of my money, not just retirement accounts.
No financial adviser is entirely conflict-free, but the ecosystem in which your adviser works matters — and will influence what type of conflicts are embedded in the way they do business. Some brokers, for example, may be paid more to sell one product over another product. Or, the firm itself might have complex revenue sharing agreements, which is when a mutual fund company makes payments to a brokerage firm — and some funds may pay a firm fatter fees than others.
Under the new rule, any financial professional making recommendations must have “policies and procedures to manage conflicts of interest and ensure providers follow these guidelines,” department officials said.
The simplest way to buy advice is to hire a “fee-only” independent certified financial planner who is a registered investment adviser, which means they are required to act as fiduciaries when providing investment advice about securities (stocks, mutual funds and the like). As part of that fiduciary duty, they must eliminate conflicts or disclose them.
“Your odds of conflicts go up, the longer their disclosures are,” said Benjamin Edwards, a professor at the William S. Boyd School of Law at the University of Las Vegas.
What questions should I ask when choosing an adviser?
There are several , but the most important: Are you a fiduciary who promises to put my interests ahead of yours 100 percent of the time with 100 percent of my money? How do you get paid — and will you get paid more for recommending one investment over another? What’s your investment philosophy — does it involve mostly low cost index-based investments?
Oh, and by the way, will you sign this fiduciary pledge ? If they refuse, find a new adviser who will.
Where can I find a trusted adviser?
There are more places now than there have been in the past: XY Planning Network , Garrett Planning Network and the National Association of Personal Financial Advisors (NAPFA ) are all trade groups whose members accept only fee-based compensation, which minimizes their conflicts of interest. They also allow you to search for professionals based on their expertise (retirement planning, for example, or stock option exercise strategies), “You don’t want the adviser to be learning about how to help you on the fly,” said Alan Moore, a financial planner and co-founder of XY Planning Network.
There are also newer entrants, including Domain Money and Facet , which connect people to independent financial planners who get paid flat fees.
Roboadvisers , or companies that lean heavily on technology to manage your investments but also often have human financial advisers, may be a solid option for people who are just starting out — or who have an investment plan they want to put into place and let run on autopilot.
One of the most valuable services an adviser can provide is saving us from ourselves, in the darkest market moments, when an individual may be most likely to give into emotion and sell investments (or buy) at the worst possible time. Just make sure the adviser is a fiduciary.
Tara Siegel Bernard writes about personal finance, from saving for college to paying for retirement and everything in between. More about Tara Siegel Bernard
A Guide to Making Better Financial Moves
Making sense of your finances can be complicated. the tips below can help..
The way advisers handle your retirement money is about to change: More investment professionals will be required to act in their customers’ best interest when providing advice about their retirement money.
The I.R.S. estimates that 940,000 people who didn’t file their tax returns in 2020 are due back money. The deadline for filing to get it is May 17.
Credit card debt is rising, and shopping for a card with a lower interest rate can help you save money. Here are some things to know .
Whether you’re looking to make your home more energy-efficient, install solar panels or buy an electric car, this guide can help you save money and fight climate change .
Starting this year, some of the money in 529 college savings accounts can be used for retirement if it’s not needed for education. Here is how it works .
Are you trying to improve your credit profile? You can now choose to have your on-time rent payments reported to the credit bureaus to enhance your score.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
This sample plan was created for a hypothetical investment company that buys other companies as investments. In this sample, the hypothetical Venture Capital firm starts with $20 million as an initial investment fund. In its early months of existence, it invests $5 million each in four companies. It receives a management fee of two percent (2% ...
Financial forecasts. Investors will inevitably want to see your financial forecasts. You'll need a sales forecast, expense budget, cash flow forecast, profit and loss, and balance sheet. If you have historical results, you should plan on sharing those too as well as any other key metrics about your business.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
Step #3: Conduct Your Market Analysis. Step #4: Research Your Competition. Step #5: Outline Your Products or Services. Step #6: Summarize Your Financial Plan. Step #7: Determine Your Marketing Strategy. Step #8: Showcase Your Organizational Chart. 14 Business Plan Templates to Help You Get Started.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 1. Create a Cover Page. The first thing investors will see is the cover page for your business plan. Make sure it looks professional. A great cover page shows that you think about first impressions. A good business plan should have the following elements on a cover page:
Learn about the best business plan software. 1. Write an executive summary. This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your ...
