- Search Search Please fill out this field.

What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
How to Write a Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples

Noah Parsons
24 min. read
Updated April 10, 2024
Writing a business plan doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to write a business plan that’s detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
- The basics of business planning
If you’re reading this guide, then you already know why you need a business plan .
You understand that planning helps you:
- Raise money
- Grow strategically
- Keep your business on the right track
As you start to write your plan, it’s useful to zoom out and remember what a business plan is .
At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow.
A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It’s also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals.
After completing your plan, you can use it as a management tool to track your progress toward your goals. Updating and adjusting your forecasts and budgets as you go is one of the most important steps you can take to run a healthier, smarter business.
We’ll dive into how to use your plan later in this article.
There are many different types of plans , but we’ll go over the most common type here, which includes everything you need for an investor-ready plan. However, if you’re just starting out and are looking for something simpler—I recommend starting with a one-page business plan . It’s faster and easier to create.
It’s also the perfect place to start if you’re just figuring out your idea, or need a simple strategic plan to use inside your business.
Dig deeper : How to write a one-page business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What to include in your business plan
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it’s a summary of the complete business plan.
Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan.
In fact, it’s common for investors to ask only for the executive summary when evaluating your business. If they like what they see in the executive summary, they’ll often follow up with a request for a complete plan, a pitch presentation , or more in-depth financial forecasts .
Your executive summary should include:
- A summary of the problem you are solving
- A description of your product or service
- An overview of your target market
- A brief description of your team
- A summary of your financials
- Your funding requirements (if you are raising money)
Dig Deeper: How to write an effective executive summary
Products and services description
This is where you describe exactly what you’re selling, and how it solves a problem for your target market. The best way to organize this part of your plan is to start by describing the problem that exists for your customers. After that, you can describe how you plan to solve that problem with your product or service.
This is usually called a problem and solution statement .
To truly showcase the value of your products and services, you need to craft a compelling narrative around your offerings. How will your product or service transform your customers’ lives or jobs? A strong narrative will draw in your readers.
This is also the part of the business plan to discuss any competitive advantages you may have, like specific intellectual property or patents that protect your product. If you have any initial sales, contracts, or other evidence that your product or service is likely to sell, include that information as well. It will show that your idea has traction , which can help convince readers that your plan has a high chance of success.
Market analysis
Your target market is a description of the type of people that you plan to sell to. You might even have multiple target markets, depending on your business.
A market analysis is the part of your plan where you bring together all of the information you know about your target market. Basically, it’s a thorough description of who your customers are and why they need what you’re selling. You’ll also include information about the growth of your market and your industry .
Try to be as specific as possible when you describe your market.
Include information such as age, income level, and location—these are what’s called “demographics.” If you can, also describe your market’s interests and habits as they relate to your business—these are “psychographics.”
Related: Target market examples
Essentially, you want to include any knowledge you have about your customers that is relevant to how your product or service is right for them. With a solid target market, it will be easier to create a sales and marketing plan that will reach your customers. That’s because you know who they are, what they like to do, and the best ways to reach them.
Next, provide any additional information you have about your market.
What is the size of your market ? Is the market growing or shrinking? Ideally, you’ll want to demonstrate that your market is growing over time, and also explain how your business is positioned to take advantage of any expected changes in your industry.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write a market analysis
Competitive analysis
Part of defining your business opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage is. To do this effectively, you need to know as much about your competitors as your target customers.
Every business has some form of competition. If you don’t think you have competitors, then explore what alternatives there are in the market for your product or service.
For example: In the early years of cars, their main competition was horses. For social media, the early competition was reading books, watching TV, and talking on the phone.
A good competitive analysis fully lays out the competitive landscape and then explains how your business is different. Maybe your products are better made, or cheaper, or your customer service is superior. Maybe your competitive advantage is your location – a wide variety of factors can ultimately give you an advantage.
Dig Deeper: How to write a competitive analysis for your business plan
Marketing and sales plan
The marketing and sales plan covers how you will position your product or service in the market, the marketing channels and messaging you will use, and your sales tactics.
The best place to start with a marketing plan is with a positioning statement .
This explains how your business fits into the overall market, and how you will explain the advantages of your product or service to customers. You’ll use the information from your competitive analysis to help you with your positioning.
For example: You might position your company as the premium, most expensive but the highest quality option in the market. Or your positioning might focus on being locally owned and that shoppers support the local economy by buying your products.
Once you understand your positioning, you’ll bring this together with the information about your target market to create your marketing strategy .
This is how you plan to communicate your message to potential customers. Depending on who your customers are and how they purchase products like yours, you might use many different strategies, from social media advertising to creating a podcast. Your marketing plan is all about how your customers discover who you are and why they should consider your products and services.
While your marketing plan is about reaching your customers—your sales plan will describe the actual sales process once a customer has decided that they’re interested in what you have to offer.
If your business requires salespeople and a long sales process, describe that in this section. If your customers can “self-serve” and just make purchases quickly on your website, describe that process.
A good sales plan picks up where your marketing plan leaves off. The marketing plan brings customers in the door and the sales plan is how you close the deal.
Together, these specific plans paint a picture of how you will connect with your target audience, and how you will turn them into paying customers.
Dig deeper: What to include in your sales and marketing plan
Business operations
The operations section describes the necessary requirements for your business to run smoothly. It’s where you talk about how your business works and what day-to-day operations look like.
Depending on how your business is structured, your operations plan may include elements of the business like:
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing processes
- Equipment and technology
- Distribution
Some businesses distribute their products and reach their customers through large retailers like Amazon.com, Walmart, Target, and grocery store chains.
These businesses should review how this part of their business works. The plan should discuss the logistics and costs of getting products onto store shelves and any potential hurdles the business may have to overcome.
If your business is much simpler than this, that’s OK. This section of your business plan can be either extremely short or more detailed, depending on the type of business you are building.
For businesses selling services, such as physical therapy or online software, you can use this section to describe the technology you’ll leverage, what goes into your service, and who you will partner with to deliver your services.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write the operations chapter of your plan
Key milestones and metrics
Although it’s not required to complete your business plan, mapping out key business milestones and the metrics can be incredibly useful for measuring your success.
Good milestones clearly lay out the parameters of the task and set expectations for their execution. You’ll want to include:
- A description of each task
- The proposed due date
- Who is responsible for each task
If you have a budget, you can include projected costs to hit each milestone. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section—just list key milestones you want to hit and when you plan to hit them. This is your overall business roadmap.
Possible milestones might be:
- Website launch date
- Store or office opening date
- First significant sales
- Break even date
- Business licenses and approvals
You should also discuss the key numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common metrics worth tracking include:
- Conversion rates
- Customer acquisition costs
- Profit per customer
- Repeat purchases
It’s perfectly fine to start with just a few metrics and grow the number you are tracking over time. You also may find that some metrics simply aren’t relevant to your business and can narrow down what you’re tracking.
Dig Deeper: How to use milestones in your business plan
Organization and management team
Investors don’t just look for great ideas—they want to find great teams. Use this chapter to describe your current team and who you need to hire . You should also provide a quick overview of your location and history if you’re already up and running.
Briefly highlight the relevant experiences of each key team member in the company. It’s important to make the case for why yours is the right team to turn an idea into a reality.
Do they have the right industry experience and background? Have members of the team had entrepreneurial successes before?
If you still need to hire key team members, that’s OK. Just note those gaps in this section.
Your company overview should also include a summary of your company’s current business structure . The most common business structures include:
- Sole proprietor
- Partnership
Be sure to provide an overview of how the business is owned as well. Does each business partner own an equal portion of the business? How is ownership divided?
Potential lenders and investors will want to know the structure of the business before they will consider a loan or investment.
Dig Deeper: How to write about your company structure and team
Financial plan
Last, but certainly not least, is your financial plan chapter.
Entrepreneurs often find this section the most daunting. But, business financials for most startups are less complicated than you think, and a business degree is certainly not required to build a solid financial forecast.
A typical financial forecast in a business plan includes the following:
- Sales forecast : An estimate of the sales expected over a given period. You’ll break down your forecast into the key revenue streams that you expect to have.
- Expense budget : Your planned spending such as personnel costs , marketing expenses, and taxes.
- Profit & Loss : Brings together your sales and expenses and helps you calculate planned profits.
- Cash Flow : Shows how cash moves into and out of your business. It can predict how much cash you’ll have on hand at any given point in the future.
- Balance Sheet : A list of the assets, liabilities, and equity in your company. In short, it provides an overview of the financial health of your business.
A strong business plan will include a description of assumptions about the future, and potential risks that could impact the financial plan. Including those will be especially important if you’re writing a business plan to pursue a loan or other investment.
Dig Deeper: How to create financial forecasts and budgets
This is the place for additional data, charts, or other information that supports your plan.
Including an appendix can significantly enhance the credibility of your plan by showing readers that you’ve thoroughly considered the details of your business idea, and are backing your ideas up with solid data.
Just remember that the information in the appendix is meant to be supplementary. Your business plan should stand on its own, even if the reader skips this section.
Dig Deeper : What to include in your business plan appendix
Optional: Business plan cover page
Adding a business plan cover page can make your plan, and by extension your business, seem more professional in the eyes of potential investors, lenders, and partners. It serves as the introduction to your document and provides necessary contact information for stakeholders to reference.
Your cover page should be simple and include:
- Company logo
- Business name
- Value proposition (optional)
- Business plan title
- Completion and/or update date
- Address and contact information
- Confidentiality statement
Just remember, the cover page is optional. If you decide to include it, keep it very simple and only spend a short amount of time putting it together.
Dig Deeper: How to create a business plan cover page
How to use AI to help write your business plan
Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT can speed up the business plan writing process and help you think through concepts like market segmentation and competition. These tools are especially useful for taking ideas that you provide and converting them into polished text for your business plan.
The best way to use AI for your business plan is to leverage it as a collaborator , not a replacement for human creative thinking and ingenuity.
AI can come up with lots of ideas and act as a brainstorming partner. It’s up to you to filter through those ideas and figure out which ones are realistic enough to resonate with your customers.
There are pros and cons of using AI to help with your business plan . So, spend some time understanding how it can be most helpful before just outsourcing the job to AI.
Learn more: 10 AI prompts you need to write a business plan
- Writing tips and strategies
To help streamline the business plan writing process, here are a few tips and key questions to answer to make sure you get the most out of your plan and avoid common mistakes .
Determine why you are writing a business plan
Knowing why you are writing a business plan will determine your approach to your planning project.
For example: If you are writing a business plan for yourself, or just to use inside your own business , you can probably skip the section about your team and organizational structure.
If you’re raising money, you’ll want to spend more time explaining why you’re looking to raise the funds and exactly how you will use them.
Regardless of how you intend to use your business plan , think about why you are writing and what you’re trying to get out of the process before you begin.
Keep things concise
Probably the most important tip is to keep your business plan short and simple. There are no prizes for long business plans . The longer your plan is, the less likely people are to read it.
So focus on trimming things down to the essentials your readers need to know. Skip the extended, wordy descriptions and instead focus on creating a plan that is easy to read —using bullets and short sentences whenever possible.
Have someone review your business plan
Writing a business plan in a vacuum is never a good idea. Sometimes it’s helpful to zoom out and check if your plan makes sense to someone else. You also want to make sure that it’s easy to read and understand.
Don’t wait until your plan is “done” to get a second look. Start sharing your plan early, and find out from readers what questions your plan leaves unanswered. This early review cycle will help you spot shortcomings in your plan and address them quickly, rather than finding out about them right before you present your plan to a lender or investor.
If you need a more detailed review, you may want to explore hiring a professional plan writer to thoroughly examine it.
Use a free business plan template and business plan examples to get started
Knowing what information to include in a business plan is sometimes not quite enough. If you’re struggling to get started or need additional guidance, it may be worth using a business plan template.
There are plenty of great options available (we’ve rounded up our 8 favorites to streamline your search).
But, if you’re looking for a free downloadable business plan template , you can get one right now; download the template used by more than 1 million businesses.
Or, if you just want to see what a completed business plan looks like, check out our library of over 550 free business plan examples .
We even have a growing list of industry business planning guides with tips for what to focus on depending on your business type.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
It’s easy to make mistakes when you’re writing your business plan. Some entrepreneurs get sucked into the writing and research process, and don’t focus enough on actually getting their business started.
Here are a few common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Not talking to your customers : This is one of the most common mistakes. It’s easy to assume that your product or service is something that people want. Before you invest too much in your business and too much in the planning process, make sure you talk to your prospective customers and have a good understanding of their needs.
- Overly optimistic sales and profit forecasts: By nature, entrepreneurs are optimistic about the future. But it’s good to temper that optimism a little when you’re planning, and make sure your forecasts are grounded in reality.
- Spending too much time planning: Yes, planning is crucial. But you also need to get out and talk to customers, build prototypes of your product and figure out if there’s a market for your idea. Make sure to balance planning with building.
- Not revising the plan: Planning is useful, but nothing ever goes exactly as planned. As you learn more about what’s working and what’s not—revise your plan, your budgets, and your revenue forecast. Doing so will provide a more realistic picture of where your business is going, and what your financial needs will be moving forward.
- Not using the plan to manage your business: A good business plan is a management tool. Don’t just write it and put it on the shelf to collect dust – use it to track your progress and help you reach your goals.
- Presenting your business plan
The planning process forces you to think through every aspect of your business and answer questions that you may not have thought of. That’s the real benefit of writing a business plan – the knowledge you gain about your business that you may not have been able to discover otherwise.
With all of this knowledge, you’re well prepared to convert your business plan into a pitch presentation to present your ideas.
A pitch presentation is a summary of your plan, just hitting the highlights and key points. It’s the best way to present your business plan to investors and team members.
Dig Deeper: Learn what key slides should be included in your pitch deck
Use your business plan to manage your business
One of the biggest benefits of planning is that it gives you a tool to manage your business better. With a revenue forecast, expense budget, and projected cash flow, you know your targets and where you are headed.
And yet, nothing ever goes exactly as planned – it’s the nature of business.
That’s where using your plan as a management tool comes in. The key to leveraging it for your business is to review it periodically and compare your forecasts and projections to your actual results.
Start by setting up a regular time to review the plan – a monthly review is a good starting point. During this review, answer questions like:
- Did you meet your sales goals?
- Is spending following your budget?
- Has anything gone differently than what you expected?
Now that you see whether you’re meeting your goals or are off track, you can make adjustments and set new targets.
Maybe you’re exceeding your sales goals and should set new, more aggressive goals. In that case, maybe you should also explore more spending or hiring more employees.
Or maybe expenses are rising faster than you projected. If that’s the case, you would need to look at where you can cut costs.
A plan, and a method for comparing your plan to your actual results , is the tool you need to steer your business toward success.
Learn More: How to run a regular plan review
Free business plan templates and examples
Kickstart your business plan writing with one of our free business plan templates or recommended tools.

