
- Science Notes Posts
- Contact Science Notes
- Todd Helmenstine Biography
- Anne Helmenstine Biography
- Free Printable Periodic Tables (PDF and PNG)
- Periodic Table Wallpapers
- Interactive Periodic Table
- Periodic Table Posters
- How to Grow Crystals
- Chemistry Projects
- Fire and Flames Projects
- Holiday Science
- Chemistry Problems With Answers
- Physics Problems
- Unit Conversion Example Problems

Chemistry Worksheets
- Biology Worksheets
- Periodic Table Worksheets
- Physical Science Worksheets
- Science Lab Worksheets
- My Amazon Books
Chemistry Worksheets and Handouts (PDF for Printing)

This is a collection of free chemistry worksheets and handouts to print. Most of the printables are PDF files, although some are available as JPG or PNG files. All of these worksheets print cleanly on normal printer paper, plus you can resize them to fit your needs.
Here is a list of worksheets. This site also has articles explaining these topics in detail.
- Label Parts of the Atom [ Google Apps worksheet ][ worksheet PDF ][ worksheet PNG ][ answers PNG ]
- Acid formulas [ PDF ][ Answers ]
- Balancing equations Worksheet #1 [ PDF ][ Answers ] Worksheet #2 [ PDF ][ Answers ] Worksheet #3 [ PDF ][ Answers ] Worksheet #4 [ PDF ][ Answers ]
- Chemical and Physical Changes [ PDF ][ Answers ]
- Chemistry scavenger hunt [ PDF clues ][ Answers ]
- Element names crossword [ PDF ][ Answers ]
- Element symbols – Symbols that make words [ PDF worksheet ][ Answers ]
- Element symbols – Countries of the world [ PDF ][ Answers ]
- More element symbol worksheets
- Homogeneous or Heterogeneous Mixtures [ PDF ][ Answers ]
- Intensive and Extensive Properties [ Worksheet ][ Answer Key ]
- Intrinsic and Extrinsic Properties [ PDF ][ Answers ]
- Ionic and Covalent Compounds (Names and Identification) [ PDF Worksheet ][ Answer Key ]
- Ionic Compound Names and Formulas [ PDF Worksheet ][ Answer Key ]
- Metric to English Unit Conversions [ PDF Worksheet ][ Answer Key ]
- Mixtures [ PDF ][ Answers ]
- Periodic table scavenger hunt [ PDF clues ][ Answers ]
- Reading a meniscus [ PDF ][ Answers ]
- Reading periodic table element information Worksheet #1 [ PDF ][ Answers ] Worksheet #2 [ PDF ][ Answers ]
- Scientific Notation [ PDF ][ Answers ]
- Significant digits Rules [ PDF ][ Answers ] Addition and subtraction [ PDF ][ Answers ] Multiplication and division [ PDF ][ Answers ]
- Types of Chemical Reactions [ Worksheet ][ Answers ]
In addition to these chemistry worksheets, there is a collection of word search puzzles .
Chemistry Handouts
These chemistry handouts illustrate chemistry concepts and offer examples.
- Amino acid side chains [ PDF ]
- Antimatter examples [ PNG ]
- Atom facts [ PNG ]
- Chemical properties [ JPG ]
- Colligative properties [ JPG ]
- Electron configurations [ PDF ]
- Element electronegativities [ PDF ]
- 118 Element Flash Cards [ PDF ]
- Element list [ PDF ]
- Endothermic reactions [ PNG ]
- Error calculations [ JPG ]
- Exothermic reactions [ JPG ]
- Heterogeneous mixtures [ JPG ]
- Hydrocarbon prefixes [ JPG ]
- Ionic compound properties [ PNG ]
- Genetic codons [ PDF ]
- Lewis structures [ JPG ]
- Litmus test [ PNG ]
- Magnetic vs non-magnetic metals [ JPG ]
- Mole ratio [ JPG ]
- Organic vs inorganic [ JPG ]
- Oxidation numbers [ JPG ]
- Periodic table Bingo game [ PDF ]
- pH indicators [ PNG ]
- Physical change [ JPG ]
- Physical properties [JPG ]
- Noble metals [ JPG ]
- Reactants and products [ JPG ]
- RNA vs DNA [ JPG ]
- States of matter [ JPG ]
- Visible spectrum [ JPG ]
Periodic Tables
There’s a printable periodic table for just about any purpose, but some of the most popular are listed here.

- 118 element vibrant periodic table [ PNG ]
- Actinides [ JPG ]
- Blank periodic table [ PDF ]
- Element charges [ JPG ]
- Element density [ PDF ]
- Element electrical conductivity [ PDF ]
- Element state of matter [ PDF ]
- Muted color 118 element periodic table [ PDF ]
- Native elements [ JPG ]
- Valence [ JPG ]

Biology Worksheets and Handouts
Is biology more your thing? We’ve got similar resources for the life sciences, including biology, biochemistry, cell biology, and anatomy.
Chemistry Worksheets Terms of Use
You are welcome to print these resources for personal or classroom use. They may be used as handouts or posters. They may not be posted elsewhere online, sold, or used on products for sale.
This page doesn’t include all of the assets on the Science Notes site. If there’s a table or worksheet you need but don’t see, just let us know!
Related Posts
Browse Course Material
Course info, instructors.
- Dr. Kimberly Berkowski
- Prof. Sarah O’Connor
Departments
As taught in.
- Organic Chemistry
Learning Resource Types
Organic chemistry i, assignments.

You are leaving MIT OpenCourseWare

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

2.8: Assignment- Chemistry in Biology
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 44300
Open Pedagogy Assignments are assignments in which students use their agency and creativity to create knowledge artifacts that can support their own learning, their classmates’ learning, and the learning of students around the world. (See this peer-reviewed article for more details.) The assignment on this page is aligned to a learning outcome of Biology for Non-Majors I and we’ve identified the module where the reading appears. The assignment can be created with basic web and computing tools, a cell phone camera or any video recording device, Google or Word documents, and your learning management system.
Learning Objectives
- Identify the principles of chemistry that are integral to biology.
In the module on Chemistry, we provide a general overview of how the principles of chemistry form the basis of biology. For this assignment, you are going to reflect upon which concept(s) in this module were most difficult for you to learn.
The product of your work will help future students to learn about some of the most difficult concepts in the course. Thus, think of your audience as friends who are taking Biology for Nonmajors in the next term. You want to help them understand a concept in the course that was particularly difficult for you.
First, identify a concept from this module that you struggled to learn regarding the basic principles of chemistry in biology. Review the content in the module and anything further you learned in class. Then, think of how you would explain the concept in your own words to a friend who is also taking the course. Keep these questions in mind:
- What was missing when you first tried to grasp the concept? In other words, did you have to read something twice?
- How could things have been phrased or framed differently? In other words, did you look up a word or concept to understand it?
- How would you rewrite an example or how the concept was presented?
Second, using your cell phone or any other recording device, create a short video explaining the topic in your own words. You don’t have to edit or create a professional-grade film. You’ve most likely have done this type of recording already on social media, so feel free to use the same informal conversational tone. Use additional images or tips that would have been helpful for you.
Lastly, share the video with your instructor. After grading and with your permission, your video may appear in future sections of the course to improve other students’ learning.
A Note To Teachers: The first time your students complete this assignment, choose the best ones and ask students for permission to include them in future sections. Just post the videos in the appropriate module in the LMS. The idea is to have students generate content that other students can learn from in this assignment.
- Book A Demo
Homework & Practice
Aktiv Chemistry is a comprehensive online homework platform that helps students build mastery of chemistry. Take advantage of over 15,000 built-in chemistry problems, scaffolded practice, a powerful instructor dashboard, LMS grade syncing, and much more.

All-in-one platform
Comprehensive learning & assessment.
From in-class active learning, homework assignments, and now secure online quizzes and exams, Aktiv Chemistry’s all-in-one platform provides a comprehensive set of features for formative and summative assessments.
In-class or Synchronous Online
Take attendance, post polls & quizzes, enhance traditional worksheets, or promote think-pair-share activities. Learn More
Assign interactive problem sets with instant feedback and automatic grading that sync with institutional LMS gradebooks.

Timed Online Quizzes & Exams
Create summative assessments with question pools, algorithmic problems, and optional integrated proctoring. Learn More
15,000 PROBLEMS OR WRITE YOUR OWN
Extensive content library.
Building engaging classroom activities has never been easier. Aktiv Chemistry provides an extensive library of questions for chemistry courses such as General Chemistry, Introductory Chemistry, GOB Chemistry, Organic Chemistry. The content library includes discipline-specific problem types such as molecule drawing, chemical equations and naming, dimensional analysis, numerical entry, and more.
Easy and flexible authoring also allows instructors to add their own questions.
Learn More About
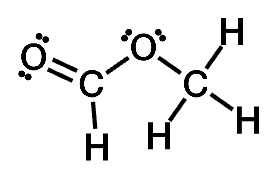
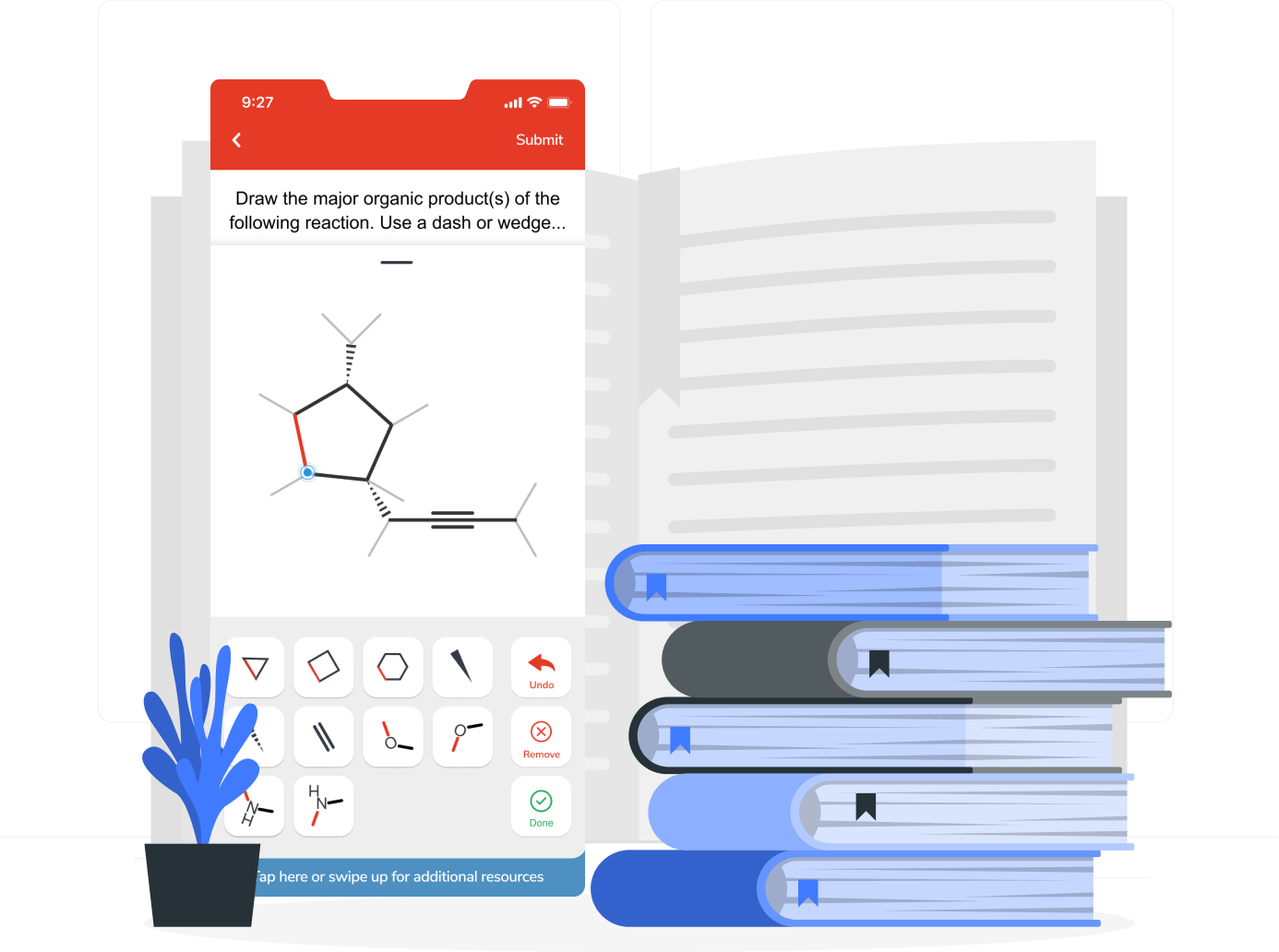
Draw the Lewis structure of (CHO)OCH₃ and then choose the appropriate set of molecular geometries of the three central atoms. Your answer choice is independent of the orientation of your drawn structure.
The solubility of He in water at 25.0 °C is 7.0 × 10⁻⁵ M when the partial pressure of He is 0.20 atm. What is the value of the Henry's law constant for He ?
- monosaccharide
- oligosaccharide
- monopolysaccharide
- heteropolysaccharide
- homopolysaccharide
According to the balanced reaction below, calculate the moles of NH₃ that form when 4.2 mol of N₂H₄ completely reacts 3 N₂H₄(l) → 4 NH₃(g) + N₂(g)
AFFORDABLE & FLEXIBLE
Built to work with any textbook.
Aktiv Chemistry ’s textbook independent approach means instructors have more flexibility for their courses. Build assignments that align to any major publisher textbook or increasingly popular OER options.
For General Chemistry courses, Aktiv Chemistry also offers seamless integration with the OpenStax Chemistry textbooks.
Student Success
More chemistry, less technology.
Drawing chemical structures, entering subscripts and superscripts, and working with significant figures just shouldn’t be hard. That’s why Aktiv Chemistry was designed from the ground up with the student experience in mind. With intuitive user interfaces and scaffolded and visual modules, our goal is to use technology to lower the barrier to chemistry.
Bring Your Own Device. Any Device.
Students and instructors can access the Aktiv Learning app from any iPhone, iPad, or Android Device. Additionally, the platform is fully accessible on Web with any Mac, PC, or Chromebook.
Aktiv Chemistry ’s mobile-first design ensures that students receive the same experience no matter where they are. Students take advantage of the Aktiv Learning mobile app to work and study on-the-go in places like riding the bus or train, or even on campus when they have downtime.
RANDOMIZATION WITH
Algorithmic problems & question pools.
Aktiv Chemistry offers additional security with both Question Pools and Algorithmic Problems. These features randomize the content that is delivered to each student during homeworks, quizzes, or exams. Instructors can also randomize the order of questions on any assignment.
Built-in variables create thousands of question variants to be delivered that randomize numbers, words, or compounds within the problem statement.
Group together a set of similar questions and deliver a subset of them at random to students.
Problem Pool 1
14 problems in this pool
- Problems to Assign
What is the correct IUPAC name for HBrO(aq)?
What is the correct IUPAC name for Ca(BrO₂)₂?
What is the correct IUPAC name for Ti(ClO₄)₄?
Success Story
Professors from over 700 colleges and universities use Aktiv Chemistry to engage students inside and outside of the classroom. Learn how some of them have transformed their courses.