Identify the three to four key factors that make your company a great opportunity and make sure they're included in this section. 3. Team Overview. This is where you introduce your team and how you'll work together to bring the business to life. An ideal Team Overview section makes the case not only that your team is the right team for the ...
Although business plans can vary greatly, there are a few essential elements. Here are eight sections that a business plan should include: Executive Summary: This is an overview of the rest of your business plan. It will summarize things like your mission statement, plans, goals, structure, and financial needs.
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
An unrealistic plan is as unattractive to investors as a lack of vision and ambition. 3. Seek professional input. Don't be afraid to ask for help. Experienced business advisors, accountants, and ...
Investment Company Business Plan. Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 1,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their investment companies. On this page, we will first give you some background information with regards to the importance of business planning. We will then go through an investment ...
You will essentially create two plans. The first is known as the internal or initial start-up business plan. This plan includes your company's mission statement, product/service description, marketing strategy plan and initial start-up goals. Most importantly, the initial plan will also include a market analysis.
Step 3: Customers. Olivia has done her research, which is the fundamentals upon which any business plan should be based. People love statistics. Olivia found statistics describing the growth in plant-based eating in the past decade, as well as the growth of flexitarian dietary choices.
PlanBuildr's Investment Company business plan template will help you to quickly and easily complete your Investment Company business plan. PlanBuildr's Investment Company business plan template will help you to quickly and easily complete your Investment Company business plan. ... Initial expenditure: $10,000: $0: $0: $0: $0: Total Expenses ...
Whether you want to launch a side gig, a solo operation or a small business, you need a simple business plan template to guide you. Forbes Advisor offers you a comprehensive and easy-to-follow ...
14 business startup costs to plan for. Although this is a typical list of business startup costs, your actual startup expenses depend entirely upon your specific business and industry. Here are ...
Writing an investment company business plan is a crucial step toward the success of your business. Here are the key steps to consider when writing a business plan: 1. Executive Summary. An executive summary is the first section planned to offer an overview of the entire business plan. However, it is written after the entire business plan is ...
Here is a basic template that any business can use when developing its business plan: Section 1: Executive Summary. Present the company's mission. Describe the company's product and/or service offerings. Give a summary of the target market and its demographics.
Initial investment. = equipment purchase price + shipment and installation + increase in working capital − disposal inflows. = $1,500 million + $200 million + ($200 million − $90 million) − $120 million. = $1,690 million. SCCL needs $1,690 million to restart the project. It needs to estimate future cash flows from the project, and ...
A major external purpose for the business plan is as an investment tool that outlines financial projections, becoming a document designed to attract investors. In many instances, a business plan can complement a formal investor's pitch. ... Off the Grid's annual report indicates the average typical initial investment ranges from $55,000 to ...
4. Write a business plan and develop financial forecasts. At this point, you need to finalize your business plan and create initial forecasts. If you've been using the one-page plan throughout the last few steps, then this shouldn't be a time-consuming process. Your goal at this point is to clearly define:
Here are the divestment demands that student protestors are making At the heart of the student protests overtaking college campuses are demands that their universities divest from companies that ...
Mark Zuckerberg is now convinced that Meta is a top artificial-intelligence company, and he has even laid out how the technology will become a significant source of profit in the years ahead. With ...
The Kroger Co. (NYSE: KR) and Albertsons Companies Inc. (NYSE: ACI) announced today that they have amended their definitive agreement with CS Wholesale Grocers, LLC (CS) for the sale of assets in connection with their proposed merger previously announced on October 14, 2022. This amended package modifies and builds on the initial divestiture package that was announced on September 8, 2023.
When Mike Henry took over as chief executive officer of BHP Group in 2020, the world's biggest mining company had lost its swagger.. Bruised by a series of painful missteps and a run-in with ...
Meta's massive $40 billion investment in AI services is part of a grand plan by CEO Mark Zuckerberg. Despite costs exceeding initial estimates, Zuckerberg is confident that the investment will pay off. Listen to Story Meta has overspent on its AI plans, with costs reaching between $35 and $40 ...
CNBC
Treasurer Jim Chalmers will set a target of 30 days to clear cases as he seeks money for build-to-rent and energy transition Foreign investment approvals will be made quicker but greater scrutiny ...
The changes, issued by the Department of Labor, which oversees retirement plans, close loopholes that made it easier for many investment professionals to avoid fiduciary status — including, for ...