Free business plan template
Download a free SBA-approved business plan template built for small businesses and startups.
Download Template

One-page plan template
Download a free one-page plan template to write a useful business plan in as little as 30-minutes.

Sample business plan library
Explore over 500 real-world business plan examples from a wide variety of industries.
View Sample Plans
How to write a business plan FAQ
What is a business plan?
A document that describes your business , the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy, how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan helps you understand where you want to go with your business and what it will take to get there. It reduces your overall risk, helps you uncover your business’s potential, attracts investors, and identifies areas for growth.
Having a business plan ultimately makes you more confident as a business owner and more likely to succeed for a longer period of time.
What are the 7 steps of a business plan?
The seven steps to writing a business plan include:
- Write a brief executive summary
- Describe your products and services.
- Conduct market research and compile data into a cohesive market analysis.
- Describe your marketing and sales strategy.
- Outline your organizational structure and management team.
- Develop financial projections for sales, revenue, and cash flow.
- Add any additional documents to your appendix.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
There are plenty of mistakes that can be made when writing a business plan. However, these are the 5 most common that you should do your best to avoid:
- 1. Not taking the planning process seriously.
- Having unrealistic financial projections or incomplete financial information.
- Inconsistent information or simple mistakes.
- Failing to establish a sound business model.
- Not having a defined purpose for your business plan.
What questions should be answered in a business plan?
Writing a business plan is all about asking yourself questions about your business and being able to answer them through the planning process. You’ll likely be asking dozens and dozens of questions for each section of your plan.
However, these are the key questions you should ask and answer with your business plan:
- How will your business make money?
- Is there a need for your product or service?
- Who are your customers?
- How are you different from the competition?
- How will you reach your customers?
- How will you measure success?
How long should a business plan be?
The length of your business plan fully depends on what you intend to do with it. From the SBA and traditional lender point of view, a business plan needs to be whatever length necessary to fully explain your business. This means that you prove the viability of your business, show that you understand the market, and have a detailed strategy in place.
If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don’t necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary information in place.
What are the different types of business plans?
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan: The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used when applying for funding or pitching to investors. This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix.
Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
One-page business plan: This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences. It’s most useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Lean Plan: The Lean Plan is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance. It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision.
However, when approached correctly, your business plan can actually function as a strategic plan as well. If kept lean, you can define your business, outline strategic steps, and track ongoing operations all with a single plan.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- Use AI to help write your plan
- Common planning mistakes
- Manage with your business plan
- Templates and examples
Related Articles

8 Min. Read
How to Write an Auto Repair Shop Business Plan + Free PDF

6 Min. Read
How to Write a Nail Salon Business Plan + Free Sample Plan PDF

7 Min. Read
Target Market Examples

8 Steps to Write a Useful Internal Business Plan
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Business Plan, Step by Step

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
What is a business plan?
1. write an executive summary, 2. describe your company, 3. state your business goals, 4. describe your products and services, 5. do your market research, 6. outline your marketing and sales plan, 7. perform a business financial analysis, 8. make financial projections, 9. summarize how your company operates, 10. add any additional information to an appendix, business plan tips and resources.
A business plan outlines your business’s financial goals and explains how you’ll achieve them over the next three to five years. Here’s a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan that will offer a strong, detailed road map for your business.

ZenBusiness
A business plan is a document that explains what your business does, how it makes money and who its customers are. Internally, writing a business plan should help you clarify your vision and organize your operations. Externally, you can share it with potential lenders and investors to show them you’re on the right track.
Business plans are living documents; it’s OK for them to change over time. Startups may update their business plans often as they figure out who their customers are and what products and services fit them best. Mature companies might only revisit their business plan every few years. Regardless of your business’s age, brush up this document before you apply for a business loan .
» Need help writing? Learn about the best business plan software .
This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your business offers and a broad summary of your financial growth plans.
Though the executive summary is the first thing your investors will read, it can be easier to write it last. That way, you can highlight information you’ve identified while writing other sections that go into more detail.
» MORE: How to write an executive summary in 6 steps
Next up is your company description. This should contain basic information like:
Your business’s registered name.
Address of your business location .
Names of key people in the business. Make sure to highlight unique skills or technical expertise among members of your team.
Your company description should also define your business structure — such as a sole proprietorship, partnership or corporation — and include the percent ownership that each owner has and the extent of each owner’s involvement in the company.
Lastly, write a little about the history of your company and the nature of your business now. This prepares the reader to learn about your goals in the next section.
» MORE: How to write a company overview for a business plan

The third part of a business plan is an objective statement. This section spells out what you’d like to accomplish, both in the near term and over the coming years.
If you’re looking for a business loan or outside investment, you can use this section to explain how the financing will help your business grow and how you plan to achieve those growth targets. The key is to provide a clear explanation of the opportunity your business presents to the lender.
For example, if your business is launching a second product line, you might explain how the loan will help your company launch that new product and how much you think sales will increase over the next three years as a result.
» MORE: How to write a successful business plan for a loan
In this section, go into detail about the products or services you offer or plan to offer.
You should include the following:
An explanation of how your product or service works.
The pricing model for your product or service.
The typical customers you serve.
Your supply chain and order fulfillment strategy.
You can also discuss current or pending trademarks and patents associated with your product or service.
Lenders and investors will want to know what sets your product apart from your competition. In your market analysis section , explain who your competitors are. Discuss what they do well, and point out what you can do better. If you’re serving a different or underserved market, explain that.
Here, you can address how you plan to persuade customers to buy your products or services, or how you will develop customer loyalty that will lead to repeat business.
Include details about your sales and distribution strategies, including the costs involved in selling each product .
» MORE: R e a d our complete guide to small business marketing
If you’re a startup, you may not have much information on your business financials yet. However, if you’re an existing business, you’ll want to include income or profit-and-loss statements, a balance sheet that lists your assets and debts, and a cash flow statement that shows how cash comes into and goes out of the company.
Accounting software may be able to generate these reports for you. It may also help you calculate metrics such as:
Net profit margin: the percentage of revenue you keep as net income.
Current ratio: the measurement of your liquidity and ability to repay debts.
Accounts receivable turnover ratio: a measurement of how frequently you collect on receivables per year.
This is a great place to include charts and graphs that make it easy for those reading your plan to understand the financial health of your business.
This is a critical part of your business plan if you’re seeking financing or investors. It outlines how your business will generate enough profit to repay the loan or how you will earn a decent return for investors.
Here, you’ll provide your business’s monthly or quarterly sales, expenses and profit estimates over at least a three-year period — with the future numbers assuming you’ve obtained a new loan.
Accuracy is key, so carefully analyze your past financial statements before giving projections. Your goals may be aggressive, but they should also be realistic.
NerdWallet’s picks for setting up your business finances:
The best business checking accounts .
The best business credit cards .
The best accounting software .
Before the end of your business plan, summarize how your business is structured and outline each team’s responsibilities. This will help your readers understand who performs each of the functions you’ve described above — making and selling your products or services — and how much each of those functions cost.
If any of your employees have exceptional skills, you may want to include their resumes to help explain the competitive advantage they give you.
Finally, attach any supporting information or additional materials that you couldn’t fit in elsewhere. That might include:
Licenses and permits.
Equipment leases.
Bank statements.
Details of your personal and business credit history, if you’re seeking financing.
If the appendix is long, you may want to consider adding a table of contents at the beginning of this section.
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
Here are some tips to write a detailed, convincing business plan:
Avoid over-optimism: If you’re applying for a business bank loan or professional investment, someone will be reading your business plan closely. Providing unreasonable sales estimates can hurt your chances of approval.
Proofread: Spelling, punctuation and grammatical errors can jump off the page and turn off lenders and prospective investors. If writing and editing aren't your strong suit, you may want to hire a professional business plan writer, copy editor or proofreader.
Use free resources: SCORE is a nonprofit association that offers a large network of volunteer business mentors and experts who can help you write or edit your business plan. The U.S. Small Business Administration’s Small Business Development Centers , which provide free business consulting and help with business plan development, can also be a resource.
On a similar note...
Find small-business financing
Compare multiple lenders that fit your business

Plan Smarter, Grow Faster:
25% Off Annual Plans! Save Now

0 results have been found for “”
Return to blog home
What Is a Business Plan? Definition and Planning Essentials Explained
Posted february 21, 2022 by kody wirth.