Helping Students Learn, Interact, and Visualize Chemistry in New Ways

¹ This quote was provided at a time where Aktiv Chemistry was named Chem101. We have replaced the use of Chem101 in any direct quotes with Aktiv Chemistry to minimize confusion.
DESIGNED TO
Support your course, flexible grading policies.
Every Aktiv Chemistry activity has a multitude of grading policies that can be customized depending on the assignment type. Settings include points per problem, participation credit, late submissions with penalties, variable attempts per problem, penalties for incorrect attempts, and more. The Aktiv Chemistry gradebook can be set up to display summary columns or individual columns depending on the assignment type as well.
Industry-leading Support
Any course using Aktiv Chemistry comes with our industry-leading support featuring average response times of 14 minutes and extended hours that include late nights and weekends. Additionally, every Aktiv Chemistry instructor works with an individual member of our Success team that helps with initial course set up, gradebook/LMS integrations, and recommendations for best practices.
LMS Integrated
Aktiv Chemistry’s gradebook can be synced with any popular campus LMS such as Canvas, Blackboard, Moodle, or D2L. The gradebook and associated columns can be customized to separate the various assignment types, to present individual assignments, or display summary columns for each type.
Speak to a Specialist
One of our Learning Specialists will give you a tour of the Aktiv Chemistry or Aktiv Mathematics learning platforms and provide a free instructor playground account with access to the content library.
I Want to Learn More About:
Home / Introduction to Assigning (R) and (S): The Cahn-Ingold-Prelog Rules
Stereochemistry and Chirality
By James Ashenhurst
- Introduction to Assigning (R) and (S): The Cahn-Ingold-Prelog Rules
Last updated: February 20th, 2024 |
Assigning R and S Configurations With the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog (CIP) Rules
- Enantiomers are stereoisomers that are non-superimposable mirror images of each other (by the way, molecules that are superimposable mirror images of each other are considered to be identical molecules).
- Enantiomers rotate plane-polarized light in equal and opposite directions, but there is no straightforward way to trace back the absolute configuration of a molecule to the direction of optical rotation
- A tetrahedral atom with four different substituents (a chiral center) can have two different configurations. A naming scheme developed by Cahn, Ingold and Prelog (CIP) is used for assigning the terms R or S to each chiral center. (When all the (R,S) designations of a molecule are specified, this is referred to as its “ absolute configuration”.)
- In the CIP protocol, each atom attached to the chiral center is ranked in order of atomic number (highest = #1, lowest = #4). (We go further down the chain in the event of ties. )
- With the #4 substituent in the back: if #1, #2, and #3 trace a clockwise path, the chiral center is assigned (R) . If they trace a counterclockwise path the chiral center is (S) .
- When #4 is in the front or on the side, some useful tips and tricks can be used to avoid having to rotate the whole molecule ( See also: How To Draw The Enantiomer of A Chiral Molecule ).
- For breaking ties, it’s useful to keep track of which carbons you’re working on with the “dot method”.
Table of Contents
- Chiral Centers And The Problem Of Naming
- The Cahn-Ingold-Prelog System For Naming Chiral Centers
- Oh No! What Do We Do When #4 Is Not In The Back?
- Assigning R/S When #4 Is In The Front: A Short Cut
- Assigning R/S When #4 Is In The Plane Of The Page
- Breaking Ties With The “Dot Technique”
- Conclusion: Assigning R and S With CIP
(Advanced) References and Further Reading
This post was co-authored by Matt Pierce of Organic Chemistry Solutions . Ask Matt about scheduling an online tutoring session here .
1. Chiral Centers And The Problem Of Naming
Previously on MOC we’ve described enantiomers : molecules that are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. Perhaps the most memorable example is these “enantiocats”.
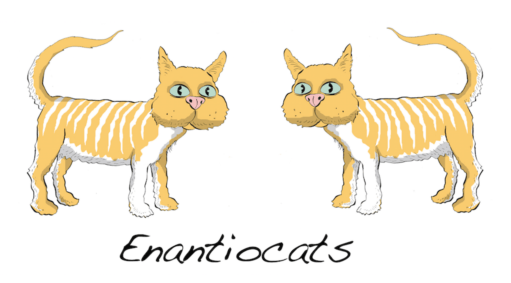
Each of these cats is said to be “chiral”: they lack a plane of symmetry.
What causes molecules to have chirality?
The most common source of chirality is a “chiral centre”: typically a tetrahedral carbon attached to four different “groups”, or “substituents”. For each chiral centre there are two (and only two!) different ways of arranging the 4 different substituents, which gives rise to two different configurations. [If you don’t believe there are only two, see Single Swap Rule ].
The purpose of this post is to introduce and describe the nomenclature we use to describe these configurations: the (R)/(S) notation, or Cahn-Ingold Prelog Rules.
Let’s look at a simple example.
Both of these molecules are 1-bromo-1-chloroethane. But they are not exactly the same molecule, in the same way that your left shoe is not exactly the same as your right. They are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. How do we communicate this difference?
One way would be to describe their physical properties. For example, although these two molecules have the same boiling point, melting point, and share many other physical properties, they rotate plane-polarized light in equal and opposite directions, a property called optical rotation ( See Optical Rotation and Optical Activity ) We could use (+)-1-bromo-1-chloroethane to refer to the isomer that rotates polarized light to the right (clockwise, or “dextrorotatory”) and use (-)-1-bromo-1-chloroethane to refer to the isomer that rotates polarized light to the left (counterclockwise, or “levorotatory”).
However this nomenclature suffers from a serious problem. There is no simple correlation between the arrangement of substituents around a chiral centre and the direction in which polarized light is rotated . Another solution is needed.
2. The Cahn Ingold Prelog (CIP) System For Naming Chiral Centers
A solution to this quandary was proposed by Robert Cahn, Chris Ingold, and Vladimir Prelog in 1966. The resulting “CIP” protocol works as follows:
- Prioritize the four groups around a chiral center according to atomic number . The highest atomic number is assigned priority #1, and the lowest atomic number is assigned priority #4.
- Orient the chiral centre such that the #4 priority substituent is pointing away from the viewer. For our purposes, it’s enough for it merely to be attached to a “dashed” bond.
- If the path traced from 1-2-3 is clockwise , the chiral center is assigned ( R ) (from Latin, rectus )
- If the path traced is counter clockwise , the chiral center is assigned ( S ) (from the Latin sinister)
- Now we have a better way to describe molecules [A] and [B] shown above. Molecule [A] is named ( R )-1-bromo-1-chloroethane, and molecule [B] is named ( S )-1-bromo-1-chloroethane:
We should reiterate that the designations (R) and (S) bear no relationship to whether a molecule rotates plane-polarized light clockwise (+) or counterclockwise (-). For example the most common naturally occurring configuration of the amino acid alanine is (S), but its optical rotation (in aqueous acid solution) is (+).
3. What About When #4 Is Not In The Back?
That seems simple enough! “Is that it?”, you might ask.
Uh, no. As it happens, there’s a few bumps in the road toward determining (R)/(S) once we get beyond the simple example above.
These “trickier cases” fall into three main categories.
- What if the #4 substituent is not helpfully pointing away from the viewer , as it was in our example above? What if it’s in the “front” (i.e. attached to a “wedged” bond) or, heaven forbid, in the plane of the page?
- Assigning priorities in complex situations . What do we do in situations where a chiral centre has two or more identical atoms attached? In other words, how do we break ties?
- What do we do if the molecule is drawn a peculiar way , such as in Fischer or Newman projections ?
We’re not going to be able to fully address all of these issues in this post. But we can certainly deal with #1 and make some headway with #2. For #3, see How To Determine R/S On A Fischer Projection and How to Determine R/S on a Newman Projection
4. Determining R/S When The #4 Substituent Is In Front (i.e. on a “Wedge”): A Short Cut
Let’s first consider the molecule below. The name of this molecule is ( R )-1-fluoroethanol. It is listed below with priorities assigned based on atomic number. In this case F>O>C>H. So F is #1 and H is #4. The tricky part here is that the #4 priority is pointing out of the page (on a “wedge”).
How do we determine (R)/(S) in this case? There are two ways to do it.
Many instructors will tell you to “simply” rotate the molecule in your head so that the #4 priority is on a dash. Then you can assign R or S in the traditional way. This “simple” advice is not always an easy task for beginners.
Thankfully, it is technically unnecessary to perform such a mental rotation.
Here’s a way around this. When the #4 priority is on a wedge you can just reverse the rules. So now we have two sets of rules:
If the #4 priority is on a dash :
- Clockwise = R
- Counterclockwise = S
If the #4 priority is on a wedge , reverse the typical rules:
- Clockwise = S
- Counterclockwise = R
R and S can easily be assigned to either picture of the molecule. I still encourage you to use a model kit and learn how to do so, however. Organic chemistry is much easier to understand, and much more beautiful, if you can master how to visualize a tetrahedral carbon atom.
See also, How To Draw The Enantiomer of A Chiral Molecule
5. Determining R/S When The #4 Group Is In The Plane Of The Page?
What if the #4 priority is in the plane of the paper, for example on a line? In this case it’s impossible to assign R and S in the traditional way. You’d have a 50:50 shot of getting it correct: not good odds. Again, if you can redraw the molecule in your head, then it’s better to just do that. If you can’t do this reliably then you need to learn the “single swap” concept.
Here’s how it works. Swapping any two groups on a chiral centre will flip the configuration of the chiral centre from R to S (and vice versa). [ We previously talked about the “single swap rule” here ]
Knowing this, we can do a nifty trick.
- Take the #4 substituent (in the plane of the page) and swap it with the substituent in the back [If the configuration is R, this will switch it to S. If the configuration is S, this will flip it to R. We’ll need to account for this in step #3].
- Redraw the chiral centre, and determine R/S on the new chiral centre which now has group #4 in the back.
- Whatever result you got, flip it to its opposite to account for the fact that you did a single swap in step #1.
Here’s an example. Note that here I first switched #4 and #3, but the main point is to switch two groups so that #4 is out of the plane of the paper.
This method always works, assuming you’ve determined the four priorities accurately. (It also works for cases when #4 is on a wedge).
However, sometimes we’re not in the position of dealing with 4 different atoms attached to a chiral carbon. For instance, it’s possible to have chiral carbons which are attached to 4 carbons . So how do we break the ties in these cases?
6. Determining CIP Priorities: Breaking “Ties” With The “Dot Technique”
The quick answer is to use the “dot technique”. Here’s how it works. Let’s do it for 4-ethyl-4-methyloctane, above.
- Go outward from the chiral centre to each of the surrounding 4 atoms and assign priorities (based on atomic number) to each of these atoms. [Sometimes it’s helpful to draw dots on each of these atoms.]
3. Compare each list, atom by atom. In our example, since C>H, (C,H,H) takes priority over (H,H,H) so the CH 3 group is assigned priority #4.
4. If there is still a tie, move the dots to the highest ranking atom in the list (i.e. the atom with highest atomic number). The dots are helpful because they help you to keep track of where you are, which can be important in complex examples.
5. In this case, we keep moving along the chain. By the way, if you ever reach the end of the chain without determining a difference, that means that the groups are identical and it isn’t a chiral centre after all.
6. By this point we have enough information to assign (R)/(S). Since priority #4 is in the front, we can also break out our “opposite rule” for good measure:
7. Conclusion: The Cahn-Ingold-Prelog Rules For Assigning R and S Configurations
In the next post we’ll go into some trickier examples with determining R/S, including how to deal with double bonds, rings, and isotopes. In a future post, we’ll get into determining R/S in the Fischer and Newman projections.
Thanks to Matt Pierce for making major contributions to this article.
Ask Matt about scheduling an online tutoring session here .
Related Articles
- Assigning Cahn-Ingold-Prelog (CIP) Priorities (2) – The Method of Dots
- How To Draw The Enantiomer Of A Chiral Molecule
- How To Determine R and S Configurations On A Fischer Projection
- Assigning R/S To Newman Projections (And Converting Newman To Line Diagrams)
- Types of Isomers: Constitutional Isomers, Stereoisomers, Enantiomers, and Diastereomers
- On Cats, Part 4: Enantiocats
- On Cats, Part 6: Stereocenters
- Stereochemistry Practice Problems and Quizzes (MOC Membership)