What is a business plan? It’s the roadmap for your business. The outline of your goals, objectives, and the steps you’ll take to get there. It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance.
A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and pursue growth. In short, a business plan is a lot of different things. It’s more than just a stack of paper and can be one of your most effective tools as a business owner.
Let’s explore the basics of business planning, the structure of a traditional plan, your planning options, and how you can use your plan to succeed.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a document that explains how your business operates. It summarizes your business structure, objectives, milestones, and financial performance. Again, it’s a guide that helps you, and anyone else, better understand how your business will succeed.
Why do you need a business plan?
The primary purpose of a business plan is to help you understand the direction of your business and the steps it will take to get there. Having a solid business plan can help you grow up to 30% faster and according to our own 2021 Small Business research working on a business plan increases confidence regarding business health—even in the midst of a crisis.
These benefits are directly connected to how writing a business plan makes you more informed and better prepares you for entrepreneurship. It helps you reduce risk and avoid pursuing potentially poor ideas. You’ll also be able to more easily uncover your business’s potential. By regularly returning to your plan you can understand what parts of your strategy are working and those that are not.
That just scratches the surface for why having a plan is valuable. Check out our full write-up for fifteen more reasons why you need a business plan .
What can you do with your plan?
So what can you do with a business plan once you’ve created it? It can be all too easy to write a plan and just let it be. Here are just a few ways you can leverage your plan to benefit your business.
Test an idea
Writing a plan isn’t just for those that are ready to start a business. It’s just as valuable for those that have an idea and want to determine if it’s actually possible or not. By writing a plan to explore the validity of an idea, you are working through the process of understanding what it would take to be successful.
The market and competitive research alone can tell you a lot about your idea. Is the marketplace too crowded? Is the solution you have in mind not really needed? Add in the exploration of milestones, potential expenses, and the sales needed to attain profitability and you can paint a pretty clear picture of the potential of your business.
Document your strategy and goals
For those starting or managing a business understanding where you’re going and how you’re going to get there are vital. Writing your plan helps you do that. It ensures that you are considering all aspects of your business, know what milestones you need to hit, and can effectively make adjustments if that doesn’t happen.
With a plan in place, you’ll have an idea of where you want your business to go as well as how you’ve performed in the past. This alone better prepares you to take on challenges, review what you’ve done before, and make the right adjustments.
Pursue funding
Even if you do not intend to pursue funding right away, having a business plan will prepare you for it. It will ensure that you have all of the information necessary to submit a loan application and pitch to investors. So, rather than scrambling to gather documentation and write a cohesive plan once it’s relevant, you can instead keep your plan up-to-date and attempt to attain funding. Just add a use of funds report to your financial plan and you’ll be ready to go.
The benefits of having a plan don’t stop there. You can then use your business plan to help you manage the funding you receive. You’ll not only be able to easily track and forecast how you’ll use your funds but easily report on how it’s been used.
Better manage your business
A solid business plan isn’t meant to be something you do once and forget about. Instead, it should be a useful tool that you can regularly use to analyze performance, make strategic decisions, and anticipate future scenarios. It’s a document that you should regularly update and adjust as you go to better fit the actual state of your business.
Doing so makes it easier to understand what’s working and what’s not. It helps you understand if you’re truly reaching your goals or if you need to make further adjustments. Having your plan in place makes that process quicker, more informative, and leaves you with far more time to actually spend running your business.
What should your business plan include?
The content and structure of your business plan should include anything that will help you use it effectively. That being said, there are some key elements that you should cover and that investors will expect to see.
Executive summary
The executive summary is a simple overview of your business and your overall plan. It should serve as a standalone document that provides enough detail for anyone—including yourself, team members, or investors—to fully understand your business strategy. Make sure to cover the problem you’re solving, a description of your product or service, your target market, organizational structure, a financial summary, and any necessary funding requirements.
This will be the first part of your plan but it’s easiest to write it after you’ve created your full plan.
Products & Services
When describing your products or services, you need to start by outlining the problem you’re solving and why what you offer is valuable. This is where you’ll also address current competition in the market and any competitive advantages your products or services bring to the table. Lastly, be sure to outline the steps or milestones that you’ll need to hit to successfully launch your business. If you’ve already hit some initial milestones, like taking pre-orders or early funding, be sure to include it here to further prove the validity of your business.
Market analysis
A market analysis is a qualitative and quantitative assessment of the current market you’re entering or competing in. It helps you understand the overall state and potential of the industry, who your ideal customers are, the positioning of your competition, and how you intend to position your own business. This helps you better explore the long-term trends of the market, what challenges to expect, and how you will need to initially introduce and even price your products or services.
Check out our full guide for how to conduct a market analysis in just four easy steps .
Marketing & sales
Here you detail how you intend to reach your target market. This includes your sales activities, general pricing plan, and the beginnings of your marketing strategy. If you have any branding elements, sample marketing campaigns, or messaging available—this is the place to add it.
Additionally, it may be wise to include a SWOT analysis that demonstrates your business or specific product/service position. This will showcase how you intend to leverage sales and marketing channels to deal with competitive threats and take advantage of any opportunities.
Check out our full write-up to learn how to create a cohesive marketing strategy for your business.
Organization & management
This section addresses the legal structure of your business, your current team, and any gaps that need to be filled. Depending on your business type and longevity, you’ll also need to include your location, ownership information, and business history. Basically, add any information that helps explain your organizational structure and how you operate. This section is particularly important for pitching to investors but should be included even if attempted funding is not in your immediate future.
Financial projections
Possibly the most important piece of your plan, your financials section is vital for showcasing the viability of your business. It also helps you establish a baseline to measure against and makes it easier to make ongoing strategic decisions as your business grows. This may seem complex on the surface, but it can be far easier than you think.
Focus on building solid forecasts, keep your categories simple, and lean on assumptions. You can always return to this section to add more details and refine your financial statements as you operate.
Here are the statements you should include in your financial plan:
- Sales and revenue projections
- Profit and loss statement
- Cash flow statement
- Balance sheet
The appendix is where you add additional detail, documentation, or extended notes that support the other sections of your plan. Don’t worry about adding this section at first and only add documentation that you think will be beneficial for anyone reading your plan.
Types of business plans explained
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. So, to get the most out of your plan, it’s best to find a format that suits your needs. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan
The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used for external purposes. Typically this is the type of plan you’ll need when applying for funding or pitching to investors. It can also be used when training or hiring employees, working with vendors, or any other situation where the full details of your business must be understood by another individual.
This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix. We recommend only starting with this business plan format if you plan to immediately pursue funding and already have a solid handle on your business information.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
The structure ditches a linear structure in favor of a cell-based template. It encourages you to build connections between every element of your business. It’s faster to write out and update, and much easier for you, your team, and anyone else to visualize your business operations. This is really best for those exploring their business idea for the first time, but keep in mind that it can be difficult to actually validate your idea this way as well as adapt it into a full plan.
One-page business plan
The true middle ground between the business model canvas and a traditional business plan is the one-page business plan. This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. It basically serves as a beefed-up pitch document and can be finished as quickly as the business model canvas.
By starting with a one-page plan, you give yourself a minimal document to build from. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences making it much easier to elaborate or expand sections into a longer-form business plan. This plan type is useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Now, the option that we here at LivePlan recommend is the Lean Plan . This is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance.
It holds all of the benefits of the single-page plan, including the potential to complete it in as little as 27-minutes . However, it’s even easier to convert into a full plan thanks to how heavily it’s tied to your financials. The overall goal of Lean Planning isn’t to just produce documents that you use once and shelve. Instead, the Lean Planning process helps you build a healthier company that thrives in times of growth and stable through times of crisis.
It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
Try the LivePlan Method for Lean Business Planning
Now that you know the basics of business planning, it’s time to get started. Again we recommend leveraging a Lean Plan for a faster, easier, and far more useful planning process.
To get familiar with the Lean Plan format, you can download our free Lean Plan template . However, if you want to elevate your ability to create and use your lean plan even further, you may want to explore LivePlan.
It features step-by-step guidance that ensures you cover everything necessary while reducing the time spent on formatting and presenting. You’ll also gain access to financial forecasting tools that propel you through the process. Finally, it will transform your plan into a management tool that will help you easily compare your forecasts to your actual results.
Check out how LivePlan streamlines Lean Planning by downloading our Kickstart Your Business ebook .
Like this post? Share with a friend!
Posted in Business Plan Writing
Join over 1 million entrepreneurs who found success with liveplan, like this content sign up to receive more.
Subscribe for tips and guidance to help you grow a better, smarter business.
You're all set!
Exciting business insights and growth strategies will be coming your way each month.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
What is a Business Plan? Definition, Tips, and Templates
Published: June 07, 2023
In an era where more than 20% of small enterprises fail in their first year, having a clear, defined, and well-thought-out business plan is a crucial first step for setting up a business for long-term success.

Business plans are a required tool for all entrepreneurs, business owners, business acquirers, and even business school students. But … what exactly is a business plan?

In this post, we'll explain what a business plan is, the reasons why you'd need one, identify different types of business plans, and what you should include in yours.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a documented strategy for a business that highlights its goals and its plans for achieving them. It outlines a company's go-to-market plan, financial projections, market research, business purpose, and mission statement. Key staff who are responsible for achieving the goals may also be included in the business plan along with a timeline.
The business plan is an undeniably critical component to getting any company off the ground. It's key to securing financing, documenting your business model, outlining your financial projections, and turning that nugget of a business idea into a reality.
What is a business plan used for?
The purpose of a business plan is three-fold: It summarizes the organization’s strategy in order to execute it long term, secures financing from investors, and helps forecast future business demands.
Business Plan Template [ Download Now ]

Working on your business plan? Try using our Business Plan Template . Pre-filled with the sections a great business plan needs, the template will give aspiring entrepreneurs a feel for what a business plan is, what should be in it, and how it can be used to establish and grow a business from the ground up.
Purposes of a Business Plan
Chances are, someone drafting a business plan will be doing so for one or more of the following reasons:
1. Securing financing from investors.
Since its contents revolve around how businesses succeed, break even, and turn a profit, a business plan is used as a tool for sourcing capital. This document is an entrepreneur's way of showing potential investors or lenders how their capital will be put to work and how it will help the business thrive.
All banks, investors, and venture capital firms will want to see a business plan before handing over their money, and investors typically expect a 10% ROI or more from the capital they invest in a business.
Therefore, these investors need to know if — and when — they'll be making their money back (and then some). Additionally, they'll want to read about the process and strategy for how the business will reach those financial goals, which is where the context provided by sales, marketing, and operations plans come into play.
2. Documenting a company's strategy and goals.
A business plan should leave no stone unturned.
Business plans can span dozens or even hundreds of pages, affording their drafters the opportunity to explain what a business' goals are and how the business will achieve them.
To show potential investors that they've addressed every question and thought through every possible scenario, entrepreneurs should thoroughly explain their marketing, sales, and operations strategies — from acquiring a physical location for the business to explaining a tactical approach for marketing penetration.
These explanations should ultimately lead to a business' break-even point supported by a sales forecast and financial projections, with the business plan writer being able to speak to the why behind anything outlined in the plan.
.webp)
Free Business Plan Template
The essential document for starting a business -- custom built for your needs.
- Outline your idea.
- Pitch to investors.
- Secure funding.
- Get to work!
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Free Business Plan [Template]
Fill out the form to access your free business plan., 3. legitimizing a business idea..
Everyone's got a great idea for a company — until they put pen to paper and realize that it's not exactly feasible.
A business plan is an aspiring entrepreneur's way to prove that a business idea is actually worth pursuing.
As entrepreneurs document their go-to-market process, capital needs, and expected return on investment, entrepreneurs likely come across a few hiccups that will make them second guess their strategies and metrics — and that's exactly what the business plan is for.
It ensures an entrepreneur's ducks are in a row before bringing their business idea to the world and reassures the readers that whoever wrote the plan is serious about the idea, having put hours into thinking of the business idea, fleshing out growth tactics, and calculating financial projections.
4. Getting an A in your business class.
Speaking from personal experience, there's a chance you're here to get business plan ideas for your Business 101 class project.
If that's the case, might we suggest checking out this post on How to Write a Business Plan — providing a section-by-section guide on creating your plan?
What does a business plan need to include?
- Business Plan Subtitle
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- The Business Opportunity
- Competitive Analysis
- Target Market
- Marketing Plan
- Financial Summary
- Funding Requirements
1. Business Plan Subtitle
Every great business plan starts with a captivating title and subtitle. You’ll want to make it clear that the document is, in fact, a business plan, but the subtitle can help tell the story of your business in just a short sentence.
2. Executive Summary
Although this is the last part of the business plan that you’ll write, it’s the first section (and maybe the only section) that stakeholders will read. The executive summary of a business plan sets the stage for the rest of the document. It includes your company’s mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals.
3. Company Description
This brief part of your business plan will detail your business name, years in operation, key offerings, and positioning statement. You might even add core values or a short history of the company. The company description’s role in a business plan is to introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way.
4. The Business Opportunity
The business opportunity should convince investors that your organization meets the needs of the market in a way that no other company can. This section explains the specific problem your business solves within the marketplace and how it solves them. It will include your value proposition as well as some high-level information about your target market.