- How To Draw A Bond Rotation
- Specification of Molecular Chirality R. S. Cahn, Sir Christopher Ingold, V. Prelog Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1966, 5 (4), 385-415 DOI: 10.1002/anie.196603851 This is not the first paper on the topic by the authors (see Refs. 4 and 5), but it is a major publication and an attempt to consolidate all the information on chirality in a single place. This paper discusses the various types of chirality possible in chemistry (not just at tetrahedral carbons!) and how to assign chirality unambiguously.
- Basic Principles of the CIP‐System and Proposals for a Revision Dr. Vladlmir Prelog and Prof. Dr. Günter Helmchen Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1982 , 21 (8), 567-583 DOI: 10.1002/anie.198205671 An update to Ref. #1, which addresses a lot of edge cases that may come up in complex stereochemical assignments.
- CHIRALITY IN CHEMISTRY Vladimir Prelog Nobel Lecture, 1975 Prelog’s Nobel Lecture. Nobel Lectures are fascinating to read as they give insight into the life of scientists and the path to discovery, which is rarely linear.
- “Absolutely” simple stereochemistry Philip S. Beauchamp Journal of Chemical Education 1984, 61 (8), 666 DOI : 10.1021/ed061p666 This paper describes a simple method for determining stereochemistry of tetrahedral carbons using the hands, suitable for undergraduate students of organic chemistry.
- A simple hand method for Cahn-Ingold-Prelog assignment of R and S configuration to chiral carbons Martin P. Aalund and James A. Pincock Journal of Chemical Education 1986, 63 (7), 600 DOI : 10.1021/ed063p600 A follow-up to the previous paper (Ref #4), but sadly it is incomplete!
- A Web-Based Stereochemistry Tool to Improve Students’ Ability to Draw Newman Projections and Chair Conformations and Assign R/S Labels Nimesh Mistry, Ravi Singh, and Jamie Ridley Journal of Chemical Education 2020, 97 (4), 1157-1161 DOI : 10.1021/acs.jchemed.9b00688 This paper discusses a web-based tool that helps students with visualization of chiral compounds and assignment of stereochemistry as per the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog (CIL) rules. See ref. 34 in the paper for the link.
00 General Chemistry Review
- Lewis Structures
- Ionic and Covalent Bonding
- Chemical Kinetics
- Chemical Equilibria
- Valence Electrons of the First Row Elements
- How Concepts Build Up In Org 1 ("The Pyramid")
01 Bonding, Structure, and Resonance
- How Do We Know Methane (CH4) Is Tetrahedral?
- Hybrid Orbitals and Hybridization
- How To Determine Hybridization: A Shortcut
- Orbital Hybridization And Bond Strengths
- Sigma bonds come in six varieties: Pi bonds come in one
- A Key Skill: How to Calculate Formal Charge
- The Four Intermolecular Forces and How They Affect Boiling Points
- 3 Trends That Affect Boiling Points
- How To Use Electronegativity To Determine Electron Density (and why NOT to trust formal charge)
- Introduction to Resonance
- How To Use Curved Arrows To Interchange Resonance Forms
- Evaluating Resonance Forms (1) - The Rule of Least Charges
- How To Find The Best Resonance Structure By Applying Electronegativity
- Evaluating Resonance Structures With Negative Charges
- Evaluating Resonance Structures With Positive Charge
- Exploring Resonance: Pi-Donation
- Exploring Resonance: Pi-acceptors
- In Summary: Evaluating Resonance Structures
- Drawing Resonance Structures: 3 Common Mistakes To Avoid
- How to apply electronegativity and resonance to understand reactivity
- Bond Hybridization Practice
- Structure and Bonding Practice Quizzes
- Resonance Structures Practice
02 Acid Base Reactions
- Introduction to Acid-Base Reactions
- Acid Base Reactions In Organic Chemistry
- The Stronger The Acid, The Weaker The Conjugate Base
- Walkthrough of Acid-Base Reactions (3) - Acidity Trends
- Five Key Factors That Influence Acidity
- Acid-Base Reactions: Introducing Ka and pKa
- How to Use a pKa Table
- The pKa Table Is Your Friend
- A Handy Rule of Thumb for Acid-Base Reactions
- Acid Base Reactions Are Fast
- pKa Values Span 60 Orders Of Magnitude
- How Protonation and Deprotonation Affect Reactivity
- Acid Base Practice Problems
03 Alkanes and Nomenclature
- Meet the (Most Important) Functional Groups
- Condensed Formulas: Deciphering What the Brackets Mean
- Hidden Hydrogens, Hidden Lone Pairs, Hidden Counterions
- Don't Be Futyl, Learn The Butyls
- Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, Quaternary In Organic Chemistry
- Branching, and Its Affect On Melting and Boiling Points
- The Many, Many Ways of Drawing Butane
- Wedge And Dash Convention For Tetrahedral Carbon
- Common Mistakes in Organic Chemistry: Pentavalent Carbon
- Table of Functional Group Priorities for Nomenclature
- Summary Sheet - Alkane Nomenclature
- Organic Chemistry IUPAC Nomenclature Demystified With A Simple Puzzle Piece Approach
- Boiling Point Quizzes
- Organic Chemistry Nomenclature Quizzes
04 Conformations and Cycloalkanes
- Staggered vs Eclipsed Conformations of Ethane
- Conformational Isomers of Propane
- Newman Projection of Butane (and Gauche Conformation)
- Introduction to Cycloalkanes (1)
- Geometric Isomers In Small Rings: Cis And Trans Cycloalkanes
- Calculation of Ring Strain In Cycloalkanes
- Cycloalkanes - Ring Strain In Cyclopropane And Cyclobutane
- Cyclohexane Conformations
- Cyclohexane Chair Conformation: An Aerial Tour
- How To Draw The Cyclohexane Chair Conformation
- The Cyclohexane Chair Flip
- The Cyclohexane Chair Flip - Energy Diagram
- Substituted Cyclohexanes - Axial vs Equatorial
- Ranking The Bulkiness Of Substituents On Cyclohexanes: "A-Values"
- Cyclohexane Chair Conformation Stability: Which One Is Lower Energy?
- Fused Rings - Cis-Decalin and Trans-Decalin
- Naming Bicyclic Compounds - Fused, Bridged, and Spiro
- Bredt's Rule (And Summary of Cycloalkanes)
- Newman Projection Practice
- Cycloalkanes Practice Problems
05 A Primer On Organic Reactions
- The Most Important Question To Ask When Learning a New Reaction
- Learning New Reactions: How Do The Electrons Move?
- The Third Most Important Question to Ask When Learning A New Reaction
- 7 Factors that stabilize negative charge in organic chemistry
- 7 Factors That Stabilize Positive Charge in Organic Chemistry
- Nucleophiles and Electrophiles
- Curved Arrows (for reactions)
- Curved Arrows (2): Initial Tails and Final Heads
- Nucleophilicity vs. Basicity
- The Three Classes of Nucleophiles
- What Makes A Good Nucleophile?
- What makes a good leaving group?
- 3 Factors That Stabilize Carbocations
- Equilibrium and Energy Relationships
- What's a Transition State?
- Hammond's Postulate
- Learning Organic Chemistry Reactions: A Checklist (PDF)
- Introduction to Free Radical Substitution Reactions
- Introduction to Oxidative Cleavage Reactions
06 Free Radical Reactions
- Bond Dissociation Energies = Homolytic Cleavage
- Free Radical Reactions
- 3 Factors That Stabilize Free Radicals
- What Factors Destabilize Free Radicals?
- Bond Strengths And Radical Stability
- Free Radical Initiation: Why Is "Light" Or "Heat" Required?
- Initiation, Propagation, Termination
- Monochlorination Products Of Propane, Pentane, And Other Alkanes
- Selectivity In Free Radical Reactions
- Selectivity in Free Radical Reactions: Bromination vs. Chlorination
- Halogenation At Tiffany's
- Allylic Bromination
- Bonus Topic: Allylic Rearrangements
- In Summary: Free Radicals
- Synthesis (2) - Reactions of Alkanes
- Free Radicals Practice Quizzes
07 Stereochemistry and Chirality
- Assigning Cahn-Ingold-Prelog (CIP) Priorities (2) - The Method of Dots
- Enantiomers vs Diastereomers vs The Same? Two Methods For Solving Problems
- The Meso Trap
- Optical Rotation, Optical Activity, and Specific Rotation
- Optical Purity and Enantiomeric Excess
- What's a Racemic Mixture?
- Chiral Allenes And Chiral Axes
- Stereochemistry Practice Problems and Quizzes
08 Substitution Reactions
- Introduction to Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
- Walkthrough of Substitution Reactions (1) - Introduction
- Two Types of Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
- The SN2 Mechanism
- Why the SN2 Reaction Is Powerful
- The SN1 Mechanism
- The Conjugate Acid Is A Better Leaving Group
- Comparing the SN1 and SN2 Reactions
- Polar Protic? Polar Aprotic? Nonpolar? All About Solvents
- Steric Hindrance is Like a Fat Goalie
- Common Blind Spot: Intramolecular Reactions
- The Conjugate Base is Always a Stronger Nucleophile
- Substitution Practice - SN1
- Substitution Practice - SN2
09 Elimination Reactions
- Elimination Reactions (1): Introduction And The Key Pattern
- Elimination Reactions (2): The Zaitsev Rule
- Elimination Reactions Are Favored By Heat
- Two Elimination Reaction Patterns
- The E1 Reaction
- The E2 Mechanism
- E1 vs E2: Comparing the E1 and E2 Reactions
- Antiperiplanar Relationships: The E2 Reaction and Cyclohexane Rings
- Bulky Bases in Elimination Reactions
- Comparing the E1 vs SN1 Reactions
- Elimination (E1) Reactions With Rearrangements
- E1cB - Elimination (Unimolecular) Conjugate Base
- Elimination (E1) Practice Problems And Solutions
- Elimination (E2) Practice Problems and Solutions
10 Rearrangements
- Introduction to Rearrangement Reactions
- Rearrangement Reactions (1) - Hydride Shifts
- Carbocation Rearrangement Reactions (2) - Alkyl Shifts
- Pinacol Rearrangement
- The SN1, E1, and Alkene Addition Reactions All Pass Through A Carbocation Intermediate
11 SN1/SN2/E1/E2 Decision
- Identifying Where Substitution and Elimination Reactions Happen
- Deciding SN1/SN2/E1/E2 (1) - The Substrate
- Deciding SN1/SN2/E1/E2 (2) - The Nucleophile/Base
- SN1 vs E1 and SN2 vs E2 : The Temperature
- Deciding SN1/SN2/E1/E2 - The Solvent
- Wrapup: The Key Factors For Determining SN1/SN2/E1/E2
- Alkyl Halide Reaction Map And Summary
- SN1 SN2 E1 E2 Practice Problems
12 Alkene Reactions
- E and Z Notation For Alkenes (+ Cis/Trans)
- Alkene Stability
- Alkene Addition Reactions: "Regioselectivity" and "Stereoselectivity" (Syn/Anti)
- Stereoselective and Stereospecific Reactions
- Hydrohalogenation of Alkenes and Markovnikov's Rule
- Hydration of Alkenes With Aqueous Acid
- Rearrangements in Alkene Addition Reactions
- Halogenation of Alkenes and Halohydrin Formation
- Oxymercuration Demercuration of Alkenes
- Hydroboration Oxidation of Alkenes
- m-CPBA (meta-chloroperoxybenzoic acid)
- OsO4 (Osmium Tetroxide) for Dihydroxylation of Alkenes
- Palladium on Carbon (Pd/C) for Catalytic Hydrogenation of Alkenes
- Cyclopropanation of Alkenes
- A Fourth Alkene Addition Pattern - Free Radical Addition
- Alkene Reactions: Ozonolysis
- Summary: Three Key Families Of Alkene Reaction Mechanisms
- Synthesis (4) - Alkene Reaction Map, Including Alkyl Halide Reactions
- Alkene Reactions Practice Problems
13 Alkyne Reactions
- Acetylides from Alkynes, And Substitution Reactions of Acetylides
- Partial Reduction of Alkynes With Lindlar's Catalyst
- Partial Reduction of Alkynes With Na/NH3 To Obtain Trans Alkenes
- Alkyne Hydroboration With "R2BH"
- Hydration and Oxymercuration of Alkynes
- Hydrohalogenation of Alkynes
- Alkyne Halogenation: Bromination, Chlorination, and Iodination of Alkynes
- Alkyne Reactions - The "Concerted" Pathway
- Alkenes To Alkynes Via Halogenation And Elimination Reactions
- Alkynes Are A Blank Canvas
- Synthesis (5) - Reactions of Alkynes
- Alkyne Reactions Practice Problems With Answers
14 Alcohols, Epoxides and Ethers
- Alcohols - Nomenclature and Properties
- Alcohols Can Act As Acids Or Bases (And Why It Matters)
- Alcohols - Acidity and Basicity
- The Williamson Ether Synthesis
- Ethers From Alkenes, Tertiary Alkyl Halides and Alkoxymercuration
- Alcohols To Ethers via Acid Catalysis
- Cleavage Of Ethers With Acid
- Epoxides - The Outlier Of The Ether Family
- Opening of Epoxides With Acid
- Epoxide Ring Opening With Base
- Making Alkyl Halides From Alcohols
- Tosylates And Mesylates
- PBr3 and SOCl2
- Elimination Reactions of Alcohols
- Elimination of Alcohols To Alkenes With POCl3
- Alcohol Oxidation: "Strong" and "Weak" Oxidants
- Demystifying The Mechanisms of Alcohol Oxidations
- Protecting Groups For Alcohols
- Thiols And Thioethers
- Calculating the oxidation state of a carbon
- Oxidation and Reduction in Organic Chemistry
- Oxidation Ladders
- SOCl2 Mechanism For Alcohols To Alkyl Halides: SN2 versus SNi
- Alcohol Reactions Roadmap (PDF)
- Alcohol Reaction Practice Problems
- Epoxide Reaction Quizzes
- Oxidation and Reduction Practice Quizzes
15 Organometallics
- What's An Organometallic?
- Formation of Grignard and Organolithium Reagents
- Organometallics Are Strong Bases
- Reactions of Grignard Reagents
- Protecting Groups In Grignard Reactions
- Synthesis Problems Involving Grignard Reagents
- Grignard Reactions And Synthesis (2)
- Organocuprates (Gilman Reagents): How They're Made
- Gilman Reagents (Organocuprates): What They're Used For
- The Heck, Suzuki, and Olefin Metathesis Reactions (And Why They Don't Belong In Most Introductory Organic Chemistry Courses)
- Reaction Map: Reactions of Organometallics
- Grignard Practice Problems
16 Spectroscopy
- Degrees of Unsaturation (or IHD, Index of Hydrogen Deficiency)
- Conjugation And Color (+ How Bleach Works)
- Introduction To UV-Vis Spectroscopy
- UV-Vis Spectroscopy: Absorbance of Carbonyls
- UV-Vis Spectroscopy: Practice Questions
- Bond Vibrations, Infrared Spectroscopy, and the "Ball and Spring" Model
- Infrared Spectroscopy: A Quick Primer On Interpreting Spectra
- IR Spectroscopy: 4 Practice Problems
- 1H NMR: How Many Signals?
- Homotopic, Enantiotopic, Diastereotopic
- Diastereotopic Protons in 1H NMR Spectroscopy: Examples
- C13 NMR - How Many Signals
- Liquid Gold: Pheromones In Doe Urine
- Natural Product Isolation (1) - Extraction
- Natural Product Isolation (2) - Purification Techniques, An Overview
- Structure Determination Case Study: Deer Tarsal Gland Pheromone
17 Dienes and MO Theory
- What To Expect In Organic Chemistry 2
- Are these molecules conjugated?
- Conjugation And Resonance In Organic Chemistry
- Bonding And Antibonding Pi Orbitals
- Molecular Orbitals of The Allyl Cation, Allyl Radical, and Allyl Anion
- Pi Molecular Orbitals of Butadiene
- Reactions of Dienes: 1,2 and 1,4 Addition
- Thermodynamic and Kinetic Products
- More On 1,2 and 1,4 Additions To Dienes
- s-cis and s-trans
- The Diels-Alder Reaction
- Cyclic Dienes and Dienophiles in the Diels-Alder Reaction
- Stereochemistry of the Diels-Alder Reaction
- Exo vs Endo Products In The Diels Alder: How To Tell Them Apart
- HOMO and LUMO In the Diels Alder Reaction
- Why Are Endo vs Exo Products Favored in the Diels-Alder Reaction?
- Diels-Alder Reaction: Kinetic and Thermodynamic Control
- The Retro Diels-Alder Reaction
- The Intramolecular Diels Alder Reaction
- Regiochemistry In The Diels-Alder Reaction
- The Cope and Claisen Rearrangements
- Electrocyclic Reactions
- Electrocyclic Ring Opening And Closure (2) - Six (or Eight) Pi Electrons
- Diels Alder Practice Problems
- Molecular Orbital Theory Practice
18 Aromaticity
- Introduction To Aromaticity
- Rules For Aromaticity
- Huckel's Rule: What Does 4n+2 Mean?
- Aromatic, Non-Aromatic, or Antiaromatic? Some Practice Problems
- Antiaromatic Compounds and Antiaromaticity
- The Pi Molecular Orbitals of Benzene
- The Pi Molecular Orbitals of Cyclobutadiene
- Frost Circles
- Aromaticity Practice Quizzes
19 Reactions of Aromatic Molecules
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution: Introduction
- Activating and Deactivating Groups In Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution - The Mechanism
- Ortho-, Para- and Meta- Directors in Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
- Understanding Ortho, Para, and Meta Directors
- Why are halogens ortho- para- directors?
- Disubstituted Benzenes: The Strongest Electron-Donor "Wins"
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitutions (1) - Halogenation of Benzene
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitutions (2) - Nitration and Sulfonation
- EAS Reactions (3) - Friedel-Crafts Acylation and Friedel-Crafts Alkylation
- Intramolecular Friedel-Crafts Reactions
- Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution (NAS)
- Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution (2) - The Benzyne Mechanism
- Reactions on the "Benzylic" Carbon: Bromination And Oxidation
- The Wolff-Kishner, Clemmensen, And Other Carbonyl Reductions
- More Reactions on the Aromatic Sidechain: Reduction of Nitro Groups and the Baeyer Villiger
- Aromatic Synthesis (1) - "Order Of Operations"
- Synthesis of Benzene Derivatives (2) - Polarity Reversal
- Aromatic Synthesis (3) - Sulfonyl Blocking Groups
- Birch Reduction
- Synthesis (7): Reaction Map of Benzene and Related Aromatic Compounds
- Aromatic Reactions and Synthesis Practice
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Practice Problems
20 Aldehydes and Ketones
- What's The Alpha Carbon In Carbonyl Compounds?
- Nucleophilic Addition To Carbonyls
- Aldehydes and Ketones: 14 Reactions With The Same Mechanism
- Sodium Borohydride (NaBH4) Reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones
- Grignard Reagents For Addition To Aldehydes and Ketones
- Wittig Reaction
- Hydrates, Hemiacetals, and Acetals
- Imines - Properties, Formation, Reactions, and Mechanisms
- All About Enamines
- Breaking Down Carbonyl Reaction Mechanisms: Reactions of Anionic Nucleophiles (Part 2)
- Aldehydes Ketones Reaction Practice
21 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
- Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution (With Negatively Charged Nucleophiles)
- Addition-Elimination Mechanisms With Neutral Nucleophiles (Including Acid Catalysis)
- Basic Hydrolysis of Esters - Saponification
- Transesterification
- Proton Transfer
- Fischer Esterification - Carboxylic Acid to Ester Under Acidic Conditions
- Lithium Aluminum Hydride (LiAlH4) For Reduction of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
- LiAlH[Ot-Bu]3 For The Reduction of Acid Halides To Aldehydes
- Di-isobutyl Aluminum Hydride (DIBAL) For The Partial Reduction of Esters and Nitriles
- Amide Hydrolysis
- Thionyl Chloride (SOCl2)
- Diazomethane (CH2N2)
- Carbonyl Chemistry: Learn Six Mechanisms For the Price Of One
- Making Music With Mechanisms (PADPED)
- Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Practice Questions
22 Enols and Enolates
- Keto-Enol Tautomerism
- Enolates - Formation, Stability, and Simple Reactions
- Kinetic Versus Thermodynamic Enolates
- Aldol Addition and Condensation Reactions
- Reactions of Enols - Acid-Catalyzed Aldol, Halogenation, and Mannich Reactions
- Claisen Condensation and Dieckmann Condensation
- Decarboxylation
- The Malonic Ester and Acetoacetic Ester Synthesis
- The Michael Addition Reaction and Conjugate Addition
- The Robinson Annulation
- Haloform Reaction
- The Hell–Volhard–Zelinsky Reaction
- Enols and Enolates Practice Quizzes
- The Amide Functional Group: Properties, Synthesis, and Nomenclature
- Basicity of Amines And pKaH
- 5 Key Basicity Trends of Amines
- The Mesomeric Effect And Aromatic Amines
- Nucleophilicity of Amines
- Alkylation of Amines (Sucks!)
- Reductive Amination
- The Gabriel Synthesis
- Some Reactions of Azides
- The Hofmann Elimination
- The Hofmann and Curtius Rearrangements
- The Cope Elimination
- Protecting Groups for Amines - Carbamates
- The Strecker Synthesis of Amino Acids
- Introduction to Peptide Synthesis
- Reactions of Diazonium Salts: Sandmeyer and Related Reactions
- Amine Practice Questions
24 Carbohydrates
- D and L Notation For Sugars
- Pyranoses and Furanoses: Ring-Chain Tautomerism In Sugars
- What is Mutarotation?
- Reducing Sugars
- The Big Damn Post Of Carbohydrate-Related Chemistry Definitions
- The Haworth Projection
- Converting a Fischer Projection To A Haworth (And Vice Versa)
- Reactions of Sugars: Glycosylation and Protection
- The Ruff Degradation and Kiliani-Fischer Synthesis
- Isoelectric Points of Amino Acids (and How To Calculate Them)
- Carbohydrates Practice
- Amino Acid Quizzes
25 Fun and Miscellaneous
- A Gallery of Some Interesting Molecules From Nature
- Screw Organic Chemistry, I'm Just Going To Write About Cats
- On Cats, Part 1: Conformations and Configurations
- On Cats, Part 2: Cat Line Diagrams
- Organic Chemistry Is Shit
- The Organic Chemistry Behind "The Pill"
- Maybe they should call them, "Formal Wins" ?
- Why Do Organic Chemists Use Kilocalories?
- The Principle of Least Effort
- Organic Chemistry GIFS - Resonance Forms
- Reproducibility In Organic Chemistry
- What Holds The Nucleus Together?
- How Reactions Are Like Music
- Organic Chemistry and the New MCAT
26 Organic Chemistry Tips and Tricks
- Common Mistakes: Formal Charges Can Mislead
- Partial Charges Give Clues About Electron Flow
- Draw The Ugly Version First
- Organic Chemistry Study Tips: Learn the Trends
- The 8 Types of Arrows In Organic Chemistry, Explained
- Top 10 Skills To Master Before An Organic Chemistry 2 Final
- Common Mistakes with Carbonyls: Carboxylic Acids... Are Acids!
- Planning Organic Synthesis With "Reaction Maps"
- Alkene Addition Pattern #1: The "Carbocation Pathway"
- Alkene Addition Pattern #2: The "Three-Membered Ring" Pathway
- Alkene Addition Pattern #3: The "Concerted" Pathway
- Number Your Carbons!
- The 4 Major Classes of Reactions in Org 1
- How (and why) electrons flow
- Grossman's Rule
- Three Exam Tips
- A 3-Step Method For Thinking Through Synthesis Problems
- Putting It Together
- Putting Diels-Alder Products in Perspective
- The Ups and Downs of Cyclohexanes
- The Most Annoying Exceptions in Org 1 (Part 1)
- The Most Annoying Exceptions in Org 1 (Part 2)
- The Marriage May Be Bad, But the Divorce Still Costs Money
- 9 Nomenclature Conventions To Know
- Nucleophile attacks Electrophile
27 Case Studies of Successful O-Chem Students
- Success Stories: How Corina Got The The "Hard" Professor - And Got An A+ Anyway
- How Helena Aced Organic Chemistry
- From a "Drop" To B+ in Org 2 – How A Hard Working Student Turned It Around
- How Serge Aced Organic Chemistry
- Success Stories: How Zach Aced Organic Chemistry 1
- Success Stories: How Kari Went From C– to B+
- How Esther Bounced Back From a "C" To Get A's In Organic Chemistry 1 And 2
- How Tyrell Got The Highest Grade In Her Organic Chemistry Course
- This Is Why Students Use Flashcards
- Success Stories: How Stu Aced Organic Chemistry
- How John Pulled Up His Organic Chemistry Exam Grades
- Success Stories: How Nathan Aced Organic Chemistry (Without It Taking Over His Life)
- How Chris Aced Org 1 and Org 2
- Interview: How Jay Got an A+ In Organic Chemistry
- How to Do Well in Organic Chemistry: One Student's Advice
- "America's Top TA" Shares His Secrets For Teaching O-Chem
- "Organic Chemistry Is Like..." - A Few Metaphors
- How To Do Well In Organic Chemistry: Advice From A Tutor
- Guest post: "I went from being afraid of tests to actually looking forward to them".
Comment section
22 thoughts on “ introduction to assigning (r) and (s): the cahn-ingold-prelog rules ”.
In a chiral molecule, two groups are attached to it with the normal line bond ,the third is shown through a wedge and hydrogen is not shown..can I conclude that the hydrogen is a dash ?
Yes! The dashed hydrogen is implied!
Thanks. Move the dots. Could not find this before.
Glad you found it useful James!
- Pingback: Terpene University: Part 8 - Limonene Effects and Benefits - Omega Equipment & Supply Blog
During my studies for 11th grade and 12th grade, we had a brilliant Organic Chemistry teacher who taught the concepts beautifully. In addition, I had a passion (more of a “study crush”) on Chemistry in general and Organic Chemistry in particular. To such an extent that this topic of R and S enantiomers is still ingrained in memory. Though I am in a completely different area now of Machine Learning and Analytics in the Healthcare space in Industry, primarily a Software Engg job. Out of sheer curiosity, I googled “Chirality Detection Machine Learning” and voila !! such cool, intereesting papers I came across where they combine Bayesian Learning and Convolutional Neural Networks (Advanced ML Theory) to detect chirality in Nanoparticles. So application of ML in cutting edge Physics. Amazing stuff :!
Most people don’t learn chirality until 2nd year university in north america, so you are ahead of the curve
- Pingback: 23 Juli: Hari Kelahiran Vladimir Prelog – Departemen Keilmiahan HMD Kimia FMIPA UI
I just only want to know the CIP system of Nomenclature
Man this website proved to be a boon for me in quarantine…keep it up🔥🔥 The best content of organic chem I could get in such an incredible way
Thank you so much!! :) This was a great refresher on chirality and you explained it in such a straightforward manner. Appreciate it!
What to do if the compound is not denoted using the dash and wedge but simple bond line notation or expanded notation ?
Can you show an example? There has to be some kind of indicator. If all four bonds from the chiral center are shown as simple line notation there is no way to tell if it is R or S. It’s ambiguous.
Thank you so much, you are a true life saver???
I have a lot of trouble rotating molecules in my head, so these tips feel like magic to me!!! Thank you soooo much :DDDD Btw I also go to McGill!
The molecule used to explain the dot technique is labelled as 3-ethyl-3-methyloctane, however shouldn’t the molecule be named as 4-ethyl-4-methyloctane? The branches are on the fourth carbon…
Shoot. You are right. Thanks for the catch. Fixed!
Thank You so much :)
Thanks!! You saved my org chem exam
I was having trouble with this when 4 was in the plane of the page. This technique is so easy. Thanks
Kindly take my work into consideration in your website.
Abstract:- “The Keval’s Method” is developed for the determination of absolute configuration of a chiral carbon in a Fisher Projection and Wedge-Dash Projection just by simple calculations. This method is easily applicable over both Fisher as well as Wedge-Dash Projection. Various methods for determining absolute configuration have been developed and published till now, some of them used fingers and hands and other used exchanging elements. “Keval’s Method” is the first method in which a chiral carbon is taken to be an origin and the branches to axes, also it is purely calculation based method where absolute configuration is found based on the nature of calculated answer without using fingers and hands and also without exchanging elements.
Your’ Thankfully Keval Chetanbhai Purohit 5th-Computer Engineering, Vishwakarma Government Engineering College, Mo- 7226953531
Thank you very much, I now understand the R/S, its not easy to rotate a compound in your mind……
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me via e-mail if anyone answers my comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