5. Competitive Analysis
Just about every industry has more than one player in the market. Even if your business owns the majority of the market share in your industry or your business concept is the first of its kind, you still have competition. In the competitive analysis section, you’ll take an objective look at the industry landscape to determine where your business fits. A SWOT analysis is an organized way to format this section.
6. Target Market
Who are the core customers of your business and why? The target market portion of your business plan outlines this in detail. The target market should explain the demographics, psychographics, behavioristics, and geographics of the ideal customer.
7. Marketing Plan
Marketing is expansive, and it’ll be tempting to cover every type of marketing possible, but a brief overview of how you’ll market your unique value proposition to your target audience, followed by a tactical plan will suffice.
Think broadly and narrow down from there: Will you focus on a slow-and-steady play where you make an upfront investment in organic customer acquisition? Or will you generate lots of quick customers using a pay-to-play advertising strategy? This kind of information should guide the marketing plan section of your business plan.
8. Financial Summary
Money doesn’t grow on trees and even the most digital, sustainable businesses have expenses. Outlining a financial summary of where your business is currently and where you’d like it to be in the future will substantiate this section. Consider including any monetary information that will give potential investors a glimpse into the financial health of your business. Assets, liabilities, expenses, debt, investments, revenue, and more are all useful adds here.
So, you’ve outlined some great goals, the business opportunity is valid, and the industry is ready for what you have to offer. Who’s responsible for turning all this high-level talk into results? The "team" section of your business plan answers that question by providing an overview of the roles responsible for each goal. Don’t worry if you don’t have every team member on board yet, knowing what roles to hire for is helpful as you seek funding from investors.
10. Funding Requirements
Remember that one of the goals of a business plan is to secure funding from investors, so you’ll need to include funding requirements you’d like them to fulfill. The amount your business needs, for what reasons, and for how long will meet the requirement for this section.
Types of Business Plans
- Startup Business Plan
- Feasibility Business Plan
- Internal Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Business Acquisition Plan
- Business Repositioning Plan
- Expansion or Growth Business Plan
There’s no one size fits all business plan as there are several types of businesses in the market today. From startups with just one founder to historic household names that need to stay competitive, every type of business needs a business plan that’s tailored to its needs. Below are a few of the most common types of business plans.
For even more examples, check out these sample business plans to help you write your own .
1. Startup Business Plan

As one of the most common types of business plans, a startup business plan is for new business ideas. This plan lays the foundation for the eventual success of a business.
The biggest challenge with the startup business plan is that it’s written completely from scratch. Startup business plans often reference existing industry data. They also explain unique business strategies and go-to-market plans.
Because startup business plans expand on an original idea, the contents will vary by the top priority goals.
For example, say a startup is looking for funding. If capital is a priority, this business plan might focus more on financial projections than marketing or company culture.
2. Feasibility Business Plan
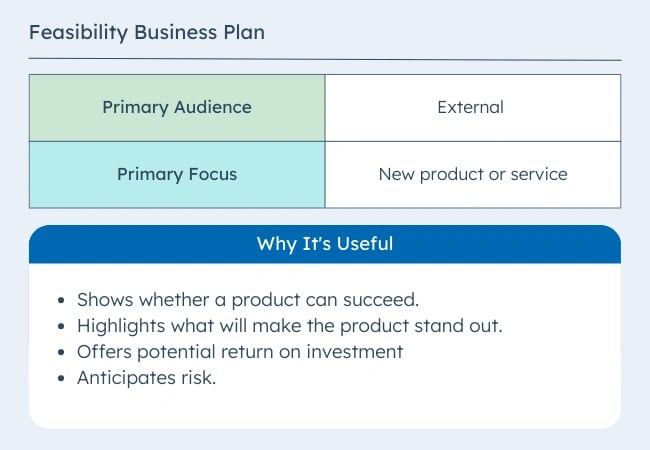
This type of business plan focuses on a single essential aspect of the business — the product or service. It may be part of a startup business plan or a standalone plan for an existing organization. This comprehensive plan may include:
- A detailed product description
- Market analysis
- Technology needs
- Production needs
- Financial sources
- Production operations
According to CBInsights research, 35% of startups fail because of a lack of market need. Another 10% fail because of mistimed products.
Some businesses will complete a feasibility study to explore ideas and narrow product plans to the best choice. They conduct these studies before completing the feasibility business plan. Then the feasibility plan centers on that one product or service.
3. Internal Business Plan

Internal business plans help leaders communicate company goals, strategy, and performance. This helps the business align and work toward objectives more effectively.
Besides the typical elements in a startup business plan, an internal business plan may also include:
- Department-specific budgets
- Target demographic analysis
- Market size and share of voice analysis
- Action plans
- Sustainability plans
Most external-facing business plans focus on raising capital and support for a business. But an internal business plan helps keep the business mission consistent in the face of change.
4. Strategic Business Plan

Strategic business plans focus on long-term objectives for your business. They usually cover the first three to five years of operations. This is different from the typical startup business plan which focuses on the first one to three years. The audience for this plan is also primarily internal stakeholders.
These types of business plans may include:
- Relevant data and analysis
- Assessments of company resources
- Vision and mission statements
It's important to remember that, while many businesses create a strategic plan before launching, some business owners just jump in. So, this business plan can add value by outlining how your business plans to reach specific goals. This type of planning can also help a business anticipate future challenges.
5. Business Acquisition Plan

Investors use business plans to acquire existing businesses, too — not just new businesses.
A business acquisition plan may include costs, schedules, or management requirements. This data will come from an acquisition strategy.
A business plan for an existing company will explain:
- How an acquisition will change its operating model
- What will stay the same under new ownership
- Why things will change or stay the same
- Acquisition planning documentation
- Timelines for acquisition
Additionally, the business plan should speak to the current state of the business and why it's up for sale.
For example, if someone is purchasing a failing business, the business plan should explain why the business is being purchased. It should also include:
- What the new owner will do to turn the business around
- Historic business metrics
- Sales projections after the acquisition
- Justification for those projections
6. Business Repositioning Plan
.webp?width=650&height=450&name=businessplan_6%20(1).webp)
When a business wants to avoid acquisition, reposition its brand, or try something new, CEOs or owners will develop a business repositioning plan.
This plan will:
- Acknowledge the current state of the company.
- State a vision for the future of the company.
- Explain why the business needs to reposition itself.
- Outline a process for how the company will adjust.
Companies planning for a business reposition often do so — proactively or retroactively — due to a shift in market trends and customer needs.
For example, shoe brand AllBirds plans to refocus its brand on core customers and shift its go-to-market strategy. These decisions are a reaction to lackluster sales following product changes and other missteps.
7. Expansion or Growth Business Plan
When your business is ready to expand, a growth business plan creates a useful structure for reaching specific targets.
For example, a successful business expanding into another location can use a growth business plan. This is because it may also mean the business needs to focus on a new target market or generate more capital.
This type of plan usually covers the next year or two of growth. It often references current sales, revenue, and successes. It may also include:
- SWOT analysis
- Growth opportunity studies
- Financial goals and plans
- Marketing plans
- Capability planning
These types of business plans will vary by business, but they can help businesses quickly rally around new priorities to drive growth.

Getting Started With Your Business Plan
At the end of the day, a business plan is simply an explanation of a business idea and why it will be successful. The more detail and thought you put into it, the more successful your plan — and the business it outlines — will be.
When writing your business plan, you’ll benefit from extensive research, feedback from your team or board of directors, and a solid template to organize your thoughts. If you need one of these, download HubSpot's Free Business Plan Template below to get started.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in August 2020 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

24 of My Favorite Sample Business Plans & Examples For Your Inspiration
![a business plan explains the idea behind your business How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/executive-summary-example_5.webp)
How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]

19 Best Sample Business Plans & Examples to Help You Write Your Own

Maximizing Your Social Media Strategy: The Top Aggregator Tools to Use

The Content Aggregator Guide for 2023
![a business plan explains the idea behind your business 7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/gantt-chart-example.jpg)
7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]
![a business plan explains the idea behind your business The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/flowchart%20templates.jpg)
The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]

16 Best Screen Recorders to Use for Collaboration

The 25 Best Google Chrome Extensions for SEO

Professional Invoice Design: 28 Samples & Templates to Inspire You
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
Everything that you need to know to start your own business. From business ideas to researching the competition.
Practical and real-world advice on how to run your business — from managing employees to keeping the books.
Our best expert advice on how to grow your business — from attracting new customers to keeping existing customers happy and having the capital to do it.
Entrepreneurs and industry leaders share their best advice on how to take your company to the next level.
- Business Ideas
- Human Resources
- Business Financing
- Growth Studio
- Ask the Board
Looking for your local chamber?
Interested in partnering with us?
Start » business ideas, the definitive guide to writing a startup business plan.
Our guide covers all the components of your startup business plan and explains why startups have unique business plan needs.

To understand what should be included in a business plan, you have to understand who the plan is for and what stage of your business you’re in. If you’ll be taking a business plan to a financial institution as part of a loan application, you’re going to want a more traditional plan. These tend to be on the longer side and should be as detailed as possible, without getting too technical.
If you’re in the early planning stages of your business or just want something to show to a few angel investors, you might consider a startup business plan format, which will be more of a summary of key points. That might only be one page long but should still hit on all the major highlights and goals of the business.
According to the Small Business Administration, the length of your business plan should be long enough to accomplish three goals: (1) excite the financing source, (2) prove that you truly understand the market, and (3) fully detail the execution strategy.
Regardless of length, your business plan must get across why you are passionate about your company and why you think it will succeed. You should have a command of your market, your subject area and be authoritative. You should include market data and financial projections, but not come across overly dry. You want the readers of your business proposal—even bank loan officers—to see your commitment to your goals and the emotional connection you have formed to your business idea. At the same time, you want your plan to appear factual and professional.
Startup business plan requirements
If you’re writing a business plan for a bank or lending institution, consider including the following major components in your plan. Keep your plan in a binder with numbered pages and provide a table of contents to make it easy to follow.
Executive summary. This is a brief (1-2 page) explanation of what your company is, what it does and why it will be successful. Although this summary will come first in the plan, you should write it last so that you have all the information to draw from. Not succinctly summarizing your business idea is one of the biggest mistakes that can be made in a business plan. If you don’t hook your reader with your executive summary, that person is not going to want to keep reading. Here are some of the pieces to include:
- The mission statement — a short statement summing up your business and explaining your product or services
- A brief overview of the structure of your company and the leadership team
- Some basic financial information, such as banking relationships and any investors
- A summary of your company growth and any financial highlights
- Company facts like number of employees, date founded and location
Mission statement. Although this is a part of the executive summary section, the mission statement deserves a separate callout because you’ll need to carefully craft your message. The statement needs to pack a punch, but remain a tight and coherent thought. Mission statements should be written in the present tense, and answer questions like who your customers are, what values are important to your business and what marker you’ll use to decide if your company is successful.
Market analysis. In your company description you started to explain why your company is a good idea. Your market analysis is where you’ll back up those statements with an authoritative understanding of your industry and target market. Address why your competitors are successful and prove that you know why what they’re doing is working. You also need to establish why your idea is better or will be more successful. The market analysis section should be between 9 and 22 pages long. In this section, include information like:
- Trends and themes in your industry
- A description and size of your target market
- Your pricing and gross margin targets
- Industry risks
- Key personnel
- Five-year projected revenues
If you need help with market research there are several free tools available. The U.S. Census is obviously data rich and can help you answer questions about the size of specific industries and businesses and which products in your industry are growing. The U.S. Census also offers Economic Indicator data that can help you digest what’s going on in different industrial sectors.
The SBA offers a tool called Sizeup that helps you process data points to get details on your competition, figure out where your competitors are located and where there might be gaps in the market. It’s important to remember that having a similar business plan as a competitor doesn’t necessarily mean you won’t be successful. It’s possible that two similar businesses can thrive, but you should be able to explain why the market you are entering is conducive to that.
Your business plan must get across why you are passionate about your company and why you think it will succeed.
You should also be able to prove that you know the customers to whom your business caters and be able define and research their habits. Know when they buy, how often they buy or how often they will need your service.
Company description. A good way to describe your company is by answering this question: What problem does your company solve? That can help determine who your customers are and what advantages your company has over your competitors. The question will also lead you to explain and highlight the expertise of your team and the benefits of your physical location. A company description is an easy place to show your commitment and passion for the company as well as boast your company's strengths.
Organization and management. Here’s another place to show your team’s competence and explain the passion behind your business. This is where you’ll outline who is running your company, how it’s structured and what you all bring to the table. The main components to include are:
- An organizational chart
- The name of all owners and percentages they own
- Resumes of some of your key staff/leaders
- The legal structure of your business (i.e., an LLC, a partnership, etc.)
Marketing and sales. It’s not enough to simply say you have a great product. In a traditional business plan, you have to explain how you intend to get this great product or service to the right customers. You should convey how your strategy is going to evolve once you have more (or any) customer data. Still, you should lay out a roadmap for how to start and potential opportunities to attract and retain customers. Consider including the following:
- An explanation of your business model and how your product leads to revenue
- How and when you will introduce new products or services
- Potential new territories for your company to enter
- The plan to boost sales on a particular product
- Potential long-term relationships with other companies or clients
- The possibility of price increases
- Improvements to your product or your processes for manufacturing or delivery
- Ideas for advertising and social media strategy
Service or product line. In this section you will need to again answer what your company does and what you’re selling. You can go into more detail about what sets your product and company apart from your competitors, as well as how you target customer benefits. Some items to include are:
- The life cycle of your product
- Information on any copyrights, patents and any other ways you protect your intellectual property
- Any non-disclosure or non-compete agreements
- Any research and development you’ve done
Funding request. If the goal of your business plan is to secure an investment or a loan, then this is where you’ll explain how much funding you need and why. In addition, you want to explain how you will pay off your debt. Also include any information that would majorly impact your future financial situation, like plans to take the company public or sell the company.
Financial information. It might seem obvious, but in your financial projections you want to show that your business is strong. If you have an established business, this is where you’ll include cash flow statements, income statements and balance sheets as well as collateral that you could put up against a loan. You should also discuss how the business is being funded and your current costs. Also, make sure that the projections clearly match up to your funding requests, avoiding overreaching. This section of your business plan should also have some heft, possibly as long as 12 to 25 pages.
Some of the documents you should provide include:
- Current financial data of all owners
- Financial data from the past three years, such as balance sheets and profit and loss statements
- A list of all your debt, including what you owe and to whom
- A five-year forecast of income and expenses
- A certification or review letter from a financial advisor saying that your information meets generally accepted accounting principles
Appendix. This section is for any supporting documents that can be used to support your plan statements. Consider including credit histories, the resumes of your staff or key leaders, product pictures, permits, patents or other relevant contracts.
Startup business plan template
For a startup business, it might be worthwhile to look at a less involved version of a traditional business plan. A popular one is the Business Model Canvas developed by Alex Osterwalder. The idea of the canvas is to explain your business model in a simple way to relevant parties, such as partners and potential investors.
Here are the main components of the Canvas model:
Key partnerships. Discuss the other businesses or services required to run your new business. This can include suppliers, contractors, manufacturers or other partners that are necessary for your company to operate.
Key activities. Format a list of how your business will gain an advantage in your industry through your chosen business model. You should highlight what makes your company more effective at reaching your target customer than your competitors.
Key resources. List your important business assets which may include staff, capital or intellectual property. These are the things that will make your chosen business model successful and help you deliver to your customer.
Value proposition. This is a good place to showcase your passion as well as your understanding of your market. You should make a compelling case for why a customer would choose you over the competition.
Customer relationships. Describe a customer’s experience working and interacting with your business. Address both customer acquisition and customer retention.
Customer segments. Explain who your customers are. You’ll want to give a clear sense of your target market and who is being served by your business. Be specific.
Channels. Describe how you will communicate with your customers and why those methods are effective. Most businesses use a mix of channels and optimize them over time.
Cost structure. Address how your company will reduce cost, maximize value and make money on your product or service. Be honest about the most significant costs that you anticipate facing.
Revenue streams. List all the revenue opportunities in your plan, including the product or service you're selling, advertising space for sale and membership fees.
See Also: Business Plan Mistakes to Avoid
CO— aims to bring you inspiration from leading respected experts. However, before making any business decision, you should consult a professional who can advise you based on your individual situation.
CO—is committed to helping you start, run and grow your small business. Learn more about the benefits of small business membership in the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, here .
Join us for our Small Business Day event!
Join us at our next event on Wednesday, May 1, at 12:00 p.m., where we’ll be kicking off Small Business Month alongside business experts and entrepreneurs. Register to attend in person at our Washington, D.C., headquarters, or join us virtually!
Subscribe to our newsletter, Midnight Oil
Expert business advice, news, and trends, delivered weekly
By signing up you agree to the CO— Privacy Policy. You can opt out anytime.
By continuing on our website, you agree to our use of cookies for statistical and personalisation purposes. Know More
Welcome to CO—
Designed for business owners, CO— is a site that connects like minds and delivers actionable insights for next-level growth.
U.S. Chamber of Commerce 1615 H Street, NW Washington, DC 20062
Social links
Looking for local chamber, stay in touch.
Chapter 8: Entrepreneurship
Reading: create your business plan, executive summary.
This written guide will help you create a business plan and map out how you will start and run your business successfully.
The executive summary is often considered the most important section of a business plan. This section briefly tells your reader where your company is, where you want to take it, and why your business idea will be successful. If you are seeking financing, the executive summary is also your first opportunity to grab a potential investor’s interest.
The executive summary should highlight the strengths of your overall plan and therefore be the last section you write. However, it usually appears first in your business plan document.
Below are several key points that your executive summary should include based on the stage of your business.
If You Are an Established Business
If you are an established business, be sure to include the following information:
- The Mission Statement —This explains what your business is all about. It should be between several sentences and a paragraph.
- Company Information —Include a short statement that covers when your business was formed, the names of the founders and their roles, your number of employees, and your business location(s).
- Growth Highlights —Include examples of company growth, such as financial or market highlights (for example, “XYZ Firm increased profit margins and market share year-over-year since its foundation). Graphs and charts can be helpful in this section.
- Your Products/Services —Briefly describe the products or services you provide.
- Financial Information —If you are seeking financing, include any information about your current bank and investors.
- Summarize future plans —Explain where you would like to take your business.
With the exception of the mission statement, all of the information in the executive summary should be covered in a concise fashion and kept to one page. The executive summary is the first part of your business plan many people will see, so each word should count.
If You Are a Startup or New Business
If you are just starting a business, you won’t have as much information as an established company. Instead, focus on your experience and background as well as the decisions that led you to start this particular enterprise.
Demonstrate that you have done thorough market analysis. Include information about a need or gap in your target market, and how your particular solutions can fill it. Convince the reader that you can succeed in your target market, then address your future plans.
Remember, your Executive Summary will be the last thing you write. So the first section of the business plan that you will tackle is the Company Description section.
Company Description
This section of your business plan provides a high-level review of the different elements of your business. This is akin to an extended elevator pitch and can help readers and potential investors quickly understand the goal of your business and its unique proposition.
What to Include in Your Company Description
- Describe the nature of your business and list the marketplace needs that you are trying to satisfy.
- Explain how your products and services meet these needs.
- List the specific consumers, organizations or businesses that your company serves or will serve.
- Explain the competitive advantages that you believe will make your business a success such as your location, expert personnel, efficient operations, or ability to bring value to your customers.
Next, you’ll need to move on to the Market Analysis section of your plan.
Market Analysis
The market analysis section of your business plan should illustrate your industry and market knowledge as well as any of your research findings and conclusions.
What to Include in Your Market Analysis
- Industry Description and Outlook —Describe your industry, including its current size and historic growth rate as well as other trends and characteristics (e.g., life cycle stage, projected growth rate). Next, list the major customer groups within your industry.
- Information About Your Target Market —Narrow your target market to a manageable size. Many businesses make the mistake of trying to appeal to too many target markets. Research and include the following information about your market:
- Distinguishing Characteristics —What are the critical needs of your potential customers? Are those needs being met? What are the demographics of the group and where are they located? Are there any seasonal or cyclical purchasing trends that may impact your business?
- Size of the Primary Target Market —In addition to the size of your market, what data can you include about the annual purchases your market makes in your industry? What is the forecasted market growth for this group?
- How Much Market Share Can You Gain? —What is the market share percentage and number of customers you expect to obtain in a defined geographic area? Explain the logic behind your calculation.
- Pricing and Gross Margin Targets —Define your pricing structure, gross margin levels, and any discount that you plan to use.
- When you include information about any of the market tests or research studies you have completed, be sure to focus only on the results of these tests. Any other details should be included in the appendix (which we will discuss later).
- Market share
- Strengths and weaknesses
- How important is your target market to your competitors?
- Are there any barriers that may hinder you as you enter the market?
- What is your window of opportunity to enter the market?
- Are there any indirect or secondary competitors who may impact your success?
- What barriers to market are there (e.g., changing technology, high investment cost, lack of quality personnel)?
- Regulatory Restrictions —Include any customer or governmental regulatory requirements affecting your business, and how you’ll comply. Also, cite any operational or cost impact the compliance process will have on your business.
Once you’ve completed this section, you can move on to the Organization and Management section of your business plan.
Organization and Management
This section should include: your company’s organizational structure, details about the ownership of your company, profiles of your management team, and the qualifications of your board of directors.
Who does what in your business? What is their background and why are you bringing them into the business as board members or employees? What are they responsible for? These may seem like unnecessary questions to answer in a one- or two-person organization, but the people reading your business plan want to know who’s in charge, so tell them. Give a detailed description of each division or department and its function.
This section should include who’s on the board (if you have an advisory board) and how you intend to keep them there. What kind of salary and benefits package do you have for your people? What incentives are you offering? How about promotions? Reassure your reader that the people you have on staff are more than just names on a letterhead.
Organizational Structure
A simple but effective way to lay out the structure of your company is to create an organizational chart with a narrative description. This will prove that you’re leaving nothing to chance, you’ve thought out exactly who is doing what, and there is someone in charge of every function of your company. Nothing will fall through the cracks, and nothing will be done three or four times over. To a potential investor or employee, that is very important.
Ownership Information
This section should also include the legal structure of your business along with the subsequent ownership information it relates to. Have you incorporated your business? If so, is it a C or S corporation? Or perhaps you have formed a partnership with someone. If so, is it a general or limited partnership? Or maybe you are a sole proprietor.
The following important ownership information should be incorporated into your business plan:
- Names of owners
- Percentage ownership
- Extent of involvement with the company
- Forms of ownership (i.e., common stock, preferred stock, general partner, limited partner)
- Outstanding equity equivalents (i.e., options, warrants, convertible debt)
- Common stock (i.e., authorized or issued)
- Management Profiles
- Experts agree that one of the strongest factors for success in any growth company is the ability and track record of its owner/management team, so let your reader know about the key people in your company and their backgrounds. Provide resumes that include the following information:
- Position (include brief position description along with primary duties)
- Primary responsibilities and authority
- Unique experience and skills
- Prior employment
- Special skills
- Past track record
- Industry recognition
- Community involvement
- Number of years with company
- Compensation basis and levels (make sure these are reasonable — not too high or too low)
- Be sure you quantify achievements (e.g. “Managed a sales force of ten people,” “Managed a department of fifteen people,” “Increased revenue by 15 percent in the first six months,” “Expanded the retail outlets at the rate of two each year,” “Improved the customer service as rated by our customers from a 60 percent to a 90 percent rating”)
Also, highlight how the people surrounding you complement your own skills. If you’re just starting out, show how each person’s unique experience will contribute to the success of your venture.
Board of Directors’ Qualifications
The major benefit of an unpaid advisory board is that it can provide expertise that your company cannot otherwise afford. A list of well-known, successful business owners/managers can go a long way toward enhancing your company’s credibility and perception of management expertise.
If you have a board of directors, be sure to gather the following information when developing the outline for your business plan:
- Positions on the board
- Extent of involvement with company
- Historical and future contribution to the company’s success
Service or Product Line
Once you’ve completed the Organizational and Management section of your plan, the next part of your business plan is where you describe your service or product, emphasizing the benefits to potential and current customers. Focus on why your particular product will fill a need for your target customers.
What to Include in Your Service or Product Line Section
- A Description of Your Product/Service —Include information about the specific benefits of your product or service – from your customers’ perspective. You should also talk about your product or service’s ability to meet consumer needs, any advantages your product has over that of the competition, and the current development stage your product is in (e.g., idea, prototype).
- Details About Your Product’s Life Cycle —Be sure to include information about where your product or service is in its life cycle, as well as any factors that may influence its cycle in the future.
- Intellectual Property —If you have any existing, pending, or any anticipated copyright or patent filings, list them here. Also disclose whether any key aspects of a product may be classified as trade secrets. Last, include any information pertaining to existing legal agreements, such as nondisclosure or non-compete agreements.
- Research and Development (R&D) Activities —Outline any R&D activities that you are involved in or are planning. What results of future R&D activities do you expect? Be sure to analyze the R&D efforts of not only your own business, but also of others in your industry.
Marketing and Sales
Once you’ve completed the Service or Product Line section of your plan, the next part of your business plan should focus on your marketing and sales management strategy for your business.
Marketing is the process of creating customers, and customers are the lifeblood of your business. In this section, the first thing you want to do is define your marketing strategy. There is no single way to approach a marketing strategy; your strategy should be part of an ongoing business-evaluation process and unique to your company. However, there are common steps you can follow which will help you think through the direction and tactics you would like to use to drive sales and sustain customer loyalty.
An overall marketing strategy should include four different strategies:
- A market penetration strategy.
- A growth strategy. This strategy for building your business might include: an internal strategy such as how to increase your human resources, an acquisition strategy such as buying another business, a franchise strategy for branching out, a horizontal strategy where you would provide the same type of products to different users, or a vertical strategy where you would continue providing the same products but would offer them at different levels of the distribution chain.
- Channels of distribution strategy. Choices for distribution channels could include original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), an internal sales force, distributors, or retailers.
- Communication strategy. How are you going to reach your customers? Usually a combination of the following tactics works the best: promotions, advertising, public relations, personal selling, and printed materials such as brochures, catalogs, flyers, etc.
After you have developed a comprehensive marketing strategy, you can then define your sales strategy. This covers how you plan to actually sell your product.
Your overall sales strategy should include two primary elements:
- A sales force strategy. If you are going to have a sales force, do you plan to use internal or independent representatives? How many salespeople will you recruit for your sales force? What type of recruitment strategies will you use? How will you train your sales force? What about compensation for your sales force?
- Your sales activities. When you are defining your sales strategy, it is important that you break it down into activities. For instance, you need to identify your prospects. Once you have made a list of your prospects, you need to prioritize the contacts, selecting the leads with the highest potential to buy first. Next, identify the number of sales calls you will make over a certain period of time. From there, you need to determine the average number of sales calls you will need to make per sale, the average dollar size per sale, and the average dollar size per vendor.
Next, if you are seeking financing for your business, you’ll need to complete the next part of your plan—Funding Request.
Funding Request
If you are seeking funding for your business venture, use this section to outline your requirements.
Your funding request should include the following information:
- Your current funding requirement
- Any future funding requirements over the next five years
- How you intend to use the funds you receive: Is the funding request for capital expenditures? Working capital? Debt retirement? Acquisitions? Whatever it is, be sure to list it in this section.
- Any strategic financial situational plans for the future, such as: a buyout, being acquired, debt repayment plan, or selling your business. These areas are extremely important to a future creditor, since they will directly impact your ability to repay your loan(s).
When you are outlining your funding requirements, include the amount you want now and the amount you want in the future. Also include the time period that each request will cover, the type of funding you would like to have (e.g., equity, debt), and the terms that you would like to have applied.
To support your funding request you’ll also need to provide historical and prospective financial information. Once you have completed your funding request, move on to the next part of your plan—Financial Projections.
Financial Projections
You should develop the Financial Projections section after you’ve analyzed the market and set clear objectives. That’s when you can allocate resources efficiently. The following is a list of the critical financial statements to include in your business plan packet.
Historical Financial Data
If you own an established business, you will be requested to supply historical data related to your company’s performance. Most creditors request data for the last three to five years, depending on the length of time you have been in business.
The historical financial data to include are your company’s income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements for each year you have been in business (usually for up to three to five years). Often, creditors are also interested in any collateral that you may have that could be used to ensure your loan, regardless of the stage of your business.
Prospective Financial Data
All businesses, whether startup or growing, will be required to supply prospective financial data. Most of the time, creditors will want to see what you expect your company to be able to do within the next five years. Each year’s documents should include forecasted income statements, balance sheets, cash flow statements, and capital expenditure budgets. For the first year, you should supply monthly or quarterly projections. After that, you can stretch it to quarterly and/or yearly projections for years two through five.
Make sure that your projections match your funding requests; creditors will be on the lookout for inconsistencies. It’s much better if you catch mistakes before they do. If you have made assumptions in your projections, be sure to summarize what you have assumed. This way, the reader will not be left guessing.
Finally, include a short analysis of your financial information. Include a ratio and trend analysis for all of your financial statements (both historical and prospective). Since pictures speak louder than words, you may want to add graphs of your trend analysis (especially if they are positive).
Next, you may want to include an Appendix to your plan. This can include items such as your credit history, resumes, letters of reference, and any additional information that a lender may request.
The Appendix should be provided to readers on an as-needed basis. In other words, it should not be included with the main body of your business plan. Your plan is your communication tool; as such, it will be seen by a lot of people. Some of the information in the business section you will not want everyone to see, but specific individuals (such as creditors) may want access to this information to make lending decisions. Therefore, it is important to have the appendix within easy reach.
The appendix would include:
- Credit history (personal and business)
- Resumes of key managers
- Product pictures
- Letters of reference
- Details of market studies
- Relevant magazine articles or book references
- Licenses, permits or patents
- Legal documents
- Copies of leases
- Building permits
- List of business consultants, including attorney and accountant
Any copies of your business plan should be controlled; keep a distribution record. This will allow you to update and maintain your business plan on an as-needed basis. Remember, too, that you should include a private placement disclaimer with your business plan if you plan to use it to raise capital.
How to Make Your Business Plan Stand Out
One of the first steps to business planning is determining your target market and why they would want to buy from you.
For example, is the market you serve the best one for your product or service? Are the benefits of dealing with your business clear and are they aligned with customer needs? If you’re unsure about the answers to any of these questions, take a step back and revisit the foundation of your business plan.
The following tips can help you clarify what your business has to offer, identify the right target market for it and build a niche for yourself.
Be Clear About What You Have to Offer
Ask yourself: Beyond basic products or services, what are you really selling? Consider this example: Your town probably has several restaurants all selling one fundamental product—food. But each is targeted at a different need or clientele.
One might be a drive-thru fast food restaurant, perhaps another sells pizza in a rustic Italian kitchen, and maybe there’s a fine dining seafood restaurant that specializes in wood-grilled fare. All these restaurants sell meals, but they sell them to targeted clientele looking for the unique qualities each has to offer. What they are really selling is a combination of product, value, ambience and brand experience.
When starting a business, be sure to understand what makes your business unique. What needs does your product or service fulfill? What benefits and differentiators will help your business stand out from the crowd?
Don’t Become a Jack of All Trades—Learn to Strategize
It’s important to clearly define what you’re selling. You do not want to become a jack-of-all trades and master of none because this can have a negative impact on business growth. As a smaller business, it’s often a better strategy to divide your products or services into manageable market niches. Small operations can then offer specialized goods and services that are attractive to a specific group of prospective buyers.
Identify Your Niche
Creating a niche for your business is essential to success. Often, business owners can identify a niche based on their own market knowledge, but it can also be helpful to conduct a market survey with potential customers to uncover untapped needs. During your research process, identify the following:
- Which areas your competitors are already well established
- Which areas are being ignored by your competitors
- Potential opportunities for your business
Check Your Understanding
Answer the question(s) below to see how well you understand the topics covered in this section. This short quiz does not count toward your grade in the class, and you can retake it an unlimited number of times.
Use this quiz to check your understanding and decide whether to (1) study the previous section further or (2) move on to the next section.
- Create Your Business Plan. Provided by : U.S. Small Business Association. Located at : https://www.sba.gov/writing-business-plan . License : Public Domain: No Known Copyright
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to footer
Better Knowledge. Your Insight Is Sharper
Turning a Business Idea into a Business Plan: Purpose, Components
Updated on August 13, 2023 by Ahmad Nasrudin