- Number of visits 1
- Number of saves 0
Balancing Chemical Equations | Assignment for OpenStax Chemistry: Atoms First 2e | Chapter 7: Stoichiometry of Chemical Reactions
- Report this resource
Description

No Alignments yet.
Evaluations
No evaluations yet.
- Balancing Chemical Equations
- Open Textbooks for Rural AZ
Version History
Review Criteria

Library Subject Guides
- Subject Guides
- Assignment Research
Chemistry: Assignment Research
- Books and ebooks
- Dictionaries, Encyclopedias, Handbooks
- Journal Articles and Databases
- Journal Title Abbreviations
- Data and Properties
- Exam Papers (via AKO | LEARN)
- Past Tests (via AKO | LEARN)
- Products and Prices
- Safety Data Sheets
- Structure Drawing Tools and Nomenclature
- Information Competencies for Chemistry Undergraduates (Wikibook)
- Stages in the Research Process
- Citation Styles and EndNote
- Writing Guides
- Web Lectures
- Stay Current
- For Academics
- Library Navigator
Introduction
This guide to basic assignment research outlines a simple but effective approach to finding information for your assignment. It is based on the resources described elsewhere in this subject guide and on the UC Library web site. Depending on your topic and your level of study, you may need to rearrange or review these steps where necessary
Check the rest of this subject guide carefully for additional subject resources and, where available, appropriate topic guides
1. Define your topic
Make sure you understand the topic. Identify the main concepts or keywords in your question to help you develop a search strategy.
2. Gather background information

Use dictionaries and encyclopedias to find definitions and background information. Articles from specialised subject encyclopedias are authoritative and often substantial
Read more on
- Dictionaries, Encyclopedias and Handbooks for Chemistry
3. Think about what information you need

- How much information do you need? Lecturers often give guidelines on the number of sources you should use
- Do you need current information or is older material relevant? Sometimes you might need both, as you might have to give both the historic background and the current situation of a topic
- Do you need primary sources that give an original account of research, or secondary sources that are interpretations of someone else's work?
If you do not understand what you have to do for an assignment, ask your lecturer, your tutor or someone at the Academic Skills Centre
4. Find books
Search the library catalogue
- Check for books on High Demand .
- Use Title and Keyword anywhere searches to find additional material.
- When you find a useful title, click its subject headings to find books on similar subjects.

Read more on:
- Finding Chemistry Books and Ebooks
5. Find journal articles

6. Find information on the Internet

- a government department (.gov or .govt.nz)
- an academic (.edu or .ac.nz or published in a reputable journal)
- a business (what are they selling?)
- or a random non-expert?
Use Google Scholar to find reliable journal articles, or the Advanced Search features of Google to restrict your search to results from more reputable sources.
- Web searching
7. Evaluate your sources

- Critically Analyzing Information Sources (Cornell University)
- How to spot fake news .
8. Cite your sources
- Citing your sources
9. Write your assignment

See our writing guides page for books that have useful hints for writing on technical subjects.
Visit the Academic Skills Centre for workshops and/or personal help.
- << Previous: Websites
- Next: Information Competencies for Chemistry Undergraduates (Wikibook) >>
- Last Updated: Apr 12, 2024 2:48 PM
- URL: https://canterbury.libguides.com/chem
StudyMonkey
Your personal ai chemistry tutor.
Learn Smarter, Not Harder with Chemistry AI
Introducing StudyMonkey, your AI-powered Chemistry tutor .
StudyMonkey AI can tutor complex Chemistry homework questions, enhance your essay writing and assess your work—all in seconds.
No more long all-nighters
24/7 solutions to Chemistry questions you're stumped on and essays you procrastinated on.
No more stress and anxiety
Get all your Chemistry assignments done with helpful answers in 10 seconds or less.
No more asking friends for Chemistry help
StudyMonkey is your new smart bestie that will never ghost you.
No more staying after school
AI Chemistry tutoring is available 24/7, on-demand when you need it most.
Chemistry is the branch of science that studies the properties and behavior of matter, the changes it undergoes during chemical reactions, and the energy that accompanies those processes.
AI Tutor for any subject
American college testing (act), anthropology, advanced placement exams (ap exams), arabic language, archaeology, biochemistry, chartered financial analyst (cfa) exam, communications, computer science, certified public accountant (cpa) exam, cultural studies, cyber security, dental admission test (dat), discrete mathematics, earth science, elementary school, entrepreneurship, environmental science, farsi (persian) language, fundamentals of engineering (fe) exam, gender studies, graduate management admission test (gmat), graduate record examination (gre), greek language, hebrew language, high school entrance exam, high school, human geography, human resources, international english language testing system (ielts), information technology, international relations, independent school entrance exam (isee), linear algebra, linguistics, law school admission test (lsat), machine learning, master's degree, medical college admission test (mcat), meteorology, microbiology, middle school, national council licensure examination (nclex), national merit scholarship qualifying test (nmsqt), number theory, organic chemistry, project management professional (pmp), political science, portuguese language, probability, project management, preliminary sat (psat), public policy, public relations, russian language, scholastic assessment test (sat), social sciences, secondary school admission test (ssat), sustainability, swahili language, test of english as a foreign language (toefl), trigonometry, turkish language, united states medical licensing examination (usmle), web development, step-by-step guidance 24/7.
Receive step-by-step guidance & homework help for any homework problem & any subject 24/7
Ask any Chemistry question
StudyMonkey supports every subject and every level of education from 1st grade to masters level.
Get an answer
StudyMonkey will give you an answer in seconds—multiple choice questions, short answers, and even an essays are supported!
Review your history
See your past questions and answers so you can review for tests and improve your grades.
It's not cheating...
You're just learning smarter than everyone else
How Can StudyMonkey Help You?
Hear from our happy students.
"The AI tutor is available 24/7, making it a convenient and accessible resource for students who need help with their homework at any time."
"Overall, StudyMonkey is an excellent tool for students looking to improve their understanding of homework topics and boost their academic success."
Upgrade to StudyMonkey Premium!
Why not upgrade to StudyMonkey Premium and get access to all features?
Module 13: Fundamental Equilibrium Concepts
Assignment: equilibrium.
- For each of the following reactions, determine whether the value of the equilibrium constant favors the formation of reactants, products, or both sides equally.
a) Br 2 (g) + Cl 2 (g) ↔ 2 BrCl(g) K eq = 3 x 10 6
b) H 2 (g) + Br 2 (g) ↔ 2 HBr(g) K eq = 1.15
c) I 2 (g) ↔ I(g) + I(g) K eq = 4.5 x 10 -7
2. Molecular chlorine decomposes into atoms according to the reaction:
Cl 2 (g) ↔ 2 Cl (g)
The equilibrium constant for the reaction at 25°C is 1.4 x 10 -38 . Would many chlorine atoms be present at this temperature? Explain how you can determine this.
3. For the following reaction at equilibrium at 2000°C, the concentration of N2 and O2 are both 4.8 M.
N 2 (g) + O 2 (g) ↔ 2 NO(g) K eq = 6.3 x 10 -4
Calculate the concentration of NO at equilibrium. Show your work; pay careful attention to exponents.
4. CaCO 3 (chalk) can produce solid CaO and CO 2 gas when heated. If 6.0 moles of carbon dioxide forms in a 4.500 L reaction vessel, what is the equilibrium constant for this reaction?
5. Le Chatelier’s Principle states that if a stress is applied to a reversible reaction at equilibrium, the reaction will undergo a shift in order to re-establish its equilibrium. Consider the following exothermic reversible reaction at equilibrium: 2 A ↔B + C In which direction (left or right) would the following stresses cause the system to shift? a. decrease the concentration of A b. increase the concentration of B c. lower the temperature
6. Chemical engineers use Le Chatêlier’s principle to predict shifts in chemical system at equilibrium resulting from changes in reaction conditions. Predict the changes needed to maximize the yield of product in each of the following industrial chemical systems:
- a) the production of ethene (ethylene)
C 2 H 6 (g) + energy ↔C 2 H 4 (g) + H 2 (g)
- b) the production of methanol
CO(g) + 2H 2 (g) ↔ CH 3 OH(g) + energy
- Acetic acid, HC 2 H 3 O 2 , is in equilibrium with its ions:
HC 2 H 3 O 2 (aq) ↔ H+(aq) + C 2 H 3 O 2 – (aq) Keq = 1.8 x 10 -5
At equilibrium, the concentration of the ions are: [H+] = 1.33 x 10 -3 M
[C 2 H 3 O 2 – ] = 1.33 x10 -3 M
Calculate the concentration of the acid, HC 2 H 3 O 2 .
8.Sulfuric acid is the most common commercial acid, with millions of tons produced each year. The second step in the production involves the oxidation of sulfur dioxide gas catalyzed with V 2 O 5 (s),
2SO 2 (g) + O 2 (g) ↔2 SO 3 (g) D H ° = -198 kJ
a) Set-up the equilibrium law for this reaction.
b) List three stresses that could shift the equilibrium to the products side of the reaction.
c) If the equilibrium constant, K eq , for the above reaction at a given temperature is 4 x 10 3 , what is the constant (K eq ) for the reverse reaction (the decomposition of sulfur trioxide)?
- Accessibility
- Main SQA Website
- Using the site
- > Subjects
- > Chemistry
- > Higher
- > Assignment
In this section
Select a subject Accounting Administration and IT Applications of Mathematics Apprenticeships Art and Design Baccalaureates Barista Skills Biology Business Management Care Chemistry Childcare & Development Classical Studies Computing Science Core Skills Dance Design and Manufacture Drama Economics Engineering Science English Environmental Science ESOL Fashion and Textiles French Gaelic Gaidhlig Geography German Graphic Communication Health and Food Technology History HN Human Biology Italian Latin Mandarin Mathematics Mathematics of Mechanics Media Modern Studies Music Music Technology National 1 & 2 Philosophy Photography Physical Education Physics Politics Practical Cake Craft Practical Cookery Practical Electronics Practical Metalworking Practical Woodworking Psychology RMPS Science NPA's Scots Language Skills for Work Sociology Spanish Statistics SVQ Urdu
- Question paper
- Advanced Higher
- Presentations
- Course Reports
- Additional resources for sessions 2020-22
Higher Chemistry - assignment
Assignment 2023 (all links open to pdf files), full project: vitamin c concentration in orange juice.
- Full Project Candidate Evidence
- Full Project Commentary
Sections: Summary, analysis, and evaluation sections
- Sections Candidate Evidence
- Sections Commentary
Assignment 2022 (All links open to PDF files)
- Candidate 1 Evidence
- Candidate 2 Evidence
- Candidate 3 Evidence
- Candidate 4 Evidence
- Candidate 5 Evidence
- Candidates 1 to 5 Commentaries
- Terms & Conditions
- Back To Top

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

Absolute Configuration - R-S Sequence Rules
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 794
To name the enantiomers of a compound unambiguously, their names must include the "handedness" of the molecule. The method for this is formally known as R/S nomenclature.
Introduction
The method of unambiguously assigning the handedness of molecules was originated by three chemists: R.S. Cahn, C. Ingold, and V. Prelog and is also often called the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rules . In addition to the Cahn-Ingold system, there are two ways of experimentally determining the absolute configuration of an enantiomer:
- X-ray diffraction analysis. Note that there is no correlation between the sign of rotation and the structure of a particular enantiomer.
- Chemical correlation with a molecule whose structure has already been determined via X-ray diffraction.
However, for non-laboratory purposes, it is beneficial to focus on the R/S system. The sign of optical rotation , although different for the two enantiomers of a chiral molecule, at the same temperature, cannot be used to establish the absolute configuration of an enantiomer; this is because the sign of optical rotation for a particular enantiomer may change when the temperature changes.
Stereocenters are labeled R or S
The "right hand" and "left hand" nomenclature is used to name the enantiomers of a chiral compound. The stereocenters are labeled as R or S.
Consider the first picture: a curved arrow is drawn from the highest priority ( 1 ) substituent to the lowest priority (4 ) substituent. If the arrow points in a counterclockwise direction ( left when leaving the 12 o' clock position), the configuration at stereocenter is considered S ("Sinister" → Latin= "left"). If, however, the arrow points clockwise,( Right when leaving the 12 o' clock position) then the stereocenter is labeled R ("Rectus" → Latin= "right"). The R or S is then added as a prefix, in parenthesis, to the name of the enantiomer of interest. For example: ( R )-2-Bromobutane and ( S )-2,3- Dihydroxypropanal.
Sequence rules to assign priorities to substituents
Before applying the R and S nomenclature to a stereocenter, the substituents must be prioritized according to the following rules:
First, examine at the atoms directly attached to the stereocenter of the compound. A substituent with a higher atomic number takes precedence over a substituent with a lower atomic number. Hydrogen is the lowest possible priority substituent, because it has the lowest atomic number.
- When dealing with isotopes, the atom with the higher atomic mass receives higher priority.
- When visualizing the molecule, the lowest priority substituent should always point away from the viewer (a dashed line indicates this). To understand how this works or looks, imagine that a clock and a pole. Attach the pole to the back of the clock, so that when when looking at the face of the clock the pole points away from the viewer in the same way the lowest priority substituent should point away.
- Then, draw an arrow from the highest priority atom to the 2nd highest priority atom to the 3rd highest priority atom. Because the 4th highest priority atom is placed in the back, the arrow should appear like it is going across the face of a clock. If it is going clockwise, then it is an R-enantiomer; If it is going counterclockwise, it is an S-enantiomer.
When looking at a problem with wedges and dashes, if the lowest priority atom is not on the dashed line pointing away, the molecule must be rotated. Remember that
- Wedges indicate coming towards the viewer.
- Dashes indicate pointing away from the viewer.
If there are two substituents with equal rank, proceed along the two substituent chains until there is a point of difference. First, determine which of the chains has the first connection to an atom with the highest priority (the highest atomic number). That chain has the higher priority.
If the chains are similar, proceed down the chain, until a point of difference.
For example : an ethyl substituent takes priority over a methyl substituent. At the connectivity of the stereocenter, both have a carbon atom, which are equal in rank. Going down the chains, a methyl has only has hydrogen atoms attached to it, whereas the ethyl has another carbon atom. The carbon atom on the ethyl is the first point of difference and has a higher atomic number than hydrogen; therefore the ethyl takes priority over the methyl.
If a chain is connected to the same kind of atom twice or three times, check to see if the atom it is connected to has a greater atomic number than any of the atoms that the competing chain is connected to.
- If none of the atoms connected to the competing chain(s) at the same point has a greater atomic number: the chain bonded to the same atom multiple times has the greater priority
- If however, one of the atoms connected to the competing chain has a higher atomic number: that chain has the higher priority.
A 1-methylethyl substituent takes precedence over an ethyl substituent. Connected to the first carbon atom, ethyl only has one other carbon, whereas the 1-methylethyl has two carbon atoms attached to the first; this is the first point of difference. Therefore, 1-methylethyl ranks higher in priority than ethyl, as shown below:
Remember that being double or triple bonded to an atom means that the atom is connected to the same atom twice. In such a case, follow the same method as above.
Caution!! Keep in mind that priority is determined by the first point of difference along the two similar substituent chains. After the first point of difference, the rest of the chain is irrelevant.
After all your substituents have been prioritized in the correct manner, you can now name/label the molecule R or S.
- Put the lowest priority substituent in the back (dashed line).
- Proceed from 1 to 2 to 3. (it is helpful to draw or imagine an arcing arrow that goes from 1--> 2-->3)
- Determine if the direction from 1 to 2 to 3 clockwise or counterclockwise.
i) If it is clockwise it is R. ii) if it is counterclockwise it is S .
USE YOUR MODELING KIT: Models assist in visualizing the structure. When using a model, make sure the lowest priority is pointing away from you. Then determine the direction from the highest priority substituent to the lowest: clockwise (R) or counterclockwise (S).
IF YOU DO NOT HAVE A MODELING KIT : remember that the dashes mean the bond is going into the screen and the wedges means that bond is coming out of the screen. If the lowest priority bond is not pointing to the back, mentally rotate it so that it is. However, it is very useful when learning organic chemistry to use models.
If you have a modeling kit use it to help you solve the following practice problems.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Are the following R or S?
- S: I > Br > F > H. The lowest priority substituent, H, is already going towards the back. It turns left going from I to Br to F, so it's a S.
- R: Br > Cl > CH 3 > H. You have to switch the H and Br in order to place the H, the lowest priority, in the back. Then, going from Br to Cl, CH 3 is turning to the right, giving you a R.
- Neither R or S : This molecule is achiral. Only chiral molecules can be named R or S.
- R: OH > CN > CH 2 NH 2 > H. The H, the lowest priority, has to be switched to the back. Then, going from OH to CN to CH 2 NH 2 , you are turning right, giving you a R. (5)
- S: \(\ce{-COOH}\) > \(\ce{-CH_2OH}\) > \(\ce{C#CH}\) > \(\ce{H}\). Then, going from \(\ce{-COOH}\) to \(\ce{-CH_2OH}\) to \(\ce{-C#CH}\) you are turning left, giving you a S configuration.
- Schore and Vollhardt. Organic Chemistry Structure and Function. New York:W.H. Freeman and Company, 2007.
- McMurry, John and Simanek, Eric. Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry . 6th Ed. Brooks Cole, 2006.
CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free
Class 10 Chemistry Assignments
We have provided below free printable Class 10 Chemistry Assignments for Download in PDF. The Assignments have been designed based on the latest NCERT Book for Class 10 Chemistry . These Assignments for Grade 10 Chemistry cover all important topics which can come in your standard 10 tests and examinations. Free printable Assignments for CBSE Class 10 Chemistry , school and class assignments, and practice test papers have been designed by our highly experienced class 10 faculty. You can free download CBSE NCERT printable Assignments for Chemistry Class 10 with solutions and answers. All Assignments and test sheets have been prepared by expert teachers as per the latest Syllabus in Chemistry Class 10. Students can click on the links below and download all Pdf Assignments for Chemistry class 10 for free. All latest Kendriya Vidyalaya Class 10 Chemistry Assignments with Answers and test papers are given below.
Chemistry Class 10 Assignments Pdf Download
We have provided below the biggest collection of free CBSE NCERT KVS Assignments for Class 10 Chemistry . Students and teachers can download and save all free Chemistry assignments in Pdf for grade 10th. Our expert faculty have covered Class 10 important questions and answers for Chemistry as per the latest syllabus for the current academic year. All test papers and question banks for Class 10 Chemistry and CBSE Assignments for Chemistry Class 10 will be really helpful for standard 10th students to prepare for the class tests and school examinations. Class 10th students can easily free download in Pdf all printable practice worksheets given below.
Topicwise Assignments for Class 10 Chemistry Download in Pdf