What’s it: A business plan is a detailed document about strategies for achieving the business’s mission and objectives. It also explains what the company should look like in the next few years.
For startups, business planning is the first step before running a business or getting a capital injection. It’s usually a short-term plan, say for a year.
For an established company, the business plan establishes business goals over the next several periods, often three, five, or ten years. Specifically, we refer to it as a corporate plan.
For this article, I will specifically discuss the business plans of new companies or startups.
Purposes of a business plan
Business planning is an essential step before executing any business strategy. Companies create them to help them consider all the elements they need for their business to be successful.
A business plan is essential to fulfilling several purposes, such as:
- Set a focus
- Exploiting potential opportunities and minimizing risks
Get funding or capital
Set business focus.
The business plan provides a guide for what to do in the future. It serves as roadmaps and guides to help businesses focus and pursue success.
The entrepreneur explains the goals, steps, and how the business achieves success and creates value. In it, you will find detailed outlines of how the business will achieve each step.
Maximizing opportunities and minimizing risks
The startup describes every aspect of the business, including the opportunities and risks faced in the future. By identifying them, they can develop strategies and tactics to maximize opportunities and minimize risks.
For startups, such identification is increasingly essential. They face higher uncertainty than established companies. Therefore, business planning reduces the risk of failure in the early years.
Entrepreneurs discuss not only internal environment aspects such as how to manufacture and design products but also the external environment. They must understand the market, potential customers, business locations, and competitive conditions. They then conduct market research to answer questions, why the company exists, and its aims and objectives.
Also, companies use market research inputs to develop appropriate strategies and tactics, including plans for product development, production, marketing, distribution, and finance.
One of the critical financial aspects to minimize risk is the cash flow forecast. Entrepreneurs predict how much money will come in and go out over the next few years.
The early years of doing business are crucial periods. Startups usually still rely on external funding. Sales are still not generating enough cash flow to finance operating activities.
Banks or potential business investors will look at the business plan before deciding to inject funds or capital. The entrepreneurs assure the capital supplier why the business will be successful and why they should provide funds.
Some successful entrepreneurs convince capital suppliers. Others failed.
By looking at the business plan, capital suppliers want to make sure they don’t lose money. Therefore, they weigh the potential risks and returns before deciding to give money. They make sure they will get more money by funding the company.
Capital suppliers may perceive the business as too risky and outside their tolerance. So, they decided not to be willing to lend money.
Business plan components
The business plan must provide detailed information and analysis of all relevant business aspects, including management, competitive position, markets, activities, products, policies, and financial projection.
For new businesses, the content structure of the business plan usually covers:
- Executive summary – overview of the business and its strategy.
- Mission statement – a brief statement of why the business exists and for what purpose.
- Business environment overview – a detailed overview of the industry background, what is sold, current and potential market size , and the competition map.
- Business operations overview – details marketing plans, teams and management, operations, and information technology systems.
- Financial projections – about future sales, costs, profits, and cash flows.
Example of a business plan
You may find a variety of business plan formats. And, here, I will present the format according to the previous discussion.
Executive summary
In this section, the entrepreneur provides a concise explanation of the new business and why it will be successful. Also, entrepreneurs try to convince investors why they should fund a business.
Investors often focus on the executive summary. They had little time to read pages of documents. When they are interested in this section, they are likely willing to read the next section.
In this section, the entrepreneur usually includes some information such as mission, products and services, target market , business location, team and management, financial information, and growth plans.
Mission statement
The mission statement helps answer the question of why new business is coming. Unlike other sections, the content in this section is usually concise. Apart from the mission, the entrepreneur might also provide some details about his short-term goals ahead.
Overview of the business environment
Entrepreneurs provide detailed information about the market in which the company will operate. They then outline opportunities through market and competition analysis. They also provide information about business challenges to inform investors about the risks inherent in the business.
Some of the content in this section includes:
- Target consumers
- Current and potential market size
- Market trends
- Market growth rate
- Competition, for example, uses Porter’s Five Forces approach
- Market profitability
- Industry cost structure
- Distribution channel
- Key success factors
Overview of business operations
Entrepreneurs provide detailed information about new businesses. They outline strategies and tactics for exploiting opportunities and minimizing risks. They also explain the competitive advantage to support business success. They then detail various aspects of the business function.
First , about organization and management. The entrepreneur explains how the company is structured and who will run it. What is a legal business entity, whether in a corporation or a general or limited partnership?
Then, the entrepreneur defines who is responsible for operating the business. It may also include information about key employees and unique experiences contributing to the business’s success going forward. In the appendix, they can include CV information in more detail.
Second , the product. Entrepreneurs explain what products they offer, why the products are successful and profitable, and why customers will buy them. They make clear and compelling statements about the value proposition that a new business brings to the market and why it does it better than other products.
They also explain other aspects such as product design and development, main product features, price, copyright or patent applications, and research and development details.
Third , marketing and sales. Entrepreneurs provide detailed information about how they will sell the product. They explain how to attract and retain customers. Other aspects are customer segments, pricing strategy, advertising campaigns, distribution channels, packaging, and customer support. They relate it all to the opportunities and challenges they have presented before.
Fourth , production and operation. In this section, the entrepreneur describes detailed aspects of production and other operating activities, including:
- Primary activities : production facilities, technology, production sites, access to raw materials, and logistics network.
- Supporting activities : accounting and finance, human resource development, information technology development, and procurement.
- Key partners : suppliers, media, subcontractors, and distributors
Financial forecast
In this section, the entrepreneur outlines the projected results of operations and funding requirements, usually for the next three or five years. It explains various aspects of business finance, such as:
- Revenue : number of customers, customer growth, price, sales volume, and market share . If the entrepreneur targets several market segments , they must break down each of these indicators by segment.
- Costs: raw materials, labor, marketing, general administration, and funding costs.
- Target capital structure : composition of debt and equity.
- Profit : product profit margin, gross profit, operating profit, financing costs, taxes, and net income.
- Cash flow: net income, working capital, depreciation, and capital expenditure budget.
Where available, entrepreneurs should study details about industry norms and competitor financial reports to provide insight into projecting finances.
Furthermore, the entrepreneur explains the future funding plan, including about:
- Target capital structure, a combination of debt and equity
- The number of funds required and details of their use
- Funding requirements
- Return on capital includes debt servicing and projected rate of return on capital.
Appendix
Employers use the appendix to provide supporting documents or other materials discussed in the previous section.
- Finding a Business Idea: Original Idea or Adaptation?
- What Are the Characteristics of a Good Business Idea?
- What Are Sources of Business Ideas?
- 7 Reasons to Start a Business
- Business Idea: Sources and Criteria for a Good Idea
5 NEW ARTICLES