Advantages of Class 10 Chemistry Assignments
- As we have the best and largest collection of Chemistry assignments for Grade 10, you will be able to easily get full list of solved important questions which can come in your examinations.
- Students will be able to go through all important and critical topics given in your CBSE Chemistry textbooks for Class 10 .
- All Chemistry assignments for Class 10 have been designed with answers. Students should solve them yourself and then compare with the solutions provided by us.
- Class 10 Students studying in per CBSE, NCERT and KVS schools will be able to free download all Chemistry chapter wise worksheets and assignments for free in Pdf
- Class 10 Chemistry question bank will help to improve subject understanding which will help to get better rank in exams
Frequently Asked Questions by Class 10 Chemistry students
At https://www.cbsencertsolutions.com, we have provided the biggest database of free assignments for Chemistry Class 10 which you can download in Pdf
We provide here Standard 10 Chemistry chapter-wise assignments which can be easily downloaded in Pdf format for free.
You can click on the links above and get assignments for Chemistry in Grade 10, all topic-wise question banks with solutions have been provided here. You can click on the links to download in Pdf.
We have provided here topic-wise Chemistry Grade 10 question banks, revision notes and questions for all difficult topics, and other study material.
We have provided the best collection of question bank and practice tests for Class 10 for all subjects. You can download them all and use them offline without the internet.
Related Posts

Class 10 Social Science Economics Assignments

Class 10 Social Science Assignments

Class 10 Mathematics Polynomials Assignments
- Study Guides
- Homework Questions
Assignment Chemical Reactions Lab Report
CHEMISTRY COMMUNITY
Created by Dr. Laurence Lavelle
Skip to content
- Register Alias and Password (Only available to students enrolled in Dr. Lavelle’s classes.)
- Board index Chem 14B Chemical Equilibrium Equilibrium Constants & Calculating Concentrations

Chemical Equilibrium 1B Post Assignment #15
Moderators: Chem_Mod , Chem_Admin
Post by Evelyn-Marian Barber » Wed Jan 11, 2023 7:27 am
Re: Chemical Equilibrium 1B Post Assignment #15
Post by kirsten clemente 1E » Wed Jan 11, 2023 7:43 am
Post by hiranya sundar 2D » Wed Jan 11, 2023 5:48 pm
Return to “Equilibrium Constants & Calculating Concentrations”
- NEWS & RESOURCES
- About The Forum
- Forum Rules and Helpful Hints
- How to make a New Post (submit a question) and use Equation Editor (click for details)
- Email Notification (click for details)
- How to Subscribe to a Forum, Subscribe to a Topic, and Bookmark a Topic (click for details)
- Endorsed Post (click for details)
- Multimedia Attachments (click for details)
- Strikethrough (click for details)
- Review of Chemical & Physical Principles
- SI Units, Unit Conversions
- Significant Figures
- Accuracy, Precision, Mole, Other Definitions
- Molarity, Solutions, Dilutions
- Empirical & Molecular Formulas
- Balancing Chemical Reactions
- Limiting Reactant Calculations
- The Quantum World
- Properties of Light
- Properties of Electrons
- Einstein Equation
- *Black Body Radiation
- Photoelectric Effect
- Bohr Frequency Condition, H-Atom , Atomic Spectroscopy
- DeBroglie Equation
- Heisenberg Indeterminacy (Uncertainty) Equation
- *Shrodinger Equation
- *Particle in a Box
- Wave Functions and s-, p-, d-, f- Orbitals
- Quantum Numbers and The H-Atom
- Electron Configurations for Multi-Electron Atoms
- Trends in The Periodic Table
- Chemical Bonds
- Ionic & Covalent Bonds
- Sigma & Pi Bonds
- Lewis Structures
- Resonance Structures
- Formal Charge and Oxidation Numbers
- Octet Exceptions
- Coordinate Covalent Bonds
- Polarisability of Anions, The Polarizing Power of Cations
- Electronegativity
- Dipole Moments
- Bond Lengths & Energies
- Forces and Liquid Structure
- Interionic and Intermolecular Forces (Ion-Ion, Ion-Dipole, Dipole-Dipole, Dipole-Induced Dipole, Dispersion/Induced Dipole-Induced Dipole/London Forces, Hydrogen Bonding)
- *Liquid Structure (Viscosity, Surface Tension, Liquid Crystals, Ionic Liquids)
- Molecular Shape and Structure
- Determining Molecular Shape (VSEPR)
- Hybridization
- *Molecular Orbital Theory (Bond Order, Diamagnetism, Paramagnetism)
- Coordination Compounds and their Biological Importance
- Naming
- Shape, Structure, Coordination Number, Ligands
- Biological Examples
- Industrial Examples
- *Stereochemistry
- *Crystal Field Theory
- *Molecular Orbital Theory Applied To Transition Metals
- Acids and Bases
- Properties & Structures of Inorganic & Organic Acids
- Properties & Structures of Inorganic & Organic Bases
- Amphoteric Compounds
- Lewis Acids & Bases
- Bronsted Acids & Bases
- Conjugate Acids & Bases
- Acidity & Basicity Constants and The Conjugate Seesaw
- Calculating pH or pOH for Strong & Weak Acids & Bases
- Polyprotic Acids & Bases
- Identifying Acidic & Basic Salts
- Calculating the pH of Salt Solutions
- Air Pollution & Acid Rain
- Chem 14A Uploaded Files (Worksheets, etc.)
- Student Social/Study Group
- Administrative Questions and Class Announcements
- General Science Questions
- *Aqueous Equilibria
- *Making Buffers & Calculating Buffer pH (Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation)
- *Biological Importance of Buffer Solutions
- *Titrations & Titration Calculations
- *Indicators
- Chemical Equilibrium
- Ideal Gases
- Equilibrium Constants & Calculating Concentrations
- Non-Equilibrium Conditions & The Reaction Quotient
- Applying Le Chatelier's Principle to Changes in Chemical & Physical Conditions
- Thermochemistry
- Phase Changes & Related Calculations
- Reaction Enthalpies (e.g., Using Hess’s Law, Bond Enthalpies, Standard Enthalpies of Formation)
- Heat Capacities, Calorimeters & Calorimetry Calculations
- Thermodynamics
- Thermodynamic Systems (Open, Closed, Isolated)
- Thermodynamic Definitions (isochoric/isometric, isothermal, isobaric)
- Calculating Work of Expansion
- Concepts & Calculations Using First Law of Thermodynamics
- Concepts & Calculations Using Second Law of Thermodynamics
- Third Law of Thermodynamics (For a Unique Ground State (W=1): S -> 0 as T -> 0) and Calculations Using Boltzmann Equation for Entropy
- Entropy Changes Due to Changes in Volume and Temperature
- Calculating Standard Reaction Entropies (e.g. , Using Standard Molar Entropies)
- Gibbs Free Energy Concepts and Calculations
- Van't Hoff Equation
- Environment, Fossil Fuels, Alternative Fuels
- Biological Examples (*DNA Structural Transitions, etc.)
- Electrochemistry
- Balancing Redox Reactions
- Galvanic/Voltaic Cells, Calculating Standard Cell Potentials, Cell Diagrams
- Work, Gibbs Free Energy, Cell (Redox) Potentials
- Appications of the Nernst Equation (e.g., Concentration Cells, Non-Standard Cell Potentials, Calculating Equilibrium Constants and pH)
- Interesting Applications: Rechargeable Batteries (Cell Phones, Notebooks, Cars), Fuel Cells (Space Shuttle), Photovoltaic Cells (Solar Panels), Electrolysis, Rust
- Chemical Kinetics
- Kinetics vs. Thermodynamics Controlling a Reaction
- General Rate Laws
- Method of Initial Rates (To Determine n and k)
- Zero Order Reactions
- First Order Reactions
- Second Order Reactions
- Reaction Mechanisms, Reaction Profiles
- Arrhenius Equation, Activation Energies, Catalysts
- *Enzyme Kinetics
- Experimental Details
- Environment, Ozone, CFCs
- Chem 14B Uploaded Files (Worksheets, etc.)
- *Thermodynamics and Kinetics of Organic Reactions
- *Electrophiles
- *Nucleophiles
- *Organic Reaction Mechanisms in General
- *Electrophilic Addition
- *Nucleophilic Substitution
- *Free Energy of Activation vs Activation Energy
- *Complex Reaction Coordinate Diagrams
- *Names and Structures of Organic Molecules
- *Alkanes
- *Cycloalkanes
- *Alkenes
- *Cycloalkenes
- *Alkynes
- *Constitutional and Geometric Isomers (cis, Z and trans, E)
- *Haloalkanes
- *Haloalkenes
- *Alcohols
- *Ethers
- *Aldehydes
- *Ketones
- *Carboxylic Acids
- *Amines
- *Identifying Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, Quaternary Carbons, Hydrogens, Nitrogens
- *Conformations of Organic Molecules
- *Alkanes and Substituted Alkanes (Staggered, Eclipsed, Gauche, Anti, Newman Projections)
- *Cyclopropanes and Cyclobutanes
- *Cyclopentanes
- *Cyclohexanes (Chair, Boat, Geometric Isomers)
- *Calculations Using ΔG° = -RT ln K
- *ChemDraw
- *Chem3D
- Chem 14C/D Topics
- Resonance in Organic Compounds
- Stereochemistry in Organic Compounds (Chirality, Stereoisomers, R/S, d/l, Fischer Projections)
Who is online
Users browsing this forum: No registered users and 22 guests
- Board index
- All times are UTC
100 Hard Words to Spell in English
Table of Contents
English is a great language with both basic and complicated vocabulary. Certain words in the language even have various spellings but the same pronunciation. In addition, several words sound different than how they should be spelled. Similarly, there are many hard words to spell in English. In this blog, we have shared a list of some of the hardest words to spell in the English language, especially for those who are always caught making spelling mistakes.
In the era of autocorrect, many people have overlooked the importance of spelling and only struggle with it while writing an essay or academic paper. If you are participating in a Spelling Bee competition, you must have a thorough understanding of English words and how to spell them. Typically, in the competition, you will be asked to write hard-to-spell words. So, feel free to explore the list and expand your vocabulary.
Why is it Difficult to Spell Certain English Words?
Have you ever thought about why some English words are misspelled often and are even hard to spell? Generally, in English, there are some spelling rules. If you are unaware of it, then chances are there for you to get locked in spelling errors out of confusion. Find here, some common reasons why certain words are hard to spell.
- Distinctions between British and American English
- Long words containing a lot of vowels
- Words that contain silent letters
- Two consonants together
- Homophones [words with similar sounds but distinct spellings and meanings]
- Homographs [words that have the same spelling but a distinct origin, pronunciation, and meaning]
- Homonyms [words with the same phoneme and spelling but distinct meanings]
- Confusion with ‘e’ and ‘i’
- The ‘c’ and ‘k’ sounds are similar
- A difficulty with the sounds “y,” “ee,” and “lee”
- Ambiguity between “ea” and “ae”
List of Hardest Words To Spell in English

The English language typically combines pronunciations and spellings from many other languages including Latin, Greek, French, and German. Moreover, different countries spell some words differently. As a result, confusion often prevails among users.
To assist you, below we have organized and listed some of the most difficult words to spell in English. Feel free to take a look.
Also Read: Top 12 Longest Words in English Language
Easy Words That Are Hard to Spell
These are some easy English words that many people find hard to spell or pronounce.
1. Necessary
One of the reasons English is difficult to spell is that some letters like c and s can generate the same sounds but do not always do so. This, paired with the usage of double consonants that do not affect how the word is spoken makes it difficult to spell. How do you recall where and how many c or s letters you will need? So have a look at the word. Do you say “c” with two s’s? Ask yourself this to ensure that a single c followed by a double “s” is necessary.
2. Narcissistic
Narcissistic, like necessary, is difficult to spell because the letters “c” and “s” sound the same way. It can be difficult to remember where to place the double “s”. It might help to know that the word narcissistic is derived from the Greek nárkissos, a plant name linked with opiates.
3. Accommodate
The word accommodate contains a double “c” and a double “m” for good measure. However, the vowels, not the consonants, are what make writing this term difficult. The word “accommodate” [uh-kom-uh-deyt] sounds like it should be spelled with three o’s, or is there a “u” in there? But there are no u’s, and the first letter is an “a”, of all things.
Speaking of words with a double “c”, the word vacuum is one that you might anticipate having this spelling but does not. Vacuum has the unusual double “u” instead of the common double c (other words with this peculiar combination are muumuu and continuum). The word’s root is vacuus, which is Latin for “empty.”
Silent g’s can come at the beginning and conclusion of words. One example is phlegm [flem]. This term is especially difficult to pronounce because it combines the letters ph and ff. This style of expressing the ff sound appears in Greek words such as phlegm and phone.
6. Spaghetti
A word with Italian origins that is difficult to spell is spaghetti. The letter “i” at the end of a word in Italian denotes that it is plural. The nearly-silent “h” may also confuse you while spelling this word.
7. Entrepreneur
Entrepreneur [ahn-truh-pruh-nur] is a French-spelled word that English speakers find difficult to pronounce. As it begins with an ah sound, you might assume it contains an “a”, but this is not the case. Next time you write this word, remind yourself that the majority of the vowel sounds are “e”, with the exception of the “eu” at the very end for the “oor” sound.
When it comes to silent letters, we employ an astonishing amount of them in English while spelling. Unless you know the word, there is no way to know these letters should be there. Asthma is a prime example of this, with a silent “th”. Yes, English will occasionally insert a silent “th” to keep you on your toes.
Another word that uses a deceptive silent letter is “indict” [in-dahyt]. You do not pronounce the letter c in this word, thus you may overlook it when spelling. The letter “c” comes from the late Latin word indictāre, which is connected to the English verb dictate.
10. Acquiesce
Another word that means “to assent tacitly; agree,” acquiesce [ak-wee-es], too has some odd letter combinations associated with its pronunciation. The Latin verb acquiēscere, which means “to find rest in,” is the source of the name. When spelling this word, bear in mind that the prefix ac-means “toward” or “to.” This may help you spell the word correctly because it indicates that it breaks down as ac-qui-esce.
Simple Words That Are Hard to Spell
Certain simple English words are frequently misspelled. Here, let us have a look at the list of the easy words that are difficult to spell.
- Accommodate
- Intelligence
- Pronunciation
- Handkerchief
Hard Words to Spell for School Students
The following are some English words that many students write incorrectly.
- Defalcation
Tough to Spell English Words
The following are some hard words to spell in English.
- Bureaucracy
Also Read: What is the Importance of Grammar in English?
Hard Words to Spell for College Students
Here is a list of hard words that college students struggle to spell.
- Contemptuous
- Superintendent
- Discernible
- Resplendent
Frequently Misspelled Words
The following are some of the most regularly misspelled English terms.
- Chronological
- Acknowledgment
Hard to Spell Long Words
Even for native speakers of the language, English is a lovely yet challenging language. In addition to errors, persons with strong fluency occasionally have trouble spelling lengthy words correctly. Some lengthy words that are challenging to spell are listed here.
- Hepaticocholangiogastrostomy
- Pneumonoultramicroscopicsilicovolcanokoniosis
- Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism
- Hippopotomonstrosesquippedaliophobia
- Psychoneuroendocrinological
- Spectrophotofluorometrically
- Pneumonoultramicroscopicsilicovolcanoconiosis
- Antidisestablishmentarianism
- Supercalifragilisticexpialidocious
- Floccinaucinihilipilification
Tricky Words to Spell in the English Language
There are a few English words that are challenging to spell. The spelling and pronunciation of certain words may not always match. So, there is a chance that you will get into trouble. Here is a list of hard words to spell.
- Chiaroscurist
- Autochthonous
- Gobbledegook
- Paraphernalia
- Chiaroscuro
- Gubernatorial
- Pochemuchka
- Kierkegaardian
- Sacrilegious
Spelling rules in English can be difficult, with many catches and exceptions. You can avoid making mistakes if you correctly follow the guidelines. Silent letters, homophones, regional variances, and double consonants are certain traps to avoid. But keep in mind that you will become more proficient at spelling words in the English language the more you study and practice.
If you are worried about receiving bad grades on your assignment due to spelling errors, approach us immediately. We have native English speakers as assignment helpers to provide you with high-quality English assignment help online . In addition, we offer proofreading as a component of our online assignment help services, so you can get aid from our language assistants to fix any spelling or grammar mistakes in your papers.
Related Post

100 Creative Graphic Design Thesis Topics and Ideas

100 Outstanding Chemistry Research Topics to Examine

90 Captivating Anthropology Research Topics and Ideas
About author.
Jacob Smith
Jacob Smith guides students with writing research paper topics and theses at greatassignmenthelp.com. Read about the author from this page
https://www.greatassignmenthelp.com/
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Featured Posts
200 Impressive Business Essay Topics
175 unique bioethics topics to consider for academic paper, apa vs. mla: know the major differences between the citation styles, top 155 java project ideas for beginners and experts, learn the difference between affect and effect, 100 unique capstone project ideas to focus on, 140 captivating public health topics for academic paper, labeling theory overview: definition, authors, examples, what are the different types of coding languages, get help instantly.
Raise Your Grades with Great Assignment Help

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
ZnO 2 and ZnCl 2. H 2 O and HCl. NO and NO 2. CH 4 and CO 2. A sample of chemical X is found to contain 5.0 grams of oxygen, 10.0 grams of carbon, and 20.0. grams of nitrogen. The law of definite proportion would predict that a 70 gram sample of chemical.
1.1: The Scope of Chemistry. Chemistry is the study of matter and the ways in which different forms of matter combine with each other. You study chemistry because it helps you to understand the world around you. Everything you touch or taste or smell is a chemical, and the interactions of these chemicals with each other define our universe.
Print free chemistry worksheets and handouts to enhance student learning. This is a collection of free chemistry worksheets and handouts to print. Most of the printables are PDF files, although some are available as JPG or PNG files. All of these worksheets print cleanly on normal printer paper, plus you can resize them to fit your needs.
Module 20: Organic Chemistry: Assignment: Nuclear Chemistry: Module 21: Nuclear Chemistry: Discussions. The following discussion assignments will also be preloaded (into the discussion-board tool) in your learning management system if you import the course. They can be used as is, modified, or removed. You can preview them below:
Module 1: Essential Ideas. Why It Matters: Essential Ideas. Chemistry in Context. Videos: History of Chemistry and the Scientific Method. Phases and Classification of Matter. Physical and Chemical Properties. Measurements. Measurement Uncertainty, Accuracy, and Precision. Videos: Significant Figures.
Book: General Chemistry - Lecture and Lab (Lumen) 1: Essential Ideas 1.15: Assignment—Matter and Measurement ... To download a copy of the assignment, please click on the link Sample Questions. As you work these matter and measurement problems, consider and explain: What type of question is it?
Assignments. Problem Set 1 Solutions (PDF) Problem Set 3 Solutions (PDF) Problem Set 4 Solutions (PDF) Problem Set 6 Solutions (PDF) Problem Set 7 Solutions (PDF) Problem Set 9 Solutions (PDF) This section contains the problems sets and their solutions.
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during reactions with other substances. ...
This assignment can be found in Google Docs: Chemistry for Majors Assignment: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions. To make your own copy to edit: If you want a Google Doc: in the file menu of the open document, click "Make a copy.". This will give you your own Google Doc to work from.
Problem Set 8 ( PDF ) ( PDF )#. Assignments section contains problem sets alonf with their solutions.
Learning Objectives. Identify the principles of chemistry that are integral to biology. In the module on Chemistry, we provide a general overview of how the principles of chemistry form the basis of biology. For this assignment, you are going to reflect upon which concept (s) in this module were most difficult for you to learn.
The Aktiv Chemistry gradebook can be set up to display summary columns or individual columns depending on the assignment type as well. Industry-leading Support Any course using Aktiv Chemistry comes with our industry-leading support featuring average response times of 14 minutes and extended hours that include late nights and weekends.
An update to Ref. #1, which addresses a lot of edge cases that may come up in complex stereochemical assignments. CHIRALITY IN CHEMISTRY Vladimir Prelog Nobel Lecture, 1975 Prelog's Nobel Lecture. Nobel Lectures are fascinating to read as they give insight into the life of scientists and the path to discovery, which is rarely linear.
This chemistry activity was created to enhance student learning around balancing chemical equations. It guides students through Phet simulations and then asks comprehension questions thereafter. Remix of: Open Textbooks for Rural AZ Publishing Template Subject: Chemistry Level: Community College / Lower Division Material Type:
This guide to basic assignment research outlines a simple but effective approach to finding information for your assignment. It is based on the resources described elsewhere in this subject guide and on the UC Library web site. Depending on your topic and your level of study, you may need to rearrange or review these steps where necessary.
A 24/7 free Chemistry homework AI tutor that instantly provides personalized step-by-step guidance, explanations, and examples for any Chemistry homework problem. Improve your grades with our AI homework helper! ... Get all your Chemistry assignments done with helpful answers in 10 seconds or less. No more asking friends for Chemistry help.
Even after Joy got her PhD, she never could finish studying. Working in Education for as long as she can remember, she now shares her extensive knowledge being a writer at AssignmentBro. Discover 70 chemistry topics for assignments that include organic, general, nuclear, physical, and engineering chemistry branches.
Assignment: Equilibrium For each of the following reactions, determine whether the value of the equilibrium constant favors the formation of reactants, products, or both sides equally. a) Br 2 (g) + Cl 2 (g) ↔ 2 BrCl(g) K eq = 3 x 10 6
This document contains instructions for teachers and lecturers, marking instructions and instructions for candidates for the National 5 Chemistry assignment. It must be read in conjunction with the course specification. This assignment is worth 20 marks (scaled to 25). The marks contribute 20% of the overall marks for the course assessment.
Higher Chemistry - assignment. Assignment 2023 (All links open to PDF files) Full project: Vitamin C Concentration in Orange Juice. Full Project Candidate Evidence. Full Project Commentary. Sections: Summary, analysis, and evaluation sections. Sections Candidate Evidence. Sections Commentary. Assignment 2022 (All links open to PDF files)
Organic Chemistry Structure and Function. New York:W.H. Freeman and Company, 2007. McMurry, John and Simanek, Eric. Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry. 6th Ed. Brooks Cole, 2006. Absolute Configuration - R-S Sequence Rules is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Ekta Patel & Ifemayowa Aworanti.
All Assignments and test sheets have been prepared by expert teachers as per the latest Syllabus in Chemistry Class 10. Students can click on the links below and download all Pdf Assignments for Chemistry class 10 for free. All latest Kendriya Vidyalaya Class 10 Chemistry Assignments with Answers and test papers are given below.
Higher Chemistry Assignment Assessment task. This document provides information for teachers and lecturers about the coursework component of this course in terms of the skills, knowledge and understanding that are assessed. It must be read in conjunction with the course specification. Valid from session 2020-21 and until further notice.
Chemistry document from Portland State University, 1 page, Assignment: Chemical Reactions Lab Report Objective: To demonstrate an understanding of chemical reactions and the factors that influence reaction rates. Procedure: 1. Choose at least three different chemical reactions to perform in the lab. Record the re
Stereochemistry in Organic Compounds (Chirality, Stereoisomers, R/S, d/l, Fischer Projections) ... "Hi, this is the problem for post-assignment question #15. "Carbonyl chloride (COCl2 ..." · "hi! try putting your answer through the calculator again because all of your work is correct. if you put the whole equation [0.14] / [1.2 x 10^-2] [0.054] into a ...
We have native English speakers as assignment helpers to provide you with high-quality English assignment help online. In addition, we offer proofreading as a component of our online assignment help services, so you can get aid from our language assistants to fix any spelling or grammar mistakes in your papers. ... 100 Outstanding Chemistry ...