Private Savings: Formula and Explanation
What's it: Private savings equal to the sum of household and business savings. And savings

How to Handle and Resolve Stakeholder Conflicts
Stakeholders have different interests and goals, which are often contradictory. Stakeholder

Where Do Comparative Advantages Come From?
The comparative advantage stems from the ability to produce goods and services at low opportunity

What are the Benefits of International Trade?
Increased access to cheaper and more varied goods and services is key benefits of international

What is the Capital Budgeting Process?
In simple terms, the capital budgeting process involves generating ideas, making proposals about
5 TRENDING ARTICLES
- Socio-cultural Factors: Examples and How They Impact Business
- Business Size: Definition, Measurement, Classification
- Values, Attitudes and Lifestyles (VALS): Categories and Why They Matter
- What are the roles and functions of management according to Mintzberg and Fayol?
EXPLORE MORE
How to create a business plan: a beginner's guide
Creating a well-written business plan is an essential first step to starting your own business

What is a business plan?
Key concepts for writing a business plan, main components of a business plan, tips for writing a business plan.
A well-written business plan holds a lot of value. It’s where your ideas start to take shape and the direction of your new enterprise becomes clear – but it can seem intimidating.
Business plans require focus: you’re stating why you’re doing what you’re doing, and how you expect to do it. There can be a lot to note down.
Ultimately, though, your business plan is going to become an essential guide for you, your team, and anyone involved in your company.
So let’s uncover what it takes to write a business plan, and find out how it can benefit you.
- Also check out our roundup of the best small business software
In short, a business plan is a description of your business and everything that goes into it.
As well as helping to clarify the business idea that you have, it brings into focus elements like financing, staffing, revenue targets, and marketing strategies.
Business plans aren’t exclusive to startups, either. If you’re regenerating an existing company, a detailed and structured plan is enormously useful.
Are you a pro? Subscribe to our newsletter
Sign up to the TechRadar Pro newsletter to get all the top news, opinion, features and guidance your business needs to succeed!

Not all success stories have required business plans, but a comprehensive plan will help you to identify any immediate routes to failure.
Although you’re putting a business concept on paper and announcing your mission statement, a plan has to be structured, not fanciful.
The first person it’s trying to convince is you. Are you ready to spend time and money on this?
After that, you should be considering any potential investors and your team members. Will they be motivated and excited? You’ll need to achieve the following with your business plan:
- A clear vision and purpose for the business – why is it important?
- A guide that can be used as a reference throughout the company’s growth.
- An objective outlook on the market potential of what it is your business is doing.

There is no one-size-fits-all business plan template, but the most successful plans have the same key components.
For small business owners writing a business plan, whether it's during the startup process or further down the road during a period of change, these are the essentials to include:
1. Executive summary
Think of your executive summary as an elevator pitch: it should be a concise, engaging, and persuasive overview of your business.
Keep this section to less than one page in length – after all, it is a summary.
While it’s the opening to your business plan, we recommend writing it last. That way, you can collate all of the key points raised in the rest of the document.
Here’s what you should summarize in this part of your business plan:
- A quick description - Outline what your business is about – if it’s a new business, what’s the mission? If you’re changing direction, what’s the concept?
- The products or services you’ll provide - Offer a brief value proposition – what makes your business idea unique?
- A picture of your target market - Give evidence that you’ve carried out market research and know who the end user should be.
- Your marketing strategy - Write a few lines about your intended marketing efforts to provide an idea of business reach.
- A snapshot of the company’s financial health - What’s the current business revenue and what are you forecasting to earn?
- A clear view of your financial needs - If you’re raising money, how much does the business require?
- The company’s key personnel - Whether you’re a startup business or an existing operation, who are the employees to mention?
- We've also featured the best online marketing services
2. Company description and overview
Next up, give a more detailed description of your business. Even if you’ve decided to write a business plan only for your own benefit, imagine what other people would want to know.
Make clear what you think is going to bring your business success in the long run.
This should help to demonstrate that the ideas you have are worth pursuing. For example, what problem can you solve? What experience can you bring to the table?
Here’s how to structure the company description part of your business plan:
Pinpoint the industry that your business is in, plus any insights or industry trends that you intend to adopt or disrupt.
Describe your business model and its structure – is it incorporated, a limited partnership, or perhaps a sole proprietorship?
Mention your target audience and highlight which problems or opportunities you have identified for the business.
Clarify your mission statement and value proposition to ensure that everyone is on the same page when it comes to business focus.
Provide some background on the company, like when it was founded, who by, and where it’s based.
Highlight the key employees in your team. If it’s a small business, that could be everyone, or maybe just a select few people.
It can be tricky to take a step back and consider your overall business goals and objectives, but remember that this is the whole point of writing a business plan.
Business plans can be great tools to use if you’re not even sure whether the venture is worth doing – writing an ambitious company description will help you to find that out.

3. Market analysis and opportunities
Whether you run a small business or a big business, you’ll have competitors. Knowing about the other companies in your industry will be invaluable.
That knowledge can inform your marketing plans, pricing decisions, and product selections.
You’ll also need to know about your target market. An understanding of your customer profile will help your business reach the right people and maintain a competitive advantage.
So, how does all of your market research come together in a business plan? Here’s how:
Illustrate your market analysis - Use charts and graphs to show where the business is going to sit within its industry. In terms of your price points, product offer, and service proposition, how will it compare to other businesses?
Explain who your potential customers are - Use survey tools to help you specify key demographics like age, profession, and location – if you’re only just starting out, it’s fine to make informed guesses about your ideal customer profile.
Include a SWOT analysis - Identifying the key strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of a business is at the heart of every competitive analysis. Present this part in a grid layout to draw attention to it within your business plan.
Be clear about the competition - It’s tough to find a market that isn’t already saturated, so show how your product or service will be different. Although it’s useful to have friendly rivals, you’ll need some competitive advantages.
4. Products and services
Earlier in your business plan, you hinted at what you’ll be selling, and now’s the time to describe it. It’s worth remembering at this point that industry jargon should be avoided.
Explaining the products or services your business offers should be clear, but exciting.
This section should describe why and how your product exists, how much money it will cost to develop, and how much business planning has gone into your decisions.
Whether you keep it brief, or go into detail about manufacturing, here’s how to shape this part:
- Outline the development process - If you’re selling products, will you be manufacturing them too, or sourcing from elsewhere? What’s the timeline?
- Overview the business model - This is particularly important for retailers, as you’ll need to clarify how your products will reach your customers.
- Cover off the costs - Financial projections and cost management will come up a lot in your business plan. In this part, discuss your profit margin expectations.
- Explain what sets your business apart - Chances are there will be versions of your product or service on the market – what’s your unique selling point (USP)?
- Talk about intellectual property - Mention any patents or copyrights you have applied for and emphasise how your work will be protected.

5. Business management and organization
By this part of your business plan, you will have described in detail the ideas behind your company or its expansion. The next step is to explain how you plan to execute them.
Start by talking about the people in your business and how they’ll contribute to its success.
You will have highlighted key employees at the start of the business plan document, so use this opportunity to go into more detail about the team.
After all, they’ll be driving the business with you – here’s what you can show:
An organizational chart - This will be a great way to sense check the structure you have created – are there too many people in senior roles? How does the team work together? Is there enough room for growth?
The backgrounds of your key players - A strong management team requires people with a range of skills and expertise. Although your employees don’t need to have years of experience, they should be bringing something interesting to the table.
Your hiring strategies - A big part of business planning is finding the right people – after all, salaries form part of the fixed costs you have to pay for. How do you expect to reach the right talent pool as you grow the company?
The company’s legal structure - If you are creating a startup, go into more detail about how your business will be run. For example, will it be a limited liability company (LLC), sole proprietorship, or partnership?
6. Marketing strategy
You have a customer profile, so now you need to think about how you’re going to manage customer relationships. Nailing this in your business plan is a really smart move.
First of all, understanding your marketing objectives will help you find the right channels.
It will also uncover the financial data around your company’s promotional efforts. What will your campaigns cost? What can you afford to spend on marketing?
Here are the key marketing components that you will need to consider:
Your website - While social media is effective, websites are essential. They’re easy to get – a website builder like Zyro or Squarespace will help you to create a bespoke platform and get online quickly and at a low cost.
Its marketing tools - The other major advantage to website builders is that they provide users with integrations, software, and insights to help drive marketing strategies. You’ll be getting an online presence and the tools to promote your business.
Third-party assistance - You can also use online marketing services to help you structure each marketing plan and drive a difference between you and your competitors. Who would you work with, and what will that cost?
Other marketing channels - Where will your audience be? You’ll most likely benefit from using social media platforms, but which ones? Find out if it’s worth investing time into Instagram, or if LinkedIn will be more profitable.
How your business will stand out - When you write a business plan, you’re making predictions about the future – what will you do if your marketing strategy fails? Understand some key digital marketing trends to help inform your ideas.
- Check out our complete list of the best small business website builders
7. Business operations and logistics
Now we’re getting really granular. Breaking down the proposed logistics in your business plan will be incredibly useful for you as you work out financial projections.
Getting a clear picture of business operations will also help you formulate a contingency plan.
It may be that your business model is very niche and needs testing – how will you account for any failures? While it isn't fun to think about worst case scenarios, it’s better to do this now.
Plus, if you need to secure funding, this section is important. Here’s what to cover:
- Business facilities - If the company plans to open retail spaces or venues, where are they and how big are they? Will there be an office for employees?
- Supply chain - Will you be sourcing products or materials from manufacturers? Explain where they are based and what policies you will implement
- Inventory management - Retailers should describe how and where they plan to manage stock and customer orders
- Fulfillment model - Another vital component for retail businesses, this covers how you expect to receive products and ship them out to customers
- Business equipment - Even small business administration costs money. How will you source office supplies? Will you need a bank loan?
- Financial operations - Before you delve into this part of the business plan, mention how you plan to track and manage cash flow

8. Financial plan
Whether you need to secure funding, take out a business loan, or simply take note of your income statements, every business plan needs to cover financial planning.
It helps to take a look at your finance software options to construct this part of the document.
Being upfront about your company’s financial outlook is critical, both for you and anyone else who is planning to invest in the organization.
There are three key components that you’ll need to include in your business plan:
An income statement , which shows the most accurate picture (or estimation) of your company’s profit and loss over a period of time.
A cash flow statement . To understand how much money you need to scale the business, and if it’s viable, you’ll need to provide cash flow statements.
Balance sheets . A balance sheet discloses your business assets and liabilities – in other words, what you owe to others.
On top of your financial statements, you should also include a breakeven analysis of your company in your business plan.
Critical for startups, this shows at what point you expect to start making a profit and for what duration you anticipate to be running at a loss.
Once you know what goes into a good business plan, you’ll need to know how to make it a document that people actually want to read.
In addition to the main segments, you can include supporting documents to help people further contextualize what it is you’re doing.
That will also help you to keep track of your plans, especially if you’re only writing the document to help yourself and your team, not investors.
Either way, you want to avoid writing a total snooze-fest. While a lot of detail goes into a business plan, it also needs to be engaging and exciting throughout.
So, to write a really solid business plan, remember to:
- Keep it brief - Nobody wants to have to flick through a 100-page manifesto, not even future you. An effective business plan is concise and memorable
- Make it shareable - Business plans written on paper won’t really go anywhere – make sure yours is published in an easily transferable format
- Be clear - Only use industry jargon when it’s totally unavoidable, otherwise you risk alienating (and boring) the readers of your business plan
- Show your research - Implement charts, provide supporting documents, and make sure that it’s abundantly clear how much thought you put into your business
- Remember your passion - Don’t be put off by traditional business plans with bland statements – make it clear in your own business plan how exciting this venture is
- We've also featured the best business plan software

Désiré has been musing and writing about technology during a career spanning four decades. He dabbled in website builders and web hosting when DHTML and frames were in vogue and started narrating about the impact of technology on society just before the start of the Y2K hysteria at the turn of the last millennium.
iDrive is adding cloud-to-cloud backup for personal Google accounts
Adobe Dreamweaver (2024) review
Intel unveils flurry of new Arc GPUs — however serious graphics users will have to wait for more powerful models, as these focus on a completely different and more lucrative market
Most Popular
- 2 You took amazing smartphone eclipse photos, but reminded me why I didn't use Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra's 100x Space Zoom
- 3 Windows 11 users are getting fed up with the performance of the OS – including an ex-Microsoft senior engineer
- 4 One of the best OLED TVs you can buy drops to a stunning price of $996 at Amazon
- 5 Microsoft pushes ahead with controversial move in Windows 11 – having Copilot appear immediately after startup
- 2 I swapped my Apple Watch for a vintage Casio Chronograph – here are 8 surprising things I learned
- 3 5 must-have features to future-proof your first or next EV purchase
- 4 Android phones finally get their first AirTag-style trackers – here's how they work
- 5 7 new movies and TV shows to stream on Netflix, Prime Video, Max, and more this weekend (April 12)

Graziadio Business Blog

Pursue Your Doctorate: DBA Program Admission
Gain valuable insights into the admission process for DBA programs and increase your chances of securing a spot in a prestigious business school.

Executive MBA Programs Cost
Learn about tuition fees, program duration, and additional expenses involved in pursuing an Executive MBA.

Navigating the Executive MBA Curriculum
Dive into the diverse range of courses offered in an Executive MBA program and understand how they enhance your leadership and strategic management skills.

Mastering Big Data Analytics: MS in Business Analytics
Discover how a Master's in Business Analytics equips you with the skills to analyze and leverage big data for actionable insights and competitive advantage.

Determining MBA Eligibility
Understand the eligibility criteria for MBA programs, including educational background, GMAT/GRE scores, language proficiency, and more.

Global Opportunities: EMBA Programs
Discover the global opportunities provided by executive MBA programs, including international study trips, global networking, and exposure to diverse business environments.

Start Your Journey: DBA Program Admission
Gain valuable insights into the admission process for DBA programs and take the first step toward advancing your expertise

Understanding the Cost of Executive MBA Programs
← Newer Posts
Learn more about how to achieve your career goals with a degree from Pepperdine Graziadio Business School.
- Student Life
- Graduate Programs
- Center for Applied Research
- Master's Degree
- Faculty Research
- Sustainability
- Entrepreneurship
- Talent Management
- Part-Time MBA
- MS in Business Analyics
Copyright © 2024 Pepperdine University
- Privacy Policy
- GDPR Privacy Notice
- Clery Notice
- Terms of Use
- Title IX
- Web Accessibility

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
A business plan covers the "who" and "what" of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains "how" the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision.
Learn about the best business plan software. 1. Write an executive summary. This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your ...
It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance. A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and pursue growth. In short, a business plan is a lot of different things. It's more than just a stack of paper and can be ...
This brief part of your business plan will detail your business name, years in operation, key offerings, and positioning statement. You might even add core values or a short history of the company. The company description's role in a business plan is to introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way. 4. The Business ...
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Most of the time, you'll start by providing a pitch deck — a presentation (PowerPoint, Keynote) version of your business plan highlighting the most basic elements of your plan in a handful of highly visual slides. Most investors will want to start here because it's much quicker to read up front than poring over your business plan.
According to the Small Business Administration, the length of your business plan should be long enough to accomplish three goals: (1) excite the financing source, (2) prove that you truly understand the market, and (3) fully detail the execution strategy.
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines ...
7. Goals. The goals portion of your business plan gives readers a better idea of where your business is headed. Try to include a mix of quarterly goals, annual goals, and goals that span five or 10 years. For each goal you share, include a few bullet points explaining: Your timeline for reaching the goal.
Describe the nature of your business and list the marketplace needs that you are trying to satisfy. Explain how your products and services meet these needs. List the specific consumers, organizations, or businesses that your company serves or will serve. Explain the competitive advantages that you believe will make your business a success such ...
1. Executive summary. This short section introduces the business plan as a whole to the people who will be reading it, including investors, lenders, or other members of your team. Start with a sentence or two about your business, development goals, and why it will succeed. If you are seeking funding, summarise the basics of the financial plan. 2.
This section of your business plan provides a high-level review of the different elements of your business. This is akin to an extended elevator pitch and can help readers and potential investors quickly understand the goal of your business and its unique proposition. ... Explain the logic behind your calculation. ... idea, prototype). Details ...
Business plan components. The business plan must provide detailed information and analysis of all relevant business aspects, including management, competitive position, markets, activities, products, policies, and financial projection. For new businesses, the content structure of the business plan usually covers: Executive summary - overview ...
1. Executive summary. Think of your executive summary as an elevator pitch: it should be a concise, engaging, and persuasive overview of your business. Keep this section to less than one page in ...
Executive Summary. The executive summary is the synopsis of the business plan, meant to be no longer than two pages, and includes a basic description of your business that sums up the five Ws and one H. Who you and your business are. What your company does and the industry it's in. When you'll start conducting business. Where you will be ...
When companies develop business plans, it allows employees at all levels to see the company as a whole enterprise. Business plans can be used to start a company, apply for a business loan, plan long-term strategies and maintain a business. Business plans vary by type, but most business plans contain the following parts:
purposes of a business plan. • 1. A business plan explains the idea behind your business and spells out your product or service will be produced and sold. • 2. A business plan sets specific objectives and describes how your business expects to achieve them. • 3. A business plan describes the backgrounds and experience of the leadership.
Explains the idea behind your business and spells out how your product or service will be produced and sold. ... A written summary of your experience is an essential part of your business plan. In the introduction. Advantages. Performance, Quality, Price, Reliability, Promotion, Distribution, Location, and Public image or reputation. ...
B. Which of the following is not a purpose of a business plan? (a) To describe the backgrounds and experience of your suppliers, (b) To explain the idea behind your business, (c) To explain how you expect to achieve specific objectives, (d) To describe the backgrounds and experience of the people who will be running the business. A.
Why does a business plan help your business? -A business plan makes you think about all aspects of your business. -It may help you secure financing for your business. -Helps you communicate your ideas to others. -A business plan can serve as a tool for managing your business. List the 5 Basic Elements of a Business Plan with a small description.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Purpose of a business plan?, Importance of a business plan?, Parts of a business plan and more. ... Explains the idea behind your business. Importance of a business plan? Makes you think about all aspects of the business. Parts of a business plan. introduction, main body ...
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like business plan, Purpose of a business plan, Why a business plan is important and more. ... 1. explains the idea behind your business 2. sets specific objectives and how your business will achieve them 3. describes the experience of the people who will run the business.